JP2007333384A - Radiographic image detector and radiographic image photographing system - Google Patents
Radiographic image detector and radiographic image photographing system Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2007333384A JP2007333384A JP2005023659A JP2005023659A JP2007333384A JP 2007333384 A JP2007333384 A JP 2007333384A JP 2005023659 A JP2005023659 A JP 2005023659A JP 2005023659 A JP2005023659 A JP 2005023659A JP 2007333384 A JP2007333384 A JP 2007333384A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- state
- image detector
- battery
- radiation image
- imaging
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 230000005855 radiation Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 160
- 238000003384 imaging method Methods 0.000 claims description 101
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 claims description 40
- 239000000725 suspension Substances 0.000 claims description 8
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000006866 deterioration Effects 0.000 abstract description 7
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 20
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 13
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 13
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 7
- OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phosphorus Chemical compound [P] OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229910052688 Gadolinium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- OJIJEKBXJYRIBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N cadmium nickel Chemical compound [Ni].[Cd] OJIJEKBXJYRIBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000003990 capacitor Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000002542 deteriorative effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000004973 liquid crystal related substance Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 2
- NDVLTYZPCACLMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N silver oxide Chemical compound [O-2].[Ag+].[Ag+] NDVLTYZPCACLMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910052716 thallium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000010409 thin film Substances 0.000 description 2
- WHXSMMKQMYFTQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Lithium Chemical compound [Li] WHXSMMKQMYFTQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HBBGRARXTFLTSG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Lithium ion Chemical compound [Li+] HBBGRARXTFLTSG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PWHULOQIROXLJO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Manganese Chemical compound [Mn] PWHULOQIROXLJO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HCHKCACWOHOZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Zinc Chemical compound [Zn] HCHKCACWOHOZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000010521 absorption reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000009825 accumulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003745 diagnosis Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005284 excitation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000284 extract Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000446 fuel Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001678 irradiating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052744 lithium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910001416 lithium ion Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052748 manganese Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011572 manganese Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011159 matrix material Substances 0.000 description 1
- QSHDDOUJBYECFT-UHFFFAOYSA-N mercury Chemical compound [Hg] QSHDDOUJBYECFT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052753 mercury Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052987 metal hydride Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052759 nickel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N nickel Substances [Ni] PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- -1 nickel metal hydride Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000002601 radiography Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052761 rare earth metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008054 signal transmission Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910001923 silver oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000007704 transition Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052725 zinc Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011701 zinc Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Radiography Using Non-Light Waves (AREA)
- Apparatus For Radiation Diagnosis (AREA)
- Transforming Light Signals Into Electric Signals (AREA)
- Measurement Of Radiation (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、放射線画像検出器及び放射線画像撮影システムに係り、特に、電池の充電又は交換を行うことにより繰り返し使用可能な放射線画像検出器及びこのような放射線画像検出器を適用した放射線画像撮影システムに関するものである。 The present invention relates to a radiographic image detector and a radiographic imaging system, and more particularly, a radiographic image detector that can be used repeatedly by charging or replacing a battery, and a radiographic imaging system to which such a radiographic image detector is applied. It is about.
従来から、医療診断を目的とする放射線撮影分野においては、被写体に放射線を照射してその被写体を透過した放射線の強度分布を検出することにより、当該被写体の放射線画像を得る放射線画像撮影システムが広く知られている。また、近年の放射線画像撮影システムでは、多数の光電変換素子をマトリクス状に配した薄型平板状の所謂「フラットパネルディテクタ(Flat Panel Detector)(以下「FPD」と称する。)」という放射線画像検出器が開発・使用されている。FPDは、被写体を透過した放射線を検出して電気信号に光電変換し、光電変換後の電気信号を画像処理することにより容易かつ迅速に被写体の放射線画像を得ることができるようになっている。 Conventionally, in the field of radiography for the purpose of medical diagnosis, there have been widely used radiographic imaging systems that obtain a radiographic image of a subject by irradiating the subject with radiation and detecting the intensity distribution of the radiation transmitted through the subject. Are known. In recent radiographic imaging systems, a so-called “Flat Panel Detector” (hereinafter referred to as “FPD”) having a thin flat plate shape in which a large number of photoelectric conversion elements are arranged in a matrix form. Is being developed and used. The FPD can easily and quickly obtain a radiation image of a subject by detecting radiation transmitted through the subject, photoelectrically converting the radiation into an electrical signal, and performing image processing on the electrical signal after the photoelectric conversion.
前記放射線画像検出器は、システムの一部として所定位置に据え置かれる据置型のものと、持ち運び自在の携帯型(カセッテ型)のものとに大別され、運搬や取扱いの容易性の見地から最近ではカセッテ型の放射線画像検出器の利用が広く検討されている。 The radiation image detectors are roughly classified into a stationary type that is installed at a predetermined position as a part of the system and a portable type (cassette type) that is portable, and has been recently used from the viewpoint of ease of transportation and handling. The use of cassette-type radiation image detectors has been widely studied.
このようなカセッテ型の放射線画像検出器においては、放射線画像検出器を駆動させるための電源を備える必要があり、内蔵型の電池や取り外し可能な電池等を備える構成が考えられる。実際、電源として着脱可能な電池を備え、この電池を適宜新しいものと交換することによって放射線画像検出器を繰り返し使用できるようにしたものが知られている(例えば、特許文献1参照)。
しかしながら、例えば、連続して撮影を行っている途中で電池を充電したり又は交換したりする必要が生じた場合には、電池の充電又は交換が完了し次第次の撮影に移行できるようにしておくことが撮影効率等の観点から望ましい。しかし、例えば、放射線画像検出器を構成するフォトダイオードや薄膜トランジスタ(以下「TFT」と称する。)等は、一旦電力供給を停止するとその後電力供給を再開してもすぐには安定せず、再度撮影可能な状態にまで立ち上げるのに時間が掛かるという問題がある。 However, for example, if it becomes necessary to charge or replace the battery during continuous shooting, it is possible to shift to the next shooting as soon as the battery is fully charged or replaced. It is desirable from the viewpoint of photographing efficiency and the like. However, for example, photodiodes and thin film transistors (hereinafter referred to as “TFTs”) that constitute the radiation image detector are not stabilized immediately after the power supply is stopped, and are not stabilized immediately after the power supply is restarted. There is a problem that it takes time to start up to a possible state.
他方で、常に放射線画像検出器の各部全体に電力を供給した状態を維持すると、消費電力が増大し、特に外部電源から電力を供給せずに内部の電池によって駆動する放射線画像検出器においては、短期間しか駆動させることができず、作業効率が落ちるという問題もある。 On the other hand, if the state in which power is always supplied to all parts of the radiation image detector is maintained, the power consumption increases, and particularly in the radiation image detector that is driven by an internal battery without supplying power from an external power source, There is also a problem that it can be driven only for a short period of time and the work efficiency is lowered.
さらに、放射線画像検出器を構成する部材の中には、フォトダイオードやTFTのように電力が供給されている状態では経時的に劣化していくものがある。このため、例えば、長期間撮影を行わないような場合にこうした部材に対して電力供給状態を維持していると、これらの部材の劣化により放射線画像検出器の寿命が短縮されてしまうという問題もある。 Furthermore, some members constituting the radiation image detector deteriorate with time in a state where electric power is supplied, such as a photodiode or a TFT. Therefore, for example, if the power supply state is maintained with respect to such a member when photographing is not performed for a long period of time, there is a problem that the life of the radiation image detector is shortened due to deterioration of these members. is there.
また、電池の充電や交換は撮影を行わない夜間に行うことが多く、このような場合には、放射線画像検出器の各部に供給する電力を全て停止させた休止状態や、できる限り消費電力の少ない動作状態にしておくことが好ましい。 Also, charging and replacement of the battery is often performed at night when shooting is not performed.In such a case, the power supplied to each part of the radiation image detector is stopped, or the power consumption is reduced as much as possible. It is preferable to keep the operating state low.
そこで、本発明は以上のような課題を解決するためになされたものであり、電池の充電や交換を行う必要のある放射線画像検出器を用いて撮影を行う場合において、電池の充電や交換後に放射線画像検出器を最適な動作状態とすることにより部材の劣化や消費電力の増大を抑えことのできる放射線画像検出器及び放射線画像撮影システムを提供することを目的とする。 Therefore, the present invention has been made to solve the above-described problems, and when performing imaging using a radiation image detector that needs to be charged or replaced, after charging or replacing the battery. It is an object of the present invention to provide a radiographic image detector and a radiographic image capturing system that can suppress deterioration of members and increase in power consumption by setting the radiographic image detector to an optimal operation state.
上記課題を解決するため、請求項1に記載の発明は、照射された放射線を検出して放射線画像情報を得る放射線画像検出器において、
複数の動作状態を有し、
充電又は交換可能な電池を備え複数の駆動部に電力を供給する電力供給源と、
前記動作状態を選択設定する選択設定手段と、
前記電池の充電又は交換が完了した際に、前記選択設定手段によって選択された動作状態となるように前記複数の駆動部の稼動状態を制御する制御部とを備えたことを特徴とする。
In order to solve the above-mentioned problem, the invention according to claim 1 is a radiological image detector that detects radiation and obtains radiographic image information.
Has multiple operating states,
A power supply source having a rechargeable or replaceable battery and supplying power to a plurality of driving units;
Selection setting means for selectively setting the operation state;
And a control unit that controls operating states of the plurality of driving units so as to be in an operation state selected by the selection setting unit when charging or replacement of the battery is completed.
請求項1に記載の発明によれば、電力供給源となる電池の充電又は交換が完了した際に、放射線画像検出器が選択設定手段によって設定された動作状態となるように制御部が各駆動部の稼動状態を制御するようになっている。 According to the first aspect of the present invention, when the charging or replacement of the battery serving as the power supply source is completed, the control unit drives each drive so that the radiation image detector enters the operation state set by the selection setting unit. The operation state of the unit is controlled.
請求項2に記載の発明は、請求項1に記載の放射線画像検出器において、前記動作状態は、撮影可能状態、前記撮影可能状態よりも消費電力量の少ない撮影待機状態及び前記各駆動部全てに対する電力供給を停止した撮影休止状態のいずれかであることを特徴とする。 According to a second aspect of the present invention, in the radiological image detector according to the first aspect, the operation state includes a photographing ready state, a photographing standby state in which power consumption is less than the photographing capable state, and all the driving units. It is one of the imaging | photography pause states which stopped the electric power supply with respect to.
請求項2に記載の発明によれば、放射線画像検出器の動作状態として、撮影可能状態と、撮影可能状態よりも消費電力量の少ない撮影待機状態及び各駆動部全てに対する電力供給を停止した撮影休止状態とを有している。 According to the second aspect of the present invention, as the operation state of the radiation image detector, the radiographable state, the radiographing standby state with less power consumption than the radiographable state, and radiographing in which the power supply to all the drive units is stopped And a dormant state.
請求項3に記載の発明は、請求項1又は請求項2に記載の放射線画像検出器において、前記撮影待機状態として、消費電力量の異なる複数のモードを有し、
前記制御部は、前記各モードごとに前記各駆動部の稼動状態を変化させることを特徴とする。
The invention according to
The control unit may change an operating state of each driving unit for each mode.
請求項3に記載の発明によれば、撮影待機状態として消費電力量の異なる複数のモードがあり、制御部が、各モードに応じた電力が電源部から供給されるように電力供給源による放射線画像検出器各部への電力供給を制御するようになっている。 According to the third aspect of the present invention, there are a plurality of modes with different power consumption amounts as the imaging standby state, and the control unit emits radiation from the power supply source so that power corresponding to each mode is supplied from the power supply unit. The power supply to each part of the image detector is controlled.
請求項4に記載の発明は、請求項1から請求項3のいずれか一項に記載の放射線画像検出器において、前記選択設定手段は、前記動作状態を予め設定する基本状態設定手段又は前記電池の充電又は交換完了後の動作状態を設定する事後状態設定手段であることを特徴とする。 According to a fourth aspect of the present invention, in the radiological image detector according to any one of the first to third aspects, the selection setting unit includes a basic state setting unit or the battery that presets the operation state. This is a post-condition setting means for setting an operation state after completion of charging or replacement.
請求項4に記載の発明によれば、選択設定手段として、動作状態を予め設定する基本状態設定手段及び電池の充電又は交換完了後の動作状態を設定する事後状態設定手段のうち少なくともいずれか一方であり、これらの選択設定手段によって放射線画像検出器の状態又は充電、交換完了後の状態を設定できるようになっている。 According to the invention described in claim 4, as the selection setting means, at least one of a basic state setting means for presetting the operating state and a post-condition setting means for setting the operating state after completion of charging or replacement of the battery Thus, the state of the radiation image detector or the state after completion of charging and replacement can be set by these selection setting means.
請求項5に記載の発明は、請求項1から請求項4のいずれか一項に記載の放射線画像検出器において、前記事後状態設定手段は、前記動作状態として、前記撮影可能状態、前記撮影待機状態、前記撮影休止状態のうちのいずれかを選択設定可能なものであることを特徴とする。 According to a fifth aspect of the present invention, in the radiological image detector according to any one of the first to fourth aspects, the posterior state setting means includes the photographing state, the photographing, as the operation state. Any one of a standby state and the photographing pause state can be selected and set.
請求項5に記載の発明によれば、事後状態設定手段によって、放射線画像検出器の動作状態を撮影可能状態、撮影待機状態、撮影休止状態のいずれかとなるように選択設定できるようになっている。
According to the invention described in
請求項6に記載の発明は、請求項1から請求項5のいずれか一項に記載の放射線画像検出器において、前記制御部は、前記電池の充電又は交換を行っている間、前記複数の撮影待機モードのうち最も消費電力量の少ない撮影待機モードとなるように前記各駆動部の稼動状態を変化させることを特徴とする。 According to a sixth aspect of the present invention, in the radiological image detector according to any one of the first to fifth aspects, the control unit performs the plurality of operations while charging or replacing the battery. The operating state of each of the drive units is changed so that the shooting standby mode with the least power consumption among the shooting standby modes is achieved.
請求項6に記載の発明によれば、電池の充電又は交換を行っている間は、最も消費電力量の少ない撮影待機モードとなるように制御部が各駆動部の稼動状態を変化させるようになっている。
According to the invention described in
請求項7に記載の発明は、請求項1から請求項5のいずれか一項に記載の放射線画像検出器において、前記制御部は、前記電池の充電又は交換を行っている間、前記撮影休止状態となるように前記各駆動部の稼動状態を制御することを特徴とする。 According to a seventh aspect of the present invention, in the radiological image detector according to any one of the first to fifth aspects, the control unit pauses the imaging while charging or replacing the battery. The operation state of each of the drive units is controlled so as to be in a state.
請求項7に記載の発明によれば、電池の充電又は交換を行っている間は、撮影休止状態となるように、制御部が各駆動部の稼動状態を制御するようになっている。 According to the seventh aspect of the present invention, the control unit controls the operating state of each driving unit so as to be in a shooting pause state while the battery is being charged or replaced.
請求項8に記載の発明は、請求項1から請求項7のいずれか一項に記載の放射線画像検出器において、照射された放射線を検出し、当該放射線を電気信号に変換して蓄積し、蓄積された電気信号を読み出して放射線画像情報を取得するカセッテ型のフラットパネルディテクタであることを特徴とする。 The invention according to claim 8 is the radiation image detector according to any one of claims 1 to 7, wherein the irradiated radiation is detected, the radiation is converted into an electrical signal and accumulated, It is a cassette type flat panel detector that reads out stored electrical signals and acquires radiation image information.
請求項8に記載の発明によれば、放射線画像検出器として、カセッテ型のフラットパネルディテクタ(FPD)を用いるようになっている。 According to the invention described in claim 8, a cassette-type flat panel detector (FPD) is used as the radiation image detector.
請求項9に記載の発明は、請求項1から請求項8のいずれか一項に記載の放射線画像検出器と、
前記放射線画像検出器との間で通信可能な通信手段を有するコンソールと、
前記放射線画像検出器の動作状態を選択設定する選択設定手段とを備え、
前記制御部は、前記電池の充電又は交換が完了した際に、前記選択設定手段によって選択された動作状態となるように前記電力供給源を制御することを特徴とする。
The invention according to
A console having communication means capable of communicating with the radiation image detector;
Selection setting means for selecting and setting the operating state of the radiation image detector,
The control unit controls the power supply source so as to be in an operation state selected by the selection setting unit when charging or replacement of the battery is completed.
請求項9に記載の発明によれば、複数の動作状態を有する放射線画像検出器の電池の充電又は交換が完了した際の動作状態を選択設定手段によって任意に選択設定するようになっている。 According to the ninth aspect of the invention, the operation state when the charging or replacement of the battery of the radiation image detector having a plurality of operation states is completed is arbitrarily selected and set by the selection setting means.
請求項10に記載の発明は、請求項9に記載の放射線画像撮影システムにおいて、前記選択設定手段は、前記コンソールに設置されることを特徴とする。 According to a tenth aspect of the present invention, in the radiographic imaging system according to the ninth aspect, the selection setting unit is installed in the console.
請求項10に記載の発明によれば、複数の動作状態を有する放射線画像検出器の電池の充電又は交換が完了した際の動作状態をコンソールの選択設定手段によって選択設定するようになっている。 According to the tenth aspect of the present invention, the operation state when the battery charging or replacement of the radiation image detector having a plurality of operation states is completed is selected and set by the selection setting means of the console.
請求項11に記載の発明は、請求項9又は請求項10に記載の放射線画像撮影システムにおいて、前記放射線画像検出器は、前記コンソールとの間で通信を行い、前記電池の残量状態、前記電池の充電又は交換の完了、前記放射線画像検出器の動作状態のうち少なくともいずれか一つを前記コンソールに送信可能な通信手段を備えたことを特徴とする。 According to an eleventh aspect of the present invention, in the radiographic image capturing system according to the ninth or tenth aspect, the radiographic image detector communicates with the console, the remaining battery level, It is characterized by comprising communication means capable of transmitting at least one of the completion of charging or replacement of the battery and the operating state of the radiation image detector to the console.
請求項11に記載の発明によれば、放射線画像検出器は、通信手段によってコンソールとの間で通信を行い、電池の残量状態、電池の充電又は交換の完了、放射線画像検出器の動作状態のうち少なくともいずれか一つをコンソールに送信するようになっている。 According to the eleventh aspect of the present invention, the radiological image detector communicates with the console through the communication means, the remaining battery level, the completion of charging or replacement of the battery, and the operating status of the radiographic image detector. At least one of them is sent to the console.
請求項12に記載の発明は、請求項11に記載の放射線画像撮影システムにおいて、前記コンソールは、前記通信手段から送信された前記電池の残量状態、前記電池の充電又は交換の完了、前記放射線画像検出器の動作状態のうち少なくともいずれか一つを表示可能な表示部を備えたことを特徴とする。 According to a twelfth aspect of the present invention, in the radiographic image capturing system according to the eleventh aspect, the console transmits the battery remaining state, completion of charging or replacement of the battery, and the radiation transmitted from the communication unit. A display unit capable of displaying at least one of the operation states of the image detector is provided.
請求項12に記載の発明によれば、放射線画像検出器の通信手段から送信された電池の残量状態、電池の充電又は交換の完了、放射線画像検出器の動作状態のうち少なくともいずれか一つを表示部に表示するようになっている。 According to the twelfth aspect of the present invention, at least one of the remaining battery level, the completion of charging or replacement of the battery, and the operating state of the radiographic image detector transmitted from the communication unit of the radiographic image detector. Is displayed on the display unit.
請求項1に記載の発明によれば、電池の充電又は交換が完了した際に、選択設定手段によって設定された動作状態となるようになっているので、電池の充電又は交換が完了後、放射線画像検出器を撮影頻度や充電等の行われる時間等に応じて所望の動作状態にすることができる。このため、無駄な消費電力を抑えフォトダイオードやTFT等の部材の劣化を防止しつつ効率的な撮影作業を行うことができるという効果を奏する。 According to the first aspect of the present invention, when the charging or replacement of the battery is completed, the operation state set by the selection setting unit is set. The image detector can be brought into a desired operation state in accordance with the frequency of photographing, the time during which charging is performed, and the like. For this reason, there is an effect that it is possible to perform efficient photographing work while suppressing wasteful power consumption and preventing deterioration of a member such as a photodiode or a TFT.
請求項2に記載の発明によれば、放射線画像検出器の動作状態として、撮影可能状態のほか、撮影待機状態、撮影休止状態がある。このため、電池の充電又は交換の完了後、放射線画像検出器をその使用状況等に応じて最も適した状態にしておくことができ、無駄な消費電力を抑えつつ効率的な撮影作業を行うことができるという効果を奏する。 According to the second aspect of the present invention, the operation state of the radiation image detector includes an imaging standby state and an imaging pause state in addition to the imaging enabled state. For this reason, after completing the charging or replacement of the battery, the radiological image detector can be put in the most suitable state according to the usage status, etc., and efficient photographing work can be performed while suppressing wasteful power consumption. There is an effect that can be.
請求項3に記載の発明によれば、撮影待機状態として、複数のモードを有している。このため、電池の充電又は交換の完了後、放射線画像検出器をその使用状況等に応じて最も適した状態にしておくことができ、無駄な消費電力を抑えつつ効率的な撮影作業を行うことができるという効果を奏する。
According to the invention described in
特に、フォトダイオードやTFT等は、一旦電力の供給を停止すると再度撮影に適した状態に安定化させるのに時間を要する。他方で、これらは、電力が供給された状態では経時的に劣化するという性質がある。したがって、短時間の休憩等を挟んで連続的に撮影が行われるような撮影環境である場合にはフォトダイオードやTFTに対する電力供給を停止しないことが好ましく、長期間撮影が行われないような撮影環境である場合にはこれらに対する電力供給を停止することが好ましい。また、信号読出し回路のように特に消費電力の多い部材については、なるべく電力供給を停止させて消費電力を抑えることが好ましい。したがって、このような部材ごとの性質に応じて電力の供給を切り替えることにより、より効率のよい撮影作業を行うことが可能となる。 In particular, photodiodes, TFTs, and the like take time to be stabilized again in a state suitable for photographing once power supply is stopped. On the other hand, these have the property of deteriorating over time when power is supplied. Therefore, it is preferable not to stop the power supply to the photodiode or TFT in a shooting environment where shooting is continuously performed with a short break, etc. When it is an environment, it is preferable to stop the power supply to these. Further, it is preferable to suppress power consumption by stopping power supply as much as possible for a member that consumes particularly high power, such as a signal readout circuit. Therefore, it is possible to perform more efficient photographing work by switching the supply of electric power according to the property of each member.
請求項4に記載の発明によれば、基本状態設定手段によって放射線画像検出器の電池の充電、交換後の動作状態を予め任意に設定できるので、撮影頻度等の条件に応じて最適の動作状態を設定しておき、充電等の完了後は必ずその動作状態になるようにできる。また、事後状態設定手段により充電等の完了後に放射線画像検出器の動作状態をどのような状態にするかを設定することができるので、例えば、電池の充電や交換の完了時間が昼間であるか夜間であるかといった時間的条件等に応じて任意に動作状態を設定することができる。このため、放射線画像検出器をその撮影の頻度や時間的条件等に応じて最も適した動作状態にしておくことができ、無駄な消費電力を抑えつつ効率的な撮影作業を行うことができるという効果を奏する。 According to the fourth aspect of the present invention, the operation state after charging and replacement of the battery of the radiographic image detector can be arbitrarily set in advance by the basic state setting means, so that the optimum operation state according to conditions such as imaging frequency Can be set to be in an operating state after the completion of charging or the like. In addition, it is possible to set the operation state of the radiation image detector after completion of charging or the like by the post-condition setting means, for example, whether the battery charging or replacement completion time is daytime The operation state can be arbitrarily set according to the time condition such as whether it is nighttime or the like. For this reason, the radiation image detector can be put into the most suitable operating state according to the frequency and time conditions of the imaging, and an efficient imaging operation can be performed while reducing wasteful power consumption. There is an effect.
請求項5に記載の発明によれば、電池の充電又は交換の完了後は撮影動作に移行する可能性が高いことから、撮影可能状態又は撮影待機状態のいずれかを設定できるようにすることにより、効率的な撮影作業を行うことができるという効果を奏する。また、すぐに撮影を行うのか、とりあえず消費電力の少ない状態で待機させておくのかを予め設定しておくことができるので、電池の充電又は交換の完了後、放射線画像検出器をその撮影の頻度や昼間であるか夜であるかといった時間的条件等に応じて最も適した動作状態にしておくことができ、無駄な消費電力を抑えることができる。 According to the fifth aspect of the present invention, since it is highly possible to shift to the shooting operation after the charging or replacement of the battery is completed, it is possible to set either the shooting enabled state or the shooting standby state. There is an effect that an efficient shooting operation can be performed. In addition, since it is possible to set in advance whether to perform imaging immediately or to stand by with low power consumption for the time being, after the battery has been charged or replaced, the radiological image detector is set to the frequency of the imaging. It is possible to keep the most suitable operating state according to time conditions such as whether it is daytime or nighttime, and wasteful power consumption can be suppressed.
放射線画像検出器には信号読出し回路等の電力を多く消費する部材が組み込まれている。また、フォトダイオードやTFT等電力供給状態を維持していると経時的に劣化していくという性質がある。請求項6に記載の発明によれば、電池の充電又は交換を行っている間という撮影を行うことがない期間の消費電力量を最小限に抑えることができるとともにフォトダイオードやTFTに対する電力供給を停止させるので、消費電力の低減及びフォトダイオードやTFT等の劣化防止を図ることができるという効果を奏する。 The radiation image detector incorporates a member that consumes much power, such as a signal readout circuit. In addition, when the power supply state such as a photodiode or TFT is maintained, it deteriorates with time. According to the sixth aspect of the present invention, it is possible to minimize the amount of power consumption during a period in which photographing is not performed during charging or replacement of the battery, and power supply to the photodiode and the TFT can be performed. Since the operation is stopped, it is possible to reduce power consumption and prevent deterioration of photodiodes, TFTs, and the like.
また、電力供給が完全に停止している状態では、外部機器からの信号を受信することもできず、再度撮影を開始する場合には、放射線技師等、撮影を行う操作者が放射線画像検出器の電源を手動で入れなければならないが、消費電力量を最小限に抑えたモードとした場合には、信号読出し回路等の電力を多く消費する部材や、フォトダイオードやTFT等への電力供給を行わないのであって、通信部には電力供給されている状態にある。このため、電池の充電や交換を行っている間も外部機器からの信号を受信して電池の充電や交換後、すぐに次の撮影に移行することも可能であり、作業効率が低減することがない。 In addition, when the power supply is completely stopped, a signal from an external device cannot be received, and when imaging is started again, a radiographer or other operator who performs imaging performs a radiation image detector. However, if the power consumption is set to a mode that minimizes power consumption, the power supply to the power consuming components such as signal readout circuits, photodiodes, TFTs, etc. The communication unit is in a state where power is supplied. For this reason, it is also possible to receive a signal from an external device while charging or replacing the battery, and immediately switch to the next shooting after charging or replacing the battery, reducing work efficiency. There is no.
請求項7に記載の発明によれば、電池の充電又は交換を行っている間という撮影を行うことがない期間は撮影休止状態となるようにするので、放射線画像検出器の消費電力量を抑えるとともにフォトダイオードやTFT等の劣化防止を図ることができるという効果を奏する。 According to the seventh aspect of the present invention, since the imaging is suspended during the period when the imaging is not performed, that is, while the battery is being charged or replaced, the power consumption of the radiation image detector is suppressed. In addition, there is an effect that it is possible to prevent the deterioration of the photodiode, the TFT and the like.
請求項8に記載の発明によれば、放射線画像検出器がカセッテ型FPDであるため、撮影場所を選ばず容易に持ち運ぶことが可能であり、撮影の自由度が向上する。また、このような放射線画像検出器を撮影に用いる場合でも、電池の充電又は交換の完了後、放射線画像検出器をその使用状況等に応じて撮影状態又は撮影待機状態にしておくので、無駄な消費電力を抑えつつ効率的な撮影作業を行うことができるという効果を奏する。 According to the eighth aspect of the present invention, since the radiation image detector is a cassette type FPD, it can be easily carried regardless of the photographing location, and the degree of freedom of photographing is improved. Even when such a radiographic image detector is used for imaging, it is useless because the radiographic image detector is placed in an imaging state or an imaging standby state in accordance with the usage state after the battery is charged or replaced. There is an effect that it is possible to perform efficient photographing work while suppressing power consumption.
請求項9に記載の発明によれば、電池の充電又は交換を行うことによって繰り返し使用することのできる放射線画像検出器を用いて放射線画像撮影を行う場合、電池の充電又は交換が完了した際に、どのような動作状態にするかを選択設定手段によって設定することができる。このため、放射線画像検出器の動作状態を任意に設定することができ、無駄な消費電力を抑えつつ効率的な撮影作業を行うことができるという効果を奏する。 According to the ninth aspect of the present invention, when radiographic imaging is performed using a radiographic image detector that can be repeatedly used by charging or exchanging the battery, the charging or exchanging of the battery is completed. The operation setting state can be set by the selection setting means. For this reason, it is possible to arbitrarily set the operation state of the radiation image detector, and there is an effect that it is possible to perform efficient imaging work while suppressing wasteful power consumption.
請求項10に記載の発明によれば、電池の充電又は交換を行うことによって繰り返し使用することのできる放射線画像検出器を用いて放射線画像撮影を行う場合、電池の充電又は交換が完了した際に、どのような動作状態にするかをコンソールから任意に設定することができる。このため、操作者はコンソールを操作することによって容易に無駄な消費電力を抑えつつ効率的な撮影作業を行うことができるという効果を奏する。
According to the invention described in
請求項11に記載の発明によれば、放射線画像検出器の電池の残量状態、電池の充電又は交換の完了、放射線画像検出器の動作状態がコンソールに送信されるようになっているので、放射線画像検出器の状態に関する情報をコンソールにおいて集約し把握することができる。このため、コンソールによって放射線画像検出器を一括的に管理する際等に便宜であるとの効果を奏する。
According to the invention described in
請求項12に記載の発明によれば、放射線画像検出器の電池の残量状態、電池の充電又は交換の完了、放射線画像検出器の動作状態を表示部に表示させることができるので、操作者が放射線画像検出器の状態に関する情報をコンソールにおいて容易に確認することができ、コンソールによって放射線画像検出器を一括的に管理する際等に便宜であるとの効果を奏する。 According to the twelfth aspect of the present invention, the battery remaining state of the radiation image detector, the completion of charging or replacement of the battery, and the operation state of the radiation image detector can be displayed on the display unit. However, the information regarding the state of the radiation image detector can be easily confirmed on the console, which is advantageous when the radiation image detector is collectively managed by the console.
以下、本発明の実施の形態を、図1から図6を参照して説明する。 Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS.
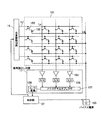
図1は、本発明に係る放射線画像検出器を適用した放射線画像撮影システムの一実施形態の概略構成を示す図である。 FIG. 1 is a diagram showing a schematic configuration of an embodiment of a radiographic imaging system to which a radiographic image detector according to the present invention is applied.
本実施形態による放射線画像撮影システム1は、例えば、病院内で行われる放射線画像撮影において適用されるシステムであり、図1に示すように、撮影や患者に関する各種の情報等を管理するサーバ2と、放射線画像撮影に関する操作を行う撮影操作装置3と、例えば無線LAN(Local Area Network)等の無線通信方式による通信を行うための基地局4と、放射線画像検出器5を操作するとともに放射線画像検出器5により検出された放射線画像の画像処理等を行うコンソール6とがネットワーク7を通じて接続されている。撮影操作装置3にはケーブル8を介して、被写体9である患者に放射線を照射して放射線画像の撮影を行う放射線画像撮影装置10が接続されている。放射線画像撮影装置10及び放射線画像検出器5は、例えば1つの撮影室11内に1つずつ設置されており、撮影操作装置3によって放射線画像撮影装置10を操作し放射線画像検出器5によって放射線画像を検出することによって放射線画像情報を得ることができるようになっている。なお、1つの撮影室11に複数の放射線画像検出器5が備えられていてもよい。
The radiographic image capturing system 1 according to the present embodiment is a system that is applied in, for example, radiographic image capturing performed in a hospital. As shown in FIG. The
ここで、ネットワーク7は、当該システム専用の通信回線であっても良いが、システム構成の自由度が低くなってしまう等の理由のため、イーサネット(Ethernet;登録商標)等の既存の回線である方が好ましい。なお、ネットワーク7には、ここに例示したものの他、他の撮影室11の放射線画像撮影装置10を操作する撮影操作装置3や放射線画像検出器5、コンソール6が複数接続されていてもよい。
Here, the
まず、撮影操作装置3は、操作パネル等から構成され放射線画像撮影装置10を操作する、例えば撮影条件等の信号を入力する入力操作部、撮影条件等の情報や各種の指示等を表示する表示部、及び放射線画像撮影装置10に対して電力を供給する電源部等(いずれも図示せず)を備えて構成されている。
First, the
放射線画像撮影装置10は、撮影室11の内部に配置され、放射線源12を有しており、この放射線源12に管電圧が印加されることによって放射線が発生するようになっている。放射線源12としては、例えば、放射線管が用いられ、放射線管は熱励起によって生ずる電子を高電圧で加速して陰極に衝突させることで、放射線を発生するようになっている。
The
次に、放射線画像検出器5は、放射線画像撮影装置10の放射線源12から照射されて被写体9を透過した放射線を検出して放射線画像を取得するものであり、撮影を行う際に放射線源12から照射される放射線の照射範囲に配置されるようになっている。なお、放射線画像検出器5は、例えば、図1に示すように、被写体9と被写体9を載置する寝台13との間に配置されるが、放射線画像検出器5を配置する位置はこれに限定されず、例えば、寝台の下方に放射線画像検出器5を装着する検出器装着口(図示しない)を設けて、放射線画像検出器5がこの検出器装着口に装着されるようにしてもよい。
Next, the
放射線画像検出器5は、フラットパネル型の放射線画像検出器5である。以下、図2及び図3を用いて、放射線画像検出器5の構造について説明する。
The
図2に示すように、放射線画像検出器5は、内部を保護する筐体14を備えており、カセッテとして携帯可能に構成されている。
As shown in FIG. 2, the
筐体14の内部には、照射された放射線を電気信号に変換する撮像パネル15が層を成して形成されている。撮像パネル15における放射線の照射面側には、入射された放射線の強度に応じて発光を行う発光層(図示せず)が設けられている。
An
発光層は、一般にシンチレータ層と呼ばれるものであり、例えば、蛍光体を主たる成分とし、入射した放射線に基づいて、波長が300nmから800nmの電磁波、すなわち、可視光線を中心に紫外光から赤外光にわたる電磁波(光)を出力するようになっている。 The light emitting layer is generally called a scintillator layer. For example, a phosphor is a main component, and based on incident radiation, an electromagnetic wave having a wavelength of 300 nm to 800 nm, that is, visible light to ultraviolet light to infrared light. It is designed to output electromagnetic waves (light).
この発光層で用いられる蛍光体は、例えば、CaWO4等を母体とするものや、CsI:TlやGd2O2S:Tb、ZnS:Ag等の母体内に発光中心物質が付活されたものを用いることができる。また、希土類元素をMとしたとき、(Gd,M,Eu)2O3の一般式で示される蛍光体を用いることができる。特に、放射線吸収及び発光効率が高いことよりCsI:TlやGd2O2S:Tbが好ましく、これらを用いることで、ノイズの低い高画質の画像を得ることができる。 The phosphor used in the light emitting layer is, for example, a material having CaWO 4 or the like as a base, or a luminescent center substance activated in a base such as CsI: Tl, Gd 2 O 2 S: Tb, or ZnS: Ag. Things can be used. Further, when the rare earth element is M, a phosphor represented by a general formula of (Gd, M, Eu) 2 O 3 can be used. In particular, CsI: Tl and Gd 2 O 2 S: Tb are preferable because of high radiation absorption and luminous efficiency, and by using these, a high-quality image with low noise can be obtained.
この発光層の放射線が照射される側の面と反対側の面には、発光層から出力された電磁波(光)を電気エネルギーに変換して蓄積し、蓄積された電気エネルギーに基づく画像信号の出力を行う信号検出部151が形成されている。
The electromagnetic wave (light) output from the light emitting layer is converted into electric energy and accumulated on the surface opposite to the surface on which the radiation of the light emitting layer is irradiated, and an image signal based on the accumulated electric energy is stored. A
ここで、撮像パネル15の回路構成について説明する。図3は、信号検出部151を構成する1画素分の光電変換部の等価回路図である。
Here, the circuit configuration of the
図3に示すように、1画素分の光電変換部の構成は、フォトダイオード152と、フォトダイオード152で蓄積された電気エネルギーをスイッチングにより電気信号として取り出す薄膜トランジスタ(以下「TFT」と称する。)153とから構成されている。取り出された電気信号は、増幅器154により信号読み出し回路17が検出可能なレベルにまで電気信号を増幅するようになっている。なお、増幅器154には、TFT153とコンデンサで構成された図示しないリセット回路が接続されており、TFT153にスイッチを入れることにより蓄積された電気信号をリセットするリセット動作が行われるようになっている。また、フォトダイオード152は、単に規制キャパシタンスを有した光ダイオードでもよいし、フォトダイオード152と光電変換部のダイナミックレンジを改良するように追加コンデンサを並列に含んでいるものでもよい。
As shown in FIG. 3, the configuration of the photoelectric conversion unit for one pixel is a
図4は、このような光電変換部を二次元に配列した等価回路図であり、画素間には、走査線Llと信号線Lrが直交するように配設されている。前述のフォトダイオード152には、TFT153が接続されており、TFT153が接続されている側のフォトダイオード152の一端は信号線Lrに接続されている。一方、フォトダイオード152の他端は、各行に配された隣接するフォトダイオード152の一端と接続されて共通のバイアス線Lbを通じてバイアス電源155に接続されている。このバイアス電源155の一端は制御部27に接続され、制御部27からの指示によりバイアス線Lbを通じてフォトダイオード152に電圧がかかるようになっている。また各行に配されたTFT153は、共通の走査線Llに接続されており、走査線Llは走査駆動回路16を介して制御部27に接続されている。同様に、各列に配されたフォトダイオード152は、共通の信号線Lrに接続されて制御部27に制御される信号読み出し回路17に接続されている。信号読み出し回路17には、撮像パネル23から近い順に、増幅器154、サンプルホールド回路156、アナログマルチプレクサ157、A/D変換機158が共通の信号線Lr上に配されている。
FIG. 4 is an equivalent circuit diagram in which such photoelectric conversion units are two-dimensionally arranged. Between the pixels, the scanning lines Ll and the signal lines Lr are arranged so as to be orthogonal to each other. A
なお、TFT153は、液晶ディスプレイ等に使用されている無機半導体系のもの、有機半導体を用いたもののいずれであってもよい。
Note that the
また、本実施形態では光電変換素子としてのフォトダイオード152を用いた場合を例示したが、光電変換素子はフォトダイオード以外の固体撮像素子を用いてもよい。
Moreover, although the case where the
この信号検出部151の側部には、図2に示すように各光電変換素子にパルスを送って当該各光電変換素子を走査・駆動させる走査駆動回路16と、各光電変換素子に蓄積された電気エネルギーを読み出す信号読出し回路17とが配されている。
As shown in FIG. 2, the side of the
また、放射線画像検出器5は、RAM(Random Access Memory)やフラッシュメモリなどの書き換え可能な読み出し専用メモリ等からなる画像記憶部18を備えており、画像記憶部18は、撮像パネル15から出力された画像信号を記憶するようになっている。画像記憶部18は内蔵型のメモリでもよいし、メモリカード等の着脱可能なメモリでもよい。
The
また、放射線画像検出器5には、放射線画像検出器5を構成する複数の駆動部(例えば、走査駆動回路16、信号読出し回路17、通信部24(後述)、画像記憶部18、充電量検出部(図示せず)、インジケータ25(後述)、入力操作部26(後述)、撮像パネル15など)に電力を供給する電力供給源として充電池21が設けられている。
Further, the
充電池21としては、例えばニカド電池、ニッケル水素電池、リチウムイオン電池、小型シール鉛電池、鉛蓄電池、燃料電池、太陽電池等の充電自在な電池を適用することができる。
As the
筐体14の一端には充電用の端子22が形成されており、例えば、図1に示すように、放射線画像検出器5を外部電源と接続されるクレードル等の充電用装置23に装着することによって充電用装置23側の端子(図示せず)と筐体側の端子22とが接続されて前記充電池21の充電が行われるようになっている。なお、電力供給源としての充電池21の形状は、図2に例示したものに限定されず、例えば、撮像パネル15と平行してプレート状の電池を設けるようにしてもよい。電池をこのような形状とすることにより、撮像パネル15の面積をより大きくすることができ、撮像可能領域を広くすることが可能となる。
A terminal 22 for charging is formed at one end of the
また、放射線画像検出器5には、コンソール6等の外部装置との間で各種信号の送受信を行う通信部24(図5参照)が設けられている。通信部24は、例えば、撮像パネル15から出力された画像信号をコンソール6に転送したり、コンソール6等から送信される撮影開始信号等を受信するようになっている。
Further, the
また、筐体14の表面一端には、充電池21の充電状況や各種の操作状況等を表示するインジケータ25が設けられており、操作者が放射線画像検出器5の充電池21の充電状況等を目視にて確認することができるようになっている。
Further, an
筐体14の外部には、放射線画像検出器5の動作状態を事前に設定する選択設定手段としての入力操作部26が設けられている。本実施形態においては、放射線画像検出器5の動作状態として、撮影可能状態、撮影待機状態、撮影休止状態という動作状態がある。
An
撮影可能状態は、放射線画像検出器5を構成する部材のうち、一連の撮影動作に用いられる各駆動部全てが稼動している状態、すなわち、走査駆動回路16、信号読出し回路17、フォトダイオード152、TFT153、画像記憶部18、通信部24といった一連の撮影動作に用いられる各駆動部全てに電力が供給されている状態であり、一連の撮影動作である画像情報の初期化、照射された放射線に応じて生成された電気エネルギーの蓄積、電気信号の読み取り、及び画像信号の転送等の各動作を行なうことが可能となっている。なお、初期化では、撮像パネル15におけるリセット動作及び空読み動作が行われるようになっている。
The imaging possible state is a state in which all the driving units used for a series of imaging operations among the members constituting the
また、本実施形態においては、撮影待機状態として、撮影可能状態よりも消費電力が少ない第1の撮影待機モードと、第1の撮影待機モードよりも消費電力の少ない第2の撮影待機モードとが選択可能となっている。 In the present embodiment, the shooting standby state includes a first shooting standby mode that consumes less power than the shooting enabled state, and a second shooting standby mode that consumes less power than the first shooting standby mode. It is selectable.
第1の撮影待機モードは、撮影可能状態への迅速な立ち上げが可能な信号読出し回路17を除いて、一連の撮影動作に用いられる各駆動部全てを立ち上げた状態であり、すぐに撮影を行うことが可能な状態にある撮影待機状態である。具体的には、走査駆動回路16、フォトダイオード152、TFT153、画像記憶部18、通信部24といった各部に対して電力が供給されている状態となる。第2の撮影待機モードは、画像保存に関わる部分である画像記憶部18や、外部への画像情報の転送、外部からの信号受信に関わる部分である通信部24のみを立ち上げた状態であり、すぐには撮影を行うことのできない消費電力の非常に低い状態にある撮影待機状態である。
The first shooting standby mode is a state in which all the drive units used for a series of shooting operations are started up except for the
さらに、撮影休止状態は、放射線画像検出器5の各駆動部に対する電力供給を全て停止した、完全な省電力状態である。
Further, the imaging suspension state is a complete power saving state in which all the power supply to each drive unit of the
まず、入力操作部26は、基本状態の選択設定手段である基本状態設定手段として、放射線画像検出器5の動作状態を撮影可能状態、各撮影待機モードのうちどの状態とするかを設定することができるようになっている。ここで基本状態とは、何らかの設定変更がなされない限り選択される動作状態である。例えば、撮影を行う頻度が低い状況で放射線画像検出器5が使用される場合には、基本状態として第2の撮影待機モードを選択設定しておくことによりフォトダイオード152やTFT153のように電力の供給により経時的に劣化していく部材を保護したり、省電力化を図ったりすることができる。これに対して、頻繁に撮影が行われるような状況で放射線画像検出器5が使用される場合には、撮影可能状態又は第1の撮影待機モードを選択設定しておくことにより立ち上げに時間のかかるフォトダイオードやTFTに電力が供給された状態となり、迅速で効率のよい撮影を行うことが可能となる。なお、本実施形態において、放射線画像検出器5は充電池21によって各駆動部に対する電力供給を行うものであるため、消費電力量を抑えつつも迅速で効率のよい撮影動作を実現するべく、基本状態としては第1の撮影待機モードが選択設定されることが好ましい。なお、撮影予定がしばらくないような場合には基本状態として撮影休止状態を選択できるようにしてもよい。
First, the
また、入力操作部26は、事後状態の選択設定手段である事後状態設定手段として、充電池21の充電後に放射線画像検出器5の動作状態を撮影可能状態とするか、いずれかの撮影待機モードとするか、又は撮影休止状態とするかを選択設定することができるようになっている。事後状態とは、充電池21の充電後の状態をいい、事後状態を任意に設定できることにより、充電池21の充電後にすぐに撮影を行う予定があるか等の状況や充電の行われる時間帯等に応じて最適な動作状態にしておくことが可能となる。
In addition, the
なお、入力操作部26から入力することのできる内容は動作状態の選択設定に限定されず、その他、放射線技師等の操作者が撮影条件や患者の識別情報等を入力設定することができるようにしてもよい。
The content that can be input from the
また、図5に示すように、放射線画像検出器5は、例えば、汎用のCPU、ROM、RAM等(いずれも図示せず)から構成された制御部27を有する制御装置28を備えており、制御部27は、ROMに格納される所定のプログラムを読み出してRAMの作業領域に展開し、当該プログラムに従ってCPUが各種処理を実行するようになっている。
As shown in FIG. 5, the
放射線画像検出器5は図示しない充電量検知手段を備えており、制御部27には、充電量検知手段によって検知された充電池21の充電状況が電気信号として送られるようになっており、制御部27は、送られた信号に基づいて充電池21の充電量等をインジケータ25に表示させるようになっている。
The
また、制御部27は、充電量検知手段による検知結果に基づいて、充電池21の充電量が低下して所定のレベル以下となり充電が必要と判断するときは、通信部24を介してその旨の信号をコンソール6に送信させるようになっている。さらに、充電量検知手段による検知結果に基づいて充電池21について充電が完了したと判断するときは、制御部27は、通信部24を介してその旨の信号をコンソール6に送信するようになっている。なお、充電池21の充電量は、随時通信部24を介してコンソール6に送信されるようにしてもよい。
Further, when the
また、放射線画像検出器5がいかなる動作状態にあるかは、制御部27により前記通信部24を介してコンソール6に随時送信されるようになっている。
In addition, the operating state of the
また、制御部27には、入力操作部26から入力された情報や通信部24から受信された信号が送られるようになっており、制御部27は、送られた信号に基づいて各部の制御を行うようになっている。
In addition, information input from the
特に、本実施形態においては、前記入力操作部26から撮影可能状態、第1の撮影待機モード、第2の撮影待機モード及び撮影休止状態を選択設定する指示が入力されると入力信号が制御部27に送られるようになっており、制御部27は放射線画像検出器5の基本状態や充電完了後の事後状態がこの入力信号に従った動作状態となるように充電池21からの電力供給を制御して放射線画像検出器5の各駆動部に適宜電力を供給するようになっている。
In particular, in the present embodiment, when an instruction to select and set the shooting enabled state, the first shooting standby mode, the second shooting standby mode, and the shooting pause state is input from the
なお、本実施形態において、制御部27は、充電池21の充電中、放射線画像検出器5が最も消費電力の少ない動作状態である第2の撮影待機モードとなるように、画像記憶部18及び通信部24のみに充電池21から電力を供給し各駆動部の稼動状態を制御するようになっている。
In the present embodiment, the
なお、例えば、入力操作部26からの選択設定によって、放射線画像検出器5の基本状態が第2の撮影待機モードに設定されているときに、さらに事後状態として撮影可能状態が選択されたり、通信部24がコンソール6等の外部装置から撮影開始を指示する撮影開始信号を受信したりしたときは、第2の撮影待機モードから第1の撮影待機モードに、さらには撮影可能状態に段階的に切り替わるように、制御部27が充電池21からの電力供給を制御して各駆動部に必要な電力を供給させるようにしてもよい。なお、この場合、段階的に切り替わるのではなく、第2の撮影待機モードから直接撮影可能状態になるように一連の撮影動作に用いられる各駆動部全てに電力が供給されるようにしてもよい。また、入力操作部26から基本状態として第1の撮影待機モードが設定されているときに、事後状態として撮影可能状態が選択されたり、撮影開始信号を受信したときは、第1の撮影待機モードから撮影可能状態に切り替わるように順次各駆動部に電力が供給されるように制御部27が充電池21からの電力供給を制御するようにしてもよい。
For example, when the basic state of the
また、制御部27は、走査駆動回路16を駆動させて各光電変換素子にパルスを送り当該各光電変換素子を走査・駆動させるようになっている。そして、各光電変換素子に蓄積された電気エネルギーを読み出す信号読出し回路17によって読み出され、読み出された画像信号は制御部27に送られるようになっている。制御部27は送られた画像信号を画像記憶部18に記憶させるようになっている。また、画像記憶部18に記憶された画像信号は通信部24を介して適宜コンソール6に送られるようになっている。
The
次に、コンソール6は、図4に示すように、例えば、汎用のCPU、ROM、RAM等(いずれも図示せず)から構成された制御部29を有する制御装置30を備えており、制御部29は、ROMに格納される所定のプログラムを読み出してRAMの作業領域に展開し、当該プログラムに従ってCPUが各種処理を実行するようになっている。
Next, as shown in FIG. 4, the
また、コンソール6は、各種の指示等を入力する入力操作部31、画像や各種のメッセージ等を表示する表示部32、放射線画像検出器5等の外部装置との間で信号の送受信を行う通信部33等を備えている。
Further, the
入力操作部31は、例えば、操作パネルやキーボードやマウス等から構成されており、操作パネル又はキーボードで押下操作されたキーの押下信号やマウスによる操作信号を入力信号として制御部29に対して出力するようになっている。
The
表示部32は、例えば、CRT(Cathode Ray Tube)やLCD(Liquid Crystal Display)等を備えて構成されており、制御部29から出力される表示信号の指示に従って、サムネイル画像等の放射線画像や入力操作部31から入力された各種の情報等の各種情報を表示するようになっている。また、本実施形態において、表示部32には、放射線画像検出器5から送られた放射線画像情報の他、放射線画像検出器5の充電池21の充電量や、充電池21の充電が完了したか否か、放射線画像検出器5の動作状態等、放射線画像検出器5の通信部24を介して送られてくる各種の情報が表示されるようになっている。なお、表示部32に表示される内容はここに例示したものに限定されず、さらに多くの情報が表示されるようにしてもよい。また、ここに例示したすべてが表示されるものでなくてもよく、これらのうち少なくともいずれか一以上が表示されるようにしてもよい。
The
通信部33は、無線LAN等の無線通信方式により、基地局4を介して、放射線画像検出器5との間で各種情報の通信を行うものである。
The communication unit 33 communicates various information with the
制御部29には、入力操作部31から入力された信号や通信部33を介して外部から受信した信号等が送られるようになっている。さらに制御部29は、例えば、放射線画像検出器5により検出された放射線画像情報に基づいて所定の画像処理を行うことによりサムネイル画像や医師等が所望する放射線画像を得るようになっている。
A signal input from the
次に、本実施形態に係る放射線画像検出器5を適用した放射線画像撮影システム1の作用について説明する。
Next, the operation of the radiation image capturing system 1 to which the
まず、放射線画像検出器5は、入力操作部26からの入力によりその基本状態が撮影可能状態なのか、撮影待機状態なのか、撮影休止状態なのかが選択設定される。
First, the
放射線画像検出器5の充電池21の充電量が撮影等を行うのに必要な所定量以下であることを充電量検知手段が検知してその旨の信号が制御部27に送られると、制御部27はその旨をインジケータ25に表示させるとともに、コンソール6に送信する。コンソール6は制御部27からの信号を受信すると、充電池21の充電が必要である旨を表示部32に表示させる等して操作者に警告する。なお、コンソール6には充電池21の充電量が信号として随時送られ、送られた信号に基づいて充電池21の充電量が表示部32に随時表示されるようにしてもよい。
When the charge amount detection means detects that the charge amount of the
インジケータ25の表示又はコンソール6による警告を受けて、操作者が充電池21の充電を行う場合には、放射線画像検出器5を充電用装置23に載置すると、充電用装置23の端子と放射線画像検出器5の端子22とが電気的に接続されて充電池21の充電が開始される。充電中は、制御部27は、放射線画像検出器5が撮影休止状態となるように各駆動部の稼動状態を制御する。
When the operator charges the
充電池21の充電が完了すると制御部27は、その旨をコンソール6に送信する。また、制御部27は設定されている事後状態になるように充電池21から各部に必要な電力を供給させ、各駆動部の稼動状態を制御する。すなわち、充電完了後の事後状態が撮影可能状態となるように入力操作部26から入力設定されている場合には、制御部27は一連の撮影動作に用いられる各駆動部全てに対して充電池21から電力を供給する。また、第1の撮影待機モードが設定されているときは、制御部27は走査駆動回路16、フォトダイオード152、TFT153、画像記憶部18、通信部24といった各部に対して充電池21から電力を供給する。さらに、第2の撮影待機モードが設定されているときは、制御部27は充電池21から画像記憶部18及び通信部24に電力が供給されるようにする。また、撮影休止状態が選択されているときは、制御部27は充電池21から各駆動部に電力を供給しないようにする。
When the charging of the
放射線画像検出器5の動作状態が予め基本状態として設定されている所定の動作状態又は事後状態として設定された動作状態となると、制御部27は、その旨を通信部24を介してコンソール6に送信する。
When the operation state of the
コンソール6には、放射線画像検出器5によって得られた放射線画像情報、充電池21の充電が完了したか否か、放射線画像検出器5の動作状態の他、放射線画像検出器5の充電池21の充電量等、各種の情報が放射線画像検出器5の制御部27から通信部24を介して随時送られており、表示部32にはこれらの情報が適宜表示される。
The
放射線画像検出器5は、撮影可能状態となると、新たな撮影に備えて蓄積されている画像情報のリセット、空読み等の初期化作業を行う。そして、撮影が開始され放射線源12から放射線が照射されると、走査駆動回路16により各光電変換素子にパルスを送って当該各光電変換素子を走査・駆動させるとともに、各光電変換素子に蓄積された電気エネルギーを信号読出し回路17によって読み出すことにより画像信号を取得する。取得した画像信号は画像記憶部18に記憶され、その後、適宜コンソール6等に転送される。
When the
以上より、本実施形態によれば、放射線画像検出器が撮影可能状態、撮影待機状態、撮影休止状態となるように各部に電力が供給されるため、すぐに撮影を行わないときにはフォトダイオード152、TFT153に電力を供給しないようにすることにより、フォトダイオード152、TFT153の劣化を防止し放射線画像検出器5の長寿命化を図ることもできる。また、撮影待機状態、撮影休止状態では消費電力の多い信号読出し回路17等に電力を供給しないので消費電力の低減を図り、1回の充電で多数回の撮影が可能となる。
As described above, according to the present embodiment, since power is supplied to each unit so that the radiation image detector is in the imaging ready state, the imaging standby state, and the imaging pause state, when the imaging is not performed immediately, the
さらに、撮影待機状態として2つの撮影待機モードを有し、第1の撮影待機モードでは、一旦電力供給を停止すると再度立ち上げるまでに時間の掛かるフォトダイオード152やTFT153等には電力を供給したままとし、消費電力の多い信号読出し回路17についてだけ電力供給を停止させるようになっている。このため、電池の充電又は交換の完了後、第1の撮影待機モードとすれば、消費電力を抑えつつすぐに撮影状態に移行することができる。他方、第2の撮影待機モードでは、外部からの信号を受信するための通信部24等最低限のものに対してのみ電力が供給されるようになっており、電力が供給された状態では経時的に劣化するフォトダイオード152やTFT153等に対する電力供給を停止させるようになっている。このため、第2の撮影待機モードとすれば、消費電力を最低限に抑えフォトダイオード152やTFT153の劣化を防止しつつ再度撮影を再開するときには外部から信号を送信することにより容易に撮影可能状態に移行させることができるため、効率的な撮影作業を行うことができる。
Furthermore, there are two shooting standby modes as shooting standby states. In the first shooting standby mode, power is supplied to the
なお、本実施形態においては、撮影待機状態として2種類の撮影待機モードを選択できるようにしたが、撮影待機モードはここに例示した2種類に限定されず、例えば、電力供給状態では経時的に劣化する性質をもつフォトダイオード152及びTFT153についてのみ電力供給を停止させる撮影待機モード、画像記憶部18及び通信部24以外に対しては全て電力供給を停止するが一旦電力供給を停止した後再度立ち上げるまでに時間のかかるフォトダイオード152及びTFT153についてのみ他の部材よりも早く電力の供給を開始させる撮影待機モード等、さらに複数の種類のモードを選択できるようにしてもよい。また、本実施形態に例示した2つの撮影待機モードのうちいずれか1つのみを有するようにしてもよい。
In the present embodiment, two types of shooting standby modes can be selected as the shooting standby state. However, the shooting standby mode is not limited to the two types illustrated here. The imaging standby mode in which the power supply is stopped only for the
また、本実施形態においては、撮影可能状態、各種の撮影待機状態及び撮影休止状態を選択する選択設定手段として入力操作部26により切り替え設定を行うように構成したが、選択設定手段を入力操作部26とは別個に設けるようにしてもよい。
Further, in the present embodiment, the
また、選択設定手段は、放射線画像検出器5に設けられている場合に限定されず、例えば、コンソール6の入力操作部31が選択設定手段として機能するように構成してもよい。すなわち、入力操作部31が基本状態設定手段として放射線画像検出器5の基本状態を設定し、又は事後状態設定手段として充電後の動作状態を設定するようにしてもよい。また、充電用装置23等に選択設定手段が設けられ、充電完了後の事後状態を設定する事後状態設定手段として機能してもよい。
Further, the selection setting unit is not limited to the case where it is provided in the
なお、本実施形態においては、放射線画像検出器5の筐体14の外部に放射線技師等の操作者が撮影条件や患者の識別情報や各種の指示等を入力設定する入力操作部26を設けるようにしたが、前記のように選択設定手段を撮影条件等を入力する手段とは別個に設ける場合や、コンソール6の入力操作部31等、放射線画像検出器5の入力操作部26以外が選択設定手段として機能する場合には、放射線画像検出器5は入力操作部26を備えない構成としてもよい。
In the present embodiment, an
また、本実施形態においては、選択設定手段として基本状態を選択設定する基本状態設定手段と事後状態を選択設定する事後状態設定手段との両方を備えるものとしたが、選択設定手段は、このうち基本状態設定手段又は事後状態設定手段のいずれかのみを備えるものとしてもよい。 Further, in the present embodiment, both the basic state setting means for selecting and setting the basic state and the posterior state setting means for selecting and setting the posterior state are provided as the selection setting means. Only either the basic state setting means or the posterior state setting means may be provided.
さらに、選択設定手段は、充電池21の充電又は交換が行われるのが1日のうちのどの時間帯であるかにより自動的に充電又は交換完了後の放射線画像検出器5の動作状態を切り替えるようにしてもよい。すなわち、例えば、充電又は交換が行われるのが昼間であれば充電又は交換完了後にすぐに次の撮影が行われる可能性が高いのに対して、夜間であればしばらく撮影が行われない可能性が高い。そこで、例えば、午前6時から午後6時までの間に充電池21の充電又は交換が行われる場合には、充電又は交換完了後に撮影可能状態又は第1の撮影待機モードとなり、午後6時から午前6時までの間に充電池21の充電又は交換が行われる場合には、充電又は交換完了後に第2の撮影待機モード又は撮影休止状態となるように予め設定できるようにしてもよい。
Further, the selection setting means automatically switches the operating state of the
また、本実施形態においては、電力供給源として充電池21を備えるものとしたが、電力供給源の構成はここに例示したものに限定されない。例えば、充電池21の替わりに、マンガン電池、アルカリ電池、アルカリボタン電池、リチウム電池、酸化銀電池、空気亜鉛電池、ニッケル・カドミウム電池、水銀電池、鉛電池等からなる交換可能な使い捨ての電池を備えるようにしてもよい。
Further, in the present embodiment, the
また、充電池21は、例えば、筐体14の側部から引き出すことにより交換可能であるように構成してもよい。
Moreover, you may comprise the
なお、電力供給源として前記のように交換可能な電池又は交換可能な充電池21を用いた場合には、例えば、操作者が交換のために電池又は充電池21を放射線画像検出器5から取り出している間は放射線画像検出器5の電源がOFFとなり、電池交換が完了して放射線画像検出器5に電池又は充電池21が装着されたことが検知されると事後状態として設定されている動作状態に移行する。なお、この場合、選択設定手段により事後状態として撮影休止状態が選択されているときには、電池又は充電池21の交換が完了して放射線画像検出器5に電池又は充電池21が装着された後も各駆動部に対する電力供給が完全に停止した撮影休止状態が維持される。
When the replaceable battery or the replaceable
この場合、電池が取り出されたかどうかは、例えば、電池の接触部分や電池を収納する収納部分の蓋部等に設けられたセンサや機械的なスイッチ等によって検知され、信号が制御部27に送られることにより判断されるようになっていてもよい。また、筐体14に電源のON/OFFを切り替えるスイッチを設け、これを操作することにより電源がOFFとなるようになっていてもよい。また、コンソール6等からの信号によって電源のON/OFFが切り替えられるようになっていてもよい。なお、このように電池交換中は放射線画像検出器5の電源がOFFとなる場合には、電池交換の完了とともに事後状態として設定されている動作状態に移行する。なお、事後状態が特に設定されていない場合には基本状態として予め設定されている動作状態に移行するようにしてもよい。
In this case, whether or not the battery has been removed is detected by, for example, a sensor or a mechanical switch provided on a contact portion of the battery or a lid portion of the storage portion for storing the battery, and a signal is sent to the
さらに、このような交換可能な電池又は交換可能な充電池21を用いた場合には、これらの電池の他に予備電源を備えるようにしてもよい。予備電源を備える場合には、例えば、電池交換中は最も消費電力の少ない動作状態である第2の撮影待機モードとなり、電池交換完了後には事後状態として設定されている動作状態に移行する。なお、この場合にも、事後状態が特に設定されていない場合には基本状態として予め設定されている動作状態に移行するようにしてもよい。このように交換可能な電池又は交換可能な充電池21の他に予備電源を備えることにより、電池又は充電池21を取り替えている間等も放射線画像検出器5に少なくとも最低限の電力を供給することが可能であり、画像記憶部18に記憶されている画像情報が誤って消えてしまったり、コンソール6等の外部装置からの信号を受信できない状態となることがない。
Furthermore, when such a replaceable battery or a replaceable
また、本実施形態においては、充電池21の充電中は、画像記憶部18及び通信部24のみに充電池21から電力が供給される第2の撮影待機モードとなるようにしたが、充電池21の充電中における放射線画像検出器5の動作状態はこれに限定されない。充電池21の充電中は、消費電力が少ない動作状態にある方が好ましく、特に最低限電力供給を維持しておくべき駆動部にのみ電力が供給されている最も消費電力の少ない動作状態であることが好ましい。
ただ、例えば、使用状況等によっては、充電中に第1の撮影待機モードや撮影可能状態となるようにしてもよい。
また、例えば、使用状況等により、充電前の動作状態を維持しておく方が望ましいような場合には、充電中も充電前の動作状態を維持するものとしてもよい。また、充電中は事後状態として設定されている動作状態になるようにしてもよい。すなわち、充電が開始されると放射線画像検出器5の動作状態が事後状態として設定されている動作状態に切り替わり、この動作状態のまま充電が行われるようにしてもよい。
さらに、事後状態として撮影休止状態が選択されているときは、充電中撮影休止状態となるようにしてもよい。
In the present embodiment, while the
However, for example, depending on the use situation or the like, the first shooting standby mode or the shooting ready state may be set during charging.
Further, for example, when it is desirable to maintain the operation state before charging depending on the use situation or the like, the operation state before charging may be maintained even during charging. Moreover, you may make it be in the operation state set as a post-condition during charge. That is, when charging is started, the operation state of the
Further, when the shooting pause state is selected as the posterior state, the charging pause state during charging may be set.
なお、放射線画像検出器5をクレードル等の充電用装置23に載置することによって充電を行う場合には、前記のようにこの充電用装置23によって充電中の放射線画像検出器5の動作状態を選択設定できるようにしてもよい。また、コンソール6等から充電中の放射線画像検出器5の動作状態を設定できるようにしてもよい。
When charging is performed by placing the
なお、前記のように電力供給源として交換可能な電池又は交換可能な充電池を備える場合であって電池交換中に予備電源から電力供給を受けることが可能な場合にも、電池交換中の放射線画像検出器5の動作状態が第2の撮影待機モードに限定されないことは同様である。
It should be noted that even when a replaceable battery or a replaceable rechargeable battery is provided as a power supply source as described above and power can be supplied from a standby power source during battery replacement, radiation during battery replacement can also be obtained. It is the same that the operation state of the
また、充電池21の充電を行うためにクレードル等の充電用装置を用いるものとしたが、放射線画像検出器の端子にコードを接続することにより外部電源から電力の供給を受けて充電されるようにしてもよい。また、充電池を放射線画像検出器から取り出した状態で充電を行う構成としてもよい。
In addition, although a charging device such as a cradle is used to charge the
また、本実施形態においては、充電中及び充電後に充電池21から各駆動部に対して電力を供給するとしたが、充電中又は充電後において放射線画像検出器5が図示しない外部電源と接続されるクレードル等の充電用装置23に載置されている場合や、前記のように充電用の端子22にコード等を介して外部電源と接続されている場合には、これらの外部電源から各駆動部に対して電力が供給されるようにしてもよい。
In the present embodiment, power is supplied from the
また、本実施形態においては、放射線画像撮影装置10を撮影操作装置3によって操作するものとしたが、放射線画像撮影装置10をコンソール6等によって操作するように構成してもよい。この場合には、撮影操作装置3を設ける必要がなく、システム構成を簡易化することができる。
In the present embodiment, the radiographic
また、本実施形態においては、制御部27が、充電池21からの電力供給の他、走査駆動回路16、信号読出し回路17、通信部24等、放射線画像検出器5各部全てを制御するものとしたが、充電池21からの電力供給、走査駆動回路16、信号読出し回路17、通信部24等、放射線画像検出器5の各部をそれぞれ別個の制御部が制御するようにしてもよい。
In the present embodiment, the
1 放射線画像撮影システム
2 サーバ
3 撮影操作装置
4 基地局
5 放射線画像検出器
6 コンソール
7 ネットワーク
10 放射線画像撮影装置
16 走査駆動回路
17 信号読出し回路
18 画像記憶部
21 充電池
23 充電用装置
24 通信部
26 入力操作部
27 制御部
DESCRIPTION OF SYMBOLS 1
Claims (12)
複数の動作状態を有し、
充電又は交換可能な電池を備え複数の駆動部に電力を供給する電力供給源と、
前記動作状態を選択設定する選択設定手段と、
前記電池の充電又は交換が完了した際に、前記選択設定手段によって選択された動作状態となるように前記複数の駆動部の稼動状態を制御する制御部とを備えたことを特徴とする放射線画像検出器。 In a radiation image detector that detects radiation and obtains radiation image information,
Has multiple operating states,
A power supply source having a rechargeable or replaceable battery and supplying power to a plurality of driving units;
Selection setting means for selectively setting the operation state;
A radiographic image comprising: a control unit that controls operating states of the plurality of driving units so as to be in an operating state selected by the selection setting unit when charging or replacement of the battery is completed. Detector.
前記制御部は、前記各モードごとに前記各駆動部の稼動状態を変化させることを特徴とする請求項1又は請求項2に記載の放射線画像検出器。 As the shooting standby state, it has a plurality of modes with different power consumption,
The radiographic image detector according to claim 1, wherein the control unit changes an operating state of each driving unit for each mode.
前記放射線画像検出器との間で通信可能な通信手段を有するコンソールと、
前記放射線画像検出器の動作状態を選択設定する選択設定手段とを備え、
前記制御部は、前記電池の充電又は交換が完了した際に、前記選択設定手段によって選択された動作状態となるように前記電力供給源を制御することを特徴とする放射線画像撮影システム。 The radiation image detector according to any one of claims 1 to 8,
A console having communication means capable of communicating with the radiation image detector;
Selection setting means for selecting and setting the operating state of the radiation image detector,
The radiographic imaging system characterized in that the control unit controls the power supply source so as to be in an operation state selected by the selection setting unit when charging or replacement of the battery is completed.
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005023659A JP2007333384A (en) | 2005-01-31 | 2005-01-31 | Radiographic image detector and radiographic image photographing system |
| PCT/JP2005/014838 WO2006030593A1 (en) | 2004-09-16 | 2005-08-12 | Radiation image detector and radiation image photographic system |
| US11/225,803 US7365337B2 (en) | 2004-09-16 | 2005-09-13 | Radiographic image detection device and radiographic imaging system |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005023659A JP2007333384A (en) | 2005-01-31 | 2005-01-31 | Radiographic image detector and radiographic image photographing system |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2007333384A true JP2007333384A (en) | 2007-12-27 |
Family
ID=38933010
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005023659A Pending JP2007333384A (en) | 2004-09-16 | 2005-01-31 | Radiographic image detector and radiographic image photographing system |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2007333384A (en) |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009180537A (en) * | 2008-01-29 | 2009-08-13 | Fujifilm Corp | Cradle for use with radiation conversion device |
| JP2009181001A (en) * | 2008-01-31 | 2009-08-13 | Fujifilm Corp | Radiation transducer |
| WO2015083312A1 (en) * | 2013-12-02 | 2015-06-11 | キヤノン株式会社 | Radiation imaging device, radiation imaging system, radiation imaging device control method, control device, control device operation method and program |
| JP2015112358A (en) * | 2013-12-13 | 2015-06-22 | コニカミノルタ株式会社 | Portable radiographic imaging apparatus and radiographic imaging system |
| WO2018190556A1 (en) * | 2017-04-10 | 2018-10-18 | 주식회사 디알텍 | Radiation detector and power management method for radiation detector |
-
2005
- 2005-01-31 JP JP2005023659A patent/JP2007333384A/en active Pending
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009180537A (en) * | 2008-01-29 | 2009-08-13 | Fujifilm Corp | Cradle for use with radiation conversion device |
| JP2009181001A (en) * | 2008-01-31 | 2009-08-13 | Fujifilm Corp | Radiation transducer |
| WO2015083312A1 (en) * | 2013-12-02 | 2015-06-11 | キヤノン株式会社 | Radiation imaging device, radiation imaging system, radiation imaging device control method, control device, control device operation method and program |
| JP2015112358A (en) * | 2013-12-13 | 2015-06-22 | コニカミノルタ株式会社 | Portable radiographic imaging apparatus and radiographic imaging system |
| WO2018190556A1 (en) * | 2017-04-10 | 2018-10-18 | 주식회사 디알텍 | Radiation detector and power management method for radiation detector |
| KR101914256B1 (en) * | 2017-04-10 | 2018-11-01 | 주식회사 디알텍 | Radiation detector and power managing method for the same |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4581713B2 (en) | Radiation imaging system | |
| US7365337B2 (en) | Radiographic image detection device and radiographic imaging system | |
| JPWO2006080377A1 (en) | Radiation image detector and radiation image capturing system | |
| CN101137327B (en) | Radiographic imaging system | |
| US8193509B2 (en) | Radiation image detector | |
| JP4715844B2 (en) | Radiation imaging system | |
| JP2006247137A (en) | Radiation image radiography system | |
| JP2008134057A (en) | Radiation image detector and radiation image photographing system | |
| JP5239623B2 (en) | Radiation image generation system and radiation image detector | |
| US20080107234A1 (en) | Radiation image radiographing system and radiation image detecting apparatus | |
| JP2006208308A (en) | Radiograph detector and radiation image photographing system | |
| JP2008145101A (en) | Cassette type radiographic image detector, and radiographic image detection system | |
| JP2010212741A (en) | Radio ray image detection device | |
| JP2006250728A (en) | Radiation image detector and radiation image photographing system | |
| JP2011101693A (en) | Radiation image forming apparatus | |
| JP4552672B2 (en) | Radiation image detector and radiation image capturing system | |
| JP2006247138A (en) | Radiation image photographing system | |
| JP2006208303A (en) | Radiographical image detector and radiographical image photographing system | |
| JP2007333384A (en) | Radiographic image detector and radiographic image photographing system | |
| JP2006208298A (en) | Radiographic image photographing system, and radiographic image detector | |
| JP2006208306A (en) | Radiographic image detector and radiographic image photographing system | |
| JP2006208319A (en) | Radiograph detector and radiation image photographing system | |
| JP4682650B2 (en) | Radiation image detector and radiation image capturing system | |
| JP2007333383A (en) | Radiographic image detector and radiographic image photographing system | |
| JP2011130878A (en) | Radiation image detector |