JP4602828B2 - In-subject information acquisition system - Google Patents
In-subject information acquisition system Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4602828B2 JP4602828B2 JP2005128556A JP2005128556A JP4602828B2 JP 4602828 B2 JP4602828 B2 JP 4602828B2 JP 2005128556 A JP2005128556 A JP 2005128556A JP 2005128556 A JP2005128556 A JP 2005128556A JP 4602828 B2 JP4602828 B2 JP 4602828B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- signal processing
- parameter
- data
- identification code
- image
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Measurement Of The Respiration, Hearing Ability, Form, And Blood Characteristics Of Living Organisms (AREA)
- Endoscopes (AREA)
Description
本発明は、複眼型のカプセル型内視鏡等の被検体内導入装置及び被検体内情報取得システムに関するものである。 The present invention relates to an in-subject introduction apparatus such as a compound eye type capsule endoscope and an in-subject information acquisition system.
近年、内視鏡の分野において、飲み込み型のカプセル型内視鏡が開発されている。このカプセル型内視鏡は、撮像機能と無線機能とを備え、体腔内の観察のために患者の口から飲み込まれた後、人体から自然排出されるまでの間、例えば食道、胃、小腸などの臓器の内部をその蠕動運動に従って移動し、順次撮像する機能を有する(例えば、特許文献1参照)。 In recent years, swallowable capsule endoscopes have been developed in the field of endoscopes. This capsule endoscope has an imaging function and a wireless function. After being swallowed from the patient's mouth for observation inside the body cavity, until it is naturally discharged from the human body, for example, the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, etc. It moves in accordance with its peristaltic movement and sequentially images (see, for example, Patent Document 1).
体腔内を移動する間、カプセル型内視鏡によって体内で撮像された画像データは、順次無線通信により体外に送信され、体外の受信装置内に設けられたメモリに蓄積される。医師もしくは看護師においては、メモリに蓄積された画像データをもとにディスプレイに表示させた画像に基づいて診断を行うことができる。 While moving inside the body cavity, image data captured inside the body by the capsule endoscope is sequentially transmitted outside the body by wireless communication, and is stored in a memory provided in a receiving apparatus outside the body. The doctor or nurse can make a diagnosis based on the image displayed on the display based on the image data stored in the memory.
ところで、この種のカプセル型内視鏡に関しては、その進行方向前方の体腔内画像のみを撮像する単眼型のカプセル型内視鏡が一般的であったが、近年では、視野範囲の拡大等を目的として進行方向前後の画像を撮像する複眼型のカプセル型内視鏡も提案されている(例えば、特許文献2参照)。この複眼型のカプセル型内視鏡は、体腔内部を照明するLED等の照明部と体腔内の画像を撮像するCCD等の撮像素子との対をそれぞれ有する複数の撮像ブロックをカプセル型筐体内の前後に配設し、体腔内におけるカプセル型筐体の進行方向前後の画像を撮像する構造とされている。 By the way, with regard to this type of capsule endoscope, a monocular capsule endoscope that captures only an image in the body cavity ahead of the traveling direction is generally used. As a purpose, a compound-eye capsule endoscope that captures images before and after the traveling direction has also been proposed (see, for example, Patent Document 2). This compound-eye capsule endoscope includes a plurality of imaging blocks each having a pair of an illumination unit such as an LED that illuminates the inside of a body cavity and an imaging element such as a CCD that images an image inside the body cavity. It is arranged in the front-rear direction, and is configured to take images before and after the capsule-type housing in the body cavity in the traveling direction.
しかしながら、特許文献2等に示される複眼型のカプセル型内視鏡は、単に、複数の撮像素子によって前後両方向の画像を撮像することが記述されているのみであり、これらの撮像素子には個々の特性の違いがあるにもかかわらず、これらの撮像素子個々の特性の違い等を考慮した処理制御等に関しては言及されておらず、それぞれの撮像素子の特性に応じた適正な撮像データの処理等が保証されないため、複眼型としての利点を必ずしも有効活用できるものとはなっていない。 However, the compound-eye capsule endoscope shown in Patent Document 2 and the like merely describes that images in both the front and rear directions are captured by a plurality of imaging elements. Although there is a difference in characteristics, there is no mention of processing control that takes into account differences in the characteristics of each of these image sensors, etc., and appropriate imaging data processing according to the characteristics of each image sensor Therefore, the advantages as a compound eye type cannot always be effectively utilized.
本発明は、上記に鑑みてなされたものであって、視野範囲が拡大される複眼型構成において、それぞれの撮像素子の特性に応じた適正な信号処理を行うことができ、複眼型の利点を最大限に発揮させることができる被検体内導入装置及び被検体内情報取得システムを提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of the above, and in a compound eye type configuration in which the field of view range is expanded, it is possible to perform appropriate signal processing according to the characteristics of each imaging element, and to obtain the advantages of the compound eye type. It is an object of the present invention to provide an intra-subject introduction apparatus and an intra-subject information acquisition system that can be maximized.
上述した課題を解決し、目的を達成するために、本発明に係る被検体内導入装置は、体腔内の異なる部位を撮像する複数の撮像素子と、前記各撮像素子の撮像データの信号処理に必要な各素子固有の信号処理用パラメータを格納した格納部と、該格納部に格納された前記信号処理用パラメータを被検体外に送信出力する送信部と、を備えたことを特徴とする。 In order to solve the above-described problems and achieve the object, an in-subject introduction apparatus according to the present invention is used for signal processing of a plurality of image sensors that image different parts in a body cavity and imaging data of each of the image sensors A storage unit that stores necessary signal processing parameters specific to each element and a transmission unit that transmits and outputs the signal processing parameters stored in the storage unit to the outside of the subject are provided.
本発明に係る被検体内導入装置は、上記発明において、前記信号処理用パラメータは、前記撮像素子の撮像データに対してホワイトバランス処理を行うためのホワイトバランス係数のデータであることを特徴とする。 In the in- subject introduction apparatus according to the present invention as set forth in the invention described above, the signal processing parameter is data of a white balance coefficient for performing white balance processing on imaging data of the imaging device. .
本発明に係る被検体内導入装置は、上記発明において、前記信号処理用パラメータは、前記撮像素子の画素欠陥のアドレスを示すデータであることを特徴とする。 In the in- vivo introduction apparatus according to the present invention as set forth in the invention described above, the signal processing parameter is data indicating an address of a pixel defect of the image sensor.
本発明に係る被検体内導入装置は、上記発明において、前記送信部は、前記各撮像素子により撮像された撮像データとともに、前記各撮像素子を識別するための識別コードに該撮像素子に対応する信号処理用パラメータを付加して送信出力することを特徴とする。 In the in- vivo introduction device according to the present invention , in the above invention, the transmission unit corresponds to the image sensor with an identification code for identifying the image sensor together with the image data captured by the image sensor. A signal processing parameter is added for transmission.
本発明に係る被検体内情報取得システムは、本発明に記載の被検体内導入装置と、該被検体内導入装置の送信部から送信出力されるデータを受信する受信装置と、を備えた被検体内情報取得システムであって、前記受信装置は、前記送信部から送信出力されるデータ中から識別コードを検出する識別コード検出手段と、前記送信部から送信出力されるデータ中から信号処理用パラメータを検出するパラメータ検出手段と、検出された識別コードに基づき前記撮像素子を識別し該撮像素子に対応する信号処理用パラメータを確定するパラメータ確定手段と、前記送信部から送信出力された該撮像素子の撮像データに対し確定された該信号処理用パラメータを用いて画像処理を施す画像処理手段と、を備えたことを特徴とする。 An in-subject information acquisition system according to the present invention includes an in-subject introduction device according to the present invention , and a reception device that receives data transmitted from a transmission unit of the in-subject introduction device. The in-sample information acquisition system, wherein the reception device detects an identification code from data transmitted and output from the transmitter, and performs signal processing from data transmitted and output from the transmitter. Parameter detection means for detecting a parameter, parameter determination means for identifying the image sensor based on the detected identification code and determining a signal processing parameter corresponding to the image sensor, and the image output transmitted from the transmitter And image processing means for performing image processing using the signal processing parameters determined for the imaging data of the element.
本発明に係る被検体内情報取得システムは、上記発明において、前記パラメータ確定手段は、前記信号処理用パラメータの確定後に入力される前記識別コードと前記信号処理用パラメータとの組合せの適正度を監視し適正でなくなった場合には確信度の高いデータに基づき該組合せに修正処理を施すことを特徴とする。 In the in- vivo information acquisition system according to the present invention as set forth in the invention described above, the parameter determination unit monitors the appropriateness of the combination of the identification code and the signal processing parameter input after the determination of the signal processing parameter. However, if the combination is no longer appropriate, the combination is corrected based on data having a high certainty factor.
本発明に係る被検体内導入装置及び被検体内情報取得システムによれば、各撮像素子の撮像データの信号処理に必要な各素子固有の信号処理用パラメータ、例えば、ホワイトバランス処理を行うためのホワイトバランス係数のデータをあらかじめ格納部に格納しておき、このような信号処理用パラメータを送信部によって被検体外に送信出力し、例えば受信装置における信号処理に供するようにしたので、それぞれの撮像素子の撮像データの信号処理に際してはそれぞれの撮像素子固有の信号処理用パラメータを用いて行うことで、素子特性の違いに応じた適正な撮像データの信号処理が可能となり、いずれの撮像素子による撮像データも適正に処理されるため、複眼型の利点を最大限に発揮させることができるという効果を奏する。また、被検体内導入装置においては、各素子固有の信号処理用パラメータを送信出力可能に保持しているだけであり、当該被検体内導入装置の内部においてホワイトバランス等の信号処理を行わないので、内部回路の回路規模が大きくなって消費電力が増大してしまうようなこともない。 According to the in-subject introduction apparatus and the in-subject information acquisition system according to the present invention, signal processing parameters specific to each element necessary for signal processing of imaging data of each imaging element, for example, white balance processing is performed. The white balance coefficient data is stored in the storage unit in advance, and such signal processing parameters are transmitted and output to the outside of the subject by the transmission unit, for example, for signal processing in the receiving apparatus. By performing signal processing of the imaging data of the elements using the signal processing parameters specific to each imaging element, it becomes possible to perform appropriate imaging data signal processing according to the difference in element characteristics, and imaging by any imaging element Since the data is also processed appropriately, there is an effect that the advantages of the compound eye type can be maximized. In addition, the intra-subject introduction apparatus only holds the signal processing parameters specific to each element so that it can be transmitted and output, and does not perform signal processing such as white balance inside the intra-subject introduction apparatus. The circuit scale of the internal circuit is not increased and the power consumption is not increased.
以下、添付図面を参照して、本発明に係る被検体内導入装置の好適な実施の形態である無線型の被検体内情報取得システムについて説明する。なお、本実施の形態により本発明が限定されるものではない。また、図面の記載において、同一部分には同一の符号を付している。 Hereinafter, a wireless in-vivo information acquiring system which is a preferred embodiment of an in-subject introducing device according to the present invention will be described with reference to the accompanying drawings. In addition, this invention is not limited by this Embodiment. In the description of the drawings, the same parts are denoted by the same reference numerals.
本発明の実施の形態について説明する。図1は、無線型の被検体内情報取得システムの全体構成を示す模式図である。この被検体内情報取得システムは、被検体内導入装置の一例として複眼型のカプセル型内視鏡を用いている。図1に示すように、無線型の被検体内情報取得システムは、被検体1の体内に導入され、体腔内画像を撮像して受信装置2に対して映像信号などのデータ送信を無線によって行うカプセル型内視鏡3と、カプセル型内視鏡3から無線送信された体腔内画像データを受信する受信装置2と、受信装置2が受信した映像信号に基づいて体腔内画像を表示する表示装置4と、受信装置2と表示装置4との間のデータ受け渡しを行うための携帯型記録媒体5とを備える。
Embodiments of the present invention will be described. FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram showing the overall configuration of a wireless in-vivo information acquiring system. This intra-subject information acquisition system uses a compound eye type capsule endoscope as an example of the intra-subject introduction apparatus. As shown in FIG. 1, the wireless in-vivo information acquiring system is introduced into the body of the
また、受信装置2は、被検体1の体外表面に貼付される複数の受信用アンテナA1〜Anを有した無線ユニット2aと、複数の受信用アンテナA1〜Anを介して受信された無線信号の処理等を行う受信本体ユニット2bとを備え、これらユニットはコネクタ等を介して着脱可能に接続される。なお、受信用アンテナA1〜Anのそれぞれは、例えば、被検体1が着用可能なジャケットに備え付けられ、被検体1は、このジャケットを着用することによって受信用アンテナA1〜Anを装着するようにしてもよい。また、この場合、受信用アンテナA1〜Anは、ジャケットに対して着脱可能なものであってもよい。
The receiving device 2 also includes a wireless unit 2a having a plurality of receiving antennas A1 to An attached to the external surface of the
表示装置4は、カプセル型内視鏡3によって撮像された体腔内画像を表示するためのものであり、携帯型記録媒体5によって得られるデータをもとに画像表示を行うワークステーション等の構成を有する。具体的には、表示装置4は、CRTディスプレイ、液晶ディスプレイ等によって直接画像を表示する構成としてもよいし、プリンタ等のように、他の媒体に画像を出力する構成としてもよい。
The display device 4 is for displaying an in-vivo image captured by the
携帯型記録媒体5は、コンパクトフラッシュ(登録商標)メモリ等が用いられ、受信本体ユニット2b及び表示装置4に対して着脱可能であって、両者に対する挿着時に情報の出力又は記録が可能な機能を有する。具体的には、携帯型記録媒体5は、カプセル型内視鏡3が被検体1の体腔内を移動している間は受信本体ユニット2bに挿着され、カプセル型内視鏡3から送信されるデータが携帯型記録媒体5に記録される。そして、カプセル型内視鏡3が被検体1から排出された後、つまり、被検体1の内部の撮像が終わった後には、受信本体ユニット2bから取り出されて表示装置4に挿着され、表示装置4によって記録されたデータが読み出される。受信本体ユニット2bと表示装置4との間のデータの受け渡しを携帯型記録媒体5によって行うことで、被検体1が体腔内の撮像中に自由に行動することが可能となり、また、表示装置4との間のデータの受け渡し期間の短縮にも寄与している。なお、受信本体ユニット2bと表示装置4との間のデータの受け渡しは、受信本体ユニット2bに内蔵型の他の記録装置を用い、表示装置4と有線又は無線接続するように構成してもよい。
The
ここで、図2を参照して、カプセル型内視鏡3について説明する。図2は、カプセル型内視鏡3の内部構成を示す断面図である。カプセル型内視鏡3は、被検体1の体腔内部を照明する照明部としての例えばLED11a,11bと、体腔内の画像を撮像する撮像素子としての例えばCCD12a,12bを有する撮像部13a,13bと、をそれぞれ対として有する2組の撮像ブロック14a,14bを、これらに電力を供給する電源部15とともに、カプセル型筐体16内に配設することにより構成されている。
Here, the
カプセル型筐体16は、撮像ブロック14a,14bをそれぞれ覆い透明で半球ドーム状の先端カバー筐体16a,16bと、これらの先端カバー筐体16a,16bと凹凸係合部17a,17bを介して水密状態に設けられ内部に電源部15を介在させて撮像ブロック14a,14bが配設される円筒状の胴部筐体16cとからなり、被検体1の口から飲み込み可能な大きさに形成されている。胴部筐体16cは、可視光が不透過な有色材質により形成されている。
The capsule-
撮像部13a,13bは、それぞれ撮像基板18a,18b上に設けられてLED11a,11bからの照明光によって照明された範囲を撮像するCCD12a,12bと、これらのCCD12a,12bに被写体像を結像する固定レンズ19a,19b及び可動レンズ20a,20bからなる結像レンズ21a,21bとよりなる。ここで、固定レンズ19a,19bは固定枠22a,22bに固定され、可動レンズ20a,20bは可動枠23a,23bに固定され、ピント調整部24a,24bを構成している。
The
また、LED11a,11bは、照明基板25a,25b上に搭載され、結像レンズ21a,21bの光軸中心に対してその上下左右の近傍4箇所に配設されている。さらに、各撮像ブロック14a,14bにおいて、撮像基板18a,18bの背面側には、ブロック毎に各部を処理又は制御するための信号処理・制御部26a,26bが搭載され、さらに、一方の撮像ブロック14aの信号処理・制御部26aには外部と無線通信を行うためのアンテナ等からなる無線部27が実装された無線基板28が配設されている。また、撮像基板18a,18bと照明基板25a,25bとは適宜ケーブルにより電気的に接続されている。
The
撮像ブロック14a,14b間に位置する電源部15は、例えば胴部筐体16cの内径にほぼ一致する直径のボタン型の電池29により構成されている。この電池29は、酸化銀電池、充電式電池、発電式電池等を用い得る。ここで、各撮像ブロック14a,14bとこの電池29との間の中心部には、撮像ブロック14a,14bをそれぞれ対向する先端カバー筐体16a,16b側、つまり、外側に付勢するねじりコイルばね形状のばね部材30a,30bが介在されている。なお、無線基板28上の無線部27と信号処理・制御部26bとは電池29外部を通したケーブル等により適宜電気的に接続され、この電池29も、信号処理・制御部26a,26b等とケーブル等により適宜電気的に接続されている。なお、無線部27は撮像ブロック14a,14bで共用とせず、撮像ブロック14a,14b毎に個別に設けてもよい。
The
ここで、先端カバー筐体16a,16bの内部外周付近には、照明基板25a,25bの外周側一部を突き当て当接させることにより撮像ブロック14a,14bのカプセル型内視鏡3における軸方向の位置決めを行う基準となる位置決め部31a,31bが一体に形成されている。また、これらの位置決め部31a,31bと照明基板25a,25bとの間には、例えば相互に係脱する凹凸形状の組み合わせからなり、軸心周り方向の位置決めをする回転止め位置決め部(図示せず)が形成されている。
Here, in the vicinity of the inner periphery of the
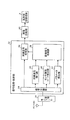
つぎに、図3を参照して、カプセル型内視鏡3の内部回路構成について説明する。図3は、カプセル型内視鏡3の内部回路構成を示す概略ブロック図である。まず、信号処理・制御部26aは、対をなすLED11aとCCD12aとを制御するためのものであり、それぞれLED11aとCCD12aに対応するLED駆動回路41a,CCD駆動回路42aを有する。また、信号処理・制御部26aは、CCD12aから出力される出力信号に対して相関二重サンプリング処理、増幅処理、A/D変換処理、多重化処理等の所定の画像処理を施す画像処理部43aを有する。さらに、信号処理・制御部26aは、各種タイミング信号や同期信号を生成するタイミングジェネレータ(TG)及びシンクジェネレータ(SG)44aを有する制御部45aを備え、タイミングジェネレータ及びシンクジェネレータ44aにより生成されたタイミング信号や同期信号に基づいて、駆動回路41a,42aや画像処理部43aの動作やその動作タイミングなどを制御する。
Next, an internal circuit configuration of the
また、信号処理・制御部26bは、対をなすLED11bとCCD12bとを制御するためのものであり、それぞれLED11bとCCD12bに対応するLED駆動回路41b,CCD駆動回路42bを有する。また、信号処理・制御部26bは、CCD12bから出力される出力信号に対して相関二重サンプリング処理、増幅処理、A/D変換処理、多重化処理等の所定の画像処理を施す画像処理部43bを有する。さらに、信号処理・制御部26bは、各種タイミング信号や同期信号を生成するタイミングジェネレータ(TG)及びシンクジェネレータ(SG)44bを有する制御部45bを備え、タイミングジェネレータ及びシンクジェネレータ44bにより生成されたタイミング信号や同期信号に基づいて、駆動回路41b,42bや画像処理部43bの動作やその動作タイミングなどを制御する。
The signal processing /
ここで、制御部45a,45bは、制御部45a側がマスタで制御部45b側がスレーブとなる主従関係にあり、制御部45bは制御部45a側からのイネーブル信号EBに従いこのイネーブル信号EBがHレベルの間だけ動作するように制御部45aに従動して制御動作を実行する。
Here, the
また、無線部27は、画像処理部43a,43bを経た撮像データの出力経路上に設けられてRF変調信号を出力する送信部としての送信モジュール46と送信アンテナ47とにより構成されている。
The
さらに、カプセル型内視鏡3は、信号処理・制御部26a,26bに対して共通な格納部としてのパラメータメモリ49を備えている。このパラメータメモリ49は、各CCD12a,12bの撮像データの信号処理に必要な各素子固有の信号処理用パラメータや当該カプセル型内視鏡3の処理に必要な共用パラメータをこれらの信号処理・制御部26a,26bにより読出し可能に格納したものであり、適宜タイミングでパラメータが画像処理部43a又は43bに対して読出されて撮像データ等との多重化処理に供され、無線部27を介して受信装置2側に送信可能とされている。
Furthermore, the
図4は、制御部45a,45bにより制御される点灯・読出し等のタイミング制御例を示す概略タイムチャートである。制御部45a,45bは、CCD12a,12bを順次交互に駆動するとともに、LED11a,11bの点灯タイミングとCCD12a,12bの読出しタイミングとが異なるようにタイミング制御する。より具体的には、例えば一方のCCD12aの読出し動作終了後に他方のCCD12bと対をなすLED11bを所定時間点灯させ、その後、CCD12bの読出し動作終了後にCCD12aと対をなすLED11aを所定時間点灯させ、以後、このような動作制御を繰り返す。
FIG. 4 is a schematic time chart showing an example of timing control such as lighting / reading controlled by the
図4に則して説明する。まず、制御部45aはタイミングジェネレータ及びシンクジェネレータ44aから出力されるパルス状のタイミング信号に従いLED駆動回路41aを介してLED11aを所定時間点灯させ、その照明部位をCCD12aにより撮像させる(LED11a点灯)。そして、LED11aが消灯したタイミングで、制御部45aはCCD駆動回路42aを介してCCD12aから画像処理部43aに対してフレーム単位の撮像信号の読出し動作を実行させる(CCD12a読出し)。この読出し動作が終了したら、制御部45aは制御部45b側に対してイネーブル信号EBを出力し(Hレベル)、制御部45b側による制御に切換える。
This will be described with reference to FIG. First, the
制御部45bは、タイミングジェネレータ及びシンクジェネレータ44bから出力されるパルス状のタイミング信号に従いLED駆動回路41bを介してLED11bを所定時間点灯させ、その照明部位をCCD12bにより撮像させる(LED11b点灯)。そして、LED11bが消灯したタイミングで、制御部45bはCCD駆動回路42bを介してCCD12bから画像処理部43bに対してフレーム単位の撮像信号の読出し動作を実行させる(CCD12b読出し)。この読出し動作が終了するタイミングで、制御部45aはイネーブル信号EBをLレベルに切換え、制御部45a側による制御に切換える。以後、これらの動作制御を交互に繰り返す。また、回路構成上、制御部45bから読出し終了時に制御部45aに対し終了信号を入力することによってイネーブル信号EBをLレベルにするようにしてもよい。
The
このような動作において、送信モジュール46に対しては、CCD12a,12bから順次交互に出力されるフレーム単位の撮像データが順次入力され(CCD12aデータ、CCD12bデータ、CCD12aデータ、…)、RFデータとしての送信出力に供される。
In such an operation, imaging data in units of frames sequentially output alternately from the
複眼型のカプセル型内視鏡3の場合、例えば胴部筐体16cが可視光に対して不透過な材質により形成され、また、中央の電池29が遮光部材として機能し得るが、CCD12aの撮像・読出し時にLED11bが点灯するとその照明光がいずれかの隙間経路等を経て迷光となってこのCCD12aの撮像画像に影響を及ぼす可能性がある。CCD12bに対するLED11aの関係も同様である。また、LED11a,11bの点灯タイミングとCCD12a,12bの読出しタイミングとが一致すると、LED11a,11bのオン・オフ時のスイッチングノイズがCCD12b,12aの撮像画像に重畳され、その画質を損なう可能性がある。
In the case of the compound-eye
ここで、本実施の形態は、上述のように、各CCD12a,12bを順次交互に駆動するとともに、LED11a,11bの点灯タイミングとCCD12a,12bの読出しタイミングとが異なるように制御することで、点灯タイミングと読出しタイミングとがタイミング的に重ならないので、体腔内の異なる部位をそれぞれのCCD12a,12bによって撮像する上で、他方のLED11b又は11aによる照明光が迷光となって一方のCCD12a又は12bの撮像画像に影響を及ぼすことや、LED11a,11b点灯時のスイッチングノイズが撮像画像に重畳されたりすることがなく、それぞれの撮像画像の品質を向上させて被検体内診察を良好に行うことができる。
Here, in the present embodiment, as described above, the
また、2つの制御部45a,45bについて、イネーブル信号EBを利用することで、制御部45a側がマスタで制御部45b側がスレーブとなる主従関係の下に制御動作を交互かつ適正に行わせることができる。さらに、信号処理・制御部26a,26bは、各CCD12a,12bが読出し動作をしない無信号時のタイミングでは出力抵抗を高抵抗(ハイインピーダンス)にすることにより、他出力に影響がないので、送信モジュール46を支障なく共通化することができる。
Further, by using the enable signal EB for the two
また、複眼型のカプセル型内視鏡を構成する上で、撮像素子や照明部は複数個個別設けることが必須であるが、本実施の形態では、上述の送信モジュール46の他に、パラメータメモリ49のように、2系統で流用できる所は流用して極力共通化を図っているので、複眼型のカプセル型内視鏡3の構成の小型・シンプル化を実現することができる。
In order to configure a compound-eye capsule endoscope, it is essential to individually provide a plurality of image sensors and illumination units. In this embodiment, in addition to the
ここで、図5−1、図5−2を参照して、パラメータメモリ49について説明する。図5−1は、パラメータメモリ49の構成の一例を示し、CCD12aに固有の信号処理用パラメータを格納するCCD12a用パラメータ領域49aと、CCD12bに固有の信号処理用パラメータを格納するCCD12b用パラメータ領域49bと、共用パラメータを格納するシステム用パラメータ領域49cとを有する。
Here, the
CCD12a用パラメータ領域49aには、固有の信号処理用パラメータとして、例えば、CCD12aの撮像データに対してホワイトバランス(WB)処理を行うためのホワイトバランス係数のデータが格納される。このデータは、各カプセル型内視鏡3の製造工程における試験によりあらかじめCCD12aに独自のホワイトバランス係数として求められたデータである。具体的には、基準となる白チャートをCCD12aにより撮像し、グリーン(G)を基準として、R(レッド)、B(ブルー)の出力が規定値となるように算出された補正係数(ホワイトバランス係数)であり、“WB係数データR1” “WB係数データB1”として格納される。
In the parameter area 49a for the
CCD12b用パラメータ領域49bには、固有の信号処理用パラメータとして、例えば、CCD12bの撮像データに対してホワイトバランス(WB)処理を行うためのホワイトバランス係数のデータが格納される。このデータも、各カプセル型内視鏡3の製造工程における試験によりあらかじめCCD12bに独自のホワイトバランス係数として求められたデータである。具体的には、基準となる白チャートをCCD12bにより撮像し、グリーン(G)を基準として、R(レッド)、B(ブルー)の出力が規定値となるように算出された補正係数(ホワイトバランス係数)であり、“WB係数データR2” “WB係数データB2”として格納される。
In the
なお、各素子固有の信号処理用パラメータとしては、このようなホワイトバランス係数のデータに限らず、例えば、各CCD12a,12bの画素欠陥のアドレスを示すデータとし、該画素欠陥のアドレスの周囲のアドレスに対応する画素データに基づいて、該アドレスに存在する画素欠陥の補正に供するようにしてもよい。さらには、撮像素子として、CCDに代えて、例えばCMOSセンサを用いた場合の各CMOSセンサに固有の値である光電変換特性のオフセット値を各素子固有の信号処理用パラメータとしてそれぞれの領域49a,49bにあらかじめ格納しておくようにしてもよい。
The signal processing parameters specific to each element are not limited to such white balance coefficient data, but are, for example, data indicating the pixel defect addresses of the
システム用パラメータ領域49cには、CCD12a,12bに固有ではないが、各カプセル型内視鏡3に固有なパラメータとして、例えば、CCD12a,12bなるセンサ毎の転送枚数(フレーム転送枚数)のデータや当該カプセルを確定するためのカプセル番号などのデータが格納される。
The
図5−2は、パラメータメモリ49の構成の別例を示し、CCD12aに固有の信号処理用パラメータを格納するCCD12a用パラメータ領域49aと、CCD12bに固有の信号処理用パラメータを格納するCCD12b用パラメータ領域49bとに二分し、これらの領域49a,49b中にさらにシステム用パラメータ領域49d,49eをそれぞれ設けておき、一方を有効、他方を無効とするようにしたものである。図示例では、制御部45a側をマスタとして制御を行うようにしているので、CCD12a用パラメータ領域49a中のシステム用パラメータ領域49d側が有効とされている。回路系によって制御部45b側をマスタにしたい等の状況が生じた場合には、CCD12b用パラメータ領域49b中のシステム用パラメータ領域49e側が有効となり、CCD12a用パラメータ領域49a中のシステム用パラメータ領域49d側が無効となるように切換えればよく、メモリに汎用性を持たせることができる。
FIG. 5B shows another example of the configuration of the
図6は、送信モジュール46に対する入力信号例を示す説明図である。送信モジュール46に対しては、まず、タイミングジェネレータ及びシンクジェネレータ44aから出力される垂直同期信号を先頭として、画像処理部43aにおいてCCD12aからの撮像データとともに、このCCD12aを識別するための識別コードであるセンサ識別コード1に、CCD12a用パラメータ領域49aから読み出したCCD12a用の信号処理パラメータであるホワイトバランス係数のデータ“WB係数データR1”“WB係数データB1”を多重化処理部で付加したデータ列がフレームデータ列として入力される。次いで、タイミングジェネレータ及びシンクジェネレータ44bから出力される垂直同期信号を先頭として、画像処理部43bにおいてCCD12bからの撮像データとともに、このCCD12bを識別するための識別コードであるセンサ識別コード2に、CCD12b用パラメータ領域49bから読み出したCCD12b用の信号処理パラメータであるホワイトバランス係数のデータ“WB係数データR2”“WB係数データB2”を多重化処理部で付加したデータ列がフレームデータ列として入力される。
FIG. 6 is an explanatory diagram illustrating an example of an input signal to the
送信モジュール46に対しては、このようなフレームデータ列が一方が奇数番目、他方が偶数番目となって交互に入力され、RF信号として、送信用アンテナ47から送信出力され、受信装置2で受信可能とされている。なお、それぞれのセンサ識別コードは、1ビット情報でよいので、垂直同期信号中の1ビットをセンサ識別コード用として兼用させることで、CCD12a用の垂直同期信号とCCD12b用の垂直同期信号とに分けるようにしてもよい。
Such a frame data sequence is alternately input to the
このように、信号処理用パラメータは、カプセル型内視鏡3の起動時だけでなく、それぞれの撮像データのフレーム単位での送信出力毎に付加して送信出力するので、例えば、カプセル型内視鏡3の起動時に受信装置2の電源が投入されていない等の事態があっても、電源投入後の任意の時点で信号処理用パラメータを取得することが可能となる。
As described above, the signal processing parameter is added and transmitted for each transmission output of each imaging data in units of frames as well as when the
つづいて、受信装置2側の構成例について図7を参照して説明する。図7は、受信装置2の回路構成例を示す概略ブロック図である。受信装置2は、受信モジュール51と、信号処理・制御部52と、画像圧縮部53とを備えている。受信モジュール51は、アンテナA1〜Anにて捕捉された電波の信号を増幅し復調する機能を果たし、無線ユニット2a部分により構成されている。画像圧縮部53は、信号処理・制御部52により画像処理後の画像データを圧縮し、この受信装置2に対して着脱自在に装着された携帯型記録媒体5に圧縮した画像データを格納する。
Next, a configuration example on the receiving device 2 side will be described with reference to FIG. FIG. 7 is a schematic block diagram illustrating a circuit configuration example of the receiving device 2. The receiving device 2 includes a receiving
信号処理・制御部52は、受信モジュール51で受信され復調された信号に対して信号分離を行う信号分離部54と、信号分離の結果に基づいて垂直同期信号、センサ識別コード、信号処理用パラメータをそれぞれ検出する検出部55,56,57と、受信モジュール51から出力される撮像データに対して画像処理を施す画像処理手段としての画像信号処理部58と、検出部55〜57による検出結果に基づいて信号処理用パラメータを確定する確定処理等を実行して画像処理部58による画像処理に供するパラメータ確定手段としての識別コード・パラメータ確定部59とを備えている。識別コード・パラメータ確定部59は、例えばパラメータ確定処理に用いる4つのレジスタR1〜R4を備えている。
The signal processing /
このような構成において、信号処理・制御部52は、概略的には、受信モジュール51で受信され復調された信号を信号分離部54で分離し、その分離信号に基づき、同期信号検出部55で垂直同期信号を検出し、センサ識別コード検出部56でセンサ識別コードを検出し、パラメータ検出部57で信号処理用パラメータとしてホワイトバランス係数のデータを検出し、これらの検出情報を識別コード・パラメータ確定部59に入力させることで、識別コード・パラメータ確定部59においてCCD12a又は12bのいずれの撮像データであるかを識別しそのCCD12a又は12bに対応する信号処理用パラメータを確定するパラメータ確定処理を実行させる。
In such a configuration, the signal processing /
図8及び図9は、識別コード・パラメータ確定部59において実行されるパラメータ確定処理例を示す概略フローチャートである。この処理は、概略的には、図8に示す奇数フレームの処理と、図9に示す偶数フレームの処理とに二分されて実行される。まず、奇数番目の垂直同期信号が入力されたか否かを判断する(ステップS1)。「奇数番目」とは、受信装置2が最初に受けたフレームデータ列が1番目であり、以降、3番目、5番目、…に受けたフレームデータ列を意味する。したがって、2番目、4番目、…に受けたフレームデータ列は偶数番目となる。
FIG. 8 and FIG. 9 are schematic flowcharts showing an example of parameter confirmation processing executed in the identification code /
奇数番目の垂直同期信号が入力されたと判断した場合には(ステップS1:Yes)、つづいて、センサ識別コードが入力されたか否かを判断し(ステップS2)、センサ識別コードが入力された場合には(ステップS2:Yes)、さらに信号処理用パラメータが入力されたか否かを判断する(ステップS3)。信号処理用パラメータが入力された場合において(ステップS3:Yes)、これらのセンサ識別コードや信号処理用パラメータが新規に入力されたものであるか否かを判断し(ステップS4)、新規に入力されたものであれば(ステップS4:Yes)、1番目の入力であるので、入力されたこれらのセンサ識別コードや信号処理用パラメータをレジスタR1に記録し(ステップS5)、ステップS1の処理に戻る。 When it is determined that an odd-numbered vertical synchronization signal has been input (step S1: Yes), it is then determined whether a sensor identification code has been input (step S2), and a sensor identification code has been input. (Step S2: Yes), it is further determined whether or not a signal processing parameter has been input (step S3). When the signal processing parameters are input (step S3: Yes), it is determined whether or not these sensor identification codes and signal processing parameters are newly input (step S4) and newly input. If so (step S4: Yes), since this is the first input, these input sensor identification codes and signal processing parameters are recorded in the register R1 (step S5), and the processing of step S1 is performed. Return.
ステップS1以降の再度の処理において、センサ識別コードや信号処理用パラメータが入力された場合には(ステップS2:Yes,ステップS3:Yes)、3番目以降であり新規ではないので(ステップS4:No)、今回入力されたセンサ識別コードや信号処理用パラメータをレジスタR2に記録する(ステップS6)。そして、レジスタR1とレジスタR2の記録内容が一致するか否かを判断する(ステップS7)。一致する場合には(ステップS7:Yes)、奇数番目同士で同一内容のセンサ識別コードと信号処理用パラメータとの入力が2回正常に連続したこととなり、奇数番目用のフレーム画像に対するセンサ識別コード及び信号処理用パラメータを確定する(ステップS8)。 If a sensor identification code or a signal processing parameter is input in the subsequent processing after step S1 (step S2: Yes, step S3: Yes), it is the third and subsequent and not new (step S4: No) ), The sensor identification code and the signal processing parameter input this time are recorded in the register R2 (step S6). Then, it is determined whether or not the recorded contents of the register R1 and the register R2 match (step S7). If they match (step S7: Yes), the input of the sensor identification code and the signal processing parameter having the same contents at odd numbers is normally continued twice, and the sensor identification code for the odd-numbered frame image is obtained. Then, the signal processing parameters are determined (step S8).
一方、レジスタR1,R2の記録内容が一致しない場合には(ステップS7:No)、レジスタR1にレジスタR2の内容を上書きし、レジスタR2の記録内容を消去し(ステップS9)、ステップS1からの処理に戻る。これにより、今度は、3番目のデータを基準に5番目のデータと一致するか比較し、一致すれば奇数番目用のフレーム画像に対するセンサ識別コード及び信号処理用パラメータを確定し(ステップS8)、一致しなければ、以降、5番目と7番目との比較を行う如く、順次、以降の奇数番目同士の比較処理を繰り返すこととなる。奇数番目用のフレーム画像に対するセンサ識別コード及び信号処理用パラメータが確定した場合には(ステップS8)、確定処理を終了する。 On the other hand, if the recorded contents of the registers R1 and R2 do not match (step S7: No), the contents of the register R2 are overwritten on the register R1, the recorded contents of the register R2 are erased (step S9), Return to processing. Thus, this time, the third data is used as a reference to compare with the fifth data, and if they match, the sensor identification code and signal processing parameters for the odd-numbered frame image are determined (step S8). If they do not coincide with each other, the subsequent odd number comparison processing is sequentially repeated so that the fifth and seventh comparisons are performed. When the sensor identification code and the signal processing parameter for the odd-numbered frame image are confirmed (step S8), the confirmation process is terminated.
次に、偶数フレームの処理について説明する。まず、偶数番目の垂直同期信号が入力されたか否かを判断する(ステップS11)。偶数番目の垂直同期信号が入力されたと判断した場合には(ステップS11:Yes)、つづいて、センサ識別コードが入力されたか否かを判断し(ステップS12)、センサ識別コードが入力された場合には(ステップS12:Yes)、さらに信号処理用パラメータが入力されたか否かを判断する(ステップS13)。信号処理用パラメータが入力された場合において(ステップS13:Yes)、これらのセンサ識別コードや信号処理用パラメータが新規に入力されたものであるか否かを判断し(ステップS14)、新規に入力されたものであれば(ステップS14:Yes)、2番目の入力であるので、入力されたこれらのセンサ識別コードや信号処理用パラメータをレジスタR3に記録し(ステップS15)、ステップS11の処理に戻る。 Next, processing of even frames will be described. First, it is determined whether or not an even-numbered vertical synchronization signal has been input (step S11). When it is determined that an even-numbered vertical synchronization signal has been input (step S11: Yes), it is then determined whether a sensor identification code has been input (step S12), and a sensor identification code has been input. (Step S12: Yes), it is further determined whether or not a signal processing parameter has been input (step S13). When the signal processing parameters are input (step S13: Yes), it is determined whether or not these sensor identification codes and signal processing parameters are newly input (step S14), and are newly input. If so (step S14: Yes), since it is the second input, these input sensor identification codes and signal processing parameters are recorded in the register R3 (step S15), and the processing of step S11 is performed. Return.
ステップS11以降の再度の処理において、センサ識別コードや信号処理用パラメータが入力された場合には(ステップS12:Yes,ステップS13:Yes)、4番目以降であり新規ではないので(ステップS14:No)、今回入力されたセンサ識別コードや信号処理用パラメータをレジスタR4に記録する(ステップS16)。そして、レジスタR3とレジスタR4の記録内容が一致するか否かを判断する(ステップS17)。一致する場合には(ステップS17:Yes)、偶数番目同士で同一内容のセンサ識別コードと信号処理用パラメータとの入力が2回連続したこととなり、偶数番目用のフレーム画像に対するセンサ識別コード及び信号処理用パラメータを確定する(ステップS18)。 If a sensor identification code or a signal processing parameter is input in the re-processing after step S11 (step S12: Yes, step S13: Yes), it is the fourth or later and not new (step S14: No). ), The sensor identification code and the signal processing parameter input this time are recorded in the register R4 (step S16). Then, it is determined whether or not the recorded contents of the register R3 and the register R4 match (step S17). If they match (step S17: Yes), the input of the sensor identification code and the signal processing parameter having the same content is repeated twice evenly, and the sensor identification code and signal for the even-numbered frame image are obtained. Processing parameters are determined (step S18).
一方、レジスタR3,R4の記録内容が一致しない場合には(ステップS17:No)、レジスタR3にレジスタR4の内容を上書きし、レジスタR4の記録内容を消去し(ステップS19)、ステップS11からの処理に戻る。これにより、今度は、4番目のデータを基準に6番目のデータと一致するか比較し、一致すれば偶数番目用のフレーム画像に対するセンサ識別コード及び信号処理用パラメータを確定し(ステップS18)、一致しなければ、以降、6番目と8番目との比較を行う如く、順次、以降の偶数番目同士の比較処理を繰り返すこととなる。偶数番目用のフレーム画像に対するセンサ識別コード及び信号処理用パラメータが確定した場合には(ステップS18)、確定処理を終了する。 On the other hand, if the recorded contents of the registers R3 and R4 do not match (step S17: No), the contents of the register R4 are overwritten in the register R3, the recorded contents of the register R4 are erased (step S19), and from step S11. Return to processing. Thus, this time, the fourth data is used as a reference to compare with the sixth data, and if they match, the sensor identification code and the signal processing parameters for the even-numbered frame image are determined (step S18). If they do not coincide with each other, the subsequent even-numbered comparison processing is sequentially repeated so that the sixth and eighth comparisons are performed. When the sensor identification code and the signal processing parameter for the even-numbered frame image are confirmed (step S18), the confirmation process is terminated.
受信装置2に入力されたセンサ識別コードと信号処理用パラメータとの組合せに関して、1回のみの受信データにより確定するようにしてもよいが、無線通信においては1回だけでは正常に送受信処理がなされていない場合もあるので、本実施の形態のように、同一データを2回連続して受信することを条件に奇数番目、偶数番目用のそれぞれのフレーム画像に対するセンサ識別コード及び信号処理用パラメータを確定するようにすることで、信頼性の高いものとなる。 The combination of the sensor identification code and the signal processing parameter input to the receiving device 2 may be determined based on the received data only once. However, in wireless communication, transmission / reception processing is normally performed only once. As in this embodiment, the sensor identification code and the signal processing parameters for the odd-numbered and even-numbered frame images are set on condition that the same data is continuously received twice. By making it fixed, it becomes highly reliable.
なお、これらの奇数番目、偶数番目用のそれぞれのフレーム画像に対するセンサ識別コード及び信号処理用パラメータを確定する上で、2回連続した場合に限らず、例えば、複数回入力させ、その中で発生頻度の多いセンサ識別コード及び信号処理用パラメータを奇数番目、偶数番目用のそれぞれのフレーム画像に対するデータとして確定するようにしてもよい。これによれば、通信エラーにより誤った信号処理用パラメータが採用されることを防止できる。さらには、多少送受信の状態が悪く、パラメータが数フレーム入力されない時には、レジスタ内容をリセットし、パラメータが再度入力された時点から確定処理を再度行うようにしてもよく、また、受信装置2側で生成した同期信号に基づいてレジスタ内容を保持し、パラメータの入力が再開されてから受信したデータを用いてレジスタ内容の一致を確認するようにしてもよい。 Note that the sensor identification code and the signal processing parameter for each of the odd-numbered and even-numbered frame images are determined, not limited to the case of two consecutive times. The sensor identification code and the signal processing parameter that are frequently used may be determined as data for the odd-numbered and even-numbered frame images. According to this, it is possible to prevent an erroneous signal processing parameter from being adopted due to a communication error. Further, when the transmission / reception state is somewhat poor and the parameter is not input for several frames, the register contents may be reset and the determination process may be performed again from the time when the parameter is input again. The register contents may be held based on the generated synchronization signal, and the matching of the register contents may be confirmed using data received after the input of parameters is resumed.
前述の画像信号処理部55では、上記のように確定された奇数番目用、偶数番目用のフレーム画像に対するセンサ識別コード及び信号処理用パラメータを用いることで、センサ識別コードの一致により特定される奇数番目のフレーム画像データの場合には上記のように確定された奇数番目用のフレーム画像に対する信号処理用パラメータを用いて画像処理を施し、偶数番目のフレーム画像データの場合には上記のように確定された偶数番目用のフレーム画像に対する信号処理用パラメータを用いて画像処理を施す。
The above-described image
具体的には、一方では、確定されたセンサ識別コード1で特定されるCCD12aによる撮像データに対して、確定されたホワイトバランス係数のデータ“WB係数データR1” “WB係数データB1”を用いてホワイトバランス処理を行い、他方では、確定されたセンサ識別コード1で特定されるCCD12bによる撮像データに対して、確定されたホワイトバランス係数のデータ“WB係数データR2” “WB係数データB2”を用いてホワイトバランス処理を行うこととなる。
Specifically, on the other hand, with respect to the imaging data by the
ところで、本実施の形態の識別コード・パラメータ確定部59は、パラメータ等の確定処理後においても、信号処理用パラメータの確定後に入力されるセンサ識別コードと信号処理用パラメータとの組合せの適正度を常に監視し適正でなくなった場合には確信度の高いデータに基づき該組合せに修正処理を施す異常パラメータ入力処理を随時実行する。
By the way, the identification code /
図10は、識別コード・パラメータ確定部59により実行されるこの異常パラメータ入力処理例を示す概略フローチャートである。まず、信号処理用パラメータの入力があるか否かを判断し(ステップS21)、入力がなければ(ステップS21:No)、入力があるまで待機する。信号処理用パラメータの入力があった場合(ステップS21:Yes)、その信号処理用パラメータとともに入力された撮像データのフレーム順(奇数番目/偶数番目)、センサ識別コードに関して、既に確定している確定パラメータと比較して異常であるか否かを判断する(ステップS22)。この判断で、一致しており、異常がなければ(ステップS22:No)、正常であり、既に確定している確定パラメータをそのまま用いるため、当該処理を終了する。
FIG. 10 is a schematic flowchart showing an example of the abnormal parameter input process executed by the identification code /
一方、確定パラメータとの比較の結果、異常がある場合(ステップS22:Yes)、その異常が、撮像データのフレーム順、センサ識別コード、信号処理用パラメータの内の1つだけが異常か、2つが異常か、3つとも異常かを判断する(ステップS23,S24)。 On the other hand, if there is an abnormality as a result of comparison with the deterministic parameter (step S22: Yes), whether the abnormality is abnormality in only one of the imaging data frame order, sensor identification code, and signal processing parameter. It is determined whether one is abnormal or all three are abnormal (steps S23 and S24).
1つだけが異常の場合(ステップS23:Yes)、異常としては軽微であるので、異常であっても、既に確定している確定パラメータをそのまま用いて信号処理を行わせる(ステップS25)。また、2つが異常の場合(ステップS23:No,ステップS24:Yes)、異常としては一応無視できないので、前フレームの処理を参照するものとし、前フレームの処理が正常であったか否かを判断する(ステップS26)。前フレームの処理がステップS22:Noのルーチンを経ることにより正常であった場合には(ステップS26:Yes)、今回の2つの異常はたまたま生じたものと判断し、既に確定している確定パラメータをそのまま用いて信号処理を行わせる(ステップS27)。すなわち、カプセル型内視鏡3の動作開始直後に、前述のように、センサ識別コードと信号処理用パラメータとの対(組合せ)を確定するが、この確定後の動作において、センサ識別コードと信号処理用パラメータとの組合せのいずれかが適正でなくなる条件となった場合には、それ以前に送られてきた信号から判断し、確信度の高いデータ、例えば既に確定している確定パラメータを用いることで、適正でなくなった今回の組合せを適正に修正できることとなる。
If only one is abnormal (step S23: Yes), since the abnormality is minor, even if it is abnormal, the signal processing is performed using the already determined parameters as they are (step S25). If the two are abnormal (step S23: No, step S24: Yes), since the abnormality cannot be ignored for the time being, the process of the previous frame is referred to, and it is determined whether or not the process of the previous frame is normal. (Step S26). If the processing of the previous frame is normal by passing through the routine of step S22: No (step S26: Yes), it is determined that the two abnormalities have occurred by this time, and the confirmation parameter that has already been confirmed. Is used for signal processing (step S27). That is, immediately after the operation of the
これに対して、前フレームの処理も正常でなかった場合には(ステップS26:No)、既に確定しているパラメータをリセットし、前述したようなパラメータ確定処理を再度行う(ステップS28)。3つとも異常であった場合も(ステップS24:No)、既に確定しているパラメータをリセットし、前述したようなパラメータ確定処理を再度行う(ステップS28)。 On the other hand, when the process of the previous frame is not normal (step S26: No), the parameter already determined is reset and the parameter determination process as described above is performed again (step S28). Even if all three are abnormal (step S24: No), the parameters already determined are reset and the parameter determination process as described above is performed again (step S28).
本発明は、上述した実施の形態に限らず、本発明の趣旨を逸脱しない範囲であれば、種々の変形が可能である。 The present invention is not limited to the above-described embodiment, and various modifications can be made without departing from the spirit of the present invention.
2 受信装置
3 カプセル型内視鏡
12a,12b CCD
46 送信モジュール
49 パラメータメモリ
56 センサ識別コード検出部
57 パラメータ検出部
58 画像信号処理部
59 識別コード・パラメータ確定部
2
46
Claims (5)
前記被検体内導入装置は、
体腔内の異なる部位を撮像する複数の撮像素子と、
前記各撮像素子の撮像データの信号処理に必要な各素子固有の信号処理用パラメータを格納した格納部と、
前記各撮像素子により撮像された撮像データとともに、前記各撮像素子を識別するための識別コードに該撮像素子に対応する前記信号処理用パラメータを付加して被検体外に送信出力する送信部と、
を備え、
前記受信装置は、
前記送信部から送信出力されるデータ中から識別コードを検出する識別コード検出手段と、
前記送信部から送信出力されるデータ中から信号処理用パラメータを検出するパラメータ検出手段と、
検出された識別コードに基づき前記撮像素子を識別し該撮像素子に対応する信号処理用パラメータを確定するパラメータ確定手段と、
前記送信部から送信出力された該撮像素子の撮像データに対し確定された該信号処理用パラメータを用いて画像処理を施す画像処理手段と、
を備え、
前記パラメータ確定手段は、前記信号処理用パラメータの確定後に入力される前記識別コードと前記信号処理用パラメータとの組合せの適正度を監視し適正でなくなった場合には確信度の高いデータに基づき該組合せに修正処理を施すことを特徴とする被検体内情報取得システム。 An in-subject introduction apparatus that transmits imaging data introduced into the subject and imaged in the subject by a wireless signal, and a receiving apparatus that receives imaging data transmitted from the introduction in the subject. An in-subject information acquisition system,
The in-subject introduction device comprises:
A plurality of image sensors for imaging different parts of the body cavity;
A storage unit storing signal processing parameters specific to each element necessary for signal processing of imaging data of each imaging element;
A transmission unit that adds the signal processing parameters corresponding to the image sensor to an identification code for identifying the image sensor together with the image data captured by the image sensor, and transmits the data outside the subject.
With
The receiving device is:
Identification code detection means for detecting an identification code from data transmitted from the transmission unit;
Parameter detection means for detecting a parameter for signal processing from data transmitted and output from the transmitter;
Parameter determining means for identifying the image sensor based on the detected identification code and determining a signal processing parameter corresponding to the image sensor;
Image processing means for performing image processing using the signal processing parameters determined for the imaging data of the imaging device transmitted and output from the transmission unit;
With
The parameter confirmation means monitors the appropriateness of the combination of the identification code and the signal processing parameter input after the signal processing parameter is confirmed. An in-subject information acquisition system, wherein correction processing is performed on the combination.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005128556A JP4602828B2 (en) | 2005-04-26 | 2005-04-26 | In-subject information acquisition system |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005128556A JP4602828B2 (en) | 2005-04-26 | 2005-04-26 | In-subject information acquisition system |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2006304885A JP2006304885A (en) | 2006-11-09 |
| JP2006304885A5 JP2006304885A5 (en) | 2008-01-24 |
| JP4602828B2 true JP4602828B2 (en) | 2010-12-22 |
Family
ID=37472477
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005128556A Expired - Fee Related JP4602828B2 (en) | 2005-04-26 | 2005-04-26 | In-subject information acquisition system |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4602828B2 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2013031300A1 (en) | 2011-08-31 | 2013-03-07 | オリンパス株式会社 | Capsule-type endoscope |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5259141B2 (en) | 2007-08-31 | 2013-08-07 | オリンパスメディカルシステムズ株式会社 | In-subject image acquisition system, in-subject image processing method, and in-subject introduction device |
| JP4918438B2 (en) * | 2007-08-31 | 2012-04-18 | オリンパスメディカルシステムズ株式会社 | In-subject information acquisition system |
| JP5156427B2 (en) * | 2008-02-13 | 2013-03-06 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | Capsule endoscope system |
| JP5513142B2 (en) * | 2010-01-20 | 2014-06-04 | オリンパス株式会社 | Endoscope device |
| US20160174809A1 (en) * | 2013-10-03 | 2016-06-23 | Capso Vision, Inc. | Robust Storage and Transmission of Capsule Images |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH11317700A (en) * | 1998-05-01 | 1999-11-16 | Es Systems:Kk | Transportation management communication system |
| JP2003038425A (en) * | 2001-07-30 | 2003-02-12 | Olympus Optical Co Ltd | Encapsulated endoscope |
| JP2004344655A (en) * | 2003-05-22 | 2004-12-09 | Siemens Ag | Endoscopic device |
| WO2004112593A1 (en) * | 2003-06-24 | 2004-12-29 | Olympus Corporation | Encapsulated endoscope and encapsulated endoscope system |
| JP2005076210A (en) * | 2003-08-28 | 2005-03-24 | Bunka Shutter Co Ltd | Opening and closing indication transmitter, indication receiver, and indication system |
-
2005
- 2005-04-26 JP JP2005128556A patent/JP4602828B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH11317700A (en) * | 1998-05-01 | 1999-11-16 | Es Systems:Kk | Transportation management communication system |
| JP2003038425A (en) * | 2001-07-30 | 2003-02-12 | Olympus Optical Co Ltd | Encapsulated endoscope |
| JP2004344655A (en) * | 2003-05-22 | 2004-12-09 | Siemens Ag | Endoscopic device |
| WO2004112593A1 (en) * | 2003-06-24 | 2004-12-29 | Olympus Corporation | Encapsulated endoscope and encapsulated endoscope system |
| JP2005076210A (en) * | 2003-08-28 | 2005-03-24 | Bunka Shutter Co Ltd | Opening and closing indication transmitter, indication receiver, and indication system |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2013031300A1 (en) | 2011-08-31 | 2013-03-07 | オリンパス株式会社 | Capsule-type endoscope |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2006304885A (en) | 2006-11-09 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4695432B2 (en) | In-subject introduction apparatus, in-subject information display apparatus, and in-subject information acquisition system | |
| JP4914600B2 (en) | In-vivo image acquisition device, reception device, and in-vivo information acquisition system | |
| US8732546B2 (en) | Radio receiver with an error correction code detector and with a correction unit | |
| US20050049461A1 (en) | Capsule endoscope and capsule endoscope system | |
| JP5265139B2 (en) | In-vivo image acquisition system | |
| JP4918438B2 (en) | In-subject information acquisition system | |
| JP4602828B2 (en) | In-subject information acquisition system | |
| JP4847075B2 (en) | Receiver | |
| AU2006288213B2 (en) | Device to be introduced into subject | |
| JP5096115B2 (en) | In-subject information acquisition system and in-subject introduction device | |
| JP3893121B2 (en) | Capsule endoscope system and capsule endoscope | |
| JP4701322B2 (en) | Intra-subject introduction apparatus and in-vivo information acquisition system | |
| JP2006288831A (en) | Apparatus introduced into subject | |
| JP4383432B2 (en) | Capsule endoscope system and capsule endoscope | |
| JP4914790B2 (en) | Intra-subject introduction device and method for producing intra-subject introduction device | |
| JP4823621B2 (en) | Receiving device, transmitting device, and transmitting / receiving system | |
| JP2006102007A (en) | Receiving device and receiving system |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20071130 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20071130 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20100630 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20100706 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20100831 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20100921 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20100930 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20131008 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R151 | Written notification of patent or utility model registration |
Ref document number: 4602828 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R151 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20131008 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| S111 | Request for change of ownership or part of ownership |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313111 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| S531 | Written request for registration of change of domicile |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313531 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |