JP2010014657A - Map information processing apparatus - Google Patents
Map information processing apparatus Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2010014657A JP2010014657A JP2008176820A JP2008176820A JP2010014657A JP 2010014657 A JP2010014657 A JP 2010014657A JP 2008176820 A JP2008176820 A JP 2008176820A JP 2008176820 A JP2008176820 A JP 2008176820A JP 2010014657 A JP2010014657 A JP 2010014657A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- map
- route
- data
- link
- lower layer
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Abstract
Description
この発明は、地図情報を処理する地図情報処理装置に関し、特に地図情報が部分的にバージョンアップされた場合に対応する技術に関する。 The present invention relates to a map information processing apparatus that processes map information, and more particularly to a technique for handling a case where map information is partially upgraded.
ナビゲーション装置は、道路データを含む地図データを保持しており、この地図データを用いて自車位置の算出および表示、ならびに、目的地までの経路探索および経路案内などの機能を実現している。 The navigation device holds map data including road data, and uses the map data to realize functions such as calculation and display of the vehicle position, route search to the destination, and route guidance.
このようなナビゲーション装置で用いられる地図データは、地図の詳細さに応じた階層構造を有し、例えば最も詳細な地図がレベル0、最も粗い地図がレベルn−1(nは2以上の整数)となる。各レベルの地図は、例えば日本全体といった作成範囲を複数のメッシュに分割した単位地図から成り、単位地図を表すデータをメッシュデータという。地図を複数のメッシュに分割して各々をメッシュデータで表すのは、複数のメッシュに分割することによって、取り扱うデータサイズを小さくし、ナビゲーション装置で扱いやすくするためである。メッシュデータは、道路データ、背景データおよび文字データなどから成る。
The map data used in such a navigation device has a hierarchical structure corresponding to the details of the map. For example, the most detailed map is
道路データは、道路を表すリンクを定義するリンクデータと、交差点などを表すノードを定義するノードデータとからなる。リンクデータは、リンクの両端のノードを表すノードレコード番号を含み、ノードデータは、ノードに接続されるリンクのリンクレコード番号を含み、これらによって道路の接続関係が表される。 The road data includes link data that defines a link representing a road and node data that defines a node representing an intersection. The link data includes node record numbers representing nodes at both ends of the link, and the node data includes link record numbers of links connected to the nodes, and these represent road connection relationships.
メッシュ境界上のノード(以下、「境界ノード」という)は、隣接情報として、接続される隣のメッシュのノードレコード番号を含み、メッシュ間での道路データの接続を実現している。 A node on the mesh boundary (hereinafter referred to as “boundary node”) includes the node record number of the adjacent mesh to be connected as adjacent information, and realizes connection of road data between the meshes.
また、実際の道路の拡張、改修または廃止などが行われた場合は、バージョンアップされた地図データがナビゲーション装置のメーカーまたは地図メーカーから提供されるが、この場合、同じ道路であってもリンクレコード番号またはノードレコード番号が変更される場合がある。このため、一部地域のみがバージョンアップされた場合は、新旧バージョンの地図データ間で隣接情報が正しく設定されない場合が発生し、その結果、新旧バージョンを混在して使用することはできない。 In addition, when an actual road is expanded, renovated, or abolished, upgraded map data is provided by the manufacturer of the navigation device or the map maker. The number or node record number may change. For this reason, when only a part of the area is upgraded, the adjacent information may not be set correctly between the map data of the old and new versions, and as a result, the old and new versions cannot be used together.
この問題を解決するために、特許文献1は、地図データを上層レベルと下層レベルの2層構造とし、目的地に至る途中にバージョンの異なる地図データが混在している場合に、上層レベルの地図データを用いて目的地の近傍の位置まで探索を行い、車両の移動によって目的地に至る途中の地図データのバージョンが等しくなったら探索をやり直す技術を開示している。また、特許文献1および特許文献2は、接続関係を示す専用データを設け、バージョンアップ時に専用データをも更新することによって新旧バージョンの地図データ間の接続関係を保証する技術を開示している。
In order to solve this problem,
しかしながら、上述した特許文献1に開示された技術では、車両の移動によって再探索を実行するため走行中に探索経路が変わってしまうという問題がある。特に、目的地を含む地図が旧バージョンであった場合は、経路探索および経路案内が不可能になったり、間違った経路が探索されて案内される可能性が高くなったりする。また、上述した特許文献1および特許文献2には、新旧バージョンの地図を跨って階層探索および誘導を行う方法は開示されていない。
However, in the technique disclosed in
この発明は、上述した問題を解消するためになされたものであり、その課題は、新旧バージョンの地図を跨って経路探索および経路案内を行うことができる地図情報処理装置を提供することにある。 The present invention has been made to solve the above-described problems, and an object thereof is to provide a map information processing apparatus capable of performing route search and route guidance across new and old versions of maps.
上記課題を解決するために、この発明に係る地図情報処理装置は、階層構造を有し、地域毎にバージョンアップされる地図データであって、下層地図のバージョンアップに応じて該下層地図に対応する上層地図がバージョンアップされた地図データを記憶する地図データ記憶部と、地図データ記憶部に記憶されている下層地図および上層地図の地図データを用いて経路探索を実行し、該経路探索によって得られた上層地図上の経路に対応する下層地図上の経路が存在する場合は該経路を表示して経路案内を行い、上層地図上の経路に対応する下層地図上の経路が存在しない場合は、目的地の方向を示した簡易案内を行う経路探索・案内部を備えている。 In order to solve the above-described problem, a map information processing apparatus according to the present invention has a hierarchical structure and is map data that is upgraded for each region, and corresponds to the lower-layer map according to the upgrade of the lower-layer map. A route search is performed using the map data storage unit that stores the upgraded map data of the upper layer map, the map data of the lower layer map and the upper layer map stored in the map data storage unit, and obtained by the route search. If there is a route on the lower layer map corresponding to the route on the upper layer map, the route is displayed and route guidance is performed, and if there is no route on the lower layer map corresponding to the route on the upper layer map, A route search / guidance unit that performs simple guidance indicating the direction of the destination is provided.
この発明に係る地図情報処理装置によれば、下層地図および上層地図の地図データを用いて経路探索を実行し、該経路探索によって得られた上層地図上の経路に対応する下層地図上の経路が存在する場合は該経路を表示して経路案内を行い、上層地図上の経路に対応する下層地図上の経路が存在しない場合は、目的地の方向を示した簡易案内を行うように構成したので、経路探索および経路案内が不可能になることはなく、新旧バージョンの地図を跨って経路探索および経路案内を行うことができる。 According to the map information processing apparatus of the present invention, a route search is executed using map data of the lower layer map and the upper layer map, and a route on the lower layer map corresponding to the route on the upper layer map obtained by the route search is obtained. When there is a route, the route is displayed and route guidance is performed. When there is no route on the lower layer map corresponding to the route on the upper layer map, simple guidance indicating the direction of the destination is performed. Route search and route guidance will not become impossible, and route search and route guidance can be performed across new and old versions of maps.
以下、この発明の実施の形態を、図面を参照しながら詳細に説明する。なお、以下では、この発明に係る地図情報処理装置が、ナビゲーション装置に適用されている場合を例に挙げて説明する。
実施の形態1.
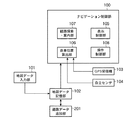
図1は、この発明の実施の形態1に係る地図情報処理装置の構成を示すブロック図である。この地図情報処理装置は、ナビゲーション制御部100、地図データ入力部101、地図データ記憶部102、GPS(Global Positioning System)受信機103および自立センサ104を備えている。
Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings. In the following, a case where the map information processing apparatus according to the present invention is applied to a navigation apparatus will be described as an example.
1 is a block diagram showing a configuration of a map information processing apparatus according to
ナビゲーション制御部100は、この発明の「制御部」に対応し、ナビゲーション機能を実現するための各種処理を実行する。このナビゲーション制御部100の詳細は後述する。
The
地図データ入力部101は、例えば、バージョンアップディスクまたはメモリカードといった記録メディア、あるいは、図示しないセンタから通信により地図データを取得する携帯電話などから構成され、新バージョンの地図データを入力する。この地図データ入力部101から入力された地図データは、地図データ記憶部102に送られる。
The map
地図データ記憶部102は、例えばHDD(Hard Disk Drive)などといった書き換え可能な記憶装置から構成されており、地図データを記憶する。この地図データ記憶部102には、ナビゲーション装置の出荷時に記憶された地図データの他、地図データ入力部101で入力された新バージョンの地図データが記憶される。この地図データ記憶部102に記憶されている地図データは、ナビゲーション制御部100によって読み出される。
The map
GPS受信機103は、GPS衛星から送信される電波を受信し、自己の現在位置を検出する。このGPS受信機103で検出された自己の現在位置は、現在位置データとしてナビゲーション制御部100に送られる。
The
自立センサ104は、速度センサおよび方位センサ(いずれも図示を省略する)を含む。速度センサで検出された自己の移動速度は、速度データとしてナビゲーション制御部100に送られる。また、方位センサで検出された自己の進行方位は、方位データとしてナビゲーション制御部100に送られる。
The self-supporting
次に、ナビゲーション制御部100の詳細を説明する。ナビゲーション制御部100は、表示制御部105、自車位置算出部106、経路探索・案内部107および操作制御部108を備えている。表示制御部105は、図示しないモニタに地図、推奨経路または各種メッセージなどを表示するための処理を実行する。
Next, details of the
自車位置算出部106は、GPS受信機103から送られてくる現在位置データ、または、自立センサ104から送られてくる速度データと方位データとに基づき自律航法により算出した自車位置データによって示される自車位置の座標を算出し、さらに、地図データ記憶部102に記憶されている地図データを用いて自車が地図上のどの道路上にいるかを算出する。この自車位置算出部106で算出された自車位置は、経路探索・案内部107における出発地として使用される他、表示制御部105で地図上に自車位置マークを表示するために使用される。
The vehicle
経路探索・案内部107は、自車位置算出部106で算出された現在位置(出発地)から、操作制御部108の制御により入力された目的地までの経路探索を行って推奨経路を表す経路データを算出するとともに、この算出した経路データによって示される推奨経路に沿って経路案内を行うための処理を実行する。
The route search /
操作制御部108は、例えば、操作パネル、リモートコントローラ(リモコン)、タッチパネルまたは音声入力装置(いずれも図示は省略する)を制御することにより、これらの操作に応じた各種情報(例えば、目的地)を入力するための処理を実行する。
The
次に、地図データ記憶部102に記憶される地図データについて説明する。図2は、各階層の地図データのフォーマットを示す図である。この地図データのフォーマットは、後述する道路データのフォーマットを除き、従来の地図データのフォーマットと同じである。すなわち、地図データは、データヘッダ、階層レベル数:nおよびレベル0〜n−1のレベルデータ(以下、「レベル0〜n−1データ」という)から成る。
Next, map data stored in the map
データヘッダは、データバージョン、データサイズおよび作成範囲を表すデータから成る。作成範囲は、作成区域左端Xs、作成区域上端Ys、作成区域右端Xeおよび作成区域下端Yeを表すデータから成る。 The data header includes data representing a data version, a data size, and a creation range. The creation range includes data representing the creation area left end Xs, the creation area upper end Ys, the creation area right end Xe, and the creation area lower end Ye.
レベルmデータは、X方向データ数:Xm、Y方向データ数:Ym、メッシュデータ(0,0)〜メッシュデータ(Xm−1,Ym−1)から成る。メッシュデータ(Xm−1,0)は、メッシュ座標(Xm−1,0)、データバージョン、ヘッダ、道路データ、背景データおよび文字データから成る。 The level m data includes X direction data number: Xm, Y direction data number: Ym, and mesh data (0, 0) to mesh data (Xm-1, Ym-1). The mesh data (Xm-1, 0) includes a mesh coordinate (Xm-1, 0), a data version, a header, road data, background data, and character data.
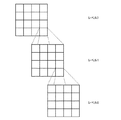
図3は、上記のように定義された地図データのレベルmデータによって表されるメッシュの例を示す図である。1つのメッシュに対応する地図を、この明細書では「単位地図」と呼ぶ。図4は、地図データの階層構造を説明するための図であり、各階層は上層のメッシュを複数に分割して構成されている。図4に示す例では、地図データがレベル0(最下層)〜レベル2(最上層)といった3階層で構成されており、レベル1のメッシュはレベル2のメッシュを4X4に分割し、レベル0のメッシュはレベル1のメッシュを4X4に分割して構成されている。
FIG. 3 is a diagram showing an example of a mesh represented by the level m data of the map data defined as described above. A map corresponding to one mesh is referred to as a “unit map” in this specification. FIG. 4 is a diagram for explaining the hierarchical structure of the map data, and each hierarchy is configured by dividing the upper mesh into a plurality of layers. In the example shown in FIG. 4, the map data is composed of three layers, level 0 (lowermost layer) to level 2 (uppermost layer), and the
図5は、図2に示した道路データのフォーマットを示す。道路データは、図5(a)に示すように、交差点などのノードを表すノードデータとノード間の道路であるリンクを表すリンクデータとから成る。 FIG. 5 shows the format of the road data shown in FIG. As shown in FIG. 5A, the road data includes node data representing nodes such as intersections and link data representing links that are roads between nodes.
ノードデータは、図5(b)に示すように、ノードレコード数と複数のノードレコード#0〜#n−1とから成る。ノードレコード#0〜#n−1の各々は、ノードの位置を示すノード座標、ノードが交差点であるか境界ノードであるかなどを示すノード属性、隣接する単位地図(以下、単に「隣接地図」という)へ接続するための隣接情報、ノードに接続されるリンクの本数を示す接続リンク数、および、接続リンク数分のリンクレコード番号から成る。隣接情報は、ノード属性が境界ノードであることを表している場合にのみ有効な情報である。なお、隣接情報は、ノード属性が境界ノードでない場合は、道路データ中に隣接情報を保持しないように構成できる。この構成によれば、道路データの全体の量を減らすことができる。
As shown in FIG. 5B, the node data is composed of the number of node records and a plurality of
リンクデータは、図5(c)に示すように、リンクレコード数と複数のリンクレコード#0〜#n−1から成る。リンクレコード#0〜#n−1の各々は、リンクの始点および終点のノードをそれぞれ示す始点ノードレコード番号および終点ノードレコード番号、リンクの種別を表すリンク種別、リンクの属性を表すリンク属性、すべてのリンクにユニークな値として付加されるリンクID番号、リンクの長さを表すリンク長、および、リンクの形を現すリンク形状から成る。リンク形状は、形状座標数と形状座標#0〜#n−1から成る。
As shown in FIG. 5C, the link data includes the number of link records and a plurality of
隣接情報は、図5(d)に示すように、リンクID番号からなる。リンクID番号は、図5(e)に示すように、始点ノードレコード側の始点側リンクID番号と終点ノードレコード側の終点側リンクID番号とから成り、所定の幅を有する。バージョンアップによってリンクが分割された場合は、始点側リンクID番号と終点側リンクID番号の範囲内でリンクID番号が振りなおされる。 As shown in FIG. 5D, the adjacency information includes a link ID number. As shown in FIG. 5E, the link ID number includes a start point side link ID number on the start point node record side and an end point side link ID number on the end point node record side, and has a predetermined width. When the link is divided due to version upgrade, the link ID number is reassigned within the range of the start side link ID number and the end point side link ID number.
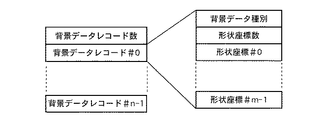
図6は、図2に示した背景データの構造を示す例であり、背景データレコード数と背景データレコード#0〜#n−1とから構成されている。背景データレコード#0〜#n−1の各々は、河川または緑地などの種別を表す背景データ種別、形状座標数、および、背景の形状を表す形状座標#0〜#m−1から構成されている。
FIG. 6 is an example showing the structure of the background data shown in FIG. 2, and is composed of the number of background data records and background
図7は、経路探索・案内部107で算出される経路データのフォーマットを示す図である。この経路データは、経路探索の出発地を表す出発地座標、目的地を表す目的地座標、経路リンク数および経路リンク#0〜#n−1からなる。経路リンク#0〜#n−1の各々は、リンクが属する地図の階層レベル、メッシュ座標(X,Y)、リンクを特定するリンクID番号およびリンクの向きと経路の向きの順逆を表す経路方向とから成る。
FIG. 7 is a diagram showing a format of route data calculated by the route search /
上述した地図データを用いて、隣接する単位地図(メッシュ)間の道路の接続関係は次のように表される。図8において、リンク603のリンクID番号は、始点側「10」、終点側「19」(以下、「10:19」と記す)であり、リンク604のリンクID番号は「20:29」であれば、境界ノード601および602の隣接情報は、それぞれ「20:29」および「10:19」とされる。
Using the map data described above, the road connection relationship between adjacent unit maps (mesh) is expressed as follows. In FIG. 8, the link ID number of the
今、図9に示すように、図8に示すリンク604がリンク702とリンク703とに分割された場合、リンクID番号として、それぞれ「20:24」および「25:29」が付与される。
As shown in FIG. 9, when the
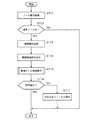
次に、上記のように構成される、この発明の実施の形態1に係る地図情報処理装置の動作を、図10および図11に示すフローチャートを参照しながら説明する。以下では、境界ノードから隣接地図のリンクを取得する処理を中心に説明する。この処理は、表示制御部105、自車位置算出部106または経路探索・案内部107からの地図データの取得要求に応じて、ナビゲーション制御部100において実行される。
Next, the operation of the map information processing apparatus configured as described above according to
境界ノードから隣接地図のリンクを取得する処理では、まず、ノード属性が取得される(ステップST11)。すなわち、ナビゲーション制御部100は、要求された地図データを地図データ記憶部102から読み込み、この読み込んだ地図データに含まれる道路データのノードデータからノード属性を取得する。
In the process of acquiring the link of the adjacent map from the boundary node, first, the node attribute is acquired (step ST11). That is, the
次いで、ステップST11で取得したノード属性が境界ノードであるかどうかが調べられる(ステップST12)。このステップST12において、ノード属性が境界ノードでないことが判断されると、境界ノードから隣接地図のリンクを取得する処理は終了する。一方、ステップST12において、ノード属性が境界ノードであることが判断されると、次いで、隣接情報が取得される(ステップST13)。すなわち、ノードデータのノードレコードの中から、隣接情報として格納されている隣接地図のリンクID番号が取得される。 Next, it is checked whether or not the node attribute acquired in step ST11 is a boundary node (step ST12). If it is determined in step ST12 that the node attribute is not a boundary node, the process of acquiring the link of the adjacent map from the boundary node ends. On the other hand, if it is determined in step ST12 that the node attribute is a boundary node, then adjacent information is acquired (step ST13). That is, the link ID number of the adjacent map stored as the adjacent information is acquired from the node record of the node data.
次いで、隣接地図が読み込まれる(ステップST14)。すなわち、当該メッシュの隣のメッシュの地図データが読み込まれる。次いで、隣接リンク取得処理が実行される(ステップST15)。この隣接リンク取得処理では、隣接地図から隣接情報に一致するリンクID番号を取得する処理が行われる。この隣接リンク取得処理の詳細は、後述する。 Next, the adjacent map is read (step ST14). That is, the map data of the mesh next to the mesh is read. Next, adjacent link acquisition processing is executed (step ST15). In this adjacent link acquisition process, a process of acquiring a link ID number that matches the adjacent information from the adjacent map is performed. Details of this adjacent link acquisition processing will be described later.
次いで、隣接リンクの取得が成功したがどうかが調べられる(ステップST16)。このステップST16において、隣接リンクの取得が成功したことが判断されると、境界ノードから隣接地図のリンクを取得する処理は終了する。一方、ステップST16において、隣接リンクの取得に成功しなかったことが判断されると、行き止まりノードであると判定され、その旨が設定される(ステップST17)。これにより、バージョンの違いによって道路データが接続されていない場合であっても、正しくナビゲーション動作を行うことができる。その後、境界ノードから隣接地図のリンクを取得する処理は終了する。 Next, it is checked whether the acquisition of the adjacent link is successful (step ST16). If it is determined in this step ST16 that the acquisition of the adjacent link is successful, the process of acquiring the link of the adjacent map from the boundary node ends. On the other hand, if it is determined in step ST16 that the acquisition of the adjacent link has not been successful, it is determined that the node is a dead end node, and that is set (step ST17). Thereby, even if the road data is not connected due to a difference in version, the navigation operation can be performed correctly. Thereafter, the process of acquiring the link of the adjacent map from the boundary node ends.
次に、上記ステップST15で実行される隣接リンク取得処理を、図11に示すフローチャートを参照しながら説明する。 Next, the adjacent link acquisition process executed in step ST15 will be described with reference to the flowchart shown in FIG.
隣接リンク取得処理では、まず、リンクデータの中の先頭リンクレコードが取得される(ステップST21)。次いで、ステップST21で取得されたリンクレコードの中からリンクID番号が取得される(ステップST22)。次いで、ステップST22で取得されたリンクID番号が、上述したステップST13で取得された隣接情報の範囲内であるかどうかが調べられる(ステップST23)。 In the adjacent link acquisition process, first, the first link record in the link data is acquired (step ST21). Next, a link ID number is acquired from the link records acquired in step ST21 (step ST22). Next, it is checked whether or not the link ID number acquired in step ST22 is within the range of the adjacent information acquired in step ST13 described above (step ST23).
このステップST23において、隣接情報の範囲内であることが判断されると、次いで、始点側ノードが取得される(ステップST24)。次いで、ステップST24で取得された始点側ノードが境界ノードであるかどうかが調べられる(ステップST25)。このステップST25において、始点側ノードが境界ノードであることが判断されると、取得成功であることが認識され、シーケンスはステップST28に進む。 If it is determined in step ST23 that it is within the range of the adjacent information, then the start point side node is acquired (step ST24). Next, it is checked whether or not the start point side node acquired in step ST24 is a boundary node (step ST25). In step ST25, when it is determined that the starting point side node is a boundary node, it is recognized that the acquisition is successful, and the sequence proceeds to step ST28.
一方、ステップST25において、始点側ノードが境界ノードでないことが判断されると、次いで、終点側ノードが取得される(ステップST26)。次いで、ステップST26で取得された終点側ノードが境界ノードであるかどうかが調べられる(ステップST27)。このステップST27において、終点側ノードが境界ノードであることが判断されると、取得成功であることが認識され、シーケンスはステップST28に進む。ステップST28においては、取得成功である旨が設定される。その後、隣接リンク取得処理は終了し、図10に示す処理にリターンする。 On the other hand, if it is determined in step ST25 that the start point side node is not a boundary node, then the end point side node is acquired (step ST26). Next, it is checked whether or not the end node obtained in step ST26 is a boundary node (step ST27). In this step ST27, when it is determined that the end node is a boundary node, it is recognized that the acquisition is successful, and the sequence proceeds to step ST28. In step ST28, the acquisition success is set. Thereafter, the adjacent link acquisition process ends, and the process returns to the process shown in FIG.
上記ステップST23において、隣接情報の範囲内でないことが判断された場合、および、上記ステップST27において、終点側ノードが境界ノードでないことが判断された場合は、次いで、最後尾のリンクレコードであるかどうかが調べられる(ステップST29)。このステップST29において、最後尾のリンクレコードでないことが判断されると、次のリンクレコードが取得される(ステップST30)。その後、シーケンスはステップST22に戻り、上述した処理が繰り返される。 If it is determined in step ST23 that it is not within the range of the adjacency information, and if it is determined in step ST27 that the end node is not a boundary node, is it the last link record? It is checked whether or not (step ST29). If it is determined in this step ST29 that it is not the last link record, the next link record is acquired (step ST30). Thereafter, the sequence returns to step ST22, and the above-described processing is repeated.
上記ステップST29において、最後尾のリンクレコードであることが判断されると、取得失敗であることが認識され、その旨が設定される(ステップST31)。その後、隣接リンク取得処理は終了し、図10に示す処理にリターンする。 If it is determined in step ST29 that it is the last link record, it is recognized that the acquisition has failed, and that fact is set (step ST31). Thereafter, the adjacent link acquisition process ends, and the process returns to the process shown in FIG.
次に、階層探索と案内について説明する。通常、ナビゲーション装置では、経路データによって示される経路のリンクを最下層(レベル0)のリンクに展開し、図12に示すような画面を表示することにより、右左折案内などが行われる。最下層のリンクに展開するのは、上層では重要度の低いリンクが省かれるために下層に存在するノードが上層に存在しない場合があり、正しい案内ができないためである。 Next, hierarchical search and guidance will be described. Usually, in the navigation device, the route link indicated by the route data is expanded into the lowest layer (level 0) link, and a screen as shown in FIG. The reason why the link is expanded to the lowest layer is that a link having low importance is omitted in the upper layer, so that a node existing in the lower layer may not exist in the upper layer, and correct guidance cannot be performed.
図13は、階層化されたリンクの対応関係を説明するための図である。リンクの対応関係は、リンクID番号の包含関係で規定され、図13において、上層のリンク801は下層のリンク804および805に対応している。この状態を「既存」という。上層のみがージョンアップされた場合は、道路の新設または延長などにより上層リンクに対応するリンクが下層に一部または全く存在しない場合がある。上層リンク802に対応する下層リンク806が一部対応している状態を「一部新設」といい、リンク803に対応する下層リンクは存在しない状態を「新設」という。
FIG. 13 is a diagram for explaining the correspondence relationship of hierarchized links. The correspondence relationship of the links is defined by the inclusion relationship of the link ID numbers. In FIG. 13, the upper layer link 801 corresponds to the
図14は、経路上を走行している場合の経路案内処理を示すフローチャートである。この案内処理は、主に、経路探索・案内部107において実行される。
FIG. 14 is a flowchart showing route guidance processing when traveling on a route. This guidance process is mainly executed in the route search /
経路案内処理では、まず、走行中のリンクが取得される(ステップST41)。すなわち、経路探索・案内部107は、自車位置算出部106で算出された自車位置が存在する道路のリンクデータを取得する。次いで、リンクID番号が取得される(ステップST42)。すなわち、ステップST41で取得されたリンクデータに含まれるリンクID番号が取得される。
In the route guidance process, first, a running link is acquired (step ST41). That is, the route search /
次いで、先頭経路リンクが取得される(ステップST43)。すなわち、経路データによって示される経路を構成する先頭のリンクデータが取得される。次いで、経路リンクのリンクID番号が取得される(ステップST44)。すなわち、ステップST43で取得した経路リンクのリンクID番号が取得される。 Next, the head route link is acquired (step ST43). That is, the head link data constituting the route indicated by the route data is acquired. Next, the link ID number of the route link is acquired (step ST44). That is, the link ID number of the route link acquired in step ST43 is acquired.
次いで、走行中のリンクのリンクID番号が包含されるかどうかが調べられる(ステップST45)。すなわち、ステップST42で取得されたリンクID番号が、ステップST44で取得された幅を有するリンクID番号の中に含まれるかどうかが調べられる。このステップST45において、走行中のリンクのリンクID番号が包含されることが判断されると、経路上を走行中であることが認識され、案内Aが実施される(ステップST46)。すなわち、図12に示すような画面が表示され、右左折案内が行われる。その後、経路案内処理は終了する。 Next, it is checked whether or not the link ID number of the running link is included (step ST45). That is, it is checked whether or not the link ID number acquired in step ST42 is included in the link ID number having the width acquired in step ST44. If it is determined in step ST45 that the link ID number of the running link is included, it is recognized that the vehicle is traveling on the route, and guidance A is implemented (step ST46). That is, a screen as shown in FIG. 12 is displayed, and left / right turn guidance is performed. Thereafter, the route guidance process ends.
一方、ステップST45において、走行中のリンクのリンクID番号が包含されないことが判断されると、次いで、最後尾の経路リンクであるかどうかが調べられる(ステップST47)。このステップST47において、最後尾の経路リンクでないことが判断されると、次の経路リンクが取得される(ステップST48)。その後、シーケンスはステップST44に戻り、上述した処理が繰り返される。 On the other hand, if it is determined in step ST45 that the link ID number of the running link is not included, it is then checked whether it is the last route link (step ST47). If it is determined in step ST47 that it is not the last route link, the next route link is acquired (step ST48). Thereafter, the sequence returns to step ST44, and the above-described processing is repeated.
ステップST47において、最後尾の経路リンクであることが判断されると、経路外を走行中であることが認識され、案内Bが実施される(ステップST49)。すなわち、図15に示すような画面が表示され、目的地の方向を示した案内が行われる。その後、経路案内処理は終了する。 If it is determined in step ST47 that the route link is at the end, it is recognized that the vehicle is traveling outside the route, and guidance B is implemented (step ST49). That is, a screen as shown in FIG. 15 is displayed, and guidance indicating the direction of the destination is performed. Thereafter, the route guidance process ends.
以上説明したように、この発明の実施の形態1に係る地図情報処理装置によれば、図9に示すように、境界ノードの隣接情報から正しくリンクレコードを取得できるので、古い地図であっても新しい地図の道路に接続することができ、これにより新しい地図と同様の経路案内を行うことができる。
As described above, according to the map information processing apparatus according to
実施の形態2.
この発明の実施の形態2に係る地図情報処理装置は、上層地図に経路の形状を表示するようにしたものである。この実施の形態2に係る地図情報処理装置の構成は、上述した実施の形態1に係る地図情報処理装置の構成(図1参照)と同じである。
Embodiment 2. FIG.
The map information processing apparatus according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention displays a route shape on an upper layer map. The configuration of the map information processing apparatus according to the second embodiment is the same as the configuration of the map information processing apparatus according to the first embodiment (see FIG. 1).
図16および図17は、実施の形態2に係る地図情報処理装置の動作を説明するための図である。図16は、下層地図に対応するリンク(以下、「下層リンク」という)が存在しない上層地図の経路リンク(以下、「上層経路リンク」という)の形状が、道路表示と異なる点線1101で下層地図に重ねて表示された例を示す図である。図12は、下層リンクが存在しない上層経路リンクの形状が、通常の道路標示と同様な線1201で下層地図に重ねて表示された例を示す図である。
16 and 17 are diagrams for explaining the operation of the map information processing apparatus according to the second embodiment. FIG. 16 shows a lower layer map in which the shape of the route link of the upper layer map (hereinafter referred to as “upper layer route link”) in which there is no link corresponding to the lower layer map (hereinafter referred to as “lower layer link”) differs from the road display. It is a figure which shows the example displayed by overlapping. FIG. 12 is a diagram illustrating an example in which the shape of the upper layer route link in which no lower layer link exists is displayed superimposed on the lower layer map with a
次に、この発明の実施の形態2に係る地図情報処理装置の動作を、図16および図17に示した表示を行うための処理を中心に、図18〜図20に示すフローチャートを参照しながら説明する。 Next, the operation of the map information processing apparatus according to the second embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to the flowcharts shown in FIGS. 18 to 20, focusing on the processing shown in FIGS. explain.
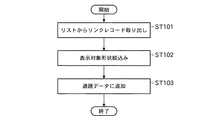
まず、表示対象となる経路リンクを選択する選択処理を、図18に示すフローチャートを参照しながら説明する。この選択処理では、表示対象として、新設および一部新設の経路リンクを選択してリスト(図示しない)に格納する処理が行われる。 First, a selection process for selecting a route link to be displayed will be described with reference to a flowchart shown in FIG. In this selection process, a process of selecting new and partially new route links as display targets and storing them in a list (not shown) is performed.
この選択処理では、まず、先頭経路リンクが取得される(ステップST51)。すなわち、経路データによって示される経路を構成する先頭のリンクデータが取得される。次いで、表示エリア内であるかどうかが調べられる(ステップST52)。すなわち、上述したステップST51または後述するステップST61で取得されたリンクデータによって示されるリンクが、モニタの表示エリア内に表示すべきリンクであるかどうかが調べられる。 In this selection process, first, a head route link is acquired (step ST51). That is, the head link data constituting the route indicated by the route data is acquired. Next, it is checked whether or not it is within the display area (step ST52). That is, it is checked whether or not the link indicated by the link data acquired in step ST51 described above or step ST61 described later is a link to be displayed in the display area of the monitor.
このステップST52において、表示エリア内でないことが判断されると、シーケンスはステップST60に進む。一方、ステップST52において、表示エリア内であることが判断されると、次いで、リンク状態が判定される(ステップST53)。すなわち、ステップST51またはステップST61で取得されたリンクレコードによって示される経路リンクが、「新規」、「一部新規」または「既存」のいずれであるかが調べられる。 If it is determined in step ST52 that it is not within the display area, the sequence proceeds to step ST60. On the other hand, if it is determined in step ST52 that it is within the display area, then the link state is determined (step ST53). That is, it is checked whether the route link indicated by the link record acquired in step ST51 or step ST61 is “new”, “partially new”, or “existing”.
このステップST53において、経路リンクが「新規」であることが判断されると、次いで、この経路リンクを含む地図が読み込まれる(ステップST54)。すなわち、経路リンクを含む地図データが地図データ記憶部102から読み込まれる。次いで、リンクレコードが取り出される(ステップST55)。すなわち、ステップST54で読み込まれた地図データに含まれる道路データを構成するリンクデータから、経路リンクに対応するリンクレコードが取り出される。次いで、新規リストに追加される(ステップST56)。すなわち、ステップST55で取り出されたリンクレコードが、図示しない新規リストに追加される。その後、シーケンスはステップST60に進む。
If it is determined in step ST53 that the route link is “new”, then a map including the route link is read (step ST54). That is, map data including a route link is read from the map
ステップST53において、経路リンクが「一部新規」であることが判断されると、次いで、この経路リンクを含む地図が読み込まれる(ステップST57)。すなわち、経路リンクを含む地図データが地図データ記憶部102から読み込まれる。次いで、リンクレコードが取り出される(ステップST58)。すなわち、ステップST57で読み込まれた地図データに含まれる道路データを構成するリンクデータから、経路リンクに対応するリンクレコードが取り出される。
If it is determined in step ST53 that the route link is “partially new”, then a map including this route link is read (step ST57). That is, map data including a route link is read from the map
次いで、一部新規リストに追加される(ステップST59)。すなわち、ステップST58で取り出されたリンクレコードが、図示しない一部新規リストに追加される。その後、シーケンスはステップST60に進む。上記ステップST53において、リンクが「既存」であることが判断された場合は、シーケンスは、ステップST60に進む。 Next, a part is added to the new list (step ST59). That is, the link record extracted in step ST58 is added to a partially new list (not shown). Thereafter, the sequence proceeds to step ST60. If it is determined in step ST53 that the link is “existing”, the sequence proceeds to step ST60.
ステップST60においては、最後尾のリンクレコードであるかどうかが調べられる。このステップST60において、最後尾のリンクレコードでないことが判断されると、次のリンクレコードが取得される(ステップST61)。その後、シーケンスはステップST52に戻り、上述した処理が繰り返される。一方、ステップST60において、最後尾のリンクレコードであることが判断されると、選択処理は終了する。 In step ST60, it is checked whether it is the last link record. If it is determined in step ST60 that it is not the last link record, the next link record is acquired (step ST61). Thereafter, the sequence returns to step ST52, and the above-described processing is repeated. On the other hand, if it is determined in step ST60 that it is the last link record, the selection process ends.
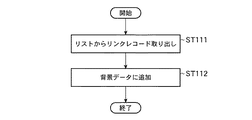
次に、上述した選択処理において新設リストに格納されたリンクレコードに基づき新設リンクの形状を表示する新設リンク表示処理を、図19に示すフローチャートを参照しながら説明する。新設リンク表示処理では、まず、リストからリストレコードが取り出される(ステップST71)。すなわち、新設リストに格納されているリンクレコードが取り出される。 Next, the new link display process for displaying the shape of the new link based on the link record stored in the new list in the selection process described above will be described with reference to the flowchart shown in FIG. In the new link display process, first, a list record is extracted from the list (step ST71). That is, the link record stored in the new list is extracted.
次いで、リンク形状が取り出される(ステップST72)。すなわち、リンクレコードに含まれるリンク形状を表すデータ、より詳しくは形状座標が取り出される。次いで、線分として表示する処理が行われる(ステップST73)。すなわち、ステップST72で取り出された形状座標を線で結ぶことにより、新規道路の形状が作成され、表示制御部105の制御によってモニタに表示される。以上により、新設リンク表示処理は終了する。
Next, the link shape is taken out (step ST72). That is, data representing the link shape included in the link record, more specifically, the shape coordinates are extracted. Next, a process of displaying as a line segment is performed (step ST73). That is, the shape of the new road is created by connecting the shape coordinates extracted in step ST72 with a line, and is displayed on the monitor under the control of the
次に、上述した選択処理において一部新設リストに格納されたリンクレコードに基づき形状表示を行う一部新設リンク表示処理を、図20に示すフローチャートを参照しながら説明する。一部新設リンク表示処理では、まず、リストからリストレコードが取り出される(ステップST81)。すなわち、一部新設リストに格納されているリンクレコードが取り出される。 Next, a partially new link display process for displaying a shape based on the link record stored in the partially new list in the selection process described above will be described with reference to the flowchart shown in FIG. In the partially new link display process, first, a list record is extracted from the list (step ST81). That is, a link record that is partially stored in the new list is extracted.
次いで、リンク形状が取り出される(ステップST82)。すなわち、リンクレコードに含まれるリンク形状を表すデータ、より詳しくは形状座標が取り出される。次いで、表示対象形状絞込みが行われる(ステップST83)。この表示対象形状絞込みにおいては、図21に示すように、上層リンク形状1301から下層リンク形状1302が減算され、その結果が表示対象形状1303とされる。
Next, the link shape is taken out (step ST82). That is, data representing the link shape included in the link record, more specifically, the shape coordinates are extracted. Next, the display target shape is narrowed down (step ST83). In narrowing down the display target shape, as shown in FIG. 21, the lower
次いで、線分として表示する処理が行われる(ステップST84)。すなわち、ステップST83で得られた表示対象形状1303に基づき、一部新規道路の形状が作成され、表示制御部105の制御によってモニタに表示される。以上により、一部新設リンク表示処理は終了する。
Next, a process of displaying as a line segment is performed (step ST84). That is, based on the
以上説明したように、この発明の実施の形態2に係る地図情報処理装置によれば、古い地図に存在しない道路であっても、探索経路の形状を把握できる。 As described above, according to the map information processing apparatus according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention, the shape of the searched route can be grasped even on a road that does not exist on an old map.
実施の形態3.
この発明の実施の形態3に係る地図情報処理装置は、実施の形態1または実施の形態2に係る地図情報処理装置において、上層地図上の経路を下層の道路データに追加するようにしたものである。
Embodiment 3 FIG.
The map information processing apparatus according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention is such that the route on the upper layer map is added to the road data of the lower layer in the map information processing apparatus according to
図22は、この発明の実施の形態3に係る地図情報処理装置の構成を示すブロック図である。この地図情報処理装置は、実施の形態1に係る地図情報処理装置に、道路データ追加部201が追加されて構成されている。道路データ追加部201は、経路探索・案内部107において、経路探索によって得られた上層地図上の経路に対応する下層地図上の経路が存在しないことが判断された場合は、上層地図の経路を構成するリンクの形状から下層地図の道路データを生成し、地図データ記憶部102に追加する。
FIG. 22 is a block diagram showing the configuration of the map information processing apparatus according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention. This map information processing apparatus is configured by adding a road data adding unit 201 to the map information processing apparatus according to the first embodiment. When the route search /
次に、この発明の実施の形態3に係る地図情報処理装置の動作を、経路リンクを道路データとして追加する処理を中心に、図23および図24に示すフローチャートを参照しながら説明する。まず、新規リンクを道路データとして追加する新規リンク追加処理を、図23に示すフローチャートを参照しながら説明する。 Next, the operation of the map information processing apparatus according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention will be described with reference to the flowcharts shown in FIGS. 23 and 24, focusing on the process of adding route links as road data. First, a new link addition process for adding a new link as road data will be described with reference to the flowchart shown in FIG.
新規リンク追加処理では、まず、リストからリンクレコードが取り出される(ステップST91)。すなわち、新規リストからリンクレコードが取り出される。次いで、道路データに追加する処理が行われる(ステップST92)。すなわち、道路データ追加部201は、ステップST91で取り出されたリンクレコードによって形成されるリンク形状から、下層地図の道路データを生成し、地図データ記憶部102に追加する。その後、新規リンク追加処理は終了する。
In the new link addition process, first, a link record is extracted from the list (step ST91). That is, the link record is extracted from the new list. Subsequently, the process added to road data is performed (step ST92). That is, the road data adding unit 201 generates road data of the lower-level map from the link shape formed by the link record extracted in step ST91 and adds it to the map
次に、一部新規リンクを道路データとして追加する一部新規リンク追加処理を、図24に示すフローチャートを参照しながら説明する。一部新規リンク追加処理では、まず、リストからリンクレコードが取り出される(ステップST101)。すなわち、一部新規リストからリンクレコードが取り出される。次いで、表示対象形状絞込みが行われる(ステップST102)。このステップST102で行われる表示対象形状絞込み処理は、実施の形態2に係る地図情報処理装置の一部新設リンク表示処理で行われる表示対象形状絞込み処理(図20に示すフローチャートのステップST83)と同じである。 Next, partial new link addition processing for adding a partial new link as road data will be described with reference to the flowchart shown in FIG. In the partial new link addition process, first, a link record is extracted from the list (step ST101). That is, a link record is extracted from a partially new list. Next, the display target shape is narrowed down (step ST102). The display target shape narrowing process performed in step ST102 is the same as the display target shape narrowing process (step ST83 of the flowchart shown in FIG. 20) performed in the partially new link display process of the map information processing apparatus according to the second embodiment. It is.
次いで、道路データに追加する処理が行われる(ステップST103)。すなわち、道路データ追加部201は、ステップST102で表示対象形状絞込み処理を行うことにより得られたリンク形状から、下層地図の道路データを生成し、地図データ記憶部102に追加する。その後、一部新規リンク追加処理は終了する。
Subsequently, the process added to road data is performed (step ST103). That is, the road data adding unit 201 generates road data of the lower layer map from the link shape obtained by performing the display target shape narrowing process in step ST102 and adds it to the map
以上説明したように、この発明の実施の形態3に係る地図情報処理装置によれば、古い地図であっても一度経路探索に使用された新道の道路データが地図データ記憶部102に格納されるので、次回からは正しい経路案内ができる。
As described above, according to the map information processing apparatus according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention, road data of a new road once used for route search is stored in the map
実施の形態4.
この発明の実施の形態4に係る地図情報処理装置は、実施の形態1または実施の形態2に係る地図情報処理装置において、上層地図上の経路を下層地図の背景データに追加するようにしたものである。
Embodiment 4 FIG.
The map information processing apparatus according to Embodiment 4 of the present invention is such that the route on the upper layer map is added to the background data of the lower layer map in the map information processing apparatus according to
図25は、この発明の実施の形態4に係る地図情報処理装置の構成を示すブロック図である。この地図情報処理装置は、実施の形態1に係る地図情報処理装置に、背景データ追加部301が追加されて構成されている。背景データ追加部301は、経路探索・案内部107において、経路探索によって得られた上層地図上の経路に対応する下層地図上の経路が存在しないことが判断された場合は、上層リンクの形状から下層地図の背景データを生成し、地図データ記憶部102に追加する。
FIG. 25 is a block diagram showing a configuration of a map information processing apparatus according to Embodiment 4 of the present invention. This map information processing apparatus is configured by adding a background data adding unit 301 to the map information processing apparatus according to the first embodiment. When the route search /
次に、この発明の実施の形態4に係る地図情報処理装置の動作を、経路リンクを道路データとして追加する処理を中心に、図26および図27に示すフローチャートを参照しながら説明する。まず、新規リンクを背景データとして追加する新規リンク追加処理を、図26に示すフローチャートを参照しながら説明する。 Next, the operation of the map information processing apparatus according to Embodiment 4 of the present invention will be described with reference to the flowcharts shown in FIGS. 26 and 27, focusing on the process of adding route links as road data. First, a new link addition process for adding a new link as background data will be described with reference to the flowchart shown in FIG.
新規リンク追加処理では、まず、リストからリンクレコードが取り出される(ステップST111)。すなわち、新規リストからリンクレコードが取り出される。次いで、背景データに追加する処理が行われる(ステップST112)。すなわち、背景データ追加部301は、ステップST111で取り出されたリンクレコードによって形成されるリンク形状から、下層地図の背景データを生成し、地図データ記憶部102に追加する。その後、新規リンク追加処理は終了する。
In the new link addition process, first, a link record is extracted from the list (step ST111). That is, the link record is extracted from the new list. Next, processing to add to the background data is performed (step ST112). That is, the background data adding unit 301 generates background data of the lower-level map from the link shape formed by the link record extracted in step ST111 and adds it to the map
次に、一部新規リンクを背景データとして追加する一部新規リンク追加処理を、図27に示すフローチャートを参照しながら説明する。一部新規リンク追加処理では、まず、リストからリンクレコードが取り出される(ステップST121)。すなわち、一部新規リストからリンクレコードが取り出される。次いで、表示対象形状絞込みが行われる(ステップST122)。このステップST122で行われる表示対象形状絞込み処理は、実施の形態2に係る地図情報処理装置の一部新設リンク表示処理で行われる表示対象形状絞込み処理(図20に示すフローチャートのステップST83)と同じである。 Next, partial new link addition processing for adding a partial new link as background data will be described with reference to the flowchart shown in FIG. In the partial new link addition process, first, a link record is extracted from the list (step ST121). That is, a link record is extracted from a partially new list. Next, the display target shape is narrowed down (step ST122). The display target shape narrowing process performed in step ST122 is the same as the display target shape narrowing process (step ST83 in the flowchart shown in FIG. 20) performed in the partially new link display process of the map information processing apparatus according to the second embodiment. It is.
次いで、背景データに追加する処理が行われる(ステップST123)。すなわち、道路データ追加部201は、ステップST102で表示対象形状絞込み処理を行うことにより得られたリンク形状から、下層地図の背景データを生成し、地図データ記憶部102に追加する。その後、一部新規リンク追加処理は終了する。
Next, processing to add to the background data is performed (step ST123). That is, the road data adding unit 201 generates background data of the lower layer map from the link shape obtained by performing the display target shape narrowing process in step ST102 and adds it to the map
以上説明したように、この発明の実施の形態4に係る地図情報処理装置によれば、古い地図であっても一度経路探索に使用された新道の表示データが地図データ記憶部102に背景データとして格納されるので、次回からは、この背景データを用いて新道の形状を表示させることができる。
As described above, according to the map information processing apparatus of the fourth embodiment of the present invention, even if an old map is used, the new road display data once used for route search is stored in the map
実施の形態5.
この発明の実施の形態5に係る地図情報処理装置は、上述した実施の形態3または実施の形態4に係る地図情報処理装置において、追加対象とする道路データまたは背景データの判定処理を具体化したものである。
Embodiment 5 FIG.
The map information processing apparatus according to Embodiment 5 of the present invention embodies the determination processing of road data or background data to be added in the map information processing apparatus according to Embodiment 3 or Embodiment 4 described above. Is.
この発明の実施の形態5に係る地図情報処理装置の構成は、図22に示した実施の形態3に係る地図情報処理装置または図25に示した実施の形態4に係る地図情報処理装置の構成と同じである。 The configuration of the map information processing apparatus according to Embodiment 5 of the present invention is that of the map information processing apparatus according to Embodiment 3 shown in FIG. 22 or the map information processing apparatus according to Embodiment 4 shown in FIG. Is the same.
次に、この発明の実施の形態5に係る地図情報処理装置の動作を、道路データおよび表示データの追加対象を判定する処理を中心に、図28に示すフローチャートを参照しながら説明する。 Next, the operation of the map information processing apparatus according to Embodiment 5 of the present invention will be described with reference to the flowchart shown in FIG. 28, centering on the process of determining the addition target of road data and display data.
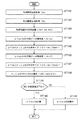
この処理では、まず、作成範囲右端が取得される(ステップST131)。すなわち、地図データのヘッダに含まれる作成範囲の中の作成区域右端:Xeが取得される。次いで、作成範囲左端が取得される(ステップST132)。すなわち、地図データのヘッダに含まれる作成範囲の中の作成区域左端:Xsが取得される。次いで、作成範囲のX方向距離が算出される(ステップST133)。すなわち、ステップST131で取得された作成区域右端:XeからステップST132で取得された作成区域左端:Xsを減じた値の絶対値がX方向距離Xdとして算出される。 In this process, first, the right end of the creation range is acquired (step ST131). That is, the creation area right end: Xe in the creation range included in the header of the map data is acquired. Next, the left end of the creation range is acquired (step ST132). That is, the creation area left end: Xs in the creation range included in the header of the map data is acquired. Next, the X-direction distance of the creation range is calculated (step ST133). That is, the absolute value of the value obtained by subtracting the creation area left end: Xs acquired in step ST132 from the creation area right end: Xe acquired in step ST131 is calculated as the X-direction distance Xd.
次いで、レベルn1のX方向データ数が取得される(ステップST134)。すなわち、レベルn1データに含まれるX方向データ数Xmn1が取得される。次いで、レベルn1メッシュのX方向のサイズが算出される(ステップST135)。すなわち、ステップST133で算出されたX方向距離Xdを、ステップST135で算出されたX方向データ数Xmn1で除することにより、レベルn1メッシュのX方向のサイズSn1が算出される。 Next, the number of X direction data of level n1 is acquired (step ST134). That is, the X direction data number Xmn1 included in the level n1 data is acquired. Next, the size of the level n1 mesh in the X direction is calculated (step ST135). That is, the X direction size Sn1 of the level n1 mesh is calculated by dividing the X direction distance Xd calculated in step ST133 by the X direction data number Xmn1 calculated in step ST135.
次いで、レベルn1より上層のレベルn2のX方向データ数が取得される(ステップST136)。すなわち、レベルn2データに含まれるX方向データ数Xmn2が取得される。次いで、レベルn2メッシュのX方向のサイズが算出される(ステップST137)。すなわち、ステップST133で算出されたX方向距離Xdを、ステップST136で算出されたX方向データ数Xmn2で除することにより、レベルn2メッシュのX方向のサイズSn2が算出される。 Next, the number of X-direction data at level n2 above level n1 is acquired (step ST136). That is, the X direction data number Xmn2 included in the level n2 data is acquired. Next, the size of the level n2 mesh in the X direction is calculated (step ST137). That is, the X-direction size Sn2 of the level n2 mesh is calculated by dividing the X-direction distance Xd calculated in step ST133 by the X-direction data number Xmn2 calculated in step ST136.
次いで、メッシュのXサイズの比が算出される(ステップST138)。すなわち、ステップST137で算出されたX方向のサイズSn2を、ステップST135で算出されたX方向のサイズSn1で除することにより、これらの比DIVが算出される。次いで、ステップST138で算出された比DIVが所定値以下であるかどうかが調べられる(ステップST139)。このステップST139において、比DIVが所定値以下であることが判断されると、レベルn2は対象とされる(ステップST140)。その後、処理は終了する。一方、ステップST139において、比DIVが所定値以下でないことが判断されると、レベルn2は対象外とされる(ステップST141)。その後、処理は終了する。 Next, the ratio of the X size of the mesh is calculated (step ST138). That is, the ratio DIV is calculated by dividing the size Sn2 in the X direction calculated in step ST137 by the size Sn1 in the X direction calculated in step ST135. Next, it is checked whether or not the ratio DIV calculated in step ST138 is equal to or less than a predetermined value (step ST139). If it is determined in step ST139 that the ratio DIV is equal to or smaller than the predetermined value, the level n2 is targeted (step ST140). Thereafter, the process ends. On the other hand, if it is determined in step ST139 that the ratio DIV is not less than or equal to the predetermined value, the level n2 is excluded (step ST141). Thereafter, the process ends.
以上の処理により、階層レベルn1に上層の階層レベルn2のリンクを追加するかどうかは、メッシュのX方向の大きさの比DIV、つまり上層地図と下層地図との精度の比が規定値以下かどうかによって判定され、規定値以下であれば、階層レベルn1に上層の階層レベルn2のリンクが追加される。 As a result of the above processing, whether or not the link of the upper hierarchy level n2 is added to the hierarchy level n1 depends on whether the ratio DIV of the size of the mesh in the X direction, that is, the accuracy ratio between the upper map and the lower map is less than the specified value. If it is determined depending on whether or not it is equal to or less than the specified value, the link of the upper hierarchy level n2 is added to the hierarchy level n1.
以上説明したように、この発明の実施の形態5に係る地図情報処理装置によれば、実際の道路形状と大きく異なる可能性がある道路データまたは背景データを地図データ記憶部102に追加しないように構成できる。
As described above, according to the map information processing apparatus according to the fifth embodiment of the present invention, road data or background data that may greatly differ from the actual road shape is not added to the map
なお、実施の形態5に係る地図情報処理装置は、実施の形態2に係る地図情報処理装置において行われる上層経路の形状の表示にも適用できる。 The map information processing apparatus according to the fifth embodiment can also be applied to the display of the shape of the upper layer route performed in the map information processing apparatus according to the second embodiment.
実施の形態6.
この発明の実施の形態6に係る地図情報処理装置は、上層地図で新旧バージョン領域を表示するようにしたものである。この発明の実施の形態6に係る地図情報処理装置の構成は、図1に示した実施の形態1に係る地図情報処理装置の構成と同じである。
Embodiment 6 FIG.
The map information processing apparatus according to the sixth embodiment of the present invention displays the old and new version areas on the upper layer map. The configuration of the map information processing apparatus according to Embodiment 6 of the present invention is the same as that of the map information processing apparatus according to
図29および図30は、実施の形態6に係る地図情報処理装置の動作を説明するための図である。図29(a)は、上層メッシュを示し、図29(b)は、上層メッシュに対応する複数の下層メッシュ(4×4)の範囲を示している。下層メッシュのメッシュ1401〜1404は最新バージョンのメッシュであり、それ以外は旧バージョンのメッシュであることを示している。 29 and 30 are diagrams for explaining the operation of the map information processing apparatus according to the sixth embodiment. FIG. 29A shows an upper layer mesh, and FIG. 29B shows a range of a plurality of lower layer meshes (4 × 4) corresponding to the upper layer mesh. The lower layer meshes 1401 to 1404 are the latest version meshes, and the other meshes are the old version meshes.
次に、この発明の実施の形態6に係る地図情報処理装置の動作を、新旧バージョン領域を表示する処理を中心に、図31に示すフローチャートを参照しながら説明する。この処理は、表示制御部105の制御によって行われる。
Next, the operation of the map information processing apparatus according to Embodiment 6 of the present invention will be described with reference to the flowchart shown in FIG. This process is performed under the control of the
この処理では、まず、範囲内の下層メッシュがリストに追加される(ステップST151)。すなわち、図29(a)に示すような上層メッシュに対応する、図29(b)に示すような下層メッシュの範囲が図示しないリストに追加される。 In this process, first, the lower layer mesh within the range is added to the list (step ST151). That is, the range of the lower layer mesh as shown in FIG. 29 (b) corresponding to the upper layer mesh as shown in FIG. 29 (a) is added to the list (not shown).
次いで、リストから1つの下層メッシュが取得される(ステップST152)。次いで、ステップST153で取り出された下層メッシュが最新バージョンであるかどうかが調べられる(ステップST153)。このステップST153において、最新バージョンであることが判断されると、シーケンスはステップST156に進む。 Next, one lower layer mesh is acquired from the list (step ST152). Next, it is checked whether or not the lower layer mesh extracted in step ST153 is the latest version (step ST153). If it is determined in step ST153 that it is the latest version, the sequence proceeds to step ST156.
一方、ステップST153において、最新バージョンでないことが判断されると、描画範囲が算出される(ステップST154)。すなわち、当該下層メッシュに対応する地図の描画範囲が算出される。次いで、網掛け表示が重畳される(ステップST155)。すなわち、ステップST154で算出された描画範囲に網掛けが施される。その後、シーケンスはステップST156に進む。 On the other hand, if it is determined in step ST153 that the version is not the latest version, a drawing range is calculated (step ST154). That is, a map drawing range corresponding to the lower layer mesh is calculated. Next, a shaded display is superimposed (step ST155). That is, the drawing range calculated in step ST154 is shaded. Thereafter, the sequence proceeds to step ST156.
ステップST156においては、全てのメッシュが取り出されたかどうかが調べられる。すなわち、ステップST151において、リストに追加された全ての下層メッシュに対する処理が終了したかどうかが調べられる。このステップST156において、全てのメッシュが取り出されていないことが判断されると、シーケンスはステップST152に戻り、上述した処理が繰り返される。一方、ステップST156において、全てのメッシュが取り出されたことが判断されると、新旧バージョン領域を表示する処理は終了する。 In step ST156, it is checked whether all the meshes have been extracted. That is, in step ST151, it is checked whether or not the processing for all lower layer meshes added to the list has been completed. If it is determined in step ST156 that all the meshes have not been extracted, the sequence returns to step ST152, and the above-described processing is repeated. On the other hand, when it is determined in step ST156 that all the meshes have been extracted, the process of displaying the old and new version areas ends.
以上の処理により、上層メッシュの範囲に対応する下層メッシュのバージョンがチェックされ、最新バージョンでない下層メッシュの範囲に網掛けが行われ、他と異なった形態で表示されるので、上層地図を、図30に示すように新旧バージョンの領域を区別して表示することができ、どの地域が新しいバージョンの地図であるかを容易に把握できる。 By the above processing, the version of the lower layer mesh corresponding to the range of the upper layer mesh is checked, the range of the lower layer mesh that is not the latest version is shaded, and displayed in a different form from the others, so the upper layer map As shown in FIG. 30, the old and new version areas can be distinguished and displayed, and it can be easily understood which area is the new version map.
実施の形態7.
この発明の実施の形態7に係る地図情報処理装置は、経路が設定されているか否かとは無関係に、上層地図の新道を下層地図に追加するようにしたものである。
Embodiment 7 FIG.
The map information processing apparatus according to Embodiment 7 of the present invention adds a new road of the upper layer map to the lower layer map regardless of whether or not a route is set.
この発明の実施の形態7に係る地図情報処理装置の構成は、図示は省略するが、図22に示した実施の形態3に係る地図情報処理装置の構成と同様に、実施の形態1に係る地図情報処理装置に道路データ追加部201を追加して構成されている。道路データ追加部201は、所定のタイミングで、上層地図の道路を構成するリンクの形状から下層地図の道路データを生成し、地図データ記憶部102に追加する。
Although the illustration of the configuration of the map information processing apparatus according to Embodiment 7 of the present invention is omitted, the configuration of the map information processing apparatus according to
次に、この発明の実施の形態7に係る地図情報処理装置の動作を、表示対象となるリンクを選択する選択処理を中心に、図32に示すフローチャートを参照しながら説明する。この選択処理では、表示対象として、新設および一部新設のリンクを選択してリスト(図示しない)に格納する処理が行われる。 Next, the operation of the map information processing apparatus according to Embodiment 7 of the present invention will be described with reference to the flowchart shown in FIG. 32, focusing on selection processing for selecting a link to be displayed. In this selection processing, processing for selecting new and partially new links as display objects and storing them in a list (not shown) is performed.
この選択処理では、まず、上層地図が読み出される(ステップST161)。すなわち、現在処理の対象としている階層の地図の上層地図が地図データ記憶部102から読み出される。次いで、先頭経路リンクが取得される(ステップST162)。すなわち、ステップST161で読み出された地図に含まれる先頭のリンクデータが取得される。次いで、下層地図のエリア内であるかどうかが調べられる(ステップST163)。すなわち、上記ステップST162または後述するステップST168で取得されたリンクデータによって示されるリンクが、下層エリア内に存在するリンクであるかどうかが調べられる。
In this selection process, first, an upper layer map is read (step ST161). That is, the upper layer map of the hierarchy map currently being processed is read from the map
このステップST163において、下層地図のエリア内でないことが判断されると、シーケンスはステップST167に進む。一方、ステップST163において、下層地図のエリア内であることが判断されると、次いで、リンク状態が判定される(ステップST164)。すなわち、ステップST162またはステップST168で取得されたリンクレコードによって示されるリンクが、「新規」、「一部新規」または「既存」のいずれであるかが調べられる。 If it is determined in step ST163 that it is not in the area of the lower layer map, the sequence proceeds to step ST167. On the other hand, if it is determined in step ST163 that it is within the area of the lower layer map, then the link state is determined (step ST164). That is, it is checked whether the link indicated by the link record acquired in step ST162 or step ST168 is “new”, “partially new”, or “existing”.
このステップST164において、リンクが「新規」であることが判断されると、次いで、新規リストに追加される(ステップST165)。すなわち、ステップST162またはステップST168で取り出されたリンクレコードが、図示しない新規リストに追加される。その後、シーケンスはステップST167に進む。 If it is determined in step ST164 that the link is “new”, it is then added to the new list (step ST165). That is, the link record extracted in step ST162 or step ST168 is added to a new list (not shown). Thereafter, the sequence proceeds to step ST167.
ステップST164において、リンクが「一部新規」であることが判断されると、次いで、一部新規リストに追加される(ステップST166)。すなわち、ステップST162またはステップST168で取り出されたリンクレコードが、図示しない一部新規リストに追加される。その後、シーケンスはステップST167に進む。ステップST164において、リンクが「既存」であることが判断されると、シーケンスは、ステップST167に進む。 If it is determined in step ST164 that the link is “partially new”, it is then added to the partly new list (step ST166). That is, the link record extracted in step ST162 or step ST168 is added to a partially new list (not shown). Thereafter, the sequence proceeds to step ST167. If it is determined in step ST164 that the link is “existing”, the sequence proceeds to step ST167.
ステップST167においては、最後尾のリンクレコードであるかどうかが調べられる。このステップST167において、最後尾のリンクレコードでないことが判断されると、次のリンクレコードが取得される(ステップST168)。その後、シーケンスはステップST163に戻り、上述した処理が繰り返される。一方、ステップST167において、最後尾のリンクレコードであることが判断されると、選択処理は終了する。以上の処理は、すべての下層メッシュに対して実施される。 In step ST167, it is checked whether it is the last link record. If it is determined in step ST167 that it is not the last link record, the next link record is acquired (step ST168). Thereafter, the sequence returns to step ST163, and the above-described processing is repeated. On the other hand, if it is determined in step ST167 that it is the last link record, the selection process ends. The above processing is performed for all lower layer meshes.
以上の選択処理が行われた後に、道路データ追加部201は、所定のタイミングで、新規リストおよび一部新規リストから読み出したリンクレコードに基づいて、上層地図の道路を構成するリンクの形状から下層地図の道路データを生成し、地図データ記憶部102に追加する。これにより、上層地図の新道を下層地図に追加することができる。
After the above selection processing is performed, the road data adding unit 201 determines, based on the link records read from the new list and the partial new list, at a predetermined timing from the shape of the link constituting the road of the upper layer map. Map road data is generated and added to the map
100 ナビゲーション制御部、101 地図データ入力部、102 地図データ記憶部、103 GPS受信機、104 自律センサ、105 表示制御部、106 自車位置算出部、107 経路探索・案内部、108 操作制御部、201 道路データ追加部、301 背景データ追加部。 100 navigation control unit, 101 map data input unit, 102 map data storage unit, 103 GPS receiver, 104 autonomous sensor, 105 display control unit, 106 own vehicle position calculation unit, 107 route search / guide unit, 108 operation control unit, 201 road data addition unit, 301 background data addition unit.
Claims (9)
前記地図データ記憶部に記憶されている下層地図および上層地図の地図データを用いて経路探索を実行し、該経路探索によって得られた上層地図上の経路に対応する下層地図上の経路が存在する場合は該経路を表示して経路案内を行い、上層地図上の経路に対応する下層地図上の経路が存在しない場合は、目的地の方向を示した簡易案内を行う経路探索・案内部
とを備えた地図情報処理装置。 A map data storage unit that has a hierarchical structure and is upgraded for each region, and stores map data in which an upper layer map corresponding to the lower layer map is upgraded in accordance with a version upgrade of the lower layer map; ,
The route search is executed using the map data of the lower layer map and the upper layer map stored in the map data storage unit, and there is a route on the lower layer map corresponding to the route on the upper layer map obtained by the route search. If there is no route on the lower layer map that corresponds to the route on the upper layer map, the route search / guidance unit that performs simple guidance indicating the direction of the destination is displayed. Map information processing device provided.
ことを特徴とする請求項1記載の地図情報処理装置。 The map information processing apparatus according to claim 1, wherein the route search / guidance unit performs simple guidance by displaying the shape of the route on the upper layer map superimposed on the lower layer map.
ことを特徴とする請求項2記載の地図情報処理装置。 3. The map information processing apparatus according to claim 2, wherein whether or not the shape of the route on the upper layer map is displayed on the lower layer map is determined based on a ratio of accuracy between the upper layer map and the lower layer map.
前記地図データ記憶部に記憶されている下層地図および上層地図の地図データを用いて経路探索を実行し、該経路探索によって得られた上層地図上の経路に対応する下層地図上の経路が存在する場合は該経路を表示して経路案内を行う経路探索・案内部と、
前記経路探索・案内部において、経路探索によって得られた上層地図上の経路に対応する下層地図上の経路が存在しないことが判断された場合は、上層地図の経路を構成するリンクの形状から下層地図の道路データを生成し、前記地図データ記憶部に追加する道路データ追加部
とを備えた地図情報処理装置。 A map data storage unit that has a hierarchical structure and is map data that is upgraded for each region, and that stores map data in which the upper layer map corresponding to the lower layer map is upgraded in accordance with the version upgrade of the lower layer map; ,
The route search is executed using the map data of the lower layer map and the upper layer map stored in the map data storage unit, and there is a route on the lower layer map corresponding to the route on the upper layer map obtained by the route search. In this case, a route search / guide unit that displays the route and provides route guidance,
In the route search / guidance unit, when it is determined that there is no route on the lower layer map corresponding to the route on the upper layer map obtained by the route search, the shape of the link constituting the route of the upper layer map is used as the lower layer. A map information processing apparatus comprising: a road data adding unit that generates road data of a map and adds the road data to the map data storage unit.
ことを特徴とする請求項4記載の地図情報処理装置。 Whether or not road data of a lower layer map is generated from the shape of a link constituting the route of the upper layer map and added to the map data storage unit is determined based on a ratio of accuracy between the upper layer map and the lower layer map. The map information processing apparatus according to claim 4.
前記地図データ記憶部に記憶されている下層地図および上層地図の地図データを用いて経路探索を実行し、該経路探索によって得られた上層地図上の経路に対応する下層地図上の経路が存在する場合は該経路を表示して経路案内を行う経路探索・案内部と、
前記経路探索・案内部において、経路探索によって得られた上層地図上の経路に対応する下層地図上の経路が存在しないことが判断された場合は、上層地図の経路を構成するリンクの形状から表示用データ生成し、前記地図データ記憶部に背景データとして追加する背景データ追加部
とを備えた地図情報処理装置。 A map data storage unit that has a hierarchical structure and is map data that is upgraded for each region, and that stores map data in which the upper layer map corresponding to the lower layer map is upgraded in accordance with the version upgrade of the lower layer map; ,
The route search is executed using the map data of the lower layer map and the upper layer map stored in the map data storage unit, and there is a route on the lower layer map corresponding to the route on the upper layer map obtained by the route search. In this case, a route search / guide unit that displays the route and provides route guidance,
In the route search / guidance unit, when it is determined that there is no route on the lower layer map corresponding to the route on the upper layer map obtained by the route search, the display is made from the shape of the link constituting the route of the upper layer map. A map information processing apparatus comprising: a background data adding unit that generates data for use and adds it as background data to the map data storage unit.
ことを特徴とする請求項6記載の地図情報処理装置。 Whether or not display data is generated from the shape of the link constituting the route of the upper layer map and added as background data to the map data storage unit is determined based on the accuracy ratio between the upper layer map and the lower layer map. The map information processing apparatus according to claim 6.
前記地図データ記憶部に記憶されている地図データに基づき上層地図を表示する場合に下層地図が旧バージョンの地域は他と異なった形態で表示させる表示制御部
とを備えた地図情報処理装置。 A map data storage unit that has a hierarchical structure and is map data that is upgraded for each region, and that stores map data in which the upper layer map corresponding to the lower layer map is upgraded in accordance with the version upgrade of the lower layer map; ,
A map information processing apparatus comprising: a display control unit that displays an area of an older version of a lower layer map in a different form from the others when displaying an upper layer map based on map data stored in the map data storage unit.
前記地図データ記憶部に記憶されている地図データに基づき上層地図上の道路に対応する下層地図上の道路が存在しないことが判断された場合は、上層地図の道路を構成するリンクの形状から下層地図の道路データを生成し、前記地図データ記憶部に追加する道路データ追加部
とを備えた地図情報処理装置。 A map data storage unit that has a hierarchical structure and is map data that is upgraded for each region, and that stores map data in which the upper layer map corresponding to the lower layer map is upgraded in accordance with the version upgrade of the lower layer map; ,
When it is determined that there is no road on the lower map corresponding to the road on the upper map based on the map data stored in the map data storage unit, the shape of the link constituting the road of the upper map is used as the lower layer. A map information processing apparatus comprising: a road data adding unit that generates road data of a map and adds the road data to the map data storage unit.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008176820A JP5127604B2 (en) | 2008-07-07 | 2008-07-07 | Map information processing device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008176820A JP5127604B2 (en) | 2008-07-07 | 2008-07-07 | Map information processing device |
Related Child Applications (3)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012074027A Division JP5409834B2 (en) | 2012-03-28 | 2012-03-28 | Map information processing device |
| JP2012074037A Division JP5383848B2 (en) | 2012-03-28 | 2012-03-28 | Map information processing device |
| JP2012074051A Division JP2012141321A (en) | 2012-03-28 | 2012-03-28 | Map information processing apparatus |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2010014657A true JP2010014657A (en) | 2010-01-21 |
| JP5127604B2 JP5127604B2 (en) | 2013-01-23 |
Family
ID=41700890
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008176820A Active JP5127604B2 (en) | 2008-07-07 | 2008-07-07 | Map information processing device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5127604B2 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016125824A (en) * | 2014-12-26 | 2016-07-11 | 日立オートモティブシステムズ株式会社 | Information processing device |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0933267A (en) * | 1995-07-18 | 1997-02-07 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Traveling-position indicator |
| JPH1124554A (en) * | 1997-07-04 | 1999-01-29 | Toyota Motor Corp | Map display device, map data memory device and map data memory medium |
| JP2003315061A (en) * | 2002-04-25 | 2003-11-06 | Aisin Aw Co Ltd | Navigation apparatus |
-
2008
- 2008-07-07 JP JP2008176820A patent/JP5127604B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0933267A (en) * | 1995-07-18 | 1997-02-07 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Traveling-position indicator |
| JPH1124554A (en) * | 1997-07-04 | 1999-01-29 | Toyota Motor Corp | Map display device, map data memory device and map data memory medium |
| JP2003315061A (en) * | 2002-04-25 | 2003-11-06 | Aisin Aw Co Ltd | Navigation apparatus |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016125824A (en) * | 2014-12-26 | 2016-07-11 | 日立オートモティブシステムズ株式会社 | Information processing device |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP5127604B2 (en) | 2013-01-23 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5001617B2 (en) | Map update data supply device, version table, map data update system, map update data supply program, and map data update program | |
| JP4954275B2 (en) | Map information processing device | |
| JP4823351B2 (en) | Map information processing device | |
| EP1477769B1 (en) | Navigation apparatus | |
| JP4757752B2 (en) | Map information processing device | |
| JP4684565B2 (en) | Guidance information retrieval apparatus and guidance information retrieval system using the same | |
| JP4786212B2 (en) | Navigation device, control method thereof, and control program | |
| JP5127604B2 (en) | Map information processing device | |
| WO2010061545A1 (en) | Facility-searching device | |
| JP5409834B2 (en) | Map information processing device | |
| JP5383848B2 (en) | Map information processing device | |
| JP2012141321A (en) | Map information processing apparatus | |
| JP5335853B2 (en) | Map information processing device | |
| JP2005326775A (en) | Navigation system | |
| JP4034113B2 (en) | Map data update system and map data update program | |
| JP2010014658A (en) | Map information processing apparatus | |
| JP2008261746A (en) | Map information processing device | |
| JP5403958B2 (en) | Map information processing device | |
| JP5300334B2 (en) | Map information processing device | |
| JP3860392B2 (en) | Route search device | |
| JPH06348996A (en) | Navigation device | |
| JP4455173B2 (en) | Navigation device | |
| JPH07244689A (en) | Device and method for route determination | |
| JP4888972B2 (en) | Navigation device | |
| JP4082799B2 (en) | Navigation apparatus and method |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20101007 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20120126 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20120131 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20120328 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20121002 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20121030 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Ref document number: 5127604 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20151109 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |