JP3762027B2 - Optical disc, optical disc playback apparatus, optical disc playback method, and optical disc recording method - Google Patents
Optical disc, optical disc playback apparatus, optical disc playback method, and optical disc recording method Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP3762027B2 JP3762027B2 JP08079697A JP8079697A JP3762027B2 JP 3762027 B2 JP3762027 B2 JP 3762027B2 JP 08079697 A JP08079697 A JP 08079697A JP 8079697 A JP8079697 A JP 8079697A JP 3762027 B2 JP3762027 B2 JP 3762027B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- sector
- track
- header
- land
- data
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Moving Of The Head For Recording And Reproducing By Optical Means (AREA)
- Optical Recording Or Reproduction (AREA)
- Signal Processing For Digital Recording And Reproducing (AREA)
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
この発明は、スパイラル状のランドトラック及びグルーブトラックの双方にデータが記録可能な光ディスクに対してデータの記録又は記録されたデータの再生を行う光ディスク記録再生装置、及び光ディスク記録再生方法に関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
光ディスクには、ランドトラック及びグルーブトラックのどちらか一方だけにデータを記録することが可能なものの他に、ランドトラック及びグルーブトラックの双方にデータを記録することが可能なものがある。
【0003】
後者の場合、データ記録再生時において、ランドトラック及びグルーブトラックを識別して、ランドトラックに応じたランドトラッキングと、グルーブトラックに応じたグルーブトラッキングとを切り替える必要ある。
従来は、光ディスクから再生された再生信号の特徴から、アナログ的にランドトラックとグルーブトラックとを識別していた。
【0004】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
とろこが、上記したようにアナログ的な識別の場合、光ディスク上の傷やビームの蛇行等の影響を受けやすく識別精度に問題があった。このため、誤検出により、誤ってランドトラッキングとグルーブトラッキングとが切り替えられてしまうようなことがあった。
【0005】
この発明の目的は、上記したような事情に鑑み成されたものであって、ランドトラッキングとグルーブトラッキングとの切り換えを正確に実行可能な光ディスク記録再生装置及び光ディスク記録再生方法を提供することにある。
【0006】
【課題を解決するための手段】
上記課題を解決し目的を達成するために、この発明の光ディスク記録再生装置は、以下のように構成されている。
(1)この発明によれば、
ランド部及びグルーブ部により形成されるスパイラル状のランドトラック及びグルーブトラックを有し、所定のトラック長から成り、かつヘッダデータが記録されるヘッダデータ領域とユーザデータが記録されるユーザデータ領域とを含む複数の連続したセクタ領域を有するフォーマットが定義された光ディスクに対してデータの記録、又は記録されたデータの再生を行う光ディスク記録再生装置において、
前記光ディスクに記録されたデータを再生する再生手段と、
この再生手段により再生された再生信号の特徴から、再生対象となっているセクタ領域が前記ランドトラック及び前記グルーブトラックのどちらのトラックに該当するセクタ領域かを識別する第1の識別手段と、
この第1の識別手段による識別結果に応じて、トラッキングを制御する第1のトラッキング制御手段と、
前記再生手段により再生されたデータであって、前記ヘッダデータに含まれた前記ランドトラック及び前記グルーブトラックのどちらのトラックに該当するセクタ領域か識別可能な識別データから、このヘッダデータを有するセクタ領域が前記ランドトラック及び前記グルーブトラックのどちらのトラックに該当するセクタ領域かを識別する第2の識別手段と、
この第2の識別手段による識別結果に応じて、トラッキングを制御する第2のトラッキング制御手段と、
を備えたことを特徴とする光ディスク記録再生装置が提供される。
【0007】
(2)この発明によれば、
ランド部及びグルーブ部により形成されるスパイラル状のランドトラック及びグルーブトラックを有し、所定のトラック長から成り、かつヘッダデータが記録されるヘッダデータ領域とユーザデータが記録されるユーザデータ領域とを含む複数の連続したセクタ領域を有するフォーマットが定義された光ディスクに対してデータの記録、又は記録されたデータの再生を行う光ディスク記録再生装置において、
前記光ディスクに記録されたデータを再生する再生手段と、
この再生手段により再生された再生信号の特徴から、再生対象となっているセクタ領域が前記ランドトラック及び前記グルーブトラックのどちらのトラックに該当するセクタ領域かを識別する第1の識別手段と、
この第1の識別手段による識別結果に応じて、前記ランドトラックに応じたランドトラッキングと前記グルーブトラックに応じたグルーブトラッキングとを切り換え制御する第1のトラッキング制御手段と、
前記再生手段により再生されたデータであって、前記ヘッダデータに含まれた複数のIDデータの関係から、これらIDデータをヘッダデータとして有するセクタ領域が前記ランドトラック及び前記グルーブトラックのどちらのトラックに該当するセクタ領域かを識別する第2の識別手段と、
この第2の識別手段による識別結果に応じて、前記ランドトラックに応じたランドトラッキングと前記グルーブトラックに応じたグルーブトラッキングとを切り換え制御する第2のトラッキング制御手段と、
を備えたことを特徴とする光ディスク記録再生装置が提供される。
【0008】
(3)この発明によれば、
ランド部及びグルーブ部により形成されるスパイラル状のランドトラック及びグルーブトラックを有し、所定のトラック長から成り、かつヘッダデータが記録されるヘッダデータ領域とユーザデータが記録されるユーザデータ領域とを含む複数の連続したセクタ領域を有するフォーマットが定義された光ディスクに対してデータの記録、又は記録されたデータの再生を行う光ディスク記録再生装置において、
前記光ディスクに記録されたデータを再生する再生手段と、
この再生手段により再生された再生信号の特徴から、再生対象となっているセクタ領域が前記ランドトラック及び前記グルーブトラックのどちらのトラックに該当するセクタ領域かを識別する第1の識別手段と、
この第1の識別手段による識別結果に応じて、前記ランドトラックに応じたランドトラッキングと前記グルーブトラックに応じたグルーブトラッキングとを切り換え制御する第1のトラッキング制御手段と、
前記再生手段により再生されたデータであって、前記ヘッダデータに含まれた第1及び第2のIDナンバーの大小関係が、第1のIDナンバー>第2のIDナンバーのとき、これらIDナンバーをヘッダデータとして有するセクタ領域を前記ランドトラックに該当するセクタ領域として識別し、第1のIDナンバー<第2のIDナンバーのとき、これらIDナンバーをヘッダデータとして有するセクタ領域を前記グルーブトラックに該当するセクタ領域として識別する第2の識別手段と、
この第2の識別手段による識別結果に応じて、前記ランドトラックに応じたランドトラッキングと前記グルーブトラックに応じたグルーブトラッキングとを切り換え制御する第2のトラッキング制御手段と、
を備えたことを特徴とする光ディスク記録再生装置が提供される。
【0009】
上記手段を講じた結果、次のような作用が生じる。
この発明の光ディスク記録再生装置においては、再生された再生信号の特徴から、再生対象となっているセクタ領域が前記ランドトラック及び前記グルーブトラックのどちらのトラックに該当するセクタ領域かを識別する第1の識別手段と、ヘッダデータに含まれたランドトラック及びグルーブトラックのどちらのトラックに該当するセクタ領域か識別可能な識別データから、このヘッダデータを有するセクタ領域がランドトラック及びグルーブトラックのどちらのトラックに該当するセクタ領域かを識別する第2の識別手段を備えているので、再生信号の特徴及び識別データから、ランドトラック及びグルーブトラックのどちらに該当するセクタ領域かが識別可能となる。さらに、第1及び第2の識別手段による識別結果に応じて、トラッキングを制御する第1及び第2のトラッキング制御手段を備えているので、再生信号の特徴及び識別データに基づくトラッキング制御が可能となる。
【0010】
【発明の実施の形態】
以下、この発明の実施の一形態について図面を参照して説明する。
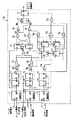
図1は、この発明の実施の一形態に係る光ディスク装置の概略構成を示す図である。この光ディスク装置は情報記録媒体としての光ディスク(DVD−RAM)1に対し集束光を用いてデータの記録、あるいは記録されているデータの再生を行うものである。
【0011】
上記光ディスク1は、例えばガラスあるいはプラスチックス等で円形に形成された基板の表面にテルルあるいはビスマス等の金属被膜層がドーナツ型にコーティングされて構成され、同心円状あるいはスパイラル状のグルーブ(凹部)およびランド(凸部)の両方を用いてデータの記録あるいは記録されているデータの再生が行われ、マスタリング工程で記録マークにより所定間隔ごとにヘッダデータ(アドレスデータなど)が記録されている相変化形で書換え形のディスクである。
【0012】
上記光ディスク1には、図2及び図3に示すように、リードインエリア2、データエリア3、リードアウトエリア4などが構成されている。リードインエリア2は、複数のトラックからなるエンボスデータゾーン5と複数のトラックからなる書換え可能なデータゾーン6とからなる。エンボスデータゾーン5には、リファレンスシグナルやコントロールデータが製造時に記録されている。書換え可能なデータゾーン6は、ガードトラック用のゾーン、ディスクテスト用のゾーン、ドライブテスト用のゾーン、ディスク識別データ用のゾーン、および交替管理エリアとしての交替管理ゾーンにより構成されている。データエリア3は、半径方向に複数のトラックからなる複数たとえば24のゾーン3a、…3xにより構成されている。リードアウトエリア4は、複数のトラックからなり、上記書換え可能なデータゾーン6と同様に、書換え可能なデータゾーンであり、データゾーン6の記録内容と同じものが記録できるようになっている。
【0013】
上記光ディスク1は、図2及び図3に示すように、内側から順に、リードインエリア2のエンボスデータゾーン5と書換え可能なデータゾーン6、データエリア3のゾーン3a、…3x、およびリードアウトエリア4のデータゾーンからなり、それぞれのゾーンに対するクロック信号は同一であり、各ゾーンに対する光ディスク1の回転数(速度)と1トラックずつのセクタ数とがそれぞれ異なったものとなっている。
【0014】
データエリア3のゾーン3a、…3xでは、光ディスク1の内周側から外周側に向かうのにしたがって、回転数(速度)が遅くなり、1トラックずつのセクタ数が増加するようになっている。上記各ゾーン3a、…3x、4、5、6に対する、速度データ(回転数)と1トラックのセクタ数との関係は、図4に示すように後述するメモリ10のテーブル10aに記録されている。
【0015】
上記データエリア3のゾーン3a、…3xのトラックには、図2及び図3に示すように、データの記録の単位としてのECC(error correction code )ブロックデータ単位(たとえば38688バイト)ごとに、あらかじめデータが記録されている。上記データエリア3のゾーン3a、…3xのトラックには、図2に示すように、各セクタごとに、それぞれアドレス等のヘッダデータが記録されているヘッダフィールド11があらかじめプリフォーマッティングされている。
【0016】
ここで、再び図1の説明に戻る。図1に示すように、光ディスク1は、モータ23によって例えば、ゾーンごとに異なった回転数で回転される。このモータ23は、モータ制御回路24によって制御されている。
【0017】
上記光ディスク1に対するデータの記録、あるいは光ディスク1に記録されているデータの再生は、再生手段としての光学ヘッド25によって行われるようになっている。この光学ヘッド25は、リニアモータ26の可動部を構成する駆動コイル27に固定されており、この駆動コイル27はリニアモータ制御回路28に接続されている。
【0018】
このリニアモータ制御回路28には、速度検出器29が接続されており、光学ヘッド25の速度信号をリニアモータ制御回路28に送るようになっている。
また、リニアモータ26の固定部には、図示しない永久磁石が設けられており、上記駆動コイル27がリニアモータ制御回路28によって励磁されることにより、光学ヘッド25は、光ディスク1の半径方向に移動されるようになっている。
【0019】
上記光学ヘッド25には、対物レンズ30が図示しないワイヤあるいは板ばねによって支持されており、この対物レンズ30は、駆動コイル31によってフォーカシング方向(レンズの光軸方向)に移動され、駆動コイル32によってトラッキング方向(レンズの光軸と直交する方向)に移動可能とされている。
【0020】
また、レーザ制御回路33によって半導体レーザ発振器39が駆動されて、レーザ光を発生するようになっている。レーザ制御回路33は、半導体レーザ発振器39のモニタ用のフォトダイオードPDからのモニタ電流に応じて半導体レーザ発振器39によるレーザ光の光量を補正するようになっている。
【0021】
レーザ制御回路33は、図示しないPLL回路からの記録用のクロック信号に同期して動作するようになっている。このPLL回路は、図示しない発振器からの基本クロック信号を分周して、記録用のクロック信号を発生するものである。
【0022】
そして、レーザ制御回路33によって駆動される半導体レーザ発振器39より発生されたレーザ光は、コリメータレンズ40、ハーフプリズム41、対物レンズ30を介して光ディスク1上に照射され、この光ディスク1からの反射光は、対物レンズ30、ハーフプリズム41、集光レンズ42、およびシリンドリカルレンズ43を介して光検出器44に導かれる。
【0023】
上記光検出器44は、4分割の光検出セル44a、44b、44c、44dによって構成されている。
上記光検出器44の光検出セル44aの出力信号は、増幅器45aを介して加算器46aの一端に供給され、光検出セル44bの出力信号は、増幅器45bを介して加算器46bの一端に供給され、光検出セル44cの出力信号は、増幅器45cを介して加算器46aの他端に供給され、光検出セル44dの出力信号は、増幅器45dを介して加算器46bの他端に供給されるようになっている。
【0024】
上記光検出器44の光検出セル44aの出力信号は、増幅器45aを介して加算器46cの一端に供給され、光検出セル44bの出力信号は、増幅器45bを介して加算器46dの一端に供給され、光検出セル44cの出力信号は、増幅器45cを介して加算器46dの他端に供給され、光検出セル44dの出力信号は、増幅器45dを介して加算器46cの他端に供給されるようになっている。
【0025】
上記加算器46aの出力信号は差動増幅器OP2の反転入力端に供給され、この差動増幅器OP2の非反転入力端には上記加算器46bの出力信号が供給される。これにより、差動増幅器OP2は、上記加算器46a、46bの差に応じてフォーカス点に関する信号(フォーカス誤差信号)をフォーカシング制御回路47に供給するようになっている。このフォーカシング制御回路47の出力信号は、駆動コイル31に供給され、レーザ光が光ディスク1上で常時ジャストフォーカスとなるように制御される。
【0026】
上記加算器46cの出力信号は差動増幅器OP1の反転入力端に供給され、この差動増幅器OP1の非反転入力端には上記加算器46dの出力信号が供給される。これにより、差動増幅器OP1は、上記加算器46c、46dの差に応じてトラッキング誤差信号をトラッキング制御手段としてのトラッキング制御回路48及びヘッダ位置検出回路60に供給するようになっている。トラッキング制御回路48は、差動増幅器OP1から供給されるトラッキング誤差信号に応じてトラック駆動信号を作成するものである。ヘッダ位置検出回路60は、ヘッダの位置を検出するものである。また、このヘッダ位置検出回路60から出力される各種信号が、ランド/グルーブ切換点検出回路70へ供給されるようになっている。このランド/グルーブ切換点検出回路70は、ランドとグルーブとの切換点を検出するものである。
【0027】
上記トラッキング制御回路48から出力されるトラック駆動信号は、前記トラッキング方向の駆動コイル32に供給される。また、上記トラッキング制御回路48で用いられたトラッキング誤差信号は、リニアモータ制御回路28に供給されるようになっている。
【0028】
上記のようにフォーカシング、トラッキングを行った状態での光検出器44の各光検出セル44a、〜44dの出力の和信号、つまり加算器46c、46dからの出力信号を加算器46eで加算した信号は、トラック上に形成されたピット(記録データ)からの反射率の変化が反映されている。この信号は、データ再生回路38に供給され、このデータ再生回路38において、記録されているデータが再生される。
【0029】
このデータ再生回路38で再生された再生データは、付与されているエラー訂正コードECCを用いてエラー訂正回路52でエラー訂正を行った後、インターフェース回路55を介して外部装置としての光ディスク制御装置56に出力される。
【0030】
また、上記トラッキング制御回路48で対物レンズ30が移動されている際、リニアモータ制御回路28は、対物レンズ30が光学ヘッド25内の中心位置近傍に位置するようにリニアモータ26つまり光学ヘッド25を移動するようになっている。
【0031】
また、レーザ制御回路33の前段には、データ生成回路34が設けられている。このデータ生成回路34には、エラー訂正回路52から供給される記録データとしてのECCブロックのフォーマットデータを、ECCブロック用の同期コードを付与した記録用のECCブロックのフォーマットデータに変換するECCブロックデータ生成回路34aと、このECCブロックデータ生成回路34aからの記録データを8−16コード変換方式で変調する変調回路34bとを有している。
【0032】
データ生成回路34には、エラー訂正回路52によりエラー訂正符号が付与された記録データやメモリ10から読出されたエラーチェック用のダミーデータが供給されるようになっている。エラー訂正回路52には外部装置としての光ディスク制御装置56からの記録データがインターフェース回路55およびバス49を介して供給されるようになっている。
【0033】
エラー訂正回路52は、光ディスク制御装置56から供給される32Kバイトの記録データを4Kバイトごとのセクタ単位の記録データに対する横方向と縦方向のそれぞれのエラー訂正符号(ECC1、ECC2)を付与するとともに、セクタID(論理アドレス番号)を付与し、ECCブロックのフォーマットデータを生成するようになっている。
【0034】
また、この光ディスク装置にはそれぞれフォーカシング制御回路47、トラッキング制御回路48、リニアモータ制御回路8と光ディスク装置の全体を制御するCPU50との間で情報の授受を行うために用いられるD/A変換器51が設けられている。
【0035】
上記モータ制御回路24、リニアモータ制御回路28、レーザ制御回路33、データ再生回路38、フォーカシング制御回路47、トラッキング制御回路48、エラー訂正回路53等は、バス49を介してCPU50によって制御されるようになっており、このCPU50はメモリ10に記録された制御プログラムによって所定の動作を行うようになされている。
【0036】
上記メモリ10は、制御プログラムが記録されていたり、データ記録用に用いられる。このメモリ10には、上記各ゾーン3a、…3x、4、5、6に対する、速度データ(回転数)と1トラックのセクタ数との関係が記録されているテーブル10aを有している。
【0037】
次に、ランドトラックとグルーブトラックの切り替わりをアナログ的に検出し、ランドトラッキングとグルーブトラッキングを切り替える方法(アナログ的トラッキング制御方法)について簡単に説明する。
【0038】
このアナログ的トラッキング制御は、ヘッダ位置検出回路60及びランド/グルーブ切換点検出回路70、及びトラッキング制御回路48により行われるものとする。ヘッダ位置検出回路60は、差動増幅器OP1から供給されるトラックエラー信号に基づき、ヘッダ位置(アウターヘッダ及びインナーヘッダ)を検出し、ヘッダ検知信号、アウターヘッダ検知信号、及びインナーヘッダ検知信号を出力する。ランド/グルーブ切換点検出回路70は、ヘッダ位置検出回路60から供給されるヘッダ検知信号、アウターヘッダ検知信号、及びインナーヘッダ検知信号を基に、ランドとグルーブの切換点を検出し、ランド/グルーブ切換信号を出力する。トラッキング制御回路48は、ランド/グルーブ切換点検出回路70から供給されるランド/グルーブ切換信号に基づき、ランドトラッキング及びグルーブトラッキングの切換を行う。
【0039】
ここで、図12〜図15を参照して、ヘッダ位置検出回路60及びランド/グルーブ切換点検出回路70について説明する。
図12に示すように、ヘッダ位置検出回路60は、ローパスフィルタ(LPF)61、ハイパスフィルタ(HPF)62、スライスレベル生成部63、差動増幅器64、MM65、AND回路66、及びOR回路67等により構成されている。このヘッダ位置検出回路60には差動増幅器OP1から供給されるトラックエラー信号が入力され、このヘッダ位置検出回路60からはヘッダ検知信号、インナーヘッダ検知信号、アウターヘッダ検知信号が出力される。図13に、これらトラックエラー信号、ヘッダ検知信号、インナーヘッダ検知信号、及びアウターヘッダ検知信号を関係を示す。
【0040】
また、図14に示すように、ランド/グルーブ切換点検出回路70は、フリップフロップ回路71、AND回路72、NAND回路73、OR回路74、NOR回路75、及びEXOR回路76等により構成されている。このランド/グルーブ切換点検出回路70にはヘッダ位置検出回路60から供給されるヘッダ検知信号、インナーヘッダ検知信号、及びアウターヘッダ検知信号、並びにクロック信号(CLK/8)及びクロック信号(CLK/256)が入力され、このランド/グルーブ切換点検出回路70からはランド/グルーブ切換信号が出力される。図15に、これらヘッダ検知信号、インナーヘッダ検知信号、アウターヘッダ検知信号、及びランド/グルーブ切換信号の関係を示す。また、この図15には、ヘッダ検知信号、インナーヘッダ検知信号、及びアウターヘッダ検知信号からランド/グルーブ切換信号を生成する過程で生じる各種信号(S1〜S7)の様子も合わせて示す。
【0041】
次に、図5を参照してセクタフォーマットについて説明する。図5は、1セクタのフォーマット及びヘッダフィールドのフォーマットを概略的に示す図である。
【0042】
図5に示すように、1セクタは、およそ2697バイトで構成され、128バイトのヘッダフィールド11、2バイトのミラーフィールド、2567バイトのレコーディングフィールドから構成されている。セクタに記録されるチャネルビットは、8ビットのデータを16ビットのチャネルビットに8−16コード変調された形式になっている。
【0043】
ヘッダフィールド11は、光ディスク1を製造する際に所定のデータが記録されているエリアである。このヘッダフィールド11は、4つのフィールド、つまりヘッダ1フィールド、ヘッダ2フィールド、ヘッダ3フィールド、及びヘッダ4フィールドにより構成されている。ヘッダ1フィールド及びヘッダ3フィールドは46バイトで、ヘッダ2フィールド及びヘッダ4フィールドは18バイトで構成され、36バイトあるいは8バイトの同期コード部VFO(Variable Frequency Oscillator )、3バイトのアドレスマークAM(Address Mark)、4バイトのアドレス部PID(Position Identifier )、2バイトの誤り検出コードIED(ID Error Detection Code)、1バイトのポストアンブルPA(Post Ambles )により構成されている。
【0044】
ヘッダ1フィールド及びヘッダ3フィールドは、36バイトの同期コード部VFO1を有し、ヘッダフィールド2及びヘッダ4フィールドは、8バイトの同期コード部VFO2を有している。この同期コード部VFO1及びVFO2は、PLLの引き込みを行うための領域で、同期コード部VFO1はチャネルビットで“010…”の連続を“36”バイト(チャネルビットで646ビット)分記録(一定間隔のパターンを記録)したものであり、同期コード部VFO2はチャネルビットで“010…”の連続を“8”バイト(チャネルビットで128ビット)分記録したものである。
【0045】
アドレスマークAMは、どこからセクタアドレスが始まるかを示す“3”バイトの同期コードである。このアドレスマークAMの各バイトのパターンは“0100100000000100”というデータ部分には現れない特殊なパターンが用いられる。
【0046】
PID1〜PID4は、4バイトから成るセクタインフォメーション(PIDナンバー含む)及びセクターナンバーが記録されている領域である。このPIDについては後に詳しく説明する。
【0047】
誤り検出コードIEDは、セクタアドレス(ID番号含む)に対するエラー(誤り)検出符号で、読み込まれたPID内のエラーの有無を検出することができる。
【0048】
ポストアンブルPA(PA1、PA2)は、復調に必要なステート情報を含んでおり、ヘッダフィールド11がスペースで終了するよう極性調整の役割も持つ。
【0049】
ミラーフィールドは、トラッキングエラー信号のオフセット補正、ランド/グルーブ切り替え信号のタイミング発生等に利用される。
レコーディングフィールドは、10〜26バイトのギャップフィールド、20〜26のガード1フィールド、35バイトのVFO3フィールド、3バイトのPS(pre-synchronous code)フィールド、2418バイトのデータフィールド、1バイトのポストアンブル3(PA3)フィールド、48〜55バイトのガード2フィールド、および9〜25バイトのバッファフィールドにより構成されている。
【0050】
ギャップフィールドは、何も記録されたない領域である。
ガード1フィールドは、相変化記録媒体特有の繰り返し記録時の終端劣化がVFO3領域にまで及ばないようにするために設けられた領域である。
【0051】
VFO3フィールドもPLLロック用の領域ではあるが、同一パターンの中に同期コードを挿入し、バイト境界の同期をとることも目的とする領域である。
PSフィールドは、データ領域につなぐための同調用の領域である。
【0052】
データフィールドは、データID、データIDエラー訂正コードIED(Data ID Error Detection Code)、同期コード、ECC(Error Collection Code )、EDC(Error Detection Code)、ユーザデータ等から構成される領域である。データIDは、各セクタの4バイト(32チャネルビット)構成のセクタID1〜ID16である。データIDエラー訂正コードIEDは、データID用の2バイト(16ビット)構成のエラー訂正コードである。
【0053】
PA(post Amble)3フィールドは、復調に必要なステート情報を含んでおり、前のデータ領域の最終バイトの終結を示す領域である。
ガード2フィールドは、相変化記録媒体特有の繰り返し記録時の終端劣化がデータ領域にまで及ばないようにするために設けられた領域である。
【0054】
バッファフィールドは、データ領域が次のヘッダフィールド11にかからないように、光ディスク1を回転するモータの回転変動などを吸収するために設けられた領域である。
【0055】
続いて、ヘッダフィールドにおけるPID(PID1〜4)について具体的に説明する。PIDは、1バイト(8ビット)のセクタインフォメーションフィールドと、3バイト(24ビット)のセクタナンバーフィールド(トラック上における論理的な位置を示す論理アドレスとしての論理セクタ番号)から構成されている。
【0056】
さらに、このセクタインフォメーションは、2ビットのリザーブフィールド、2ビットのPIDナンバーフィールド、3ビットのセクタタイプフィールド、1ビットのレイヤーナンバーフィールドにより構成されている。
【0057】
この実施形態では、リザーブフィールドには特に何も記録されない。
PIDナンバーフィールドには、PIDナンバーが記録される。例えば、ヘッダ1フィーフィールド中におけるPIDナンバーフィールドにはPID1を示す“00”、ヘッダ2フィーフィールド中におけるPIDナンバーフィールドにはPID2を示す“01”、ヘッダ3フィーフィールド中におけるPIDナンバーフィールドにはPID3を示す“10”、ヘッダ4フィーフィールド中におけるPIDナンバーフィールドにはPID4を示す“11”が記録される。
【0058】
この発明では、ヘッダ1フィールド〜ヘッダ4フィールド中のPIDナンバーフィールドに記録された各PIDナンバーの関係から、ランドトラッキングとグルーブトラッキングとが切り替えられる。このPIDナンバーを利用したランドトラッキングとグルーブトラッキングの切り換えを、PIDナンバーによるトラッキング制御方法と称し、後に詳しく説明する。
【0059】
セクタタイプフィールドには、読み出し専用セクタ(Read only sector)であることを示す“000”、リザーブセクタ(Reserved)であることを示す“001”、“010”、又は“011”、ランド又はグルーブトラックの書き換え可能な先頭セクタ(Rewritable first sector )であることを示す“100”、ランド又はグルーブトラックの書き換え可能な最終セクタ(Rewritable last sector)であることを示す“101”、ランド又はグルーブトラックの書き換え可能な最終セクタの一つ手前のセクタ(Rewritable before last sector )であることを示す“110”、ランド又はグルーブトラックの書き換え可能なその他のセクタ(Rewritable other sector )であることを示す“111”が記録される。
【0060】
この発明では、セクタタイプフィールドに記録されたセクタタイプを基にして、ランドトラッキングとグルーブトラッキングとが切り替えられる。このセクタタイプによるランドトラッキングとグルーブトラッキングの切り換えを、セクタタイプによるトラッキング制御方法と称し、後に詳しく説明する。
【0061】
レイヤーナンバーフィールドには、レイヤー1又は0を示す“1”又は“0”が記録される。
次に、図6〜図9を参照して、PIDナンバーによるトラッキング制御方法について説明する。
【0062】
先ず、図6及び図7を参照して、グルーブセクタとグルーブセクタ、又はランドセクタとランドセクタの間に設けられたヘッダフィールド11のPIDナンバーによるトラッキング制御方法について説明する。
【0063】
ヘッダフィールド11は、図6に示すように、複数のピットPにより構成されている。ヘッダH12−1及びH12−2を構成するピットの中心は、ランドセクタL02とグルーブセクタG12(又はランドセクタL01とグルーブセクタG11)の接線の同一線上の位置に存在する。ヘッダH22−3及びヘッダH22−4を構成するピットの中心は、グルーブセクタG12とランドセクタL22(又はグルーブセクタG11とランドセクタL21)の接線の同一線上の位置に存在する。ヘッダH32−1及びヘッダH32−2を構成するピットの中心は、ランドセクタL22とグルーブセクタG32(又はランドセクタL21とグルーブセクタG31)の接線の同一線上の位置に存在する。ヘッダH42−3及びヘッダH42−4を構成するピットの中心は、グルーブセクタG32とランドセクタL42(又はグルーブセクタG31とランドセクタL41)の接線の同一線上の位置に存在する。ヘッダH52−1及びヘッダH52−2を構成するピットの中心は、ランドセクタL42とグルーブセクタG52(又はランドセクタL41とグルーブセクタG51)の接線の同一線上の位置に存在する。ヘッダH62−3及びヘッダH62−4を構成するピットの中心は、グルーブセクタG52とランドセクタL62(又はグルーブセクタG51とランドセクタL61)の接線の同一線上の位置に存在する。
【0064】
また、グルーブセクタとグルーブセクタの間に設けられたヘッダフィールド11の各ヘッダのPID(physical ID number)ナンバーは、図7に示すような関係となる。例えば、グルーブセクタG11とグルーブセクタG12の間に設けられた各ヘッダのPIDナンバーを例に取り説明する。グルーブセクタG11とグルーブセクタG12の間には、ヘッダH12−1(ヘッダ1フィールド)、ヘッダH12−2(ヘッダ2フィールド)、ヘッダH22−3(ヘッダ3フィールド)、及びヘッダH22−4(ヘッダ4フィールド)が設けられている。また、ヘッダH12−1のPIDナンバーは(n+3N)、ヘッダH12−2のPIDナンバーは(n+3N)、ヘッダH22−3のPIDナンバーは(n+2N)、ヘッダH22−4のPIDナンバーは(n+2N)である。つまり、グルーブセクタとグルーブセクタの間に設けられた各ヘッダのPIDを比較すると、(ヘッダ1フィールド又はヘッダ2フィールドのPIDナンバー)>(ヘッダ3フィールド又はヘッダ4フィールドのPIDナンバー)の関係が成立する。
【0065】
一方、ランドセクタとランドセクタの間に設けられたヘッダフィールド11の各ヘッダのPIDナンバーは、図7に示すような関係となる。例えば、ランドセクタL21とランドセクタL22の間に設けられた各ヘッダのPIDナンバーを例に取り説明する。ランドセクタL21とランドセクタL22の間には、ヘッダH32−1(ヘッダ1フィールド)、ヘッダH32−2(ヘッダ2フィールド)、ヘッダH22−3(ヘッダ3フィールド)、及びヘッダH22−4(ヘッダ4フィールド)が設けられている。また、ヘッダH32−1のPIDナンバーは(n+N)、ヘッダH32−2のPIDナンバーは(n+N)、ヘッダH22−3のPIDナンバーは(n+2N)、ヘッダH22−4のPIDナンバーは(n+2N)である。つまり、ランドセクタとランドセクタの間に設けられた各ヘッダのPIDを比較すると、(ヘッダ1フィールド又はヘッダ2フィールドのPIDナンバー)<(ヘッダ3フィールド又はヘッダ4フィールドのPIDナンバー)の関係が成立する。
【0066】
つまり、ヘッダ再生により、(ヘッダ1フィールド又はヘッダ2フィールドのPIDナンバー)>(ヘッダ3フィールド又はヘッダ4フィールドのPIDナンバー)の関係が判明すれば、このヘッダの後のセクタがグルーブセクタであるものとして識別され、グルーブセクタに応じた再生処理を行うことができる。逆に、ヘッダ再生により、(ヘッダ1フィールド又はヘッダ2フィールドのPIDナンバー)<(ヘッダ3フィールド又はヘッダ4フィールドのPIDナンバー)の関係が判明すれば、このヘッダの後のセクタがランドセクタであるものとして識別され、ランドセクタに応じた再生処理を行うことができる。
【0067】
なお、上記したランドセクタ及びグルーブセクタの識別は、識別手段としてのCPU50によりなされるものとする。また、識別結果に応じた再生処理、つまり、ランドトラックに応じたランドトラッキング、及びグルーブセクタに応じたグルーブトラッキングは、トラッキング制御手段としてのトラッキング制御回路により行われるものとする。
【0068】
続いて、図8及び図9を参照して、グルーブセクタとランドセクタの間、つまりグルーブとランドの変わり目に設けられたヘッダフィールド11のPIDナンバーによるトラッキング制御方法について説明する。
【0069】
ヘッダフィールド11は、図8に示すように、複数のピットPにより構成されている。ヘッダH20−3及びヘッダH20−4を構成するピットの中心は、グルーブセクタG10とランドセクタL20の接線の同一線上の位置に存在する。ヘッダH30−1及びH30−2を構成するピットの中心は、ランドセクタL20とグルーブセクタG30(又はグルーブセクタG1nとランドセクタL2n)の接線の同一線上の位置に存在する。ヘッダH40−3及びヘッダH40−4を構成するピットの中心は、グルーブセクタG30とランドセクタL40(又はランドセクタL2nとグルーブセクタG3n)の接線の同一線上の位置に存在する。ヘッダH50−1及びヘッダH50−2を構成するピットの中心は、ランドセクタL40とグルーブセクタG50(又はグルーブセクタG3nとランドセクタL4n)の接線の同一線上の位置に存在する。ヘッダH60−3及びヘッダH60−4を構成するピットの中心は、グルーブセクタG50とランドセクタL60(又はランドセクタL4nとグルーブセクタG5n)の接線の同一線上の位置に存在する。ヘッダH70−1及びヘッダH70−2を構成するピットの中心は、ランドセクタL60とグルーブセクタG70の接線の同一線上の位置に存在する。
【0070】
また、ランドセクタとグルーブセクタの間(ランドセクタからグルーブセクタへ変化するとき)に設けられたヘッダフィールド11の各ヘッダのPID(physical ID number)ナンバーは、図9に示すような関係となる。例えば、ランドセクタL2nとグルーブセクタG30の間に設けられた各ヘッダのPIDナンバーを例に取り説明する。ランドセクタL2nとグルーブセクタG30の間には、ヘッダH30−1(ヘッダ1フィールド)、ヘッダH30−2(ヘッダ2フィールド)、ヘッダH40−3(ヘッダ3フィールド)、及びヘッダH40−4(ヘッダ4フィールド)が設けられている。また、ヘッダH30−1のPIDナンバーは(m+3N)、ヘッダH30−2のPIDナンバーは(m+3N)、ヘッダH40−3のPIDナンバーは(m+2N)、ヘッダH40−4のPIDナンバーは(m+2N)である。つまり、ランドセクタとグルーブセクタの間に設けられた各ヘッダのPIDを比較すると、(ヘッダ1フィールド又はヘッダ2フィールドのPIDナンバー)>(ヘッダ3フィールド又はヘッダ4フィールドのPIDナンバー)の関係が成立する。
【0071】
一方、グルーブセクタとランドセクタの間(グルーブセクタからランドセクタへ変化するとき)に設けられたヘッダフィールド11の各ヘッダのPIDナンバーは、図9に示すような関係となる。例えば、グルーブセクタG3nとランドセクタL40の間に設けられた各ヘッダのPIDナンバーを例に取り説明する。グルーブセクタG3nとランドセクタL40の間には、ヘッダH50−1(ヘッダ1フィールド)、ヘッダH50−2(ヘッダ2フィールド)、ヘッダH40−3(ヘッダ3フィールド)、及びヘッダH40−4(ヘッダ4フィールド)が設けられている。また、ヘッダH50−1のPIDナンバーは(m+N)、ヘッダH50−2のPIDナンバーは(m+N)、ヘッダH40−3のPIDナンバーは(m+2N)、ヘッダH40−4のPIDナンバーは(m+2N)である。つまり、グルーブセクタとランドセクタの間に設けられた各ヘッダのPIDを比較すると、(ヘッダ1フィールド又はヘッダ2フィールドのPIDナンバー)<(ヘッダ3フィールド又はヘッダ4フィールドのPIDナンバー)の関係が成立する。
【0072】
つまり、ヘッダ再生により、(ヘッダ1フィールド又はヘッダ2フィールドのPIDナンバー)>(ヘッダ3フィールド又はヘッダ4フィールドのPIDナンバー)の関係が判明すれば、このヘッダの後のセクタがグルーブセクタであるものとして識別され、グルーブセクタに応じた再生処理を行うことができる。逆に、ヘッダ再生により、(ヘッダ1フィールド又はヘッダ2フィールドのPIDナンバー)<(ヘッダ3フィールド又はヘッダ4フィールドのPIDナンバー)の関係が判明すれば、このヘッダの後のセクタがランドセクタであるものとして識別され、ランドセクタに応じた再生処理を行うことができる。
【0073】
なお、上記したランドセクタ及びグルーブセクタの識別は、識別手段としてのCPU50によりなされるものとする。また、識別結果に応じた再生処理、つまり、ランドトラックに応じたランドトラッキング、及びグルーブセクタに応じたグルーブトラッキングは、トラッキング制御手段としてのトラッキング制御回路により行われるものとする。
【0074】
以上、図6〜図9で説明したように、ヘッダ再生により得られるヘッダ1フィールド(又はヘッダ2フィールド)とヘッダ3フィールド(又はヘッダ4フィールド)との大小関係から、その後のセクタがランドセクタなのか、グルーブセクタなのかを識別することができる。この識別結果を基にして、トラッキング制御回路28から出力されるトラック駆動信号により駆動コイル32が駆動され、ランドトラッキングとグルーブトラッキングとが切り替えられる。
【0075】
次に、図10を参照して、セクタータイプによるトラッキング制御方法について説明する。
図10に示すように、1トラック(ランドトラック又はグルーブトラック)中における各セクタには上記したようにセクタタイプの情報が記録されている。つまり、トラックの先頭セクタには「先頭セクタ」、トラックの最終セクタには「最終セクタ」、トラックの最終セクタの一つ手前のセクタには「最終前のセクタ」、トラックの先頭セクタとトラックの最終セクタの一つ手前のセクタとの間のセクタには「その他のセクタ」がセクタタイプ情報として記録される。
【0076】
よって、トラックとトラックの変わり目、つまりランドトラックとグルーブトラックの変わり目の前後のセクタに記録されたセクタタイプ情報を基にしてトラックの変わり目を検出することができる。例えば、再生されたセクタタイプ情報から、このセクタが最終前のセクタであることが判明すれば、次のセクタの次でトラックが切り替わることが検出できる。また、再生されたセクタタイプ情報から、このセクタが最終セクタであることが判明すれば、次のセクタでトラックが切り替わることが検出できる。さらに、再生されたセクタタイプ情報から、このセクタが先頭セクタでることが判明すれば、トラックが切り替わったことが検出できる。なお、これら検出は、検出手段としてのCPU50によりなされるものとする。また、検出結果に応じた再生処理、つまり、ランドトラックに応じたランドトラッキング、及びグルーブセクタに応じたグルーブトラッキングは、トラッキング制御手段としてのトラッキング制御回路により行われるものとする。
【0077】
この発明では、セクタタイプフィールドに記録されたセクタタイプを基にして、ランドトラックからグルーブトラック、又はグルーブトラックからランドトラックへの切り替わりを検出することができる。この検出結果を基にして、トラッキング制御回路28から出力されるトラック駆動信号により駆動コイル32が駆動されランドトラッキングとグルーブトラッキングが切り換えられる。
【0078】
次に、図11のフローチャートを参照して、アナログ的トラッキング制御方法、PIDナンバーによるトラッキング制御方法、及びセクタタイプによるトラッキング制御方法を利用したトラッキング制御について説明する。
【0079】
図11に示すように、シーク動作(ST10)、トラックオン(ST12)の順に処理が進められ、上記説明したアナログ的トラッキング制御が実行される(ST14)。
【0080】
続いて、ヘッダ再生が行われ(ST16)、正常にヘッダが再生されると(ST18、YES)、上記説明したPIDナンバーによるトラッキング制御が実行される(ST20)。このPIDナンバーによるトラッキング制御は、PID1及びPID2の少なくとも一方、PID3及びPID4の少なくとも一方が再生できれば実行できる。何故なら、このPIDナンバーによるトラッキング制御では、PID1又はPID2とPID3又はPID4との大小関係が制御のポイントとなるからである。PIDナンバーによるトラッキング制御が正常に実行されると(ST22、YES)、トラッキング制御は終了する。
【0081】
PIDナンバーによるトラッキング制御が正常に実行されなかった場合(ST22、NO)で、かつ少なくとも一つのPIDが再生された場合には(ST24、YES)、この再生されたPIDに含まれるセクタタイプの情報から上記説明したセクタタイプによるトラッキング制御が実行される(ST26)。
【0082】
PIDナンバーによるトラッキング制御が正常に実行されなかった場合(ST22、NO)で、かつPIDが再生できなかった場合(ST24、NO)、つまり、現在のセクタのセクタタイプが再生できない場合には、前回のセクタのセクタタイプの情報から現在のセクタタイプが予測され(ST28)、この予測結果によりトラッキング制御が行われる。つまり、前回のセクタが最終セクタである場合には現在のセクタは先頭セクタであると予測され、ランドトラッキングからグルーブトラッキングへ、又はグルーブトラッキングからランドトラッキングへ切り替えられる(ST30)。また、現在のセクタのセクタタイプ及び前回のセクタのセクタタイプが不明な場合には、前々回のセクタのセクタタイプの情報から現在のセクタタイプが予測される。
【0083】
【発明の効果】
この発明によれば、ランドトラッキングとグルーブトラッキングとの切り換えを正確に実行可能な光ディスク記録再生装置及び光ディスク記録再生方法を提供することができる。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】この発明の実施の一形態に係る光ディスク装置の概略構成を示す図。
【図2】光ディスクの概略構成を示す平面図。
【図3】光ディスクの概略構成を示すブロック図。
【図4】光ディスクの各ゾーンにおける回転数及び1トラックあたりのセクタ数を説明する図。
【図5】セクタフィールドのレイアウト、ヘッダフィールドのレイアウト、PIDフィールドのレイアウト、及びセクターインフォーメーションのレイアウトを示す図。
【図6】グルーブセクタとグルーブセクタ、又はランドセクタとランドセクタの間に設けられたヘッダフィールドを概略的に示す図。
【図7】グルーブセクタとグルーブセクタ、又はランドセクタとランドセクタの間に設けられたヘッダフィールドを概略的に示す図。
【図8】グルーブセクタとランドセクタとの間に設けられたヘッダフィールドを概略的に示す図。
【図9】グルーブセクタとランドセクタとの間に設けられたヘッダフィールドを概略的に示す図。
【図10】セクタタイプによるトラッキング制御を説明するための図。
【図11】アナログ的トラッキング制御、PIDナンバーによるトラッキング制御、及びセクタタイプによるトラッキング制御を利用したトラッキング制御を説明するためのフローチャート。
【図12】ヘッダ位置検出回路の概略構成を示す図。
【図13】トラックエラー信号、ヘッダ検知信号、インナーヘッダ検知信号、及びアウターヘッダ検知信号の関係を示す図。
【図14】ランド/グルーブ切換点検出回路の概略構成を示す図。
【図15】ヘッダ検知信号、インナーヘッダ検知信号、アウターヘッダ検知信号、及びランド/グルーブ切換信号の関係を示す図。
【符号の説明】
1…光ディスク
10…メモリ
25…光学ヘッド
31、32…駆動コイル
33…レーザ制御回路
38…データ再生回路
48…トラッキング制御回路
50…CPU[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to an optical disc recording / reproducing apparatus and an optical disc recording / reproducing method for recording data on an optical disc capable of recording data on both a spiral land track and a groove track or reproducing the recorded data.
[0002]
[Prior art]
Some optical discs can record data on only one of a land track and a groove track, and others can record data on both a land track and a groove track.
[0003]
In the latter case, at the time of data recording / reproducing, it is necessary to identify the land track and the groove track and switch between land tracking corresponding to the land track and groove tracking corresponding to the groove track.
Conventionally, a land track and a groove track are identified in an analog manner from the characteristics of a reproduction signal reproduced from an optical disk.
[0004]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
In the case of analog identification as described above, there is a problem in the identification accuracy because the corn is easily affected by scratches on the optical disk or meandering of the beam. For this reason, land tracking and groove tracking may be erroneously switched due to erroneous detection.
[0005]
An object of the present invention is to provide an optical disc recording / reproducing apparatus and an optical disc recording / reproducing method capable of accurately executing switching between land tracking and groove tracking. .
[0006]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
In order to solve the above problems and achieve the object, an optical disc recording / reproducing apparatus of the present invention is configured as follows.
(1) According to the present invention,
A spiral land track and a groove track formed by the land portion and the groove portion, each having a predetermined track length, and a header data area in which header data is recorded and a user data area in which user data is recorded In an optical disc recording / reproducing apparatus for recording data on an optical disc in which a format having a plurality of continuous sector areas is defined or reproducing the recorded data,
Reproducing means for reproducing data recorded on the optical disc;
From the characteristics of the reproduced signal reproduced by the reproducing means, first identifying means for identifying which sector area of the land track or the groove track corresponds to the sector area to be reproduced;
First tracking control means for controlling tracking according to the identification result by the first identification means;
Sector area having the header data from the data reproduced by the reproducing means and identifying data that can identify the sector area corresponding to either the land track or the groove track included in the header data A second identification means for identifying which of the land track and the groove track the sector area corresponds to;
Second tracking control means for controlling tracking according to the identification result by the second identification means;
An optical disc recording / reproducing apparatus characterized by comprising:
[0007]
(2) According to the present invention,
A spiral land track and a groove track formed by the land portion and the groove portion, each having a predetermined track length, and a header data area in which header data is recorded and a user data area in which user data is recorded In an optical disc recording / reproducing apparatus for recording data on an optical disc in which a format having a plurality of continuous sector areas is defined or reproducing the recorded data,
Reproducing means for reproducing data recorded on the optical disc;
From the characteristics of the reproduced signal reproduced by the reproducing means, first identifying means for identifying which sector area of the land track or the groove track corresponds to the sector area to be reproduced;
First tracking control means for switching and controlling land tracking corresponding to the land track and groove tracking corresponding to the groove track in accordance with the identification result by the first identifying means;
It is data reproduced by the reproducing means, and the sector area having these ID data as header data is located on either the land track or the groove track from the relationship of a plurality of ID data included in the header data. A second identification means for identifying the sector area,
A second tracking control means for switching between land tracking corresponding to the land track and groove tracking corresponding to the groove track in accordance with an identification result by the second identifying means;
An optical disc recording / reproducing apparatus characterized by comprising:
[0008]
(3) According to the present invention,
A spiral land track and a groove track formed by the land portion and the groove portion, each having a predetermined track length, and a header data area in which header data is recorded and a user data area in which user data is recorded In an optical disc recording / reproducing apparatus for recording data on an optical disc in which a format having a plurality of continuous sector areas is defined or reproducing the recorded data,
Reproducing means for reproducing data recorded on the optical disc;
From the characteristics of the reproduced signal reproduced by the reproducing means, first identifying means for identifying which sector area of the land track or the groove track corresponds to the sector area to be reproduced;
First tracking control means for switching and controlling land tracking corresponding to the land track and groove tracking corresponding to the groove track in accordance with the identification result by the first identifying means;
The data reproduced by the reproducing means, and when the first and second ID numbers included in the header data have a first ID number> a second ID number, the ID numbers are A sector area having header data is identified as a sector area corresponding to the land track, and when first ID number <second ID number, a sector area having these ID numbers as header data corresponds to the groove track. A second identification means for identifying the sector area;
A second tracking control means for switching between land tracking corresponding to the land track and groove tracking corresponding to the groove track in accordance with an identification result by the second identifying means;
An optical disc recording / reproducing apparatus characterized by comprising:
[0009]
As a result of taking the above-mentioned means, the following operation occurs.
In the optical disk recording / reproducing apparatus of the present invention, the first discriminating whether the sector area to be reproduced is the sector area corresponding to the land track or the groove track from the feature of the reproduced signal reproduced. From the identification means and the identification data that can identify which of the land track and groove track included in the header data, the sector area having this header data is either the land track or the groove track. Since the second identification means for identifying the sector area corresponding to is provided, the sector area corresponding to the land track or the groove track can be identified from the characteristics of the reproduction signal and the identification data. Furthermore, since the first and second tracking control means for controlling tracking according to the identification results by the first and second identification means are provided, tracking control based on the characteristics of the reproduction signal and the identification data is possible. Become.
[0010]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
An embodiment of the present invention will be described below with reference to the drawings.
FIG. 1 is a diagram showing a schematic configuration of an optical disc apparatus according to an embodiment of the present invention. This optical disc apparatus records data on an optical disc (DVD-RAM) 1 as an information recording medium using focused light or reproduces recorded data.
[0011]
The
[0012]
As shown in FIGS. 2 and 3, the
[0013]
As shown in FIG. 2 and FIG. 3, the
[0014]
In the
[0015]
As shown in FIGS. 2 and 3, the tracks of the
[0016]
Here, it returns to description of FIG. 1 again. As shown in FIG. 1, the
[0017]
Recording of data on the
[0018]
A speed detector 29 is connected to the linear
In addition, a permanent magnet (not shown) is provided in the fixed portion of the
[0019]
An
[0020]
Further, the laser control circuit 33 drives the
[0021]
The laser control circuit 33 operates in synchronization with a recording clock signal from a PLL circuit (not shown). This PLL circuit divides a basic clock signal from an oscillator (not shown) to generate a recording clock signal.
[0022]
The laser light generated from the
[0023]
The
The output signal of the light detection cell 44a of the
[0024]
The output signal of the photodetector cell 44a of the
[0025]
The output signal of the adder 46a is supplied to the inverting input terminal of the differential amplifier OP2, and the output signal of the
[0026]
The output signal of the adder 46c is supplied to the inverting input terminal of the differential amplifier OP1, and the output signal of the adder 46d is supplied to the non-inverting input terminal of the differential amplifier OP1. Thus, the differential amplifier OP1 supplies a tracking error signal to the
[0027]
The track drive signal output from the
[0028]
A signal obtained by adding the output signals from the adders 46c and 46d by the
[0029]
The reproduction data reproduced by the
[0030]
When the
[0031]
In addition, a
[0032]
The
[0033]
The
[0034]
Further, in this optical disc apparatus, a D / A converter used for transferring information between the focusing control circuit 47, the
[0035]
The
[0036]
The
[0037]
Next, a method of detecting the switching between the land track and the groove track in an analog manner and switching between the land tracking and the groove tracking (analog tracking control method) will be briefly described.
[0038]
This analog tracking control is performed by the header
[0039]
Here, the header
As shown in FIG. 12, the header
[0040]
As shown in FIG. 14, the land / groove switching
[0041]
Next, the sector format will be described with reference to FIG. FIG. 5 is a diagram schematically showing the format of one sector and the format of the header field.
[0042]
As shown in FIG. 5, one sector is composed of approximately 2697 bytes, and is composed of a 128-
[0043]
The
[0044]
The
[0045]
The address mark AM is a “3” byte synchronization code indicating where the sector address starts. As a pattern of each byte of the address mark AM, a special pattern that does not appear in the data portion “0100100000000100” is used.
[0046]
PID1 to PID4 are areas in which sector information (including a PID number) consisting of 4 bytes and a sector number are recorded. This PID will be described in detail later.
[0047]
The error detection code IED is an error (error) detection code for a sector address (including an ID number), and can detect the presence or absence of an error in the read PID.
[0048]
The postamble PA (PA1, PA2) includes state information necessary for demodulation, and also has a role of polarity adjustment so that the
[0049]
The mirror field is used for offset correction of a tracking error signal, timing generation of a land / groove switching signal, and the like.
The recording field includes a 10-26 byte gap field, a 20-26
[0050]
The gap field is an area where nothing is recorded.
The
[0051]
The VFO3 field is also an area for PLL lock, but it is also an area intended to synchronize byte boundaries by inserting a synchronization code into the same pattern.
The PS field is a tuning area for connecting to the data area.
[0052]
The data field is an area composed of a data ID, a data ID error correction code IED (Data ID Error Detection Code), a synchronization code, an ECC (Error Collection Code), an EDC (Error Detection Code), user data, and the like. The data ID is sector ID1 to ID16 having a 4-byte (32 channel bit) configuration of each sector. The data ID error correction code IED is an error correction code having a 2-byte (16 bits) configuration for data ID.
[0053]
A PA (post Amble) 3 field includes state information necessary for demodulation, and is an area indicating the end of the last byte of the previous data area.
The
[0054]
The buffer field is an area provided to absorb rotational fluctuations of a motor that rotates the
[0055]
Subsequently, PIDs (PID1 to PID4) in the header field will be specifically described. The PID is composed of a 1-byte (8-bit) sector information field and a 3-byte (24-bit) sector number field (a logical sector number as a logical address indicating a logical position on a track).
[0056]
Further, this sector information is composed of a 2-bit reserve field, a 2-bit PID number field, a 3-bit sector type field, and a 1-bit layer number field.
[0057]
In this embodiment, nothing is recorded in the reserved field.
A PID number is recorded in the PID number field. For example, “00” indicating PID1 is indicated in the PID number field in the
[0058]
In the present invention, land tracking and groove tracking are switched based on the relationship between the PID numbers recorded in the PID number field in the
[0059]
In the sector type field, “000” indicating a read-only sector, “001”, “010”, or “011” indicating a reserved sector (Reserved), a land or groove track “100” indicating the rewritable first sector, “101” indicating the rewritable last sector of the land or groove track, and rewriting of the land or groove track “110” indicating that it is a sector immediately before the last possible sector (Rewritable before last sector), and “111” indicating that it is a rewritable other sector of the land or groove track. To be recorded.
[0060]
In the present invention, land tracking and groove tracking can be switched based on the sector type recorded in the sector type field. This switching between land tracking and groove tracking by sector type is called a tracking control method by sector type and will be described in detail later.
[0061]
In the layer number field, “1” or “0” indicating
Next, a tracking control method based on PID numbers will be described with reference to FIGS.
[0062]
First, a tracking control method based on the PID number of the
[0063]
The
[0064]
Also, the PID (physical ID number) number of each header of the
[0065]
On the other hand, the PID number of each header in the
[0066]
That is, if the relationship of (PID number of
[0067]
Note that the land sector and the groove sector are identified by the
[0068]
Next, a tracking control method based on the PID number of the
[0069]
The
[0070]
Also, the PID (physical ID number) number of each header of the
[0071]
On the other hand, the PID number of each header in the
[0072]
That is, if the relationship of (PID number of
[0073]
Note that the land sector and the groove sector are identified by the
[0074]
As described above with reference to FIGS. 6 to 9, the subsequent sector is a land sector because of the size relationship between the
[0075]
Next, a tracking control method by sector type will be described with reference to FIG.
As shown in FIG. 10, sector type information is recorded in each sector in one track (land track or groove track) as described above. That is, the first sector of the track is the “first sector”, the last sector of the track is the “last sector”, the sector immediately before the last sector of the track is “the last sector”, the first sector of the track and the track In the sector between the sector immediately before the last sector, “other sector” is recorded as sector type information.
[0076]
Therefore, the track change can be detected based on the sector type information recorded in the sectors before and after the change between the tracks, that is, the land track and the groove track. For example, if it is found from the reproduced sector type information that this sector is the last sector, it can be detected that the track is switched after the next sector. If it is found from the reproduced sector type information that this sector is the last sector, it can be detected that the track is switched in the next sector. Furthermore, if it is determined from the reproduced sector type information that this sector is the first sector, it can be detected that the track has been switched. These detections are performed by the
[0077]
In the present invention, switching from a land track to a groove track or from a groove track to a land track can be detected based on the sector type recorded in the sector type field. Based on the detection result, the
[0078]
Next, tracking control using an analog tracking control method, a tracking control method based on a PID number, and a tracking control method based on a sector type will be described with reference to the flowchart of FIG.
[0079]
As shown in FIG. 11, the processing proceeds in the order of seek operation (ST10) and track-on (ST12), and the analog tracking control described above is executed (ST14).
[0080]
Subsequently, header playback is performed (ST16), and when the header is normally played back (ST18, YES), tracking control based on the PID number described above is executed (ST20). The tracking control based on the PID number can be executed if at least one of PID1 and PID2 and at least one of PID3 and PID4 can be reproduced. This is because in tracking control using this PID number, the magnitude relationship between PID1 or PID2 and PID3 or PID4 is the point of control. When tracking control by the PID number is normally executed (ST22, YES), the tracking control ends.
[0081]
When the tracking control by the PID number is not normally executed (ST22, NO) and at least one PID is reproduced (ST24, YES), information on the sector type included in the reproduced PID The tracking control based on the sector type described above is executed (ST26).
[0082]
When the tracking control by the PID number is not normally executed (ST22, NO) and the PID cannot be reproduced (ST24, NO), that is, when the sector type of the current sector cannot be reproduced, The current sector type is predicted from the sector type information of this sector (ST28), and tracking control is performed based on the prediction result. That is, if the previous sector is the last sector, the current sector is predicted to be the first sector, and switching from land tracking to groove tracking or from groove tracking to land tracking is performed (ST30). When the sector type of the current sector and the sector type of the previous sector are unknown, the current sector type is predicted from the sector type information of the previous sector.
[0083]
【The invention's effect】
According to the present invention, it is possible to provide an optical disc recording / reproducing apparatus and an optical disc recording / reproducing method capable of accurately executing switching between land tracking and groove tracking.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a diagram showing a schematic configuration of an optical disc apparatus according to an embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 2 is a plan view showing a schematic configuration of an optical disc.
FIG. 3 is a block diagram showing a schematic configuration of an optical disc.
FIG. 4 is a diagram for explaining the number of rotations and the number of sectors per track in each zone of the optical disc.
FIG. 5 shows a layout of a sector field, a header field, a PID field, and a sector information layout.
FIG. 6 is a diagram schematically showing a header field provided between a groove sector and a groove sector, or between a land sector and a land sector.
FIG. 7 is a diagram schematically showing a header field provided between a groove sector and a groove sector, or between a land sector and a land sector.
FIG. 8 is a diagram schematically showing a header field provided between a groove sector and a land sector.
FIG. 9 is a diagram schematically showing a header field provided between a groove sector and a land sector.
FIG. 10 is a diagram for explaining tracking control by sector type.
FIG. 11 is a flowchart for explaining tracking control using analog tracking control, tracking control by PID number, and tracking control by sector type.
FIG. 12 is a diagram showing a schematic configuration of a header position detection circuit.
FIG. 13 is a diagram showing a relationship among a track error signal, a header detection signal, an inner header detection signal, and an outer header detection signal.
FIG. 14 is a diagram showing a schematic configuration of a land / groove switching point detection circuit;
FIG. 15 is a diagram illustrating a relationship among a header detection signal, an inner header detection signal, an outer header detection signal, and a land / groove switching signal.
[Explanation of symbols]
1 ... Optical disc
10 ... Memory
25. Optical head
31, 32 ... Driving coil
33 ... Laser control circuit
38. Data reproduction circuit
48 ... Tracking control circuit
50 ... CPU
Claims (4)
各ゾーンが、ランドトラックとグルーブトラックにより形成されるスパイラルトラックを有し、 Each zone has a spiral track formed by land tracks and groove tracks,
前記ランドトラック及び前記グルーブトラックは、夫々、セクタ領域を複数個有し、 Each of the land track and the groove track has a plurality of sector regions,
同一ゾーンの前記ランドトラック又は前記グルーブトラックが有する前記セクタ領域の数は同一であり、異なるゾーンの前記ランドトラック又は前記グルーブトラックが有する前記セクタ領域の数は異なり、 The number of the sector areas included in the land track or the groove track in the same zone is the same, the number of the sector areas included in the land track or the groove track in a different zone is different,
前記セクタ領域は、ヘッダデータが記録されたヘッダデータ領域とユーザデータが記録されるユーザデータ領域とを含み、 The sector area includes a header data area in which header data is recorded and a user data area in which user data is recorded,
前記ヘッダデータ領域は、セクタタイプフィールド及びセクタナンバーフィールドを含み、 The header data area includes a sector type field and a sector number field,
前記セクタナンバーフィールドは、アドレスを含み、 The sector number field includes an address,
前記ランドトラック及び前記グルーブトラックの最終に位置する前記セクタ領域の前記セクタタイプフィールドは、1トラックにおける最終セクタであることを示すデータを含む、 The sector type field of the sector area located at the end of the land track and the groove track includes data indicating the last sector in one track.
ことを特徴とする光ディスク。 An optical disc characterized by the above.
前記光ディスクに記録されたデータを再生する再生手段と、 Reproducing means for reproducing data recorded on the optical disc;
前記再生手段により再生されたデータであって、前記ヘッダデータに含まれる前記セクタタイプフィールドのデータに基づき、このヘッダデータを有するセクタ領域が1トラックにおける最終セクタに該当するか否かを識別する識別手段と、 Identification for identifying whether the sector area having the header data corresponds to the last sector in one track based on the data of the sector type field included in the header data, which is data reproduced by the reproducing means Means,
前記識別手段による識別結果に基づき、トラッキングを制御するトラッキング制御手段と、 Tracking control means for controlling tracking based on the identification result by the identification means;
を備えたことを特徴とする光ディスク再生装置。 An optical disc reproducing apparatus comprising:
前記光ディスクに記録されたデータを再生し、 Play back the data recorded on the optical disc,
前記再生されたデータであって、前記ヘッダデータに含まれる前記セクタタイプフィールドのデータに基づき、このヘッダデータを有するセクタ領域が1トラックにおける最終セクタに該当するか否かを識別し、 Identifying whether the sector area having the header data corresponds to the last sector in one track based on the data of the sector type field included in the header data, the reproduced data.
前記識別結果に基づき、トラッキングを制御する、 Based on the identification result, tracking is controlled.
ことを特徴とする光ディスク再生方法。 An optical disc reproducing method characterized by the above.
前記光ディスクに記録されたデータを再生し、 Play back the data recorded on the optical disc,
前記再生されたデータであって、前記ヘッダデータに含まれる前記セクタタイプフィールドのデータに基づき、このヘッダデータを有するセクタ領域が1トラックにおける最終セクタに該当するか否かを識別し、 Identifying whether the sector area having the header data corresponds to the last sector in one track based on the data of the sector type field included in the header data, the reproduced data.
前記識別結果に基づき、トラッキングを制御する、 Based on the identification result, tracking is controlled.
ことを特徴とする光ディスク記録方法。 An optical disc recording method.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP08079697A JP3762027B2 (en) | 1997-03-31 | 1997-03-31 | Optical disc, optical disc playback apparatus, optical disc playback method, and optical disc recording method |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP08079697A JP3762027B2 (en) | 1997-03-31 | 1997-03-31 | Optical disc, optical disc playback apparatus, optical disc playback method, and optical disc recording method |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JPH10275347A JPH10275347A (en) | 1998-10-13 |
| JP3762027B2 true JP3762027B2 (en) | 2006-03-29 |
Family
ID=13728432
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP08079697A Expired - Lifetime JP3762027B2 (en) | 1997-03-31 | 1997-03-31 | Optical disc, optical disc playback apparatus, optical disc playback method, and optical disc recording method |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP3762027B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN100369130C (en) * | 2005-12-12 | 2008-02-13 | 威盛电子股份有限公司 | Sevo controller, optic disc machine and servo control method |
-
1997
- 1997-03-31 JP JP08079697A patent/JP3762027B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JPH10275347A (en) | 1998-10-13 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR100301191B1 (en) | Optical disk apparatus and a replacement processing method | |
| KR100284966B1 (en) | Information recording medium and information reproducing apparatus | |
| JPH07262566A (en) | Optical disk and optical disk device | |
| KR100243457B1 (en) | Optical disk device and tracking control circuit and method for changing tracking position thereof | |
| JP3707833B2 (en) | Optical disk device | |
| JP3959147B2 (en) | Optical disc, optical disc playback apparatus, optical disc playback method, and optical disc recording method | |
| JP3959149B2 (en) | Optical disc, optical disc playback apparatus, optical disc playback method, and optical disc recording method | |
| JP3762027B2 (en) | Optical disc, optical disc playback apparatus, optical disc playback method, and optical disc recording method | |
| JP3762029B2 (en) | Optical disc, optical disc playback apparatus, optical disc playback method, and optical disc recording method | |
| JP3762028B2 (en) | Optical disc, optical disc playback apparatus, optical disc playback method, and optical disc recording method | |
| JP3959148B2 (en) | Optical disc, optical disc playback apparatus, optical disc playback method, and optical disc recording method | |
| JP3875399B2 (en) | Tracking method for optical disk device and tracking method for DVD-RAM drive device | |
| JP2002319246A (en) | Recording medium and thereof and method for manufacture thereof, recording and reproducing device and reproducing method | |
| JP3872887B2 (en) | Optical disk device | |
| JP3707834B2 (en) | Optical disk device | |
| JPH10247325A (en) | Tracking method for data recorder and optical disk device, and signal processing method for optical disk device | |
| EP1356464A1 (en) | Record carrier of the optical type and a device for recording and/or playback for use with such a record carrier | |
| JPH11213392A (en) | Optical disk and optical disk device | |
| JP2954130B2 (en) | Information recording / reproducing medium, information recording / reproducing medium format device, and information recording / reproducing device | |
| JP2954131B2 (en) | Information recording / reproducing medium, information recording / reproducing medium format device, and information recording / reproducing device | |
| JP2954129B2 (en) | Information recording / reproducing medium, information recording / reproducing medium format device, and information recording / reproducing device | |
| JP2954135B2 (en) | Information recording / reproducing medium, information recording / reproducing medium format device, and information recording / reproducing device | |
| JP2954133B2 (en) | Information recording / reproducing medium, information recording / reproducing medium format device, and information recording / reproducing device | |
| JPH1064168A (en) | Data recorder | |
| JPH0773519A (en) | Magneto-optical recording medium and magneto-optical recording method using the same |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20040324 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20040324 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20050331 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20050405 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20050601 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20060110 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20060112 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20100120 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110120 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120120 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130120 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130120 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20140120 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| EXPY | Cancellation because of completion of term |