JP4386812B2 - X-ray inspection equipment - Google Patents
X-ray inspection equipment Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4386812B2 JP4386812B2 JP2004248706A JP2004248706A JP4386812B2 JP 4386812 B2 JP4386812 B2 JP 4386812B2 JP 2004248706 A JP2004248706 A JP 2004248706A JP 2004248706 A JP2004248706 A JP 2004248706A JP 4386812 B2 JP4386812 B2 JP 4386812B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- ray
- inspection
- axis
- inspection object
- image
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Analysing Materials By The Use Of Radiation (AREA)
- Electric Connection Of Electric Components To Printed Circuits (AREA)
Description
本発明は、X線検査装置、例えば、プリント回路基板上に実装された部品の接合状態、樹脂若しくは金属によりパッケージングされた部品内部の接合状態、及びプリント回路基板内に実装された部品の接合状態等を検査するX線検査装置及びX線検査方法に関するものである。 The present invention relates to an X-ray inspection apparatus, for example, a bonding state of components mounted on a printed circuit board, a bonding state inside components packaged with resin or metal, and a bonding of components mounted in a printed circuit board. The present invention relates to an X-ray inspection apparatus and an X-ray inspection method for inspecting a state and the like.
近年の携帯情報端末等においては小型、高機能化が進み、使用される電子部品の実装においても、小さい空間に出来るだけ多くの電子部品を実装させるために、実装密度を高める高密度化、電極が電子部品の下面に設けられてプリント回路基板のランド上に接合されるフェイスダウン接合化、プリント回路基板の内部に電子部品を実装する部品内蔵化が進んでいる。 In recent portable information terminals, etc., miniaturization and high functionality have progressed, and in mounting electronic components to be used, in order to mount as many electronic components as possible in a small space, increasing the mounting density, electrodes Are being mounted on the lower surface of the electronic component and are being joined to the land of the printed circuit board, and face-down bonding, and the incorporation of components for mounting electronic components inside the printed circuit board has been progressing.
前記のフェイスダウン接合における接合部分、又はプリント回路基板の内部に実装されている場合の接合部分に対しては、直接目視することが出来ないため、その接合部分の断面を露呈させて観察する検査方法や、非破壊により検査対象物の内部状態を観察するX線検査方法が用いられている。X線検査方法を用いた場合には、検査対象物内部の接合状態等を観察することが可能であるが、複数個の部品が重なって実装されている場合には、部品が重なり合ったX線画像となり、各部品の状態を正確に観察することが困難であった。このため、従来のX線検査装置においては、X線の照射方向と、検査対象物への照射角度とを変更して複数の位置で撮像し、その撮像されたX線画像をトモグラフィ法やラミノグラフィ法を用いて観察したい断層部分を切り出し、観察、検査していた。
以下、添付の図面を参照しながら従来のX線検査装置及びその問題点について説明する。なお、各従来例において共通する部分は同一符号を用いて説明する。 A conventional X-ray inspection apparatus and its problems will be described below with reference to the accompanying drawings. In addition, the part which is common in each conventional example is demonstrated using the same code | symbol.
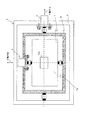
図18はトモグラフィ法を用いた従来のX線検査装置の概略構成を示すブロック図である。図18に示した従来のX線検査装置としては、例えば、特許文献1に開示された装置がある。
FIG. 18 is a block diagram showing a schematic configuration of a conventional X-ray inspection apparatus using the tomography method. As a conventional X-ray inspection apparatus shown in FIG. 18, for example, there is an apparatus disclosed in
図18に示すように、X線照射装置103からのX線は、回転装置101に保持された検査対象物102、例えばプリント回路基板に照射され、その検査対象物102を透過したX線がX線検出装置100により検出されるよう構成されている。X線照射装置103は、回転装置101の回転中心と、X線検出装置100の撮像中心位置との延長線上に配置され、X線検出装置100に向けてX線を発生させている。制御装置104は、回転装置101の回転位置を制御するとともに、X線検出装置100及びX線照射装置103を駆動制御している。制御装置104は、検査対象物102を保持する回転装置101が所定の回転角度の位置において、X線照射装置103からX線を照射させて、検査対象物102を透過したX線画像をX線検出装置100に取り込むよう駆動制御する。このとき、制御装置104は、回転装置101を1回転若しくは半回転させてX線検出装置100に撮像させて、観察したい断層部分のX線画像を作成し、表示するよう構成されている。
As shown in FIG. 18, X-rays from the
上記のように、図18に示す従来のX線検査装置は、検査対象物102をX線の照射軸と直交する軸を回転軸として回転させる構成である。図18に示す従来のX線検査装置の構成においては、X線照射装置103のX線が出射するX線源のX線焦点(スポット位置)から検査対象物102の回転軸の位置までの距離Aと、この回転軸の位置からX線検出装置100の検出部までの距離Bが、検査対象物102の外形寸法により制約を受ける。この制約とは、検査対象物102であるプリント回路基板の外形(図18においてCで示す寸法)が回転できるように、距離Aの最小値が、A>C/2の条件を満たさなければならないことである。この制約により。検査対象物102をX線照射装置103にあまり近づけることができなかった。図18に示した従来のX線検査装置において、検査対象配置空間を規定するA+Bの距離を小さくした場合には、X線画像の倍率である(A+B)/AにおけるAの値が制限され、倍率を上げることができない。このため、図18に示した従来のX線検査装置では、各部品の詳細な状態を観察することが困難であるという問題点を有していた。
As described above, the conventional X-ray inspection apparatus shown in FIG. 18 is configured to rotate the
図19はラミノグラフィ法を用いた従来のX線検査装置の概略構成を示すブロック図である。図19に示した従来のX線検査装置としては、例えば、特許文献2に開示された装置がある。
FIG. 19 is a block diagram showing a schematic configuration of a conventional X-ray inspection apparatus using a laminography method. As a conventional X-ray inspection apparatus shown in FIG. 19, for example, there is an apparatus disclosed in
図19において、回転X線照射装置105は熱電子を回転磁界により制御し、所定の位置でX線を回転して放射させる機能を有している。X線検出装置109は、検査対象物102、例えばプリント回路基板等を透過したX線を、シンチレータ107において可視光に変換した後に回転ミラー機構108を通して検出している。制御装置106は回転X線照射装置105の回転磁界と回転ミラー機構108とを同期して駆動制御している。また、制御装置106は回転X線照射装置105とX線検出装置109とを制御して撮像し、X線検査装置では高速度で検査対象物102の断層画像を取得して、検査を行っている。
In FIG. 19, a rotating
図19に示す従来のX線検査装置においては、検査対象物102に対するX線の照射角度βは物理的に予め決まっており、固定値である。従って、検査対象物102を回転X線照射装置105に近づけると、例えば図19においてWで示す位置では、X線の照射範囲から外れてしまう。このため、検査対象物102を回転X線照射装置105に近づけてX線画像を拡大しようとしても、倍率が制限されるという問題がある。また、図19に示す従来のX線検査装置においては、構造が複雑であり高価であった。
In the conventional X-ray inspection apparatus shown in FIG. 19, the X-ray irradiation angle β with respect to the
従来のX線検査装置の他の例としては、X線照射装置を傾斜させ、且つ回転させて、検査対象物内で重なった接合部分を分離して各接合部分の接合状態を検査するものがある。このような従来のX線検査装置としては、例えば特許文献3に開示された装置がある。
As another example of the conventional X-ray inspection apparatus, the X-ray irradiation apparatus is tilted and rotated to separate the overlapping joint portions in the inspection object and inspect the joint state of each joint portion. is there. As such a conventional X-ray inspection apparatus, there is an apparatus disclosed in
図20は、X線照射装置を傾斜、回転させて接合状態を検査する従来のX線検査装置の概略構成を示す図である。 FIG. 20 is a diagram showing a schematic configuration of a conventional X-ray inspection apparatus that inspects the bonding state by tilting and rotating the X-ray irradiation apparatus.
図20に示すX線検査装置は、X線照射装置110が検出対象物102であるプリント回路基板等に対して斜めにX線を照射させるよう構成されている。X線照射装置110からのX線は、検出対象物102を透過してX線検出装置115により受け取るよう構成されている。この従来のX線検査装置において行われるX線斜め撮影は、X線照射装置110を傾けることにより実施される。このように、検出対象物102に対して様々な角度からX線を照射して、X線検出装置115により検出対象物102のX線透視画像を撮像している。従って、これらのX線透視画像から、検出対象物102における所望の位置の部品の状態を検査することが可能となる。
The X-ray inspection apparatus shown in FIG. 20 is configured such that the
図21は、図20に示した従来のX線検査装置の主要部分を示すブロック図である。図21において、検査対象物102は、フェイスダウン接合部分を有するボールグリッドアレイ(以下BGAという)111と、プリント回路基板112と、電子部品113とにより構成された回路形成体である。この検査対象物102に対してX線照射装置110を傾斜させて検査対象物102がX線検出装置115において撮像される。図21においては、X線検出装置115におけるシンチレータ114を示す。
FIG. 21 is a block diagram showing a main part of the conventional X-ray inspection apparatus shown in FIG. In FIG. 21, an
図21においてFで示したX線撮像画像は、X線照射装置110が検査対象物102の真下にある時のX線画像の一例であり、X線照射装置110からのX線が検査対象物102の回路形成体において部品が重なった状態を示している。また、図21においてGで示したX線撮像画像は、X線照射装置110を斜めに配置して検査対象物102を照射し、X線検出装置115により検出されたX線画像の一例を表している。検査対象物102である回路形成体の内部では異なる位置に電子部品と接合部分等が存在するため、X線撮像画像FとX線撮像画像Gとでは撮影角度の違いにより異なった画像を表す。
The X-ray captured image indicated by F in FIG. 21 is an example of an X-ray image when the
図21に示すように、X線撮影画像Fのみでは電子部品の陰に隠れて、BGA111の接合部分の全てを検査できないが、X線照射装置110を傾斜させて撮影したX線画像Gを用いることにより、BGA111の全ての接合部分の接合状態を検査することが可能となる。すなわち、撮影された複数のX線画像において、電子部品113の位置を検査範囲から除いてBGAの接合部分を検査することにより、BGAの全ての接合状態を検査することができる。
As shown in FIG. 21, only the X-ray image F is hidden behind the electronic component and cannot inspect all the joint portions of the
しかしながら、図20に示す従来のX線検査装置においては、電子部品間の実装間隔がさらに狭くなると、どの角度においても検査対象の断層と異なる高さにある電子部品の影響を除外することが出来ず、検査対象の断層における正確な情報を取得できないという問題を有していた。 However, in the conventional X-ray inspection apparatus shown in FIG. 20, when the mounting interval between the electronic components is further reduced, the influence of the electronic components at a different height from the tomographic object to be inspected at any angle can be excluded. Therefore, there is a problem that accurate information on the fault to be examined cannot be obtained.
本発明は、従来の各種X線検査装置における問題点を解決することを課題とするものであり、検査対象物における部品間隔が狭くなり、実装が高密度になっても、所望の断層における情報を正確に取得することが可能なX線検査装置及びX線検査方法を提供することを目的とする。また、本発明においては、検査対象物の形状により分解能の制限を受けることがなく、比較的安価でありながら高分解能で鮮明な断層画像を入手することができ、この断層画像に用いて非破壊検査を精度高く行うことができるX線検査装置及びX線検査方法を提供することを目的とする。 An object of the present invention is to solve the problems in various conventional X-ray inspection apparatuses, and information on a desired fault is obtained even when the interval between parts in an inspection object is narrowed and the mounting density is high. An object of the present invention is to provide an X-ray inspection apparatus and an X-ray inspection method capable of accurately acquiring the above. In the present invention, the resolution is not limited by the shape of the inspection object, and a high-resolution and clear tomographic image can be obtained while being relatively inexpensive. An object of the present invention is to provide an X-ray inspection apparatus and an X-ray inspection method capable of performing inspection with high accuracy.
本発明のX線検査装置は、上記目的を達成するために、
保持面に保持された検査対象物にX線を照射するX線照射手段と、
前記検査対象物を透過したX線を検出するX線検出手段と、
前記X線照射手段と前記X線検出手段との間において、前記保持面と平行かつ前記保持面上で直交するX軸とY軸の2軸をそれぞれ中心として、前記保持面を2方向に下記式(1)および式(2)の条件で往復揺動させる揺動手段と、
前記X線検出手段の検出結果に基づいて前記検査対象物の検査を行う検査手段と、を具備する。
TAN(θ)=TAN(φX)/TAN(φY) (1)
TAN 2 (α)=TAN 2 (φX)+TAN 2 (φY) (2)
ただし、θ:X軸と保持面法線との成す角、α:Z軸と保持面法線との成す角、φX:X軸中心の回転角度、φY:Y軸中心の回転角度、である。
In order to achieve the above object, the X-ray inspection apparatus of the present invention provides:
X-ray irradiation means for irradiating the inspection object held on the holding surface with X-rays;
X-ray detection means for detecting X-rays transmitted through the inspection object;
In between the X-ray irradiation unit and the X-ray detecting means, following the two axes of the X axis and Y axis perpendicular on the holding surface and parallel and the holding surface around each said holding surface in two directions Oscillating means for reciprocally oscillating under the conditions of the equations (1) and (2) ;
Inspection means for inspecting the inspection object based on a detection result of the X-ray detection means.
TAN (θ) = TAN (φX) / TAN (φY) (1)
TAN 2 (α) = TAN 2 (φX) + TAN 2 (φY) (2)
Where θ is an angle formed by the X axis and the holding surface normal, α is an angle formed by the Z axis and the holding surface normal, φX is a rotation angle about the X axis, and φY is a rotation angle about the Y axis. .
このように構成された本発明においては、保持面に保持された検査対象物における部品間隔が狭くなり、実装が高密度になっても、所望の断層における情報を正確に取得することが可能となる。また、本発明においては、小型で安価な構成により検査対象物を任意の傾き方向、任意の傾き角度の状態で高精度なX線画像を取得することが可能となる。
In the present invention configured as described above, it is possible to accurately acquire information on a desired fault even when the interval between parts in the inspection object held on the holding surface becomes narrow and the mounting becomes dense. Become. Further, in the present invention, it is possible to acquire a highly accurate X-ray image of an inspection object in an arbitrary tilt direction and an arbitrary tilt angle with a small and inexpensive configuration.
本発明に関連する参考例としてのX線検査装置は、基板にX線を照射するX線照射手段と、
前記基板を透過したX線を検出するX線検出手段と、
前記X線照射手段と前記X線検出手段との間において前記基板を揺動させる揺動手段と、
前記X線検出手段の駆動と前記揺動手段の駆動とを同期させるX線検出用揺動手段と、
前記揺動手段の直交2軸をそれぞれ位相の異なる所定角度内で揺動させる制御手段と、
前記X線検出手段の検出結果に基づいて前記基板の検査を行う検査手段と、を具備する。
An X-ray inspection apparatus as a reference example related to the present invention includes an X-ray irradiation means for irradiating a substrate with X-rays,
X-ray detection means for detecting X-rays transmitted through the substrate;
Rocking means for rocking the substrate between the X-ray irradiation means and the X-ray detection means;
X-ray detection swinging means for synchronizing the drive of the X-ray detection means and the swinging means;
Control means for swinging two orthogonal axes of the swing means within predetermined angles with different phases;
Inspection means for inspecting the substrate based on the detection result of the X-ray detection means.
このように構成された本発明に関連する参考例としてのX線検査装置においては、小型で安価な構成により、検査対象物である基板を任意の傾き方向、任意の傾き角度の状態で高精度なX線画像を取得することが可能となり、制御手段での複数の傾き画像から断層画像を演算により求めることによってボケや虚像の少ない断層画像を取得することができる。また、実装密度の高いプリント回路基板や薄い基板での断層情報を確実に取得することができるため、高分解能で鮮明な断層画像を用いた検査が可能となる。
In the X-ray inspection apparatus as a reference example related to the present invention configured as described above, a substrate that is an inspection object is highly accurate in an arbitrary tilt direction and an arbitrary tilt angle with a small and inexpensive configuration. X-ray images can be acquired, and a tomographic image with few blurs and virtual images can be acquired by calculating a tomographic image from a plurality of tilt images by the control means. In addition, since it is possible to reliably acquire tomographic information on a printed circuit board having a high mounting density or a thin board, inspection using a high-resolution and clear tomographic image is possible.
本発明に関連する参考例としてのX線検査装置は、X線焦点を頂点とする円錐状にX線を照射するX線照射手段と、
X線の照射範囲内で基板をX線照射軸の直交方向に移動させる基板用移動手段と、
前記基板を透過したX線を検出する検出面を有するX線検出手段と、
前記X線検出手段を前記X線照射軸の直交方向に移動させるX線検出用移動手段と、
前記基板用移動手段と前記X線検出用移動手段とを同期駆動制御するモータ制御手段と、
前記X線検出手段により形成されたX線画像から前記基板の任意断層面のX線画像を抽出する画像処理手段と、
前記X線画像に基づいて前記基板の任意断層面を検査する検査手段と、を具備し、
前記基板用移動手段は、前記X線検出用移動手段と同期して前記検出面の中心点を前記X線焦点と前記基板の中心点とを結ぶ直線上に配置させる構成である。
また、本発明の他の観点のX線検査装置は、X線焦点を頂点とする円錐状にX線を照射するX線照射手段と、
X線の照射範囲内で基板をX線照射軸の直交方向に移動させる基板用移動手段と、
前記基板を透過したX線を検出する検出面を有するX線検出手段と、
前記X線検出手段を前記X線照射軸の直交方向に移動させるX線検出用移動手段と、
前記基板用移動手段と前記X線検出用移動手段とを同期駆動制御する制御手段と、
前記X線検出手段により形成されたX線画像から前記基板の任意断層面のX線画像を抽出する画像処理手段と、
前記X線画像に基づいて前記基板の任意断層面の検査を行う検査手段と、を具備し、
前記X線検出手段は、前記基板用移動手段と前記X線検出用移動手段とのそれぞれでの水平面での同期回転動作における1回転の期間にX線撮影を行う構成である。
さらに、本発明の他の観点のX線検査装置は、X線焦点を頂点とする円錐状にX線を照射するX線照射手段と、
X線の照射範囲内で基板をX線照射軸の直交方向に移動させる基板用移動手段と、
前記基板を透過したX線を検出する検出面を有するX線検出手段と、
前記X線検出手段を前記X線照射軸の直交方向に移動させるX線検出用移動手段と、
前記基板用移動手段と前記X線検出用移動手段とを同期駆動制御する制御手段と、
前記X線検出手段により形成されたX線画像から前記基板の任意断層面のX線画像を抽出する画像処理手段と、
前記X線画像から前記基板の任意断層面を検査する検査手段と、を具備し、
前記X線検出手段は、前記基板用移動手段と前記X線検出用移動手段との同期回転動作中の回転停止時にX線撮影を行う構成である。
An X-ray inspection apparatus as a reference example related to the present invention includes an X-ray irradiation means for irradiating X-rays in a conical shape having an X-ray focal point as a vertex,
A substrate moving means for moving the substrate in a direction orthogonal to the X-ray irradiation axis within the X-ray irradiation range;
X-ray detection means having a detection surface for detecting X-rays transmitted through the substrate;
X-ray detection moving means for moving the X-ray detection means in a direction orthogonal to the X-ray irradiation axis;
Motor control means for synchronously driving and controlling the substrate moving means and the X-ray detection moving means;
Image processing means for extracting an X-ray image of an arbitrary tomographic plane of the substrate from the X-ray image formed by the X-ray detection means;
An inspection means for inspecting an arbitrary tomographic plane of the substrate based on the X-ray image,
The substrate moving means is configured to arrange the center point of the detection surface on a straight line connecting the X-ray focal point and the center point of the substrate in synchronization with the X-ray detection moving means.
An X-ray inspection apparatus according to another aspect of the present invention includes an X-ray irradiation unit that irradiates X-rays in a conical shape having an X-ray focal point as a vertex,
A substrate moving means for moving the substrate in a direction orthogonal to the X-ray irradiation axis within the X-ray irradiation range;
X-ray detection means having a detection surface for detecting X-rays transmitted through the substrate;
X-ray detection moving means for moving the X-ray detection means in a direction orthogonal to the X-ray irradiation axis;
Control means for synchronously driving and controlling the substrate moving means and the X-ray detection moving means;
Image processing means for extracting an X-ray image of an arbitrary tomographic plane of the substrate from the X-ray image formed by the X-ray detection means;
An inspection means for inspecting an arbitrary tomographic plane of the substrate based on the X-ray image,
The X-ray detection means is configured to perform X-ray imaging during a period of one rotation in the synchronous rotation operation on the horizontal plane in each of the substrate moving means and the X-ray detection moving means.
Furthermore, an X-ray inspection apparatus according to another aspect of the present invention includes an X-ray irradiation unit that irradiates X-rays in a conical shape having an X-ray focal point as a vertex,
A substrate moving means for moving the substrate in a direction orthogonal to the X-ray irradiation axis within the X-ray irradiation range;
X-ray detection means having a detection surface for detecting X-rays transmitted through the substrate;
X-ray detection moving means for moving the X-ray detection means in a direction orthogonal to the X-ray irradiation axis;
Control means for synchronously driving and controlling the substrate moving means and the X-ray detection moving means;
Image processing means for extracting an X-ray image of an arbitrary tomographic plane of the substrate from the X-ray image formed by the X-ray detection means;
An inspection means for inspecting an arbitrary tomographic plane of the substrate from the X-ray image,
The X-ray detection means is configured to perform X-ray imaging when the rotation is stopped during the synchronous rotation operation of the substrate moving means and the X-ray detection moving means.
このように構成された本発明に関連する参考例としてのX線検査装置においては、検査箇所がモニタ画面の中心から移動することなく撮影方向及び撮影倍率を変更して観察することができ、さらに検査箇所の断層面のX線画像から、検査対象である基板、例えばプリント回路基板の接合部のオープン不良を含む様々な接合不良の検査を行うことができる。
In the X-ray inspection apparatus as a reference example related to the present invention configured as described above, the inspection location can be observed by changing the imaging direction and the imaging magnification without moving from the center of the monitor screen. From the X-ray image of the tomographic plane of the inspection location, it is possible to inspect various bonding defects including an open defect at a bonding portion of a substrate to be inspected, for example, a printed circuit board.
本発明に関連する参考例としてのX線検査方法は、基板にX線を照射する照射工程と、
前記基板を透過したX線を検出する検出工程と、
検出した前記X線のX線画像データから前記基板の任意断層面のデータを抽出する抽出工程と、
前記基板を揺動させる揺動工程と、
前記抽出工程の抽出結果に基づいて前記基板を検査する検査工程と、を有する。
An X-ray inspection method as a reference example related to the present invention includes an irradiation step of irradiating a substrate with X-rays,
A detection step of detecting X-rays transmitted through the substrate;
An extraction step of extracting data of an arbitrary tomographic plane of the substrate from the detected X-ray image data of the X-ray;
A swinging step of swinging the substrate;
And an inspection step of inspecting the substrate based on the extraction result of the extraction step.
このような工程を有する本発明に関連する参考例としてのX線検出方法においては、検査対象物である基板における部品間隔が狭くなり、実装が高密度になっても、所望の断層における情報を正確に取得することが可能となる。また、本発明に関連する参考例としてのX線検出方法においては、検査対象物である基板を任意の傾き方向、任意の傾き角度の状態で高精度なX線画像を取得することが可能となる。
In the X-ray detection method as a reference example related to the present invention having such a process, information on a desired fault is obtained even when the component interval on the substrate as the inspection object is narrowed and the mounting becomes high density. It becomes possible to acquire accurately. In addition, in the X-ray detection method as a reference example related to the present invention , it is possible to acquire a highly accurate X-ray image of the substrate as an inspection object in an arbitrary tilt direction and an arbitrary tilt angle. Become.
本発明に関連する参考例としてのX線検査方法は、X線焦点を頂点とする円錐状にX線を照射する照射工程と、
基板を透過した前記X線をX線検出手段の検出面で検出する検出工程と、
検出された前記X線により形成されたX線画像から前記基板の任意断層面のX線画像を抽出する抽出工程と、
前記基板をX線の照射範囲内でX線照射軸と垂直方向に移動させる移動工程と、
前記移動工程の移動に同期して前記基板と同一平面上においてX線画像中心に目標点を配置する第1配置工程と、
前記X線焦点と前記基板の検査箇所の中心点とを結ぶ直線上に前記検出面の中心点を配置する第2配置工程と、
前記抽出工程の抽出結果に基づいて前記基板の検査を行う検査工程と、を有する。
An X-ray inspection method as a reference example related to the present invention includes an irradiation step of irradiating X-rays in a conical shape having an X-ray focal point as a vertex,
A detection step of detecting the X-ray transmitted through the substrate on a detection surface of the X-ray detection means;
An extraction step of extracting an X-ray image of an arbitrary tomographic plane of the substrate from an X-ray image formed by the detected X-ray;
A moving step of moving the substrate in a direction perpendicular to the X-ray irradiation axis within an X-ray irradiation range;
A first arrangement step of arranging a target point at the center of the X-ray image on the same plane as the substrate in synchronization with the movement of the movement step;
A second arrangement step of arranging the center point of the detection surface on a straight line connecting the X-ray focal point and the center point of the inspection location of the substrate;
An inspection step of inspecting the substrate based on the extraction result of the extraction step.
このような工程を有する本発明に関連する参考例としてのX線検出方法においては、検査箇所がモニタ画面の中心から移動することなく撮影方向及び撮影倍率を変更して観察することができ、さらに検査箇所の断層面のX線画像から、検査対象物である基板、例えばプリント回路基板の接合部のオープン不良を含む様々な接合不良の検査を行うことができる。
In the X-ray detection method as a reference example related to the present invention having such a process, the inspection location can be observed by changing the imaging direction and the imaging magnification without moving from the center of the monitor screen. From the X-ray image of the tomographic plane of the inspection location, it is possible to inspect various bonding defects including an open defect in a bonding portion of a substrate that is an inspection object, for example, a printed circuit board.
発明の新規な特徴は添付の請求の範囲に特に記載したものに他ならないが、構成及び内容の双方に関して本発明は、他の目的や特徴と合わせて図面と共に以下の詳細な説明を読むことにより、より良く理解され評価されるであろう。 The novel features of the invention are nonetheless specifically set forth in the appended claims, but the invention, both in terms of structure and content, should be read in conjunction with the drawings and in the detailed description that follows. Will be better understood and appreciated.
本発明のX線検査装置においては、後述の各実施の形態において詳細に説明するように、安価で、高分解能でかつ鮮明な検査対象物の断層情報を容易に取得することができ、この断層情報に基づく正確な検査を行うことができる。 In the X-ray inspection apparatus of the present invention, as will be described in detail in each embodiment described later, the tomographic information of the inspection object can be easily acquired at low cost, with high resolution, and with this tomography. Accurate inspection based on information can be performed.
以下、本発明のX線検査装置及びX線検査方法の好適な実施の形態について、添付の図面を参照しつつ説明する。 DESCRIPTION OF EXEMPLARY EMBODIMENTS Hereinafter, preferred embodiments of an X-ray inspection apparatus and an X-ray inspection method of the present invention will be described with reference to the accompanying drawings.
《実施の形態1》
図1は本発明に係る実施の形態1のX線検査装置の概略構成を示す図である。
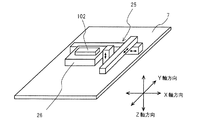
図1に示すように、X線照射装置3から出射されたX線は、揺動装置2に保持された検査対象物102、例えばプリント回路基板等の回路形成体に照射され、その検査対象物102を透過したX線がX線検出装置1により検出される。X線照射装置3は、揺動装置2の中心と、X線検出装置1の撮像中心位置との延長線(X線経路)上に配置され、X線検出装置1に向けてX線を発生させている。制御装置6は、揺動装置2のZ軸方向(X線照射軸方向)への移動と、揺動装置2のX軸とY軸に関する傾斜角度を制御するとともに、X線検出装置1及びX線照射装置3を駆動制御している。図1に示す状態において、左右方向がY軸方向であり、このY軸方向に直交する方向がX軸方向である。Z軸方向はX線照射装置3のX線焦点(スポット位置)の鉛直線方向であり、この方向がX線照射軸方向である。
FIG. 1 is a diagram showing a schematic configuration of an X-ray inspection apparatus according to
As shown in FIG. 1, X-rays emitted from the
制御装置6は、検査対象物102を保持する揺動装置2が所定の角度において、X線照射装置3からX線を照射させて、検査対象物102を透過したX線画像をX線検出装置1に取り込むよう駆動制御する。
The
実施の形態1のX線検査装置においては、検査対象物102を透過したX線がX線検出装置1に取り込まれてX線画像が形成され、そのX線画像が制御装置6において演算され、その演算結果が制御装置6において表示されるよう構成されている。
In the X-ray inspection apparatus according to the first embodiment, X-rays transmitted through the
実施の形態1において用いたX線照射装置3は、加速された熱電子をターゲットに衝突させることにより発生するX線を利用する方式のものであり、内部が常にほぼ真空状態に密封されている密封管方式のものである。しかし、本発明においては、この方式に限定されるものではなく、熱電子を発生させるフィラメントをユーザ側で交換する方法であり、使用する際にその都度内部を真空にする開放管方式のX線照射装置を用いてもよい。ただし、拡大率を大きくして、分解能を上げるためには、X線源のX線焦点サイズ(スポット径)はできる限り小さい方が望ましい。このため、実施の形態1においてはX線焦点サイズが1μmのX線照射装置3を使用し、表示時のX線画像のボケを極力小さくしている。
The
実施の形態1において、検査対象物102としての回路形成体には、プリント回路基板、電子部品のいずれか、もしくはそれらを組み合わせた複合品、もしくはそれらを接合した実装部品を示している。プリント回路基板は、紙フェノールの片面基板、多数層のガラスエポキシ基板、フィルム状基板、電子部品内蔵基板、樹脂の表面に回路パターンを形成した基板等の各種基板が含まれる。
In the first embodiment, the circuit forming body as the
図2は実施の形態1における揺動装置2の概略構成を示す平面図である。揺動装置2は、検査対象物102である前記回路形成体を保持する検査対象物用移動機構であるXYステージ7と、このXYステージ7をX軸を中心に回動させるX軸モータ4が固定された内枠8と、内枠8を介してXYステージ7をY軸を中心に回動させるY軸モータ5が固定された外枠9とを有する。XYステージ7は内枠8に対してX軸を中心に回動するよう、カップリングを介して接続されている。また、内枠8は外枠9に対してY軸を中心に回動するよう、カップリングを介して接続されている。なお、図2に示す状態において、XYステージ7の縦方向がX軸方向であり、横方向がY軸方向である。
FIG. 2 is a plan view showing a schematic configuration of the
次に、実施の形態1における揺動装置2により駆動される検査対象物102の揺動状態を説明する。図3は実施の形態1のX線検査装置における検査対象物102の揺動状態を示す説明する図である。図4は実施の形態1のX線検査装置における検査対象物102の傾き方向Tと傾き角度αを示す概念図である。
Next, the swinging state of the
図3に示すように、実施の形態1における揺動装置2により検査対象物102は揺動動作を行う。ここで、揺動動作とは、検査対象物102を保持するXYステージ7の保持面7aの中心点の法線がX線照射軸に対して所定角度を有して保持面7aの中心を回転中心点(揺動中心点)として回転することをいう。実施の形態1においては、X線照射装置3が揺動装置2の中心位置とX線検出装置1の撮像中心位置との延長線上に配置されており、この延長線がX線照射軸でありZ軸となる。従って、このZ軸に対して所定角度を有してXYステージ7の保持面7aの中心点(揺動中心点)の法線が揺動している。なお、揺動中心は、X軸モータ4とY軸モータ5との回転軸の交点位置であり、固定である。しかし、XYステージ7上で検査対象物102の位置を変更することにより、検査対象物102の所望の位置を検査が可能である。
As shown in FIG. 3, the
図4は実施の形態1のX線検査装置における検査対象物102の傾き方向Tと傾き角度αを示す概念図である。ここで、傾き方向Tとは、XYステージ7の保持面(XY面)7aにおいて、検査対象物102の中心点(保持面7aの中心点)の法線がX軸となす角度θを持つ方向をいう。また、傾き角度αとは、検査対象物102の中心点の法線がZ軸となす角度をいう。図4において、角度φXは、X軸モータ4の回転軸の回転角度を示し、YZ面におけるZ軸に対する角度を示している。また、角度φYは、Y軸モータ5の回転軸の回転角度を示し、ZX面におけるZ軸に対する角度を示している。
FIG. 4 is a conceptual diagram showing the inclination direction T and the inclination angle α of the
傾き方向Tを規定する角度θは、下記式(1)に示すように、X軸モータ4の回転角度φXとY軸モータ5の回転角度φYにより表される。また、傾き角度αは、下記式(2)に示すように、X軸モータ4の回転角度φXとY軸モータ5の回転角度φYにより表される。
The angle θ that defines the tilt direction T is represented by the rotation angle φX of the
以上のように、X軸モータ4の回転角度φXとY軸モータ5の回転角度φYとを規定することにより、任意の傾き方向T及び任意の傾き角度αを設定することが可能となる。
As described above, by defining the rotation angle φX of the
実施の形態1においては、X軸モータ4の回転角度φXとY軸モータ5の回転角度φYとを規定して、XYステージ7の保持面(XY面)7a、すなわち検査対象物102に対する揺動動作を行っている。図5は実施の形態1のX線検査装置においてX軸モータ4とY軸モータ5の駆動動作を示す波形図である。図5においては、傾き角度αが45度の場合であり、この場合にはTAN45°=1、となりTANφXとTANφYの最大値が1となる。
In the first embodiment, the rotation angle φX of the
実施の形態1においては、傾き角度αを45度とし、傾き方向Tを規定する角度を0度から360度まで移動させている。この場合、X軸モータ4が所定角度内で往復動作を行い、Y軸モータ5がX軸モータ4と図5に示すように位相のずれた関係を保ちつつ動作を行う。例えば、Y軸モータ5はX軸モータ4と位相が90度ずれた状態で同じ振幅及び周期で往復動作を行ってもよい。
In the first embodiment, the inclination angle α is 45 degrees, and the angle defining the inclination direction T is moved from 0 degrees to 360 degrees. In this case, the
なお、上記の揺動動作において、傾き角度αを変更した場合には、TANφXとTANφYの振幅が変わる。また、実施の形態1においては、傾き角度αは、0度から75度以下の範囲内で設定できるよう構成されている。但し、30度以上75度以下の範囲内で比較的良好な画像を取得することが可能である。 In the above swinging operation, when the tilt angle α is changed, the amplitudes of TANφX and TANφY change. In the first embodiment, the inclination angle α is configured to be set within a range of 0 degree to 75 degrees or less. However, it is possible to obtain a relatively good image within a range of 30 degrees to 75 degrees.
実施の形態1において、上記のように検査対象物102は揺動装置2により所定の揺動動作を行い、その揺動動作において、所定の位置に到達したときX線照射装置3からX線が照射されて、検査対象物102を透過したX線がX線検出装置1に取り込まれる。このとき、制御装置6は、揺動装置2により傾き方向Tが360度変わる間、すなわち揺動動作が1回転する間にX線検出装置1に複数回撮像させて、断層X線画像を作成し、表示する。
In the first embodiment, the
実施の形態1のX線検査装置においては、検査対象物102を揺動動作させる構成であるため、前述の図18に示したトモグラフィ法を用いた従来のX線検査装置のように、検査対象物102の全体を一回転させる必要がなく、検査対象物102をX線源のX線焦点(スポット位置)に近づけることが可能となる。この結果、実施の形態1のX線検査装置は、小型で高分解能を有する装置となる。
Since the X-ray inspection apparatus according to the first embodiment is configured to swing the
実施の形態1のX線検査装置において、揺動装置2のXYステージ7における検査対象物102の保持手段としては、ねじ等の物理的固定手段を用いている。また、揺動装置2において、揺動装置2の全体がX線照射軸方向(Z軸方向)へ任意に移動できるよう、ラックとピニオンによる駆動機構が設けられている。なお、X線検出装置1及びX線照射装置3に駆動機構を設けて、X線検出装置1及びX線照射装置3を同時もしくは個別にX線照射軸方向(Z軸方向)に移動できるよう構成して、X線画像の倍率をさらに大きく設定変更できる構成としてもよい。
In the X-ray inspection apparatus of the first embodiment, a physical fixing means such as a screw is used as the holding means for the
実施の形態1におけるX線検出装置1は、X線の線量を電気信号に変換する機能を有するものである。X線検出装置1において、X線を可視光に変換するシンチレータが設けられており、このシンチレータより入射したX線を可視光に変換した後、その光をレンズで集光し、CCD、CMOS等の光電子変換素子に入光させている。従って、実施の形態1においては、シンチレータとレンズによりX線の分解能を決めた後に、X線の線量を電気信号に変換するよう構成されている。
The
また、別のX線検出装置として、次のような構成、動作の装置でもよい。X線イメージインテンシファイヤのように、X線を荷電粒子に変換する第1のシンチレータにより入射したX線を荷電粒子に変換し、その後、荷電粒子を磁界制御して集中させる。そして、集中した荷電粒子を可視光に変換する第2のシンチレータにあてて光に変換し、その光をCCD、CMOS等の光電子変換素子を用いて電気信号に変換する。また、X線フラットパネルのように、X線を可視光に変換するシンチレータによりX線を光に変換した後、その光をCCD、CMOS等の光電子変換素子に直接入光させて、電気信号に変換してもよい。 Another X-ray detection apparatus may be an apparatus having the following configuration and operation. Like the X-ray image intensifier, incident X-rays are converted into charged particles by a first scintillator that converts X-rays into charged particles, and then the charged particles are concentrated by controlling the magnetic field. Then, the concentrated charged particles are applied to a second scintillator that converts visible light into light and converted into light, and the light is converted into an electrical signal using a photoelectric conversion element such as a CCD or CMOS. Moreover, after converting X-rays into light by a scintillator that converts X-rays into visible light, such as an X-ray flat panel, the light is directly incident on a photoelectric conversion element such as a CCD or CMOS, and converted into an electrical signal. It may be converted.
実施の形態1において、制御装置6は、X線照射装置3のX線発生のON/OFF制御、管電圧設定、管電流設定、エラー監視を行い、揺動装置2の傾き方向T及び傾き角度αを制御している。また、制御装置6は、X線検出装置1から入力されたX線画像データである電気信号を演算処理し、演算処理した電気信号の状態を表示する。制御装置6は、複数枚のX線画像からトモグラフィ法を用いて断層データを表示する機能を有している。また、制御装置6における検査方法としては、X線検出装置1が取得した傾いた画像をそのまま表示して、作業者が判定する方法と、複数のX線画像からトモグラフィ法により立体画像を作成し、その立体画像から任意の断層面を表示して、作業者が判定する方法である。
In the first embodiment, the
図6は、実施の形態1のX線検査装置における検査動作を示すフローチャートである。 FIG. 6 is a flowchart showing an inspection operation in the X-ray inspection apparatus of the first embodiment.
図6に示すように、実施の形態1のX線検査装置においては、まずステップ201で揺動装置2をZ軸方向(X線照射軸方向)に移動し所望の倍率とする。次に、ステップ202において、X軸モータ4とY軸モータ5を回転駆動して検査対象物102を固定したXYステージ7を揺動動作させる。この揺動動作中において、XYステージ7の保持面7aが所定の傾き方向Tと所定の傾き角度αに到達したとき、X線照射装置3からX線を照射させて、検査対象物102を透過したX線画像がX線検出装置1に取り込まれる撮像動作を行う(ステップ203)。この撮像動作は、予め決めた複数の位置において行われる。すなわち、保持面7aの傾き方向Tが360度変わる間(1回転の間)に、X線検出装置1に複数回撮像させて、所定枚数のX線画像を取得する。取得された複数枚のX線画像から当該検査対象物102の立体画像(三次元画像)を作成し、制御装置6の表示部に表示する(ステップ204)。作成された立体画像から所望の断層面の状態を検出し、良否を判定する(ステップ205)。この良否判定においては、予め取得している良品状態の断層面のデータと当該検査対象物102の断層面のデータとの差分をとり、その差分画像をもとに検査してもよい。
As shown in FIG. 6, in the X-ray inspection apparatus according to the first embodiment, first, in
以上のように、実施の形態1のX線検査装置によれば、小型で安価な構成により、検査対象物102を任意の傾き方向、任意の傾き角度の状態で高精度なX線画像を取得することが可能となり、制御装置6での複数の傾き画像から断層画像を演算により求めることによってボケや虚像の少ない断層画像を取得することができる。また、実装密度の高いプリント回路基板や薄い基板での断層データを確実に取得することができるため、高分解能で鮮明な断層画像を用いた検査が可能となる。
As described above, according to the X-ray inspection apparatus of the first embodiment, a high-accuracy X-ray image is obtained with the
なお、実施の形態1において、揺動装置2として、X軸モータ4とY軸モータ5を用いる揺動機構を用いた例で説明したが、3軸以上の多軸制御装置10を用いて構成することも可能である。図7は実施の形態1における揺動装置2の変形例であり、検査対象物102を固定するステージ7Aが3つの多軸制御装置10により駆動される。また、各多軸制御装置10はX軸方向、Y軸方向及びZ軸方向にステージ7Aを移動できるよう構成されている。図8は揺動装置2のさらに別の変形例である。図8に示す揺動装置2においては、検査対象物102を固定するステージ7Bが6軸ロボットである多軸制御装置10により駆動される。従って、ステージ7Bは6軸ロボットのアームにより、検査対象物102をX軸、Y軸及びZ軸方向に関して揺動動作とスライド動作を行うことができる。図7や図8に示すように、多軸制御機構301を用いて、検査対象物102を固定したステージ7A又は7Bを揺動動作させ、X軸、Y軸及びZ軸方向に関して揺動動作とスライド動作を行うよう構成することにより、検査対象物102に対して所望の動作をさせることが可能となり、検査位置の変更機能や倍率変更機能を容易に実施することが可能となる。
In the first embodiment, the example of using the swing mechanism using the
《実施の形態2》
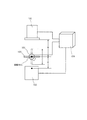
図9は本発明に係る実施の形態2のX線検査装置の概略構成を示す図である。図10は実施の形態2のX線検査装置における検査対象物の駆動機構を示す構成図である。実施の形態2のX線検査装置は、前述の実施の形態1のX線検査装置の揺動装置2にさらにX線検出装置1を揺動させるX線検出用揺動装置20を設けるとともに、X軸、Y軸及びZ軸に移動可能なXYZ移動テーブル26を設けている。実施の形態2において、前述の実施の形態1における構成要素と同じ機能、構成を有するものには同じ符号を付し、その説明は省略する。
<<
FIG. 9 is a diagram showing a schematic configuration of the X-ray inspection apparatus according to the second embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 10 is a configuration diagram showing a driving mechanism of the inspection object in the X-ray inspection apparatus of the second embodiment. The X-ray inspection apparatus according to the second embodiment is further provided with an X-ray
図9に示すように、実施の形態2のX線検査装置においても、X線照射装置3から出射されたX線は、揺動装置2に保持された検査対象物102に照射され、その検査対象物102を透過したX線がX線検出装置1により検出される。X線照射装置3のX線焦点(スポット位置)は、揺動装置2の中心と、X線検出装置1の撮像中心位置との延長線上に配置され、X線検出装置1に向けてX線を発生させている。
As shown in FIG. 9, also in the X-ray inspection apparatus of the second embodiment, the X-rays emitted from the
実施の形態2のX線検査装置においては、図10に示すように、揺動装置2のXYステージ7に検査対象物駆動機構である多軸制御装置25が設けられている。この多軸制御装置25は図9においては省略する。実施の形態2のX線検査装置においては、多軸制御装置25によりXYステージ7上のXYZ移動テーブル26がX軸、Y軸及びZ軸に移動可能に構成されている。このXYZ移動テーブル26の上に検査対象物102である、例えばプリント回路基板、電子部品等の回路形成体が固定される。
In the X-ray inspection apparatus according to the second embodiment, as shown in FIG. 10, the
また、実施の形態2のX線検査装置においては、X線検出装置1を揺動させるX線検出用揺動装置20が設けられている。X線検出用揺動装置20は、検出対象物102を揺動させる揺動装置2と同様に、X線検出装置1が固定されたXYステージ27と、このXYステージ27をX軸を中心に回動させるX軸モータ21と、XYステージ27をY軸を中心に回動させるY軸モータ22を有している。ただし、XYステージ27はZ軸方向には移動しない構成である。実施の形態2におけるX線検出用揺動装置20は、揺動装置2と同期して同じ方向に駆動される。すなわち、X線検出用揺動装置20におけるXYステージ27と揺動装置2のXYステージ7は常に同じ向きとなるよう揺動する。
In the X-ray inspection apparatus according to the second embodiment, an X-ray
実施の形態2における制御装置23は、揺動装置2のZ軸方向への移動と、XYステージ7のX軸とY軸に関する傾斜角度と、X線検出用揺動装置20におけるXYステージ27のX軸とY軸に関する傾斜角度とを制御している。また、制御装置23は、X線検出装置1及びX線照射装置3を駆動制御している。制御装置23は、検査対象物102を保持する揺動装置2が所定の角度において、X線照射装置3からX線を照射させて、検査対象物102を透過したX線をX線検出装置1に取り込むよう駆動制御する。そして、X線検出装置1に取り込まれたX線画像のデータが制御装置23に入力され、そのX線画像のデータが制御装置23において演算され、その演算結果が表示される。また、制御装置23において作成された断層面の情報の良否が自動的に判断されて表示されるよう構成されている。
The
実施の形態2のX線検査装置においては、揺動装置2のXYステージ7に多軸制御装置25とXYZ移動テーブル26が設けられており、XYZ移動テーブル26が単独でX軸、Y軸及びZ軸に移動可能に構成されている。これにより、検査対象物102をXYステージ7に対して任意の位置(X軸方向の位置、Y軸方向の位置及びZ軸方向の位置)に設定することができる。従って、XYステージ7におけるX線照射基準位置に対して、検査対象物102の任意の部分を所定の傾き角度及び傾き方向に設定することができる。この結果、実施の形態2のX線検査装置によれば、検査対象物102の全ての位置を容易に検査することが可能となる。
In the X-ray inspection apparatus of the second embodiment, the
実施の形態2のX線検査装置においては、X線検出装置1を揺動させるX線検出用揺動装置20が設けられており、X線検出用揺動装置20は揺動装置2と同期して同じ方向に駆動される。すなわち、X線検出用揺動装置20におけるXYステージ27と揺動装置2のXYステージ7が同一の傾き方向Tと、同一の傾き角度αに設定されている。この結果、実施の形態2のX線検査装置は、X線画像の歪みを防止することが可能となる。実施の形態2のX線検査装置において、X線検出用揺動装置20におけるXYステージ27と揺動装置2のXYステージ7の両者を同一に制御する方法として、各モータの回転位置を検出し、その回転位置に基づいて制御装置23においてフィードバック制御して駆動している。
In the X-ray inspection apparatus of the second embodiment, an X-ray
なお、揺動装置2とX線検出用揺動装置20とを同一に制御する手段としては、物理的に両者を接続し、片方の揺動機構をモータ制御することにより、同一の傾き方向T、同一の傾き角度αを実現することも可能である。
As means for controlling the
実施の形態2のX線検査装置においては、制御装置23がアルゴリズムによる自動検査機能を有している。このため、検査品質のばらつきのない信頼性の高い安定したX線検査を実現できる。
In the X-ray inspection apparatus according to the second embodiment, the
図11は実施の形態2のX線検査装置において、制御装置23が有するアルゴリズムによる自動検査機能の動作を示すフローチャートである。
FIG. 11 is a flowchart showing the operation of the automatic inspection function by the algorithm of the
図11の揺動動作ステップ301において、多軸制御装置25によりXYZ移動テーブル26を所望の位置に設定し、揺動装置2をZ軸方向(X線照射軸方向)に移動して所望の倍率とする。そして、検査対象物102を固定したXYステージ7とX線検出用揺動装置20とを同期して揺動動作させる。この揺動動作中において、XYステージ7の保持面7aが所定の傾き方向Tと所定の傾き角度αに到達したとき、X線照射装置3からX線を照射させて、検査対象物102を透過したX線がX線検出装置1に取り込まれる。この撮像動作は、予め決めた所定の傾き方向Tと所定の角度αの複数の位置において行われる。すなわち、XYステージ7の保持面7aの傾き方向Tが360度変わる間(1回転の間)に、X線検出装置1に複数回撮像させて、所定枚数のX線画像を取得する(画像取得ステップ302)。
In the
設定データ格納部401には、予め所定の傾き方向Tと所定の角度αに関する各断層面の良品状態における全てのX線画像を取得して格納されている。従って、画像取得ステップ302において、設定データ格納部401から揺動装置2及びX線検出用揺動装置20を駆動制御する制御装置23に対して傾き方向Tと角度αに関する情報が送られる。
In the setting
立体画像作成ステップ303において、トモグラフィ法を用いて、立体画像データ格納部402からのアルゴリズムにより、当該検査対象物102の立体画像データを作成する。
In the stereoscopic
次に、検査画像設定ステップ304において、設定データ格納部401から送られた情報に基づき所定の断層面を指定して、作成された立体画像データにおける一部の情報を選択する。この選択された情報により形成される所定の断層面のデータと、保存されている当該検査対象物に関する良品状態の立体画像データにおける断層面のデータとを比較する。良品状態の立体画像データは良品画像データ格納部403から選択して送られる。検査画像設定ステップ304において、比較した際の相関値により、設定データ格納部401に保存された良否判定基準値に基づいて、良否判定を実施する。
Next, in the inspection
上記のように、実施の形態2のX線検査装置においては、制御装置23が有する自動検査機能により、X線検査を確実に、且つ容易に行うことができる。
As described above, in the X-ray inspection apparatus according to the second embodiment, the X-ray inspection can be reliably and easily performed by the automatic inspection function of the
実施の形態2のX線検査装置は、画像認識装置を用いて自動検査システムを構築することができる。これら自動検査システムにおいては、生産ラインにX線検査装置をインラインで設置し、生産中のプリント回路基板等の回路形成体をコンベアで自動搬送して連続検査することができる。 The X-ray inspection apparatus according to the second embodiment can construct an automatic inspection system using an image recognition apparatus. In these automatic inspection systems, an X-ray inspection apparatus can be installed in-line on a production line, and a circuit formed body such as a printed circuit board under production can be automatically conveyed by a conveyor for continuous inspection.
実施の形態2のX線検査装置においては、揺動装置2のXYステージ7にXYZ移動テーブル26が設けられているため、検査対象物102をXYステージ7に対して任意の位置に設定することができ、XYステージ7におけるX線照射基準位置に対して、検査対象物102の任意の部分を、所定の傾き角度及び傾き方向に設定することができる。この結果、実施の形態2のX線検査装置によれば、取得したX線画像からボケや虚像の少ない高精度の断層画像を作成することが可能となり、検査対象物102の全体を容易にかつ、より正確に検査することが可能となる。
In the X-ray inspection apparatus of the second embodiment, since the XYZ movement table 26 is provided on the
なお、実施の形態2において、X線検出用遥動装置装置20及びX線照射装置3に駆動機構を設けて、X線検出用遥動装置装置20及びX線照射装置3を同時もしくは個別にX線照射軸方向(Z軸方向)に移動できるよう構成して、X線画像の倍率をさらに大きく設定変更できる構成としてもよい。
In the second embodiment, a drive mechanism is provided in the X-ray
《実施例3》
図12は本発明に係る実施の形態3のX線検査装置の主要な内部構成を示す平面断面図であり、図13はその正面断面図である。図14乃至図17は実施の形態3のX線検査装置におけるX線撮影及び画像合成の説明図である。実施の形態3において、前述の実施の形態1及び実施の形態2における構成要素と同じ機能、構成を有するものには同じ符号を付し、その説明は省略する。
Example 3
12 is a plan sectional view showing the main internal configuration of the X-ray inspection apparatus according to the third embodiment of the present invention, and FIG. 13 is a front sectional view thereof. 14 to 17 are explanatory diagrams of X-ray imaging and image synthesis in the X-ray inspection apparatus according to the third embodiment. In the third embodiment, components having the same functions and configurations as the components in the first embodiment and the second embodiment are denoted by the same reference numerals, and the description thereof is omitted.
図12及び図13において、X線遮蔽箱30内にはX線検出装置1、X線照射装置3、検査対象物用移動機構である基板用XYステージ31、及びX線検出用移動機構であるX線検出用XYステージ32等が配設されている。X線照射装置3の真上に設けられた基板用XYステージ31には検査対象物102であるプリント回路基板等が装着される基板保持機構40が設けられている。基板保持機構40は基板用XYステージ31に対してX軸方向とY軸方向へ移動可能に構成されている。基板用XYステージ31には基板用X軸モータ33を有する基板用X軸駆動機構41と基板用Y軸モータ34を有する基板用Y軸駆動機構42が設けられている。基板保持機構40は基板用X軸駆動機構41と基板用Y軸駆動機構42とによりX軸方向とY軸方向へ駆動される。
12 and 13, the
X線検出用XYステージ32にはX線検出装置1が固定されている。X線検出用XYステージ32には、X線検出用X軸モータ35を有するX線検出用X軸駆動機構43とX線検出用Y軸モータ36を有するX線検出用Y軸駆動機構44が設けられている。このため、X線検出装置1が固定されたX線検出用XYステージ32は、X軸方向とY軸方向へ移動可能に構成されている。また、X線検出用XYステージ32はZ軸方向(図13における上下方向)へ移動可能にX線検出用Z軸駆動機構39が設けられている。
The
モータ制御装置37(図13においてブロックで示す)は、基板用XYステージ31及びX線検出用XYステージ32を駆動する各モータを同時に制御する。また、表示装置38(図13においてブロックで示す)は、X線検出装置1からのX線画像のデータ及び算出されたX線断層画像のデータが表示される。
A motor control device 37 (shown as a block in FIG. 13) controls the motors that drive the
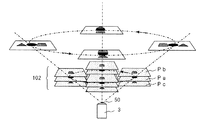
実施の形態3のX線検査装置において、X線照射装置3はX線遮蔽箱30内における下部に固定されている。X線はX線照射装置3のX線焦点(X線スポット)50から上方に向けて広い照射角度で円錐状に照射される。X線焦点50から放射されたX線は、検査対象物102である、例えばプリント回路基板を透過してX線検出装置1に入射される。このX線が検査対象物102を透過する際、その検査対象物102の物質のX線吸収率に応じて減衰される。X線検出装置1においては、取り込まれたX線の強度に比例した濃淡画像に変換してX線画像を作成する。作成されたX線画像は表示装置38において表示される。
In the X-ray inspection apparatus according to the third embodiment, the
実施の形態3のX線検査装置において、検査対象物102は基板用XYステージ31の基板保持機構40により固定されて、X軸方向とY軸方向へ移動できるよう構成されている。検査対象物102は基板用X軸駆動機構41と基板用Y軸駆動機構42により基板用XYステージ31の水平面上の任意の位置に移動できる。一方、X線検出装置1が固定されたX線検出用ステージ32は、X線検出用Z軸駆動機構39に固定されている。さらに、X線検出用Z軸駆動機構39はX線検出用X軸駆動機構43及びX線検出用Y軸駆動機構44に取付けられている。このため、実施の形態3におけるX線検出装置1は、X線検出用X軸駆動機構43、X線検出用Y軸駆動機構44、及びX線検出用Z軸駆動機構39による移動範囲内の任意の空間上の位置に移動できる。図12において、破線で示す円Qが基板保持機構40の中心点の軌跡を示し、円RがX線検出装置1の検出面の中心点の軌跡を示す。
In the X-ray inspection apparatus according to the third embodiment, the
次に、実施の形態3のX線検査装置におけるX線撮影について図14を参照して説明する。図14は検査対象物102としてボールグリッドアレイ(以下BGAという)接合部を有するプリント回路基板であり、図14においてP1、P2はBGA接合部のX線画像を示している。
Next, X-ray imaging in the X-ray inspection apparatus of
図14において、X線画像P1はBGA接合部を有するプリント回路基板(102)を基板用XYステージ31に固定し、BGA接合部の中心のボール接合部がX線検出装置1のX線画像の中心に撮影されるように垂直方向に透視した画像である。このとき、BGA接合部を有するプリント回路基板(102)の上部にコンデンサ等のX線透過率の低い部品が実装されている。このため、BGA接合部の中心のボール接合部の観察が妨げられている。また、X線画像P2は、BGA接合部を有するプリント回路基板(102)を図14の左方向に移動し、且つBGA接合部の中心のボール接合部が撮影されるX線画像の中心となるよう、X線検出装置1をさらに左方向に移動した画像である。X線画像P2では、コンデンサ等のX線透過率の低い部品が中心のボール接合部と重ならないため、BGA接合部の中心のボール接合部を観察することができる。
In FIG. 14, an X-ray image P <b> 1 fixes a printed circuit board (102) having a BGA bonding portion to the
上記のプリント回路基板(102)の移動とX線検出装置1の移動は、作業者が操作装置60(図13においてブロックで示す)における検査対象物102のX軸方向及び/又はY軸方向の移動スイッチを押すだけで、検査対象物102の移動量に応じてX線検出用XYステージ32を自動的に移動させる。このとき、X線検出用XYステージ32は、基板用XYステージ31における基板保持機構40の移動量にX線撮影の拡大率を乗じた分だけ移動する。この結果、常にBGA接合部の中心のボール接合部が撮像されたX線画像の中心の位置となる。ここで、X線撮影の拡大率とは、X線焦点50からX線検出装置1の画像形成位置までの距離Gを、X線焦点50から検出対象物102の検出位置までの距離Fで除した値(G/F)である。なお、X線検出用Z軸駆動機構39によりX線検出装置1を移動させて拡大率が変化した場合には、自動的に拡大率が再計算され、その算出された拡大率に応じてX線検出用XYステージ32を動作させる。
The above-described movement of the printed circuit board (102) and the movement of the
上記のように、実施の形態3のX線検査装置においては、基板用XYステージ31の基板保持機構40の移動量に応じてX線検出用XYステージ32を自動的に移動させて、観察したい注目点を常にX線画像の中心となるよう構成している。
As described above, in the X-ray inspection apparatus according to the third embodiment, the X-ray
次に、上記のように構成された実施の形態3のX線検査装置におけるX線断層検査方法について図15から図17を用いて説明する。実施の形態3のX線検査装置におけるX線断層検査方法として2つの検査方法がある。
Next, an X-ray tomographic inspection method in the X-ray inspection apparatus according to
[第1のX線断層検査方法]
まず、第1のX線断層検査方法について図15と図16を用いて説明する。図15は実施の形態3のX線検査装置におけるX線断層撮影の説明図である。図16は実施の形態3のX線検査装置における第1のX線断層検査方法により撮影したX線画像P3を示している。
[First X-ray tomography method]
First, the first X-ray tomography method will be described with reference to FIGS. 15 and 16. FIG. 15 is an explanatory diagram of X-ray tomography in the X-ray inspection apparatus according to the third embodiment. FIG. 16 shows an X-ray image P3 imaged by the first X-ray tomographic inspection method in the X-ray inspection apparatus of the third embodiment.
図15における検査対象物102は、一例として3層構造のプリント回路基板を示している。このプリント回路基板は、3層構造として、観察面である中間層に円形パターンPaがあり、中間層の上に四角形パターンPbがあり、中間層の下に三角形パターンPcで構成されている。このプリント回路基板は基板用XYステージ31の基板保持機構40に取り付けられており、基板用X軸駆動機構41と基板用Y軸駆動機構42により基板用XYステージ31の基板保持機構40が水平面上で円運動を行う。この時、基板保持機構40の移動量にX線撮影の拡大率を乗じた分だけX線検出用XYステージ32を自動的に移動させている。この結果、X線検出用XYステージ32は基板保持機構40の円運動の直径にX線撮影の拡大率を乗じた大きさの直径で円運動を行う。上記の拡大率の計算においては、X線焦点50から検出対象物102の観察面である目標位置までの距離は、X線焦点50からプリント回路基板の中間層である円形パターンPaまでの距離で計算する。これにより、3層構造のプリント回路基板の円形パターンPaが図16のX線画像P3に示すように、常にX線検出装置1によるX線画像の中心に撮影される。この撮影動作において、検査対象物102であるプリント回路基板とX線検出装置1の回転運動の中心は、X線焦点50を通る鉛直線上にある。この回転運動において、基板用XYステージ31とX線検出用XYステージ32のそれぞれの回転角度が常に同じになるように、それぞれを駆動する各軸のモータがモータ制御装置37により同期制御されている。
The
実施の形態3におけるX線検出装置1は、蓄積型のカメラを用いることにより、シャッタが開いている時間とX線強度の積に比例した濃淡画像が得られる構造である。図16に示したX線画像P3は、プリント回路基板とX線検出装置1の円運動が1回転する間、シャッタを開いた状態で撮影したX線画像である。回転角度が0度のときカメラのシャッタを開き、1回転したときシャッタを閉じれば、プリント回路基板のX線画像において、円形パターンPaは常にX線画像の中心に投影されて鮮明なパターンが撮影される。一方、別の断層面にある四角形パターンPbや三角形パターンPcは回転運動に応じてX線画像の異なる位置に投影されるため、画像がぼけてしまいはっきりとした像とならない。
The
従って、実施の形態3におけるX線検出装置1を用いて第1のX線断層検査方法を行うことにより、合成水平断層画像を形成して、検査対象物102における指定した断層面の状態が確実に検査可能となる。
Therefore, by performing the first X-ray tomography method using the
[第2のX線断層検査方法]
次に、実施の形態3のX線検査装置における第2のX線断層検査方法について図15及び図17を参照して説明する。
[Second X-ray Tomography Method]
Next, a second X-ray tomographic inspection method in the X-ray inspection apparatus of
前述の第1のX線断層検査方法においては、検査対象物102であるプリント回路基板とX線検出装置1の1回転の円運動においてシャッタを開放して1回の撮影を行っている。第2のX線断層検査方法においては、円運動における一定の角度毎に、プリント回路基板とX線検出装置1とを停止させて、その静止状態で撮影を行っている。従って、第2のX線断層検査方法においては、1回転の円運動の間に複数回撮影し、複数のX線画像を作成している。このため、第2のX線断層検査方法は、複数のX線画像を重ね合わせることにより、前述の第1のX線断層検査方法と同様に合成水平断層画像を得ることができる。
In the first X-ray tomographic inspection method described above, one image is taken by opening the shutter in the circular motion of one rotation of the printed circuit board as the
第2のX線断層検査方法においても、図15に示した3層構造のプリント回路基板を検査対象物102として説明する。 Also in the second X-ray tomographic inspection method, the printed circuit board having the three-layer structure shown in FIG.
プリント回路基板は基板用XYステージ31の基板保持機構40に取付けられている。撮影動作の最初において、基板用XYステージ31は、予め決められている検査対象物102の水平面上の円運動における円周上の角度0度の位置まで移動して停止する。この時、基板用XYステージ31の移動量にX線撮影の拡大率を乗じた分だけX線検出用XYステージ32は自動的に移動している。この状態において撮影を行い最初のX線画像を作成する。次に、基板用XYステージ31を、予め決められている円運動における円周上の所望の角度の位置まで移動して停止し、撮影する。以下、順次基板用XYステージ31を円運動における円周上の所望の角度毎に撮影する。このように撮影することにより、円運動の円周上の全ての停止位置で3層構造のプリント回路基板の円形パターンPaが常にX線検出装置1によるX線画像の中心に撮像される。
The printed circuit board is attached to the
上記のように、第2のX線断層検査方法において、検査対象物102であるプリント回路基板の円運動の中心点と、X線検出装置1の円運動の中心点は、X線焦点50を通る鉛直線上にある。また、プリント回路基板とX線検出装置1のそれぞれの円運動における円周上の位置は、各円における中心角度が常に同じである。このように、プリント回路基板とX線検出装置1が円運動するよう、基板用X軸モータ33、基板用Y軸モータ34、X線検査用X軸モータ35及びX線検査用Y軸モータ36は、モータ制御装置37により同期制御されている。
As described above, in the second X-ray tomographic inspection method, the center point of the circular motion of the printed circuit board that is the
第2のX線断層検査方法において、シャッタが開いている時間とX線強度の積に比例した濃淡画像のX線画像が、X線検出装置1により作成されるのは前述の第1のX線断層検査方法と同様である。ただし、第2のX線断層検査方法においては、シャッタの開放時間が短時間であるため撮影できる高感度カメラを使用するほうが望ましい。
In the second X-ray tomography method, an X-ray image of a grayscale image proportional to the product of the time when the shutter is open and the X-ray intensity is created by the
図17は、プリント回路基板とX線検出装置1を90度毎に停止して撮影し、4枚のX線画像を作成した例である。図17において、P0は角度0度のときのX線画像であり、P90は角度90度のときのX線画像であり、P180は角度180度のときのX線画像であり、P270は角度270度のときのX線画像である。図17において中央に記載したPAは、4枚のX線画像を実施の形態3のX線検査装置における画像処理装置70(図13においてブロックで示す)において重ね合わせることにより形成した合成X線画像であり、合成水平断層画像である。
FIG. 17 shows an example in which the printed circuit board and the
なお、第2のX線断層検査方法においては、円運動における停止位置を多くし、停止角度を小さくして撮影し、多くのX線画像を作成して、それらを合成することにより、さらなる鮮明なX線画像が得られる。ただ、停止位置が多くなるに従い撮影のための時間が長くなり、X線検査に長時間が必要となる。 In the second X-ray tomography method, the number of stop positions in a circular motion is increased, images are taken with a reduced stop angle, many X-ray images are created, and these are combined, thereby further sharpening. X-ray image can be obtained. However, as the stop position increases, the time for imaging becomes longer, and a longer time is required for the X-ray inspection.
第2のX線断層検査方法においては、画像処理装置70により所望の角度毎に得られた複数のX線画像の情報を用いてCT技術によるX線画像の再構成演算を行うことにより、3次元の立体画像を作成することもできる。このように作成された立体画像を用いて検査対象物102における各断面層の情報を正確に検出することが可能となる。従って、第2のX線断層検査方法を用いることにより検査対象物102の各断面層に関する内部情報を軸移動を行うことなく、容易に検査することが可能となる。
In the second X-ray tomographic examination method, by performing reconstruction calculation of an X-ray image by CT technique using information of a plurality of X-ray images obtained for each desired angle by the
以上のように、実施の形態3のX線検査装置によれば、検査対象物102の検査箇所をX線照射角の範囲内の任意の方向から容易に観察でき、拡大率を変更しても常に同じ検査箇所を観察できるばかりでなく、検査箇所を含む水平断面の画像だけを抽出することができる。さらに、実施の形態3のX線検査装置によれば、検査対象物102の各断面層の情報も容易に取得することが可能となる。
As described above, according to the X-ray inspection apparatus of the third embodiment, the inspection location of the
実施の形態3のX線検査装置によれば、X線照射装置3及びX線焦点を固定したX線検出装置1により、X検査の注目点である検査箇所がモニタ画面の中心から移動することなく撮影方向及び撮影倍率を変更して観察することができる。また、実施の形態3のX線検査装置によれば、検査箇所の水平断層画像を合成することにより、例えばプリント回路基板の接合部のオープン不良を含む様々な接合不良を検査することができる。
According to the X-ray inspection apparatus of the third embodiment, the
本発明のX線検査装置においては、各実施の形態において詳細に説明したように、安価で、高分解能でかつ鮮明な検査対象物の断層情報を容易に取得することができ、この断層情報に基づく正確な検査を行うことができる。 In the X-ray inspection apparatus of the present invention, as described in detail in each embodiment, it is possible to easily acquire the tomographic information of the inspection object that is inexpensive, high resolution, and clear. Based on the accurate inspection can be done.
近年においては、携帯情報機器等の電子機器の市場では商品の小型、軽量化が強く求められており、電子機器を構成する回路基板に対しても小型、軽量化の要望が強くなっている。そのため、従来のようなパッケージの周辺に電極リードを配置したQFP(Quad Flat Package)やSOP(Small Outline Package)等のリニア接合型の電子部品から、パッケージの裏面全体にポール電極等を配置したBGA(Ball grid array)やCSP(Chip Size Package)等のエリア接合型の電子部品が広く使われるようになっている。エリア接合型パッケージは、リニア接合型に比べて狭い面積の中に多くの電極を持てるので回路基板を小型化できる利点があるが、接合部が外から見えないため光学的外観検査装置が使用できない。そこで、これらの部品の接合検査には回路基板内部の状態を透視できるX線撮影法が用いられるようになってきている。このような部品に対して、本発明のX線検査装置は有用である。 In recent years, there has been a strong demand for smaller and lighter products in the market of electronic devices such as portable information devices, and there has been a strong demand for smaller and lighter circuit boards constituting electronic devices. Therefore, BGA with pole electrodes etc. arranged on the entire back surface of the package from linear junction type electronic parts such as QFP (Quad Flat Package) and SOP (Small Outline Package) with electrode leads arranged around the package as in the past. Area junction type electronic components such as (Ball grid array) and CSP (Chip Size Package) are widely used. The area junction type package has the advantage that the circuit board can be miniaturized because it can have many electrodes in a narrow area compared to the linear junction type, but the optical appearance inspection device cannot be used because the junction part cannot be seen from the outside. . Therefore, an X-ray imaging method capable of seeing through the state inside the circuit board has been used for bonding inspection of these components. The X-ray inspection apparatus of the present invention is useful for such components.
発明をある程度の詳細さをもって好適な形態について説明したが、この好適形態の現開示内容は構成の細部において変化してしかるべきものであり、各要素の組合せや順序の変化は請求された発明の範囲及び思想を逸脱することなく実現し得るものである。 Although the invention has been described in its preferred form with a certain degree of detail, the present disclosure of this preferred form should vary in the details of construction, and combinations of elements and changes in order may vary in the claimed invention. It can be realized without departing from the scope and spirit.
本発明係るX線検査装置は、安価で、高分解能でかつ鮮明な検査対象物の断層情報を容易に取得することができるため、X線検査において有用である。 The X-ray inspection apparatus according to the present invention is useful in X-ray inspection because it is inexpensive, has high resolution, and can easily acquire clear tomographic information of the inspection object.
1 X線検出装置
2 揺動装置
3 X線照射装置
4 X軸モータ
5 Y軸モータ
6 制御装置
7 XYステージ
8 内枠
9 外枠
10 多軸制御装置
20 X線検出用揺動装置
21 X軸モータ
22 Y軸モータ
23 制御装置
102 検査対象物
1
4 X-axis motor 5 Y-
Claims (7)
前記検査対象物を透過したX線を検出するX線検出手段と、
前記X線照射手段と前記X線検出手段との間において、前記保持面と平行かつ前記保持面上で直交するX軸とY軸の2軸をそれぞれ中心として、前記保持面を2方向に下記式(1)および式(2)の条件で往復揺動させる揺動手段と、
前記X線検出手段の検出結果に基づいて前記検査対象物の検査を行う検査手段と、
を具備することを特徴とするX線検査装置。
TAN(θ)=TAN(φX)/TAN(φY) (1)
TAN 2 (α)=TAN 2 (φX)+TAN 2 (φY) (2)
ただし、θ:X軸と保持面法線との成す角、α:Z軸と保持面法線との成す角、φX:X軸中心の回転角度、φY:Y軸中心の回転角度、である。
X-ray irradiation means for irradiating the inspection object held on the holding surface of the inspection object moving mechanism with X-rays;
X-ray detection means for detecting X-rays transmitted through the inspection object;
In between the X-ray irradiation unit and the X-ray detecting unit, the two axes of the X axis and Y axis perpendicular on the holding surface and parallel or One the holding surface around each said holding surface in two directions Rocking means for reciprocating rocking under the conditions of the following formula (1) and formula (2) ;
Inspection means for inspecting the inspection object based on the detection result of the X-ray detection means;
An X-ray inspection apparatus comprising:
TAN (θ) = TAN (φX) / TAN (φY) (1)
TAN 2 (α) = TAN 2 (φX) + TAN 2 (φY) (2)
Where θ is an angle formed by the X axis and the holding surface normal, α is an angle formed by the Z axis and the holding surface normal, φX is a rotation angle about the X axis, and φY is a rotation angle about the Y axis. .
を特徴とする請求項1に記載のX線検査装置。The X-ray inspection apparatus according to claim 1.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004248706A JP4386812B2 (en) | 2003-08-27 | 2004-08-27 | X-ray inspection equipment |
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003303188 | 2003-08-27 | ||
| JP2003330180 | 2003-09-22 | ||
| JP2004248706A JP4386812B2 (en) | 2003-08-27 | 2004-08-27 | X-ray inspection equipment |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2005121633A JP2005121633A (en) | 2005-05-12 |
| JP2005121633A5 JP2005121633A5 (en) | 2007-04-26 |
| JP4386812B2 true JP4386812B2 (en) | 2009-12-16 |
Family
ID=34623546
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004248706A Expired - Fee Related JP4386812B2 (en) | 2003-08-27 | 2004-08-27 | X-ray inspection equipment |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4386812B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (20)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB0415053D0 (en) * | 2004-07-05 | 2004-08-04 | Dage Prec Ind Ltd | X-ray manipulator |
| JP4926645B2 (en) * | 2006-10-24 | 2012-05-09 | 名古屋電機工業株式会社 | Radiation inspection apparatus, radiation inspection method, and radiation inspection program |
| JP2008298480A (en) * | 2007-05-29 | 2008-12-11 | Beamsense Co Ltd | Stereo fluoroscopic device, and stereo observation method using therefor |
| JP5125423B2 (en) * | 2007-11-01 | 2013-01-23 | オムロン株式会社 | Method of inspecting solder electrode by X-ray tomographic image and board inspection apparatus using this method |
| JP4818245B2 (en) * | 2007-11-14 | 2011-11-16 | 株式会社 コアーズ | Heating X-ray observation device |
| WO2009078415A1 (en) * | 2007-12-17 | 2009-06-25 | Uni-Hite System Corporation | X-ray examining apparatus and method |
| JP5396751B2 (en) * | 2008-06-18 | 2014-01-22 | オムロン株式会社 | Board inspection equipment using X-rays |
| EP2378279A4 (en) * | 2008-12-22 | 2013-05-29 | Omron Tateisi Electronics Co | X-ray inspection method and x-ray inspection apparatus |
| JP5444718B2 (en) * | 2009-01-08 | 2014-03-19 | オムロン株式会社 | Inspection method, inspection device, and inspection program |
| JP4574718B1 (en) | 2009-04-22 | 2010-11-04 | 株式会社アドバンテスト | Electromagnetic wave measuring apparatus, measuring method, program, recording medium |
| JP5569061B2 (en) * | 2010-03-15 | 2014-08-13 | オムロン株式会社 | X-ray inspection method, X-ray inspection apparatus and X-ray inspection program |
| JP5220060B2 (en) * | 2010-06-02 | 2013-06-26 | 株式会社アドバンテスト | Electromagnetic wave measuring apparatus, measuring method, program, recording medium |
| CN103733053B (en) * | 2011-08-05 | 2016-08-17 | 株式会社岛津制作所 | Radiation tomography device |
| JP2013061257A (en) * | 2011-09-14 | 2013-04-04 | Omron Corp | X-ray inspection device, x-ray inspection device control method, program for controlling x-ray inspection device, and recording medium storing program therein |
| KR101181845B1 (en) * | 2011-12-22 | 2012-09-11 | 주식회사 쎄크 | Automatic x-ray inspection apparatus for surface mount technology in-line |
| KR101381927B1 (en) * | 2013-09-13 | 2014-04-24 | 김선택 | Apparatus and method for obliquely scanning circuit elements using x-ray |
| KR101467478B1 (en) * | 2013-09-13 | 2014-12-01 | (주)시스트 | Apparatus and method for scanning circuit elements using x-ray |
| EP2927945B1 (en) * | 2014-04-04 | 2023-05-31 | Nordson Corporation | X-ray inspection apparatus for inspecting semiconductor wafers |
| WO2017133847A1 (en) | 2016-02-04 | 2017-08-10 | Yxlon International Gmbh | Method for the reconstruction of a test part in an x-ray ct method in an x-ray ct system by means of an intelligent path curve |
| DK3690429T3 (en) | 2019-02-04 | 2021-12-13 | Microtec Srl | Tunnel ct scanner |
-
2004
- 2004-08-27 JP JP2004248706A patent/JP4386812B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2005121633A (en) | 2005-05-12 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4386812B2 (en) | X-ray inspection equipment | |
| US7099432B2 (en) | X-ray inspection apparatus and X-ray inspection method | |
| JP5444718B2 (en) | Inspection method, inspection device, and inspection program | |
| JPH06100451B2 (en) | Automatic laminograph system for electronics inspection. | |
| JP4711759B2 (en) | X-ray inspection equipment | |
| JP5104962B2 (en) | X-ray inspection method and X-ray inspection apparatus | |
| TW200848723A (en) | X ray inspecting method and X ray inspecting device | |
| CN111247424A (en) | Inspection position specifying method, three-dimensional image generating method, and inspection device | |
| WO2009121051A2 (en) | X-ray inspection systems and methods | |
| JP5045134B2 (en) | X-ray CT system | |
| JP3643722B2 (en) | X-ray inspection method and apparatus | |
| JP2007170926A (en) | X-ray inspection device, abnormality display device for tomographic image, x-ray inspection method, abnormality display method for tomographic image, program and recording medium | |
| WO2021215217A1 (en) | Inspection apparatus | |
| JP5125297B2 (en) | X-ray inspection apparatus and X-ray inspection method | |
| JP5251264B2 (en) | X-ray CT system | |
| JP2005292047A (en) | X-ray tomographic imaging device, and x-ray tomographic imaging method | |
| JP4155866B2 (en) | X-ray tomography system | |
| JP2019060808A (en) | Method for specifying inspection position and inspection device | |
| TW201312102A (en) | X-ray inspecting device, method for controlling the same, program for controlling the same and recording media for stroing the program thereof | |
| JP5544636B2 (en) | Tomography equipment | |
| JP2007101247A (en) | X-ray tomographic imaging apparatus and x-ray tomographic imaging method | |
| JP2001153819A (en) | X-ray laminographic device | |
| JP2004340630A (en) | Computer tomography, and computer tomographic device | |
| JP2005055274A (en) | Apparatus for inspecting soldered appearance | |
| JP2006214841A (en) | X-ray ct apparatus |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A821 Effective date: 20050523 |
|
| RD02 | Notification of acceptance of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7422 Effective date: 20050523 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20070308 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20070308 |
|
| RD03 | Notification of appointment of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7423 Effective date: 20070308 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20080626 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20080729 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20080925 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20081209 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20090203 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20090901 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20090929 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20121009 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20131009 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |