JP4059971B2 - Glass run channel - Google Patents
Glass run channel Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4059971B2 JP4059971B2 JP03870998A JP3870998A JP4059971B2 JP 4059971 B2 JP4059971 B2 JP 4059971B2 JP 03870998 A JP03870998 A JP 03870998A JP 3870998 A JP3870998 A JP 3870998A JP 4059971 B2 JP4059971 B2 JP 4059971B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- molecular weight
- parts
- weight
- run channel
- glass run
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
Images
Description
【0001】
【発明の技術分野】
本発明は、ガラスランチャンネルに関し、さらに詳しくは、熱可塑性エラストマー製基体層と滑性樹脂表面層とからなる積層体により構成される窓ガラス摺動部を備えたガラスランチャンネルに関する。
【0002】
【発明の技術的背景】
一般に自動車の車輌における窓ガラスでは、通風換気のために、あるいは車輌外部との通話などのために、昇降による開閉操作が必要である。窓ガラスの昇降開閉操作を容易にしながら、しかも窓ガラスと窓枠との緊密的(液密的)な密閉操作を可能とするために、窓ガラスと窓枠との間にガラスランチャンネルと呼ばれる案内部材を設けている。
【0003】
従来のガラスランチャンネルは、軟質塩化ビニル樹脂のような軟質合成樹脂や、エチレン−プロピレン−ジエン共重合ゴム等の加硫ゴムで形成されており、底壁と底壁の両端部から延設した側壁とから構成され、断面略U字状で溝部が形成されたガラスランチャンネル本体と、該ガラスランチャンネル本体の両側壁の先端近傍から該底壁に向かって相互に近接するように張設した舌片状の水切り部とから構成されている。
【0004】
従来のガラスランチャンネルでは、窓ガラスの水切り部からの離れを良好にし、また窓ガラスの汚れを防止するために、窓ガラス摺動部は、その表面にナイロンフィルム等が接着により貼合わせられており、また窓ガラスとの接触面積を少なくするために、上記ナイロンフィルム等の積層の前または後に、エンボス加工が施されている。
【0005】
このようなガラスランチャンネルでは、上述した軟質合成樹脂または加硫ゴムとナイロン類の表面素材との間に接着性がないため、軟質合成樹脂または加硫ゴムでガラスランチャンネル本体を成形し、得られた成形物に接着剤を塗布してナイロンなどのフィルムを貼合わせるという工程が必要であり、さらに、この接着の前または後にエンボス加工を行なわなければならない等、工程数が多く、しかも手間を要するという不都合がある。
【0006】
また、このようなガラスランチャンネルでは、接着剤による積層工程があることから、耐久性にも問題があり、経時および屋外曝露等により表面フィルム層と基体との間で剥離を生じやすいという欠点もある。さらに、エンボス加工で形成させ得る凹凸模様は未だ微細さと均一さとの組合せにおいて十分満足のいくものではなく、閉鎖時における窓ガラス摺動部と窓ガラスとの間の緊密接触性、および開放時における窓ガラス摺動部と窓ガラスとの間の軽快摺動性についても未だ改善すべき余地が残されている。
【0007】
そこで、本発明者らは、ガラスランチャンネルの上記のような問題を解決すべく鋭意研究し、ガラスランチャンネルの少なくとも窓ガラス摺動部を構成するエラストマーとして結晶性ポリオレフィンとゴムとから構成される熱可塑性エラストマーを選択し、その熱可塑性エラストマー層上に特定の超高分子量ポリオレフィン組成物層を熱融着させて積層すれば、製造作業が容易であり、しかも、耐久性、閉鎖時における窓ガラスとの緊密接触性、および開放時における窓ガラスとの軽快摺動性に優れたガラスランチャンネルを得ることができることを見出し、新規なガラスランチャンネルを提案した。(特開平5−4522号公報、特開平5−4308号公報)
【0008】
しかしながら、このガラスランチャンネルは、超高分子量ポリオレフィン組成物層に超高分子量ポリオレフィン、たとえば超高分子量ポリエチレンを単独で用いると、剛性が高いために、製品(ガラスランチャンネル)を車体に組み込む過程等においてガラスランチャンネルをねじったり、折り曲げたときに超高分子量ポリオレフィン組成物層に皺が発生し、製品の外観を損ねる場合があった。
【0009】
本発明者らは、この点を改良すべく検討を重ねた結果、超高分子量ポリオレフィン組成物として超高分子量ポリオレフィンとオレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマーとからなる組成物を用いることにより、超高分子量ポリオレフィンの性能を持ち、かつ、ねじったり、折り曲げても超高分子量ポリオレフィン組成物層に皺が発生しないガラスランチャンネルが得られることを見出し、本発明を完成するに至った。
【0010】
【発明の目的】
本発明は、上記のような従来技術に伴う問題点を解決しようとするものであって、製造工程を簡略化して製造することができ、耐久性、閉鎖時における窓ガラスとの緊密接触性、および開放時における窓ガラスとの軽快摺動性に優れ、ねじたり折り曲げたりしても超高分子量ポリオレフィン組成物層に皺が発生しないガラスランチャンネルを提供することを目的としている。
【0011】
【発明の概要】
本発明に係るガラスランチャンネルは、
底壁と底壁の両端部から延設した側壁とから構成され、断面略U字状で溝部が形成されたガラスランチャンネル本体と、該ガラスランチャンネル本体の両側壁の先端近傍から該底壁に向かって相互に近接するように張設した舌片状の水切り部とから構成されたガラスランチャンネルであって、
該水切り部の窓ガラスと接触する表面である窓ガラス接触部が、
結晶性ポリオレフィンとゴムとから構成される熱可塑性エラストマー(A)層と、超高分子量ポリオレフィン組成物(B)層とからなり、かつ、
超高分子量ポリオレフィン組成物(B)層が窓ガラスと接触するように構成されており、
該超高分子量ポリオレフィン組成物(B)が、
135℃デカリン溶媒中で測定した極限粘度[η]が7〜40dl/gの範囲内にある超高分子量ポリオレフィン(a−1)と、135℃デカリン溶媒中で測定した極限粘度[η]が0.1〜5dl/gの範囲内にあるポリオレフィン(a−2)とから実質的になり、該超高分子量ポリオレフィン(a−1)が、超高分子量ポリオレフィン(a−1)とポリオレフィン(a−2)との総重量100重量%に対して15〜40重量%の割合で存在し、かつ、135℃デカリン溶媒中で測定した極限粘度[η]が3.5〜8.3dl/gの範囲内にあるポリオレフィン(a)’10〜90重量部、および
結晶性オレフィン系樹脂とオレフィン系ゴムとからなるオレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー(b)90〜10重量部[成分(a)’および(b)の合計は100重量部]からなることを特徴としている。
【0012】
本発明で用いられる熱可塑性エラストマー(A)の好ましい例としては、
結晶性ポリプロピレン(A−1)70〜10重量部と、
エチレン・プロピレン共重合体ゴムまたはエチレン・プロピレン・ジエン共重合体ゴムからなるゴム(A−2)30〜90重量部[成分(A−1)および(A−2)の合計量は100重量部とする]と
からなる混合物を、有機ペルオキシドの存在下で動的に熱処理して得られる、上記ゴム(A−2)が架橋された熱可塑性エラストマーが挙げられる。
【0013】
また本発明で好ましく用いられる超高分子量ポリオレフィン組成物(B)は、
135℃デカリン溶媒中で測定した極限粘度[η]が7〜40dl/gの範囲内にある超高分子量ポリオレフィン(a−1)と、135℃デカリン溶媒中で測定した極限粘度[η]が0.1〜5dl/gの範囲内にあるポリオレフィン(a−2)とから実質的になり、該超高分子量ポリオレフィン(a−1)が、超高分子量ポリオレフィン(a−1)とポリオレフィン(a−2)との総重量100重量%に対して15〜40重量%の割合で存在し、かつ、135℃デカリン溶媒中で測定した極限粘度[η]が3.5〜8.3dl/gの範囲内にあるポリオレフィン組成物(a)’10〜90重量部、
結晶性オレフィン系樹脂とオレフィン系ゴムとからなるオレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー(b)85〜5重量部、および
スチレンまたはその誘導体の重合体ブロック(c−1)と、イソプレン重合体ブロックおよび/またはイソプレン・ブタジエン共重合体ブロックであって、全イソプレン単位に対する1,2−位および3,4−位で結合しているイソプレン単位含有量が40%以上である重合体および/または共重合体ブロック(c−2)とからなる水素添加されていてもよいブロック共重合体(c)5〜60重量部[成分(a)’、(b)および(c)の合計は100重量部]からなる組成物である。
【0014】
また、前記超高分子量ポリオレフィン組成物(B)は、前記ポリオレフィン(a)もしくはポリオレフィン組成物(a)’、およびオレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー(b)のほかに、
スチレンまたはその誘導体の重合体ブロック(c−1)と、イソプレン重合体ブロックおよび/またはイソプレン・ブタジエン共重合体ブロックであって、全イソプレン単位に対する1,2−位および3,4−位で結合しているイソプレン単位含有量が40%以上である重合体および/または共重合体ブロック(c−2)とからなる水素添加されていてもよいブロック共重合体(c)、および/または
高級脂肪酸アミド(d)、シリコーンオイル(e)、脂肪族アルコールとジカルボン酸あるいはモノカルボン酸とのエステル(f)、およびフッ素系ポリマー(g)からなる群から選ばれる少なくとも1種の成分を含有していてもよい。
【0015】
前記超高分子量ポリオレフィン組成物(B)を構成するオレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー(b)の好ましい例としては、
結晶性ポリプロピレン(A−1)70〜10重量部と、
エチレン・プロピレン共重合体ゴムまたはエチレン・プロピレン・ジエン共重合体ゴムからなるゴム(A−2)30〜90重量部[成分(A−1)および(A−2)の合計量は100重量部とする]と
からなる混合物を、有機ペルオキシドの存在下で動的に熱処理して得られる、上記ゴム(A−2)が架橋された熱可塑性エラストマーが挙げられる。本発明では、熱可塑性エラストマー(A)とオレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー(b)は、同一であってもよいし、異なっていてもよい。
【0016】
前記超高分子量ポリオレフィン組成物(B)は、超高分子量ポリオレフィン組成物(B)当たり1〜20重量%の液体ないし固体の潤滑油を含有していてもよい。
【0017】
【発明の具体的説明】
以下、本発明に係るガラスランチャンネルの一例を図に基づいて具体的に説明する。
【0018】
図1は、本発明に係るガラスランチャンネルの一例の断面構造を示す断面図である。
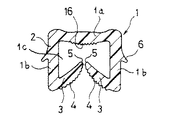
図1において、1は全体で本発明のガラスランチャンネルを示している。このガラスランチャンネル1は、底壁1aと底壁1aの両端部から延設した側壁1bとから構成されており、断面略U字状(コの字形状)であり、その内部に溝部1cが形成されたガラスランチャンネル本体2を備えている。ガラスランチャンネル本体2の両側壁1b,1bの先端近傍から前記底壁1aに向かって相互に近接するように舌片状の水切り部3,3が張設されており、これらの水切り部3,3の先端5,5が、相互に開閉可能な位置関係にあるように構成されている。また、これらの水切り部3,3の外面側が、自動車などの車両の窓ガラスと接触する表面となっており、窓ガラス接触部4,4を構成している。さらに、ガラスランチャンネル本体2には、その両側壁1b,1bの外側に側壁1bの先端部側に傾斜するように突設した取付け用フック6が形成されている。
【0019】
この本体2および水切り部3はエラストマーで一体に成形されているが、本発明によれば、少なくとも窓ガラス接触部4を、特定の熱可塑性エラストマー(A)からなる基体層と特定の超高分子量ポリオレフィン組成物(B)からなる滑性樹脂層とで構成する。この窓ガラス接触部4を拡大して示す図2のように、上記基体層7の表面8は、微細な凹凸の繰返し模様が施されていることが好ましい。このようなシャークスキン状の微小凹凸模様を有する表面8に対して、上記滑性樹脂層9が熱融着により積層され、その外表面10には同様の微細な凹凸の繰返し模様が施されていることが好ましい。
【0020】
図3〜図5は、このように構成されるガラスランチャンネルを自動車の窓枠への装着方法を説明するそれぞれドアを示す斜視図、窓枠部分の断面図である。
図3〜図5に示したように、自動車のドア11には、昇降動させることによって開閉可能なように窓ガラス12が装着されている。一方、ドア11の窓枠13の内周部分に、ガラスランチャンネル1が固定されている。
【0021】
このガラスランチャンネル1を窓枠13の内周部分に固定するために、図4および図5に示したように、窓枠13は全体にわたってその断面が略U字状(コの字形状)に成形されており、その凹部14を構成する両側板部14aの凹部14の入口部分には、内側に突設する突起部15が形成されている。そして、この窓枠13の凹部14内に、ガラスランチャンネル1をそのガラスランチャンネル本体2の底壁側から挿入して、その取付け用フック6が窓枠13の突起部15を越えるように挿入すれば、取付け用フック6が突起部15にて係止され、ガラスランチャンネル本体2が窓枠13の凹部14から抜け落ちるのが防止されるため、その結果、ガラスランチャンネル1を窓枠13に固定することができる。
【0022】
そして、図4に示したように、窓ガラス12を降下させた状態では、ガラスランチャンネル1のガラス摺動部を構成する水切り部3,3の先端5,5は、相互に対面して閉じた状態となっており、溝部内に塵埃などが侵入して、窓ガラス12の表面を汚損するのが防止できるようになっている。一方、図5に示したように、窓ガラス12を上昇させた状態では、窓ガラス摺動部を構成する水切り部3,3の先端5,5は、窓ガラス12がこれらの間に嵌挿された状態となり、相互に分離した状態となっているが、窓ガラス12の表面とは接触状態となっており、液密状態が確保されるようになっている。
【0023】
本発明によれば、ガラスランチャンネル1の内、少なくとも窓ガラスと接触する部分に熱可塑性エラストマー(A)からなる基体層7と、この基体層7の表面に熱融着された超高分子量ポリオレフィン組成物(B)からなる滑性樹脂層9とを設ける。
【0024】
すなわち、本発明で用いられる熱可塑性エラストマー(A)は、任意の形状および寸法に熱成形することが可能であるとともに、ガラスランチャンネルの窓ガラス摺動部に要求される弾性、柔軟性、可圧縮性などの特性に優れており、しかも、耐久性、耐候性、耐水性などの性質にも優れている。熱可塑性エラストマー(A)は、表面材層となる超高分子量ポリオレフィン組成物(B)からなる滑性樹脂層9に対し、強い接着性を示し、この滑性樹脂層9との熱融着により、接着直後および経時の層間接着強度、さらには、耐候試験後の層間接着強度に優れた積層構造を形成させることができる。しかも、本発明で基体層7として用いられる熱可塑性エラストマー(A)は、シャークスキン状の成形外観を呈するように成形することも可能であり、この成形工程と、表面材層としての超高分子量ポリオレフィン組成物(B)からなる滑性樹脂層9と基体層7との熱融着工程とを組合わせることにより、滑性樹脂層9の外表面にシャークスキン状の微小凹凸模様を忠実に再現することもできる。このようなシャークスキン状の微小凹凸模様表面の写し出しは、従来の接着剤塗布方式では極めて困難であり、上記成形工程と熱融着工程との組合せによりはじめて可能となった。
【0025】
本発明によれば、上述した構成を採用することにより、接着剤の塗布工程、接着剤の硬化ないし焼付工程、その前あるいは後におけるエンボス加工工程がすべて省略され、少ない工程数と少ない手間とでガラスランチャンネルを能率よく製造することができる。また、超高分子量ポリオレフィン組成物(B)からなる滑性樹脂層9を表面材層としてを設けることにより、窓ガラスとの摩擦係数を低減させることができるだけでなく、従来のエンボス加工による凹凸模様に比して、ピッチが均一で、しかもシャークスキン状の微細な凹凸を表面に形成させることが可能となった。したがって、本発明に係るガラスランチャンネルにおいては、窓ガラスの閉鎖時には窓ガラスとの緊密(液密)な接触が可能となるとともに、窓ガラスの開放時にはその摺動抵抗を低減させて、円滑軽快な開閉操作が可能となる。
【0026】
熱可塑性エラストマー(A)
本発明で用いられる熱可塑性エラストマー(A)は、結晶性ポリオレフィンとゴムとから構成されている。
【0027】
本発明で用いられる結晶性ポリオレフィンとしては、炭素原子数2〜20のα- オレフィンの単独重合体または共重合体が挙げられる。
上記結晶性ポリオレフィンの具体的な例としては、以下のような(共)重合体が挙げられる。
(1)エチレン単独重合体
(製法は、低圧法、高圧法のいずれでも良い)
(2)エチレンと、10モル%以下の他のα- オレフィンまたは酢酸ビニル、エチルアクリレートなどのビニルモノマーとの共重合体
(3)プロピレン単独重合体
(4)プロピレンと10モル%以下の他のα- オレフィンとのランダム共重合体
(5)プロピレンと30モル%以下の他のα- オレフィンとのブロック共重合体
(6)1-ブテン単独重合体
(7)1-ブテンと10モル%以下の他のα- オレフィンとのランダム共重合体
(8)4-メチル-1- ペンテン単独重合体
(9)4-メチル-1- ペンテンと20モル%以下の他のα- オレフィンとのランダム共重合体
上記のα- オレフィンとしては、具体的には、エチレン、プロピレン、1-ブテン、4-メチル-1- ペンテン、1-ヘキセン、1-オクテンなどが挙げられる。
【0028】
本発明で用いられるゴムとしては、特に制限はないが、オレフィン系共重合体ゴムが好ましい。
上記のオレフィン系共重合体ゴムは、炭素原子数2〜20のα- オレフィンを主成分とする無定形ランダムな弾性共重合体であって、2種以上のα- オレフィンからなる非晶性α- オレフィン共重合体、2種以上のα- オレフィンと非共役ジエンとからなるα- オレフィン・非共役ジエン共重合体などがある。
【0029】
このようなオレフィン系共重合体ゴムの具体的な例としては、以下のようなゴムが挙げられる。
(1)エチレン・α- オレフィン共重合体ゴム
[エチレン/α- オレフィン(モル比)=約90/10〜50/50]
(2)エチレン・α- オレフィン・非共役ジエン共重合体ゴム
[エチレン/α- オレフィン(モル比)=約90/10〜50/50]
(3)プロピレン・α- オレフィン共重合体ゴム
[プロピレン/α- オレフィン(モル比)=約90/10〜50/50]
(4)ブテン・α- オレフィン共重合体ゴム
[ブテン/α- オレフィン(モル比)=約90/10〜50/50]
上記α- オレフィンとしては、具体的には、上記した結晶性ポリオレフィンを構成するα- オレフィンの具体的な例と同様のα- オレフィンが挙げられる。
【0030】
上記非共役ジエンとしては、具体的には、ジシクロペンタジエン、1,4-ヘキサジエン、シクロオクタジエン、メチレンノルボルネン、エチリデンノルボルネンなどが挙げられる。
【0031】
これらの共重合体ゴムのムーニー粘度ML1+4 (100℃)は、10〜250、特に40〜150が好ましい。また、上記非共役ジエンが共重合している場合のヨウ素価は、25以下が好ましい。
【0032】
上記のオレフィン系共重合体ゴムは、熱可塑性エラストマー中において、未架橋、部分架橋、全体架橋など、すべての架橋状態で存在することができるが、本発明においては、架橋状態で存在していることが好ましく、特に部分架橋状態で存在していることが好ましい。
【0033】
本発明において用いられるゴムとしては、上記のオレフィン系共重合体ゴムのほかに、他のゴム、たとえばスチレン- ブタジエンゴム(SBR)、ニトリルゴム(NBR)、天然ゴム(NR)、ブチルゴム(IIR)等のジエン系ゴム、SEBS、ポリイソブチレンなどが挙げられる。
【0034】
本発明で用いられる熱可塑性エラストマー(A)において、結晶性ポリオレフィンとゴムとの重量配合比(結晶性ポリオレフィン/ゴム)は、通常90/10〜5/95、好ましくは70/30〜10/90の範囲である。
【0035】
またゴムとして、オレフィン系共重合体ゴムとその他のゴムを組合わせて用いる場合には、その他のゴムは、結晶性ポリオレフィンとゴムとの合計量100重量部に対して、40重量部以下、好ましくは5〜20重量部の割合で配合する。
【0036】
本発明で好ましく用いられる熱可塑性エラストマー(A)は、結晶性ポリプロピレンと、エチレン・α- オレフィン共重合体ゴムもしくはエチレン・α- オレフィン・非共役ジエン共重合体ゴムとからなり、熱可塑性エラストマー中においてこれらが部分架橋された状態で存在し、かつ、結晶性ポリプロピレンとゴムとの重量配合比(結晶性ポリプロピレン/ゴム)が70/30〜10/90の範囲内にある。
【0037】
上記の熱可塑性エラストマー(A)には、必要に応じて、鉱物油系軟化剤、耐熱安定剤、帯電防止剤、耐候安定剤、老化防止剤、充填剤、着色剤、滑剤などの添加物を、本発明の目的を損なわない範囲で配合することができる。
【0038】
本発明で好ましく用いられる熱可塑性エラストマー(A)のより具体的な例としては、
結晶性ポリプロピレン(A−1)70〜10重量部と、
エチレン・プロピレン共重合体ゴムまたはエチレン・プロピレン・ジエン共重合体ゴムからなるゴム(A−2)30〜90重量部[成分(A−1)および(A−2)の合計量は、100重量部とする]と、
このゴム(A−2)以外のゴム(A−3)および/または鉱物油系軟化剤(A−4)5〜100重量部と
からなる混合物を、有機ペルオキシドの存在下で動的に熱処理して得られる、上記ゴム(A−2)が架橋された熱可塑性エラストマーが挙げられる。
【0039】
上記有機ペルオキシドとしては、具体的には、ジクミルペルオキシド、ジ-tert-ブチルペルオキシド、2,5-ジメチル-2,5- ジ-(tert-ブチルペルオキシ)ヘキサン、2,5-ジメチル-2,5- ジ-(tert-ブチルペルオキシ)ヘキシン-3、1,3-ビス(tert- ブチルペルオキシイソプロピル)ベンゼン、1,1-ビス(tert- ブチルペルオキシ)-3,3,5- トリメチルシクロヘキサン、n-ブチル-4,4- ビス(tert- ブチルペルオキシ)バレレート、ベンゾイルペルオキシド、p-クロロベンゾイルペルオキシド、2,4-ジクロロベンゾイルペルオキシド、tert- ブチルペルオキシベンゾエート、tert- ブチルペルベンゾエート、tert- ブチルペルオキシイソプロピルカーボネート、ジアセチルペルオキシド、ラウロイルペルオキシド、tert- ブチルクミルペルオキシドなどが挙げられる。
【0040】
これらの内では、臭気性、スコーチ安定性の点で、2,5-ジメチル-2,5- ジ-(tert-ブチルペルオキシ)ヘキサン、2,5-ジメチル-2,5- ジ-(tert-ブチルペルオキシ)ヘキシン-3、1,3-ビス(tert- ブチルペルオキシイソプロピル)ベンゼン、1,1-ビス(tert- ブチルペルオキシ)-3,3,5- トリメチルシクロヘキサン、n-ブチル-4,4- ビス(tert- ブチルペルオキシ)バレレートが好ましく、なかでも、1,3-ビス(tert- ブチルペルオキシイソプロピル)ベンゼンが最も好ましい。
【0041】
本発明においては、有機ペルオキシドは、結晶性ポリオレフィンとゴムとの合計量100重量%に対して、0.05〜3重量%、好ましくは0.1〜1重量%の割合で用いられる。
【0042】
上記有機ペルオキシドによる部分架橋処理に際し、硫黄、p-キノンジオキシム、p,p'- ジベンゾイルキノンジオキシム、N-メチル-N-4- ジニトロソアニリン、ニトロソベンゼン、ジフェニルグアニジン、トリメチロールプロパン-N,N'-m-フェニレンジマレイミドのようなペルオキシ架橋用助剤、あるいはジビニルベンゼン、トリアリルシアヌレート、エチレングリコールジメタクリレート、ジエチレングリコールジメタクリレート、ポリエチレングリコールジメタクリレート、トリメチロールプロパントリメタクリレート、アリルメタクリレートのような多官能性メタクリレートモノマー、ビニルブチラート、ビニルステアレートのような多官能性ビニルモノマーを配合することができる。
【0043】
上記のような化合物を用いることにより、均一かつ緩和な架橋反応が期待できる。特に、本発明においては、ジビニルベンゼンが最も好ましい。ジビニルベンゼンは、取扱い易く、上記の被架橋処理物の主成分である結晶性ポリオレフィンおよびゴムとの相溶性が良好であり、かつ、有機ペルオキシドを可溶化する作用を有し、有機ペルオキシドの分散剤として働くため、熱処理による架橋効果が均質で、流動性と物性とのバランスのとれた熱可塑性エラストマーが得られる。
【0044】
上記のような架橋助剤もしくは多官能性ビニルモノマーは、上記の被架橋処理物全体に対して、0.1〜2重量%、特に0.3〜1重量%の割合で用いるのが好ましい。架橋助剤もしくは多官能性ビニルモノマーの配合割合が2重量%を超えると、有機ペルオキシドの配合量が多い場合には、架橋反応が速く進行し過ぎるため、得られる熱可塑性エラストマーは、流動性に劣り、一方、有機ペルオキシドの配合量が少ない場合には、架橋助剤および多官能性ビニルモノマーが、熱可塑性エラストマー中に未反応のモノマーとして残存し、熱可塑性エラストマーは、加工成形の際に熱履歴による物性の変化が生じたりする。したがって、架橋助剤および多官能性ビニルモノマーは、過剰に配合すべきではない。
【0045】
上記の「動的に熱処理する」とは、上記のような各成分を融解状態で混練することをいう。
混練装置としては、従来公知の混練装置、たとえば開放型のミキシングロール、非開放型のバンバリーミキサー、押出機、ニーダー、連続ミキサーなどが用いられる。これらの内では、非開放型の混練装置が好ましく、混練は、窒素ガス、炭酸ガスなどの不活性ガスの雰囲気下で行なうことが好ましい。
【0046】
また、混練は、使用する有機ペルオキシドの半減期が1分未満となる温度で行なうのが望ましい。混練温度は、通常150〜280℃、好ましくは170〜240℃であり、混練時間は、1〜20分間、好ましくは3〜10分間である。また、加えられる剪断力は、剪断速度として100sec-1以上、好ましくは500〜10,000sec-1の範囲内で決定される。
【0047】
本発明で特に好ましく用いられる熱可塑性エラストマー(A)は、部分的に架橋されているが、この「部分的に架橋された」とは、下記の方法で測定したゲル含量が20〜98%の範囲内にある場合をいい、本発明においては、ゲル含量が40〜98%の範囲内にあることが好ましい。
【0048】
[ゲル含量の測定法]
熱可塑性エラストマーの試料を約100mg秤量して0.5mm×0.5mm×0.5mmの細片に裁断し、次いで、得られた細片を、密閉容器中にて30mlのシクロヘキサンに、23℃で48時間浸漬する。
【0049】
次に、この試料を濾紙上に取り出し、室温にて72時間以上恒量になるまで乾燥する。
この乾燥残渣の重量からポリマー成分以外のシクロヘキサン不溶性成分(繊維状フィラー、充填剤、顔料等)の重量を減じた値を、「補正された最終重量(Y)」とする。
【0050】
一方、試料の重量からポリマー成分以外のシクロヘキサン可溶性成分(たとえば軟化剤)の重量およびポリマー成分以外のシクロヘキサン不溶性成分(繊維状フィラー、充填剤、顔料等)の重量を減じた値を、「補正された初期重量(X)」とする。
【0051】
ここに、ゲル含量(シクロヘキサン不溶解分)は、次式により求められる。
ゲル含量[重量%]=[補正された最終重量(Y)]÷[補正された初期重量(X)]×100
本発明で用いられる熱可塑性エラストマー(A)は、結晶性ポリオレフィンとゴムとからなるため、流動性に優れている。
【0052】
上記のような熱可塑性エラストマー(A)は、圧縮成形、トランスファー成形、射出成形、押出成形等の従来使用されている成形装置を用いて成形することができる。
【0053】
超高分子量ポリオレフィン組成物(B)
本発明で用いられる超高分子量ポリオレフィン組成物(B)の具体的な例としては、以下のような超高分子量ポリオレフィン組成物が挙げられる。
【0054】
(1)135℃デカリン溶媒中で測定した極限粘度[η]が3.5〜8.3dl/gの範囲にあるポリオレフィン(a)と、
結晶性オレフィン系樹脂とオレフィン系ゴムからなるオレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー(b)と、必要に応じて、
スチレンまたはその誘導体の重合体ブロック(c−1)と、イソプレン重合体ブロックおよび/またはイソプレン・ブタジエン共重合体ブロックであって、全イソプレン単位に対する1,2−位および3,4−位で結合しているイソプレン単位含有量が40%以上である重合体および/または共重合体ブロック(c−2)とからなる水素添加されていてもよいブロック共重合体(c)、および/または
高級脂肪酸アミド(d)、シリコーンオイル(e)、脂肪族アルコールとジカルボン酸あるいはモノカルボン酸とのエステル(f)、およびフッ素系ポリマー(g)からなる群から選ばれる少なくとも1種の成分と
からなる組成物。
【0055】
(2)135℃デカリン溶媒中で測定した極限粘度[η]が7〜40dl/g、好ましくは10〜35dl/gの範囲内にある超高分子量ポリオレフィン(a−1)と、135℃デカリン溶媒中で測定した極限粘度[η]が0.1〜5dl/g、好ましくは0.1〜2dl/gの範囲内にある低分子量ないし高分子量ポリオレフィン(a−2)とから実質的になり、超高分子量ポリオレフィン(a−1)が、超高分子量ポリオレフィン(a−1)とポリオレフィン(a−2)との総重量100重量%に対して15〜40重量%、好ましくは18〜35重量%の割合で存在し、かつ、135℃デカリン溶媒中で測定した極限粘度[η]が3.5〜8.3dl/gの範囲にあるポリオレフィン組成物(a)’と、
結晶性オレフィン系樹脂とオレフィン系ゴムからなるオレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー(b)と、必要に応じて、
上記ブロック共重合体(c)、および/または
高級脂肪酸アミド(d)、シリコーンオイル(e)、脂肪族アルコールとジカルボン酸あるいはモノカルボン酸とのエステル(f)、およびフッ素系ポリマー(g)からなる群から選ばれる少なくとも1種の成分と
からなる組成物。
【0056】
(3)上記(1)または(2)の超高分子量ポリオレフィン組成物と、この超高分子量ポリオレフィン組成物当り1〜20重量%の液体ないし固体の潤滑油とからなる組成物。
【0057】
[ポリオレフィン(a)、超高分子量ポリオレフィン(a−1)およびポリオレフィン(a−2)]
上記(1)の組成物を構成するポリオレフィン(a)、上記(2)の組成物を構成する超高分子量ポリオレフィン(a−1)およびポリオレフィン(a−2)は、たとえばエチレン、プロピレン、1-ブテン、1-ペンテン、1-ヘキセン、1-オクテン、1-デセン、1-ドデセン、4-メチル-1- ペンテン、3-メチル-1- ペンテンなどのα- オレフィンの単独重合体または共重合体からなる。本発明においては、エチレン単独重合体、およびエチレンと他のα- オレフィンとからなる、エチレンを主成分とする共重合体が望ましい。
【0058】
[オレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー(b)]
上記オレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー(b)は、上述したオレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー(A)と同様の材料を用いることができる。成分(b)と(A)とは全く同じでもよいし、異なっていてもよい。
【0059】
[ブロック共重合体(c)]
本発明で用いられるブロック共重合体(c)は、スチレンまたはその誘導体の重合体ブロック(c−1)と、特定のイソプレン重合体または特定のイソプレン・ブタジエン共重合体からなるブロック(c−2)とからなり、水素添加されていてもよい。
【0060】
上記ブロック(c−1)を構成する重合体成分は、スチレンまたはその誘導体である。
スチレンの誘導体としては、具体的には、α- メチルスチレン、1-ビニルナフタレン、2-ビニルナフタレン、3-メチルスチレン、4-プロピルスチレン、4-シクロヘキシルスチレン、4-ドデシルスチレン、2-エチル-4- ベンジルスチレン、4-(フェニルブチル)スチレンなどが挙げられる。ブロック(c−1)を構成する重合体成分としては、スチレン、α- メチルスチレンが好ましい。
【0061】
上記ブロック(c−2)を構成する重合体または共重合体は、イソプレン重合体またはイソプレン・ブタジエン共重合体であって、下記に示すイソプレン単位全体に対する1,2−位および3,4−位で結合しているイソプレン単位含有量が40%以上、好ましくは45%以上である。
【0062】
【化1】
【0063】
本発明において、全イソプレン単位に対する1,2−位および3,4−位で結合しているイソプレン単位含有量が40%以上であるとき、耐傷付き性に優れた成形体を提供し得る熱可塑性エラストマーを得ることができる。
【0064】
ブロック共重合体(c)におけるスチレンまたはその誘導体の重合体ブロック(c−1)の割合は、好ましくは5〜50重量%、さらに好ましくは10〜45重量%の範囲である。すなわち、上記のイソプレン重合体ブロックまたはイソプレン・ブタジエン共重合体ブロック(c−2)の割合は、好ましくは95〜50重量%、さらに好ましくは90〜55重量%の範囲である。
【0065】
本発明においては、水素添加されたブロック共重合体(c)が好ましい。水素添加されたブロック共重合体(c)を用いると、耐候性と耐熱性により優れた成形体を提供し得る熱可塑性エラストマーが得られる。
本発明で用いられるブロック共重合体(c)のメルトフローレート(MFR;ASTM D 1238、230℃、2.16kg荷重、以下同じ)は、好ましくは0.01〜30g/10分、さらに好ましくは0.01〜10g/10分の範囲にある。メルトフローレートが上記のような範囲にあるブロック共重合体(c)を用いると、耐傷付き性に優れた成形体を提供し得る熱可塑性エラストマーが得られる。
【0066】
本発明で用いられるブロック共重合体(c)のブロック形態としては、ブロック(c−1)−ブロック(c−2)−ブロック(c−1)の形態が最も好ましいが、これに限られるものではない。
【0067】
このようなブロック共重合体(c)は、たとえば、以下のような方法により製造することができる。
(1) アルキルリチウム化合物を開始剤としてスチレンまたはその誘導体、イソプレンまたはイソプレン・ブタジエン混合物を逐次重合させる方法。
(2) スチレンまたはその誘導体、次いで、イソプレンまたはイソプレン・ブタジエン混合物を重合し、これをカップリング剤によりカップリングする方法。
(3) ジリチウム化合物を開始剤としてイソプレンまたはイソプレン・ブタジエン混合物、次いで、スチレンまたはその誘導体を逐次重合させる方法。
【0068】
上記ブロック共重合体(c)の製造方法の詳細は、たとえば特開平2−300250号公報に記載されている。
また、上記のような方法により得られたブロック共重合体(c)に水添処理を行なえば、水素添加されたブロック共重合体(c)が得られる。水添されるブロックは、イソプレン重合体ブロックまたはイソプレン・ブタジエン共重合体ブロック(c−2)である。
【0069】
本発明においては、ブロック共重合体(c)は、必要に応じて、上記の成分(a)、(b)および(c)の合計量100重量部に対して、5〜60重量部、好ましくは10〜50重量部、さらに好ましくは10〜40重量部の割合で用いられる。
【0070】
ブロック共重合体(c)を上記のような割合で用いると、特に耐摩耗性に優れた成形体を提供し得る熱可塑性エラストマーが得られる。
[高級脂肪酸アミド(d)、シリコーンオイル(e)、エステル(f)およびフッ素系ポリマー(g)]
本発明で用いられる高級脂肪酸アミド(d)としては、具体的には、ラウリル酸アミド、パルミチン酸アミド、ステアリン酸アミド、ベへミン酸アミド等の飽和脂肪酸アミド;
エルカ酸アミド、オレイン酸アミド、ブラシジン酸アミド、エライジン酸アミド等の不飽和脂肪酸アミド;
メチレンビスステアリン酸アミド、メチレンビスオレイン酸アミド、エチレンビスステアリン酸アミド、エチレンビスオレイン酸アミド等のビス脂肪酸アミドなどが挙げられる。これらの中では、エルカ酸アミド、オレイン酸アミド、エチレンビスオレイン酸アミドが好ましい。
【0071】
本発明で用いられるシリコーンオイル(e)としては、具体的には、ジメチルシリコーンオイル、フェニルメチルシリコーンオイル、フルオロシリコーンオイル、テトラメチルテトラフェニルトリシロキサン、変性シリコーン油などが挙げられる。これらの中では、ジメチルシリコーンオイル、フェニルメチルシリコーンオイルが好ましく用いられる。
【0072】
このシリコーンオイル(e)の動粘度[JIS K 2283、25℃]は、10〜30,000cSt、好ましくは50〜10,000cSt、さらに好ましくは100〜5,000cStの範囲である。
【0073】
本発明で用いられるエステル(f)は、脂肪族アルコールと、ジカルボン酸あるいはモノカルボン酸とのエステルである。
このようなエステル(f)としては、具体的には、セチルアルコールと酢酸とのエステル、セチルアルコールとプロピオン酸とのエステル、セチルアルコールと酪酸とのエステル、牛脂アルコールと酢酸とのエステル、牛脂アルコールとプロピオン酸とのエステル、牛脂アルコールと酪酸とのエステル、ステアリルアルコールと酢酸とのエステル、ステアリルアルコールとプロピオン酸とのエステル、ステアリルアルコールと酪酸とのエステル、ジステアリルアルコールとフタル酸とのエステル、グリセリンモノオレート、グリセリンモノステアレート、12- 水酸化ステアレート、グリセリントリステアレート、トリメチロールプロパントリステアレート、ペンタエリスリトールテトラステアレート、ブチルステアレート、イソブチルステアレート、ステアリン酸エステル、オレイン酸エステル、ベヘン酸エステル、カルシウムソープ含有エステル、イソトリデシルステアレート、セチルパルミテート、セチルステアレート、ステアリールステアレート、ベヘニルベヘネート、モンタン酸エチレングリコールエステル、モンタン酸グリセリンエステル、モンタン酸ペンタエリスリトールエステル、カルシウム含有モンタン酸エステルなどが挙げられる。これらの中では、ジステアリルアルコールとフタル酸とのエステル、グリセリンモノオレート、グリセリンモノステアレート、ステアリン酸エステル、モンタン酸グリセリンエステルが好ましい。特にジステアリルアルコールとフタル酸とのエステル、グリセリンモノステアレート、モンタン酸グリセリンエステルが好ましい。
【0074】
本発明で用いられるフッ素系ポリマ−(g)としては、具体的には、ポリテトラフルオロエチレン、ビニリデンフルオライド共重合物などが挙げられる。これらの中では、ポリテトラフルオロエチレンが好ましい。
【0075】
本発明においては、上記の高級脂肪酸アミド(d)、シリコーンオイル(e)、エステル(f)およびフッ素系ポリマー(g)からなる群から選ばれる少なくとも1種の成分は、必要に応じて用いられ、ポリオレフィン(a)もしくはポリオレフィン組成物(a)’とオレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー(b)とブロック共重合体(c)との合計量100重量部に対して、0.01〜10重量部、好ましくは0.05〜5重量部、さらに好ましくは0.1〜5重量部の割合で用いられる。上記ブロック共重合体(c)は任意成分であるので、0重量部となる場合がある。
【0076】
[液体ないし固体の潤滑油]
前記(3)の組成物で用いられる液体潤滑油としては、石油系潤滑油、合成潤滑油などが使用される。
【0077】
石油系潤滑油としては、具体的には、流動パラフィン、スピンドル油、冷凍機油、ダイナモ油、タービン油、マシン油、シリンダー油などが使用される。
合成潤滑油としては、具体的には、合成炭化水素油、ポリグリコール油、ポリフェニルエーテル油、エステル油、リン酸エステル油、ポリクロロトリフルオロエチレン油、フルオロエステル油、塩素化ビフェニル油、シリコーン油などが使用される。
【0078】
また、前記(3)の組成物で用いられる固体潤滑油としては、具体的には、黒鉛、二硫化モリブデンが主に使用されるが、他に窒化ホウ素、二硫化タングステン、酸化鉛、ガラス粉、金属石けんなども、使用することができる。固体潤滑油は、単独でも使用することができ、また、液体潤滑油と組み合わせて使用することができ、たとえば粉末、ゾル、ゲル、サスペンソイドなどの形態で超高分子量ポリオレフィンに配合することができる。
【0079】
本発明で用いられる超高分子量ポリオレフィン組成物(B)には、必要に応じて、鉱物油系軟化剤、耐熱安定剤、帯電防止剤、耐候安定剤、老化防止剤、充填剤、着色剤、滑剤などの添加物を、本発明の目的を損なわない範囲で配合することができる。
【0080】
上記(1)〜(3)の超高分子量ポリオレフィン組成物(B)は、上記熱可塑性エラストマー(A)との共押出積層加工が行なえるため、本発明のガラスランチャンネルの製造に際し、フィルム(シート)成形工程を経ることなく、直接、熱可塑性エラストマー(A)層と超高分子量ポリオレフィン組成物(B)層とを積層することができ、経済的である。
【0081】
一方、超高分子量ポリオレフィン、たとえば上記(2)における135℃デカリン溶媒中で測定した極限粘度[η]が7〜40dl/gの範囲内にある超高分子量ポリオレフィン(a−1)単独では、上記熱可塑性エラストマー(A)との共押出積層加工を行なうことはできず、したがって、上記の熱可塑性エラストマー層と超高分子量ポリオレフィン層との積層に際しては、少なくとも一方を予めフィルム(シート)にしておく必要があり、上記超高分子量ポリオレフィン組成物(B)の場合と比較すると経済性に劣る。
【0082】
本発明に係るガラスランチャンネルにおいて、水切り部3はガラスランチャンネル本体2と同一材質からなることが好ましい。
ガラスランチャンネル本体2が熱可塑性エラストマー(A)からなっている場合には、水切り部3も同一材質で成形すれば、耐久性の点でも、滑性樹脂層9との接合強度の点でも十分に実用に耐える。
【0083】
本発明に係るガラスランチャンネルにおいて用いることのできるシャークスキン(サメ肌)は、原料熱可塑性エラストマー(A)の性状を適当に選ぶことにより、成形時に発現させ得る。
【0084】
得られたシャークスキンの外観は、樹脂やエラストマーの押出成形時に見られることのあるメルトフラクチャーとは異なり、成形品の肌が周期的に荒れて微細な凹凸を生じている。
【0085】
また、このシャークスキンの上に施された滑性樹脂層9表面にも、シャークスキンが現出していることが必要で、滑性樹脂層9の厚さは、通常3〜50μmとなるように積層する。また、本発明においては、必要に応じて、滑性樹脂層9の厚さをさらに厚くすることもできるし、また薄くすることもできる。
【0086】
なお、水切り部3が窓ガラス12と接触する部位は、窓ガラス12の進入時と退出時とでは一般に異なるから、超高分子量ポリオレフィン組成物(B)による被覆および必要に応じて施されるシャークスキンの形成は、水切り部3の比較的広い範囲に施しておくことが好ましい。
【0087】
また、図1に示す具体例では、ガラスランチャンネル本体2の内部には、窓ガラス端部と当接する部分16があるが、この部分16にも、熱可塑性エラストマー(A)からなるガラスランチャンネル本体2表面に、超高分子量ポリオレフィン組成物(B)からなる滑性樹脂層9を設けることができる。
【0088】
さらに、本発明においては、上記滑性樹脂層9の表面に起毛が存在していてもよい。上記起毛の加飾方法としては、(a)エメリーペーパーによるバフ掛けをして滑性樹脂層表面を起毛加飾する方法、(b)針布ロール通しをして滑性樹脂層表面を起毛加飾する方法、(c)ベルトサンダーもしくはドラムサンダーなどによるサンディングをして滑性樹脂層表面を起毛加飾する方法、(d)特開昭62−275,732号公報に記載されている熱微小体を衝突させて滑性樹脂層表面を起毛加飾する方法など、従来公知の起毛加飾方法が用いられる。
【0089】
【発明の効果】
本発明によれば、接着剤の塗布工程、接着剤の硬化ないし焼付工程、およびその前後のエンボス加工工程をすべて省略することができ、その結果、工程数が少なくて済み、また、作業時間を短縮することができるため、経済性に優れたガラスランチャンネルを製造することができるとともに、耐久性、閉鎖時における窓ガラスとの緊密接触性、および開閉操作時における軽快摺動性に優れ、ねじったり折り曲げたりしても超高分子量ポリオレフィン組成物層に皺が生じないガラスランチャンネルを提供することができる。
【0090】
以下、本発明を実施例により説明するが、本発明は、これら実施例に限定されるものではない。
【0091】
【実施例1】
エチレン含有量70モル%、ヨウ素価12、ムーニー粘度ML1+4 (100℃)120のエチレン・プロピレン・5-エチリデン-2- ノルボルネン共重合体ゴム[以下、EPDMと略す]80重量部と、MFR(ASTM D 1238−65T、230℃)13g/10分、密度0.91g/cm3 のポリプロピレン[以下、PPと略す]20重量部とを、バンバリーミキサーを用いて、窒素雰囲気中、180℃で5分間混練した後、この混練物をロールに通してシート状にし、これをシートカッターで裁断して角ペレットを製造した。
【0092】
次いで、この角ペレットと、1,3-ビス(tert- ブチルペルオキシイソプロピル)ベンゼン[以下、ペルオキシドと略す]0.3重量部と、ジビニルベンゼン[以下、DVBと略す]0.5重量部とをヘンシェルミキサーで攪拌混合した。
【0093】
次いで、この混合物を、L/D=40、スクリュー径50mmの2軸押出機を用いて、窒素雰囲気中、220℃で押出して熱可塑性エラストマー(A−1)を得た。
【0094】
得られた熱可塑性エラストマー(A−1)のゲル含量は、上記方法により求めたところ、85重量%であった。
この熱可塑性エラストマー(A−1)を230℃の温度で押出成形してガラスランチャンネル本体および水切り部を成形するとともに、その表面に、135℃デカリン溶媒中で測定した極限粘度[η]が28dl/gの超高分子量ポリエチレン(a−1)23重量%と、135℃デカリン中で測定した極限粘度[η]が0.73dl/gの低分子量ポリエチレン(a−2)77重量%とからなるポリエチレン組成物(a)’[135℃デカリン中で測定した極限粘度[η]:7.0dl/g]75重量部と熱可塑性エラストマー(A−1)25重量部を上述の2軸押出機で混練した超高分子量ポリエチレン組成物(B−1)を250℃で共押出積層してガラスランチャンネルを得た。
【0095】
得られたガラスランチャンネルは、ほぼ台形状の形状をしており、図3において窓枠13に固定されるガラスランチャンネル1の傾斜部と水平部との合計長さが1500mm、垂直部の長さが900mmであり、図1において本体2の底部外幅が15mm、側部外高が20mm、水切り部3の長さが10mmであり、図1に示された断面形状にほぼ等しく、超高分子量ポリエチレン組成物層の厚みは平均30μmであった。
【0096】
得られたガラスランチャンネルを試験窓枠に装着し、厚さ3.2mmの窓ガラスを嵌装して耐久試験(窓ガラス上下繰返し試験)を行なった。その結果、このガラスランチャンネルは、50,000回の窓ガラス上下繰返し試験にも耐え、ガラスランチャンネルとしての機能を維持していた。
【0097】
しかしながら、従来品のガラスランチャンネル(窓ガラス摺動部が軟質塩化ビニル樹脂層にナイロンフィルムを接着した積層構造になっている)は、25,000回で窓ガラス接触面において破壊を生じ、その結果、窓ガラスとの摩擦抵抗が著しく増大して使用に耐えられなくなった。
【0098】
また、この実施例1で得られたガラスランチャンネルの直線部を長さ30cmに切り、中央から水切り部を外側にして180度折り曲げたが、超高分子量ポリエチレン組成物層(滑性樹脂層)に顕著な皺は見られなかった。
【0099】
【実施例2】
実施例1において、ポリエチレン組成物(a)’60重量部、熱可塑性エラストマー(A−1)15重量部、およびスチレン・イソプレン・スチレンブロック共重合体[スチレン含有量:20重量%、イソプレン重合体部分における1,2−位および3,4−位で結合しているイソプレン単位含有量:55%、メルトフローレート:2.5g/10分](c)25重量部を上述の2軸押出機で混練した超高分子量ポリエチレン組成物(B−2)を用いた以外は、実施例1と同様に行なった。
【0100】
得られたガラスランチャンネルを用いて、窓ガラス上下繰返し試験を実施例1と同様にして行なった結果、50,000回に耐えた。また、上述の折り曲げに対しても、超高分子量ポリエチレン組成物層に顕著な皺は見られなかった。
【0101】
【実施例3】
実施例1において、EPDMおよびPPのほかに、ブチルゴム[エッソ社製、IIR−065、不飽和度0.8モル%、以下、IIRと略す]10重量部およびパラフィン系プロセスオイル[出光興産(株)製、商品名 ダイアナプロセスオイル]30重量部を配合して熱可塑性エラストマー(A−2)を製造した以外は、実施例1と同様に行なった。得られた熱可塑性エラストマー(A−2)のゲル含量は、70%であった。
【0102】
得られたガラスランチャンネルは、窓ガラス上下繰返し試験50,000回に耐えた。また、上述の折り曲げに対して、超高分子量ポリエチレン組成物層に顕著な皺は見られなかった。
【0103】
【実施例4】
実施例1において、ポリエチレン組成物(a)’75重量部および熱可塑性エラストマー(A−1)25重量部の他に、エルカ酸アミド0.5重量部から超高分子量ポリエチレン組成物(B−3)を調製した以外は、実施例1と同様に行なった。
【0104】
得られたガラスランチャンネルは、窓ガラス上下繰返し試験50,000回に耐えた。また、上述の折り曲げに対しても、超高分子量ポリエチレン組成物層に顕著な皺は見られなかった。
【0105】
【比較例1】
実施例1において、超高分子量ポリエチレン組成物(B−1)の代わりに、ポリエチレン組成物(a)’を単独で用いた以外は、実施例1と同様に行なった。
【0106】
得られたガラスランチャンネルは、窓ガラス上下繰返し試験50,000回に耐えた。しかしながら、上述の折り曲げに対しては、超高分子量ポリエチレン組成物層の部分に皺が生じ白化が見られた。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】図1は、本発明に係るガラスランチャンネルの断面図である。
【図2】図2は、図1に示すガラスランチャンネルの窓ガラスとの接触部の拡大断面図である。
【図3】図3は、ガラスランチャンネルの自動車ドアへの取付けを説明する図である。
【図4】図4は、窓ガラスの開放時におけるガラスランチャンネルの状態を示す断面図である。
【図5】図5は、窓ガラスの閉鎖時におけるガラスランチャンネルの状態を示す断面図である。
【符号の説明】
1 ・・・・・ガラスランチャンネル
1a ・・・底壁
1b ・・・側壁
1c ・・・溝部
2 ・・・・・ガラスランチャンネル本体
3 ・・・・・水切り部
4 ・・・・・窓ガラス接触部
7 ・・・・・熱可塑性エラストマーからなる基体層
8 ・・・・・微小凹凸の繰返し模様(必要に応じて施される)を有する基体層表面
9 ・・・・・超高分子量ポリオレフィン組成物からなる滑性樹脂層
10 ・・・微小凹凸の繰り返し模様(必要に応じて施される)を有する滑性樹脂層表面[0001]
TECHNICAL FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a glass run channel, and more particularly, to a glass run channel provided with a window glass sliding portion constituted by a laminate made of a thermoplastic elastomer base layer and a slipping resin surface layer.
[0002]
TECHNICAL BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
In general, a window glass in a vehicle of an automobile needs to be opened and closed by raising and lowering for ventilation and ventilation or for talking with the outside of the vehicle. It is called a glass run channel between the window glass and the window frame in order to make it possible to perform a close (liquid-tight) sealing operation between the window glass and the window frame while facilitating the opening and closing operation of the window glass. A guide member is provided.
[0003]
The conventional glass run channel is formed of a soft synthetic resin such as a soft vinyl chloride resin or a vulcanized rubber such as an ethylene-propylene-diene copolymer rubber, and is extended from both ends of the bottom wall and the bottom wall. A glass run channel main body having a substantially U-shaped cross section and having a groove formed therein, and stretched so as to be close to each other toward the bottom wall from the vicinity of the tip of both side walls of the glass run channel main body. It consists of a tongue-shaped draining part.
[0004]
In the conventional glass run channel, the window glass sliding part has a nylon film or the like bonded to the surface to improve the separation from the drainage part of the window glass and to prevent the window glass from becoming dirty. In order to reduce the contact area with the window glass, embossing is performed before or after lamination of the nylon film or the like.
[0005]
In such a glass run channel, since there is no adhesion between the above-mentioned soft synthetic resin or vulcanized rubber and the surface material of nylons, the glass run channel main body is molded by using a soft synthetic resin or vulcanized rubber. It requires a process of applying an adhesive to the molded product and laminating a film such as nylon, and also requires embossing before or after this bonding. There is an inconvenience that it takes.
[0006]
In addition, since such a glass run channel has a lamination process with an adhesive, there is also a problem in durability, and there is a drawback that peeling between the surface film layer and the substrate is likely to occur due to aging and outdoor exposure. is there. Furthermore, the uneven pattern that can be formed by embossing is not yet satisfactory in the combination of fineness and uniformity, close contact between the window glass sliding part and the window glass at the time of closing, and at the time of opening There is still room for improvement in the light sliding property between the window glass sliding portion and the window glass.
[0007]
Therefore, the present inventors have intensively studied to solve the above-described problems of the glass run channel, and are composed of crystalline polyolefin and rubber as an elastomer constituting at least the sliding portion of the glass run channel. If a thermoplastic elastomer is selected and a specific ultra-high molecular weight polyolefin composition layer is laminated on the thermoplastic elastomer layer by heat-sealing, the manufacturing operation is easy, and durability and window glass when closed It was found that a glass run channel excellent in close contact with the glass and light sliding property with the window glass when opened could be obtained, and a new glass run channel was proposed. (JP-A-5-4522, JP-A-5-4308)
[0008]
However, this glass run channel has a high rigidity when an ultra high molecular weight polyolefin, for example, ultra high molecular weight polyethylene is used alone in the ultra high molecular weight polyolefin composition layer. When the glass run channel is twisted or bent, wrinkles are generated in the ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin composition layer, which may impair the appearance of the product.
[0009]
As a result of repeated studies to improve this point, the present inventors have used an ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin composition and an olefin-based thermoplastic elastomer as the ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin composition. The inventors have found that a glass run channel having performance and capable of generating no wrinkles in the ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin composition layer even when twisted or bent is obtained, and the present invention has been completed.
[0010]
OBJECT OF THE INVENTION
The present invention is intended to solve the problems associated with the prior art as described above, can be manufactured by simplifying the manufacturing process, durability, close contact with the window glass when closed, Another object of the present invention is to provide a glass run channel which is excellent in light slidability with a window glass at the time of opening and does not generate wrinkles in an ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin composition layer even when twisted or bent.
[0011]
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
The glass run channel according to the present invention is:
A glass run channel body comprising a bottom wall and side walls extending from both ends of the bottom wall, having a substantially U-shaped cross section and having grooves formed therein, and the bottom wall from the vicinity of the ends of both side walls of the glass run channel body A glass run channel composed of a tongue-shaped drainer stretched so as to be close to each other toward the
A window glass contact portion which is a surface in contact with the window glass of the draining portion,
A thermoplastic elastomer (A) layer composed of crystalline polyolefin and rubber, an ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin composition (B) layer, and
The ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin composition (B) layer is configured to come into contact with the window glass,
The ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin composition (B) is
Ultra high molecular weight polyolefin (a-1) having an intrinsic viscosity [η] measured in a decalin solvent of 135 ° C. within a range of 7 to 40 dl / g, and an intrinsic viscosity [η] measured in a decalin solvent of 135 ° C. of 0. 0.1 to 5 dl / g of the polyolefin (a-2), and the ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin (a-1) comprises the ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin (a-1) and the polyolefin (a- 2) with respect to the total weight of 100% by weight and 15 to 40% by weight, andPolyolefin having an intrinsic viscosity [η] measured in a decalin solvent of 135 ° C. within a range of 3.5 to 8.3 dl / g(A) '10 to 90 parts by weight, and
90 to 10 parts by weight of olefinic thermoplastic elastomer (b) comprising a crystalline olefinic resin and an olefinic rubber [component(A) 'And (b) is 100 parts by weight].
[0012]
As a preferable example of the thermoplastic elastomer (A) used in the present invention,
70 to 10 parts by weight of crystalline polypropylene (A-1),
30 to 90 parts by weight of rubber (A-2) made of ethylene / propylene copolymer rubber or ethylene / propylene / diene copolymer rubber [the total amount of components (A-1) and (A-2) is 100 parts by weight And
And a thermoplastic elastomer in which the rubber (A-2) is crosslinked, which is obtained by dynamically heat-treating a mixture of the above in the presence of an organic peroxide.
[0013]
MaThe ultra-high molecular weight polyolefin composition (B) preferably used in the present invention is
Ultra high molecular weight polyolefin (a-1) having an intrinsic viscosity [η] measured in a decalin solvent of 135 ° C. within a range of 7 to 40 dl / g, and an intrinsic viscosity [η] measured in a decalin solvent of 135 ° C. of 0. 0.1 to 5 dl / g of the polyolefin (a-2), and the ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin (a-1) comprises the ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin (a-1) and the polyolefin (a- 2) and the intrinsic viscosity [η] measured in a decalin solvent at 135 ° C. is in the range of 3.5 to 8.3 dl / g. The polyolefin composition (a) within 10 to 90 parts by weight,
85 to 5 parts by weight of an olefinic thermoplastic elastomer (b) comprising a crystalline olefinic resin and an olefinic rubber, and
A polymer block (c-1) of styrene or a derivative thereof and an isoprene polymer block and / or an isoprene-butadiene copolymer block, which are bonded at 1,2-position and 3,4-position with respect to all isoprene units. 5 to 60 parts by weight of a block copolymer (c) which may be hydrogenated with a polymer and / or copolymer block (c-2) having an isoprene unit content of 40% or more [ The total of components (a) ′, (b) and (c) is 100 parts by weight].
[0014]
Further, the ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin composition (B) includes, in addition to the polyolefin (a) or the polyolefin composition (a) ', and the olefinic thermoplastic elastomer (b),
A polymer block (c-1) of styrene or a derivative thereof and an isoprene polymer block and / or an isoprene-butadiene copolymer block, which are bonded at 1,2-position and 3,4-position with respect to all isoprene units. A block copolymer (c) which may be hydrogenated and comprising a polymer and / or copolymer block (c-2) having an isoprene unit content of 40% or more, and / or
Contains at least one component selected from the group consisting of higher fatty acid amide (d), silicone oil (e), ester (f) of aliphatic alcohol and dicarboxylic acid or monocarboxylic acid, and fluorine-based polymer (g) You may do it.
[0015]
As a preferred example of the olefinic thermoplastic elastomer (b) constituting the ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin composition (B),
70 to 10 parts by weight of crystalline polypropylene (A-1),
30 to 90 parts by weight of rubber (A-2) made of ethylene / propylene copolymer rubber or ethylene / propylene / diene copolymer rubber [the total amount of components (A-1) and (A-2) is 100 parts by weight And
And a thermoplastic elastomer in which the rubber (A-2) is crosslinked, which is obtained by dynamically heat-treating a mixture of the above in the presence of an organic peroxide. In the present invention, the thermoplastic elastomer (A) and the olefinic thermoplastic elastomer (b) may be the same or different.
[0016]
The ultra high molecular weight polyolefin composition (B) may contain 1 to 20% by weight of a liquid or solid lubricating oil per ultra high molecular weight polyolefin composition (B).
[0017]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
Hereinafter, an example of the glass run channel according to the present invention will be specifically described with reference to the drawings.
[0018]
FIG. 1 is a cross-sectional view showing a cross-sectional structure of an example of a glass run channel according to the present invention.
In FIG. 1, 1 indicates the glass run channel of the present invention as a whole. The
[0019]
Although the
[0020]
FIGS. 3 to 5 are a perspective view and a sectional view of a window frame portion for explaining a method of mounting the glass run channel configured as described above to a window frame of an automobile.
As shown in FIGS. 3 to 5, a
[0021]
In order to fix the
[0022]
As shown in FIG. 4, when the
[0023]
According to the present invention, the
[0024]
That is, the thermoplastic elastomer (A) used in the present invention can be thermoformed into an arbitrary shape and size, and has elasticity, flexibility, and flexibility required for the window slide portion of the glass run channel. It has excellent properties such as compressibility, and also has excellent properties such as durability, weather resistance, and water resistance. The thermoplastic elastomer (A) exhibits strong adhesiveness to the slipping resin layer 9 made of the ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin composition (B) serving as the surface material layer, and is thermally bonded to the slipping resin layer 9. It is possible to form a laminated structure excellent in interlayer adhesive strength immediately after bonding and over time, and further in interlayer adhesive strength after a weather resistance test. Moreover, the thermoplastic elastomer (A) used as the
[0025]
According to the present invention, by adopting the above-described configuration, the adhesive application process, the adhesive curing or baking process, and the embossing process before or after it are all omitted, with a small number of processes and a small amount of labor. A glass run channel can be produced efficiently. In addition, by providing the slippery resin layer 9 made of the ultra-high molecular weight polyolefin composition (B) as a surface material layer, not only can the friction coefficient with the window glass be reduced, but also an uneven pattern by conventional embossing Compared to the above, it was possible to form a uniform shark-skin-like unevenness on the surface with a uniform pitch. Therefore, in the glass run channel according to the present invention, when the window glass is closed, close contact (liquid tight) with the window glass is possible, and when the window glass is opened, its sliding resistance is reduced, so that it is smooth and light. Open and close operation is possible.
[0026]
Thermoplastic elastomer (A)
The thermoplastic elastomer (A) used in the present invention is composed of crystalline polyolefin and rubber.
[0027]
Examples of the crystalline polyolefin used in the present invention include homopolymers or copolymers of α-olefins having 2 to 20 carbon atoms.
Specific examples of the crystalline polyolefin include the following (co) polymers.
(1) Ethylene homopolymer
(Manufacturing method may be either low pressure method or high pressure method)
(2) Copolymers of ethylene and other α-olefins up to 10 mol% or vinyl monomers such as vinyl acetate and ethyl acrylate
(3) Propylene homopolymer
(4) Random copolymers of propylene and other α-olefins up to 10 mol%
(5) Block copolymer of propylene and other α-olefin of 30 mol% or less
(6) 1-butene homopolymer
(7) Random copolymers of 1-butene and other α-olefins of 10 mol% or less
(8) 4-Methyl-1-pentene homopolymer
(9) Random copolymers of 4-methyl-1-pentene and other α-olefins of 20 mol% or less
Specific examples of the α-olefin include ethylene, propylene, 1-butene, 4-methyl-1-pentene, 1-hexene, and 1-octene.
[0028]
The rubber used in the present invention is not particularly limited, but olefin copolymer rubber is preferable.
The olefin copolymer rubber is an amorphous random elastic copolymer mainly composed of an α-olefin having 2 to 20 carbon atoms, and is an amorphous α composed of two or more α-olefins. -Olefin copolymer, α-olefin / non-conjugated diene copolymer composed of two or more kinds of α-olefin and non-conjugated diene.
[0029]
Specific examples of such olefin copolymer rubbers include the following rubbers.
(1) Ethylene / α-olefin copolymer rubber
[Ethylene / α-olefin (molar ratio) = about 90/10 to 50/50]
(2) Ethylene / α-olefin / non-conjugated diene copolymer rubber
[Ethylene / α-olefin (molar ratio) = about 90/10 to 50/50]
(3) Propylene / α-olefin copolymer rubber
[Propylene / α-olefin (molar ratio) = about 90/10 to 50/50]
(4) Butene / α-olefin copolymer rubber
[Butene / α-olefin (molar ratio) = about 90/10 to 50/50]
Specific examples of the α-olefin include α-olefins similar to the specific examples of the α-olefin constituting the crystalline polyolefin.
[0030]
Specific examples of the non-conjugated diene include dicyclopentadiene, 1,4-hexadiene, cyclooctadiene, methylene norbornene, and ethylidene norbornene.
[0031]
Mooney viscosity ML of these copolymer rubbers1 + 4 (100 ° C.) is preferably 10 to 250, particularly preferably 40 to 150. The iodine value when the non-conjugated diene is copolymerized is preferably 25 or less.
[0032]
In the thermoplastic elastomer, the olefin copolymer rubber can exist in all cross-linked states such as uncrosslinked, partially cross-linked, and overall cross-linked, but in the present invention, it exists in a cross-linked state. It is preferable that it exists in a partially crosslinked state.
[0033]
In addition to the above olefin copolymer rubber, other rubbers such as styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR), nitrile rubber (NBR), natural rubber (NR), butyl rubber (IIR) are used as the rubber used in the present invention. And diene rubbers such as SEBS and polyisobutylene.
[0034]
In the thermoplastic elastomer (A) used in the present invention, the weight blending ratio of crystalline polyolefin and rubber (crystalline polyolefin / rubber) is usually 90/10 to 5/95, preferably 70/30 to 10/90. Range.
[0035]
When the olefin copolymer rubber and other rubber are used in combination as the rubber, the other rubber is preferably 40 parts by weight or less, preferably 100 parts by weight or less of the total amount of crystalline polyolefin and rubber. Is blended at a ratio of 5 to 20 parts by weight.
[0036]
The thermoplastic elastomer (A) preferably used in the present invention comprises crystalline polypropylene and ethylene / α-olefin copolymer rubber or ethylene / α-olefin / non-conjugated diene copolymer rubber. These are present in a partially crosslinked state, and the weight blending ratio of crystalline polypropylene to rubber (crystalline polypropylene / rubber) is in the range of 70/30 to 10/90.
[0037]
The thermoplastic elastomer (A) may contain additives such as mineral oil softeners, heat stabilizers, antistatic agents, weathering stabilizers, anti-aging agents, fillers, colorants, and lubricants as necessary. , And can be blended as long as the object of the present invention is not impaired.
[0038]
As a more specific example of the thermoplastic elastomer (A) preferably used in the present invention,
70 to 10 parts by weight of crystalline polypropylene (A-1),
30 to 90 parts by weight of rubber (A-2) made of ethylene / propylene copolymer rubber or ethylene / propylene / diene copolymer rubber [the total amount of components (A-1) and (A-2) is 100% by weight Part]
5 to 100 parts by weight of rubber (A-3) and / or mineral oil softener (A-4) other than this rubber (A-2)
And a thermoplastic elastomer in which the rubber (A-2) is crosslinked, which is obtained by dynamically heat-treating a mixture of the above in the presence of an organic peroxide.
[0039]
Specific examples of the organic peroxide include dicumyl peroxide, di-tert-butyl peroxide, 2,5-dimethyl-2,5-di- (tert-butylperoxy) hexane, 2,5-dimethyl-2, 5-di- (tert-butylperoxy) hexyne-3, 1,3-bis (tert-butylperoxyisopropyl) benzene, 1,1-bis (tert-butylperoxy) -3,3,5-trimethylcyclohexane, n -Butyl-4,4-bis (tert-butylperoxy) valerate, benzoyl peroxide, p-chlorobenzoyl peroxide, 2,4-dichlorobenzoyl peroxide, tert-butylperoxybenzoate, tert-butylperbenzoate, tert-butylperoxyisopropyl Examples include carbonate, diacetyl peroxide, lauroyl peroxide, tert-butyl cumyl peroxide and the like.
[0040]
Among these, in terms of odor and scorch stability, 2,5-dimethyl-2,5-di- (tert-butylperoxy) hexane, 2,5-dimethyl-2,5-di- (tert- Butylperoxy) hexyne-3, 1,3-bis (tert-butylperoxyisopropyl) benzene, 1,1-bis (tert-butylperoxy) -3,3,5-trimethylcyclohexane, n-butyl-4,4- Bis (tert-butylperoxy) valerate is preferred, and 1,3-bis (tert-butylperoxyisopropyl) benzene is most preferred.
[0041]
In the present invention, the organic peroxide is used in a proportion of 0.05 to 3% by weight, preferably 0.1 to 1% by weight, based on 100% by weight of the total amount of crystalline polyolefin and rubber.
[0042]
In the partial crosslinking treatment with the above organic peroxide, sulfur, p-quinonedioxime, p, p'-dibenzoylquinonedioxime, N-methyl-N-4-dinitrosoaniline, nitrosobenzene, diphenylguanidine, trimethylolpropane- Peroxy crosslinking aids such as N, N'-m-phenylene dimaleimide, or divinylbenzene, triallyl cyanurate, ethylene glycol dimethacrylate, diethylene glycol dimethacrylate, polyethylene glycol dimethacrylate, trimethylolpropane trimethacrylate, allyl methacrylate Polyfunctional methacrylate monomers such as, polyfunctional vinyl monomers such as vinyl butyrate and vinyl stearate can be blended.
[0043]
By using such a compound, a uniform and mild crosslinking reaction can be expected. In particular, divinylbenzene is most preferred in the present invention. Divinylbenzene is easy to handle, has a good compatibility with the crystalline polyolefin and rubber, which are the main components of the cross-linked product, and has an action of solubilizing the organic peroxide. Therefore, a thermoplastic elastomer having a uniform crosslinking effect by heat treatment and a balance between fluidity and physical properties can be obtained.
[0044]
It is preferable to use the crosslinking aid or polyfunctional vinyl monomer as described above in a proportion of 0.1 to 2% by weight, particularly 0.3 to 1% by weight, based on the entire cross-linked product. When the blending ratio of the crosslinking aid or the polyfunctional vinyl monomer exceeds 2% by weight, the crosslinking reaction proceeds too quickly when the blending amount of the organic peroxide is large. On the other hand, when the amount of the organic peroxide is small, the crosslinking aid and the polyfunctional vinyl monomer remain as unreacted monomers in the thermoplastic elastomer, and the thermoplastic elastomer is heated during processing and molding. Changes in physical properties due to history may occur. Therefore, the crosslinking aid and the polyfunctional vinyl monomer should not be added in excess.
[0045]
The above “dynamic heat treatment” means kneading the above components in a molten state.
As the kneading device, a conventionally known kneading device, for example, an open type mixing roll, a non-open type Banbury mixer, an extruder, a kneader, a continuous mixer, or the like is used. Among these, a non-open type kneading apparatus is preferable, and kneading is preferably performed in an atmosphere of an inert gas such as nitrogen gas or carbon dioxide gas.
[0046]
The kneading is desirably performed at a temperature at which the half-life of the organic peroxide used is less than 1 minute. The kneading temperature is usually 150 to 280 ° C., preferably 170 to 240 ° C., and the kneading time is 1 to 20 minutes, preferably 3 to 10 minutes. The applied shear force is 100 sec as the shear rate.-1Or more, preferably 500 to 10,000 sec-1It is determined within the range.
[0047]
The thermoplastic elastomer (A) particularly preferably used in the present invention is partially crosslinked. This “partially crosslinked” means that the gel content measured by the following method is 20 to 98%. In the present invention, the gel content is preferably in the range of 40 to 98%.
[0048]
[Measurement method of gel content]
About 100 mg of a sample of thermoplastic elastomer is weighed and cut into 0.5 mm × 0.5 mm × 0.5 mm strips, and the resulting strips are then placed in 30 ml of cyclohexane in a sealed container at 23 ° C. Soak for 48 hours.
[0049]
Next, the sample is taken out on a filter paper and dried at room temperature until a constant weight is obtained for 72 hours or more.
A value obtained by subtracting the weight of the cyclohexane insoluble component (fibrous filler, filler, pigment, etc.) other than the polymer component from the weight of the dry residue is defined as “corrected final weight (Y)”.
[0050]
On the other hand, the value obtained by subtracting the weight of the cyclohexane-soluble component (for example, softener) other than the polymer component and the weight of the cyclohexane-insoluble component (fibrous filler, filler, pigment, etc.) other than the polymer component from the weight of the sample is corrected. Initial weight (X) ”.
[0051]
Here, the gel content (cyclohexane insoluble matter) is determined by the following formula.
Gel content [wt%] = [corrected final weight (Y)] / [corrected initial weight (X)] × 100
Since the thermoplastic elastomer (A) used in the present invention is composed of crystalline polyolefin and rubber, it has excellent fluidity.
[0052]
The thermoplastic elastomer (A) as described above can be molded using a conventionally used molding apparatus such as compression molding, transfer molding, injection molding or extrusion molding.
[0053]
Ultra-high molecular weight polyolefin composition (B)
Specific examples of the ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin composition (B) used in the present invention include the following ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin compositions.
[0054]
(1) a polyolefin (a) having an intrinsic viscosity [η] measured in a decalin solvent at 135 ° C. in the range of 3.5 to 8.3 dl / g;
An olefin thermoplastic elastomer (b) comprising a crystalline olefin resin and an olefin rubber, and if necessary,
A polymer block (c-1) of styrene or a derivative thereof and an isoprene polymer block and / or an isoprene-butadiene copolymer block, which are bonded at 1,2-position and 3,4-position with respect to all isoprene units. A block copolymer (c) which may be hydrogenated and comprising a polymer and / or copolymer block (c-2) having an isoprene unit content of 40% or more, and / or
At least one component selected from the group consisting of higher fatty acid amide (d), silicone oil (e), ester (f) of aliphatic alcohol and dicarboxylic acid or monocarboxylic acid, and fluorine-based polymer (g);
A composition comprising:
[0055]
(2) Ultra high molecular weight polyolefin (a-1) having an intrinsic viscosity [η] measured in a 135 ° C. decalin solvent of 7 to 40 dl / g, preferably 10 to 35 dl / g, and a 135 ° C. decalin solvent The intrinsic viscosity [η] measured in 0.1 to 5 dl / g, preferably consisting of low to high molecular weight polyolefin (a-2) in the range of 0.1 to 2 dl / g, The ultra high molecular weight polyolefin (a-1) is 15 to 40% by weight, preferably 18 to 35% by weight, based on 100% by weight of the total weight of the ultra high molecular weight polyolefin (a-1) and the polyolefin (a-2). And a polyolefin composition (a) ′ having an intrinsic viscosity [η] measured in a decalin solvent of 135 ° C. in the range of 3.5 to 8.3 dl / g,
An olefin thermoplastic elastomer (b) comprising a crystalline olefin resin and an olefin rubber, and if necessary,
The block copolymer (c), and / or
At least one component selected from the group consisting of higher fatty acid amide (d), silicone oil (e), ester (f) of aliphatic alcohol and dicarboxylic acid or monocarboxylic acid, and fluorine-based polymer (g);
A composition comprising:
[0056]
(3) A composition comprising the ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin composition according to (1) or (2) above and 1 to 20% by weight of a liquid or solid lubricating oil per ultra high molecular weight polyolefin composition.
[0057]
[Polyolefin (a), ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin (a-1) and polyolefin (a-2)]
The polyolefin (a) constituting the composition (1), the ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin (a-1) and the polyolefin (a-2) constituting the composition (2) are, for example, ethylene, propylene, 1- Homopolymers or copolymers of α-olefins such as butene, 1-pentene, 1-hexene, 1-octene, 1-decene, 1-dodecene, 4-methyl-1-pentene, 3-methyl-1-pentene Consists of. In the present invention, an ethylene homopolymer and a copolymer composed mainly of ethylene and composed of ethylene and another α-olefin are desirable.
[0058]
[Olefin-based thermoplastic elastomer (b)]
The said olefin type thermoplastic elastomer (b) can use the material similar to the olefin type thermoplastic elastomer (A) mentioned above. Components (b) and (A) may be exactly the same or different.
[0059]
[Block copolymer (c)]
The block copolymer (c) used in the present invention is a block (c-2) comprising a polymer block (c-1) of styrene or a derivative thereof and a specific isoprene polymer or a specific isoprene-butadiene copolymer. And may be hydrogenated.
[0060]
The polymer component constituting the block (c-1) is styrene or a derivative thereof.
Specific examples of styrene derivatives include α-methylstyrene, 1-vinylnaphthalene, 2-vinylnaphthalene, 3-methylstyrene, 4-propylstyrene, 4-cyclohexylstyrene, 4-dodecylstyrene, 2-ethyl- 4-Benzylstyrene, 4- (phenylbutyl) styrene and the like can be mentioned. As the polymer component constituting the block (c-1), styrene and α-methylstyrene are preferable.
[0061]
The polymer or copolymer constituting the block (c-2) is an isoprene polymer or an isoprene-butadiene copolymer, and is in the 1,2-position and 3,4-position with respect to the entire isoprene unit shown below. The content of the isoprene unit bonded at is 40% or more, preferably 45% or more.
[0062]
[Chemical 1]
[0063]
In the present invention, when the content of isoprene units bonded at 1,2-position and 3,4-position with respect to all isoprene units is 40% or more, thermoplasticity capable of providing a molded article having excellent scratch resistance. An elastomer can be obtained.
[0064]
The proportion of the polymer block (c-1) of styrene or a derivative thereof in the block copolymer (c) is preferably 5 to 50% by weight, more preferably 10 to 45% by weight. That is, the proportion of the isoprene polymer block or isoprene-butadiene copolymer block (c-2) is preferably in the range of 95 to 50% by weight, more preferably 90 to 55% by weight.
[0065]
In the present invention, a hydrogenated block copolymer (c) is preferred. When the hydrogenated block copolymer (c) is used, a thermoplastic elastomer capable of providing a molded article superior in weather resistance and heat resistance can be obtained.
The melt flow rate (MFR; ASTM D 1238, 230 ° C., 2.16 kg load, the same applies hereinafter) of the block copolymer (c) used in the present invention is preferably 0.01 to 30 g / 10 minutes, more preferably It exists in the range of 0.01-10 g / 10min. When the block copolymer (c) having a melt flow rate in the above range is used, a thermoplastic elastomer capable of providing a molded article having excellent scratch resistance can be obtained.
[0066]
As the block form of the block copolymer (c) used in the present invention, the form of block (c-1) -block (c-2) -block (c-1) is most preferable, but is not limited thereto. is not.
[0067]
Such a block copolymer (c) can be produced, for example, by the following method.
(1) A method of sequentially polymerizing styrene or a derivative thereof, isoprene or an isoprene-butadiene mixture using an alkyllithium compound as an initiator.
(2) A method of polymerizing styrene or a derivative thereof, then isoprene or an isoprene-butadiene mixture, and coupling this with a coupling agent.
(3) A method of sequentially polymerizing isoprene or an isoprene-butadiene mixture and then styrene or a derivative thereof using a dilithium compound as an initiator.
[0068]
Details of the method for producing the block copolymer (c) are described, for example, in JP-A-2-300250.
Moreover, if the block copolymer (c) obtained by the above methods is hydrogenated, the hydrogenated block copolymer (c) will be obtained. The hydrogenated block is an isoprene polymer block or an isoprene / butadiene copolymer block (c-2).
[0069]
In the present invention, the block copolymer (c) is preferably 5 to 60 parts by weight based on 100 parts by weight of the total amount of the components (a), (b) and (c), if necessary. Is used in a proportion of 10 to 50 parts by weight, more preferably 10 to 40 parts by weight.
[0070]
When the block copolymer (c) is used in the above ratio, a thermoplastic elastomer that can provide a molded article having particularly excellent wear resistance can be obtained.
[Higher fatty acid amide (d), silicone oil (e), ester (f) and fluorine-based polymer (g)]
Specific examples of the higher fatty acid amide (d) used in the present invention include saturated fatty acid amides such as lauric acid amide, palmitic acid amide, stearic acid amide, and behemic acid amide;
Unsaturated fatty acid amides such as erucic acid amide, oleic acid amide, brassic acid amide, elaidic acid amide;
Examples thereof include bis fatty acid amides such as methylene bis stearic acid amide, methylene bis oleic acid amide, ethylene bis stearic acid amide, and ethylene bis oleic acid amide. Of these, erucic acid amide, oleic acid amide, and ethylenebisoleic acid amide are preferable.
[0071]
Specific examples of the silicone oil (e) used in the present invention include dimethyl silicone oil, phenylmethyl silicone oil, fluorosilicone oil, tetramethyltetraphenyltrisiloxane, and modified silicone oil. Of these, dimethyl silicone oil and phenylmethyl silicone oil are preferably used.
[0072]
The kinematic viscosity [JIS K 2283, 25 ° C.] of the silicone oil (e) is in the range of 10 to 30,000 cSt, preferably 50 to 10,000 cSt, more preferably 100 to 5,000 cSt.
[0073]
The ester (f) used in the present invention is an ester of an aliphatic alcohol and a dicarboxylic acid or a monocarboxylic acid.
Specific examples of such esters (f) include esters of cetyl alcohol and acetic acid, esters of cetyl alcohol and propionic acid, esters of cetyl alcohol and butyric acid, esters of beef tallow alcohol and acetic acid, tallow alcohol Ester of beryllic acid and propionic acid, ester of beef tallow alcohol and butyric acid, ester of stearyl alcohol and acetic acid, ester of stearyl alcohol and propionic acid, ester of stearyl alcohol and butyric acid, ester of distearyl alcohol and phthalic acid, Glycerol monooleate, glycerin monostearate, 12-hydroxystearate, glycerin tristearate, trimethylolpropane tristearate, pentaerythritol tetrastearate, butyl stearate, isobutyl stearate , Stearic acid ester, oleic acid ester, behenic acid ester, calcium soap-containing ester, isotridecyl stearate, cetyl palmitate, cetyl stearate, stearyl stearate, behenyl behenate, montanic acid ethylene glycol ester, Examples include glycerin montanate, pentaerythritol ester of montanate, and montanic acid ester containing calcium. Among these, esters of distearyl alcohol and phthalic acid, glycerin monooleate, glycerin monostearate, stearic acid ester, and montanic acid glycerin ester are preferable. Particularly preferred are esters of distearyl alcohol and phthalic acid, glycerin monostearate, and glycerin montanate.
[0074]
Specific examples of the fluorine-based polymer (g) used in the present invention include polytetrafluoroethylene and vinylidene fluoride copolymer. Of these, polytetrafluoroethylene is preferred.
[0075]
In the present invention, at least one component selected from the group consisting of the above higher fatty acid amide (d), silicone oil (e), ester (f), and fluorine-based polymer (g) is used as necessary. , 0.01 to 10 parts by weight, preferably 100 parts by weight of the total amount of polyolefin (a) or polyolefin composition (a) ′, olefinic thermoplastic elastomer (b) and block copolymer (c), Is used in a proportion of 0.05 to 5 parts by weight, more preferably 0.1 to 5 parts by weight. Since the said block copolymer (c) is an arbitrary component, it may become 0 weight part.
[0076]
[Liquid or solid lubricant]
As the liquid lubricating oil used in the composition (3), petroleum-based lubricating oil, synthetic lubricating oil and the like are used.
[0077]
Specifically, liquid paraffin, spindle oil, refrigerating machine oil, dynamo oil, turbine oil, machine oil, cylinder oil and the like are used as the petroleum-based lubricating oil.
Specific examples of the synthetic lubricating oil include synthetic hydrocarbon oil, polyglycol oil, polyphenyl ether oil, ester oil, phosphate ester oil, polychlorotrifluoroethylene oil, fluoroester oil, chlorinated biphenyl oil, silicone Oil is used.
[0078]
Specifically, as the solid lubricating oil used in the composition of (3), specifically, graphite and molybdenum disulfide are mainly used. In addition, boron nitride, tungsten disulfide, lead oxide, glass powder Metal soaps can also be used. The solid lubricating oil can be used alone or in combination with a liquid lubricating oil, and can be blended with the ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin in the form of powder, sol, gel, suspension, etc.
[0079]
In the ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin composition (B) used in the present invention, a mineral oil softener, a heat stabilizer, an antistatic agent, a weathering stabilizer, an antiaging agent, a filler, a colorant, Additives such as a lubricant can be blended within a range that does not impair the object of the present invention.
[0080]
Since the ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin composition (B) of the above (1) to (3) can be co-extruded and laminated with the thermoplastic elastomer (A), the film ( Sheet) The thermoplastic elastomer (A) layer and the ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin composition (B) layer can be directly laminated without going through the molding step, which is economical.
[0081]
On the other hand, an ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin, for example, an ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin (a-1) alone having an intrinsic viscosity [η] measured in a decalin solvent at 135 ° C. in the above (2) in the range of 7 to 40 dl / g, Coextrusion laminating with the thermoplastic elastomer (A) cannot be performed. Therefore, at the time of laminating the thermoplastic elastomer layer and the ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin layer, at least one of them is previously formed into a film (sheet). It is necessary and is inferior in economic efficiency as compared with the case of the ultra-high molecular weight polyolefin composition (B).
[0082]
In the glass run channel according to the present invention, the draining
When the glass run channel
[0083]
The shark skin (shark skin) that can be used in the glass run channel according to the present invention can be expressed at the time of molding by appropriately selecting the properties of the raw thermoplastic elastomer (A).
[0084]
The appearance of the obtained shark skin is different from the melt fracture that may be seen during extrusion molding of resins and elastomers, and the skin of the molded product is periodically roughened to produce fine irregularities.
[0085]
Further, it is necessary that the sharkskin appears on the surface of the slippery resin layer 9 applied on the sharkskin, and the thickness of the slippery resin layer 9 is usually 3 to 50 μm. Laminate. In the present invention, the thickness of the slipping resin layer 9 can be further increased or decreased as necessary.
[0086]
In addition, since the site | part which the draining
[0087]
In the specific example shown in FIG. 1, the glass run channel
[0088]
Furthermore, in the present invention, napping may exist on the surface of the sliding resin layer 9. As for the above-mentioned raising decoration method, (a) buffing with emery paper and raising the surface of the sliding resin layer, (b) passing through the needle cloth roll and raising the sliding resin layer surface. A method of decorating, (c) a method of sanding with a belt sander or a drum sander to decorate the surface of the slipping resin layer, and (d) a thermal micrometer described in JP-A-62-275732. Conventionally known brushed decoration methods such as a method of brushing the surface of the sliding resin layer by colliding the body are used.
[0089]
【The invention's effect】
According to the present invention, it is possible to omit the adhesive application process, the adhesive curing or baking process, and the embossing process before and after the process. As a result, the number of processes can be reduced, and the working time can be reduced. Because it can be shortened, it is possible to produce a glass run channel with excellent economy, durability, close contact with the window glass when closed, and light sliding performance during opening and closing operations. It is possible to provide a glass run channel that does not cause wrinkles in the ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin composition layer even when bent or folded.
[0090]
EXAMPLES Hereinafter, although an Example demonstrates this invention, this invention is not limited to these Examples.
[0091]
[Example 1]
Ethylene content 70mol%,
[0092]
Next, this rectangular pellet, 0.3 parts by weight of 1,3-bis (tert-butylperoxyisopropyl) benzene [hereinafter abbreviated as peroxide], and 0.5 parts by weight of divinylbenzene [hereinafter abbreviated as DVB] The mixture was stirred and mixed with a Henschel mixer.
[0093]
Next, this mixture was extruded at 220 ° C. in a nitrogen atmosphere using a twin screw extruder having L / D = 40 and a screw diameter of 50 mm to obtain a thermoplastic elastomer (A-1).
[0094]
The gel content of the obtained thermoplastic elastomer (A-1) was 85% by weight as determined by the above method.
The thermoplastic elastomer (A-1) is extruded at a temperature of 230 ° C. to form a glass run channel main body and a draining portion, and the intrinsic viscosity [η] measured in a 135 ° C. decalin solvent is 28 dl on the surface. / G of ultra high molecular weight polyethylene (a-1) 23% by weight and low molecular weight polyethylene (a-2) 77% by weight having an intrinsic viscosity [η] measured in decalin of 135 ° C. of 0.73 dl / g. Polyethylene composition (a) ′ [Intrinsic viscosity [η] measured in decalin at 135 ° C .: 7.0 dl / g] 75 parts by weight and thermoplastic elastomer (A-1) 25 parts by weight using the above-mentioned twin screw extruder. The kneaded ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene composition (B-1) was coextruded at 250 ° C. to obtain a glass run channel.
[0095]
The obtained glass run channel has a substantially trapezoidal shape. The total length of the inclined portion and the horizontal portion of the
[0096]
The obtained glass run channel was attached to a test window frame, and a window glass having a thickness of 3.2 mm was fitted thereto, and an endurance test (window glass up and down repeated test) was performed. As a result, this glass run channel withstood the 50,000 times window glass up-and-down repetition test and maintained its function as a glass run channel.
[0097]
However, the conventional glass run channel (the window glass sliding part has a laminated structure in which a nylon film is bonded to a soft vinyl chloride resin layer) is broken at the window glass contact surface after 25,000 times. As a result, the frictional resistance with the window glass increased significantly, making it unusable.
[0098]
In addition, the straight portion of the glass run channel obtained in Example 1 was cut into a length of 30 cm and bent 180 degrees from the center with the draining portion on the outside. The ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene composition layer (sliding resin layer) There was no noticeable wrinkle.
[0099]
[Example 2]
In Example 1, 60 parts by weight of polyethylene composition (a), 15 parts by weight of thermoplastic elastomer (A-1), and styrene / isoprene / styrene block copolymer [styrene content: 20% by weight, isoprene polymer The content of isoprene units bonded at the 1,2- and 3,4-positions in the portion: 55%, melt flow rate: 2.5 g / 10 min] (c) 25 parts by weight of the above-described twin-screw extruder This was carried out in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene composition (B-2) kneaded in (1) was used.
[0100]
Using the obtained glass run channel, the window glass up / down repetition test was conducted in the same manner as in Example 1. As a result, it withstood 50,000 times. In addition, no remarkable wrinkle was observed in the ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene composition layer even with respect to the above-described bending.
[0101]
[Example 3]
In Example 1, in addition to EPDM and PP, 10 parts by weight of butyl rubber [manufactured by Esso, IIR-065, unsaturation degree 0.8 mol%, hereinafter abbreviated as IIR] and paraffinic process oil [Idemitsu Kosan Co., Ltd. Product name Diana Process Oil] The same procedure as in Example 1 was conducted except that 30 parts by weight of the thermoplastic elastomer (A-2) was produced. The gel content of the obtained thermoplastic elastomer (A-2) was 70%.
[0102]
The resulting glass run channel withstood 50,000 repetitions of the window glass up / down repetition test. In addition, no remarkable wrinkles were observed in the ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene composition layer with respect to the above-described bending.
[0103]
[Example 4]
In Example 1, in addition to 75 parts by weight of the polyethylene composition (a) and 25 parts by weight of the thermoplastic elastomer (A-1), 0.5 parts by weight of erucamide is added to the ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene composition (B-3). ) Was carried out in the same manner as in Example 1, except that
[0104]
The resulting glass run channel withstood 50,000 repetitions of the window glass up / down repetition test. In addition, no remarkable wrinkle was observed in the ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene composition layer even with respect to the above-described bending.
[0105]
[Comparative Example 1]
In Example 1, it carried out like Example 1 except having used polyethylene composition (a) 'independently instead of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene composition (B-1).
[0106]
The resulting glass run channel withstood 50,000 repetitions of the window glass up / down repetition test. However, with respect to the above-described bending, wrinkles occurred in the ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene composition layer, and whitening was observed.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a cross-sectional view of a glass run channel according to the present invention.
2 is an enlarged cross-sectional view of a contact portion of the glass run channel shown in FIG. 1 with a window glass.
FIG. 3 is a view for explaining attachment of a glass run channel to an automobile door.
FIG. 4 is a cross-sectional view showing a state of a glass run channel when the window glass is opened.
FIG. 5 is a cross-sectional view showing a state of the glass run channel when the window glass is closed.
[Explanation of symbols]
1 ・ ・ ・ ・ ・ Glass run channel
1a ... bottom wall
1b: side wall
1c: Groove
2 ・ ・ ・ ・ ・ Glass run channel body
3 ...... Drainer
4 ... Window glass contact area
7 ・ ・ ・ ・ ・ Base layer made of thermoplastic elastomer
8... Base layer surface having a repetitive pattern of minute irregularities (applied as necessary)
9 ・ ・ ・ ・ ・ Sliding resin layer made of ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin composition
10 ... Surface of the resin layer having a repetitive pattern of minute irregularities (applied as necessary)
Claims (5)
該水切り部の窓ガラスと接触する表面である窓ガラス接触部が、
結晶性ポリオレフィンとゴムとから構成される熱可塑性エラストマー(A)層と、超高分子量ポリオレフィン組成物(B)層とからなり、かつ、
超高分子量ポリオレフィン組成物(B)層が窓ガラスと接触するように構成されており、
該超高分子量ポリオレフィン組成物(B)が、
135℃デカリン溶媒中で測定した極限粘度[η]が7〜40dl/gの範囲内にある超高分子量ポリオレフィン(a−1)と、135℃デカリン溶媒中で測定した極限粘度[η]が0.1〜5dl/gの範囲内にあるポリオレフィン(a−2)とから実質的になり、該超高分子量ポリオレフィン(a−1)が、超高分子量ポリオレフィン(a−1)とポリオレフィン(a−2)との総重量100重量%に対して15〜40重量%の割合で存在し、かつ、135℃デカリン溶媒中で測定した極限粘度[η]が3.5〜8.3dl/gの範囲内にあるポリオレフィン(a)’10〜90重量部、および
結晶性オレフィン系樹脂とオレフィン系ゴムとからなるオレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー(b)90〜10重量部[成分(a)’および(b)の合計は100重量部]からなることを特徴とするガラスランチャンネル。A glass run channel body comprising a bottom wall and side walls extending from both ends of the bottom wall, having a substantially U-shaped cross section and having grooves formed therein, and the bottom wall from the vicinity of the ends of both side walls of the glass run channel body A glass run channel composed of a tongue-shaped drainer stretched so as to be close to each other toward the
A window glass contact portion which is a surface in contact with the window glass of the draining portion,
A thermoplastic elastomer (A) layer composed of crystalline polyolefin and rubber, an ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin composition (B) layer, and
The ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin composition (B) layer is configured to come into contact with the window glass,
The ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin composition (B) is
Ultra high molecular weight polyolefin (a-1) having an intrinsic viscosity [η] measured in a decalin solvent of 135 ° C. within a range of 7 to 40 dl / g, and an intrinsic viscosity [η] measured in a decalin solvent of 135 ° C. of 0. 0.1 to 5 dl / g of the polyolefin (a-2), and the ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin (a-1) comprises the ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin (a-1) and the polyolefin (a- 2) and the intrinsic viscosity [η] measured in a decalin solvent at 135 ° C. is in the range of 3.5 to 8.3 dl / g. polyolefins located within (a) '10 to 90 parts by weight, and the olefin-based thermoplastic elastomer comprising a crystalline olefin resin and an olefin rubber (b) 90 to 10 parts by weight [the component (a)' and (b) Total glass run channel, characterized in that it consists of 100 parts by weight.
135℃デカリン溶媒中で測定した極限粘度[η]が7〜40dl/gの範囲内にある超高分子量ポリオレフィン(a−1)と、135℃デカリン溶媒中で測定した極限粘度[η]が0.1〜5dl/gの範囲内にあるポリオレフィン(a−2)とから実質的になり、該超高分子量ポリオレフィン(a−1)が、超高分子量ポリオレフィン(a−1)とポリオレフィン(a−2)との総重量100重量%に対して15〜40重量%の割合で存在し、かつ、135℃デカリン溶媒中で測定した極限粘度[η]が3.5〜8.3dl/gの範囲内にあるポリオレフィン組成物(a)’10〜90重量部、
結晶性オレフィン系樹脂とオレフィン系ゴムとからなるオレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー(b)85〜5重量部、および
スチレンまたはその誘導体の重合体ブロック(c−1)と、イソプレン重合体ブロックおよび/またはイソプレン・ブタジエン共重合体ブロックであって、全イソプレン単位に対する1,2−位および3,4−位で結合しているイソプレン単位含有量が40%以上である重合体および/または共重合体ブロック(c−2)とからなる水素添加されていてもよいブロック共重合体(c)5〜60重量部[成分(a)’、(b)および(c)の合計は100重量部]からなることを特徴とする請求項1に記載のガラスランチャンネル。The ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin composition (B) is
Ultra high molecular weight polyolefin (a-1) having an intrinsic viscosity [η] measured in a decalin solvent of 135 ° C. within a range of 7 to 40 dl / g, and an intrinsic viscosity [η] measured in a decalin solvent of 135 ° C. of 0. 0.1 to 5 dl / g of the polyolefin (a-2), and the ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin (a-1) comprises the ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin (a-1) and the polyolefin (a- 2) and the intrinsic viscosity [η] measured in a decalin solvent at 135 ° C. is in the range of 3.5 to 8.3 dl / g. The polyolefin composition (a) within 10 to 90 parts by weight,
85 to 5 parts by weight of an olefin thermoplastic elastomer (b) composed of a crystalline olefin resin and an olefin rubber, a polymer block (c-1) of styrene or a derivative thereof, an isoprene polymer block and / or isoprene A butadiene copolymer block in which the content of isoprene units bonded at 1,2-position and 3,4-position with respect to all isoprene units is 40% or more and / or copolymer block ( c-2) optionally hydrogenated block copolymer (c) 5 to 60 parts by weight [total of components (a) ′, (b) and (c) is 100 parts by weight] The glass run channel according to claim 1 .
結晶性ポリプロピレン(A−1)70〜10重量部と、
エチレン・プロピレン共重合体ゴムまたはエチレン・プロピレン・ジエン共重合体ゴムからなるゴム(A−2)30〜90重量部[成分(A−1)および(A−2)の合計量は100重量部とする]と
からなる混合物を、有機ペルオキシドの存在下で動的に熱処理して得られる、上記ゴム(A−2)が架橋された熱可塑性エラストマーであることを特徴とする請求項1〜3のいずれかに記載のガラスランチャンネル。The olefinic thermoplastic elastomer (b) constituting the ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin composition (B) is:
70 to 10 parts by weight of crystalline polypropylene (A-1),
30 to 90 parts by weight of rubber (A-2) made of ethylene / propylene copolymer rubber or ethylene / propylene / diene copolymer rubber [the total amount of components (A-1) and (A-2) is 100 parts by weight the to] from become mixture obtained by dynamic heat treatment in the presence of an organic peroxide, claim 1-3 in which the rubber (a-2) is characterized in that it is a thermoplastic elastomer which is crosslinked The glass run channel according to any one of the above.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP03870998A JP4059971B2 (en) | 1997-02-21 | 1998-02-20 | Glass run channel |
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP9-37217 | 1997-02-21 | ||
| JP3721797 | 1997-02-21 | ||
| JP03870998A JP4059971B2 (en) | 1997-02-21 | 1998-02-20 | Glass run channel |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JPH10291418A JPH10291418A (en) | 1998-11-04 |
| JP4059971B2 true JP4059971B2 (en) | 2008-03-12 |
Family
ID=26376333
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP03870998A Expired - Lifetime JP4059971B2 (en) | 1997-02-21 | 1998-02-20 | Glass run channel |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4059971B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001001450A (en) * | 1999-06-24 | 2001-01-09 | Mitsui Chemicals Inc | Laminate |
| JP4118716B2 (en) * | 2003-03-12 | 2008-07-16 | 株式会社クラレ | Thermoplastic elastomer composition and molded article thereof |
| JP4388355B2 (en) * | 2003-12-04 | 2009-12-24 | 株式会社アステア | Resin lower sash |
| US20060059799A1 (en) * | 2004-08-24 | 2006-03-23 | Cooper-Standard Automotive Inc. | Invisible division bar modular assembly |
| JP2005037965A (en) * | 2004-10-04 | 2005-02-10 | Naoto Denda | Toner sealing structure and sealing material |
| JP2005025225A (en) * | 2004-10-04 | 2005-01-27 | Naoto Denda | Toner sealing structure and sealing material |
| KR20060068493A (en) * | 2004-12-16 | 2006-06-21 | 에스케이 주식회사 | Coating composition for weatherstrips of automobile vehicles |
| JP6420642B2 (en) * | 2014-11-28 | 2018-11-07 | 日本板硝子株式会社 | Glass plate and method for producing glass plate |
| DE102019134264A1 (en) | 2019-12-13 | 2021-06-17 | Zf Airbag Germany Gmbh | GAS GENERATOR IN PARTICULAR FOR A VEHICLE SAFETY SYSTEM |
| WO2021193554A1 (en) * | 2020-03-27 | 2021-09-30 | 三井化学株式会社 | Thermoplastic elastomer composition and molded body thereof |
-
1998
- 1998-02-20 JP JP03870998A patent/JP4059971B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JPH10291418A (en) | 1998-11-04 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CA2230332C (en) | Glass run channel | |
| US5424135A (en) | Thermoplastic elastomer laminates and glass run channels molded therefrom | |
| US7999038B2 (en) | Weatherstrip | |
| US20070077375A1 (en) | Weatherstrip | |
| JP4059971B2 (en) | Glass run channel | |
| EP1063084B1 (en) | Laminate comprising a sliding member layer and a substrate layer | |
| EP1095764A2 (en) | Laminated products of olefinic thermoplastic elastomer and constructional gaskets | |
| JP5014725B2 (en) | Weather Strip | |
| JP3945248B2 (en) | Olefinic foam laminates and applications | |
| JP4226772B2 (en) | Olefin-based thermoplastic elastomer laminate and architectural gasket | |
| JP3994611B2 (en) | Olefin-based thermoplastic elastomer laminate and automotive glass run channel | |
| JP3210066B2 (en) | Glass run channel | |
| JPH0994925A (en) | Successively injection molded automobile interior and exterior trim using thermoplastic elastomer laminate | |
| JP3055113B2 (en) | Glass run channel | |
| JP3465421B2 (en) | Thermoplastic elastomer composition | |
| JP3910313B2 (en) | Resin composition for skin member and laminate thereof | |
| JP2001316487A (en) | Thermoplastic olefin elastomer and its use | |
| JP2000281845A (en) | Cross-linked thermoplastic elastomer composition for injection molding | |
| JP2023014023A (en) | Thermoplastic elastomer composition | |
| JPH04320838A (en) | Layered body of thermoplastic elastomer | |
| JP2023033118A (en) | Thermoplastic elastomer composition and automobile weather strip | |
| JPH054522A (en) | Glass run channel | |
| JP2022063030A (en) | Resin composition, dynamic-crosslinking resin composition, method for producing resin composition, and extrusion-molded product and method for producing the same | |
| JPH11323044A (en) | Thermoplastic elastomer composition for surface skin member | |
| JP2004168117A (en) | Glass run channel |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20041006 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20041006 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20070426 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20070508 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20070614 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20071211 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20071219 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20101228 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20111228 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20111228 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20121228 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20121228 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20131228 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| EXPY | Cancellation because of completion of term |