JP2010016013A - Method for mounting semiconductor device, semiconductor element module, and electronic information apparatus - Google Patents
Method for mounting semiconductor device, semiconductor element module, and electronic information apparatus Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2010016013A JP2010016013A JP2008171815A JP2008171815A JP2010016013A JP 2010016013 A JP2010016013 A JP 2010016013A JP 2008171815 A JP2008171815 A JP 2008171815A JP 2008171815 A JP2008171815 A JP 2008171815A JP 2010016013 A JP2010016013 A JP 2010016013A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- semiconductor device
- ball
- substrate
- semiconductor element
- semiconductor
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 223
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 59
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 155
- 229910000679 solder Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 104
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 86
- 238000003384 imaging method Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 80
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 46
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 46
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 claims description 71
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 claims description 71
- 229920001187 thermosetting polymer Polymers 0.000 claims description 37
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 claims description 19
- 235000011837 pasties Nutrition 0.000 claims description 14
- 238000007747 plating Methods 0.000 claims description 14
- 239000007769 metal material Substances 0.000 claims description 9
- 230000008646 thermal stress Effects 0.000 claims description 9
- 238000005476 soldering Methods 0.000 claims description 4
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000002844 melting Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000008018 melting Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000005452 bending Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000017525 heat dissipation Effects 0.000 abstract description 6
- 230000002950 deficient Effects 0.000 abstract 1
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 description 42
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 description 42
- 239000002245 particle Substances 0.000 description 27
- 239000000945 filler Substances 0.000 description 26
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 16
- 230000007547 defect Effects 0.000 description 10
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 description 9
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 9
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 8
- 239000004593 Epoxy Substances 0.000 description 6
- 239000003822 epoxy resin Substances 0.000 description 5
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 5
- 239000004973 liquid crystal related substance Substances 0.000 description 5
- 229920000647 polyepoxide Polymers 0.000 description 5
- 238000012937 correction Methods 0.000 description 4
- 229920006375 polyphtalamide Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 238000007639 printing Methods 0.000 description 4
- 229910045601 alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000000956 alloy Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000012766 organic filler Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000035882 stress Effects 0.000 description 3
- 229920001169 thermoplastic Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 239000004416 thermosoftening plastic Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000004954 Polyphthalamide Substances 0.000 description 2
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000000919 ceramic Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000006866 deterioration Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000011888 foil Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000011810 insulating material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910000881 Cu alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910001030 Iron–nickel alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910004298 SiO 2 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- BQCADISMDOOEFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silver Chemical compound [Ag] BQCADISMDOOEFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ATJFFYVFTNAWJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tin Chemical compound [Sn] ATJFFYVFTNAWJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000013144 data compression Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007667 floating Methods 0.000 description 1
- LNEPOXFFQSENCJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N haloperidol Chemical compound C1CC(O)(C=2C=CC(Cl)=CC=2)CCN1CCCC(=O)C1=CC=C(F)C=C1 LNEPOXFFQSENCJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000005355 lead glass Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000088 plastic resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000003825 pressing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000191 radiation effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002040 relaxant effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 235000012239 silicon dioxide Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000000377 silicon dioxide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052709 silver Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000004332 silver Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000007779 soft material Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/10—Bump connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/15—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/16—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process of an individual bump connector
- H01L2224/161—Disposition
- H01L2224/16151—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/16221—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/16225—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/26—Layer connectors, e.g. plate connectors, solder or adhesive layers; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/31—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/32—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors after the connecting process of an individual layer connector
- H01L2224/321—Disposition
- H01L2224/32151—Disposition the layer connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/32221—Disposition the layer connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/32225—Disposition the layer connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/73—Means for bonding being of different types provided for in two or more of groups H01L2224/10, H01L2224/18, H01L2224/26, H01L2224/34, H01L2224/42, H01L2224/50, H01L2224/63, H01L2224/71
- H01L2224/732—Location after the connecting process
- H01L2224/73201—Location after the connecting process on the same surface
- H01L2224/73203—Bump and layer connectors
- H01L2224/73204—Bump and layer connectors the bump connector being embedded into the layer connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/91—Methods for connecting semiconductor or solid state bodies including different methods provided for in two or more of groups H01L2224/80 - H01L2224/90
- H01L2224/92—Specific sequence of method steps
- H01L2224/921—Connecting a surface with connectors of different types
- H01L2224/9212—Sequential connecting processes
- H01L2224/92122—Sequential connecting processes the first connecting process involving a bump connector
- H01L2224/92125—Sequential connecting processes the first connecting process involving a bump connector the second connecting process involving a layer connector
Landscapes
- Solid State Image Pick-Up Elements (AREA)
- Transforming Light Signals Into Electric Signals (AREA)
- Wire Bonding (AREA)
- Die Bonding (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、基板上に半導体素子を有する半導体デバイスを実装する半導体デバイスの実装方法、この半導体デバイスの実装方法により実装され、被写体からの画像光を光電変換して撮像する複数の受光部を有する半導体素子としての撮像素子または、出射光を発生させるための半導体素子としての発光素子および入射光を受光するための半導体素子としての受光素子がモジュール化された半導体素子モジュール、この半導体素子モジュールとしての固体撮像モジュールを画像入力デバイスとして撮像部に用いた例えばデジタルビデオカメラおよびデジタルスチルカメラなどのデジタルカメラや、画像入力カメラ、スキャナ装置、ファクシミリ装置、カメラ付き携帯電話装置や、この半導体素子モジュールを情報記録再生部に用いたピックアップ装置などの電子情報機器に関する。 The present invention includes a semiconductor device mounting method for mounting a semiconductor device having a semiconductor element on a substrate, and a plurality of light receiving units that are mounted by the semiconductor device mounting method and that photoelectrically convert image light from a subject to image it. A semiconductor element module in which an imaging element as a semiconductor element or a light emitting element as a semiconductor element for generating emitted light and a light receiving element as a semiconductor element for receiving incident light are modularized, and as this semiconductor element module Information on digital cameras such as digital video cameras and digital still cameras, image input cameras, scanner devices, facsimile devices, camera-equipped mobile phone devices, and semiconductor element modules that use solid-state imaging modules as image input devices in the imaging unit Pickup used in the recording / playback unit Apparatus and an electronic information device, such as a.
この種の従来の半導体素子モジュールとしての固体撮像モジュールは、主に、カメラモジュールとして、カメラ付き携帯電話装置や携帯端末装置(PDA)、さらにはカードカメラなどに用いられ、セラミックスやガラス入りエポキシ樹脂などのマウント基板上に、被写体からの画像光をそれぞれ光電変換して被写体を撮像する複数の受光部を有する半導体素子としての固体撮像素子を有する半導体デバイスとしての固体撮像チップと、入射光を撮像素子上に結像するための集光レンズを固定したホルダー部材とが設けられている。この場合に、固体撮像チップの各端子はマウント基板の配線パターン上に配設されて半田付けされ、互いに電気的に接続されている。また、これらの集光レンズと撮像素子との間の結像距離を正確に平行に固定して入射光を撮像素子上に精度よく結像させることは、鮮明な画像を得るために重要である。 Solid-state imaging modules as conventional semiconductor element modules of this type are mainly used as camera modules in mobile phone devices with cameras, personal digital assistants (PDAs), card cameras, etc., and ceramic and glass-filled epoxy resins A solid-state imaging chip as a semiconductor device having a solid-state imaging element as a semiconductor element having a plurality of light-receiving portions that photoelectrically convert image light from the subject and image the subject on a mounting substrate, and the like, and imaging incident light And a holder member to which a condenser lens for imaging on the element is fixed. In this case, each terminal of the solid-state imaging chip is disposed on the wiring pattern of the mount substrate, soldered, and electrically connected to each other. In addition, it is important to obtain a clear image by accurately fixing the imaging distance between these condenser lenses and the image sensor in parallel and forming the incident light on the image sensor with high accuracy. .
このマウント基板上に、半導体デバイスとしてのセンサデバイスをマウント基板上に実装する場合について図12および図13を参照しながら説明する。 A case where a sensor device as a semiconductor device is mounted on the mount substrate will be described with reference to FIGS.
図12(a)〜図12(d)は、従来の固体撮像素子を有するセンサデバイスの実装方法について説明するための各工程を模式的に示す斜視図である。図13(a)〜図13(d)は、図12(a)〜図12(d)にそれぞれ対応した各工程の縦断面図である。 12 (a) to 12 (d) are perspective views schematically showing respective steps for explaining a mounting method of a sensor device having a conventional solid-state imaging device. FIG. 13A to FIG. 13D are longitudinal sectional views of respective steps corresponding to FIG. 12A to FIG. 12D, respectively.
従来のセンサデバイスの実装方法は、図12(a)および図13(a)に示すように、まず、配線パターン150aが表面側に形成されたマウント基板150を実装装置の所定位置にセットする。
In the conventional sensor device mounting method, as shown in FIGS. 12A and 13A, first, the
次に、配線150aの半田付け箇所に対応したランド位置に穴がパターニングされた樹脂製または金属製の薄板状のマスク(図示せず)を、マウント基板150上に重ねて置き、そのマスクの上からペイスト状半田材料を塗布する。その後、マスクをマウント基板150上から取り除くと、図12(b)および図13(b)に示すように、配線パターン150aの半田付け箇所に対応したランド位置に、ペイスト状半田材料151が配設される。ここでは、各ペイスト状半田材料151は、左右3本づつの配線150aの中央側の端部上に6箇所配置される。また、マスクの板厚は、0.5mm程度である。
Next, a resin or metal thin plate mask (not shown) having holes patterned at land positions corresponding to the soldered portions of the
さらに、図12(c)および図13(c)に示すように、ロボットアームにより、表面側中央部分に固体撮像素子152が搭載されたセンサデバイス153を、センサデバイス153の裏面側の各端子153aと各ペイスト状半田材料151とをそれぞれ位置合せをしてマウント基板150上に載置する。センサデバイス153がペイスト状半田材料151上に載置されると、ペイスト状半田材料151はペイスト状であるため、センサデバイス153の自重で、ある程度沈み込む。
Further, as shown in FIG. 12C and FIG. 13C, the
その後、マウント基板150、各ペイスト状半田材料151および、固体撮像素子152が搭載されたセンサデバイス153に摂氏230度の温度をかけて、図12(d)および図13(d)に示すように各ペイスト状半田材料151を溶かして、センサデバイス153の裏面側の各金属端子153aと、配線パターン150aの中央側の各ランド部とをそれぞれ、各ペイスト状半田材料151による半田接合部151bにより電気的に接合する。
Thereafter, a temperature of 230 degrees Celsius is applied to the
次に、別の従来の固体撮像モジュールの事例として、接着剤の充填材として、例えば1辺が2〜8μm(0.002〜0.008mm)の矩形画素よりも小さい微細なフィラーを用いたものが特許文献1に開示されている。 Next, as an example of another conventional solid-state imaging module, a fine filler smaller than a rectangular pixel having a side of 2 to 8 μm (0.002 to 0.008 mm), for example, is used as an adhesive filler. Is disclosed in Patent Document 1.
図14は、特許文献1に開示されている従来の撮像装置の要部構成例を示す縦断面図である。 FIG. 14 is a longitudinal sectional view showing an example of the configuration of the main part of a conventional imaging device disclosed in Patent Document 1. As shown in FIG.
図14において、特許文献1に開示されている従来の撮像装置100は、光軸Lに沿って配置された非球面レンズ103、光学フィルタ104および半導体撮像素子105と、これらを保持する立体基板102と、立体基板102に接続されるプリント基板(FPC)110とを有している。なお、立体基板102の開口部を取り囲む部分108は、ガラス強化PPA(ポリフタルアミド樹脂)などによって構成され、光の透過を防ぐため黒色にしてある。
In FIG. 14, a
立体基板102は、半導体撮像素子105を固定する役割を有すると共に光学フィルタ104を保持する保持部材としての役割を兼ね備えている。立体基板102は、筒形の鏡筒部102aと、鏡筒部102aの一端面に連続する底部102bとからなっている。
The three-
光学フィルタ104は、鉛ガラスからなる基材の片面にIR(InfraRed)カットコートが施され、他面に反射防止のAR(Anti Reflection)コートが施されている。
The
光学フィルタ104を立体基板102に接着するための接着剤106について説明する。立体基板102には、ガラス強化PPA(ポリフタルアミド樹脂)が用いられており、その線膨張係数は約40×10−6mm/℃である。一方、光学フィルタ104の線膨張係数は約10×10−6mm/℃である。この両者を適切に固定するため、接着剤106の線膨張係数が立体基板102の線膨張係数と光学フィルタ104の線膨張係数との間の値となるように、接着剤106には図示しないフィラーが含まれている。また、このフィラーは、光学用に適するように二酸化ケイ素(SiO2)からなっている。さらに、接着剤106が硬化した後に異方性を有しないように、フィラーは球形のものを用いることが好ましい。
The
このフィラーの大きさは、その径が半導体撮像素子5の画素サイズより小さく、画素サイズの1/2以上である。以下、この大きさのフィラーを含む接着剤106を用いる理由について説明する。
The size of the filler is smaller than the pixel size of the
フィラーの径についての説明に先立ってフィラーを含む接着剤106に起因する問題点について述べる。接着剤106が硬化する際には、接着剤106の中に含まれるフィラーが飛散したり、特に端面部分においてフィラーの一部がむき出しになったりすることがある。また、光学フィルタ104を立体基板102に取付けた後に、撮像素子105や光学系のレンズ103を取り付けたり、FPC110を実装し、必要によってはフォーカスの調整工程が行われるが、これらの工程におけるハンドリングや衝撃などによって端面部分におけるフィラーが脱落することがある。飛散・脱落したフィラーが撮像素子105の表面に付着して画素からの信号出力を低下させる原因になることが、撮像装置100の分析によって明らかになった。特に最近では、撮像装置100が小型化してきたことに伴って、装置分解のために必要な部分の寸法を確保することが困難となり、分解できない装置が多く見られる。このような撮像装置100では、飛散・脱落したフィラーが撮像素子105の表面に付着した場合、撮像装置100を廃棄せざるを得ない事態も起きていた。
Prior to the description of the diameter of the filler, problems caused by the
この撮像装置100では、フィラーの径が画素サイズ以下の接着剤106を用いて光フィルタ104を接着したので、飛散・脱落したフィラーが半導体撮像素子105の表面に付着してもキズ補正によってフィラーのない状態と同じ画像を得ることができる。
In this
このように、CCDの欠陥などによるキズを補正する機能(キズ補正機能)を用いて、フィラーに起因して生じ得る画像の黒点などを補正することができるので、工程・工法・設備などの変更をする必要がない。すなわち、撮像装置組み立ての作業性を低下させることなく、フィラーによる画質劣化を低減させることができる。 In this way, it is possible to correct black spots or the like of images that can be caused by fillers using a function that corrects defects due to CCD defects (scratch correction function), so changes in processes, construction methods, equipment, etc. There is no need to do. That is, it is possible to reduce image quality deterioration due to the filler without reducing the workability of assembling the imaging device.
特許文献1の場合よりも大きさが大きい平均粒径が10〜80μm(0.01〜0.08mm)のフィラーを接着剤の充填材として用いたものが特許文献2に開示されている。
特許文献2に開示されている従来のダイボンディングペーストにおいて、エポキシ樹脂、このエポキシ樹脂の硬化剤、球形熱可塑性有機フィラーより平均粒径が小さい充填剤および平均粒径が10〜80μm(0.01〜0.08mm)で、その粒度分布が±5μm以下である球形熱可塑性有機フィラーを必須成分とする。また、そのダイボンディングペーストにおいて、熱可塑性有機フィラーが、成分の全合計量に対して0.1〜10重量%の割合で含有されている。
In the conventional die bonding paste disclosed in
更に別の従来の固体撮像モジュールの事例として、接着剤の充填材として、粒状に丸い微細なバンプを用いたものが特許文献3、4にそれぞれ開示されている。
Further, as another example of the conventional solid-state imaging module,
図15は、特許文献3に開示されている従来の撮像装置の要部構成例を示す縦断面図である。
FIG. 15 is a longitudinal sectional view showing an example of the configuration of the main part of a conventional imaging device disclosed in
図15において、特許文献3に開示されている従来の撮像装置200は、内側領域に開口部202が形成された枠状の平面形状を有し絶縁性材料からなる基台201と、基台201の一方の面に付設され開口部202側の領域から基台201の外周端に向かって延在する複数本の配線204と、基台201の配線が付設された面に、開口部202に受光領域205aが面するように搭載された撮像素子205とを備え、各配線における基台201の開口部201側および外周端側の各端部が各々内部端子部204aおよび外部端子部204bを形成し、撮像素子の電極と配線の内部端子部とが電気的に接続されている。配線は金属薄板リードにより形成され、基台201は金属薄板リードを埋め込んだ樹脂成型体により構成され、金属薄板リードは、端面の少なくとも一部が基台201中に埋設されている。なお、透光板206は、基台201の開口部201上を覆うように設けられている。
In FIG. 15, a
撮像素子205における受光領域205aと同一の面に、受光領域205aの回路と接続された電極パッド(図示せず)が配置され、電極パッド上にAuからなるバンプ208が設けられている。各配線204における開口部202に隣接した端部が内部端子部204aを形成しており、内部端子部204aがバンプ208を介して撮像素子205の電極パッドと電気的に接続されている。各配線204における、基台201の外周端部(凹部203の外側の部分)の下面に配置された部分が外部端子部204bを形成し、回路基板上の電極と接続するために用いられる。
An electrode pad (not shown) connected to the circuit of the
図16は、特許文献4に開示されている従来の撮像装置の要部構成例を示す縦断面図である。
FIG. 16 is a longitudinal sectional view showing an example of the configuration of the main part of a conventional imaging device disclosed in
図16において、特許文献4に開示されている従来の撮像装置300の基台301は、絶縁性の材料、例えばエポキシ樹脂などの可塑性樹脂からなり、平面形状が中央部に矩形の開口部302を有する矩形枠状である。基台301の断面形状は、全体として実質的に一様な厚みを有する平板状である。基台301の下面には、開口部302の周縁から基台301の外周端に亘って、金属箔リードからなる複数本の配線303が配置されている。金属箔リードとしては、通常のリードフレームに使用される材料と同様な、例えばCu合金、42アロイ(Fe−Ni42合金)などが用られ、厚さは概ね2〜3μmである。
In FIG. 16, a
基台301における配線303が形成された面に、Si基板に形成されたCCDなどの撮像素子304が固定され、その電極が配線303と接続されている。各配線303における開口部302に隣接した端部が内部端子部303aを形成しており、内部端子部303aがバンプ307を介して撮像素子304の電極パッドと電気的に接続されている。各配線303における、基台301の外周端部の下面に配置された部分が外部端子部303bを形成し、回路基板上の電極と接続するために用いられる。撮像素子304の表面側の中央部分には受光領域304aが設けられ、撮像素子304の表面側の周囲部と内部端子部303aとの間にバンプ307が設けられている。撮像素子304と内部端子部303aとがシール樹脂306により接着されている。なお、透光板305は基台301の開口部302上を覆うように設けられている。
An
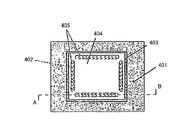
図17は、特許文献5に開示されている従来の半導体装置の要部構成例を示す平面図、図18は、図17のA−B線の縦断面図である。
FIG. 17 is a plan view showing a configuration example of a main part of a conventional semiconductor device disclosed in
図17および図18において、特許文献4に開示されている従来の半導体装置400は、樹脂基板401と、半導体チップ404と、樹脂基板401と半導体チップ404との間に配置されかつ粒子形状の揃った平均粒径が0.01〜0.08mmの粒子402と、樹脂基板401と半導体チップ404とを接着させるためのダイボンドペースト403とから構成されている。
17 and 18, a conventional semiconductor device 400 disclosed in
樹脂基板401における半導体チップ404の搭載領域の外縁部分には溝405が形成されており、この溝405の内部が粒子402によって埋められている。半導体チップ404は平面視した場合、矩形であるため、4本の溝405が樹脂基板401に形成される。効果として粒子形状の揃った粒子402を入れることによりチップの均一高さ制御が可能になる。
A
樹脂基板401に掘り込まれた溝405の深さは粒子402の大きさよりも浅く、溝405の広さは粒子402の直径よりも広く設定されている。このため、溝405に粒子402を入れた場合、樹脂基板401の表面に対して粒子402の一部が突出するようになっている。樹脂基板401上にある粒子402を覆うようにダイボンドペースト403を塗布し、その上に半導体チップ404を押し付けるように配置する。
The depth of the
このとき、粒子402が溝405によって保持され、半導体チップ404と樹脂基板401との間には、粒子402の大きさと溝405の深さとの差分と略同じ分だけの均一高さのギャップが形成されることになる。
上記従来の構成では、被写体を撮像する固体撮像素子152が設けられたセンサデバイス153をマウント基板150上に実装する場合には、マウント基板150上に印刷した配線パターン150aの半田位置にセンサデバイス153の各端子を位置合せして、センサデバイス153をマウントし、熱処理により半田をリフローさせている。ところが、センサデバイス153をマウント基板150上に密着させて実装すると、放熱効果が低減し、暗電流不良が発生するため、センサデバイス153はマウント基板150上から浮かして実装する。一方、半田の量は、配線パターン150aの印刷ばらつきや、配線パターン150aによって差があり、図19に示すように熱処理時に半田接合部151bの高さに差が発生する。この半田接合部151bの高さの差は、マウント基板150の表面に対してセンサデバイス153の表面に傾き(煽り)を発生させてしまい、カメラモジュール本体のレンズ焦点距離がセンサデバイス153の固体撮像素子152におけるの受光面の位置(中央部とその周辺部)により異なることによる画質不良(部分的にピンボケ)を引き起こす。
In the above-described conventional configuration, when the
特許文献1、2のように、接着剤の充填材としての微細なフィラーでは、フィラーが微細過ぎてセンサデバイスの高さ制御をするのに、全く適していないし、センサデバイスをマウント基板上に密着させて実装してしまい、これによって、半田の接着強度と共に放熱効果が低減し、暗電流不良も発生する虞がある。
As in
特許文献3、4では、バンプは均一な球形ではなく、大きさもそれぞれ異なることから、センサデバイスのマウント基板に対する高さ制御材として用いることは難しい。特許文献3、4では、軟らかい材料を用いて、別工程で平行に押さえ付けて高さ制御しているものと考えられるが、それでも、バンプのサイズが異なることから、センサデバイスの表面に平行度を出すことは困難でセンサデバイスが傾く虞がある。
In
特許文献5では、樹脂基板401上に多数の粒子402を介在させて半導体チップ404が配置されており、平面視矩形の半導体チップ404における4辺の内側に沿った溝405内に多数の粒子402を入れて半導体チップ404の高さ制御をしているが、樹脂基板401に形成される溝405の加工深さにばらつきがあると、粒子402の直径のばらつきだけでなく、半導体チップ404の高さ制御に誤差が生じて半導体チップ404の表面が傾く虞がある。この溝405の加工は、深さがばらつきやすく、加工精度が高いレーザ光で溝加工すると、コストの高いレーザ加工機を別途用意する必要が生じる。また、多数の粒子402を溝405内に入れるのに、溝405内に一つ一つ粒子402を入れると工数が多くなるし、樹脂基板401を傾けて一括して粒子402を溝405内に入れる場合には、工数が少なくなるものの、溝405内に入りきれない粒子402は、その傾きによって落ちて樹脂基板401の表面から排除されるが、樹脂基板401の表面に粒子402が残った場合には、溝405の深さだけ高さ制御に差が生じ、樹脂基板401上の半導体チップ404の表面に傾きが生じてしまう。しかも、この場合の樹脂基板401と半導体チップ404との隙間は極めて微小であり、半導体チップ404を樹脂基板401上に密着させて実装してしまい、これによって、半田の接着強度と共に放熱効果が低減し、暗電流不良も発生する虞がある。
In
本発明は、上記従来の問題を解決するもので、半田の接着強度と共に放熱効果を維持しつつ、基板面と撮像素子を水平に保ちながら容易かつ確実に実装できて画質不良を防止することができる半導体デバイスの実装方法、この半導体デバイスを用いた半導体素子モジュール、この半導体素子モジュールを画像入力デバイスとして撮像部に用いた例えばカメラ付き携帯電話装置や、この半導体素子モジュールを情報記録再生部に用いたピックアップ装置などの電子情報機器を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention solves the above-described conventional problems, and can easily and reliably mount the substrate surface and the image sensor while maintaining the heat radiation effect as well as the adhesive strength of the solder, thereby preventing image quality defects. Semiconductor device mounting method that can be used, semiconductor element module using this semiconductor device, mobile phone device with camera using this semiconductor element module as an image input device in an imaging unit, and using this semiconductor element module for an information recording / reproducing unit An object of the present invention is to provide an electronic information device such as a pickup device.
本発明の半導体デバイスの実装方法は、基板上に半導体素子を有する半導体デバイスを実装する半導体デバイスの実装方法において、該基板と該半導体デバイスとの間に、目標間隔保持用のボールを介在させた状態で、該基板の配線パターンのランド部と該半導体デバイスの各端子とを接合部により接合する半導体デバイス実装工程を有するものであり、そのことにより上記目的が達成される。 The semiconductor device mounting method of the present invention is a semiconductor device mounting method in which a semiconductor device having a semiconductor element is mounted on a substrate. A ball for holding a target interval is interposed between the substrate and the semiconductor device. In this state, the semiconductor device mounting step of bonding the land portion of the wiring pattern of the substrate and each terminal of the semiconductor device by the bonding portion, thereby achieving the above object.
また、好ましくは、本発明の半導体デバイスの実装方法における半導体デバイス実装工程は、前記配線パターンの各ランド部上にそれぞれ、各ペイスト状半田材料をそれぞれ配置する半田材料配置工程と、該各ペイスト状半田材料上の一部または全部にそれぞれ、前記ボールを載置するボール載置工程と、前記半導体デバイスを、該半導体デバイスの各端子と該配線パターンの各ランド部とをそれぞれ位置合せして、前記ボール上に載置する半導体デバイス載置工程と、該各ペイスト状半田材料を溶融させて、該半導体デバイスの各端子と該配線パターンの各ランド部とをそれぞれ接合する半導体デバイス接合工程とを有する。 Preferably, the semiconductor device mounting step in the semiconductor device mounting method of the present invention includes a solder material placement step of placing each paste-like solder material on each land portion of the wiring pattern, and each paste-like shape. A ball placing step for placing the ball on part or all of the solder material, and the semiconductor device, each terminal of the semiconductor device and each land portion of the wiring pattern are aligned, A semiconductor device mounting step of mounting on the ball, and a semiconductor device bonding step of melting each paste-like solder material and bonding each terminal of the semiconductor device and each land portion of the wiring pattern, respectively. Have.
さらに、好ましくは、本発明の半導体デバイスの実装方法における半導体デバイス実装工程は、前記基板上の半導体デバイス実装用の所定位置に、各ペイスト状熱硬化樹脂材料を一または複数箇所配置するペイスト状熱硬化樹脂材料配置工程と、該ペイスト状熱硬化樹脂材料上にそれぞれ、前記ボールを載置するボール載置工程と、前記半導体デバイスの各端子と該基板の配線パターンの各ランド部とをそれぞれ位置合せし、該半導体デバイスを該ボール上に載置する半導体デバイス載置工程と、該ペイスト状熱硬化樹脂材料を熱硬化させると共に、該半導体デバイスの各端子と該配線パターンの各ランド部とを半田によりそれぞれ接合する半導体デバイス接合工程とを有する。 Further preferably, in the semiconductor device mounting step of the semiconductor device mounting method of the present invention, the paste-like heat in which one or a plurality of paste-like thermosetting resin materials are arranged at predetermined positions for mounting the semiconductor device on the substrate. Positioning the cured resin material placement step, the ball placement step of placing the ball on the paste-like thermosetting resin material, and the terminals of the semiconductor device and the land portions of the wiring pattern of the substrate, respectively A semiconductor device placement step of placing the semiconductor device on the ball, thermosetting the paste-like thermosetting resin material, and each terminal of the semiconductor device and each land portion of the wiring pattern. And a semiconductor device bonding step in which each is bonded by solder.
さらに、好ましくは、本発明の半導体デバイスの実装方法における半導体デバイス実装用の所定位置は、前記配線パターンの各ランド部以外の位置である。 Further preferably, the predetermined position for mounting the semiconductor device in the semiconductor device mounting method of the present invention is a position other than each land portion of the wiring pattern.
さらに、好ましくは、本発明の半導体デバイスの実装方法におけるボールは、樹脂製球体、該樹脂製球体の表面に金属めっきが施された球体および金属製球体のうちの少なくともいずれかである。 More preferably, the ball in the semiconductor device mounting method of the present invention is at least one of a resin sphere, a sphere having a metal plating applied to the surface of the resin sphere, and a metal sphere.
さらに、好ましくは、本発明の半導体デバイスの実装方法におけるボールが樹脂製球体の表面に金属めっきが施された球体または金属製球体の場合に、該金属めっきの金属材料または該金属製球体の金属材料が前記半田の材料と同じ材料である。 Further preferably, when the ball in the semiconductor device mounting method of the present invention is a sphere or metal sphere in which the surface of the resin sphere is subjected to metal plating, the metal material of the metal plating or the metal of the metal sphere The material is the same material as that of the solder.
さらに、好ましくは、本発明の半導体デバイスの実装方法におけるボールは、前記配線パターンの複数のランド部のうち、最も支持面積が広く取れる4箇所以上のランド部の位置で前記半導体デバイスを支持している。 Further preferably, the ball in the semiconductor device mounting method of the present invention supports the semiconductor device at positions of four or more land portions having the largest support area among the plurality of land portions of the wiring pattern. Yes.
さらに、好ましくは、本発明の半導体デバイスの実装方法における半田の材料はペイスト状半田材料である。 Further preferably, the solder material in the semiconductor device mounting method of the present invention is a paste-like solder material.
さらに、好ましくは、本発明の半導体デバイスの実装方法における半導体デバイス実装工程の後に、前記基板と前記半導体デバイスとの間の隙間内に充填樹脂を注入する充填樹脂注入工程をさらに有する。 Preferably, the method further includes a filling resin injection step of injecting a filling resin into the gap between the substrate and the semiconductor device after the semiconductor device mounting step in the semiconductor device mounting method of the present invention.
さらに、好ましくは、本発明の半導体デバイスの実装方法におけるボールの直径は、前記半田材料または前記ペイスト状熱硬化樹脂材料の厚さよりも大きく設定されている。 Further preferably, the diameter of the ball in the semiconductor device mounting method of the present invention is set to be larger than the thickness of the solder material or the paste-like thermosetting resin material.
さらに、好ましくは、本発明の半導体デバイスの実装方法におけるボールの直径は0.2〜0.8mmである。 Further, preferably, the diameter of the ball in the semiconductor device mounting method of the present invention is 0.2 to 0.8 mm.
さらに、好ましくは、本発明の半導体デバイスの実装方法における目標間隔は、前記基板の配線パターンのランド部と前記半導体デバイスの各端子とを接合する接合部が所定の集中熱応力条件により接合不良にならない程度の間隔である。 Further preferably, in the semiconductor device mounting method of the present invention, the target interval is such that the joint portion that joins the land portion of the wiring pattern of the substrate and each terminal of the semiconductor device causes poor bonding due to a predetermined concentrated thermal stress condition. This is an interval that does not become necessary.
本発明の半導体素子モジュールは、表面側に一または複数の配線パターンが形成された基板と、半導体素子が表面側に搭載された半導体デバイスと、該基板と該半導体デバイスとの間に介在して、該半導体デバイスの表面と該基板の表面を、平行に配置すると共に目標間隔に保持するためのボールと、該配線パターンの所定のランド部と該半導体デバイスの各端子を電気的に接合する接合部とを有するものであり、そのことにより上記目的が達成される。 The semiconductor element module of the present invention includes a substrate having one or more wiring patterns formed on the front surface side, a semiconductor device having a semiconductor element mounted on the front surface side, and interposed between the substrate and the semiconductor device. , A ball for arranging the surface of the semiconductor device and the surface of the substrate in parallel and maintaining a target distance, and a junction for electrically joining a predetermined land portion of the wiring pattern and each terminal of the semiconductor device The above object is achieved by this.
また、好ましくは、本発明の半導体素子モジュールにおけるボールは、前記配線パターンの所定のランド部上に載置されているかまたは、該配線パターンのランド部以外の該基板上に載置されている。 Preferably, the ball in the semiconductor element module of the present invention is placed on a predetermined land portion of the wiring pattern or placed on the substrate other than the land portion of the wiring pattern.
さらに、好ましくは、本発明の半導体素子モジュールにおけるボールは、樹脂製球体、該樹脂製球体の表面に金属めっきが施された球体および金属製球体のうちの少なくともいずれかである。 Further preferably, the ball in the semiconductor element module of the present invention is at least one of a resin sphere, a sphere having a metal plating applied to the surface of the resin sphere, and a metal sphere.
さらに、好ましくは、本発明の半導体素子モジュールにおけるボールが樹脂製球体の表面に金属めっきが施された球体または金属製球体の場合で、前記接合部が半田接合部の場合に、該金属めっきの金属材料または該金属製球体の金属材料が該半田接合部の材料と同じ材料により構成されている。 Further preferably, when the ball in the semiconductor element module of the present invention is a sphere or metal sphere in which the surface of the resin sphere is subjected to metal plating, and the joint is a solder joint, the metal plating The metal material or the metal material of the metal sphere is made of the same material as that of the solder joint.
さらに、好ましくは、本発明の半導体素子モジュールにおけるボールは、前記配線パターンの複数のランド部のうち、最も支持面積が広く取れる4箇所以上のランド部の位置で前記半導体デバイスを支持している。 Further, preferably, the ball in the semiconductor element module of the present invention supports the semiconductor device at positions of four or more land portions having the largest support area among the plurality of land portions of the wiring pattern.
さらに、好ましくは、本発明の半導体素子モジュールにおける接合部の半田材料はペイスト状半田材料である。 Further preferably, the solder material of the joint in the semiconductor element module of the present invention is a paste-like solder material.
さらに、好ましくは、本発明の半導体素子モジュールにおいて、前記基板と前記半導体デバイスとの間の隙間内に充填樹脂が配設されている。 Further preferably, in the semiconductor element module of the present invention, a filling resin is disposed in a gap between the substrate and the semiconductor device.
さらに、好ましくは、本発明の半導体素子モジュールにおけるボールの直径は、前記接合部の半田材料の厚さよりも大きく設定されている。 Further preferably, the diameter of the ball in the semiconductor element module of the present invention is set larger than the thickness of the solder material of the joint.
さらに、好ましくは、本発明の半導体素子モジュールにおけるボールが前記配線パターンの所定のランド部上に載置される場合は、該ボールがペイスト状半田材料内に配置されており、該ボールが該配線パターンのランド部以外の該基板上に載置される場合は該ボールがペイスト状熱硬化樹脂材料内に配置されている。 Further preferably, when the ball in the semiconductor element module of the present invention is placed on a predetermined land portion of the wiring pattern, the ball is disposed in a paste-like solder material, and the ball is connected to the wiring When placed on the substrate other than the land portion of the pattern, the ball is disposed in the pasty thermosetting resin material.
さらに、好ましくは、本発明の半導体素子モジュールにおけるボールの直径は、前記ペイスト状熱硬化樹脂材料の厚さよりも大きく設定されている。 Further preferably, the diameter of the ball in the semiconductor element module of the present invention is set to be larger than the thickness of the pasty thermosetting resin material.
さらに、好ましくは、本発明の半導体素子モジュールにおけるボールの直径は0.2〜0.8mmである。 Further, preferably, the diameter of the ball in the semiconductor element module of the present invention is 0.2 to 0.8 mm.
さらに、好ましくは、本発明の半導体素子モジュールにおける目標間隔は、前記基板の配線パターンのランド部と前記半導体デバイスの各端子とを接合する接合部が所定の集中熱応力条件により接合不良にならない程度の間隔である。 Further, preferably, the target interval in the semiconductor element module of the present invention is such that the bonding portion where the land portion of the wiring pattern of the substrate and each terminal of the semiconductor device are bonded does not cause poor bonding due to a predetermined concentrated thermal stress condition. Is the interval.
さらに、好ましくは、本発明の半導体素子モジュールにおける半導体素子は、被写体からの画像光を光電変換して撮像する複数の受光部を有する撮像素子である。 Still preferably, in a semiconductor element module according to the present invention, the semiconductor element is an imaging element having a plurality of light receiving units that perform image conversion by photoelectrically converting image light from a subject.
さらに、好ましくは、本発明の半導体素子モジュールにおける半導体素子は、出射光を発生させるための発光素子および入射光を受光するための受光素子である。 Further preferably, the semiconductor element in the semiconductor element module of the present invention is a light emitting element for generating outgoing light and a light receiving element for receiving incident light.
さらに、好ましくは、本発明の半導体素子モジュールにおいて、本発明の上記半導体素子モジュールの基板上の所定位置に、前記撮像素子上に入射光を結像するための集光レンズを固定したホルダー部材が設けられている。 Further preferably, in the semiconductor element module of the present invention, a holder member in which a condensing lens for imaging incident light on the imaging element is fixed at a predetermined position on the substrate of the semiconductor element module of the present invention. Is provided.
さらに、好ましくは、本発明の半導体素子モジュールにおいて、本発明の上記半導体素子モジュールの基板上に、出射光を直進させたり入射光を所定方向に曲げて導いたりする一または複数の光学機能素子を固定したホルダー部材が設けられている。 Further preferably, in the semiconductor element module according to the present invention, one or a plurality of optical functional elements for directing the emitted light or bending the incident light in a predetermined direction on the substrate of the semiconductor element module according to the present invention are provided. A fixed holder member is provided.
本発明の電子情報機器は、本発明の上記半導体素子モジュールを画像入力デバイスとして撮像部に用いたものであり、そのことにより上記目的が達成される。 An electronic information device of the present invention uses the semiconductor element module of the present invention as an image input device in an imaging unit, and thereby achieves the above object.
本発明の電子情報機器は、本発明の上記半導体素子モジュールを情報記録再生部に用いたものであり、そのことにより上記目的が達成される。 An electronic information device according to the present invention uses the semiconductor element module according to the present invention for an information recording / reproducing unit, thereby achieving the above object.
上記構成により、以下、本発明の作用を説明する。 With the above configuration, the operation of the present invention will be described below.
本発明においては、基板面と半導体デバイスとの間に間隔保持用のボールを介在させるので、基板面と半導体デバイスとがボールによって平行に位置している。これによって、半導体素子モジュールの半導体素子の受光面が基板面と平行になることにより、受光面の中央部とその周辺部など如何なる場所でもレンズ焦点距離が一定になり、受光面内のフォーカス差による画質不良が防止される。 In the present invention, since the spacing ball is interposed between the substrate surface and the semiconductor device, the substrate surface and the semiconductor device are positioned in parallel by the ball. As a result, the light receiving surface of the semiconductor element of the semiconductor element module is parallel to the substrate surface, so that the lens focal length is constant at any location such as the central portion and the peripheral portion of the light receiving surface, and due to the focus difference in the light receiving surface. Image quality defects are prevented.
また、基板面の配線パターンの接合部と半導体デバイスの各端子とを接合するための半田中に同一径のボールが埋め込まれているので、半導体デバイスの基板面に対する高さ制御と同時に、基板面の配線パターンの接合部(ランド部)と半導体デバイスの各端子とを半田により電気的に接合することが可能となる。 Also, since balls of the same diameter are embedded in the solder for joining the wiring pattern joints on the board surface and the respective terminals of the semiconductor device, the board surface is simultaneously controlled with the height of the semiconductor device on the board surface. It becomes possible to electrically join the joint portion (land portion) of the wiring pattern and each terminal of the semiconductor device with solder.
さらに、ボールの径に応じて基板面と半導体デバイスとの間に所望のクリアランスを設けることが可能となる。半導体デバイスの各端子と、基板の各配線パターンのランド部とが半田で接続される場合に、所望のクリアランスとは、半導体デバイスと基板の熱膨張の差が半田(フィレット)に影響しない隙間である。半田(フィレット)の体積によって、半導体デバイスと基板との熱応力緩和が可能な所望のクリアランスが必要になる。したがって、特許文献1〜5の粒子の大きさでは全く半導体デバイスと基板との熱集中応力の緩和ができない微細なクリアランスになってしまう。 Furthermore, a desired clearance can be provided between the substrate surface and the semiconductor device in accordance with the diameter of the ball. When each terminal of a semiconductor device is connected to the land portion of each wiring pattern of the substrate by soldering, the desired clearance is a gap where the difference in thermal expansion between the semiconductor device and the substrate does not affect the solder (fillet). is there. Depending on the volume of the solder (fillet), a desired clearance capable of relaxing the thermal stress between the semiconductor device and the substrate is required. Therefore, the size of the particles of Patent Documents 1 to 5 results in a fine clearance that cannot completely relieve the heat concentration stress between the semiconductor device and the substrate.
この半導体デバイスと基板との熱集中応力の緩和のために、クリアランス内にエポキシ系の充填樹脂を介在させてもよい。この場合には、充填樹脂によって半導体デバイスと基板とが接合されるので、半導体デバイスと基板との半田接合部分の集中熱応力が大幅に緩和されて、半導体デバイスと基板の半田接合部分の破壊が防止される。 In order to relieve the heat concentration stress between the semiconductor device and the substrate, an epoxy-based filling resin may be interposed in the clearance. In this case, since the semiconductor device and the substrate are joined by the filling resin, the concentrated thermal stress at the solder joint portion between the semiconductor device and the substrate is greatly reduced, and the solder joint portion between the semiconductor device and the substrate is destroyed. Is prevented.
特許文献5のように溝加工する必要もなく、半導体デバイスの基板面に対する高さ制御がより容易かつ正確になるし、小さいチップを載置するノズルを共用すれば、ノズルを別途用意することなくボールを半田上または接着材上に容易かつ正確に置くことが可能となる。
There is no need for groove processing as in
以上により、本発明によれば、撮像素子を表面側に有する半導体デバイスを基板面上にマウントする前に、半田部上または、半導体デバイスを支持可能とする基板面の接着材上に、同一径のボールを載せて実装して、基板面と半導体デバイスとの間に間隔保持用のボールを介在させるため、基板面に対する半導体デバイスの撮像素子の傾きを、治具による補助的な制御や、実装後に修正などを施すことなく、半導体デバイスの撮像素子を基板面に対して所望の均一な目標高さに揃えることができる。これによって、半田の接着強度と共に放熱効果を維持しつつ、基板面と撮像素子を水平に保ちながら容易かつ確実に実装できて画質不良を防止することができる。 As described above, according to the present invention, before mounting the semiconductor device having the imaging element on the surface side on the substrate surface, the same diameter is provided on the solder portion or the adhesive on the substrate surface capable of supporting the semiconductor device. Since the ball for holding the gap is interposed between the substrate surface and the semiconductor device, the tilt of the image pickup device of the semiconductor device relative to the substrate surface is controlled by a jig or mounted. The image sensor of the semiconductor device can be aligned at a desired uniform target height with respect to the substrate surface without any subsequent correction. As a result, while maintaining the heat dissipation effect as well as the adhesive strength of the solder, it is possible to easily and reliably mount the substrate surface and the image pickup device horizontally and prevent image quality defects.
以下に、本発明の半導体デバイスの実装方法および、この半導体デバイスの実装方法により半導体デバイスが実装された半導体素子モジュールを撮像素子モジュールに適用した場合の撮像素子モジュールの実施形態1,2および、この撮像素子モジュールの実施形態1,2に更に光学部材をモジュール化した撮像素子モジュールの実施形態3、さらに、これらの撮像素子モジュールの実施形態1〜3のいずれかを撮像部に用いた電子情報機器の実施形態4について図面を参照しながら詳細に説明する。 Embodiments 1 and 2 of an image sensor module when a semiconductor device mounting method of the present invention, and a semiconductor element module on which a semiconductor device is mounted by the semiconductor device mounting method, are applied to an image sensor module. An image sensor module according to a third embodiment in which an optical member is further modularized in the first and second embodiments of the image sensor module, and an electronic information device using any one of the first to third embodiments of the image sensor module as an imaging unit The fourth embodiment will be described in detail with reference to the drawings.
(実施形態1)
図1は、本発明の実施形態1に係る撮像素子モジュールの構成例を模式的に示す斜視図である。図2は、図1の撮像素子モジュールの要部縦断面図である。図3は、図1の撮像素子モジュールの要部の拡大縦断面図である。
(Embodiment 1)
FIG. 1 is a perspective view schematically illustrating a configuration example of an imaging element module according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. FIG. 2 is a longitudinal sectional view of a main part of the image sensor module of FIG. FIG. 3 is an enlarged vertical cross-sectional view of a main part of the image sensor module of FIG.
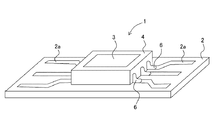
図1〜図3において、本実施形態1の撮像素子モジュール1は、配線幅0.2〜1mm(ここでは0.5mm)の配線パターン2aが中央部分を空けて左右に3行づつ形成されたマウント基板2と、入射光を光電変換して信号電荷を生成する固体撮像素子3が表面側中央部分に搭載された半導体デバイスとしてのセンサデバイス4と、マウント基板2とセンサデバイス4との間に介在して、センサデバイス4をマウント基板2と平行に配置するためのボールとしてのパールボール5と、このパールボール5を内部に含み、マウント基板2の配線パターン2aとセンサデバイス4の各接続端子4aを電気的に接合している半田接合部6とを有している。
In FIG. 1 to FIG. 3, in the image sensor module 1 according to the first embodiment, the
パールボール5は、樹脂製で球状のものでもよく、樹脂製の球体表面に金属めっきが為されているものでもよく、金属製の球体であってもよいが、ここでは、樹脂製の球体表面に金属めっき材料として、半田接合部6のペイスト状半田材料と同じすず(Sn)と銀(Ag)との合金メッキが施されている。要するに、パールボール5が樹脂製球体の表面に金属めっきが施された球体または金属製球体の場合に、金属めっきの材料または金属製球体の金属材料が半田材料と同じ材料により構成されていれば、半田材料と金属材料が互いに親和性があり、熱応力にも強く接合強度が高く、互いに剥がれ難い。
The
また、パールボール5は、センサデバイス4を、最も支持面積が広く取れる配線パターン2aの最も外側の4箇所で支持するようにしているが、最も支持面積が広く取れる3箇所または5箇所以上の複数箇所によるセンサデバイス4への支持でもよい。このパールボール5は、単に3箇所だけの支持では、センサデバイス4が倒れて傾く可能性も捨てきれず、センサデバイス4に対して、最も支持面積が広く取れる4箇所以上の複数箇所による支持が安定している。パールボール5は、半田接合部6となるペイスト状半田材料上に置かれると、ロボットアーム(搭載機)の搭載荷重およびパールボール5の自重によりパールボール5がペイスト状半田材料内を沈むので、パールボール5がペイスト状半田材料上から脱落し難い。
In addition, the
このパールボール5により、マウント基板2とセンサデバイス4との間に所望のクリアランスを設けている。このクリアランス内にエポキシ系の充填樹脂を介在させてもよく、この場合には、エポキシ系の充填樹脂によってセンサデバイス4とマウント基板2とが上下で接合されるので、センサデバイス4とマウント基板2の半田接合部6の集中熱応力が大幅に緩和されてセンサデバイス4とマウント基板2の半田接合部6の破壊が防止される。このクリアランスは、小さければ小さいほど、センサデバイス4とマウント基板2との間に充填樹脂が必要になるし、クリアランスが大きければ大きいほど、その充填樹脂が必要ではなくなる。流動性のよいエポキシ系の充填樹脂を細いノズル先端部から、センサデバイス4とマウント基板2との間に注入すると、毛細管現象で容易にそのクリアランス内部に流入する。
The
上記構成により、以下、半導体デバイスとしてのセンサデバイス4のマウント基板2への実装方法について説明する。
Hereinafter, a method of mounting the
図5(a)〜図5(e)は、図1のセンサデバイス4のマウント基板2への実装方法について説明するための各工程を模式的に示す斜視図である。図6(a)〜図6(e)は、図5(a)〜図5(e)にそれぞれ対応した各工程の縦断面図である。
FIG. 5A to FIG. 5E are perspective views schematically showing respective steps for explaining a method of mounting the
図1のセンサデバイス4のマウント基板2への実装方法は、図5(a)および図6(a)に示すように、まず、配線幅0.2〜1mm(ここでは0.5mm)の配線パターン2aが形成されたマウント基板2を実装装置のテーブル上の所定位置にセットする。
As shown in FIGS. 5 (a) and 6 (a), the
次に、配線パターン2aの半田付け箇所に対応したランド位置に穴がパターニングされた樹脂製または金属製の薄板状のマスク(図示せず)を、マウント基板2上に重ねて置き、そのマスクの上から半田接合部6となるペイスト状半田材料を塗布する。その後、マスクをマウント基板2上から取り除くと、図5(b)および図6(b)に示すように、配線パターン2aの半田付け箇所に対応したランド位置に、ペイスト状半田材料6aが配置される。ここでは、各ペイスト状半田材料6aは、左右3本づつの配線パターン2aの中央側の端部(ランド部またはフットパターン;半田が溶融して電気的に接着するための接着部分)上に厚さ0.1〜0.3mm(ここでは、0.25mm)高さで6箇所配置される。また、マスクの板厚は、ここでは、0.3mm程度である。
Next, a resin or metal thin plate mask (not shown) having holes patterned at the land positions corresponding to the soldered portions of the
さらに、図5(c)および図6(c)に示すように、ロボットアームの先端部に設けられたノズルにより、左右の各3箇所のペイスト状半田材料6aのうち、外側の4箇所のペイスト状半田材料6a上にそれぞれ、直径が0.2〜0.8mm(ここでは0.3mm)の球状のパールボール5を吸引して移動させた後に排気して順次載置する。ロボットアーム(搭載機)の搭載荷重およびパールボール5の自重によりパールボール5がペイスト状半田材料内に沈む。このペイスト状半田材料6aの厚さ0.25mmよりも、パールボール5の直径0.3mmの方が大きく構成されており、ペイスト状半田材料6a内にパールボール5が自重で沈んでもパールボール5の上面部分が露出する寸法関係になっている。
Further, as shown in FIGS. 5 (c) and 6 (c), the four paste pastes on the outer side of the three paste-
さらに、図5(d)および図6(d)に示すように、ロボットアームの先端部に設けられたノズルにより、表面側中央部分に固体撮像素子3が搭載されたセンサデバイス4を、センサデバイス4の裏面側の各金属接合端子4aと、各ペイスト状半田材料6aとをそれぞれ位置合せをして、4箇所のパールボール5上に載置する。センサデバイス4がペイスト状半田材料6a上のパールボール5上に載置されると、ペイスト状半田材料6aはペイスト状であるため、センサデバイス4の自重で、パールボール5と共にある程度または完全にペイスト状半田材料6a内に沈み込む。
Further, as shown in FIGS. 5D and 6D, a
その後、マウント基板2、各ペイスト状半田材料6aおよび、固体撮像素子3が搭載されたセンサデバイス4をリフロー炉に入れて、周囲温度を摂氏230度にする。これによって、図5(e)および図6(e)に示すように各ペイスト状半田材料6aを溶かし、センサデバイス4の裏面側の各金属接合端子4aと、配線パターン2aの中央部側の各端部(ランド部)とをそれぞれ、各ペイスト状半田材料6aにより半田接合部6として電気的に接合する。
Thereafter, the
以上により、本実施形態1によれば、マウント基板2とセンサデバイス4との間に間隔保持用のパールボール5を介在させるため、マウント基板2とセンサデバイス4とをパールボール5によって目標とする間隔で平行に位置させることができる。これによって、半導体素子モジュールとしての撮像素子モジュール1の固体撮像素子3の受光面がマウント基板2の表面と平行になることにより、受光面の中央部とその周辺部など如何なる場所でもレンズ焦点距離が一定になり、受光面内のフォーカス差による画質不良を防止することができる。
As described above, according to the first embodiment, since the
また、マウント基板2の表面の配線パターン2aの接合部とセンサデバイス4の各端子とを接合するための半田中に同一径のパールボール5が埋め込まれているため、センサデバイス4の基板面に対する高さ制御と同時に、マウント基板2の表面の配線パターン2aの接合部(ランド部)とセンサデバイス4の各端子とを半田により電気的に接合することができる。
Further, since the
さらに、パールボール5の径に応じてマウント基板2の基板面とセンサデバイス4との間に所望のクリアランス(隙間)を設けることができる。センサデバイス4の各端子と、マウント基板2の各配線パターン2aのランド部とが半田で接続される場合に、所望のクリアランスとは、センサデバイス4とマウント基板2の熱膨張の差が半田(フィレット)に影響しない隙間である。
Furthermore, a desired clearance (gap) can be provided between the substrate surface of the
このセンサデバイス4とマウント基板2との熱集中応力の緩和のために、このクリアランス内にエポキシ系の充填樹脂を介在させてもよい。この場合には、充填樹脂によってセンサデバイス4とマウント基板2とが接合されるので、センサデバイス4とマウント基板2との半田接合部6の集中熱応力が大幅に緩和されて、センサデバイス4とマウント基板2の半田接合部分の破壊が防止される。このクリアランスが小さければ小さいほど、充填樹脂が必要になるし、クリアランスが大きければ大きいほど、充填樹脂が必要ではなくなる。流動性のよいエポキシ系の充填樹脂を細いノズル先端部から注入すると、毛細管現象で容易にクリアランス内部に流入する。
(実施形態2)
上記実施形態1では、マウント基板2の各配線パターン2a上にペイスト状半田材料6aを載置し、そのペイスト状半田材料6a上にパールボール5を載置し、マウント基板2の各配線パターン2aとセンサデバイス4の各金属接合端子4aとを半田により接合すると同時に、パールボール5によりマウント基板2とセンサデバイス4との距離を一定の目標距離に高さ制御したが、本実施形態2では、マウント基板2の各配線パターン2aとは別に、マウント基板2上の左右の各配線パターン2a間の中央部分に、後述する熱硬化型ペイスト状樹脂材料としての熱硬化型ペイスト状接着剤7を4箇所配置して、その上にパールボール5を載置し、更にその上にセンサデバイス4を置き、マウント基板2の各配線パターン2aとセンサデバイス4の各金属接合端子4aとの電気的な接続を、別途、ハンダ付けにより行う場合について説明する。
In order to relieve the heat concentration stress between the
(Embodiment 2)
In the first embodiment, the paste-
図7(a)〜図7(e)は、本発明の実施形態2に係る撮像素子モジュールのセンサデバイス4のマウント基板2への実装方法について説明するための各工程を模式的に示す斜視図である。図8(a)〜図8(e)は、図7(a)〜図7(e)にそれぞれ対応した各工程の縦断面図である。なお、上記図5と同様の作用効果を奏する部材には同一の符号番号を付けて説明する。
FIG. 7A to FIG. 7E are perspective views schematically showing respective steps for explaining a method of mounting the
本実施形態2の撮像素子モジュール1Aのセンサデバイス4のマウント基板2への実装方法は、図7(a)および図8(a)に示すように、まず、配線幅0.2〜1mm(ここでは0.5mm)の配線パターン2aが形成されたマウント基板2を実装装置のテーブル上の所定位置にセットする。
As shown in FIGS. 7A and 8A, the mounting method of the
次に、図7(b)および図8(b)に示すように、ピン転写方式(または注射器等によるディスペンス方式:微量時はピン転写方式を用い、それよりも多い量の時はディスペン方式を用いる。量に応じて両者を使い分ける。)により熱硬化型ペイスト状接着剤7をピン先端部分で掬い取って、配線パターン2aの半田付け箇所の内側中央領域に、熱硬化型ペイスト状接着剤7をそれぞれ順次塗布する。これによって、配線パターン2aの内側中央領域に、4つの熱硬化型ペイスト状接着剤7が配置されるとともに、更にこれらの中央位置に、これらよりも高く、センサデバイス4を固定するための一つの熱硬化型ペイスト状接着剤7aが配置される。ここでは、各熱硬化型ペイスト状接着剤7は、左右3本づつの配線パターン2aの内側の中央部(中央領域)上に厚さ0.1〜0.3mm(ここでは、0.25mm)高さで4箇所配置される。
Next, as shown in FIGS. 7B and 8B, a pin transfer method (or a dispensing method using a syringe or the like: a pin transfer method is used when the amount is small, and a dispense method is used when the amount is larger than that. The thermosetting paste-
さらに、図7(c)および図8(c)に示すように、ロボットアームの先端部に設けられたノズルにより、左右の4箇所の熱硬化型ペイスト状接着剤7上にそれぞれ、直径が0.2〜0.8mm(ここでは0.3mm)の球状のパールボール5を吸引して移動させた後に排気して順次載置する。ロボットアーム(搭載機)の搭載荷重およびパールボール5の自重によりパールボール5がペイスト状接着剤7内に沈む。この熱硬化型ペイスト状接着剤7の厚さ0.25mmよりも、パールボール5の直径0.3mmの方が大きく構成されており、熱硬化型ペイスト状接着剤7内に、パールボール5が、ロボットアームの搭載荷重およびパールボール5の自重により沈んでも、パールボール5の上面部分が露出する寸法関係になっている。また、中央部分の一つの熱硬化型ペイスト状接着剤7aの厚さは、このときのパールボール5の高さ位置(直径寸法)と略同等以上の高さになる厚さ寸法(熱硬化型ペイスト状接着剤7aの表面がセンサデバイス4の底面に必ず接着する厚さ寸法)に設定されている。
Further, as shown in FIGS. 7 (c) and 8 (c), the nozzle provided at the tip of the robot arm has a diameter of 0 on each of the left and right
さらに、図7(d)および図8(d)に示すように、ロボットアームの先端部に設けられたノズルにより、表面側中央部分に固体撮像素子3が搭載されたセンサデバイス4を、センサデバイス4の裏面側の各金属接合端子4aと、マウント基板2の配線パターン2aとをそれぞれ位置合せをして、それらの内側の中央部分の4箇所のパールボール5上に載置すると共に、センサデバイス固定用の熱硬化型ペイスト状接着剤7a上に載置する。センサデバイス4が、熱硬化型ペイスト状接着剤7上のパールボール5上に載置されると共に、熱硬化型ペイスト状接着剤7a上に載置されると、熱硬化型ペイスト状接着剤7はペイスト状であるため、ロボットアーム(搭載機)の搭載荷重、パールボール5およびセンサデバイス4の自重で、更にパールボール5と共に熱硬化型ペイスト状接着剤7内に完全に沈み込む。
Further, as shown in FIGS. 7 (d) and 8 (d), the
その後、マウント基板2、各熱硬化型ペイスト状接着剤7および、固体撮像素子3が搭載されたセンサデバイス4をリフロー炉(高温炉)に入れて、周囲温度を比較的低温度の摂氏120度にする。これによって、図7(e)および図8(e)に示すように各熱硬化型ペイスト状接着剤7を硬貨させてパールボール5をマウント基板2上に固定する。
Thereafter, the mounting
続いて、センサデバイス4の裏面側の各金属接合端子4aと、配線パターン2aの中央部側の各端部(ランド部)とにそれぞれ、各ペイスト状半田材料を位置させてレーザ光によりスポット的に熱を加えて溶融させて電気的に接合して半田接合部6とする。
Subsequently, each paste-like solder material is positioned on each metal
以上により、本実施形態2によれば、周囲温度を比較的低温度の摂氏120度に設定して各熱硬化型ペイスト状接着剤7を硬貨させてパールボール5をマウント基板2上に固定するため、センサデバイス4の固体撮像素子3に、上記実施形態1のような摂氏230度の高温度をかけないので固体撮像素子3の熱による変質が抑制される。
(実施形態3)
図9は、本発明の実施形態3に係る撮像素子モジュールの要部構成例を模式的に示す縦断面図である。図1と同様の作用効果を奏する部材には同一の部材番号を付して説明することにする。
As described above, according to the second embodiment, the ambient temperature is set to 120 degrees Celsius, which is a relatively low temperature, and each
(Embodiment 3)
FIG. 9 is a vertical cross-sectional view schematically illustrating an exemplary configuration of a main part of an image sensor module according to
図9において、本実施形態3の固体撮像モジュール10は、カメラモジュールとして、セラミックスやガラス入りエポキシ樹脂などのマウント基板2と、このマウント基板2上に、被写体からの画像光をそれぞれ光電変換して被写体を撮像する複数の受光部を有する半導体素子としての固体撮像素子3をパッケージ内に有するセンサデバイス4と、このマウント基板2とセンサデバイス4間に介在しているパールボール5と、入射光を撮像素子上に結像するための集光レンズ11を固定したホルダー部材12と、ホルダー部材12内の集光レンズ11とセンサデバイス4間に設けられ、表面に赤外線カットフィルタがコーティングされたガラス基板13とを有している。
(実施形態4)
図10は、本発明の実施形態4として、本発明の実施形態1〜3の固体撮像モジュール1または1Aまたは10を含む固体撮像装置を撮像部に用いた電子情報機器の概略構成例を示すブロック図である。
In FIG. 9, the solid-
(Embodiment 4)
FIG. 10 is a block diagram illustrating a schematic configuration example of an electronic information device using, as an imaging unit, a solid-state imaging device including the solid-state imaging module 1, 1 </ b> A, or 10 according to Embodiments 1 to 3 of the present invention as
図10において、本実施形態4の電子情報機器90は、上記実施形態1〜3の固体撮像モジュール1または1Aまたは10からの撮像信号を各種信号処理してカラー画像信号を得る固体撮像装置91と、この固体撮像装置91からのカラー画像信号を記録用に所定の信号処理した後にデータ記録可能とする記録メディアなどのメモリ部92と、この固体撮像装置91からのカラー画像信号を表示用に所定の信号処理した後に液晶表示画面などの表示画面上に表示可能とする液晶表示装置などの表示手段93と、この固体撮像装置91からのカラー画像信号を通信用に所定の信号処理をした後に通信処理可能とする送受信装置などの通信手段94と、この固体撮像装置91からのカラー画像信号を印刷用に所定の信号処理をした後に印刷処理可能とする画像出力手段95とを有している。なお、この電子情報機器90として、これに限らず、固体撮像装置91の他に、メモリ部92と、表示手段93と、通信手段94と、プリンタなどの画像出力手段95とのうちの少なくともいずれかを有していてもよい。
In FIG. 10, an
この電子情報機器90としては、前述したように例えばデジタルビデオカメラ、デジタルスチルカメラなどのデジタルカメラや、監視カメラ、ドアホンカメラ、車載用後方監視カメラなどの車載用カメラおよびテレビジョン電話用カメラなどの画像入力カメラ、スキャナ装置、ファクシミリ装置、カメラ付き携帯電話装置および携帯端末装置(PDA)などの画像入力デバイスを有した電子機器が考えられる。
As described above, the
したがって、本実施形態4によれば、この固体撮像装置91からのカラー画像信号に基づいて、これを表示画面上に良好に表示したり、これを紙面にて画像出力手段95により良好にプリントアウト(印刷)したり、これを通信データとして有線または無線にて良好に通信したり、これをメモリ部92に所定のデータ圧縮処理を行って良好に記憶したり、各種データ処理を良好に行うことができる。
Therefore, according to the fourth embodiment, on the basis of the color image signal from the solid-
なお、上記実施形態4の電子情報機器90に限らず、図11に示すように、本発明の電子素子モジュール20を情報記録再生部に用いたピックアップ装置91Aなどの電子情報機器90Aであってもよい。この場合のピックアップ装置91Aの光学素子としては、出射光を直進させて出射させると共に、入射光を曲げて所定方向に入射させる光学機能素子(例えばホログラム光学素子)である。また、ピックアップ装置91Aの電子素子としては、出射光を発生させるための発光素子(例えば半導体レーザ素子またはレーザチップ)および入射光を受光するための受光素子(例えばフォトIC)を有している。したがって、電子素子モジュール20としての半導体素子モジュールは、光学機能素子(例えばホログラム光学素子)と、その下部に設けられた発光素子および受光素子とを有している。
In addition to the
この場合も同様に、電子情報機器90Aは、上記本発明の電子素子モジュール20を情報記録再生部に用いたピックアップ装置91Aと、このピックアップ装置91Aからのカラー画像信号を記録用に所定の信号処理した後にデータ記録可能とする記録メディアなどのメモリ部92と、このピックアップ装置91Aからのカラー画像信号を表示用に所定の信号処理した後に液晶表示画面などの表示画面上に表示可能とする液晶表示装置などの表示手段93と、このピックアップ装置91Aからのカラー画像信号を通信用に所定の信号処理をした後に通信処理可能とする送受信装置などの通信手段94と、このピックアップ装置91Aからのカラー画像信号を印刷用に所定の信号処理をした後に印刷処理可能とする画像出力手段95とを有している。なお、この電子情報機器90Aとして、これに限らず、ピックアップ装置91Aの他に、メモリ部92と、表示手段93と、通信手段94と、プリンタなどの画像出力手段95とのうちの少なくともいずれかを有していてもよい。
Similarly, in this case, the
以上のように、本発明の好ましい実施形態1〜4を用いて本発明を例示してきたが、本発明は、この実施形態1〜4に限定して解釈されるべきものではない。本発明は、特許請求の範囲によってのみその範囲が解釈されるべきであることが理解される。当業者は、本発明の具体的な好ましい実施形態1〜4の記載から、本発明の記載および技術常識に基づいて等価な範囲を実施することができることが理解される。本明細書において引用した特許、特許出願および文献は、その内容自体が具体的に本明細書に記載されているのと同様にその内容が本明細書に対する参考として援用されるべきであることが理解される。 As mentioned above, although this invention has been illustrated using preferable Embodiment 1-4 of this invention, this invention should not be limited and limited to this Embodiment 1-4. It is understood that the scope of the present invention should be construed only by the claims. It is understood that those skilled in the art can implement an equivalent range from the description of specific preferred embodiments 1 to 4 of the present invention based on the description of the present invention and the common general technical knowledge. Patents, patent applications, and documents cited herein should be incorporated by reference in their entirety, as if the contents themselves were specifically described herein. Understood.
本発明は、基板上に半導体素子を有する半導体デバイスを実装する半導体デバイスの実装方法、この半導体デバイスの実装方法により実装され、被写体からの画像光を光電変換して撮像する複数の受光部を有する半導体素子としての撮像素子または、出射光を発生させるための半導体素子としての発光素子および入射光を受光するための半導体素子としての受光素子がモジュール化された半導体素子モジュール、この半導体素子モジュールとしての固体撮像モジュールを画像入力デバイスとして撮像部に用いた例えばデジタルビデオカメラおよびデジタルスチルカメラなどのデジタルカメラや、画像入力カメラ、スキャナ装置、ファクシミリ装置、カメラ付き携帯電話装置や、この半導体素子モジュールを情報記録再生部に用いたピックアップ装置などの電子情報機器の分野において、撮像素子を表面側に有する半導体デバイスを基板面上にマウントする前に、半田部上または、半導体デバイスを支持可能とする基板面の接着材上に、同一径のボールを載せて実装して、基板面と半導体デバイスとの間に間隔保持用のボールを介在させるため、基板面に対する半導体デバイスの撮像素子の傾きを、治具による補助的な制御や、実装後に修正などを施すことなく、半導体デバイスの撮像素子を基板面に対して所望の均一な目標高さに揃えることができる。これによって、半田の接着強度と共に放熱効果を維持しつつ、基板面と撮像素子を水平に保ちながら容易かつ確実に実装できて画質不良を防止することができる。 The present invention includes a semiconductor device mounting method for mounting a semiconductor device having a semiconductor element on a substrate, and a plurality of light receiving units that are mounted by the semiconductor device mounting method and that photoelectrically convert image light from a subject to image it. A semiconductor element module in which an imaging element as a semiconductor element or a light emitting element as a semiconductor element for generating emitted light and a light receiving element as a semiconductor element for receiving incident light are modularized, and as this semiconductor element module Information on digital cameras such as digital video cameras and digital still cameras, image input cameras, scanner devices, facsimile devices, camera-equipped mobile phone devices, and semiconductor element modules that use solid-state imaging modules as image input devices in the imaging unit Pickup used in the recording / playback unit In the field of electronic information equipment such as devices, before mounting a semiconductor device having an imaging element on the surface side on the substrate surface, the same on the solder part or the adhesive on the substrate surface that can support the semiconductor device In order to mount a ball of a diameter and interpose a spacing ball between the substrate surface and the semiconductor device, the tilt of the image sensor of the semiconductor device relative to the substrate surface is controlled by a jig, It is possible to align the image pickup element of the semiconductor device with a desired uniform target height with respect to the substrate surface without performing correction or the like after mounting. As a result, while maintaining the heat dissipation effect as well as the adhesive strength of the solder, it is possible to easily and reliably mount the substrate surface and the image pickup device horizontally and prevent image quality defects.
1、1A、10 固体撮像モジュール
2 マウント基板(基板)
2a 配線パターン
3 固体撮像素子
4 センサデバイス
4a 接続端子(端子)
5 パールボール(ボール)
6 半田接合部
6a ペイスト状半田材料
7 熱硬化型ペイスト状接着剤(熱硬化型ペイスト状樹脂材料)
11 集光レンズ
12 ホルダー部材
13 ガラス基板
90、90A 電子情報機器
91 固体撮像装置
91A ピックアップ装置
20 電子素子モジュール(半導体素子モジュール)
92 メモリ部
93 表示手段
94 通信手段
95 画像出力手段
1, 1A, 10 Solid-
5 Pearl ball (ball)
6 Solder joint 6a Paste-
DESCRIPTION OF
92
Claims (30)
該基板と該半導体デバイスとの間に、目標間隔保持用のボールを介在させた状態で、該基板の配線パターンのランド部と該半導体デバイスの各端子とを接合部により接合する半導体デバイス実装工程を有する半導体デバイスの実装方法。 In a semiconductor device mounting method for mounting a semiconductor device having a semiconductor element on a substrate,
A semiconductor device mounting step of joining a land portion of a wiring pattern of the substrate and each terminal of the semiconductor device by a joint portion with a ball for holding a target interval interposed between the substrate and the semiconductor device. A method for mounting a semiconductor device comprising:
前記配線パターンの各ランド部上にそれぞれ、各ペイスト状半田材料をそれぞれ配置する半田材料配置工程と、
該各ペイスト状半田材料上の一部または全部にそれぞれ、前記ボールを載置するボール載置工程と、
前記半導体デバイスを、該半導体デバイスの各端子と該配線パターンの各ランド部とをそれぞれ位置合せして、前記ボール上に載置する半導体デバイス載置工程と、
該各ペイスト状半田材料を溶融させて、該半導体デバイスの各端子と該配線パターンの各ランド部とをそれぞれ接合する半導体デバイス接合工程とを有する請求項1に記載の半導体デバイスの実装方法。 The semiconductor device mounting step includes
Solder material placement step of placing each paste-like solder material on each land portion of the wiring pattern,
A ball placing step of placing the ball on part or all of the paste-like solder material;
A semiconductor device placement step of placing the semiconductor device on the ball by aligning each terminal of the semiconductor device and each land portion of the wiring pattern;
The semiconductor device mounting method according to claim 1, further comprising: a semiconductor device bonding step of melting each paste-like solder material and bonding each terminal of the semiconductor device and each land portion of the wiring pattern.
前記基板上の半導体デバイス実装用の所定位置に、各ペイスト状熱硬化樹脂材料を一または複数箇所配置するペイスト状熱硬化樹脂材料配置工程と、
該ペイスト状熱硬化樹脂材料上にそれぞれ、前記ボールを載置するボール載置工程と、
前記半導体デバイスの各端子と該基板の配線パターンの各ランド部とをそれぞれ位置合せし、該半導体デバイスを該ボール上に載置する半導体デバイス載置工程と、
該ペイスト状熱硬化樹脂材料を熱硬化させると共に、該半導体デバイスの各端子と該配線パターンの各ランド部とを半田によりそれぞれ接合する半導体デバイス接合工程とを有する請求項1に記載の半導体デバイスの実装方法。 The semiconductor device mounting step includes
A paste-like thermosetting resin material arrangement step of arranging one or a plurality of paste-like thermosetting resin materials at a predetermined position for mounting a semiconductor device on the substrate;
A ball placing step of placing the ball on the pasty thermosetting resin material,
A semiconductor device placement step of aligning each terminal of the semiconductor device and each land portion of the wiring pattern of the substrate, and placing the semiconductor device on the ball,
The semiconductor device bonding step according to claim 1, further comprising a step of thermosetting the paste-like thermosetting resin material and bonding each terminal of the semiconductor device and each land portion of the wiring pattern by soldering. Implementation method.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008171815A JP5511156B2 (en) | 2008-06-30 | 2008-06-30 | Semiconductor device mounting method, semiconductor element module, and electronic information device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008171815A JP5511156B2 (en) | 2008-06-30 | 2008-06-30 | Semiconductor device mounting method, semiconductor element module, and electronic information device |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2010016013A true JP2010016013A (en) | 2010-01-21 |
| JP5511156B2 JP5511156B2 (en) | 2014-06-04 |
Family
ID=41701894
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008171815A Active JP5511156B2 (en) | 2008-06-30 | 2008-06-30 | Semiconductor device mounting method, semiconductor element module, and electronic information device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5511156B2 (en) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012028433A (en) * | 2010-07-21 | 2012-02-09 | Nec Network Products Ltd | Packaging method of electronic component |
| JP2019050418A (en) * | 2018-11-29 | 2019-03-28 | 株式会社ニコン | Imaging apparatus |
| CN114271038A (en) * | 2019-08-23 | 2022-04-01 | 株式会社富士 | Electronic circuit device and method for manufacturing the same |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH08139097A (en) * | 1994-11-10 | 1996-05-31 | World Metal:Kk | Flip chip use connection ball and bonding of semiconductor chip |
| JP2001094002A (en) * | 1999-09-21 | 2001-04-06 | Nec Corp | Method and structure for mounting bga |
| JP2001110825A (en) * | 1999-10-08 | 2001-04-20 | Nec Corp | Manufacturing method of semiconductor device |
| JP2009283628A (en) * | 2008-05-21 | 2009-12-03 | Tamura Seisakusho Co Ltd | Method for mounting semiconductor element |
-
2008
- 2008-06-30 JP JP2008171815A patent/JP5511156B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH08139097A (en) * | 1994-11-10 | 1996-05-31 | World Metal:Kk | Flip chip use connection ball and bonding of semiconductor chip |
| JP2001094002A (en) * | 1999-09-21 | 2001-04-06 | Nec Corp | Method and structure for mounting bga |
| JP2001110825A (en) * | 1999-10-08 | 2001-04-20 | Nec Corp | Manufacturing method of semiconductor device |
| JP2009283628A (en) * | 2008-05-21 | 2009-12-03 | Tamura Seisakusho Co Ltd | Method for mounting semiconductor element |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012028433A (en) * | 2010-07-21 | 2012-02-09 | Nec Network Products Ltd | Packaging method of electronic component |
| JP2019050418A (en) * | 2018-11-29 | 2019-03-28 | 株式会社ニコン | Imaging apparatus |
| CN114271038A (en) * | 2019-08-23 | 2022-04-01 | 株式会社富士 | Electronic circuit device and method for manufacturing the same |
| CN114271038B (en) * | 2019-08-23 | 2024-05-03 | 株式会社富士 | Electronic circuit device and method for manufacturing the same |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP5511156B2 (en) | 2014-06-04 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US7780365B2 (en) | Camera module and method of manufacturing the same | |
| CA2571345C (en) | System and method for mounting an image capture device on a flexible substrate | |
| CN100484199C (en) | Camera assembly package | |
| US7414663B2 (en) | Imaging element, imaging device, camera module and camera system | |
| KR0172142B1 (en) | Use of anisotropically conductive film for connecting leads of wiring board with electrode pads of photoelectric transducer | |
| JP3695583B2 (en) | Imaging semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP2007288755A (en) | Camera module | |
| JP2007208793A (en) | Small-sized camera | |
| JP5913284B2 (en) | Device with optical module and support plate | |
| JP2009095000A (en) | Camera module and method for manufacturing imaging apparatus | |
| JP2009515435A (en) | Small lens turret assembly | |
| JP5511156B2 (en) | Semiconductor device mounting method, semiconductor element module, and electronic information device | |
| CN100369468C (en) | Image sensor module of camera apparatus and assembling method thereof | |
| JP2006294720A (en) | Camera module | |
| JP2005242242A (en) | Image sensor package and camera module | |
| JP2005051535A (en) | Imaging apparatus and manufacturing method therefor | |
| JPH04137663A (en) | Solid-state image sensor | |
| JP5732238B2 (en) | Solid-state imaging device and electronic information device | |
| JP2009158873A (en) | Optical device and manufacturing method of optical device | |
| JP2012079984A (en) | Mounting method of semiconductor device, semiconductor module, and electronic information device | |
| TWI543613B (en) | Image sensor module | |
| KR20100027857A (en) | Wafer level camera module and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP2009088650A (en) | Image sensor module and method of manufacturing the same | |
| TWI607554B (en) | Image module structure | |
| WO2024009694A1 (en) | Semiconductor device, electronic apparatus, and method for producing semiconductor device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20100826 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20110228 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20120822 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20120927 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20130118 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20130214 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20130418 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20130709 |
|
| A911 | Transfer to examiner for re-examination before appeal (zenchi) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A911 Effective date: 20130716 |
|
| A912 | Re-examination (zenchi) completed and case transferred to appeal board |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A912 Effective date: 20130913 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20140210 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20140325 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5511156 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| RD04 | Notification of resignation of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R3D04 |