JP4479343B2 - Programs and devices for system usability study support - Google Patents
Programs and devices for system usability study support Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4479343B2 JP4479343B2 JP2004152058A JP2004152058A JP4479343B2 JP 4479343 B2 JP4479343 B2 JP 4479343B2 JP 2004152058 A JP2004152058 A JP 2004152058A JP 2004152058 A JP2004152058 A JP 2004152058A JP 4479343 B2 JP4479343 B2 JP 4479343B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- questionnaire
- function
- user
- log
- question
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Management, Administration, Business Operations System, And Electronic Commerce (AREA)
Description
本発明は、システムの有用性の調査のための技術に関し、特に調査のためのアンケート質問票の自動作成に関する。 The present invention relates to a technique for investigating the usefulness of a system, and more particularly to automatic creation of a questionnaire questionnaire for investigation.
利用者(ユーザ)が利用するシステムは、小は単一の機器・ソフトウエアから大は多くの機器やソフトウエアから構成される大規模システムに至るまでのどのようなシステムでも、利用者が利用する以上、利用者にとって使いやすいかどうかが重要な問題となる。また、個々の機能が使いやすくても、利用者達が必要とする機能が足りなければ、システム全体としての使いやすさは減じられるし、利用者達が使わない機能があれば、それは無駄であるばかりか、その機能が使う資源のために必要な機能のための資源が圧迫されるという問題も出てくる。このように、システム全体の有用性は、システムの使い勝手やシステムの機能の過不足性の面から評価することができる。 The system used by the user (user) can be used by the user in any system, ranging from a single device / software to a large system composed of many devices and software. As a result, whether it is easy for users to use is an important issue. Even if individual functions are easy to use, if the functions required by users are not sufficient, the ease of use of the system as a whole will be reduced, and if there are functions that users do not use, it will be useless. In addition, there is a problem that resources for functions necessary for the resources used by the functions are compressed. As described above, the usefulness of the entire system can be evaluated from the viewpoint of usability of the system and excess / deficiency of the functions of the system.
従来、システムの有用性の評価を行うには、ユーザモデリング、利用者の操作やそれに対するシステム側の応答などのログの分析、利用者に対するアンケート調査などを、多大な工数を掛けて実施しなければならなかった。 Conventionally, in order to evaluate the usefulness of a system, user modeling, analysis of logs such as user operations and system responses to them, and questionnaire surveys for users, etc. must be performed with a great deal of man-hours. I had to.
このようなシステム有用性の調査の一部としてのログの分析を支援するための技術として、特許文献1に示されるものが知られている。この従来装置では、対話型システムに対する入力を入力モニター部により監視して入力履歴を記録し、この入力に関連する対話型システムの出力を出力モニター部で監視して出力履歴に記録している。そして、この装置では、履歴参照指示部からの指示により所望の入力履歴を指示して画面表示させると共に、表示させた入力履歴に関連づけられた出力履歴を表示させることができる。 As a technique for supporting log analysis as part of such a system usability study, a technique disclosed in Patent Document 1 is known. In this conventional apparatus, the input to the interactive system is monitored by the input monitor unit and the input history is recorded, and the output of the interactive system related to this input is monitored by the output monitor unit and recorded in the output history. In this apparatus, a desired input history can be instructed and displayed on the screen by an instruction from the history reference instruction unit, and an output history associated with the displayed input history can be displayed.
また、システム有用性の評価に関するものではないが、特許文献2には、対話型システムの入出力の監視を利用した装置として、特許文献2に示すものがある。この装置は、利用者に的確なタイミングでヘルプ情報を提示するアクティブ・ヘルプ装置を目指すものである。この装置では、対話モニタ部が利用者とシステムの間の入出力信号を監視、記録して対話履歴を更新し、画面停留実測・判定部が、対話履歴の更新のたびに、その対話履歴に基づいて、表示画面ごとの連続的な表示時間を算出し、表示画面毎の標準表示時間と比較することによって、利用者とシステムとの対話に異常な遅延や膠着が生じているか否かを評価する。そして、異常な遅延等が生じている場合、ヘルプ情報格納部からヘルプ情報を選択し、そのヘルプ情報をヘルプ画面出力部を介して利用者に提示する。 Further, although not related to evaluation of system usability, Patent Document 2 discloses an apparatus using input / output monitoring of an interactive system as disclosed in Patent Document 2. This device aims to be an active help device that presents help information at a precise timing to the user. In this device, the dialog monitor unit monitors and records the input / output signals between the user and the system and updates the dialog history, and the screen stop measurement / determination unit updates the dialog history every time the dialog history is updated. Based on this, the continuous display time for each display screen is calculated and compared with the standard display time for each display screen to evaluate whether there is an abnormal delay or stalemate in the interaction between the user and the system. To do. When an abnormal delay or the like occurs, help information is selected from the help information storage unit, and the help information is presented to the user via the help screen output unit.
このように、システムの入力や出力のログを自動的に収集したり、利用者がそのログの分析しやすくするために対応する入力と出力を関連づけて表示したりする技術は従来から存在する。 As described above, there are techniques for automatically collecting system input and output logs, and displaying corresponding input and output in association with each other so that a user can easily analyze the log.
しかしながら、システムの有用性評価は、ログ分析だけでは十分でない場合が多く、アンケート調査も併用される。ところが、従来、システム有用性評価のためのアンケート調査は、ログ分析等の他の情報収集・分析とは独立して行われていたので、いきおい無駄な質問項目や適切な選択肢のない質問項目を少なからず含んだアンケートが行われる傾向にあった。無駄な項目が多く含まれているとアンケート回答者の取組意欲を殺ぐことになり、また適切な選択肢がない項目が含まれていると回答者は無理に回答することになり、いずれにしてもアンケート結果の信頼性を低下させることに繋がりかねない。調査者がログ分析等の情報を見てアンケートの質問項目を絞り込んだり、回答の選択肢を調整したりするようにすれば、このような問題はかなり解消されるが、調査者の負担が大きいという問題がある。 However, log analysis alone is often not sufficient for evaluating the usefulness of the system, and a questionnaire survey is also used. However, since questionnaire surveys for evaluating system usability have been conducted independently of other information collection / analysis, such as log analysis, it has been difficult to identify useless question items or question items without appropriate options. There was a tendency for questionnaires to be included. If a lot of useless items are included, the survey respondents' willingness to work will be killed, and if there are items that do not have an appropriate option, the respondent will respond unreasonably. Can also reduce the reliability of questionnaire results. If the investigator narrows down the questionnaire questions and adjusts the answer options by looking at information such as log analysis, such problems will be solved considerably, but the investigator's burden is heavy. There's a problem.
本発明は、コンピュータシステムを、調査対象システムが提供する機能に対し利用者が行った操作を検知して、当該操作を行った利用者と特定する情報と当該操作の行われた時刻の情報とを少なくとも含む、当該操作についてのログデータを記録するログ記録手段、前記ログ記録手段により記録されたログデータを解析し、前記機能の利用状況を示す利用状況指標を求めるログ解析手段であって、前記機能の利用状況指標が所定の条件を満足する場合に、更に前記ログ記録手段に記録された各ログデータに含まれる、当該ログデータに係る操作を行った利用者を特定する情報と当該操作の行われた時刻の情報とに基づき、同一の利用者が行った当該機能の利用のための一連の操作における各操作の行われた時刻から、当該利用者が行った当該機能の利用のための前記一連の操作に要した操作時間を計算し、計算した各利用者による当該機能の利用のための当該一連の操作に要した操作時間の分散を計算し、計算した分散が分散しきい値より大きい場合に、前記機能の利用のための前記一連の操作に要した操作時間が操作時間しきい値より大きい利用者を特定するログ解析手段、前記調査対象システムの有用性に関するアンケート質問票データを生成する質問票生成手段であって、前記ログ解析手段により求められた前記機能の利用状況指標に基づきアンケート質問票データに組み込む質問項目を選択する質問票生成手段、前記ログ解析手段が計算した各利用者による当該機能の利用のための当該一連の操作に要した操作時間の分散が分散しきい値より大きい場合に、前記質問票生成手段が生成したアンケート質問票データを、前記機能の利用のための前記一連の操作に要した操作時間が操作時間しきい値より大きい利用者に提供する質問票提供手段、として機能させるためのプログラムを提供する。 According to the present invention, the computer system detects the operation performed by the user for the function provided by the investigation target system, identifies the user who performed the operation , and information on the time when the operation was performed. the at least, logging means for logging data about the operation, the analyzes recorded log data by logging means, a log analyzing means for calculating a usage index indicating a use status of the function, When the usage status index of the function satisfies a predetermined condition, information for identifying a user who has performed an operation related to the log data and the operation included in each log data recorded in the log recording unit Based on the information on the time at which the user was performed, from the time at which each operation was performed in a series of operations for use of the function performed by the same user Calculate the operation time required for the series of operations for using the function, calculate the variance of the operation time required for the series of operations for using the function by each calculated user, and calculate the variance Log analysis means for identifying a user whose operation time required for the series of operations for using the function is larger than an operation time threshold when the function is larger than a dispersion threshold , usefulness of the investigation target system Questionnaire generating means for generating questionnaire questionnaire data relating to the questionnaire, the questionnaire generating means for selecting the question items to be incorporated into the questionnaire questionnaire data based on the usage status index of the function obtained by the log analyzing means, the log When the variance of the operation time required for the series of operations for use of the function by each user calculated by the analysis means is larger than the variance threshold, the questionnaire is generated The survey questionnaire data stage is generated, the program to function as a questionnaire providing means, for the operation time required for a series of operations are provided to the operation time threshold is greater than the user for the use of the function I will provide a.
本発明の好適な態様では、前記コンピュータシステムを、前記調査対象システムが提供する機能の利用状況指標についての条件ごとに該条件に対応する質問項目の情報を示した質問条件情報が登録されたデータベース、として更に機能させ、前記質問票生成手段は、前記ログ解析手段により求められた前記機能の利用状況指標が満たす条件が前記データベースにあれば、該条件に対応する質問項目をアンケート質問票データに組み込む質問項目として選択する。 In a preferred aspect of the present invention, the computer system is a database in which question condition information indicating information of question items corresponding to the conditions is registered for each condition regarding the usage status index of the function provided by the survey target system. , to further function as, the questionnaire generating means, if usage index satisfies the condition of the features that have been determined by the log analysis unit in the database, the question items corresponding to the conditions in the questionnaire questionnaire data Select as a question item to include.
更に好適な態様では、前記質問条件情報には、前記条件ごとに該条件に対応する質問項目の対象とする利用者を特定するための対象者情報が含まれ、前記質問票生成手段は、前記ログ解析手段により求められた前記機能の利用状況指標が満たす条件が前記データベースにあれば、該条件に対応する対象者情報に基づき、該条件に対応する質問項目の対象とする利用者を特定し、特定した利用者に対するアンケート質問票データとして該質問項目を含んだアンケート質問票データを生成する。
In a further preferred embodiment, the question condition information, subject information for specifying a user of interest question item corresponding to the conditions included in each of the conditions, the questionnaire generating means, said if conditions satisfying the usage index of the features that have been determined by the log analysis unit in the database, based on the subject information corresponding to the condition, and specifying the user of interest question item corresponding to the conditions Then, questionnaire questionnaire data including the question item is generated as questionnaire questionnaire data for the identified user.
更に好適な態様では、前記データベースには、前記調査対象システムが提供する機能ごとに前記質問条件情報が登録され、前記ログ解析手段は、前記調査対象システムが提供する機能ごとにその利用状況指標を求め、前記質問票生成手段は、前記ログ解析手段が求めた各機能の利用状況指標と各機能についての質問条件情報とに基づき、利用者ごとに、該利用者を対象とする質問項目を集めたアンケート質問票データを生成する。 In a further preferred aspect, the question condition information is registered in the database for each function provided by the survey target system, and the log analysis unit displays a usage status index for each function provided by the survey target system. The questionnaire generating means collects, for each user, a question item for the user based on the usage status index of each function obtained by the log analyzing means and the question condition information for each function. Generate questionnaire questionnaire data.
また本発明の別の好適な態様では、前記機能の利用状況指標は、該機能の利用者数及び利用頻度を含む。 In another preferred aspect of the present invention, the usage status index of the function includes the number of users and the usage frequency of the function.
また本発明の別の好適な態様では、前記質問票提供手段は、前記ログ解析手段が計算した前記分散が前記分散しきい値以下である場合には、前記質問票生成手段が生成したアンケート質問票データを、前記ログ記録手段に記録された前記ログデータから求められる前記機能を利用した利用者全員に提供する。 In another preferred embodiment of the present invention is also the questionnaire providing means, when said log analysis unit has calculated variance is less than said variance threshold, questionnaire that the questionnaire generating means has generated The vote data is provided to all users who use the function obtained from the log data recorded in the log recording means .
また本発明の別の好適な態様では、前記ログ解析手段は、前記機能の利用状況指標が所定の条件を満足する場合に、更に利用者のプロファイル情報により区別される利用者のグループごとに前記ログから該グループの該機能の利用状況を求め、前記質問票生成手段は、グループごとの利用状況の差の程度に応じ、質問項目の対象とする利用者を限定する。 In another preferred aspect of the present invention, the log analysis unit further includes the log analysis unit for each group of users further distinguished by user profile information when the usage status index of the function satisfies a predetermined condition. The usage status of the function of the group is obtained from the log, and the questionnaire generation means limits the users who are the target of the question item according to the degree of the difference in usage status for each group.
以下、図面を参照して、本発明を実施するための最良の形態(以下「実施形態」と呼ぶ)について説明する。 The best mode for carrying out the present invention (hereinafter referred to as “embodiment”) will be described below with reference to the drawings.
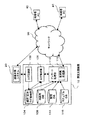
図1は、本発明に係るシステム有用性調査支援装置の概略構成を説明するための図である。 FIG. 1 is a diagram for explaining a schematic configuration of a system usability investigation support apparatus according to the present invention.
図1において、調査支援装置10は、調査対象システム20の有用性を調査する際の支援を行う装置である。
In FIG. 1, a survey support device 10 is a device that provides support when investigating the usefulness of the
ここで調査対象システム20は、利用者に対して所定のサービスを提供するシステムであり、利用者が利用可能な1以上の機能を提供する。図示の例では、調査対象システム20は、インターネット等のネットワーク30を介し、利用者PC(パーソナルコンピュータ)40を操作する各利用者にサービスを提供するサービス形態のシステムを示している。例えば、基幹業務システムはグループウエアなどがそのようなシステムの一例である。しかし、これは一例であり、調査支援装置10が適用可能な調査対象システム20の形態は特に限定されない。調査対象システム20は、ハードウエアのシステムで、ソフトウエアのシステムでも、それら両者の組合せでもよいし、規模も問わない。
Here, the
調査支援装置10において、ログ記録部102は、調査対象システム20に対する利用者からの操作及びその操作に対するシステム20からの応答を監視し、操作指示や応答を検知すると、それを示すログデータを作成し、操作・応答ログ格納部104に格納する。操作及び応答の内容は、調査対象システム20に対する入力及び出力の信号又はデータを監視することにより検知することができる。
In the investigation support apparatus 10, the
個々の操作・応答のログデータには、当該操作・応答が行われた日時、当該操作を行った(したがって応答の対象である)利用者の識別情報、当該操作と応答の内容を示す識別情報が含まれる。例えば、「1/1 10:00 19415 Press B, Page B Open」が1つの操作・応答ログデータであり、これは1月1日10時0分に("1/1 10:00")、利用者ID19415の利用者が("19415")、調査対象システム20の機能Bにアクセスし("Press B")、これに対して調査対象システム20が機能Bの画面を利用者に提供(すなわち利用者PCに画面表示)したこと("Page B Open")を示している。もちろんこれは一例であり、この他のデータ項目を含んでもよい。また、以上の例では操作とこれに対する応答とを1つのログデータに記述したが、これらを分けて記述してももちろんよい。
The log data of each operation / response includes the date and time when the operation / response was performed, the identification information of the user who performed the operation (and therefore the response target), and the identification information indicating the content of the operation / response Is included. For example, “1/1 10:00 19415 Press B, Page B Open” is one operation / response log data, which is at 10:00 on January 1 ("1/1 10:00"), The user with the user ID 19415 ("19415") accesses the function B of the survey target system 20 ("Press B"), and the
このようなログ記録部102の操作・応答の監視、及びログの記録の動作は、特許文献1に示される従来装置の場合と同様の仕組みで実現できる。
Such monitoring of the operation / response of the
ログ解析部106は、操作ログ格納部104に格納されたログデータ群の解析を行う。ログ解析では、調査対象システム20が提供する各機能の利用状況を示す利用状況指標を求める。利用状況指標には、例えば利用者達がその機能を利用した総回数(利用頻度)や、その機能を利用した利用者の総数(利用者数)などがある。解析により求められた利用状況指標は、アンケート質問票の作成に利用される。ここに示したのはあくまで一例であり、ログ解析の詳細な内容は後で改めて説明する。
The
利用者DB(データベース)108は、各利用者のプロファイル情報を登録したデータベースである。プロファイル情報には、例えば、利用者ID、氏名、性別、年齢、役職、利き手などの個人の特徴情報が含まれる。 A user DB (database) 108 is a database in which profile information of each user is registered. The profile information includes, for example, personal feature information such as user ID, name, gender, age, title, and dominant hand.
質問DB114は、アンケート質問票に組み込む質問項目のデータが登録されるデータベースである。個々の質問項目のデータは、その質問項目が質問票に採用されるべき条件に対応づけて登録される。この条件は、調査対象システム20の各機能に対する利用者達の利用状況についての条件として表現される。
The
図2に、質問DB114に登録されるデータ内容の一例を示す。図示例では、質問DB114の1つのレコードは、「機能」、「利用状況条件」、「質問項目情報」、「付随表示情報」、「対象者情報」を含んでいる。「機能」は、調査対象システム20が提供する1以上の機能のうち、当該レコードに該当する機能を示す識別情報である。「利用状況条件」は、当該レコードに該当する利用状況指標についての条件を示すデータである。例えば図の1行目のレコードでは、利用状況条件が、利用頻度と利用者数に関する条件の形で規定されている。「質問項目情報」は、当該レコードに該当する質問項目の情報である。質問項目の情報は、質問文やそれに対する回答を受け付けるためのオブジェクトの情報などを含む。例えば、回答のためのオブジェクトは、例えば、回答の選択肢の選択を受け付けるチェックボックスやラジオボタン、或いは自由記入のための入力欄などである。アンケート質問票をウェブページのかたちで作成する場合、質問項目の情報は、例えば、HTML(HyperText Markup Language)の記述、或いはそのようなHTML記述を生成するメソッドなどとなる。なお、図示のテーブルには、質問項目の情報としてそのような質問項目の情報の名称を示している。「付随表示情報」は、「質問項目情報」が示す質問項目に付随してアンケート質問票に示すべき情報である。例えば、機能についての説明を示したマニュアル情報などが、付随表示情報の一例である。付随表示情報には、いくつかの種類が存在するが、そのうちの機能の説明を示したマニュアル情報は、マニュアルDB116に登録されている。また、操作・応答ログ格納部104に格納されたログデータから、ある個人のある機能の利用履歴の情報を付随表示情報として作成することもできる。「対象者情報」は、「質問項目情報」が示す質問項目を提示する対象となる利用者を特定するための情報である。言い換えれば、その質問項目の提示対象の利用者が満たすべき条件を規定した情報である。
FIG. 2 shows an example of data contents registered in the
図には、1つの機能についてのレコード群しか示していないが、質問DB114には、調査対象システム20が提供する各機能について同様のレコードが登録されている。
Although only the record group for one function is shown in the figure, similar records are registered in the
すなわちこの装置10では、システム20の「機能」と、その「機能」についての利用状況指標が満足する「利用状況条件」との組合せにより、アンケート質問票に載せるべき「質問項目情報」及び「付随表示情報」が選択される。ある機能についての利用状況指標が、質問DB114に登録されている当該機能のどの「利用状況条件」にも該当しない場合は、アンケート質問票にはその機能についての質問項目が組み込まれないことになる。また、利用者DB108に登録された利用者のうち、その組合せに対応する「対象者情報」を満足する利用者が、その質問項目の対象として選ばれることになる。
In other words, in this device 10, “question item information” and “accompanying” to be put on the questionnaire questionnaire by combining the “function” of the
アンケート処理部110は、アンケート処理のための各種処理を実行する手段であり、アンケート質問票を生成するための質問票生成部112を備えている。
The
この質問票生成部112は、ログ解析部106の解析により求められた各機能についての利用状況指標に該当する質問項目を質問DB114から求め、求められた1以上の質問項目を組み込んだアンケート質問票のデータを作成する。このとき、アンケート質問票に組み込む質問項目に付随する付随表示情報が質問DB114に登録されていれば、その付随表示情報をマニュアルDB116のマニュアル情報や操作・応答ログ格納部104に格納されたログ情報から作成し、アンケート質問票に組み込む。アンケート質問票のデータは、例えばHTMLで記述されたウェブページとして作成することができる。ここで、複数の機能についての質問項目をまとめたアンケート質問票を作成する場合、各利用者ごとに、その利用者に対する質問項目をまとめた、カスタマイズされたアンケート質問票が作成される。これには「機能」と「利用状況条件」の組合せにより選択された各「質問項目」がそれぞれどの利用者向けのものなのかを「対象者情報」から判定し、この結果求められた質問項目と対象の利用者との組合せを、利用者ごとに整理することで、各利用者宛のアンケート質問票に組み込むべき質問項目群が特定できる。
The
アンケート処理部110は、質問票生成部112で作成されたアンケート質問票のデータを用いてアンケート調査を実行する。ウェブページを利用してアンケート調査を行う場合、アンケート処理部110は、質問票生成部112が生成したアンケート質問票のウェブページをウェブサーバに登録し、それらアンケート調査票のURL(Uniform Resource Locator)を、例えば電子メールなどの形で、対象となる利用者宛に送信する。利用者は、そのURLを用いて利用者PC40にてそのアンケート質問票のページを取得し、各質問項目に対する回答を入力した上で、入力結果をウェブサーバ宛に送信する。アンケート処理部110は、この入力結果を集計することで、アンケート結果をまとめる。
The
調査支援装置10は、まとめたアンケート結果やログ解析の結果を画面表示することができ、その画面表示は、調査者が各機能の有用性、すなわち各機能の使い勝手や各機能が必要なのか否か、を判断する際の判断材料となる。 The survey support apparatus 10 can display the collected questionnaire results and log analysis results on the screen, and the screen display indicates whether the investigator needs the usefulness of each function, that is, whether the use of each function or each function is necessary. It becomes a judgment material when judging.
また、調査支援装置10に、ログ解析結果やアンケート回答の集計結果に基づき、機能についての施策を提案する機能を設けることも好適である。例えば、ログ解析の結果、ある機能が余り使われていないことが分かり、アンケートの結果、利用者のほとんどがその機能を余り使いたいと思っていないことが分かれば、その機能は不要であると判断できる。そこで、調査支援装置10は、ログ解析で利用頻度が所定のしきい値より少ないと判定した機能につき、その機能を使いたいかどうかを問うアンケートを利用者DB108に登録された全利用者に行い、その結果使いたいと回答した利用者が所定のしきい値より少なければ、その機能は不要である可能性が高いので削除した方がよい、等の施策を示すメッセージをアンケート結果などに加え表示する。なお、このような施策提案のためには、質問DB114と同様、施策内容と、その施策内容を提案に採用するための条件をデータベース化しておけばよい。施策内容を採用するための条件は、アンケートの集計結果に関する条件、或いはアンケート集計結果とログ解析結果についての条件として記述することができる。
It is also preferable to provide the survey support apparatus 10 with a function for proposing measures for functions based on the log analysis results and the results of questionnaire responses. For example, if the log analysis shows that a certain function is not used much, and the questionnaire shows that most users do not want to use that function too much, that function is unnecessary. I can judge. Therefore, the survey support apparatus 10 conducts a questionnaire asking whether or not to use the function for which the usage frequency is determined to be less than a predetermined threshold in the log analysis to all users registered in the
次に、具体例を挙げて、本実施形態の調査支援装置10の処理動作を説明する。 Next, the processing operation of the survey support apparatus 10 of the present embodiment will be described with a specific example.
本実施形態の調査支援装置10では、ログ記録部102が、調査対象システム20に対する操作及び応答を常にモニタし、そのログを操作・応答ログ格納部104に記録している。そして、調査者が装置10に対して調査の開始を指示すると、ログ解析部106が、まず操作・応答ログ格納部104のデータを解析して、各機能ごと、利用状況指標として、全体の利用頻度と利用者数を求める。機能の利用頻度は、その機能を含んだログデータの数を合計すればよい。これにより利用者全体における当該機能の利用頻度が求められる。また機能の利用者数は、その機能を示したログデータに現れる異なる利用者の数を合計すればよい。この合計では、同じ利用者が当該機能を複数回利用していたとしても、その利用者は1回のみカウントする。各機能の利用頻度と利用者数の組合せは、図3のチャート200のように、利用頻度と利用者数をそれぞれ座標軸とした2次元座標にプロットすることができる。
In the investigation support device 10 of the present embodiment, the
典型的な例では、機能ごとの利用頻度と利用者数の組合せに従い、質問票生成部112がアンケート質問票を作成する。利用頻度と利用者数との組合せに応じて作成される質問票の例を図3〜図5に示す。
In a typical example, the
図3は、利用者数も利用頻度も共に少ない機能A(図ではこの機能の名称を「タスクレポート」としてる)についての質問項目を示すアンケート質問票300を示す図である。これは、図2に例示した質問DB114のデータ内容のうちの第1行目のレコードに対応する。「少ない」か否かを判定するためのしきい値として、利用者数及び利用頻度に対してそれぞれしきい値t1,T1が定められている。利用者数がt1より少なく、かつ利用頻度がT1より少ない場合、このレコードの利用状況条件が満足されるので、このレコードが検索されることになる。図3では、チャート200において斜線ハッチングを施した部分がその条件を満足する部分である。
FIG. 3 is a diagram showing a
しきい値の値は、調査者が決めればよい。以降の例で述べる他のしきい値も同様である。 The investigator may determine the threshold value. The same applies to other threshold values described in the following examples.
この例のように機能の利用者数も利用頻度も共に少ない場合、それは機能自体が利用者達にあまり知られていないからかも知れないし、また利用者達はその機能を知っているが必要性を感じないからかもしれない。そこで、質問票生成部112は、その機能を知っているかどうかを確認するために、「認知度・期待度調査」(図2参照)のための質問項目310を組み込んだアンケート質問票300を作成する。組み込むべき質問項目の情報は、機能とこの機能についての利用状況指標とに該当するレコードを質問DB114から検索することにより特定される。
If both the number of users and the frequency of use of the function are low as in this example, it may be because the function itself is not well known to the user, and the user knows the function but needs to It may be because you do not feel. Accordingly, the
質問票300中の質問項目欄310には、質問文312と、その質問文に対する回答欄314とが示される。図示例では、回答欄314は、複数の選択肢から該当するものを1つ選択する形式のものであり、各選択肢に対しラジオボタン316が設けられている。質問票をウェブページとして作成する場合、この回答欄314の情報は、HTMLにおける選択肢リストの記述方式に従って記述しておけばよい。複数選択可能な選択肢や、自由記入欄も、同様にHTMLに従って記述することができる。
In the
この質問項目欄310には、複数の質問文312を組み込むこともできる。図示例では、質問項目欄310のなかに、当該機能を知っているかを問う質問Q1(認知度の質問)に加え、知らない人に対する付加的な質問としてその機能に対する期待を尋ねる質問Q2も含まれている。これら複数の質問からなる集合が、「利用者数がt1より少なく、かつ利用頻度がT1より少ない」という1つの利用状況条件に対する1つの質問項目を構成している。なお、1つの質問項目を構成する複数の質問は、例示のような主たる質問と付随する質問といった組合せだけでなく、独立した複数の質問の組合せでもよい。
A plurality of
また、質問DB114から検索されたレコードに「付随表示情報」が登録されている場合には、その付随表示情報320が質問票300に組み込まれる。図示例では、対象である「タスクレポート」機能の説明用マニュアル文書がマニュアルDB116から読み出され、質問票300に組み込まれる。
Further, when “accompanying display information” is registered in the record retrieved from the
このように図3に例示した質問票300は、機能が利用者達に周知されていない可能性を調べるものなので、図2の例の第1行目のレコードの「対象者情報」に規定されるように、対象者は利用者全員となる。
As described above, the
図3に例示した質問票300によるアンケートによれば、まず、当該機能Aが余り使われていない理由が、利用者達がその機能Aを知らないからなのかどうかを判断することができる。利用者達の多くが質問Q1に対し「知っている」と回答した場合、機能Aを知っているのに使っていない人が多いということになる。この場合、機能Aがそもそも必要とされていない可能性が高くなる。したがって、調査支援装置10は、機能Aを削除するという施策を提案する。また、利用者達の多くが質問Q1に「知らない」と回答した場合は、それら利用者達の期待度の質問Q2に対する回答の分析が問題となる。質問Q2に対し、「使いたい」と回答した人が多ければ、機能Aの利用実績が少ないのは、単に機能Aが知られていなかったからだということが分かる。この場合、機能Aの便利な利用法を利用者達に紹介するという施策を装置10から提案することもできる。また、質問Q2に対し、「使いたくない」と回答した人が多い場合は、機能Aがそもそも必要とされていない可能性が高いので、機能Aを削除するという施策を装置10から提案することが考えられる。
According to the questionnaire using the
次に図4は、利用頻度は多いが利用者数は少ない機能B(図ではその機能名を「タスクレポート」としている)についての質問項目を示すアンケート質問票400の例を示す。これは、図2に例示したデータのうち、第2行目のレコードに対応する。このレコードに示されるように、利用頻度がしきい値T2より多く、利用者数がしきい値t2より小さいという条件が満足される場合、図4に示すようなアンケート質問票400が作成される。
Next, FIG. 4 shows an example of a
この例のように利用頻度は多いが利用者数は少ない機能は、少数の利用者が頻繁に使用している機能と捉えることができる。このような機能については、1つの方向として、頻繁に使っている利用者の利用目的や頻繁に利用する理由などを調べることで、この機能のセールスポイントを見つけて未利用者への宣伝に利用したり、この機能の改良の方向性を定めたりするのに役立てることが考えられる。そこで、このような場合、質問票生成部112は、「利用実態調査」のための質問項目欄410を含んだアンケート質問票400を作成する。この例では、質問項目欄410には、当該機能の利用目的を尋ねる質問Q1や当該機能の良い点(便利な点)を尋ねる質問Q2など、当該機能の利用実態を問う1以上の質問412が含まれる。この例では、各質問412の回答欄には複数の選択肢が示されており、複数の選択肢を選択可能とするため、ラジオボタンではなくチェックボックス414が設けられている。また、選択肢に挙げられていない回答を記入するための自由記入欄416も設けられている。このように質問項目410に挙げるべき質問412と各選択肢の情報は、質問DB114に登録されており、これが読み出されて質問票400に組み込まれる。
A function that is frequently used but has a small number of users as in this example can be regarded as a function that is frequently used by a small number of users. About such a function, as one direction, by finding out the purpose of use of frequent users and the reason for frequent use, etc., find the selling point of this function and use it for advertising to non-users It may be useful to determine the direction of improvement of this function. Therefore, in such a case, the
図4の例では、質問項目欄410に組み込む質問文や質問文の回答欄の内容(選択肢など)は、該質問項目の対象である機能の内容に関連したものなので、機能ごとに異なったものとなることが多い。利用目的や良い点を聞く質問など、機能に依らず共通した質問もあるが、選択肢については、機能ごとに個別内容となることが多い。例えば、「タスクレポート」という機能については図4に示したような選択肢になるのに対し、別の「文書登録」という機能については別の選択肢になるであろう。したがって、質問項目の内容は、図2に例示したごとく、機能ごとに別々に登録しておくことが望ましい。
In the example of FIG. 4, the question text to be incorporated in the
なお、これに対し、図3の例のように機能を知っているかどうかを問う質問の場合、『「***」機能を知っていますか』というように、機能名を示す「***」の部分以外は機能に依らず共通の文章となり、選択肢の方も「知っている」及び「知らない」というように機能に依存しない。したがって、このようなものについては、質問DB114には、機能に依らず共通の質問文テンプレート及び選択肢情報を登録しておき、質問文テンプレートに当該機能の機能名を差し込むことで個別の質問文を生成するようにすることもできる。この場合、図2の質問DB114のデータ内容における「質問項目情報」には、共通の質問文テンプレート及び選択肢情報を指す情報を登録すればよい。
On the other hand, in the case of a question asking whether the user knows the function as in the example of FIG. 3, “***” indicating the function name is used, such as “Do you know the“ *** ”function”? The part other than “” is a common sentence regardless of the function, and the options are not dependent on the function such as “I know” and “I don't know”. Therefore, for such items, a common question sentence template and option information are registered in the
また、図2の例では、利用頻度がT2より多く利用者数がt2より少ない場合には、「利用者自身の利用履歴」を付随表示情報として質問票に組み込むことが規定されている。そこで、質問票生成部112は、操作・応答ログ格納部104のログデータを解析し、この質問票400の対象である利用者の利用履歴チャート422を求め、このチャートを含んだ付随表示情報420を質問票400に組み込む。利用履歴チャート422は、当該利用者が当該機能の利用回数の時系列変化を所定期間にわたって(図示例では過去6ヶ月)表示したものである。
In the example of FIG. 2, it is defined that “user's own usage history” is incorporated into the questionnaire as accompanying display information when the usage frequency is higher than T2 and the number of users is lower than t2. Therefore, the
利用者は、この利用履歴チャートを参照することで、自分の当該機能B「タスクレポート」の利用状況を知ることができる。これは、例えば質問項目欄410の各質問への回答に生かすことができる。例えば、質問Q1は、機能「タスクレポート」の利用目的を問うものであるが、その選択肢の一つである「グループ月報作成」が利用者自身の目的に該当するかどうかを判断する際、利用履歴チャート422の利用パターンは参考になる。例えば、利用履歴チャート422から、ほぼ月末にこの機能の利用が多いことが分かれば、利用者はこの機能を月報作成に利用している可能性を考慮することができる。
The user can know the usage status of his / her function B “task report” by referring to the usage history chart. This can be used, for example, in answering each question in the
このように、質問票400は利用者個別の情報である利用履歴チャート422を含むので、質問票400は利用者ごとの個別に生成することになる。質問票400の対象とする利用者は、質問DB114の「対象者情報」に示されるように、当該機能Bを高い頻度で利用している利用者であり、これは各利用者の当該機能Bの利用頻度をしきい値と比較することで判別すればよい。この判別しきい値は、調査者が本装置10に登録しておけばよい。
Thus, since the
なお、1つの態様では、利用者の利用履歴のパターンに応じ、その利用者に対する質問票400の質問項目欄410に載せる質問文を切り替えたり、質問文自体は同じでもその回答欄に載せる選択肢を切り替えたりすることも可能である。例えば、機能の利用目的を問う質問の選択肢としてどのようなものを回答欄に組み込むかを、利用履歴パターンに応じて自動決定することができる。すなわち、例えば、当該機能の利用が各月末に多いことが利用履歴のパターンから分かれば「月報作成」を選択肢に入れ、各週末に多ければ「週報作成」を選択肢に入れる、等といった切替を行う等である。
In one aspect, according to the usage history pattern of the user, the question text to be placed in the
図4に例示した質問票400によるアンケートによれば、機能Bを使う目的やその機能Bのセールスポイントを求めることができる。したがって、利用目的やセールスポイントを広く利用者達に宣伝する等の施策を提案することができる。
According to the questionnaire based on the
次に、図5の例を説明する。これは、利用者数が多く、利用頻度が少なくも多くもない場合のアンケート質問票500の例である。これは、図2に例示したデータのうち第3行目のレコードに対応する。ここでの利用状況条件は、このレコードに示されるように、利用者数がt3より多く、利用頻度がT3〜T4の範囲にある、という条件である。
Next, the example of FIG. 5 will be described. This is an example of the
このように、利用者は多いのだが全体の利用頻度は伸び悩んでいる状況は、かなりの利用者達が当該機能を使ったことがあるにもかかわらず、その後その機能が利用者全体で見てそれほど頻繁に使われていないことであり、その原因としてその機能の使い勝手(使いやすさ)が悪いのではないかという可能性が考えられる。そこで、この場合には、図5に示すように、使い勝手についての質問を並べた質問項目欄510を含むアンケート質問票500を作成する。この例では、対象である機能C「文書登録」が使いやすいかどうかを問う質問Q1と、この質問で使いにくいと答えた人に対する追加の質問として、その機能の使い勝手の問題点を尋ねる質問Q2が示されている。質問Q1については、回答欄512は、使いやすいかどうかを「はい」か「いいえ」かで答える形式となっている。一方、質問Q2の回答欄514には、この機能Cの使い勝手について想定される問題点が選択肢として列挙され、該当するものを選択(複数選択も可能)できるようになっている。
In this way, there are many users, but the overall frequency of use is sluggish. Even though a large number of users have used the function, the function can be viewed by the entire user. The reason for this is that it is not used so frequently, and the cause may be that its functionality is not easy to use. Therefore, in this case, as shown in FIG. 5, a
これら質問のうち、質問Q1は、機能が使いやすいか否かを問うだけのものなので、機能名以外の質問文の文章と、選択肢は、機能に依らず共通化できる。一方、質問Q2については、回答欄514に挙げる選択肢は機能に依るので、機能ごとに別途作成し、質問DB114に登録しておく。
Of these questions, the question Q1 only asks whether or not the function is easy to use. Therefore, the sentence of the question sentence other than the function name and the options can be made common regardless of the function. On the other hand, as for the question Q2, the choices listed in the
また、質問票500には、付随表示情報520として、当該機能Cのマニュアル情報が示される。これは、機能Cを余り多くは使っていない人が、その機能を余り使用していない原因がどこにあるかを考える際の参考のために提供したものである。図2のデータ内容例の第3行目も参照されたい。
Also, the
このような質問票500は、当該機能Cを使ったことのない人に送っても余り意味がないので、対象は機能Cの利用経験者に限定する(図2のデータ内容例の第3行目のレコード参照)。利用経験者は、操作・応答ログ格納部104のログデータの解析により求めることができる。
Since such a
なお、このような使い勝手の問題は、慣れると使いやすくなってくる場合もあれば、何度使っても使いにくい場合もある。後者の場合、利用経験者皆が問題を感じていると考えられるので、上述のように利用経験者全員に質問票500に回答してもらうことが好適である。一方前者の場合は、使い慣れたベテランは余り当該機能の使い勝手に問題を感じていない可能性が高い。したがって、機能Cの使い勝手を改善し、初心者段階でのつまずきを少なくするには、初心者段階で当該機能を利用しなくなった人の回答が重要である。そこで、前者の場合には、質問票500の対象を当該機能Cの初心者に限定することも考えられる。
Such usability problems may be easier to use as you get used to, and may be difficult to use no matter how many times you use them. In the latter case, it is considered that all the experienced users feel a problem. Therefore, it is preferable to have all the experienced users answer the
このように質問の対象範囲を利用経験者全員にするか初心者のみに限定するかは、各利用者が当該機能を利用するための操作に要した時間(操作時間と呼ぶ)のばらつきにより判定することができる。1つの機能を利用するには、一般に複数の操作を順にこなす必要がある。例えば「文書登録」機能の場合、メニューの選択等で「文書登録」機能を呼び出し、登録する文書を指定し、登録先のフォルダ等のような登録のためのパラメータを指定し、指定した文書を指定したパラメータに従って登録する旨の登録ボタンを押下する、という一連の操作が必要となる。機能を利用するためのユーザインタフェースが使いやすければ、それら一連の操作に要する操作時間は短くなると考えられる。このように、操作時間は、当該機能が使いやすいかどうかの判断指標となる。 In this way, whether the target range of the question is limited to all experienced users or limited to beginners is determined by the variation in time (referred to as operation time) required for each user to use the function. be able to. In order to use one function, it is generally necessary to sequentially perform a plurality of operations. For example, in the case of the “document registration” function, the “document registration” function is called by selecting a menu, the document to be registered is designated, the registration parameters such as the registration destination folder are designated, and the designated document is designated. A series of operations of pressing the registration button for registering according to the specified parameter is required. If the user interface for using the function is easy to use, the operation time required for the series of operations will be shortened. As described above, the operation time is a determination index as to whether or not the function is easy to use.
そして、操作時間のばらつきが大きい場合、ベテランと初心者の分化が生じていると考えられるので、質問対象を初心者のみに限定する。一方、各人の機能Cの利用回数に差があるにもかかわらず操作時間のばらつきが小さい場合は、慣れてもそれほど使いやすくなっていないことを意味すると考えられるので、利用経験者全員に質問を行う。 If the variation in operation time is large, it is considered that there is a differentiation between veterans and beginners, so the question target is limited to only beginners. On the other hand, if the variation in operation time is small even though there is a difference in the number of times each person uses function C, it may mean that it is not so easy to use even if you are used to it. I do.
このような判定のため、ログ解析部106は、ログデータから、各利用者が当該機能Cを利用した都度、その利用のための一連の操作に要した操作時間を計算する。そして、利用ごとの操作時間を、操作時間ごとに集計することで、操作時間ごとの利用の頻度を求める。図5のチャート250はこれを図式化したものである。図示の例では、操作時間のばらつきが大きく、操作時間ごとに整理した利用の回数の分布に2つのピークが現れている。操作時間が短い方のピーク近傍がベテランのものであり、長い方のピーク近傍が初心者のものと考えられる。このように明確にピークが分離する場合でなくても、操作時間のばらつきが大きければ、初心者とベテランの差があると考えることができる。
For such determination, the
操作時間のばらつきの度合いは、各利用ごとの操作時間の分散で示すことができる。したがって、ログ解析部106は、操作時間の分散を計算し、その分散が所定のしきい値(これは調査者等が予め登録しておく)より小さければ、ベテランと初心者の差がないので、利用経験者全員に質問票500を提供する。また、分散がしきい値より大きい場合には、初心者のみに質問票500を提供する。この場合、例えば操作時間の平均値を求め、その平均値よりも平均操作時間が長い利用者を初心者と判定すればよい。利用者の平均操作時間は、その利用者が当該機能Cを利用した際の操作時間の平均である。なお、この例では、初心者を判定するしきい値として全利用者についての操作時間の平均値を用いたが、これは一例に過ぎない。操作時間が長い方から30%をしきい値とするなど、他の決め方でしきい値を決めることもできる。
The degree of variation in operation time can be indicated by the dispersion of operation time for each use. Therefore, the
図5の質問票500を用いてアンケートを行えば、機能Cを利用する上で利用者がつまずいている点を求め、それを調査者に提示することができる。
If a questionnaire is conducted using the
以上、図3〜図5を参照して、利用状況条件とそれに該当した場合のアンケート質問票の具体例を説明した。ただし、当該機能が提供され始めた当初は利用頻度自体が少なく、上に例示したようなログ解析及び質問票生成の処理を行っても意味がない場合が多い。したがって、上記の処理は、利用者達に提供され始めてからある程度の期間が経過した機能(これを判別するための期間のしきい値を本装置10に登録しておけばよい)についてのみ行うようにすることも好適である。 In the above, with reference to FIGS. 3 to 5, specific examples of the usage condition and the questionnaire questionnaire when it corresponds to the usage condition have been described. However, at the beginning of the provision of the function, the frequency of use itself is low, and there are many cases where it does not make sense to perform the log analysis and questionnaire generation processing as exemplified above. Therefore, the above-described processing is performed only for a function for which a certain period of time has elapsed since the start of provision to users (the threshold value of the period for determining this may be registered in the apparatus 10). It is also suitable to make it.
図3〜図5の例では、1つの機能に関するアンケート質問票300、400、500を例示したが、前述のように、各機能についての質問項目を列挙して1つのアンケート質問票を作成することもできる。この場合、各利用者ごとに、その利用者が該当する質問項目が選択され、アンケート質問票に組み込まれる。
3 to 5
以上説明したように、調査支援装置10によれば、ログ解析により求めた調査対象システム20の利用状況に基づき、アンケート質問票に組み込むべき質問項目を切り替えることができ、無駄な質問を減らすことができる。また、利用者ごとに、その利用者が該当する質問項目のみからなる質問票を作成できるので、この点からも無駄な質問を減らすことができる。このように無駄な質問の少ないアンケートにより、より信頼性の高いアンケート結果が得られるものと期待できる。
As described above, according to the survey support apparatus 10, the question items to be incorporated into the questionnaire questionnaire can be switched based on the usage status of the
また、調査支援装置10は、ログデータから機能の利用頻度と利用者数を求めるという大まかな解析を行い、その後、その結果に基づきアンケートを行ったり、あるいは更なるログ解析により操作時間の分布を求めたりなどという具合に、段階的に調査を進めていく。したがって、調査のための処理に無駄が少ない。 In addition, the survey support apparatus 10 performs a rough analysis of obtaining the function usage frequency and the number of users from the log data, and then performs a questionnaire based on the result, or further distributes the operation time by further log analysis. We will proceed with the survey step by step, such as asking for it. Therefore, there is little waste in processing for investigation.
以上の実施形態は例示的なものであり、本発明の範囲内で様々な変形が可能である。 The above embodiments are exemplary, and various modifications are possible within the scope of the present invention.
例えば、利用者数及び利用頻度の解析の後に、更に利用者のプロファイル情報を利用した解析を加え、それを反映したアンケートを行うことも可能である。この例を以下に示す。 For example, after analyzing the number of users and usage frequency, it is also possible to add a further analysis using user profile information and conduct a questionnaire reflecting the analysis. An example of this is shown below.
この例では、ログ解析部106の解析で、ある機能の利用者数は多いが利用頻度はそれほど多くない(図5のケースに類似)ことが判明した場合、更にログ解析部106がログデータを解析して利用者の利き手別に利用頻度を集計する。そしてログ解析部106は、の集計結果から、右利きと左利きとで利用者1人当たりの利用回数に有意な差がないかを調べる。これには、右利きと左利きの間での1人当たりの利用回数の差を、所定のしきい値と比較すればよい。しきい値より多ければ、当該機能が一方の利き手の人にとって使いにくくなっている可能性がある。そこで、その利き手の人に、図5に示したのと同様の質問票を用いて使い勝手のアンケートを行えば、本当にその利き手の人に使いにくくなっているかどうかが確認できる。
In this example, if the analysis by the
ここでは、利き手に着目した解析を行ったが、この他にも年齢層別など、プロファイル情報から利用者達を様々にグループ分けすることができ、ログデータからそれらグループごとの利用状況(上述の利用回数に限らず、例えば操作時間など他のものでももちろんよい)を解析し、それらからグループごとでの差がないかを求めることができる。グループ間で差があれば、グループの特性によって当該機能の使い勝手に差がある可能性があるので、それを確認するアンケート質問票を作成すればよい。 Here, analysis focusing on the dominant hand was performed, but in addition to this, users can be grouped in various groups based on profile information, such as by age group, and the usage status of each group from the log data (see above) It is possible to analyze not only the number of times of use but also other things such as operation time, for example, and determine whether there is a difference between groups. If there is a difference between groups, there may be a difference in usability of the function depending on the characteristics of the group, so a questionnaire questionnaire to confirm it may be created.
以上の例では、ウェブを利用したオンラインでのアンケート調査を例にとって説明したが、本実施形態の仕組みは、紙のアンケート質問票でアンケート調査を行う場合にも、アンケート質問票をカスタマイズするのに利用できる。 In the above example, the online questionnaire survey using the web has been described as an example. However, the mechanism of this embodiment can be used to customize the questionnaire questionnaire even when conducting a questionnaire survey using a paper questionnaire questionnaire. Available.
以上に説明した調査支援装置10は、典型的には、以上に説明した各機能モジュールの動作・処理を記述したプログラムを、コンピュータシステムに実行させることにより、実現することができる。 The survey support apparatus 10 described above can typically be realized by causing a computer system to execute a program that describes the operation and processing of each functional module described above.
10 調査支援装置、20 調査対象システム、30 ネットワーク、40 利用者PC、102 ログ記録部、104 操作・応答ログ格納部、106 ログ解析部、108利用者DB、110 アンケート処理部、112 質問票生成部、114 質問DB、116 マニュアルDB。 10 Survey support device, 20 Survey target system, 30 Network, 40 User PC, 102 Log recording unit, 104 Operation / response log storage unit, 106 Log analysis unit, 108 User DB, 110 Questionnaire processing unit, 112 Questionnaire generation Part, 114 question DB, 116 manual DB.
Claims (9)
調査対象システムが提供する機能に対し利用者が行った操作を検知して、当該操作を行った利用者と特定する情報と当該操作の行われた時刻の情報とを少なくとも含む、当該操作についてのログデータを記録するログ記録手段、
前記ログ記録手段により記録されたログデータを解析し、前記機能の利用状況を示す利用状況指標を求めるログ解析手段であって、前記機能の利用状況指標が所定の条件を満足する場合に、更に前記ログ記録手段に記録された各ログデータに含まれる、当該ログデータに係る操作を行った利用者を特定する情報と当該操作の行われた時刻の情報とに基づき、同一の利用者が行った当該機能の利用のための一連の操作における各操作の行われた時刻から、当該利用者が行った当該機能の利用のための前記一連の操作に要した操作時間を計算し、計算した各利用者による当該機能の利用のための当該一連の操作に要した操作時間の分散を計算し、計算した分散が分散しきい値より大きい場合に、前記機能の利用のための前記一連の操作に要した操作時間が操作時間しきい値より大きい利用者を特定するログ解析手段、
前記調査対象システムの有用性に関するアンケート質問票データを生成する質問票生成手段であって、前記ログ解析手段により求められた前記機能の利用状況指標に基づきアンケート質問票データに組み込む質問項目を選択する質問票生成手段、
前記ログ解析手段が計算した各利用者による当該機能の利用のための当該一連の操作に要した操作時間の分散が分散しきい値より大きい場合に、前記質問票生成手段が生成したアンケート質問票データを、前記機能の利用のための前記一連の操作に要した操作時間が操作時間しきい値より大きい利用者に提供する質問票提供手段、
として機能させるためのプログラム。 Computer system
Detects the operation performed by the user for the function provided by the investigation target system , and includes at least information identifying the user who performed the operation and information on the time when the operation was performed. Log recording means for recording log data ,
Analyzing the log data recorded by the log recording unit, a log analyzing means for calculating a usage index indicating usage of the function, if the usage index of the function satisfies a predetermined condition, further Based on the information included in each log data recorded in the log recording means for identifying the user who performed the operation related to the log data and the information on the time when the operation was performed, the same user performs The operation time required for the series of operations for use of the function performed by the user is calculated from the time when each operation in the series of operations for use of the function is performed. When the variance of the operation time required for the series of operations for use of the function by the user is calculated and the calculated variance is larger than the dispersion threshold, the series of operations for use of the function is performed. Necessary operations Log analysis means that the time to identify the operation time threshold greater than the user,
Questionnaire generating means for generating questionnaire questionnaire data relating to the usefulness of the survey target system, wherein a question item to be incorporated into the questionnaire questionnaire data is selected based on a usage status index of the function obtained by the log analyzing means Questionnaire generation means,
Questionnaire questionnaire generated by the questionnaire generation means when the variance of the operation time required for the series of operations for use of the function by each user calculated by the log analysis means is larger than a dispersion threshold Questionnaire providing means for providing data to a user whose operation time required for the series of operations for using the function is greater than an operation time threshold;
Program to function as.
前記調査対象システムが提供する機能の利用状況指標についての条件ごとに該条件に対応する質問項目の情報を示した質問条件情報が登録されたデータベース、
として更に機能させ、
前記質問票生成手段は、前記ログ解析手段により求められた前記機能の利用状況指標が満たす条件が前記データベースにあれば、該条件に対応する質問項目をアンケート質問票データに組み込む質問項目として選択する、
ことを特徴とする請求項1記載のプログラム。 The computer system;
A database in which question condition information indicating information of question items corresponding to the condition is registered for each condition about the usage status index of the function provided by the survey target system;
Further function as
The questionnaire generation unit selects a question item corresponding to the condition as a question item to be incorporated into the questionnaire questionnaire data when the condition satisfied by the function usage status index obtained by the log analysis unit is satisfied in the database. ,
The program according to claim 1.
前記質問票生成手段は、前記ログ解析手段により求められた前記機能の利用状況指標が満たす条件が前記データベースにあれば、該条件に対応する対象者情報に基づき、該条件に対応する質問項目の対象とする利用者を特定し、特定した利用者に対するアンケート質問票データとして該質問項目を含んだアンケート質問票データを生成する、
ことを特徴とする請求項2記載のプログラム。 The question condition information includes target person information for identifying a user as a target of a question item corresponding to the condition for each condition,
If the condition that the usage status index of the function obtained by the log analysis unit satisfies is in the database, the questionnaire generation unit generates a question item corresponding to the condition based on target person information corresponding to the condition. Specify the target user, and generate questionnaire questionnaire data including the question items as questionnaire questionnaire data for the specified user.
The program according to claim 2.
前記ログ解析手段は、前記調査対象システムが提供する機能ごとにその利用状況指標を求め、
前記質問票生成手段は、前記ログ解析手段が求めた各機能の利用状況指標と各機能についての質問条件情報とに基づき、利用者ごとに、該利用者を対象とする質問項目を集めたアンケート質問票データを生成する、
ことを特徴とする請求項3記載のプログラム。 In the database, the question condition information is registered for each function provided by the survey target system,
The log analysis means obtains a usage status index for each function provided by the survey target system,
The questionnaire generating means is a questionnaire that collects the question items for each user based on the usage status index of each function obtained by the log analyzing means and the question condition information for each function. Generate questionnaire data,
The program according to claim 3.
前記質問票生成手段は、グループごとの利用状況の差の程度に応じ、質問項目の対象とする利用者を限定する、
ことを特徴とする請求項1記載のプログラム。 The log analysis means, when the usage status index of the function satisfies a predetermined condition, further determines the usage status of the function of the group from the log for each user group distinguished by the user profile information. Seeking
The questionnaire generation means limits the users targeted for the question items according to the degree of difference in the usage situation for each group,
The program according to claim 1.
前記ログ記録手段により記録されたログデータを解析し、前記機能の利用状況を示す利用状況指標を求めるログ解析手段であって、前記機能の利用状況指標が所定の条件を満足する場合に、更に前記ログ記録手段に記録された各ログデータに含まれる、当該ログデータに係る操作を行った利用者を特定する情報と当該操作の行われた時刻の情報とに基づき、同一の利用者が行った当該機能の利用のための一連の操作における各操作の行われた時刻から、当該利用者が行った当該機能の利用のための前記一連の操作に要した操作時間を計算し、計算した各利用者による当該機能の利用のための当該一連の操作に要した操作時間の分散を計算し、計算した分散が分散しきい値より大きい場合に、前記機能の利用のための前記一連の操作に要した操作時間が操作時間しきい値より大きい利用者を特定する、ログ解析手段と、
前記調査対象システムの有用性に関するアンケート質問票データを生成する質問票生成手段であって、前記ログ解析手段により求められた前記機能の利用状況指標に基づきアンケート質問票データに組み込む質問項目を選択する質問票生成手段と、
前記ログ解析手段が計算した各利用者による当該機能の利用のための当該一連の操作に要した操作時間の分散が分散しきい値より大きい場合に、前記質問票生成手段が生成したアンケート質問票データを、前記機能の利用のための前記一連の操作に要した操作時間が操作時間しきい値より大きい利用者に提供する質問票提供手段と、
を備えるシステム有用性調査支援装置。 Detects the operation performed by the user for the function provided by the investigation target system , and includes at least information identifying the user who performed the operation and information on the time when the operation was performed. Log recording means for recording log data ;
Analyzing the log data recorded by the log recording unit, a log analyzing means for calculating a usage index indicating usage of the function, if the usage index of the function satisfies a predetermined condition, further Based on the information included in each log data recorded in the log recording means for identifying the user who performed the operation related to the log data and the information on the time when the operation was performed, the same user performs The operation time required for the series of operations for use of the function performed by the user is calculated from the time when each operation in the series of operations for use of the function is performed. When the variance of the operation time required for the series of operations for use of the function by the user is calculated and the calculated variance is larger than the dispersion threshold, the series of operations for use of the function is performed. Necessary operations Time to identify the operation time threshold is greater than the user, a log analysis unit,
Questionnaire generating means for generating questionnaire questionnaire data relating to the usefulness of the survey target system, wherein a question item to be incorporated into the questionnaire questionnaire data is selected based on a usage status index of the function obtained by the log analyzing means Questionnaire generation means;
Questionnaire questionnaire generated by the questionnaire generation means when the variance of the operation time required for the series of operations for use of the function by each user calculated by the log analysis means is larger than a dispersion threshold Questionnaire providing means for providing data to a user whose operation time required for the series of operations for use of the function is greater than an operation time threshold;
System usability investigation support device comprising:
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004152058A JP4479343B2 (en) | 2004-05-21 | 2004-05-21 | Programs and devices for system usability study support |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004152058A JP4479343B2 (en) | 2004-05-21 | 2004-05-21 | Programs and devices for system usability study support |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2005332327A JP2005332327A (en) | 2005-12-02 |
| JP2005332327A5 JP2005332327A5 (en) | 2007-06-14 |
| JP4479343B2 true JP4479343B2 (en) | 2010-06-09 |
Family
ID=35486932
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004152058A Expired - Fee Related JP4479343B2 (en) | 2004-05-21 | 2004-05-21 | Programs and devices for system usability study support |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4479343B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008059182A (en) * | 2006-08-30 | 2008-03-13 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Authentication device and method |
| JP4810479B2 (en) * | 2007-03-23 | 2011-11-09 | Necビッグローブ株式会社 | Questionnaire system, questionnaire control server, questionnaire control method, and program |
| JP2011002870A (en) * | 2009-06-16 | 2011-01-06 | Hitachi Ltd | Method for evaluating and improving operability of web application, and web system |
| JP6085575B2 (en) * | 2014-02-18 | 2017-02-22 | 三菱重工業株式会社 | Questionnaire processing apparatus, questionnaire processing method, program, and questionnaire processing system |
| JP7410687B2 (en) * | 2019-10-25 | 2024-01-10 | 株式会社Jtbコミュニケーションデザイン | Organizational change support system, organizational change support method, and organizational change support program |
-
2004
- 2004-05-21 JP JP2004152058A patent/JP4479343B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2005332327A (en) | 2005-12-02 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US6853966B2 (en) | Method for categorizing, describing and modeling types of system users | |
| Hasan et al. | A comparison of usability evaluation methods for evaluating e-commerce websites | |
| Bevan et al. | Usability measurement in context | |
| Nowack | 360-degree feedback: The whole story | |
| WO2012177791A2 (en) | System and method for building and managing user experience for computer software interfaces | |
| Bradley et al. | Rating Scales in Survey Research: Using the Rasch model to illustrate the middle category measurement flaw | |
| US20170323316A1 (en) | Method for Documenting a Customer's Journey Using an Online Survey Platform | |
| US20070288246A1 (en) | In-line report generator | |
| JP2002092291A (en) | Method for investigating questionnaire, questionnaire system and recording medium | |
| JPWO2004072883A1 (en) | Usability evaluation support method and system | |
| Heerwegh | Internet survey paradata | |
| JP4335251B2 (en) | Online expert selection methods and systems | |
| JP3580497B2 (en) | Company diagnosis system, company diagnosis method, company diagnosis server, and recording medium | |
| Menezes et al. | Development, validation, and reliability testing of the brief instrument to assess workers› productivity during a working day (IAPT) | |
| JP4795496B1 (en) | Questionnaire counting system | |
| JP4479343B2 (en) | Programs and devices for system usability study support | |
| Abdullah et al. | Usability measurement of Malaysia online news websites | |
| JP4029654B2 (en) | Answer system, answer device, answer method and answer program | |
| JP6626170B1 (en) | Health evaluation system, health evaluation server and health evaluation program | |
| JP2005209042A (en) | Questionnaire system and questionnaire page forming method | |
| US11120404B2 (en) | Method and system for dynamic data collection while optimize a smart device | |
| JP2006171817A (en) | Web site evaluation system and method | |
| JP2005346171A (en) | Recruitment information provision system | |
| Nussbaumer et al. | An evaluation system for digital libraries | |
| JP2006338697A (en) | Method, device and program for creating questionnaire item |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20070425 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20070425 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20090819 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20090901 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20091029 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20100223 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20100308 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130326 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 4479343 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130326 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20140326 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |