JP3898399B2 - Assembly including lancet and body fluid component detection unit - Google Patents
Assembly including lancet and body fluid component detection unit Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP3898399B2 JP3898399B2 JP32246599A JP32246599A JP3898399B2 JP 3898399 B2 JP3898399 B2 JP 3898399B2 JP 32246599 A JP32246599 A JP 32246599A JP 32246599 A JP32246599 A JP 32246599A JP 3898399 B2 JP3898399 B2 JP 3898399B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- lancet
- body fluid
- opening
- fluid component
- housing
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Investigating Or Analysing Biological Materials (AREA)
- Measurement Of The Respiration, Hearing Ability, Form, And Blood Characteristics Of Living Organisms (AREA)
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、血液などの体液の臨床検査等をする体液成分測定装置に接続して用いるランセットを備えた組立体に関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
近年の糖尿病患者の増加に伴い日頃の血糖値の変動を患者自身モニターする自己血糖測定が推奨されてきており、最近では容易かつ衛生的に測定を行えるように、特開平6−339473号や特開平9−276235号、及び米国特許4787398号などに穿刺具や測定装置とが一体化された装置が開示されている。しかし、特開平6−339473号や特開平9−276235号は装置としては一体のものであるが、穿刺機構と測定機構とが別個のものであり、穿刺針を含むランセットと試験紙を含む検出部とを別々にセットしなければならず操作にある程度の手間を必要とする。また、米国特許4787398号は、穿刺機構と測定機構とが一体化されており、穿刺針を含むランセットと試験紙を含む検出部とを備えた一つのアダプターをセットすることで容易に操作を行うことができるが、使用前に前記アダプターを滅菌処理すると試験紙に含浸されている試薬などが変性してしまうため、穿刺針の滅菌状態が維持された状態で製品を提供することが困難であった。
【0003】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
そこで本発明の目的は、穿刺機構と測定機構とが一体化されている装置に使用するための、穿刺針を含むランセットと試験紙を含む検出部とを備えたアダプターであって、穿刺針の滅菌が維持されながら、試験紙などの検出部の機能が維持されているものを提供することにある。
【0004】
【課題を解決するための手段】
上記目的は以下の本発明によって達成される。
(1)本発明は、体液成分測定装置に接続して用いるランセット及び体液成分検出部を備えた組立体において、
先端に穿刺針、基端に前記体液成分測定装置内の穿刺機構との接続部を備えたランセットと、
内部を前記ランセットが移動し、かつ前記穿刺針が突出する先端開口部を形成する第一開口部、及び前記ランセットの接続部と前記体液成分測定装置内の穿刺機構とを接続させるための基端開口部とが設けらた筒状部を有する第一ハウジングと、
体液成分測定検出部、および前記第一開口部と重なり前記先端開口部を形成する第二開口部を有する第二ハウジングと、
前記第一開口部を封止する封止部材とからなり、
前記第一ハウジングは、前記ランセットが移動前において、前記ランセットが前記筒状部の基端付近において前記基端開口部を気密に塞ぐように固定され、かつ前記第一開口部が前記封止部材で封止された状態で滅菌処理されたものであり、
前記第一開口部と前記第二開口部とが先端開口部を形成するように前記第一ハウジングと前記第二ハウジングが固定されてなるランセット及び体液成分検出部を備えた組立体である。
【0005】
(2)本発明は、前記ランセット及び体液成分検出部を備えた組立体の全体が保護部材によって密封されていることを特徴とする上記(1)に記載のランセット及び体液成分検出部を備えた組立体である。
【0006】
(3)本発明は、前記封止部材が前記保護部材に接続されており、前記保護部材を除去すると同時に前記第一開口部から前記封止部材が除去できる上記(1)乃至(2)に記載のランセット及び体液成分検出部を備えた組立体である。
【0007】
(4)本発明は、前記第一開口部から前記封止部材が除去されるまで、前記穿刺針の滅菌状態が保たれている上記(1)乃至(3)に記載のランセット及び体液成分検出部を備えた組立体である。
【0008】
(5)本発明は、前記第二ハウジングに設けた前記流路部は、一の流路と他の流路が角度を持って交わるものであって、当該交わる箇所付近には前記流路部内に向って延び、当該交わる箇所付近に発生するメニィスカスに接触する凸部を有するものである上記(1)乃至(4)に記載のランセット及び体液成分検出部を備えた組立体である。
【0009】
(6)本発明は、前記第一ハウジングに使用後のランセットの脱落防止機構を設けた上記(1)乃至(5)に記載のランセット及び体液成分検出部を備えた組立体である。
【0010】
(7)本発明は、前記脱落防止機構が前記基端開口部の封止機構を兼ねる上記(1)乃至(6)に記載のランセット及び体液成分検出部を備えた組立体である。
【0011】
(8)本発明は、体液成分測定装置に接続して用いるランセット及び体液成分検出部を備えた組立体において、
先端に穿刺針、基端に前記体液成分測定装置内の穿刺機構との接続部を備えたランセットと、
内部を前記ランセットが移動し、かつ前記穿刺針が突出する先端開口部を形成する第一開口部、及び前記ランセットの接続部と前記体液成分測定装置内の穿刺機構とを接続させるための基端開口部とが設けらた筒状部を有する第一ハウジングと、
体液成分測定検出部、および前記第一開口部と重なり前記先端開口部を形成する第二開口部を有する第二ハウジングと、
前記第一開口部を封止する第一封止部材と、
前記基端開口部を封止する第二封止部材とからなり、
前記第一ハウジングは、前記ランセットが前記筒状部に収納され、前記第一開口部が前記第一封止部材で、前記基端開口部が前記第二封止部材で封止された状態で滅菌処理されたものであり、
前記第一開口部と前記第二開口部とが先端開口部を形成するように前記第一ハウジングと前記第二ハウジングが固定されてなるランセット及び体液成分検出部を備えた組立体である。
【0012】
(9)本発明は、前記ランセット及び体液成分検出部を備えた組立体の全体が保護部材によって密封されていることを特徴とする上記(8)に記載のランセット及び体液成分検出部を備えた組立体である。
【0013】
(10)本発明は、前記第一封止部材及び前記第二封止部材とが前記保護部材に接続されており、前記保護部材を除去すると同時に前記第一開口部から前記第一封止部材が除去でき、前記基端開口部から前記第二封止部材が除去できる上記(8)乃至(9)に記載のランセット及び体液成分検出部を備えた組立体である。
【0014】
(11)本発明は、前記第一開口部から前記第一封止部材が除去、および前記基端開口部から前記第二封止部材が除去されるまで前記穿刺針の滅菌状態が保たれている上記(8)乃至(10)に記載のランセット及び体液成分検出部を備えた組立体である。
【0015】
(12)本発明は、前記第二ハウジングに設けた前記流路部は、一の流路と他の流路が角度を持って交わるものであって、当該交わる箇所付近には前記流路部内に向って延び、当該交わる箇所付近に発生するメニィスカスに接触する凸部を有するものである上記(8)乃至(11)に記載のランセット及び体液成分検出部を備えた組立体である。
