JP3749661B2 - Color image display apparatus and color image display method - Google Patents
Color image display apparatus and color image display method Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP3749661B2 JP3749661B2 JP2000344632A JP2000344632A JP3749661B2 JP 3749661 B2 JP3749661 B2 JP 3749661B2 JP 2000344632 A JP2000344632 A JP 2000344632A JP 2000344632 A JP2000344632 A JP 2000344632A JP 3749661 B2 JP3749661 B2 JP 3749661B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- color image
- image display
- color
- light source
- display device
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Liquid Crystal (AREA)
- Liquid Crystal Display Device Control (AREA)
- Control Of Indicators Other Than Cathode Ray Tubes (AREA)
- Devices For Indicating Variable Information By Combining Individual Elements (AREA)
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、複数の基本色を用いてカラー画像を再現するカラー画像表示装置に関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
近年、一例として図7に示すような構成のカラーシーケンシャル型ディスプレイが用いられている。このディスプレイは、3原色を順次発光する光源11と、前記光源の発光に同期して画像を透過率変化として表示するライトバルブ12と、から構成されている。光源11は、散乱板などにより面全体に輝度を均一化され、面発光光源として使用される。
【0003】
タイムシーケンスを図8に示す。1枚のカラー画像全体を表示する1フレーム21の間に、3原色(R:赤、G:緑、B:青)の光源を順次発光22させ、それに同期して対応する色の画像をライトバルブに表示23するサブフレーム24を設けている。サブフレーム内では、第一にライトバルブ各画素へのデータの電気的な書き込み23が行われる。第二に各画素にデータが書き込まれると、各画素の液晶が応答するが、応答には一定の時間を要する。通常ライトバルブの上部から順次書き込みがなされるため、上部から順に液晶応答を開始するが、ライトバルブ全体の液晶が応答を完了して、画像が透過率のパターンとしてライトバルブ上に準備されるのは、最下部の最後に書き込まれた画素が、書き込み終わり、その位置の液晶が応答を完了するタイミングである。従って第三にカラーシーケンシャルディスプレイでは、このタイミング22で、バックライトが発光し、画像を輝度パターンとして表示する。
【0004】
一例としてビデオ信号の場合は、1フレームは約16.7msecであるから、各サブフレーム24は、約5.6msecとなる。1フレーム時間を十分短くすることによって、人間の視覚では、各原色が弁別不可能になるので、色が重なり合って、カラー表示が達成される。
【0005】
この方式は、結果として1ドットが、1ピクセルのカラー画素に相当するため、液晶パネルにカラーフィルターを備える方式に比べて、3倍の高解像度を得られ、またカラーフィルターを用いないため、この吸収を省けることから、透過率を3倍に高め、結果として消費電力を1/3に削減できる特徴がある。
【0006】
なお、以下では、サブフレーム間に光源が発する色を基本色と呼ぶことにする。
【0007】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
しかし、従来のカラーシーケンシャル型ディスプレイには、下記の課題がある。
【0008】
(1)カラーブレイクの発生
図9に示すように、移動物体表示時に視線がこれを追跡すると、輪郭31に色づきが見えるカラーブレイク現象があり、カラーシーケンシャル方式では、原理的に発生する。フレーム周波数を上げれば、軽減されるが、表示デバイスに高速応答性が要求され、代わりに下記(2)の課題が発生する。
【0009】
(2)液晶パネル高速駆動性能および液晶高速応答性能の不足
カラーフィルター方式に比べ3倍の液晶パネル高速駆動と、液晶の応答性が必要である。これが、不足した場合、コントラスト低下等の不具合を生じる。
【0010】
(3)フィールドシーケンシャル信号に変換するためのメモリー追加のコストアップ
フィールドシーケンシャル方式では、図10に示す駆動回路が必要である。42はRGB同期分離回路、43から45はそれぞれメモリを含むR,G,B用走査速度変換回路、47は光源11を順次発光させるバックライト駆動回路である。
【0011】
図10に示されるように、入力された映像信号41をRGBの3原色の画像信号に分離42し、これを順次、3倍速で液晶パネルに表示するために、走査速度変換回路43,44,45を設け、この回路中に一時情報を蓄積するメモリーを必要とする。上記、従来例では、メモリーは、3原色分3画面分が必要になる。
【0012】
本発明は、上記従来のカラーシーケンシャル方式の課題を解決し、実現容易なカラーシーケンシャル型ディスプレイ装置を提供するものである。
【0013】
【課題を解決するための手段】
第1の発明は、基本色を発光する光源と、前記光源の発光に同期して、画素毎に透過率を制御するライドバルブと、を備えたカラー画像表示装置において、前記光源は、少なくとも1つの基本色を、その他の基本色と異なるタイミングで発光し、且つ、前記その他の基本色のうち複数の基本色を同時に発光し、前記ライドバルブは、前記光源が同時に発光する複数の基本色のそれぞれを透過する複数種類の画素を有することを特徴とする。
第2の発明は、前記基本色が、赤、緑、青の3原色であり、前記光源が、赤と青とを、緑とは異なるタイミングで同時に発光し、前記ライトバルブが、赤と緑を透過する画素と、青と緑を透過する画素とを有することを特徴とする。
第3の発明は、前記光源が、発光ダイオード(LED)からなることを特徴とする。
【0014】
第4の発明は、基本色を発光する光源と、前記光源の発光に同期して、画素毎に透過率を制御するライトバルブと、を備えたカラー画像表示装置において、1枚のカラー画像全体を表示する1フレームは、第一及び第二のサブフレームからなり、前記光源は、第一のサブフレームで少なくとも1つの基本色を発光し、第二のサブフレームでその他の複数の基本色を同時に発光し、前記ライドバルブは、前記光源が同時に発光する複数の基本色のそれぞれを透過する複数種類の画素を有することを特徴とする。
第5の発明は、前記1フレームの間に、前記第一のサブフレームと前記第二のサブフレームとを複数回繰り返すことを特徴とする。
【0015】
第6の発明は、複数の基本色を用いて画像表示を行なうカラー画像表示方法であって、1枚のカラー画像全体を表示する1フレームを、第一及び第二のサブフレームに分割し、第1のサブフレームにおいて、少なくとも1つの基本色を表示するとともに、第2のサブフレームにおいて、前記第1のサブフレームで表示される少なくとも1つの基本色を除く、その他の複数の基本色を同時に表示することを特徴とする。
【0016】
【発明の実施の形態】
以下図面に従って本発明の実施例を詳細にあの説明する。
【0017】
図1は本発明におけるカラー画像表示装置の構成例を示す図である。
【0018】
本実施例は、バックライト(光源)51と、ライトバルブとしての液晶パネル52と、カラーシーケンシャル駆動回路53からなっている。さらにバックライト51は、赤、緑、青の3原色を発光する3種のLED(発光ダイオード)54を、必要な輝度を発するのに十分な個数配置している。LEDの上には、光線の色ムラを防止するための散乱板55が配置されている。この構成によって、LEDバックライトは、駆動回路からの信号に従って、必要な原色を発光し、散乱板55で均一な輝度となって、上部に配置された液晶パネル52を照明56する働きをする。
【0019】
LEDは、応答速度が1μsec程度と高速駆動が可能なため、カラーシーケンシャル方式で求められる1msec程度のパルス発光に最適である。さらに、そのスペトル巾が狭いことから、本発明に用いる2色透過性のフィルター設計が容易になるメリットがある。
【0020】
次に液晶パネル52は、本実施例では通常のTN(ツイストネマティック)モードTFT(薄膜トランジスタ)液晶パネルを用いた。その構成は、偏光板と画素駆動回路を備えたTFTガラス基板と対向ガラス基板と、TNモード液晶と、カラーフィルターである。
【0021】
しかし、本発明の適用範囲は、上記に限定されない。画素毎に光の透過率を制御するライトバルブすべてに対して、下記の方法が適用できる。
【0022】
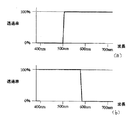
本発明の第一の特徴は、カラーフィルター61,62にある。カラーフィルターは、図2に示すように2画素を1組として配置され、それぞれの分光透過特性は、図3のようになっている。第一のフィルター61は、図3(a)の分光透過特性を示すように赤と緑を透過し、第二のフィルター62は、図3(b)の分光特性を示すように緑と青を透過する。2次元的な配置方法は、各フィルター61,62を一列交代に並べる図4(a)、あるいは一フィルター毎交互に並べる図4(b)のいずれでも可能であり使用目的によって選択できる。
【0023】
本発明の第二の特徴は、バックライトの発光方法と、液晶パネルへの画像表示方法にある。図5にタイミングチャートを示す。
【0024】
画像全体を構成する1フレーム91は、2種のサブフレーム92,93からなる。第一のサブフレーム92では、まず液晶パネル52に、あらかじめ入力信号からカラーシーケンシャル駆動回路53内で、分離された緑の信号が供給され、緑の画像が表示94される。タイミングチャートで書き込みとバックライト発光の間にインターバル95があるのは、液晶応答時間を確保するためであり、使用する液晶によって変更できる。このようにして液晶パネル52上に緑画像に対応する透過率パターンが準備された状態で、第一サブフレームの最後に緑のLED510のみが発光96する。すると液晶パネルのカラーフィルターは、上記2種類のカラーフィルター61,62のいずれも緑を透過するので、緑画像が表示される。
【0025】
次に第二のサブフレーム93においては、カラーシーケンシャル駆動回路53で分離された赤と青の2種の映像信号が供給され、赤と緑を透過するフィルター61を備えた画素には赤の信号が書き込まれ、緑と青を透過するフィルター62を備えた画素には青の信号が書き込まれるように液晶パネル内の回路が構成されている。その結果、液晶応答時間98後には、液晶パネル52上に赤と青の画像に対応する透過率パターンが準備されることになる。そこで、第二のサブフレーム93の最後に赤と青のLED511,512を同時に点灯すると、画素の対応するフィルターを透過して正しく赤と青の画像が同時に表示されることになる。
【0026】
もちろん、赤と青の画像の解像度は、緑の半分となるが、人間の視感度は緑が最も高く、解像度も主に緑が決定するので、赤と青の表示解像度低下は全体の解像度への影響が少ない。
【0027】
また、上記サブフレーム92,93の構成は、上記実施例の構成に限定されない。第一と第二のサブフレーム92,93の順序を交換することも可能であるし、またサブフレーム92,93を複数回繰り返して、カラーブレイクを防ぐこともできる。
【0028】
次に、本実施例のカラーシーケンシャル駆動回路53の回路構成例を図6に示す。71はRGB同期分離回路、72はメモリを含むG用走査速度変換回路、73はR及びB用走査速度変換回路、74はタイミング制御回路、75はバックライト駆動回路である。従来と異なっているのは、上記説明のように、本実施例では、2種のサブフィールドで構成されているので、メモリは2画面分に削減されている点である。
【0029】
最後に、表により、本方式と、従来のカラーシーケンシャル方式とカラーフィルター方式の性能を比較する。
【0030】
【表1】
【0031】
表1から明らかなように、本実施例では、解像度、輝度を決める最も重要な緑は、従来のシーケンシャル方式同様、カラーフィルター方式に比べて3倍としたまま、カラーブレイク、サブフレーム周波数、メモリー使用量は、それぞれ1/2,2/3,2/3に低減している。以上の結果から、本方式を用いれば、カラーシーケンシャル方式の利点をほとんど維持したまま、カラーブレイク、サブフレーム周波数、メモリー使用量といった課題を解決して、実現容易なカラーシーケンシャル型ディスプレイ装置を提供できる。
【0032】
【発明の効果】
本発明によれば、従来のカラーシーケンシャル型ディスプレイ方式に比べ、サブフレーム、カラーブレイク、使用メモリのそれぞれを低減することが可能となり、デメリットの少ないカラー画像表示を実現できる。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】本発明の一構成例を示す図である。
【図2】カラーフィルターの構成例を説明する図である。
【図3】カラーフィルターの分光特性を説明する図である。
【図4】カラーフィルターの配置例を説明する図である。
【図5】表示方法を説明するタイミングチャートである。
【図6】駆動回路の構成例を説明するブロック図である。
【図7】従来の構成例を示す図である。
【図8】従来の表示方法を説明するタイミングチャートである。
【図9】従来技術のカラーブレイクを説明する図である。
【図10】従来の駆動回路の構成例を説明するブロック図である。
【符号の説明】
51 バックライト
52 液晶パネル
510 赤色LED
511 緑色LED
512 青色LED
53 カラーシーケンシャル駆動回路
61 第1のカラーフィルター
62 第2のカラーフィルター[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a color image display device that reproduces a color image using a plurality of basic colors.
[0002]
[Prior art]
In recent years, a color sequential display having a configuration as shown in FIG. 7 is used as an example. This display includes a
[0003]
A time sequence is shown in FIG. During one
[0004]
As an example, in the case of a video signal, since one frame is about 16.7 msec, each
[0005]
As a result, one dot corresponds to one pixel of color pixel. As a result, three times higher resolution can be obtained compared to a method with a color filter on the liquid crystal panel, and no color filter is used. Since the absorption can be omitted, the transmittance can be increased by a factor of 3, and as a result, the power consumption can be reduced to 1/3.
[0006]
Hereinafter, a color emitted from a light source between subframes is referred to as a basic color.
[0007]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
However, the conventional color sequential display has the following problems.
[0008]
(1) Occurrence of color break As shown in FIG. 9, when a line of sight tracks this when a moving object is displayed, there is a color break phenomenon in which a color appears on the
[0009]
(2) Insufficient liquid crystal panel high-speed drive performance and liquid crystal high-speed response performance The liquid crystal panel high-speed drive and liquid crystal responsiveness three times that of the color filter system are required. If this is insufficient, problems such as a decrease in contrast occur.
[0010]
(3) Increase in cost of adding a memory for conversion to a field sequential signal In the field sequential method, the drive circuit shown in FIG. 10 is required. 42 is an RGB synchronous separation circuit, 43 to 45 are R, G, and B scanning speed conversion circuits each including a memory, and 47 is a backlight driving circuit for sequentially causing the
[0011]
As shown in FIG. 10, the input video signal 41 is separated into RGB three primary
[0012]
The present invention solves the problems of the conventional color sequential method and provides a color sequential display device that is easy to implement.
[0013]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
The first invention is provided with a light source for emitting light of primary colors, in synchronization with light emission of the light source, the color image display device and a ride valve for controlling the transmittance for each pixel, the light source, at least One basic color is emitted at a timing different from that of the other basic colors, and a plurality of basic colors among the other basic colors are simultaneously emitted, and the ride bulb has a plurality of basic colors that the light source emits simultaneously. Rukoto to have a plurality of types of pixels passing through the respective you characterized.
In a second aspect of the invention, the basic colors are three primary colors of red, green, and blue, the light source emits red and blue simultaneously at a timing different from green, and the light valve is red and green. And a pixel that transmits blue and green.
A third invention is characterized in that the light source is a light emitting diode (LED).
[0014]
According to a fourth aspect of the present invention, there is provided a color image display device comprising: a light source that emits a basic color; and a light valve that controls transmittance for each pixel in synchronization with the light emission of the light source. 1 frame comprising a first subframe and a second subframe, the light source emits at least one basic color in the first subframe, and a plurality of other basic colors in the second subframe. At the same time light emission, and the ride valve, characterized in that have a plurality of types of pixels transmitted through each of the plurality of basic colors the light source emits light at the same time.
The fifth invention is characterized in that the first subframe and the second subframe are repeated a plurality of times during the one frame.
[0015]
A sixth invention is a color image display method for displaying an image using a plurality of basic colors, wherein one frame displaying the entire color image is divided into first and second sub-frames, In the first subframe, at least one basic color is displayed, and in the second subframe , a plurality of other basic colors other than at least one basic color displayed in the first subframe are simultaneously displayed. It is characterized by displaying.
[0016]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
Embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below with reference to the drawings.
[0017]
FIG. 1 is a diagram showing a configuration example of a color image display apparatus according to the present invention.
[0018]
This embodiment includes a backlight (light source) 51, a
[0019]
Since the LED can be driven at a high speed with a response speed of about 1 μsec, it is optimal for pulsed emission of about 1 msec required by the color sequential method. Further, since the spectrum width is narrow, there is an advantage that the two-color transmissive filter used in the present invention can be easily designed.
[0020]
Next, in this embodiment, the
[0021]
However, the application range of the present invention is not limited to the above. The following method can be applied to all the light valves that control the light transmittance for each pixel.
[0022]
The first feature of the present invention resides in the
[0023]
The second feature of the present invention resides in a backlight emission method and an image display method on a liquid crystal panel. FIG. 5 shows a timing chart.
[0024]
One
[0025]
Next, in the
[0026]
Of course, the resolution of red and blue images is half that of green, but human visibility is the highest in green, and the resolution is mainly determined by green, so the reduction in red and blue display resolution is reduced to the overall resolution. Is less affected.
[0027]
The configuration of the
[0028]
Next, FIG. 6 shows a circuit configuration example of the color
[0029]
Finally, the table compares the performance of this method with the conventional color sequential method and color filter method.
[0030]
[Table 1]
[0031]
As is apparent from Table 1, in this embodiment, the most important green for determining the resolution and luminance is the color break, the subframe frequency, the memory while maintaining the triple of the color filter method as in the conventional sequential method. The amount used is reduced to 1/2, 2/3, and 2/3, respectively. From the above results, if this method is used, it is possible to solve the problems such as color break, subframe frequency, and memory usage while maintaining most of the advantages of the color sequential method, and to provide an easy-to-implement color sequential display device. .
[0032]
【The invention's effect】
According to the present invention, compared with the conventional color sequential display method, subframes, color BREAK, it is possible to reduce the respective use memory can be realized disadvantage less color image display.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a diagram illustrating a configuration example of the present invention.
FIG. 2 is a diagram illustrating a configuration example of a color filter.
FIG. 3 is a diagram illustrating spectral characteristics of a color filter.
FIG. 4 is a diagram illustrating an example of arrangement of color filters.
FIG. 5 is a timing chart illustrating a display method.
FIG. 6 is a block diagram illustrating a configuration example of a drive circuit.
FIG. 7 is a diagram illustrating a conventional configuration example.
FIG. 8 is a timing chart illustrating a conventional display method.
FIG. 9 is a diagram for explaining a color break in the prior art.
FIG. 10 is a block diagram illustrating a configuration example of a conventional drive circuit.
[Explanation of symbols]
51
511 Green LED
512 Blue LED
53 Color
Claims (6)
前記光源の発光に同期して、画素毎に透過率を制御するライドバルブと、を備えたカラー画像表示装置において、
前記光源は、少なくとも1つの基本色を、その他の基本色と異なるタイミングで発光し、且つ、前記その他の基本色のうち複数の基本色を同時に発光し、
前記ライドバルブは、前記光源が同時に発光する複数の基本色のそれぞれを透過する複数種類の画素を有することを特徴とするカラー画像表示装置。A light source that emits basic colors;
In a color image display device comprising a ride valve that controls transmittance for each pixel in synchronization with light emission of the light source,
The light source emits at least one basic color at a timing different from the other basic colors, and simultaneously emits a plurality of basic colors among the other basic colors,
The color image display device, wherein the ride valve has a plurality of types of pixels that transmit each of a plurality of basic colors emitted simultaneously by the light source.
前記基本色は、赤、緑、青の3原色であり、
前記光源は、赤と青とを、緑とは異なるタイミングで同時に発光し、
前記ライトバルブは、赤と緑を透過する画素と、青と緑を透過する画素とを有することを特徴とするカラー画像表示装置。The color image display device according to claim 1,
The basic colors are three primary colors of red, green and blue,
The light source emits red and blue simultaneously at a timing different from green,
The light valve has a pixel that transmits red and green and a pixel that transmits blue and green.
前記光源は、発光ダイオード(LED)からなることを特徴とするカラー画像表示装置。In the color image display device according to claim 1 or 2,
A color image display device, wherein the light source comprises a light emitting diode (LED).
前記光源の発光に同期して、画素毎に透過率を制御するライトバルブと、を備えたカラー画像表示装置において、
1枚のカラー画像全体を表示する1フレームは、第一及び第二のサブフレームからなり、
前記光源は、第一のサブフレームで少なくとも1つの基本色を発光し、第二のサブフレームでその他の複数の基本色を同時に発光し、
前記ライドバルブは、前記光源が同時に発光する複数の基本色のそれぞれを透過する複数種類の画素を有することを特徴とするカラー画像表示装置。A light source that emits basic colors;
In a color image display device provided with a light valve that controls transmittance for each pixel in synchronization with light emission of the light source,
One frame displaying the entire color image is composed of first and second sub-frames,
The light source emits at least one basic color in a first subframe, and simultaneously emits a plurality of other basic colors in a second subframe ,
The ride valve, a color image display device which is characterized in that have a plurality of types of pixels transmitted through each of the plurality of basic colors the light source emits light at the same time.
前記1フレームの間に、前記第一のサブフレームと前記第二のサブフレームとを複数回繰り返すことを特徴とするカラー画像表示装置。In the color image display device according to claim 4,
The color image display device, wherein the first subframe and the second subframe are repeated a plurality of times during the one frame.
1枚のカラー画像全体を表示する1フレームを、第一及び第二のサブフレームに分割し、
第1のサブフレームにおいて、少なくとも1つの基本色を表示するとともに、
第2のサブフレームにおいて、前記第1のサブフレームで表示される少なくとも1つの基本色を除く、その他の複数の基本色を同時に表示することを特徴とするカラー画像表示方法。A color image display method for displaying an image using a plurality of basic colors,
One frame displaying the entire color image is divided into first and second sub-frames;
Displaying at least one basic color in the first sub-frame;
In the second subframe , a plurality of other basic colors other than at least one basic color displayed in the first subframe are simultaneously displayed.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000344632A JP3749661B2 (en) | 2000-11-13 | 2000-11-13 | Color image display apparatus and color image display method |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000344632A JP3749661B2 (en) | 2000-11-13 | 2000-11-13 | Color image display apparatus and color image display method |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2002149129A JP2002149129A (en) | 2002-05-24 |
| JP2002149129A5 JP2002149129A5 (en) | 2005-01-27 |
| JP3749661B2 true JP3749661B2 (en) | 2006-03-01 |
Family
ID=18818800
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000344632A Expired - Fee Related JP3749661B2 (en) | 2000-11-13 | 2000-11-13 | Color image display apparatus and color image display method |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP3749661B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (17)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4611604B2 (en) * | 2002-09-30 | 2011-01-12 | 独立行政法人情報通信研究機構 | Image display device |
| KR100560445B1 (en) | 2004-03-15 | 2006-03-13 | 삼성에스디아이 주식회사 | Light emitting display device and driving method thereof |
| KR100560446B1 (en) | 2004-03-15 | 2006-03-13 | 삼성에스디아이 주식회사 | Light emitting display device and driving method thereof |
| JP2006301043A (en) * | 2005-04-18 | 2006-11-02 | Agilent Technol Inc | Display device |
| KR100662998B1 (en) | 2005-11-04 | 2006-12-28 | 삼성에스디아이 주식회사 | Organic electroluminescent display and its driving method |
| CN101317210B (en) * | 2006-02-27 | 2011-09-21 | 夏普株式会社 | Display |
| JP2008020611A (en) * | 2006-07-12 | 2008-01-31 | M & S Fine Tec Kk | Liquid crystal display device and method for reducing afterimage in same |
| US7952544B2 (en) * | 2007-02-15 | 2011-05-31 | Cree, Inc. | Partially filterless liquid crystal display devices and methods of operating the same |
| US8836624B2 (en) | 2007-02-15 | 2014-09-16 | Cree, Inc. | Partially filterless and two-color subpixel liquid crystal display devices, mobile electronic devices including the same, and methods of operating the same |
| WO2008129722A1 (en) * | 2007-03-30 | 2008-10-30 | Sharp Kabushiki Kaisha | Display unit and electric apparatus |
| JP2009128455A (en) * | 2007-11-20 | 2009-06-11 | National Central Univ | How to expand the color display color reproduction range |
| CN100580762C (en) * | 2007-12-06 | 2010-01-13 | 友达光电股份有限公司 | Driving method of color-sequence liquid crystal display backlight source |
| JP4720865B2 (en) * | 2008-07-25 | 2011-07-13 | ソニー株式会社 | Display device, display method, and electronic apparatus |
| JP5674757B2 (en) * | 2009-03-17 | 2015-02-25 | コーニンクレッカ フィリップス エヌ ヴェ | How to drive a color sequential display |
| WO2010143330A1 (en) * | 2009-06-10 | 2010-12-16 | シャープ株式会社 | Driving device, driving method, image display device, television receiver, display monitor device, program and record medium |
| WO2012111471A1 (en) * | 2011-02-14 | 2012-08-23 | シャープ株式会社 | Display device |
| WO2013150913A1 (en) * | 2012-04-02 | 2013-10-10 | シャープ株式会社 | Image display device and method for displaying image |
-
2000
- 2000-11-13 JP JP2000344632A patent/JP3749661B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2002149129A (en) | 2002-05-24 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP3749661B2 (en) | Color image display apparatus and color image display method | |
| US7629988B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for driving liquid crystal display | |
| US8581887B2 (en) | Color-sequential display method | |
| US20100079366A1 (en) | Method of driving a backlight module and a display | |
| TWI524321B (en) | Color display device and method | |
| US20090058794A1 (en) | Liquid crystal display device with improved display luminance | |
| US20090059581A1 (en) | Display Device | |
| JP2008083204A (en) | Liquid crystal display device and driving method thereof | |
| JP2002244626A (en) | Color sequential type display device | |
| JP2002149129A5 (en) | ||
| JP2001318363A (en) | Driving method for liquid crystal device and liquid crystal device driven by the same driving method | |
| KR101251377B1 (en) | FSC LCD and driving method thereof | |
| JP2002221702A (en) | Field sequential liquid crystal display device | |
| CN101887183A (en) | Liquid crystal display device | |
| JPH10186310A (en) | Method for driving display device | |
| CN100405453C (en) | Electro-optical device, driving method thereof, and electronic device | |
| JP5349773B2 (en) | Liquid crystal display | |
| US20100039359A1 (en) | Adjustment circuit for color sequential liquid crystal display and adjustment method thereof | |
| KR100950517B1 (en) | LCD panel and driving method thereof | |
| JP2003295833A (en) | Image display device and driving method thereof | |
| US20160049122A1 (en) | Display apparatus and method of driving the same | |
| CN100445813C (en) | Liquid crystal display element and driving method thereof | |
| CN101169927A (en) | Driving method of color-sequence liquid crystal display backlight source | |
| JP3627831B2 (en) | Liquid crystal display | |
| JPH01179914A (en) | Liquid crystal color display device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20040224 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20040224 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20050921 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20051004 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20051024 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20051122 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20051202 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| RD05 | Notification of revocation of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7425 Effective date: 20051213 |
|
| A072 | Dismissal of procedure |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A072 Effective date: 20060207 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20091209 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20091209 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20101209 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20101209 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20111209 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20111209 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20121209 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20121209 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |