JP4330477B2 - Gradient magnetic field coil and magnetic resonance imaging apparatus using the same - Google Patents
Gradient magnetic field coil and magnetic resonance imaging apparatus using the same Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4330477B2 JP4330477B2 JP2004101999A JP2004101999A JP4330477B2 JP 4330477 B2 JP4330477 B2 JP 4330477B2 JP 2004101999 A JP2004101999 A JP 2004101999A JP 2004101999 A JP2004101999 A JP 2004101999A JP 4330477 B2 JP4330477 B2 JP 4330477B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- coil
- magnetic field
- gradient
- gradient magnetic
- cooling
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 238000002595 magnetic resonance imaging Methods 0.000 title claims description 22
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 claims description 107
- 239000003507 refrigerant Substances 0.000 claims description 23
- 230000003068 static effect Effects 0.000 claims description 21
- 238000003384 imaging method Methods 0.000 claims description 13
- 239000002356 single layer Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000002826 coolant Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000000498 cooling water Substances 0.000 description 9
- 238000004804 winding Methods 0.000 description 9
- 230000020169 heat generation Effects 0.000 description 7
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 description 6
- 230000001939 inductive effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000000523 sample Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000003822 epoxy resin Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000001965 increasing effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 229920000647 polyepoxide Polymers 0.000 description 3
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical compound [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000005481 NMR spectroscopy Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000010292 electrical insulation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000005011 phenolic resin Substances 0.000 description 2
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000000903 blocking effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000919 ceramic Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012937 correction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007797 corrosion Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005260 corrosion Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000006866 deterioration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007599 discharging Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005288 electromagnetic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000005674 electromagnetic induction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000004907 flux Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012535 impurity Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000006698 induction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000011810 insulating material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001208 nuclear magnetic resonance pulse sequence Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01R—MEASURING ELECTRIC VARIABLES; MEASURING MAGNETIC VARIABLES
- G01R33/00—Arrangements or instruments for measuring magnetic variables
- G01R33/20—Arrangements or instruments for measuring magnetic variables involving magnetic resonance
- G01R33/28—Details of apparatus provided for in groups G01R33/44 - G01R33/64
- G01R33/38—Systems for generation, homogenisation or stabilisation of the main or gradient magnetic field
- G01R33/385—Systems for generation, homogenisation or stabilisation of the main or gradient magnetic field using gradient magnetic field coils
- G01R33/3856—Means for cooling the gradient coils or thermal shielding of the gradient coils
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging Apparatus (AREA)
Description
本発明は磁気共鳴イメージング装置(以下、MRI装置)、特にオープン型のMRI装置に用いられる傾斜磁場コイルに係り、特に傾斜磁場コイルの通電発熱を効率良く冷却するための冷却構造に関するものである。 The present invention relates to a gradient magnetic field coil used in a magnetic resonance imaging apparatus (hereinafter referred to as an MRI apparatus), particularly an open type MRI apparatus, and more particularly to a cooling structure for efficiently cooling energization heat generation of the gradient magnetic field coil.
MRI装置では、NMR信号に位置情報を付与するために、静磁場に重畳して傾斜磁場を加える必要があり、X、Y、Zの3軸方向に傾斜磁場を発生する3組のコイルを組み合わせた傾斜磁場コイルが広く使用されている。傾斜磁場コイルには撮像の際に繰り返し電流が印加され、これによりジュール熱が発生する。近年、高速撮像法の普及に伴い傾斜磁場の磁場強度も増加する傾向にあり、コイルに流れる電流値や導体ターン数が大きくなり、結果として通電時に生じるジュール発熱が増加している。特に、傾斜磁場が発生する変動磁場が、均一磁場空間以外のコイル周辺に漏洩しないようにシールドコイルを併有させたアクティブシールド型の傾斜磁場コイルにおいては、磁場発生の効率が悪いため、通電時の発熱量は非常に大きなものになる。 In order to give position information to NMR signals, it is necessary to apply a gradient magnetic field superimposed on a static magnetic field in an MRI apparatus, and combine three sets of coils that generate gradient magnetic fields in the X, Y, and Z directions. Gradient field coils are widely used. A current is repeatedly applied to the gradient coil during imaging, thereby generating Joule heat. In recent years, with the spread of high-speed imaging methods, the magnetic field strength of the gradient magnetic field tends to increase, and the current value flowing through the coil and the number of conductor turns increase, resulting in an increase in Joule heat generated during energization. In particular, the active shield type gradient magnetic field coil combined with the shield coil so that the magnetic field generated by the gradient magnetic field does not leak around the coil other than the uniform magnetic field space has a low magnetic field generation efficiency. The calorific value of is very large.
また上述したように通常の傾斜磁場コイルは、3軸方向に傾斜磁場を発生する3種類のコイルの組合せで構成されており、各々の発熱量と面内分布が異なるため、コイル集合体内部の発熱と温度は大きな分布を有する。
このような傾斜磁場コイルによる発熱量の増加や分布は、傾斜磁場コイル自体に熱変形を生じさせたり静磁場磁石等の性能を劣化させる原因となるため、傾斜磁場コイルを冷却するための技術が種々提案されている。
In addition, as described above, a normal gradient magnetic field coil is composed of a combination of three types of coils that generate gradient magnetic fields in three axial directions, and the amount of generated heat and in-plane distribution are different. The exotherm and temperature have a large distribution.
Such an increase or distribution of the amount of heat generated by the gradient magnetic field coil causes thermal deformation in the gradient magnetic field coil itself or deteriorates the performance of the static magnetic field magnet, etc. Therefore, there is a technique for cooling the gradient magnetic field coil. Various proposals have been made.
例えば特許文献1には、メインの傾斜磁場コイルとシールドコイルとを備えたアクティブシールド型の傾斜磁場コイルにおいて、メインコイルとシールドコイルの中間部に冷却配管を配置することで、コイル全体を冷却する構造が提案されている。また特許文献2には、傾斜磁場コイルの断面方向に熱伝導率の異なる層を積層するとともに最外層に冷却部を配置し、発熱部から冷却部に向かって熱伝導率が低くなるようにして熱流束を改善した傾斜磁場コイルが提案されている。さらに特許文献3には、傾斜磁場コイルを構成する導体を、冷却媒体を流通させるために中空円筒状にした構成が開示されている。
しかし特許文献1に記載されたものでは、コイル内部における発熱密度が最も大きな領域に冷却機構を設けていないため、効率良く、かつ全面にわたって均等に冷却することは困難である。また特許文献2に記載されたものでは熱伝導率の異なる層を積層した構造になっているため、傾斜磁場コイル自体の厚さが大きくなり、撮像空間を確保するためには最外層に設ける冷却部の厚さにはおのずと限界があり、冷却効率にも限界がある。さらに特許文献3に記載されたものでは、コイル導体の特性から形状、太さには制限があり、冷却効率にも限界がある。また特許文献3に記載されたものでは、複数のコイルを組み合わせた傾斜磁場コイルについては考慮されておらず、この種のコイルの熱分布を改善することができない。 However, since the cooling mechanism is not provided in the region having the largest heat generation density inside the coil, it is difficult to efficiently and evenly cool the entire surface described in Patent Document 1. In addition, since the structure described in Patent Document 2 has a structure in which layers having different thermal conductivities are laminated, the thickness of the gradient magnetic field coil itself is increased, and cooling provided in the outermost layer in order to secure an imaging space. The thickness of the part naturally has a limit, and the cooling efficiency also has a limit. Furthermore, in what is described in Patent Document 3, the shape and thickness are limited due to the characteristics of the coil conductor, and the cooling efficiency is also limited. Moreover, in the thing described in patent document 3, the gradient magnetic field coil which combined several coils is not considered, and the heat distribution of this kind of coil cannot be improved.
そこで本発明は、傾斜磁場コイルを効率良く、かつ全面にわたって均等に冷却することが可能な冷却構造を備えた傾斜磁場コイルを提供することを目的とする。 Then, an object of this invention is to provide the gradient magnetic field coil provided with the cooling structure which can cool a gradient magnetic field coil efficiently and uniformly over the whole surface.
上記目的を達成するため本発明のMRI装置用傾斜磁場コイルは、実質的に平坦な形状を有し、異なる方向の傾斜磁場を発生する複数のコイルを含むものであって、主な特徴として次の特徴を備える。 In order to achieve the above object, a gradient coil for an MRI apparatus of the present invention has a substantially flat shape and includes a plurality of coils that generate gradient magnetic fields in different directions. With the features of
(1)少なくとも一方の面に電磁気的な機能を有しない冷却配管が配置されるとともに、傾斜磁場コイルを構成する複数のコイルの一つは内部に冷媒の流路を有する冷却コイルである。
(2) 傾斜磁場コイルを構成する複数のコイルの一つは内部に冷媒の流路を有する冷却コイル(電磁気的な機能を有する冷却配管)であって、他のコイルの間に配置されている。
(3) 傾斜磁場コイルが、電磁気的な機能を有しない冷却配管と冷却コイルとを有するものである場合、冷却配管と冷却コイルの各配管系統は圧力損失が同等であって、同じ冷媒循環系に接続されている。
(4) 傾斜磁場コイルが、電磁気的な機能を有しない冷却配管と冷却コイルとを有するものである場合、冷却配管は、無誘導巻きされた単層からなる。
(5) 冷却配管が無誘導巻きされたものである場合、往路と復路との間隔が互いの熱交換を防止する距離に保たれている。
(6) 傾斜磁場コイルが、メインコイルと前記メインコイルの磁場漏洩を防止するシールドコイルとを備えている場合、メインコイル及びシールドコイルの少なくとも一方が上記特徴(1)〜(6)のいずれかを備えている。
(7) メインコイルとシールドコイルの両方に冷却配管を備える場合、両冷却配管は直列接続されている。
(8) メインコイルとシールドコイルの両方に冷却配管を備える場合、両冷却配管は直列接続されており、シールドコイル側の冷却配管が冷媒流入側に接続されている。
(9) 上記(1)〜(8)の特徴が任意に組み合わされている。
また本発明のMRI装置は、傾斜磁場コイルとして、これら特徴(1)〜(9)のいずれかと、熱交換器と循環ポンプとを有して前記冷媒を循環させる手段とを備えたものである。
(1) A cooling pipe not having an electromagnetic function is disposed on at least one surface, and one of the plurality of coils constituting the gradient coil is a cooling coil having a refrigerant flow path therein.
(2) One of the plurality of coils constituting the gradient magnetic field coil is a cooling coil (cooling pipe having an electromagnetic function) having a refrigerant flow path therein, and is disposed between other coils. .
(3) When the gradient coil has a cooling pipe and a cooling coil that do not have an electromagnetic function, each piping system of the cooling pipe and the cooling coil has the same pressure loss, and the same refrigerant circulation system It is connected to the.
(4) When the gradient magnetic field coil has a cooling pipe and a cooling coil that do not have an electromagnetic function, the cooling pipe is made of a single layer wound non-inductively.
(5) When the cooling pipe is non-inductively wound, the distance between the forward path and the return path is maintained at a distance that prevents mutual heat exchange.
(6) In the case where the gradient magnetic field coil includes a main coil and a shield coil for preventing magnetic field leakage of the main coil, at least one of the main coil and the shield coil is any one of the features (1) to (6). It has.
(7) When both the main coil and the shield coil are provided with cooling pipes, both cooling pipes are connected in series.
(8) When both the main coil and the shield coil are provided with cooling pipes, both the cooling pipes are connected in series, and the cooling pipe on the shield coil side is connected to the refrigerant inflow side.
(9) The features (1) to (8) above are arbitrarily combined.
The MRI apparatus of the present invention includes any one of these features (1) to (9) as a gradient magnetic field coil, and a means for circulating the refrigerant having a heat exchanger and a circulation pump. .
本発明の傾斜磁場コイルによれば、上記構成を採用することにより、傾斜磁場コイルが発生する熱を効率よく且つ全面に亘って均等に冷却することができる。 According to the gradient coil of the present invention, the heat generated by the gradient coil can be efficiently and uniformly cooled over the entire surface by adopting the above configuration.
以下、本発明の傾斜磁場コイル及びそれを備えたMRI装置の実施の形態を説明する。 Embodiments of a gradient coil and an MRI apparatus having the same according to the present invention will be described below.
図1(a)は、本発明が適用されるMRI装置の全体概要を示すブロック図である。
このMRI装置は、被検体101の体軸方向に対し垂直な傾斜磁場を発生する垂直磁場方式オープンタイプのMRI装置であり、被検体101が挿入される撮像空間に静磁場を発生する上下一対の磁石102と、この空間に傾斜磁場を発生する傾斜磁場コイル103と、被検体の撮像領域に高周波磁場を発生するRFコイル104と、被検体101が発生する核磁気共鳴(MR)信号を検出するRFプローブ105と、静磁場空間に被検体101を挿入するためのベッド112を備えている。
FIG. 1A is a block diagram showing an overall outline of an MRI apparatus to which the present invention is applied.
This MRI apparatus is a vertical magnetic field type open type MRI apparatus that generates a gradient magnetic field perpendicular to the body axis direction of the
このオープンタイプのMRI装置では、上下一対の磁石102の各々に、平板状の傾斜磁場コイル103及び平板状のRFコイル104が固定されており、磁石102を支持する支柱(図示せず)の間から撮像空間にアクセスできるようになっている。
傾斜磁場コイル103は、互いに直交する3方向(X,Y,Z)の傾斜磁場コイルで構成され、傾斜磁場電源109からの信号に応じてそれぞれ傾斜磁場を発生する。また傾斜磁場コイル103は冷却手段(後述)を備えており、冷却手段は、図1(b)に示すように、冷却のための配管を介して熱交換器113及び循環ポンプ114に接続されている。
In this open type MRI apparatus, a flat
The gradient
RFコイル104はRF送信部110の信号に応じて高周波磁場を発生する。RFプローブ105は、RFコイル104と兼用とすることも可能であるが、図示する実施例ではRFコイル104とは別に被検体101の測定部位に近接して配置されている。RFプローブ105からの信号は、信号検出部106で検出され、信号処理部107で信号処理され、また計算により画像信号に変換される。画像は表示部108で表示される。
傾斜磁場電源109、RF送信部110、信号検出部106は、撮像方法によって決まるパルスシーケンスに従い制御部111で制御される。
The
The gradient magnetic
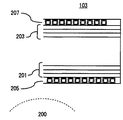
図2は、傾斜磁場コイル103の一部の詳細を模式的に示す部分断面図であり、上下に配置される傾斜磁場コイルの一方(上側に配置されるもの)のみを示している。この傾斜磁場コイル103は、アクティブシールド型の傾斜磁場コイルで、撮像空間200に傾斜磁場を与えるメインの傾斜磁場コイル201(以下、メインコイルともいう)のほかに、メインコイル201が発生する磁場が静磁場磁石側へ漏洩しないように逆向きの磁場を発生させるシールドコイル203が備えられている。シールドコイル203も、メインコイルと同様にX、Y、Zの3方向の傾斜磁場を発生する傾斜磁場コイルであり、メインコイル201と同様にこれら3方向のコイルを一体化した平板形状を有している。シールドコイル203は、メインコイル201の磁場を効果的にキャンセルするために、所定の間隔を持って配置されている。
FIG. 2 is a partial sectional view schematically showing a part of the gradient
また傾斜磁場コイル103は、メインコイル201及びシールドコイル203が発生する熱を冷却するために、メインコイル201の撮像空間側およびシールドコイル203の静磁場磁石側にそれぞれ冷却用配管205、207が固定されている。これら冷却用配管205、207は、それぞれ往路と復路が同一面内にあり、冷媒供給用及び排出用の口出し部がコイル外側面に設けられている。一般に冷却配管の構造としては、蛇腹状或いは渦巻状があるが、蛇腹状のものは傾斜磁場コイルの一端から他端に向かって温度勾配を生じ、渦巻状のものは復路のために全体の厚みが管自体の厚みの2倍以上となり、傾斜磁場コイルの冷却配管として好ましくない。このため本発明では、渦巻状であって往路と復路が同一平面内にある構造の冷却配管を採用する。図3にこのような構造の冷却配管の一例を示す。
The gradient
図3に示す冷却配管は、平板の端部を冷媒入口とする渦巻状の往路が中央近傍で折り返し、往路に平行した渦巻状の復路となって平板の端部の冷媒出口につながっている構造で、無誘導巻きと呼ばれるものである。このような無誘導巻きでは、往路の巻き方向と復路の巻き方向とは全く逆方向となるので、銅管やアルミ管のような導電性の材料で構成した場合にも電磁誘導による磁場の発生がなく実質的に電磁気的な作用を有しない。また同一平面内に冷媒の往路と復路が形成されているので、冷却配管に要する厚みは配管の厚みのみであり、冷却配管による傾斜磁場コイルの厚みの増加を極力抑えることができる。その結果、撮像空間として十分な広さを確保することができる。 The cooling pipe shown in FIG. 3 has a structure in which a spiral outward path having a refrigerant inlet at the end of a flat plate is folded back in the vicinity of the center, and a spiral return path parallel to the outward path is connected to the refrigerant outlet at the end of the flat plate. This is called non-inductive winding. In such a non-inductive winding, the winding direction of the forward path and the winding direction of the return path are completely opposite directions, so even when it is made of a conductive material such as a copper tube or an aluminum tube, a magnetic field is generated by electromagnetic induction. There is no substantial electromagnetic effect. Further, since the refrigerant forward and return paths are formed in the same plane, the thickness required for the cooling pipe is only the thickness of the pipe, and an increase in the thickness of the gradient magnetic field coil due to the cooling pipe can be suppressed as much as possible. As a result, a sufficient area as an imaging space can be ensured.
冷却配管の無誘導巻きの形状は、冷却管によって除熱したい熱量から、巻線される配管内部を流れる冷媒の流量及び流路の断面寸法と全長から決定される圧力損失が冷媒供給装置と適合するように設計される。この際、無誘導巻きした冷却配管の往路と復路との間は、往路・復路間で熱交換が起こることを防止するために、所定の間隔が設けられる。この往路と復路との間隔(ターン間隔)は、流量が多ければ間隔は狭くてもよく、流量が少なければ広くする必要がある。従って流量に応じて適宜設計する。 The shape of the non-inductive winding of the cooling pipe is compatible with the refrigerant supply device from the amount of heat to be removed by the cooling pipe, the flow rate of the refrigerant flowing inside the coiled pipe, the pressure loss determined from the cross-sectional dimensions and the total length of the flow path Designed to do. At this time, a predetermined interval is provided between the forward path and the return path of the cooling pipe that has been wound without induction in order to prevent heat exchange between the forward path and the return path. The distance between the forward path and the return path (turn interval) may be narrow if the flow rate is large, and wide if the flow rate is small. Therefore, it is designed appropriately according to the flow rate.
例として、銅配管の断面形状が外径10mm(内径8mm)、長さ50mであり、ターン間にエポキシ樹脂を充填した冷却配管の場合を図4に示す。図中、1.5kWの発熱量に対し配管内部に約0.5L/分で冷却水を流した場合(実線)及び流量を倍の約1L/分にした場合(点線)について、冷却配管長手方向の冷却水温度の変化を示すグラフで、それぞれターン間隔(4mm〜14mm)を異ならせて測定したものを示している。図示するように、流量約0.5L/分ではターン間隔を14mm以上設ける必要があり、流量約1L/分ではターン間隔は10mm以上設ける必要がある。 As an example, FIG. 4 shows a case where a copper pipe has a cross-sectional shape having an outer diameter of 10 mm (inner diameter of 8 mm) and a length of 50 m, and a cooling pipe filled with epoxy resin between turns. In the figure, when the cooling water is flowed at about 0.5 L / min to the heat generation of 1.5 kW (solid line) and when the flow rate is doubled to about 1 L / min (dotted line), It is a graph showing the change of the cooling water temperature, and shows the values measured with different turn intervals (4 to 14 mm). As shown in the figure, it is necessary to provide a turn interval of 14 mm or more at a flow rate of about 0.5 L / min, and a turn interval of 10 mm or more at a flow rate of about 1 L / min.
なお図4の例では、往路と復路との間にエポキシ樹脂が介在する場合を示したが、これらの間に存在する空気のみでもよいし、エポキシ樹脂以外の熱を遮断する材料(例えばフェノール樹脂やマシナブルセラミックス)を介在させてもよい。さらに往路を熱伝導性のよい材料で形成し、復路を熱伝導性の低い材料で形成することも可能である。このように往路と復路との間、特に冷媒入口と冷媒出口の近傍での熱交換を遮断することにより、配管内部を流れる冷媒や配管の温度が、配管入口から出口に向かって一様に上昇するようにすることができ、傾斜磁場コイルを冷却効率を高めることができる。 In the example of FIG. 4, the case where an epoxy resin is interposed between the forward path and the return path is shown, but only air existing between these may be used, or a material that blocks heat other than the epoxy resin (for example, a phenol resin). Or machinable ceramics). Further, it is possible to form the forward path with a material having good thermal conductivity and to form the return path with a material having low thermal conductivity. Thus, by blocking the heat exchange between the forward path and the return path, particularly in the vicinity of the refrigerant inlet and the refrigerant outlet, the temperature of the refrigerant flowing in the pipe and the temperature of the pipe rise uniformly from the pipe inlet to the outlet. Thus, the cooling efficiency of the gradient coil can be increased.
なお冷媒は特に限定されないが、通常、冷却水を用いる。冷却水は、電気絶縁性や腐食の観点から導電率が50μS/cm以下であることが好ましい。このような導電率は冷却水の循環路に不純物を除去するイオン交換器を設置することにより達成することができる。 The refrigerant is not particularly limited, but usually cooling water is used. The cooling water preferably has a conductivity of 50 μS / cm or less from the viewpoint of electrical insulation and corrosion. Such conductivity can be achieved by installing an ion exchanger for removing impurities in the circulation path of the cooling water.
メインコイル側の冷却配管205とシールドコイル側の冷却配管207は、別個の配管系統としてもよいが、直列に接続することにより配管系統を簡素にすることができる。その場合には、比較的温度上昇の少ないシールドコイル側の冷却配管を冷媒の流入側とすることが好ましい。またこれら両配管は好適には長さ及び形状を同一とする。これにより、冷却管の巻線工程が共通化し、作業を簡略化することができる。或いは発熱量の大きいメインコイル側の冷却配管205の長さをシールドコイル側より長くすることも可能であり、この場合には、メインコイル側の前面を効率よく冷却できるため、傾斜磁場コイル全体の温度勾配を小さくすることができる。
The
このように本実施形態の傾斜磁場コイルによれば、傾斜磁場コイルの少なくとも一方の面に冷却配管を固定し、且つ冷却配管として典型的には無誘導巻きのような往路と復路を同一平面に有する配管を採用したことにより、傾斜磁場コイルの厚みを増やすことなく効果的に傾斜磁場コイルの温度上昇を抑制できる。またシールドコイルを備えたアクティブシールド傾斜磁場コイルの場合には、メインコイルのみならずシールドコイルの静磁場磁石側側面にも冷却配管を配置することにより、静磁場磁石への熱の伝達を効果的に抑制し、熱による磁石特性の変化や性能の劣化を防止できる。この場合、メインコイル側とシールドコイル側の冷却配管の長さや冷媒流量を調整することにより、傾斜磁場全体の温度勾配を小さくすることができる。 As described above, according to the gradient magnetic field coil of the present embodiment, the cooling pipe is fixed to at least one surface of the gradient magnetic field coil, and the forward path and the return path such as a non-inductive winding are typically coplanar as the cooling pipe. By adopting the piping having, it is possible to effectively suppress the temperature rise of the gradient magnetic field coil without increasing the thickness of the gradient magnetic field coil. In addition, in the case of an active shield gradient magnetic field coil equipped with a shield coil, heat transfer to the static magnetic field magnet can be effectively performed by arranging a cooling pipe not only on the main coil but also on the side surface of the shield coil on the static magnetic field magnet side. It is possible to suppress the change in the magnetic characteristics and the deterioration of the performance due to heat. In this case, the temperature gradient of the entire gradient magnetic field can be reduced by adjusting the length of the cooling pipes on the main coil side and the shield coil side and the refrigerant flow rate.
本発明の別の実施形態を図5に示す。図5に示す実施形態の傾斜磁場コイル103は、冷却配管205、207の構成は図2と同様であるが、これらに加えてX、Y、Zのメインコイル201の一つ2011が冷却コイルを兼ねている。即ち図示する実施形態では、メインZコイル2011を中空導体で構成し、その内部に冷媒を通すとともに、冷却配管205とメインZコイル2011とでメインXコイル及びメインYコイルを挟む構成としている。
Another embodiment of the present invention is shown in FIG. In the gradient
一般に垂直磁場方式のMRI装置の傾斜磁場コイル103では、垂直方向をZ方向とすると、Xコイル及びYコイルは傾斜磁場コイル103の面と平行な方向に磁場勾配を発生するための複雑なパターンに巻かれているため、電気抵抗がZコイルより高く、従って発熱量も多い。またシールドコイル203に比べメインコイル201の発熱量が高い。表1に、典型的なアクティブシールド傾斜磁場コイルの発熱量の一例を示す。
本実施形態の傾斜磁場コイル103は、比較的単純な巻きパターンであって冷媒の流路としての抵抗が小さいメインZコイル2011を冷却配管としても機能させるとともに、最も発熱量の多いメインXコイル及びメインYコイルを、このメインZコイルを含む2つの冷却配管2011、205で挟んだ構造とすることにより、さらに効果的に傾斜磁場コイル103の温度上昇と傾斜磁場コイルの熱変形を抑制することができる。
The gradient
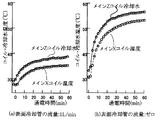
冷却配管及びメインZコイルの断面寸法を6mm×6mm、肉厚1mm、冷却水の流量を約1L(リットル)/分とした場合の冷却効果を図6に示す。図6(a)のグラフは冷却配管とメインZコイルに冷却水を流した場合、(b)のグラフは冷却配管には冷却水を流さなかった場合で、それぞれメインZコイル内の冷却水温度及びメインXコイルの温度の実測値を、メインXコイルに対する通電時間(200A)に対しプロットしたものである。(a)、(b)のグラフから明らかなように、メインZコイルを傾斜磁場コイルの一方の面に配置した構成では、メインの冷却コイルのみでは冷却効果が十分ではないが、他方の面に冷却配管を配置して他のコイルを挟む構造にしたことにより、高い冷却効果を上げることができる。 FIG. 6 shows the cooling effect when the cross-sectional dimensions of the cooling pipe and the main Z coil are 6 mm × 6 mm, the wall thickness is 1 mm, and the cooling water flow rate is about 1 L (liter) / min. The graph of FIG. 6A shows the case where the cooling water flows through the cooling pipe and the main Z coil, and the graph of FIG. 6B shows the case where the cooling water does not flow through the cooling pipe. The measured values of the temperature of the main X coil are plotted against the energization time (200 A) for the main X coil. As is clear from the graphs (a) and (b), in the configuration in which the main Z coil is disposed on one surface of the gradient magnetic field coil, the cooling effect is not sufficient with only the main cooling coil, but on the other surface. By arranging the cooling pipe to sandwich another coil, a high cooling effect can be achieved.
メインZコイルも含めた冷却配管の配管系統の一例を図7に示す。図示するように、この実施形態では、冷却専用の配管系統701と、通電時に電圧が印加される配管系統702とを備え、それぞれの口出しC1〜C4が傾斜磁場コイルの外周部に設けられる。メインコイル側の冷却配管205とシールドコイル側の冷却配管207は配管系統701に属し、メインZコイル2011は配管系統702に属している。配管系統702の口出しC1、C2には撮像シーケンスに従い電圧が印加される。このためC1、C2は、絶縁性材料からなるホース等を用いて外部配管に接続される。或いはメインZコイルの配管として電気絶縁処理を施したものを用いてもよく、この場合には外部との接続には導電体を用いてもよい。
An example of the piping system of the cooling piping including the main Z coil is shown in FIG. As shown in the figure, this embodiment includes a
また冷却専用の配管系統701とメインZコイルの配管系統702を別系統にするのではなく、口出しC1とC2及びC3とC4をそれぞれ一つにまとめ、傾斜磁場コイル内で分岐するようにしてもよい。この場合、冷却専用の配管205、207とメインZコイル2011の両者の圧力損失を同等にすることが好ましい。それにより外部に流量調整用のバルブ等を設けることなく両配管系統に流れる冷却水の流量を同等にすることができる。
Rather than separate the cooling
本実施形態の傾斜磁場コイルによれば、メインZコイルに冷却管としての機能を持たせ、最も発熱量の多いXコイル及びYコイルをメインZコイルと冷却専用の冷却管とで挟む構造にしたことにより、さらに効果的に傾斜磁場コイルの温度上昇を抑制できる。この場合、メインZコイルである冷却管と冷却専用冷却管の圧力損失を同等にすることにより、流量調節用バルブ等を不要とし配管系統を簡略にすることができる。 According to the gradient magnetic field coil of the present embodiment, the main Z coil has a function as a cooling pipe, and the X coil and the Y coil that generate the most heat are sandwiched between the main Z coil and a cooling pipe dedicated to cooling. Thus, the temperature rise of the gradient coil can be more effectively suppressed. In this case, by equalizing the pressure loss of the cooling pipe that is the main Z coil and the cooling dedicated cooling pipe, a flow rate adjusting valve or the like is not required and the piping system can be simplified.
次に本発明のさらに別の実施形態を説明する。
図8は、本発明の傾斜磁場コイルの別の実施形態を示す図で、この実施形態の傾斜磁場コイルもメインコイル801のほかにシールドコイル803を備えたアクティブシールド傾斜磁場コイルであることは図2の実施形態と同じであるが、この実施形態では、メイン及びシールドのZコイル8011、8031をそれぞれ内部に冷媒流路を設けた冷却コイルとするとともに、これら冷却コイル8011、8031をXコイルとYコイルとの間に設けたことを特徴としている。これら冷却コイル8011、8031は、傾斜磁場コイルの外端部に冷媒供給用及び排出用の口出し部が設けられ、それぞれ電気的に絶縁されて冷却循環系に接続されている。メインコイルとシールドコイルは電気的には直列に接続され、通電時に所定の電圧が印加されるように傾斜磁場電源に接続されている。冷却コイル8011、8031の配管系統は、別個でもよいし、並列又は直列に接続して同じ系統にすることも可能である。但し、これらの接続においては各冷却コイルの電磁気的な機能を阻害しないことが重要である。
Next, still another embodiment of the present invention will be described.
FIG. 8 is a diagram showing another embodiment of the gradient coil according to the present invention. The gradient coil of this embodiment is also an active shield gradient coil including a
本実施形態の傾斜磁場コイルでは、発熱量の大きいXコイルとYコイルとの間に冷却コイルを配置したことにより、冷却専用の配管を表面に配置しなくても、メインコイル或いはシールドコイル全体の温度勾配を小さくすることができ、温度勾配に起因する熱変形を効果的に防止することができる。またメインコイル及びシールドコイルの両方に冷却コイルを採用したことにより、静磁場磁石側の温度上昇を抑えることができる。
この実施形態では、冷却専用の配管は必須ではないが、図2或いは図5に示す実施形態と同様に、シールドコイル803の静磁場磁石側及びメインコイル801の撮像空間側に冷却配管を備えることができ、これら冷却専用の冷却配管として無誘導巻きを採用することができる。
In the gradient magnetic field coil of the present embodiment, the cooling coil is arranged between the X coil and the Y coil that generate a large amount of heat, so that the entire main coil or shield coil can be obtained without arranging a cooling-dedicated pipe on the surface. The temperature gradient can be reduced, and thermal deformation due to the temperature gradient can be effectively prevented. Further, by adopting the cooling coil for both the main coil and the shield coil, the temperature rise on the static magnetic field magnet side can be suppressed.
In this embodiment, piping dedicated for cooling is not essential, but cooling piping is provided on the static magnetic field magnet side of the
以上、本発明の傾斜磁場コイルの実施形態を説明したが、本発明はこれら実施形態に限定されることなく、特許請求の範囲に記載される範囲において種々の変更を採用できる。例えば、上記実施形態ではシールドコイルを備えたアクティブシールド型傾斜磁場コイルについて説明したが、シールドコイルを備えていない傾斜磁場コイルや静磁場均一性を補正する補正用コイルを備えた傾斜磁場コイルにも同様に適用することができる。また本発明を他の冷却手段や熱遮断手段と併用することも可能である。例えば、図3に示したように、コイル面内の冷却配管のみならず、コイル外側面に冷却配管を設けてもよいし、図9に示すように、静磁場磁石への取り付け面に熱伝導率の低い材料(例えばフェノール樹脂板など)からなる薄板901を配置することも可能である。
As mentioned above, although embodiment of the gradient magnetic field coil of this invention was described, this invention is not limited to these embodiment, A various change is employable in the range described in a claim. For example, although the active shield type gradient magnetic field coil provided with the shield coil has been described in the above embodiment, the gradient magnetic field coil not provided with the shield coil or the gradient magnetic field coil provided with the correction coil for correcting the static magnetic field uniformity is also described. The same can be applied. Further, the present invention can be used in combination with other cooling means and heat shut-off means. For example, as shown in FIG. 3, not only cooling pipes in the coil surface but also cooling pipes may be provided on the outer surface of the coil, and heat conduction is performed on the mounting surface to the static magnetic field magnet as shown in FIG. It is also possible to arrange a
本発明の傾斜磁場コイルのMRI装置への組み込み例を図10に示す。図10は図5と同様の構成の傾斜磁場コイル103を静磁場磁石102に組み込んだ例を示すもので、図示するように、傾斜磁場コイル103のシールドコイル側が静磁場磁石102に接するように、静磁場磁石102に形成された凹部に固定する。この際、静磁場磁石102とシールドコイルの表面冷却配管207との間に熱絶縁板901を配置する。この構成では、シールドコイルの表面冷却配管207によって傾斜磁場コイルの発熱を除去するとともに傾斜磁場コイル103と静磁場磁石102とを熱的に遮断したことにより、静磁場磁石102の特性の変動を防止することができる。
An example of incorporating the gradient magnetic field coil of the present invention into an MRI apparatus is shown in FIG. FIG. 10 shows an example in which the gradient
102・・・静磁場磁石、103・・・傾斜磁場コイル、201・・・メインコイル、2011・・・メインZコイル(冷却コイル)、203・・・シールドコイル、205、207・・・冷却配管
102 ... Static magnetic field magnet, 103 ... Gradient magnetic field coil, 201 ... Main coil, 2011 ... Main Z coil (cooling coil), 203 ... Shield coil, 205, 207 ... Cooling piping
Claims (6)
前記冷却配管と冷却コイルの各配管は圧力損失が同等で同じ冷媒循環系に接続されていることを特徴とする傾斜磁場コイル。 The gradient coil according to claim 2,
Each of the cooling pipe and the cooling coil has the same pressure loss and is connected to the same refrigerant circulation system.
前記メインコイル及びシールドコイルの少なくとも一方が請求項1から3いずれか1項記載の傾斜磁場コイルであることを特徴とする磁気共鳴イメージング装置用傾斜磁場コイル。 A main coil comprising a plurality of coils having a substantially flat shape and generating gradient magnetic fields in different directions, and a gradient magnetic field having a substantially flat shape and canceling the gradient magnetic field generated by the main coil. A gradient coil for a magnetic resonance imaging apparatus comprising a generated shield coil,
The gradient magnetic field coil for a magnetic resonance imaging apparatus, wherein at least one of the main coil and the shield coil is the gradient magnetic field coil according to any one of claims 1 to 3.
前記メインコイル及び前記シールドコイルは、それぞれ、冷却配管を備え、前記メインコイル及び前記シールドコイルの冷却配管は直列接続されていることを特徴とする傾斜磁場コイル。 The gradient coil according to claim 4,
The main coil and the shield coil each include a cooling pipe, and the main coil and the cooling pipe for the shield coil are connected in series.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004101999A JP4330477B2 (en) | 2004-03-31 | 2004-03-31 | Gradient magnetic field coil and magnetic resonance imaging apparatus using the same |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004101999A JP4330477B2 (en) | 2004-03-31 | 2004-03-31 | Gradient magnetic field coil and magnetic resonance imaging apparatus using the same |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2005279168A JP2005279168A (en) | 2005-10-13 |
| JP2005279168A5 JP2005279168A5 (en) | 2007-05-17 |
| JP4330477B2 true JP4330477B2 (en) | 2009-09-16 |
Family
ID=35178161
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004101999A Expired - Lifetime JP4330477B2 (en) | 2004-03-31 | 2004-03-31 | Gradient magnetic field coil and magnetic resonance imaging apparatus using the same |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4330477B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7339376B2 (en) * | 2006-04-09 | 2008-03-04 | General Electric Company | MRI/MRS gradient coil with integrated cooling circuits |
| JP5100199B2 (en) * | 2006-05-17 | 2012-12-19 | 株式会社東芝 | Gradient magnetic field coil, method of manufacturing the gradient magnetic field coil, and magnetic resonance imaging apparatus provided with the gradient magnetic field coil |
| WO2008096628A1 (en) * | 2007-02-06 | 2008-08-14 | Hitachi Medical Corporation | Magnetic resonance imaging device, and inclined magnetic field coil |
| JP5613379B2 (en) * | 2008-03-13 | 2014-10-22 | 株式会社東芝 | Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and cooling apparatus |
| JP5570910B2 (en) | 2009-09-28 | 2014-08-13 | 株式会社東芝 | Magnetic resonance imaging system |
| JP6058612B2 (en) * | 2009-09-28 | 2017-01-11 | 東芝メディカルシステムズ株式会社 | Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and gradient coil |
| JP2011087904A (en) * | 2009-09-28 | 2011-05-06 | Toshiba Corp | Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus |
| JP5911338B2 (en) * | 2012-03-02 | 2016-04-27 | 株式会社東芝 | Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and cooling apparatus thereof |
| DE112015006201T5 (en) * | 2015-02-23 | 2017-11-02 | Synaptive Medical (Barbados) Inc. | System and method for arranging magnetic resonance coils |
| US10761162B2 (en) * | 2018-09-18 | 2020-09-01 | General Electric Company | Gradient coil cooling systems |
| CN112858972A (en) * | 2019-11-28 | 2021-05-28 | 西门子(深圳)磁共振有限公司 | Gradient coil and magnetic resonance imaging system |
| CN113050005B (en) * | 2019-12-26 | 2024-01-30 | 西门子(深圳)磁共振有限公司 | Gradient coil cooling component and gradient coil |
-
2004
- 2004-03-31 JP JP2004101999A patent/JP4330477B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2005279168A (en) | 2005-10-13 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4719438B2 (en) | Apparatus for active cooling of an MRI patient bore in a cylindrical MRI system | |
| JP5100994B2 (en) | Inclined bore cooling and RF shielding | |
| US7135863B2 (en) | Thermal management system and method for MRI gradient coil | |
| JP4330477B2 (en) | Gradient magnetic field coil and magnetic resonance imaging apparatus using the same | |
| JP6055306B2 (en) | Reactor | |
| JP5209277B2 (en) | Gradient magnetic field coil unit, gantry for MRI apparatus, and MRI apparatus | |
| US6236207B1 (en) | Coil system for magnetic resonance systems with integrated cooling unit | |
| JP3771947B2 (en) | Magnet assembly of superconducting magnetic resonance imaging system | |
| JP2005058770A (en) | Method and apparatus for directly cooling hollow conductor wound around transverse gradient coil boards | |
| JP2004202245A (en) | Conduction cooled passive shield mri magnet | |
| JP5226930B2 (en) | Thermal management device and manufacturing method thereof | |
| EP0921537B1 (en) | Magnet coil assembly | |
| JPS60189204A (en) | Cooler for magnet system | |
| JP2024041051A (en) | High frequency coil assembly for magnetic resonance imaging system and its manufacturing method | |
| JP2012011060A (en) | Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus | |
| WO2013175928A1 (en) | Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and magnet for magnetic resonance imaging apparatus | |
| JP2005279168A5 (en) | ||
| JP5222735B2 (en) | Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and gradient coil | |
| US7495442B2 (en) | Method for cooling coils and shim iron | |
| JP2008028146A (en) | Thermal shield for superconducting magnet, superconducting magnet device, and magnetic resonance imaging apparatus | |
| JP2005288044A (en) | Magnetic resonance imaging device | |
| JP2609346B2 (en) | Gradient magnetic field coil device | |
| JP2024508859A (en) | Shielded slope assembly | |
| JP2001149337A (en) | Magnetic resonance imaging device | |
| JPH04367650A (en) | Magnetoresonance imaging device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20070328 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20070328 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20090205 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20090217 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20090407 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20090616 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20090616 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 4330477 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120626 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120626 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130626 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| S111 | Request for change of ownership or part of ownership |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313111 |
|
| S533 | Written request for registration of change of name |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313533 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| S111 | Request for change of ownership or part of ownership |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313111 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| EXPY | Cancellation because of completion of term |