JP3944377B2 - Focus detection device - Google Patents
Focus detection device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP3944377B2 JP3944377B2 JP2001324035A JP2001324035A JP3944377B2 JP 3944377 B2 JP3944377 B2 JP 3944377B2 JP 2001324035 A JP2001324035 A JP 2001324035A JP 2001324035 A JP2001324035 A JP 2001324035A JP 3944377 B2 JP3944377 B2 JP 3944377B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- light
- subject
- focus detection
- image
- reflected
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Length Measuring Devices By Optical Means (AREA)
- Microscoopes, Condenser (AREA)
- Automatic Focus Adjustment (AREA)
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、例えばIC基板や材料などの加工面に対して光学的に焦点を合わせる焦点検出装置に関するものである。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
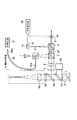
従来、この種の焦点検出装置として、図5に示すように構成したものがある。図において、1は測定光としての赤外域のレーザー光を発生する半導体レーザーで、この半導体レーザー1から発せられたレーザー光は、偏光ビームスプリッタ2に照射される。偏光ビームスプリッタ2で反射された光は、結像レンズ3で平行ビームに変換され、1/4波長板4、ダイクロイックミラー5を介して対物レンズ6に入射し、被検体である被測定表面7(例えば、IC基板表面あるいは材料の加工表面など)に集光される。そして、この被測定表面7で反射された反射光は、再び対物レンズ6、ダイクロイックミラー5、1/4波長板4および結像レンズ3を介して偏光ビームスプリッタ2に照射される。
【0003】
この場合、反射光は、1/4波長板4を透過する際、その偏光方向が90°ずれるので、反射光は、偏光ビームスプリッタ2を透過してビームスプリッタ8に入射され、ここで2方向に振り分けられる。
【0004】
このうちビームスプリッタ8を透過した光は、合焦点より前に置かれた第1の絞り9を介して受光手段としての第1の受光素子10により受光され、また、ビームスプリッタ8を反射した光は、合焦点より後に置かれた第2の絞り11を介して受光手段としての第2の受光素子12により受光される。これら第1および第2の受光素子10、12は、それぞれ受光した反射光の光量に応じた電気信号a、bを出力するもので、これら電気信号a、bを信号処理系13に入力する。信号処理系13は、入力された電気信号a、bに対して所定の演算を実行し、被測定表面7の変位に対応した変位信号を出力する。
【0005】
この場合、第1および第2の受光素子10、12より、図6に示すような特性を有する電気信号a、bが出力されたとすると、信号処理系13により図7に示すような特性を有する変位信号cが出力され、この変位信号cに基づいて被測定表面7の変位が測定されるとともに、この被測定表面7に対する焦点検出が行われる。
【0006】
ところで、通常、このような焦点検出は、被測定表面7を観察しながら行われる。この場合、上述したダイクロイックミラー5は、赤外波長域以上の光成分を反射するとともに、可視域の光を透過するような特性のものが用いられ、観察光学系14には、レーザー光の入射を阻止し、可視光のみを取り込むことができるようになっている。
【0007】
そして、被測定表面7の観察には、被測定表面7を可視光で照明する。被測定表面7からの反射光は、対物レンズ6を介してダイクロイックミラー5に照射され、ダイクロイックミラー5を透過した光は、観察光学系14の結像レンズ14aにより集光され、被測定表面7の観察像が図示しない接眼レンズやCCDカメラにより観察される。
【0008】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
このような焦点検出装置では、被測定表面7に集光される半導体レーザー1のスポットは、理論上回折限界まで絞られ、極めて微小な集光スポットとなり、焦点検出は、このような微小な集光スポットが照射される被測定表面7上の極微小な領域を対象にして行われる。
【0009】
ところが、焦点検出の際に、被測定表面7で反射されたレーザー光のスポットは、ダイクロイックミラー5により観察光学系14への入射を阻止されているので、被測定表面7を観察している観察者には、レーザー光のスポット位置を知ることができない。つまり、観察者は、焦点検出を行っている状態で、被測定表面7を観察しているものの、被測定表面7上のどの領域を対象にして焦点検出が行われているかを全く知ることができない。
【0010】
このため、従来では、例えば、被測定表面7の微小な領域の焦点検出を行うような場合は、経験的に覚えているレーザー光のスポット位置に対して検出対象の領域を正確に移動させなければならず、このための作業に熟練を要するという問題があった。
【0011】
また、熟練した技術を持たない観察者は、検出対象の領域が十分な大きさの像になるように高倍の対物レンズに切換え、この拡大された領域像をレーザー光のスポット位置に移動させるようにしているが、高倍の対物レンズを用いることで視野自体が著しく狭くなるため、さらに作業性が悪化するという問題があった。
【0012】
一方、レーザースポットの位置を明確にするため、CCDカメラにより撮像した観察像をTVモニタ上で観察し、TVモニタ上でおおよそのレーザースポットの位置に印を付けるような場合も合ったが、TVシステムを必要とするため、装置が大掛かりとなるとともに、価格的にも高価であった。
【0013】
本発明は上記事情に鑑みてなされたもので、優れた作業性が得られ、しかも微小な領域の焦点検出も確実に行うことができる焦点検出装置を提供することを目的とする。
【0014】
【課題を解決するための手段】
請求項1記載の発明は、半導体レーザーから出射された赤外域の測定光を被検体に対し集光スポットとして照射するとともに、前記被検体から反射した反射光を受光手段で受光し、該受光手段の出力により前記被検体面の合焦を検出する焦点検出装置において、前記測定光の投影像と光学的に共役の位置に配置された指標と、前記指標を照明する可視光域の光を発光する光源と、を具備し、前記可視光域の光を発光する光源により照明された前記指標の像の光を前記測定光の光路を通して前記被検体に対し照射するとともに、前記被検体から反射した前記指標の像の位置と前記被検体上に照射される前記測定光の集光スポット位置を一致させ、前記指標の像の位置を前記測定光の集光スポット位置として観察可能にしたことを特徴としている。
【0015】
請求項2記載の発明は、請求項1記載の発明において、前記測定光は、レーザー光からなり、前記指標は円形又は十字線パターンのピンホールからなることを特徴としている。
【0016】
請求項3記載の発明は、請求項1記載の発明において、前記可視光域の光を発光する光源は、LEDであることを特徴としている。
請求項4記載の発明は、半導体レーザーから出射された赤外域の測定光を被検体に対し集光スポットとして照射するとともに、前記被検体から反射した反射光を受光手段で受光し、該受光手段の出力により前記被検体面の合焦を検出する焦点検出装置において、前記測定光の発光点の投影像と光学的に共役の位置に出射端が配置されるとともに、前記出射端より可視光域の光を発する光ファイバを具備し、前記可視光域の光を発光する光ファイバの出射端からの光を前記測定光の光路を通して前記被検体に対し照射するとともに、前記被検体から反射した前記出射端の像の位置と前記被検体上に照射される前記測定光の集光スポット位置を一致させ、前記出射端の像の位置を前記測定光の集光スポット位置として観察可能にしたことを特徴としている。
請求項5記載の発明は、請求項1または4記載の発明において、前記可視光域の光を発する光源は、常時点灯、または前記被検体面の合焦を検出する時のみ点灯することを特徴としている。
請求項6の発明は、請求項1記載の発明において、前記赤外域の測定光の透過を阻止し、且つ、前記可視光域の光を発光する光源により照明された前記指標の像の光を透過させるIRカットフィルタを備えることを特徴としている。
請求項7の発明は、請求項4記載の発明において、前記赤外域の測定光の透過を阻止し、且つ、前記可視光域の光を発光する光源により照明された前記出射端の像の光を透過させるIRカットフィルタを備えることを特徴としている。
【0017】
この結果、本発明によれば、焦点検出のための測定光の被検体上での集光スポットの位置を指標の像位置から容易に知ることができるので、観察者は、測定光の位置を経験的に覚えるような必要がなくなり、焦点検出のための一連の作業を簡単にすることができる。
【0018】
また、本発明によれば、被検体上の焦点検出したい領域が極めて小さい場合も、指標の像位置を目的の領域に移動させるだけで対応することができる。
【0019】
さらに、本発明によれば、光ファイバにより外部からの光を導くことができるので、外部光源を選択することで被検体面に合わせた色の選択や光量の調整を行うことが可能となり、これらを組み合わせることで様々なユーザ要求に答えることができる。
【0020】
【発明の実施の形態】
以下、本発明の実施の形態を図面に従い説明する。
【0021】
(第1の実施の形態)
図1は、本発明が適用される共焦点型の焦点検出装置の概略構成を示すもので、図5と同一部分には同符号を付している。
【0022】
この場合、図5で述べたダイクロイックミラー5に代えてハーフミラー20が配置されている。
【0023】
半導体レーザー1と偏光ビームスプリッタ2との間の光路にビームスプリッタ21が配置されている。また、ビームスプリッタ21より分割された光路には、指標として円形のピンホール22が配置され、このピンホール22の後方に、ピンホール22を照明する可視光域の光を発光するLEDなどの光源23が配置されている。この場合、ピンホール22は、半導体レーザー1の発光点の投影像と光学的に共役の位置に配置されている。
【0024】
なお、光源23については、常時点灯されていても焦点検出時のみ点灯するようにしてもよい。
【0025】
ハーフミラー20と対物レンズ6の間の光路には、ハーフミラー24が配置され、このハーフミラー24の分割光路には、被測定表面7を照明する可視光域の光を発光する光源25が配置されている。
【0026】
また、ハーフミラー20と観察光学系14との間の光路には、IRカットフィルタ26が配置されている。このIRカットフィルタ26は、被測定表面7で反射しハーフミラー20を透過した反射光のうち、赤外波長域以上の光成分の透過を阻止し、可視光域の光のみを観察光学系14側に透過させるためのものである。
【0027】
さらに、偏光ビームスプリッタ2とビームスプリッタ8との間の光路には、バンドパスフィルタ27が配置されている。このバンドパスフィルタ27は、被測定表面7で反射しハーフミラー20で反射した反射光のうち、可視光域の光の透過を阻止し、赤外波長域以上の光成分を第1および第2の受光素子10、12側に透過させるためのものである。
【0028】
このような構成において、いま、半導体レーザー1からレーザー光が発せられると、ビームスプリッタ21を透過して偏光ビームスプリッタ2に照射される。偏光ビームスプリッタ2で反射された光は、結像レンズ3で平行ビームに変換され、1/4波長板4を透過し、ハーフミラー20で反射して対物レンズ6に入射し、被測定表面7にスポット状に集光される。
【0029】
また、被測定表面7で反射された反射光は、再び対物レンズ6を透過し、ハーフミラー20で反射して1/4波長板4および結像レンズ3を介して偏光方向が90°ずれて偏光ビームスプリッタ2に照射される。
