JP2012196643A - Apparatus for producing hypochlorous acid water or the like - Google Patents
Apparatus for producing hypochlorous acid water or the like Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2012196643A JP2012196643A JP2011063587A JP2011063587A JP2012196643A JP 2012196643 A JP2012196643 A JP 2012196643A JP 2011063587 A JP2011063587 A JP 2011063587A JP 2011063587 A JP2011063587 A JP 2011063587A JP 2012196643 A JP2012196643 A JP 2012196643A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- electrode
- tank
- diaphragm
- hypochlorous acid
- electrolysis
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Water Treatment By Electricity Or Magnetism (AREA)
- Electrolytic Production Of Non-Metals, Compounds, Apparatuses Therefor (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、除菌、消臭などに使用する消臭力、殺菌力の強い弱酸性から中性域の次亜塩素酸や次亜塩素酸塩の水溶液(次亜塩素酸や次亜塩素酸塩を総称して次亜塩素酸等、次亜塩素酸等の水溶液を次亜塩素酸水等と定義し、以下、呼称する。)の生成を行う次亜塩素酸水等の生成装置に関する。 The present invention relates to an aqueous solution (hypochlorous acid or hypochlorous acid) of a weakly acidic to neutral hypochlorous acid or hypochlorite used for sterilization, deodorization and the like. The present invention relates to an apparatus for producing hypochlorous acid water or the like, which generally produces salts such as hypochlorous acid and the like, and hypochlorous acid and the like as an aqueous solution of hypochlorous acid.
昨今、塩素ガス発生がなく、アルカリによる皮膚腐食のない弱酸性から中性付近の次亜塩素酸水等による強い殺菌、消臭力が注目されて、口内の殺菌、口臭予防、手指の洗浄などに使用する次亜塩素酸水等がボトルに詰められ販売されるようになってきている。 Recently, there is no generation of chlorine gas, there is no skin corrosion due to alkali, and strong sterilization and deodorizing power with hypochlorous acid water etc. near neutrality has attracted attention, sterilization of mouth, prevention of bad breath, washing of fingers, etc. Hypochlorous acid water used for sachets is packed in bottles and sold.
また、従来、食塩水を電気分解によって次亜塩素酸や次亜塩素酸塩の水溶液を生成する次亜塩素酸水等の生成装置が知られており、広く利用されている(例えば、特許文献1〜3)。 Further, conventionally, a device for producing hypochlorous acid water or the like that produces an aqueous solution of hypochlorous acid or hypochlorite by electrolysis of saline is known and widely used (for example, patent documents). 1-3).
しかし、特許文献1に開示する次亜塩素酸水等の生成装置にあっては、酸性水およびアルカリ性水が流れる通水路に流水量を調整するバルブを設け、流量比率でPHを決めているため、微量調整が難しく、バルブの流量経時変化もあり、PHを長時間安定させて使用することは難しく、PH計を備え自動調整するか頻繁にPHを測定し流量調整をしなければならなかった。特許文献2に開示する次亜塩素酸水等の生成装置にあっては、電解する原水に塩酸を添加することを要し、劇物である濃塩酸を希釈して用いるか、希塩酸を頻繁に取り扱わなければならず、次亜塩素酸水等の生成装置の利用者が限定された。特許文献3に開示する次亜塩素酸水等の生成装置にあっては、塩化ナトリウムなどの水溶液を使用し、隔膜電解法及び無隔膜電解法を組合わせて生成される2種類以上の電解水を混合し、中性域の次亜塩素酸水等を得るものであるが、電解槽を2つ以上持つため装置が大きくなり、またコストアップになるという欠点があった。
However, in the apparatus for generating hypochlorous acid water or the like disclosed in
本発明は、上述の課題を解決するためになされたものであり、利用者が安全、簡易に、殺菌力の強い弱酸性から中性域の次亜塩素酸水等をつくることができる、低廉な次亜塩素酸水等の生成装置を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in order to solve the above-mentioned problems, and allows a user to produce a hypochlorous acid water or the like in a neutral region from a weakly acidic, strong sterilizing power to a neutral region. An object of the present invention is to provide a device for producing hypochlorous acid water or the like.
このため第1の発明は、塩素イオンを含む電気分解液を電気分解して次亜塩素酸水等を生成する生成装置であって、隔膜でA槽とB槽に区切られた電解槽と、A槽内に設けられた電極1及び電極2と、前記隔膜を隔ててA槽内に設けられた電極3およびB槽内に設けられた電極4と、電極1及び電極2を陽極陰極として電極1及び電極2に直流の定電流値I1、電極3を陽極及び電極4を陰極として電極3および電極4に直流の定電流値I2を流す電気制御装置とからなることを特徴とする。
For this reason, the first invention is a generating device that electrolyzes an electrolytic solution containing chlorine ions to generate hypochlorous acid water and the like, and an electrolytic cell partitioned into a tank A and a tank B by a diaphragm, Electrode 1 and
第2の発明は、前記定電流値I1と前記定電流値I2の比が、定電流値I2/定電流値I1=0.06〜10であり、前記電気制御装置に定電流値I1及び定電流値I2の通電時間制御が組み込まれていることを特徴とする。 In a second aspect of the invention, the ratio between the constant current value I1 and the constant current value I2 is constant current value I2 / constant current value I1 = 0.06 to 10, and the electric control device includes the constant current value I1 and the constant current value I2. It is characterized in that energization time control of the current value I2 is incorporated.
第3の発明は、前記電気制御装置が前記電極3及び前記電極4を流れる直流の極性を所定時間ごとに反転する機能を有することを特徴とする。
The third invention is characterized in that the electric control device has a function of inverting the polarity of the direct current flowing through the
第4の発明は、前記B槽に塩水を加える装置を有し、所定時間毎にもしくは連続して前記B槽に塩水を加え、B槽から出水することを特徴とする。 4th invention has the apparatus which adds salt water to the said B tank, salt water is added to the said B tank every predetermined time or continuously, and it drains from B tank, It is characterized by the above-mentioned.
第5の発明は、塩素イオンを含む電気分解液を電気分解して次亜塩素酸水等を生成する生成装置であって、隔膜でA槽とB槽に区切られた電解槽と、前記隔膜を隔ててA槽内に設けられた電極3およびB槽内に設けられた電極4と、電極3を陽極及び電極4を陰極として電極3および電極4に直流の定電流を流す電気制御装置と、前記B槽に塩水を加える装置及び排水装置とからなり、所定時間毎にもしくは連続して前記B槽に塩水を加え、略同量のB槽電解液を排水し、電解電流量Q(クーロン)に対し前記排水量が0.016×Q(クーロン)ml以下であることを特徴とする。
5th invention is the production | generation apparatus which produces | generates hypochlorous acid water etc. by electrolyzing the electrolysis solution containing a chlorine ion, Comprising: The electrolytic cell divided into A tank and B tank by the diaphragm, The said diaphragm An
第6の発明は、前記隔膜が陽イオン交換膜であることを特徴とする。 The sixth invention is characterized in that the diaphragm is a cation exchange membrane.
第7の発明は、前記隔膜または隔膜近傍に振動を与える装置を付設していることを特徴とする。 The seventh invention is characterized in that a device for applying vibration to the diaphragm or the vicinity of the diaphragm is attached.
本発明は、一つの電解槽内で、塩素イオンを含む電気分解液(以下、「電解液」と略称する。)の無隔膜電気分解(隔膜を隔てない陰陽2極による電気分解で、これを「無隔膜電解」と呼ぶ、以下呼称する。)及び有隔膜電気分解(隔膜で仕切られた2槽のそれぞれに配置した陽極と陰極による電気分解で、これを有隔膜電解と呼ぶ、以下呼称する。)または有隔膜電気分解のみを行い、無隔膜の電解電流値および電解時間と有隔膜の電解電流値および電解時間を調節することにより、またB槽アルカリ性の電解液を一部入れ換えることにより、PH,残留塩素濃度を設定できる、利用者が安全,簡易に殺菌力の強い弱酸性から中性域の次亜塩素酸水等をつくることができる次亜塩素酸水等の生成装置を提供することができる。 The present invention is a non-diaphragm electrolysis of an electrolytic solution containing chlorine ions (hereinafter abbreviated as “electrolytic solution”) in a single electrolytic cell. (Hereinafter referred to as “non-diaphragm electrolysis”) and diaphragm electrolysis (electrolysis by an anode and a cathode disposed in each of two tanks partitioned by a diaphragm, which is referred to as “diaphragm electrolysis”. .) Or by performing only electrolysis of the diaphragm, adjusting the electrolysis current value and electrolysis time of the non-diaphragm and the electrolysis current value and electrolysis time of the diaphragm, and by partially replacing the B-cell alkaline electrolyte, Providing a device for generating hypochlorite water, etc. that can set PH and residual chlorine concentration, and that allows users to safely and easily produce hypochlorous acid water in a neutral range from weakly acidic to strong acidity be able to.
また本発明は、電気分解により発生する気泡が隔膜に付着し通電を阻害するのを、隔膜に付着した気泡に動揺を与えて脱離させ、通電の阻害を防止することにより、安定した発生量の次亜塩素酸水等の生成装置を提供することができる。 In addition, the present invention prevents the bubbles generated by electrolysis from adhering to the diaphragm and impeding energization by swaying the bubbles adhering to the diaphragm and releasing them, thereby preventing the energization from being inhibited, thereby generating a stable amount of generation. An apparatus for producing hypochlorous acid water or the like can be provided.
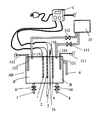
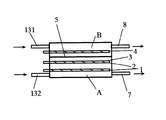
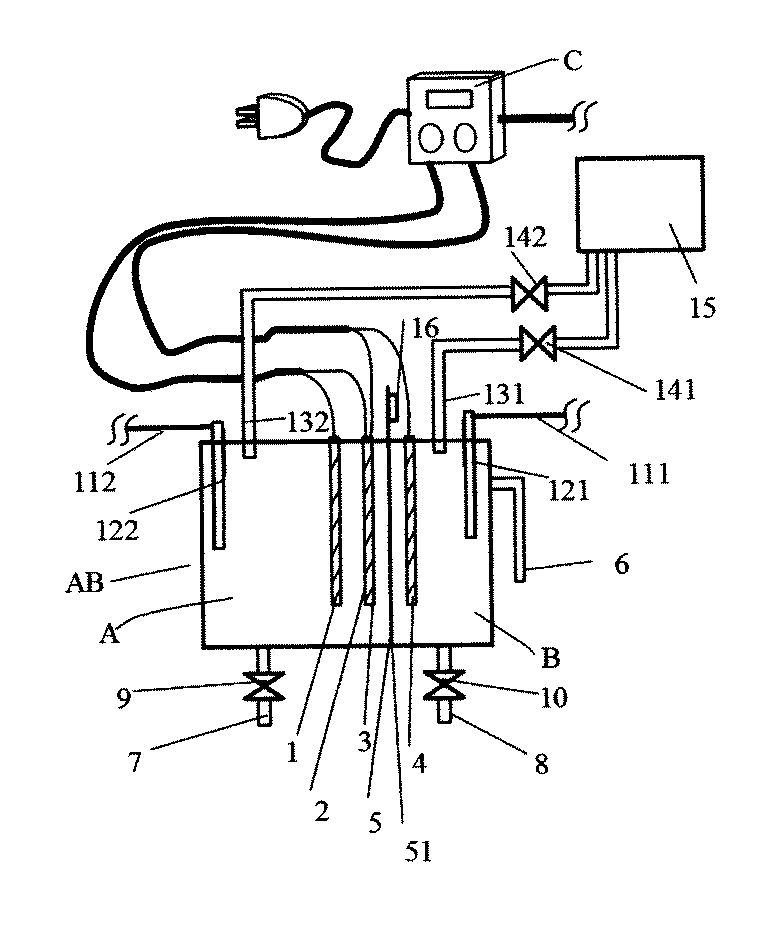
以下、本発明を実施するための第1の形態について図1を用いて説明する。まず、構造の概略について説明する。電解槽ABには電解用電極1,2,3,4、電解槽AB内を2つに区切る隔膜5、アルカリ水出水管6、次亜塩素酸水等出水管7、アルカリ水出水管8、電解液水位センサー121,122が付設されている。また、電極への通電を制御する電気制御装置C、水槽に電解液を供給する電解液供給管131,132及び電解液タンク15が付設されている。
Hereinafter, a first embodiment for carrying out the present invention will be described with reference to FIG. First, an outline of the structure will be described. The electrolytic cell AB includes
次に構造の詳細について説明する。電気分解を行う電解槽ABは隔膜5によりA槽とB槽に区切られている。電解により、A槽には次亜塩素酸水等が生成され、B槽内の水はアルカリ性となる。A槽には電極1および電極2が対峙して設けられ、また、前記隔膜を隔ててA槽に電極3、B槽に電極4が設けられている。ここで対峙してとは液抵抗を大きくしない配置をすることを言い、厳密に向き合うことを要しない。電極1と電極2の極性は陰陽どちらも可能であるが、電極3を陽極とすることから隔膜5寄りの電極2を陽極とするのが好ましい。図1ではA槽内の陰陽電極のうち前記隔膜に近い側の電極2を陽極とし、電極2の背面を電極3として用い、該隔膜5を隔てて近接してB槽の電極4に陰極を設け、1つの電極で電極2と電極3の2つの役割をさせているが、図2のように別々に電極2と電極3を設けてもかまわない。
Next, details of the structure will be described. The electrolytic cell AB that performs electrolysis is divided into a tank A and a tank B by a
電極2、電極3など陽極は強い酸化環境の中でも耐久性を求められることから、チタン基材に白金または酸化イリジウムなどの白金族酸化物の被覆をして用いる。電極1は陽極として用いる場合にはチタン基材に白金または酸化イリジウムなどの白金族酸化物の被覆をして用い、陰極として用いる場合には陽極と同じ材質であっても良いがチタン材でも良い。食塩などの電解質を溶解するとき、逆浸透膜通過水、イオン交換樹脂通過水のようにカルシウムイオン、マグネシウムイオンなどのスケール成分を含まない水を用いた場合には、スケール除去のための逆電解が不要なので電極1、電極4の材質はチタン材でもよい。使用する水がスケール成分を含む場合には電極4の材質は直流の極性反転をするため陽極と同じ白金または白金族酸化物の被覆材など耐久性素材を用いる。
Since the anodes such as the
隔膜5はイオン泳動ができ、液が容易に行き来できない素材、たとえば、素焼き板、不織布、イオン交換膜などを用いる。不織布、イオン交換膜は耐久性の点からフッ素樹脂製のものが良い。不織布はPE,PP,PET製など次亜塩素酸水等に耐える他の素材あっても良い。撥水性の素材は湿潤処理をして用いる。隔膜5は電解電圧を低くするため、薄くし補強の支材51を用いて形成すると良いが、支材51は無くても良い。
The
A槽B槽に食塩などの塩素イオンを含む電解液を入れ、電極1、電極2に直流電流を流して電気分解を行う。また、電極3,電極4に直流電流を流して電気分解を行う。隔膜5を陽イオン交換膜にするとB槽に発生したOH−イオンの通過が防止され、A槽はより酸性に傾きやすくなる。
An electrolytic solution containing chlorine ions such as salt is placed in the A tank and the B tank, and a direct current is passed through the
電気分解により水素ガス、酸素ガスが発生し、隔膜5に気泡が付着して通電を阻害するので、隔膜5の補強支材51には隔膜5から気泡を脱離させるため振動装置16が付設されている。気泡を脱離させるための振動装置は、本実施例では電磁石を用い補強支材51への打撃を利用したが、オルゴールのように弾く方法であっても良く、隔膜5付近の電解槽容器を叩いても良く、水流、気流で隔膜5および付近に動揺を与えても良い。
Hydrogen gas and oxygen gas are generated by electrolysis, and bubbles are attached to the
電気制御装置Cには、電源へのコンセント、電極、振動装置、開閉弁、水位センサーなど電装部品と繋ぐ配線、電流値制御ボタン、時間制御ボタン、各種表示が設けられている。また、電解電流値、電解時間、その他電装部品を制御する電気回路が設けられている。無隔膜電解電流値、有隔膜電解電流値、電流値比の設定は、本実施例では無隔膜電解電流値、有隔膜電解電流値で設定しているが、無隔膜電解電流値と電流値比で設定するなど別の組合せで設定する構造としても良い。 The electrical control device C is provided with a power outlet, an electrode, a vibration device, an on-off valve, a wiring connecting to an electrical component such as a water level sensor, a current value control button, a time control button, and various displays. In addition, an electric circuit for controlling the electrolysis current value, electrolysis time, and other electrical components is provided. The setting of the diaphragm electrolysis current value, the diaphragm electrolysis current value, and the current value ratio is set by the diaphragm electrolysis current value and the diaphragm electrolysis current value in this embodiment, but the ratio of the diaphragm electrolysis current value and the current value ratio is set. It is good also as a structure set with another combination, such as setting by.
A槽,B槽に付設され、電解槽に入る液量を制御する電解液水位センサー121,122はチタンなどの耐食性金属を用い、一方を水位に一方を深く沈めて、2極の通電の有無で電気制御装置Cにより電解液水位が所定水位にあることを判断している。本例では電解液水位センサーに電極式を用いているが、フロート式、超音波式その他の方法であっても良い。また、本実施例では水位センサーを設けているが、定量ポンプなどで電解液流量を制御できる場合には水位センサーを設けなくても良い。
Electrolyte
A槽,B槽への電解液の供給のため電解液供給管131,132及び電解液タンク15が設けられ、電解液供給管131,132にはそれぞれ電磁弁141,142が設けられており、電解液水位センサー121,122の信号を受けて電気制御装置Cが電磁弁141,142の開閉を行う構造となっている。本例では電磁弁を用いたが、ポンプ、定量ポンプその他の方法であっても良い。また、電解液は少量の濃厚塩水を定量ポンプで入れ、浄水を加える方法であっても良い。
また、A槽には次亜塩素酸水等出水管7, B槽にはアルカリ水出水管8が設けられ、それぞれに電磁弁9、10が付設され、電気制御装置Cの指示により開閉を行う構造となっている。本実施例では弁に電磁弁を用いているが、モーターによる開閉、レバーによる開閉など他の方法による開閉であっても良く、これにより本発明は制限されない。また、電解液水位センサー121,122、電解液供給管131,132及び電解液タンク15、次亜塩素酸水等出水管7, アルカリ水出水管8の付設は必ずしも必要でなく、手動で供給、排出を行うなど電解液の供給、排出を他の方法で行っても本発明を免れるものではない。また、B槽の電解液のアルカリ濃度の過上昇防止およびA槽の電解液PH制御のためB槽の電解液の一部入れ換えを行うが、この排出のため排水装置を設けている。排水装置は排水できる構造物であれば良く、本実施例ではアルカリ水出水管6を設けている。なお、電解電流量に比し、B槽容量が大きい場合には水酸化物イオン濃度が高くならないのでアルカリ水出水管6は無くても良い。
The tank A is provided with a
次に動作について図1に基づいて説明する。電磁弁141,142が開き電解液タンク15より電解液が電解液供給管131,132を通って電解槽ABに供給される。電解液には塩化ナトリウム、塩化カリウムなどの塩化物塩を水道水などの浄水、精製水、逆浸透膜通過水など不純物の少ない水に溶解して用いる。電解液が所定水位に達すると電解液水位センサー121,122の信号により電磁弁141,142が閉じ電解液の供給が停止する。電気制御装置Cの指示により電極1,電極2に所定電流値I1、電極3,電極4に所定電流値I2、が流れ電解液の電気分解が始まる。電気分解を継続すると電極から発生した酸素ガスと水素ガスの一部が隔膜5に付着するので、振動装置16に通電して振動を起こし気泡を脱離する。振動装置16への必要な通電間隔は電解電流に左右されるが、10分程度の間隔で気泡を脱離してやればほとんど問題ない。電解中のB槽の電解液の水酸化物イオン濃度の変化でA槽の電解液のPHが左右されるのを防ぐため、所定時間間隔で所定量の電解液を電磁弁141を開いて供給し、またアルカリ水出水管6から同量を排出する。所定時間電解液の電気分解を行った後、電気制御装置Cの指示により電気分解は停止する。電気分解終了後、A槽の次亜塩素酸水等は電磁弁9が開き、次亜塩素酸水等出水管7を通って出水され容器に貯えもしくは直接利用に供される。B槽のアルカリ水は電磁弁10が開き、出水管8を通って出水され、油脂汚れ洗浄剤などとして利用されるか、廃棄される。回分式で説明したが本発明は回分式に限らず、小刻みの供給出水、連続供給出水する方法であっても良い。ここで前記定電流値I1,定電流値I2は所要電解時間内の平均電流値であって、所要電解時間内、一定電流値であることが望ましいが、所要電解時間に比し短時間内での電流値変化があっても、本発明を免れるものではない。
Next, the operation will be described with reference to FIG. The
次に本発明を実施するための第2の形態について図3を用いて説明する。この場合、第1の実施形態と異なる部分について特に説明する。本実施形態では第1の実施形態のうち、A槽の電極1を除いた構造をしている。電極1、電極2を用いる電気分解がなくなるので、それに必要な電気回路も不必要となり低コスト化できる。その反面A槽の電解液の次亜塩素酸水等のPH調整範囲は5〜7程度に抑えられ、次亜塩素酸水等の濃度とPHを選択する範囲が狭められる。本実施例ではB槽の電解液の入換によりB槽の電解液の水酸化物イオン濃度を調整し、これによりA槽の電解液のPHを調整するので、B槽の電解液の入換は必須であり、B槽容量は少ないほうが有利である。B槽の電解液の入換はB槽の電解液の水酸化物イオン濃度が大きく変化しない程度の水量で行う。一度の供給出水は同量であることを要しないが、B槽の水酸化物イオン濃度、電解液量の変化を避けるため、略同量とし、同量とすることがさらに好ましい。
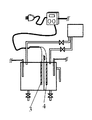
Next, a second embodiment for carrying out the present invention will be described with reference to FIG. In this case, a different part from 1st Embodiment is demonstrated especially. In this embodiment, the structure which remove | excluded the
次に本発明を実施するための第3の形態について図4を用いて説明する。この場合、第1の実施形態と異なる部分について特に説明する。本実施形態では第1の実施形態を横向きにした構造をしている。本実施形態では回分式としても使用できるが、連続して次亜塩素酸水等を生成する場合に適する。電気分解により酸素ガス、水素ガスが発生し、同じ電流量なら塩濃度が低いほどガス発生量が多くなるが、ガスの発生量が多い場合には、電極面が立て向きになるよう配置し上方に気泡を逃がし、排気ガス口を設けると良い。 Next, a third embodiment for carrying out the present invention will be described with reference to FIG. In this case, a different part from 1st Embodiment is demonstrated especially. In the present embodiment, the first embodiment is structured horizontally. In this embodiment, it can be used as a batch system, but is suitable for continuously producing hypochlorous acid water or the like. Oxygen gas and hydrogen gas are generated by electrolysis. If the amount of current is the same, the amount of gas generated increases as the salt concentration decreases. However, if the amount of gas generated is large, the electrode surface is placed upright. It is advisable to provide an exhaust gas outlet by letting bubbles escape.
次に本発明の生成装置を用いて生成した次亜塩素酸水等性状等について、前記生成装置の仕様及び電解条件とともに表す。ここで使用した水道水は埼玉県熊谷市の浄水(水道水)である。残留塩素濃度測定には柴田科学(株)製の機種名AQ−102、PH測定には堀場製作所製の機種名B−211を用いた。PH標準液は東亜ディケーケー(株)製の中性燐酸塩標準液(PH6.86)を用いた。残留塩素は塩素、次亜塩素酸及び次亜塩素酸ソーダを塩素に換算し加算したものであるが、弱酸性から中性付近では塩素の比率は極めて低いので残留塩素測定値は次亜塩素酸及び次亜塩素酸ソーダの和であるとして説明する。本実施例で用いた電解電極はチタン基材に酸化イリジウムで表面被覆。電極1、電極2の電解面積2cm2、面間隔10mm、電極3、電極4の電解面積2cm2、面間隔20mm、電解液の温度は8±2℃である。
Next, properties such as hypochlorous acid water produced using the production apparatus of the present invention are shown together with specifications of the production apparatus and electrolysis conditions. The tap water used here is clean water (tap water) in Kumagaya City, Saitama Prefecture. The model name AQ-102 manufactured by Shibata Kagaku Co., Ltd. was used for residual chlorine concentration measurement, and the model name B-211 manufactured by Horiba Seisakusho was used for PH measurement. As the PH standard solution, a neutral phosphate standard solution (PH 6.86) manufactured by Toa Decay Co., Ltd. was used. Residual chlorine is the sum of chlorine, hypochlorous acid and sodium hypochlorite converted to chlorine, but the residual chlorine measurement is hypochlorous acid because the ratio of chlorine is very low from weakly acidic to neutral. And the sum of sodium hypochlorite. The electrolytic electrode used in this example is a titanium base material coated with iridium oxide. Electrode area of
無隔膜電解電流値を350mAとし、有隔膜電解電流値を変化させたときのA槽電解液のPHの変化を表1に示す。食塩濃度10g/l、食塩溶解にはRO水(逆浸透膜を通過した水)を使用、液量:A槽B槽とも1000ml、電流値比は有隔膜電解電流値を無隔膜電解電流値350mAで割った値、0H〜10Hは電解時間、空欄は測定せず。無隔膜電解電流値(電極1と電極2による電解の電流値I1、以下同じ)と有隔膜電解電流値(電極3と電極4による電解の電流値I2、以下同じ)の電流値比I2/I1を変化させることによりA槽電解液のPHを約3.5〜8.3の範囲で変化させることができる。また、次亜塩素酸水等発生量は総電解電流量にほぼ比例して増減するので、無隔膜電解電流値と前記電流値比I2/I1を調整することにより、PH5.8〜8.3の範囲で次亜塩素酸水等濃度とPHを独立にほぼ自由に変えることができる。更にPH6.2〜7.6の範囲でより精度良く設定することができる。
Table 1 shows changes in PH of the A-cell electrolyte when the diaphragm electrolysis current value was 350 mA and the diaphragm electrolysis current value was changed. Salt concentration is 10g / l, RO water (water that has passed through reverse osmosis membrane) is used for salt dissolution, Liquid volume: 1000ml for both tank A and tank B, current value ratio is diaphragm membrane current value 350mA The value divided by, 0H to 10H is the electrolysis time, and the blank is not measured. Current value ratio I2 / I1 between the diaphragm electrolysis current value (current value I1 of electrolysis by
無隔膜電解と有隔膜電解の電解時間を変え、また、電流値比I2/I1を大きく変化させたときのA槽電解液のPHの変化を表2に示す。食塩濃度10g/l、食塩溶解にはRO水(逆浸透膜を通過した水)を使用、液量:A槽B槽とも1000ml、電流値比は有隔膜電解電流値を無隔膜電解電流値で割った値、0H〜10Hは電解時間、無隔膜電解時間は連続10時間、−欄は有隔膜電解をしていない時間帯、−数値(例:−10.7)は有隔膜電解を始める直前のA槽の電解液のPH、*1は無隔膜電解9時間30分後に無隔膜電解とともに有隔膜電解を30分行った。表2からわかるように、電流値比及びそれぞれの電解時間、電流値を制御することにより、A槽電解液のPHを弱酸性から中性付近に制御できる。 Table 2 shows the change in pH of the A-cell electrolyte when the electrolysis time of the diaphragm electrolysis and the diaphragm electrolysis is changed and the current value ratio I2 / I1 is greatly changed. Salt concentration is 10 g / l, RO water (water that has passed through reverse osmosis membrane) is used for salt dissolution, liquid volume: 1000 ml for both tank A and tank A, current value ratio is the diaphragm electrolysis current value as the diaphragm electrolysis current value Divided values, 0H to 10H are electrolysis time, non-diaphragm electrolysis time is continuous 10 hours,-column is a time zone when diaphragm electrolysis is not performed,-numerical value (example: -10.7) is just before starting electrolysis of diaphragm The pH of the electrolyte in tank A, * 1, was 9 hours and 30 minutes after the diaphragm electrolysis, and the diaphragm electrolysis was performed for 30 minutes together with the diaphragm electrolysis. As can be seen from Table 2, by controlling the current value ratio, each electrolysis time, and the current value, the pH of the A tank electrolyte can be controlled from weakly acidic to near neutral.
前記電極3及び前記電極4を流れる直流の極性を所定時間ごとに反転し電気分解を続けたときの、前記有隔膜電解電流値と前記電極4の電解面に析出するスケールとの関係を表3に示す。食塩濃度10g/l、食塩溶解には熊谷市水道水を使用、液量:A槽B槽とも1000ml、無隔膜電解電流値350mA、電流値比は有隔膜電解電流値を無隔膜電解電流値で割った値、0H〜10Hは電解時間、電解時間は無隔膜電解、有隔膜電解とも連続10時間。有隔膜電解は電極3を陽極(正電解)として60分、陰極(逆電解)として6分の繰り返し。有隔膜電解電流値50mA〜200mAの範囲で電極4の電解面に析出するスケールは認められなかった。
Table 3 shows the relationship between the diaphragm electrolysis current value and the scale deposited on the electrolytic surface of the
前記電極3及び前記電極4を流れる直流の極性を所定時間ごとに反転し電気分解を続けたときに、前記電極4が陽極となる時間と前記電極4の電解面に析出するスケールとの関係を表4に示す。食塩濃度10g/l、食塩溶解には熊谷市水道水を使用、液量:A槽B槽とも1000ml、無隔膜電解電流値350mA、有隔膜電解電流値150mA、0H〜10Hは電解時間、電解時間は無隔膜電解、有隔膜電解とも連続10時間。有隔膜電解は電極3を陽極(正電解)として60分、陰極(逆電解)としてx分の繰り返し、x分を1〜60分とした。逆電解時間1〜60分の範囲で電極4の電解面に析出するスケールは認められなかった。
When the polarity of the direct current flowing through the
電気分解中、前記B槽の電解液に60分毎に所定量の塩水を加え、同量を排水したときの加える塩水量とA槽の電解液のPHの関係を表5に示す。電解液:食塩濃度10g/l、食塩溶解には熊谷市水道水を使用、液量:A槽1000ml、B槽370ml、無隔膜電解電流値350mA、有隔膜電解電流値250mA、電解時間は無隔膜電解、有隔膜電解とも連続10時間。有隔膜電解は電極3を陽極として60分、陰極として4.2分の繰り返し。加える塩水は電解液と同じもの。B槽への塩水の追加、同量の排水(B槽入換液量と呼ぶ、以下同じ)により、B槽入換液量の増加とともにA槽の電解液PHが低い方へ変化している。
Table 5 shows the relationship between the amount of salt water to be added and the pH of the electrolyte solution in the A tank when a predetermined amount of salt water is added to the electrolyte solution in the B tank during the electrolysis and the same amount is drained. Electrolyte solution: salt concentration 10 g / l, use Kumagaya City tap water for salt dissolution, liquid volume: A tank 1000 ml, B tank 370 ml, diaphragm electrolysis current value 350 mA, diaphragm electrolysis current value 250 mA, electrolysis time is diaphragm Continuous 10 hours for both electrolysis and diaphragm electrolysis. The diaphragm electrolysis was repeated for 60 minutes using the
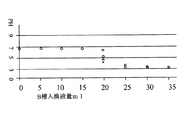
無隔膜電解の無い、A槽とB槽の液量を変えておこなった場合の、電気分解中前記B槽の電解液に60分毎に所定量の塩水を加え、同量を排水したときの加える塩水量とA槽の電解液のPHの関係を表6に示す。電解液:食塩濃度10g/l、食塩溶解には熊谷市水道水を使用、液量:A槽850ml、B槽85ml、有隔膜電解電流値350mA、連続10時間。有隔膜電解は電極3を陽極として60分、陰極として4.2分の繰り返し。加える塩水は電解液と同じもの、空欄は測定せず。B槽への塩水の追加、同量の排水により、A槽の電解液PHがB槽入換液量の増加とともに低い方へ変化している。食塩濃度50g/l(有隔膜電解電流値350mA△印)、食塩濃度10g/l(有隔膜電解電流値350mA○印)、食塩濃度5g/l(有隔膜電解電流値300mA□印)、食塩濃度2g/l(有隔膜電解電流値150mA×印)のPHとB槽入換液量(すべて電解電流量1260クーロンに換算)の関係を図5に示す。PHが弱酸性から中性付近の条件はB槽電解液の排水量が20ml以下であり、0.016×電解電流量(クーロン)ml以下が適する。(0.35A×3600Sec=1260クーロン、20ml/1260クーロン≒0.016ml/クーロンが得られる。)また、低電圧で電解するためと所定PHに達する時間を短くするために食塩濃度5g/l以上がさらに適する。ここでは塩に食塩を用いたが塩化カリウムなど他の塩化物塩であっても良い。B槽入換液として用いた塩水はここでは電解液を用いたが、必ずしも電解液と同じものでなくても良く、通常電解圧が確保できる導電率の塩水であれば良い。
When there is no diaphragm electrolysis and the amount of liquid in tank A and tank B is changed, a predetermined amount of salt water is added to the electrolyte in tank B during electrolysis every 60 minutes, and the same amount is drained. Table 6 shows the relationship between the amount of salt water to be added and the pH of the electrolytic solution in tank A. Electrolyte solution: Salt concentration of 10 g / l, Kumagaya city tap water was used for salt dissolution, Liquid volume: A tank 850 ml, B tank 85 ml, diaphragm electrolysis current value 350 mA, continuous 10 hours. The diaphragm electrolysis was repeated for 60 minutes using the
本発明の次亜塩素酸水等の生成装置は、塩酸などの劇物を使用することなく、塩酸ガスの発生もなく、また、小型化、低コストにできるので、清掃、除菌、消臭を要する調理場、介護施設などに適する。 The apparatus for producing hypochlorous acid water or the like of the present invention does not use deleterious substances such as hydrochloric acid, does not generate hydrochloric acid gas, and can be reduced in size and cost. Suitable for kitchens and nursing care facilities that require cooking.
AB 電解槽
A 隔膜で区切られた電解槽の1部分A槽
B 隔膜で区切られた電解槽の1部分B槽
C 電気制御装置
1、2、3、4 電極
5 隔膜
51 支材
6 アルカリ水出水管
7 次亜塩素酸水等出水管
8 アルカリ水出水管
9、10 電磁弁
111、112 水位センサー配線
121、122 電解液水位センサー
131、132 電解液供給管
141、142 電磁弁
15 電解液タンク
16 振動装置
AB Electrolyzer A A Part of an electrolytic cell separated by a diaphragm A Tank B A part of an electrolytic cell separated by a diaphragm B Tank C
Claims (7)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011063587A JP2012196643A (en) | 2011-03-23 | 2011-03-23 | Apparatus for producing hypochlorous acid water or the like |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011063587A JP2012196643A (en) | 2011-03-23 | 2011-03-23 | Apparatus for producing hypochlorous acid water or the like |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2012196643A true JP2012196643A (en) | 2012-10-18 |
Family
ID=47179412
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011063587A Pending JP2012196643A (en) | 2011-03-23 | 2011-03-23 | Apparatus for producing hypochlorous acid water or the like |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2012196643A (en) |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20140209454A1 (en) * | 2013-01-28 | 2014-07-31 | Yoshihisa ISHII | Deodorization and sterilization apparatus |
| KR101579044B1 (en) * | 2015-09-10 | 2015-12-21 | 주식회사 동일그린시스 | Apparatus for Generating Electrolyzed Water |
| CN113355683A (en) * | 2021-05-21 | 2021-09-07 | 珠海格力电器股份有限公司 | Solution electrolysis circuit, control method thereof and solution electrolysis system |
| JP2021188065A (en) * | 2020-05-26 | 2021-12-13 | 株式会社日本トリム | Electrolytic water generating device and hypochlorous acid water generating method |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH06165985A (en) * | 1992-11-30 | 1994-06-14 | Nippon Intetsuku Kk | Ionized water forming device |
| JPH06246266A (en) * | 1993-02-22 | 1994-09-06 | Nippon Intetsuku Kk | Device for producing electrolyte |
| JPH0985250A (en) * | 1995-09-22 | 1997-03-31 | Hoshizaki Electric Co Ltd | Electrolytic water preparation device |
| JPH09122649A (en) * | 1995-11-01 | 1997-05-13 | Hoshizaki Electric Co Ltd | Method and apparatus for producing electrolytic water |
| JP2003088865A (en) * | 2001-09-18 | 2003-03-25 | Sanyo Electric Co Ltd | Water treatment apparatus |
-
2011
- 2011-03-23 JP JP2011063587A patent/JP2012196643A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH06165985A (en) * | 1992-11-30 | 1994-06-14 | Nippon Intetsuku Kk | Ionized water forming device |
| JPH06246266A (en) * | 1993-02-22 | 1994-09-06 | Nippon Intetsuku Kk | Device for producing electrolyte |
| JPH0985250A (en) * | 1995-09-22 | 1997-03-31 | Hoshizaki Electric Co Ltd | Electrolytic water preparation device |
| JPH09122649A (en) * | 1995-11-01 | 1997-05-13 | Hoshizaki Electric Co Ltd | Method and apparatus for producing electrolytic water |
| JP2003088865A (en) * | 2001-09-18 | 2003-03-25 | Sanyo Electric Co Ltd | Water treatment apparatus |
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20140209454A1 (en) * | 2013-01-28 | 2014-07-31 | Yoshihisa ISHII | Deodorization and sterilization apparatus |
| JP2014144031A (en) * | 2013-01-28 | 2014-08-14 | Yoshihisa Ishii | Deodorant sterilization device |
| US9222180B2 (en) * | 2013-01-28 | 2015-12-29 | Yoshihisa ISHII | Deodorization and sterilization apparatus |
| TWI582360B (en) * | 2013-01-28 | 2017-05-11 | 石井義久 | Deodorization and sterilization apparatus |
| KR101579044B1 (en) * | 2015-09-10 | 2015-12-21 | 주식회사 동일그린시스 | Apparatus for Generating Electrolyzed Water |
| JP2021188065A (en) * | 2020-05-26 | 2021-12-13 | 株式会社日本トリム | Electrolytic water generating device and hypochlorous acid water generating method |
| JP7280854B2 (en) | 2020-05-26 | 2023-05-24 | 株式会社日本トリム | Electrolyzed water generator and hypochlorous acid water generation method |
| CN113355683A (en) * | 2021-05-21 | 2021-09-07 | 珠海格力电器股份有限公司 | Solution electrolysis circuit, control method thereof and solution electrolysis system |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5688103B2 (en) | Electrolyzed water production method and apparatus | |
| TWI608129B (en) | Electrolysis device and electrolytic ozone water production device | |
| JP5716100B2 (en) | Electrolysis apparatus and electrolysis method | |
| JP4090665B2 (en) | Electrolyzed water production method | |
| JP2003024943A (en) | Water treatment apparatus | |
| JP5597855B2 (en) | Apparatus and method for preparing toilet flush water | |
| JP6268383B2 (en) | ELECTROLYTIC WATER GENERATION DEVICE AND METHOD FOR OPERATING THE SAME | |
| JP2014046227A (en) | Electrolyzed water generating apparatus and electrolyzed water generating method | |
| US20200140295A1 (en) | Electrochemical cell | |
| JP2012196643A (en) | Apparatus for producing hypochlorous acid water or the like | |
| JP2003024941A (en) | Method and apparatus for generating hypochlorous acid | |
| JP4597263B1 (en) | Electrolyzed water production apparatus and electrolyzed water production method using the same | |
| JP5244038B2 (en) | Electrolyzed water mixing device | |
| JP2005177671A (en) | Electrolysis type ozonizer | |
| KR20170104893A (en) | Chlorine water electrolysis apparatus capable of regulating chloride dosage and temperature | |
| JP6831570B2 (en) | Electrolyzed water generator | |
| JP2003034889A (en) | Method for electrolysis in device for generating strong- electrolyzed water | |
| JP6675112B2 (en) | Electrolysis raw water storage type electrolyzer | |
| WO2022014127A1 (en) | Electrolyzed water generation device | |
| JPH09206755A (en) | Formation of alkaline ionized and hypochlorous acid sterilizing water and device therefor | |
| JP2004223497A (en) | Method for cleaning electrode of running water type apparatus for forming strongly acidic water | |
| JP6896259B1 (en) | Sterilization wash water production equipment and sterilization wash water production method | |
| KR20070075624A (en) | Electrolytic water generation apparatus | |
| JP2005152867A (en) | Electrolytic water manufacturing means | |
| JP2005081345A (en) | Electrolytic cell comprising two or more electrolytic chambers |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20140130 |
|
| RD03 | Notification of appointment of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7423 Effective date: 20140130 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20141111 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20150421 |