JP4474455B2 - Refrigerant filling apparatus for refrigeration air conditioner and refrigerant filling method for refrigeration air conditioner - Google Patents
Refrigerant filling apparatus for refrigeration air conditioner and refrigerant filling method for refrigeration air conditioner Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4474455B2 JP4474455B2 JP2007284640A JP2007284640A JP4474455B2 JP 4474455 B2 JP4474455 B2 JP 4474455B2 JP 2007284640 A JP2007284640 A JP 2007284640A JP 2007284640 A JP2007284640 A JP 2007284640A JP 4474455 B2 JP4474455 B2 JP 4474455B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- refrigerant
- charging
- amount
- temperature
- heat exchanger
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25B—REFRIGERATION MACHINES, PLANTS OR SYSTEMS; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS
- F25B45/00—Arrangements for charging or discharging refrigerant
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25B—REFRIGERATION MACHINES, PLANTS OR SYSTEMS; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS
- F25B13/00—Compression machines, plants or systems, with reversible cycle
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25B—REFRIGERATION MACHINES, PLANTS OR SYSTEMS; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS
- F25B2345/00—Details for charging or discharging refrigerants; Service stations therefor
- F25B2345/003—Control issues for charging or collecting refrigerant to or from a cycle
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Thermal Sciences (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Air Conditioning Control Device (AREA)
Description
この発明は、冷凍空調装置への冷媒充填装置及び冷凍空調装置への冷媒充填方法に関するものである。 The present invention relates to a refrigerant charging device for a refrigeration air conditioner and a refrigerant charging method for a refrigeration air conditioning device.
冷凍サイクルを構成する冷凍空調装置は、一般に室内機と、室外機と、室内機と室外機との間を接続する配管とにより構成されている。室内機は、室内側熱交換器等を有する。また、室外機は、室外側熱交換器、圧縮機、減圧電磁弁等を有し、それぞれが室外機内部で配管接続されている。これらで構成された室内機と、室外機とは、据え付け現場にて配管接続され、冷凍空調装置として機能する。 A refrigerating and air-conditioning apparatus constituting a refrigeration cycle is generally composed of an indoor unit, an outdoor unit, and a pipe connecting between the indoor unit and the outdoor unit. The indoor unit includes an indoor heat exchanger and the like. The outdoor unit includes an outdoor heat exchanger, a compressor, a pressure reducing electromagnetic valve, and the like, and each is connected by piping inside the outdoor unit. The indoor unit constituted by these and the outdoor unit are connected by piping at the installation site and function as a refrigeration air conditioner.
冷凍空調装置の据え付け環境は多種多様である。その据え付け環境に応じた長さの接続配管を接続する。そのため、接続配管長によって冷凍サイクル内の容積は異なる。また、室内側熱交換器3も設置する室内機Bによって異なる容積を持つことから、据え付け環境ごとに冷媒回路容積は異なることになる。
There are many different installation environments for refrigeration air conditioners. Connect a connection pipe with a length appropriate for the installation environment. Therefore, the volume in the refrigeration cycle differs depending on the length of the connecting pipe. Moreover, since the indoor
冷凍空調装置を機能させる為には冷媒回路を循環する冷媒が必要である。上記据え付け環境による冷媒回路容積の違いから必要冷媒量が異なるため、予め冷媒回路内に容積に応じて必要な全冷媒量を充填しておくことは困難である。 In order for the refrigeration air conditioner to function, a refrigerant circulating in the refrigerant circuit is necessary. Since the required amount of refrigerant differs due to the difference in the refrigerant circuit volume depending on the installation environment, it is difficult to preliminarily fill the refrigerant circuit with the necessary total amount of refrigerant according to the volume.
従来、冷凍空調装置の設置状態に対して適正な追加冷媒量を自動で充填し、冷凍サイクルの信頼性を確保するために、圧縮機、室外熱交換器、減圧装置、受液器を有する室外ユニットと、室内熱交換器、減圧装置を有する室内ユニットと、を配管接続した冷凍サイクルに対して、所定量の冷媒を室外ユニット内に充填、又は冷媒を追加充填する冷媒充填装置において、室内ユニットの受液器と室内ユニットの間に副流部を備えた過冷却熱交換器の主流部を配置し、副流部の一方は冷媒充填電磁弁を介して冷媒ボンベに、他方は圧縮機の吸入側に接続し、主流部出口側の冷媒過冷却度に関連して冷媒充填電磁弁の開閉を制御する冷媒充填装置及び冷媒充填方法が提案されている(例えば、特許文献1参照)。 Conventionally, an outdoor unit having a compressor, an outdoor heat exchanger, a pressure reducing device, and a liquid receiver in order to automatically fill an additional refrigerant amount appropriate for the installation state of the refrigeration air conditioner and ensure the reliability of the refrigeration cycle. In a refrigerant charging apparatus for filling a predetermined amount of refrigerant into an outdoor unit or additionally charging a refrigerant with respect to a refrigeration cycle in which the unit, an indoor heat exchanger, and an indoor unit having a decompression device are connected by piping, the indoor unit The main flow part of the supercooling heat exchanger having a secondary flow part is arranged between the liquid receiver and the indoor unit, and one of the secondary flow parts is placed in the refrigerant cylinder via the refrigerant filling electromagnetic valve, and the other is in the compressor. A refrigerant charging device and a refrigerant charging method that are connected to the suction side and control the opening and closing of the refrigerant charging electromagnetic valve in relation to the degree of refrigerant supercooling on the outlet side of the main flow portion have been proposed (for example, see Patent Document 1).
また、冷凍サイクルの現場据え付け時に追加充填する冷媒量を適切且つ自動的に調整し得る冷凍サイクルに対する冷媒充填方法を提供するために、室外側のユニット及び室内側のユニットを連結管で連結した後の試運転の際、冷媒循環系路に冷媒を補充しつつ冷媒循環路の各点での冷媒圧力、冷媒温度を規定する所定の運転パラメータをモニタして冷媒の過熱度及び/又は過冷却度を検出し、これら過熱度及び/又は過冷却度に達したことで適量の冷媒が充填されたとして冷媒の補充を自動的に停止するようにした冷凍サイクルに対する冷媒充填方法及びその装置が提案されている(例えば、特許文献2参照)。
しかしながら、上記特許文献1、2の冷媒充填方法では、冷凍空調装置の冷媒回路に冷媒を自動で充填し適正量充填後にその後の冷媒充填を抑制する為に、冷媒回路と冷媒ボンベの接続間に自動制御弁を備えなければならない。これは、コスト・資源の課題だけでなく、使用できる冷凍空調装置の範囲も限定される。
However, in the refrigerant filling method of
この発明は、上記のような課題を解決するためになされたもので、冷凍空調装置と冷媒を充填するために必要な冷媒ボンベとの接続間に、冷媒ボンベに備えられたバルブ以外の弁を設けずに、適正冷媒量を充填後に自動で冷媒充填を終了することができる冷凍空調装置への冷媒充填装置及び冷凍空調装置への冷媒充填方法を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made to solve the above-described problems. Between the refrigeration air conditioner and a refrigerant cylinder necessary for charging the refrigerant, a valve other than the valve provided in the refrigerant cylinder is provided. An object of the present invention is to provide a refrigerant charging device for a refrigeration air conditioner and a refrigerant charging method for the refrigeration air conditioning device that can automatically end the refrigerant charging after charging with an appropriate amount of refrigerant without providing it.
この発明に係る冷媒充填装置は、冷凍空調装置への冷媒充填装置において、圧縮機、四方弁、室内側熱交換器、減圧装置、室外側熱交換器、液溜め装置を有する冷媒回路と、冷媒回路の低圧側にボンベに備えられたバルブ以外に弁を設けずに接続される冷媒ボンベと、冷媒回路の冷媒充填量の適正を判定する際、室内側熱交換器を内設した室内機と室外側熱交換器を内設した室外機とを接続する接続配管の液側配管に液冷媒状態で存在する運転モードとして充填状態を判定し、冷媒回路へ前記冷媒ボンベから冷媒を充填する制御を行なう制御装置と、制御装置に設けられ、冷媒の充填状態を表示する表示装置とを備え、当該冷凍空調装置を運転しながら、冷媒回路へ冷媒ボンベから冷媒を充填して、冷媒量が適正と判定すると自動的に圧縮機を停止するとともに四方弁を切り替えることを特徴とする。 A refrigerant charging device according to the present invention is a refrigerant charging device for a refrigerating and air-conditioning device, a refrigerant circuit having a compressor, a four-way valve, an indoor heat exchanger, a pressure reducing device, an outdoor heat exchanger, a liquid reservoir, and a refrigerant A refrigerant cylinder connected without providing a valve other than a valve provided on the low pressure side of the circuit, and an indoor unit provided with an indoor heat exchanger when determining the appropriate refrigerant charging amount of the refrigerant circuit; Control is performed to determine a filling state as an operation mode existing in a liquid refrigerant state in a liquid side pipe of a connection pipe connecting an outdoor unit provided with an outdoor heat exchanger, and to fill the refrigerant circuit with the refrigerant from the refrigerant cylinder. A control device for performing the operation, and a display device provided in the control device for displaying a refrigerant charging state. While operating the refrigerating and air-conditioning apparatus, the refrigerant circuit is filled with the refrigerant from the refrigerant cylinder so that the refrigerant amount is appropriate. Compressor automatically when judged And it switches the four-way valve to stop.
この発明に係る冷凍空調装置への冷媒充填装置は、冷凍空調装置と冷媒を充填するために必要な冷媒ボンベとの接続間に、冷媒ボンベに備えられたバルブ以外の弁を設けずに、冷媒ボンベから冷凍空調装置へ冷媒を充填できる。 The refrigerant filling device for the refrigeration air-conditioning apparatus according to the present invention provides a refrigerant without providing a valve other than the valve provided in the refrigerant cylinder between the connection of the refrigeration air-conditioning apparatus and the refrigerant cylinder necessary for charging the refrigerant. The refrigerant can be charged from the cylinder to the refrigeration air conditioner.
実施の形態1.
以下、冷凍空調装置の一例である空気調和機を例に説明する。冷凍空調装置としては、空気調和機以外に、例えば、冷蔵ショーケース等がある。
Hereinafter, an air conditioner which is an example of a refrigeration air conditioner will be described as an example. As a refrigerating and air-conditioning apparatus, for example, there is a refrigerated showcase in addition to an air conditioner.
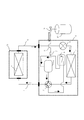
図1乃至図8は実施の形態1を示す図で、図1は空気調和機の冷媒充填時の冷媒回路図、図2は冷媒充填方法を示す冷媒充填フローチャート、図3は冷媒充填量判定運転モードが選択された場合の制御装置30の制御対象を示す図、図4は外気温と冷凍サイクル安定までに至る時間の関係を示す図、図5は冷媒充填時における圧縮機1の回転数の制御方法を示す図、図6は冷媒充填時における四方弁2の制御方法を示す図、図7は冷媒充填時における冷媒の充填方法を示す図、図8は空気調和機の冷媒充填時の変形例の冷媒回路図である。
1 to 8 are
図1において、空気調和機は、室外機Aと室内機Bとを備える。室外機Aは、圧縮機1、四方弁2、減圧電磁弁4(減圧装置の一例)、室外側熱交換器5、及びアキュームレータ6(液溜め装置の一例)等を内蔵している。また、室内機Bは、室内側熱交換器3等を内蔵している。
In FIG. 1, the air conditioner includes an outdoor unit A and an indoor unit B. The outdoor unit A includes a
室外機Aの一端と室内機Bの一端とをガス側接続配管Cで接続する。一方、室外機Aの他端と室内機Bの他端を液側接続配管Dで接続する。これにより、冷媒回路が形成される。 One end of the outdoor unit A and one end of the indoor unit B are connected by a gas side connection pipe C. On the other hand, the other end of the outdoor unit A and the other end of the indoor unit B are connected by a liquid side connection pipe D. Thereby, a refrigerant circuit is formed.
形成された冷媒回路の中で、室外機Aに内蔵されている四方弁2は、冷媒回路の進路方向を変更する役割を持つ。通常、冷房及び暖房の両方の機能を有する冷凍空調装置は、圧縮機1から吐出された高温・高圧の冷媒を室外側熱交換器5に送り込んだ場合に冷房運転を行い、室内側熱交換器3に送り込んだ場合に暖房運転を行う。四方弁2はこの運転サイクルを切り替える役割を有し、四方弁2内にあるスライド弁を切り替えることで運転サイクルを自由に切り替えることが出来る。
In the formed refrigerant circuit, the four-
一方、室外機Aに内蔵された減圧電磁弁4は、熱交換器によって凝縮された低温・高圧の液冷媒を、蒸発しやすい圧力まで減圧させる役割を持つ。つまり、圧縮機1から吐出された後、冷房、または暖房の運転サイクルに応じた冷媒回路の所定の流路を通過し、減圧電磁弁4に到達するまでは、冷媒は高圧を維持しており、減圧電磁弁4通過以降より圧縮機1の吸入口に到達するまでに通過する冷媒回路では、低圧となる。
On the other hand, the pressure reducing
上記の通り形成した冷媒回路を持つ装置が、空気調和機として機能するためには、冷媒回路内に冷媒を充填する必要がある。空気調和機の冷媒回路に冷媒を充填する方法は、一般的に冷媒ボンベ10を冷媒回路中にある低圧側チャージポート7にホース8を介して接続し、冷媒ボンベ10に備え付けられた冷媒ボンベバルブ9を開くことで、回路内に冷媒が充填される。
In order for an apparatus having a refrigerant circuit formed as described above to function as an air conditioner, it is necessary to fill the refrigerant circuit with a refrigerant. In general, a refrigerant circuit of an air conditioner is filled with a refrigerant by connecting a
本実施の形態の冷媒充填方法においても、冷媒を充填する前準備としては、同様の接続を行う。すなわち、冷媒ボンベバルブ9を有する冷媒ボンベ10を冷媒回路(低圧側である圧縮機1の吸入側)にホース8を介して接続することを、本実施の形態で提供する冷媒充填方法の準備段階とする。
Also in the refrigerant filling method of the present embodiment, the same connection is performed as preparation before filling the refrigerant. That is, the refrigerant filling method provided in the present embodiment includes connecting the
上記準備が完了した後における、空気調和機への冷媒充填方法を図2に従って説明する。図2は冷媒充填方法を示す冷媒充填フローチャートである。 The refrigerant filling method for the air conditioner after the above preparation is completed will be described with reference to FIG. FIG. 2 is a refrigerant charging flowchart showing a refrigerant charging method.
先ず、予め室外機Aの制御装置30に設けられた所定のスイッチ(図示せず)を入れると、冷媒充填量判定運転モードが選択される(S1)。
First, when a predetermined switch (not shown) provided in the
冷媒充填量判定運転モードが選択された場合、図1に示すように減圧電磁弁4が室外機Aに内蔵されている場合は、暖房運転を開始する(S2)。暖房運転は、室外機Aに内蔵されたアキュームレータ6内に必要最小限で封入された冷媒が、冷媒回路を図1の矢印で示された方向に循環する。暖房運転で冷媒充填量判定を行う理由は、次の通りである。室外機Aには、工場出荷時においてその冷媒回路内(アキュームレータ6)に必要最小限の冷媒が封入されている。室内機Bには冷媒は充填されていない。従って、空気調和機の据付時には、先ず室外機Aと室内機Bとを冷媒回路が遮断された状態で接続する。室内機Bのエアーを放出した後、真空引きを行う。その状態で、室外機Aと室内機Bとを冷媒回路が遮断された状態を解除(開放)する。すると室内機Bには、予め室外機Aに充填されている必要最小限の冷媒が流入し、空気調和機の運転が可能な状態になる。
When the refrigerant charging amount determination operation mode is selected, the heating operation is started when the pressure reducing
室外機Aと室内機Bとを接続する接続配管(延長配管)は、据付状況により長さが変化する。この接続配管(延長配管)に液冷媒が存在する状態で、冷媒充填量判定を行うことにより、判定精度を上げている。図1のように、減圧電磁弁4が室外機Aにある場合は、暖房運転を行うことにより、接続配管(延長配管)の一つである液側接続配管Dに液冷媒が存在するようにすることができる。これを冷房運転にすると、液側接続配管Dには気液二相冷媒が流れ、室外側熱交換器5が凝縮器となり、液冷媒は室外側熱交換器5と減圧電磁弁4との間に存在する。従って、冷房運転では接続配管(延長配管)の長さに応じた冷媒充填量判定が困難である。
The length of the connection pipe (extended pipe) that connects the outdoor unit A and the indoor unit B varies depending on the installation status. The determination accuracy is improved by performing the refrigerant filling amount determination in a state where the liquid refrigerant is present in the connection pipe (extension pipe). As shown in FIG. 1, when the pressure reducing
冷媒充填量判定運転モードが選択された場合の制御対象を図3に示す。空気調和機は環境によって最適な運転状態を選択する為、室外機A、室内機Bの制御を行っている。 FIG. 3 shows a control target when the refrigerant charging amount determination operation mode is selected. The air conditioner controls the outdoor unit A and the indoor unit B in order to select an optimal operating state depending on the environment.
冷媒回路内の冷媒温度を把握するための温度検知装置として、以下に示すものが設けられる。
(1)室外機Aの圧縮機1の吐出管の温度を検知する圧縮機吐出管温度検知装置21;
(2)室内機Bの室内側熱交換器の温度を検知する室内側熱交換器温度検知装置22;
(3)室内機Bの室内側熱交換器出口の温度を検知する室内側熱交換器出口温度検知装置23;
(4)室内機Bの吹出口の空気温度を温度を検知する室内側吹出口温度検知装置24;
(5)室外機Aの室外側熱交換器入口の温度を検知する室外側熱交換器入口温度検知装置25;
(6)室外機Aの室外側熱交換器の温度を検知する室外側熱交換器温度検知装置26;
(7)室外機Aの吹出口の空気温度を温度を検知する室外側吹出口温度検知装置27。
What is shown below is provided as a temperature detection device for grasping the refrigerant temperature in the refrigerant circuit.
(1) A compressor discharge pipe
(2) Indoor heat exchanger
(3) The indoor side heat exchanger outlet
(4) The indoor side outlet
(5) an outdoor heat exchanger inlet
(6) The outdoor heat exchanger
(7) The outdoor air outlet
また、室内機Bの周囲温度を検出する温度検出装置及び室外機Aの周囲温度を検出する温度検出装置が、夫々室内機B及び室外機Aの空気吸込み側に設けられる。 Further, a temperature detection device that detects the ambient temperature of the indoor unit B and a temperature detection device that detects the ambient temperature of the outdoor unit A are provided on the air suction side of the indoor unit B and the outdoor unit A, respectively.
制御装置30が、上記(1)乃至(7)等の温度検知装置をリアルタイムで検知し、その状況に応じて圧縮機1、減圧電磁弁4、室内側ファン11及び室外側ファン12を制御することで、安定した運転状態を確保し、空気調和機としての役割を果たす。
The
制御装置30は、冷媒充填状態等を表示する表示装置40(例えば、LED(発光ダイオード))を有する。制御装置30は、室外機Aに装着される基板にマイコン(マイクロコンピュータ)等を実装して構成される。制御装置30は、少なくとも冷媒回路へ冷媒ボンベ10から冷媒を充填する際の制御を行うものである。
The
本実施の形態による冷媒充填方法も、空気調和機を制御する上記(1)乃至(7)の温度検知装置が検知する各温度を使用し、適切な暖房運転状態を確保出来ているかを判断することで、冷媒回路の冷媒量の状態を判断する。 The refrigerant charging method according to the present embodiment also uses each temperature detected by the temperature detection devices (1) to (7) that control the air conditioner to determine whether an appropriate heating operation state can be secured. Thus, the state of the refrigerant amount in the refrigerant circuit is determined.
S2の暖房運転により、圧縮機1が運転を開始し、冷媒が回路内を循環する。ここで、外気温が低く、且つガス側接続配管C及び液側接続配管Dが長く、アキュームレータ6内に封入された冷媒量では極端に不足している場合、冷媒量過少の状態で運転する。
By the heating operation of S2, the
この場合、冷媒回路内に必要最低限の充填量を満たしておらず、圧縮機1が冷媒を吐出する一方、吸入する冷媒が循環されてこない為、アキュームレータ6から圧縮機1へと繋がる配管経路が真空になる。以上の運転状態は圧縮機1の故障に繋がる可能性がある為、冷媒量過少の場合は、すぐに冷媒が極端に不足している旨を通知し、速やかな冷媒充填を促す。表示装置40が冷媒が過少(X=1、後述する)であることを表示する(S4)。制御装置30から信号を受けた表示装置40(LED)が、例えば点滅することにより作業者に通知し、速やかな冷媒充填を促す。
In this case, the refrigerant circuit does not satisfy the minimum required filling amount, and the
S3で冷媒量が過少でない場合は、冷凍サイクルが安定し、適正な冷媒量状態を判定するまでの間、冷媒量を追加しないまま運転を行う(S5)。 If the refrigerant amount is not too small in S3, the operation is performed without adding the refrigerant amount until the refrigeration cycle is stabilized and an appropriate refrigerant amount state is determined (S5).
S5の運転は、現在冷媒回路内で循環している冷媒量が適正であるか判断するのに必要なだけでなく、冷凍サイクル自体の信頼性確保にも重要である。 The operation of S5 is not only necessary for determining whether the amount of refrigerant currently circulating in the refrigerant circuit is appropriate, but is also important for ensuring the reliability of the refrigeration cycle itself.
冷凍サイクルが安定するまでの運転時間は、外気温によって左右される。 The operation time until the refrigeration cycle is stabilized depends on the outside air temperature.
S6で外気温度を所定値α℃と比較する。所定値α℃は、例えば、10℃である。 In S6, the outside air temperature is compared with a predetermined value α ° C. The predetermined value α ° C. is, for example, 10 ° C.
外気温が低い場合、圧縮機1で吐出された高温・高圧の冷媒は、室内側熱交換器3(凝縮器)に至るまでの配管を通過する過程で外気によって冷やされるため、凝縮温度と室温との差が小さい値となり、且つ過冷却度もほとんど0となる。この場合、外気温の影響を受けず、また冷媒温度を上昇させる為には圧縮機1の周波数を上げる必要がある為、冷凍サイクルが安定し、凝縮温度が上昇するまでには時間を要する。
When the outside air temperature is low, the high-temperature and high-pressure refrigerant discharged from the
S6で外気温度が所定値α℃より低い場合は、S7に進み所定時間F(分)経過したか判定する。S7で所定時間F(分)経過していない場合は、冷媒充填量判定中時間とし、冷媒の充填を控えてさらに運転を行う。所定時間F(分)は、冷凍サイクルが安定し、凝縮温度が上昇するまでの時間であり、例えば20分である。所定時間F(分)の決定は、各外気温条件において、冷凍空調装置の安定運転に至るまでの時間を実験的に求めた数値である。外気温と冷凍サイクル安定までに至る時間の関係を図4に示す。図4に示すように、外気温が運転保証温度範囲では、外気温が低い場合は冷凍空調装置の安定運転に至るまでの時間が、外気温が高い場合よりも長くなる。 When the outside air temperature is lower than the predetermined value α ° C. in S6, the process proceeds to S7 and it is determined whether a predetermined time F (minute) has elapsed. When the predetermined time F (minutes) has not elapsed in S7, it is determined that the refrigerant charging amount is being determined, and the operation is further performed while the refrigerant is not charged. The predetermined time F (minutes) is a time until the refrigeration cycle is stabilized and the condensation temperature rises, and is, for example, 20 minutes. The determination of the predetermined time F (minutes) is a numerical value obtained experimentally by determining the time required for stable operation of the refrigeration air conditioner under each outside air temperature condition. FIG. 4 shows the relationship between the outside air temperature and the time required to stabilize the refrigeration cycle. As shown in FIG. 4, when the outside air temperature is within the guaranteed operating temperature range, when the outside air temperature is low, the time until stable operation of the refrigeration air conditioner is longer than when the outside air temperature is high.
一方、外気温が高い場合は、上記外気温が低い場合に比べて、凝縮温度は圧縮機1の周波数が低い状態から高い為、冷凍サイクルの安定までの時間は短縮される。
On the other hand, when the outside air temperature is high, the condensation temperature is high from a low frequency of the
S6で外気温度が所定値α℃より高い場合は、S8に進み所定時間E(分)経過したか判定する。所定時間E(分)は、S7のF(分)より短い時間である。所定時間E(分)は、冷凍サイクルが安定し、凝縮温度が上昇するまでの時間であり、例えば12分である。S8で所定時間E(分)経過していない場合は、冷媒充填量判定中時間とし、冷媒の充填を控えてさらに運転を行う。 When the outside air temperature is higher than the predetermined value α ° C. in S6, the process proceeds to S8 and it is determined whether a predetermined time E (minute) has elapsed. The predetermined time E (minute) is shorter than F (minute) in S7. The predetermined time E (minutes) is a time until the refrigeration cycle is stabilized and the condensation temperature rises, and is, for example, 12 minutes. If the predetermined time E (minutes) has not elapsed in S8, it is determined that the refrigerant charging amount is being determined, and the operation is further performed while the refrigerant is not charged.
このように、冷凍サイクルの安定時間の差異を考慮し、外気温によって冷媒量を追加しないまま運転する時間を変更する。 In this way, in consideration of the difference in the stabilization time of the refrigeration cycle, the operation time is changed without adding the refrigerant amount depending on the outside air temperature.
次に、図2に示す冷媒充填方法フローチャートのS9の冷媒量状態判定値Xの表示方法について説明を行う。 Next, the display method of the refrigerant quantity state determination value X in S9 of the refrigerant charging method flowchart shown in FIG. 2 will be described.
外気温によって指定された待機時間(E、F(分))を経過すると、冷凍サイクル状態を示す各因子のうち、過冷却度及び凝縮温度パラメータにより演算された冷媒量状態判定値Xが出力される。冷媒量状態判定値Xは、刻々と変化する冷凍サイクル状態に従ってリアルタイムで算出し、算出するパラメータとしては、冷凍サイクル安定状態移行後における過冷却度、および凝縮温度と室温の差を利用し、過冷却度を凝縮温度と室温の差で除した値の範囲によって、冷媒量状態判定値Xを決定する。 When the standby time (E, F (minutes)) specified by the outside air temperature has elapsed, among the factors indicating the refrigeration cycle state, the refrigerant quantity state determination value X calculated by the subcooling degree and the condensation temperature parameter is output. The The refrigerant quantity state determination value X is calculated in real time according to the refrigeration cycle state that changes every moment, and as a parameter to be calculated, the degree of supercooling after transition to the refrigeration cycle stable state and the difference between the condensation temperature and room temperature are used. The refrigerant quantity state determination value X is determined by the range of the value obtained by dividing the degree of cooling by the difference between the condensation temperature and room temperature.
結果の表示は、室外機Aの制御装置30(基板)に設置された表示装置40(LED)によって行われる。LEDの表示方法としては、1つのLEDの点滅パターンを変化させることによって様々な信号を明確に伝達する。例えば、6秒間を1セットと考えた場合、その中で点滅1回、2回、3回、4回と割り振ることで、冷媒回路内に存在する冷媒量が過少、小、適正または過充填かをリアルタイムに出力した冷媒量状態判定値を伝達する。 The display of the result is performed by the display device 40 (LED) installed on the control device 30 (substrate) of the outdoor unit A. As an LED display method, various signals are clearly transmitted by changing the blinking pattern of one LED. For example, if 6 seconds is considered as one set, the amount of refrigerant existing in the refrigerant circuit is too small, small, appropriate or overfilled by allocating blinking once, twice, three times, and four times. Is transmitted in real time.
即ち、S7で運転時間がF(分)以上の場合、S8で運転時間がE(分)以上の場合は、S9に進み過冷却度及び凝縮温度パラメータにより演算された冷媒量状態判定値Xを出力する。冷媒量状態判定値Xは、次の4レベルに分かれる。
X=1(冷媒量が過少)
X=2(冷媒量が小)
X=3(冷媒量が適正)
X=4(冷媒量が過充填)
That is, when the operation time is F (min) or more in S7, and when the operation time is E (min) or more in S8, the process proceeds to S9 and the refrigerant amount state determination value X calculated by the subcooling degree and the condensation temperature parameter is set. Output. The refrigerant quantity state determination value X is divided into the following four levels.
X = 1 (Insufficient amount of refrigerant)
X = 2 (small amount of refrigerant)
X = 3 (the amount of refrigerant is appropriate)
X = 4 (overflow of refrigerant)
冷媒量状態判定値Xは、刻々と変化する冷凍サイクル状態に従ってリアルタイムで制御装置30が算出する。制御装置30の算出結果は、室外機Aの基板(図示せず)に設置された表示装置40(例えば、LED(発光ダイオード))に表示される。
The refrigerant quantity state determination value X is calculated by the
次に、図2に示す冷媒充填方法フローチャートのS10で冷媒量判定の結果冷媒不足と判断された際の、冷媒充填方法について説明を行う。 Next, the refrigerant charging method when it is determined that the refrigerant is insufficient as a result of the refrigerant amount determination in S10 of the refrigerant charging method flowchart shown in FIG. 2 will be described.
判定の結果、冷媒量が少ないと判断された場合、冷媒を充填する作業へと移行する。 As a result of the determination, when it is determined that the amount of the refrigerant is small, the operation shifts to an operation for charging the refrigerant.
S10でX=1又はX=2かを判定する。X=1又はX=2の場合は、S11に進み冷媒を充填する。 In S10, it is determined whether X = 1 or X = 2. In the case of X = 1 or X = 2, it progresses to S11 and is filled with a refrigerant | coolant.
冷媒量過少(X=1)の場合は、冷媒量過少(X=1)を表示装置40に表示する(S11)。 If the amount of refrigerant is too small (X = 1), the amount of refrigerant (X = 1) is displayed on the display device 40 (S11).
そして、予め冷媒回路(例えば、アキュームレータ6)に必要最小限充填された冷媒量の3%以内の冷媒を充填する(S13)。これを約1分毎に行う。1回に充填する冷媒量を予め充填された冷媒量の3%以内にする理由は、次の通りである。 And the refrigerant | coolant within 3% of the refrigerant | coolant amount with which the refrigerant | coolant circuit (for example, accumulator 6) was filled minimum required previously is filled (S13). This is done about every minute. The reason why the amount of refrigerant charged at one time is within 3% of the amount of refrigerant charged in advance is as follows.
即ち、冷凍空調装置が安定した運転状態に移行している場合、冷媒回路内を循環している冷媒の分布は場所によって差はあるものの、拡散している状態にある。この運転状態において、初期冷媒量に対して3%以上の冷媒充填を行った場合、局所的に冷媒密度の高い冷凍サイクル運転となり、冷凍サイクルとして安定した運転状態から逸脱する。この状態では、正確な判定を行うことは困難であり、運転状態を安定に移行するまでに時間がかかるデメリットを生じる。以上のことから、冷媒充填を行う際の1分間当りの最大値を規制することとする。 That is, when the refrigerating and air-conditioning apparatus has shifted to a stable operating state, the distribution of the refrigerant circulating in the refrigerant circuit is in a diffuse state although there is a difference depending on the location. In this operation state, when the refrigerant charging of 3% or more with respect to the initial refrigerant amount is performed, the refrigeration cycle operation with a high refrigerant density is locally performed and deviates from the stable operation state as the refrigeration cycle. In this state, it is difficult to make an accurate determination, resulting in a demerit that takes time until the operating state is stably shifted. From the above, the maximum value per minute when charging the refrigerant is regulated.
冷媒量小(X=2)の場合は、冷媒量小(X=2)を表示装置40に表示し、予め冷媒回路(例えば、アキュームレータ6)に必要最小限充填された冷媒量の1%以内の冷媒を充填する(S12)。
When the refrigerant quantity is small (X = 2), the refrigerant quantity is small (X = 2) is displayed on the
冷媒量を追加し、追加冷媒量を反映した冷凍サイクルの安定状態になるまでには、追加から時間差が生じる。このため、冷媒量が冷媒量小(X=2)の状態から、予め冷媒回路に必要最小限充填された冷媒量の1%以内の冷媒を充填を追加し続けた場合、冷媒量を適正と判断した時点において実際の冷媒量は過多の状態である可能性がある。従って、判定値が適正冷媒量に近似するにつれて追加冷媒量を順次減らしていく必要がある。 There is a time difference from the addition until the refrigerant quantity is added and the refrigeration cycle is in a stable state reflecting the additional refrigerant quantity. For this reason, if the refrigerant amount is kept small (X = 2) and charging is continued with a refrigerant within 1% of the minimum refrigerant amount that has been charged in the refrigerant circuit in advance, the refrigerant amount is regarded as appropriate. There is a possibility that the actual refrigerant amount is excessive at the time of determination. Therefore, it is necessary to sequentially reduce the additional refrigerant amount as the determination value approximates the appropriate refrigerant amount.
次に、図2に示す冷媒充填方法フローチャートのS14の冷媒充填量判定時、冷媒量適正(X=3)、または冷媒量過充填(X=4)と判断し、冷媒充填量判定運転モードを停止するステップについて説明を行う。 Next, when determining the refrigerant charging amount in S14 of the refrigerant charging method flowchart shown in FIG. 2, it is determined that the refrigerant amount is appropriate (X = 3) or the refrigerant amount is overfilled (X = 4), and the refrigerant charging amount determination operation mode is set. The step of stopping will be described.
上記冷媒充填方法により、S14で、初回の判定時にまたは追加冷媒充填を繰り返した結果、冷媒量適正(X=3)、または冷媒量過充填(X=4)と判断された場合、冷媒量を判定する運転を停止するモードへと移行する。 If it is determined in S14 that the refrigerant amount is appropriate (X = 3) or the refrigerant amount is overfilled (X = 4) as a result of the first determination or repeated additional refrigerant filling in S14 by the refrigerant filling method, Transition to the mode to stop the operation to judge.
即ち、S14でXを判定し、S14でX=3又はX=4の場合、S15に進み冷媒量が適正であるから、運転停止モードに移行し冷媒充填量判定運転を停止する(S15)。運転停止モードに移行した場合、圧縮機1は自動で停止する。圧縮機1が停止すると同時に室外機Aの基板に設置された表示装置40(LED)には適正判定結果が表示される(S16)。これにより、冷媒充填作業が終了した旨を作業者が把握することができる。
That is, if X is determined in S14 and X = 3 or X = 4 in S14, the process proceeds to S15 and the refrigerant amount is appropriate, so that the operation is shifted to the operation stop mode and the refrigerant charging amount determination operation is stopped (S15). When shifting to the operation stop mode, the
さらに、冷媒充填量判定運転を停止すると、圧縮機1が停止するとともに、四方弁2が切替る。さらに減圧電磁弁4が全開となる(S15)。図1で示されるような冷媒回路の場合、四方弁2の内部に備えられた仕切りを挟み、圧縮機1の吐出側から流入する高温高圧の冷媒と、室外側熱交換器5から流入する常温低圧の冷媒の、状態の異なる冷媒が通過している。
Further, when the refrigerant charging amount determination operation is stopped, the
本実施の形態の冷媒充填方法は、冷媒ボンベ10をホース8によって介して冷媒回路の低圧側に接続し、空気調和機を運転することで生じる、接続した冷媒回路中の配管の圧力低下を利用し、圧力差からスムーズに冷媒が回路内に充填することを特徴としている。
The refrigerant filling method of the present embodiment uses the pressure drop of the piping in the connected refrigerant circuit that occurs when the
しかし、冷媒が適正に充填された後も、冷媒ボンベ10と冷媒回路の間に制御弁がないことから、そのまま冷媒が充填され続けてしまう恐れが生じる。
However, even after the refrigerant is properly filled, there is no control valve between the
そこで、上記のように状態の異なる冷媒が通過している四方弁2を切替え、互いの冷媒をバイパスすることで、冷媒回路内の圧力は均一となる。このことで冷媒回路と冷媒ボンベ10の圧力差はなくなり、冷媒充填運転完了後の必要以上の冷媒充填を抑制することが出来る。
Thus, the pressure in the refrigerant circuit becomes uniform by switching the four-
さらに、圧力差を生じる装置として、冷媒回路内には減圧電磁弁4がある。図1のような暖房運転において、減圧電磁弁4は、室内側熱交換器3から流れてくる低温高圧の液冷媒を、流路の断面積を調整することで低温低圧の気液二相冷媒へと変換する役割を持つ。
Further, as a device for generating a pressure difference, there is a pressure reducing
つまり、空気調和機の運転中において、減圧電磁弁4の前後では圧力差が生じる構造となっている。この減圧電磁弁4を、冷媒充填運転が完了すると同時に全開にする。すなわち回路上の流路の断面積を均一にすることにより、圧力差を生じることがなくなり、四方弁2と同様に冷媒回路中の圧力を均一にすることが出来る。このことも、冷媒充填運転完了後の必要以上の冷媒充填を抑制する役割を果たす。
That is, a pressure difference is generated before and after the pressure reducing
次に、図2に示す冷媒充填方法フローチャートのS17の冷媒量判定運転モード終了後の運転履歴の記録について説明を行う。 Next, the recording of the operation history after the end of the refrigerant amount determination operation mode of S17 in the refrigerant charging method flowchart shown in FIG. 2 will be described.
冷媒充填運転を完了した後、室外機Aの基板に運転履歴を記録する(S17)。直前の冷媒充填運転作業の状況を記録することにより、空気調和機の点検時など、冷媒の充填作業がどのように行われていたかと把握することができ、冷媒量がどのような状態で冷凍サイクルが運転されていたかを瞬時に検討することが出来る。このことは、空気調和機のメンテナンスに関して負担を減らし、且つ制度の向上に役立てることが可能である。 After completing the refrigerant charging operation, the operation history is recorded on the substrate of the outdoor unit A (S17). By recording the status of the previous refrigerant charging operation, it is possible to determine how the refrigerant charging operation was performed, such as when checking the air conditioner. You can instantly examine whether the cycle was operating. This can reduce the burden on the maintenance of the air conditioner and can help improve the system.
本実施の形態における冷媒充填方法を実施するにあたり、冷媒量状態判定運転モード時における、冷媒充填過程と、運転中に制御を行う圧縮機1、四方弁2の動作について説明を行う。
In carrying out the refrigerant charging method in the present embodiment, the refrigerant charging process and the operations of the
冷媒量状態判定運転モード中における、圧縮機1が行う周波数制御の一例を図5に、四方弁2が行う切り替え制御の一例を図6に、冷媒充填状況を図7にそれぞれ示す。
An example of frequency control performed by the
図2に示すフローチャート上のS1、S2に示すように、冷媒充填判定運転モードが選択されることにより、暖房運転がスタートする。同時に、制御装置30から信号を受けた圧縮機1も運転を開始し、四方弁2も切替ることにより、暖房運転としての冷媒回路での冷媒の流路方向を確保する。
As shown in S1 and S2 on the flowchart shown in FIG. 2, the heating operation starts when the refrigerant charging determination operation mode is selected. At the same time, the
運転開始から、時間経過とともに圧縮機1は周波数を上昇させ、冷媒の循環を促すことにより、置かれた温度環境下での安定した冷凍サイクル運転を確保しようとする。この時、冷凍サイクルの安定状態を確保したかを判定する要素として、図3に示す各温度検知装置、圧縮機吐出管温度検知装置21、室内側熱交換器温度検知装置22、室内側熱交換器出口温度検知装置23、室内側吹出口温度検知装置24、室外側熱交換器入口温度検知装置25、室外側熱交換器温度検知装置26、室外側吹出口温度検知装置27を利用し、その検知状況に応じて圧縮機1は周波数を刻々と変化させる。
The
冷凍サイクルが安定し、図2のS7、S8にて選択された所定の運転時間経過後、判定結果がS9のように出力される。冷媒過少(X=1)と判断された場合、この段階が図5〜図7の運転時間アに当るが、その段階から図7に示すように冷媒充填を開始する。 After the refrigeration cycle is stabilized and the predetermined operation time selected in S7 and S8 in FIG. 2 has elapsed, the determination result is output as in S9. When it is determined that the refrigerant is insufficient (X = 1), this stage corresponds to the operation time A in FIGS. 5 to 7, and refrigerant charging starts from that stage as shown in FIG. 7.
指示された冷媒を充填後、図5〜図7の運転時間イに到達し、1分当りの冷媒充填量を変化する表示を確認した後、図7に示すように指示通りの冷媒量をさらに充填する。 After filling the instructed refrigerant, the operation time a in FIGS. 5 to 7 is reached, and after confirming the display of changing the refrigerant filling amount per minute, the refrigerant amount as indicated is further increased as shown in FIG. Fill.
本冷媒充填作業を繰り返し、冷媒充填量適正と判断された場合、図2のフローチャートのS15に示す通り、冷媒量充填判定運転の停止モードに移行する。 When this refrigerant charging operation is repeated and it is determined that the refrigerant charging amount is appropriate, as shown in S15 of the flowchart of FIG.
この段階は、図5〜図7に示す運転時間ウに対応しており、圧縮機1が運転停止モード移行の信号を受けるとほぼ同時に停止し、四方弁2も切り替えを即時行う。それにより、冷媒の現在量以上の充填を抑制するようにする。
This stage corresponds to the operation time c shown in FIG. 5 to FIG. 7. When the
さらに、図8に空気調和機の冷媒充填時の第1の変形例の冷媒回路図を示す。図8に示す冷媒回路は、パワーレシーバー13を持つレシーバー回路である。そして、図1に示す冷媒回路に比し、アキュームレータ6の代わりに取り付けられたパワーレシーバー13は、室内側熱交換器3と室外側熱交換器5との間の接続配管をその内部に取り込むとともに、前後に減圧電磁弁4、2次減圧電磁弁14を持つ構成である。
Furthermore, the refrigerant circuit diagram of the 1st modification at the time of the refrigerant | coolant filling of an air conditioner is shown in FIG. The refrigerant circuit shown in FIG. 8 is a receiver circuit having a
アキュームレータ6の代わりに取り付けられたパワーレシーバー13は、アキュームレータ6で有する余剰冷媒の蓄積タンクの役割を持つ。さらに、減圧電磁弁4で低温、低圧となった気液二相冷媒をパワーレシーバー13に入れ、出口で液のみを回収して2次減圧電磁弁14でさらに減圧を行うことで、液冷媒を2段で効率的に低圧化し、運転効率を増加させる役割を持つ。
The
図8の構成の冷媒回路であっても、2次減圧電磁弁14を全開とすることによって、図1に示したアキュームレータ回路に酷似した冷凍サイクルとなることから、実施の形態1と同様の冷媒充填方法が利用できることはいうまでもない。
Even in the refrigerant circuit having the configuration shown in FIG. 8, since the refrigeration cycle very similar to the accumulator circuit shown in FIG. 1 is obtained by fully opening the secondary pressure reducing
実施の形態2.
図9は実施の形態2を示す図で、空気調和機の冷媒充填時の冷媒回路図である。図1と異なるのは、減圧電磁弁4が室内機B側に内蔵されている点である。
FIG. 9 is a diagram showing the second embodiment and is a refrigerant circuit diagram when the air conditioner is filled with refrigerant. The difference from FIG. 1 is that the pressure reducing
室内機Bに減圧電磁弁4が内蔵されている場合、図9の矢印の方向に従って冷媒回路を循環させることで、実施の形態1で示した内容と同様な冷媒充填方法が可能である。つまり、冷媒量状態を把握する為には、減圧電磁弁4が室外機A側にある場合は、暖房運転する必要があるが、室内機B側にある場合は、冷房運転する必要があるということを示している。
When the decompression
これは、冷媒の密度が最も高くなる、つまり冷媒量を最も必要とする冷媒回路上の区間は、凝縮器(室外側熱交換器5)から液側接続配管Dまでの通路である。このことは上記区間で冷媒が液化することに起因する。言うまでもなく、ガス状態と液状態の密度には大きな違いがある。冷媒回路内においては、ガス状態で通過する部分がほとんどであるが、冷媒量として考えた場合、上記液化区間が最も冷媒量を保有する区間である。よって、減圧電磁弁4の調整によって冷媒量状態を検討する本発明の冷媒充填方法を適用する場合、上記区間の密度を把握することができる冷凍サイクル(冷房運転)とするのが適切である。
This is the passage from the condenser (outdoor heat exchanger 5) to the liquid side connection pipe D in the section on the refrigerant circuit where the density of the refrigerant is the highest, that is, the amount of refrigerant most required. This is due to the liquefaction of the refrigerant in the above section. Needless to say, there is a big difference between the density of the gas state and the liquid state. In the refrigerant circuit, the portion that passes through in the gas state is mostly, but when considered as the refrigerant quantity, the liquefaction section is the section that holds the refrigerant quantity most. Therefore, when applying the refrigerant charging method of the present invention in which the refrigerant amount state is examined by adjusting the pressure reducing
実施の形態3.
一方、図1と同様の冷媒回路を持ち、冷媒ボンベ10と冷媒回路の間に開閉を可能とする自動制御弁15を持つ図10に示すような冷媒充填方法であっても、前述までの運転方法は利用可能である。
On the other hand, even in the refrigerant charging method as shown in FIG. 10 which has the same refrigerant circuit as in FIG. 1 and has an
図10は実施の形態3を示す図で、空気調和機の冷媒充填時の冷媒回路図である。 FIG. 10 shows the third embodiment, and is a refrigerant circuit diagram when the air conditioner is charged with refrigerant.
本発明による冷媒充填方法は、冷媒量が適正と判断した段階で、暖房運転モードを停止し、圧縮機1を停止すると同時に四方弁2を切替え、さらに減圧電磁弁4を全開にすることで、暖房運転を行うことで生じる冷媒回路中の圧力差を無くし、その結果以降の過度な冷媒充填を抑制するものである。
In the refrigerant charging method according to the present invention, when the refrigerant amount is determined to be appropriate, the heating operation mode is stopped, the
それに対し、冷媒ボンベ10と冷媒回路の間に、開閉の切替を室外機運転制御により可能とした自動制御弁15を追加した図10に示す回路は、冷媒充填量判定運転を行っている段階では冷媒を充填するために自動制御弁15は開いており、冷媒量適正判定により停止する際に自動制御弁15を閉じることで運転停止以降の冷媒充填を即時中止することが出来る。
On the other hand, the circuit shown in FIG. 10 in which an
図10の冷媒回路の最も重要な利点は、自動制御弁15を閉じることによる冷媒充填量判定運転停止以降の冷媒充填を完全に止めることが可能なことである。そのため、冷媒量をより正確に充填でき、製品の信頼性向上が図れる。
The most important advantage of the refrigerant circuit of FIG. 10 is that it is possible to completely stop the refrigerant charging after the refrigerant charging amount determination operation stop by closing the
A 室外機、B 室内機、C ガス側接続配管、D 液側接続配管、1 圧縮機、2 四方弁、3 室内側熱交換器、4 減圧電磁弁、5 室外側熱交換器、6 アキュームレータ、7 低圧側チャージポート、8 ホース、9 冷媒ボンベバルブ、10 冷媒ボンベ、11 室内側ファン、12 室外側ファン、13 パワーレシーバー、14 2次減圧電磁弁、15 自動制御弁、21 圧縮機吐出管温度検知装置、22 室内側熱交換器温度検知装置、23 室内側熱交換器出口温度検知装置、24 室内側吹出口温度検知装置、25 室外側熱交換器入口温度検知装置、26 室外側熱交換器温度検知装置、27 室外側吹出口温度検知装置、30 制御装置、40 表示装置。 A outdoor unit, B indoor unit, C gas side connection piping, D liquid side connection piping, 1 compressor, 2 4-way valve, 3 indoor heat exchanger, 4 pressure reducing solenoid valve, 5 outdoor heat exchanger, 6 accumulator, 7 Low pressure side charge port, 8 hose, 9 refrigerant cylinder valve, 10 refrigerant cylinder, 11 indoor fan, 12 outdoor fan, 13 power receiver, 14 secondary pressure reducing solenoid valve, 15 automatic control valve, 21 compressor discharge pipe temperature Detection device, 22 Indoor heat exchanger temperature detection device, 23 Indoor heat exchanger outlet temperature detection device, 24 Indoor air outlet temperature detection device, 25 Outdoor heat exchanger inlet temperature detection device, 26 Outdoor heat exchanger Temperature detection device, 27 outdoor air outlet temperature detection device, 30 control device, 40 display device.
Claims (11)
圧縮機、四方弁、室内側熱交換器、減圧装置、室外側熱交換器、液溜め装置を有する冷媒回路と、
前記冷媒回路の低圧側にボンベに備えられたバルブ以外に弁を設けずに接続される冷媒ボンベと、
前記冷媒回路の冷媒充填量の適正を判定する際、前記室内側熱交換器を内設した室内機と前記室外側熱交換器を内設した室外機とを接続する接続配管の液側配管に液冷媒状態で存在する運転モードとして充填状態を判定し、前記冷媒回路へ前記冷媒ボンベから冷媒を充填する制御を行なう制御装置と、
前記制御装置に設けられ、前記冷媒の充填状態を表示する表示装置とを備え、
当該冷凍空調装置を運転しながら、前記冷媒回路へ前記冷媒ボンベから冷媒を充填して、冷媒量が適正と判定すると自動的に前記圧縮機を停止するとともに前記四方弁を切り替えることを特徴とする冷凍空調装置への冷媒充填装置。 In the refrigerant filling device to the refrigeration air conditioner,
A refrigerant circuit having a compressor, a four-way valve, an indoor heat exchanger, a pressure reducing device, an outdoor heat exchanger, a liquid reservoir, and
A refrigerant cylinder connected without providing a valve other than a valve provided in the cylinder on the low pressure side of the refrigerant circuit;
When determining the appropriateness of the refrigerant charge amount in the refrigerant circuit, the liquid side pipe of the connecting pipe that connects the indoor unit with the indoor heat exchanger and the outdoor unit with the outdoor heat exchanger A control device that determines a charging state as an operation mode that exists in a liquid refrigerant state, and performs control for charging the refrigerant into the refrigerant circuit from the refrigerant cylinder;
A display device that is provided in the control device and displays a charging state of the refrigerant ;
While operating the refrigerating and air-conditioning apparatus, the refrigerant circuit is filled with refrigerant from the refrigerant cylinder, and when it is determined that the amount of refrigerant is appropriate, the compressor is automatically stopped and the four-way valve is switched. Refrigerant filling equipment for refrigeration air conditioners.
前記温度検出装置により検出された温度から冷媒量状態判定値を算出してその値が適正の場合、前記圧縮機を停止すると共に前記四方弁を切替えて冷媒回路内の圧力を均一として冷媒充填量判定運転を停止することを特徴とする冷凍空調装置への冷媒充填方法。 A refrigerant circuit having a compressor, a four-way valve, an indoor heat exchanger, a decompression device, an outdoor heat exchanger, a liquid storage device, and the indoor heat serving as at least room temperature, outside air temperature, condensation temperature, evaporation temperature, and condenser A temperature detecting device for detecting an outlet temperature of the exchanger or the outdoor heat exchanger, a refrigerant cylinder connected to the low pressure side of the refrigerant circuit when the refrigerant is charged, and charging the refrigerant from the refrigerant cylinder to the refrigerant circuit In the refrigerant charging method to the refrigerating and air-conditioning apparatus having the control device for performing the control at the time and determining the charging state,
When the refrigerant quantity state determination value is calculated from the temperature detected by the temperature detection device and the value is appropriate, the compressor is stopped and the four-way valve is switched to make the pressure in the refrigerant circuit uniform, and the refrigerant charge amount A refrigerant charging method for a refrigerating and air-conditioning apparatus, wherein the determination operation is stopped.
冷媒量が過少の場合は、冷媒が極端に不足している旨を前記表示装置に表示し、速やかに冷媒充填を行うことを特徴とする請求項2又は請求項3記載の冷凍空調装置への冷媒充填方法。 The control device has a display device,
The refrigerant air conditioning apparatus according to claim 2 or 3 , wherein when the amount of the refrigerant is too small, the display device displays that the refrigerant is extremely insufficient, and the refrigerant is quickly charged. Refrigerant filling method.
前記減圧装置が前記室外機に設けられる場合は、当該冷凍空調装置の運転は暖房運転であることを特徴とする請求項2乃至4のいずれかに記載の冷凍空調装置への冷媒充填方法。 An indoor unit and an outdoor unit,
5. The refrigerant charging method for a refrigeration air conditioner according to any one of claims 2 to 4 , wherein when the decompression device is provided in the outdoor unit, the operation of the refrigeration air conditioner is a heating operation.
前記減圧装置が前記室内機に設けられる場合は、当該冷凍空調装置の運転は冷房運転であることを特徴とする請求項2乃至4のいずれかに記載の冷凍空調装置への冷媒充填方法。 An indoor unit and an outdoor unit,
The refrigerant charging method for a refrigerating and air-conditioning apparatus according to any one of claims 2 to 4 , wherein when the decompression device is provided in the indoor unit, the operation of the refrigerating and air-conditioning apparatus is a cooling operation.
前記制御装置は、前記冷媒量状態判定値をリアルタイムで算出し、当該制御装置の算出結果は前記表示装置に表示されることを特徴とする請求項2乃至8のいずれかに記載の冷凍空調装置への冷媒充填方法。 The control device has a display device,
The refrigerating and air-conditioning apparatus according to any one of claims 2 to 8 , wherein the control device calculates the refrigerant quantity state determination value in real time, and a calculation result of the control device is displayed on the display device. Refrigerant filling method.
Priority Applications (6)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007284640A JP4474455B2 (en) | 2007-11-01 | 2007-11-01 | Refrigerant filling apparatus for refrigeration air conditioner and refrigerant filling method for refrigeration air conditioner |
| EP08252574.2A EP2056046B1 (en) | 2007-11-01 | 2008-07-29 | Refrigerant filling apparatus of refrigerating and air conditioning apparatus and refrigerant filling method of refrigerating and air conditioning apparatus |
| ES08252574.2T ES2690822T3 (en) | 2007-11-01 | 2008-07-29 | Refrigerant filling apparatus of refrigeration and air conditioning apparatus and refrigerant filling method of refrigeration and air conditioning apparatus |
| CN2008101441059A CN101424469B (en) | 2007-11-01 | 2008-07-29 | Refrigerant filling apparatus of refrigerating and air conditioning apparatus and refrigerant filling method of refrigerating and air conditioning apparatus |
| CN201010134532.6A CN101762133B (en) | 2007-11-01 | 2008-07-29 | Refrigerant filling method for refrigerating air conditioning apparatus |
| US12/183,121 US8215119B2 (en) | 2007-11-01 | 2008-07-31 | Refrigerant filling apparatus of refrigerating and air conditioning apparatus and refrigerant filling method of refrigerating and air conditioning apparatus |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007284640A JP4474455B2 (en) | 2007-11-01 | 2007-11-01 | Refrigerant filling apparatus for refrigeration air conditioner and refrigerant filling method for refrigeration air conditioner |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2009109156A JP2009109156A (en) | 2009-05-21 |
| JP2009109156A5 JP2009109156A5 (en) | 2009-07-23 |
| JP4474455B2 true JP4474455B2 (en) | 2010-06-02 |
Family
ID=40615243
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007284640A Expired - Fee Related JP4474455B2 (en) | 2007-11-01 | 2007-11-01 | Refrigerant filling apparatus for refrigeration air conditioner and refrigerant filling method for refrigeration air conditioner |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4474455B2 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN101424469B (en) |
Families Citing this family (16)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103629794B (en) * | 2012-08-27 | 2016-05-04 | 珠海格力电器股份有限公司 | Air-filling device of air conditioner, air conditioner and air-filling control method of air conditioner |
| CN103671044B (en) * | 2012-08-29 | 2017-06-13 | 珠海格力电器股份有限公司 | Method and device for controlling frequency of compressor |
| JP5948237B2 (en) * | 2012-12-27 | 2016-07-06 | ジョンソンコントロールズ ヒタチ エア コンディショニング テクノロジー(ホンコン)リミテッド | Air conditioner |
| JP6293647B2 (en) * | 2014-11-21 | 2018-03-14 | ヤンマー株式会社 | heat pump |
| CN104566830A (en) * | 2015-01-20 | 2015-04-29 | 三菱重工海尔(青岛)空调机有限公司 | Method for detecting quantity of refrigerant in multiple online systems |
| CN104990320A (en) * | 2015-07-16 | 2015-10-21 | 广东美的暖通设备有限公司 | Control method and system capable of automatically filling refrigerants |
| JP6123878B1 (en) * | 2015-12-22 | 2017-05-10 | ダイキン工業株式会社 | Air conditioner |
| JP6112189B1 (en) * | 2015-12-22 | 2017-04-12 | ダイキン工業株式会社 | Air conditioner |
| CN111094877B (en) * | 2017-09-14 | 2021-08-10 | 三菱电机株式会社 | Refrigeration cycle device and refrigeration device |
| CN109028672B (en) * | 2018-08-13 | 2020-06-30 | 奥克斯空调股份有限公司 | Automatic fluoridation control method of air conditioner and air conditioner |
| CN110925592A (en) * | 2019-11-05 | 2020-03-27 | 上海酷奥制冷设备有限公司 | Refrigerant filling process |
| JP7457244B2 (en) * | 2020-04-27 | 2024-03-28 | ダイキン工業株式会社 | Air conditioning management system and refrigerant recovery management device |
| CN111829208A (en) * | 2020-07-31 | 2020-10-27 | 张瑞麟 | Noise reduction type heat exchange system of air heat source pump |
| CN113932503B (en) * | 2021-11-24 | 2023-04-07 | 宁波奥克斯电气股份有限公司 | Refrigerant charging device and control method |
| CN114183952B (en) * | 2021-12-21 | 2023-09-15 | 宁波奥克斯电气股份有限公司 | Refrigerant recovery control method and refrigerant recovery unit |
| CN114719435B (en) * | 2022-03-30 | 2023-12-08 | 浙江中广电器集团股份有限公司 | Control method of heat pump water heater using jet enthalpy-increasing compressor |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH1163745A (en) * | 1997-08-08 | 1999-03-05 | Hitachi Ltd | Refrigerant feeding amount indicating device for air conditioner and monitoring device |
| JP3855901B2 (en) * | 2002-09-26 | 2006-12-13 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Refrigeration and air-conditioning cycle device handling method, refrigeration and air-conditioning cycle device refrigerant recovery mechanism |
| WO2007049372A1 (en) * | 2005-10-25 | 2007-05-03 | Mitsubishi Electric Corporation | Air-conditioning apparatus, method of refrigerant filling in air-conditioning apparatus, method of judging state of refrigerant filling in air-conditioning apparatus, and method of refrigerant filling/piping cleaning for air-conditioning apparatus |
| JP4165566B2 (en) * | 2006-01-25 | 2008-10-15 | ダイキン工業株式会社 | Air conditioner |
-
2007
- 2007-11-01 JP JP2007284640A patent/JP4474455B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2008
- 2008-07-29 CN CN2008101441059A patent/CN101424469B/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN101424469A (en) | 2009-05-06 |
| JP2009109156A (en) | 2009-05-21 |
| CN101424469B (en) | 2011-07-27 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4474455B2 (en) | Refrigerant filling apparatus for refrigeration air conditioner and refrigerant filling method for refrigeration air conditioner | |
| US8215119B2 (en) | Refrigerant filling apparatus of refrigerating and air conditioning apparatus and refrigerant filling method of refrigerating and air conditioning apparatus | |
| US7980086B2 (en) | Air conditioner | |
| JP5247833B2 (en) | Air conditioner | |
| JP4114691B2 (en) | Air conditioner | |
| JP4705878B2 (en) | Air conditioner | |
| US7954333B2 (en) | Air conditioner | |
| US9303908B2 (en) | Air conditioner | |
| KR101917941B1 (en) | Air conditioner and control method thereof | |
| US8069682B2 (en) | Air conditioner that corrects refrigerant quantity determination based on refrigerant temperature | |
| US20090126379A1 (en) | Air conditioner | |
| US20090100849A1 (en) | Air conditioner | |
| JP2008089292A (en) | Air conditioner | |
| JP2008232579A (en) | Refrigerant filling method | |
| JP2007212134A (en) | Air conditioner | |
| JP2008064456A (en) | Air conditioner | |
| JP2007198680A (en) | Air conditioner | |
| JP2000337740A (en) | Refrigerant amount regulating method and refrigerant amount judging device | |
| JP4434260B2 (en) | Refrigerant filling method for refrigeration air conditioner, refrigerant filling device for refrigeration air conditioner | |
| JP2007163102A (en) | Air conditioning system | |
| JP2010133636A (en) | Refrigerating device | |
| JP2010025545A (en) | Refrigerant filling method for refrigerating air conditioner and refrigerant charge device for refrigerating air conditioner | |
| JP4655107B2 (en) | Air conditioner | |
| JP2007187442A (en) | Air conditioner | |
| JP3824009B2 (en) | Supercooling device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20090605 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20090605 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20091112 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20091124 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20100114 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20100216 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20100308 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130312 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 4474455 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130312 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20140312 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |