JP2009297290A - Endoscope apparatus and image processing method thereof - Google Patents
Endoscope apparatus and image processing method thereof Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2009297290A JP2009297290A JP2008155597A JP2008155597A JP2009297290A JP 2009297290 A JP2009297290 A JP 2009297290A JP 2008155597 A JP2008155597 A JP 2008155597A JP 2008155597 A JP2008155597 A JP 2008155597A JP 2009297290 A JP2009297290 A JP 2009297290A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- light
- endoscope apparatus
- image
- endoscope
- illumination
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Abandoned
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B1/00—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor
- A61B1/06—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor with illuminating arrangements
- A61B1/063—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor with illuminating arrangements for monochromatic or narrow-band illumination
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B1/00—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor
- A61B1/00163—Optical arrangements
- A61B1/00165—Optical arrangements with light-conductive means, e.g. fibre optics
- A61B1/0017—Details of single optical fibres, e.g. material or cladding
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B1/00—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor
- A61B1/04—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor combined with photographic or television appliances
- A61B1/043—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor combined with photographic or television appliances for fluorescence imaging
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B1/00—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor
- A61B1/06—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor with illuminating arrangements
- A61B1/0638—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor with illuminating arrangements providing two or more wavelengths
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B1/00—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor
- A61B1/06—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor with illuminating arrangements
- A61B1/0653—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor with illuminating arrangements with wavelength conversion
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B1/00—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor
- A61B1/06—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor with illuminating arrangements
- A61B1/0655—Control therefor
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B1/00—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor
- A61B1/06—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor with illuminating arrangements
- A61B1/0661—Endoscope light sources
- A61B1/0684—Endoscope light sources using light emitting diodes [LED]
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B1/00—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor
- A61B1/06—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor with illuminating arrangements
- A61B1/07—Instruments for performing medical examinations of the interior of cavities or tubes of the body by visual or photographical inspection, e.g. endoscopes; Illuminating arrangements therefor with illuminating arrangements using light-conductive means, e.g. optical fibres
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Radiology & Medical Imaging (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Endoscopes (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、内視鏡装置およびその画像処理方法に関する。 The present invention relates to an endoscope apparatus and an image processing method thereof.
従来より広く使用されている内視鏡装置は、光源装置内のランプからの照明光を内視鏡挿入部に沿って設けたライトガイドにより導光し,このライトガイドで導光された照明光を内視鏡挿入部の先端の照明窓から出射して検査対象部位を照明する構成になっている。これに対し、光源としてランプに代えてLED素子を用いたものがいくつか提案されている(例えば特許文献1、2)。
特許文献1の光源装置では、LED素子を内視鏡の操作部またはその近傍に配置して、光ファイバ束であるライトガイドを通じて内視鏡挿入部の先端から光出力している。また、特許文献2に記載の光源装置では、LED素子を内視鏡挿入部の先端に配置して、ストロボ撮影時にだけ発光照射し、通常はライトガイドを通して供給されるキセノン光源の光を照射するようにしている。
また、LED素子の他にもレーザ光により照明を行うものがある。特許文献3の光源装置は、青色レーザ光を光ファイバーにより内視鏡挿入部先端に導き、光ファイバー先端に配置された蛍光体を励起発光させることで、白色照明光を照射する構成となっている。
An endoscope apparatus that has been widely used conventionally guides illumination light from a lamp in a light source device by a light guide provided along an endoscope insertion portion, and the illumination light guided by the light guide. Is emitted from the illumination window at the tip of the endoscope insertion portion to illuminate the region to be inspected. On the other hand, some which used the LED element instead of the lamp | ramp as a light source are proposed (for example,
In the light source device of
In addition to the LED element, there is one that performs illumination with laser light. The light source device of
ところで、内視鏡診断においては、上記の白色照明光による観察に加えて、特定の波長帯域の光で照明した画像を利用する分光診断と呼ばれる手法がある。その場合の照明光は、特定の狭い波長帯域の光が用いられる。分光診断では、例えば粘膜層あるいは粘膜下層に発生する新生血管を明瞭に観察でき、通常の観察像では得られない粘膜表面の微細構造の描写が可能であるため、例えば、病変の診断や癌の早期発見等に有益に供されている。分光診断に用いる特定の波長帯域の照明光は、波長が短いほど散乱特性が強くなるので、短波長では比較的浅い層の情報、長波長では比較的深い層からの情報が得られるようになる。そのため、光の深達度を表層に限定して表面微細構造を観察する場合には、照明光を狭帯域化することが撮像画像のコントラストを向上させる上で重要となる。
ところで、内視鏡を用いて上部消化管の診断を行う際、従来の経口内視鏡でなく、患者にとってより負担の少ない経鼻内視鏡が用いられつつある。しかし、一般的なランプとライトガイドを用いる構成や、特許文献1のように内視鏡の操作部にLED素子を配置してLED素子の発光光を操作部から内視鏡先端部へライトガイドを通じて導光させる構成では、内視鏡挿入部の細径化には限度がある。つまり、光源が一般的なランプの場合は、照明光を小さく絞ることが困難であり、LEDの場合は、一般的なランプに対して発光光源の面積は小さいが、高輝度を得ようとすると発光面の面積が増大するので、細径化できない。また、光源からの発光をライトガイドに導入する際の光の損失もあり、光の伝送効率(利用効率)が低下する不利があった。
また、特許文献2のように内視鏡挿入部の先端にLED素子を配置した場合、ライトガイドが不要となる。しかし、白色照明用として所定の光量を得るためにはLED素子からの発熱は、電気エネルギーを青色光に変換するための発熱と青色から蛍光体光を発生させるための発熱が非常に大きく、これを抑える必要があるが、コンパクトな構成のまま十分に放熱させることは困難であった。特に経鼻内視鏡は、内視鏡挿入部が細く、ライトガイドの太さを確保することが困難になる。そこで、照明光量を十分確保するには単位面積あたりの光量を増やせばよいが、発熱が増大するので好ましくない。そのため、内視鏡挿入部の先端に配置したLED素子は、ライトガイドを通じて光源装置から供給される照明光と併用して低輝度で発光させるか、あるいは一時的な点灯であるストロボ撮影時のみに利用する等、使用条件が限られていた。
さらに、特許文献3のように、レーザ光を細径の光ファイバーで導光することで電気エネルギーを青色励行に変換する発熱は先端部ではなく外部になり、先端部では青色の励起光から蛍光体発光への発熱だけとなり、内視鏡挿入部の細径化は図れるが、レーザ光を蛍光体により白色光に変換する際に、所望の発光波長幅を得ること、特に波長幅の狭い発光を得ることは困難であった。また、レーザ光を直接照明光として利用する場合に、そのコヒーレンシーの高さから、スペックル(干渉)により撮影画像にノイズが重畳したり、動画でちらつきが発生しやすくなることがあった。
By the way, when diagnosing the upper gastrointestinal tract using an endoscope, a nasal endoscope that is less burdensome for a patient is being used instead of a conventional oral endoscope. However, in a configuration using a general lamp and a light guide, or as disclosed in
Moreover, when an LED element is disposed at the tip of the endoscope insertion portion as in
Furthermore, as disclosed in
本発明は、このような状況に鑑みてなされたもので、内視鏡挿入部の細径化を図り、内視鏡挿入部の先端に配置したLED素子の発熱を抑えつつ、白色光と特定の狭い可視波長帯域の光とを簡単な構成で選択的に照射して観察することができる内視鏡装置、およびこの内視鏡装置からの画像情報に基づいてより精度の高い分光診断を可能とする画像処理方法を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of such a situation. The diameter of the endoscope insertion portion is reduced, and the generation of the LED element disposed at the distal end of the endoscope insertion portion is suppressed, while white light is specified. Endoscope device capable of selectively irradiating and observing light with a narrow visible wavelength band with a simple configuration, and more accurate spectroscopic diagnosis based on image information from this endoscope device An object of the present invention is to provide an image processing method.
本発明は、下記構成からなる。
(1) レーザ光を出射する第1光源と、前記レーザ光を光入射側に入射して内視鏡挿入部先端へ伝送する光ファイバーと、該光ファイバーの光出射側に配置され前記レーザ光により励起発光する少なくとも1種の蛍光材料を含む波長変換部材と、を有し、前記レーザ光と前記波長変換部材からの励起発光光とを混合して前記内視鏡挿入部先端から白色光を出射する第1の照明光学系と、
前記内視鏡挿入部先端に配置され特定の可視波長帯域で発光する発光素子を備えた第2の照明光学系と、
を具備する内視鏡装置。
The present invention has the following configuration.
(1) A first light source that emits laser light, an optical fiber that transmits the laser light to the light incident side and transmits it to the distal end of the endoscope insertion portion, and is arranged on the light emitting side of the optical fiber and is excited by the laser light A wavelength conversion member including at least one type of fluorescent material that emits light, and the laser light and excitation light emitted from the wavelength conversion member are mixed to emit white light from the distal end of the endoscope insertion portion. A first illumination optical system;
A second illumination optical system provided with a light emitting element disposed at the distal end of the endoscope insertion portion and emitting light in a specific visible wavelength band;
An endoscope apparatus comprising:
この内視鏡装置によれば、第1光源によるレーザ光を光ファイバーにより導光し、光ファイバーの出射端に配置した波長変換部材に照射して、波長変換部材を励起発光させることで、もともとの第1光源からのレーザ光と、励起発光光とにより白色光が生成されて、白色光照明用の光学系となる。また、特定の可視波長帯域で発光する発光素子を有する第2の照明光学系を備えたことで、白色光照明と、特定の可視波長帯域の光による照明とを簡素な構成で選択的に出射させることができる。
そして、レーザ光を用いて白色照明光を生成するため、高輝度な光が得られ、しかも光ファイバーにより導光するために内視鏡挿入部の細径化が図られる。
According to this endoscope apparatus, the laser light from the first light source is guided by the optical fiber, irradiated to the wavelength conversion member disposed at the output end of the optical fiber, and the wavelength conversion member is excited to emit light. White light is generated by the laser light from one light source and the excitation light, and an optical system for white light illumination is obtained. In addition, by providing the second illumination optical system having a light emitting element that emits light in a specific visible wavelength band, white light illumination and illumination with light in a specific visible wavelength band are selectively emitted with a simple configuration. Can be made.
Since white illumination light is generated using laser light, high-luminance light is obtained, and the diameter of the endoscope insertion portion is reduced in order to guide the light through the optical fiber.
(2) (1)記載の内視鏡装置であって、
前記第2の照明光学系の前記発光素子が、LED素子である内視鏡装置。
(2) The endoscope apparatus according to (1),
An endoscope apparatus in which the light emitting element of the second illumination optical system is an LED element.
この内視鏡装置によれば、高効率で高輝度の光が得られる。また、第1の照明光学系のレーザ光と併用することで、内視鏡挿入部先端からのLED素子の光量を抑制でき、これにより、内視鏡挿入部先端の小型化と発熱の抑制が図られる。 According to this endoscope apparatus, light with high efficiency and high luminance can be obtained. Moreover, by using together with the laser light of the first illumination optical system, the light quantity of the LED element from the distal end of the endoscope insertion portion can be suppressed, thereby reducing the size of the distal end of the endoscope insertion portion and suppressing heat generation. Figured.
(3) (1)または(2)記載の内視鏡装置であって、
前記第2の照明光学系が、それぞれ異なる中心波長で発光する複数の発光素子を備えた内視鏡装置。
(3) The endoscope apparatus according to (1) or (2),
An endoscope apparatus in which the second illumination optical system includes a plurality of light emitting elements that emit light at different center wavelengths.
この内視鏡装置によれば、複数の発光素子を備えることで、観察目的に応じて種々の照明光を出射することができる。 According to this endoscope apparatus, by providing a plurality of light emitting elements, various illumination lights can be emitted according to the observation purpose.
(4) (1)〜(3)のいずれか1項記載の内視鏡装置であって、
前記第2の照明光学系が、少なくとも緑色光を発光する発光素子を有する内視鏡装置。
(4) The endoscope apparatus according to any one of (1) to (3),
An endoscope apparatus in which the second illumination optical system includes a light emitting element that emits at least green light.
この内視鏡装置によれば、緑色光を出射させることで、分光診断における強調画像の生成が行える。 According to this endoscope apparatus, it is possible to generate an emphasized image in spectroscopic diagnosis by emitting green light.
(5) (1)〜(4)のいずれか1項記載の内視鏡装置であって、
前記第2の照明光学系が、少なくとも青色光を発光する発光素子を有する内視鏡装置。
(5) The endoscope apparatus according to any one of (1) to (4),
An endoscope apparatus in which the second illumination optical system includes a light emitting element that emits at least blue light.
この内視鏡装置によれば、青色光を出射させることで、分光診断における強調画像の生成が行える。 According to this endoscope apparatus, it is possible to generate an enhanced image in spectroscopic diagnosis by emitting blue light.
(6) (1)〜(5)のいずれか1項記載の内視鏡装置であって、
前記第2の照明光学系が、少なくとも赤色光乃至赤外光を発光する発光素子を有する内視鏡装置。
(6) The endoscope apparatus according to any one of (1) to (5),
An endoscope apparatus in which the second illumination optical system includes a light emitting element that emits at least red light or infrared light.
この内視鏡装置によれば、赤色光乃至赤外光を出射させることで、赤外光が吸収されやすい薬剤を静脈注射した状態で観察する、いわゆる赤外光観察を実施できる。 According to this endoscope apparatus, by emitting red light or infrared light, it is possible to perform so-called infrared light observation in which a medicine that easily absorbs infrared light is observed in a state of being intravenously injected.
(7) (1)〜(6)のいずれか1項記載の内視鏡装置であって、
前記内視鏡挿入部先端に設けた観察窓を通して被観察部位からの光を受光して撮像信号を出力する撮像素子を含む撮像手段と、
前記第1の照明光学系による白色光と前記第2の照明光学系による特定の可視波長帯域の光とを切り換えて照明する照明光制御手段と、
を備えた内視鏡装置。
(7) The endoscope apparatus according to any one of (1) to (6),
An imaging means including an imaging element that receives light from a site to be observed through an observation window provided at a distal end of the endoscope insertion unit and outputs an imaging signal;
Illumination light control means for switching and illuminating white light by the first illumination optical system and light of a specific visible wavelength band by the second illumination optical system;
An endoscopic apparatus comprising:
この内視鏡装置によれば、内視鏡挿入部を細径化でき、また、照射する光を、白色光と特定の可視波長帯域の光とを選択的に出射制御できるので、分光診断等を容易に行うことができる。 According to this endoscope apparatus, the diameter of the endoscope insertion portion can be reduced, and the emitted light can be selectively controlled to emit white light and light in a specific visible wavelength band. Can be easily performed.
(8) (7)記載の内視鏡装置であって、
前記第1の照明光学系による白色光の照明光下において撮像した撮像信号を保存する第1のメモリと、
前記第2の照明光学系による前記特定の可視波長帯域の光を含む照明光下において撮像した撮像信号を保存する第2のメモリと、
前記第1のメモリと前記第2のメモリに保存された各撮像信号をそれぞれ異なる表示領域に表示する撮像画像表示手段と、
を備えた内視鏡装置。
(8) The endoscope apparatus according to (7),
A first memory for storing an imaging signal imaged under illumination light of white light by the first illumination optical system;
A second memory for storing an imaging signal imaged under illumination light including light of the specific visible wavelength band by the second illumination optical system;
Picked-up image display means for displaying the picked-up image signals stored in the first memory and the second memory in different display areas;
An endoscopic apparatus comprising:
この内視鏡装置によれば、照明光の種類に対応して撮像信号をそれぞれ異なるメモリに保存し、各メモリの撮像信号をそれぞれ異なる表示領域に表示させることで、例えば、白色光による照明光下の観察像と、特定の可視波長帯域の光による照明光下の観察像とを、それぞれ別々に表示させることができる。これにより、通常の観察像と特定波長で観察される像とを比較しながら診断することができる。 According to this endoscope apparatus, the imaging signals are stored in different memories corresponding to the types of illumination light, and the imaging signals of each memory are displayed in different display areas. A lower observation image and an observation image under illumination light with light in a specific visible wavelength band can be displayed separately. Thereby, diagnosis can be performed while comparing a normal observation image with an image observed at a specific wavelength.
(9) (8)記載の内視鏡装置であって、
前記照明光制御手段が、前記白色光の照明と、前記特定の可視波長帯域の光を含む照明とを、前記撮像素子による撮像フレーム毎に交互に切り換えることを特徴とする内視鏡装置。
(9) The endoscope apparatus according to (8),
The endoscope apparatus characterized in that the illumination light control means alternately switches the illumination of the white light and the illumination including the light in the specific visible wavelength band for each imaging frame by the imaging element.
この内視鏡によれば、白色光の照明下の撮像画像と、特定の可視波長帯域の光を含む照明下の撮像画像を交互に撮像することで、双方を略同時に画像取得することができ、2種類の画像情報をリアルタイムで同時に表示させることができる。 According to this endoscope, by alternately capturing a captured image under illumination of white light and a captured image under illumination including light in a specific visible wavelength band, both images can be acquired substantially simultaneously. Two types of image information can be displayed simultaneously in real time.
(10) (7)〜(9)のいずれか1項記載の内視鏡装置であって、
前記撮像素子が特定検出色成分を検出するためのカラーフィルタを備えており、
前記発光素子が発光する前記特定の可視波長帯域の発光スペクトル曲線のピークの半値幅が、前記カラーフィルタの前記特定検出色を検出する波長帯域のスペクトル感度曲線のピークの半値幅より狭い波長幅にされた内視鏡装置。
(10) The endoscope apparatus according to any one of (7) to (9),
The image sensor includes a color filter for detecting a specific detection color component;
The half width of the peak of the emission spectrum curve of the specific visible wavelength band emitted by the light emitting element is narrower than the half width of the peak of the spectral sensitivity curve of the wavelength band of the color filter for detecting the specific detection color. Endoscopic device.
この内視鏡装置によれば、発光素子が発光する特定の可視波長帯域の発光ピークの半値幅を、カラーフィルタの検出波長帯域ピークの半値幅より狭くすることで、発光素子の発光光が対応する一つの波長帯域のピーク内で検出され、他の波長帯域に影響を及ぼさない。したがって、混色等の影響を受けることがない。また、光の深達度を観察目的とする領域に合わせやすくなり、観察したい層からの情報を確実に取得できるとともに、撮像画像の高コントラスト化が図られる。 According to this endoscope apparatus, the half-value width of the emission peak of a specific visible wavelength band emitted by the light-emitting element is made narrower than the half-value width of the detection wavelength band peak of the color filter, so that the light emitted from the light-emitting element can be used. Are detected within the peak of one wavelength band and do not affect the other wavelength bands. Therefore, there is no influence of color mixing or the like. In addition, it becomes easy to adjust the depth of light to a region intended for observation, information from the layer to be observed can be acquired with certainty, and the contrast of the captured image can be increased.
(11) (7)〜(10)のいずれか1項記載の内視鏡装置を用い、それぞれ異なる特定の波長帯域光を検出した検出色画面を複数画面有して構成されるフレーム画像を、複数回にわたって撮像する一方、各フレーム画像の撮像タイミングに同期して複数種の光源からの光をそれぞれ異なる条件で照射する内視鏡装置の画像処理方法であって、
前記第1光源により被検体を照明したときの観察画像を第1フレーム画像、前記第2光源により被検体を照明したときの観察画像を第2フレーム画像として、前記第1フレーム画像と前記第2フレーム画像とを繰り返し撮像し、
前記第1フレーム画像の特定の検出色画面の輝度情報と、前記第2フレーム画像の特定の検出画面の輝度情報とを組み合わせて、前記光源装置からの特定の波長成分の光による観察画像を解析的に求めることを特徴とする内視鏡装置の画像処理方法。
(11) Using the endoscope device according to any one of (7) to (10), a frame image configured by including a plurality of detection color screens each detecting light having a different specific wavelength band, An image processing method for an endoscopic device that irradiates light from a plurality of types of light sources in different conditions in synchronization with imaging timing of each frame image while imaging multiple times,
An observation image when the subject is illuminated with the first light source is a first frame image, an observation image when the subject is illuminated with the second light source is a second frame image, and the first frame image and the second frame Frame images are taken repeatedly,
The luminance information of the specific detection color screen of the first frame image and the luminance information of the specific detection screen of the second frame image are combined to analyze the observation image by the light of the specific wavelength component from the light source device. An image processing method for an endoscopic device, characterized in that the image processing is obtained automatically.
この内視鏡装置の画像処理方法によれば、第1フレーム画像と第2フレーム画像の各検出色画面の情報を組み合わせることで、所望の波長成分の光による観察画像を選択的に抽出することができる。すなわち、1回の撮像によるフレーム画像から直接的に得られない特定の波長成分の光による観察画像を、時間軸前後のフレーム画像を用いることで解析的に求めることができる。 According to the image processing method of the endoscope apparatus, an observation image by light of a desired wavelength component can be selectively extracted by combining information on each detection color screen of the first frame image and the second frame image. Can do. That is, an observation image with light of a specific wavelength component that cannot be obtained directly from a frame image obtained by one imaging can be analytically obtained by using frame images around the time axis.
(12) (11)記載の内視鏡装置の画像処理方法であって、
前記特定の波長成分の光による観察画像が、波長帯域幅の狭い出射光による観察画像を少なくとも含むことを特徴とする内視鏡装置の画像処理方法。
(12) The image processing method for an endoscope apparatus according to (11),
The image processing method for an endoscope apparatus, wherein the observation image with light of the specific wavelength component includes at least an observation image with outgoing light having a narrow wavelength bandwidth.
この内視鏡装置の画像処理方法によれば、狭波長帯域の光成分による観察画像を解析的に求められ、例えば血管や腺管構造の観察を行う際に、光の深達度が狭い範囲に限定されて、よりコントラストの高い画像を得ることができる。 According to the image processing method of this endoscope apparatus, an observation image based on a light component in a narrow wavelength band is analytically obtained. For example, when observing a blood vessel or a gland duct structure, the light penetration depth is narrow. The image with higher contrast can be obtained.
(13) (11)記載の内視鏡装置の画像処理方法であって、
前記特定の波長成分の光による観察画像が、波長帯域幅の広い出射光による観察画像を少なくとも含むことを特徴とする内視鏡の画像処理方法。
(13) The image processing method for an endoscope apparatus according to (11),
An image processing method for an endoscope, wherein the observation image with light of the specific wavelength component includes at least an observation image with outgoing light having a wide wavelength bandwidth.
この内視鏡装置の画像処理方法によれば、広い波長帯域幅の光成分による観察画像を解析的に求められ、より演色性の高い白色照明下での画像を得ることができる。 According to the image processing method of the endoscope apparatus, an observation image using a light component having a wide wavelength bandwidth can be analytically obtained, and an image under white illumination with higher color rendering can be obtained.
(14) (11)〜(13)のいずれか1項記載の内視鏡装置の画像処理方法であって、
前記特定の波長成分の光による観察画像を、それぞれ特定の色調に変換して疑似カラー画像を生成することを特徴とする内視鏡装置の画像処理方法。
(14) The image processing method for an endoscope apparatus according to any one of (11) to (13),
An image processing method for an endoscope apparatus, wherein a pseudo color image is generated by converting an observation image with light having a specific wavelength component into a specific color tone.
この内視鏡装置の画像処理方法によれば、組織表面の毛細血管や腺管構造等を強調表示することができ、観察対象の確認を容易にし、診断精度を向上できる。 According to the image processing method of the endoscope apparatus, it is possible to highlight the capillaries and gland duct structures on the tissue surface, facilitate confirmation of the observation target, and improve diagnosis accuracy.
本発明の内視鏡装置によれば、内視鏡挿入部の細径化を図り、内視鏡挿入部の先端に配置したLED素子の発熱を抑えつつ、白色光と特定の狭い可視波長帯域の光とを簡単な構成で選択的に照射して観察することができる。また、内視鏡装置の画像処理方法によれば、この内視鏡装置からの画像情報に基づいてより精度の高い分光診断が可能となる。 According to the endoscope apparatus of the present invention, the diameter of the endoscope insertion portion is reduced, and the white light and a specific narrow visible wavelength band are suppressed while suppressing the heat generation of the LED element disposed at the distal end of the endoscope insertion portion. Can be selectively irradiated with a simple structure and observed. Further, according to the image processing method of the endoscope apparatus, it is possible to perform spectroscopic diagnosis with higher accuracy based on the image information from the endoscope apparatus.
以下に、光源装置およびこれを用いた内視鏡装置ならびに画像処理方法の好適な実施の形態について、図面を参照して詳細に説明する。
図1に本実施形態の内視鏡装置の概念的な構成図を示した。
本実施形態の内視鏡装置100は、主に、内視鏡10、光源装置20、画像処理装置30、モニタ40を備えて構成される。
内視鏡10は、本体操作部11と、この本体操作部11に連設され、被検体(体腔)内に挿入される内視鏡挿入部13とを備える。内視鏡挿入部13の先端部には撮像光学系である撮像素子15と撮像レンズ17が配置され、また、撮像光学系の近傍には照明光学系の照明用光学部材19とこれに接続される光ファイバー21が配置されている。光ファイバー21は詳細を後述する光源装置20に接続され、撮像素子15からの撮像信号は画像処理装置30に入力される。
Hereinafter, preferred embodiments of a light source device, an endoscope device using the same, and an image processing method will be described in detail with reference to the drawings.
FIG. 1 shows a conceptual configuration diagram of the endoscope apparatus of the present embodiment.
The
The
撮像素子15は、CCD(charge coupled device)やCMOS(Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor)等の撮像素子が使用され、その撮像信号は、制御部29からの指令に基づいて撮像信号処理部27によって画像データに変換されて適宜の画像処理が施される。制御部29は、撮像信号処理部27から出力される画像データを撮像画像表示手段であるモニタ40に映出したり、図示しないLAN等のネットワークに接続して画像データを含む情報を配信する。また、制御部29には、撮像信号を保存するための第1のメモリ51と、第2のメモリ52が接続されている。これら第1のメモリ51,第2のメモリ52については後述する。
The
次に、照明光学系の構成例を説明する。
図2は図1に示す内視鏡装置の内視鏡挿入部先端における照明光学系の概略的な断面構成図である。
照明光学系は、白色光を出射するための白色光照明系61と、緑色光、青色光等の特色光を出射するための特色光照明系63とからなる。白色光照明系61は、中心波長445nmの青色レーザ光源(第1光源)33と、青色レーザ光源33からのレーザ光を集光する集光レンズ41とを励起光源部65に備え、内視鏡挿入部13の先端に配される照明用光学部材19はレーザ光を可視光に変換する波長変換部材45からなる。また、励起光源部65と照明用光学部材19との間は光ファイバー21により接続されている。
Next, a configuration example of the illumination optical system will be described.
FIG. 2 is a schematic cross-sectional configuration diagram of the illumination optical system at the distal end of the endoscope insertion portion of the endoscope apparatus shown in FIG.
The illumination optical system includes a white
青色レーザ光源33は、白色光駆動部67からの指令に基づいて出射光量を制御されつつ青色レーザ光を出射し、この出射光が光ファイバー21を通じて内視鏡挿入部13の波長変換部材45に照射される。
波長変換部材45は、青色レーザ光源33からのレーザ光の一部を吸収して緑色〜黄色に励起発光する複数種の蛍光体(例えばYAG系蛍光体、あるいはBAM(BaMgAl10O37)等を含む蛍光体等)を含んで構成される。これにより、青色レーザ光源33からのレーザ光と、このレーザ光から変換された緑色〜黄色の励起光とが合波されて、白色光が生成される。
The blue
The
この青色レーザ光源33としては、ブロードエリア型のInGaN系レーザダイオードが使用できる。また、光ファイバー21は、内視鏡挿入部13の先端硬質部(金属製ブロック)に形成された開口孔13aに挿通され、この開口孔13aに嵌挿される固定用治具75に光軸を合わせて固定される。この固定用治具75は、光ファイバー21の光出射側に波長変換部材45を固定し、光ファイバー21からの出射光を受けて波長変換部材45が励起発光する光を光路前方へ出射する。このとき、波長変換部材45を波長変換せずに透過する青色レーザ光は、波長変換部材45内の蛍光体により拡散され、直進性の高いレーザ光から光軸に対して60°〜70°の拡散角を有する拡散光として出射される。
As the blue
一方、特色光照明系63は、LED(Light Emitting Diode:発光ダイオード)素子を光源として用いており、特色光駆動部69に接続された青色発光LED素子71と緑色発光LED素子73とを備えて構成される。
青色発光LED素子71と緑色発光LED素子73は、先端硬質部に窪んで形成され側壁が反射面とされた収容座13b、13cに配置され、これら収容座13b、13cの近傍には電極パッド77A,77Bがそれぞれ配置されて、各LED素子のN型電極とP型電極にワイヤーボンディングによって接続されている。さらに、これら各LED素子71,73と電極パッド77A,77B、と金ワイヤー線は、透明樹脂によりモールドされて、このモールドされた透明樹脂79A,79Bがレンズとして機能する。なお、青色LED、緑色LEDと記載したが、例えば緑色LEDは発光効率が低いので、405nm紫色LEDを用いて、透明樹脂に緑色で発光する蛍光体や、染料あるいは顔料等を混入してもよい。また、同様に375nmの紫外LEDと青紫色で発光する蛍光体を樹脂に混入して封止しても良い。
On the other hand, the
The blue light-emitting
特色光駆動部69は、青色発光LED素子71と緑色発光LED73とを個別に出射光量を制御して、白色光駆動部67と共に制御部29(図1)により統括制御される。これら白色光駆動部67および特色光駆動部69ならびに制御部29が、照明光の切り換え等を行う照明光制御手段として機能する。
上記構成により、光ファイバー21から出射される青色レーザ光源33からの青色レーザ光は、波長変換部材45に照射され、波長変換部材45は、青色レーザ光の一部を吸収して、この青色レーザ光よりも長波長の光(緑色〜黄色の光)を励起発光する。
The spot color
With the above configuration, the blue laser light emitted from the
図3は、青色レーザ光が波長変換部材45により波長変換された後の光のスペクトル分布を示すグラフである。青色レーザ光源33からの青色レーザ光は、中心波長445nmの輝線で表され、このレーザ光により波長変換部材45が励起発光する光によって、概ね450nm〜700nmの波長帯域で発光強度が増大する。この波長帯域の光と青色レーザ光とによって白色光が形成される。
FIG. 3 is a graph showing the spectral distribution of light after the blue laser light has been wavelength-converted by the
図4は、特色光照明系63の青色発光LED素子71と、緑色発光LED素子73の発光スペクトルである。青色発光LED素子71による発光スペクトルは、半値幅で波長450〜480nm程度の狭波長帯域の光で、緑色発光LED素子73による発光スペクトルは、半値幅で520〜560nm程度の狭波長帯域の光である。
FIG. 4 shows emission spectra of the blue light-emitting
なお、波長変換部材45から出射する青色、緑色、他の波長域の発光は同時に出射されるが、各光成分による照明光の観察光を検出する際は、撮像素子15が有するカラーフィルタにより、例えば緑色光成分のみを撮像素子15で検出することで、緑色光成分と他の光成分とを容易に分離することができる。また、青色光成分も同様に分離できる。したがって、後段の信号処理で混色の問題を生じることはない。
The blue, green, and other wavelengths of light emitted from the
次に、上記構成の光源装置20が内視鏡10に組み込まれた内視鏡装置100の使用例を説明する。
図1に示すように、内視鏡装置100においては、内視鏡挿入部13を体腔内に挿入して、内視鏡挿入部13の先端から白色照明光を照明用光学部材19を通して出射させ、また、特色光による照明光を各LED素子71,73から出射させる。白色光と特色光はそれぞれ切り換えて、いずれか一方のみを出射させる。そして、この出射光が被検体に照射された反射光を、撮像レンズ17を通して撮像素子15で撮像する。撮像して得た撮像信号は、撮像信号処理部27によって適宜な画像処理が施されて、モニタ40に出力される。あるいは記録媒体に保存する。
Next, a usage example of the
As shown in FIG. 1, in the
このような撮像素子15を用いた撮像の際、体腔内で白色の照明光を照射して観察する通常の内視鏡診断時には、制御部29は、図2に示す白色光駆動部67により、青色レーザ光源33からのレーザ光の出力をONにし、特色光駆動部69により青色発光LED素子71、緑色発光LED素子73の各出力をOFFにする。この場合には、青色レーザ光源33からのレーザ光と、波長変換部材45の励起発光光とによって生成される白色照明光が被検体に照射される。また、内視鏡装置100による分光診断を行う際は、制御部29は、特色光駆動部69により青色発光LED素子71、緑色発光LED素子73の各出力をONにし、白色光駆動部67により青色レーザ光源33の出力をOFFにする。この場合には、青色発光LED素子71,緑色発光LED素子73による狭波長帯域の青色光および緑色光が被検体に照射される。そして、これら緑色光と青色光とを同時に照射した被検体からの反射光を撮像素子15により撮像し、撮像信号処理部27は、分光診断用の疑似カラー画像を生成する。例えば、撮像素子15による緑検出信号(狭帯域の緑色光の反射光成分)を赤色の色調、青検出信号を青色と緑色の色調に変換して疑似カラー画像を生成する。この疑似カラー画像によれば、被検体の表層の表面微細構造(毛細血管や粘膜微細構造等)を明瞭に観察することができる。
At the time of imaging using such an
ここで、分光診断を行う場合の具体的な制御例を説明する。
図5は、撮像光学系により撮像して時系列的に得た複数のフレーム画像(a)と、これらフレーム画像を並べ替えて表示する様子(b)を概念的に示す説明図である。ここでは、白色光による照明光下の観察像と、特定の可視波長帯域(緑色、青色)の光による照明光下の観察像とを、それぞれ別々にモニタ40に表示する制御を行う。
制御部29は、図5(a)に示すように、光源装置20による出射光を制御して、第1フレーム目では、中心波長445nmの青色レーザ光を出射させて白色光を被検体に照射する。撮像素子15は、白色光で照明された被検体を撮像し、その撮像信号を第1のメモリ51(図1参照)に保存する。
Here, a specific control example when performing spectral diagnosis will be described.
FIG. 5 is an explanatory diagram conceptually showing a plurality of frame images (a) obtained in time series by imaging with an imaging optical system and a state (b) in which these frame images are rearranged and displayed. Here, control is performed to separately display an observation image under illumination light with white light and an observation image under illumination light with light in a specific visible wavelength band (green, blue) on the
As shown in FIG. 5A, the
次に、制御部29は、光源装置20による出射光を制御して、第2フレーム目では、青色発光LED素子71と緑色発光LED素子73による狭波長帯域の緑色光と青色光をそれぞれ被検体に照射する。撮像素子15は、緑色光と青色光で照明された被検体を撮像し、その撮像信号を第2のメモリ53に保存する。
Next, the
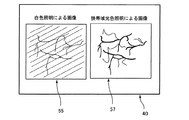
以降、同様にして、第3フレーム(奇数フレーム)では第1フレーム目と同様に、第4フレーム(偶数フレーム)では第2フレームと同様に照明・撮像・撮像信号保存の処理を行うことを繰り返す。つまり、白色光の照明と、特定の可視波長帯域の光を含む照明とを撮像素子15の撮像フレーム毎に交互に切り換える。すると、図5(b)に示すように、第1のメモリ51には白色光による照明画像が蓄積され、第2のメモリ53には緑色光と青色光による狭帯域診断用画像が蓄積される。これら2種類の撮像信号による画像情報を、図6に示すように、モニタ40上の異なる表示領域55、57に、第1のメモリ51と第2のメモリ53に保存された撮像信号をそれぞれ表示する。各表示領域のサイズは図示例では同一にしているが、いずれか一方を他方より大きく表示したり、いずれか一方の画像表示領域内に、他方の画像を小さく表示する等、任意に設定することができる。
Thereafter, similarly, the third frame (odd frame) repeats the processing of illumination / imaging / image signal storage in the same manner as the first frame in the third frame (odd frame) and the second frame in the fourth frame (even frame). . That is, the illumination of white light and the illumination including light in a specific visible wavelength band are alternately switched for each imaging frame of the
このように、白色光の照明下の撮像画像と、特定の可視波長帯域の光を含む照明下の撮像画像とを交互に撮像することで、双方を略同時に画像取得することができ、2種類の画像情報をリアルタイムで同時に表示させることができる。また、それぞれの撮像画像を並べて表示することで、観察位置とその部位の性状が同時に把握でき、分光診断による診断精度を一層高められる。 Thus, by alternately capturing a captured image under illumination of white light and a captured image under illumination including light in a specific visible wavelength band, both images can be acquired substantially simultaneously. The image information can be displayed simultaneously in real time. Further, by displaying the captured images side by side, the observation position and the properties of the part can be grasped at the same time, and the diagnostic accuracy by the spectroscopic diagnosis can be further enhanced.
また、特定の可視波長帯域の光を照射して撮像し、分光診断を行う際に、上記のように青色発光LED素子による青色光、緑色発光LED素子による緑色光の照明光の組み合わせ以外にも、種々の光成分の組み合わせが可能である。
例えば、青色発光LED素子71による青色光に代えて、白色照明用の青色レーザ光源33による青色レーザ光を狭帯域の特色光として用いて疑似カラー画像を生成することもできる。これにより得られる疑似カラー画像は、出射光の波長帯域がLED素子よりレーザの方が狭いため、分光診断に有益な画像となる場合がある。
In addition to the combination of blue light emitted by a blue light emitting LED element and green light emitted by a green light emitting LED element as described above, when imaging is performed by irradiating light in a specific visible wavelength band and performing spectroscopic diagnosis, Various combinations of light components are possible.
For example, instead of the blue light emitted from the blue light emitting
このような光成分の組み合わせを行うには、撮像光学系により撮像して時系列的に得た複数のフレーム画像に対して、撮像タイミングの異なるフレーム画像に跨った画像演算処理を行う。
つまり、図5で説明したように、それぞれ異なる特定の波長帯域光を検出した検出色画面(青、緑、赤の3原色の画面)を複数画面有して構成されるフレーム画像を、複数回にわたって撮像する一方、各フレーム画像の撮像タイミングに同期して複数種の光源からの光をそれぞれ異なる条件で照射する。第1光源により被検体を照明したときの観察画像を第1フレーム画像、第2光源により被検体を照明したときの観察画像を第2フレーム画像としたとき、第1フレーム画像と第2フレーム画像とを繰り返し撮像し、第1フレーム画像の特定の検出色画面の輝度情報と、第2フレーム画像の特定の検出画面の輝度情報とを組み合わせて、特定の波長成分の光による観察画像を解析的に求める。
In order to perform such a combination of light components, an image calculation process across frame images with different imaging timings is performed on a plurality of frame images captured in time series by imaging with an imaging optical system.
That is, as described with reference to FIG. 5, a frame image having a plurality of detection color screens (screens of three primary colors of blue, green, and red) that detect different specific wavelength band lights is displayed a plurality of times. On the other hand, light from a plurality of types of light sources is irradiated under different conditions in synchronization with the imaging timing of each frame image. When the observation image when the subject is illuminated with the first light source is the first frame image, and the observation image when the subject is illuminated with the second light source is the second frame image, the first frame image and the second frame image And the luminance information of the specific detection color screen of the first frame image and the luminance information of the specific detection screen of the second frame image are combined to analyze the observation image by the light of the specific wavelength component. Ask for.
図7に、図5と同様に撮像した各フレーム画像に対して特定の検出色の画面に含まれる主要な光成分を示した。ここでは、波長変換部材45の蛍光体として、YAG蛍光体とした例で説明する。
中心波長445nmの青色レーザ光を照射して撮像して得た撮像信号である第1フレームは、青色の検出光画面B1では、青色レーザ光源33からの中心波長445nmの青色レーザ光による照明光下での観察光が含まれ、緑色の検出光画面G1では、波長変換部材45のYAG蛍光体による緑光蛍光による照明光下での観察光が含まれ、赤色の検出光画面R1では、波長変換部材45のYAG蛍光体による赤色蛍光による照明光下での観察光が含まれる。
FIG. 7 shows main light components included in the screen of a specific detection color for each frame image captured in the same manner as in FIG. Here, an example in which the phosphor of the
The first frame, which is an imaging signal obtained by irradiating with blue laser light having a central wavelength of 445 nm, is illuminated by blue laser light having a central wavelength of 445 nm from the blue
また、次に青色発光LED素子71と緑色発光LED素子73を発光させて撮像して得た撮像信号である第2フレームは、青色の検出光画面B2では、青色発光LED素子71による照明光下での観察光が含まれ、緑色の検出光画面G2では、緑色発光LED素子73による照明光下での観察光が含まれる。
Further, the second frame, which is an imaging signal obtained by causing the blue light emitting
ここで、白色光による観察画像について考えると、照明に用いる白色光は、特定の狭い範囲の波長成分が強くなると、実際の見え方と異なる色調となる。そのため、理想的には、可視波長帯域が比較的平坦なスペクトルの光で照明することが望ましい。しかし、本構成による白色照明は、輝線となる青色レーザ光を白色照明用としているので、これをレーザ光より波長幅の広い青色発光LED71による発光と入れ替えると、照明光のスペクトルをより平坦化できる。つまり、白色照明時では、輝線成分となるレーザ光が混在する照明光よりも、むしろ第2フレームにおけるLED素子による比較的波長帯域幅の広い青色光を用いた方が演色性を向上できる。そこで、白色光による観察光画像として、第1フレームをそのまま用いることなく、第1フレームのG1,R1と、第2フレームのB2を組み合わせることで、より演色性のよい白色光による観察光画像を得ることができる。
Here, considering an observation image using white light, the white light used for illumination has a color tone different from the actual appearance when the wavelength component in a specific narrow range becomes strong. Therefore, ideally, it is desirable to illuminate with light having a spectrum with a relatively flat visible wavelength band. However, since the white illumination according to the present configuration uses the blue laser light as a bright line for white illumination, the spectrum of the illumination light can be flattened by replacing it with the light emitted by the blue
また、狭帯域照明光による観察光画像として、B1で得られる青色レーザ光による観察光と、G2で得られる緑色発光LED素子73の発光による狭帯域光による観察光を組み合わせ、これを強調処理用画像として用いることができる。その場合には、青色光の波長幅が狭くされるので、観察対象となる組織表層部を、表面側のより浅い領域に限定することができる。
Further, as the observation light image by the narrow band illumination light, the observation light by the blue laser light obtained in B1 and the observation light by the narrow band light by the light emission of the green light emitting
上記のように、撮像して得られる各フレームの各検出光画面のそれぞれを適宜組み合わせて利用することで、診断に都合のよい画像情報を簡単に提供することができる。また、粘膜の深い部分に到達しにくい青色光が組織の表層部の毛細血管を、また、組織の内部にまで行き届く緑色光が深部の血管をそれぞれ鮮明に映し出した画像を簡単にして得ることができる。 As described above, it is possible to easily provide image information convenient for diagnosis by using each detection light screen of each frame obtained by imaging in an appropriate combination. In addition, it is possible to easily obtain an image in which the blue light that is difficult to reach the deep part of the mucosa clearly shows the capillaries in the surface layer of the tissue, and the green light that reaches the inside of the tissue clearly shows the deep blood vessels. it can.
また、白色照明光と特定の狭い可視波長帯域の光とを、内視鏡10の本体操作部11に設けたスイッチ12等により、簡単な手元操作により切り換え自在とする構成としてもよい。この場合、照明光を手動により任意のタイミングで切り換えることができ、使い勝手を向上することができる。
Further, the configuration may be such that the white illumination light and the light with a specific narrow visible wavelength band can be switched by a simple hand operation by a
以上説明したように、本実施形態の内視鏡装置100によれば、照明光学系の白色光源としてレーザ光を用いることで、光ファイバーにより導光でき、高輝度の光を拡散を抑えて高効率で伝搬させることができる。また、白色用の導光路を光ファイバーで構成できるため、従前のライトガイド(光ファイバー束)を要することなく、内視鏡挿入部の細径化が図り易くなる。すなわち、ライトガイドで必要な光を内視鏡挿入部13の先端に導くためには、ライトガイドの径が少なくとも約1mm以上必要となるが、単線の光ファイバーを用いる本実施形態の構成では、外皮の保護材を含めた外径で0.3mm程度の細径にできる。また、LED素子は、必要な波長帯域に直接エネルギを変換して照明するので、高効率で高照度の光が得られ、内視鏡で一般的に用いられるキセノンランプにより狭波長帯域の光をフィルタリングして取り出す場合と比較すると、1/20程度の消費電力で同等の明るさを実現できる。さらに、排熱も少なくできることから、冷却ファン等の小型化、静音化が図られる。
そして、蛍光体励起光を照明光として使用するため、レーザ光を直接照明光として利用する場合に生じやすい、スペックル(干渉)によるノイズの重畳がなく、動画でのちらつきも発生しない。
As described above, according to the
Since phosphor excitation light is used as illumination light, there is no noise superposition due to speckle (interference), which is likely to occur when laser light is used directly as illumination light, and flickering in moving images does not occur.
また、本実施形態の内視鏡装置100の構成によれば、内視鏡挿入部13の細径化に伴って熱容量が小さくなり、LED素子71,73からの発熱が危惧されるが、比較的光量を多く必要とする白色照明光をレーザ光を利用して供給し、分光診断に必要となる特色照明光をLED素子71,73を利用して供給するので、LED素子を常時高出力で点灯する場合と比較して、発熱量を抑えることができる。
Further, according to the configuration of the
また、LED素子71,73からの出射光は、透明樹脂79A,79Bで形成されたレンズにより集光され、所望の照射位置に向けて出射される。そのため、図8に観察領域と特色光照射領域の関係を示すように、撮像素子15による観察領域81の全領域をLED素子71,73で照明することなく、観察領域81の一部を特色光照明領域83とすることができる。特色光照明領域83を狭い領域に選択的に照射することにすれば、LED素子71,73からの出射光量が小さくて済み、これにより、発熱量を抑えることができる。
In addition, light emitted from the
次に、上記構成の内視鏡装置100の変形例を説明する。
<変形例1>
図9に内視鏡挿入部の他の断面構成図を示した。
上記の内視鏡装置100の内視鏡挿入部13に形成したLED素子71,73の収容座は、各LED素子71,73にそれぞれ設ける以外にも、複数のLED素子71,73を一つの収容座13dに配置することもできる。この場合、複数のLED素子71,73を纏めて透明樹脂79Cでモールドすることができ、製造工程を簡略化して、しかも各LED素子71,73が1つの集光レンズを共有することで、出射光の照射むらが抑えられる。
Next, a modification of the
<
FIG. 9 shows another cross-sectional configuration diagram of the endoscope insertion portion.
The housing seats for the
<変形例2>
図10に光源装置の他の光学系の構成図を示した。
この場合のLED素子は、青色発光LED素子71,73(いずれか一方は紙面垂直方向に並設している)と、赤外(780nm)発光LED素子76である。これらLED素子71,73,74は同一の収容座13eに配置されて透明樹脂79Dでモールドされている。青色発光LED素子71、緑色発光LED素子73、赤外発光LED素子74は、共に特色光駆動部69に接続され、発光状態がそれぞれ制御される。
<
FIG. 10 shows a configuration diagram of another optical system of the light source device.
The LED elements in this case are blue light emitting
図11は、この場合の青色発光LED素子71、緑色発光LED素子73、赤外発光LED素子74の発光スペクトルである。この構成によれば、分光診断に用いる青色光〜緑色光に加えて、赤外光が出射可能となるので、例えば赤外光観察による診察が可能となる。赤外光観察とは、赤外光が吸収されやすいICG(インドシアニンググリーン)を静脈注射した上で、赤外光を照射することで、人間の目では視認が難しい粘膜深部の血管や肥厚を強調表示する技術である。また、血流情報も表示させることができる。
FIG. 11 shows emission spectra of the blue light emitting
以上説明した、各内視鏡装置においては、分光診断等に用いる狭波長帯域の光、すなわち、青色発光LED素子71、緑色発光LED素子73等の発光は、波長帯域が半値幅で40nm以下に設定されることが好ましい。これは次の理由による。
CCDやCMOS等の撮像素子は、カラーフィルタを備えており、例えばR(赤)、G(緑)、B(青)の各原色(他にも補色としてシアン、マゼンタ、イエロー等の組み合わせもある)を特定検出色としてフルカラー画像情報を生成している。各検出色の光強度検出は、ある波長幅の有感度波長帯内の光強度を検出するが、実際には各検出色の波長が近接しており、有感度波長帯の一部が相互にオーバーラップしている。しかし、オーバーラップする領域が多いと混色が生じるため、通常、このオーバーラップする領域を狭めることがなされている。
In each of the endoscope apparatuses described above, light in a narrow wavelength band used for spectroscopic diagnosis or the like, that is, light emitted from the blue light emitting
An image sensor such as a CCD or CMOS has a color filter, for example, R (red), G (green), and B (blue) primary colors (in addition, there are combinations such as cyan, magenta, and yellow as complementary colors). ) Is generated as the specific detection color. The light intensity detection of each detection color detects the light intensity within a sensitive wavelength band of a certain wavelength width, but in reality the wavelengths of each detection color are close to each other, and some of the sensitive wavelength bands are mutually It overlaps. However, when there are many overlapping areas, color mixing occurs, and thus the overlapping areas are usually narrowed.
有感度波長帯は、例えば、Bでは100nm以下、Gでは80nm以下、RではGとの混色防止のため100nm以下に設計される(本明細書では、これを実質的な有感度波長帯と呼称する)。したがって、撮像素子に混色の影響なく各検出色を検出するには、LED素子の発光の波長帯域をこの実質的な有感度波長帯よりも狭い波長幅にすればよい。換言すれば、LED素子が発光する特定の可視波長帯域の発光スペクトル曲線のピークの半値幅が、カラーフィルタの特定検出色(LED素子の発光色を検出するための検出色)成分を検出する波長帯域のスペクトル感度曲線のピークの半値幅より狭い波長幅にする。これにより、特定の波長帯域の発光光が複数の有感度波長帯に跨って検出されることがなくなる。また、観察したい被検体に合わせてスペクトルの中心をカラーフィルタの中心からずらす場合もあり、その場合には、発光光の波長帯域の幅をより狭くする必要がある。 The sensitive wavelength band is designed to be, for example, 100 nm or less for B, 80 nm or less for G, and 100 nm or less for R to prevent color mixing with G (in this specification, this is called a substantially sensitive wavelength band). To do). Therefore, in order to detect each detected color without the influence of color mixing in the image sensor, the wavelength band of light emission of the LED element may be set to a wavelength width narrower than this substantially sensitive wavelength band. In other words, the wavelength at which the half width of the peak of the emission spectrum curve in the specific visible wavelength band emitted by the LED element detects the specific detection color component (detection color for detecting the emission color of the LED element) of the color filter. The wavelength width is narrower than the half width of the peak of the spectral sensitivity curve in the band. Thereby, the emitted light in a specific wavelength band is not detected across a plurality of sensitive wavelength bands. In some cases, the center of the spectrum is shifted from the center of the color filter in accordance with the subject to be observed. In this case, it is necessary to narrow the width of the wavelength band of the emitted light.
このため、各LED素子71,73の発光光の波長帯域の幅は、60nm以下、好ましくは40nm以下、さらに好ましくは20nm以下に設定する。また、光強度の観点からは10nm以上であることが好ましい。
For this reason, the width of the wavelength band of the emitted light of each
また、狭帯域化の理由は、撮像素子の光強度検出による理由の他に、狭帯域内視鏡(narrow band imaging :NBI)による診断を行う際に、狭帯域化が必要となる点も挙げられる。生体組織に照明光が照射されると、光は拡散的に伝播する。吸収や散乱特性が強いと、光は生体組織内の深くまで伝播されずに反射光として観察される。その吸収・散乱特性は、強い波長依存性を有し、波長が短いほど散乱特性が強くなり、光の生体組織への深達度は照射する光の波長によって決定される。特に、早期病変の診断に重要となる粘膜表面の微細構造の観察には、表面から浅い層内からの情報が重要となるので、その場合には、LED素子の発光光の波長帯域を、所望の波長でしかも帯域を狭くすることで、観察目的とする層からの情報を選択的に抽出することが可能となる。 In addition to the reason for the detection of the light intensity of the image sensor, the reason for narrowing the band is that it is necessary to narrow the band when performing diagnosis with a narrow band imaging (NBI). It is done. When illumination light is irradiated onto a living tissue, the light propagates diffusely. When the absorption and scattering characteristics are strong, the light is observed as reflected light without being propagated deep inside the living tissue. The absorption / scattering characteristics have a strong wavelength dependence, and the shorter the wavelength, the stronger the scattering characteristics, and the penetration depth of light into the living tissue is determined by the wavelength of the irradiated light. In particular, for observation of the fine structure of the mucosal surface, which is important for the diagnosis of early lesions, information from within the shallow layer from the surface is important. In this case, the wavelength band of the emitted light of the LED element is desired. It is possible to selectively extract information from the observation target layer by narrowing the band with the wavelength of.
以上、各実施形態の内視鏡装置によれば、レーザ光と蛍光体の励起発光光とを含んで形成される白色光と、特定の狭い可視波長帯域の光とを、細径化を図りつつ簡単な構成で選択的に照射することができる。
なお、本光源装置およびこれを用いた内視鏡装置は、前述した各実施形態に限定されるものではなく、適宜、変形や改良等が可能である。
As described above, according to the endoscope apparatus of each embodiment, the diameter of the white light formed including the laser light and the excitation light emitted from the phosphor and the light of a specific narrow visible wavelength band is reduced. However, it can selectively irradiate with a simple configuration.
Note that the light source device and the endoscope device using the light source device are not limited to the above-described embodiments, and can be appropriately modified and improved.
10 内視鏡
11 本体操作部
13 挿入部
15 撮像素子
19 照明用光学部材
20 光源装置
21 光ファイバー
27 撮像信号処理部
29 制御部
30 画像処理装置
33 青色レーザ光源
45 波長変換部材
51 第1のメモリ
53 第2のメモリ
55,57 表示領域
61 白色光照明系
63 特色光照明系
65 励起光源部
67 白色光駆動部
69 特色光駆動部
71 青色発光LED素子
73 緑色発光LED素子
74 赤外発光LED素子
79A,79B 透明樹脂
81 観察領域
83 特色光照射領域
100 内視鏡装置
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (14)
前記内視鏡挿入部先端に配置され特定の可視波長帯域で発光する発光素子を備えた第2の照明光学系と、
を具備する内視鏡装置。 A first light source that emits laser light; an optical fiber that is incident on the light incident side to transmit the laser light to the distal end of the endoscope insertion portion; and is disposed at the light emitting side of the optical fiber and emits excitation light by the laser light. A wavelength conversion member including one type of fluorescent material, and mixing the laser light and excitation light emitted from the wavelength conversion member to emit white light from the distal end of the endoscope insertion portion Illumination optics,
A second illumination optical system provided with a light emitting element disposed at the distal end of the endoscope insertion portion and emitting light in a specific visible wavelength band;
An endoscope apparatus comprising:
前記第2の照明光学系の前記発光素子が、LED素子である内視鏡装置。 The endoscope apparatus according to claim 1,
An endoscope apparatus in which the light emitting element of the second illumination optical system is an LED element.
前記第2の照明光学系が、それぞれ異なる中心波長で発光する複数の発光素子を備えた内視鏡装置。 The endoscope apparatus according to claim 1 or 2,
An endoscope apparatus in which the second illumination optical system includes a plurality of light emitting elements that emit light at different center wavelengths.
前記第2の照明光学系が、少なくとも緑色光を発光する発光素子を有する内視鏡装置。 The endoscope apparatus according to any one of claims 1 to 3,
An endoscope apparatus in which the second illumination optical system includes a light emitting element that emits at least green light.
前記第2の照明光学系が、少なくとも青色光を発光する発光素子を有する内視鏡装置。 The endoscope apparatus according to any one of claims 1 to 4,
An endoscope apparatus in which the second illumination optical system includes a light emitting element that emits at least blue light.
前記第2の照明光学系が、少なくとも赤色光乃至赤外光を発光する発光素子を有する内視鏡装置。 The endoscope apparatus according to any one of claims 1 to 5,
An endoscope apparatus in which the second illumination optical system includes a light emitting element that emits at least red light or infrared light.
前記内視鏡挿入部先端に設けた観察窓を通して被観察部位からの光を受光して撮像信号を出力する撮像素子を含む撮像手段と、
前記第1の照明光学系による白色光と前記第2の照明光学系による特定の可視波長帯域の光とを切り換えて照明する照明光制御手段と、
を備えた内視鏡装置。 The endoscope apparatus according to any one of claims 1 to 6,
An imaging means including an imaging element that receives light from a site to be observed through an observation window provided at a distal end of the endoscope insertion unit and outputs an imaging signal;
Illumination light control means for switching and illuminating white light by the first illumination optical system and light of a specific visible wavelength band by the second illumination optical system;
An endoscopic apparatus comprising:
前記第1の照明光学系による白色光の照明光下において撮像した撮像信号を保存する第1のメモリと、
前記第2の照明光学系による前記特定の可視波長帯域の光を含む照明光下において撮像した撮像信号を保存する第2のメモリと、
前記第1のメモリと前記第2のメモリに保存された各撮像信号をそれぞれ異なる表示領域に表示する撮像画像表示手段と、
を備えた内視鏡装置。 The endoscope apparatus according to claim 7,
A first memory for storing an imaging signal imaged under illumination light of white light by the first illumination optical system;
A second memory for storing an imaging signal imaged under illumination light including light of the specific visible wavelength band by the second illumination optical system;
Picked-up image display means for displaying the picked-up image signals stored in the first memory and the second memory in different display areas;
An endoscopic apparatus comprising:
前記照明光制御手段が、前記白色光の照明と、前記特定の可視波長帯域の光を含む照明とを、前記撮像素子による撮像フレーム毎に交互に切り換えることを特徴とする内視鏡装置。 The endoscope apparatus according to claim 8, wherein
The endoscope apparatus characterized in that the illumination light control means alternately switches the illumination of the white light and the illumination including the light in the specific visible wavelength band for each imaging frame by the imaging element.
前記撮像素子が特定検出色成分を検出するためのカラーフィルタを備えており、
前記発光素子が発光する前記特定の可視波長帯域の発光スペクトル曲線のピークの半値幅が、前記カラーフィルタの前記特定検出色を検出する波長帯域のスペクトル感度曲線のピークの半値幅より狭い波長幅にされた内視鏡装置。 The endoscope apparatus according to any one of claims 7 to 9,
The image sensor includes a color filter for detecting a specific detection color component;
The half width of the peak of the emission spectrum curve of the specific visible wavelength band emitted by the light emitting element is narrower than the half width of the peak of the spectral sensitivity curve of the wavelength band of the color filter for detecting the specific detection color. Endoscopic device.
前記第1光源により被検体を照明したときの観察画像を第1フレーム画像、前記第2光源により被検体を照明したときの観察画像を第2フレーム画像として、前記第1フレーム画像と前記第2フレーム画像とを繰り返し撮像し、
前記第1フレーム画像の特定の検出色画面の輝度情報と、前記第2フレーム画像の特定の検出画面の輝度情報とを組み合わせて、前記光源装置からの特定の波長成分の光による観察画像を解析的に求めることを特徴とする内視鏡装置の画像処理方法。 Using the endoscope apparatus according to any one of claims 7 to 10, a frame image having a plurality of detection color screens each detecting a different specific wavelength band light is provided a plurality of times. An image processing method for an endoscope apparatus that irradiates light from a plurality of types of light sources under different conditions in synchronization with imaging timing of each frame image,
An observation image when the subject is illuminated with the first light source is a first frame image, an observation image when the subject is illuminated with the second light source is a second frame image, and the first frame image and the second frame Frame images are taken repeatedly,
The luminance information of the specific detection color screen of the first frame image and the luminance information of the specific detection screen of the second frame image are combined to analyze the observation image by the light of the specific wavelength component from the light source device. An image processing method for an endoscopic device, characterized in that the image processing is obtained automatically.
前記特定の波長成分の光による観察画像が、波長帯域幅の狭い出射光による観察画像を少なくとも含むことを特徴とする内視鏡装置の画像処理方法。 An image processing method for an endoscope apparatus according to claim 11,
The image processing method for an endoscope apparatus, wherein the observation image with light of the specific wavelength component includes at least an observation image with outgoing light having a narrow wavelength bandwidth.
前記特定の波長成分の光による観察画像が、波長帯域幅の広い出射光による観察画像を少なくとも含むことを特徴とする内視鏡の画像処理方法。 An image processing method for an endoscope apparatus according to claim 11,
An image processing method for an endoscope, wherein the observation image with light of the specific wavelength component includes at least an observation image with outgoing light having a wide wavelength bandwidth.
前記特定の波長成分の光による観察画像を、それぞれ特定の色調に変換して疑似カラー画像を生成することを特徴とする内視鏡装置の画像処理方法。 An image processing method for an endoscope apparatus according to any one of claims 11 to 13,
An image processing method for an endoscope apparatus, wherein a pseudo color image is generated by converting an observation image with light having a specific wavelength component into a specific color tone.
Priority Applications (7)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008155597A JP2009297290A (en) | 2008-06-13 | 2008-06-13 | Endoscope apparatus and image processing method thereof |
| EP10171389A EP2241244A1 (en) | 2008-06-04 | 2009-06-04 | Illumination device for use in endoscope |
| DE602009001103T DE602009001103D1 (en) | 2008-06-04 | 2009-06-04 | Lighting device for use in endoscopes |
| AT09007428T ATE506000T1 (en) | 2008-06-04 | 2009-06-04 | LIGHTING DEVICE FOR USE IN ENDOSCOPES |
| EP09007428A EP2130484B1 (en) | 2008-06-04 | 2009-06-04 | Illumination device for use in endoscope |
| US12/478,704 US8506478B2 (en) | 2008-06-04 | 2009-06-04 | Illumination device for use in endoscope |
| US12/837,124 US8337400B2 (en) | 2008-06-04 | 2010-07-15 | Illumination device for use in endoscope |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008155597A JP2009297290A (en) | 2008-06-13 | 2008-06-13 | Endoscope apparatus and image processing method thereof |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2009297290A true JP2009297290A (en) | 2009-12-24 |
| JP2009297290A5 JP2009297290A5 (en) | 2011-03-03 |
Family
ID=41544813
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008155597A Abandoned JP2009297290A (en) | 2008-06-04 | 2008-06-13 | Endoscope apparatus and image processing method thereof |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2009297290A (en) |
Cited By (21)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102119846A (en) * | 2010-01-08 | 2011-07-13 | 富士胶片株式会社 | Medical apparatus and endoscope apparatus |
| JP2011244951A (en) * | 2010-05-25 | 2011-12-08 | Fujifilm Corp | Endoscope system |
| JP2012016545A (en) * | 2010-07-09 | 2012-01-26 | Fujifilm Corp | Endoscope apparatus |
| JP2012070822A (en) * | 2010-09-28 | 2012-04-12 | Fujifilm Corp | Light source device and endoscopic diagnostic systen |
| JP2012070839A (en) * | 2010-09-28 | 2012-04-12 | Fujifilm Corp | Light source device and endoscopic diagnostic system |
| JP2012070935A (en) * | 2010-09-28 | 2012-04-12 | Fujifilm Corp | Endoscopic image display apparatus |
| WO2012056860A1 (en) * | 2010-10-26 | 2012-05-03 | オリンパスメディカルシステムズ株式会社 | Endoscope |
| JP2012115514A (en) * | 2010-12-01 | 2012-06-21 | Fujifilm Corp | Endoscope unit |
| JP2012115513A (en) * | 2010-12-01 | 2012-06-21 | Fujifilm Corp | Endoscope unit |
| JP2012205849A (en) * | 2011-03-30 | 2012-10-25 | Fujifilm Corp | Electronic endoscope |
| WO2013136565A1 (en) * | 2012-03-16 | 2013-09-19 | スカラ株式会社 | Video camera |
| EP2407088A3 (en) * | 2010-07-15 | 2015-03-04 | Fujifilm Corporation | Endoscope beam source apparatus and endoscope system |
| EP2856925A1 (en) | 2013-10-03 | 2015-04-08 | Fujifilm Corporation | Light source apparatus and endoscope system |
| JP2016067378A (en) * | 2014-09-26 | 2016-05-09 | オリンパス株式会社 | Endoscope apparatus and endoscope adaptor |
| JP2017060860A (en) * | 2016-12-14 | 2017-03-30 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | Endoscope system |
| JPWO2016098444A1 (en) * | 2014-12-17 | 2017-04-27 | オリンパス株式会社 | Endoscope system |
| WO2018109995A1 (en) * | 2016-12-12 | 2018-06-21 | オリンパス株式会社 | Light source device |
| JP2018171540A (en) * | 2013-08-27 | 2018-11-08 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | Endoscope system |
| WO2021131447A1 (en) * | 2019-12-25 | 2021-07-01 | Hoya株式会社 | Endoscope |
| JP2023536643A (en) * | 2020-08-05 | 2023-08-28 | ジャイラス エーシーエムアイ インク ディー/ビー/エー オリンパス サージカル テクノロジーズ アメリカ | Identification of the composition of anatomical targets |
| JP7546204B2 (en) | 2020-10-26 | 2024-09-06 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | Light emitting device and endoscope system |
Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005198794A (en) * | 2004-01-15 | 2005-07-28 | Pentax Corp | Endoscope |
| JP2006068488A (en) * | 2004-08-31 | 2006-03-16 | Olympus Corp | Capsule type endoscope |
| JP2006166940A (en) * | 2004-12-10 | 2006-06-29 | Olympus Corp | Lighting device for endoscope |
| JP2006288535A (en) * | 2005-04-07 | 2006-10-26 | Olympus Medical Systems Corp | Endoscopic apparatus |
| JP2007229262A (en) * | 2006-03-01 | 2007-09-13 | Fujinon Corp | Endoscopic apparatus |
| JP2008113967A (en) * | 2006-11-07 | 2008-05-22 | Pentax Corp | Endoscope processor, endoscope and endoscope system |
| JP2009118988A (en) * | 2007-11-14 | 2009-06-04 | Hoya Corp | Endoscope apparatus |
| JP2009297141A (en) * | 2008-06-11 | 2009-12-24 | Fujifilm Corp | Light source device, endoscope and image processing method using the same |
-
2008
- 2008-06-13 JP JP2008155597A patent/JP2009297290A/en not_active Abandoned
Patent Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005198794A (en) * | 2004-01-15 | 2005-07-28 | Pentax Corp | Endoscope |
| JP2006068488A (en) * | 2004-08-31 | 2006-03-16 | Olympus Corp | Capsule type endoscope |
| JP2006166940A (en) * | 2004-12-10 | 2006-06-29 | Olympus Corp | Lighting device for endoscope |
| JP2006288535A (en) * | 2005-04-07 | 2006-10-26 | Olympus Medical Systems Corp | Endoscopic apparatus |
| JP2007229262A (en) * | 2006-03-01 | 2007-09-13 | Fujinon Corp | Endoscopic apparatus |
| JP2008113967A (en) * | 2006-11-07 | 2008-05-22 | Pentax Corp | Endoscope processor, endoscope and endoscope system |
| JP2009118988A (en) * | 2007-11-14 | 2009-06-04 | Hoya Corp | Endoscope apparatus |
| JP2009297141A (en) * | 2008-06-11 | 2009-12-24 | Fujifilm Corp | Light source device, endoscope and image processing method using the same |
Cited By (31)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011156339A (en) * | 2010-01-08 | 2011-08-18 | Fujifilm Corp | Medical apparatus and endoscope apparatus |
| CN102119846A (en) * | 2010-01-08 | 2011-07-13 | 富士胶片株式会社 | Medical apparatus and endoscope apparatus |
| JP2011244951A (en) * | 2010-05-25 | 2011-12-08 | Fujifilm Corp | Endoscope system |
| JP2012016545A (en) * | 2010-07-09 | 2012-01-26 | Fujifilm Corp | Endoscope apparatus |
| EP2407088A3 (en) * | 2010-07-15 | 2015-03-04 | Fujifilm Corporation | Endoscope beam source apparatus and endoscope system |
| JP2012070822A (en) * | 2010-09-28 | 2012-04-12 | Fujifilm Corp | Light source device and endoscopic diagnostic systen |
| JP2012070839A (en) * | 2010-09-28 | 2012-04-12 | Fujifilm Corp | Light source device and endoscopic diagnostic system |
| JP2012070935A (en) * | 2010-09-28 | 2012-04-12 | Fujifilm Corp | Endoscopic image display apparatus |
| US9066676B2 (en) | 2010-09-28 | 2015-06-30 | Fujifilm Corporation | Endoscopic image display apparatus |
| WO2012056860A1 (en) * | 2010-10-26 | 2012-05-03 | オリンパスメディカルシステムズ株式会社 | Endoscope |
| US9179829B2 (en) | 2010-10-26 | 2015-11-10 | Olympus Corporation | Endoscope |
| JP5028550B2 (en) * | 2010-10-26 | 2012-09-19 | オリンパスメディカルシステムズ株式会社 | Endoscope |
| JP2012115514A (en) * | 2010-12-01 | 2012-06-21 | Fujifilm Corp | Endoscope unit |
| JP2012115513A (en) * | 2010-12-01 | 2012-06-21 | Fujifilm Corp | Endoscope unit |
| JP2012205849A (en) * | 2011-03-30 | 2012-10-25 | Fujifilm Corp | Electronic endoscope |
| WO2013136565A1 (en) * | 2012-03-16 | 2013-09-19 | スカラ株式会社 | Video camera |
| JPWO2013136565A1 (en) * | 2012-03-16 | 2015-08-03 | スカラ株式会社 | Video camera |
| JP2018171540A (en) * | 2013-08-27 | 2018-11-08 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | Endoscope system |
| EP2856925A1 (en) | 2013-10-03 | 2015-04-08 | Fujifilm Corporation | Light source apparatus and endoscope system |
| CN104510435B (en) * | 2013-10-03 | 2018-04-03 | 富士胶片株式会社 | Light source device for endoscope and use its endoscopic system |
| CN104510435A (en) * | 2013-10-03 | 2015-04-15 | 富士胶片株式会社 | Light source apparatus used for endoscope and endoscope system using same |
| US11246195B2 (en) | 2013-10-03 | 2022-02-08 | Fujifilm Corporation | Light source apparatus and endoscope system |
| JP2016067378A (en) * | 2014-09-26 | 2016-05-09 | オリンパス株式会社 | Endoscope apparatus and endoscope adaptor |
| JPWO2016098444A1 (en) * | 2014-12-17 | 2017-04-27 | オリンパス株式会社 | Endoscope system |
| WO2018109995A1 (en) * | 2016-12-12 | 2018-06-21 | オリンパス株式会社 | Light source device |
| JP6384889B1 (en) * | 2016-12-12 | 2018-09-05 | オリンパス株式会社 | Endoscope light source device |
| US10834791B2 (en) | 2016-12-12 | 2020-11-10 | Olympus Corporation | Light source device |
| JP2017060860A (en) * | 2016-12-14 | 2017-03-30 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | Endoscope system |
| WO2021131447A1 (en) * | 2019-12-25 | 2021-07-01 | Hoya株式会社 | Endoscope |
| JP2023536643A (en) * | 2020-08-05 | 2023-08-28 | ジャイラス エーシーエムアイ インク ディー/ビー/エー オリンパス サージカル テクノロジーズ アメリカ | Identification of the composition of anatomical targets |
| JP7546204B2 (en) | 2020-10-26 | 2024-09-06 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | Light emitting device and endoscope system |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP2009297290A (en) | Endoscope apparatus and image processing method thereof | |
| JP5216429B2 (en) | Light source device and endoscope device | |
| JP7280394B2 (en) | Endoscope light source device | |
| JP5997676B2 (en) | Endoscope light source device and endoscope system using the same | |
| JP5460507B2 (en) | Endoscope apparatus operating method and endoscope apparatus | |
| JP6505792B2 (en) | LIGHT SOURCE DEVICE FOR ENDOSCOPE AND ENDOSCOPE SYSTEM | |
| JP5285967B2 (en) | LIGHT SOURCE DEVICE AND ENDOSCOPE DEVICE USING THE SAME | |
| US20110172492A1 (en) | Medical apparatus and endoscope apparatus | |
| JP5508959B2 (en) | Endoscope device | |
| EP2241244A1 (en) | Illumination device for use in endoscope | |
| US20070213593A1 (en) | Endoscope system | |
| JP5371858B2 (en) | Electronic endoscope device | |
| JP2012016545A (en) | Endoscope apparatus | |
| JP2011036361A (en) | Endoscopic device | |
| JP2014171511A (en) | Subject observation system and method thereof | |
| JP2010022700A (en) | Endoscope system | |
| JP2012050641A (en) | Endoscope system | |
| JP2009291347A (en) | Light source unit and endoscope system using it | |
| JP6203127B2 (en) | Endoscope light source device and endoscope system | |
| JP5677555B2 (en) | Endoscope device | |
| JP2012115372A (en) | Endoscope apparatus | |
| JP2014014716A (en) | Endoscopic apparatus | |
| JP2012070822A (en) | Light source device and endoscopic diagnostic systen | |
| JP5879422B2 (en) | Endoscope device | |
| JP2022031393A (en) | Endoscope apparatus |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20110117 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20110117 |
|
| RD04 | Notification of resignation of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7424 Effective date: 20111216 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20120828 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20120904 |
|
| RD03 | Notification of appointment of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7423 Effective date: 20120907 |
|
| RD04 | Notification of resignation of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7424 Effective date: 20121004 |
|
| A762 | Written abandonment of application |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A762 Effective date: 20121102 |