JP2011049598A - Semiconductor device, and method of manufacturing the same - Google Patents
Semiconductor device, and method of manufacturing the same Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2011049598A JP2011049598A JP2010267184A JP2010267184A JP2011049598A JP 2011049598 A JP2011049598 A JP 2011049598A JP 2010267184 A JP2010267184 A JP 2010267184A JP 2010267184 A JP2010267184 A JP 2010267184A JP 2011049598 A JP2011049598 A JP 2011049598A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- dummy patterns
- length
- dummy
- pattern
- semiconductor device
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 77
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 17
- 239000011229 interlayer Substances 0.000 claims description 69
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 claims description 59
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 39
- 230000000149 penetrating effect Effects 0.000 claims description 8
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 claims 4
- 238000005530 etching Methods 0.000 description 19
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 16
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 16
- 229910021420 polycrystalline silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 11
- 229920005591 polysilicon Polymers 0.000 description 11
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 9
- 238000000206 photolithography Methods 0.000 description 8
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 7
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 7
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 7
- BOTDANWDWHJENH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tetraethyl orthosilicate Chemical compound CCO[Si](OCC)(OCC)OCC BOTDANWDWHJENH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 239000005380 borophosphosilicate glass Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000005498 polishing Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000007547 defect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 229910016570 AlCu Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- ATJFFYVFTNAWJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tin Chemical compound [Sn] ATJFFYVFTNAWJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000004888 barrier function Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000002950 deficient Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000002955 isolation Methods 0.000 description 2
- WNUPENMBHHEARK-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon tungsten Chemical compound [Si].[W] WNUPENMBHHEARK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012938 design process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000006866 deterioration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000035515 penetration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Semiconductor Memories (AREA)
- Internal Circuitry In Semiconductor Integrated Circuit Devices (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、半導体装置及びその製造方法に係り、特に、配線層の段差を抑制するうえで好適な構造を有する半導体装置及びその製造方法に関する。 The present invention relates to a semiconductor device and a manufacturing method thereof, and more particularly, to a semiconductor device having a structure suitable for suppressing a step of a wiring layer and a manufacturing method thereof.
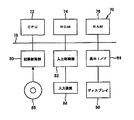
図8は、従来の半導体装置10の断面図を示す。半導体装置10は、ロジック回路とDRAM(Dynamic Random Access Memory)とを同一基板上に備える混載デバイスである。半導体装置10は、シリコン基板12を備えている。シリコン基板12には、シャロートレンチプロセスで形成された分離酸化膜14が埋め込まれている。
FIG. 8 shows a cross-sectional view of a conventional semiconductor device 10. The semiconductor device 10 is a mixed device including a logic circuit and a DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory) on the same substrate. The semiconductor device 10 includes a
シリコン基板12の上部には、ロジック回路の構成要素であるゲート電極16やサイドウォール18、並びにDRAMの構成要素であるトランスファゲート(TG)20やサイドウォール22が形成されている。ゲート電極16やTG20の上層には、BPSGで構成された第1の層間膜24が形成されている。第1の層間膜24には、DRAMの活性領域と導通する複数のコンタクトプラグ26が設けられている。
Formed on the
コンタクトプラグ26は、以下の手順で形成される。すなわち、コンタクトプラグ26の形成工程では、先ず、第1の層間膜24にDRAMの活性領域に開口するコンタクトホール28が形成される。次に、そのコンタクトホール28の内部が充填されるようにドープトポリシリコンが堆積される。最後に、第1の層間膜24の上面とコンタクトプラグ26の端面とが平坦となるようにCMP(Chemical Mechanical Polishing)が行われる。
The
第1の層間膜24の上層には、TEOSで構成された第2の層間膜30が形成されている。半導体装置10は、第2の層間膜30を貫通して一部のコンタクトプラグ26に導通するビットライン32と、第1および第2の層間膜24,30を貫通してロジック回路の活性領域と導通する金属配線34とを備えている。ビットライン32および金属配線34は以下の手順で形成される。すなわち、それらの形成工程では、先ず、第2の層間膜24を貫通するコンタクトホール36と、第1および第2の層間膜24,30を貫通するコンタクトホール38とが形成される。次に、それらのコンタクトホール36,38の内部が充填されるように、第2の層間膜30の全面にタングステンシリサイド(WSi)が堆積される。最後に、写真製版とエッチングとによりそのWSiが所望の形状にパターニングされる。
On the upper layer of the
第2の層間膜30の上層には、TEOSで構成された第3の層間膜40が形成されている。半導体装置10は、第2および第3の層間膜30、40を貫通して一部のコンタクトプラグ26と導通するストレージノードコンタクトプラグ(SCプラグ)42を備えている。SCプラグ42は以下の手順で形成される。すなわち、SCプラグの形成工程では、先ず、第2および第3の層間膜30,40を貫通するコンタクトホール44が形成される。次に、そのコンタクトホール44の内部が充填されるようにドープトポリシリコンが堆積される。最後に、第3の層間膜40の上面とSCプラグ42の端面とが平坦となるようにCMPが行われる。
A third interlayer film 40 made of TEOS is formed on the
第3の層間膜40の上層には、BPSGで構成された第4の層間膜46が形成されている。第4の層間膜46にはSCプラグ42に通じる開口部48が設けられている。開口部48の内壁およびSCプラグ42の表面は、絶縁膜50により覆われている。絶縁膜50で囲まれる空間の内部、および第4の層間膜46の上部には、ドープトポリシリコンで構成されたセルプレート52が形成されている。セルプレート52は以下の手順で形成される。すなわち、セルプレート52の形成工程では、先ず、第4の層間膜46を貫通する開口部48が形成される。次に、その開口部48の内部が充填されるように、第4の層間膜46の全面にドープトポリシリコンが堆積される。最後に、写真製版とエッチングとによりそのドープトポリシリコンが所望の形状にパターニングされる。
A
半導体装置10のような混載デバイスにおいて、セルプレート52はDRAMの領域にのみ形成される。このため、セルプレート52が形成されると、DRAMの領域とロジック回路の領域とに、セルプレート52の膜厚に起因する段差が発生する。
In a hybrid device such as the semiconductor device 10, the
第4の層間膜46の上層には、セルプレート52が覆われるように第5の層間膜54が形成される。半導体装置10は、セルプレート52や金属配線34と導通する複数の金属配線56を備えている。金属配線56の形成工程では、先ず、第5の層間膜54や第4の層間膜46に開口部が設けられる。次に、それらの開口部が充填されるように、第5の層間膜54の全面にバリアメタル(TiN:15nmなど)および配線部材(AlCu:150nmなど)が成膜される。最後に、写真製版とエッチングとによりそれらの積層膜が所望の形状にパターニングされる。以後、必要に応じて上記のような処理が繰り返されることにより多層の配線構造が形成される。
A
半導体装置10のような混載デバイスには、上述したセルプレート52のように、DRAMおよびロジック回路の一方にのみ形成されるパターンが存在する。このため、そのようなパターンの上層では、DRAMの領域とロジック回路の領域とに段差が生ずる。このような段差が発生すると、写真製版におけるマージンが小さくなり、コンタクトホールの開口不良や配線パターンの精度劣化などが生じ易くなる。また、段差を減らすためにCMPを行うと、被研磨面の凹凸の影響で、研磨のされ方が不均一となるという不都合が生ずる。
A mixed device such as the semiconductor device 10 has a pattern formed only in one of the DRAM and the logic circuit, like the
本発明は、上記のような課題を解決するためになされたもので、配線層の平坦性を保つためのダミーパターンを有する半導体装置及びその製造方法を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made to solve the above-described problems, and it is an object of the present invention to provide a semiconductor device having a dummy pattern for maintaining the flatness of a wiring layer and a method for manufacturing the same.
本願の発明に係る半導体装置は、多層配線構造を有する半導体装置であって、半導体装置の機能を実現するうえで必要な機能パターンと、半導体装置の所定の層に、該機能パターンと共に形成される複数のダミーパターンとを備え、該複数のダミーパターンは、第一の大きさの複数のダミーパターンと、該第一の大きさよりも小さい第二の大きさの複数のダミーパターンとで構成され、該第一の大きさの複数のダミーパターンが規則的に配置され、該第一の大きさの複数のダミーパターンが規則的に配置されない領域に、該第二の大きさの複数のダミーパターンが規則的に配置され、該第一の大きさの複数のダミーパターンと該機能パターンとの間に該第二の大きさの複数のダミーパターンが配置され、第一所定方向に配置された該第一の大きさの複数のダミーパターンそれぞれと、第二所定方向に配置された該第二の大きさの複数のダミーパターンそれぞれとは隣り合うように配置され、該第一の大きさのダミーパターン間の幅は、該第二の大きさのダミーパターン間の幅よりも大きいことを特徴とする。 The semiconductor device according to the invention of the present application is a semiconductor device having a multilayer wiring structure, and is formed with a functional pattern necessary for realizing the function of the semiconductor device and a predetermined layer of the semiconductor device together with the functional pattern. A plurality of dummy patterns, the plurality of dummy patterns is composed of a plurality of dummy patterns of a first size and a plurality of dummy patterns of a second size smaller than the first size, The plurality of dummy patterns of the first size are regularly arranged, and the plurality of dummy patterns of the second size are in areas where the plurality of dummy patterns of the first size are not regularly arranged. The plurality of dummy patterns arranged in a regular manner, the plurality of dummy patterns of the second size arranged between the plurality of dummy patterns of the first size and the functional pattern, and arranged in a first predetermined direction. One big Each of the plurality of dummy patterns arranged adjacent to each of the plurality of dummy patterns of the second size arranged in the second predetermined direction, and the width between the dummy patterns of the first size. Is larger than the width between the dummy patterns of the second size.
本発明によれば、多層配線構造に含まれる各層が、機能パターンと複数種類のダミーパターンとによって、高い充填率で占有されている。従って、本発明によれば、各層が優れた平坦性を有する半導体装置を実現することができる。 According to the present invention, each layer included in the multilayer wiring structure is occupied with a high filling rate by the functional pattern and the plurality of types of dummy patterns. Therefore, according to the present invention, a semiconductor device in which each layer has excellent flatness can be realized.
以下、図面を参照してこの発明の実施の形態について説明する。尚、各図において共通する要素には、同一の符号を付して重複する説明を省略する。 Embodiments of the present invention will be described below with reference to the drawings. In addition, the same code | symbol is attached | subjected to the element which is common in each figure, and the overlapping description is abbreviate | omitted.
実施の形態1.
図1は、本発明の実施の形態1の半導体装置60の断面図を示す。半導体装置60は、ロジック回路とDRAM(Dynamic Random Access Memory)とを同一基板上に備える混載デバイスである。半導体装置60は、シリコン基板12を備えている。シリコン基板12には、シャロートレンチプロセスで形成された分離酸化膜14が埋め込まれている。
Embodiment 1 FIG.
FIG. 1 is a sectional view of a
シリコン基板12の上部には、ロジック回路の構成要素であるゲート電極16やサイドウォール18、並びにDRAMの構成要素であるTG20やサイドウォール22が形成されている。ゲート電極16やTG20の上層には、BPSGで構成された第1の層間膜24が形成されている。第1の層間膜24には、DRAMの活性領域と導通する複数のコンタクトプラグ26が設けられている。
On the upper part of the
コンタクトプラグ26は、以下の手順で形成される。すなわち、コンタクトプラグ26の形成工程では、先ず、第1の層間膜24にDRAMの活性領域に開口するコンタクトホール28が形成される。次に、そのコンタクトホール28の内部が充填されるようにドープトポリシリコンが堆積される。最後に、第1の層間膜24の上面とコンタクトプラグ26の端面とが平坦となるようにCMPが行われる。
The
第1の層間膜24の上層には、TEOSで構成された第2の層間膜30が形成されている。半導体装置60は、第2の層間膜30を貫通して一部のコンタクトプラグ26に導通するビットライン32と、第1および第2の層間膜24,30を貫通してロジック回路の活性領域と導通する金属配線34とを備えている。ビットライン32および金属配線34は以下の手順で形成される。すなわち、それらの形成工程では、先ず、第2の層間膜24を貫通するコンタクトホール36と、第1および第2の層間膜24,30を貫通するコンタクトホール38とが形成される。次に、それらのコンタクトホール36,38の内部が充填されるように、第2の層間膜30の全面にタングステンシリサイド(WSi)が堆積される。最後に、写真製版とエッチングとによりそのWSiが所望の形状にパターニングされる。
On the upper layer of the
第2の層間膜30の上層には、TEOSで構成された第3の層間膜40が形成されている。半導体装置60は、第2および第3の層間膜30を貫通して一部のコンタクトプラグ26と導通するSCプラグ42を備えている。SCプラグ42は以下の手順で形成される。すなわち、SCプラグの形成工程では、先ず、第2および第3の層間膜30,40を貫通するコンタクトホール44が形成される。次に、そのコンタクトホール44の内部が充填されるようにドープトポリシリコンが堆積される。最後に、第3の層間膜40の上面とSCプラグ42の端面とが平坦となるようにCMPが行われる。
A third interlayer film 40 made of TEOS is formed on the
第3の層間膜40の上層には、BPSGで構成された第4の層間膜46が形成されている。第4の層間膜46にはSCプラグ42に通じる開口部48が設けられている。開口部48の内壁およびSCプラグ42の表面は、絶縁膜50により覆われている。絶縁膜50で囲まれる空間の内部、および第4の層間膜46の上部には、ドープトポリシリコンで構成されたセルプレート52が形成されている。
A
また、本実施形態において、第4の層間膜46の上層には、セルプレート52と同じ材質(すなわち、ドープトポリシリコン)で構成されたダミーパターン62が形成されている。ダミーパターン62は、半導体装置10が備える他の配線部材の何れとも干渉しないようにロジック回路の領域に設けられている。尚、本明細書において、「ダミーパターン」とは、半導体装置60の本質的な機能を確保する上では不必要なパターンを指す。これに対して、半導体装置60の機能上必要な全てのパターン(ビットライン32や金属配線34、並びにサイドウォール18,22等を含む)を、以下「機能パターン」と称す。
In the present embodiment, a dummy pattern 62 made of the same material as the cell plate 52 (ie, doped polysilicon) is formed on the
セルプレート52、およびダミーパターン62は以下の手順で形成される。すなわち、それらの形成工程では、先ず、第4の層間膜46を貫通する開口部48が形成される。次に、その開口部48の内部が充填されるように、第4の層間膜46の全面にドープトポリシリコンが堆積される。最後に、写真製版とエッチングとによりそのドープトポリシリコンが、予め設計された形状に、すなわち、セルプレート52の形状とダミーパターンの形状とにパターニングされる。
The
半導体装置60のような混載デバイスにおいて、セルプレート52はDRAMの領域にのみ形成される。このため、ダミーパターン62が存在しない場合は、セルプレート52が形成されることにより、DRAMの領域とロジック回路の領域とに段差が発生する。これに対して、本実施形態のようにロジック回路の領域にダミーパターン64を設けることとすると、DRAMの領域とロジック回路の領域とに上記の段差が生ずるのを有効に防止することができる。
In a hybrid device such as the
第4の層間膜46の上層には、セルプレート52およびダミーパターン62が覆われるように第5の層間膜54が形成される。第5の層間膜54の表面は、CMPにより平坦化される。本実施形態では、第5の層間膜54の下層が上記の如く平坦化されている。このため、第5の層間膜54を平坦化するためのCMPの研磨特性は、その全面においてほぼ均一となる。その結果、第5の層間膜54の表面には、ダミーパターン62が形成されない場合に比して顕著に良好な平坦性が確保される。
A
半導体装置60は、セルプレート52や金属配線34と導通する複数の金属配線56を備えている。金属配線56の形成工程では、先ず、第5の層間膜54や第4の層間膜46に開口部が設けられる。次に、それらの開口部が充填されるように、第5の層間膜54の全面にバリアメタル(TiN:15nmなど)および配線部材(AlCu:150nmなど)が成膜される。最後に、写真製版とエッチングとによりそれらの積層膜が所望の形状にパターニングされる。
The
以後、必要に応じて上記のような処理が繰り返されることにより多層の配線構造が形成される。ところで、図1では、セルプレート52を含む配線層にのみダミーパターン62を発生させることとしているが、ダミーパターンはこの配線層にのみ含まれるものではない。すなわち、半導体装置60は、機能パターンの影響で平坦性の悪化する全ての配線層に、その平坦性を向上させるためのダミーパターンを有している。
Thereafter, the above processing is repeated as necessary to form a multilayer wiring structure. In FIG. 1, the dummy pattern 62 is generated only in the wiring layer including the
次に、図2乃至図6を参照して、本実施形態の半導体装置60に含まれるダミーパターン(ダミーパターン62を含む)の特徴やその設計方法、並びにそれらのダミーパターンを自動的に設計するパターン設計装置について説明する。
Next, referring to FIG. 2 to FIG. 6, the features of dummy patterns (including dummy patterns 62) included in the
図2は、本実施形態のパターン設計装置70のブロック図を示す。パターン設計装置70は、一般的なコンピュータシステムのハードウェア構成を利用して実現することができる。すなわち、パターン設計装置70は、CPU72、ROM74、およびRAM76を備えている。それらの構成要素はバスライン78を介して互いに接続されている。バスライン78には、更に、記録制御部80、入力制御部82、および表示インターフェース(表示I/F)84などが接続されている。
FIG. 2 is a block diagram of the
記録制御部80は、ハードディスクやCD−ROMなどの記録媒体86からデータを読み出したり、或いはそれらの記録媒体86へデータを書き込んだりする装置である。入力制御部82は、キーボードやマウスなどの入力装置88からの入力信号をバスライン78に出力する装置である。また、表示I/F84は、ディスプレイ90に表示する画像の生成などを行うインターフェースである。
The recording control unit 80 is a device that reads data from a
パターン設計装置70において、CPU72は、記録媒体86からRAM76にロードされたプログラムやデータを用いて後述する処理を実行することにより、ダミーパターン等の設計を行う。以下、パターン設計装置70が、ダミーパターンを含むパターンを設計する手順について説明する。
In the
図3は、パターン設計装置70においてダミーパターンを発生させるために実行される第1のルーチンのフローチャートを示す。図3に示すルーチンは、各配線層に含まれる機能パターンの設計が終了した後に実行される。図1に示す半導体装置60の設計過程では、例えば、第4の層間膜46上に形成すべきセルプレート52の設計が終了した後に、図3に示すルーチンが実行される。
FIG. 3 shows a flowchart of a first routine executed for generating a dummy pattern in the
ステップ100では、処理の対象とされている層に含まれる空き領域(機能パターンによって占有されていない領域)の中から、ダミーパターンを配置する領域として抽出すべきスペースの大きさが設定される。以下、このようなスペースを「探索スペース」と称す。本ステップでは、例えば、「一辺が10μmの正方形領域」のように探索スペースの大きさが設定される。
In
ステップ102では、上記の如く設定された探索スペースのサイズに対応するダミーパターンの大きさが設定される。本ステップでは、例えば、一辺10μmの探索スペースに対して「一辺7μmの正方形領域」がダミーパターンの大きさとして設定される。
In
ステップ104では、処理の対象である配線層に含まれる空き領域の中から、上記ステップ100で設定された探索スペースを抽出する処理が実行される。ステップ106では、抽出された探索スペースの中に、上記ステップ102で設定されたダミーパターンを発生させる処理が行われる。
In
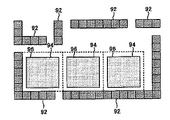
図4は、上述した一連の処理により設計された配線パターンの一例を示す。図4において、符号92を付して表すパターンは半導体装置60の機能パターンである。また、符号94を付して表す領域は、一辺が10μmの空き領域である。更に、符号96を付して表すパターンは、上記ステップ106の処理により設定されたダミーパターンである。図4に示すように、本実施形態のパターン設計方法によれば、配線層の空き領域に、サイズと形状の等しい複数のダミーパターン96を規則正しく配置することができる。
FIG. 4 shows an example of a wiring pattern designed by the series of processes described above. In FIG. 4, a pattern denoted by
ステップ108では、ダミーパターンの発生終了条件が成立しているか否かが判別される。本実施形態では、例えば、上記ステップ106で生成されたダミーパターンの大きさが、所定の大きさ以下である場合、或いは処理の対象である配線層におけるパターンの充填率(機能パターンおよびダミーパターンが、配線層の中に占める割合)が所定値以上である場合に、ダミーパターンの発生終了条件が成立していると判断される。上記の判別の結果、未だ終了条件が成立していないと判別された場合は、再び上記ステップ100以降の処理が実行される。一方、終了条件が既に成立していると判別された場合は、今回の処理サイクルが終了される。
In
上記ステップ100の処理が再び実行される場合は、探索スペースのサイズが、前回の処理サイクル時に設定されたサイズに比して小さなサイズに変更される。例えば、1回目の処理サイクル時に「一辺が10μmの正方形領域」と設定された探索スペースは、2回目の処理サイクル時には「一辺が4μmの正方形領域」に変更される。
When the process in
上記ステップ102の処理が再び実行される場合は、ダミーパターンのサイズも変更される。例えば、1回目の処理サイクル時に「一辺が7μmの正方形領域」と設定されたダミーパターンは、2回目の処理サイクル時には、一辺が4μmの探索スペースに合わせて「一辺が3μmの正方形領域」に変更される。
When the process of
図5は、探索スペースおよびダミーパターンが上記の如く設定された後にステップ104および106が実行されることにより設計された配線パターンの一例を示す。図5において、符号97を付して表す領域は、一辺が4μmの空き領域である。また、符号98を付して表すパターンは、一辺が3μmのダミーパターンである。図5に示すように、上述した方法によれば、ダミーパターン96を配置することのできなかった空き領域に、サイズと形状の等しい複数のダミーパターン98を規則正しく配置することができる。
FIG. 5 shows an example of a wiring pattern designed by executing
大きなダミーパターン96が配置できない空き領域に、小さなダミーパターン98を配置することによれば、配線層におけるパターンの充填率をより一層高めることができる。パターンの充填率を高めると、機能パターンの分布に関わらず、配線層の全面におけるパターン密度を均一化することができる。更に、本実施形態の方法では、大きさおよび形状の等しい複数のダミーパターンを規則正しく配置することでパターン充填率の向上が図られている。
By disposing the
配線層の上に形成される層間膜をCMPで研磨する際に、CMPのパターン依存性が現れるのを防止するうえでは、配線層のパターン充填率が高く、また、パターンの分布が配線層の全面において均一であることが望ましい。本実施形態の方法によれば、複数種類のダミーパターンを規則正しく配置することで、それらの要求を有効に満たすことができる。従って、本実施形態の方法によれば、ダミーパターンが形成されない場合や、ダミーパターンが単一のルールに従って設計されるに過ぎない場合に比べて、多層配線構造に含まれる個々の層に優れた平坦性を与えることができる。 When polishing the interlayer film formed on the wiring layer by CMP, the pattern filling rate of the wiring layer is high in order to prevent the CMP pattern dependence from appearing, and the pattern distribution is It is desirable to be uniform over the entire surface. According to the method of the present embodiment, by arranging a plurality of types of dummy patterns regularly, those requirements can be satisfied effectively. Therefore, according to the method of the present embodiment, each layer included in the multilayer wiring structure is superior to the case where the dummy pattern is not formed or the case where the dummy pattern is only designed according to a single rule. Flatness can be given.
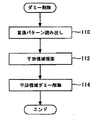
図6は、パターン設計装置70においてダミーパターンの一部を削除するために実行されるルーチンのフローチャートを示す。図6に示すルーチンは、各配線層に含まれるダミーパターンの設計が終了した後に実行される。より具体的には、処理対象の配線層について上記図3に示すルーチンが終了した後に実行される。
FIG. 6 shows a flowchart of a routine executed in the
ステップ110では、処理対象の配線層を貫通するパターンが読み出される。本ステップでは、例えば、図1に示す金属配線56などのパターンが読み出される。以下、上記の処理で読み出されたパターンを「貫通パターン」と称す。
In
ステップ112では、設計されたダミーパターンのうち、貫通パターンと干渉する可能性のある領域(以下、「干渉領域」と称す)が探索される。尚、本実施形態では、貫通パターンの大きさに、写真製版のずれなどを考慮したプロセスマージンを加えた領域が干渉領域とされる。
In
ステップ114では、設計済みのダミーパターンから干渉領域を削除する処理が行われる。上記の処理が実行されることにより、図1に示すダミーパターン62のように、金属配線56などの配線部材と干渉することのないダミーパターンが設計される。上述した一連の処理が終了すると、今回の処理サイクルが終了される。
In
上述の如く、本実施形態のパターン設計装置70によれば、個々の配線層に、他の配線部材と干渉せず、かつ、CMPのパターン依存性を防止する上で有効なダミーパターンを設計することができる。このようなダミーパターンを用いることによれば、半導体装置60の機能に影響を与えることなく、各配線層を精度良く形成することが可能となる。このため、本実施形態によれば、安定した品質を有し、かつ、高い歩留まりで製造し得る半導体装置60を実現することができる。
As described above, according to the
実施の形態2.
次に、図7を参照して、本発明の実施の形態2のパターン設計装置について説明する。本実施形態のパターン設計装置は、上記図2に示す構成を有する装置に、図7に示すルーチンを実行させることにより実現することができる。
Embodiment 2. FIG.
Next, a pattern design apparatus according to the second embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIG. The pattern design apparatus of the present embodiment can be realized by causing the apparatus having the configuration shown in FIG. 2 to execute the routine shown in FIG.
半導体装置が十分に微細化されている場合は、写真製版の際に用いられるマスクの開口率に応じて、エッチングのプロセスウィンドウ、すなわち、適正な加工精度を得ることのできるエッチング条件の範囲が変化する。表1は、上記図1に示すコンタクトホール28を開口するためのエッチングに対するプロセスウィンドウを示す。表1において、「OK」の表示はエッチング残渣を生ずることなくコンタクトホールを適正に開口し得ることを表す。表1に示す結果は、マスクの開口率が小さくなるほどコンタクトホールの開口不良が生じ易くなること、および、エッチングチャンバーの使用時間が長くなるほどコンタクトホールの開口不良が発生し易くなることを表している。
When the semiconductor device is sufficiently miniaturized, the etching process window, that is, the range of etching conditions that can obtain appropriate processing accuracy, changes according to the aperture ratio of the mask used during photolithography. To do. Table 1 shows a process window for etching to open the
半導体装置60のような混載デバイスについては、製品毎に専用の生産ラインが敷設されることは希である。換言すると、半導体装置60のような混載デバイスは、生産効率上の観点より、一般に汎用の生産ライン、すなわち、複数の製品を生産するためのラインで生産される。
For mixed devices such as the
混載デバイスの中でロジック回路やDRAMが占める割合は、製品の仕様等に応じて大きく変化する。更に、ロジック回路やDRAMに含まれる機能パターンが、個々の配線層の中に占める割合も、製品の仕様等に応じて大きく変化する。このため、混載デバイスの機能パターンを転写するためのマスクの開口率は、製品の仕様に応じて大きく変化する。 The ratio of the logic circuit and DRAM in the embedded device varies greatly depending on the product specifications and the like. Furthermore, the ratio of the functional pattern included in the logic circuit or DRAM to the individual wiring layers also varies greatly depending on the product specifications and the like. For this reason, the aperture ratio of the mask for transferring the functional pattern of the embedded device varies greatly depending on the product specifications.
汎用の生産ラインでは、プロセスウィンドウが重複しない複数の配線層がエッチングの対象となることがある。この場合、エッチングの条件が常に一定であると、一部の配線層についてはエッチングの条件がプロセスウィンドウ外となり、その配線層の機能パターンに不良が生じ易くなる。このような機能パターンの不良は、例えば、各配線層について用いられるマスクの開口率に応じてエッチングの条件を変えることにより防止することができる。しかしながら、上記の手法によると、エッチング条件の変更が要求される度に条件確認が必要となり、混載デバイスの生産性が悪化する。 In a general-purpose production line, a plurality of wiring layers having process windows that do not overlap may be subject to etching. In this case, if the etching conditions are always constant, the etching conditions for some of the wiring layers are outside the process window, and the functional pattern of the wiring layers is likely to be defective. Such a defective functional pattern can be prevented, for example, by changing the etching conditions in accordance with the aperture ratio of the mask used for each wiring layer. However, according to the above method, it is necessary to check the condition every time a change in the etching condition is required, and the productivity of the embedded device deteriorates.
混載デバイスの機能パターンを転写するためのマスクの開口率は、機能パターンに加えてダミーパターンを設けることにより高めることができる。従って、個々の配線層に適宜ダミーパターンを設けることによれば、複数の配線層についてのマスク開口率を合わせて、汎用の生産ラインで処理すべき全ての製品に対するエッチングのプロセスウィンドウを整合させることができる。全ての製品に対するプロセスウィンドウが整合していると、エッチングの条件を常に一定に維持しつつ、全ての製品の機能パターンを適正にエッチングすることが可能となる。従って、このような手法によれば、複数の混載デバイスを単一の汎用ラインで効率的に生産することが可能となる。 The aperture ratio of the mask for transferring the functional pattern of the mixed device can be increased by providing a dummy pattern in addition to the functional pattern. Therefore, by appropriately providing dummy patterns in individual wiring layers, the mask opening ratios for a plurality of wiring layers are matched, and the etching process window for all products to be processed in a general-purpose production line is matched. Can do. When the process windows for all products are matched, it is possible to properly etch the functional patterns of all products while keeping the etching conditions constant. Therefore, according to such a method, it is possible to efficiently produce a plurality of mixed devices on a single general-purpose line.
図7は、本実施形態のパターン設計装置が上記の手法で配線パターンを設計するために実行するルーチンのフローチャートを示す。図7に示すルーチンは、パターンの形成がエッチングにより行われる配線層の全てについて、その配線層の機能パターンが設計された後に実行される。 FIG. 7 shows a flowchart of a routine executed by the pattern design apparatus of the present embodiment to design a wiring pattern by the above method. The routine shown in FIG. 7 is executed after the functional pattern of the wiring layer is designed for all the wiring layers in which the pattern is formed by etching.
ステップ116では、目標のマスク開口率が設定される。目標開口率は、同じ汎用ラインで処理される全ての配線層について共通に用いられる値である。
In
ステップ118では、処理の対象である配線層に含まれる空き領域の中から、ダミーパターンを発生させるべき空き領域が探索される。 In step 118, a vacant area where a dummy pattern is to be generated is searched from vacant areas included in the wiring layer to be processed.
ステップ120では、空き領域に発生させるダミーパターンの大きさや配置が設定される。本ステップでは、処理の対象である配線層に含まれる機能パターンの大きさおよび配置が、ダミーパターンの大きさや配置として設定される。より具体的には、例えば、空き領域がロジック回路の領域に見出されている場合は、DRAM領域上の機能パターンの大きさや配置がダミーパターンの大きさや配置として設定される。
In
ダミーパターンの大きさや配置を上記の如く設定すると、同じ配線層に含まれる全てのパターンの大きさや配置を統一することができる。また、機能パターンについては、信頼性などの確認が行われるため、ダミーパターンを上記の如く機能パターンに倣って設計すると、間接的にダミーパターンの信頼性などを保証することが可能である。 When the size and arrangement of the dummy patterns are set as described above, the sizes and arrangements of all patterns included in the same wiring layer can be unified. Further, since the reliability and the like of the function pattern is confirmed, if the dummy pattern is designed following the function pattern as described above, it is possible to indirectly guarantee the reliability of the dummy pattern.
ステップ122では、探索された空きスペースの中に、上記の如く設定されたダミーパターンを発生させる処理が行われる。上記の処理が終了すると、今回の処理サイクルが終了される。
In
上記の処理によれば、配線層の空き領域に、その層に含まれている機能パターンと同様のダミーパターンを発生させることができる。機能パターンだけではマスク開口率が低い場合(例えば、表1における8%以下のような場合)でも、上記の手法でダミーパターンを発生させれば、マスク開口率を十分に大きな値とすることができる。従って、本実施形態のパターン設計方法によれば、複数の製品に含まれる全ての配線層のプロセスウィンドウを重複させて、混合デバイスの生産性を高めることができる。 According to the above processing, a dummy pattern similar to the functional pattern included in the layer can be generated in the empty area of the wiring layer. Even when the functional pattern alone has a low mask aperture ratio (for example, 8% or less in Table 1), if the dummy pattern is generated by the above method, the mask aperture ratio can be set to a sufficiently large value. it can. Therefore, according to the pattern design method of this embodiment, the process windows of all the wiring layers included in a plurality of products can be overlapped to increase the productivity of the mixed device.
ところで、実施の形態2においては、空き領域に、ダミーパターンを1種類だけ形成することとしているが、本発明はこれに限定されるものではなく、実施の形態1の手法で、複数種類のダミーパターンを設けることとしても良い。複数種類のダミーパターンを設けることとすると、配線パターンの充填率を高めることができ、マスクの開口率を高めると共に、配線層の平坦性を向上させることが可能となる。 In the second embodiment, only one type of dummy pattern is formed in the empty area. However, the present invention is not limited to this, and a plurality of types of dummy patterns can be obtained using the method of the first embodiment. A pattern may be provided. When a plurality of types of dummy patterns are provided, the filling rate of the wiring pattern can be increased, the mask aperture ratio can be increased, and the flatness of the wiring layer can be improved.
また、上述した実施の形態1および2では、混載デバイスにDRAMとロジック回路とが搭載されることとしているが、本発明はこれに限定されるものではなく、混載デバイスには、DRAMに代えて、またはDRAMと共に、SRAMを搭載してもよい。 In the first and second embodiments described above, the DRAM and the logic circuit are mounted on the embedded device. However, the present invention is not limited to this, and the embedded device is replaced with the DRAM. Alternatively, an SRAM may be mounted together with the DRAM.
12 シリコン基板、 16 ゲート電極、 18,22 サイドウォール、 20 トランスファゲート、 24 第1の層間膜、 26 コンタクトプラグ、 30 第2の層間膜、 32 ビットライン、 34,56 金属配線、 40 第3の層間膜、 46 第4の層間膜、 50絶縁膜、 52 セルプレート、 54 第5の層間膜、 60 半導体装置、 62,96,98 ダミーパターン、 70 パターン設計装置、92 機能パターン、 94,97 空き領域。 12 silicon substrate, 16 gate electrode, 18, 22 sidewall, 20 transfer gate, 24 first interlayer film, 26 contact plug, 30 second interlayer film, 32 bit line, 34,56 metal wiring, 40 third Interlayer film, 46 4th interlayer film, 50 insulating film, 52 cell plate, 54 5th interlayer film, 60 semiconductor device, 62, 96, 98 dummy pattern, 70 pattern design device, 92 function pattern, 94, 97 empty region.
Claims (24)
半導体装置の機能を実現するうえで必要な機能パターンと、
半導体装置の所定の層に、前記機能パターンと共に形成される複数のダミーパターンとを備え、
前記複数のダミーパターンは、第一の大きさの複数のダミーパターンと、前記第一の大きさよりも小さい第二の大きさの複数のダミーパターンとで構成され、
前記第一の大きさの複数のダミーパターンが規則的に配置され、
前記第一の大きさの複数のダミーパターンが規則的に配置されない領域に、前記第二の大きさの複数のダミーパターンが規則的に配置され、
前記第一の大きさの複数のダミーパターンと前記機能パターンとの間に前記第二の大きさの複数のダミーパターンが配置され、
第一所定方向に配置された前記第一の大きさの複数のダミーパターンそれぞれと、第二所定方向に配置された前記第二の大きさの複数のダミーパターンそれぞれとは隣り合うように配置され、
前記第一の大きさのダミーパターン間の幅は、前記第二の大きさのダミーパターン間の幅よりも大きいことを特徴とする半導体装置。 A semiconductor device having a multilayer wiring structure,
Functional patterns necessary for realizing the functions of semiconductor devices,
A plurality of dummy patterns formed together with the functional pattern in a predetermined layer of the semiconductor device,
The plurality of dummy patterns includes a plurality of dummy patterns having a first size and a plurality of dummy patterns having a second size smaller than the first size,
The plurality of dummy patterns of the first size are regularly arranged,
In the region where the plurality of dummy patterns of the first size are not regularly arranged, the plurality of dummy patterns of the second size are regularly arranged,
A plurality of dummy patterns of the second size are arranged between the plurality of dummy patterns of the first size and the functional pattern;
Each of the plurality of dummy patterns of the first size arranged in the first predetermined direction and each of the plurality of dummy patterns of the second size arranged in the second predetermined direction are arranged adjacent to each other. ,
2. A semiconductor device according to claim 1, wherein a width between the first-size dummy patterns is larger than a width between the second-size dummy patterns.
前記ダミーパターンは、前記配線部材と干渉しないように形成されていることを特徴とする請求項1記載の半導体装置。 The functional pattern includes a wiring member penetrating at least one wiring layer,
2. The semiconductor device according to claim 1, wherein the dummy pattern is formed so as not to interfere with the wiring member.
ロジック回路の構成要素となる機能パターンが形成されるロジック回路領域とを備え、
前記ロジック回路領域に形成される前記ダミーパターンは、そのダミーパターンと同じ層に形成されるメモリ回路用の機能パターンと同じパターンを含むことを特徴とする請求項2記載の半導体装置。 A memory area in which a functional pattern as a component of the memory device is formed;
A logic circuit area in which a functional pattern as a component of the logic circuit is formed,
3. The semiconductor device according to claim 2, wherein the dummy pattern formed in the logic circuit region includes the same pattern as a functional pattern for a memory circuit formed in the same layer as the dummy pattern.
前記第二の大きさのダミーパターンは、第三の方向の一辺が第三の長さで、前記第三の方向と異なる第四の方向の一辺が第四の長さの四角形であり、
前記第一の長さは前記第三の長さよりも長く、前記第二の長さは前記第四の長さよりも長いことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の半導体装置。 The dummy pattern of the first size is a quadrangle whose one side in the first direction has a first length and whose one side in the second direction different from the first direction has a second length,
The dummy pattern of the second size is a quadrangle whose one side in the third direction is a third length and whose one side in the fourth direction different from the third direction is a fourth length,
The semiconductor device according to claim 1, wherein the first length is longer than the third length, and the second length is longer than the fourth length.
前記第一の大きさの複数のダミーパターンそれぞれの形状は等しく、前記第二の大きさの複数のダミーパターンそれぞれの形状は等しいことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の半導体装置。 The predetermined layer is a layer formed on an interlayer insulating film covering the gate electrode,
2. The semiconductor device according to claim 1, wherein each of the plurality of dummy patterns having the first size has the same shape, and each of the plurality of dummy patterns having the second size has the same shape.
前記第一所定方向に配置された前記第一の大きさの複数のダミーパターンそれぞれは前記複数の機能パターンの一部と隣接するように配置され、
前記第二所定方向に配置された前記第二の大きさの複数のダミーパターンそれぞれは前記複数の機能パターンの他の一部と隣接するように配置されることを特徴とする請求項6に記載の半導体装置。 There are a plurality of the functional patterns,
Each of the plurality of dummy patterns of the first size arranged in the first predetermined direction is arranged adjacent to a part of the plurality of functional patterns,
The plurality of dummy patterns of the second size arranged in the second predetermined direction are arranged so as to be adjacent to other parts of the plurality of functional patterns. Semiconductor device.
半導体装置の機能を実現するうえで必要な機能パターンと、
半導体装置の所定の層に、前記機能パターンと共に形成される複数のダミーパターンとを備え、
前記複数のダミーパターンは、第一の面積の複数のダミーパターンと、前記第一の面積よりも小さい第二の面積の複数のダミーパターンとで構成され、
前記第一の面積の複数のダミーパターンが規則的に第一の領域に配置され、
前記第二の面積の複数のダミーパターンが規則的に第二の領域に配置され、
前記機能パターンと前記第一の領域の間に前記第二の領域が設けられ、
前記第一の領域内の前記第一の面積の複数のダミーパターンそれぞれと、前記第二の領域内の前記第二の面積の複数のダミーパターンそれぞれとは隣接するように配置され、
前記第一の面積のダミーパターン間の距離は、前記第二の面積のダミーパターン間の距離よりも大きいことを特徴とする半導体装置。 A semiconductor device having a multilayer wiring structure,
Functional patterns necessary for realizing the functions of semiconductor devices,
A plurality of dummy patterns formed together with the functional pattern in a predetermined layer of the semiconductor device,
The plurality of dummy patterns includes a plurality of dummy patterns having a first area and a plurality of dummy patterns having a second area smaller than the first area.
The plurality of dummy patterns of the first area are regularly arranged in the first region,
The plurality of dummy patterns of the second area are regularly arranged in the second region,
The second region is provided between the functional pattern and the first region;
Each of the plurality of dummy patterns of the first area in the first region and each of the plurality of dummy patterns of the second area in the second region are arranged adjacent to each other,
The distance between the dummy patterns of the first area is larger than the distance between the dummy patterns of the second area.
前記第二の面積のダミーパターンは、第三の方向の一辺が第三の長さで、前記第三の方向と異なる第四の方向の一辺が第四の長さの四角形であり、
前記第一の長さは前記第三の長さよりも長く、前記第二の長さは前記第四の長さよりも長いことを特徴とする請求項8に記載の半導体装置。 The dummy pattern of the first area is a quadrangle whose one side in the first direction is the first length and whose one side in the second direction different from the first direction is the second length,
The dummy pattern of the second area is a quadrangle whose one side in the third direction is a third length, and whose one side in the fourth direction different from the third direction is a fourth length,
9. The semiconductor device according to claim 8, wherein the first length is longer than the third length, and the second length is longer than the fourth length.
前記第一の面積の複数のダミーパターンそれぞれの形状は等しく、前記第二の面積の複数のダミーパターンそれぞれの形状は等しいことを特徴とする請求項8に記載の半導体装置。 The predetermined layer is a layer formed on an interlayer insulating film covering the gate electrode,
9. The semiconductor device according to claim 8, wherein each of the plurality of dummy patterns having the first area has the same shape, and each of the plurality of dummy patterns having the second area has the same shape.
前記第一の領域内の前記第一の面積の複数のダミーパターンそれぞれは前記複数の機能パターンの一部と隣接するように配置され、
前記第二の領域内の前記第二の面積の複数のダミーパターンそれぞれは前記複数の機能パターンの他の一部と隣接するように配置されることを特徴とする請求項8に記載の半導体装置。 There are a plurality of the functional patterns,
Each of the plurality of dummy patterns of the first area in the first region is disposed adjacent to a part of the plurality of functional patterns,
9. The semiconductor device according to claim 8, wherein each of the plurality of dummy patterns of the second area in the second region is disposed adjacent to another part of the plurality of functional patterns. .
半導体装置の機能を実現するうえで必要な機能パターンと、
半導体装置の所定の層に、前記機能パターンと共に形成される複数のダミーパターンとを備え、
平面視で見た際に前記複数のダミーパターンは、それぞれが第一の大きさの領域を有する複数の第一ダミーパターンと、それぞれが前記第一の大きさよりも小さい第二の大きさの領域を有する複数の第二ダミーパターンとで構成され、
前記複数の第一ダミーパターンが規則的に配置され、
前記複数の第一ダミーパターンが規則的に配置されない領域に、前記複数の第二ダミーパターンが規則的に配置され、
前記複数の第一ダミーパターンと前記機能パターンとの間に前記複数の第二ダミーパターンが配置され、
第一所定方向に配置された前記複数の第一ダミーパターンそれぞれと、第二所定方向に配置された前記複数の第二ダミーパターンそれぞれとは隣り合うように配置され、
前記第一ダミーパターン間の距離は、前記第二ダミーパターン間の距離よりも大きいことを特徴とする半導体装置。 A semiconductor device having a multilayer wiring structure,
Functional patterns necessary for realizing the functions of semiconductor devices,
A plurality of dummy patterns formed together with the functional pattern in a predetermined layer of the semiconductor device,
When viewed in plan, the plurality of dummy patterns include a plurality of first dummy patterns each having a first size region, and a second size region that is smaller than the first size. A plurality of second dummy patterns having
The plurality of first dummy patterns are regularly arranged,
In a region where the plurality of first dummy patterns are not regularly arranged, the plurality of second dummy patterns are regularly arranged,
The plurality of second dummy patterns are disposed between the plurality of first dummy patterns and the functional pattern,
Each of the plurality of first dummy patterns arranged in the first predetermined direction and each of the plurality of second dummy patterns arranged in the second predetermined direction are arranged adjacent to each other,
The distance between said 1st dummy patterns is larger than the distance between said 2nd dummy patterns, The semiconductor device characterized by the above-mentioned.
前記第二ダミーパターンは、第三の方向の一辺が第三の長さで、前記第三の方向と異なる第四の方向の一辺が第四の長さの四角形であり、
前記第一の長さは前記第三の長さよりも長く、前記第二の長さは前記第四の長さよりも長いことを特徴とする請求項13に記載の半導体装置。 In the first dummy pattern, one side in a first direction is a first length, and one side in a second direction different from the first direction is a quadrangle having a second length,
The second dummy pattern is a quadrangle whose one side in the third direction is a third length and whose one side in the fourth direction different from the third direction is a fourth length;
14. The semiconductor device according to claim 13, wherein the first length is longer than the third length, and the second length is longer than the fourth length.
前記第一ダミーパターンそれぞれの形状は等しく、前記第二ダミーパターンそれぞれの形状は等しいことを特徴とする請求項13に記載の半導体装置。 The predetermined layer is a layer formed on an interlayer insulating film covering the gate electrode,
14. The semiconductor device according to claim 13, wherein the first dummy patterns have the same shape, and the second dummy patterns have the same shape.
前記第一所定方向に配置された前記複数の第一ダミーパターンそれぞれは前記複数の機能パターンの一部と隣接するように配置され、
前記第二所定方向に配置された前記複数の第二ダミーパターンそれぞれは前記複数の機能パターンの他の一部と隣接するように配置されることを特徴とする請求項13に記載の半導体装置。 There are a plurality of the functional patterns,
Each of the plurality of first dummy patterns arranged in the first predetermined direction is arranged to be adjacent to a part of the plurality of functional patterns,
The semiconductor device according to claim 13, wherein each of the plurality of second dummy patterns arranged in the second predetermined direction is arranged adjacent to another part of the plurality of functional patterns.
前記複数のトランジスタが形成された層上に、半導体装置の機能を実現するのに必要な機能パターンと、複数のダミーパターンとを形成する工程とを有する半導体装置の製造方法であって、
前記複数のダミーパターンは、第一の面積の複数のダミーパターンと、前記第一の面積よりも小さい第二の面積の複数のダミーパターンとで構成され、
前記第一の面積の複数のダミーパターンが規則的に配置され、
前記第一の面積の複数のダミーパターンが規則的に配置されない領域に、前記第二の面積の複数のダミーパターンが規則的に配置され、
前記第一の面積の複数のダミーパターン間の距離は、前記第二の面積の複数のダミーパターン間の距離よりも大きく、
前記第一の面積の複数のダミーパターンと前記機能パターンとの間に前記第二の面積の複数のダミーパターンが配置され、
第一所定方向に配置された前記第一の面積の複数のダミーパターンそれぞれと、第二所定方向に配置された前記第二の面積の複数のダミーパターンそれぞれとは隣り合うように配置されていることを特徴とする半導体装置の製造方法。 Forming a plurality of transistors;
A method of manufacturing a semiconductor device, comprising: forming a functional pattern necessary for realizing a function of the semiconductor device on the layer where the plurality of transistors are formed; and a plurality of dummy patterns.
The plurality of dummy patterns includes a plurality of dummy patterns having a first area and a plurality of dummy patterns having a second area smaller than the first area.
A plurality of dummy patterns of the first area are regularly arranged,
In the region where the plurality of dummy patterns of the first area are not regularly arranged, the plurality of dummy patterns of the second area are regularly arranged,
The distance between the plurality of dummy patterns of the first area is greater than the distance between the plurality of dummy patterns of the second area,
A plurality of dummy patterns of the second area are arranged between the plurality of dummy patterns of the first area and the functional pattern;
Each of the plurality of dummy patterns having the first area arranged in the first predetermined direction and each of the plurality of dummy patterns having the second area arranged in the second predetermined direction are arranged adjacent to each other. A method for manufacturing a semiconductor device.
前記ダミーパターンは、前記配線部材と干渉しないように形成されていることを特徴とする請求項18記載の半導体装置の製造方法。 The functional pattern includes a wiring member penetrating at least one wiring layer,
19. The method of manufacturing a semiconductor device according to claim 18, wherein the dummy pattern is formed so as not to interfere with the wiring member.
前記ロジック回路領域に形成される前記ダミーパターンは、そのダミーパターンと同じ層に形成されるメモリ回路用の機能パターンと同じパターンを含むことを特徴とする請求項18記載の半導体装置の製造方法。 A memory region in which a functional pattern serving as a component of the memory device is formed; and a logic circuit region in which a functional pattern serving as a component of the logic circuit is formed,
19. The method of manufacturing a semiconductor device according to claim 18, wherein the dummy pattern formed in the logic circuit region includes the same pattern as a functional pattern for a memory circuit formed in the same layer as the dummy pattern.
前記第二の面積のダミーパターンは、第三の方向の一辺が第三の長さで、前記第三の方向と異なる第四の方向の一辺が第四の長さの四角形であり、
前記第一の長さは前記第三の長さよりも長く、前記第二の長さは前記第四の長さよりも長いことを特徴とする請求項18に記載の半導体装置の製造方法。 The dummy pattern of the first area is a quadrangle whose one side in the first direction is the first length and whose one side in the second direction different from the first direction is the second length,
The dummy pattern of the second area is a quadrangle whose one side in the third direction is a third length, and whose one side in the fourth direction different from the third direction is a fourth length,
19. The method of manufacturing a semiconductor device according to claim 18, wherein the first length is longer than the third length, and the second length is longer than the fourth length.
前記第一所定方向に配置された前記第一の面積の複数のダミーパターンそれぞれは前記複数の機能パターンの一部と隣接するように配置され、
前記第二所定方向に配置された前記第二の面積の複数のダミーパターンそれぞれは前記複数の機能パターンの他の一部と隣接するように配置されることを特徴とする請求項23に記載の半導体装置。 A plurality of the functional patterns exist,
Each of the plurality of dummy patterns of the first area arranged in the first predetermined direction is arranged adjacent to a part of the plurality of functional patterns,
24. Each of the plurality of dummy patterns having the second area arranged in the second predetermined direction is arranged adjacent to another part of the plurality of functional patterns. Semiconductor device.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010267184A JP2011049598A (en) | 2010-11-30 | 2010-11-30 | Semiconductor device, and method of manufacturing the same |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010267184A JP2011049598A (en) | 2010-11-30 | 2010-11-30 | Semiconductor device, and method of manufacturing the same |
Related Parent Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP33843799A Division JP4703807B2 (en) | 1999-11-29 | 1999-11-29 | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2011049598A true JP2011049598A (en) | 2011-03-10 |
| JP2011049598A5 JP2011049598A5 (en) | 2011-04-21 |
Family
ID=43835550
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010267184A Pending JP2011049598A (en) | 2010-11-30 | 2010-11-30 | Semiconductor device, and method of manufacturing the same |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2011049598A (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN111259613A (en) * | 2018-11-14 | 2020-06-09 | 华邦电子股份有限公司 | Electronic device and layout method of integrated circuit |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0661230A (en) * | 1992-05-28 | 1994-03-04 | Nec Corp | Semiconductor integrated circuit device |
| JPH08306771A (en) * | 1995-04-27 | 1996-11-22 | Yamaha Corp | Semiconductor device and its fabrication |
| JP2000114258A (en) * | 1998-09-29 | 2000-04-21 | Toshiba Corp | Semiconductor device |
| JP4703807B2 (en) * | 1999-11-29 | 2011-06-15 | ルネサスエレクトロニクス株式会社 | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof |
-
2010
- 2010-11-30 JP JP2010267184A patent/JP2011049598A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0661230A (en) * | 1992-05-28 | 1994-03-04 | Nec Corp | Semiconductor integrated circuit device |
| JPH08306771A (en) * | 1995-04-27 | 1996-11-22 | Yamaha Corp | Semiconductor device and its fabrication |
| JP2000114258A (en) * | 1998-09-29 | 2000-04-21 | Toshiba Corp | Semiconductor device |
| JP4703807B2 (en) * | 1999-11-29 | 2011-06-15 | ルネサスエレクトロニクス株式会社 | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN111259613A (en) * | 2018-11-14 | 2020-06-09 | 华邦电子股份有限公司 | Electronic device and layout method of integrated circuit |
| CN111259613B (en) * | 2018-11-14 | 2023-08-15 | 华邦电子股份有限公司 | Electronic device and layout method of integrated circuit |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN110223982B (en) | Dynamic random access memory and manufacturing method thereof | |
| KR101186038B1 (en) | Method of fabricating semiconductor device | |
| US20050272256A1 (en) | Semiconductor device and fabricating method thereof | |
| US9601588B2 (en) | Method for fabricating semiconductor device | |
| US8716777B2 (en) | Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same | |
| TWI553780B (en) | Contact structure and semiconductor memory device using the same | |
| JP2006216649A (en) | Semiconductor device and its manufacturing method | |
| TWI455250B (en) | Low parasitic capacitance contact and gate structure and process for dynamic random access memory | |
| US11610611B2 (en) | Dynamic random access memory and method for manufacturing the dram having a bottom surface of a bit line contact structure higher than a top surface of a dielectric layer formed on a buried word line | |
| TWI447857B (en) | Fabricating method of dram structrue | |
| TW201947707A (en) | Memory devices and methods of fabricating the same | |
| JP4703807B2 (en) | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof | |
| KR100950553B1 (en) | Method for forming contact in semiconductor device | |
| US20150214234A1 (en) | Semiconductor device and method for fabricating the same | |
| US8148250B2 (en) | Method for manufacturing semiconductor device for preventing occurrence of short circuit between bit line contact plug and storage node contact plug | |
| TW201322255A (en) | Structure of dynamic random access memory and fabrication method thereof | |
| US11830567B2 (en) | Integrated circuit device | |
| JP2011049598A (en) | Semiconductor device, and method of manufacturing the same | |
| US9059194B2 (en) | High-K and metal filled trench-type EDRAM capacitor with electrode depth and dimension control | |
| JP2014175647A (en) | Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same | |
| US20240284664A1 (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| US9349813B2 (en) | Method for fabricating semiconductor device | |
| US8030203B2 (en) | Method of forming metal line of semiconductor device | |
| JP2013187398A (en) | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method of the same | |
| KR101076813B1 (en) | Semiconductor Device and Method for Manufacturing the same |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20101130 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20110217 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20130117 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20130122 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20130903 |