【0030】
これにより、反射光は、偏光ビームスプリッタ2を透過してビームスプリッタ8に入射され、ここで2方向に振り分けられる。そして、ビームスプリッタ8を透過した光は、合焦点より前に置かれた第1の絞り9を介して第1の受光素子10により受光され、また、ビームスプリッタ8を反射した光は、合焦点より後に置かれた第2の絞り11を介して第2の受光素子12により受光される。また、これら受光された光量に応じた第1および第2の受光素子10、12からの電気信号が信号処理系13に入力され、ここで、所定の演算が実行され、被測定表面7の変位に対応した変位信号が出力され、被測定表面7に対する焦点検出が行われる。
【0031】
この場合、半導体レーザー1のレーザー光の被測定表面7で反射される反射光の一部は、ハーフミラー20を透過されるが、IRカットフィルタ26により観察光学系14側への入射は阻止される。
【0032】
一方、この状態で、光源25より可視光域の光が発せられると、この光は、ハーフミラー24で反射し、対物レンズ6を透過して被測定表面7に照射される。また、被測定表面7からの反射光は、対物レンズ6を介してハーフミラー24、20を順に透過し、これらハーフミラー24、20を透過した光は、IRカットフィルタ26を透過して観察光学系14の結像レンズ14aにより集光され、焦点検出が行われる被測定表面7の観察像が図示しない接眼レンズやCCDカメラにより観察される。
【0033】
また、これと同時に、光源23より可視光域の光が発せられると、この光により照明されたピンホール22の像が、ビームスプリッタ21に入射される。その後は、半導体レーザー1からの光と同じ光路を通って被測定表面7に結像される。また、被測定表面7で反射されたピンホール22の像は、対物レンズ6を介してハーフミラー24、20を順に透過し、これらハーフミラー24、20を透過した光は、IRカットフィルタ26を透過して観察光学系14の結像レンズ14aにより集光され、上述した接眼レンズやCCDカメラにより観察される被測定表面7の観察像上に重ねて表示される。
【0034】
この場合、ピンホール22の位置は、半導体レーザー1の発光点の投影像と光学的に共役な位置にあるので、観察光学系14で観察されるピンホール22の像位置は、被測定表面7上に集光されレーザー光のスポット位置と一致している。
【0035】
これにより、観察者は、焦点検出が行われる被測定表面7の観察像を観察しながら、この観察像上に重ねて表示されるピンホール22の像位置からレーザー光のスポットの位置を容易に知ることができるので、被測定表面7上のどの領域を対象にして焦点検出が行われているかを簡単に確認でき、また、ピンホール22の像位置を被測定表面7上の焦点検出したい測定ポイントに移動させるだけで、微小な領域に対するレーザー光のスポットの位置決めを正確に行うことができる。
【0036】
この場合、光源25からの可視光域の光および光源23からの可視光域の光により照明されたピンホール22の像の被測定表面7で反射される光の一部は、ハーフミラー20で反射されるが、バンドパスフィルタ27により第1および第2の受光素子10、12側への入射は阻止される。
【0037】
従って、このようにすれば、半導体レーザー1からのレーザー光の被測定表面7上でのスポットの位置を、観察像上に重ねて表示されるピンホール22の像位置から容易に知ることができるので、従来と比べ、観察者は、レーザースポットの位置を経験的に覚えるような必要がなく、焦点検出のための作業に熟練する必要もなくなり、焦点検出のための一連の作業を簡単にすることができる。
【0038】
また、対物レンズ6の倍率が低く、被測定表面7上の焦点検出したい領域が極めて小さい場合も、ピンホール22の像位置を目的の領域に移動させるだけで対応できるので、優れた作業性、操作性が得られる。
【0039】
さらに、TVシステムなどによりレーザースポットの位置に印を付けるような必要もないので、これらTVシステム等を用いたものと比べてシステム構成が簡単で、価格的にも安価にできる。
【0040】
(変形例)
上述した実施の形態では、指標として円形のピンホール22を用いた例を述べたが、この形状に限らず、例えば十字線パターンなど、観察像中で目印になるようなパターンであれば、どのような形状であってもよい。
【0041】
(第2の実施の形態)
次に、本発明の第2の実施の形態を説明する。
【0042】
図2は、第2の実施の形態の概略構成を示すもので、図1と同一部分には同符号を付している。
【0043】
この場合、図1で述べたピンホール22と光源23に代えて光ファイバ30が用いられている。この光ファイバ30は、ビームスプリッタ21より分割された光路に出射端30aが配置されている。この出射端30aは、半導体レーザー1の発光点の投影像と光学的に共役の位置に配置されている。
【0044】
また、光ファイバ30の入射端30bには、装置外部に配置された可視光域の光を発する外部光源31が接続されている。この外部光源31は、常時点灯されていても焦点検出時のみ点灯するようにしてもよい。
【0045】
このような構成においても、外部光源31より可視光域の光が発せられると、光ファイバ30の出射端30aからの光がビームスプリッタ21に入射される。その後は、半導体レーザー1からの光と同じ光路を通って被測定表面7に結像される。また、被測定表面7で反射された光ファイバ30の出射端30aの像は、対物レンズ6を介してハーフミラー24、20を順に透過し、これらハーフミラー24、20を透過した光は、IRカットフィルタ26を透過して観察光学系14の結像レンズ14aにより集光され、上述した接眼レンズやCCDカメラにより観察される被測定表面7の観察像上に重ねて表示される。
【0046】
この場合、光ファイバ30の出射端30aの位置は、半導体レーザー1の発光点の投影像と光学的に共役な位置にあるので、観察光学系14で観察される出射端30aの像位置は、被測定表面7上に集光されレーザー光のスポット位置と一致している。
【0047】
これにより、観察者は、焦点検出が行われる被測定表面7の観察像を観察しながら、この観察像上に重ねて表示される出射端30aの像位置からレーザー光のスポットの位置を容易に知ることができるので、被測定表面7上のどの領域を対象にして焦点検出が行われているかを簡単に確認でき、また、出射端30aの像位置を被測定表面7上の焦点検出したい測定ポイントに移動させるだけで、微小な領域に対するレーザー光のスポットの位置決めを正確に行うことができる。
【0048】
従って、このようにしても上述した第1の実施の形態と同様な効果を期待でき、さらに、光ファイバ30により外部光源31からの光を導くようにしているので、外部光源31を選択することで被測定表面7に合わせた色の選択や光量の調整を行うことが可能となり、これらを組み合わせることにより様々なユーザ要求に答えることができる。
【0049】
(第3の実施の形態)
次に、本発明の第3の実施の形態を説明する。
【0050】
図3は、第3の実施の形態の概略構成を示すもので、図1と同一部分には同符号を付している。
【0051】
この場合、図1で述べたビームスプリッタ21、ピンホール22および光源23に代えて、1/4波長板4とハーフミラー20との間の光路にビームスプリッタ40が配置され、このビームスプリッタ40より分割された光路には、結像レンズ41が配置されている。また、結像レンズ41の焦点位置には、指標として円形のピンホール42が配置され、このピンホール42の後方に、ピンホール42を照明する可視光域の光を発光するLEDなどの光源43が配置されている。この場合、ピンホール42は、半導体レーザー1の発光点の投影像と光学的に共役の位置に配置されている。
【0052】
なお、光源43についても、常時点灯されていても焦点検出時のみ点灯するようにしてもよい。
【0053】
このような構成によっても、光源43より可視光域の光が発せられると、この光により照明されたピンホール42の像の光が、結像レンズ41に入射され、平行光となってビームスプリッタ40に入射される。その後は、半導体レーザー1からの光と同じ光路を通って被測定表面7に投影される。また、被測定表面7で反射されたピンホール42の像は、対物レンズ6を介してハーフミラー24、20を順に透過し、これらハーフミラー24、20を透過した光は、IRカットフィルタ26を透過して観察光学系14の結像レンズ14aにより集光され、上述した接眼レンズやCCDカメラにより観察される被測定表面7の観察像上に重ねて表示される。
【0054】
この場合、ピンホール42の位置は、半導体レーザー1の発光点の投影像と光学的に共役な位置にあるので、観察光学系14で観察されるピンホール42の像位置は、被測定表面7上に集光されレーザー光のスポット位置と一致している。
【0055】
これにより、観察者は、焦点検出が行われる被測定表面7の観察像を観察しながら、この観察像上に重ねて表示されるピンホール42の像位置からレーザー光のスポットの位置を容易に知ることができるので、被測定表面7上のどの領域を対象にして焦点検出が行われているかを簡単に確認でき、また、ピンホール42の像位置を被測定表面7上の焦点検出したい測定ポイントに移動させるだけで、微小な領域に対するレーザー光のスポットの位置決めを正確に行うことができる。
【0056】
従って、このようにしても上述した第1の実施の形態と同様な効果を期待でき、さらに、ピンホール42を被測定表面7上に投影するための結像レンズ41は、半導体レーザー1からのレーザー光の光路と無関係な位置に配置しているので、結像レンズ41の焦点距離を適当に変更しても焦点検出光学系の特性は変化しない。このことは、焦点検出光学系の特性を変化させることなく被測定表面7上でのピンホール42の投影倍率を変更できるので、使い勝手のよい投影倍率を設定することができる。
【0057】
(第4の実施の形態)
ところで、上述した第1乃至第3の実施の形態では、共焦点型の焦点検出装置について述べたが、この第4の実施の形態では、瞳分割方式の焦点検出装置に本発明を適用した例を示している。
【0058】
図4は、第4の実施の形態の概略構成を示すもので、図1と同一部分には同符号を付している。
【0059】
この場合、半導体レーザー1から出射されるレーザー光の光路中に、コリメータレンズ51、遮蔽板52、集光レンズ53が配置されており、レーザー光は、コリメータレンズ51により平行光に変換され、遮蔽板52により半分の光束が遮蔽され、残り半分の光束が集光レンズ53により中間結像位置Pに投影された後、偏光ビームスプリッタ2に照射される。そして、偏光ビームスプリッタ2で反射された光は、結像レンズ3、1/4波長板4、ハーフミラー20の図示光路Cを介して対物レンズ6に入射し、被測定表面7に集光し、この被測定表面7で反射された反射光は、再び対物レンズ6、ハーフミラー20、1/4波長板4および結像レンズ3の図示光路Dを介して偏光方向が90°ずれて偏光ビームスプリッタ2に照射される。これにより、反射光は、偏光ビームスプリッタ2を透過してバンドパスフィルタ27を介して2分割受光素子54に結像される。
【0060】
この2分割受光素子54は、2つの光電変換部A、Bを有しており、これら光電変換部A、Bは、それぞれ受光した反射光の光量に応じた電気信号a、bを出力するもので、これら電気信号a、bを信号処理系55に入力する。信号処理系55は、入力された電気信号a、bに対して所定の演算を実行し、被測定表面7の変位に対応した変位信号を出力する。
【0061】
この場合も、光電変換部A、Bより、図6に示すような特性を有する電気信号a、bが出力されたとすると、信号処理系55により図7に示すような特性を有する変位信号cが出力され、この変位信号cに基づいて被測定表面7の変位が測定されるとともに、この被測定表面7に対する焦点検出が行われる。
【0062】
一方、集光レンズ53と偏光ビームスプリッタ2との間の光路にビームスプリッタ56が配置されている。また、ビームスプリッタ56より分割された光路には、指標として円形のピンホール57が配置され、このピンホール57の後方に、ピンホール57を照明する可視光域の光を発光するLEDなどの光源58が配置されている。この場合、ピンホール57は、半導体レーザー1の発光点の投影像と光学的に共役の位置に配置されている。
【0063】
なお、光源58についても、常時点灯されていても焦点検出時のみ点灯するようにしてもよい。
【0064】
このような構成によっても、光源58より可視光域の光が発せられると、この光により照明されたピンホール57の像の光が、ビームスプリッタ56に入射される。その後は、半導体レーザー1からの光と同じ光路を通って被測定表面7に照射される。また、被測定表面7で反射されたピンホール57の像は、対物レンズ6を介してハーフミラー24、20を順に透過し、これらハーフミラー24、20を透過した光は、IRカットフィルタ26を透過して観察光学系14の結像レンズ14aにより集光され、上述した接眼レンズやCCDカメラにより観察される被測定表面7の観察像上に重ねて表示される。
【0065】
この場合、ピンホール57の位置は、半導体レーザー1の発光点の投影像と光学的に共役な位置にあるので、観察光学系14で観察されるピンホール57の像位置は、被測定表面7上に集光されレーザー光のスポット位置と一致している。
【0066】
これにより、観察者は、焦点検出が行われる被測定表面7の観察像を観察しながら、この観察像上に重ねて表示されるピンホール57の像位置からレーザー光のスポットの位置を容易に知ることができるので、被測定表面7上のどの領域を対象にして焦点検出が行われているかを簡単に確認でき、また、ピンホール57の像位置を被測定表面7上の焦点検出したい測定ポイントに移動させるだけで、微小な領域に対するレーザー光のスポットの位置決めを正確に行うことができる。
【0067】
従って、このようにしても上述した第1の実施の形態と同様な効果を期待することができる。
【0068】
なお、本発明は、上記実施の形態に限定されるものでなく、実施段階では、その要旨を変更しない範囲で種々変形することが可能である。
【0069】
さらに、上記実施の形態には、種々の段階の発明が含まれており、開示されている複数の構成要件における適宜な組み合わせにより種々の発明が抽出できる。例えば、実施の形態に示されている全構成要件から幾つかの構成要件が削除されても、発明が解決しようとする課題の欄で述べた課題を解決でき、発明の効果の欄で述べられている効果が得られる場合には、この構成要件が削除された構成が発明として抽出できる。
【0070】
【発明の効果】
以上述べたように本発明によれば、優れた作業性が得られ、しかも微小な領域の焦点検出も確実に行うことができる焦点検出装置を提供できる。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】本発明の第1の実施の形態の概略構成を示す図。
【図2】本発明の第2の実施の形態の概略構成を示す図。
【図3】本発明の第3の実施の形態の概略構成を示す図。
【図4】本発明の第4の実施の形態の概略構成を示す図。
【図5】従来の焦点検出装置の一例の概略構成を示す図。
【図6】焦点検出装置の受光素子より出力される電気信号の特性を示す図。
【図7】焦点検出装置の信号処理系より出力される変位信号の特性を示す図。
【符号の説明】
1…半導体レーザー
2…偏光ビームスプリッタ
3…結像レンズ
4…1/4波長板
5…ダイクロイックミラー
6…対物レンズ
7…被測定表面
8…ビームスプリッタ
9…第1の絞り
10…第1の受光素子
11…第2の絞り
12…第2の受光素子
13…信号処理系
14…観察光学系
14a…結像レンズ
20…ハーフミラー
21…ビームスプリッタ
22…ピンホール
23…光源
24…ハーフミラー
25…光源
26…IRカットフィルタ
27…バンドパスフィルタ
30…光ファイバ
30a…出射端
30b…入射端
31…外部光源
40…ビームスプリッタ
41…結像レンズ
42…ピンホール
43…光源
51…コリメータレンズ
52…遮蔽板
53…集光レンズ
54…分割受光素子
55…信号処理系
56…ビームスプリッタ
57…ピンホール
58…光源[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a focus detection apparatus that optically focuses a processing surface such as an IC substrate or a material.
[0002]
[Prior art]
Conventionally, this type of focus detection apparatus is configured as shown in FIG. In the figure, reference numeral 1 denotes a semiconductor laser that generates laser light in the infrared region as measurement light. Laser light emitted from the semiconductor laser 1 is applied to the
[0003]
In this case, when the reflected light is transmitted through the quarter-
[0004]
Of these, the light transmitted through the
[0005]
In this case, assuming that the electrical signals a and b having the characteristics shown in FIG. 6 are output from the first and second
[0006]
Incidentally, such focus detection is usually performed while observing the surface 7 to be measured. In this case, the dichroic mirror 5 described above has a characteristic that reflects light components in the infrared wavelength region or more and transmits light in the visible region, and the observation optical system 14 receives laser light. And only visible light can be captured.
[0007]
For observation of the surface 7 to be measured, the surface 7 to be measured is illuminated with visible light. Reflected light from the surface to be measured 7 is applied to the dichroic mirror 5 through the
[0008]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
In such a focus detection apparatus, the spot of the semiconductor laser 1 focused on the surface 7 to be measured is theoretically narrowed to the diffraction limit and becomes a very small focused spot. The measurement is performed on a very small area on the surface to be measured 7 irradiated with the light spot.
[0009]
However, since the spot of the laser beam reflected by the surface to be measured 7 is prevented from entering the observation optical system 14 by the dichroic mirror 5 at the time of focus detection, the observation for observing the surface to be measured 7 is observed. A person cannot know the spot position of the laser beam. That is, the observer observes the surface to be measured 7 while performing focus detection, but can completely know which region on the surface to be measured 7 is subjected to focus detection. Can not.
[0010]
For this reason, conventionally, for example, when focus detection is performed on a minute area of the surface 7 to be measured, the detection target area must be accurately moved with respect to the spot position of the laser light that is empirically remembered. In other words, there is a problem that the work for this requires skill.
[0011]
In addition, an observer who does not have a skillful technique switches to a high-magnification objective lens so that the detection target area becomes a sufficiently large image, and moves the enlarged area image to the spot position of the laser beam. However, since the field of view itself becomes extremely narrow by using a high-magnification objective lens, there is a problem that workability is further deteriorated.
[0012]
On the other hand, in order to clarify the position of the laser spot, the observation image captured by the CCD camera is observed on the TV monitor and the approximate position of the laser spot is marked on the TV monitor. Since a system is required, the apparatus becomes large and expensive in price.
[0013]
The present invention has been made in view of the above circumstances, and an object of the present invention is to provide a focus detection apparatus that can obtain excellent workability and can reliably perform focus detection in a minute region.
[0014]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
The invention described in claim 1In the infrared region emitted from the semiconductor laserIn a focus detection apparatus that irradiates a subject with measurement light as a focused spot, receives reflected light reflected from the subject with a light receiving means, and detects the focus of the subject surface by the output of the light receiving means An index placed at a position optically conjugate with the projected image of the measurement light, and a light source that emits light in a visible light range that illuminates the index,Emits light in the visible light rangeThe light of the index image illuminated by the light source is irradiated to the subject through the optical path of the measurement light, and the position of the index image reflected from the subject and the measurement irradiated onto the subject Light focusing spotThe position of the index image is matched with the position of the index image.It is characterized by being made observable.
[0015]
According to a second aspect of the present invention, in the first aspect of the invention, the measurement light is a laser beam, and the index isPinhole with circular or cross patternIt is characterized by consisting of.
[0016]
The invention described in claim 3The invention according to claim 1 is characterized in that the light source that emits light in the visible light region is an LED.
The invention according to
According to a fifth aspect of the present invention, in the first or fourth aspect of the invention, the light source that emits light in the visible light region is always turned on or only when the in-focus state of the subject surface is detected. It is said.
According to a sixth aspect of the present invention, in the first aspect of the invention, the light of the index image illuminated by a light source that blocks the transmission of the measurement light in the infrared region and emits the light in the visible light region. An IR cut filter that transmits the light is provided.
The invention according to claim 7 is the light of the image of the emission end illuminated by a light source that blocks transmission of the measurement light in the infrared region and emits light in the visible light region. It is characterized by comprising an IR cut filter that transmits light.
[0017]
As a result, according to the present invention, since the position of the focused spot on the subject of the measurement light for focus detection can be easily known from the image position of the index, the observer can determine the position of the measurement light. There is no need to memorize empirically, and a series of operations for focus detection can be simplified.
[0018]
Further, according to the present invention, even when the region on the subject on which the focus is to be detected is extremely small, it is possible to cope with it by simply moving the image position of the index to the target region.
[0019]
Furthermore, according to the present invention, since light from the outside can be guided by the optical fiber, it is possible to select the color and adjust the light amount according to the subject surface by selecting the external light source. Various user requests can be answered by combining.
[0020]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
[0021]
(First embodiment)
FIG. 1 shows a schematic configuration of a confocal focus detection apparatus to which the present invention is applied, and the same parts as those in FIG.
[0022]
In this case, a
[0023]
A
[0024]
It should be noted that the
[0025]
A
[0026]
An IR cut
[0027]
Further, a
[0028]
In such a configuration, when a laser beam is emitted from the semiconductor laser 1, the laser beam is transmitted through the
[0029]
The reflected light reflected by the surface 7 to be measured is transmitted again through the
[0030]
As a result, the reflected light passes through the
[0031]
In this case, a part of the reflected light reflected by the surface 7 to be measured of the laser light of the semiconductor laser 1 is transmitted through the
[0032]
On the other hand, when light in the visible light range is emitted from the
[0033]
At the same time, when light in the visible light range is emitted from the
[0034]
In this case, since the position of the
[0035]
Thereby, the observer can easily locate the spot of the laser beam from the image position of the
[0036]
In this case, a part of the light reflected by the measured surface 7 of the image of the
[0037]
Therefore, in this way, the position of the spot of the laser light from the semiconductor laser 1 on the surface to be measured 7 can be easily known from the image position of the
[0038]
Further, even when the magnification of the
[0039]
Furthermore, since it is not necessary to mark the position of the laser spot with a TV system or the like, the system configuration is simpler and less expensive than those using these TV systems.
[0040]
(Modification)
In the above-described embodiment, an example using the
[0041]
(Second embodiment)
Next, a second embodiment of the present invention will be described.
[0042]
FIG. 2 shows a schematic configuration of the second embodiment, and the same parts as those in FIG.
[0043]
In this case, an
[0044]
In addition, an external
[0045]
Even in such a configuration, when light in the visible light range is emitted from the external
[0046]
In this case, since the position of the
[0047]
Thereby, the observer can easily locate the spot of the laser beam from the image position of the
[0048]
Therefore, even in this way, the same effect as that of the first embodiment described above can be expected. Furthermore, since the light from the external
[0049]
(Third embodiment)
Next, a third embodiment of the present invention will be described.
[0050]
FIG. 3 shows a schematic configuration of the third embodiment, and the same parts as those in FIG.
[0051]
In this case, instead of the
[0052]
Note that the
[0053]
Even in such a configuration, when light in the visible light range is emitted from the
[0054]
In this case, since the position of the
[0055]
Thus, the observer can easily determine the position of the laser light spot from the image position of the
[0056]
Therefore, even in this way, the same effect as that of the first embodiment described above can be expected. Further, the
[0057]
(Fourth embodiment)
In the first to third embodiments described above, the confocal focus detection device has been described. However, in the fourth embodiment, the present invention is applied to a pupil division type focus detection device. Is shown.
[0058]
FIG. 4 shows a schematic configuration of the fourth embodiment, and the same parts as those in FIG.
[0059]
In this case, a
[0060]
The two-divided
[0061]
Also in this case, assuming that the electrical signals a and b having the characteristics shown in FIG. 6 are output from the photoelectric conversion units A and B, the displacement signal c having the characteristics shown in FIG. The displacement of the surface 7 to be measured is measured based on the displacement signal c, and the focus detection for the surface 7 to be measured is performed.
[0062]
On the other hand, a
[0063]
Note that the
[0064]
Even in such a configuration, when light in the visible light range is emitted from the
[0065]
In this case, since the position of the
[0066]
Thus, the observer can easily determine the position of the laser light spot from the image position of the
[0067]
Therefore, even in this way, the same effect as that of the first embodiment described above can be expected.
[0068]
In addition, this invention is not limited to the said embodiment, In the implementation stage, it can change variously in the range which does not change the summary.
[0069]
Furthermore, the above embodiments include inventions at various stages, and various inventions can be extracted by appropriately combining a plurality of disclosed constituent elements. For example, even if some constituent requirements are deleted from all the constituent requirements shown in the embodiment, the problem described in the column of the problem to be solved by the invention can be solved, and is described in the column of the effect of the invention. If the above effect is obtained, a configuration from which this configuration requirement is deleted can be extracted as an invention.
[0070]
【The invention's effect】
As described above, according to the present invention, it is possible to provide a focus detection apparatus that can obtain excellent workability and can reliably perform focus detection in a minute region.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a diagram showing a schematic configuration of a first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 2 is a diagram showing a schematic configuration of a second embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 3 is a diagram showing a schematic configuration of a third embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 4 is a diagram showing a schematic configuration of a fourth embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 5 is a diagram showing a schematic configuration of an example of a conventional focus detection apparatus.
FIG. 6 is a view showing characteristics of an electric signal output from a light receiving element of the focus detection device.
FIG. 7 is a diagram illustrating characteristics of a displacement signal output from a signal processing system of the focus detection apparatus.
[Explanation of symbols]
1 ... Semiconductor laser
2 ... Polarizing beam splitter
3. Imaging lens
4 ... 1/4 wavelength plate
5 ... Dichroic mirror
6 ... Objective lens
7 ... surface to be measured
8 ... Beam splitter
9 ... 1st aperture
10: First light receiving element
11 ... Second aperture
12 ... Second light receiving element
13 ... Signal processing system
14 ... Observation optical system
14a ... Imaging lens
20 ... half mirror
21 ... Beam splitter
22 ... pinhole
23 ... Light source
24 ... Half mirror
25 ... Light source
26 ... IR cut filter
27 ... Band pass filter
30: Optical fiber
30a: emitting end
30b ... Incident end
31 ... External light source
40. Beam splitter
41 ... Imaging lens
42 ... pinhole
43 ... Light source
51 ... Collimator lens
52 ... Shield plate
53 ... Condensing lens
54. Split light receiving element
55. Signal processing system
56 ... Beam splitter
57 ... pinhole
58 ... Light source
Claims (7)
前記測定光の発光点の投影像と光学的に共役の位置に配置された指標と、
前記指標を照明する可視光域の光を発光する光源と、を具備し、
前記可視光域の光を発光する光源により照明された前記指標の像の光を前記測定光の光路を通して前記被検体に対し照射するとともに、前記被検体から反射した前記指標の像の位置と前記被検体上に照射される前記測定光の集光スポット位置を一致させ、前記指標の像の位置を前記測定光の集光スポット位置として観察可能にしたことを特徴とする焦点検出装置。 Infrared measurement light emitted from the semiconductor laser is irradiated to the subject as a focused spot, and reflected light reflected from the subject is received by the light receiving means, and the output of the light receiving means is used to output the surface of the subject. In a focus detection device that detects in-focus,
An index placed at a position optically conjugate with the projected image of the emission point of the measurement light;
A light source that emits light in a visible light range that illuminates the indicator,
The light of the index image illuminated by the light source that emits light in the visible light range is irradiated to the subject through the optical path of the measurement light, and the position of the index image reflected from the subject and the position A focus detection apparatus characterized in that the position of the condensing spot of the measurement light irradiated on the subject is matched so that the position of the index image can be observed as the position of the condensing spot of the measurement light .
前記測定光の発光点の投影像と光学的に共役の位置に出射端が配置されるとともに、前記出射端より可視光域の光を発する光ファイバを具備し、
前記可視光域の光を発光する光ファイバの出射端からの光を前記測定光の光路を通して前記被検体に対し照射するとともに、前記被検体から反射した前記出射端の像の位置と前記被検体上に照射される前記測定光の集光スポット位置を一致させ、前記出射端の像の位置を前記測定光の集光スポット位置として観察可能にしたことを特徴とする焦点検出装置。 Infrared measurement light emitted from the semiconductor laser is irradiated to the subject as a focused spot, and reflected light reflected from the subject is received by the light receiving means, and the output of the light receiving means is used to output the surface of the subject. In a focus detection device that detects in-focus,
An emission end is disposed at a position optically conjugate with the projected image of the emission point of the measurement light, and an optical fiber that emits light in the visible light region from the emission end is provided.
The light from the output end of the optical fiber that emits light in the visible light range is irradiated to the subject through the optical path of the measurement light, and the position of the image of the output end reflected from the subject and the subject A focus detection apparatus characterized in that the position of the condensing spot of the measurement light irradiated thereon is made coincident so that the position of the image at the exit end can be observed as the position of the condensing spot of the measurement light .
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001324035A JP3944377B2 (en) | 2001-10-22 | 2001-10-22 | Focus detection device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001324035A JP3944377B2 (en) | 2001-10-22 | 2001-10-22 | Focus detection device |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2003131116A JP2003131116A (en) | 2003-05-08 |
| JP2003131116A5 JP2003131116A5 (en) | 2005-06-30 |
| JP3944377B2 true JP3944377B2 (en) | 2007-07-11 |
Family
ID=19140839
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001324035A Expired - Fee Related JP3944377B2 (en) | 2001-10-22 | 2001-10-22 | Focus detection device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP3944377B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4869727B2 (en) * | 2006-02-15 | 2012-02-08 | オリンパス株式会社 | Measuring microscope equipment |
| JP5424064B2 (en) * | 2008-07-09 | 2014-02-26 | 株式会社ニコン | measuring device |
| WO2010054318A1 (en) * | 2008-11-07 | 2010-05-14 | Hamilton Thorne, Inc. | Modular objective assembly |
| US10247910B1 (en) * | 2018-03-14 | 2019-04-02 | Nanotronics Imaging, Inc. | Systems, devices and methods for automatic microscopic focus |
| US10146041B1 (en) * | 2018-05-01 | 2018-12-04 | Nanotronics Imaging, Inc. | Systems, devices and methods for automatic microscope focus |
| JP7219463B2 (en) * | 2019-04-15 | 2023-02-08 | 大塚電子株式会社 | Optical unit, optical measuring device and optical measuring method |
| KR102368468B1 (en) | 2020-07-13 | 2022-03-02 | 주식회사 에타맥스 | Automatic Optical Focus Control Device and Optical Instrument Comprising The Same |
-
2001
- 2001-10-22 JP JP2001324035A patent/JP3944377B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2003131116A (en) | 2003-05-08 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5341386B2 (en) | Ophthalmic imaging equipment | |
| US9804029B2 (en) | Microspectroscopy device | |
| JPH1068866A (en) | Microscope provided with autofocusing device | |
| CN110720986A (en) | Multimode microsurgery navigation system | |
| JP3944377B2 (en) | Focus detection device | |
| JP2008262100A (en) | Sample scanner device, and sample position detecting method using device | |
| JP2008116900A (en) | Interference objective lens, and interference microscope apparatus with interference objective lens | |
| KR101283814B1 (en) | Microscope device | |
| JPS60100114A (en) | Focusing detecting device | |
| JP2007264322A (en) | Infrared microscope | |
| JP5336959B2 (en) | Probe microscope | |
| JP2003185914A (en) | Focus detector, optical device equipped with the same and focus detecting method | |
| JP4228125B2 (en) | microscope | |
| JP2736780B2 (en) | Fundus camera | |
| JP2006110113A (en) | Ophthalmic imaging system | |
| JPS63194634A (en) | Alignment apparatus of ophthalmic machinery | |
| US20190155010A1 (en) | Microscope | |
| JP3599754B2 (en) | Confocal scanning optical microscope | |
| JP2002156578A (en) | Focus detector as well as objective lens, optical microscope or optical test apparatus having the same | |
| JP3542171B2 (en) | Microscope equipment | |
| JP2003015048A (en) | Lattice illumination microscope | |
| JP6211261B2 (en) | Ranging device | |
| JP2011102817A (en) | Microscope device | |
| JP4809731B2 (en) | Fundus imaging device | |
| JPH0720651Y2 (en) | Optical device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20041013 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20041013 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20060912 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20060926 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20061116 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20070403 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20070409 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110413 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120413 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130413 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20140413 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| S531 | Written request for registration of change of domicile |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313531 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |