JP2008015139A - Optical scanner and image forming device using the same - Google Patents
Optical scanner and image forming device using the same Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2008015139A JP2008015139A JP2006185333A JP2006185333A JP2008015139A JP 2008015139 A JP2008015139 A JP 2008015139A JP 2006185333 A JP2006185333 A JP 2006185333A JP 2006185333 A JP2006185333 A JP 2006185333A JP 2008015139 A JP2008015139 A JP 2008015139A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- optical
- sub
- imaging
- scanning
- optically
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 title claims abstract description 181
- 230000004907 flux Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 12
- 238000003384 imaging method Methods 0.000 claims description 93
- 239000003086 colorant Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000000969 carrier Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 43
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 9
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 9
- 230000001360 synchronised effect Effects 0.000 description 9
- 230000006866 deterioration Effects 0.000 description 8
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 7
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 7
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000000465 moulding Methods 0.000 description 6
- 230000004075 alteration Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000005452 bending Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000012937 correction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000001105 regulatory effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008602 contraction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002542 deteriorative effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002452 interceptive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Mechanical Optical Scanning Systems (AREA)
- Facsimile Scanning Arrangements (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は光走査装置及びそれを用いた画像形成装置に関し、例えば電子写真プロセスを有するレーザービームプリンタやデジタル複写機、マルチファンクションプリンタ(多機能プリンタ)等の画像形成装置に好適なものである。 The present invention relates to an optical scanning device and an image forming apparatus using the same, and is suitable for an image forming apparatus such as a laser beam printer, a digital copying machine, or a multi-function printer (multi-function printer) having an electrophotographic process.
従来よりレーザービームプリンター(LBP)等の光走査装置においては画像信号に応じて光源手段から光変調され出射した光束を、例えば回転多面鏡(ポリゴンミラー)より成る光偏向器により周期的に偏向させている。そして偏向された光束をfθ特性を有する結像光学系によって感光性の記録媒体(感光ドラム)面上にスポット状に集束させ、その面上を光走査して画像記録を行っている。 Conventionally, in an optical scanning device such as a laser beam printer (LBP), a light beam that is light-modulated and emitted from a light source means according to an image signal is periodically deflected by, for example, an optical deflector composed of a rotating polygon mirror (polygon mirror). ing. The deflected light beam is focused in a spot shape on the surface of a photosensitive recording medium (photosensitive drum) by an imaging optical system having fθ characteristics, and image recording is performed by optically scanning the surface.
図17は従来の光走査装置の要部概略図である。 FIG. 17 is a schematic view of a main part of a conventional optical scanning device.
同図において光源手段1から出射した発散光束はコリメーターレンズ3により平行光束に変換され、絞り2によって該光束を制限して副走査方向にのみ有限の屈折力を有するシリンドリカルレンズ4に入射している。シリンドリカルレンズ4に入射した平行光束のうち主走査断面内においてはそのままの状態で射出する。また副走査断面内においては集束して偏向手段としての光偏向器(回転多面鏡)5の偏向面(反射面)5aに線像として結像している。
In the figure, a divergent light beam emitted from the light source means 1 is converted into a parallel light beam by a
そして光偏向器5の偏向面5aで偏向された光束をfθ特性を有する結像光学系(結像レンズ系)6を介して被走査面としての感光ドラム面8上に導光している。そして光偏向器5を矢印A方向に回転させることによって該感光ドラム面8上を矢印B方向(主走査方向)に光走査して画像情報の記録を行なっている。
Then, the light beam deflected by the
上記の光走査装置においては感光ドラム面8上を光スポットで走査する前に該感光ドラム8面上における画像形成を開始するタイミングを調整するために、光検出器としての同期検出用(beam detector)センサ−96が設けられている。この同期検出用センサー96は光偏向器5で反射偏向された光束の一部である同期検出用光束、即ち感光ドラム8面上の画像形成領域を走査する前の画像形成領域外の領域を走査している時の光束を受光する。
In the above optical scanning device, in order to adjust the timing for starting image formation on the surface of the
この同期検出用光束は同期検出用ミラー95で反射され、同期検出用レンズ(不図示)で集光されて同期検出用センサー96に入射する。そしてこの同期検出用センサー95の出力信号から同期検出用信号(同期信号)を検出し、この同期検出用信号に基づいて感光ドラム8面における画像記録の開始タイミングを調整している。
The synchronization detection light beam is reflected by the
同図における結像光学系6は副走査断面内において光偏向器5の偏向面5aと感光ドラム面8とが共役関係となるように構成しており、これより偏向面5aの面倒れを補正している。
The imaging
この様な光走査装置において、印刷速度の速い印刷機が年々望まれている。例えばカラーLBPの場合では、印刷速度を考えると、1つの感光ドラムに4回走査させて転写させるタイプより、4色に対応する感光ドラムに対してそれぞれ走査させて転写ドラムに転写させるタンデム型の方が望まれている。 In such an optical scanning device, a printing machine with a high printing speed is desired year by year. For example, in the case of a color LBP, considering the printing speed, a tandem type in which a photosensitive drum corresponding to four colors is scanned and transferred to a transfer drum, rather than a type in which a photosensitive drum is scanned four times and transferred. Is desired.
また、オフィス内での省スペース化のために、コンパクトな光走査装置が望まれており、ミラーで光路を折り曲げることで装置全体を小型化している。 Further, in order to save space in the office, a compact optical scanning device is desired, and the entire device is downsized by bending the optical path with a mirror.
ところで近年、さらなる小型化が望まれており、走査光学系を構成するレンズやモータなどの光学部品の簡素化及び光学系全体の小型化が要望されている。 In recent years, further miniaturization is desired, and simplification of optical components such as lenses and motors constituting the scanning optical system and miniaturization of the entire optical system are desired.
そこでレンズ枚数を少なく、光偏向器(ポリゴンミラー)の高さを小さくするために、光偏向器の偏向面に対して斜め方向から光束を入射させて光偏向器側の結像レンズを共通(ダブルパス)にして通過させる構成がとられている。この種の光走査装置は従来から種々と提案されている(特許文献1参照)。 Therefore, in order to reduce the number of lenses and reduce the height of the optical deflector (polygon mirror), a light beam is incident on the deflecting surface of the optical deflector from an oblique direction so that the imaging lens on the optical deflector side is shared ( Double pass) is used. Various types of optical scanning devices of this type have been conventionally proposed (see Patent Document 1).
さらにレンズの枚数を削減するための方法として、被走査面(感光ドラム面)に近い側の結像レンズも共通化(ダブルパス)する方法がある。ただし、斜入射光学系においては、光偏向器の偏向面に対する入射光束の出入り量の差によって生じるスポットの回転および走査線曲がりを補正するために結像レンズを斜入射する方向に向けて副走査方向に偏芯させている。この種の光走査装置は従来から種々と提案されている(特許文献2参照)。 Further, as a method for reducing the number of lenses, there is a method in which an imaging lens closer to the surface to be scanned (photosensitive drum surface) is also shared (double pass). However, in the oblique incidence optical system, the sub-scanning is performed in the direction in which the imaging lens is obliquely incident in order to correct the rotation of the spot and the bending of the scanning line caused by the difference in the amount of incident light entering and exiting the deflection surface of the optical deflector. It is eccentric in the direction. Various kinds of optical scanning devices of this type have been conventionally proposed (see Patent Document 2).
このとき被走査面に近い側の結像レンズをそれぞれの感光ドラムに向かう光束に対して共通化しようとすると、レンズを上下(副走査方向)に積み重ねたようなレンズになる。この種の光走査装置は従来から種々と提案されている(特許文献3参照)。
結像光学系をコンパクトで、かつ簡易に製作にするための方法として、該結像光学系を構成する複数の結像レンズを光偏向器に近づける(拡大光学系)方法がある。このとき上下に積み重ねた結像レンズの頂点間(面頂点間)の距離は比較的短くなる。 As a method for making the imaging optical system compact and simple, there is a method of bringing a plurality of imaging lenses constituting the imaging optical system close to an optical deflector (enlargement optical system). At this time, the distance between the apexes (between surface apexes) of the imaging lenses stacked vertically is relatively short.
図18は上下に積み重ねたレンズ(結像レンズ)181のレンズ面181a、181bを各々2本の光線が通過する様子を示した拡大説明図である。
FIG. 18 is an enlarged explanatory view showing a state in which two light beams pass through
この結像レンズ181を実際に成形を行う際には、副走査断面で考えると2つの円弧のつなぎ目部分(B1)の転写性は角度変化がきついため、それ以外の部分よりも劣化することが考えられる。上述したように拡大光学系で2つのA部(光学有効部)の頂点A11間が狭い光学系の場合、B部(光学非有効部)の転写性の劣化が光線通過位置の形状に影響を及ぼす。この結果、感光ドラム面上での波面収差に影響を及ぼし、図19に示すように感光ドラム面上でのスポットのスポット形状が劣化することが懸念される。
When the
したがってB部(光学非有効部)の転写性を向上するためには結像レンズ181の副走査断面内での形状を考慮する必要がある。
Therefore, in order to improve the transferability of the B part (optical ineffective part), it is necessary to consider the shape of the
本発明はコンパクトで簡易でありながら結像レンズの共通化を図っても被走査面上でのスポットの形状が劣化することがなく光学性能を劣化させることのない光走査装置及びそれを用いた画像形成装置の提供を目的とする。 The present invention uses an optical scanning device that is compact and simple, and that does not deteriorate the optical performance without deteriorating the spot shape on the surface to be scanned even if the imaging lens is used in common, and the same. An object is to provide an image forming apparatus.
請求項1の発明の光走査装置は、
複数の光源手段と、該複数の光源手段から発せられた複数の光束を偏向走査する偏向手段と、該偏向手段により偏向走査された複数の光束をそれぞれの光源手段に対応した被走査面上に結像させる1つ以上の結像光学素子を有する結像光学系と、を有する走査ユニットを1つ以上具備する光走査装置であって、
該偏向手段の同一の偏向面には、副走査断面内において該複数の光束が該偏向手段の回転軸に垂直な平面に対して異なる角度をもって入射しており、該1つ以上の結像光学素子は、複数の光学有効部と、該複数の光学有効部間であって光束が通過しない光学非有効部が1つ以上存在しており、
該1つ以上の結像光学素子は副走査断面内において該同一の偏向面で偏向された複数の光束が互いに異なる光学有効部を通過しており、
副走査断面内において、該複数の光学有効部の各頂点を結んだ線分から該複数の光学有効部間の光学非有効部の頂点までの該結像光学素子の光軸方向の距離が1.0mm以下となるように構成されていることを特徴としている。
The optical scanning device of the invention of
A plurality of light source means, a deflecting means for deflecting and scanning a plurality of light beams emitted from the plurality of light source means, and a plurality of light beams deflected and scanned by the deflecting means on a surface to be scanned corresponding to each light source means An optical scanning device comprising one or more scanning units each having an imaging optical system having one or more imaging optical elements to form an image,
The plurality of light beams are incident on the same deflection surface of the deflecting unit at different angles with respect to a plane perpendicular to the rotation axis of the deflecting unit in the sub-scan section, and the one or more imaging optics The element has a plurality of optically effective portions and one or more optically ineffective portions between the plurality of optically effective portions and through which light flux does not pass,
In the one or more imaging optical elements, a plurality of light beams deflected by the same deflection surface in a sub-scan section pass through different optical effective portions,
In the sub-scan section, the distance in the optical axis direction of the imaging optical element from the line segment connecting the vertices of the plurality of optically effective portions to the vertex of the optically ineffective portion between the plurality of optically effective portions is 1. It is characterized by being configured to be 0 mm or less.
請求項2の発明は請求項1の発明において、
複数の光源手段と、該複数の光源手段から発せられた複数の光束を偏向走査する偏向手段と、該偏向手段により偏向走査された複数の光束をそれぞれの光源手段に対応した被走査面上に結像させる1つ以上の結像光学素子を有する結像光学系と、を有する走査ユニットを1つ以上具備する光走査装置であって、
該偏向手段の同一の偏向面には、副走査断面内において該複数の光束が該偏向手段の回転軸に垂直な平面に対して異なる角度をもって入射しており、該1つ以上の結像光学素子は複数の光学有効部と、該複数の光学有効部間であって光束が通過しない光学非有効部が1つ以上存在しており、
該1つ以上の結像光学素子は副走査断面内において該同一の偏向面で偏向された複数の光束が互いに異なる光学有効部を通過しており、 副走査断面内において、該複数の光学有効部を各光束の主光線が通過する位置から該複数の光学有効部間の光学非有効部の頂点までの該結像光学素子の光軸方向の距離が1.0mm以下となるように構成されていることを特徴としている。
The invention of
A plurality of light source means, a deflecting means for deflecting and scanning a plurality of light beams emitted from the plurality of light source means, and a plurality of light beams deflected and scanned by the deflecting means on a surface to be scanned corresponding to each light source means An optical scanning device comprising one or more scanning units each having an imaging optical system having one or more imaging optical elements to form an image,
The plurality of light beams are incident on the same deflection surface of the deflecting unit at different angles with respect to a plane perpendicular to the rotation axis of the deflecting unit in the sub-scan section, and the one or more imaging optics The element has a plurality of optically effective portions and one or more optically ineffective portions between the plurality of optically effective portions and through which the light beam does not pass,
In the one or more imaging optical elements, a plurality of light beams deflected by the same deflection surface in the sub-scan section pass through different optical effective portions, and the plurality of optical effective elements in the sub-scan section. The distance in the optical axis direction of the imaging optical element from the position through which the principal ray of each light beam passes through the apex of the optically ineffective portion between the plurality of optically effective portions is 1.0 mm or less. It is characterized by having.
請求項3の発明は請求項1又は2の発明において、
前記複数の光学有効部と前記光学非有効部は傾きが連続となるように接続されていることを特徴としている。
The invention of
The plurality of optically effective portions and the optically ineffective portion are connected so that the inclination is continuous.
請求項4の発明は請求項1、2又は3の発明において、
前記複数の光源手段からの光束が前記偏向手段の同一の偏向面に入射するときの副走査方向の離間量が0mm以上1.0mm以下であることを特徴としている。
The invention of
The separation amount in the sub-scanning direction when the light beams from the plurality of light source units are incident on the same deflection surface of the deflection unit is 0 mm or more and 1.0 mm or less.
請求項5の発明は請求項1から4のいずれか1項の発明において、
前記結像光学系の副走査断面内の結像倍率をβsとするとき、
1.8≦|βs|≦3.0
なる条件を満足することを特徴としている。
The invention of
When the imaging magnification in the sub-scan section of the imaging optical system is βs,
1.8 ≦ | βs | ≦ 3.0
It is characterized by satisfying the following conditions.
請求項6の発明のカラー画像形成装置は、
各々が請求項1から5の何れか1項に記載の光走査装置の被走査面に配置され、互いに異なった色の画像を形成する複数の像担持体とを有することを特徴としている。
The color image forming apparatus of the invention of
Each of the optical scanning devices according to any one of
請求項7の発明は請求項6の発明において、
外部機器から入力した色信号を異なった色の画像データに変換して各々の光走査装置に入力せしめるプリンタコントローラを有していることを特徴としている。
The invention of
It is characterized by having a printer controller that converts color signals input from an external device into image data of different colors and inputs them to each optical scanning device.
本発明によれば装置全体のコンパクト化やレンズの個数の削減化を図ることができ、またレンズの転写性を向上させて波面収差の劣化による画像の劣化を抑えることができる光走査装置及びそれを用いた画像形成装置を達成することができる。 According to the present invention, it is possible to reduce the overall size of the apparatus and reduce the number of lenses, and to improve the transferability of the lenses and to suppress image deterioration due to the deterioration of wavefront aberration, and the same An image forming apparatus using can be achieved.
以下、図面を用いて本発明の実施例を説明する。 Embodiments of the present invention will be described below with reference to the drawings.
図1は本発明の実施例1の主走査方向の要部断面図(主走査断面図)である。図2は本発明の実施例1の光偏向器を挟み一方のみの走査ユニット(走査光学系)S1の副走査方向の要部断面図(副走査断面図)である。図3は本発明の実施例1の平面ミラーを含めた副走査方向の要部断面図(副走査断面図)である。 FIG. 1 is a sectional view (main scanning sectional view) of the main part in the main scanning direction according to the first embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 2 is a sectional view (sub-scanning sectional view) of the principal part in the sub-scanning direction of only one scanning unit (scanning optical system) S1 with the optical deflector according to the first embodiment of the present invention interposed therebetween. FIG. 3 is a cross-sectional view (sub-scanning cross-sectional view) of the main part in the sub-scanning direction including the plane mirror according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
尚、以下の説明において、主走査方向とは光偏向器の回転軸および結像光学系(結像レンズ系)の光軸に垂直な方向(光偏向器で光束が反射偏向(偏向走査)される方向)である。副走査方向とは光偏向器の回転軸と平行な方向である。また主走査断面とは主走査方向と結像光学系の光軸を含む平面である。また副走査断面とは主走査断面と垂直な断面である。 In the following description, the main scanning direction is a direction perpendicular to the rotation axis of the optical deflector and the optical axis of the imaging optical system (imaging lens system) (the light deflector reflects and deflects (deflects and scans) the optical deflector). Direction). The sub-scanning direction is a direction parallel to the rotation axis of the optical deflector. The main scanning section is a plane including the main scanning direction and the optical axis of the imaging optical system. The sub-scanning section is a section perpendicular to the main scanning section.
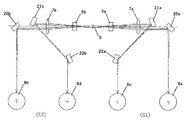
本実施例の光走査装置は光偏向器(ポリゴンミラー)5を挟み2つの結像レンズ系(結像光学系)15a,15bを備え、夫々の結像レンズ系15a,15bへ2本の光束を入射させて1つの光偏向器5により同時に4本の光束を反射偏向する。そしてし4本の光束を夫々に対応した感光ドラム面8a,8b,8c,8dに導光し、該感光ドラム面8a,8b,8c,8d上を光走査するタンデム型の光走査装置である。
The optical scanning device of the present embodiment includes two imaging lens systems (imaging optical systems) 15a and 15b with an optical deflector (polygon mirror) 5 interposed therebetween, and two light beams to the
図中、S1,S2は各々第1、第2の走査ユニット(以下、「ステーション」または「走査光学系」とも称す。)である。 In the figure, S1 and S2 are first and second scanning units (hereinafter also referred to as “station” or “scanning optical system”).
以下、第1、第2の走査ユニットS1,S2の各部材については第1の走査ユニットS1を中心に述べる。そして第2の走査ユニットS2の各部材のうち第1の走査ユニットS1と同じ部材については括弧を付して示す。 Hereinafter, each member of the first and second scanning units S1 and S2 will be described focusing on the first scanning unit S1. Of the members of the second scanning unit S2, the same members as those of the first scanning unit S1 are shown in parentheses.
第1(第2)の走査ユニットS1(S2)は、各々光源手段1a,1c(1b,1d)からの光束を規制する開口絞り2a,2c(2b,2d)と、該光束の状態を他の光束の状態に変換する第1の光学素子3a,3c(3b,3d)とを有している。さらに第1(第2)の走査ユニットS1(S2)は、主走査方向に長い線像として結像させる第2の光学素子4a,4c(4b,4d)と、偏向手段としての光偏向器5とを有している。さらに光偏向器5からの光束を被走査面8a,8c(8b,8d)にスポットに形成する結像レンズ系15a(15b)とを有している。
The first (second) scanning unit S1 (S2) includes aperture stops 2a and 2c (2b and 2d) for restricting light beams from the light source means 1a and 1c (1b and 1d), and other states of the light beams. The first
本実施例においては第1、第2の走査ユニットS1,S2が同一の光偏向器5を併用しており、かつ第1、第2の走査ユニットS1,S2は、該光偏向器5の異なった偏向面で反射偏向(偏向走査)した光束を用いている。
In the present embodiment, the first and second scanning units S1 and S2 use the same
また本実施例においては第1(第2)の走査ユニットS1(S2)の被走査面としての感光ドラム面8a,8c(8b,8d)への書き出しタイミングを、光偏向器5の偏向面からの光束を書き出し位置検知手段(同期検出用光学系)16で検出している。そして書き出し位置検知手段16からの信号を用いて感光ドラム面(8a,8c・8b,8d)への書き出しタイミングを決定している。
In this embodiment, the writing timing to the
また第1、第2の走査ユニットS1,S2は光束が光偏向器5に対して同一方向から入射するように構成されている。
The first and second scanning units S1 and S2 are configured such that the light beam enters the
上記第1、第2の走査ユニットS1,S2において、光源手段(1a,1c・1b,1d)は各々半導体レーザより成り、また光源手段(1a,1c・1b,1d)は同一の平面基板12に配置されている。尚、光源手段(1a,1c・1b,1d)は各々独立に配置しても良い。
In the first and second scanning units S1 and S2, the light source means (1a, 1c, 1b, 1d) are each composed of a semiconductor laser, and the light source means (1a, 1c, 1b, 1d) are the same
開口絞り(2a,2c・2b,2d)は各々光源手段(1a,1c・1b,1d)から出射された光束を特定の最適なビーム形状に成形している。 The aperture stops (2a, 2c, 2b, 2d) respectively shape the light beams emitted from the light source means (1a, 1c, 1b, 1d) into a specific optimum beam shape.
第1の光学素子(3a,3c・3b,3d)は各々コリメーターレンズより成り、開口絞り(2a,2c・2b,2d)を通過した光束を平行光束(もしくは発散光束もしくは収束光束)に変換している。 The first optical elements (3a, 3c, 3b, 3d) are each composed of a collimator lens, and convert the light beam that has passed through the aperture stop (2a, 2c, 2b, 2d) into a parallel light beam (or a divergent light beam or a convergent light beam). is doing.
第2の光学素子(4a,4c・4b,4d)は各々シリンドリカルレンズより成り、副走査方向のみに有限の屈折力を有している。本実施例においてはこの4つのシリンドリカルレンズ(4a,4c・4b,4d)をプラスティックモールド等で一体的に成形している。 Each of the second optical elements (4a, 4c, 4b, 4d) is formed of a cylindrical lens and has a finite refractive power only in the sub-scanning direction. In the present embodiment, these four cylindrical lenses (4a, 4c, 4b, 4d) are integrally formed by a plastic mold or the like.
尚、光源手段1a,1c(1b,1d)、開口絞り2a,2c(2b,2d)、コリメーターレンズ3a,3c(3b,3d)、シリンドリカルレンズ4a,4c(4b,4d)等の各要素は入射光学系の一要素を構成している。
The light source means 1a, 1c (1b, 1d), aperture stops 2a, 2c (2b, 2d),
光偏向器5は、例えば偏向面数が4面より成る回転多面鏡(ポリゴンミラー)より成り、モーター等の駆動手段(不図示)により図中矢印A方向に一定速度で回転している。本実施例においては上記の如く第1、第2の走査ユニットS1,S2がこの光偏向器5を併用しており、かつ第1、第2の走査ユニットS1,S2は、該光偏向器5の異なった偏向面5a,5bで反射偏向した光束を用いている。
The
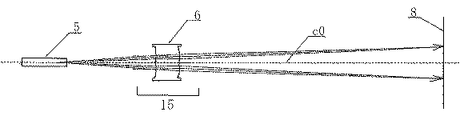
15a(15b)は集光機能とfθ特性とを有する結像レンズ系(fθレンズ系)であり、第1、第2の2枚の結像レンズ6a,7a(6b,7b)より成っている。結像レンズ系15a(15b)は光偏向器5により反射偏向された複数の光束を対応する被走査面8a,8c(8b,8d)上にスポット状に結像させている。また結像レンズ系15a(15b)は副走査断面内において光偏向器5の偏向面と被走査面8a,8c(8b,8d)との間を共役関係にすることにより、面倒れ補正機能を有している。第1、第2の結像レンズ6a,7a(6b,7b)は各々主走査方向と副走査方向とで互いに異なる屈折力(パワー)を有するプラスチック樹脂製のトーリックレンズ(結像光学素子)より成っている。
尚、第1の結像レンズ6a、6bをアナモフィックレンズ1とも称し、また第2の結像レンズ7a、7bをアナモフィックレンズ2とも称す。
The
また本実施例における第1、第2の結像レンズ6a,7a(6b,7b)は各々複数の光束が通過する領域が存在している。
Further, the first and
20a,21a,22a(20b,21b,22b)は各々折返しミラーであり、結像レンズ系15a(15b)を通過した光束を対応する感光ドラム8a,8c(8b,8d)側へ折り返している。
16は書き出し位置検知手段(同期検出用光学系)である。同期検出用光学系16は同期検出用レンズ(以下、「同期検出用レンズ」と記す。)9と、直線状のエッジ部(以下、「同期検出用エッジ」と記す。)11と、同期検知センサー(以下、「同期検出用センサー」と記す。)10とを有している。この同期検出用光学系16は走査ユニットS1(S2)の被走査面8a,8c(8b,8d)への書き出しタイミングを決定している。
本実施例における同期検出用レンズ9は各走査ユニットS1(S2)のシリンドリカルレンズ4a,4c(4b,4d)と一体で構成されており、偏向面5aで反射偏向された同期検出用の光束(同期検出用光束)を同期検出用エッジ11面上に結像させている。また同期検出用レンズ9は主走査断面内では同期検出用エッジ11上を走査し、副走査断面内では偏向面と同期検出用エッジ11とが共役であるため、偏向面の面倒れ補正系となっている。
The
同期検出用エッジ11は画像の書き出し位置を決めている。 The synchronization detection edge 11 determines the image writing position.
同期検出用センサー10は複数の素子が一次元方向に配置されたセンサーより成っている。本実施例ではこの同期検出用センサー10と、4つの光源手段(1a,1c・1b,1d)とを同一の平面基板12上に一体で構成している。尚、同期検出用センサー10と、4つの光源手段(1a,1c・1b,1d)とを各々独立に構成しても良い。
The
本実施例においては、まず第1のステーションS1において、画像情報に応じて光源手段1a、1cから光変調され出射した2本の光束が開口絞り2a、2cにより規制される。そして規制された2本の光束はコリメーターレンズ3a、3cにより平行光束もしくは収束光束に変換され、シリンドリカルレンズ4a、4cに入射する。シリンドリカルレンズ4a、4cに入射した光束のうち主走査断面内においてはそのままの状態で出射する。また副走査断面内(光偏向器の回転軸に垂直な平面)においては収束して光偏向器5の偏向面5aに対し互いに異なる角度をもって入射(斜入射)し、線像(主走査方向に長手の線像)として結像する。そして光偏向器5の偏向面5aで反射偏向された2本の光束は結像レンズ系15aにより対応する折返しミラー20a,21a,22aを介して感光ドラム面8a、8c上にスポット状に結像される。そして光偏向器5を矢印A方向に回転させることによって、感光ドラム面8a、8c上を矢印B方向(主走査方向)に等速度で光走査している。これにより記録媒体である感光ドラム面8a、8c上に画像記録を行っている。
In the present embodiment, first, in the first station S1, the two light beams emitted and modulated from the light source means 1a and 1c according to the image information are regulated by the aperture stops 2a and 2c. The two regulated light beams are converted into parallel light beams or convergent light beams by the
このとき感光ドラム面8a、8c上を光走査する前に該感光ドラム面8a、8c上の走査開始位置のタイミングを調整する為に、光偏向器5の偏向面5aで反射偏向された光束の一部(同期検出用光束)を同期検出用レンズ9により同期検出用エッジ11面上に集光させる。その後、同期検出用エッジ11面上に集光させた光束を同期検出用センサー10に導光している。そして同期検出用センサー10からの出力信号を検知して得られた書き出し位置検知信号(同期検出用信号)を用いて感光ドラム面8a上への画像記録の走査開始位置のタイミングを調整している。
At this time, in order to adjust the timing of the scanning start position on the
第2のステーションS2においては、光源手段1b、1dから出射した2本の光束が第1の走査ユニットS1の入射方向と同一方向から光偏向器5の偏向面5bに対し互いに異なる角度をもって入射する。そして偏向面5bで反射偏向された2本の光束が結像レンズ系15bにより対応する折返しミラー20b,21b,22bを介して感光ドラム面8b、8d上にスポット状に結像され、光走査される。これにより4つの感光ドラム面8a,8b,8c,8d上に夫々1本ずつの走査線を形成し、画像記録を行っている。
In the second station S2, the two light beams emitted from the light source means 1b and 1d are incident on the deflecting
次に本実施例の目的を達成するための手段と効果について説明する。 Next, means and effects for achieving the object of the present embodiment will be described.
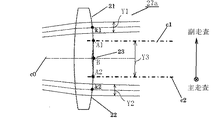
第2の結像レンズ7a(7b)は各々副走査断面内において斜入射によって発生するスポット回転や走査線曲がりを補正するために図4に示すようにレンズ面20を副走査方向に上下に偏芯させて2つに分離したレンズ面(出射面)21、22を有している。この2つのレンズ面21、22の断面は円弧であり、図4に示すような状態を考えると、2つのレンズ面21、22を繋いでいる部分(繋ぎ部)23の連続性がなく角度がきついために、成形後に繋ぎ部23の中央部24において収縮の向きが異なる。このために中央部24における副走査方向の形状が元の円弧形状に対して非球面成分(4次以上)を含んだクセのようなものが発生して、レンズ面21及びレンズ面22の光線が通過する位置の形状にまで影響を及ぼすことで光束の波面収差を劣化させる可能性がある。
As shown in FIG. 4, the
尚、図4においてY1、Y2は各々光学有効部(光学有効面)である。本実施例では偏向面5aで偏向された2本の光束が対応する光学有効部Y1、Y2にそれぞれ入射している。この光学有効部Y1、Y2は各々レンズ面21,22に含まれている。
In FIG. 4, Y1 and Y2 are optically effective portions (optically effective surfaces). In this embodiment, the two light beams deflected by the deflecting
Y3は光束が通過しない光学非有効部(光学非有効面)であり、光学有効部Y1、Y2間にある。この光学非有効部Y3は繋ぎ部23に含まれている。
Y3 is an optical ineffective portion (optical ineffective surface) through which the light beam does not pass, and is between the optical effective portions Y1 and Y2. The optically ineffective portion Y3 is included in the connecting
本実施例では図4に示すようにレンズ面21とレンズ面22とを傾きが連続になるように滑らかな曲線(例えば、円弧や多項式など)で接続することにより、前述した成形後の収縮による繋ぎ目のクセの影響を少なくしている。
In this embodiment, as shown in FIG. 4, the
ここで述べている傾きの連続性とは、2つの曲線の接続点での傾きが等しくなるということである。また、繋ぎ部23からレンズ面21及びレンズ面22までの距離を小さくすることでもクセの影響を少なくできる。
The continuity of the slope described here means that the slopes at the connection points of the two curves are equal. In addition, the influence of the habit can be reduced by reducing the distance from the connecting
次に具体的な内容について説明する。 Next, specific contents will be described.
図4において、レンズ面21の頂点をA21、レンズ面22の頂点をA22、また繋ぎ部23の頂点をBとする。考え方を簡単にするため、レンズ面21及びレンズ面22と繋ぎ部23を円弧として考える。レンズ面21及びレンズ面22の曲率半径をR21、光学有効部Y1、Y2の曲率半径も同様R21とする。また繋ぎ部23の曲率半径をR23、光学非有効部Y3の曲率半径も同様R23とする。さらに頂点A21から頂点A22までの距離をHとすると、頂点A21と頂点A22を結ぶ線分から頂点Bまでの光軸方向の距離(サグ量)zは以下のように表すことができる。
In FIG. 4, the vertex of the
光偏向器5の回転軸に垂直な平面に対して、副走査方向に上下に±γ度で斜入射する光束L1,L2がレンズ面21及びレンズ面22に入射する位置から偏向面5aまでの距離をLとすると、2つの光束の通過位置間距離hは
h=2L・tanγ
で表される。走査光学系(走査ユニット)をコンパクトにしようとすると、結像レンズ系15a(15b)を光偏向器5に近づける(拡大光学系)のがよい。また平面ミラーによって折り返された光束が結像レンズ系15a(15b)と干渉しないようにするためには、光偏向器5から結像レンズ系15a(15b)までの距離を60mm程度に近づける必要がある。
With respect to a plane perpendicular to the rotation axis of the
It is represented by In order to make the scanning optical system (scanning unit) compact, it is preferable to bring the
また、結像レンズ系15a(15b)を出射したのちの各光束の分離を考えると斜入射角度γは2.5度以上であることが望ましい。これらから結像レンズ系15a(15b)における2つの光束の離間量hは2〜3mm程度と比較的小さい。結像レンズ系15a(15b)が光偏向器5に近いと光線通過がレンズ面頂点に比較的近いのでH≒hとすると(式A)は以下のように書き換えられる。
Considering the separation of each light beam after exiting the
スポット回転や走査線曲がりの補正のために結像レンズ系15a(15b)の出射面のパワーは強くなり曲率半径Rは一般的に10〜50程度になる。レンズを2段に積み重ねた場合、曲率がきつくなるほど光学非有効部Y3(繋ぎ部23)の曲率半径R23を光学有効部Y1(レンズ面21,22)の曲率半径R21に近づける必要があるので、
R21=10、
R23≧R21/4
とすると(式B)から
z≦1.0mm ‥‥‥(1)
となる。
The power of the exit surface of the
R 21 = 10,
R 23
From (Equation B), z ≦ 1.0mm (1)
It becomes.
但し、サグ量zは、0mm<zである。 However, the sag amount z is 0 mm <z.
このように、レンズ面21の頂点A21とレンズ面22の頂点A22を結ぶ線分から繋ぎ部23の頂点Bまでの光軸方向の距離zを1.0mm以下に抑えるように2つのレンズ面21、22を滑らかに接続することで成形後の収縮の影響を少なくできる。これにより波面収差の劣化を低減することができる。また、結像レンズ系15a(15b)を光偏向器5に近づけて第2の結像レンズ7a(7b)を2本の光束で共通化することにより、従来よりもコンパクトな光走査装置を提供することができる。
Thus, the two
尚、上記条件式(1)を、さらに
z≦0.5mm ‥‥‥(1a)
に設定すれば成形後の収縮における影響をさらに低減できるので望ましい。
The above conditional expression (1) is further changed to z ≦ 0.5 mm (1a)
If it is set to, the influence on shrinkage after molding can be further reduced, which is desirable.
表1に本発明の実施例1の光学系の諸量を示す。 Table 1 shows various amounts of the optical system of Example 1 of the present invention.
本実施例においては図5に示すように第2の結像レンズ(アナモフィックレンズ2)7a(7b)の出射面21及び出射面22の面頂点軸c1及び面頂点軸c2がレンズ光軸c0に対して副走査方向に上下に1.4mm偏芯している。
In this embodiment, as shown in FIG. 5, the
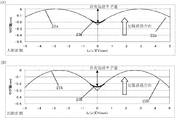
本実施例では出射面21を副走査方向に上下に偏芯させることで図6に示すようにスポットの回転を補正している。尚、スポットはピーク光量に対して5%,10%,13.5%,36.8%,50%の等高線で表している。
In this embodiment, the rotation of the spot is corrected as shown in FIG. 6 by decentering the emitting
図7は本発明の実施例1の繋ぎ目部分のサグ量を示す説明図である。同図に示すように面頂点部に対して繋ぎ目部分までの光学非有効部Y3のサグ量zは50μmと小さい。そのままレンズ面21とレンズ面22を接続しても良いが成形型を加工するときの便宜性を考えると、光線が通過する光学有効部Y1、Y2と光線が通過しない光学非有効部Y3の傾きが連続になるように小径(緩い曲率)Rもしくは多項式で調整するのが望ましい。
FIG. 7 is an explanatory diagram showing the amount of sag at the joint portion according to the first embodiment of the present invention. As shown in the figure, the sag amount z of the optically ineffective portion Y3 up to the joint portion with respect to the surface apex portion is as small as 50 μm. The
このとき、光学非有効部Y3のサグ量zがさらに小さくなるので成形による繋ぎ目の影響は小さく波面収差の劣化によるスポット形状の劣化を防ぐことができる。また第2の結像レンズ7a(7b)が光偏向器5に近いのでレンズの長さを従来に対して短くできる。
At this time, since the sag amount z of the optically ineffective portion Y3 is further reduced, the influence of the joint by the molding is small, and the deterioration of the spot shape due to the deterioration of the wavefront aberration can be prevented. Further, since the
光偏向器5から第2の結像レンズ7a(7b)までの距離をある程度まで抑えて光線の折り返しによるレンズとの干渉を避けるには、結像レンズ系15a(15b)の副走査断面内の結像倍率βsを1.8以上にするのが望ましい。また、結像倍率βsが大きくなりすぎると第2の結像レンズ7a(7b)が光偏向器5に近づきすぎて光束の分離が不利になるので副走査倍率βsは3.0以下に抑えることが望ましい。即ち、結像レンズ系15a(15b)の副走査断面内の結像倍率βsを、
1.8≦|βs|≦3.0 ‥‥‥(2)
なる条件を満足させることが良い。
In order to suppress the distance from the
1.8 ≦ | βs | ≦ 3.0 (2)
It is better to satisfy the following conditions.
光束分離を容易にするには、複数の光束が偏向面を反射するときの光束離間量を大きくすることが考えられるが、偏向面の副走査方向の高さが大きくなる。よってモータの回転抵抗が増加すること、また第2の結像レンズ7a(7b)の高さが増えることを考慮すると、偏向面上での複数の光束の離間量は0mm以上1.0mm以下にすることが望ましい。
In order to facilitate light beam separation, it is conceivable to increase the amount of light beam separation when a plurality of light beams reflect the deflection surface, but the height of the deflection surface in the sub-scanning direction increases. Therefore, considering the increase in the rotational resistance of the motor and the increase in the height of the
本実施例においては第2の結像レンズ7a(7b)のレンズ面が2段の場合を示したが、これに限らず、3段以上のレンズ面であっても良い。例えば3本以上の光束を第2の結像レンズ7a,7bを通過後に光束を分離するような系の場合、レンズ面が3段以上になることもあり、この場合でも、本実施例と同様に滑らかに接続することで成形時のクセの影響を低減できる。
[変形例]
図8は本発明の実施例1の変形例の副走査方向の要部断面図(副走査断面図)である。同図において図2に示した要素と同一要素には同符番を付している。
In the present embodiment, the case where the lens surface of the
[Modification]
FIG. 8 is a sectional view (sub-scanning sectional view) of the principal part in the sub-scanning direction of a modification of the first embodiment of the present invention. In the figure, the same elements as those shown in FIG.
変形例において前述の実施例1と異なる点は結像光学系15を単一の結像レンズ(アナモフィックレンズ1)6より構成したことである。その他の構成及び光学的作用は実施例1と同様である。
The modification differs from the first embodiment described above in that the imaging
表2に変形例の光学系の諸量を示す。 Table 2 shows various amounts of the optical system of the modification.
変形例においては結像光学系15を構成するレンズ枚数が1枚になっていることで、レンズ面の被走査面上での光学性能の補正の自由度が減少している。従って、本実施例ではスポットの回転を図10に示すように補正するために、図9に示すように結像レンズ6の入射面21a、22aの面頂点軸c3、c4をレンズ光軸(レンズ中心)c0に対して副走査方向に上下に2.9mm偏芯させている。また出射面21b、22bの面頂点軸c5、c6を同じくレンズ光軸c0に対して副走査方向に上下に2.7mm偏芯させている。
In the modification, since the number of lenses constituting the imaging
尚、図10においてスポットはピーク光量に対して5%,10%,13.5%,36.8%,50%の等高線で表している。 In FIG. 10, spots are represented by contour lines of 5%, 10%, 13.5%, 36.8%, and 50% with respect to the peak light quantity.
ここで結像レンズ6の入射面21a、22a及び出射面21b、22bにおける繋ぎ目の光軸方向の距離(サグ量)zを図11(A)、(B)に示す。同図(A)、(B)より面頂点部に対して繋ぎ目部分までのサグ量zは両面とも約0.3mmである。
Here, the distance (sag amount) z in the optical axis direction of the joint between the incident surfaces 21a and 22a and the exit surfaces 21b and 22b of the
図9に示すように光線通過位置がレンズ光軸c0に近いため、繋ぎ部23a、23bの影響を小さくするためには光線が通過する光学有効部Y1、Y2と光線が通過しない光学非有効部Y3の傾きが連続になるように小径(緩い曲率)Rもしくは多項式で調整するのが望ましい。
Since the light beam passing position is close to the lens optical axis c0 as shown in FIG. 9, in order to reduce the influence of the connecting
このように繋ぎ部23a、23bの面頂点に対するサグ量を小さくすることで両面とも繋ぎ部23a、23bでの成形時のクセによる影響を低減することができる。
Thus, by reducing the sag amount with respect to the surface apexes of the connecting
図12は本発明の実施例2の光偏向器を挟み一方のみの走査ユニット(走査光学系)S1の副走査方向の要部断面図(副走査断面図)、図13は第2の結像レンズ(アナモフィックレンズ2)の副走査断面図である。図12、図13において図2、図5に示した要素と同一要素には同符番を付している。 FIG. 12 is a sectional view (sub-scanning sectional view) of the principal part in the sub-scanning direction of only one scanning unit (scanning optical system) S1 with the optical deflector according to the second embodiment of the present invention interposed therebetween, and FIG. It is a sub-scan sectional view of a lens (anamorphic lens 2). 12 and 13, the same elements as those shown in FIGS. 2 and 5 are denoted by the same reference numerals.
本実施例において前述の実施例1と異なる点は第2の結像レンズ27aの面頂点Bを1つより構成したことである。その他の構成及び光学的作用は実施例1と同様であり、これにより同様な効果を得ている。
This embodiment is different from the first embodiment described above in that the surface apex B of the
即ち、図中、27aは第2の結像レンズ(アナモフィックレンズ2)であり、本実施例では図13に示すように第2の結像レンズ27aの面頂点Bを1つより構成している。
That is, in the drawing,
k1、k2は各々主光線の光線通過位置である。 k1 and k2 are the principal ray passing positions, respectively.
光線分離のため斜入射角度γが大きくなる場合、スポット回転と走査線曲がりを補正するためにレンズ面の傾斜がよりきつい位置を光束が通過しようとするので、光束が元のレンズ面21の頂点A1に対してかなり離れた位置を通過する。
When the oblique incident angle γ is increased due to the light beam separation, the light beam tends to pass through a position where the inclination of the lens surface is tighter in order to correct the spot rotation and the scanning line curve, so that the light beam is the apex of the
したがって2つのレンズ面21、22を積み重ねた場合、元のレンズ面21の頂点A1は他方のレンズ面22の光学有効部Y2内にあるので、実質存在しない。ただし、成形後の収縮による繋ぎ部23のヒケは起こりうるので、2つのレンズ面21、22を滑らかに接続する必要があるので、図13に示すような面頂点が中央に存在するような形状をもつレンズ面となる。
Therefore, when the two
表3に実施例2の光学系の諸量を示す。 Table 3 shows various amounts of the optical system of Example 2.
本実施例においては、第2の結像レンズ27aの出射面21の面頂点軸c1及び出射面22の面頂点軸c2を図13に示すようにレンズ光軸c0に対して副走査方向に上下に3.3mm偏芯させている。それとともに子線方向の頂点を50μm程度曲げることで、斜入射によるスポット回転を図14に示すように抑えている。
In this embodiment, the surface vertex axis c1 of the
尚、図14においてスポットはピーク光量に対して5%,10%,13.5%,36.8%,50%の等高線で表している。 In FIG. 14, the spots are represented by contour lines of 5%, 10%, 13.5%, 36.8%, and 50% with respect to the peak light quantity.
図15は本発明の実施例2の繋ぎ目部分のサグ量を示す説明図である。同図において図13に示した要素と同一要素には同符番を付している。 FIG. 15 is an explanatory diagram showing a sag amount at a joint portion according to the second embodiment of the present invention. In the figure, the same elements as those shown in FIG.
同図に示すように繋ぎ目に対して主光線の光線通過位置k1及びk2までの距離がレンズ光軸c0に対して4.7mmと長いので繋ぎ部23を残す必要がない。 As shown in the figure, since the distance from the joint to the light ray passing positions k1 and k2 is as long as 4.7 mm with respect to the lens optical axis c0, there is no need to leave the joint 23.
したがって、光線が通過しない光学非有効部Y3を直線で結ぶか、光線が通過する光学有効部Y1、Y2と光学非有効部Y3との傾きが連続になるように緩い曲率(R)もしくは多項式で繋ぐようにすれば良い。このとき副走査断面内において、主光線の光線通過位置k1及びk2から光学非有効部Y3の面頂点Bまでの光軸方向の距離(サグ量)zは0.1mm以下と小さく、成形において光学非有効部Y3の影響は非常に小さい。 Therefore, the optically ineffective portion Y3 through which the light beam does not pass is connected by a straight line, or the optically effective portion Y1, Y2 through which the light beam passes and the optical ineffective portion Y3 has a gentle curvature (R) or a polynomial so that the inclination is continuous. Just connect them. At this time, in the sub-scan section, the distance (sag amount) z in the optical axis direction from the ray passing positions k1 and k2 of the principal rays to the surface apex B of the optical ineffective portion Y3 is as small as 0.1 mm or less. The influence of the ineffective portion Y3 is very small.
尚、サグ量zは1.0mm以下なら本発明の目的は達せられる。さらに好ましくはサグ量zを0.5mm以下に設定するのが良い。但し、サグ量zは、0mm<zである。 If the sag amount z is 1.0 mm or less, the object of the present invention can be achieved. More preferably, the sag amount z is set to 0.5 mm or less. However, the sag amount z is 0 mm <z.
また、第2の結像レンズ27aが光偏向器5に近いのでレンズの長さを従来に対して短くできる。また、斜入射角度γが大きくなることで副走査方向の上下の光線の分離に有利となる。
Further, since the
尚、上記本実施例1,2では光偏向器5を挟んで走査ユニット(走査光学系)をそれぞれ設けたが、これに限らず、どちらか一方のみでも良い。
In the first and second embodiments, the scanning unit (scanning optical system) is provided with the
[カラー画像形成装置]
図16は本発明の実施例のカラー画像形成装置の要部概略図である。本実施例は、光走査装置を4個並べ各々並行して像担持体である感光ドラム面上に画像情報を記録するタンデムタイプのカラー画像形成装置である。図16において、360はカラー画像形成装置、311,312は各々実施例1、2に示したいずれかの構成を有する走査ユニットである。341,342,343,344は各々像担持体としての感光ドラム、321,322,323,324は各々現像器、351は搬送ベルトである。
[Color image forming apparatus]
FIG. 16 is a schematic view of a main part of a color image forming apparatus according to an embodiment of the present invention. This embodiment is a tandem type color image forming apparatus in which four optical scanning devices are arranged in parallel and image information is recorded on a photosensitive drum surface as an image carrier. In FIG. 16, 360 is a color image forming apparatus, and 311 and 312 are scanning units each having one of the configurations shown in the first and second embodiments. 341, 342, 343, and 344 are photosensitive drums as image carriers, 321, 322, 323, and 324 are developing units, and 351 is a conveyor belt.
図16において、カラー画像形成装置360には、パーソナルコンピュータ等の外部機器352からR(レッド)、G(グリーン)、B(ブルー)の各色信号が入力する。これらの色信号は、装置内のプリンタコントローラ353によって、C(シアン),M(マゼンタ),Y(イエロー)、B(ブラック)の各画像データ(ドットデータ)に変換される。これらの画像データは、それぞれ走査ユニット311,312に入力される。そして、これらの走査ユニットからは、各画像データに応じて変調された光ビーム331,332,333,334が出射され、これらの光ビームによって感光ドラム341,342,343,344の感光面が主走査方向に走査される。
In FIG. 16, R (red), G (green), and B (blue) color signals are input to the color
本実施例におけるカラー画像形成装置は走査ユニット311,312を2個並べ、各々がC(シアン),M(マゼンタ),Y(イエロー)、B(ブラック)の各色に対応している。そして各々平行して感光ドラム341,342,343,344面上に画像信号(画像情報)を記録し、カラー画像を高速に印字している。
The color image forming apparatus according to the present embodiment has two scanning
本実施例におけるカラー画像形成装置は上述の如く2つの走査ユニット311,312により各々の画像データに基づいた光ビームを用いて各色の潜像を各々対応する感光ドラム341,342,343,344面上に形成している。その後、記録材に多重転写して1枚のフルカラー画像を形成している。
As described above, the color image forming apparatus according to the present embodiment uses the light beams based on the respective image data by the two scanning
前記外部機器352としては、例えばCCDセンサを備えたカラー画像読取装置が用いられても良い。この場合には、このカラー画像読取装置と、カラー画像形成装置360とで、カラーデジタル複写機が構成される。
As the external device 352, for example, a color image reading device including a CCD sensor may be used. In this case, the color image reading apparatus and the color
1a,1b,1c,1d 光源手段
2a,2b,2c,2d 開口絞り
3a,3b,3c,3d 集光レンズ(コリメーターレンズ)
4a,4b,4c,4d シリンドリカルレンズ
5 偏向手段(ポリゴンミラー)
15a,15b 結像光学系(fθレンズ系)
6a,6b 第1の結像レンズ(fθレンズ)
7a,7b 第2の結像レンズ(fθレンズ)
8a,8b,8c,8d 被走査面(感光ドラム面)
9 同期検出用レンズ
11 同期検出用エッジ
10 同期検出用センサー
311,312 走査ユニット
341,342,343,344 像担持体(感光ドラム)
321,322,323,324 現像器
331,332,333,334 光ビーム
351 搬送ベルト
352 外部機器
353 プリンタコントローラ
360 カラー画像形成装置
1a, 1b, 1c, 1d Light source means 2a, 2b, 2c,
4a, 4b, 4c,
15a, 15b Imaging optical system (fθ lens system)
6a, 6b First imaging lens (fθ lens)
7a, 7b Second imaging lens (fθ lens)
8a, 8b, 8c, 8d Scanned surface (photosensitive drum surface)
DESCRIPTION OF
321, 322, 323, 324
Claims (7)
該偏向手段の同一の偏向面には、副走査断面内において該複数の光束が該偏向手段の回転軸に垂直な平面に対して異なる角度をもって入射しており、該1つ以上の結像光学素子は、複数の光学有効部と、該複数の光学有効部間であって光束が通過しない光学非有効部が1つ以上存在しており、
該1つ以上の結像光学素子は副走査断面内において該同一の偏向面で偏向された複数の光束が互いに異なる光学有効部を通過しており、
副走査断面内において、該複数の光学有効部の各頂点を結んだ線分から該複数の光学有効部間の光学非有効部の頂点までの該結像光学素子の光軸方向の距離が1.0mm以下となるように構成されていることを特徴とする光走査装置。 A plurality of light source means, a deflecting means for deflecting and scanning a plurality of light beams emitted from the plurality of light source means, and a plurality of light beams deflected and scanned by the deflecting means on a surface to be scanned corresponding to each light source means An optical scanning device comprising one or more scanning units each having an imaging optical system having one or more imaging optical elements to form an image,
The plurality of light beams are incident on the same deflection surface of the deflecting unit at different angles with respect to a plane perpendicular to the rotation axis of the deflecting unit in the sub-scan section, and the one or more imaging optics The element has a plurality of optically effective portions and one or more optically ineffective portions between the plurality of optically effective portions and through which light flux does not pass,
In the one or more imaging optical elements, a plurality of light beams deflected by the same deflection surface in a sub-scan section pass through different optical effective portions,
In the sub-scan section, the distance in the optical axis direction of the imaging optical element from the line segment connecting the vertices of the plurality of optically effective portions to the vertex of the optically ineffective portion between the plurality of optically effective portions is 1. An optical scanning device configured to be 0 mm or less.
該偏向手段の同一の偏向面には、副走査断面内において該複数の光束が該偏向手段の回転軸に垂直な平面に対して異なる角度をもって入射しており、該1つ以上の結像光学素子は複数の光学有効部と、該複数の光学有効部間であって光束が通過しない光学非有効部が1つ以上存在しており、
該1つ以上の結像光学素子は副走査断面内において該同一の偏向面で偏向された複数の光束が互いに異なる光学有効部を通過しており、 副走査断面内において、該複数の光学有効部を各光束の主光線が通過する位置から該複数の光学有効部間の光学非有効部の頂点までの該結像光学素子の光軸方向の距離が1.0mm以下となるように構成されていることを特徴とする光走査装置。 A plurality of light source means, a deflecting means for deflecting and scanning a plurality of light beams emitted from the plurality of light source means, and a plurality of light beams deflected and scanned by the deflecting means on a surface to be scanned corresponding to each light source means An optical scanning device comprising one or more scanning units each having an imaging optical system having one or more imaging optical elements to form an image,
The plurality of light beams are incident on the same deflection surface of the deflecting unit at different angles with respect to a plane perpendicular to the rotation axis of the deflecting unit in the sub-scan section, and the one or more imaging optics The element has a plurality of optically effective portions and one or more optically ineffective portions between the plurality of optically effective portions and through which the light beam does not pass,
In the one or more imaging optical elements, a plurality of light beams deflected by the same deflection surface in the sub-scan section pass through different optical effective portions, and the plurality of optical effective elements in the sub-scan section. The distance in the optical axis direction of the imaging optical element from the position through which the principal ray of each light beam passes through the apex of the optically ineffective portion between the plurality of optically effective portions is 1.0 mm or less. An optical scanning device characterized by comprising:
1.8≦|βs|≦3.0
なる条件を満足することを特徴とする請求項1から4のいずれか1項に記載の光走査装置。 When the imaging magnification in the sub-scan section of the imaging optical system is βs,
1.8 ≦ | βs | ≦ 3.0
5. The optical scanning device according to claim 1, wherein the following condition is satisfied.
7. The color image forming apparatus according to claim 6, further comprising a printer controller that converts color signals input from an external device into image data of different colors and inputs the converted image data to each optical scanning device.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006185333A JP2008015139A (en) | 2006-07-05 | 2006-07-05 | Optical scanner and image forming device using the same |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006185333A JP2008015139A (en) | 2006-07-05 | 2006-07-05 | Optical scanner and image forming device using the same |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2008015139A true JP2008015139A (en) | 2008-01-24 |
| JP2008015139A5 JP2008015139A5 (en) | 2009-08-20 |
Family
ID=39072232
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006185333A Pending JP2008015139A (en) | 2006-07-05 | 2006-07-05 | Optical scanner and image forming device using the same |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2008015139A (en) |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011081369A (en) * | 2009-09-08 | 2011-04-21 | Ricoh Co Ltd | Plastic optical element, optical scanning device, and image forming apparatus |
| US8743444B2 (en) | 2011-03-16 | 2014-06-03 | Ricoh Company, Limited | Optical scanning device, image forming apparatus, scanning lens, and molding method of the scanning lens |
| US20140307037A1 (en) * | 2013-04-15 | 2014-10-16 | Canon Kabushiki Kaisha | Optical scanning apparatus and image forming apparatus equipped with scanning apparatus |
| JP2015219495A (en) * | 2014-05-21 | 2015-12-07 | キヤノン株式会社 | Optical scanning device |
| US9547152B2 (en) | 2011-09-15 | 2017-01-17 | Ricoh Company, Ltd. | Plastic optical element and optical scanner and imaging forming device including the same |
| US10218871B2 (en) | 2015-11-20 | 2019-02-26 | Hp Printing Korea Co., Ltd. | Light scanning unit and image forming apparatus having the same |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002365532A (en) * | 2001-06-05 | 2002-12-18 | Ricoh Co Ltd | Resin aspherical optical element, optical scanner and imaging apparatus |
| JP2004070110A (en) * | 2002-08-08 | 2004-03-04 | Canon Inc | Optical scanner and image forming apparatus using the same |
| JP2004294713A (en) * | 2003-03-26 | 2004-10-21 | Minolta Co Ltd | Ftheta OPTICAL SYSTEM, LENS, AND SCANNING OPTICAL APPARATUS |
-
2006
- 2006-07-05 JP JP2006185333A patent/JP2008015139A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002365532A (en) * | 2001-06-05 | 2002-12-18 | Ricoh Co Ltd | Resin aspherical optical element, optical scanner and imaging apparatus |
| JP2004070110A (en) * | 2002-08-08 | 2004-03-04 | Canon Inc | Optical scanner and image forming apparatus using the same |
| JP2004294713A (en) * | 2003-03-26 | 2004-10-21 | Minolta Co Ltd | Ftheta OPTICAL SYSTEM, LENS, AND SCANNING OPTICAL APPARATUS |
Cited By (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011081369A (en) * | 2009-09-08 | 2011-04-21 | Ricoh Co Ltd | Plastic optical element, optical scanning device, and image forming apparatus |
| US8743444B2 (en) | 2011-03-16 | 2014-06-03 | Ricoh Company, Limited | Optical scanning device, image forming apparatus, scanning lens, and molding method of the scanning lens |
| US9547152B2 (en) | 2011-09-15 | 2017-01-17 | Ricoh Company, Ltd. | Plastic optical element and optical scanner and imaging forming device including the same |
| US20140307037A1 (en) * | 2013-04-15 | 2014-10-16 | Canon Kabushiki Kaisha | Optical scanning apparatus and image forming apparatus equipped with scanning apparatus |
| JP2014206673A (en) * | 2013-04-15 | 2014-10-30 | キヤノン株式会社 | Optical scanner and image forming apparatus using the same |
| US9217948B2 (en) | 2013-04-15 | 2015-12-22 | Canon Kabushiki Kaisha | Optical scanning apparatus and image forming apparatus equipped with scanning apparatus |
| JP2015219495A (en) * | 2014-05-21 | 2015-12-07 | キヤノン株式会社 | Optical scanning device |
| US9395537B2 (en) | 2014-05-21 | 2016-07-19 | Canon Kabushiki Kaisha | Optical scanning apparatus |
| US10218871B2 (en) | 2015-11-20 | 2019-02-26 | Hp Printing Korea Co., Ltd. | Light scanning unit and image forming apparatus having the same |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4769734B2 (en) | Optical scanning device and image forming apparatus using the same | |
| JP5171029B2 (en) | Optical scanning device and image forming apparatus using the same | |
| JP2009271353A (en) | Optical scanner and image forming apparatus using the same | |
| JP3667286B2 (en) | Optical scanning apparatus, image forming apparatus, and color image forming apparatus | |
| JP2008015139A (en) | Optical scanner and image forming device using the same | |
| JP2004240266A (en) | Light scanner and color image forming apparatus using the same | |
| JP5197045B2 (en) | Optical scanning device and image forming apparatus using the same | |
| JP2010049061A (en) | Optical scanning apparatus and image forming apparatus using the same | |
| JP2004070108A (en) | Optical scanner and image forming apparatus using the same | |
| JP2004070109A (en) | Optical scanner and image forming apparatus using the same | |
| JP4227335B2 (en) | Optical scanning device and image forming apparatus using the same | |
| JP2006330688A (en) | Optical scanner and image forming apparatus using the same | |
| JP4250572B2 (en) | Optical scanning device and image forming apparatus using the same | |
| JP2003241126A (en) | Scanning optical device and image forming apparatus using it | |
| JP2013142744A (en) | Multibeam optical scanner and image formation apparatus | |
| JP2005134624A (en) | Optical scanner and image forming apparatus using same | |
| JP2006337792A (en) | Optical scanner and image forming apparatus using the same | |
| JP2007316115A (en) | Optical scanner and image forming apparatus using the same | |
| JP2008170487A (en) | Optical scanner and image forming apparatus using the same | |
| JP2010072050A (en) | Optical scanner and method of adjusting optical scanner | |
| JP2005091966A (en) | Optical scanner and color image forming apparatus using it | |
| JP6132701B2 (en) | Optical scanning device and image forming apparatus using the same | |
| JP2013064857A (en) | Optical scanner, and image forming apparatus | |
| JP4902279B2 (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| JP2009271384A (en) | Optical scanning apparatus and image forming apparatus using the same |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20090702 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20090702 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20110516 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20110524 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20110721 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20120207 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20120605 |