【0016】
(13)本発明は、前記第一ハウジングに使用後のランセットの脱落防止機構を設けた上記(8)乃至(12)に記載のランセット及び体液成分検出部を備えた組立体である。
【0017】
(14)本発明は、先端に穿刺針と、基端に穿刺機構との接続部を備えたランセットと、体液成分検出部とが一体となっており、前記ランセットは滅菌状態で密封包装されているランセット及び体液成分検出部を備えた組立体である。
【0018】
(15)本発明は、前記ランセット及び体液成分検出部を備えた組立体の全体が保護部材で包装されている上記(14)に記載のランセット及び体液成分検出部を備えた組立体である。
【0019】
(16)本発明は、前記ランセットの密封包装の一部と、前記保護部材の一部が連結されており、前記保護部材を除去すると同時に前記密封包装も除去される上記(14)乃至(15)に記載のランセット及び体液成分検出部を備えた組立体である。
【0020】
なお、メニィスカスとは、毛細管内の液体が毛細管内の表面張力により留まってしまい、その液体表面が毛管現象により管壁に沿った周囲が中央部に比して上がるかまたは下がり、曲面を形成する現象をいう。特に毛細管に角度を設けた場合にそう周囲で起き易い現象である。
【0021】
【発明の実施の形態】
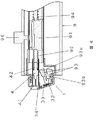
本発明の実施の形態の第一例を図面を参照しながら説明する。図1は、本発明の実施形態の第一例である組立体1の断面を示す。組立体1は、第一ハウジング2及び第二ハウジング3とから構成される。第一ハウジング2は、その断面である図2に示すとおり、筒状部21を有し、筒状部21は先端に第一開口部22、基端に基端開口部23が設けられ、その内部をランセット4が移動する。第二ハウジング3は、平面を示す図3、および線分X−Xの断面である図4に示すとおり、第二開口部31と、体液成分測定検出部としての試験紙32が設けられている。
【0022】
第一ハウジング2と第二ハウジング3とは、第一開口部22と第二開口部31とが重なりあい先端開口部5を形成するように固定され、組立体1となる。第一ハウジング2と第二ハウジング3との固定は、第一ハウジング2の係止部24a,bと、第二ハウジング3の係合部35a,bの係合により行われるが、第一ハウジング2と第二ハウジング3との接触面を接着や融着させてもよい。この構造により、使用時に操作者が、第一ハウジング2と第二ハウジング3とを別々に体液成分測定装置9にセットする必要はなく、組立体1として同時ににセットすることが可能となり、さらに使用後にも別々ではなく、一つの組立体1として体液成分測定装置9から取り外す事が可能となる。
【0023】
第一ハウジング2は、筒状部21を有し、その内部には移動可能なランセット4が収納されている。筒状部21の形状としては、円筒でも角型でも構わないが、構造的に製造しやすいことから円筒が望ましい。ランセット4は、先端に穿刺針41、基端に体液成分測定装置9内の穿刺機構91と接続するための接続部42が設けられている。接続部42の形状は図に示す凸状のものに限定されず、穿刺機構91の形状と対応するものであればよく、基端開口部23から突出している必要はない。
【0024】
ランセット4は、筒状部21の基端付近すなわち少なくとも穿刺針41が第一開口部22から突出しない位置で固定される。なお、この固定の固定力は、使用前は穿刺針41が第一開口部22から突出せず、かつ穿刺機構91と接続部42を接続する時にはその作業が可能であり、使用時すなわちランセット4が移動する際は穿刺機構91の押出し力により、その固定が解除される程度の固定力を必要とする。固定方法は、特に限定されず、筒状部21の内面および/またはランセット4外面に係止手段を設けたり、筒状部21の内面とランセット4外面との接触面の摩擦力を使用したり、前記接触面を弱接着、弱融着するものであってもよい。
【0025】
基端開口部23を後述する第二封止部材で封止しない場合には、使用前ランセット4は基端開口部23付近に基端開口部23を封止するように固定される。封止する方法は、基本的には上述したランセット4の固定方法と同様であるが、具体的には図示するように筒状部21の内面に設けられた円周状に延びる凸部25にランセット4を嵌合する方法があげられるが、これに限らず筒状部21内面の基端付近を狭くし、そこにランセット4を嵌合する方法や、筒状部21の内面に部分的に設けられた凸部にランセット4を嵌合し、筒状部21基端付近の内面とランセット4の基端付近の外面とを気密に接触させておく方法などがあげられる。
【0026】
ランセット4は筒状部21の基端付近で嵌合し基端開口部23を封止するため、筒状部21と同様な断面形状とし、材質も基本的には後述する第一ハウジング2及び第二ハウジング3と同様なものでよいが、その中でも可撓性を有するものを使用することが望ましい。
【0027】
第一ハウジング2は、筒状部21の内部にランセット4を収納し基端開口部23を封止した状態で滅菌処理をした後、または少なくともその内部を滅菌処理した筒状部21の内部に滅菌処理したランセット4を無菌条件下で収納した後、筒状部21の内部を使用時まで密封状態を維持するこで滅菌状態を維持するものである。なお、滅菌方法としては、特に限定しないが、EOG滅菌、γ線滅菌、電子線滅菌などがあげられる。第一ハウジング2は、上述したとおり筒状部21の内部を使用時まで滅菌状態を維持できる状態とした後、第二ハウジング3と組み合わされて、組立体1を構成する。
【0028】
第一ハウジング2の構成材質は、ABS、ポリエチレン、ポリプロピレン、ポリスチレン、ポリ塩化ビニル、ポリ塩化ビニリデン樹脂、ポリフェニレンオキサイド、熱可塑性ポリウレタン、ポリメチレンメタクリレート、ポリオキシエチレン、フッ素樹脂、ポリカーボネート、ポリアミド、アセタール樹脂、アクリル樹脂、ポリエチレンテレフタレート等の射出成形で用いられる熱可塑性樹脂やフェノール樹脂、エポキシ樹脂、シリコーン樹脂、不飽和ポリエステル等の熱硬化性などがあげられる。
【0029】
筒状部21内は、第一開口部22および基端開口部23を封止することにより密封状態に保たれる。第一開口部22の封止は第一封止部材6により行われる。第一封止部材6は図示するように、フィルム状のものであり第一開口部22の周囲と接着や融着などで固定されている。なお、第一封止部材6は、接着や融着しやすく、かつ剥がし易いようにフイルム状の物が好ましいが、蓋状や栓状のものでもよい。基端開口部23は上述したとおり、ランセット4を固定して密封状態を保つことが望ましいが、第一封止部材6と同様な第二封止部材(図示しない)で封止してもよい。
【0030】
第二ハウジング3は、第二開口部31と、体液成分測定検出部としての試験紙32が設けられている。なお、体液成分測定検出部は試験紙に限定されることなく、体液成分測定装置9の体液成分測定手段に適した媒体を使用できる。本実施形態においては、第二開口部31の周縁に体液導入口33aと、体液を毛細管現象によって体液導入口33aから試験紙32まで導く流路33が設けられている。第二ハウジング3の構成材質は、上述した第一ハウジング2と同様なものがあげられるが、体液成分測定装置9の体液成分測定手段が試験紙での呈色反応を捉える光学的な測定手段である場合には、その中でも測定精度の関係から外乱光の影響を受けにくくするように非透明なものが望ましいが、流路33の体液の移動を確認するするため半透明な色つきの樹脂でも良い。
【0031】
流路33は、その断面形状及び長さは測定に必要とする体液量によりことなるが体液の残存量を少なくなるよう設計するのが望ましい。具体的には、断面形状としては管状、V字溝、長方形溝でも構わないが、体液の残存量を少なくできるため薄型の長方形が好ましい。厚みは0.05〜0.5mm程度、幅は0.5〜3mm程度が好ましい。長さは、体液成分測定装置9の体液成分測定手段93の位置配置にもよるがなるべく短い方が望ましく5mm〜15mm程度が適当である。
【0032】
また、体液を流路33の体液導入口33aから試験紙32まで導くときに、密閉系では毛細管現象が途中で止り、体液が試験紙32までに届かない場合がある。そのため空気抜けを必要とし、具体的には第二ハウジング3内面に凹状に設けられる試験紙固定部36を、その平面である図5に示すような構造とすることが望ましい。すなわち、試験紙32の周縁と試験紙固定部36の周縁の間に隙間39a、及び試験紙32の一面と試験紙固定部36の平面の間に隙間39bを形成するように試験紙32を固定する(図4の状態)ために、測定試験紙固定台38と、流路試験紙側端部33bに空気抜け部37を有する構造とすることが望ましい。なお、試験紙32は測定試験紙固定台38と流路試験紙側端部33bとで支持される。
【0033】
流路33の構成材料としては第二ハウジング3と同様の材料で構わないが、アクリル樹脂等の親水性の高い材料が望ましい。またアクリル樹脂等の材料でない場合は、その表面を親水性処理することで吸引力を高めても良い。親水性処理の方法としては、オゾン処理、プラズマ処理、グロー放電、コロナ放電、紫外線照射等の物理活性化処理や、界面活性剤、水溶性シリコン、ヒドロキシプロピルセルロース、ポリエチレングリコール、ポリプロピレングリコール等の塗布等により行うことができる。なお 流路33は射出成形により第二ハウジング3と一体成形、または第二ハウジング3を切り欠き加工やプレス加工することにより第二ハウジング3と一体的に設けられるものでも、管状体や溝部材を固定して得られるものであっても良い。
【0034】
体液導入口33aの縁には、体液導入ガイド部34を設けることが望ましい。体液導入ガイド部34は、そこに体液が接触すると体液導入口33aまで体液を導く機能を有する。構成材料は、第二ハウジング3や流路部4と同様で構わなく、さらに流路33のように親水化処理をしてあることが望ましい。形状的には、多量のため体液導入口33aで吸引しきれない体液が第二開口部31の周囲に広がり非衛生的となり、かつ流路33の吸引力の低下が起き測定に必要な体液量が多くなり使用者の負担が多くなるため、体液導入口33aまで迅速に体液を導き、多量の体液を保持し他の部分に流出しない構造が望ましい。具体的には、体液導入口33aの周縁の左右両方にレール状のガイド34a,bを突出させるよう設けたものがあげられる。
【0035】
具体的な体液導入ガイド34の内部空間の大きさは、幅は1〜3mm程度、高さは0.5〜3mm程度、長さは1〜3mm程度が望ましい。これは、体液を4μl程度を絞り出したときの大きさが約3mm程度の滴になるため、ガイドとしては最大で必要な体液量と同等の大きさが望ましいからである。ガイド34a,bの高さは、体液導入口33aの最大径と同程度の高さであることが望ましい。また、図示する二本のガイド34a,bの他に体液導入口33aの上下左右の4方向全てを覆うもの、下左右の3方向を覆ものでも構わない。なお、二本のガイド34a,bは、その内面が図のように平行ではなく、第二開口部31の中心に向ってハの字状に開いた形状でも構わない。
【0036】
穿刺針41は、体液導入ガイド34先端部付近、もしくはその間を通過し穿刺することになる。穿刺位置から流出した体液が必要量の滴状になると体液導入ガイド34に接触し、流路33を通り試験紙32に導かれる。穿刺針41の通る位置としては、測定に必要な体液量から考えて遠くても体液導入ガイド34先端部から3mm程度が望ましく、より望ましくは先端部から1mm以内である。体液導入ガイド34が、図示するようなガイド34a,bからなるような場合には、その間を通ってもよい。
【0037】
第二ハウジング3は、先端開口部5を穿刺位置(例えば指先やお腹など)に導くための役割を果たさせるために、第二開口部31から角度αを有するテーパーが設けられていることが望ましい。これに穿刺位置に当てる部分を先端開口部5のみにでき、穿刺箇所の周囲全体が押されることがなくなるため、その感触で使用者が穿刺位置を限定できる。角度αは、10〜45度が望ましい。なお、角度αを有するテーパーではなく、第二開口部31が第二ハウジング3本体から突起するような形状であっても構わない。
【0038】
体液成分検出部または試験紙32は、特に限定されず、体液成分測定手段により適したものを選んで使用することができれる。例えば、体液成分測定手段が試験紙での呈色反応を捉える光学的な測定手段で、血液中のグルコースを測定する場合などは、試薬としてグルコースオキシダーゼ、ペルオキシダーゼと呈色試薬を試験紙に含浸させ乾燥させておけば良い。試験紙としては、多孔性の膜が望ましく、形態としては不織布、織布、延伸処理したシートなどがあげられる。材質としては、ポリエステル類、ポリアミド類、ポリオレフィン類、ポリスルホン類、またはセルロース類等があげられる。また、試薬を含浸させたり体液をしみ込ませるので、親水性の材料または親水処理したものが望ましい。試験紙は単層のシートでも多層のシートでも構わない。
【0039】
組立体1は、上述した筒状部21内が密封状態に保たれ少なくとも穿刺針41の滅菌状態が保たれた第一ハウジング2と、上述した体液成分測定検出部を有する第二ハウジングとが、先端開口部5を形成するように固定されて形成された後、さらに全体が保護部材8によって密封されることが望ましい。保護部材8の形態としては、組立体1の他の構成が密封できるものであれば、特に限定されない。図示する形態は、シート状のものであり切り込み部81から使用直前に破いて除去することができる。なお、この時、第一封止部材6の保護部材接続部61を保護部材8の内面の一部に接続し、さらに第二封止部材を有する場合は第二封止部材の保護部材接続部を保護部材8の内面の一部に接続することにより、保護部材8を除去すると同時に第一開口部から第一封止部材を除去し、さらに基端開口部から前記第二封止部材を除去することができる。
【0040】
保護部材8は、シート状のもの他に硬質プラスチック製のケースであってもよい。保護部材8の構成材質としては、特に限定されず、シート状のものであれば、上述した第一封止部材や第二封止部材と同様なもの、硬質プラスチック製のケースであれば第一ハウジングや第二ハウジングと同様なものが使用できる。
【0041】
次に組立体1の使用方法について説明する。まず、組立体1が保護部材8で密封されている場合には保護部材8を除去し、同時に第一封止部材6(第二封止部材を有する場合は同時に第二封止部材)も除去する。次に、組立体1を体液成分測定装置9の先端に接続する。その際、ランセット4の接続部42と穿刺機構91の先端凹部92が嵌合し、穿刺手段91に連結されるバネ94を圧縮させる。なお、体液成分測定装置9の先端には接続した組立体1の固定力を高めるためにOリング95などを有することが望ましい。これで、測定前の準備が完了する。
【0042】
体液成分測定装置9を組立体1の先端開口部5が穿刺位置に当るように押し当てる。そして、ボタン96をバネ94の圧縮が解除され、穿刺手段91が先端方向に移動し、その勢いでランセット4が押出され、穿刺針41が穿刺位置を穿刺する。その後、バネ94が元の長さに戻ること、または別のバネ(図示しない)で引き戻されることにより、穿刺針41は組立体1内に収納される。この時の状態を、図6に示す。
【0043】
穿刺後、穿刺位置から体液(血液)が流出すると、その体液は、体液導入ガイド部34から流路33を経て試験紙32に導かれる。試験紙32に導かた体液は呈色反応し、体液成分測定手段の一部である発光素子93a、受光素子93bにより吸光度(もしくは発光度)を測定し、体液成分を算出する。一連の操作完了後、組立体1を体液成分測定装置9の先端から取り外す。この時、ランセット4等が一体となった状態で取り外すことができる。
【0044】
本発明の実施の形態の第二例を図面を参照しながら説明する。図7は、本発明の実施形態の第二例である組立体101の断面を示す。組立体101は、第一ハウジング102及び第二ハウジング103とから構成される。第一ハウジング102は、その断面である図8に示すとおり、筒状部121を有し、筒状部121は先端に第一開口部122、基端に基端開口部123が設けられ、その内部をランセット104が移動する。第二ハウジング103は、正面を示す図9、および上面である図10に示すとおり、第二開口部131と、体液成分測定検出部としての試験紙132が設けられている。
【0045】
第一ハウジング102と第二ハウジング103とは、第一開口部122と第二開口部131とが重なりあい先端開口部105を形成するように固定され、組立体101となる。第一ハウジング102と第二ハウジング103との固定は、第一ハウジング102を第二ハウジング103に圧入して行われるが、第一ハウジング102と第二ハウジング103との接触面を接着や融着させても構わなく、また係合部を第一ハウジング102と第二ハウジング103に設け嵌合させても構わない。この構造により、使用時に操作者が、第一ハウジング102と第二ハウジング103とを別々に体液成分測定装置(図示しない。本第二例の体液成分測定装置およびその内部機構は、上記第一例の体液成分測定装置9と同様なものである。)にセットする必要はなく、組立体101として同時にセットすることが可能となり、さらに使用後にも別々ではなく、一つの組立体101として体液成分測定装置から取り外す事が可能となる。
【0046】
第一ハウジング102は、筒状部121を有し、その内部には移動可能なランセット104が収納されている。筒状部121の形状としては、円筒でも角型でも構わないが、構造的に製造しやすいことから円筒が望ましい。ランセット104は、先端に穿刺針141、基端に体液成分測定装置内の穿刺機構(図示しない。穿刺機構91と同様なものである。)と接続するための接続部142が設けられている。接続部142の形状は図に示す凸状のものに限定されず、穿刺機構の形状と対応するものであればよく、図のように基端開口部123から突出してなくても、突出していても構わない。
【0047】
ランセット104は、筒状部121の基端付近すなわち少なくとも穿刺針141が第一開口部122から突出しない位置で固定される。なお、この固定の固定力は、使用前は穿刺針141が第一開口部122から突出せず、かつ穿刺機構と接続部142を接続する時にはその作業が可能であり、使用時すなわちランセット104が移動する際は穿刺機構の押出し力により、その固定が解除される程度の固定力を必要とする。固定方法は、特に限定されず、筒状部121の内面および/またはランセット104外面に係止手段を設けたり、筒状部121の内面とランセット104外面との接触面の摩擦力を使用したり、前記接触面を弱接着、弱融着するものであってもよい。
【0048】
基端開口部123を後述する第二封止部材で封止しない場合には、使用前ランセット104は基端開口部123付近に基端開口部123を封止するように固定される。封止する方法は、基本的には上述したランセット104の固定方法と同様であるが、具体的には図示するように筒状部21の内面に設けられた円周状に延びる凸部125にランセット104を嵌合する方法があげられるが、これに限らず筒状部121内面の基端付近を狭くし、そこにランセット104を嵌合する方法や、筒状部121の内面に部分的に設けられた凸部にランセット104を嵌合し、筒状部121基端付近の内面とランセット104の基端付近の外面とを気密に接触させておく方法などがあげられる。
【0049】
なお、組立体101を体液成分測定装置から取り外す際には、ランセット104は接続部142により体液成分測定装置の穿刺機構と接続されているため、第一ハウジング102の基端方向に引き戻されていく。そして、ランセット104が円周状に延びる凸部125などの上述した固定・封止する方法による手段と嵌合し固定されることで、接続部142が穿刺機構から外され、最終的に組立体101を体液成分測定装置から取り外すことができる。また、このとき穿刺針141が筒状部121にしっかりと固定され、第二開口部131よりも穿刺針141の先端が出ないようになるため、使用後の誤刺などを防ぐことができる。
【0050】
ランセット104は筒状部121の基端付近で嵌合し基端開口部123を封止するため、筒状部121と同様な断面形状とし、材質も基本的には後述する第一ハウジング102及び第二ハウジング103と同様なものでよいが、その中でも可撓性を有するものを使用することが望ましい。
【0051】
第一ハウジング102は、筒状部121の内部にランセット104を収納し基端開口部123を封止した状態で滅菌処理をした後、または少なくともその内部を滅菌処理した筒状部121の内部に滅菌処理したランセット104を無菌条件下で収納した後、筒状部121の内部を使用時まで密封状態を維持するこで滅菌状態を維持するものである。なお、滅菌方法としては、特に限定しないが、EOG滅菌、γ線滅菌、電子線滅菌などがあげられる。第一ハウジング102は、上述したとおり筒状部121の内部を使用時まで滅菌状態を維持できる状態とした後、第二ハウジング103と組み合わされて、組立体101を構成する。
【0052】
第一ハウジング102の構成材質は、ABS、ポリエチレン、ポリプロピレン、ポリスチレン、ポリ塩化ビニル、ポリ塩化ビニリデン樹脂、ポリフェニレンオキサイド、熱可塑性ポリウレタン、ポリメチレンメタクリレート、ポリオキシエチレン、フッ素樹脂、ポリカーボネート、ポリアミド、アセタール樹脂、アクリル樹脂、ポリエチレンテレフタレート等の射出成形で用いられる熱可塑性樹脂やフェノール樹脂、エポキシ樹脂、シリコーン樹脂、不飽和ポリエステル等の熱硬化性などがあげられる。
【0053】
筒状部121内は、第一開口部122および基端開口部123を封止することにより密封状態に保たれる。第一開口部122の封止は第一封止部材106により行われる。第一封止部材106は図示するように、栓状のものであり第一開口部122に圧入され固定され、筒状部121内部の気密性を保っている。なお、第一封止部材106は、蓋状のようなものでも接着や融着しやすく、かつ剥がし易いようにフイルム状の物でもよい。基端開口部123は上述したとおり、ランセット104を固定して密封状態を保つことが望ましいが、第一封止部材106と同様な第二封止部材(図示しない)で封止してもよい。
【0054】
第二ハウジング103は、第二開口部131と、体液成分測定検出部としての試験紙132が設けられる。本第二例では、試験紙132は後述するとおり第一ハウジング102に第二ハウジング103を固定し組立体101とした時に、試験紙132の面方向が筒状部121の軸方向とほぼ平行となるように設けられるものである。また、本第二例では、試験紙132は試験紙ハウジング132aに組み合わせられた状態で第二ハウジング103に固定される。なお、体液成分測定検出部は試験紙に限定されることなく、体液成分測定装置の体液成分測定手段に適した媒体を使用できる。
【0055】
第二ハウジング103の構成材質は、上述した第一ハウジング102と同様なものがあげられるが、体液成分測定装置の体液成分測定手段が試験紙での呈色反応を捉える光学的な測定手段である場合には、その中でも測定精度の関係から外乱光の影響を受けにくくするように非透明なものが望ましいが、流路133の体液の移動を確認するするため半透明な色つきの樹脂でも良い。
【0056】
本実施形態においては、第二開口部131の周縁に体液導入口133aと、体液を毛細管現象によって体液導入口133aから試験紙132まで導く流路133が設けられている。なお、本第二例の図10における第二ハウジング103の線分Y−Yの拡大断面図を図12を示す。図12に示すとおり、流路133は、体液導入口133aから延びる流路133cと、第二ハウジング103の軸方向へ延びる流路133dとが角度を持って交わり、さらに流路133dと試験紙132方向へ延びる流路133eとが角度を持って交わるものである。本第二例において流路133は、試験紙ハウジング132aと第二ハウジング3とを組み合わせるときに、その隙間に形成させるように作成するものである。
【0057】
流路133は、その断面形状及び長さは測定に必要とする体液量によりことなるが体液の残存量を少なくなるよう設計するのが望ましい。具体的には、断面形状としては管状、V字溝、長方形溝でも構わないが、体液の残存量を少なくするできるため薄型の長方形が好ましい。厚みは0.05〜0.5mm程度、幅は0.5〜3mm程度が好ましい。長さは、体液成分測定装置の体液成分測定手段の位置配置にもよるがなるべく短い方が望ましく5mm〜15mm程度が適当である。
【0058】
また、体液を流路133の体液導入口133aから試験紙132まで導くときに、密閉系では毛細管現象が途中で止り、体液が試験紙132までに届かない場合がある。そのため空気抜けを必要とし、具体的には第二ハウジング103内面に凹状に設けられる試験紙固定部136を、その平面である図11に示すような構造とすることが望ましい。すなわち、試験紙132の周縁と試験紙固定部136の周縁の間に隙間139a、及び試験紙132の一面と試験紙固定部136の平面の間に隙間139bを形成するように試験紙132を固定する(図12の状態)ために、測定試験紙固定台138と、流路試験紙側端部133bに空気抜け部137を有する構造とすることが望ましい。なお、試験紙132は測定試験紙固定台138と流路試験紙側端部133bとで支持される。
【0059】
なお、本第二例では図12に示すとおり、流路133は、体液導入口133aから延びる流路133cと第二ハウジング103の軸方向へ延びる流路133dとが角度を持って交わり、さらに流路133dと試験紙132方向へ延びる流路133eとが角度を持って交わるものであり、このような流路形状であると体液等の粘度の高い液体が管状内を流れるときにその端面では表面張力によりメニィスカスが形成される可能性がある。したがって、本第二例においては、当該交わる箇所付近には前記流路部133内に向って延び、当該交わる箇所付近に発生するメニィスカスに接触する凸部135a、試験紙132に流路部133内に向って延びる突起135bを形成するものであることが望ましい。凸部135aと突起135bの表面張力によってメニィスカスが解消される。
【0060】
流路133の構成材料としては第二ハウジング103と同様の材料で構わないが、アクリル樹脂等の親水性の高い材料が望ましい。またアクリル樹脂等の材料でない場合は、その表面を親水性処理することで吸引力を高めても良い。親水性処理の方法としては、オゾン処理、プラズマ処理、グロー放電、コロナ放電、紫外線照射等の物理活性化処理や、界面活性剤、水溶性シリコン、ヒドロキシプロピルセルロース、ポリエチレングリコール、ポリプロピレングリコール等の塗布等により行うことができる。
【0061】
体液導入口133aの縁には、体液導入ガイド部134を設けることが望ましい。体液導入ガイド部134は、そこに体液が接触すると体液導入口133aまで体液を導く機能を有する。構成材料は、第二ハウジング103や流路部133と同様で構わなく、さらに流路133のように親水化処理をしてあることが望ましい。形状的には、多量のため体液導入口133aで吸引しきれない体液が第二開口部131の周囲に広がり非衛生的となり、かつ流路133の吸引力の低下が起き測定に必要な体液量が多くなり使用者の負担が多くなるため、体液導入口133aまで迅速に体液を導き、多量の体液を保持し他の部分に流出しない構造が望ましい。具体的には、体液導入口133aの周縁の左右両方にレール状のガイド134a,bを突出させたものがあげられる。なお、二本のガイド134a,bは、その内面が、第二開口部31の中心に向ってハの字状に開いた形状でも、平行のものでも構わないが、より血液吸引を確実且つ迅速に行うためには、ハの字状に開いた方が好ましい。さらに、体液導入口133aの下部側を塞ぐ下板を設けたものが望ましい。また、体液導入ガイド部134の他の形状としては、体液導入口133aの上下左右の4方向全てをガイドで覆うものでも構わない。
【0062】
具体的な体液導入ガイド134の内部空間の大きさは、幅は1〜3mm程度、高さは0.5〜3mm程度、長さは1〜3mm程度が望ましい。これは、体液を4μl程度を絞り出したときの大きさが約3mm程度の滴になるため、ガイドとしては最大で必要な体液量と同等の大きさが望ましいからである。ガイド134a,bの高さは、体液導入口133aの最大径と同程度の高さであることが望ましい。
【0063】
穿刺針141は、体液導入ガイド134先端部付近、もしくはその間を通過し穿刺することになる。穿刺位置から流出した体液が必要量の滴状になると体液導入ガイド134に接触し、流路133を通り試験紙132に導かれる。穿刺針141の通る位置としては、測定に必要な体液量から考えて遠くても体液導入ガイド134先端部から3mm程度が望ましく、より望ましくは先端部から1mm以内である。
【0064】
第二ハウジング103は、先端開口部105を穿刺位置(例えば指先やお腹など)に導くための役割を果たさせるために、第二開口部131付近を穿刺位置付近に対応した曲面形状部105aに形成しても構わない。図9では、指と同じような曲面形状部105aを設け、これにより先端開口部105が窪んだ状態となり、指の穿刺位置と先端開口部105とを合わせ易くなる。
【0065】
体液成分検出部または試験紙132は、特に限定されず、体液成分測定手段により適したものを選んで使用することができれる。例えば、体液成分測定手段が試験紙での呈色反応を捉える光学的な測定手段で、血液中のグルコースを測定する場合などは、試薬としてグルコースオキシダーゼ、ペルオキシダーゼと呈色試薬を試験紙に含浸させ乾燥させておけば良い。試験紙としては、多孔性の膜が望ましく、形態としては不織布、織布、延伸処理したシートなどがあげられる。材質としては、ポリエステル類、ポリアミド類、ポリオレフィン類、ポリスルホン類、またはセルロース類等があげられる。また、試薬を含浸させたり体液をしみ込ませるので、親水性の材料または親水処理したものが望ましい。試験紙は単層のシートでも多層のシートでも構わない。多層シートの場合には、図示しているように各層間を密着させる必要がある。
【0066】
組立体101は、上述した筒状部121内が密封状態に保たれ少なくとも穿刺針141の滅菌状態が保たれた第一ハウジング102と、上述した体液成分測定検出部を有する第二ハウジングとが、先端開口部105を形成するように固定されて形成された後、さらに全体が保護部材108によって密封されることが望ましい。保護部材108の形態としては、組立体101の他の構成が密封できるものであれば、特に限定されない。図示する形態は、シート状のものであり切り込み部181から使用直前に破いて除去することができる。なお、この時、第一封止部材106の保護部材接続部161を保護部材108の内面の一部に接続し、さらに第二封止部材を有する場合は第二封止部材の保護部材接続部を保護部材108の内面の一部に接続することにより、保護部材108を除去すると同時に第一開口部から第一封止部材を除去し、さらに基端開口部から前記第二封止部材を除去することができる。
【0067】
保護部材108は、シート状のもの他に硬質プラスチック製のケースであってもよい。保護部材108の構成材質としては、特に限定されず、シート状のものであれば、アルミコーティングしたフイルム等、上述した第一封止部材や第二封止部材と同様なもの、硬質プラスチック製のケースであれば第一ハウジングや第二ハウジングと同様なものが使用できる。
【0068】
本第二例の組立体101は、第一例とほぼ同様に使用することができる。
【0069】
【発明の効果】
本発明は、穿刺針が滅菌処理され、かつ使用前まで滅菌状態が維持されながらも、穿刺針以外の部分の滅菌処理による悪影響、例えば、各種滅菌処理による試験紙の試薬等の劣化を起こすことのないランセットを備えた組立体を提供する。本発明のランセットを備えた組立体により、ランセットの滅菌が維持されているために安全に測定が行え、さらにランセット及び試験紙などの体液成分検出部を同時に体液成分測定装置に脱着できるため容易かつ確実に操作が行える。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】本発明の実施形態の第一例である組立体1の断面図である。
【図2】第一ハウジング2の断面図である。
【図3】第二ハウジング3の平面図である。
【図4】図3における第二ハウジング3の線分X−Xの断面図である。
【図5】第二ハウジング3の試験紙固定部36(試験紙なし状態)の平面図である。
【図6】本発明の組立体1の使用形態の一例を示す断面図である。
【図7】本発明の実施形態の第二例である組立体101の断面を示す。
【図8】第一ハウジング102の断面図である。
【図9】第二ハウジング103の正面図である。
【図10】第二ハウジング103の上面図である。
【図11】第二ハウジング103の試験紙固定部136(試験紙なし状態)の平面図である。
【図12】図10における第二ハウジング103の線分Y−Yの断面図である。
【符号の説明】
1、101 組立体
2、102 第一ハウジング
21、121 筒状部
22、122 第一開口部
23、123 基端開口部
3、103 第二ハウジング
31、131 第二開口部
32、132 試験紙
33、133 流路
34、134 体液導入ガイド
4、104 ランセット
41、141 穿刺針
42、142 接続部
5、105 先端開口部
6、106 第一封止部材
61、161 保護部材接続部
8、108 保護部材
9 体液成分測定装置
91 穿刺機構[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to an assembly including a lancet that is used by being connected to a body fluid component measuring apparatus for performing a clinical examination of body fluid such as blood.
[0002]
[Prior art]
As the number of diabetic patients increases in recent years, self-blood glucose measurement in which daily fluctuations in blood glucose level are monitored has been recommended. Japanese Laid-Open Patent Application No. 9-276235 and US Pat. No. 4,787,398 disclose a device in which a puncture tool and a measurement device are integrated. However, although JP-A-6-339473 and JP-A-9-276235 are integrated as an apparatus, the puncture mechanism and the measurement mechanism are separate, and the detection includes a lancet including a puncture needle and a test paper. The parts have to be set separately, and some effort is required for the operation. In US Pat. No. 4,787,398, a puncture mechanism and a measurement mechanism are integrated, and the operation is easily performed by setting one adapter including a lancet including a puncture needle and a detection unit including a test paper. However, if the adapter is sterilized before use, the reagent impregnated in the test paper will be denatured, making it difficult to provide the product while maintaining the sterilized state of the puncture needle. It was.
[0003]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
Therefore, an object of the present invention is an adapter including a lancet including a puncture needle and a detection unit including a test paper for use in an apparatus in which the puncture mechanism and the measurement mechanism are integrated. An object of the present invention is to provide a device in which the function of a detection unit such as a test paper is maintained while sterilization is maintained.
[0004]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
The above object is achieved by the present invention described below.
(1) The present invention relates to an assembly including a lancet and a humor component detection unit used by being connected to a humor component measuring device.
A lancet provided with a puncture needle at the distal end and a connection portion with a puncture mechanism in the body fluid component measuring device at the proximal end;
A first opening for forming a distal end opening through which the lancet moves and the puncture needle protrudes, and a base end for connecting the connection portion of the lancet and the puncture mechanism in the body fluid component measuring device A first housing having a cylindrical portion provided with an opening;
A body fluid component measurement detector, and a second housing having a second opening that overlaps the first opening and forms the tip opening;
A sealing member for sealing the first opening,
The first housing is fixed so that the lancet closes the base end opening in the vicinity of the base end of the cylindrical portion before the lancet is moved, and the first opening is the sealing member. Sterilized in a sealed state with,
It is an assembly including a lancet and a body fluid component detection unit in which the first housing and the second housing are fixed such that the first opening and the second opening form a tip opening.
[0005]
(2) The present invention includes the lancet and body fluid component detection unit according to (1) above, wherein the entire assembly including the lancet and body fluid component detection unit is sealed by a protective member. It is an assembly.
[0006]
(3) According to the above (1) or (2), the sealing member is connected to the protection member, and the sealing member can be removed from the first opening at the same time as the protection member is removed. It is an assembly provided with the described lancet and a body fluid component detection part.
[0007]
(4) The lancet and body fluid component detection according to (1) to (3), wherein the puncture needle is kept in a sterilized state until the sealing member is removed from the first opening. It is an assembly provided with a part.
[0008]
(5) In the present invention, the flow path portion provided in the second housing is such that one flow path and another flow path intersect with each other at an angle. It is an assembly including the lancet and the body fluid component detection unit according to the above (1) to (4), which has a projection that extends toward the surface and contacts a meniscus generated in the vicinity of the intersection.
[0009]
(6) The present invention is an assembly including the lancet and the body fluid component detection unit according to the above (1) to (5), wherein the first housing is provided with a mechanism for preventing the lancet from falling off after use.
[0010]
(7) The present invention is an assembly including the lancet and the body fluid component detection unit according to (1) to (6), in which the drop-off prevention mechanism also serves as a sealing mechanism for the base end opening.
[0011]
(8) The present invention relates to an assembly including a lancet and a body fluid component detection unit that are used by being connected to a body fluid component measurement device.
A lancet provided with a puncture needle at the distal end and a connection portion with a puncture mechanism in the body fluid component measuring device at the proximal end;
A first opening for forming a distal end opening through which the lancet moves and the puncture needle protrudes, and a base end for connecting the connection portion of the lancet and the puncture mechanism in the body fluid component measuring device A first housing having a cylindrical portion provided with an opening;
A body fluid component measurement detector, and a second housing having a second opening that overlaps the first opening and forms the tip opening;
A first sealing member for sealing the first opening;
A second sealing member for sealing the proximal end opening,
In the first housing, the lancet is accommodated in the cylindrical portion, the first opening is sealed with the first sealing member, and the proximal end opening is sealed with the second sealing member. Sterilized,
It is an assembly including a lancet and a body fluid component detection unit in which the first housing and the second housing are fixed such that the first opening and the second opening form a tip opening.
[0012]
(9) The present invention includes the lancet and the humor component detection unit according to (8), wherein the entire assembly including the lancet and the humor component detection unit is sealed by a protective member. It is an assembly.
[0013]
(10) In the present invention, the first sealing member and the second sealing member are connected to the protection member, and the first sealing member is removed from the first opening at the same time as the protection member is removed. The lancet described in the above (8) to (9) and the body fluid component detection unit can be removed, and the second sealing member can be removed from the proximal end opening.
[0014]
(11) In the present invention, the sterilization state of the puncture needle is maintained until the first sealing member is removed from the first opening and the second sealing member is removed from the proximal opening. An assembly including the lancet and the body fluid component detection unit according to (8) to (10).
[0015]
(12) In the present invention, the flow path portion provided in the second housing is such that one flow path and another flow path intersect with each other at an angle. It is an assembly including the lancet and the body fluid component detection unit according to the above (8) to (11), which has a convex portion that extends toward the surface and contacts a meniscus generated in the vicinity of the intersection.
[0016]
(13) The present invention is an assembly including the lancet and the body fluid component detection unit according to (8) to (12), wherein the first housing is provided with a mechanism for preventing the lancet from falling off after use.
[0017]
(14) According to the present invention, a lancet provided with a puncture needle at the distal end, a connection portion with a puncture mechanism at the proximal end, and a body fluid component detection unit are integrated, and the lancet is sealed and packaged in a sterilized state. An assembly including a lancet and a body fluid component detection unit.
[0018]
(15) The present invention is an assembly including the lancet and the humor component detection unit according to (14), in which the entire assembly including the lancet and the humor component detection unit is packaged with a protective member.
[0019]
(16) In the present invention, a part of the sealed package of the lancet is connected to a part of the protective member, and the sealed package is removed simultaneously with the removal of the protective member. ) And a body fluid component detection unit.
[0020]
It should be noted that the meniscus is that the liquid in the capillary tube stays due to the surface tension in the capillary tube, and the liquid surface rises around the tube wall due to capillary action compared to the central part. Or A phenomenon that falls and forms a curved surface. This phenomenon is particularly likely to occur around the capillary tube when an angle is provided.
[0021]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
A first example of an embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. FIG. 1 shows a cross section of an
[0022]
First housing N The
[0023]
The
[0024]
The
[0025]
When the base end opening 23 is not sealed with a second sealing member to be described later, the
[0026]
The
[0027]
The
[0028]
The constituent material of the
[0029]
The inside of the
[0030]
The
[0031]
Although the cross-sectional shape and length of the
[0032]
Further, when the body fluid is guided from the
[0033]
The material of the
[0034]
It is desirable to provide a body fluid
[0035]
The specific size of the internal space of the body
[0036]
The
[0037]
The
[0038]
The body fluid component detection unit or the
[0039]
The
[0040]
The
[0041]
Next, a method for using the
[0042]
The body fluid
[0043]
After puncturing, when body fluid (blood) flows out from the puncturing position, the body fluid is guided from the body fluid
[0044]
A second example of the embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. FIG. 7 shows a cross section of an
[0045]
The
[0046]
The
[0047]
The
[0048]
When the
[0049]
When the
[0050]
The
[0051]
The
[0052]
The constituent material of the
[0053]
The inside of the
[0054]
The
[0055]
The constituent material of the
[0056]
In the present embodiment, a body
[0057]
It is desirable that the
[0058]
Further, when the body fluid is led from the
[0059]
In the second example, as shown in FIG. 12, the
[0060]
The material of the
[0061]
It is desirable to provide a body fluid
[0062]
Specifically, it is desirable that the internal space of the body
[0063]
The
[0064]
The
[0065]
The body fluid component detection unit or the
[0066]
The
[0067]
The
[0068]
The
[0069]
【The invention's effect】
While the puncture needle is sterilized and maintained in a sterilized state before use, the present invention causes adverse effects due to sterilization of parts other than the puncture needle, for example, deterioration of test paper reagents and the like due to various sterilization processes. Provided is an assembly with a lancet. Since the lancet sterilization is maintained by the assembly provided with the lancet of the present invention, the measurement can be performed safely, and the body fluid component detection unit such as the lancet and the test paper can be detached from the body fluid component measuring device at the same time. It can be operated reliably.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a cross-sectional view of an
FIG. 2 is a sectional view of the
3 is a plan view of a
4 is a cross-sectional view taken along line XX of the
5 is a plan view of a test paper fixing portion 36 (without test paper) of the
FIG. 6 is a cross-sectional view showing an example of a usage pattern of the
FIG. 7 shows a cross section of an
8 is a cross-sectional view of the
9 is a front view of the
10 is a top view of the
11 is a plan view of a test paper fixing portion 136 (without test paper) of the
12 is a cross-sectional view taken along line YY of the
[Explanation of symbols]
1,101 Assembly
2,102 first housing
21, 121 Tubular part
22, 122 First opening
23, 123 Base end opening
3, 103 Second housing
31, 131 Second opening
32, 132 Test paper
33, 133 flow path
34, 134 Body fluid introduction guide
4, 104 lancet
41, 141 Puncture needle
42, 142 connections
5, 105 Tip opening
6, 106 First sealing member
61, 161 Protection member connection
8,108 Protective member
9 Body fluid component measuring device
91 Puncture mechanism
Claims (10)
先端に穿刺針、基端に前記体液成分測定装置内の穿刺機構との接続部を備えたランセットと、
内部を前記ランセットが移動し、かつ前記穿刺針が突出する先端開口部を形成する第一開口部、及び前記ランセットの接続部と前記体液成分測定装置内の穿刺機構とを接続させるための基端開口部が設けられた筒状部を有する第一ハウジングと、
体液成分測定検出部、および前記第一開口部と重なり前記先端開口部を形成する第二開口部を有する第二ハウジングと、
前記第一開口部を封止する封止部材とからなり、
前記第一ハウジングは、前記筒状部の内面に設けられた円周状に延びる凸部を有し、前記ランセットが前記凸部に嵌合することによって、前記ランセットが移動前において、前記ランセットが前記筒状部の基端付近において前記基端開口部を封止するように固定され、かつ前記第一開口部が前記封止部材で封止された状態で滅菌処理されたものであり、
前記第一開口部と前記第二開口部とが先端開口部を形成するように前記第一ハウジングと前記第二ハウジングが固定されてなるランセット及び体液成分検出部を備えた組立体。In an assembly including a lancet and a body fluid component detection unit used in connection with a body fluid component measurement device,
A lancet provided with a puncture needle at the distal end and a connection portion with a puncture mechanism in the body fluid component measuring device at the proximal end;
A first opening for forming a distal end opening through which the lancet moves and the puncture needle protrudes, and a base end for connecting the connection portion of the lancet and the puncture mechanism in the body fluid component measuring device A first housing having a cylindrical portion provided with an opening;
A body fluid component measurement detector, and a second housing having a second opening that overlaps the first opening and forms the tip opening;
A sealing member for sealing the first opening,
The first housing has a circumferentially extending convex portion provided on an inner surface of the cylindrical portion, and the lancet is fitted with the convex portion, so that the lancet is moved before the lancet is moved. It is fixed so as to seal the proximal end opening in the vicinity of the proximal end of the cylindrical portion, and is sterilized in a state where the first opening is sealed with the sealing member,
An assembly comprising a lancet and a body fluid component detection unit in which the first housing and the second housing are fixed so that the first opening and the second opening form a tip opening.
先端に穿刺針、基端に前記体液成分測定装置内の穿刺機構との接続部を備えたランセットと、
内部を前記ランセットが移動し、かつ前記穿刺針が突出する先端開口部を形成する第一開口部、前記ランセットの接続部と前記体液成分測定装置内の穿刺機構とを接続させるための基端開口部、及び使用後のランセットを嵌合する凸部が設けられた筒状部を有する第一ハウジングと、
体液成分測定検出部、および前記第一開口部と重なり前記先端開口部を形成する第二開口部を有する第二ハウジングと、
前記第一開口部を封止する第一封止部材と、
前記基端開口部を封止する第二封止部材とからなり、
前記第一ハウジングは、前記ランセットが前記筒状部に収納され、前記第一開口部が前記第一封止部材で、前記基端開口部が前記第二封止部材で封止された状態で滅菌処理されたものであり、
前記第一開口部と前記第二開口部とが先端開口部を形成するように前記第一ハウジングと前記第二ハウジングが固定されてなるランセット及び体液成分検出部を備えた組立体。In an assembly including a lancet and a body fluid component detection unit used in connection with a body fluid component measurement device,
A lancet provided with a puncture needle at the distal end and a connection portion with a puncture mechanism in the body fluid component measuring device at the proximal end;
Internal to the move the lancet, and the puncture needle first opening for forming the distal end opening portion which projects, before Symbol proximal end for connecting the lancing mechanism in the body fluid in the component measuring apparatus and the connection portion of the lancet a first housing having openings, and a cylindrical portion projecting portions are found provided for fitting the lancet after use,
A body fluid component measurement detector, and a second housing having a second opening that overlaps the first opening and forms the tip opening;
A first sealing member for sealing the first opening;
A second sealing member for sealing the proximal end opening,
In the first housing, the lancet is accommodated in the cylindrical portion, the first opening is sealed with the first sealing member, and the proximal end opening is sealed with the second sealing member. Sterilized,
An assembly comprising a lancet and a body fluid component detection unit in which the first housing and the second housing are fixed so that the first opening and the second opening form a tip opening.
前記ランセット及び体液成分検出部を備えた組立体の全体が保護部材で包装されており、前記封止部材の一部と前記保護部材の一部とが連結され、前記保護部材を除去すると同時に前記封止部材も除去されることを特徴とするランセット及び体液成分検出部を備えた組立体。The entire assembly including the lancet and the body fluid component detection unit is packaged with a protective member, and a part of the sealing member and a part of the protective member are connected, and at the same time as the protective member is removed, An assembly comprising a lancet and a body fluid component detection unit, wherein the sealing member is also removed.
前記封止部材は栓状物であり、前記先端開口部に圧入固定されている請求項9に記載のランセット及び体液成分検出部を備えた組立体。The assembly including the lancet and the body fluid component detection unit according to claim 9, wherein the sealing member is a plug-like object and is press-fitted and fixed to the tip opening.
Priority Applications (9)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP32246599A JP3898399B2 (en) | 1999-07-07 | 1999-11-12 | Assembly including lancet and body fluid component detection unit |
| AT99961409T ATE408372T1 (en) | 1999-01-04 | 1999-12-27 | LANDZET ARRANGEMENT FOR COLLECTION AND DETECTION OF BODY FLUID |
| EP99961409A EP1139873B1 (en) | 1999-01-04 | 1999-12-27 | Body fluid collecting and detecting lancet assembly |
| CNB2004101019923A CN1315432C (en) | 1999-01-04 | 1999-12-27 | Body fluid collecting and detecting device |
| PCT/JP1999/007325 WO2000040150A1 (en) | 1999-01-04 | 1999-12-27 | Assembly having lancet and means for collecting and detecting body fluid |
| KR1020017008535A KR100621944B1 (en) | 1999-01-04 | 1999-12-27 | Assembly having lancet and means for collecting and detecting body fluid |
| DE69939598T DE69939598D1 (en) | 1999-01-04 | 1999-12-27 | LANDZETTENANORDNUNG FOR REMOVAL AND FOR DETECTION OF BODY FLUIDS |
| CNB998164232A CN1191786C (en) | 1999-01-04 | 1999-12-27 | Assembly having lancet and means for collecting and detecting body fluid |
| US09/475,125 US6315738B1 (en) | 1999-01-04 | 1999-12-30 | Assembly having lancet and means for collecting and detecting body fluid |
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP11-193754 | 1999-07-07 | ||
| JP19375499 | 1999-07-07 | ||
| JP32246599A JP3898399B2 (en) | 1999-07-07 | 1999-11-12 | Assembly including lancet and body fluid component detection unit |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2001074731A JP2001074731A (en) | 2001-03-23 |
| JP2001074731A5 JP2001074731A5 (en) | 2004-12-24 |
| JP3898399B2 true JP3898399B2 (en) | 2007-03-28 |
Family
ID=26508073
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP32246599A Expired - Fee Related JP3898399B2 (en) | 1999-01-04 | 1999-11-12 | Assembly including lancet and body fluid component detection unit |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP3898399B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP1404232B1 (en) * | 2001-06-12 | 2009-12-02 | Pelikan Technologies Inc. | Blood sampling apparatus and method |
| US7050157B2 (en) * | 2001-11-08 | 2006-05-23 | Optiscan Biomedical Corp. | Reagent-less whole-blood glucose meter |
| AU2003244015A1 (en) * | 2002-07-01 | 2004-01-19 | Terumo Kabushiki Kaisha | Body fluid sampling device |
| AU2003246222A1 (en) | 2002-07-02 | 2004-01-23 | Arkray, Inc. | Unit for piercing, and piercing device |
| JP4537049B2 (en) * | 2003-12-24 | 2010-09-01 | テルモ株式会社 | Chip packaging |
| US7201740B2 (en) * | 2004-07-01 | 2007-04-10 | Becton, Dickinson And Company | Forward-shielding blood collection set |
| EP1723907B1 (en) * | 2005-05-20 | 2008-05-14 | F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ag | Lancet device with sterile protection |
| GB2440119A (en) * | 2006-07-18 | 2008-01-23 | Owen Mumford Ltd | Skin Pricking Device |
| US7766846B2 (en) * | 2008-01-28 | 2010-08-03 | Roche Diagnostics Operations, Inc. | Rapid blood expression and sampling |
| JP5266798B2 (en) | 2008-03-04 | 2013-08-21 | 株式会社リコー | Optical scanning apparatus and image forming apparatus |
| CN108968982B (en) * | 2018-06-07 | 2024-08-02 | 杭州博拓生物科技股份有限公司 | Device for detecting analyte in sample |
Family Cites Families (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS61286738A (en) * | 1985-06-14 | 1986-12-17 | オ−デイオバイオニクス インコ−ポレイテツド | Medical system |
| JPH01185245A (en) * | 1988-01-19 | 1989-07-24 | Terumo Corp | Blood collecting piercing tool |
| JPH0723935A (en) * | 1993-07-08 | 1995-01-27 | Apurusu Kk | Assembly comprising lancet assembly and container |
| JP3752278B2 (en) * | 1995-09-20 | 2006-03-08 | 大日本印刷株式会社 | Blood analyzer |
| JPH09168530A (en) * | 1995-10-17 | 1997-06-30 | Dainippon Printing Co Ltd | Body fluid collecting tool and body fluid analyzer using the same |
| JP3605225B2 (en) * | 1996-04-01 | 2004-12-22 | 大日本印刷株式会社 | Body fluid analyzer |
| JP3604821B2 (en) * | 1996-07-18 | 2004-12-22 | 大日本印刷株式会社 | Body fluid analyzer |
| JP3873093B2 (en) * | 1998-06-15 | 2007-01-24 | アークレイ株式会社 | Lancet-integrated body fluid measuring device and attached body to be used by attaching to this body fluid measuring device |
-
1999
- 1999-11-12 JP JP32246599A patent/JP3898399B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2001074731A (en) | 2001-03-23 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US6315738B1 (en) | Assembly having lancet and means for collecting and detecting body fluid | |
| JP3898399B2 (en) | Assembly including lancet and body fluid component detection unit | |
| EP0931507B1 (en) | Body-fluid inspection device | |
| CA2538677C (en) | Analytical aid | |
| KR101198054B1 (en) | Body fluid sampling device | |
| US20130280696A1 (en) | Devices and methods for detecting analyte in bodily fluid | |
| JP3659832B2 (en) | Body fluid component measuring device | |
| KR20190100417A (en) | Delivering and/or receiving fluids | |
| JPH07213925A (en) | Fixed volume blood sampling tool | |
| JP3648081B2 (en) | Body fluid component measuring device | |
| EP1437093A1 (en) | Apparatus for measuring component and chip | |
| JP4953139B2 (en) | Biosensor chip | |
| US20040210247A1 (en) | Apparatus for measuring component and chip | |
| JP2005017280A (en) | Disposable pipet and blood collector | |
| JP4957121B2 (en) | Biosensor cartridge | |
| JP3648098B2 (en) | Body fluid component measuring instrument | |
| JP2007082954A (en) | Component measurement tip | |
| JP2005017281A (en) | Disposable pipet and infinitestimal blood collector | |
| JP2024537926A (en) | Urine test kit | |
| US20220308051A1 (en) | Lateral flow test apparatus | |
| WO2016079770A1 (en) | Blood test plate equipped with biochip | |
| KR102223629B1 (en) | Blood collection device adaptive to size of capillary tube | |
| JP2007078403A (en) | Component measuring chip | |
| US20240023852A1 (en) | Blood collection instrument and blood collection plate | |
| JP4924932B2 (en) | Biosensor cartridge, method of using biosensor cartridge, and biosensor device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20040122 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20040122 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20060905 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20061106 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20061128 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20061221 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 3898399 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110105 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110105 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120105 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130105 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130105 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |