JP4034932B2 - Semiconductor device, LED print head, and wire bonding method - Google Patents
Semiconductor device, LED print head, and wire bonding method Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4034932B2 JP4034932B2 JP2000382222A JP2000382222A JP4034932B2 JP 4034932 B2 JP4034932 B2 JP 4034932B2 JP 2000382222 A JP2000382222 A JP 2000382222A JP 2000382222 A JP2000382222 A JP 2000382222A JP 4034932 B2 JP4034932 B2 JP 4034932B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- bonding
- bonding pad
- width
- pads
- led array
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/02—Bonding areas ; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/04—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process
- H01L24/06—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process of a plurality of bonding areas
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/02—Bonding areas ; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/04—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process
- H01L24/05—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process of an individual bonding area
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/02—Bonding areas; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/04—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/04042—Bonding areas specifically adapted for wire connectors, e.g. wirebond pads
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/02—Bonding areas; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/04—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/05—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process of an individual bonding area
- H01L2224/0554—External layer
- H01L2224/0555—Shape
- H01L2224/05552—Shape in top view
- H01L2224/05553—Shape in top view being rectangular
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/02—Bonding areas; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/04—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/05—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process of an individual bonding area
- H01L2224/0554—External layer
- H01L2224/0555—Shape
- H01L2224/05552—Shape in top view
- H01L2224/05554—Shape in top view being square
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/02—Bonding areas; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/04—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/06—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process of a plurality of bonding areas
- H01L2224/0601—Structure
- H01L2224/0603—Bonding areas having different sizes, e.g. different heights or widths
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/02—Bonding areas; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/04—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/06—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process of a plurality of bonding areas
- H01L2224/061—Disposition
- H01L2224/0612—Layout
- H01L2224/0615—Mirror array, i.e. array having only a reflection symmetry, i.e. bilateral symmetry
- H01L2224/06153—Mirror array, i.e. array having only a reflection symmetry, i.e. bilateral symmetry with a staggered arrangement, e.g. depopulated array
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/47—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/48—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/481—Disposition
- H01L2224/48135—Connecting between different semiconductor or solid-state bodies, i.e. chip-to-chip
- H01L2224/48137—Connecting between different semiconductor or solid-state bodies, i.e. chip-to-chip the bodies being arranged next to each other, e.g. on a common substrate
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/47—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/48—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/484—Connecting portions
- H01L2224/48463—Connecting portions the connecting portion on the bonding area of the semiconductor or solid-state body being a ball bond
- H01L2224/48465—Connecting portions the connecting portion on the bonding area of the semiconductor or solid-state body being a ball bond the other connecting portion not on the bonding area being a wedge bond, i.e. ball-to-wedge, regular stitch
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/47—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/48—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/484—Connecting portions
- H01L2224/4847—Connecting portions the connecting portion on the bonding area of the semiconductor or solid-state body being a wedge bond
- H01L2224/48471—Connecting portions the connecting portion on the bonding area of the semiconductor or solid-state body being a wedge bond the other connecting portion not on the bonding area being a ball bond, i.e. wedge-to-ball, reverse stitch
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/47—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/49—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process of a plurality of wire connectors
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/47—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/49—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process of a plurality of wire connectors
- H01L2224/491—Disposition
- H01L2224/4912—Layout
- H01L2224/49175—Parallel arrangements
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/47—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/49—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process of a plurality of wire connectors
- H01L2224/494—Connecting portions
- H01L2224/4943—Connecting portions the connecting portions being staggered
- H01L2224/49431—Connecting portions the connecting portions being staggered on the semiconductor or solid-state body
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/47—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/49—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process of a plurality of wire connectors
- H01L2224/494—Connecting portions
- H01L2224/4945—Wire connectors having connecting portions of different types on the semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. regular and reverse stitches
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L2224/85—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a wire connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L2224/85—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a wire connector
- H01L2224/8512—Aligning
- H01L2224/85148—Aligning involving movement of a part of the bonding apparatus
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L2224/85—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a wire connector
- H01L2224/8512—Aligning
- H01L2224/85148—Aligning involving movement of a part of the bonding apparatus
- H01L2224/85169—Aligning involving movement of a part of the bonding apparatus being the upper part of the bonding apparatus, i.e. bonding head, e.g. capillary or wedge
- H01L2224/8518—Translational movements
- H01L2224/85191—Translational movements connecting first both on and outside the semiconductor or solid-state body, i.e. regular and reverse stitches
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01004—Beryllium [Be]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01005—Boron [B]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01006—Carbon [C]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01033—Arsenic [As]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01079—Gold [Au]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/10—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/11—Device type
- H01L2924/12—Passive devices, e.g. 2 terminal devices
- H01L2924/1204—Optical Diode
- H01L2924/12041—LED
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/10—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/11—Device type
- H01L2924/14—Integrated circuits
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Wire Bonding (AREA)
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、LEDアレイIC(Light Emitting Diode Array Integrated Circuit)と、このLEDアレイICを駆動する駆動ICとを有する半導体装置、LEDプリントヘッドに関し、特にLEDアレイIC上に形成されたボンディングパッドと、駆動IC上に形成されたボンディングパッドの配置に関するものである。
【0002】
さらに本発明は、LEDアレイIC上に形成されたボンディングパッドと、駆動IC上に形成されたボンディングパッドとを接続するためのワイヤボンディング方法に関するものである。
【0003】
【従来の技術】
LEDアレイICと、このLEDアレイICを駆動する駆動ICとを有する半導体装置として、LEDプリントヘッドと呼ばれるものがある。このLEDプリントヘッドは、実装基板と、この実装基板上に実装されたLEDアレイICおよび駆動ICとで構成されている。
【0004】
LEDアレイIC上および駆動IC上には、複数のボンディングパッドが各々形成されている。これらのボンディングパッドは例えば1列に配置されている。駆動ICのボンディングパッドは、ボンディングワイヤによってLEDアレイICの対応するボンディングパッドと接続され、さらに配線層を介して駆動IC内に形成された制御回路とも接続されている。
【0005】
この制御回路は、LEDアレイを駆動するための制御信号を生成する。この制御信号は、駆動ICのボンディングパッドからボンディングワイヤを介してLEDアレイICへ伝達される。LEDアレイIC中のLEDは、この伝達された制御信号に応答して発光動作を行う。
【0006】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
従来のLEDプリントヘッドでは、まず最初に駆動IC上のボンディングパッドにワイヤボンディングが実行され(ファーストボンディングと称される)、次にLEDアレイIC上のボンディングパッドにワイヤボンディングが実行される。(セカンドボンディングと称される)すなわち、ファーストボンディングが駆動IC上の全てのボンディングパッドに適用され、セカンドボンディングがLEDアレイIC上の全てのボンディングパッドに適用される。
【0007】
従来の他のLEDプリントヘッドでは、まず最初にLEDアレイIC上のボンディングパッドにワイヤボンディングが実行され(ファーストボンディングと称される)、次に駆動IC上のボンディングパッドにワイヤボンディングが実行される。(セカンドボンディングと称される)すなわち、ファーストボンディングがLEDアレイIC上の全てのボンディングパッドに適用され、セカンドボンディングが駆動IC上の全てのボンディングパッドに適用される。
【0008】
ファーストボンディングではボンディングパッド上にボールが形成されるため、ボンディングパッドの横方向の長さ(ボンディングパッドの幅)はこのボールの大きさに依存する。
【0009】
LEDアレイICの集積度を上げるためには、ボンディングパッド間の距離を短くすることが考えられる。しかしながら、ボンディングパッド間の距離を短くすることにも限界がある。
さらに、LEDアレイICの集積度を上げるためにボンディングパッドの横方向の長さを短くすることが考えられる。しかしながら、上述したように、ファーストボンディングが実行される時に形成されるボールのためのエリア(ボンディングパッドの横方向の長さ)がボンディングパッドには必要である。
【0010】
よって、LEDアレイICの集積度を上げることは単純ではない。これは、結果として、駆動ICを含めた半導体装置全体の大きさを縮小することが困難であることを意味する。
【0011】
従って、集積度が改善された半導体装置が望まれていた。
【0012】
【課題を解決するための手段】
本発明は、上記課題を克服するために、ボンディングパッドの配置を変更したものである。本願において開示される発明のうち、代表的なものの概要は以下の通りである。
【0013】
実装基板と、前記実装基板上に配置された第1の辺を有する第1の半導体基板と、前記実装基板上に配置され、前記第1の辺に対向する第2の辺を有する第2の半導体基板と、 第1の幅を有する第1のボンディングパッドと、該第1のボンディングパッドと前記第1の辺に沿って隣接し前記第1の幅よりも短い第2の幅を有する第2のボンディングパッドとを含み、前記第1の半導体基板上に配置された第1のボンディングパッドユニットと、前記第2の幅を有する第3のボンディングパッドと、該第3のボンディングパッドと前記第2の辺に沿って隣接し前記第1の幅を有する第4のボンディングパッドとを含み、前記第2の半導体基板上に配置された第2のボンディングパッドユニットと、前記第1のボンディングパッドと前記第3のボンディングパッドとを接続する第1のボンディングワイヤーと、前記第2のボンディングパッドと前記第4のボンディングパッドとを接続する第2のボンディングワイヤーとを備え、前記第1のボンディングパッドユニットの前記第1の辺方向の両端は、前記第2のボンディングパッドユニットの前記第2の辺方向の両端と略等しい位置となるよう対向して配置されたものである。
【0014】
【発明の実施の形態】
以下、本発明の実施の形態を図面を参照して詳細に説明する。
【0015】
なお、説明を容易にするため、同様の構成には同様の符号を付与する。また、重複した構成の説明は省略する。
【0016】
(第1の実施の形態)
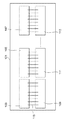
図1は本発明の第1の実施の形態の半導体装置(LEDプリントヘッド)の全体を示す平面図である。
【0017】
この半導体装置は、実装基板101と、この実装基板101上にダイボンディングされた複数のLEDアレイIC103、105、107と、複数の駆動IC109、111、113とを有している。複数のLEDアレイICと複数の駆動ICはボンディングワイヤ115で各々接続されている。
図1では、説明を容易にするため、LEDアレイIC103、105、107と、駆動IC109、111、113のみが示されている。
【0018】
図2は、図1に示されたLEDアレイIC103と駆動IC109の接続状態を示す平面図である。
【0019】
図2に示すように、LEDアレイIC103は略長方形状を有している。このLEDアレイICの一辺には、ボンディングパッド形成領域201が存在し、複数のボンディングパッド205、207がこのボンディングパッド形成領域201に一列に形成されている。
【0020】
図2において、黒丸はファーストボンディングが実行されていることを示しており、×印はセカンドボンディングが実行されていることを示している。このようなファーストボンディングは、複数のボンディングパッドのうち、ボンディングパッド205に適用されており、このようなセカンドボンディングは、複数のボンディングパッドのうち、ボンディングパッド207に適用されている。
【0021】
つまり、LEDアレイICのボンディングパッドには、ファーストボンディングとセカンドボンディングとが交互に適用されている。
【0022】
複数の配線層213がLEDアレイIC103上に形成されている。第1の実施の形態では、配線層213の配線幅は20μmである。
【0023】
ボンディングパッド205、207には、この配線層213が接続されている。この配線層213は、図示しない各LED素子の電極に接続されている。
【0024】
駆動IC109もLEDアレイICと同様に略長方形状を有している。この駆動ICの一辺には、ボンディングパッド形成領域203が存在し、複数のボンディングパッド209、211がこのボンディングパッド形成領域203に一列に形成されている。
【0025】
図2において、黒丸はファーストボンディングが実行されていることを示しており、×印はセカンドボンディングが実行されていることを示している。このようなファーストボンディングは、複数のボンディングパッドのうち、ボンディングパッド211に適用されており、このようなセカンドボンディングは、複数のボンディングパッドのうち、ボンディングパッド209に適用されている。
【0026】
つまり、駆動ICのボンディングパッドには、ファーストボンディングとセカンドボンディングとが交互に適用されている。複数の配線層215が駆動IC109上に形成されている。ボンディングパッド209、211には、この配線層215が接続されている。この配線層215は、駆動IC109内に形成された制御回路に接続されている。
【0027】
図3は、LEDアレイIC103の隣り合った2つのボンディングパッド205、207のワイヤボンディングの状態を示す平面図である。図3に示されているように、ボンディングパッド205には、ファーストボンディングが実行されているため、ボンディングワイヤ115の先端につぶれたボール301が存在する。ワイヤ115には例えば金が使用されているので、ファーストボンディング後のボールのつぶれ幅(このつぶれ幅は、ボール圧着径とも称される)は約80μmになる。
【0028】
従って、ファーストボンディングが実行されるボンディングパッド205の幅(紙面のx軸方向の長さ)には、少なくともこのボールのつぶれ幅とほぼ同じ幅(約80μm)が要求される。
【0029】
一方、ボンディングパッド207には、セカンドボンディングが実行されているため、ボンディングパッド207上にはボールが形成されない。ボンディングパッド207には、図3に示されているように三日月状のセカンドボンディング形状が代りに形成される。この形状はクレセントと称されている。このクレセントは、先に説明したボールのつぶれ幅よりも小さな幅を有している。具体的には、この幅は約50μmである。
今、ボンディングパッドとボンディングパッドとの間に要求される幅(ボンディングパッドの間隔)が約40μmである場合、一対のボンディングパッドのためのボンディング領域201として必要な幅は約170μmである。また、ボンディングワイヤ間に必要な距離は、約105μmである。
【0030】
図2に示される第1の実施の形態においては、LEDアレイIC103全体に関して、ボンディング領域201として必要な幅は1220μmである。
【0031】
この値は、以下の式によって計算される。
【0032】
105×(12−1)+80/2+50/2=1220
一方、図4に示されているように、従来技術においては、ボンディングパッドとボンディングパッドとの間に要求される幅(ボンディングパッドの間隔)が約40μmである場合、一対のボンディングパッドのためのボンディング領域201として必要な幅は約200μmである。また、ボンディングワイヤ間に必要な距離は、約120μmである。
従来技術においては、12個のボンディングパッドを有するLEDアレイIC103全体に関して、ボンディング領域201として必要な幅は1400μmである。
【0033】
この値は、以下の式によって計算される。
【0034】
120×(12−1)+80/2+50/2=1400
ボンディング領域203として必要な幅を減少させることができる点は、LEDアレイIC103と同様であるということは容易に理解できるであろう。
【0035】
第1の実施の形態は、ファーストボンディング用のボンディングパッドと、セカンドボンディング用のボンディングパッドとを単に交互に配置したものではない。この点を図5を参照して説明する。
【0036】
図5は、図2の部分拡大図を示す図である。図5において、ボンディングワイヤ115は省略されている。
【0037】
図5に示すように、LEDアレイIC103において、ファーストボンディングが実行されるボンディングパッド205は、幅B(80μm)を有する。 セカンドボンディングが実行されるボンディングパッド207は幅Bよりも短い幅C(50μm)を有する。
【0038】
ボンディングパッド205とボンディングパッド207との間の距離はD(40μm)である。
【0039】
ボンディングパッド205とボンディングパッド207の互いに隣接していないエッジ間の距離Aは、距離Bと距離Cと距離Dとの合計であり、170μmである。
【0040】
駆動IC109において、セカンドボンディングが実行されるボンディングパッド209は、幅B(80μm)よりも短い幅C(50μm)を有する。
【0041】
ファーストボンディングが実行されるボンディングパッド211は、幅B(80μm)を有する。
【0042】
ボンディングパッド209とボンディングパッド211との間の距離はD(40μm)である。ボンディングパッド209とボンディングパッド211の互いに隣接していないエッジ間の距離Aは、距離Cと距離Dと距離Bとの合計であり、170μmである。
【0043】
今、ファーストボンディングが実行されるボンディングパッドと、セカンドボンディングが実行されるボンディングパッドとをボンディングパッドユニットU1(U2)として定義する。
【0044】
この場合、LEDアレイIC103側のボンディングパッドユニットU1の両エッジと駆動IC109側のボンディングパッドユニットU2の両エッジは、紙面のx軸方向において一致するように配置される。そして同一基板上に形成されたボンディングパッドユニット間の距離はEであり、その値は40μmである。
【0045】
なお、図13に示すように、LEDアレイIC103のボンディングパッドと、これと対をなす駆動IC109のボンディングパッドとのx軸方向の相対位置を、下式に示す距離Fだけ平行移動して実装基板に実装することにより、ワイヤーボンディング時に対となるLEDアレイIC103のボンディングパッド205のx軸方向の中心と、駆動IC109のボンディングパッド209のx軸方向の中心とを合わせることも可能である。
【0046】
F=(B−C)/2
このとき、LEDアレイIC103と駆動IC109の対となるボンディングパッド間の距離を最短にすることができる。
【0047】
以上のように、幅の異なるボンディングパッドを隣接して配置することにより、ボンディングパッド形成領域の寸法を縮小させることができる。
【0048】
次に、第1の実施の形態におけるボンディングパッドの配置方法と、LEDプリントヘッドの実装方法について図6及び図7を使用して説明する。
【0049】
図6及び図7は、第1の実施の形態のボンディングパッドの配置方法及びプリントヘッドの実装方法のフローチャートを示す図である。ステップ1からステップ5では、コンピュータ上で計算が行われている。
【0050】
(ステップ1)
まず、ファーストボンディングパッド及びセカンドボンディングパッドの幅を定義する。さらに、ファーストボンディングパッドとセカンドボンディングパッドとの間の距離を決定する。
【0051】
(ステップ2)
次に、ステップ1で得られたデータに基づき、1つのファーストボンディングパッドと1つのセカンドボンディングパッドとで構成されたボンディングパッドユニットを決定する。
【0052】
(ステップ3)
次に、ボンディングパッドユニット間の距離(間隔)を決定する。
【0053】
(ステップ4)
ボンディングパッドユニットをLEDアレイICの一辺に沿って一列に配置する。さらに、ボンディングパッドユニットを駆動ICの一辺に沿って一列に配置する。
【0054】
(ステップ5)
LEDアレイIC上のボンディングパッドユニットの両エッジが、駆動ICのボンディングパッドユニットの両エッジとx軸方向において一致するように、これらのボンディングパッドユニットを配置する。
【0055】
(ステップ6)
ステップ5で得られたデータに基づき、ボンディングパッドを含むLEDアレイIC及び駆動ICを製造する。
【0056】
(ステップ7)
複数のLEDアレイIC及び複数の駆動ICを実装基板に実装する。
【0057】
(ステップ8)
LEDアレイICのボンディングパッドと駆動ICのボンディングパッドとの間をワイヤーボンディングする。
【0058】
以上のように、本実施の形態によれば、ファーストボンディング用のボンディングパッドと、ファーストボンディング用のボンディングパッドよりも幅が短いセカンドボンディング用のボンディングパッドとを交互に配置したので、ボンディングパッド形成領域の寸法を縮小することが可能である。
【0059】
ボンディングパッド形成領域を縮小することができるので、LEDアレイICおよび駆動ICの集積度を上げることができる。結果として、集積度が改善された半導体装置を得ることができるのである。
さらに第1の実施の形態は、1つのボンディングパッドユニットのデータを基礎として複数のボンディングパッドを配置するようにした。したがって、必要最小限のデータでボンディングパッドの配置を行うことができる。
【0060】
よってボンディングパッドの配置のためのデータ量を減少させることができる。
【0061】
(第2の実施の形態)
以下、本発明の第2の実施の形態を図面を参照して詳細に説明する。
図8は本発明の第2の実施の形態の半導体装置の全体を示す平面図である。
【0062】
図8に示された半導体装置は、LEDアレイIC上に形成されたボンディングパッドと、駆動IC上に形成されたボンディングパッドとが、各々2列に配置されている。このような配置は、千鳥状配置とも称される。
【0063】
図9は、図8に示されたLEDアレイIC103と駆動IC109の接続状態を示す平面図である。
【0064】
図9に示すように、LEDアレイIC103は略長方形状を有している。このLEDアレイIC103の一辺には、ボンディングパッド形成領域201が存在する。このボンディングパッド形成領域201には、ファーストボンディングが適用される複数のボンディングパッド205−1と、セカンドボンディングが適用される複数のボンディングパッド207−1とで構成された外側列のボンディングパッド群が形成されている。
【0065】
さらにこのボンディングパッド形成領域201には、ファーストボンディングが適用される複数のボンディングパッド205−2と、セカンドボンディングが適用される複数のボンディングパッド207−2とで構成された内側列のボンディングパッド群が形成されている。
【0066】
外側列のボンディングパッドには、ファーストボンディングとセカンドボンディングとが交互に適用されている。内側列のボンディングパッドにも、ファーストボンディングとセカンドボンディングとが交互に適用されている。
【0067】
外側列のボンディングパッド205−1、207−1には、配線層901が接続されている。この配線層901は、内側列のボンディングパッド間を通り図示しない対応するLED素子の電極に接続されている。
【0068】
内側列のボンディングパッド205−2、207−2には、配線層903が接続されている。この配線層903は図示しない対応するLED素子の電極に接続されている。
【0069】
駆動IC109もLEDアレイICと同様に略長方形状を有している。この駆動ICの一辺には、ボンディングパッド形成領域203が存在している。
【0070】
このボンディングパッド形成領域203には、セカンドボンディングが適用される複数のボンディングパッド209−1と、ファーストボンディングが適用される複数のボンディングパッド211−1とで構成された外側列のボンディングパッド群が形成されている。
【0071】
さらにこのボンディングパッド形成領域203には、セカンドボンディングが適用される複数のボンディングパッド209−2と、ファーストボンディングが適用される複数のボンディングパッド211−2とで構成された内側列のボンディングパッド群が形成されている。
【0072】
外側列のボンディングパッドには、セカンドボンディングとファーストボンディングとが交互に適用されている。内側列のボンディングパッドにも、セカンドボンディングとファーストボンディングとが交互に適用されている。
【0073】
外側列のボンディングパッド209−1、211−1には、配線層905が接続されている。この配線層905は、内側列のボンディングパッド間を通り対応する図示しない制御回路の電極に接続されている。内側列のボンディングパッド209−2、211−2には、配線層907が接続されている。この配線層907は対応する図示しない制御回路の電極に接続されている。
【0074】
図10は、図9の部分拡大図を示す図である。図9において、ボンディングワイヤ115は省略されている。
図10に示すように、LEDアレイIC103において、ファーストボンディングが実行されるボンディングパッド205−1、205−2は、幅B(80μm)を有する。セカンドボンディングが実行されるボンディングパッド207−1、207−2は、幅Bよりも短い幅C(50μm)を有する。
【0075】
ボンディングパッド205−2とボンディングパッド207−2との間の距離はDである。この距離D(40μm)は、配線901の幅によって決定される。第2の実施の形態では、配線901の幅は20μmである。
【0076】
ボンディングパッド205−2とボンディングパッド207−2の互いに隣接しないエッジ間の距離Aは、距離Bと距離Cと距離Dとの合計であり、170μmである。
【0077】
今、ファーストボンディングが実行されるボンディングパッドと、セカンドボンディングが実行されるボンディングパッドとをボンディングパッドユニットとして定義する。
【0078】
図10においては、LEDアレイIC103の外側列に複数のボンディングパッドユニットU1が配置され、内側列に複数のボンディングパッドユニットU2が配置されている。
【0079】
複数のボンディングパッドユニットU1は互いに距離E(40μm)だけ離れて配置されている。同様に複数のボンディングパッドユニットU2も互いに距離E(40μm)だけ離れて配置されている。
【0080】
駆動IC109の外側列には複数のボンディングパッドユニットU3が配置され、内側列に複数のボンディングパッドユニットU4が配置されている。
【0081】
複数のボンディングパッドユニットU3は互いに距離E(40μm)だけ離れて配置されている。同様に複数のボンディングパッドユニットU4も互いに距離E(40μm)だけ離れて配置されている。
【0082】
ボンディングパッドユニットU2の両エッジと、ボンディングパッドユニットU4の両エッジは、紙面のx軸方向において一致している。ボンディングパッドユニットU1の両エッジと、ボンディングパッドユニットU3の両エッジも面のx軸方向において一致している。
【0083】
ボンディングパッドユニットU2、U3、U4における上記距離A、B、C、D、Eは、ボンディングパッドユニットU1のそれらと同じである。
【0084】
幅の異なるボンディングパッドを同一列内において隣接して配置させることにより、ボンディングパッド形成領域の寸法を縮小させることができる。
【0085】
複数のボンディングパッドがこのように配置されることで、ボンディング領域を効率的に縮小することができるのである。
【0086】
次に、第2の実施の形態におけるボンディングパッドの配置方法と、LEDプリントヘッドの実装方法について図11及び図12を使用して説明する。
【0087】
図11及び図12は、第2の実施の形態のボンディングパッドの配置方法及びプリントヘッドの実装方法のフローチャートを示す図である。ステップ1からステップ8では、コンピュータ上で計算が行われている。
【0088】
(ステップ1)
まず、ファーストボンディングパッドの幅B及びセカンドボンディングパッドの幅Cを決定する。さらに、配線層の幅を考慮することによりファーストボンディングパッドとセカンドボンディングパッドとの間の距離Dを決定する。
(ステップ2)
次に、ステップ1で得られたデータに基づき、1つのファーストボンディングパッドと1つのセカンドボンディングパッドとで構成されたボンディングパッドユニットを定義する。
【0089】
(ステップ3)
次に、配線層の幅を考慮することによりボンディングパッドユニット間の距離(間隔)Eを決定する。
【0090】
(ステップ4)
ボンディングパッドユニットU1をLEDアレイICの一辺に沿って一列に配置し、外側列のボンディングパッド群を形成する。さらに、ボンディングパッドユニットU3を駆動ICの一辺に沿って一列に配置し、外側列のボンディングパッド群を形成する。
【0091】
(ステップ5)
ボンディングパッドユニットU2をLEDアレイICの外側列のボンディングパッド群に沿って一列に配置し、内側列のボンディングパッド群を形成する。さらに、ボンディングパッドユニットU4を駆動ICの外側列のボンディングパッド群に沿って一列に配置し、内側列のボンディングパッド群を形成する。
【0092】
(ステップ6)
LEDアレイIC上の外側列のボンディングパッドユニットU1の両エッジが、駆動ICの外側列のボンディングパッドユニットU3の両エッジと一致するように、これらのボンディングパッドユニットを配置する。
【0093】
(ステップ7)
LEDアレイIC上の内側列のボンディングパッドユニットU2のエッジが、駆動ICの内側列のボンディングパッドユニットU4のエッジと一致するように、これらのボンディングパッドユニットを配置する。
【0094】
(ステップ8)
LEDアレイIC及び駆動ICの内側列のボンディングパッドユニットを外側列のボンディングパッドユニットに対してX軸方向に所定の距離移動させる。
【0095】
(ステップ9)
ステップ8で得られたデータに基づき、ボンディングパッドを含むLEDアレイIC及び駆動ICを製造する。
【0096】
(ステップ10)
複数のLEDアレイIC及び複数の駆動ICを実装基板に実装する。
【0097】
(ステップ11)
LEDアレイICのボンディングパッドと駆動ICのボンディングパッドとの間をワイヤーボンディングする。
【0098】
以上のように、第2の実施の形態によれば、千鳥配置においても効率的にボンディングパッド形成領域を縮小することが可能である。
【0099】
【発明の効果】
本願において開示される発明のうち、代表的なものによって得られる効果の概要を簡単に説明すると以下の通りである。
【0100】
すなわち、本発明は、ファーストボンディングが実行されるボンディングパッドと、セカンドボンディングが実行されるボンディングパッドとを同一列内において交互に配置したので、ボンディング領域を縮小することが可能である。
【0101】
さらに、本発明は、幅が異なる1対のボンディングパッドで構成されるボンディングパッドユニットを定義し、このボンディングパッドユニットを基礎としてボンディングパッドを配置した。したがって、必要最小限のデータでボンディングパッドの配置を行うことができる。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】本発明の第1の実施の形態の半導体装置の全体を示す平面図である
【図2】図1に示されたLEDアレイIC103と駆動IC109の接続状態を示す平面図である。
【図3】本発明のワイヤボンディングの状態を示す平面図である。
【図4】従来のワイヤボンディングの状態を示す平面図である。
【図5】図2の部分拡大図を示す図である。
【図6】本発明の第1の実施の形態のボンディングパッドの配置方法及びプリントヘッド実装方法のフローチャートを示す図である。
【図7】本発明の第1の実施の形態のボンディングパッドの配置方法及びプリントヘッド実装方法のフローチャートを示す図である。
【図8】本発明の第2の実施の形態の半導体装置の全体を示す平面図である
【図9】図8に示されたLEDアレイIC103と駆動IC109の接続状態を示す平面図である。
【図10】図9の部分拡大図を示す図である。
【図11】本発明の第2の実施の形態のボンディングパッドの配置方法及びプリントヘッド実装方法のフローチャートを示す図である。
【図12】本発明の第2の実施の形態のボンディングパッドの配置方法及びプリントヘッド実装方法のフローチャートを示す図である。
【図13】図5に示されたLEDアレイIC103と駆動IC109の実装基板上の配置例を示す平面図である。
【符号の説明】
103・・・LEDアレイIC
109・・・駆動IC
115・・・ボンディングワイヤ
201、203・・・ボンディング領域
205、211・・・ファーストボンディング用ボンディングパッド
207、209・・・セカンドボンディング用ボンディングパッド[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a semiconductor device having an LED array IC (Light Emitting Diode Array Integrated Circuit) and a drive IC for driving the LED array IC, LED print head In particular, the present invention relates to an arrangement of bonding pads formed on the LED array IC and bonding pads formed on the driving IC.
[0002]
The present invention further relates to a wire bonding method for connecting a bonding pad formed on an LED array IC and a bonding pad formed on a driving IC.
[0003]
[Prior art]
As a semiconductor device having an LED array IC and a driving IC for driving the LED array IC, there is an LED print head. This LED print head is composed of a mounting substrate, and an LED array IC and a driving IC mounted on the mounting substrate.
[0004]
A plurality of bonding pads are formed on the LED array IC and the driving IC, respectively. These bonding pads are arranged in one row, for example. The bonding pads of the driving IC are connected to the corresponding bonding pads of the LED array IC by bonding wires, and are further connected to a control circuit formed in the driving IC through a wiring layer.
[0005]
The control circuit generates a control signal for driving the LED array. This control signal is transmitted from the bonding pad of the driving IC to the LED array IC via the bonding wire. The LEDs in the LED array IC perform a light emission operation in response to the transmitted control signal.
[0006]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
In the conventional LED print head, first, wire bonding is performed on the bonding pad on the driving IC (referred to as first bonding), and then wire bonding is performed on the bonding pad on the LED array IC. That is, first bonding is applied to all bonding pads on the driving IC, and second bonding is applied to all bonding pads on the LED array IC.
[0007]
In other conventional LED print heads, wire bonding is first performed on the bonding pads on the LED array IC (referred to as first bonding), and then wire bonding is performed on the bonding pads on the driving IC. That is, first bonding is applied to all bonding pads on the LED array IC, and second bonding is applied to all bonding pads on the driving IC.
[0008]
In the first bonding, since a ball is formed on the bonding pad, the lateral length of the bonding pad (bonding pad width) depends on the size of the ball.
[0009]
In order to increase the integration degree of the LED array IC, it is conceivable to shorten the distance between the bonding pads. However, there is a limit to shortening the distance between bonding pads.
Furthermore, in order to increase the integration degree of the LED array IC, it is conceivable to reduce the lateral length of the bonding pad. However, as described above, an area for the ball (the lateral length of the bonding pad) formed when the first bonding is performed is necessary for the bonding pad.
[0010]
Therefore, it is not simple to increase the integration degree of the LED array IC. As a result, this means that it is difficult to reduce the size of the entire semiconductor device including the driving IC.
[0011]
Therefore, a semiconductor device with improved integration has been desired.
[0012]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
In the present invention, in order to overcome the above-described problems, the arrangement of bonding pads is changed. Among the inventions disclosed in the present application, outlines of typical ones are as follows.
[0013]
A mounting substrate; a first semiconductor substrate having a first side disposed on the mounting substrate; and a second semiconductor layer disposed on the mounting substrate and having a second side facing the first side. A semiconductor substrate; a first bonding pad having a first width; and a second bonding pad adjacent to the first bonding pad along the first side and having a second width shorter than the first width. A first bonding pad unit disposed on the first semiconductor substrate, a third bonding pad having the second width, and the third bonding pad. No bo A second bonding pad unit disposed on the second semiconductor substrate, the second bonding pad unit including a bonding pad and a fourth bonding pad adjacent to the second side and having the first width; A first bonding wire that connects the first bonding pad and the third bonding pad; and a second bonding wire that connects the second bonding pad and the fourth bonding pad. Both ends of the first bonding pad unit in the first side direction are arranged so as to face each other at positions substantially equal to both ends of the second bonding pad unit in the second side direction.
[0014]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings.
[0015]
For ease of explanation, the same reference numerals are given to the same components. Further, the description of the duplicate configuration is omitted.
[0016]
(First embodiment)
FIG. 1 is a plan view showing the entire semiconductor device (LED print head) according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
[0017]
The semiconductor device includes a
In FIG. 1, only the
[0018]
FIG. 2 is a plan view showing a connection state between the
[0019]
As shown in FIG. 2, the LED array IC 103 has a substantially rectangular shape. A bonding
[0020]
In FIG. 2, black circles indicate that the first bonding is being performed, and x marks indicate that the second bonding is being performed. Such first bonding is applied to the
[0021]
That is, the first bonding and the second bonding are alternately applied to the bonding pads of the LED array IC.
[0022]
A plurality of
[0023]
The
[0024]
Similarly to the LED array IC, the
[0025]
In FIG. 2, black circles indicate that the first bonding is being performed, and x marks indicate that the second bonding is being performed. Such first bonding is applied to the
[0026]
That is, first bonding and second bonding are alternately applied to the bonding pads of the driving IC. A plurality of
[0027]
FIG. 3 is a plan view showing a wire bonding state of two
[0028]
Accordingly, the width (length in the x-axis direction of the paper surface) of the
[0029]
On the other hand, since the second bonding is performed on the
If the required width between the bonding pads (bonding pad spacing) is about 40 μm, the width required for the
[0030]
In the first embodiment shown in FIG. 2, the width necessary for the
[0031]
This value is calculated by the following formula.
[0032]
105 × (12−1) + 80/2 + 50/2 = 1220
On the other hand, as shown in FIG. 4, in the prior art, when the required width (interval between bonding pads) between the bonding pads is about 40 μm, for the pair of bonding pads, The required width for the
In the prior art, the width required for the
[0033]
This value is calculated by the following formula.
[0034]
120 × (12−1) + 80/2 + 50/2 = 1400
It can be easily understood that the width required for the
[0035]
In the first embodiment, bonding pads for first bonding and bonding pads for second bonding are not simply arranged alternately. This point will be described with reference to FIG.
[0036]
FIG. 5 is a partial enlarged view of FIG. In FIG. 5, the
[0037]
As shown in FIG. 5, in the
[0038]
The distance between the
[0039]
The distance A between the non-adjacent edges of the
[0040]
In the driving
[0041]
The
[0042]
The distance between the
[0043]
Now, a bonding pad on which first bonding is performed and a bonding pad on which second bonding is performed are defined as a bonding pad unit U1 (U2).
[0044]
In this case, both edges of the bonding pad unit U1 on the
[0045]
As shown in FIG. 13, the relative position in the x-axis direction between the bonding pad of the
[0046]
F = (B−C) / 2
At this time, the distance between the bonding pads forming the pair of the
[0047]
As described above, the bonding pad forming region can be reduced in size by arranging bonding pads having different widths adjacent to each other.
[0048]
Next, a bonding pad arrangement method and an LED print head mounting method in the first embodiment will be described with reference to FIGS.
[0049]
6 and 7 are flowcharts illustrating the bonding pad arrangement method and the print head mounting method according to the first embodiment. In
[0050]
(Step 1)
First, the widths of the first bonding pad and the second bonding pad are defined. Further, the distance between the first bonding pad and the second bonding pad is determined.
[0051]
(Step 2)
Next, based on the data obtained in
[0052]
(Step 3)
Next, the distance (interval) between the bonding pad units is determined.
[0053]
(Step 4)
Bonding pad units are arranged in a line along one side of the LED array IC. Further, the bonding pad units are arranged in a line along one side of the driving IC.
[0054]
(Step 5)
These bonding pad units are arranged so that both edges of the bonding pad unit on the LED array IC coincide with both edges of the bonding pad unit of the driving IC in the x-axis direction.
[0055]
(Step 6)
Based on the data obtained in step 5, an LED array IC and a driving IC including bonding pads are manufactured.
[0056]
(Step 7)
A plurality of LED array ICs and a plurality of driving ICs are mounted on a mounting substrate.
[0057]
(Step 8)
Wire bonding is performed between the bonding pad of the LED array IC and the bonding pad of the driving IC.
[0058]
As described above, according to the present embodiment, the bonding pads for the first bonding and the bonding pads for the second bonding shorter in width than the bonding pads for the first bonding are alternately arranged. It is possible to reduce the dimensions.
[0059]
Since the bonding pad formation region can be reduced, the integration degree of the LED array IC and the driving IC can be increased. As a result, a semiconductor device with improved integration can be obtained.
Furthermore, in the first embodiment, a plurality of bonding pads are arranged based on data of one bonding pad unit. Therefore, the bonding pads can be arranged with the minimum necessary data.
[0060]
Therefore, the amount of data for arranging the bonding pads can be reduced.
[0061]
(Second Embodiment)
Hereinafter, a second embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings.
FIG. 8 is a plan view showing the entire semiconductor device according to the second embodiment of the present invention.
[0062]
In the semiconductor device shown in FIG. 8, bonding pads formed on the LED array IC and bonding pads formed on the driving IC are arranged in two rows. Such an arrangement is also called a staggered arrangement.
[0063]
FIG. 9 is a plan view showing a connection state between the
[0064]
As shown in FIG. 9, the
[0065]
Further, in this bonding
[0066]
First bonding and second bonding are alternately applied to the bonding pads in the outer row. The first bonding and the second bonding are alternately applied to the bonding pads in the inner row.
[0067]
A
[0068]
A
[0069]
Similarly to the LED array IC, the
[0070]
In this bonding
[0071]
Further, in this bonding
[0072]
Second bonding and first bonding are alternately applied to the bonding pads in the outer row. The second bonding and the first bonding are alternately applied to the bonding pads in the inner row.
[0073]
A
[0074]
FIG. 10 is a diagram showing a partially enlarged view of FIG. In FIG. 9, the
As shown in FIG. 10, in the
[0075]
The distance between the bonding pad 205-2 and the bonding pad 207-2 is D. This distance D (40 μm) is determined by the width of the
[0076]
The distance A between the non-adjacent edges of the bonding pad 205-2 and the bonding pad 207-2 is the sum of the distance B, the distance C, and the distance D, and is 170 μm.
[0077]
Now, a bonding pad in which first bonding is performed and a bonding pad in which second bonding is performed are defined as bonding pad units.
[0078]
In FIG. 10, a plurality of bonding pad units U1 are arranged in the outer row of the
[0079]
The plurality of bonding pad units U1 are arranged at a distance E (40 μm) from each other. Similarly, the plurality of bonding pad units U2 are also separated from each other by a distance E (40 μm).
[0080]
A plurality of bonding pad units U3 are arranged in the outer row of the
[0081]
The plurality of bonding pad units U3 are arranged apart from each other by a distance E (40 μm). Similarly, the plurality of bonding pad units U4 are also arranged apart from each other by a distance E (40 μm).
[0082]
Both edges of the bonding pad unit U2 and both edges of the bonding pad unit U4 coincide with each other in the x-axis direction on the paper surface. Both edges of the bonding pad unit U1 and both edges of the bonding pad unit U3 also coincide with each other in the x-axis direction of the surface.
[0083]
The distances A, B, C, D, and E in the bonding pad units U2, U3, and U4 are the same as those of the bonding pad unit U1.
[0084]
By arranging the bonding pads having different widths adjacent to each other in the same row, the size of the bonding pad forming region can be reduced.
[0085]
By arranging a plurality of bonding pads in this manner, the bonding area can be efficiently reduced.
[0086]
Next, a bonding pad arrangement method and an LED print head mounting method in the second embodiment will be described with reference to FIGS.
[0087]
FIGS. 11 and 12 are flowcharts illustrating the bonding pad arrangement method and the print head mounting method according to the second embodiment. In
[0088]
(Step 1)
First, the width B of the first bonding pad and the width C of the second bonding pad are determined. Further, the distance D between the first bonding pad and the second bonding pad is determined by considering the width of the wiring layer.
(Step 2)
Next, based on the data obtained in
[0089]
(Step 3)
Next, the distance (interval) E between the bonding pad units is determined by considering the width of the wiring layer.
[0090]
(Step 4)
The bonding pad units U1 are arranged in a line along one side of the LED array IC to form a bonding pad group in the outer line. Further, the bonding pad units U3 are arranged in a line along one side of the drive IC to form a bonding pad group in the outer line.
[0091]
(Step 5)
The bonding pad units U2 are arranged in a line along the bonding pad group in the outer row of the LED array IC to form the bonding pad group in the inner row. Further, the bonding pad units U4 are arranged in a line along the bonding pad group in the outer row of the driving ICs to form the bonding pad group in the inner row.
[0092]
(Step 6)
These bonding pad units are arranged so that both edges of the bonding pad unit U1 in the outer row on the LED array IC coincide with both edges of the bonding pad unit U3 in the outer row of the driving IC.
[0093]
(Step 7)
These bonding pad units are arranged so that the edge of the bonding pad unit U2 in the inner row on the LED array IC coincides with the edge of the bonding pad unit U4 in the inner row of the driving IC.
[0094]
(Step 8)
The bonding pad units in the inner row of the LED array IC and the driving IC are moved by a predetermined distance in the X-axis direction with respect to the bonding pad units in the outer row.
[0095]
(Step 9)
Based on the data obtained in step 8, an LED array IC and a driving IC including bonding pads are manufactured.
[0096]
(Step 10)
A plurality of LED array ICs and a plurality of driving ICs are mounted on a mounting substrate.
[0097]
(Step 11)
Wire bonding is performed between the bonding pad of the LED array IC and the bonding pad of the driving IC.
[0098]
As described above, according to the second embodiment, it is possible to efficiently reduce the bonding pad formation region even in the staggered arrangement.
[0099]
【The invention's effect】
The following is a brief description of an outline of the effects obtained by the typical inventions among the inventions disclosed in the present application.
[0100]
That is, according to the present invention, since the bonding pads on which the first bonding is performed and the bonding pads on which the second bonding is performed are alternately arranged in the same column, the bonding area can be reduced.
[0101]
Furthermore, the present invention defines a bonding pad unit composed of a pair of bonding pads having different widths, and the bonding pads are arranged based on the bonding pad unit. Therefore, the bonding pads can be arranged with the minimum necessary data.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a plan view showing an entire semiconductor device according to a first embodiment of the present invention;
2 is a plan view showing a connection state between the
FIG. 3 is a plan view showing a state of wire bonding according to the present invention.
FIG. 4 is a plan view showing a state of conventional wire bonding.
FIG. 5 is a diagram showing a partially enlarged view of FIG. 2;
FIG. 6 is a flowchart of a bonding pad arrangement method and a print head mounting method according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 7 is a diagram showing a flowchart of a bonding pad arrangement method and a print head mounting method according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 8 is a plan view showing the entirety of a semiconductor device according to a second embodiment of the present invention;
9 is a plan view showing a connection state between the
10 is a diagram showing a partially enlarged view of FIG. 9. FIG.
FIG. 11 is a flowchart illustrating a bonding pad arrangement method and a print head mounting method according to a second embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 12 is a flowchart illustrating a bonding pad arrangement method and a print head mounting method according to a second embodiment of the present invention.
13 is a plan view showing an arrangement example of the
[Explanation of symbols]
103 ... LED array IC
109 ... Drive IC
115: Bonding wire
201, 203 ... Bonding area
205, 211 ... Bonding pads for first bonding
207, 209 ... Bonding pads for second bonding
Claims (3)
前記実装基板上に配置された第1の辺を有する第1の半導体基板と、
前記実装基板上に配置され、前記第1の辺に対向する第2の辺を有する第2の半導体基板と、
第1の幅を有する第1のボンディングパッドと、該第1のボンディングパッドと前記第1の辺に沿って隣接し前記第1の幅よりも短い第2の幅を有する第2のボンディングパッドとを含み、前記第1の半導体基板上に配置された第1のボンディングパッドユニットと、
前記第2の幅を有する第3のボンディングパッドと、該第3のボンディングパッドと前記第2の辺に沿って隣接し前記第1の幅を有する第4のボンディングパッドとを含み、前記第2の半導体基板上に配置された第2のボンディングパッドユニットと、
前記第1のボンディングパッドと前記第3のボンディングパッドとを接続する第1のボンディングワイヤーと、
前記第2のボンディングパッドと前記第4のボンディングパッドとを接続する第2のボンディングワイヤーとを備え、
前記第1のボンディングパッドユニットの前記第1の辺方向の両端は、前記第2のボンディングパッドユニットの前記第2の辺方向の両端と略等しい位置となるよう対向して配置されたことを特徴とする半導体装置。A mounting board;
A first semiconductor substrate having a first side disposed on the mounting substrate;
A second semiconductor substrate disposed on the mounting substrate and having a second side facing the first side;
A first bonding pad having a first width; a second bonding pad adjacent to the first bonding pad along the first side and having a second width shorter than the first width; A first bonding pad unit disposed on the first semiconductor substrate; and
Wherein it comprises third and bonding pads having a second width, and a fourth bonding pad having adjacent along the Bonn loading pad and the second side of the third and the first width, the second A second bonding pad unit disposed on two semiconductor substrates;
A first bonding wire connecting the first bonding pad and the third bonding pad;
A second bonding wire connecting the second bonding pad and the fourth bonding pad;
Both ends of the first bonding pad unit in the first side direction are arranged to face each other so as to be substantially equal to both ends of the second bonding pad unit in the second side direction. A semiconductor device.
前記第1の半導体基板、または、前記第2の半導体基板の何れか一方はLED素子が複数形成されたLEDアレイ装置であることを特徴とするLEDプリントヘッド。A semiconductor device according to claim 1,
One of the first semiconductor substrate and the second semiconductor substrate is an LED array device in which a plurality of LED elements are formed.
第1の幅を有する第1のボンディングパッドに関する第1ボンディングパッドデータを生成する工程と、
前記第1の幅よりも短い第2の幅を有する第2のボンディングパッドに関する第2ボンディングパッドデータを生成する工程と、
前記第1のボンディングパッドデータと前記第2のボンディングパッドデータとを使用して、前記第1及び第2のボンディングパッドに関するボンディングパッドユニットデータを生成する工程と、
前記ボンディングパッドユニットデータを複数個一列に並べた第1のデータ及び第2のデータを生成する工程と、
前記第1のデータに基づき、前記第1の辺に沿って前記第1の半導体基板上に複数のボンディングパッドを形成する工程と、
前記前記第2のデータに基づき、前記第2の辺に沿って前記第2の半導体基板上に複数のボンディングパッドを形成する工程と、
前記第1のボンディングパッドにファーストボンディングを実行し、その後前記第2のボンディングパッドにセカンドボンディングを実行する工程とを備えたことを特徴とするワイヤボンディング方法。Preparing a first semiconductor substrate having a first side; preparing a second semiconductor substrate having a second side opposite to the first side;
Generating first bonding pad data for a first bonding pad having a first width;
Generating second bonding pad data relating to a second bonding pad having a second width shorter than the first width;
Generating bonding pad unit data for the first and second bonding pads using the first bonding pad data and the second bonding pad data;
Generating a first data and a second data in which a plurality of the bonding pad unit data are arranged in a line;
Forming a plurality of bonding pads on the first semiconductor substrate along the first side based on the first data;
Forming a plurality of bonding pads on the second semiconductor substrate along the second side based on the second data;
A wire bonding method comprising: performing a first bonding on the first bonding pad and then performing a second bonding on the second bonding pad.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000382222A JP4034932B2 (en) | 2000-12-15 | 2000-12-15 | Semiconductor device, LED print head, and wire bonding method |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000382222A JP4034932B2 (en) | 2000-12-15 | 2000-12-15 | Semiconductor device, LED print head, and wire bonding method |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2002184805A JP2002184805A (en) | 2002-06-28 |
| JP2002184805A5 JP2002184805A5 (en) | 2006-10-12 |
| JP4034932B2 true JP4034932B2 (en) | 2008-01-16 |
Family
ID=18850087
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000382222A Expired - Fee Related JP4034932B2 (en) | 2000-12-15 | 2000-12-15 | Semiconductor device, LED print head, and wire bonding method |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4034932B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4522079B2 (en) * | 2003-11-20 | 2010-08-11 | イビデン株式会社 | IC chip mounting substrate |
| KR101475314B1 (en) * | 2009-03-30 | 2014-12-23 | 엘지디스플레이 주식회사 | Light emitting diode backlight unit and liquid crystal display device module using the same |
| JP6196092B2 (en) * | 2013-07-30 | 2017-09-13 | ルネサスエレクトロニクス株式会社 | Semiconductor device |
| JP7249302B2 (en) * | 2020-03-19 | 2023-03-30 | 株式会社東芝 | semiconductor equipment |
| WO2021187101A1 (en) * | 2020-03-19 | 2021-09-23 | 京セラ株式会社 | Light-emitting element array and light print head provided with same, and image forming device |
-
2000
- 2000-12-15 JP JP2000382222A patent/JP4034932B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2002184805A (en) | 2002-06-28 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US20060131757A1 (en) | Light emitting module | |
| JP4034932B2 (en) | Semiconductor device, LED print head, and wire bonding method | |
| JP2000289250A (en) | Led array chip and led array print head | |
| JP2901223B2 (en) | Imaging device | |
| JPS61105851A (en) | Wire bonding method | |
| WO2000037255A1 (en) | Driver ic chip and print head | |
| JPS62191161A (en) | Thermal recording head | |
| JPH0694216B2 (en) | Optical print head | |
| JP3357810B2 (en) | Optical print head | |
| JP2633701B2 (en) | Thermal head | |
| JPS60182756A (en) | Ic device | |
| KR920016256A (en) | LED Printhead | |
| JPH06278313A (en) | Image device | |
| JP2911351B2 (en) | Structure of semiconductor chip for driving in thermal print head | |
| JP2914643B2 (en) | Imaging device | |
| JP2511654B2 (en) | Liquid crystal display | |
| KR920003079B1 (en) | Printer head | |
| JPH09270535A (en) | Semiconductor element and linear light source using it | |
| EP0581330B1 (en) | Drive IC for printing head | |
| JPH0323734Y2 (en) | ||
| JPH07266617A (en) | Structure of led array semiconductor chip used in led array printing head | |
| JPH04313283A (en) | Mounting method of semiconductor device and ic chip | |
| JPH11219961A (en) | Mounting structure and method of optical semiconductor module | |
| JP2586009Y2 (en) | Thermal head | |
| KR930000704B1 (en) | Driving ic roading method |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20060828 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20060828 |
|
| RD02 | Notification of acceptance of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7422 Effective date: 20061025 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20061130 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20070515 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20070713 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20070807 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20071002 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20071023 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20071026 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20101102 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20101102 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20111102 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20111102 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20121102 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20121102 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20131102 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |