JP4520126B2 - Capsule type medical device system - Google Patents
Capsule type medical device system Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4520126B2 JP4520126B2 JP2003338260A JP2003338260A JP4520126B2 JP 4520126 B2 JP4520126 B2 JP 4520126B2 JP 2003338260 A JP2003338260 A JP 2003338260A JP 2003338260 A JP2003338260 A JP 2003338260A JP 4520126 B2 JP4520126 B2 JP 4520126B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- medical device
- capsule
- marking
- drug
- capsule medical
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61M—DEVICES FOR INTRODUCING MEDIA INTO, OR ONTO, THE BODY; DEVICES FOR TRANSDUCING BODY MEDIA OR FOR TAKING MEDIA FROM THE BODY; DEVICES FOR PRODUCING OR ENDING SLEEP OR STUPOR
- A61M31/00—Devices for introducing or retaining media, e.g. remedies, in cavities of the body
Description
本発明は、生体内に投入され表在疾患等の目的部位に、容易且つ直接的にアプローチすることができるカプセル型医療装置システムに関する。 The present invention relates to a capsule medical device system that can be introduced into a living body and easily and directly approach a target site such as a superficial disease.
現在、患者に対してより安全且つ効果的に薬物を投与する手段として、薬剤送達システム(DDS;Drug Delivery System)が注目されている。該薬剤送達システムは、医薬品の生物活性、副作用、患部への標的指向(ターゲティング)、薬剤の放出制御(コントロールドリリース)、薬剤の吸収改善、薬剤の化学的安定性及び代謝活性等を調整して、生体内の表在疾患に対して、必要な量の薬剤を必要な時間だけ作用させ、薬剤をより効果的に使用するものである。この薬剤送達システムは、疾患種類に応じて、利用される技術が異なるものであり、例えば、患部である表在疾患が悪性腫瘍の場合には、ターゲティング、コントロールドリリース等の技術が求められる。 At present, a drug delivery system (DDS) is attracting attention as a means for safely and effectively administering a drug to a patient. The drug delivery system regulates the biological activity, side effects, targeted targeting (targeting) to the affected area, controlled release of the drug, improved drug absorption, chemical stability and metabolic activity of the drug. Thus, a necessary amount of a drug is allowed to act on a superficial disease in a living body for a necessary time to use the drug more effectively. This drug delivery system uses different technologies depending on the type of disease. For example, when a superficial disease that is an affected area is a malignant tumor, technologies such as targeting and controlled release are required.
一方、容易に健康状態を検査するものとして、経口から生体内に投入可能なカプセル状のカプセル型医療装置が知られている。この種のカプセル型医療装置は、様々なものが提供されており、例えば、生体内の各部を無作為的に撮影するものや、生体内からサンプル等を採取するものや、薬剤を放出するもの等が知られている。その1つとして、体内の所定位置(大腸)で発泡剤を放出して生体内の管腔部分を拡張した後、撮像することができるカプセル内視鏡が知られている(例えば、特許文献1参照)。 On the other hand, a capsule-type capsule medical device that can be put into a living body from the oral cavity is known as an apparatus for easily examining a health condition. Various types of capsule-type medical devices are provided. For example, a device that randomly images each part of the living body, a device that collects a sample from the living body, or a device that releases a drug. Etc. are known. As one of them, a capsule endoscope is known that can take an image after releasing a foaming agent at a predetermined position (large intestine) in the body to expand a lumen portion in the living body (for example, Patent Document 1). reference).
上記カプセル内視鏡は、一方の端面側に透明且つ半球状の透明部材を有し、他方の端面側に半球状のメッシュ部材を有するカプセル状に形成されたカプセル枠体を有している。また、カプセル枠体の内部であって透明部材の内側には、生体内に照明光を照射するLED及び生体内を撮像する撮像光学系を有している。
また、カプセル枠体には、外表面に露出するようにpHセンサが設けられている。このpHセンサで検出されたpH値は、制御処理回路に送られ、pH値の変化から大腸に達したと判断されたときに、送信アンテナから体外に向けて送信されるようになっている。また、上記撮像光学系で撮像した画像データも、所定処理された後、送信アンテナから体外に送信されるようになっている。更に、メッシュ部材の内側には、超音波の照射により破壊される複数のマイクロカプセルが内蔵されており、該マイクロカプセル内には水と反応してガスを発生する発泡剤が内蔵されている。
The capsule endoscope has a capsule frame formed in a capsule shape having a transparent and hemispherical transparent member on one end face side and a hemispherical mesh member on the other end face side. In addition, inside the capsule frame and inside the transparent member, there are an LED that irradiates the living body with illumination light and an imaging optical system that images the inside of the living body.
The capsule frame body is provided with a pH sensor so as to be exposed on the outer surface. The pH value detected by the pH sensor is sent to the control processing circuit, and is transmitted from the transmitting antenna toward the outside of the body when it is determined that the large intestine has been reached from the change in pH value. The image data picked up by the image pickup optical system is also transmitted from the transmitting antenna to the outside after predetermined processing. Furthermore, inside the mesh member, a plurality of microcapsules that are destroyed by the irradiation of ultrasonic waves are incorporated, and a foaming agent that reacts with water to generate gas is incorporated in the microcapsules.
このカプセル内視鏡により検査を行う場合には、患者は、まずカプセル内視鏡を飲み込んで体内に投入する。投入されたカプセル内視鏡は、pHセンサで体内のpH値を検出しながら消化器官を移動する。ここで、大腸に達すると、制御処理回路は、pHセンサで検出されたpH値の変化により大腸に達したと判断して、送信アンテナから体外にその旨を知らせる。この送信された信号を、体外にて医療スタッフ等が受信すると、医療スタッフ等は、超音波発生器により体内に向けて超音波を照射する。超音波が照射されると、マイクロカプセルが破壊されるので、内部の発泡剤がメッシュ部材から大腸内に放出される。そして、発泡剤は、大腸内の水分と反応してガスを発生して、大腸内を拡張する。これにより、撮像光学系で、拡張された大腸内を広範囲にわたって撮像することが可能となる。 When performing an examination using this capsule endoscope, the patient first swallows the capsule endoscope and puts it into the body. The inserted capsule endoscope moves the digestive organ while detecting the pH value in the body with a pH sensor. Here, when reaching the large intestine, the control processing circuit determines that the large intestine has been reached due to a change in pH value detected by the pH sensor, and notifies the outside of the body from the transmitting antenna. When a medical staff or the like receives this transmitted signal outside the body, the medical staff or the like irradiates the body with ultrasonic waves using an ultrasonic generator. When the ultrasonic wave is irradiated, the microcapsule is broken, and the internal foaming agent is released from the mesh member into the large intestine. The foaming agent reacts with moisture in the large intestine to generate gas and expands in the large intestine. Thereby, it is possible to image the expanded large intestine over a wide range with the imaging optical system.
このように、上述したカプセル内視鏡は、体内の所望する位置(大腸)でマイクロカプセルから発泡剤を放出するという上述したターゲティング、コントロールドリリースの機能を有しているものである。特に、このようなカプセル型医療装置は、簡便に患者の体内に投入できるため、上記薬剤送達システムの1つの手段として新たに注目されている。
ところで、上記特許文献1に記載のカプセル内視鏡は、生体内の所定位置である大腸に達したときに生体外にその旨の信号を送り、該信号を受けて生体外から送られてきた超音波により発泡剤を大腸内に放出するので、所定位置に達してから発泡剤を放出するまでに時間を要するものであった。このカプセル内視鏡においては、発泡剤を放出する被対象物が長さを有する大腸であるため、大腸に達してから発泡剤を放出する時間の影響をシビアに考慮しなくても良いが、例えば、生体内の表在疾患付近という限られた範囲内で作動させたい場合には、表在疾患を発見してから反応するまでに時間がかかるので、作動したときには所望する範囲を通り過ぎてしまうという不都合があった。
By the way, the capsule endoscope described in
この発明は、このような事情を考慮してなされたもので、その目的は、生体内の表在疾患等の所望する部位に対して、容易且つ直接的にアプローチすることができるカプセル型医療装置システムを提供することである。 The present invention has been made in view of such circumstances, and its purpose is a capsule medical device that can easily and directly approach a desired site such as a superficial disease in a living body. Is to provide a system .
本発明のカプセル型医療装置システムは、体腔内の生体情報を得る生体情報取得手段と前記体腔内に間欠的に複数の指標を残すマーキング手段とを有する医療装置と、カプセル状の外装部と、前記医療装置が前記体腔内に残した前記複数の指標を検出する指標検出手段と、薬剤を保持する薬剤保持部と、該薬剤保持部内の前記薬剤を放出する薬剤放出部と、前記指標検出手段の情報に基づき前記薬剤放出部を制御する制御部とを有するカプセル型医療装置と、を備え、前記制御部は、前記複数の指標のうちの前記薬剤の放出を行う指標の順番を予め記憶すると共に、前記指標検出手段が前記指標を検出した数が前記制御部に記憶された前記薬剤の放出を行う前記指標の順番に一致したときに、前記薬剤放出部に前記薬剤を放出させることを特徴としている。 The capsule medical device system of the present invention includes a medical device having biological information acquisition means for obtaining biological information in a body cavity and marking means for intermittently leaving a plurality of indices in the body cavity, a capsule-shaped exterior part, Index detecting means for detecting the plurality of indices left in the body cavity by the medical device, a drug holding part for holding a drug, a drug releasing part for releasing the drug in the drug holding part, and the index detecting means A capsule medical device having a control unit that controls the drug release unit based on the information of the information, and the control unit stores in advance the order of the index for releasing the drug among the plurality of indexes with, when the number of said index detecting means detects said index matches the order of the index for performing release of the drug stored in the control unit, especially that to release the drug in the drug-releasing unit It is set to.
また、上記のカプセル型医療装置システムにおいて、前記医療装置が、カプセル状の外装部に、前記生体情報取得手段と、前記マーキング手段と、前記生体情報取得手段で取得した前記生体情報と前記マーキング手段の動作情報とを前記外装部の外部に伝達する情報伝達部とを有する第2のカプセル型医療装置と、前記情報伝達部で前記外装部の外部に伝達された情報を受信する受信装置とで構成されることがより好ましい。Further, in the above capsule medical device system, the medical device has a capsule-shaped exterior part, the biological information acquisition means, the marking means, the biological information acquired by the biological information acquisition means, and the marking means. A second capsule medical device having an information transmission unit that transmits the operation information to the outside of the exterior unit, and a reception device that receives information transmitted to the outside of the exterior unit by the information transmission unit. More preferably, it is configured.
この発明に係るカプセル型医療装置システムにおいては、第2のカプセル型医療装置を経口投入することで、情報伝達部が、生体情報取得手段で取得した生体情報とマーキング手段の動作情報とを外装部の外部に対して伝達する。また、受信装置が、伝達された生体情報と動作情報とを受信すると共に、これらの情報から体腔内の所望する部位を指標として検出する。その後、経口投入されたカプセル型医療装置により、指標位置を検出して該指標位置で薬剤の放出が行える。このように、医療装置を第2のカプセル型医療装置で構成できるので、小型化を図ることができ、簡便に患者等に経口投入することができる。In the capsule medical device system according to the present invention, the second capsule medical device is orally added, so that the information transmission unit obtains the biological information acquired by the biological information acquisition unit and the operation information of the marking unit. Communicate to outside. The receiving device receives the transmitted biological information and motion information, and detects a desired site in the body cavity from these information as an index. Thereafter, the position of the index can be detected and the drug can be released at the position of the index by the capsule medical device that has been orally introduced. Thus, since the medical device can be constituted by the second capsule medical device, it can be miniaturized and can be easily orally injected into a patient or the like.
また、上記のカプセル型医療装置システムにおいて、前記医療装置は、前記生体情報と前記指標を残した位置とを関連づけて記憶する記憶手段を有することがより好ましい。In the capsule medical device system, it is more preferable that the medical device has a storage unit that stores the biological information and the position where the index is left in association with each other.
本発明に係るカプセル型医療装置システムによれば、生体内の所望する部位(患部)に、容易且つ直接的にアプローチすることができると共に、さらに投薬を行うことができる。特に、患部を検出してから投薬を行うのではなく、患部の位置を示す指標を検出して投薬を行うので、投薬前に患部を通過することがなく、患部に対して効率良く投薬を行うことができる。 The desired site of the capsule medical device by the system lever, the body according to the present invention (affected area), it is possible to approach easily and directly, it is possible to further carry out the medication. In particular, dosing is not performed after the affected area is detected, but is performed by detecting an index indicating the position of the affected area, so that the affected area can be efficiently administered without passing through the affected area before dosing. be able to.
以下、本発明に係る第1実施形態を、図1から図10を参照して説明する。
本実施形態のカプセル型医療装置システム1は、図1に示すように、患者Pの体内(生体内)に経口投入される投薬用カプセル(カプセル型医療装置)2と、体腔内の生体情報である撮像画像を得る観察系12(生体情報取得手段)及び体腔内にマーキング(指標)Mを残す吐出機構(マーキング手段)13を有する医療装置3とを備えている。
A first embodiment according to the present invention will be described below with reference to FIGS.
As shown in FIG. 1, the capsule
上記医療装置3は、図1及び図2に示すように、カプセル状に形成された筐体(外装部)11内に、上記観察系12と、上記吐出機構13と、観察系12で取得した生体情報と吐出機構13の動作情報とを筐体11の外部に伝達する無線送信手段(伝達手段、情報伝達部)14とを有するカプセル型医療装置(第2のカプセル型医療装置)10と、無線送信手段14で筐体11の外部に伝達された情報を受信する観察情報受信機31を有するパーソナルコンピュータ(以下PC)(受信装置)30とを備えている。
As shown in FIGS. 1 and 2, the
上記カプセル型医療装置10の筐体11は、プラスチック等で内部を密閉するように形成され、一端側に透明カバー11aが設けられている。この透明カバー11aの内側には、体内の各部を撮像する対物レンズ15が配されており、該対物レンズ15の結像位置には、例えば、CMOSイメージャやCCD等の撮像素子16が配されている。また、対物レンズ15の周囲には、照明光を照射して対物レンズ15の視野範囲を照明するLED17が配設されている。即ち、これら対物レンズ15、撮像素子16及びLED17は、上記観察系12を構成している。
The
また、筐体11の一部には、微小な吐出口18が形成されており、該吐出口18の内側には、染料、磁性体、放射線体等のマーキング剤Wを収納するリザーバ19が配されている。該リザーバ19の一部は、弾性変形可能とされており、該弾性位置には、ピエゾ素子20が設けられている。つまり、ピエゾ素子20に作動信号等を送ることにより、該ピエゾ素子20が伸張してリザーバ19を押圧し、マーキング剤Wを吐出口18から筐体11の外部に向けて吐出できるようになっている。こうすることで、生体内に点墨のような上記マーキングMを施すことができるようになっている。即ち、これら吐出口18、リザーバ19及びピエゾ素子20は、上記吐出機構13を構成している。なお、マーキング剤Wは、生体内にマーキングMとして施されてから所定時間経過すると自然に消えるようになっている。例えば、小腸においてマーキングMを施した場合、組織の代謝によりマーキングMは、小腸組織をと共に管壁からはがれることになる。
In addition, a
また、筐体11内には、上記観察系12及び吐出機構13を制御すると共に、観察系12で取得した生体情報を所定処理する制御処理部21と、該制御処理部21で処理した生体情報等を記憶するメモリ22及び上述した各構成品に電力を供給する電池23が内蔵されている。
上記制御処理部21は、体内に投入された後、ピエゾ素子20に作動信号を送り、体内を移動している間に、定期的、例えば、5分に1回毎にマーキングMを体内に施すように吐出機構13を作動させる機能を有している。また、同時に観察系12を制御して、体内を、例えば、1秒に2回毎に無作為的に撮像して、生体情報を取得させる機能を有している。更に、制御処理部21は、観察系12から送られてきた生体情報を所定処理すると共に、該生体情報をピエゾ素子20を作動させたタイミングと関連付けて上記メモリ22に逐次記憶させる機能を有している。つまり、体内に施したマーキングMの位置と生体情報とを関連付けて、メモリ22に記憶させる機能を有している。
In addition, in the
The
また、カプセル型医療装置10は、患者Pの体内から排出され、回収された後、上記PC30にメモリ22内に記憶されている生体情報を出力できるようになっている。これにより、医師は、PC30に入力された生体情報に基づいて診断を行うことができる。
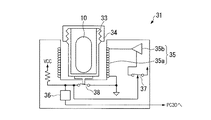
即ち、上記PC30は、図3及び図4に示すように、カプセル型医療装置10と無線通信を行って、生体情報を得る上記観察情報受信機31を備えている。該観察情報受信機31は、PC30とケーブル32によって接続されており、カプセル型医療装置10を内部に収納する容器33を設置する容器設置部34と、容器33に収納されたカプセル型医療装置10に電力を供給する電力供給手段35と、無線受信手段36とを備えている。
In addition, the capsule
That is, as shown in FIGS. 3 and 4, the
上記電力供給手段35は、例えば、上記容器設置部34を取り囲むように配置されたコイル35a、該コイル35aに交流電流を流すドライバ35b、該ドライバ35bの電源をON/OFFするスイッチ37とから構成されている。このスイッチ37は、容器設置部34の底面に配された設置検知スイッチ38に接続されており、容器33が容器設置部34に配置されたことを設置検知スイッチ38が検知したときに作動するようになっている。即ち、容器33を容器設置部34に設置したときに、ドライバ35bからコイル35aに交流電源が流れるようになっている。
また、上記無線受信手段36は、カプセル型医療装置10から送信される信号を受信すると共に、ケーブル32を介して上記PC30に伝達するようになっている。
The power supply means 35 includes, for example, a
The wireless receiving means 36 receives a signal transmitted from the capsule
更に、図2に示すように、カプセル型医療装置10は、筐体11内に、観察情報受信機31の無線受信手段36に信号を送信する上記無線送信手段14及び電力供給手段35から電力を受信する電力受信手段24を備えている。
該電力受信手段24は、受信用コイル24aとAC−DCコンバータ24bとから構成されている。この電力受信手段24は、上記電力供給手段35から電力の供給を受けると、無線送信手段14及びメモリ22に電力を分配し、メモリ22に蓄えられた生体情報を無線送信手段14を介して無線受信手段36に送るようになっている。また、送られた生体情報は、PC30に送られるようになっている。
これにより、上述したように、以下PC30に、メモリ22内に記憶されている生体情報を出力できるようになっている。
Furthermore, as shown in FIG. 2, the capsule
The power receiving means 24 includes a receiving
Thereby, as described above, the biometric information stored in the
次に、上記投薬用カプセル2を、図5及び図6に示す。図5は外観を示し、図6は断面図である。上記投薬用カプセル2は、患者Pの体内(生体内)に経口投入されるカプセル状の筐体(外装部)内40に、薬剤Aを保持するリザーバ(薬剤保持部)41と、該リザーバ41に保持された薬剤Aを放出する放出手段(薬剤放出部)42と、該放出手段42を作動させる制御部(放出制御手段)43と、体内に施された薬剤放出位置を示すマーキングMを検出するセンサ(検出手段、指標検出手段)44と、これら各構成品に電力を供給する電池45とを備えている。
Next, the
上記筐体40は、プラスチック等で内部を密閉するように形成されており、一端側の内部には、壁部40aと筐体40の内周面とで囲まれた上記リザーバ41が設けられている。該リザーバ41の周囲であって筐体40の外表面には、複数の薬剤口46が筐体40の軸回りに形成されている。該薬剤口46には、図示していない薄膜が形成されておりリザーバ41内に保持された薬剤Aが薬剤口46から漏れないようになっている。また、リザーバ41内には、ヒータ47が設けられている。該ヒータ47は、瞬間的な加熱により気泡を発生させ、その圧力で上記薬剤口46の薄膜を破り、薬剤Aを薬剤口46から放出させる機能を有している。即ち、これら薬剤口46及びヒータ47は、上記放出手段42を構成している。
The
上記センサ44は、筐体40の他端側の外表面であって、筐体40の軸回りに複数形成されており、生体内を移動中に上記マーキングMを検出して上記制御部43に送る機能を有している。即ち、センサ44は、図7に示すように、LED等で構成された発光素子44aと、光ディティクタ44bと、プリズム44cとで構成されている。なお、マーキングMが点墨であるとしてセンサ44を説明する。発光素子44aで発した光は、プリズム44cで反射され、筐体40に形成された窓40aを通し生体に照射される。照射された光は、生体で反射され、窓40a及びプリズム44cを透過して光ディティクタ44bに入射されるようになっている。また、光ディティクタ44bは、入射した光のレベルを検出するようになっている。
The
ここで、点墨されていない組織の位置で上記センサ44を動作させた場合には、照射された光は、生体組織で反射され、光ディティクタ44cにより反射光が検出される。
一方、点墨された組織の位置で上記センサ44を動作させた場合には、生体組織が点墨されているため、光は生体組織で吸収されてしまい(または、点墨されていない組織に比べ反射率が大幅に低くなる)、光ディティクタ44cでは反射光より弱い光を検出する。また、光ディティクタ44cは、入射された光のレベルに対応した電圧出力を制御部43に伝達するようになっている。制御部43は、前記電圧出力が点墨の施された組織からの信号か、点墨されていない組織からの信号化を判断するようになっている。ここで、制御部43が、点墨の施された組織からの信号であると判断した場合には、該制御部43に内蔵された図示しないカウンタを1進める。これにより、マーキングMのカウントができるようになっている。
Here, when the
On the other hand, when the
また、本実施例では、点墨を採用したが、検出可能であればいかなる色素を使用しても同様の効果が得られる。一例としては、メチレンブルー等の内視鏡検査に使用される色素がある。また、その際には、光ディティクタ44cの検出波長領域を最適になるように選択すれば良い。また、マーキングMとしては、蛍光発生材料を含有する薬剤を使用しても良い。この場合には、蛍光を励起する波長の光を発生させる発光素子44aを使用し、発生する蛍光の波長の光を検出する光ディティクタ44cを使用すれば良い。
また、マーキングMとしては、放射性同位元素を含有する薬剤を使用しても良い。この場合には、センサ44としてシンチレータ等を使用すれば良い。
また、マーキングMとしては、磁性材料を含有する薬剤を使用しても良い。また、磁性体そのものを薬剤の代わりに使用しても良い。この場合には、センサ44として磁気センサを使用すれば良い。
また、マーキングMとしては、金属材料を使用しても良い。この場合の動作については、第2実施例にて記載してある。
Further, in this embodiment, ink is used, but the same effect can be obtained by using any dye as long as it can be detected. An example is a dye used for endoscopy such as methylene blue. In this case, the detection wavelength region of the optical detector 44c may be selected to be optimal. Further, as the marking M, a chemical containing a fluorescence generating material may be used. In this case, a
In addition, as the marking M, a medicine containing a radioisotope may be used. In this case, a scintillator or the like may be used as the
As the marking M, a medicine containing a magnetic material may be used. Moreover, you may use a magnetic body itself instead of a chemical | medical agent. In this case, a magnetic sensor may be used as the
Further, as the marking M, a metal material may be used. The operation in this case is described in the second embodiment.
また、上記制御部43は、患部Xの位置を示す指標である特定のマーキングMを、マーキングMの数として予め記憶されているメモリ43aを有しており、センサ44によって検出されたマーキングMをカウントし、メモリ43aに記憶されている数と一致したときに上記ヒータ47を作動させて加熱させる機能を有している。つまり、制御部43は、センサ44により検出されたマーキングMが特定のマーキングであるか否かを判断している。
Further, the
このように構成されたカプセル型医療装置システム1、投薬用カプセル2及びカプセル型医療装置10により、患者Pの体内の患部Xに対して薬剤Aを投薬する場合について以下に説明する。
まず、患者Pは、病院等の医療機関にて医師の指示のもとカプセル型医療装置10を飲み込んで経口投入する。この際、カプセル型医療装置10は、投入時に図示しないスイッチが入るようになっており、電池23から電力供給された制御処理部21が作動し始める。経口投入されたカプセル型医療装置10は、図8に示すように、患者Pの体内を移動する間に、制御処理部21が吐出機構13を作動させて、体内の消化器官に対して、例えば、5分に1回毎にマーキングMを施す。即ち、制御処理部21は、ピエゾ素子20に作動信号等を送って伸張させる。これにより、リザーバ19が押圧されて吐出口18からマーキング剤Wが吐出されるので、消化器官にマーキングMが施される。また、同時に制御処理部21は、観察系12を作動させて、体内各部を、例えば、1秒に2回毎に撮像して生体情報を取得する。更に、制御処理部21は、観察系12で取得された生体情報とマーキングMの位置とを関連付けて、逐次メモリ22に記憶する。
The case where the medicine A is administered to the affected part X in the body of the patient P by the capsule
First, the patient P swallows the capsule
そして、カプセル型医療装置10の排泄により体内の観察が終了した後、該カプセル型医療装置10を回収する。回収後、メモリ22に記憶されているマーキングMの位置に関連付けられた生体情報を、図3に示すPC30に入力する。
即ち、患者Pの体内から排出された観察用カプセル10を回収した後、容器33に収納する。容器33に収納することにより、その後操作する人が不潔感をもつことなく操作を行うことができる。そして、容器33を容器設置部34に設置すると、設置検知スイッチ38がONになる。これにより、スイッチ37がONになり、電力供給手段35及び無線受信手段36が駆動される。電力供給手段35が動作すると、カプセル型医療装置10に向けて電力を供給する。カプセル型医療装置10の電力受信手段24は、この供給された電力を受け、無線送信手段14及びメモリ22に分配して供給する。この電力を受けて無線送信手段14は、メモリ22に蓄えられた生体情報を観察情報受信機31に向けて無線送信する。そして、無線送信手段36は、送信された生体情報を受信すると共に、ケーブル32を介してPC30に伝達する。
Then, after the observation inside the body is completed by excretion of the capsule
That is, the
PC30で受けた生体情報は、操作者が確認し投薬位置を決定する。また、生体情報は、マーキングMの位置(個数)と関連付けられて保存されているため、投薬位置を決定すると、直ちにマーキングMの何個目で投薬を開始すればよいか判断することができる。マーキングMの個数を判断するのは、操作者でも良いが、PC30が自動的にマーキングMの個数を認識し、後述するように、投薬用カプセル2に設定するように構成しても構わない。
なお、本実施形態では、無線送信手段14は、電磁波を使用した通信方式を採用しているが、通信方式は電磁波以外の方法で実施しても良く、例えば、カプセル型医療装置10及び容器33を、赤外線透過型の材料で構成すると共に、容器33を容器設置部34に設置したときに、観察情報受信機31に設けられた赤外線センサと、カプセル型医療装置10に設けられた赤外線発光素子とが対向するように配置すれば、赤外線通信にて生体情報を伝達することが可能となる。
The biological information received by the
In the present embodiment, the
また、医師等の操作者は、PC30に入力された生体情報である撮像画像に基づいて、体内に異常がないか診断を行う。その結果、撮像画像に病変等を発見した場合には、該病変等から投薬が必要な表在疾患等の患部Xを特定する。患部Xを特定した後、医師は、患部Xの位置を示すマーキングMを特定する。即ち、生体情報とマーキングMの位置とが関連付けられて送られてくるので、患部Xを特定した生体情報から該生体情報に関連したマーキングMの特定が行える。つまり、特定のマーキングMを、何番目のマーキングMであるというようなマーキングMの数で特定する。
なお、本実施形態の説明においては、図9に示すように、患部Xの位置が、10番目のマーキングMと11番目のマーキングMとの間に位置しているものとし、患部Xの位置を示す特定のマーキングMを10番目のマーキングとしている。
An operator such as a doctor diagnoses whether there is an abnormality in the body based on a captured image that is biometric information input to the
In the description of the present embodiment, as shown in FIG. 9, it is assumed that the position of the affected part X is located between the tenth marking M and the eleventh marking M, and the position of the affected part X is The specific marking M shown is the tenth marking.
次いで、医師は、図3に示すように、投薬用カプセル2をPC30に接続された通信機39に載置して、PC30からメモリ43aに特定のマーキングMの情報を設定値として入力する。即ち、10番目のマーキングMが特定のマーキングMであることを示すデータをPC30から通信機39を介して、通信機39に載置された投薬用カプセル2に送信する。入力後、患者Pは、医師等から投薬用カプセル2を入手する。なお、患者Pは、投薬用カプセル2の入手後、医療機関等を離れても構わない。
その後、患者Pは、決められた投薬時間に従って、投薬用カプセル2を飲み込んで経口投入する。経口投入された投薬用カプセル2は、体内を移動する間に、カプセル型医療装置10によって施されたマーキングMをセンサ44が検出する。センサ44は、管腔の情報を取得し、制御部43でマーキングMの有無を判断する。
Next, as shown in FIG. 3, the doctor places the
Thereafter, the patient P swallows the
制御部43は、マーキングMの情報と、メモリ43aに予め設定されている特定のマーキングMの情報とを比較して判断する。即ち、制御部43は、送られてくるマーキングMの数をカウントすることにより、特定のマーキングMであるか否かを判断する。例えば、特定のマーキングが10番目のマーキングMであると予め設定されているので、最初に検出されたマーキングMは、特定のマーキングMではないと判断する。また、次に送られてくるマーキングMは、カウント数により2番目のマーキングMであるので、特定のマーキングMではないと判断する。
The
このように、投薬用カプセル2は、各マーキングMを検出しながら生体内を移動する。ここで、投薬用カプセル2が、10番目のマーキングMを検出した場合には、制御部43は、カウント数により送られてきたマーキングMが10番目のマーキングM、即ち、特定のマーキングMであると判断してヒータ47を作動させる。該ヒータ47は、制御部43からの信号を受けて、瞬間的に加熱して気泡を発生させ、該気泡の圧力により薬剤口46の薄膜を破る。
薬剤口46の薄膜が破れると、図10に示すように、リザーバ41内の薬剤Aが薬剤口46から筐体40外部に放出される。即ち、特定のマーキングMは、患部Xの位置を示しているので、患部Xに対して直接的に投薬を行うことができる。
Thus, the
When the thin film of the
上述したカプセル型医療装置システム1、投薬用カプセル2及びカプセル型医療装置10によれば、カプセル型医療装置10を経口投入することで、体腔内にマーキングMを残しながら生体情報の取得を行え、無線送信手段14を介してPC30にて、生体情報とマーキングMの情報との受信が行える。これらの情報から、体内の患部XをマーキングMにより容易に検出することができる。また、その後経口投入された投薬用カプセル2により、投薬を行う特定のマーキングMの位置で薬剤Aの放出を行える。このように、体腔内の所望する部位(患部)に、容易且つ直接的にアプローチすることができると共に、投薬を行うことができる。また、患部Xを検出してから投薬を行うのではなく、特定のマーキングMを検出して投薬を行うので、投薬を行う前に患部Xを通過することがなく、患部Xに対して効率良く投薬を行うことができる。
According to the capsule
また、患部の位置を示す指標を、生体内の特徴のある形状や色等の部位ではなく、カプセル型医療装置10によって施されたマーキングとしているので、より明確な指標とすることできる。従って、センサ44が、確実且つ高精度にマーキング(特定のマーキング)の検出を行うので、投薬の信頼性を向上することができる。
更に、医療装置3をカプセル型医療装置10により構成するので、簡便に患者Pに経口投入することができる。
また、制御部43は、センサ44によって検出されたマーキングの数をカウントし、メモリ43aに予め記憶されている数と一致したときに、いま検出したマーキングMが特定のマーキングであると判断して薬剤Aの放出を行なっている。このように、制御部43は、特定のマーキングMを単なるマーキングMのカウントによって判断するので、複雑な判断回路等を備える必要がなく、構成を容易にすることができると共に、検出ミスが低減されて信頼性を向上することができる。
In addition, since the index indicating the position of the affected part is not a site having a characteristic shape or color in the living body but a marking applied by the capsule
Furthermore, since the
Further, the
また、本実施例では、カプセル型医療装置10を体内から排出されてから回収してメモリ22に蓄えられた生体情報を取り出したが、生体観察中に随時無線通信手段を使い、カプセル外部に伝達する構成としても構わない。
また、本実施では、一定時間間隔で間欠的にマーキングMを施すこととしたが、一定時間間隔でなくても構わない。例えば、体内での一定移動距離間隔でマーキングMを施すようにしても構わない。この場合には、例えば、図11に示すように、筐体11内に、観察用計測手段(移動量検出手段)50を設ければ良い。該観察用計測手段50は、体内の消化管内腔壁の表面情報である表面画像を取得する情報取得手段51と、該情報取得手段51により取得した表面情報の経時的変化に基づいて移動距離を算出する画像処理部52とを備えている。また、情報取得手段51は、消化管内腔壁の表面に光Lを照射するLED53と、消化管内腔壁の表面で反射された光Lの画像、即ち、表面画像を読み取る光学センサ54とを有している。LED53は、筐体11の軸方向に光Lを照射するように例えば、水平配置されている。また、照射された光Lは、反射ミラー55a、55bによって照射方向が変更され、消化管内腔壁の表面に向けて斜めに照射できるようになっている。また、光学センサ54は、反射した光Lを受光できる位置に配されている。なお、光学的に光Lを透過できるように、情報取得手段50近傍の筐体11には、透明カバー11aを設ければ良い。
Further, in this embodiment, the capsule
In the present embodiment, the marking M is intermittently performed at regular time intervals. However, the markings may not be regular time intervals. For example, the marking M may be applied at a constant movement distance interval in the body. In this case, for example, as shown in FIG. 11, an observation measurement means (movement amount detection means) 50 may be provided in the
上記画像処理部52は、光学センサ54で読み取った消化管内腔壁の表面画像を、例えば、毎秒1500〜6000回の高速で撮影(スキャン)すると共に、撮影した各画像の色や形状等の特徴に着目し、これらの経時的変化から移動距離を算出するようになっている。そして、算出した移動距離を制御処理部21に知らせるように構成すれば良い。こうすることで、制御処理部21は、上述したように、体内の一定移動距離毎に吐出機構13を作動させて、マーキングMを施すことができる。
このように、一定移動距離でマーキングMを施すことで、マーキングM同士が接近しすぎることがなく、体腔内にマーキングMを施すことができる。
更に、筐体11内に、位置センサを設けて、該位置センサの出力に基づいて一定間隔毎にマーキングMを施しても構わない。この場合には、位置センサには、例えば、NDI社のAURORA等が使用することができる。
The
In this manner, by applying the marking M at a constant movement distance, the markings M can be applied in the body cavity without the markings M being too close to each other.
Furthermore, a position sensor may be provided in the
次に、本発明に係る第2実施形態について、図12及び図13を参照して説明する。なお、第2実施形態において第1実施形態と同一の構成要素については、同一の符号を付しその説明を省略する。
第2実施形態と第1実施形態との異なる点は、第1実施形態のカプセル型医療装置システム1では、カプセル型医療装置10により体内にマーキングMを施していたのに対し、第2実施形態のカプセル型医療装置システム60では、内視鏡装置(医療装置)61により患部Xを特定すると共に該患部Xの位置を示す特定のマーキングMを施し、該特定のマーキングMを検出したときに投薬を行う点である。なお、本実施形態において、特定のマーキングMは、磁性体の性質を有しているものである。
このマーキングMについては、磁性体薬剤の他、内視鏡で行う処置で使用されているクリップ等が使用できる。
Next, a second embodiment according to the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS. In the second embodiment, the same components as those in the first embodiment are denoted by the same reference numerals, and the description thereof is omitted.
The difference between the second embodiment and the first embodiment is that, in the capsule
For this marking M, in addition to the magnetic drug, a clip or the like used in a procedure performed with an endoscope can be used.
即ち、本実施形態のカプセル型医療装置システム60は、図12に示すように、上記内視鏡装置61及び経口投入される投薬用カプセル70を備えている。
内視鏡装置61は、体内に挿入可能な可撓性を有する内視鏡挿入部62を有しておる。該内視鏡挿入部62は、先端に体内を観察する図示しない観察手段(生体情報取得手段)を有している。また、内視鏡挿入部62内には、先端の開口から基端側に配された図示しない処置具挿入孔に亘って挿通するように形成された、図示しない処置具チャンネルが形成されている。そして、この処置具チャンネル内に、上記磁性体のマーキングMを体腔内に施す処置具(マーキング手段)63を挿入できるようになっている。
That is, as shown in FIG. 12, the capsule
The
また、上記投薬用カプセル70は、図13に示すように、筐体40内に、リザーバ41、放出手段42、制御部43、電池45及び上記特定のマーキングMを検出する磁気センサ(検出手段)71とを備えている。また、制御部43は、磁気センサ71が、特定のマーキングMを検出したときに放出手段42を作動させるようになっている。
Further, as shown in FIG. 13, the
本実施形態のカプセル型医療装置システム60により、患者Pの体内の患部Xに対して薬剤Aを投薬する場合について、以下に説明する。
まず、患者Pは、病院等の医療機関にて、内視鏡検査を受診し、体内に異常がないか診断を受ける。即ち、内視鏡装置61の内視鏡挿入部62を体内に挿入して、観察系により体内を観察する。この内視鏡検査により、消化器官に表在疾患等の患部Xが発見された場合には、医師は、処置具63を処置具チャンネル内に挿入して、患部Xの位置を示す磁性体である特定のマーキングMを消化気管内に施す。この内視鏡検査後、患者Pは、医師から投薬用カプセル70を入手する。なお、患者Pは、投薬用カプセル70を入手した後、医療機関等を離れても構わない。
The case where the medicine A is administered to the affected part X in the body of the patient P by the capsule
First, a patient P undergoes an endoscopic examination at a medical institution such as a hospital and is diagnosed for any abnormality in the body. That is, the
次いで、患者Pは、投薬用カプセル70を飲み込んで経口投入する。経口投入された投薬用カプセル70は、磁気センサ71により消化器官内を観察しながら移動する。ここで、特定のマーキングMに到達すると、磁気センサ71が、磁性体である特定のマーキングMに反応してその位置を検出する。特定のマーキングMを検出すると、磁気センサ71は、その旨を制御部43に送る。該制御部43は、磁気センサ71からの信号を受けて、ヒータ47を作動させる。該ヒータ47は、制御部43からの信号を受けて、瞬間的に加熱して気泡を発生させ、該気泡の圧力により薬剤口46の薄膜を破る。これにより、リザーバ41内の薬剤Aが薬剤口46より筐体40外部に放出される。従って、患部Xに対して直接的に投薬を行うことができる。また、体内を移動している間において、特定マーキングMを検出したと同時に薬剤Aの放出が行えるので、検出から放出に至る時間を必要としない。従って、より特定のマーキングAの近傍で薬剤の放出が行えるので、高精度に患部Xに対して投薬を行うことができる。
Next, the patient P swallows the
また、本実施例では、磁気センサ71を用いたが、上記クリップを使用した場合では、
図14に示すように、処置具63として、体腔内に内視鏡用クリップを施すことができるクリップ装着用処置具を採用すれば良い。また、投薬用カプセル70に、発光素子及び受光素子を設け、発光素子で発した光の反射率の変化を検出しても良い。(クリップは、金属でできているので、クリップがあれば反射光量が増大する)また、受光素子は、CMOS画像センサやCCD等のイメージセンサでも良い。その場合には、画像処理技術を使用してマーキングM(クリップ)を検出しても良い。
In this embodiment, the
As shown in FIG. 14, as the
なお、本発明の技術分野は、上記実施形態に限定されるものではなく、本発明の趣旨を逸脱しない範囲において種々の変更を加えることが可能である。
例えば、上記第1実施形態において、制御部が、センサから送られてきたマーキングの数をカウントすることにより、特定のマーキングであるか否かを判断したが、これに限られることはない。例えば、生体内にマーキングを施す際に、異なる形状、大きさや色等のマーキングを施し、この形状、大きさや色等の違いで特定のマーキングを判断しても構わない。
また、患部に位置を示す指標を特定のマーキングとしたが、これに限られず、例えば、生体内の特徴のある形状や色等の部位を指標としても構わない。
The technical field of the present invention is not limited to the above embodiment, and various modifications can be made without departing from the spirit of the present invention.
For example, in the first embodiment, the control unit determines whether the marking is a specific marking by counting the number of markings sent from the sensor. However, the present invention is not limited to this. For example, when marking a living body, markings with different shapes, sizes, colors, and the like may be performed, and specific markings may be determined based on differences in the shapes, sizes, colors, and the like.
In addition, although the index indicating the position of the affected part is the specific marking, the present invention is not limited to this, and for example, a part having a characteristic shape or color in the living body may be used as the index.
また、上記各実施形態において、ヒータを利用して薬剤を放出したが、これに限られるものではなく、制御部によって放出手段を制御することができる構成
であれば構わない。例えば、カプセル型医療装置の吐出機構のようにピエゾ素子を利用して薬剤を放出させても構わない。また、浸透圧を駆動力として薬剤を放出させても良いし、親水性高分子等が吸水して膨潤する時に発生する膨潤圧を利用して薬剤を放出させるようにしても構わない。
また、特定のマーキングを1つとしたが、これに限られず、患部が数個所ある場合には、それぞれの患部の位置を示す特定のマーキングを検出したときに、投薬するようにしても構わない。更に、患部を挟んで前後のマーキングを特定のマーキングとし、最初の特定のマーキングで投薬を開始し、次のマーキングで投薬を停止するよう設定しても構わない。こうすることで、薬剤を効率よく患部に対して投与することができ、複数の患部がある場合には有効である。
また、投薬用カプセルに複数のリザーバを設け、各リザーバに異なる種類の薬剤を収納させ、患部に応じた投薬を行なっても構わない。
また、第2実施形態において、投薬用カプセルは、磁気センサを利用して磁性体である特定のマーキングを検出したが、これに限られず、内視鏡検査等によって特定の形状や色等の特定のマーキングを施し、該特定のマーキングを検出できるように構成されていれば良い。
In each of the above embodiments, the drug is released using the heater. However, the present invention is not limited to this, and any configuration may be used as long as the control unit can control the release means. For example, the medicine may be released using a piezo element like a discharge mechanism of a capsule medical device. Further, the drug may be released using osmotic pressure as a driving force, or the drug may be released using a swelling pressure generated when the hydrophilic polymer or the like absorbs water and swells.
In addition, the number of specific markings is one. However, the present invention is not limited to this, and when there are several affected parts, medication may be administered when specific markings indicating the positions of the affected parts are detected. Furthermore, the markings before and after the affected part may be set as specific markings, and the medication may be set to start at the first specific marking and stopped at the next marking. By carrying out like this, a chemical | medical agent can be efficiently administered with respect to an affected part, and when there exists a several affected part, it is effective.
Further, a plurality of reservoirs may be provided in the medication capsule, and different types of medicines may be accommodated in each reservoir to perform medication according to the affected area.
In the second embodiment, the medication capsule uses a magnetic sensor to detect a specific marking that is a magnetic substance. However, the present invention is not limited to this, and a specific shape, color, or the like can be specified by endoscopy or the like. It is only necessary to be configured so that the specific marking can be detected.
更に、上記各実施形態においては、体内の各部を撮像した撮像画像を生体情報としたが、これに限られず、pH値や圧力や体液等でも構わない。この場合には、撮像部に変えて各生体情報を取得可能とするように構成すれば良い。
また、撮像部は、患者の体内を一定時間の間隔で断続的且つ無作為に撮影するものを適用したが、これに限られず、例えば、ビデオ等のように体内を連続的に撮影するものでも構わない。この場合は、ビデオ信号が記憶される。
また、ビデオ等により体内を撮影するものに限定されず、患者の体内情報を検出して体外装置にデータ送信可能なものであれば構わない。例えば、ヘモグロビンセンサを内蔵した出血検査用カプセルや、pH値、圧力値、温度、微生物量、酵素及び遺伝子異常等の体内情報を断続的に長時間取得する体内情報検査用カプセルや、超音波画像等の断続的に取得する超音波カプセルでも適用可能である。
Furthermore, in each of the above-described embodiments, the captured image obtained by capturing each part in the body is used as the biological information. In this case, the biometric information may be acquired instead of the imaging unit.
In addition, the imaging unit is a device that intermittently and randomly captures a patient's body at regular time intervals, but is not limited thereto, and may be, for example, a device that continuously images the body such as a video. I do not care. In this case, a video signal is stored.
Moreover, it is not limited to what image | photographs the inside of a body by a video etc., What is necessary is that it can detect in-vivo information of a patient and can transmit data to an external device. For example, a hemorrhage test capsule with a built-in hemoglobin sensor, an in-vivo information test capsule that intermittently acquires in-vivo information such as pH value, pressure value, temperature, microbial load, enzyme and gene abnormality, and ultrasonic image It is also possible to apply ultrasonic capsules acquired intermittently.
なお、本発明には、以下のものが含まれる。
〔付記項1〕
生体内に経口投入されるカプセル状の筐体内に、薬剤を保持する薬剤保持部と、
前記薬剤保持部に保持された前記薬剤を放出する放出手段と、
前記放出手段を動作させる放出制御手段と、
薬剤放出位置を示す指標を検出する検出手段とを備え、
前記放出制御手段は、前記検出手段の出力に基づき前記放出制御手段を動作させることを特徴とする投薬用カプセル。
〔付記項2〕
付記項1に記載の投薬用カプセルにおいて、
前記指標が、生体内に施された特定のマーキングであることを特徴とする投薬用カプセル。
〔付記項3〕
付記項2に記載の投薬用カプセルにおいて、
前記検出手段が、生体内に施された複数のマーキングを検出するものであり、
前記放出制御手段が、前記特定のマーキングを前記マーキングの数として予め記憶するメモリを有し、前記検出手段によって検出された前記マーキングをカウントすることにより、前記メモリに記憶されている数と一致したときに前記放出手段を動作させることを特徴とする投薬用カプセル。
〔付記項4〕
生体内に経口投入されるカプセル状の筐体と、
生体情報を取得する生体情報取得手段と、
体腔内に指標を残すマーキング手段と、
前記生体情報取得手段で取得した生体情報と前記マーキング手段で体腔内に残した前記指標とを前記筐体の外部に伝達する伝達手段とを有することを特徴とするカプセル型医療装置。
〔付記項5〕
付記項4に記載のカプセル型医療装置において、
前記生体情報取得手段で取得した生体情報と、前記マーキング手段で生体内に残した指標情報とを関連付ける情報処理部を有することを特徴とするカプセル型医療装置。
〔付記項6〕
付記項5に記載のカプセル型医療装置において、
前記情報処理部で処理された情報を記憶する記憶手段を有することを特徴とするカプセル型医療装置。
〔付記項7〕
付記項4から6のいずれか1項に記載のカプセル型医療装置において、
前記マーキング手段が、間欠動作を行うことを特徴とするカプセル型医療装置。
〔付記項8〕
付記項4に記載のカプセル型医療装置において、
前記指標が、磁性体材料、蛍光薬剤、色素、放射性同位体又は金属材料の少なくともいずれか1つを含有することを特徴とするカプセル型医療装置。
〔付記項9〕
体腔内の生体情報を得る生体情報取得手段と体腔内に指標を残すマーキング手段とを有する医療装置と、
カプセル状の外装部と、前記医療装置が体腔内に残した指標を検出する指標検出手段と、薬剤収納部と、前記薬剤収納部内の薬剤を放出する薬剤放出部と、前記指標検出手段の情報に基づき薬剤放出部を制御する制御部とを有するカプセル型医療装置とを有するカプセル型医療装置システム。
〔付記項10〕
付記項9に記載のカプセル型医療装置システムにおいて、
前記医療装置が、内視鏡であることを特徴とするカプセル型医療装置システム。
〔付記項11〕
付記項10に記載のカプセル型医療装置システムにおいて、
前記マーキング手段が、内視鏡用クリップであることを特徴とするカプセル型医療装置。
〔付記項12〕
付記項9に記載のカプセル型医療装置システムにおいて、
前記医療装置が、カプセル状の外装部に、前記生体情報取得手段と、前記マーキング手段と、前記生体情報取得手段で検出した生体情報と前記マーキング手段の動作情報とを前記外装部の外部に伝達する情報伝達部とを有する第2のカプセル型医療装置と、
前記情報伝達部で前記外装部の外部に伝達された情報を受信する受信装置とで構成されることを特徴とするカプセル型医療装置システム。
〔付記項13〕
付記項12に記載のカプセル型医療装置システムにおいて、
前記第2のカプセル型医療装置が、前記生体情報取得手段で検出した生体情報と、前記マーキング手段の動作情報とを関連付けて保存する記憶手段とを有しており、
前記情報伝達部が、前記記憶手段に記憶された情報を前記外装部の外部に伝達することを特徴とするカプセル型医療装置システム。
〔付記項14〕
付記項12又は13に記載のカプセル型医療装置システムにおいて、
前記情報伝達部が、赤外線通信手段を有することを特徴とするカプセル型医療装置システム。
〔付記項15〕
付記項12又は13に記載のカプセル型医療装置システムにおいて、
前記情報伝達部が、電磁波による通信手段を有することを特徴とするカプセル型医療装置システム。
〔付記項16〕
付記項12から14のいずれか1項に記載のカプセル型医療装置システムにおいて、
前記第2のカプセル型医療装置が、間欠的に指標を残すことを特徴とするカプセル型医療装置システム。
〔付記項17〕
付記項9に記載のカプセル型医療装置システムにおいて、
前記マーキング手段が、間欠的に指標を残すことを特徴とするカプセル型医療装置システム。
〔付記項18〕
付記項17に記載のカプセル型医療装置システムにおいて、
前記マーキング手段が、一定時間間隔で指標を残すことを特徴とするカプセル型医療装置システム。
〔付記項19〕
付記項17に記載のカプセル型医療装置システムにおいて、
位置検出手段を備え、
該位置検出手段で得た位置情報を元に、前記マーキング手段が指標を残すことを特徴とするカプセル型医療装置システム。
〔付記項20〕
付記項17に記載のカプセル型医療装置システムにおいて、
前記第2のカプセル型医療装置が、移動量検出手段を有し、該移動量検出手段の出力に基づいて前記マーキング手段が指標を残すことを特徴とするカプセル型医療装置システム。
〔付記項21〕
付記項17から20のいずれか1項に記載のカプセル型医療装置システムにおいて、
前記指標が、生体体腔内組織に対し反射率の低い薬剤であることを特徴とするカプセル型医療装置システム。
〔付記項22〕
付記項17から20のいずれか1項に記載のカプセル型医療装置システムにおいて、
前記指標が、生体体腔内組織に対し反射率の高い薬剤であることを特徴とするカプセル型医療装置システム。
〔付記項23〕
付記項17から20のいずれか1項に記載のカプセル型医療装置システムにおいて、
前記指標が、磁性体材料であることを特徴とするカプセル型医療装置システム。
〔付記項24〕
付記項17から20のいずれか1項に記載のカプセル型医療装置システムにおいて、
前記指標が、蛍光材料であることを特徴とするカプセル型医療装置システム。
〔付記項25〕
生体内を観察するステップと、
生体内での投薬位置を決定するステップと、
前記投薬位置近傍に指標をつけるステップと、
前記指標を検出する手段と、薬剤収納部と、薬剤放出部と、薬剤放出制御部とを有する投薬用カプセルを体腔内に挿入するステップと、
前記指標を検出するステップと、
前記薬剤放出部の制御を行うステップとを備えることを特徴とする制御方法。
〔付記項26〕
生体内を観察するステップと、
指標を生体内に残すステップと、
生体内を観察するステップで得た生体情報と、指標を生体内に残すステップを行ったことを関連付けて生体情報として記録するステップと、
前記生体情報から投薬位置を決定するステップと、
前記指標を検出する手段と、薬剤収納部と、薬剤放出部と、薬剤放出制御手段とを有する投薬用カプセルに投薬位置を指定するステップと、
投薬用カプセルを体腔内に挿入するステップと、
前記指標を検出するステップと、
投薬位置を検出するステップと、
前記薬剤放出部の制御を行うステップとを有することを特徴とする制御方法。
The present invention includes the following.
[Additional Item 1]
In a capsule-like casing that is orally injected into a living body, a drug holding unit that holds the drug,
A release means for releasing the drug held in the drug holding unit;
Release control means for operating the release means;
A detection means for detecting an index indicating the drug release position,
The administration capsule characterized in that the release control means operates the release control means based on the output of the detection means.
[Appendix 2]
In the capsule for medication according to
The medication capsule, wherein the index is a specific marking applied in a living body.
[Additional Item 3]
In the capsule for medication according to
The detection means detects a plurality of markings applied in the living body,
The release control means has a memory that pre-stores the specific marking as the number of markings, and by counting the markings detected by the detection means, it coincides with the number stored in the memory A capsule for dispensing characterized in that the release means is sometimes operated.
[Additional Item 4]
A capsule-like housing that is orally injected into a living body;
Biometric information acquisition means for acquiring biometric information;
Marking means for leaving an indicator in the body cavity;
A capsule medical apparatus, comprising: a transmission unit configured to transmit the biological information acquired by the biological information acquisition unit and the index left in the body cavity by the marking unit to the outside of the housing.
[Additional Item 5]
In the capsule medical device according to
A capsule medical device, comprising: an information processing unit that associates the biological information acquired by the biological information acquisition unit with the index information left in the living body by the marking unit.
[Additional Item 6]
In the capsule medical device according to
A capsule medical device comprising storage means for storing information processed by the information processing unit.
[Additional Item 7]
In the capsule medical device according to any one of
The capsule medical device, wherein the marking means performs an intermittent operation.
[Additional Item 8]
In the capsule medical device according to
The capsule medical device, wherein the index contains at least one of a magnetic material, a fluorescent agent, a dye, a radioisotope, or a metal material.
[Additional Item 9]
A medical device having biological information acquisition means for obtaining biological information in a body cavity and marking means for leaving an index in the body cavity;
Capsule-shaped exterior part, index detection means for detecting the index left in the body cavity by the medical device, drug storage part, drug release part for releasing the drug in the drug storage part, and information of the index detection means Capsule type medical device system comprising: a capsule type medical device having a control unit for controlling the drug release unit based on the above.
[Appendix 10]
In the capsule medical device system according to
A capsule medical device system, wherein the medical device is an endoscope.
[Additional Item 11]
In the capsule medical device system according to
The capsule medical device, wherein the marking means is an endoscope clip.
[Additional Item 12]
In the capsule medical device system according to
The medical device transmits the biological information acquisition means, the marking means, the biological information detected by the biological information acquisition means, and the operation information of the marking means to the outside of the exterior portion in a capsule-shaped exterior portion. A second capsule medical device having an information transmission unit for
A capsule medical device system comprising: a receiving device that receives information transmitted to the outside of the exterior unit by the information transmitting unit.
[Additional Item 13]
In the capsule medical device system according to
The second capsule medical device has storage means for storing the biological information detected by the biological information acquisition means and the operation information of the marking means in association with each other,
The capsule medical device system, wherein the information transmission unit transmits information stored in the storage unit to the outside of the exterior unit.
[Additional Item 14]
In the capsule medical device system according to
The capsule medical device system, wherein the information transmission unit includes infrared communication means.
[Appendix 15]
In the capsule medical device system according to
The capsule medical device system, wherein the information transmission unit includes communication means using electromagnetic waves.
[Additional Item 16]
The capsule medical device system according to any one of
The capsule-type medical device system, wherein the second capsule-type medical device leaves an index intermittently.
[Additional Item 17]
In the capsule medical device system according to
The capsule medical device system, wherein the marking means leaves an index intermittently.
[Appendix 18]
In the capsule medical device system according to
The capsule medical device system, wherein the marking means leaves an index at regular time intervals.
[Appendix 19]
In the capsule medical device system according to
A position detecting means;
A capsule medical device system, wherein the marking means leaves an index based on position information obtained by the position detection means.
[Additional Item 20]
In the capsule medical device system according to
The capsule-type medical device system, wherein the second capsule-type medical device has a movement amount detection unit, and the marking unit leaves an index based on an output of the movement amount detection unit.
[Appendix 21]
In the capsule medical device system according to any one of
The capsule medical device system, wherein the index is a drug having a low reflectance with respect to a tissue in a living body cavity.
[Appendix 22]
In the capsule medical device system according to any one of
The capsule medical device system, wherein the index is a drug having a high reflectance with respect to a tissue in a living body cavity.
[Additional Item 23]
In the capsule medical device system according to
The capsule medical device system, wherein the index is a magnetic material.
[Appendix 24]
In the capsule medical device system according to any one of
The capsule medical device system, wherein the index is a fluorescent material.
[Appendix 25]
Observing the inside of the living body;
Determining a dosing position in vivo;
Marking the vicinity of the dosing position;
Inserting a medication capsule having a means for detecting the index, a medicine storage section, a medicine release section, and a medicine release control section into the body cavity;
Detecting the indicator;
And a step of controlling the medicine release unit.
[Additional Item 26]
Observing the inside of the living body;
Leaving the indicator in vivo,
Correlating the biological information obtained in the step of observing the inside of the living body with the fact that the step of leaving the index in the living body is performed, and recording as biological information;
Determining a medication position from the biological information;
Designating a dosing position on a dosing capsule having means for detecting the indicator, a medicine storage section, a medicine release section, and a medicine release control means;
Inserting a medication capsule into the body cavity;
Detecting the indicator;
Detecting a dosing position;
And a control method for controlling the medicine release section.
A 薬剤
M マーキング、クリップ(指標)
1、60 カプセル型医療装置システム
2、70 投薬用カプセル(カプセル型医療装置)
3 医療装置
10 カプセル型医療装置(第2のカプセル型医療装置)
11、40 筐体(外装部)
12 観察系(生体情報取得手段)
13 吐出機構(マーキング手段)
14 無線送信手段(伝達手段、情報伝達部)
30 パーソナルコンピュータ(受信装置)
41 リザーバ(薬剤保持部)
42 放出手段(薬剤放出部)
43 制御部(放出制御手段)
44 センサ(検出手段、指標検出手段)
61 内視鏡装置(医療装置)
63 処置具(マーキング手段)
A medicine M marking, clip (indicator)
1, 60 Capsule type
3
11, 40 Case (exterior part)
12 Observation system (biological information acquisition means)
13 Discharge mechanism (marking means)
14 Wireless transmission means (transmission means, information transmission part)
30 Personal computer (receiving device)
41 Reservoir (drug holder)
42 Release means (drug release part)
43 Control unit (release control means)
44 sensors (detection means, index detection means)
61 Endoscopic device (medical device)
63 Treatment tool (marking means)
Claims (3)
カプセル状の外装部と、前記医療装置が前記体腔内に残した前記複数の指標を検出する指標検出手段と、薬剤を保持する薬剤保持部と、該薬剤保持部内の前記薬剤を放出する薬剤放出部と、前記指標検出手段の情報に基づき前記薬剤放出部を制御する制御部とを有するカプセル型医療装置と、
を備え、
前記制御部は、前記複数の指標のうちの前記薬剤の放出を行う指標の順番を予め記憶すると共に、前記指標検出手段が前記指標を検出した数が前記制御部に記憶された前記薬剤の放出を行う前記指標の順番に一致したときに、前記薬剤放出部に前記薬剤を放出させることを特徴とするカプセル型医療装置システム。 A medical device having biological information acquisition means for obtaining biological information in the body cavity and marking means for intermittently leaving a plurality of indices in the body cavity;
Capsule-shaped exterior part, index detection means for detecting the plurality of indices left in the body cavity by the medical device, a drug holding part for holding a drug, and drug release for releasing the drug in the drug holding part And a capsule medical device having a control unit that controls the drug release unit based on information of the index detection unit,
With
The control unit stores in advance the order of the indices for releasing the drug among the plurality of indices, and the number of the indices detected by the index detection unit is stored in the control unit. The capsule medical device system causes the medicine release unit to release the medicine when the order of the indices is determined.
前記医療装置が、カプセル状の外装部に、前記生体情報取得手段と、前記マーキング手段と、前記生体情報取得手段で取得した前記生体情報と前記マーキング手段の動作情報とを前記外装部の外部に伝達する情報伝達部とを有する第2のカプセル型医療装置と、
前記情報伝達部で前記外装部の外部に伝達された情報を受信する受信装置とで構成されることを特徴とするカプセル型医療装置システム。 The capsule medical device system according to claim 1 ,
The medical device is arranged in a capsule-shaped exterior part with the biological information acquisition means, the marking means, and the biological information acquired by the biological information acquisition means and the operation information of the marking means outside the exterior part. A second capsule medical device having an information transmitting unit for transmitting;
A capsule medical device system comprising: a receiving device that receives information transmitted to the outside of the exterior unit by the information transmitting unit.
前記医療装置は、前記生体情報と前記指標を残した位置とを関連づけて記憶する記憶手段を有することを特徴とするカプセル型医療装置システム。 The capsule medical device system according to claim 1 ,
The capsule medical device system, characterized in that the medical device has storage means for storing the biological information and the position where the index is left in association with each other.
Priority Applications (6)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003338260A JP4520126B2 (en) | 2003-09-29 | 2003-09-29 | Capsule type medical device system |
| US10/951,099 US8021356B2 (en) | 2003-09-29 | 2004-09-27 | Capsule medication administration system, medication administration method using capsule medication administration system, control method for capsule medication administration system |
| CN2004800278990A CN1856290B (en) | 2003-09-29 | 2004-09-28 | Capsule dosing system |
| EP04788441A EP1669052A4 (en) | 2003-09-29 | 2004-09-28 | Capsule dosing system, dosing method using capsule dosing system, and control method for capsule dosing system |
| KR1020067005829A KR101139082B1 (en) | 2003-09-29 | 2004-09-28 | Capsule dosing system, dosing method using capsule dosing system, and control method for capsule dosing system |
| PCT/JP2004/014557 WO2005030114A1 (en) | 2003-09-29 | 2004-09-28 | Capsule dosing system, dosing method using capsule dosing system, and control method for capsule dosing system |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003338260A JP4520126B2 (en) | 2003-09-29 | 2003-09-29 | Capsule type medical device system |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2005102851A JP2005102851A (en) | 2005-04-21 |
| JP2005102851A5 JP2005102851A5 (en) | 2006-11-30 |
| JP4520126B2 true JP4520126B2 (en) | 2010-08-04 |
Family
ID=34533831
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003338260A Expired - Fee Related JP4520126B2 (en) | 2003-09-29 | 2003-09-29 | Capsule type medical device system |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4520126B2 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN1856290B (en) |
Families Citing this family (29)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPWO2007037158A1 (en) * | 2005-09-28 | 2009-04-09 | Tti・エルビュー株式会社 | Capsule type drug release device and capsule type drug release device system |
| CN101342067B (en) * | 2007-07-11 | 2010-08-25 | 重庆特奥科技有限公司 | Medical tool capsule |
| US9017248B2 (en) * | 2007-11-08 | 2015-04-28 | Olympus Medical Systems Corp. | Capsule blood detection system and method |
| JP5291955B2 (en) | 2008-03-10 | 2013-09-18 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | Endoscopy system |
| JP2009226066A (en) * | 2008-03-24 | 2009-10-08 | Olympus Corp | Capsule medical device |
| EP2398374A1 (en) * | 2009-02-17 | 2011-12-28 | Siemens Aktiengesellschaft | Endoscopic capsule |
| EP2394565B1 (en) | 2009-08-07 | 2013-05-01 | Olympus Medical Systems Corp. | Medical system |
| JP4723048B2 (en) * | 2009-08-19 | 2011-07-13 | オリンパスメディカルシステムズ株式会社 | Inspection apparatus and medical control method |
| CN102724907A (en) * | 2010-01-27 | 2012-10-10 | 奥林巴斯株式会社 | Power supply system and medical capsule device mounted with same |
| JP2011177339A (en) * | 2010-03-01 | 2011-09-15 | Panasonic Corp | Capsule type dosage apparatus |
| CN102397052B (en) * | 2011-11-30 | 2014-01-15 | 西交利物浦大学 | Image-recognition-technology-based shooting-speed-adjustable wireless capsule endoscope system and method |
| RU2502482C2 (en) * | 2011-12-19 | 2013-12-27 | Федеральное государственное автономное образовательное учреждение высшего профессионального образования "Национальный исследовательский технологический университет "МИСиС" | Method of surgical treatment of intestinal obstruction of small and large intestine and device for its realisation |
| CN102551643B (en) * | 2012-02-16 | 2014-03-19 | 金纯� | Self-assembling type medical serpentiform endoscopic capsule |
| US9511211B2 (en) | 2012-03-27 | 2016-12-06 | Sony Corporation | Medical system including a plurality of capsule type medical devices |
| US20150141752A1 (en) | 2012-05-19 | 2015-05-21 | Capso Vision, Inc. | Optical Wireless Docking System for Capsule Camera |
| US10264972B2 (en) | 2012-05-21 | 2019-04-23 | International Business Machines Corporation | Dispensing drugs from a companion diagnostic linked smart pill |
| CN104379049A (en) | 2012-06-26 | 2015-02-25 | 索尼公司 | Imaging control device, storage system, and storage medium |
| CN104720735B (en) * | 2014-12-02 | 2016-10-05 | 上海理鑫光学科技有限公司 | virtual reality capsule endoscope |
| KR102589081B1 (en) | 2016-09-09 | 2023-10-17 | 비오라 쎄라퓨틱스, 인크. | Electromechanical ingestible device for delivery of a dispensable substance |
| US10610104B2 (en) | 2016-12-07 | 2020-04-07 | Progenity, Inc. | Gastrointestinal tract detection methods, devices and systems |
| EP3600009B1 (en) | 2017-03-31 | 2020-12-30 | Progenity, Inc. | Ingestible device with localization capabilities |
| CN107252353B (en) * | 2017-06-01 | 2021-01-26 | 上海联影医疗科技股份有限公司 | Control method of medical imaging equipment and medical imaging equipment |
| US11253221B2 (en) | 2017-06-01 | 2022-02-22 | Shanghai United Imaging Healthcare Co., Ltd. | Systems and methods for configuring medical device |
| CN108056747A (en) * | 2017-12-12 | 2018-05-22 | 重庆财玺科技有限公司 | A kind of capsule endoscope with drug release |
| CN108324231A (en) * | 2018-03-14 | 2018-07-27 | 潍坊学院 | A kind of automatically cleaning medicine-feeding capsule endoscope |
| CN109091749A (en) * | 2018-07-12 | 2018-12-28 | 纪维忠 | A kind of Internal Medicine-Oncology drug interventional therapy device and its application method |
| EP4275601A3 (en) * | 2019-04-18 | 2024-01-17 | Enterasense Limited | Biosensor capsule and system |
| CN115666704A (en) | 2019-12-13 | 2023-01-31 | 比奥拉治疗股份有限公司 | Ingestible device for delivery of therapeutic agents to the gastrointestinal tract |
| CN117159147A (en) * | 2020-07-27 | 2023-12-05 | 彭志军 | Wire-control magnetic force ultrasonic cavitation motion body internal physiotherapy robot device |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH05168680A (en) * | 1991-12-03 | 1993-07-02 | Olympus Optical Co Ltd | Capsule device for medical treatment |
| JP2835051B2 (en) * | 1988-07-06 | 1998-12-14 | オリンパス光学工業株式会社 | Medical capsule |
| JP2003038424A (en) * | 2001-07-30 | 2003-02-12 | Olympus Optical Co Ltd | Encapsulated endoscope |
Family Cites Families (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20020099310A1 (en) * | 2001-01-22 | 2002-07-25 | V-Target Ltd. | Gastrointestinal-tract sensor |
| US7160258B2 (en) * | 2001-06-26 | 2007-01-09 | Entrack, Inc. | Capsule and method for treating or diagnosing the intestinal tract |
-
2003
- 2003-09-29 JP JP2003338260A patent/JP4520126B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2004
- 2004-09-28 CN CN2004800278990A patent/CN1856290B/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2835051B2 (en) * | 1988-07-06 | 1998-12-14 | オリンパス光学工業株式会社 | Medical capsule |
| JPH05168680A (en) * | 1991-12-03 | 1993-07-02 | Olympus Optical Co Ltd | Capsule device for medical treatment |
| JP2003038424A (en) * | 2001-07-30 | 2003-02-12 | Olympus Optical Co Ltd | Encapsulated endoscope |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2005102851A (en) | 2005-04-21 |
| CN1856290B (en) | 2012-03-14 |
| CN1856290A (en) | 2006-11-01 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4520126B2 (en) | Capsule type medical device system | |
| JP4733918B2 (en) | Capsule dosing system | |
| KR101139082B1 (en) | Capsule dosing system, dosing method using capsule dosing system, and control method for capsule dosing system | |
| KR101066820B1 (en) | Capsule medical treatment device and capsule medical treatment device collecting system | |
| JP4744026B2 (en) | Capsule endoscope and capsule endoscope system | |
| US10064544B2 (en) | Endoscopic capsule and endoscopic system | |
| JP4643089B2 (en) | Capsule medical device | |
| JP4716922B2 (en) | Capsule type medical device and drug introduction system using the same | |
| JP4868720B2 (en) | Capsule dosing system | |
| JP4578740B2 (en) | Capsule medical device | |
| WO2005023102A1 (en) | In-subject introducing device and wireless in-subject information capturing system | |
| JP2004041709A (en) | Capsule medical care device | |
| JP2003116781A (en) | Capsule type medical instrument | |
| JP2005334331A5 (en) | ||
| JP2005102851A5 (en) | ||
| US8439851B2 (en) | Lumen passability checking device, lumen passability checking method, and method of manufacturing lumen passability checking device | |
| CN102843954A (en) | Medical diagnostic apparatus and method of marking and/or treating area of interest in the body of human or animal | |
| JP2005131012A (en) | Capsule medication system | |
| KR20100073489A (en) | Capsuled diagnosing device with vibration element |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20060928 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A821 Effective date: 20060929 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20061012 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A821 Effective date: 20061013 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20090901 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20091027 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A821 Effective date: 20091028 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20100126 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20100323 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A821 Effective date: 20100324 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20100506 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20100520 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130528 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20140528 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| S531 | Written request for registration of change of domicile |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313531 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |