JP2016204635A - Polyurethane integral skin foam and manufacturing method therefor - Google Patents
Polyurethane integral skin foam and manufacturing method therefor Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2016204635A JP2016204635A JP2016058313A JP2016058313A JP2016204635A JP 2016204635 A JP2016204635 A JP 2016204635A JP 2016058313 A JP2016058313 A JP 2016058313A JP 2016058313 A JP2016058313 A JP 2016058313A JP 2016204635 A JP2016204635 A JP 2016204635A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- integral skin
- organic polyisocyanate
- skin foam
- polyurethane integral
- polyisocyanate composition
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08G—MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS OBTAINED OTHERWISE THAN BY REACTIONS ONLY INVOLVING UNSATURATED CARBON-TO-CARBON BONDS
- C08G18/00—Polymeric products of isocyanates or isothiocyanates
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08G—MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS OBTAINED OTHERWISE THAN BY REACTIONS ONLY INVOLVING UNSATURATED CARBON-TO-CARBON BONDS
- C08G18/00—Polymeric products of isocyanates or isothiocyanates
- C08G18/06—Polymeric products of isocyanates or isothiocyanates with compounds having active hydrogen
- C08G18/08—Processes
- C08G18/10—Prepolymer processes involving reaction of isocyanates or isothiocyanates with compounds having active hydrogen in a first reaction step
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Polymers & Plastics (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Polyurethanes Or Polyureas (AREA)
Abstract
【課題】 高反発弾性率を幅広い温度帯域で有し、機械的強度や生産性に優れるポリウレタンインテグラルスキンフォーム、及び当該ポリウレタンインテグラルスキンフォームの製造方法を提供する。【解決手段】 ポリウレタンインテグラルスキンフォームが、少なくとも有機ポリイソシアネート組成物(A)、ポリオール成分(B)、触媒(C)、及び発泡剤(D)を原料とするポリウレタンインテグラルスキンフォームにおいて、有機ポリイソシアネート組成物(A)が、ジフェニルメタンジイソシアネートを数平均分子量1,000〜3,500のポリテトラメチレンエーテルグリコールにてウレタン変性したイソシアネート基含有率7〜25質量%の有機ポリイソシアネート(a1)であることを特徴とする。【選択図】 なしPROBLEM TO BE SOLVED: To provide a polyurethane integral skin foam having a high rebound resilience in a wide temperature range and excellent in mechanical strength and productivity, and a method for producing the polyurethane integral skin foam. SOLUTION: The polyurethane integral skin foam is organic in a polyurethane integral skin foam using at least an organic polyisocyanate composition (A), a polyol component (B), a catalyst (C), and a foaming agent (D) as raw materials. The polyisocyanate composition (A) is an organic polyisocyanate (a1) having an isocyanate group content of 7 to 25% by mass obtained by urethane-modifying diphenylmethane diisocyanate with polytetramethylene ether glycol having a number average molecular weight of 1,000 to 3,500. It is characterized by being. [Selection figure] None
Description
本発明は,ポリウレタンインテグラルスキンフォーム(以下、「ISF」と称する場合がある。)及び当該ISFの製造方法に関するものである。さらに詳しくは,幅広い温度帯域において高い反発弾性を有しつつ、生産性や成形物としての機械的強度に優れたISFの製造方法に関するものである。 The present invention relates to a polyurethane integral skin foam (hereinafter sometimes referred to as “ISF”) and a method for producing the ISF. More specifically, the present invention relates to a method for producing an ISF having high resilience in a wide temperature range and excellent in productivity and mechanical strength as a molded product.
ISFは、その生産性の良さ、機械的強度、感触の良さ等から、靴底用素材やステアリングホイールをはじめとする自動車の内装部品として広く使用されているが、高性能な靴底等に好適な高い反発弾性率を常用の温度帯で有しつつ、良好な機械的強度を有するISFの技術はこれまで知られていなかった。 ISF is widely used as an interior part for automobiles, including materials for shoe soles and steering wheels, because of its good productivity, mechanical strength, and good touch, but it is suitable for high-performance shoe soles. Until now, no ISF technology has been known which has a high rebound resilience in a normal temperature range and good mechanical strength.
特許文献1には、ジフェニルメタンジイソシアネート(以下、「MDI」と称する場合がある。)を使用した比較的高い密度を有する高弾性軟質ポリウレタンフォームが提案されている。 Patent Document 1 proposes a highly elastic flexible polyurethane foam having a relatively high density using diphenylmethane diisocyanate (hereinafter sometimes referred to as “MDI”).
しかしながら、当該ポリウレタンフォームは架橋剤を使用し、化学的架橋量を増やすことで高い弾性率を実現しているものであり、靴底用樹脂等として十分な伸び率や引き裂き強度等の機械的強度を実現することができない。 However, the polyurethane foam uses a cross-linking agent and realizes a high elastic modulus by increasing the amount of chemical cross-linking, and mechanical strength such as sufficient elongation and tear strength as a resin for shoe soles, etc. Cannot be realized.
また、特許文献2には、靴底部材としての低密度ポリウレタン成形物を与える方法が記載されているが複雑な工程であり、さらに開示されている弾性率では十分なものではなかった。 Further, Patent Document 2 describes a method for providing a low-density polyurethane molded product as a shoe sole member, but it is a complicated process, and the disclosed elastic modulus is not sufficient.
本発明の目的は、高反発弾性率を幅広い温度帯域で有し、機械的強度や生産性に優れるISFの提供及びISFの製造方法を提供することである。 An object of the present invention is to provide an ISF having a high rebound resilience in a wide temperature range and excellent in mechanical strength and productivity and a method for producing the ISF.
本発明者等は、これらの問題点を解決することを目的として鋭意検討研究を重ねた結果、有機ポリイソシアネート組成物として特定分子量範囲のポリテトラメチレンエーテルグリコール(以下、「PTMEG」と称する場合がある。)でウレタン変性した特定のイソシアネート基含有率を有する有機ポリイソシアネート組成物を使用することにより本発明を完成するに至った。 As a result of intensive studies and studies aimed at solving these problems, the present inventors have found that polytetramethylene ether glycol (hereinafter referred to as “PTMEG”) having a specific molecular weight range as an organic polyisocyanate composition. The present invention has been completed by using an organic polyisocyanate composition having a specific isocyanate group content modified with urethane.
すなわち本発明は,以下の(1)〜(12)の実施形態を含む。 That is, the present invention includes the following embodiments (1) to (12).
(1)少なくとも有機ポリイソシアネート組成物(A)、ポリオール成分(B)、触媒(C)、発泡剤(D)を原料とするポリウレタンインテグラルスキンフォームであって、有機ポリイソシアネート組成物(A)が、ジフェニルメタンジイソシアネートと数平均分子量1,000〜3,500のポリテトラメチレンエーテルグリコールとのウレタン変性体であり、イソシアネート基含有率7〜25質量%の有機ポリイソシアネート(a1)であることを特徴とするポリウレタンインテグラルスキンフォーム。 (1) A polyurethane integral skin foam using at least an organic polyisocyanate composition (A), a polyol component (B), a catalyst (C) and a foaming agent (D) as raw materials, the organic polyisocyanate composition (A) Is a urethane-modified product of diphenylmethane diisocyanate and polytetramethylene ether glycol having a number average molecular weight of 1,000 to 3,500, and is an organic polyisocyanate (a1) having an isocyanate group content of 7 to 25% by mass. Polyurethane integral skin foam.
(2)有機ポリイソシアネート組成物(A)が、常温において液状であるジフェニルメタンジイソシアネートと数平均分子量1,000〜3,500のポリテトラメチレンエーテルグリコールとのウレタン変性体であり、イソシアネート基含有率7〜25質量%の有機ポリイソシアネート(a2)であることを特徴とする上記(1)に記載のポリウレタンインテグラルスキンフォーム。 (2) The organic polyisocyanate composition (A) is a urethane-modified product of diphenylmethane diisocyanate which is liquid at room temperature and polytetramethylene ether glycol having a number average molecular weight of 1,000 to 3,500, and has an isocyanate group content of 7 The polyurethane integral skin foam according to (1) above, which is ˜25% by mass of organic polyisocyanate (a2).
(3)有機ポリイソシアネート組成物(A)中に粘度低減剤(F)を含むことを特徴とする上記(1)又は(2)に記載のポリウレタンインテグラルスキンフォーム。 (3) The polyurethane integral skin foam as described in (1) or (2) above, wherein the organic polyisocyanate composition (A) contains a viscosity reducing agent (F).
(4)ポリオール成分(B)が、数平均分子量600〜3,500のポリテトラメチレンエーテルグリコール(b1)を含み、ポリオール成分(B)中の(b1)の比率が50質量%以上であることを特徴とする、上記(1)乃至(3)のいずれかに記載のポリウレタンインテグラルスキンフォーム。 (4) The polyol component (B) contains polytetramethylene ether glycol (b1) having a number average molecular weight of 600 to 3,500, and the ratio of (b1) in the polyol component (B) is 50% by mass or more. The polyurethane integral skin foam according to any one of (1) to (3) above,
(5)ポリオール成分(B)が、(b1)以外のポリエーテルポリオール(b2)を含み、(b2)が、平均官能基数2〜4の重合開始剤と、プロピレンオキサイド及びエチレンオキサイドからなる群より選ばれる少なくとも1種の重合生成物であり、水酸基当量1,000〜3,000のポリエーテルポリオールであることを特徴とする上記(1)乃至(4)のいずれかに記載のポリウレタンインテグラルスキンフォーム。 (5) The polyol component (B) contains a polyether polyol (b2) other than (b1), and (b2) is a group consisting of a polymerization initiator having an average functional group number of 2 to 4, propylene oxide and ethylene oxide. The polyurethane integral skin according to any one of (1) to (4) above, wherein the polyurethane integral skin is a polyether polyol having a hydroxyl group equivalent of 1,000 to 3,000, which is at least one selected polymerization product. Form.
(6)フォーム密度が150〜500kg/m3であることを特徴とする上記(1)乃至(5)のいずれかに記載のポリウレタンインテグラルスキンフォーム。 (6) The polyurethane integral skin foam according to any one of (1) to (5) above, wherein the foam density is 150 to 500 kg / m 3.
(7)反発弾性率が60%以上であり、伸び率が200%以上であり、且つ引裂強さが30N/cm以上であることを特徴とする上記(1)乃至(6)のいずれかに記載のポリウレタンインテグラルスキンフォーム。 (7) Any one of (1) to (6) above, wherein the impact resilience is 60% or more, the elongation is 200% or more, and the tear strength is 30 N / cm or more. Polyurethane integral skin foam as described.
(8)有機ポリイソシアネート組成物(A)とポリオール成分(B)とを、触媒(C)、発泡剤(D)の存在下で反応させるポリウレタンインテグラルスキンフォームの製造方法であって、有機ポリイソシアネート組成物(A)が、ジフェニルメタンジイソシアネートを数平均分子量1,000〜3,500のポリテトラメチレンエーテルグリコールにてウレタン変性したイソシアネート基含有率7〜25質量%の有機ポリイソシアネート(a1)であることを特徴とするポリウレタンインテグラルスキンフォームの製造方法。 (8) A method for producing a polyurethane integral skin foam comprising reacting an organic polyisocyanate composition (A) with a polyol component (B) in the presence of a catalyst (C) and a foaming agent (D), The isocyanate composition (A) is an organic polyisocyanate (a1) having an isocyanate group content of 7 to 25% by mass obtained by urethane modification of diphenylmethane diisocyanate with polytetramethylene ether glycol having a number average molecular weight of 1,000 to 3,500. A process for producing a polyurethane integral skin foam, characterized in that
(9)有機ポリイソシアネート組成物(A)が、常温で液状であるジフェニルメタンジイソシアネートを数平均分子量1,000〜3,500のポリテトラメチレンエーテルグリコールにてウレタン変性したイソシアネート基含有率7〜25質量%の有機ポリイソシアネート(a2)であることを特徴とする上記(8)に記載のポリウレタンインテグラルスキンフォームの製造方法。 (9) Organic polyisocyanate composition (A) is a diphenylmethane diisocyanate that is liquid at room temperature and is urethane-modified with polytetramethylene ether glycol having a number average molecular weight of 1,000 to 3,500. % Of the organic polyisocyanate (a2), The method for producing a polyurethane integral skin foam as described in (8) above.
(10)有機ポリイソシアネート組成物(A)中に粘度低減剤(F)を含むことを特徴とする上記(8)又は(9)に記載のポリウレタンインテグラルスキンフォームの製造方法。 (10) The method for producing a polyurethane integral skin foam as described in (8) or (9) above, wherein the organic polyisocyanate composition (A) contains a viscosity reducing agent (F).
(11)ポリオール成分(B)が、数平均分子量600〜3,500のポリテトラメチレンエーテルグリコール(b1)を含み、ポリオール成分(B)中の(b1)の比率が50質量%以上であることを特徴とする、上記(8)乃至(10)のいずれかに記載のポリウレタンインテグラルスキンフォームの製造方法。 (11) The polyol component (B) contains polytetramethylene ether glycol (b1) having a number average molecular weight of 600 to 3,500, and the ratio of (b1) in the polyol component (B) is 50% by mass or more. The method for producing a polyurethane integral skin foam according to any one of the above (8) to (10), wherein:
(12)ポリオール成分(B)が、(b1)以外のポリエーテルポリオール(b2)を含み、(b2)が、平均官能基数2〜4の重合開始剤に、プロピレンオキサイド及びエチレンオキサイドからなる群より選ばれる少なくとも1種を重合した、水酸基当量1,000〜3,000のポリエーテルポリオールであることを特徴とする上記(8)乃至(11)のいずれかに記載のポリウレタンインテグラルスキンフォームの製造方法。 (12) The polyol component (B) includes a polyether polyol (b2) other than (b1), and (b2) is a polymerization initiator having an average functional group number of 2 to 4, from the group consisting of propylene oxide and ethylene oxide. The production of the polyurethane integral skin foam according to any one of the above (8) to (11), wherein the polyol is a polyether polyol having a hydroxyl equivalent of 1,000 to 3,000, which is obtained by polymerizing at least one selected from the above. Method.
本発明では、ISFにおいて機械的強度等の物性を低下させずに幅広い温度帯域で反発弾性率を顕著に向上させることができる。また、本発明により製造されたISFは靴底用樹脂等高い弾性性能が必要な素材に広く利用でき非常に有用である。さらに、ISF製造の際、一般的な発泡装置での高い生産安定性を実現することができる。 In the present invention, the rebound resilience can be remarkably improved in a wide temperature range without lowering physical properties such as mechanical strength in ISF. The ISF produced according to the present invention can be widely used for materials that require high elastic performance such as a resin for shoe soles, and is very useful. Furthermore, high production stability in a general foaming apparatus can be realized during ISF production.
本発明をさらに詳細に説明する。 The present invention will be described in further detail.
本発明のポリウレタンインテグラルスキンフォームは、少なくとも有機ポリイソシアネート組成物(A)、ポリオール成分(B)、触媒(C)、及び発泡剤(D)を原料とするポリウレタンインテグラルスキンフォームにおいて、有機ポリイソシアネート組成物(A)が、ジフェニルメタンジイソシアネートを数平均分子量1,000〜3,500のポリテトラメチレンエーテルグリコールにてウレタン変性したイソシアネート基含有率7〜25質量%の有機ポリイソシアネート(a1)であることをその特徴とする。 The polyurethane integral skin foam of the present invention is a polyurethane integral skin foam using at least an organic polyisocyanate composition (A), a polyol component (B), a catalyst (C), and a foaming agent (D) as raw materials. The isocyanate composition (A) is an organic polyisocyanate (a1) having an isocyanate group content of 7 to 25% by mass obtained by urethane modification of diphenylmethane diisocyanate with polytetramethylene ether glycol having a number average molecular weight of 1,000 to 3,500. It is characterized by that.
本発明で使用する有機ポリイソシアネート組成物(A)は、MDIをPTMEGにてウレタン変性した有機ポリイソシアネート(a1)又は、常温において液状であるMDI(以下、「液状MDI」と称する。)をPTMEGでウレタン変性した有機ポリイソシアネート(a2)である。ここで常温とは、JIS Z8703(試験場所の標準状態)に準じており、20℃±15℃を意味する。 The organic polyisocyanate composition (A) used in the present invention is an organic polyisocyanate (a1) obtained by urethane-modifying MDI with PTMEG or MDI that is liquid at room temperature (hereinafter referred to as “liquid MDI”). The organic polyisocyanate (a2) modified with urethane. Here, normal temperature is in accordance with JIS Z8703 (standard state of test place) and means 20 ° C. ± 15 ° C.
本発明で使用している有機ポリイソシアネート(a1)、(a2)のイソシアネート基含有率は、7〜25質量%であり、好ましくは10〜20質量%である。イソシアネート基含有率が下限を下回る場合,有機ポリイソシアネートの粘度が非常に高くなり、発泡装置への導入が困難になると共に、一般的な発泡装置のイソシアネートやポリオール類の混合能力では十分均一に混合されない問題がある。一方上限以上のイソシアネート基含有率では、イソシアネートとポリオール、発泡剤としての水との反応がランダムとなり、特にイソシアネートと水との反応によって生じるウレア結合繰り返し単位の巨大化が原因として推定される反発弾性率の顕著な低下が見られる。 The isocyanate group content of the organic polyisocyanate (a1) or (a2) used in the present invention is 7 to 25% by mass, preferably 10 to 20% by mass. When the isocyanate group content is below the lower limit, the viscosity of the organic polyisocyanate becomes very high, making it difficult to introduce into the foaming device, and mixing with the general foaming device with sufficient mixing ability of isocyanates and polyols. There is no problem. On the other hand, when the isocyanate group content exceeds the upper limit, the reaction between the isocyanate and the polyol and the water as the blowing agent becomes random, and in particular, the resilience estimated due to the enlargement of the urea bond repeating unit caused by the reaction between the isocyanate and water. There is a noticeable drop in rate.
本発明で使用している有機ポリイソシアネート(a1)及び(a2)のウレタン変性用ポリオールは、数平均分子量1,000〜3,500のPTMEGであり、好ましくは数平均分子量1,500〜3,500のPTMEGである。数平均分子量が下限を下回ると、PTMEG鎖がソフトセグメントとして十分機能しなくなるために反発弾性率目標値の達成が困難となる。一方で、上限値以上の分子量では靴底等の用途に好適なISFとしての硬さが得られなくなると共に、PTMEG鎖の結晶性が高まり、有機ポリイソシアネートの低温貯蔵安定性が悪化するという問題がある。 The polyol for urethane modification of the organic polyisocyanate (a1) and (a2) used in the present invention is PTMEG having a number average molecular weight of 1,000 to 3,500, and preferably a number average molecular weight of 1,500 to 3, 500 PTMEG. If the number average molecular weight is below the lower limit, the PTMEG chain will not function sufficiently as a soft segment, making it difficult to achieve the rebound elastic modulus target value. On the other hand, when the molecular weight is equal to or higher than the upper limit, hardness as an ISF suitable for uses such as shoe soles cannot be obtained, the crystallinity of the PTMEG chain is increased, and the low-temperature storage stability of the organic polyisocyanate is deteriorated. is there.
有機ポリイソシアネート(a1)及び(a2)のウレタン変性用PTMEGは、テトラヒドロフランのみを開環重合した数平均分子量1,000〜3,500、さらに好ましくは数平均分子量1,500〜3,500の2官能ポリオールであることが、反発弾性率、伸び率、引裂き強度を中心とした機械物性の面で好ましい。ただし、重合前モノマーとして10モル%までの範囲であれば他のエーテル単位を分子内に導入しても本技術の効果を大きく損なうことは無い。一般的にはPTMEGの常温液状化を目的とした1,3−プロパンジオール、3−メチル−1,5−ペンタンジオール、ネオペンチルグリコール等の導入が可能である。 The PTMEG for urethane modification of the organic polyisocyanates (a1) and (a2) is a number average molecular weight of 1,000 to 3,500 obtained by ring-opening polymerization of only tetrahydrofuran, more preferably a number average molecular weight of 1,500 to 3,500. A functional polyol is preferred from the standpoint of mechanical properties such as rebound resilience, elongation, and tear strength. However, as long as the pre-polymerization monomer is in the range of up to 10 mol%, even if other ether units are introduced into the molecule, the effect of the present technology is not greatly impaired. In general, 1,3-propanediol, 3-methyl-1,5-pentanediol, neopentyl glycol, etc. for the purpose of liquefying PTMEG at room temperature can be introduced.
有機ポリイソシアネート(a1)に用いるMDIは、4,4’−MDIを主成分とすることが好ましい。MDIには4,4’−MDI以外に異性体として2,2’−MDI、2,4’−MDIが存在するが、これら異性体のMDI中の含有率は、60質量%以下が好ましい。MDI異性体が大量に含まれる場合、ISF硬度の低下、反応性低下による生産性の悪化等が生じる恐れがある。 The MDI used for the organic polyisocyanate (a1) is preferably composed mainly of 4,4'-MDI. MDI includes 2,2'-MDI and 2,4'-MDI as isomers in addition to 4,4'-MDI. The content of these isomers in MDI is preferably 60% by mass or less. When a large amount of the MDI isomer is contained, there is a risk that productivity decreases due to a decrease in ISF hardness or a decrease in reactivity.
また、(a1)に用いるMDIは、類似構造体のポリフェニレンポリメチルポリイソシアネート(p−MDI)を含むことも可能であるが、イソシアネート官能基数増大によるISFの伸び率低下、p−MDI由来のISF着色等が生じるため、有機ポリイソシアネート(a1)に使用されるMDIに対し、p−MDIの含有率は10質量%以下とすることが好ましく、5質量%以下であることがさらに好ましい。 The MDI used in (a1) can also contain polyphenylene polymethyl polyisocyanate (p-MDI) having a similar structure. However, the increase in the number of isocyanate functional groups reduces the ISF elongation rate, and the p-MDI-derived ISF. Since coloring or the like occurs, the content of p-MDI is preferably 10% by mass or less, and more preferably 5% by mass or less with respect to MDI used in the organic polyisocyanate (a1).
有機ポリイソシアネート(a2)に用いられる液状MDIは、
(1)MDIを200℃以上で反応させる、
(2)MDIにトリメチルホスフェート、トリエチルホスフェート等を触媒として添加した上で170℃以上で反応させる、又は
(3)MDIに3−メチル−1−フェニル−2−ホスホレン1−オキシド等のホスホレン化合物を触媒として添加した上で、70℃以上で反応させ、所定の反応率で反応停止剤を添加する、
等の方法で得られるMDIの部分カルボジイミド及び部分ウレトンイミン変性物からなる群より選ばれる少なくとも1種を含有するものである。本発明に用いられる液状MDIは、ISFの着色を防止するという観点からホスホレン系触媒により低温で反応を進行させた液状MDIが望ましい。
The liquid MDI used for the organic polyisocyanate (a2) is:
(1) MDI is reacted at 200 ° C. or higher.
(2) Add trimethyl phosphate, triethyl phosphate or the like as a catalyst to MDI and react at 170 ° C. or higher, or (3) Add a phospholene compound such as 3-methyl-1-phenyl-2-phospholene 1-oxide to MDI. After adding as a catalyst, react at 70 ° C. or higher, and add a reaction terminator at a predetermined reaction rate.
It contains at least one selected from the group consisting of a partial carbodiimide and a partial uretonimine modified product of MDI obtained by the above method. The liquid MDI used in the present invention is preferably liquid MDI that has been reacted at a low temperature with a phospholene-based catalyst from the viewpoint of preventing the coloring of ISF.
また、上記反応が終了し、反応停止剤を添加した後、50℃以下の温度で24時間以上保管し、カルボジイミド結合の大部分をウレトンイミン結合へ変換した状態において、ゲルパーミエーションクロマトグラフィー等、ウレトンイミン結合を分解しない方法で測定される液状MDI中のカルボジイミド変性MDI及びウレトンイミン変性MDIの含有率の合計は、5〜40質量%が好ましく、さらに好ましくは10〜35質量%である。カルボジイミド変性MDI及びウレトンイミン変性MDI含有率の合計が前記範囲内であることにより好適なイソシアネート官能基数とすることが可能となり、使用に際しての粘度も適切にすることができる。さらにISFとした場合にも伸び率や強度を満足することができる。 In addition, after the above reaction is completed and a reaction terminator is added, it is stored at a temperature of 50 ° C. or lower for 24 hours or more, and in a state in which most of the carbodiimide bonds are converted to uretonimine bonds, uretonimine, etc. The total content of the carbodiimide-modified MDI and the uretonimine-modified MDI in the liquid MDI measured by a method that does not decompose the bond is preferably 5 to 40% by mass, and more preferably 10 to 35% by mass. When the total content of the carbodiimide-modified MDI and the uretonimine-modified MDI is within the above range, it is possible to obtain a suitable number of isocyanate functional groups, and the viscosity at the time of use can be made appropriate. Furthermore, when it is set to ISF, the elongation and strength can be satisfied.
有機ポリイソシアネート(a2)に用いられる液状MDIは、(a1)同様、カルボジイミド変性前又はウレトンイミン変性前のMDIとして、2,2’−MDI、2,4’−MDIの含有率合計は、60質量%以下が好ましい。これは(a1)と同様の理由による。 The liquid MDI used for the organic polyisocyanate (a2) is, as in (a1), the total content of 2,2′-MDI and 2,4′-MDI as MDI before carbodiimide modification or uretonimine modification is 60 mass. % Or less is preferable. This is for the same reason as in (a1).
さらに有機ポリイソシアネート(a2)に用いられる液状MDIは、カルボジイミド変性前又はウレトンイミン変性前のMDIに少量のp−MDIを含むことが可能である。 Furthermore, the liquid MDI used for the organic polyisocyanate (a2) can contain a small amount of p-MDI in the MDI before carbodiimide modification or uretonimine modification.
しかし、(a1)に比較し(a2)は高いイソシアネート平均官能基数を有しており、カルボジイミド変性前又はウレトンイミン変性前のMDIとして、最大5質量%、さらに好ましくは3質量%以下に留める必要がある。 However, compared with (a1), (a2) has a higher number of isocyanate average functional groups, and as MDI before carbodiimide modification or uretonimine modification, it is necessary to keep it at most 5% by mass, more preferably 3% by mass or less. is there.
本発明で使用するポリオール成分(B)としては、数平均分子量600〜3,500のPTMEGが好適に使用できる。さらに好ましくは1,000〜3,500である。また、ポリオール成分(B)中の(b1)含有量は50質量%以上が好ましい。さらに好ましくは60〜90質量%である。下限以下では、得られるISFの反発弾性率が十分高くならず、引裂き強度等の機械物性が低下する。また、上限以上では、常温における反発弾性率や機械物性は向上するが、PTMEGの結晶性から得られるISFの反発弾性率が0℃付近の低温域で大幅に低下する。 As the polyol component (B) used in the present invention, PTMEG having a number average molecular weight of 600 to 3,500 can be suitably used. More preferably, it is 1,000-3,500. Further, the content of (b1) in the polyol component (B) is preferably 50% by mass or more. More preferably, it is 60-90 mass%. Below the lower limit, the rebound resilience of the resulting ISF is not sufficiently high, and mechanical properties such as tear strength are reduced. Above the upper limit, the rebound resilience and mechanical properties at room temperature are improved, but the rebound resilience of ISF obtained from the crystallinity of PTMEG is greatly reduced in the low temperature range near 0 ° C.
本発明に使用する(b1)以外のポリオール成分(b2)としては、平均官能基数2〜4の重合開始剤に、プロピレンオキサイド及びエチレンオキサイドからなる群より選ばれる少なくとも1種を重合した、水酸基当量1,000〜3,000の一般的に軟質ポリウレタンフォーム製造に使用されるポリエーテルポリオールを用いることができる。具体的には、開始剤として、水、エチレングリコール、プロパンジオール、ジエチレングリコール、ジプロピレングリコール、ブタンジオール、ヘキサンジオール、ヒドロキノン、グリセリン、トリメチロールプロパン、ヘキサントリオール、ペンタエリスリトール、エチレンジアミン、トルエンジアミン、メチレンジフェニルジアミン等を使用し、エチレンオキサイド(EO)、プロピレンオキサイド(PO)又はその両方を付加重合したポリエーテルポリオールである。さらには、上記ポリオールの中でアクリロニトリルやスチレン等のビニル化合物をラジカル重合することやアミンとイソシアネートの反応によりウレア化合物を生成させることによって得られるポリマーポリオールを使用することも可能である。 As the polyol component (b2) other than (b1) used in the present invention, a hydroxyl group equivalent obtained by polymerizing at least one selected from the group consisting of propylene oxide and ethylene oxide on a polymerization initiator having an average functional group number of 2 to 4. Polyether polyols generally used for producing 1,000 to 3,000 flexible polyurethane foams can be used. Specifically, as an initiator, water, ethylene glycol, propanediol, diethylene glycol, dipropylene glycol, butanediol, hexanediol, hydroquinone, glycerin, trimethylolpropane, hexanetriol, pentaerythritol, ethylenediamine, toluenediamine, methylenediphenyl A polyether polyol obtained by addition polymerization of ethylene oxide (EO), propylene oxide (PO) or both using diamine or the like. Furthermore, it is also possible to use a polymer polyol obtained by radical polymerization of a vinyl compound such as acrylonitrile or styrene in the polyol, or by generating a urea compound by a reaction between an amine and an isocyanate.
触媒(C)としては、当該分野において公知である各種ウレタン化触媒が使用できる。例えば、トリエチルアミン、トリプロピルアミン、トリブチルアミン、N−メチルモルフォリン、N−エチルモルフォリン、ジメチルベンジルアミン、N,N,N’,N’−テトラメチルヘキサメチレンジアミン、N,N,N’,N”,N”−ペンタメチルジエチレントリアミン、ビス−(2−ジメチルアミノエチル)エーテル、トリエチレンジアミン、1,8−ジアザビシクロ[5.4.0]ウンデセン−7、1,2−ジメチルイミダゾール、1−ブチル−2−メチルイミダゾール等の3級アミン及びこれらの有機酸塩、ジメチルエタノールアミン、N−トリオキシエチレン−N,N−ジメチルアミン、N,N−ジメチル−N−ヘキサノールアミン等のアミノアルコール類、及びこれらの有機酸塩、スタナスオクトエート、ジブチルチンジラウレート、ジオクチルチンジラウレート、ナフテン酸亜鉛等の有機金属化合物類等が挙げられる。これら触媒は、必要に応じて2種類以上を混合して使用することができる。また、これら触媒を低粘度化、液状化、成形機械の計量精度向上のための増容、等の理由で各種溶媒、ポリオール、可塑剤、等に溶解して使用することも可能である。 As the catalyst (C), various urethanization catalysts known in the art can be used. For example, triethylamine, tripropylamine, tributylamine, N-methylmorpholine, N-ethylmorpholine, dimethylbenzylamine, N, N, N ′, N′-tetramethylhexamethylenediamine, N, N, N ′, N ″, N ″ -pentamethyldiethylenetriamine, bis- (2-dimethylaminoethyl) ether, triethylenediamine, 1,8-diazabicyclo [5.4.0] undecene-7, 1,2-dimethylimidazole, 1-butyl Tertiary alcohols such as 2-methylimidazole and their organic acid salts, amino alcohols such as dimethylethanolamine, N-trioxyethylene-N, N-dimethylamine, N, N-dimethyl-N-hexanolamine, And their organic acid salts, stannous octoate, dibutyltin di Ureto, dioctyl dilaurate, organometallic compounds such as zinc naphthenate and the like. These catalysts can be used as a mixture of two or more if necessary. Further, these catalysts can be used by dissolving them in various solvents, polyols, plasticizers, etc. for reasons such as viscosity reduction, liquefaction, and volume increase for improving measurement accuracy of the molding machine.
本発明に使用される発泡剤(D)としては水が望ましいが、必要に応じて地球環境等に重大な影響を及ぼすことが少ない公知のものも使用することができる。この公知の発泡剤には不活性低沸点溶剤と反応性発泡剤の二種があり、前者としてはジクロルメタン、ハイドロフルオロカーボン、ハイドロフルオロオレフィン、アセトン、蟻酸メチル、ヘキサン、ペンタン、イソペンタン、シクロペンタン等、さらに窒素ガス、炭酸ガスや空気等を挙げることができる。後者の例としては、室温より高い温度等により分解して気体を発生する、例えばアゾ化合物や炭酸水素ナトリウム等を挙げることができる。 As the foaming agent (D) used in the present invention, water is desirable, but known ones that do not significantly affect the global environment and the like can be used as necessary. There are two types of known blowing agents, inert low-boiling solvents and reactive blowing agents. The former includes dichloromethane, hydrofluorocarbon, hydrofluoroolefin, acetone, methyl formate, hexane, pentane, isopentane, cyclopentane, etc. Furthermore, nitrogen gas, carbon dioxide gas, air, etc. can be mentioned. Examples of the latter include, for example, azo compounds and sodium bicarbonate, which decompose to generate gas at a temperature higher than room temperature.
本発明において、必要に応じて助剤(E)を使用してもよい。このような助剤(E)としては、例えば、整泡剤、減粘剤、顔料又は染料、マイカ、ガラス繊維等の補強材又は充填剤、難燃剤、酸化防止剤、紫外線吸収剤、光安定化剤、防カビ剤、抗菌剤、VOCキャッチャー剤等が挙げられ、必要に応じて使用することができる。 In the present invention, an auxiliary agent (E) may be used as necessary. Examples of such auxiliaries (E) include foam stabilizers, thickeners, pigments or dyes, mica, reinforcing materials or fillers such as glass fibers, flame retardants, antioxidants, ultraviolet absorbers, and light stabilizers. An agent, an antifungal agent, an antibacterial agent, a VOC catcher agent and the like can be mentioned, and can be used as necessary.
整泡剤としては、一般にポリウレタンフォーム製造に使用されている公知のものを挙げることができる。例えば、ポリジメチルシロキサン−ポリアルキレンオキシドブロックポリマー、ビニルシラン−ポリアルキレンポリオール重合体等を挙げる事ができる。 Examples of the foam stabilizer include known ones generally used for producing polyurethane foam. For example, a polydimethylsiloxane-polyalkylene oxide block polymer, a vinyl silane-polyalkylene polyol polymer, etc. can be mentioned.
本発明に使用される粘度低減剤(F)としては、一般に高粘度液体の粘度低減に使用される液状物質の内、イソシアネート基と反応する活性水素基、カルボジイミド基、ホルミル基などを含有しないものを使用することができる。好ましくは、粘度低減効果の面から25℃における粘度が100mPa・s以下、取扱いの面から融点が0℃以下、安全性の面からJIS K2265の方法で計測される引火点が70℃以上、毒性、環境汚染性等が低いものであることが好ましい。具体的には、フタル酸ジエチル、フタル酸ジプロピル、フタル酸ジブチル、フタル酸系ジオクチル、フタル酸ジイソノニル、アジピン酸ジエチル、アジピン酸ジプロピル、アジピン酸ジブチル、アジピン酸ジオクチル、アジピン酸ジイソノニル、マレイン酸ジエチル、マレイン酸ジプロピル、マレイン酸ジブチル、マレイン酸ジオクチル、リン酸トリクレジル、リン酸トリスβクロロプロピル、アセチルクエン酸トリブチル、ジベンジルエーテル等が上げられる。 The viscosity reducing agent (F) used in the present invention does not contain an active hydrogen group, a carbodiimide group, a formyl group, etc., which react with isocyanate groups, among liquid substances generally used for viscosity reduction of high viscosity liquids. Can be used. Preferably, the viscosity at 25 ° C. is 100 mPa · s or less from the viewpoint of the viscosity reduction effect, the melting point is 0 ° C. or less from the handling aspect, and the flash point measured by the method of JIS K2265 is 70 ° C. or more from the safety aspect. In addition, it is preferable that it is low in environmental pollution. Specifically, diethyl phthalate, dipropyl phthalate, dibutyl phthalate, dioctyl phthalate, diisononyl phthalate, diethyl adipate, dipropyl adipate, dibutyl adipate, dioctyl adipate, diisononyl adipate, diethyl maleate, Examples thereof include dipropyl maleate, dibutyl maleate, dioctyl maleate, tricresyl phosphate, tris β-chloropropyl phosphate, tributyl acetylcitrate, dibenzyl ether and the like.
粘度低減剤(F)の含有量は有機ポリイソシアネート組成物中に25質量%以下であることが好ましい。上限を超えると、ISF成形物の成形性悪化や反発弾性率及び引裂き強度等の機械物性低下が見られる場合がある。 The content of the viscosity reducing agent (F) is preferably 25% by mass or less in the organic polyisocyanate composition. When the upper limit is exceeded, there are cases where deterioration of the formability of the ISF molded product and mechanical properties such as rebound resilience and tear strength are reduced.
本発明によるISFは、例えば、有機ポリイソシアネート組成物(A)とポリオール成分(B)とを、触媒(C)、発泡剤(D)、及び必要に応じて助剤(E)の存在下、攪拌混合後、金型内に注入して得られるモールドフォーム、又は上下左右に壁面を有するコンベアーに注入することで得られる連続シート状フォーム等として製造される。両製造方法とも、有機ポリイソシアネート組成物(A)以外の成分をあらかじめ混合してポリオールプレミックスを準備し、これと(A)との2成分を混合発泡させる方法、一部又は全ての成分を別々に攪拌混合機の混合ヘッドに導入し、発泡する方法が可能である。 The ISF according to the present invention comprises, for example, an organic polyisocyanate composition (A) and a polyol component (B) in the presence of a catalyst (C), a foaming agent (D), and optionally an auxiliary agent (E). After stirring and mixing, it is produced as a molded foam obtained by pouring into a mold or a continuous sheet-like foam obtained by pouring on a conveyor having wall surfaces on the top, bottom, left and right. In both production methods, a component other than the organic polyisocyanate composition (A) is mixed in advance to prepare a polyol premix, and the two components (A) and this are mixed and foamed. A method of separately introducing into a mixing head of a stirring mixer and foaming is possible.
本発明の有機ポリイソシアネート組成物中の全イソシアネート基と水を含むイソシアネート反応性化合物中の全イソシアネート反応性基のモル比(イソシアネート基/NCO反応性基)としては、0.5〜1.2(イソシアネートインデックス(NCO INDEX)=50〜120)であることが好ましく、0.6〜1.1(NCO INDEX=60〜110)であることがより好ましい。 The molar ratio (isocyanate group / NCO reactive group) of all isocyanate reactive groups in the isocyanate reactive compound containing water and all isocyanate groups in the organic polyisocyanate composition of the present invention is 0.5 to 1.2. (Isocyanate index (NCO INDEX) = 50 to 120) is preferable, and 0.6 to 1.1 (NCO INDEX = 60 to 110) is more preferable.
本発明のISFは、その用途を特に限定するものではないが、通常、反発弾性率として40%前後を有する靴底、靴底の一部、靴の中敷等に用いられる発泡樹脂や従来のISFを本発明によるISFに置き換えることで、非常に優れた使用感を得ることができる。なお、このような用途に求められるISFの機械的強度は、伸び率200%以上,引裂強さ25N/cm以上であり、これを実現するためには、本発明によるISFの密度を最低でも150kg/m3とする必要がある。また、一方で経済性や生産性を考慮するとISF密度の上限は500kg/m3以下が好ましい。触媒(C)の種類や配合量にもよるが、水のみを発泡剤として使用する場合、この密度帯域を達成するために必要な水の添加部数は、ポリオール成分(B)100質量部に対し0.3〜2.5質量部である。 The ISF of the present invention is not particularly limited in its use, but is usually a foamed resin used for a shoe sole having a rebound resilience of around 40%, a part of the shoe sole, a shoe insole, or the like. By replacing the ISF with the ISF according to the present invention, a very excellent feeling of use can be obtained. The mechanical strength of ISF required for such applications is an elongation of 200% or more and a tear strength of 25 N / cm or more. In order to realize this, the density of the ISF according to the present invention is at least 150 kg. / M 3 is required. On the other hand, in consideration of economy and productivity, the upper limit of the ISF density is preferably 500 kg / m 3 or less. Although depending on the type and blending amount of the catalyst (C), when only water is used as the blowing agent, the number of added water necessary to achieve this density band is based on 100 parts by mass of the polyol component (B). 0.3 to 2.5 parts by mass.
以下、さらに本発明の具体的実施例について述べるが、本実施例のみによって本発明が限定されることはない。なお実施例において、すべての部及び%は特に断りの無い限り質量によるものである。 Specific examples of the present invention will be further described below, but the present invention is not limited to the examples. In the examples, all parts and percentages are by mass unless otherwise specified.
[有機ポリイソシアネート組成物 合成例I−1]
攪拌機、温度計、冷却器及び窒素ガス導入管のついた容量1Lの反応器に、異性体含有率1%のMDI:439gを仕込み、75℃まで昇温した後、数平均分子量1000のPTMEG(PTG−1000SN:保土ヶ谷化学工業社製)を561g仕込み、温度を維持したまま攪拌羽根で均一に混合しながら2時間ウレタン化反応を行った。室温まで冷却して有機ポリイソシアネート組成物「I−1」(NCO基含有率10%)を得た。
[Organic Polyisocyanate Composition Synthesis Example I-1]
A reactor having a volume of 1 L equipped with a stirrer, a thermometer, a cooler, and a nitrogen gas inlet tube was charged with 439 g of MDI having an isomer content of 1%, heated to 75 ° C., and then PTMEG (number average molecular weight 1000) 561 g of PTG-1000SN (manufactured by Hodogaya Chemical Co., Ltd.) was charged, and the urethanization reaction was performed for 2 hours while uniformly mixing with a stirring blade while maintaining the temperature. After cooling to room temperature, an organic polyisocyanate composition “I-1” (NCO group content 10%) was obtained.
[有機ポリイソシアネート組成物 合成例I−2]
攪拌機、温度計、冷却器及び窒素ガス導入管のついた容量1Lの反応器に、異性体含有率1%のMDIをカルボジイミド変性及びウレトンイミン変性して得られた、MDI含有率68%、イソシアネート基含有率28.9%の液状MDI:819gを仕込み、75℃まで昇温した後、数平均分子量2000のPTMEG(PTG−2000SN:保土谷化学工業社製)を182g仕込み、温度を維持したまま攪拌羽根で均一に混合しながら2時間ウレタン化反応を行った。室温まで冷却して有機ポリイソシアネート組成物「I−2」(NCO基含有率23%)を得た。
[Organic Polyisocyanate Composition Synthesis Example I-2]
A 1 L reactor equipped with a stirrer, thermometer, condenser and nitrogen gas inlet tube was obtained by modifying MDI having an isomer content of 1% with carbodiimide modification and uretonimine modification. After charging 819 g of liquid MDI having a content rate of 28.9% and raising the temperature to 75 ° C., 182 g of PTMEG having a number average molecular weight of 2000 (PTG-2000SN: manufactured by Hodogaya Chemical Co., Ltd.) was added and stirred while maintaining the temperature. The urethanization reaction was carried out for 2 hours while uniformly mixing with a blade. After cooling to room temperature, an organic polyisocyanate composition “I-2” (NCO group content 23%) was obtained.
[イソシアネート合成例I−3〜I−18]
表1〜表3に示した原料を用い、I−1、I−2と同様の操作を行うことで有機ポリイソシアネート組成物I−3〜I−18を得た。なお、粘度低減剤は、反応終了後に添加し均一に混合した。表中の原料配合は、質量部にて示した。
[Isocyanate Synthesis Examples I-3 to I-18]
Using the raw materials shown in Tables 1 to 3, organic polyisocyanate compositions I-3 to I-18 were obtained by performing the same operations as I-1 and I-2. The viscosity reducing agent was added after the reaction was completed and mixed uniformly. The raw material composition in the table is shown in parts by mass.
PTG−1000SN:保土谷化学工業社製PTMEG、数平均分子量=1000.
PTG−2000SN:保土谷化学工業社製PTMEG、数平均分子量=2000.
PTG−3000SN:保土谷化学工業社製PTMEG、数平均分子量=3200.
PTG-1000SN: PTMEG manufactured by Hodogaya Chemical Co., Ltd., number average molecular weight = 1000.
PTG-2000SN: PTMEG manufactured by Hodogaya Chemical Co., Ltd., number average molecular weight = 2000.
PTG-3000SN: PTMEG manufactured by Hodogaya Chemical Co., Ltd., number average molecular weight = 3200.
PTG−650SN:数平均分子量=650 PTG-650SN: number average molecular weight = 650
[ポリオール成分の調整]
表4〜表6に示す割合で原料を均一に混合し、ポリオールプレミックスとして、ポリオール成分P−1〜P−18を調整した。なお、原料配合は質量部にて示した。
[Polyol component adjustment]
The raw materials were uniformly mixed at the ratios shown in Tables 4 to 6, and polyol components P-1 to P-18 were prepared as a polyol premix. In addition, raw material mixing | blending was shown by the mass part.
表4〜表6で使用した原料は以下の通り。 The raw materials used in Tables 4 to 6 are as follows.
ポリオール1:グリセリンのプロピレンオキサイド付加重合物、水酸基当量1000.
ポリオール2:エチレングリコールのプロピレンオキサイド、エチレンオキサイド付加重合物、プロピレンオキサイド/エチレンオキサイド=55/45(質量比)、水酸基当量1000.
ポリオール3:ペンタエリスリトールのプロピレンオキサイド、エチレンオキサイド付加重合物、プロピレンオキサイド/エチレンオキサイド=86/14(質量比)、水酸基当量2000.
ポリオール4:グリセリンのプロピレンオキサイド、エチレンオキサイド付加重合物、
プロピレンオキサイド/エチレンオキサイド=86/14(質量比)、水酸基当量2300.
ポリオール5:エチレングリコールのプロピレンオキサイド付加重合物、水酸基当量3000.
ポリオール6:グリセリンのプロピレンオキサイド付加重合物、水酸基当量500.
ポリオール7:エチレングリコールのプロピレンオキサイド付加重合物、水酸基当量5000.
Toyocat ET:ビス−(2−ジメチルアミノエチル)エーテルの70質量%DPG溶液.
DABCO NCIM:1−イソブチル−2−メチルイミダゾール.
DOTDL:ジオクチルチンジラウレート
Polyol 1: Propylene oxide addition polymer of glycerol, hydroxyl equivalent 1000.
Polyol 2: Propylene oxide of ethylene glycol, ethylene oxide addition polymer, propylene oxide / ethylene oxide = 55/45 (mass ratio), hydroxyl group equivalent 1000.
Polyol 3: propylene oxide of pentaerythritol, ethylene oxide addition polymer, propylene oxide / ethylene oxide = 86/14 (mass ratio), hydroxyl group equivalent 2000.
Polyol 4: Propylene oxide of glycerol, ethylene oxide addition polymer,
Propylene oxide / ethylene oxide = 86/14 (mass ratio), hydroxyl group equivalent 2300.
Polyol 5: propylene oxide addition polymer of ethylene glycol, hydroxyl group equivalent 3000.
Polyol 6: propylene oxide addition polymer of glycerin, hydroxyl group equivalent 500.
Polyol 7: propylene oxide addition polymer of ethylene glycol, hydroxyl equivalent 5000.
Toyocat ET: 70 mass% DPG solution of bis- (2-dimethylaminoethyl) ether.
DABCO NCIM: 1-isobutyl-2-methylimidazole.
DOTDL: Dioctyltin dilaurate
有機ポリイソシアネート組成物としてイソシアネートプレポリマーI−1〜I−18、ポリオールプレミックスP−1〜P−18を用いISFを作製した。 ISF was prepared using isocyanate prepolymers I-1 to I-18 and polyol premixes P-1 to P-18 as the organic polyisocyanate composition.
即ち、表7〜10に示す割合で温度45℃に温調した各有機ポリイソシアネート組成物とポリオールプレミックスを7000r.p.m.の回転数で卓上ミキサーにより混合撹拌した。60℃に加熱し、離型剤塗布後、乾燥した300mm×300mm×5mmサイズの金属モールドにこの混合物を注入した後、蓋をして7分間硬化させた。硬化後、金型から取り出し、ISFのテストピース(以下TPと略す)を得た。得られたTPについては、密度、硬さ、機械物性等の評価を実施した。 That is, each organic polyisocyanate composition and the polyol premix which were adjusted to a temperature of 45 ° C. at a ratio shown in Tables 7 to 10 were mixed at 7000 r. p. m. Were mixed and stirred by a tabletop mixer. After heating to 60 ° C. and applying a release agent, the mixture was poured into a dried metal mold of 300 mm × 300 mm × 5 mm size, then covered and cured for 7 minutes. After curing, the product was removed from the mold to obtain an ISF test piece (hereinafter abbreviated as TP). About obtained TP, density, hardness, mechanical physical properties, etc. were evaluated.
<機械物性の測定方法>
密度は、JIS K7222に、硬さ(アスカーC、スキン付き表面硬度)、TB(引張強度、3号ダンベル使用)、EB(引張伸び、3号ダンベル使用)、TR(引裂き強度、B型ダンベル使用)、反発弾性率(リュプケ式)は、JIS K7312に準じて測定を行った。0℃における反発弾性率は、24時間0±1℃に温度調節された恒温槽に保管したサンプルを取り出した後、10秒以内に上記常温の場合と同じ方法にて測定した。
<Measuring method of mechanical properties>
Density is JIS K7222, Hardness (Asker C, surface hardness with skin), TB (Tensile strength, No. 3 dumbbell used), EB (Tensile elongation, No. 3 dumbbell used), TR (Tear strength, B-type dumbbell used) ), The impact resilience (Lupke type) was measured according to JIS K7312. The rebound resilience at 0 ° C. was measured by the same method as at room temperature within 10 seconds after taking out a sample stored in a thermostatic chamber adjusted to 0 ± 1 ° C. for 24 hours.
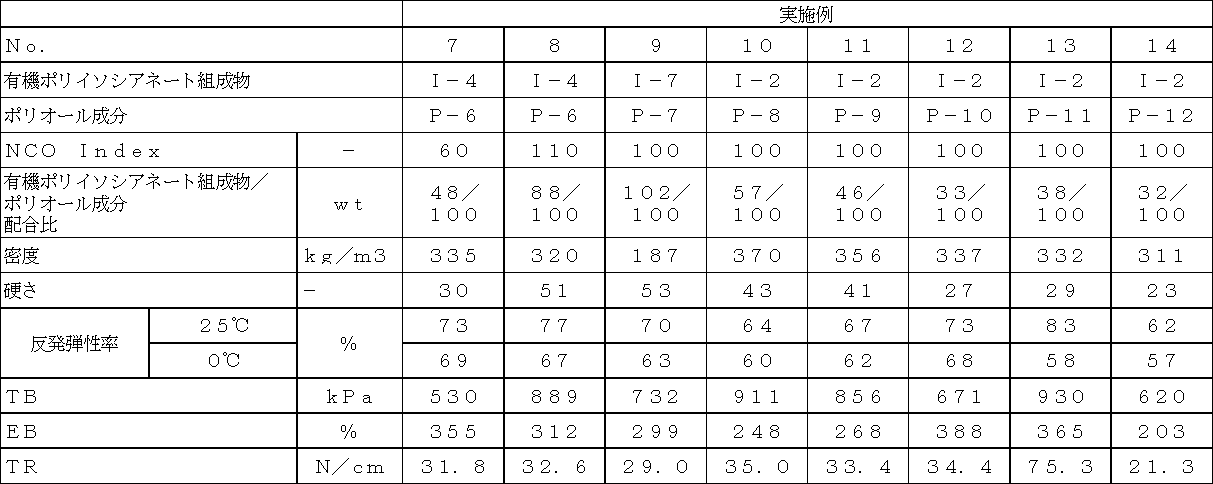
作製したISFの評価結果を表7〜表10に記載する。 The evaluation results of the produced ISF are shown in Tables 7 to 10.
表7〜10から明らかなように、本願発明により得られるISFは、高い反発弾性率、優れた機械的強度を有する。具体的に述べると、表7〜10おいてアスカ−C硬度を20〜60程度に調整したISFの実施例1〜24は、比較例の中で成形が可能であった比較例1、3、5に比べ、反発弾性率が顕著に向上している。 As is clear from Tables 7 to 10, the ISF obtained by the present invention has a high rebound resilience and excellent mechanical strength. Specifically, in Tables 7 to 10, ISF Examples 1 to 24 in which Asuka-C hardness was adjusted to about 20 to 60 were Comparative Examples 1 and 3, which could be molded among the Comparative Examples. Compared to 5, the rebound resilience is significantly improved.
本発明による従来市場に無い低密度かつ高い反発弾性率と良好な機械的物性を有するポリウレタンインテグラルスキンフォームは、靴底、靴のインソール、産業用機械の部品、玩具、楽器等に、使用感の向上、軽量化等の優れた効果をもたらす。 Polyurethane integral skin foam with low density and high rebound resilience and good mechanical properties that are not available on the market according to the present invention is used in shoe soles, shoe insoles, parts of industrial machinery, toys, musical instruments, etc. This brings about excellent effects such as improvement of the weight and weight reduction.
Claims (12)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015083399 | 2015-04-15 | ||
| JP2015083399 | 2015-04-15 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2016204635A true JP2016204635A (en) | 2016-12-08 |
| JP6759648B2 JP6759648B2 (en) | 2020-09-23 |
Family
ID=57127111
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016058313A Active JP6759648B2 (en) | 2015-04-15 | 2016-03-23 | Polyurethane integral skin foam and its manufacturing method |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6759648B2 (en) |
| TW (1) | TW201710315A (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2016167312A1 (en) |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017105913A (en) * | 2015-12-09 | 2017-06-15 | アキレス株式会社 | Polyurethane foam |
| JP2018203921A (en) * | 2017-06-07 | 2018-12-27 | アキレス株式会社 | Polyurethane foam |
| CN111072889A (en) * | 2018-10-18 | 2020-04-28 | 东曹株式会社 | Composition for integral skin polyurethane foam, integral skin polyurethane foam, and method for producing the same |
| JP2020537013A (en) * | 2017-10-10 | 2020-12-17 | ビーエーエスエフ ソシエタス・ヨーロピアBasf Se | Elastic membrane |
| JP2022123350A (en) * | 2021-02-12 | 2022-08-24 | 株式会社イノアックコーポレーション | Polyurethane foam and sole material |
| JP2023051463A (en) * | 2021-09-30 | 2023-04-11 | 日本発條株式会社 | Polyurethane foam material |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP7224713B2 (en) * | 2018-03-08 | 2023-02-20 | アキレス株式会社 | Polyurethane foam and sole material |
| CN111961184B (en) * | 2019-05-20 | 2022-04-22 | 万华化学集团股份有限公司 | Low-density ultraviolet radiation-resistant polyurethane sponge and preparation method thereof |
| CN111518252B (en) * | 2020-04-09 | 2022-04-05 | 上海抚佳精细化工有限公司 | Polyurethane self-skinning foam and preparation method thereof |
| JP2021178915A (en) * | 2020-05-13 | 2021-11-18 | アキレス株式会社 | Polyurethane foam and shoe sole member |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5234961A (en) * | 1992-12-07 | 1993-08-10 | Basf Corporation | Polyurethane water-blown integral skin system produced with a polyterahydrofuran prepolymer |
| JPH05306325A (en) * | 1992-04-10 | 1993-11-19 | Dow Chem Japan Ltd | Polyurethane foam molding |
| JPH05306324A (en) * | 1992-04-10 | 1993-11-19 | Dow Chem Japan Ltd | Polyurethane foam molding |
| JPH06322058A (en) * | 1993-05-12 | 1994-11-22 | Dow Chem Japan Ltd | Polyurethane foam molding |
| JPH06322057A (en) * | 1993-05-12 | 1994-11-22 | Dow Chem Japan Ltd | Polyurethane foam molding |
Family Cites Families (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE3113690A1 (en) * | 1981-04-04 | 1982-10-28 | Elastogran GmbH, 2844 Lemförde | "METHOD FOR PRODUCING CLOSED-CELL POLYURETHANE MOLDED PARTS WITH A COMPRESSED EDGE ZONE" |
| JPH0649298B2 (en) * | 1989-09-25 | 1994-06-29 | 東海ゴム工業株式会社 | Foam molding method |
| IT1240635B (en) * | 1990-05-04 | 1993-12-17 | Dow Italia | MICROCELLULAR POLYURETHANE POLYMERS PREPARED FROM THREE POLY POLYMERS (TETRAMETHYLENE) GLYCOLS WITH ISOCYANATE GROUPS TERMINALS |
| JP2652339B2 (en) * | 1994-02-18 | 1997-09-10 | 三洋化成工業株式会社 | Production method of polyurethane foam |
| JPH10182777A (en) * | 1996-12-25 | 1998-07-07 | Mitsui Chem Inc | Skin-integral head rest |
| JP2003026754A (en) * | 2001-07-17 | 2003-01-29 | Kao Corp | Polyurethane foam elastomer |
| JP2009096858A (en) * | 2007-10-16 | 2009-05-07 | Nippon Polyurethane Ind Co Ltd | Polyisocyanate composition for producing rigid polyurethane slab foam, and method for producing rigid polyurethane slab foam using the composition |
| JP2014141594A (en) * | 2013-01-24 | 2014-08-07 | Nippon Polyurethane Ind Co Ltd | Integral skin polyurethane foam |
-
2016
- 2016-03-23 JP JP2016058313A patent/JP6759648B2/en active Active
- 2016-04-14 WO PCT/JP2016/061985 patent/WO2016167312A1/en not_active Ceased
- 2016-04-15 TW TW105111777A patent/TW201710315A/en unknown
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH05306325A (en) * | 1992-04-10 | 1993-11-19 | Dow Chem Japan Ltd | Polyurethane foam molding |
| JPH05306324A (en) * | 1992-04-10 | 1993-11-19 | Dow Chem Japan Ltd | Polyurethane foam molding |
| US5234961A (en) * | 1992-12-07 | 1993-08-10 | Basf Corporation | Polyurethane water-blown integral skin system produced with a polyterahydrofuran prepolymer |
| JPH06322058A (en) * | 1993-05-12 | 1994-11-22 | Dow Chem Japan Ltd | Polyurethane foam molding |
| JPH06322057A (en) * | 1993-05-12 | 1994-11-22 | Dow Chem Japan Ltd | Polyurethane foam molding |
Cited By (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017105913A (en) * | 2015-12-09 | 2017-06-15 | アキレス株式会社 | Polyurethane foam |
| JP2018203921A (en) * | 2017-06-07 | 2018-12-27 | アキレス株式会社 | Polyurethane foam |
| JP2020537013A (en) * | 2017-10-10 | 2020-12-17 | ビーエーエスエフ ソシエタス・ヨーロピアBasf Se | Elastic membrane |
| JP7483602B2 (en) | 2017-10-10 | 2024-05-15 | ビーエーエスエフ ソシエタス・ヨーロピア | Elastic membrane |
| CN111072889A (en) * | 2018-10-18 | 2020-04-28 | 东曹株式会社 | Composition for integral skin polyurethane foam, integral skin polyurethane foam, and method for producing the same |
| CN111072889B (en) * | 2018-10-18 | 2023-04-21 | 东曹株式会社 | Composition for polyurethane integral skin foam, and method for producing same |
| JP2022123350A (en) * | 2021-02-12 | 2022-08-24 | 株式会社イノアックコーポレーション | Polyurethane foam and sole material |
| JP7550073B2 (en) | 2021-02-12 | 2024-09-12 | 株式会社イノアックコーポレーション | Polyurethane foam and shoe sole materials |
| JP2023051463A (en) * | 2021-09-30 | 2023-04-11 | 日本発條株式会社 | Polyurethane foam material |
| JP7692327B2 (en) | 2021-09-30 | 2025-06-13 | 株式会社東洋クオリティワン | Polyurethane foam material |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| TW201710315A (en) | 2017-03-16 |
| JP6759648B2 (en) | 2020-09-23 |
| WO2016167312A1 (en) | 2016-10-20 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6759648B2 (en) | Polyurethane integral skin foam and its manufacturing method | |
| KR101327721B1 (en) | Carbon dioxide blown low density, flexible microcellular polyurethane elastomers | |
| WO2016017628A1 (en) | Polyisocyanate composition for producing flexible polyurethane foam, and flexible polyurethane foam production method using same | |
| JP2008274051A (en) | Polyisocyanate composition for flexible polyurethane foam and method for producing flexible polyurethane foam using the composition | |
| CN111072889B (en) | Composition for polyurethane integral skin foam, and method for producing same | |
| JP2006519918A (en) | Low amine release polyurethane foam | |
| JP6631069B2 (en) | Polyisocyanate composition for flexible polyurethane foam | |
| WO2009098966A1 (en) | Low-resilience flexible polyurethane foam | |
| JP2001172349A (en) | Process for preparing polyurethane foam | |
| JP2009185155A5 (en) | ||
| JP7110586B2 (en) | Polyurethane integral skin foam and its manufacturing method | |
| JPH0461885B2 (en) | ||
| CN109937220B (en) | Polyurethane foam having sufficient hardness and good flexibility | |
| JP3587051B2 (en) | Method for producing flexible polyurethane foam | |
| JP2003119236A (en) | Polyurethane foam elastomer | |
| JP2007145983A (en) | Production method of polyurethane foam | |
| WO2017135289A1 (en) | Polyisocyanate composition for soft polyurethane foam | |
| JP2014141594A (en) | Integral skin polyurethane foam | |
| JPH11310624A (en) | Manufacturing method of polyurethane foam | |
| JP2016060896A (en) | High durability flexible polyurethane foam molding composition | |
| JP7470889B2 (en) | Composition for polyurethane integral skin foam, polyurethane integral skin foam, and method for producing same | |
| JPH0718055A (en) | Flexible polyurethane foam | |
| JP2018165292A (en) | Polyisocyanate composition for soft polyurethane foam | |
| JP5732845B2 (en) | Catalyst composition for producing flexible polyurethane foam, and method for producing flexible polyurethane foam using the same | |
| JP2024158563A (en) | Polyol premix, foam, and thermal storage |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20190214 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20191216 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20191224 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20200217 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20200804 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20200817 |
|
| R151 | Written notification of patent or utility model registration |
Ref document number: 6759648 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R151 |