JP4248714B2 - Crawler car - Google Patents
Crawler car Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4248714B2 JP4248714B2 JP34586699A JP34586699A JP4248714B2 JP 4248714 B2 JP4248714 B2 JP 4248714B2 JP 34586699 A JP34586699 A JP 34586699A JP 34586699 A JP34586699 A JP 34586699A JP 4248714 B2 JP4248714 B2 JP 4248714B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- steering
- speed
- crawler
- traveling
- turning
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 claims description 101
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 claims description 92
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 claims description 19
- 230000001965 increasing effect Effects 0.000 claims description 15
- 230000035945 sensitivity Effects 0.000 claims description 11
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 25
- 230000007935 neutral effect Effects 0.000 description 19
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 17
- 235000013339 cereals Nutrition 0.000 description 15
- 238000003306 harvesting Methods 0.000 description 13
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000003028 elevating effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000001133 acceleration Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000012937 correction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000009193 crawling Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000005096 rolling process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000002699 waste material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 240000007594 Oryza sativa Species 0.000 description 1
- 235000007164 Oryza sativa Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 235000014676 Phragmites communis Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000006096 absorbing agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000969 carrier Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000006866 deterioration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000446 fuel Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012423 maintenance Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000003801 milling Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 1
- 235000009566 rice Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 210000004935 right thumb Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000000630 rising effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000009987 spinning Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007723 transport mechanism Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Guiding Agricultural Machines (AREA)
- Harvester Elements (AREA)
- Non-Deflectable Wheels, Steering Of Trailers, Or Other Steering (AREA)
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は例えば圃場の穀稈を連続的に刈取って脱穀するコンバインまたは耕耘トラクタまたは圃場管理車などのクローラ走行車に関する。
【0002】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
従来、走行変速レバーの操作によって左右走行クローラの駆動速度を無段階に変更して車速を変速させると共に、操向ハンドルの操作によって左右走行クローラの駆動速度の差を無段階に変更して走行進路を変更させる技術がある。しかし乍ら、操向ハンドルの操作により、旋回内側走行クローラを逆転させるスピンターン動作を行わせると、旋回半径が小さい方向転換を容易に行えるが、湿田など泥土層が多い路面ではスピンターン動作によって走行クローラの走行力が低下し、希望する方向の旋回移動を容易に行い得ない等の問題がある。また、乾田または湿田など走行路面条件によって走行クローラのスピンターン動作を人為的に禁止する場合、本機姿勢を水平に保つ水平制御を自動的に行うことにより、スピンターン動作の禁止及び許可操作を自動水平制御動作に対応して行って走行機能を維持する必要がある。また、左右走行クローラを駆動する変速部材及び操向部材を設ける場合、変速部材及び操向部材を変速レバー及び操向ハンドルにリンク機構を介して連結させて制御することにより、前記リンク機構などの操作構造の簡略化並びに変速及び操向などの走行機能の変更などを容易に行い得ない等の問題がある。また、操向ハンドルの操作によって左右走行クローラの回転が連続的に変化することにより、旋回内側走行クローラ回転が低下するブレーキターンと旋回内側走行クローラが逆転するスピンターンを容易に判別し得ず、超湿田などで走行クローラをスピンターン動作させて走行機能を低下させる不具合がある。また、変速部材または操向部材を油圧ポンプ及び油圧モータを用いた油圧無段変速機構によって形成することにより、油圧ポンプ及びモータの伝動損失によって走行クローラの駆動力が必要以下に低下する不具合がある。このように、走行変速及び旋回機能の向上並びに運転操作性の向上などを容易に図り得ない等の問題がある。
【0003】
【課題を解決するための手段】
然るに、本発明は、機体に左右走行クローラを備え、前記機体の前後方向の直進走行を変速する変速部材と、前記機体を旋回させる操向部材とを変速操向コントローラを介して接続したクローラ走行車において、走行クローラの走行路面条件によって走行クローラのスピンターンを許可または禁止操作するスピンターンスイッチを設けるとともに、操向部材のスピンターン動作領域の操向ハンドル操作によってエンジン出力を自動的に大きくするように構成したもので、スピンターンスイッチ操作によって湿田などでの走行クローラのスピンターンを容易に阻止し得、同一の圃場で全体的に乾田で一部が湿田のときでも作業を中断させることなくスピンターンスイッチ操作によってスピンターンの禁止及び許可の切換を行い得、走行クローラの走行性能を路面条件に適応させて維持し得るものである。また、走行クローラの走行負荷が増大する旋回時に走行クローラを安定して駆動し得、出力不足によるエンジン回転低下などを容易に防止し得、運転操作性の向上並びにエンジン等の耐久性向上などを容易に図り得るものである。
【0004】
また、左右走行クローラ速度を検出する車速センサと、操向ハンドル切角を検出する操向角度センサと、変速レバー操作位置を検出する変速センサを設け、操向ハンドル切角によって決定される旋回半径になるように左右走行クローラ速度を自動制御するように構成したもので、操向ハンドル及び変速レバーなどの操作構造の簡略化並びに走行クローラの操向機能及び変速機能の向上または変更を容易に行い得、旋回性能の向上並びに運転操作性の向上などを容易に図り得るものである。
【0005】
また、変速部材または操向部材の出力が、停止乃至最大出力の途中で、直線的な変化よりも大きくなるように構成したもので、変速部材または操向部材の動力伝達損失などによって走行クローラ駆動力が不足する不具合を容易になくし得、走行クローラの走行性能の維持並びに運転操作性の向上などを容易に図り得、特に損失割合が大きくなる微速走行時の走行性能を容易に向上し得るものである。
【0006】
また、操向角度センサ及び変速センサの検出結果に基づき決定される左右走行クローラ速度変化の制御基準値を予め記憶させ、前記制御基準値を旋回感度設定器によって補正するように構成したもので、前記制御基準値(制御マップ)に基づく平均的な走行クローラの操向または変速制御と、走行路面(圃場)条件または作業者の希望走行フィーリングに適応した操向または変速制御を容易に得られ、運転操作性の向上などを容易に図り得るものである。
【0007】
また、操向ハンドル切角を検出する操向角度センサと、変速レバー切換位置を検出する変速センサと、変速部材及び操向部材の出力回転を検出するクローラ回転センサを設け、前記各センサの検出結果に基づき左右走行クローラ速度を演算して左右走行クローラ速度を自動制御するように構成したもので、クローラ回転センサによる変速部材または操向部材出力回転の直接検出によって回転センサの損傷を容易に防止し得、かつ左右走行クローラ速度の表示によって運転状況を容易に確認し得るものである。
【0008】
【発明の実施の形態】
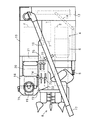
以下、本発明の実施例を図面に基づいて詳述する。図1はコンバインの全体側面図、図2は同平面図であり、図中(1)は左右一対の走行クローラ(2)を装設するトラックフレーム、(3)は前記トラックフレーム(1)に架設する機台、(4)はフィードチェン(5)を左側に張架し扱胴(6)及び処理胴(7)を内蔵している脱穀部、(8)は刈刃(9)及び穀稈搬送機構(10)などを備える刈取部、(11)は刈取フレーム(12)を介して刈取部(8)を昇降させる油圧昇降シリンダ、(13)は排藁チェン(14)終端を臨ませる排藁処理部、(15)は脱穀部(4)からの穀粒を揚穀筒(16)を介して搬入する穀物タンク、(17)は前記タンク(15)の穀粒を機外に搬出する排出オーガ、(18)は丸形操向ハンドル(19)及び運転席(20)などを備える運転台、(21)は運転席(20)下方に設けるエンジンであり、連続的に穀稈を刈取って脱穀するように構成している。
【0009】
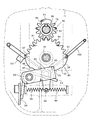
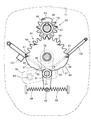
さらに、図3に示す如く、前記走行クローラ(2)を駆動するミッションケース(22)は、1対の第1油圧ポンプ(23)及び第1油圧モータ(24)を備えて走行主変速用の油圧式無段変速機構を形成する変速部材(25)と、1対の第2油圧ポンプ(26)及び第2油圧モータ(27)を備えて旋回用の油圧式無段変速機構を形成する操向部材(28)とを備え、前記エンジン(21)の出力軸(21a)に第1及び第2油圧ポンプ(23)(26)の入力軸(29a)(29b)を伝達ベルト(30a)(30b)によって連結させ、前記各油圧ポンプ(23)(26)を駆動するように構成している。
【0010】
また、前記第1油圧モータ(24)の変速出力軸(31)に、副変速機構(32)及び差動機構(33)を介して左右走行クローラ(2)の各駆動輪(34)を連動連結させるもので、前記差動機構(33)は左右対称の1対の遊星ギヤ機構(35)(35)を有し、各遊星ギヤ機構(35)は1つのサンギヤ(36)と、該サンギヤ(36)の外周で噛合う3つのプラネタリギヤ(37)と、これらプラネタリギヤ(37)に噛合うリングギヤ(38)などで形成している。
【0011】
前記プラネタリギヤ(37)はサンギヤ軸(39)と同軸線上とのキャリヤ軸(40)のキャリヤ(41)にそれぞれ回転自在に軸支させ、左右のサンギヤ(36)(36)を挾んで左右のキャリヤ(41)を対向配置させると共に、前記リングギヤ(38)は各プラネタリギヤ(37)に噛み合う内歯(38a)を有してサンギヤ軸(39)とは同一軸芯上に配置させ、キャリヤ軸(40)に回転自在に軸支させ、キャリヤ軸(40)を延設して車軸を形成して走行クローラ(2)の駆動輪(34)を軸支させている。
【0012】
また、走行用の油圧式無段変速部材(25)は、第1油圧ポンプ(23)の回転斜板の角度変更調節により第1油圧モータ(24)の正逆回転と回転数の制御を行うもので、第1油圧モータ(24)の回転出力を出力軸(31)の伝達ギヤ(42)より各ギヤ(43)(44)(45)及び副変速機構(32)を介して、サンギヤ軸(39)に固定したセンタギヤ(46)に伝達してサンギヤ(36)を回転するように構成している。前記副変速機構(32)は、前記ギヤ(44)を有する副変速軸(47)と、前記ギヤ(45)を介してセンタギヤ(46)に噛合うギヤ(48)を有する駐車ブレーキ軸(49)とを備え、副変速軸(47)とブレーキ軸(49)間に各1対の低速用ギヤ(50)(51)・中速用ギヤ(52)(53)・高速用ギヤ(54)(48)を設けて、低中速スライダ(55)及び高速スライダ(56)のスライド操作によって副変速の低速・中速・高速の切換を行うように構成している。なお低速・中速間及び中速・高速間には中立を有する。また前記ブレーキ軸(49)に駐車ブレーキ(57)を設けると共に、刈取部(8)に回転力を伝達する刈取PTO軸(58)にギヤ(59)(60)及び一方向クラッチ(61)を介して副変速軸(47)を連結させ、刈取部(8)を車速同調速度で駆動している。
【0013】
上記のように、前記センタギヤ(46)を介しサンギヤ軸(39)に伝達された第1油圧モータ(24)からの駆動力を、左右の遊星ギヤ機構(35)を介して左右キャリヤ軸(40)に伝達させると共に、左右キャリヤ軸(40)に伝達された回転を左右の駆動輪(34)にそれぞれ伝え、左右走行クローラ(2)を駆動するように構成している。
【0014】
さらに、旋回用の油圧式無段変速機構で形成する操向部材(28)は、第2油圧ポンプ(26)の回転斜板の角度変更調節により第2油圧モータ(27)の正逆回転と回転数の制御を行うもので、操向出力ブレーキ(62)を有するブレーキ軸(63)と、操向出力クラッチ(64)を有するクラッチ軸(65)と、前記の左右リングギヤ(38)の外歯(38b)に常時噛合させる左右入力ギヤ(66)(67)を設け、第2油圧モータ(27)の操向出力軸(68)に前記ブレーキ軸(63)及び操向出力クラッチ(64)を介してクラッチ軸(65)を連結させ、クラッチ軸(65)に正転ギヤ(69)を介して右入力ギヤ(67)を連結させ、またクラッチ軸(65)に正転ギヤ(69)及び逆転ギヤ(70)を介して左入力ギヤ(66)を連結させている。そして、副変速スライダ(55)(56)の中立によって前記ブレーキ(62)を入にしかつクラッチ(64)を切にする一方、前記中立以外の副変速出力時にブレーキ(62)を切にしかつクラッチ(64)を入にし、右側のリングギヤ(38)の外歯(38b)に正転ギヤ(69)を介してモータ(27)回転力を伝え、また左側のリングギヤ(38)の外歯(38b)に正転ギヤ(69)及び逆転ギヤ(70)を介してモータ(27)回転を伝え、第2油圧モータ(27)を正転(逆転)時、左右同一回転数で、左リングギヤ(38)を逆転(正転)させ、かつ右リングギヤ(38)を正転(逆転)とさせるように構成している。
【0015】
而して、旋回用の第2油圧モータ(27)を停止させて左右リングギヤ(38)を静止固定させた状態で、走行用の第1油圧モータ(24)を駆動すると、第1油圧モータ(24)からの回転出力はセンタギヤ(46)から左右のサンギヤ(36)に同一回転数で伝達され、左右遊星ギヤ機構(35)のプラネタリギヤ(37)・キャリヤ(41)を介して左右の走行クローラ(2)が左右同一回転方向で同一回転数によって駆動され、機体の前後方向直進走行が行われる。一方、走行用の第1油圧モータ(24)を停止させて左右のサンギヤ(36)を静止固定させた状態で、旋回用の第2油圧モータ(27)を正逆回転駆動すると、左側の遊星ギヤ機構(35)が正或いは逆回転、また右側の遊星ギヤ機構(35)が逆或いは正回転し、左右走行クローラ(2)を逆方向に駆動し、機体を左或いは右に旋回させる。また、走行用の第1油圧モータ(24)を駆動させながら、旋回用の第2油圧モータ(27)を駆動することにより、機体が左右に旋回して進路が修正されるもので、機体の旋回半径は第2油圧モータ(27)の出力回転数によって決定される。
【0016】
さらに、図2、図4乃至図6に示す如く、前記運転台(18)の前部上面にステアリングコラム(71)を立設固定させ、ステアリングコラム(71)上面上方側に操向ハンドル(19)を縦軸回りに回転自在に取付けると共に、運転台(18)左側にサイドコラム(72)を設け、サイドコラム(72)下方にミッション(22)を配設させ、主変速レバー(73)、副変速レバー(74)、刈取クラッチレバー(75)、脱穀クラッチレバー(76)を前記サイドコラム(72)に取付ける。
【0017】
また、前記ステアリングコラム(71)上部に操向入力軸(78)上端部を回転自在に軸支させ、操向ハンドル(19)に連結させるハンドル軸(79)のギヤ(80)と操向入力軸(78)のセクタギヤ(81)を噛合させて各軸(78)(79)を連結させるもので、前記ギヤ(80)は、270度の外周範囲に複数の歯(82)を形成し、90度の外周範囲を円弧(83)に形成し、操向ハンドル(19)の全回転角度を270度とし、左操向回転または右操向回転の角度を135度に設定し、操向ハンドル(19)回転操作を片手で作業者が容易に行えるように形成する。また、前記セクタギヤ(81)は、130度の外周範囲に複数の歯(84)を形成し、230度の外周範囲を円弧カム(85)に形成し、前記ギヤ(80)の歯(82)とセクタギヤ(81)の歯(83)を噛合せ、各ギヤ(80)(81)の最大正逆転時、前記円弧(83)両端のストッパ(86)と前記円弧カム(85)両端のストッパ(87)を当接させ、操向ハンドル(19)の回転を規制する。
【0018】
また、前記セクタギヤ(81)の円弧カム(85)中央に直進ノッチ(88)を形成すると共に、前記ステアリングコラム(71)デテント軸(89)を介してデテントアーム(90)を回転自在に軸支させ、デテントアーム(90)にローラ軸(91)を介してデテントローラ(92)を回転自在に軸支させ、前記円弧カム(85)にデテントローラ(92)を当接させ、直進ノッチ(88)に係脱自在にデテントローラ(92)を係合させ、操向ハンドル(19)を直進位置に支持させる。また、前記デテント軸(89)に巻装させる中立バネ(93)の一端をデテントアーム(90)に係止させ、ステアリングコラム(71)の受板(94)に中立バネ(93)の他端を当接させ、円弧カム(85)及び直進ノッチ(88)にデテントローラ(92)を中立バネ(93)によって弾圧当接させている。
【0019】
さらに、前記セクタギヤ(81)に形成する円弧カム(85)をブレーキカム(95)とスピンカム(96)とに分けて設け、各カム(95)(96)を段差(97)で連結させ、操向ハンドル(19)の直進乃至約90度の操作角度のブレーキターン位置でデテントローラ(92)をブレーキカム(95)に当接させ、旋回内側走行クローラ(2)が逆転駆動される直前でデテントローラ(92)を段差(97)に当接させ、旋回内側走行クローラ(2)が逆転駆動されるスピンターン位置でデテントローラ(92)をスピンカム(96)に当接させるもので、中立バネ(93)力によって決定される操向ハンドル(19)の操作力を段階的に大きくしてブレーキターン動作からスピンターン動作に移行させ、ブレーキターンとスピンターンのデテント手段として前記段差(92)を形成し、操向ハンドル(19)の最大ブレーキターン操作角度で操作力を大きく変化させ、ブレーキターンとスピンターンの境界を作業者に認識させ、例えば超湿田での収穫作業時、操向ハンドル(19)のスピンターン操作を防止し、スピンターンによる走行性能の低下を未然に阻止する。このように、操向部材(28)を操作する操向ハンドル(19)の操作力を段階的に変化させるように構成し、左右走行クローラ(2)を同一方向に駆動するブレーキターン並びに旋回内側走行クローラ(2)を逆転させるスピンターンなどの切換え位置を操向ハンドル(19)操作力の変化によって作業者が認識し、例えば走行性能が低下し易い軟弱泥土路面(湿田)でのスピンターンなどを防止し、運転操作性の向上などを図る。
【0020】
また、前記操向入力軸(78)に操向出力アーム(98)の一端を固定させ、操向ハンドル(19)を直進位置に戻す左右一対の直進バネ(99)(99)と、前記バネ(99)に抗して操向ハンドル(19)の回転速度を遅くする戻り抵抗アブソーバ(100)を、前記出力アーム(98)に連結させ、操向ハンドル(19)を左右に回転させる手動操作を行ったとき、ハンドル(19)から作業者が手を離すことにより、ハンドル(19)を緩やかに直進位置に自動的に戻し、作業者によるハンドル(19)直進戻し操作を省くと共に、スライドポテンショメータ型操向角度センサ(101)を前記出力アーム(98)に連結させ、操向ハンドル(19)の操向操作量を操向角度センサ(101)によって検出させる。
【0021】
さらに、図7に示す如く、前記の左右トラックフレーム(1)を機台(3)に左右スイングアーム(102)を介して連結させ、機台(3)に左右スイングアーム(102)を油圧左側及び右側シリンダ(103)によって連結させ、左側及び右側シリンダ(103)制御によって機台(3)と左右トラックフレーム(1)の上下間隔を変更自在に構成すると共に、機台(3)の左右傾動を検出する傾斜センサ(104)を設け、傾斜センサ(104)の検出結果に基づき左側及び右側シリンダ(103)を自動的に作動させ、各シリンダ(103)によって左右スイングアーム(102)を揺動させて左右トラックフレーム(1)を昇降させ、走行クローラ(2)の接地側を昇降させて機台(3)を略水平に支持させる自動水平制御を行わせる。
【0022】
さらに、図3、図8に示す如く、主変速レバー(73)手動操作によって作動させる電動変速モータ(105)と、前記変速出力軸(31)を制動する変速ブレーキ(106)を操作する変速ブレーキシリンダ(107)を設ける。そして、前記主変速レバー(73)を操作して変速モータ(105)を作動させて第1油圧ポンプ(23)の斜板角度を変更させ、第1油圧モータ(24)の変速出力軸(31)の回転数を無段階に変化させる変速動作と、第1油圧モータ(24)の出力軸(31)を逆転させる前後進切換動作を行わせると共に、前記主変速レバー(73)の中立操作によって変速ブレーキシリンダ(107)を作動させ、変速ブレーキ(106)によって第1油圧モータ(24)の出力軸(31)を制動し、中立操作時の出力軸(31)の前後進回転を阻止するように構成している。
【0023】
さらに、前記操向ハンドル(19)手動操作によって作動させる電動操向モータ(108)と、操向ハンドル(19)の直進操作並びに副変速機構(32)中立切換によって作動させる操向ブレーキシリンダ(109)及びクラッチシリンダ(110)を設ける。そして、前記操向ハンドル(19)を操作して操向モータ(108)を作動させて第2油圧ポンプ(26)の斜板角度を変更させ、第2油圧モータ(27)の操向出力軸(68)の回転数を無段階に変化させたり、逆転させる左右操向動作を行わせ、走行方向を左右に変更して圃場枕地で方向転換したり進路を修正すると共に、前記操向ハンドル(19)の直進操作並びに副変速機構(32)の中立操作により、操向ブレーキシリンダ(109)を作動させ、操向出力ブレーキ(62)によって第2油圧モータ(27)の操向出力軸(68)を制動し、直進操作時の出力軸(68)の左右操向回転を阻止する一方、クラッチシリンダ(110)を作動させて操向出力クラッチ(64)を切動作させ、入力ギヤ(66)(67)に伝える操向駆動出力を中止させるように構成している。
【0024】
さらに、図8に示す如く、前記主変速レバー(73)の変速操作位置及び中立位置及び前後進切換動作を検出するポテンショメータ型主変速センサ(111)と、前記副変速機構(32)を切換える副変速レバー(74)の変速操作位置及び中立位置を検出するポテンショメータ型副変速センサ(112)と、操向ハンドル(19)の左右操向操作位置及び直進位置を検出するポテンショメータ型操向角度センサ(113)と、作業者が切換える撮形手元操作部材(114)の操作によって操向ハンドル(19)の切れ角(操向量)に対する車速の増減速量(第1油圧モータ(24)の変速出力比)を変更させるボリューム形減速感度設定器(115)と、作業者が切換える撮形手元操作部材(116)の操作によって主変速レバー(73)の変速量(第1油圧モータ(24)の変速出力)に対する第2油圧モータ(27)の操向出力(左右走行クローラ(2)の速度比)を変更させるボリューム形旋回感度設定器(117)と、前記左右キャリア軸(40)の回転数を検出する左右車速センサ(118)(119)を、マイクロコンピュータで形成する変速操向コントローラ(120)に入力接続させる。
【0025】
さらに、前記変速モータ(105)を正転または逆転させる増速及び減速回路(121)(122)を前記コントローラ(120)に接続させ、主変速レバー(73)操作量(操作角度)に対して変速モータ(105)による第1油圧ポンプ(23)の斜板角を略正比例させて変化させ、主変速レバー(73)の傾き操作に応じた車速を得ると共に、前記変速ブレーキシリンダ(107)を作動させる主変速回路(123)を前記コントローラ(120)に接続させ、主変速レバー(73)中立時に第1油圧モータ(24)の変速出力軸(31)を停止維持させ、主変速レバー(73)中立操作状態下での第1油圧モータ(24)による走行クローラ(2)の駆動を阻止している。
【0026】
さらに、前記操向モータ(47)を正転または逆転させる左右旋回回路(124)(125)を前記コントローラ(120)に接続させ、操向ハンドル(19)の操向操作量(左右回転角度)に対して操向モータ(108)による第2油圧ポンプ(26)の斜板を略正比例させて変化させ、また主変速レバー(73)の前進操作時と後進操作時とでは、操向ハンドル(19)の左右回転に対して左右旋回出力を逆にし、前進時と後進時とで逆ハンドルになるのを防ぎ、四輪自動車と同じ操向動作を行わせて前後進させる。また、主変速レバー(73)が中立のときは、第2油圧ポンプ(26)の斜板角を零に保ち、第2油圧モータ(27)の操向出力軸(68)を停止維持し、主変速中立状態下でのハンドル(19)操作による旋回動作を阻止すると共に、操向ハンドル(19)切れ角に応じて大きくなる第2油圧ポンプ(26)の斜板角の絶対値を主変速レバー(73)操作角度の絶対値と比例するように制御し、操向ハンドル(19)切れ角が一定のときに車速を変化させても旋回半径を一定に保ち、四輪自動車と同じ操向動作で旋回させる。また、操向ブレーキシリンダ(109)及びクラッチシリンダ(110)を作動させる直進回路(126)を前記コントローラ(120)に接続させ、副変速中立またはハンドル(19)直進によって出力軸(68)を自動的に停止させ、操向出力を中止させる。また、未刈り穀稈列に対する刈取部(8)の位置を検出させる操向センサ(127)と、前記センサ(127)の検出結果に基づき操向モータ(108)を自動制御する操向回路(128)を設け、操向ハンドル(19)の手動操作による操向角度センサ(113)入力を優先させ乍ら操向センサ(127)入力によって操向モータ(108)を作動させ、未刈り穀稈列に沿わせて進路を自動的に修正させ、収穫作業を行わせる。
【0027】
さらに、前記操向ハンドル(19)最大操作によって旋回内側走行クローラ(2)を逆転させるスピンターン許可動作と左右走行クローラ(2)を同一方向にだけ駆動させるスピンターン禁止動作とに切換えるスピンターンスイッチ(129)を設け、スピンターンによって走行性能が低下し易い超湿田作業時にスピンターンスイッチ(129)操作によって走行クローラ(2)のスピンターン動作を禁止する。また、前記脱穀クラッチレバー(76)または脱穀スイッチ(130)の操作によって脱穀部(4)に対するエンジン(21)動力伝達を入切する脱穀クラッチモータ(131)と、脱穀部(4)の駆動を検出する脱穀センサ(132)を設けると共に、前記刈取クラッチレバー(75)または刈取スイッチ(133)の操作によって刈取部(8)に対するエンジン(21)動力伝達を入切する刈取クラッチモータ(134)と、刈取部(8)の駆動を検出する刈取センサ(135)を設け、脱穀部(4)並びに刈取部(8)の駆動を前記コントローラ(120)によって検出させる。
【0028】
さらに、前記エンジン(21)の回転数を検出する回転センサ(136)と、エンジン(21)の回転数を増減制御する燃料ソレノイド(137)を、エンジン(21)の回転数をアクセル操作量に基づき自動制御してエンジン(21)回転を略一定に保つ電子ガバナ(138)に設け、図9に示す如く、前記操向ハンドル(19)のスピンターン領域操作時に電子ガバナ(138)制御が通常モードから旋回モードに切換わり、アクセル操作量よりもエンジン(21)回転を自動的に上げて出力を一時的に大きくするもので、操向部材(28)のスピンターン動作領域の操向ハンドル(19)操作によってエンジン(21)出力を自動的に大きくするように構成し、走行クローラ(2)の走行負荷が増大する旋回時に走行クローラ(2)を安定して駆動し、出力不足によるエンジン(21)回転低下などを防止し、運転操作性の向上並びにエンジン(21)等の耐久性向上などを図る。
【0029】
さらに、前記機台(3)の対地左右傾斜を検出する前記傾斜センサ(104)と、機台(3)の左右傾斜角を設定する傾斜設定器(139)を、機台(3)の左右傾斜を自動修正する水平制御コントローラ(140)に設けると共に、前記の左側及び右側シリンダ(103)(103)を作動させる電磁左側及び右側バルブ(141)(142)と、トラックフレーム(1)に対する機台(3)の左右昇降量を検出するポテンショメータ型左側及び右側センサ(143)(144)を、変速操向コントローラ(120)に接続させ、傾斜センサ(104)の検出結果に基づき左側及び右側シリンダ(103)(103)を自動制御して機台(3)を水平に保つ一方、スピンターンスイッチ(129)の切換によって前記シリンダ(103)の乾田または湿田制御を選択させ、かつ機台(3)高さによって走行クローラ(2)のスピンターン動作の許可と禁止を選択させる。
【0030】
上記のように、本機の左右傾斜を検出する傾斜センサ(104)と、本機の対地高さを検出する対地高さセンサである左側及び右側センサ(143)(144)と、本機の左右傾斜及び対地高さを変更させるローリング部材である左側及び右側シリンダ(103)を設け、作業スイッチであるスピンターンスイッチ(129)の乾田切換操作によって本機を低位置支持させて左側及び右側シリンダ(103)制御が行われるように構成し、本機傾斜を自動的に修正する水平制御動作と走行クローラ(2)の旋回制御動作を乾田に最適な状態に設定し、運転操作の簡略化並びに運転操作性の向上などを図る。
【0031】
また、本機の左右傾斜を検出する傾斜センサ(104)と、本機の対地高さを検出する左側及び右側センサ(143)(144)と、本機の左右傾斜及び対地高さを変更させる左側及び右側シリンダ(103)を設け、スピンターンスイッチ(129)の湿田切換操作によって本機を高位置支持させて左側及び右側シリンダ(103)制御が行われるように構成し、本機傾斜を自動的に修正する水平制御動作と走行クローラ(2)の旋回制御動作を湿田に最適な状態に設定し、運転操作の簡略化並びに運転操作性の向上などを図る。
【0032】
さらに、前記刈取部(8)の対地高さを検出するポテンショメータ型刈高センサ(145)と、刈取部(8)を非作業位置(枕地旋回高さ)または作業位置(刈高センサ(145)検出高さ)に上昇または下降させる昇降スイッチ(146)と、刈取部(8)を手動昇降させる手動スイッチ(147)を、刈取部(8)を自動昇降させるリフト制御コントローラ(148)に設けると共に、前記昇降シリンダ(11)を作動させる電磁昇降バルブ(149)と、刈取部(8)の対機台(3)高さを検出する刈取部高さセンサ(150)を、変速操向コントローラ(120)に接続させ、刈高センサ(145)の検出結果に基づき昇降シリンダ(11)を自動制御して穀稈の刈取り高さを略一定に保つ一方、昇降スイッチ(146)の作業位置下降操作によって走行クローラ(2)のスピンターン動作を禁止し、かつ昇降スイッチ(146)の非作業位置上昇操作によって走行クローラ(2)のスピンターン動作を許可し、刈取部(8)が低い位置に支持されている状態でのスピンターン旋回を阻止している。
【0033】
さらに、前記第1及び第2油圧モータ(24)(27)の出力回転数を検出する変速回転センサ(151)及び操向回転センサ(152)と、左右走行クローラ(2)の回転速度を表示する旋回インジケータ(153)を、変速操向コントローラ(120)に接続させ、前記各センサ(151)(152)の検出結果に基づき左右走行クローラ(2)の回転速度を演算してインジケータ(153)に表示させ、図10に示す如く、走行クローラ(2)の駆動状態を、停止、直進(前進及び後進)、緩旋回、ブレーキターン(左右旋回)、スピンターン(左右方向転換)に分けて作業者に知らせるもので、操向ハンドル(19)切角を検出する操向角度センサ(113)と、主変速レバー(73)切換位置を検出する主変速センサ(111)と、変速部材(25)及び操向部材(28)の出力回転を検出するクローラ回転センサ(151)(152)を設け、前記各センサ(111)(113)(151)(152)の検出結果に基づき左右走行クローラ(2)速度を演算して左右走行クローラ(2)速度を自動制御し、クローラ回転センサ(151)(152)による変速部材(25)または操向部材(28)出力回転の直接検出によって回転センサ(151)(152)の損傷を防止し、かつ左右走行クローラ(2)速度の表示によって運転状況を確認できるものである。
【0034】
さらに、図11乃至図15に示す如く、主変速レバー(73)を前進(後進)方向に傾ける操作により、変速モータ(105)を作動させて変速部材(25)を出力制御し、前進(後進)変速が行われて前進(後進)移動するもので、主変速レバー(73)を操作している状態で、操向ハンドル(19)を左(右)側に回転させて左(右)旋回操作を行うことにより、変速モータ(105)を制御する変速入力操作量が二次曲線形に変化すると共に、前記変速入力操作量に対して90度の位相差で直進位置を起点に操向モータ(108)を制御する操向入力操作量が二次曲線形に変化し、立上りが緩傾斜の二次曲線となる変速入力操作量によって操向ハンドル(19)操向角度に比例して変速部材(25)が減速制御されると共に、立上りが急傾斜の二次曲線となる操向入力操作量によって操向ハンドル(19)操向角度に比例して操向部材(28)が増速制御される。
【0035】
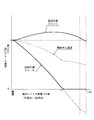
また、図11は、主変速レバー(73)の前(後)進操作量が最大のとき並びに2分の1のとき並びに4分の1のときの操向ハンドル(19)の操作により、操向部材(28)が増速制御される操向モータ(108)の出力変位量を操向増速操作量として表わしたもので、操向ハンドル(19)の回転と操向操作出力との関係を示している。前記操向モータ(108)の出力変位量である操向増速操作量は、操向ハンドル(19)の角度変化に対し、略直線的な比例変化よりも大きく設定され、操向部材(28)の出力を大きくして油圧動力伝達損失を補い、操向部材(28)の実際の出力が設定適正範囲(効率100パーセント出力状態)になるように構成している。
【0036】
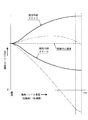
また、図12は、主変速レバー(73)の前(後)進操作量が最大のとき並びに2分の1のとき並びに4分の1のときの操向ハンドル(19)の回転と、操向部材(28)の油圧モータ(27)の旋回出力回転数との関係を示すもので、主変速レバー(73)の操作(車速の変更)に対して操向ハンドル(19)操作量が一定のときに操向部材(28)の旋回出力回転数を比例して変化させるから、図13のように、旋回内側走行クローラ(2)の速度(V1)と旋回外側走行クローラ(2)の速度(V2)との比が、操向ハンドル(19)回転角度が一定のとき、主変速レバー(73)操作によって車速が変更されても一定に保たれ、主変速レバー(73)の車速変更に対して旋回半径(R)が一定に保たれる。即ち、図3のように、変速部材(25)の回転出力を左右遊星ギヤ機構(35)を介して左右走行クローラ(2)に伝えて左右走行クローラ(2)を同一方向に同一速度で駆動すると共に、操向部材(28)の回転出力を入力操向ギヤ(66)(67)によって左右逆転させて左右遊星ギヤ機構(35)に伝え、左右走行クローラ(2)を反対方向に同一速度で駆動する(強制差動構造)場合、主変速レバー(73)操作によって変速部材(25)の回転出力を変化させて車速を変更したとき、仮りに操向部材(28)の回転出力が一定に保たれていると、車速の変更に対して左右走行クローラ(2)の速度差(V2−V1)が一定に保たれることになり、車速の増速(減速)によって旋回半径(R)が拡大(縮少)され、操向ハンドル(19)の回転角度を一定に保っていても、車速の変更によって旋回半径(R)が変化する。これに対し、図11及び図12から明らかなように、操向ハンドル(19)の回転角度を一定に保っているとき、変速部材(25)の回転出力を変化させて車速を変更する主変速レバー(73)の操作により、操向部材(28)の回転出力が比例して変化し、左右走行クローラ(2)の旋回半径(R)が一定に保たれるもので、四輪自動車のアクセルペダル及びハンドル操作と略同一操作感覚で主変速レバー(73)の変速と操向ハンドル(19)の操向の各操作を行える。
【0037】
上記のように、変速具である主変速レバー(73)操作によって変速部材(25)を作動させて左右走行クローラ(2)の両方を同一方向に同一速度で駆動して増速または減速させると共に、操向具である操向ハンドル(19)操作によって操向部材(28)を作動させて左右走行クローラ(2)を逆方向に同一速度で駆動して駆動速度に差を生じさせるクローラ作業車において、旋回外側走行クローラ(2)の回転数と旋回内側走行クローラ(2)の回転数の比を略一定に保ち乍ら左右走行クローラ(2)を変速制御する。そして、操向ハンドル(19)操作によって左または右方向に旋回しているとき、主変速レバー(73)操作によって左右走行クローラ(2)を増速または減速させて車速を変更しても旋回半径が略一定に維持され、四輪自動車と略同様の運転感覚で操向及び変速の各操作を行え、走行変更操作に伴う進路の修正などを不要にし、例えば作物列に沿わせる走行または圃場枕地での次作業工程位置への方向転換などを容易に行える。
【0038】
さらに、図14は、主変速レバー(73)の前(後)進操作量が最大のとき並びに2分の1のとき並びに4分の1のときの操向ハンドル(19)の操作により、変速部材(25)が減速制御される変速モータ(105)の出力変位量を変速減速操作量として表わしたもので、操向ハンドル(19)の回転と変速操作出力との関係を示している。前記変速モータ(105)の出力変位量である変速減速操作量は、操向ハンドル(19)の角度変化に対し、略直線的な比例変化よりも小さく設定され、変速部材(28)の出力を大きくして油圧動力伝達損失を補い、変速部材(28)の実際の出力が設定適正範囲(効率100パーセント出力状態)になるように構成している。前記の図11及び図14から明らかなように、変速部材(25)または操向部材(28)の出力が、停止乃至最大出力の途中で、直線的な変化よりも大きくなるように構成し、変速部材(25)または操向部材(28)の動力伝達損失などによって走行クローラ(2)駆動力が不足する不具合をなくし、走行クローラ(2)の走行性能の維持並びに運転操作性の向上などを図り、特に損失割合が大きくなる微速走行時の走行性能を向上させる。
【0039】
また、図15は、主変速レバー(73)の前(後)進操作量が最大のとき並びに2分の1のとき並びに4分の1のときの操向ハンドル(19)の回転と、変速部材(25)の油圧モータ(24)の変速出力回転数との関係を示すもので、主変速レバー(73)の操作量が一定のとき、操向ハンドル(19)操向操作に対して変速部材(25)の変速出力回転数を比例して変化させるから、図16に示す如く、副変速レバー(74)が一定位置で副変速が同一速度に保たれているとき、直進位置の操向ハンドル(19)を左方向(右方向)に約15度回転させる刈取り進路修正範囲では、操向ハンドル(19)の回転に対して変速モータ(105)が減速方向に微少動作し、変速部材(25)が直進と略同一出力状態に維持されると共に、操向部材(28)の第2油圧ポンプ(26)によって第2油圧モータ(27)を正転(逆転)させる操向出力によって左方向(右方向)に旋回させ、未刈り穀稈(作物)列の湾曲に合せる進路修正を行う。このとき、旋回内側の走行クローラ(2)の減速量と、旋回外側の走行クローラ(2)の増速量が略等しくなり、機体中心速度が直進と略同一速度に保たれる。また、操向ハンドル(19)を直進位置から15度以上回転させると、操向ハンドル(19)の回転に比例して変速モータ(105)が減速方向に動作し、変速部材(25)が左旋回及び右旋回のいずれでも減速動作し、第1油圧ポンプ(23)及びモータ(24)の走行変速出力を減速させ、左右走行クローラ(2)を同一方向に回転駆動させて前進(または後進)させ、左右走行クローラ(2)の走行速度差により左方向(右方向)に旋回するブレーキターン動作を行わせ、未刈り穀稈(作物)列から外れたときに元の列に戻したり隣の列に移動させる進路修正を行う。さらに、操向ハンドル(19)を約116度回転させると、旋回部材(28)が最大出力になって旋回出力が最高出力維持され、135度の切角範囲で機体中心速度が直進時の約4分の1に減速され、旋回内側の走行クローラ(2)が逆転駆動され、左右走行クローラ(2)の間の旋回中心回りに機体が旋回するスピンターン動作が行われ、左右走行クローラ(2)の左右幅だけ旋回方向にずらせて機体を180度方向転換させるもので、ハンドル切角0度からハンドル切角135度の範囲で操向ハンドル(19)を回転させて左または右方向の旋回操作を行い、直進位置を中心とした左右15度のハンドル(19)回転範囲で未刈り穀稈(作物)列に沿って移動する条合せ進路修正を、直進時の走行速度を維持し乍ら行うと共に、左右116度乃至135度のハンドル(19)回転により、旋回部材(28)を最高出力維持し乍ら、圃場枕地で機体を方向転換させて次作業工程に移動させるスピンターン動作を、直進時の約4分の1の走行速度(減速率25パーセント)に自動的に減速して行う。
【0040】
上記から明らかなように、左右走行クローラ(2)速度を検出する車速センサ(118)(119)と、操向ハンドル(19)切角を検出する操向角度センサ(113)と、変速レバー(73)操作位置を検出する変速センサ(111)を設け、操向ハンドル(19)切角によって決定される旋回半径になるように左右走行クローラ(2)速度を自動制御するように構成し、操向ハンドル(19)及び変速レバー(73)などの操作構造の簡略化並びに走行クローラ(2)の操向機能及び変速機能の向上または変更を行い、旋回性能の向上並びに運転操作性の向上などを図るもので、前記変速部材(25)の変速量の変更を検出する主変速センサ(111)または左右車速センサ(118)(119)の一方または両方の検出結果によって操向部材(28)の操向量を自動的に変化させ、車速の変更だけで旋回内側走行クローラ(2)と旋回外側走行クローラ(2)の速度差を変化させ、増速に伴う旋回半径の拡大量だけ左右走行クローラ(2)の速度差を大きくする一方、減速に伴う旋回半径の縮少量だけ左右走行クローラ(2)の速度差を小さくし、旋回半径を変化させることなく車速を変更し、四輪自動車の車速増減速と略同様の運転感覚で走行クローラ(2)の車速変更を行い、走行クローラ(2)の走行変速及び操向機能の向上などを図る。
【0041】
また、変速部材(25)の変速量である左右キャリア軸(40)の同一方向の増減速回転変化に比例させて主変速センサ(111)または左右車速センサ(118)(119)のいずれか一方または両方の検出結果に基づき操向部材(28)の操向量を前記コントローラ(120)の演算出力によって自動的に変化させ、操向操作が一定のとき、変速操作だけで、旋回半径を一定に保って、車速を増減速変化させ、車速の変更に対して旋回内側走行クローラ(2)の速度と旋回外側走行クローラ(2)の速度の比が一定に保たれ、走行クローラ(2)の走行変速及び操向機能の向上並びに走行変速及び操向制御の簡略化などを図る。また、変速部材(25)の変速量に対する操向部材(28)の操向量の変化率(左右走行クローラ(2)の車速比)を旋回感度設定器(117)により変更自在に構成し、走行路面条件または本機重量の左右バランスなどにより、車速の変更に対する旋回内側走行クローラ(2)と旋回外側走行クローラ(2)の速度比を変更し、走行クローラ(2)の横滑り低減並びに本機の左右不均一重量による蛇行防止などを行う。また、操向ハンドル(19)の操向操作量と、主変速レバー(73)の変速操作量とにより、左右走行クローラ(2)の駆動速度を決定させ、図16の出力線図のように操向操作量と変速操作量の関係を演算で求めて形成した制御基準値(制御マップ)に基づき、変速部材(25)の変速量に関係なく、操向ハンドル(19)の操作量と左右走行クローラ(2)の旋回半径を一致させるもので、操向角度センサ(113)及び変速センサ(111)の検出結果に基づき決定される左右走行クローラ(2)速度変化の制御基準値を予め記憶させ、前記制御基準値を旋回感度設定器(117)によって補正するように構成し、前記制御基準値(制御マップ)に基づく平均的な走行クローラ(2)の操向または変速制御と、走行路面(圃場)条件または作業者の希望走行フィーリングに適応した操向または変速制御を得られ、運転操作性の向上などを図る。
【0042】
さらに、副変速高速切換によって路上走行モードで旋回制御を行い、副変速標準切換並びに副変速低速切換によって操向ハンドル(19)操作に基づき主変速減速制御及び操向制御を行わせるもので、図16のように、操向ハンドル(19)及び主変速レバー(73)の操作により、左右走行クローラ(2)の駆動速度を変更して条合せ進路修正並びに圃場枕地でのスピンターンによる方向転換を行い、連続的に穀稈を刈取って脱穀する収穫作業を行うと共に、図17に示す如く、副変速レバー(74)を操作して副変速機構(32)を高速または標準(刈取作業)または低速に切換えたとき、左右走行クローラ(2)の速度差が略一定に保たれて車速が変更され、車速の変更にともなって左右走行クローラ(2)の旋回半径(R)も変化する。
【0043】
また、図18に示す如く、前記手元操作部材(56)によって減速感度設定器(115)を操作することにより、操向ハンドル(19)の切れ角(操向量)に基づく変速部材(25)の減速量の変化率が変化するもので、走行抵抗が大きくスリップし易い湿田泥土路面走行(低速走行作業)のとき、操向ハンドル(19)の切れ角に対する減速変化率を小さくし、またはスピンターンが不要なときに減速変化率を零にすることにより、操向動作全域での車速の減速を少なくし、または図18の実線で示すように減速をなくして略一定車速とし、走行性能を確保する。一方、走行抵抗が小さい乾田走行(高速走行作業)のとき、操向ハンドル(19)の切れ角に対する減速変化率を大きくすることにより、図18の仮想線で示すように、操向操作だけでスピンターンなどの方向転換を安定良く行え、操向(方向転換乃至直進)操作に伴う車速減速操作及び車速復帰操作を省ける。
【0044】
さらに、図16、図19に示す如く、乾田作業で走行クローラ(2)をスピンターン動作させ、かつ湿田作業で走行クローラ(2)のスピンターン動作を中止させる操作を作業スイッチであるスピンターンスイッチ(129)によって行わせるように構成し、同一の圃場で全体的に乾田で一部が湿田のときでも作業を中断させることなくスピンターンスイッチ(129)操作によってスピンターンの禁止及び許可の切換を行い、走行クローラ(2)の走行性能を路面条件に適応させて維持するもので、走行クローラ(2)の走行路面条件によって操向部材(28)の制御動作を切換えるスピンターンスイッチ(129)を設け、スピンターンスイッチ(129)操作によって走行クローラ(2)の走行制御を図16または図19に変更し、超湿田での走行クローラ(2)の旋回機能の維持並びに運転操作性の向上などを図る。
【0045】
また、前記図19のようにスピンターンスイッチ(129)をスピンターン禁止操作したとき、旋回内側走行クローラ(2)が逆転するまでのブレーキターンの速度変化を、図16のスピンターンスイッチ(129)のスピンターン許可操作と同一速度変化にすると共に、スピンターンスイッチ(129)のスピンターン許可操作によって旋回内側走行クローラ(2)が逆転する操向ハンドル(19)のスピンターン操作領域(切角100度〜135度)の範囲で、旋回内側走行クローラ(2)の速度を略零に保ち、スピンターンを禁止することができる一方、図20に示す如く、操向ハンドル(19)の切角最大(135度)位置で旋回内側走行クローラ(2)を停止させるブレーキターンを行わせ、操向ハンドル(19)の操作範囲全域で旋回内側走行クローラ(2)の速度を二次曲線的に緩やかに減速させ、スピンターンを禁止することも行える。
【0046】
さらに、図21、図22に示す如く、前記操向ハンドル(19)の主スポーク(19a)にスピンターンスイッチ(129)を取付けると共に、前記スピンターンスイッチ(129)に並列接続させる副スピンターンスイッチ(129a)を主変速レバー(73)の握り部(73a)に取付け、操向ハンドル(19)または主変速レバー(73)を握る手でスピンターンスイッチ(129)または副スピンターンスイッチ(129a)を操作し、収穫作業中に前記ハンドル(19)またはレバー(73)を握って運転操作し乍ら上記したスピンターンの許可または禁止の切換を行う。また、前記操向ハンドル(19)の右側スポーク(19b)に脱穀スイッチ(130)と刈取スイッチ(133)を取付けると共に、操向ハンドル(19)の中心寄りに脱穀スイッチ(130)を配置させ、脱穀スイッチ(130)に対して刈取スイッチ(133)を外側寄りに配置させ、脱穀スイッチ(130)または脱穀クラッチレバー(76)の脱穀クラッチ入操作によって脱穀部(4)を駆動しているときにだけ、刈取スイッチ(133)の刈取クラッチ入操作によって刈取部(8)が作動するように構成し、作業者が左手で主変速レバー(73)を握り、右手で各スイッチ(130)(133)を行え、また収穫作業中に入切頻度が高い刈取スイッチ(133)を操向ハンドル(19)側の右手親指の操作可能範囲に位置させ、かつ誤操作によって作業中に脱穀スイッチ(130)が操作される不具合をなくしている。
【0047】
上記のように、操向ハンドル(19)にスピンターンスイッチ(129)を設け、操向ハンドル(19)を握る手で操作可能な範囲にスピンターンスイッチ(129)を配置させ、作業中に操向ハンドル(19)を握って運転し乍らスピンターンスイッチ(129)を操作し、走行クローラ(2)が沈下し易い泥土の多い場所でのスピンターンの禁止を緊急に行い、運転操作性の向上などを容易に図る。
【0048】
また、主変速レバー(73)に副スピンターンスイッチ(129a)を設け、主変速レバー(73)を握る手で操作可能な範囲に副スピンターンスイッチ(129a)を配置させ、作業中に主変速レバー(73)を握って運転し乍ら副スピンターンスイッチ(129a)を操作し、走行クローラ(2)が沈下し易い泥土の多い場所でのスピンターンの禁止を緊急に行い、運転操作性の向上などを容易に図る。
【0049】
本実施例は上記の如く構成するもので、図23の旋回制御フローチャートに示す如く、減速感度設定器(115)の旋回時の減速フィーリング入力と、旋回感度設定器(117)の操向ハンドル(19)の旋回フィーリング入力と、スピンターンスイッチ(129)のスピンターン許可(乾田)または禁止(湿田)判断入力と、左側及び右側センサ(143)(144)の機台(3)高さに基づく乾田または湿田判断入力と、刈取部高さセンサ(150)の刈取部(8)の作業位置または非作業判断入力とにより、図16、図18、図19(または図20)の出力線図に基づく走行クローラ(2)の速度制御基準値(制御マップ)の出力を自動的に修正し、前記減速フィーリング及び旋回フィーリング並びに乾田と湿田の切換によって演算された制御マップを形成すると共に、主変速センサ(111)の主変速レバー(73)操作入力と、副変速センサ(112)の副変速レバー(74)切換入力と、操向角度センサ(113)の操向ハンドル(19)操作(切角)入力と、左右車速センサ(118)(119)の左右キャリア軸(40)回転入力とにより、主及び副変速レバー(73)(74)の一方または両方が中立のときに操向ブレーキ(62)を入にして第2油圧モータ(27)を停止維持し、かつ操向クラッチ(40)を切動作させると共に、主変速レバー(73)が中立のとき、変速ブレーキ(106)を入にして第1油圧モータ(24)の出力軸(31)を停止させる。また、副変速が中速または低速で、主変速が中立以外で、操向ハンドル(19)が直進以外に操作されることにより、主変速センサ(53)入力と操向角度センサ(55)入力によって走行速度(車速)及び操向角度及び操向方向が修正後の制御マップによって決定され、主変速及び操向制御によって変速モータ(105)及び操向モータ(108)を作動させ、図16の乾田作業状態で左右走行クローラ(2)の駆動速度を変更して条合せ進路修正並びに圃場枕地でのスピンターンによる方向転換を行い、連続的に穀稈を刈取って脱穀する収穫作業を行う。また、スピンターンスイッチ(129)が禁止操作のとき、または機台(3)が湿田作業状態で高位置のとき、または刈取部(8)が作業状態で低位置のとき、図19(または図20)のスピンターンを禁止する湿田作業状態で左右走行クローラ(2)の駆動速度を制御して条合せ進路修正並びにブレーキターンによる方向転換を行う。
【0050】
さらに、図24は水平制御フローチャートであり、傾斜センサ(104)の機台(3)左右傾き向き入力と、傾斜設定器(139)の設定傾き入力と、左側及び右側センサ(143)(144)の機台(3)左右高さ入力と、刈取部高さセンサ(150)の刈取部(8)の作業位置または非作業位置判断入力と、スピンターンスイッチ(129)のスピンターン許可(乾田)または禁止(湿田)判断入力とにより、機台(3)の左側及び右側の昇降量を演算し、乾田作業の判断によって機台(3)を下げ動作させかつスピンターン動作を許可し、図16の出力線図に基づく旋回及び走行減速を行い乍ら、機台(3)の対地高さを低くして機台(3)の左傾または右傾を左側及び右側シリンダ(103)の上げ動作と下げ動作によって修正する一方、湿田作業の判断によって機台(3)を上げ動作させかつスピンターン動作を禁止し、図19(図20)の出力線図に基づく旋回及び走行減速を行い乍ら、機台(3)の対地高さを高くして機台(3)の左傾または右傾を左側及び右側シリンダ(103)の上げ動作と下げ動作によって修正する。また、左側及び右側センサ(143)(144)の検出結果に基づき、前記シリンダ(103)の自動水平制御によって機台(3)の対地高さが一定以下になったとき、旋回内側走行クローラ(2)を逆転させる図16のスピンターン動作を自動的に許可する一方、機台(3)の対地高さが一定以上になったとき、図19(図20)のスピンターン禁止動作で図21の旋回制御を行わせる。
【0051】
さらに、図25はエンジン制御フローチャートであり、回転センサ(136)のエンジン(21)回転数入力と、左右車速センサ(118)(119)の左右キャリア軸(40)回転数入力と、操向角度センサ(113)の操向ハンドル(19)切角入力とにより、旋回内側走行クローラ(2)が逆転するピンターン動作であるか否かを判断し、スピンターン以外のときは図9の通常モードでエンジン(21)回転数を自動制御する一方、スピンターンのときは図9の旋回モードに切換え、通常モードよりも高出力になるようにエンジン(21)回転数を自動制御し、エンジン(21)を高出力状態に一定時間維持し、スピンターン動作を行わせる。
【0052】
さらに、図26は圃場の未刈り穀稈列に追従させる操向制御フローチャートであり、脱穀部(4)及び刈取部(8)がクラッチ入によって作動しているとき、主変速センサ(111)の主変速位置入力と、副変速センサ(112)の副変速位置入力と、操向角度センサ(113)の操向ハンドル(19)切角入力と、刈取部高さセンサ(150)の刈取部(8)対地高さ入力とにより、走行変速及び操向の各手動操作がオフの状態で操向センサ(127)の未刈り穀稈列検出入力によって左または右旋回を判断し、前記操向センサ(127)の検出結果に基づき操向モータ(108)を自動制御し、左または右旋回動作を行わせ、圃場の未刈り穀稈列に沿わせて自動的に走行移動させて収穫作業を行わせる。
【0053】
さらに、図27は刈取部(8)を昇降させる昇降制御フローチャートであり、刈取部(8)を手動操作で昇降させる手動スイッチ(147)がオフのとき、刈高センサ(145)の刈取部(8)対地高さ入力と、昇降スイッチ(146)の自動昇降入力と、刈取部高さセンサ(150)の刈取部(8)対本機高さ入力と、スピンターンスイッチ(129)のスピンターン許可または禁止入力と、刈取スイッチ(133)の刈取部(8)作動入力とにより、刈取部(8)が刈取作業位置よりも上昇しているとき、昇降スイッチ(146)のオンによって昇降シリンダ(11)が自動的に下降動作し、刈取部(8)が刈高センサ(145)制御範囲まで下降し、かつ図16のスピンターン動作が禁止される。また、刈取部(8)が刈取作業位置に下降しているとき、スピンターン動作が禁止された状態で刈高センサ(145)の検出結果に基づき昇降シリンダ(11)の自動制御が行われ、刈取部(8)を略一定高さに支持して収穫作業が行われると共に、刈取作業位置に刈取部(8)が下降している状態で昇降スイッチ(146)のオンによって昇降シリンダ(11)が自動的に上昇動作し、スピンターン動作が許可されて図16の出力線図に基づき操向ハンドル(19)操作によってスピンターン動作し、圃場枕地で方向転換して次作業工程位置に移動する。
【0054】
【発明の効果】
以上実施例から明らかなように本発明は、機体に左右走行クローラを備え、前記機体の前後方向の直進走行を変速する変速部材と、前記機体を旋回させる操向部材とを変速操向コントローラを介して接続したクローラ走行車において、走行クローラの走行路面条件によって走行クローラのスピンターンを許可または禁止操作するスピンターンスイッチを設けたもので、スピンターンスイッチ操作によって湿田などでの走行クローラのスピンターンを容易に阻止でき、同一の圃場で全体的に乾田で一部が湿田のときでも作業を中断させることなくスピンターンスイッチ操作によってスピンターンの禁止及び許可の切換を行うことができ、走行クローラの走行性能を路面条件に適応させて維持できるものである。また、操向部材のスピンターン動作領域の操向ハンドル操作によってエンジン出力を自動的に大きくするように構成したもので、走行クローラ(2)の走行負荷が増大する旋回時に走行クローラ(2)を安定して駆動でき、出力不足によるエンジン(21)回転低下などを容易に防止でき、運転操作性の向上並びにエンジン(21)等の耐久性向上などを容易に図ることができるものである。
【0055】
また、左右走行クローラ(2)速度を検出する車速センサ(118)(119)と、操向ハンドル(19)切角を検出する操向角度センサ(113)と、変速レバー(73)操作位置を検出する変速センサ(111)を設け、操向ハンドル(19)切角によって決定される旋回半径になるように左右走行クローラ(2)速度を自動制御するように構成したもので、操向ハンドル(19)及び変速レバー(73)などの操作構造の簡略化並びに走行クローラ(2)の操向機能及び変速機能の向上または変更を容易に行うことができ、旋回性能の向上並びに運転操作性の向上などを容易に図ることができるものである。
【0056】
また、変速部材(25)または操向部材(28)の出力が、停止乃至最大出力の途中で、直線的な変化よりも大きくなるように構成したもので、変速部材(25)または操向部材(28)の動力伝達損失などによって走行クローラ(2)駆動力が不足する不具合を容易になくすことができ、走行クローラ(2)の走行性能の維持並びに運転操作性の向上などを容易に図ることができ、特に損失割合が大きくなる微速走行時の走行性能を容易に向上させることができるものである。
【0057】
また、操向角度センサ(113)及び変速センサ(111)の検出結果に基づき決定される左右走行クローラ(2)速度変化の制御基準値を予め記憶させ、前記制御基準値を旋回感度設定器(117)によって補正するように構成したもので、前記制御基準値(制御マップ)に基づく平均的な走行クローラ(2)の操向または変速制御と、走行路面(圃場)条件または作業者の希望走行フィーリングに適応した操向または変速制御を容易に得ることができ、運転操作性の向上などを容易に図ることができるものである。
【0058】
また、操向ハンドル(19)切角を検出する操向角度センサ(113)と、変速レバー(73)切換位置を検出する変速センサ(111)と、変速部材(25)及び操向部材(28)の出力回転を検出するクローラ回転センサ(151)(152)を設け、前記各センサ(111)(113)(151)(152)の検出結果に基づき左右走行クローラ(2)速度を演算して左右走行クローラ(2)速度を自動制御するように構成したもので、クローラ回転センサ(151)(152)による変速部材(25)または操向部材(28)出力回転の直接検出によって回転センサ(151)(152)の損傷を容易に防止でき、かつ左右走行クローラ(2)速度の表示によって運転状況を容易に確認できるものである。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】コンバインの側面図。
【図2】同平面図。
【図3】ミッションケースの説明図。
【図4】操向ハンドル取付部の平面説明図。
【図5】同部分平面図。
【図6】同作動説明図。
【図7】走行クローラ部の正面説明図。
【図8】操向及び変速制御回路図。
【図9】エンジンの出力線図。
【図10】旋回インジケータの表示説明図。
【図11】操向ハンドルと操向操作出力の関係を示す出力線図。
【図12】操向ハンドル回転角度と操向部材出力の関係を示す出力線図。
【図13】左右走行クローラの旋回説明図。
【図14】操向ハンドルと変速操作出力の関係を示す出力線図。
【図15】操向ハンドル回転角度と変速部材出力の関係を示す出力線図。
【図16】操向及び主変速切換と走行クローラ回転の関係を示す出力線図。
【図17】操向及び副変速切換と走行クローラ回転の関係を示す出力線図。
【図18】走行減速を省いた操向出力線図。
【図19】スピンターンを禁止した操向出力線図。
【図20】図19の変形例を示す操向出力線図。
【図21】操向ハンドル部の平面図。
【図22】同部の側面図。
【図23】旋回制御フローチャート。
【図24】水平制御フローチャート。
【図25】エンジン制御フローチャート。
【図26】操向制御フローチャート。
【図27】昇降制御フローチャート。
【符号の説明】
(2) 走行クローラ
(19) 操向ハンドル
(21) エンジン
(25) 変速部材
(28) 操向部材
(73) 主変速レバー
(103) 左側・右側シリンダ(ローリング部材)
(104) 傾斜センサ
(111) 主変速センサ
(113) 操向角度センサ
(117) 旋回感度設定器
(118)(149) 左・右車速センサ
(129) スピンターンスイッチ
(143)(144) 左側・右側センサ
(151)(152) クローラ回転センサ[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a crawler traveling vehicle such as a combine, a tilling tractor, or a field management vehicle that continuously harvests and thresh cereals in a field.
[0002]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
Conventionally, the driving speed of the left and right traveling crawlers is changed steplessly by operating the traveling shift lever to change the vehicle speed, and the difference in the driving speed of the left and right traveling crawlers is changed steplessly by operating the steering handle. There is a technology to change. However, if the spin turn operation that reverses the crawler on the inside of the turn is performed by operating the steering handle, it is possible to easily change the direction of the turn radius, but on the road surface with many mud layers such as wet fields, the spin turn operation There is a problem that the traveling force of the traveling crawler is reduced and the turning movement in a desired direction cannot be easily performed. In addition, when artificially prohibiting the crawler's spin turn operation depending on the road surface conditions such as dry fields or wet fields, the spin turn operation is prohibited and permitted by automatically performing horizontal control to keep the machine posture horizontal. It is necessary to maintain the running function in response to the automatic horizontal control operation. Further, when providing a speed change member and a steering member for driving the left and right traveling crawlers, the speed change member and the steering member are connected to the speed change lever and the steering handle via the link mechanism and controlled, so that the link mechanism etc. There are problems such as simplification of the operation structure and changes in traveling functions such as gear shifting and steering. In addition, by continuously changing the rotation of the left and right traveling crawlers by the operation of the steering handle, it is not possible to easily discriminate between the brake turn in which the turning inner traveling crawler rotation decreases and the spin turn in which the turning inner traveling crawler reverses, There is a problem that a traveling crawler is spin-turned in a super wet field and the traveling function is lowered. In addition, since the speed change member or the steering member is formed by a hydraulic continuously variable transmission mechanism using a hydraulic pump and a hydraulic motor, there is a problem that the driving force of the traveling crawler is reduced to an unnecessary level due to transmission loss of the hydraulic pump and the motor. . As described above, there are problems in that it is not possible to easily improve the traveling speed change and turning functions and the driving operability.
[0003]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
However, the present inventionThe aircraft is equipped with a left and right traveling crawler, and shifts the straight traveling in the front-rear direction of the aircraft.A transmission member;A steering member for turning the airframe is connected via a shift steering controller.In crawler traveling vehicles,A spin turn switch that allows or prohibits the spin turn of the travel crawler according to the travel road surface condition of the travel crawler is provided, and the engine output is automatically increased by operating the steering handle in the spin turn operation area of the steering member.It is configured so that the spin crawler's spin turn can easily be prevented by operating the spin turn switch, and the work can be interrupted even when the field is entirely dry and partly wet. In other words, the spin turn can be prohibited and permitted by operating the spin turn switch, and the traveling performance of the traveling crawler can be adapted to the road surface condition and maintained.In addition, the traveling crawler can be stably driven during turning when the traveling load of the traveling crawler increases, and it is possible to easily prevent the engine rotation from being reduced due to insufficient output, improving the driving operability and the durability of the engine, etc. It can be easily planned.
[0004]
In addition, a turning speed determined by the steering handle turning angle is provided, which includes a vehicle speed sensor that detects the left / right traveling crawler speed, a steering angle sensor that detects the steering handle turning angle, and a shift sensor that detects the shift lever operating position. The left and right traveling crawler speed is automatically controlled so that the operation structure such as the steering handle and shift lever can be simplified, and the traveling crawler steering function and shifting function can be easily improved or changed. Thus, it is possible to easily improve the turning performance and the driving operability.
[0005]
In addition, the output of the speed change member or the steering member is configured to be larger than the linear change during the stop or maximum output, and the traveling crawler is driven by the power transmission loss of the speed change member or the steering member. It can easily eliminate the problem of insufficient power, can easily maintain the traveling performance of the traveling crawler and improve the driving operability, and can easily improve the traveling performance especially at very low speeds where the loss ratio increases. It is.
[0006]
Further, the control reference value of the left and right traveling crawler speed change determined based on the detection results of the steering angle sensor and the shift sensor is stored in advance, and the control reference value is corrected by the turning sensitivity setting device. Steering or shifting control of the average traveling crawler based on the control reference value (control map) and steering or shifting control adapted to the traveling road surface (field) conditions or the operator's desired traveling feeling can be easily obtained. It is possible to easily improve driving operability.
[0007]
Further, a steering angle sensor for detecting a steering handle turning angle, a shift sensor for detecting a shift lever switching position, and a crawler rotation sensor for detecting output rotation of the transmission member and the steering member are provided, and the detection of each of the sensors is provided. The left and right traveling crawler speed is calculated based on the result and the left and right traveling crawler speed is automatically controlled. Damage to the rotation sensor can be easily prevented by directly detecting the output of the speed change member or the steering member by the crawler rotation sensor. In addition, the driving situation can be easily confirmed by displaying the left and right traveling crawler speeds.
[0008]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
Embodiments of the present invention will be described below in detail with reference to the drawings. 1 is an overall side view of the combine, and FIG. 2 is a plan view thereof. In FIG. 1, (1) is a track frame on which a pair of left and right traveling crawlers (2) are installed, and (3) is the track frame (1). A machine base to be installed, (4) is a threshing section that stretches the feed chain (5) to the left and incorporates a handling cylinder (6) and a processing cylinder (7), (8) is a cutting blade (9) and grains A cutting part provided with a reed transport mechanism (10), (11) is a hydraulic lifting cylinder that lifts and lowers the cutting part (8) via a cutting frame (12), and (13) faces the end of the waste chain (14) A waste disposal section, (15) is a grain tank that carries the grain from the threshing section (4) through the milling cylinder (16), and (17) carries the grain from the tank (15) out of the machine. A discharge auger, (18) a cab with a round steering handle (19) and a driver seat (20), 21) is an engine provided in the driver's seat (20) downward, and configured to threshing continuously harvests culms.
[0009]
Further, as shown in FIG. 3, the transmission case (22) for driving the traveling crawler (2) includes a pair of first hydraulic pump (23) and first hydraulic motor (24) for traveling main transmission. A speed change member (25) forming a hydraulic continuously variable transmission mechanism, a pair of second hydraulic pump (26) and a second hydraulic motor (27) are provided to form a hydraulic continuously variable transmission mechanism for turning. Direction member (28), and input shafts (29a) (29b) of the first and second hydraulic pumps (23), (26) to the output shaft (21a) of the engine (21). 30b) and the hydraulic pumps (23) and (26) are driven.
[0010]
In addition, the drive wheels (34) of the left and right traveling crawler (2) are interlocked with the transmission output shaft (31) of the first hydraulic motor (24) via the auxiliary transmission mechanism (32) and the differential mechanism (33). The differential mechanism (33) includes a pair of symmetrical planetary gear mechanisms (35) and (35), and each planetary gear mechanism (35) includes one sun gear (36) and the sun gear. These are formed by three planetary gears (37) meshing with the outer periphery of (36) and a ring gear (38) meshing with these planetary gears (37).
[0011]
The planetary gear (37) is rotatably supported by the carrier (41) of the carrier shaft (40) coaxial with the sun gear shaft (39), and the left and right sun gears (36) (36) are sandwiched between the left and right carriers. The ring gear (38) has an inner tooth (38a) that meshes with each planetary gear (37) and is arranged on the same axis as the sun gear shaft (39), so that the carrier shaft (40 ), The carrier shaft (40) is extended to form an axle, and the driving wheel (34) of the traveling crawler (2) is pivotally supported.
[0012]
The traveling hydraulic continuously variable transmission member (25) controls forward / reverse rotation and rotation speed of the first hydraulic motor (24) by adjusting and changing the angle of the rotary swash plate of the first hydraulic pump (23). Therefore, the rotation output of the first hydraulic motor (24) is transmitted from the transmission gear (42) of the output shaft (31) via the gears (43) (44) (45) and the auxiliary transmission mechanism (32) to the sun gear shaft. The sun gear (36) is rotated by being transmitted to the center gear (46) fixed to (39). The sub-transmission mechanism (32) includes a sub-transmission shaft (47) having the gear (44) and a parking brake shaft (49) having a gear (48) meshing with the center gear (46) via the gear (45). ), And a pair of low speed gears (50) (51), medium speed gears (52) (53), and high speed gears (54) between the auxiliary transmission shaft (47) and the brake shaft (49). (48) is provided, and the sub-shift is switched between low speed, medium speed, and high speed by the sliding operation of the low and medium speed slider (55) and the high speed slider (56). There is neutrality between low speed and medium speed and between medium speed and high speed. In addition, a parking brake (57) is provided on the brake shaft (49), and gears (59) (60) and a one-way clutch (61) are provided on a cutting PTO shaft (58) that transmits rotational force to the cutting portion (8). The sub-transmission shaft (47) is coupled to the cutting part (8) at the vehicle speed synchronization speed.
[0013]
As described above, the driving force from the first hydraulic motor (24) transmitted to the sun gear shaft (39) via the center gear (46) is transmitted to the left and right carrier shafts (40) via the left and right planetary gear mechanisms (35). ) And the rotation transmitted to the left and right carrier shafts (40) to the left and right drive wheels (34), respectively, to drive the left and right traveling crawler (2).
[0014]
Further, the steering member (28) formed by the turning hydraulic continuously variable transmission mechanism is configured to rotate the second hydraulic motor (27) forward and backward by adjusting the angle of the rotary swash plate of the second hydraulic pump (26). The rotation speed is controlled by a brake shaft (63) having a steering output brake (62), a clutch shaft (65) having a steering output clutch (64), and the left and right ring gears (38). Left and right input gears (66) and (67) that are always meshed with the teeth (38b) are provided, and the brake shaft (63) and the steering output clutch (64) are provided on the steering output shaft (68) of the second hydraulic motor (27). The clutch shaft (65) is connected to the clutch shaft (65), the right input gear (67) is connected to the clutch shaft (65) via the forward rotation gear (69), and the forward rotation gear (69) is connected to the clutch shaft (65). And the left input gear ( And by connecting the 6). Then, the brake (62) is turned on and the clutch (64) is turned off by the neutral of the auxiliary transmission sliders (55) and (56), while the brake (62) is turned off and the clutch is turned off at the time of the auxiliary transmission other than the neutral. (64) is turned on, the rotational force of the motor (27) is transmitted to the external teeth (38b) of the right ring gear (38) via the forward rotation gear (69), and the external teeth (38b) of the left ring gear (38) ) Is transmitted to the rotation of the motor (27) via the forward rotation gear (69) and the reverse rotation gear (70), and when the second hydraulic motor (27) rotates forward (reverse rotation), the left ring gear (38 ) In the reverse direction (forward rotation) and the right ring gear (38) in the forward direction (reverse rotation).
[0015]
Thus, when the traveling first hydraulic motor (24) is driven in a state where the second hydraulic motor (27) for turning is stopped and the left and right ring gears (38) are stationary and fixed, the first hydraulic motor ( The rotational output from 24) is transmitted from the center gear (46) to the left and right sun gears (36) at the same rotational speed, and the left and right traveling crawlers are transmitted via the planetary gear (37) and carrier (41) of the left and right planetary gear mechanism (35). (2) is driven at the same rotational speed in the same rotational direction on the left and right, and the machine body travels straight forward and backward. On the other hand, when the second hydraulic motor (27) for rotation is driven to rotate in the forward and reverse directions with the first hydraulic motor (24) for traveling stopped and the left and right sun gears (36) stationary and fixed, the planet on the left side The gear mechanism (35) rotates forward or backward, and the right planetary gear mechanism (35) rotates backward or forward, driving the left and right traveling crawler (2) in the reverse direction and turning the aircraft to the left or right. Further, by driving the second hydraulic motor (27) for turning while driving the first hydraulic motor (24) for traveling, the aircraft turns left and right to correct the course. The turning radius is determined by the output rotational speed of the second hydraulic motor (27).
[0016]
Further, as shown in FIGS. 2 and 4 to 6, a steering column (71) is vertically fixed on the upper surface of the front portion of the cab (18), and a steering handle (19) is disposed on the upper surface of the steering column (71). ) Rotatably mounted around the vertical axis, a side column (72) is provided on the left side of the cab (18), a transmission (22) is disposed below the side column (72), a main transmission lever (73), The auxiliary transmission lever (74), the cutting clutch lever (75), and the threshing clutch lever (76) are attached to the side column (72).
[0017]
Further, the steering column (71) has an upper end portion of a steering input shaft (78) rotatably supported on the steering column (71), and a steering shaft (79) gear (80) connected to the steering handle (19) and steering input. The shaft (78) is engaged with the sector gear (81) to connect the shafts (78) and (79). The gear (80) forms a plurality of teeth (82) in an outer peripheral range of 270 degrees, The outer peripheral range of 90 degrees is formed in an arc (83), the total rotation angle of the steering handle (19) is 270 degrees, the angle of left steering rotation or right steering rotation is set to 135 degrees, and the steering handle (19) It is formed so that the operator can easily perform the rotation operation with one hand. Further, the sector gear (81) forms a plurality of teeth (84) in the outer peripheral range of 130 degrees, forms an outer peripheral range of 230 degrees in the arc cam (85), and the teeth (82) of the gear (80). And the teeth (83) of the sector gear (81) are meshed, and when the respective gears (80) (81) are maximally forward / reversely rotated, stoppers (86) at both ends of the arc (83) and stoppers at both ends of the arc cam (85) ( 87) is abutted to regulate the rotation of the steering handle (19).
[0018]
A straight notch (88) is formed in the center of the arc cam (85) of the sector gear (81), and the detent arm (90) is rotatably supported via the steering column (71) detent shaft (89). The detent roller (92) is rotatably supported by the detent arm (90) via the roller shaft (91), the detent roller (92) is brought into contact with the arc cam (85), and the rectilinear notch (88 The detent roller (92) is detachably engaged with the steering handle (19), and the steering handle (19) is supported in the straight movement position. Further, one end of a neutral spring (93) wound around the detent shaft (89) is engaged with a detent arm (90), and the other end of the neutral spring (93) is placed on a receiving plate (94) of the steering column (71). The detent roller (92) is brought into elastic contact with the arc cam (85) and the rectilinear notch (88) by the neutral spring (93).
[0019]
Further, an arc cam (85) formed on the sector gear (81) is provided separately for a brake cam (95) and a spin cam (96), and the cams (95) (96) are connected by a step (97) to be operated. The detent roller (92) is brought into contact with the brake cam (95) at the brake turn position of the operation angle of about 90 degrees straight from the direction handle (19), and the detent immediately before the turning inner traveling crawler (2) is driven in reverse. The roller (92) is brought into contact with the step (97), and the detent roller (92) is brought into contact with the spin cam (96) at the spin turn position where the turning inner traveling crawler (2) is driven in reverse rotation. 93) The operation force of the steering handle (19) determined by the force is increased stepwise to shift from the brake turn operation to the spin turn operation. As the detent means, the step (92) is formed, the operating force is greatly changed at the maximum brake turn operating angle of the steering handle (19), and the operator recognizes the boundary between the brake turn and the spin turn. During the harvesting operation, the spin turn operation of the steering handle (19) is prevented, and the deterioration of the running performance due to the spin turn is prevented. In this way, the operation force of the steering handle (19) for operating the steering member (28) is changed stepwise, the brake turn for driving the left and right traveling crawler (2) in the same direction and the inside of the turn The operator recognizes the switching position of the spin turn that reverses the traveling crawler (2) by the change of the steering handle (19) operating force, for example, a spin turn on a soft mud road surface (wet paddy field) where traveling performance tends to deteriorate To improve driving operability.
[0020]
Further, one end of a steering output arm (98) is fixed to the steering input shaft (78), and a pair of left and right straight springs (99) (99) for returning the steering handle (19) to a straight position, and the springs The return resistance absorber (100) that slows down the rotational speed of the steering handle (19) against (99) is connected to the output arm (98), and the steering handle (19) is rotated left and right manually. When the operator removes the handle (19) from the handle (19), the handle (19) is automatically and gently returned to the straight-ahead position, and the operator does not need to return the handle (19) to the straight-ahead position. The mold steering angle sensor (101) is connected to the output arm (98), and the steering operation amount of the steering handle (19) is detected by the steering angle sensor (101).
[0021]
Further, as shown in FIG. 7, the left and right track frames (1) are connected to the machine base (3) via the left and right swing arms (102), and the left and right swing arms (102) are hydraulically connected to the machine base (3). And the right and left cylinders (103) are connected, and the vertical distance between the machine base (3) and the left and right track frames (1) can be freely changed by the left and right cylinder (103) control, and the machine table (3) is tilted left and right. The left and right cylinders (103) are automatically operated based on the detection result of the tilt sensor (104), and the left and right swing arms (102) are swung by each cylinder (103). The left and right track frames (1) are raised and lowered, and the grounding side of the traveling crawler (2) is raised and lowered to perform automatic horizontal control for supporting the machine base (3) substantially horizontally. That.
[0022]
Further, as shown in FIGS. 3 and 8, an electric transmission motor (105) that is operated by manual operation of the main transmission lever (73) and a transmission brake that operates a transmission brake (106) that brakes the transmission output shaft (31). A cylinder (107) is provided. Then, the main transmission lever (73) is operated to operate the transmission motor (105) to change the swash plate angle of the first hydraulic pump (23), and the transmission output shaft (31) of the first hydraulic motor (24). ) In a stepless manner, and a forward / reverse switching operation in which the output shaft (31) of the first hydraulic motor (24) is reversed, and a neutral operation of the main transmission lever (73) is performed. The shift brake cylinder (107) is operated, the output brake (106) of the first hydraulic motor (24) is braked by the shift brake (106), and the forward / reverse rotation of the output shaft (31) during the neutral operation is prevented. It is configured.
[0023]
Furthermore, the steering steering wheel (19) is operated by manual operation, and the steering steering cylinder (109) is operated by linear operation of the steering steering handle (19) and neutral switching of the auxiliary transmission mechanism (32). ) And a clutch cylinder (110). Then, the steering handle (19) is operated to operate the steering motor (108) to change the swash plate angle of the second hydraulic pump (26), and the steering output shaft of the second hydraulic motor (27). The left and right steering operation is performed to change the rotation number of (68) steplessly or reversely, change the traveling direction to the left and right to change the direction on the field headland, correct the course, and the steering handle The steering brake cylinder (109) is actuated by the straight operation of (19) and the neutral operation of the subtransmission mechanism (32), and the steering output shaft (2) of the second hydraulic motor (27) is operated by the steering output brake (62). 68) is braked to prevent the left and right steering rotation of the output shaft (68) during the straight running operation, while the clutch cylinder (110) is operated to disengage the steering output clutch (64) and the input gear (66 ) Steering to tell (67) It is configured so as to stop the output.
[0024]
Further, as shown in FIG. 8, a potentiometer-type main transmission sensor (111) for detecting a shift operation position, a neutral position, and a forward / reverse switching operation of the main transmission lever (73) and a sub transmission mechanism (32) for switching the sub transmission mechanism (32). A potentiometer-type sub-shift sensor (112) for detecting a shift operation position and a neutral position of the shift lever (74), and a potentiometer-type steering angle sensor (for detecting a left / right steering operation position and a rectilinear position of the steering handle (19)). 113) and a speed change output ratio of the first hydraulic motor (24) with respect to the turning angle (steering amount) of the steering handle (19) by the operation of the photographing hand operating member (114) switched by the operator ) To change the main speed change lever (73) by operating the volume type deceleration sensitivity setting device (115) and the photographing hand operating member (116) to be switched by the operator. A volume type turning sensitivity setting device (117) for changing the steering output (speed ratio of the left and right traveling crawler (2)) of the second hydraulic motor (27) with respect to the speed change amount (shifting output of the first hydraulic motor (24)); The left and right vehicle speed sensors (118) and (119) for detecting the rotational speed of the left and right carrier shafts (40) are connected to a shift steering controller (120) formed by a microcomputer.
[0025]
Further, an acceleration / deceleration circuit (121) (122) for normal rotation or reverse rotation of the transmission motor (105) is connected to the controller (120), and the operation amount (operation angle) for the main transmission lever (73) is connected. The swash plate angle of the first hydraulic pump (23) by the transmission motor (105) is changed in an approximately direct proportion to obtain a vehicle speed according to the tilting operation of the main transmission lever (73), and the transmission brake cylinder (107) is operated. The main transmission circuit (123) to be operated is connected to the controller (120), and when the main transmission lever (73) is neutral, the transmission output shaft (31) of the first hydraulic motor (24) is stopped and maintained, and the main transmission lever (73 ) The traveling crawler (2) is prevented from being driven by the first hydraulic motor (24) under the neutral operation state.
[0026]
Further, a left / right turning circuit (124) (125) for rotating the steering motor (47) forward or backward is connected to the controller (120), and the steering operation amount (left / right rotation angle) of the steering handle (19) is connected. The swash plate of the second hydraulic pump (26) by the steering motor (108) is changed in an approximately direct proportion, and the steering handle ( The left / right turning output is reversed with respect to the left / right rotation of 19) to prevent reverse steering during forward traveling and reverse traveling, and the same steering operation as that of a four-wheeled vehicle is performed to move forward and backward. When the main transmission lever (73) is neutral, the swash plate angle of the second hydraulic pump (26) is kept at zero, the steering output shaft (68) of the second hydraulic motor (27) is stopped and maintained, The absolute value of the swash plate angle of the second hydraulic pump (26), which is prevented from turning by the operation of the handle (19) in the main shift neutral state and increases with the turning angle of the steering handle (19), is the main shift. The lever (73) is controlled to be proportional to the absolute value of the operating angle, and the steering handle (19) keeps the turning radius constant even if the vehicle speed is changed when the turning angle is constant, and the same steering as a four-wheeled vehicle Turn by movement. Further, a straight circuit (126) for operating the steering brake cylinder (109) and the clutch cylinder (110) is connected to the controller (120), and the output shaft (68) is automatically operated by the sub-shift neutral or the steering wheel (19). The steering output is stopped. In addition, a steering sensor (127) for detecting the position of the cutting unit (8) with respect to the uncut grain row and a steering circuit for automatically controlling the steering motor (108) based on the detection result of the sensor (127) ( 128), giving priority to the steering angle sensor (113) input by manual operation of the steering handle (19), and operating the steering motor (108) by the steering sensor (127) input, The course is automatically corrected along the line, and the harvesting work is performed.
[0027]
Further, a spin turn switch for switching between a spin turn permission operation for reversing the turning inner traveling crawler (2) by a maximum operation of the steering handle (19) and a spin turn prohibiting operation for driving the left and right traveling crawler (2) only in the same direction. (129) is provided, and the spin turn operation of the traveling crawler (2) is prohibited by operating the spin turn switch (129) during the super wet field work where the traveling performance is likely to be deteriorated by the spin turn. The threshing clutch motor (131) for turning on and off the power transmission to the threshing portion (4) by operating the threshing clutch lever (76) or the threshing switch (130), and driving the threshing portion (4). A reaping sensor (132) for detecting, and a reaping clutch motor (134) for turning on and off the power transmission of the engine (21) to the reaping part (8) by operating the reaping clutch lever (75) or the reaping switch (133); The cutting sensor (135) for detecting the driving of the cutting unit (8) is provided, and the driving of the threshing unit (4) and the cutting unit (8) is detected by the controller (120).
[0028]
Further, a rotation sensor (136) for detecting the rotation speed of the engine (21), a fuel solenoid (137) for increasing / decreasing the rotation speed of the engine (21), and the rotation speed of the engine (21) as an accelerator operation amount. The electronic governor (138) is automatically controlled based on the electronic governor (138) to keep the rotation of the engine (21) substantially constant. As shown in FIG. 9, the electronic governor (138) is normally controlled when the steering handle (19) is operated in the spin turn region. The mode is switched from the mode to the turning mode, and the engine (21) rotation is automatically increased from the accelerator operation amount to temporarily increase the output, and the steering handle (28) 19) The engine (21) output is automatically increased by operation, and the traveling crawler (2) is turned during turning when the traveling load of the traveling crawler (2) increases. Constant and is driven, to prevent such engine (21) rotation reduction by insufficient output, achieving and improving driving operation as well as the engine (21) durability of such.
[0029]
Furthermore, the tilt sensor (104) for detecting the horizontal tilt of the machine base (3) with respect to the ground, and the tilt setter (139) for setting the horizontal tilt angle of the machine base (3) are provided. An electromagnetic left and right valve (141) (142) for operating the left and right cylinders (103) (103) and a mechanism for the track frame (1) are provided in the horizontal control controller (140) for automatically correcting the inclination. Potentiometer-type left and right sensors (143) and (144) for detecting the amount of left and right elevation of the platform (3) are connected to the shift steering controller (120), and the left and right cylinders are detected based on the detection result of the tilt sensor (104). (103) The machine (3) is automatically controlled to keep the machine base (3) horizontal, while the cylinder (103) is controlled by switching the spin turn switch (129) To select the field or Shitsuden control, and machine base (3) permit the spin turn operation of the traveling crawlers (2) by the height and to select permission or prohibition.
[0030]
As described above, the tilt sensor (104) that detects the left / right tilt of the machine, the left and right sensors (143) (144) that are the ground height sensors that detect the height of the machine, and the Left and right cylinders (103) that are rolling members that change the horizontal tilt and height to the ground are provided, and the left and right cylinders are supported at a low position by a dry field switching operation of a spin turn switch (129) that is a work switch. (103) It is configured so that the control is performed, and the horizontal control operation for automatically correcting the inclination of the machine and the turning control operation of the traveling crawler (2) are set to the optimum state for the dry paddy, Improve driving operability.
[0031]
In addition, the tilt sensor (104) for detecting the horizontal tilt of the machine, the left and right sensors (143) (144) for detecting the ground height of the machine, and the horizontal tilt and the ground height of the machine are changed. The left and right cylinders (103) are provided, and the machine is supported at a high position by the wet-field switching operation of the spin turn switch (129) so that the left and right cylinders (103) are controlled to automatically tilt the machine. The horizontal control operation to be corrected and the turning control operation of the traveling crawler (2) are set to the optimum state for the wet field, thereby simplifying the driving operation and improving the driving operability.
[0032]
Furthermore, the potentiometer type cutting height sensor (145) for detecting the height of the cutting portion (8) with respect to the ground, and the cutting portion (8) are set to a non-working position (headland turning height) or a working position (cutting height sensor (145). ) A lift switch (146) for raising or lowering the detection height) and a manual switch (147) for manually raising and lowering the cutting part (8) are provided in the lift control controller (148) for automatically raising and lowering the cutting part (8). In addition, an electromagnetic elevating valve (149) for operating the elevating cylinder (11) and a mowing unit height sensor (150) for detecting the height of the machine base (3) of the mowing unit (8) are provided with a shift steering controller. (120), the lifting cylinder (11) is automatically controlled based on the detection result of the cutting height sensor (145) to keep the cutting height of the cereals substantially constant, while the working position of the lifting switch (146) The spin crawling operation of the traveling crawler (2) is prohibited by the descending operation, and the spinning crawler operation of the traveling crawler (2) is permitted by the lifting operation of the lift switch (146), and the cutting part (8) is at a low position. This prevents spin-turning while it is supported.
[0033]
Furthermore, the rotational speed of the variable speed rotation sensor (151) and the steering rotation sensor (152) for detecting the output rotation speed of the first and second hydraulic motors (24), (27) and the rotation speed of the left and right traveling crawler (2) are displayed. The turning indicator (153) to be connected is connected to the shift steering controller (120), and the rotational speed of the left and right traveling crawler (2) is calculated based on the detection results of the sensors (151) and (152) to calculate the indicator (153). As shown in FIG. 10, the driving state of the traveling crawler (2) is divided into stop, straight ahead (forward and reverse), slow turn, brake turn (left and right turn), and spin turn (right and left direction change). A steering angle sensor (113) for detecting a steering angle of the steering handle (19), and a main transmission sensor (111) for detecting a switching position of the main transmission lever (73). A crawler rotation sensor (151) (152) for detecting the output rotation of the transmission member (25) and the steering member (28) is provided, and based on the detection results of the sensors (111) (113) (151) (152). The left / right traveling crawler (2) speed is calculated to automatically control the left / right traveling crawler (2) speed, and the output rotation of the speed change member (25) or steering member (28) is directly detected by the crawler rotation sensor (151) (152). Thus, the rotation sensors (151) and (152) can be prevented from being damaged, and the driving condition can be confirmed by displaying the left and right traveling crawler (2) speed.
[0034]
Further, as shown in FIGS. 11 to 15, by operating the main speed change lever (73) in the forward (reverse) direction, the speed change motor (105) is operated to control the output of the speed change member (25), and the forward (reverse) ) Moves forward (backward) after shifting, and turns the left (right) by rotating the steering handle (19) to the left (right) while operating the main shift lever (73). By performing the operation, the speed change input operation amount for controlling the speed change motor (105) changes into a quadratic curve, and the steering motor starts from the straight position with a phase difference of 90 degrees with respect to the speed change input operation amount. The steering input operation amount for controlling (108) changes into a quadratic curve shape, and the shift member is proportional to the steering angle of the steering handle (19) by the shift input operation amount in which the rising is a gently curved quadratic curve. (25) is decelerated and the rise is Steering member (28) is accelerated controlled in proportion to the steering wheel (19) steering angle by the steering input operation amount as the quadratic curve slope.
[0035]
Further, FIG. 11 shows the operation by operating the steering handle (19) when the forward (reverse) forward operation amount of the main transmission lever (73) is maximum, half, and quarter. The output displacement amount of the steering motor (108) in which the steering member (28) is speed-up controlled is expressed as the steering speed-increasing operation amount, and the relationship between the rotation of the steering handle (19) and the steering operation output. Is shown. The steering acceleration operation amount, which is the output displacement amount of the steering motor (108), is set to be larger than the substantially linear proportional change with respect to the angle change of the steering handle (19), and the steering member (28 ) Is increased to compensate for the hydraulic power transmission loss, and the actual output of the steering member (28) is within the set appropriate range (100% efficiency output state).
[0036]
FIG. 12 shows the rotation of the steering handle (19) when the forward (reverse) forward operation amount of the main transmission lever (73) is the maximum, half, and quarter. It shows the relationship with the turning output rotation speed of the hydraulic motor (27) of the direction member (28), and the operation amount of the steering handle (19) is constant with respect to the operation of the main transmission lever (73) (change of the vehicle speed). Since the turning output speed of the steering member (28) is changed proportionally at the time, the speed (V1) of the turning inner traveling crawler (2) and the speed of the turning outer traveling crawler (2) as shown in FIG. When the steering wheel (19) rotation angle is constant, the ratio to (V2) is kept constant even if the vehicle speed is changed by operating the main transmission lever (73), and the vehicle speed of the main transmission lever (73) is changed. On the other hand, the turning radius (R) is kept constant. That is, as shown in FIG. 3, the rotation output of the speed change member (25) is transmitted to the left and right traveling crawler (2) via the left and right planetary gear mechanism (35) to drive the left and right traveling crawler (2) at the same speed in the same direction. At the same time, the rotational output of the steering member (28) is reversed left and right by the input steering gears (66) and (67) and transmitted to the left and right planetary gear mechanism (35), and the left and right traveling crawler (2) is moved in the opposite direction at the same speed. When the vehicle is driven (forced differential structure), when the vehicle speed is changed by changing the rotational output of the transmission member (25) by operating the main transmission lever (73), the rotational output of the steering member (28) is constant. When the vehicle speed is maintained, the speed difference (V2-V1) between the left and right traveling crawlers (2) is kept constant with respect to the change in the vehicle speed, and the turning radius (R) is increased by the increase (deceleration) of the vehicle speed. Is enlarged (reduced) and the steering handle (1 Even keeping the rotational angle of the constant), the turning radius (R) is changed by a change in the vehicle speed. On the other hand, as is apparent from FIGS. 11 and 12, when the rotation angle of the steering handle (19) is kept constant, the main shift that changes the vehicle speed by changing the rotation output of the transmission member (25). By operating the lever (73), the rotational output of the steering member (28) changes in proportion, and the turning radius (R) of the left and right traveling crawler (2) is kept constant. Each operation of shifting the main transmission lever (73) and steering the steering handle (19) can be performed with substantially the same operation feeling as the pedal and handle operations.
[0037]
As described above, the speed change member (25) is operated by operating the main speed change lever (73), which is a speed changer, and both the left and right traveling crawlers (2) are driven at the same speed in the same direction to increase or decrease the speed. A crawler work vehicle that operates the steering member (28) by operating the steering handle (19), which is a steering tool, and drives the left and right traveling crawlers (2) at the same speed in the opposite directions to cause a difference in driving speed. The left and right traveling crawlers (2) are shift-controlled while maintaining the ratio of the rotational speed of the turning outer traveling crawler (2) and the rotational speed of the turning inner traveling crawler (2) substantially constant. When the steering wheel (19) is turned left or right, the turning radius can be changed even if the vehicle speed is changed by increasing or decreasing the left / right traveling crawler (2) by operating the main shift lever (73). Is maintained at a substantially constant level, and the steering and shifting operations can be performed with a driving feeling similar to that of a four-wheeled vehicle. It is easy to change direction to the next work process position on the ground.
[0038]
Further, FIG. 14 shows that the shift by the operation of the steering handle (19) when the forward (reverse) forward operation amount of the main shift lever (73) is the maximum, half, and quarter. The amount of output displacement of the speed change motor (105) whose member (25) is controlled to be decelerated is expressed as a speed change / deceleration operation amount, and shows the relationship between the rotation of the steering handle (19) and the speed change operation output. The speed reduction operation amount, which is the output displacement amount of the speed change motor (105), is set smaller than a substantially linear proportional change with respect to the angle change of the steering handle (19), and the output of the speed change member (28) is set. The transmission power loss is increased to compensate for the hydraulic power transmission loss, and the actual output of the speed change member (28) is configured to be within the set appropriate range (
[0039]
FIG. 15 shows the rotation of the steering handle (19) when the forward (reverse) forward operation amount of the main transmission lever (73) is maximum, half, and quarter, This shows the relationship with the shift output speed of the hydraulic motor (24) of the member (25). When the operation amount of the main shift lever (73) is constant, the steering handle (19) shifts with respect to the steering operation. Since the speed change output speed of the member (25) is changed proportionally, as shown in FIG. 16, when the sub speed change lever (74) is kept at a constant position and the sub speed is maintained at the same speed, the straight position is steered. In the cutting path correction range in which the handle (19) is rotated about 15 degrees leftward (rightward), the speed change motor (105) slightly moves in the deceleration direction with respect to the rotation of the steering handle (19), and the speed change member ( 25) is maintained in almost the same output state as straight running and steering The second hydraulic pump (26) of the material (28) turns the second hydraulic motor (27) in the forward direction (reverse direction) to turn leftward (rightward), and the uncut cereal (crop) row The course is corrected to match the curve. At this time, the deceleration amount of the traveling crawler (2) inside the turning and the acceleration amount of the traveling crawler (2) outside the turning become substantially equal, and the body center speed is kept at substantially the same speed as the straight traveling. Further, when the steering handle (19) is rotated by 15 degrees or more from the straight traveling position, the transmission motor (105) operates in the deceleration direction in proportion to the rotation of the steering handle (19), and the transmission member (25) is rotated counterclockwise. The vehicle is decelerated in both rotation and right turn, decelerates the traveling shift output of the first hydraulic pump (23) and the motor (24), and drives the left and right traveling crawlers (2) to rotate forward in the same direction. ), And a brake turn operation that turns leftward (rightward) due to the difference in traveling speed between the left and right traveling crawlers (2) is performed, and when it comes off the uncut grain row, it returns to the original row or next to it. The course is moved to the next row. Further, when the steering handle (19) is rotated about 116 degrees, the turning member (28) reaches the maximum output and the turning output is maintained at the maximum output. The traveling crawler (2) on the inner side of the turn is driven in reverse, and a spin turn operation is performed in which the aircraft turns around the turning center between the left and right traveling crawlers (2). ) To shift the direction of the aircraft by 180 degrees in the turning direction. Turn the steering handle (19) in the range of 0 to 135 degrees and turn left or right. The operation is performed, and the alignment course correction that moves along the uncut grain culm (crop) row within the rotation range of the left and right 15 degrees handle (19) centered on the straight traveling position, while maintaining the traveling speed during straight traveling And left and right 11 By rotating the handle (19) at a degree from 135 degrees to 135 degrees, while maintaining the maximum output of the swivel member (28), the spin turn operation that changes the direction of the aircraft on the field headland and moves to the next work step is performed. The vehicle is automatically decelerated to a quarter of the traveling speed (a deceleration rate of 25%).
[0040]
As is apparent from the above, the vehicle speed sensors (118) and (119) for detecting the left and right traveling crawler (2) speed, the steering angle sensor (113) for detecting the steering angle (19) and the shift lever ( 73) A shift sensor (111) for detecting the operation position is provided, and the speed of the left and right traveling crawler (2) is automatically controlled so that the turning radius determined by the turning angle of the steering handle (19) is set. Simplify the operating structure of the direction handle (19) and the speed change lever (73) and improve or change the steering function and speed change function of the traveling crawler (2) to improve turning performance and driving operability. For example, the operation is performed according to the detection result of one or both of the main transmission sensor (111) and the left and right vehicle speed sensors (118) (119) that detect a change in the transmission amount of the transmission member (25). The steering amount of the member (28) is automatically changed, and the speed difference between the turning inner traveling crawler (2) and the turning outer traveling crawler (2) is changed only by changing the vehicle speed. While increasing the speed difference between the left and right traveling crawlers (2) only, the speed difference between the left and right traveling crawlers (2) is decreased by a small amount of the turning radius due to deceleration, and the vehicle speed is changed without changing the turning radius. The vehicle speed of the traveling crawler (2) is changed with substantially the same driving feeling as the speed increase / decrease of the wheeled vehicle to improve the traveling speed change and steering function of the traveling crawler (2).
[0041]
Further, either the main transmission sensor (111) or the left and right vehicle speed sensors (118) (119) in proportion to the increase / decrease / rotation change in the same direction of the left / right carrier shaft (40), which is the shift amount of the transmission member (25). Alternatively, the steering amount of the steering member (28) is automatically changed by the calculation output of the controller (120) based on both detection results, and when the steering operation is constant, the turning radius is made constant only by the speed change operation. The vehicle speed is increased / decreased, and the ratio of the speed of the inner crawler (2) to the outer crawler (2) is kept constant with respect to the change of the vehicle speed. Improvement of gear shifting and steering functions and simplification of traveling gear shifting and steering control. Further, the rate of change of the steering amount of the steering member (28) with respect to the transmission amount of the transmission member (25) (the vehicle speed ratio of the left and right traveling crawler (2)) is configured to be freely changeable by the turning sensitivity setting device (117). By changing the speed ratio of the inner traveling crawler (2) and the outer traveling crawler (2) with respect to the change in vehicle speed according to the road surface condition or the left-right balance of the weight of the machine, the skid of the traveling crawler (2) is reduced and the Prevents meandering due to uneven weight on the left and right. Further, the driving speed of the left and right traveling crawler (2) is determined by the steering operation amount of the steering handle (19) and the transmission operation amount of the main transmission lever (73), as shown in the output diagram of FIG. Based on the control reference value (control map) formed by calculating the relationship between the steering operation amount and the shift operation amount, the operation amount of the steering handle (19) and the left and right are controlled regardless of the shift amount of the transmission member (25). A control reference value for the speed change of the left and right traveling crawler (2), which is determined based on the detection results of the steering angle sensor (113) and the speed change sensor (111), is stored in advance. And the control reference value is corrected by the turning sensitivity setter (117), and the steering or shift control of the average traveling crawler (2) based on the control reference value (control map), and the traveling road surface (Field) condition It is obtained a steer or shift control adapted to the desired driving feeling of an operator, achieving and improving driving operability.
[0042]
Furthermore, turning control is performed in the road traveling mode by sub-shift high-speed switching, and main shift deceleration control and steering control are performed based on the steering handle (19) operation by sub-shift standard switching and sub-shift low-speed switching. As shown in FIG. 16, the driving speed of the left and right traveling crawler (2) is changed by operating the steering handle (19) and the main speed change lever (73) to correct the alignment course and change the direction by spin turn on the field headland. And performing a harvesting operation for continuously harvesting and threshing the grains, and operating the auxiliary transmission lever (74) to operate the auxiliary transmission mechanism (32) at high speed or standard (reaping operation) as shown in FIG. Alternatively, when the speed is switched to a low speed, the speed difference between the left and right traveling crawlers (2) is kept substantially constant and the vehicle speed is changed, and the turning radius (R) of the left and right traveling crawlers (2) also changes as the vehicle speed changes. .
[0043]
Further, as shown in FIG. 18, by operating the deceleration sensitivity setter (115) by the hand operating member (56), the speed change member (25) based on the turning angle (steering amount) of the steering handle (19). The rate of change of the deceleration amount changes, and when traveling on a swampy mud road surface (low-speed traveling work) where the running resistance is large and slips easily, the deceleration change rate with respect to the turning angle of the steering handle (19) is reduced, or the spin turn By reducing the rate of change in deceleration to zero when vehicle speed is unnecessary, the vehicle speed is reduced throughout the entire steering operation, or as shown by the solid line in FIG. To do. On the other hand, in dry field traveling (high speed traveling work) with low traveling resistance, by increasing the deceleration change rate with respect to the turning angle of the steering handle (19), as shown by the phantom line in FIG. A direction change such as a spin turn can be performed stably, and a vehicle speed reduction operation and a vehicle speed return operation associated with a steering operation (direction change or straight advance) can be omitted.
[0044]
Further, as shown in FIGS. 16 and 19, a spin turn switch that is a work switch is an operation that causes the traveling crawler (2) to perform a spin turn operation in the dry paddy field operation and stops the spin turn operation of the traveling crawler (2) in the wet paddy field operation. (129) is configured to perform the spin turn prohibition and permission switching by operating the spin turn switch (129) without interrupting the operation even when the field is entirely dry and partly wet. A spin turn switch (129) for switching the control operation of the steering member (28) according to the traveling road surface condition of the traveling crawler (2). The traveling control of the traveling crawler (2) is changed to FIG. 16 or FIG. 19 by operating the spin turn switch (129). Achieving such maintenance and improvement of the driving operation of the turning function of the travel crawler in field (2).
[0045]
In addition, when the spin turn switch (129) is operated to prohibit the spin turn as shown in FIG. 19, the change in the speed of the brake turn until the turning inner traveling crawler (2) is reversed is shown in FIG. The spin turn operation area (cutting angle 100) of the steering handle (19) in which the turning crawler (2) is rotated in reverse by the spin turn permission operation of the spin turn switch (129). In the range of degrees to 135 degrees, the speed of the crawler inside traveling crawler (2) can be kept substantially zero and the spin turn can be prohibited, while the steering wheel (19) has a maximum turning angle as shown in FIG. Brake turn is performed to stop the crawling inner traveling crawler (2) at the (135 degrees) position, and the entire operating range of the steering handle (19) The speed of the turning inner running crawlers (2) is a quadratic curve slowly decelerated, also performed to prohibit spin turn.
[0046]
Furthermore, as shown in FIG. 21 and FIG. 22, a spin turn switch (129) is attached to the main spoke (19a) of the steering handle (19) and is connected in parallel to the spin turn switch (129). (129a) is attached to the grip part (73a) of the main transmission lever (73), and the spin turn switch (129) or the auxiliary spin turn switch (129a) is held by the hand of the steering handle (19) or the main transmission lever (73). Is operated and the handle (19) or the lever (73) is gripped during the harvesting operation to allow or prohibit the spin turn as described above. In addition, the threshing switch (130) and the cutting switch (133) are attached to the right spoke (19b) of the steering handle (19), and the threshing switch (130) is disposed near the center of the steering handle (19), When the cutting switch (133) is arranged on the outer side with respect to the threshing switch (130) and the threshing part (4) is driven by the threshing clutch engaging operation of the threshing switch (130) or the threshing clutch lever (76). Only, the cutting part (8) is operated by the cutting clutch engaging operation of the cutting switch (133), the operator holds the main transmission lever (73) with the left hand, and the switches (130) (133) with the right hand. The harvesting switch (133), which is frequently turned on and off during harvesting, is positioned within the operable range of the right thumb on the steering handle (19) side. Erroneous eliminating the trouble of threshing switch during work (130) is operated by.
[0047]
As described above, the steering handle (19) is provided with the spin turn switch (129), and the spin turn switch (129) is disposed in a range that can be operated by a hand holding the steering handle (19), so that the steering handle (129) can be operated during work. While driving while holding the direction handle (19), the spin turn switch (129) is operated, and the spin crawler (2) is urgently prohibited from being turned in mud where the crawler (2) is likely to sink. Make improvements easily.
[0048]
In addition, a sub-spin turn switch (129a) is provided on the main transmission lever (73), and the sub-spin turn switch (129a) is disposed within a range that can be operated by a hand that holds the main transmission lever (73), so that the main transmission is shifted during the work. While operating while holding the lever (73), the secondary spin turn switch (129a) is operated, and the spin crawler (2) is urgently prohibited from being turned in a place with a lot of mud where it can easily sink. Make improvements easily.
[0049]
This embodiment is configured as described above. As shown in the turning control flowchart of FIG. 23, the deceleration feeling input during turning of the deceleration sensitivity setting device (115) and the steering handle of the turning sensitivity setting device (117). The turning feeling input of (19), the spin turn permission (dry field) or prohibition (wet field) determination input of the spin turn switch (129), and the machine base (3) height of the left and right sensors (143) (144) Output line of FIG. 16, FIG. 18, FIG. 19 (or FIG. 20) by the dry field or wet field determination input based on the cutting position and the work position or non-work determination input of the cutting part (8) of the cutting part height sensor (150). The output of the speed control reference value (control map) of the traveling crawler (2) based on the figure is automatically corrected and calculated by the deceleration feeling, turning feeling, and switching between the dry field and the wet field. The control map is formed, the main transmission lever (73) operation input of the main transmission sensor (111), the auxiliary transmission lever (74) switching input of the auxiliary transmission sensor (112), and the steering angle sensor (113). One or both of the main and auxiliary transmission levers (73) and (74) by the steering handle (19) operation (cut angle) input and the left and right vehicle shaft (40) rotation input of the left and right vehicle speed sensors (118) and (119). When the vehicle is neutral, the steering brake (62) is turned on to keep the second hydraulic motor (27) stopped and the steering clutch (40) is disengaged, and the main speed change lever (73) is neutral. Then, the shift brake (106) is turned on to stop the output shaft (31) of the first hydraulic motor (24). Further, when the sub-shift is at medium speed or low speed, the main shift is other than neutral, and the steering handle (19) is operated other than straight travel, the main shift sensor (53) and steering angle sensor (55) are input. 16 determines the traveling speed (vehicle speed), steering angle and steering direction based on the corrected control map, and operates the transmission motor (105) and steering motor (108) by the main shift and steering control. Change the driving speed of the left and right traveling crawler (2) in the dry paddy state, correct the alignment course and change the direction by spin turn on the field headland, and perform the harvesting work to continuously harvest and thresh the grain. . Further, when the spin turn switch (129) is prohibited, or when the machine base (3) is in the wet position and in the high position, or when the cutting part (8) is in the low position in the work state, FIG. 20) In the wet field operation state where the spin turn is prohibited, the driving speed of the left and right traveling crawler (2) is controlled to change the alignment course and change the direction by the brake turn.
[0050]
Further, FIG. 24 is a horizontal control flowchart, in which the machine base (3) of the tilt sensor (104) is input to the left / right tilt direction, the set tilt input of the tilt setter (139), and the left and right sensors (143) (144). Machine base (3) Left / right height input, cutting position height sensor (150) cutting position (8) working position or non-working position determination input, spin turn switch (129) spin turn permission (dry field) Alternatively, the amount of lift of the left and right sides of the machine base (3) is calculated based on the prohibition (wet field) judgment input, and the machine base (3) is lowered according to the dry rice field work and the spin turn operation is permitted. While turning and traveling on the basis of the output diagram of Fig. 4, the ground height of the machine base (3) is lowered and the left or right inclination of the machine base (3) is raised and lowered with the raising and lowering operations of the left and right cylinders (103). Correct by action On the other hand, the machine base (3) is raised by the judgment of the wet field work and the spin turn operation is prohibited, and the machine base (3) is turned while performing the turning and traveling deceleration based on the output diagram of FIG. 19 (FIG. 20). Is increased by raising and lowering the left and right cylinders (103). Further, based on the detection results of the left and right sensors (143) and (144), when the ground height of the machine base (3) becomes below a certain level by the automatic horizontal control of the cylinder (103), 16 is automatically permitted, and when the ground height of the machine base (3) becomes equal to or higher than a certain level, the spin turn prohibiting operation of FIG. The turning control is performed.
[0051]
Further, FIG. 25 is an engine control flowchart, in which the engine (21) rotation speed input of the rotation sensor (136), the left and right carrier shaft (40) rotation speed inputs of the left and right vehicle speed sensors (118) (119), and the steering angle. It is determined whether or not the turning inner traveling crawler (2) is in a pin-turn operation in reverse by the steering handle (19) turning angle input of the sensor (113). While automatically controlling the engine (21) rotational speed, the engine (21) rotational speed is automatically controlled to switch to the turning mode shown in FIG. Is maintained in a high output state for a certain period of time to perform a spin turn operation.
[0052]
Furthermore, FIG. 26 is a steering control flowchart for following an uncut grain row in the field. When the threshing part (4) and the cutting part (8) are operated by clutch engagement, the main transmission sensor (111) The main shift position input, the sub shift position input of the sub shift sensor (112), the steering handle (19) cutting angle input of the steering angle sensor (113), and the cutting part ( 8) Based on the ground height input, the left or right turn is determined by the uncut grain row detection input of the steering sensor (127) in the state where each manual operation of traveling speed change and steering is off, and the steering Based on the detection result of the sensor (127), the steering motor (108) is automatically controlled to perform a left or right turning operation, and is automatically moved along an uncut grain row in the field to harvest. To do.
[0053]
Further, FIG. 27 is an elevation control flowchart for raising and lowering the cutting part (8). When the manual switch (147) for raising and lowering the cutting part (8) by manual operation is off, the cutting part ( 8) Ground height input, automatic lifting input of lifting switch (146), cutting part height sensor (150) cutting part (8) machine height input, and spin turn switch (129) spin turn When the cutting part (8) is raised above the cutting work position by the permission or prohibition input and the cutting part (8) operation input of the cutting switch (133), the lifting cylinder (146) is turned on by turning on the lifting switch (146). 11) is automatically lowered, the cutting part (8) is lowered to the cutting height sensor (145) control range, and the spin turn operation of FIG. 16 is prohibited. Further, when the cutting unit (8) is lowered to the cutting work position, the lift cylinder (11) is automatically controlled based on the detection result of the cutting height sensor (145) in a state where the spin turn operation is prohibited. The harvesting operation is performed with the mowing unit (8) supported at a substantially constant height, and the elevating cylinder (11) is turned on when the elevating switch (146) is turned on while the mowing unit (8) is lowered to the mowing operation position. Is automatically lifted, spin-turn operation is permitted, and based on the output diagram of FIG. 16, a spin-turn operation is performed by operating the steering handle (19), the direction is changed at the field headland and moved to the next work process position. To do.
[0054]
【The invention's effect】
As apparent from the above examples, the present inventionThe aircraft is equipped with a left and right traveling crawler, and shifts the straight traveling in the front-rear direction of the aircraft.A transmission member;A steering member for turning the airframe is connected via a shift steering controller.In crawler traveling vehicles,A spin turn switch that allows or prohibits the spin crawler's spin turn depending on the running road surface conditionTherefore, the spin turn switch operation can easily prevent the crawler's spin turn in a wet field, etc., and even if the entire field is dry and partly wet, it can be operated without interrupting the work. It is possible to switch between prohibition and permission of the spin turn, and to maintain the traveling performance of the traveling crawler in accordance with the road surface condition. Further, the engine output is automatically increased by the steering handle operation in the spin turn operation area of the steering member, and the traveling crawler (2) is turned during turning when the traveling load of the traveling crawler (2) increases. It is possible to drive stably, easily prevent a decrease in rotation of the engine (21) due to insufficient output, etc., and easily improve driving operability and durability of the engine (21).
[0055]
Further, vehicle speed sensors (118) and (119) for detecting the left and right traveling crawler (2) speed, a steering angle sensor (113) for detecting the steering wheel (19) cutting angle, and the operating position of the shift lever (73). A shift sensor (111) for detecting is provided, and the left and right traveling crawler (2) speed is automatically controlled so as to have a turning radius determined by the steering handle (19) cutting angle. 19) and the operation structure of the shift lever (73), etc., and the steering function and the shift function of the traveling crawler (2) can be easily improved or changed to improve turning performance and driving operability. Etc. can be easily achieved.
[0056]
Further, the transmission member (25) or the steering member (28) is configured such that the output of the transmission member (25) or the steering member (28) is larger than the linear change during the stop or maximum output. The problem that the driving crawler (2) driving force is insufficient due to the power transmission loss of (28) can be easily eliminated, and the driving performance of the driving crawler (2) can be easily maintained and the driving operability can be easily improved. In particular, it is possible to easily improve the running performance during slow speed running where the loss ratio is large.
[0057]
In addition, a control reference value for the left and right traveling crawler (2) speed change determined based on the detection results of the steering angle sensor (113) and the shift sensor (111) is stored in advance, and the control reference value is stored in the turn sensitivity setting device ( 117), the steering or shift control of the average traveling crawler (2) based on the control reference value (control map), the traveling road surface (field) condition, or the operator's desired traveling Steering or shift control adapted to feeling can be easily obtained, and driving operability can be easily improved.
[0058]
Further, the steering angle sensor (113) for detecting the steering angle of the steering handle (19), the shift sensor (111) for detecting the shift lever (73) switching position, the transmission member (25), and the steering member (28). Crawler rotation sensors (151) (152) for detecting the output rotation of the left and right crawlers (2) are calculated based on the detection results of the sensors (111) (113) (151) (152). The crawler rotation sensor (151) (152) is configured to automatically control the speed of the left and right traveling crawler (2), and the rotation sensor (151) is detected by directly detecting the output rotation of the speed change member (25) or the steering member (28). ) (152) can be easily prevented from being damaged, and the driving condition can be easily confirmed by displaying the left and right traveling crawler (2) speed.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a side view of a combine.
FIG. 2 is a plan view of the same.
FIG. 3 is an explanatory diagram of a mission case.
FIG. 4 is an explanatory plan view of a steering handle mounting portion.
FIG. 5 is a partial plan view of the same.
FIG. 6 is an explanatory diagram of the operation.
FIG. 7 is an explanatory front view of a traveling crawler unit.
FIG. 8 is a steering and shift control circuit diagram.
FIG. 9 is an output diagram of the engine.
FIG. 10 is an explanatory view of the display of a turning indicator.
FIG. 11 is an output diagram showing a relationship between a steering handle and a steering operation output.
FIG. 12 is an output diagram showing the relationship between the steering handle rotation angle and the steering member output.
FIG. 13 is an explanatory view of turning of the left and right traveling crawlers.
FIG. 14 is an output diagram showing a relationship between a steering handle and a shift operation output.
FIG. 15 is an output diagram showing the relationship between the steering wheel rotation angle and the speed change member output.
FIG. 16 is an output diagram showing the relationship between steering and main shift switching and traveling crawler rotation.
FIG. 17 is an output diagram showing the relationship between steering and sub-shift switching and traveling crawler rotation.
FIG. 18 is a steering output diagram without traveling deceleration.
FIG. 19 is a steering output diagram in which spin turn is prohibited.
FIG. 20 is a steering output diagram showing a modification of FIG. 19;
FIG. 21 is a plan view of the steering handle portion.
FIG. 22 is a side view of the same part.
FIG. 23 is a turning control flowchart;
FIG. 24 is a horizontal control flowchart.
FIG. 25 is an engine control flowchart.
FIG. 26 is a steering control flowchart.
FIG. 27 is an elevation control flowchart.
[Explanation of symbols]
(2) Traveling crawler
(19) Steering handle
(21) Engine
(25) Speed change member
(28) Steering member
(73) Main transmission lever
(103) Left and right cylinders (rolling members)
(104) Tilt sensor
(111) Main transmission sensor
(113) Steering angle sensor
(117) Turn sensitivity setting device
(118) (149) Left / Right vehicle speed sensor
(129) Spin turn switch
(143) (144) Left / Right sensor
(151) (152) Crawler rotation sensor
Claims (5)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP34586699A JP4248714B2 (en) | 1999-12-06 | 1999-12-06 | Crawler car |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP34586699A JP4248714B2 (en) | 1999-12-06 | 1999-12-06 | Crawler car |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006059985A Division JP2006151387A (en) | 2006-03-06 | 2006-03-06 | Crawler traveling vehicle |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2001163243A JP2001163243A (en) | 2001-06-19 |
| JP2001163243A5 JP2001163243A5 (en) | 2006-04-27 |
| JP4248714B2 true JP4248714B2 (en) | 2009-04-02 |
Family
ID=18379535
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP34586699A Expired - Fee Related JP4248714B2 (en) | 1999-12-06 | 1999-12-06 | Crawler car |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4248714B2 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US11148714B2 (en) | 2019-02-04 | 2021-10-19 | Caterpillar Inc. | Steering a differential steering machine while commanded to be in neutral |
-
1999
- 1999-12-06 JP JP34586699A patent/JP4248714B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US11148714B2 (en) | 2019-02-04 | 2021-10-19 | Caterpillar Inc. | Steering a differential steering machine while commanded to be in neutral |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2001163243A (en) | 2001-06-19 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP3028481B1 (en) | Moving agricultural machine | |
| JP4248715B2 (en) | Crawler car | |
| JP4430181B2 (en) | Crawler work vehicle | |
| JP4249197B2 (en) | Traveling crawler turning mechanism | |
| JP4313802B2 (en) | Travel crawler control mechanism | |
| JP4248714B2 (en) | Crawler car | |
| JP4390960B2 (en) | Crawler car | |
| JP4417500B2 (en) | Crawler car | |
| JP2001138944A (en) | Crawler traveling vehicle | |
| JP3998109B2 (en) | Mobile farm machine | |
| JP4417498B2 (en) | Crawler car | |
| JP4248713B2 (en) | Crawler car | |
| JP3028482B1 (en) | Moving agricultural machine | |
| JP4485623B2 (en) | Mobile farm machine | |
| JP2001163247A (en) | Crawler traveling vehicle | |
| JP4422254B2 (en) | Crawler car | |
| JP2006151387A (en) | Crawler traveling vehicle | |
| JP4267774B2 (en) | Mobile farm machine | |
| JP4422241B2 (en) | Mobile farm machine | |
| JP4112738B2 (en) | Mobile farm machine | |
| JP2001122148A (en) | Tending work vehicle | |
| JP4329400B2 (en) | Rice transplanter | |
| JP3013179B1 (en) | Traveling equipment for mobile farm machines | |
| JP3363271B2 (en) | Steering device for traveling crawlers on mobile agricultural machines | |
| JPH1132512A (en) | Combine harvester |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| RD04 | Notification of resignation of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7424 Effective date: 20040610 |
|
| RD04 | Notification of resignation of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7424 Effective date: 20040810 |
|
| A072 | Dismissal of procedure |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A073 Effective date: 20050222 |
|
| RD02 | Notification of acceptance of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7422 Effective date: 20060123 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20060307 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20060307 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20080725 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20080729 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20080926 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20090113 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20090114 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120123 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120123 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| S111 | Request for change of ownership or part of ownership |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313111 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120123 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |