JP2007206464A - Spontaneous display device, estimation degradation information correction device, input display data compensation device, and program - Google Patents
Spontaneous display device, estimation degradation information correction device, input display data compensation device, and program Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2007206464A JP2007206464A JP2006026419A JP2006026419A JP2007206464A JP 2007206464 A JP2007206464 A JP 2007206464A JP 2006026419 A JP2006026419 A JP 2006026419A JP 2006026419 A JP2006026419 A JP 2006026419A JP 2007206464 A JP2007206464 A JP 2007206464A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- correction
- value
- pixels
- pixel
- sample
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 238000012937 correction Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 170
- 230000015556 catabolic process Effects 0.000 title claims abstract description 21
- 238000006731 degradation reaction Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 21
- 230000002269 spontaneous effect Effects 0.000 title 1
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 57
- 230000006866 deterioration Effects 0.000 claims description 201
- 230000001186 cumulative effect Effects 0.000 claims description 60
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 32
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 claims description 25
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 claims description 17
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 claims description 15
- 238000004364 calculation method Methods 0.000 claims description 11
- 238000004590 computer program Methods 0.000 claims 4
- 230000002688 persistence Effects 0.000 abstract 2
- 230000002035 prolonged effect Effects 0.000 abstract 1
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 description 12
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 10
- 238000009825 accumulation Methods 0.000 description 8
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 8
- 239000003086 colorant Substances 0.000 description 6
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 4
- 239000004973 liquid crystal related substance Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000007796 conventional method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000003111 delayed effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000002123 temporal effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229910021417 amorphous silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000295 complement effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002542 deteriorative effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007613 environmental effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000002474 experimental method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000020169 heat generation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003384 imaging method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000010365 information processing Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011159 matrix material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003672 processing method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000004043 responsiveness Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Electroluminescent Light Sources (AREA)
- Control Of Indicators Other Than Cathode Ray Tubes (AREA)
- Control Of El Displays (AREA)
Abstract
Description
この明細書で説明する発明は、入力表示データに基づいて算出された累積劣化情報の見積もり値を、累積劣化情報の実測値に基づいて修正する技術に関する。
なお、発明者らが提案する発明は、自発光表示装置、見積もり劣化情報修正装置、入力表示データ補正装置及びプログラムとしての側面を有する。
The invention described in this specification relates to a technique for correcting an estimated value of cumulative deterioration information calculated based on input display data based on an actual measurement value of cumulative deterioration information.
The invention proposed by the inventors has aspects such as a self-luminous display device, an estimated deterioration information correction device, an input display data correction device, and a program.
フラットパネルディスプレイは、コンピュータディスプレイ、携帯端末、テレビジョン受像機その他の電子機器に広く用いられている。現在のところ、フラットパネルディスプレイには、主に液晶ディスプレイパネルが用いられている。しかし、液晶ディスプレイパネルは、依然として、視野角の狭さや応答速度の遅さが指摘されている。 Flat panel displays are widely used in computer displays, portable terminals, television receivers and other electronic devices. At present, liquid crystal display panels are mainly used for flat panel displays. However, it has been pointed out that the liquid crystal display panel still has a narrow viewing angle and a slow response speed.
このため、液晶ディスプレイパネルに代わるフラットパネルディスプレイの登場が期待されている。
その最有力候補が、有機EL素子をマトリクス状に配列した有機ELディスプレイパネルである。有機ELディスプレイパネルは、視野角や応答性が良好であるだけでなく、バックライトが不要、高輝度、高コントラストといった優れた特性を備えている。
For this reason, the appearance of a flat panel display replacing the liquid crystal display panel is expected.
The most promising candidate is an organic EL display panel in which organic EL elements are arranged in a matrix. The organic EL display panel not only has a good viewing angle and responsiveness, but also has excellent characteristics such as no backlight, high brightness, and high contrast.
ところで、有機ELディスプレイパネルを構成する自発光素子は、その発光量と時間に比例して劣化する特性があることが一般的にも知られている。
一方で、フラットパネルディスプレイに表示される画像の内容は一様ではない。このため、発光体(有機EL素子)の劣化が部分的に進行しやすい。例えば、時刻表示領域に位置する発光体は、他の表示領域の発光体に比べて劣化の進行が速い。
By the way, it is generally known that the self-luminous elements constituting the organic EL display panel have a characteristic of deteriorating in proportion to the light emission amount and time.
On the other hand, the content of the image displayed on the flat panel display is not uniform. For this reason, deterioration of the light emitter (organic EL element) is likely to partially proceed. For example, the light emitter located in the time display area is more rapidly deteriorated than the light emitters in the other display areas.
劣化の進行した発光体の輝度は、他の表示領域の輝度に比して相対的に低下する。一般に、この現象は「焼きつき」と呼ばれる。以下、部分的な発光体の劣化を「焼きつき」と表記する。
「焼きつき」の改善策には、従来から様々な手法が提案されている。焼きつきを精度良く、性能良く補正するには、発光体の実際の劣化状態を正しく検出する必要がある。
The luminance of the light-emitting body that has deteriorated is relatively lowered as compared with the luminance of other display areas. In general, this phenomenon is called “burn-in”. Hereinafter, partial deterioration of the light emitter is referred to as “burn-in”.
Various methods have been proposed for improving “burn-in”. In order to correct burn-in with high accuracy and high performance, it is necessary to correctly detect the actual deterioration state of the light emitter.
従って、劣化状態を検出せずに行う焼きつきの改善策は全て、焼きつきの発生を単に抑制しているのにすぎない。
このうち特許文献1と特許文献2は、発光体の劣化状態を入力表示データ(階調値)の積算値によって予測し、その予測結果に基づいて入力表示データを補正する技術を開示する。すなわち、これらの特許文献は、劣化特性の予測値に基づいて焼きつきを補正する手法を開示する。このため、予測結果に基づく補正後も、焼きつきが解消されない可能性がある。
Among these,
その大きな要因は、発光体の劣化特性は、入力階調値だけでは一様に決定できないためである。例えば、周囲の環境、駆動方法、輝度条件、発熱条件、劣化の程度など様々な条件が複雑に影響する。しかも、有機ELディスプレイパネル間の個体誤差をも考慮する必要がある。このように、全ての条件を正確に関連付けて発光体の劣化状態を予測することは、事実上ほぼ不可能に近い。 The main factor is that the deterioration characteristics of the light emitter cannot be uniformly determined only by the input gradation value. For example, various conditions such as the surrounding environment, the driving method, the luminance condition, the heat generation condition, and the degree of deterioration have a complicated influence. Moreover, it is necessary to consider individual errors between organic EL display panels. Thus, it is virtually impossible to predict the deterioration state of the light emitter by accurately associating all the conditions.
一方、特許文献3に示す手法では、画素回路内に配置した光検出素子により発光体の劣化特性を精度良く検出することができる。しかし、画素毎に光検出素子を利用した補正回路を配置することにより1画素当たりのトランジスタ数が増加し、生産歩留まりの低下や高解像化に不利になる問題がある。
On the other hand, in the technique disclosed in
そこで、発明者らは、有効表示領域の外側に複数個のダミー画素を配置して、有効表示領域内の任意のダミー画素に関する累積劣化情報を実測し、その実測結果と対応する見積もり結果との差分を修正する仕組みと修正後の累積劣化情報に基づいて各画素に対応する補正値を決定する仕組みとを提案する。 Therefore, the inventors have arranged a plurality of dummy pixels outside the effective display area, measured the accumulated deterioration information regarding any dummy pixel in the effective display area, and measured the measured result and the corresponding estimated result. A mechanism for correcting the difference and a mechanism for determining a correction value corresponding to each pixel based on the corrected cumulative deterioration information are proposed.
(仕組み1)
まず、累積劣化情報を修正する仕組みとして、以下に示す処理機能を搭載する手法を提案する。
(a)測定タイミング以外は、有効表示領域内で任意に選択されたサンプル画素に対応する階調値と全画素の平均階調値とをそれぞれ対応するダミー画素に与える一方で、測定タイミングには測定用の階調値を複数個のダミー画素全てに与える処理
(b)輝度検出センサーにより検出された検出輝度に基づいて、各ダミー画素の累積劣化情報を測定する処理
(c)複数個のサンプル画素について算出された累積劣化情報の見積もり値と、これらに対応する累積劣化情報の実測値に基づいて各サンプル画素に対応する修正倍率を求める処理
(d)複数個のサンプル画素について算出された累積劣化情報の見積もり値を大きさ順に並べた際に隣接する2つのサンプル画素に対応する各修正倍率の平均値を、対応する見積もり範囲に対する修正値に決定する処理
(Mechanism 1)
First, as a mechanism for correcting the cumulative deterioration information, a method for mounting the processing functions shown below is proposed.
(A) Except for the measurement timing, the gradation value corresponding to the sample pixel arbitrarily selected in the effective display area and the average gradation value of all the pixels are given to the corresponding dummy pixels, while the measurement timing includes (B) Processing for measuring accumulated deterioration information of each dummy pixel based on the detected luminance detected by the luminance detection sensor (c) Multiple samples A process for obtaining a correction magnification corresponding to each sample pixel based on an estimated value of the accumulated deterioration information calculated for the pixel and an actual measurement value of the accumulated deterioration information corresponding to the estimated value. (D) Accumulation calculated for a plurality of sample pixels. When the estimated values of the deterioration information are arranged in order of size, the average value of each correction magnification corresponding to two adjacent sample pixels is set as a correction value for the corresponding estimated range. Processing constant to
(仕組み2)
また、修正後の累積劣化情報に基づいて各画素に対応する補正値を決定する仕組みとして、以下に示す処理機能を搭載する手法を提案する。
(a)測定タイミング以外は、有効表示領域内で任意に選択されたサンプル画素に対応する階調値と全画素の平均階調値とをそれぞれ対応するダミー画素に与える一方で、測定タイミングには測定用の階調値を複数個のダミー画素全てに与える処理
(b)輝度検出センサーにより検出された検出輝度に基づいて、各ダミー画素の累積劣化情報を測定する処理
(c)複数個のサンプル画素について算出された累積劣化情報の見積もり値と、これらに対応する累積劣化情報の実測値に基づいて各サンプル画素に対応する修正倍率を求める処理
(d)複数個のサンプル画素について算出された累積劣化情報の見積もり値を大きさ順に並べた際に隣接する2つのサンプル画素に対応する各修正倍率の平均値を、対応する見積もり範囲に対する修正値に決定する処理
(e)修正値による修正済みの累積劣化情報に基づいて、各画素に対応する補正量を決定する処理
(f)決定された補正量に基づいて、有効表示領域に対応する入力階調値を補正する処理
(Mechanism 2)
In addition, as a mechanism for determining a correction value corresponding to each pixel based on the corrected accumulated deterioration information, a method of mounting the processing functions shown below is proposed.
(A) Except for the measurement timing, the gradation value corresponding to the sample pixel arbitrarily selected in the effective display area and the average gradation value of all the pixels are given to the corresponding dummy pixels, while the measurement timing includes (B) Processing for measuring accumulated deterioration information of each dummy pixel based on the detected luminance detected by the luminance detection sensor (c) Multiple samples A process for obtaining a correction magnification corresponding to each sample pixel based on an estimated value of the accumulated deterioration information calculated for the pixel and an actual measurement value of the accumulated deterioration information corresponding to the estimated value. (D) Accumulation calculated for a plurality of sample pixels. When the estimated values of the deterioration information are arranged in order of size, the average value of each correction magnification corresponding to two adjacent sample pixels is set as a correction value for the corresponding estimated range. (E) A process for determining a correction amount corresponding to each pixel based on the corrected cumulative deterioration information by the correction value (f) An input floor corresponding to the effective display area based on the determined correction amount Processing to correct key values
発明者らの提案する発明では、有効表示領域の外側に配置された複数個のダミー画素の累積劣化情報を実測し、実測値と対応する見積もり値との差分に基づいて有効表示領域を構成する全画素の累積劣化情報が実際の劣化状態に追従するように修正する。この結果、入力表示データの補正精度が向上し、焼き付き現象を確実に抑制又は改善することが可能になる。 In the invention proposed by the inventors, the accumulated deterioration information of a plurality of dummy pixels arranged outside the effective display area is actually measured, and the effective display area is configured based on the difference between the actually measured value and the corresponding estimated value. Correction is made so that the cumulative deterioration information of all pixels follows the actual deterioration state. As a result, the correction accuracy of the input display data is improved, and the burn-in phenomenon can be reliably suppressed or improved.
以下、発明に係る自発光表示装置の形態例を説明する。
なお、本明細書で特に図示又は記載されない部分には、当該技術分野の周知又は公知技術を適用する。
また以下に説明する形態例は、発明の一つの形態例であって、これらに限定されるものではない。
Hereinafter, embodiments of the self-luminous display device according to the invention will be described.
In addition, the well-known or well-known technique of the said technical field is applied to the part which is not specifically illustrated or described in this specification.
Moreover, the form example demonstrated below is one form example of invention, Comprising: It is not limited to these.
(A)発光特性の変動を劣化量の見積もり時に正確に反映する技術
(A−1)基本的な考え方
階調値と劣化量は必ずしも比例関係にない。これは、パネル間の特性誤差、環境温度、パネル面の発光温度その他の影響で発光特性が変化するという特性が有機EL素子にあるためである。
このため、階調値を画素毎に累積加算しても、対応画素の劣化量を正確に見積もることはできない。
(A) Technology for accurately reflecting fluctuations in light emission characteristics when estimating the deterioration amount (A-1) Basic concept The gradation value and the deterioration amount are not necessarily in a proportional relationship. This is because the organic EL element has a characteristic that the light emission characteristic changes due to the characteristic error between panels, the environmental temperature, the light emission temperature of the panel surface, and the like.
For this reason, even if the gradation value is cumulatively added for each pixel, the deterioration amount of the corresponding pixel cannot be accurately estimated.
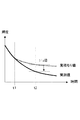
そこで、発明者らは、有機EL素子の発光特性の経時的な変動を実測し、実測結果を劣化量の見積もりに反映する仕組みを提案する。
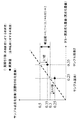
図1に、発光時点の違いによる劣化速度(率)の変動を示す。図1は、ある画素を構成する発光体を、一定の階調値で点灯制御する場合の発光輝度の時間変化を示す。曲線DAPL は、ある画素(例えば、劣化特性測定用のダミー画素)を画面全体の平均階調値で点灯制御する場合の劣化曲線を示す。
In view of this, the inventors propose a mechanism for measuring the temporal variation of the light emission characteristics of the organic EL element and reflecting the measurement result in the estimation of the deterioration amount.
FIG. 1 shows the variation of the deterioration rate (rate) due to the difference in the light emission point. FIG. 1 shows temporal changes in light emission luminance in the case where lighting of a light emitter constituting a certain pixel is controlled with a constant gradation value. A curve D APL represents a deterioration curve when lighting control is performed on a certain pixel (for example, a dummy pixel for measuring deterioration characteristics) with an average gradation value of the entire screen.
図1に示す矢印D100 は、画素に100%信号レベルの階調値を与えた場合の輝度劣化の進行速度(劣化率)を示す。時点t1を基点とする矢印D100の傾きと時点t2を基点とする矢印D100の傾きとを比べて分かるように、同じ階調値によりある画素の発光を制御する場合でも、発光開始時の輝度劣化が異なると劣化速度は同じにならない。 An arrow D 100 shown in FIG. 1 indicates a progress rate (deterioration rate) of luminance degradation when a gradation value of 100% signal level is given to a pixel. As can be seen by comparing the slope of the arrow D 100 with the time point t1 as the base point and the slope of the arrow D 100 with the time point t2 as the base point, even when the light emission of a certain pixel is controlled by the same gradation value, If the brightness deterioration is different, the deterioration speed is not the same.
劣化速度が異なれば、発光時間長は同じでも該当期間内に発生する劣化量は異なる値になる。すなわち、階調値と劣化量との対応関係は時間の経過と共に変化する。
そこで、発明者らは、固定的な対応関係に基づいて算出された各画素の累積劣化量の見積もり値を、サンプル画素について実測された累積劣化量に基づいて逐次修正する手法を採用する。
If the deterioration rate is different, the amount of deterioration occurring in the corresponding period is different even if the light emission time length is the same. That is, the correspondence between the gradation value and the deterioration amount changes with the passage of time.
In view of this, the inventors adopt a method of sequentially correcting the estimated value of the cumulative deterioration amount of each pixel calculated based on a fixed correspondence relationship based on the cumulative deterioration amount actually measured for the sample pixel.
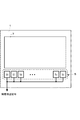
(A−2)表示パネルの構成例
図2に、有機ELパネルモジュールの構成例を示す。図2は、主に画素配置の観点から表した図であり、駆動回路その他の周辺回路は省略して表している。
有機ELパネルモジュール1は、有効表示領域3とダミー画素領域5で構成する。
有効表示領域3は、発光が外部から観察できる領域である。一方、ダミー画素領域5は、発光が外部から観察されないように遮光された領域であり、有効表示領域3の外側に配置される。
(A-2) Configuration Example of Display Panel FIG. 2 shows a configuration example of the organic EL panel module. FIG. 2 is a diagram mainly showing from the viewpoint of pixel arrangement, and the drive circuit and other peripheral circuits are omitted.
The organic
The
図2に示すように、ダミー画素領域5には、複数個のダミー画素51を配置する。配置する個数は任意である。なお、後述するように、ダミー画素51の1つには、有効表示領域を構成する全画素(基本発光色別)の平均階調値が与えられる。また、その他のダミー画素51には、有効表示領域内で任意に選択されたサンプル画素と全く同じ階調値が与えられる。
As shown in FIG. 2, a plurality of
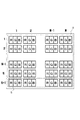
図3に、有機ELパネルモジュールの具体的な画素配置例を示す。図3の場合、1行目からn行目までが有効表示領域3であり、n+1行目がダミー画素領域5である。この例の場合、各ダミー画素51は、ブランキング期間に発光制御する。図3に示すように、発明者らの提案する表示パネルは、一般的な表示パネルに選択線(ゲート駆動線)を1本追加するだけで実現できる。すなわち、ダミー画素領域5は、有効表示領域3内の各画素と同じ構造で良く、既存の駆動回路を流用することができる。すなわち、ダミー画素の駆動に、専用の駆動回路又は大規模な駆動回路を必要としない。
FIG. 3 shows a specific pixel arrangement example of the organic EL panel module. In the case of FIG. 3, the
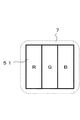
図4に、ダミー画素領域5を構成するダミー画素51の構造例を示す。ダミー画素51は、有効表示領域内の表示画素と同一の構造を有し、赤(R)、緑(G)、青(B)のそれぞれに対応する単位ダミー画素で構成される。
これら各単位ダミー画素の発光輝度は、輝度検出センサー7により検出される。図4の場合、1つの輝度検出センサー7が表示画素の全体を覆うように配置される。
FIG. 4 shows a structural example of the
The light emission luminance of each unit dummy pixel is detected by the
もっとも、3つの輝度検出センサー7を構成する各単位ダミー画素と対面するように配置することも可能であるし、各単位ダミー画素内に配置することもできる。
この形態例の場合、輝度検出センサー7を構成する光検出素子には、アモルファスシリコン半導体を用いた可視光センサーを使用する。輝度検出センサー7は、電流値として検出した光量情報を増幅して電圧値に変換し、光検出信号として出力する。
However, it can be arranged so as to face each unit dummy pixel constituting the three
In the case of this embodiment, a visible light sensor using an amorphous silicon semiconductor is used as the light detection element constituting the
(B)好適な形態例
以下、前述した累積劣化情報の修正技術を採用する有機ELディスプレイ装置の形態例を説明する。
(a)システム構成
図5に、この形態例で説明する有機ELディスプレイ装置11のシステム構成例の概要を示す。有機ELディスプレイ装置11は、有機ELパネルモジュール13、入力表示データ補正部15及び見積もり劣化量修正部17で構成する。
(B) Preferred Embodiment Hereinafter, an embodiment of an organic EL display device that employs the above-described technique for correcting cumulative deterioration information will be described.
(A) System Configuration FIG. 5 shows an outline of a system configuration example of the organic
有機ELパネルモジュール13には、図4に示す構成を採用する。
入力表示データ補正部15は、有効表示領域3を構成する各画素の劣化量が基準画素の劣化量に揃うように又は入力階調値が同じ場合に、各画素の発光輝度が基準画素の発光輝度に揃うように入力表示データを個別に補正する処理を実行する。ここでの基準画素には、入力表示データの平均階調値で継続的に発光制御される画素を想定する。
The organic
The input display
見積もり劣化量修正部17は、ダミー画素データを生成する処理と、ダミー画素についての実測結果である累積劣化量差に基づいて入力表示データ補正部15の見積もり劣化量を修正する処理とを実行する。
例えば図6に示すように、時点t2にあるサンプル画素について算出された累積劣化量差の見積もり値と対応する実測値との間に1/a倍の差が確認される場合、見積もり劣化量修正部17は、見積もり値をa倍して現状に近づける処理を実行する。
The estimated deterioration
For example, as shown in FIG. 6, when a difference of 1 / a times is confirmed between the estimated value of the accumulated deterioration amount difference calculated for the sample pixel at time t2 and the corresponding actual measurement value, the estimated deterioration amount correction is performed. The
(b)入力表示データ補正部の構成
図7に、入力表示データ補正部15の詳細構成例を示す。入力表示データ補正部15は、階調値/劣化量変換テーブル151、劣化量差算出部153、修正前累積劣化量差蓄積部155、修正後累積劣化量差蓄積部157、補正量決定部159及び映像信号補正部161で構成する。
(B) Configuration of Input Display Data Correction Unit FIG. 7 shows a detailed configuration example of the input display
階調値/劣化量変換テーブル151は、入力表示データ(階調値)を劣化量に変換するテーブルである。変換テーブルを用いるのは、前述したように有機EL素子の劣化の進行が階調値と比例関係にないためである。図8に、階調値/劣化量変換テーブル151の一例を示す。階調値/劣化量変換テーブル151には、入力表示データが採り得る全ての階調値と、これらに対応する劣化量とが対応付けられて記憶されている。劣化量Rは、各階調値に対応する劣化速度(劣化率)と発光期間tとの積として与えられる。発光期間tは、固定でも可変でも良い。 The gradation value / degradation amount conversion table 151 is a table for converting input display data (gradation value) into a deterioration amount. The reason why the conversion table is used is that the progress of the deterioration of the organic EL element is not proportional to the gradation value as described above. FIG. 8 shows an example of the gradation value / degradation amount conversion table 151. In the gradation value / degradation amount conversion table 151, all gradation values that can be taken by the input display data and the corresponding degradation amounts are stored in association with each other. The deterioration amount R is given as the product of the deterioration rate (deterioration rate) corresponding to each gradation value and the light emission period t. The light emission period t may be fixed or variable.
劣化量差算出部153は、基準画素の劣化量に対する各画素の劣化量の差分を算出する処理デバイスである。この形態例の場合、基準画素には、有効表示領域を構成する全画素のフレーム単位の平均階調値が与えられる。なお、基準画素に対応する劣化量は、当該平均階調値に対応する劣化量として階調値/劣化量変換テーブル151から読み出される。 The deterioration amount difference calculation unit 153 is a processing device that calculates the difference in the deterioration amount of each pixel with respect to the deterioration amount of the reference pixel. In the case of this embodiment, the reference pixel is given an average gradation value in units of frames of all the pixels constituting the effective display area. The deterioration amount corresponding to the reference pixel is read from the gradation value / deterioration amount conversion table 151 as the deterioration amount corresponding to the average gradation value.
修正前累積劣化量差蓄積部155は、画素毎に算出された累積劣化量差を蓄積する記憶デバイスである。ここでの累積劣化量差は見積もり値である。なお、蓄積されている累積劣化量差は、見積もり精度の修正値を決定する際に、見積もり精度修正部177に読み出される。
修正後累積劣化量差蓄積部157は、累積劣化量差の実測値に基づいて修正された累積劣化量差を蓄積する記憶デバイスである。勿論、ここでの累積劣化量差は、基本発光色別に記憶される。
The pre-correction cumulative deterioration amount difference accumulation unit 155 is a storage device that accumulates the cumulative deterioration amount difference calculated for each pixel. The cumulative deterioration amount difference here is an estimated value. The accumulated accumulated deterioration amount difference is read to the estimation
The corrected cumulative deterioration amount difference accumulation unit 157 is a storage device that accumulates the cumulative deterioration amount difference corrected based on the actual measurement value of the cumulative deterioration amount difference. Of course, the accumulated deterioration amount difference here is stored for each basic emission color.
補正量決定部159は、各画素に対応する補正値を累積劣化量差に基づいて決定する処理デバイスである。この形態例の場合、補正量の決定方法には、基準画素の累積劣化量との差が無くなるように補正値を決定する方法又は入力階調値が同じ場合に、各画素の発光輝度が基準画素の発光輝度に揃うように補正値を決定する方法を適用する。
映像信号補正部161は、入力表示データを補正表示データに変換する処理を実行する処理デバイスとして機能する。
The correction amount determination unit 159 is a processing device that determines a correction value corresponding to each pixel based on the accumulated deterioration amount difference. In the case of this embodiment, the correction amount determination method is a method for determining a correction value so that there is no difference from the cumulative deterioration amount of the reference pixel, or when the input gradation value is the same, the emission luminance of each pixel is the reference. A method of determining a correction value so as to match the light emission luminance of the pixel is applied.
The video signal correction unit 161 functions as a processing device that executes processing for converting input display data into corrected display data.
この形態例の場合、映像信号補正部161は、有効表示領域内の各画素に対応する入力表示データに、各画素に対応する補正値を加減算することにより入力表示データを補正表示データに変換する。
補正値は、補正量決定部159より与えられる。変換後の補正表示データは、階調値/劣化量変換テーブル151、ダミー画素決定部171及びダミー画素データ多重部173に与えられる。
In the case of this embodiment, the video signal correction unit 161 converts the input display data into corrected display data by adding / subtracting the correction value corresponding to each pixel to / from the input display data corresponding to each pixel in the effective display area. .
The correction value is given from the correction amount determination unit 159. The corrected display data after the conversion is given to the gradation value / degradation amount conversion table 151, the dummy pixel determining unit 171 and the dummy pixel
(c)見積もり劣化量修正部の構成
図7に、見積もり劣化量修正部の詳細構成例を示す。見積もり劣化量修正部17は、ダミー画素データ決定部171、ダミー画素データ多重部173、実劣化量測定部175及び見積もり精度修正部177で構成する。
ダミー画素データ決定部171は、任意に選択されたn個の表示画素と基準画素に対応する計n+1個のダミー画素に供給するダミー画素データを決定する処理デバイスである。なお、ダミー画素データは、測定タイミング時とそれ以外とで異なる値を使用する。
(C) Configuration of Estimated Degradation Amount Correction Unit FIG. 7 shows a detailed configuration example of the estimated degradation amount correction unit. The estimated deterioration
The dummy pixel data determination unit 171 is a processing device that determines dummy pixel data to be supplied to a total of n + 1 dummy pixels corresponding to arbitrarily selected n display pixels and reference pixels. The dummy pixel data uses different values at the measurement timing and other times.
図9に、発生するダミー画素データとダミー画素との対応関係を示す。なお、図9に示す対応関係は、測定タイミング以外の期間に使用する対応関係である。図9に示すように、ダミー画素データ決定部171は、ダミー画素の1つに有効表示領域内の全画素に対応する平均階調値DAPL を与える。また、ダミー画素データ決定部171は、その他のn個のダミー画素に対し、任意に設定されたn個のサンプル画素に対応する各階調値(RGBデータ)を与える。
一方、測定タイミングには、ダミー画素データ決定部171は、n+1個の全ダミー画素に対し、測定用に設定された固定の階調値(例えば100%階調値)を与える。
FIG. 9 shows the correspondence between generated dummy pixel data and dummy pixels. The correspondence relationship shown in FIG. 9 is a correspondence relationship used during a period other than the measurement timing. As shown in FIG. 9, the dummy pixel data determination unit 171 gives an average gradation value D APL corresponding to all the pixels in the effective display area to one of the dummy pixels. In addition, the dummy pixel data determination unit 171 gives gradation values (RGB data) corresponding to arbitrarily set n sample pixels to the other n dummy pixels.
On the other hand, at the measurement timing, the dummy pixel data determination unit 171 gives a fixed gradation value (for example, 100% gradation value) set for measurement to all the n + 1 dummy pixels.
ダミー画素データ多重部173は、ダミー画素データを補正表示データに多重して有機ELパネルモジュール13に出力する処理デバイスである。
実劣化量測定部175は、測定タイミングにおける各ダミー画素の発光輝度値を検出し、検出輝度に基づいてダミー画素別の累積劣化量を求める処理デバイスである。累積劣化量は、初期輝度(100%輝度)に対する輝度の低下割合として与えられる。
The dummy pixel
The actual deterioration amount measuring unit 175 is a processing device that detects the light emission luminance value of each dummy pixel at the measurement timing and obtains the cumulative deterioration amount for each dummy pixel based on the detected luminance. The cumulative deterioration amount is given as a luminance reduction rate with respect to the initial luminance (100% luminance).
また、実劣化量測定部175は、画面全体の平均的な累積劣化量に対する各サンプル画素の累積劣化量の差分を算出する処理を実行する。図10に、サンプル画素別の累積劣化量差ΔD1 〜ΔDn の例を示す。なお、ΔDi
は、サンプル画素i(1〜n)に対応する累積劣化量差の実測値を表している。図10に示すように、サンプル画素は、ランダムに選択されているため、劣化の程度にはバラツキがある。すなわち、あるサンプル画素については、画面全体の平均的な累積劣化量よりも劣化が進んでいる画素もあれば、あるサンプル画素については、画面全体の平均的な累積劣化量よりも劣化が遅れる画素もある。
In addition, the actual deterioration amount measurement unit 175 performs a process of calculating a difference of the cumulative deterioration amount of each sample pixel with respect to the average cumulative deterioration amount of the entire screen. FIG. 10 shows an example of cumulative deterioration amount differences ΔD 1 to ΔD n for each sample pixel. ΔD i
Represents an actual measurement value of the accumulated deterioration amount difference corresponding to the sample pixel i (1 to n). As shown in FIG. 10, since the sample pixels are selected at random, the degree of deterioration varies. That is, for some sample pixels, some pixels are more deteriorated than the average accumulated deterioration amount of the entire screen, and for some sample pixels, pixels whose deterioration is delayed from the average accumulated deterioration amount of the entire screen. There is also.
見積もり精度修正部177は、サンプル画素について算出された累積劣化量差の見積もり値と実測値との差分に基づいて、全ての画素について算出されている累積劣化量差の見積もり値を修正する処理デバイスである。
図11に、見積もり精度修正部177の内部構成例を示す。図11に示すように、見積もり精度修正部177は、見積もり劣化量差格納部1771、実劣化量差格納部1773、サンプル画素別修正倍率算出部1775、見積もり範囲別修正値決定部1777及び累積劣化量差再計算部1779で構成される。
The estimation
FIG. 11 shows an internal configuration example of the estimation
見積もり劣化量差格納部1771は、修正前累積劣化量差蓄積部155から読み出された測定タイミング時点での累積劣化量差のうちサンプル画素に対応する累積劣化量差を格納する記憶デバイスである。
実劣化量差格納部1773は、実劣化量測定部175でサンプル画素別に算出された累積劣化量差の実測値を格納する記憶デバイスである。
The estimated deterioration amount difference storage unit 1771 is a storage device that stores the accumulated deterioration amount difference corresponding to the sample pixel among the accumulated deterioration amount differences at the measurement timing read from the pre-correction accumulated deterioration amount difference storage unit 155. .
The actual deterioration amount
サンプル画素別修正倍率算出部1775は、各サンプル画素について見積もり値と実測値との修正倍率を算出する処理デバイスである。図12に、修正倍率の算出原理を示す。例えば、サンプル画素1の場合、見積もり値が0.3であるのに対し、実測値が0.25である。この場合、サンプル画素別修正倍率算出部1775は、見積もり値の方が実測値よりも劣化が進んでいるので、実測値に近づくように修正倍率を0.83に決定する。同様に、サンプル画素2についての修正倍率は0.7に決定する。勿論、見積もり値の方が実測値よりも劣化が遅れいている場合の修正倍率は1より大きな値に決定される。
The sample pixel correction magnification calculation unit 1775 is a processing device that calculates a correction magnification between an estimated value and an actual measurement value for each sample pixel. FIG. 12 shows the calculation principle of the correction magnification. For example, in the case of the
見積もり範囲別修正値決定部1777は、複数個のサンプル画素について算出された累積劣化情報の見積もり値を図10に示すように大きさ順に並べた際に隣接する2つのサンプル画素に対応する各修正倍率の平均値を、隣接する2つの見積もり値の間(区間)に対する修正値に決定する処理デバイスである。
修正値の決定原理を図12を用いて説明する。図12の場合、累積劣化量差の見積もり値の0.3と0.5が隣り合う場合について表している。
この場合、見積もり範囲別修正値決定部1777は、サンプル画素1の修正倍率0.83とサンプル画素2の修正倍率0.7の平均値である0.77をこの区間に対する修正値に決定する。
The correction
The principle of determining the correction value will be described with reference to FIG. In the case of FIG. 12, the estimated value of the cumulative deterioration amount difference of 0.3 and 0.5 is shown as being adjacent.
In this case, the estimated value-by-estimated-range correction
累積劣化量差再計算部1779は、各サンプル画素の累積劣化量差を大きさ順に並べ替えた各区間の修正値に基づいて、各画素について算出されている累積劣化量の見積もり値を再計算する処理デバイスである。図13に、再計算時に使用される見積もり劣化量差の範囲と修正値との対応関係を示す。なお、図13は、サンプル画素が5個の場合について表している。修正前累積劣化量差蓄積部155に蓄積されている累積劣化量差は、全てこれら6つの区間のいずれかに分類される。 The accumulated deterioration amount difference recalculation unit 1779 recalculates the estimated value of the accumulated deterioration amount calculated for each pixel based on the correction values of the respective sections in which the accumulated deterioration amount differences of the respective sample pixels are rearranged in order of magnitude. Processing device. FIG. 13 shows the correspondence between the range of estimated deterioration amount difference used at the time of recalculation and the correction value. FIG. 13 shows a case where there are five sample pixels. The accumulated deterioration amount difference accumulated in the pre-correction accumulated deterioration amount difference accumulation unit 155 is all classified into one of these six sections.
因みに、この形態例の場合、a未満の修正値には隣の区間a−bと同じ修正値を使用し、e以上の修正値には隣の区間d−eと同じ修正値を使用する。
累積劣化量差再計算部1779は、修正値を用いて再計算した各画素の累積劣化量差を修正後累積劣化量差蓄積部157に記録する処理も実行する。
Incidentally, in the case of this embodiment, the same correction value as that of the adjacent section a-b is used for the correction value less than a, and the same correction value as that of the adjacent section de is used for the correction value of e or more.
The cumulative deterioration amount difference recalculation unit 1779 also executes a process of recording the cumulative deterioration amount difference of each pixel recalculated using the correction value in the corrected cumulative deterioration amount difference storage unit 157.
(d)累積劣化量差の修正動作
以下、この形態例で採用する累積劣化量差の修正動作を簡単に説明する。
有機ELパネルモジュールの使用開始と同時に、n+1個のダミー画素は、有効表示領域内の平均階調値又はn個のサンプル画素と同じ階調値で発光制御される。
これにより、n+1個のダミー画素の発光輝度は、有効表示領域全体の平均的な輝度劣化に伴って又は各サンプル画素の輝度劣化に伴って変化する。
(D) Correction Operation for Cumulative Degradation Amount Difference Hereinafter, the operation for correcting the accumulated deterioration amount difference employed in this embodiment will be briefly described.
Simultaneously with the start of use of the organic EL panel module, n + 1 dummy pixels are controlled to emit light with an average gradation value in the effective display area or with the same gradation value as the n sample pixels.
As a result, the light emission luminance of the n + 1 dummy pixels changes with the average luminance deterioration of the entire effective display area or with the luminance deterioration of each sample pixel.
このダミー画素の累積劣化量が測定タイミング毎に検出され、各サンプル画素の画面平均に対する累積劣化量差が算出される。測定タイミングは任意である。例えば固定周期でも良いし、任意の間隔でも良い。
ところで、前述したように、サンプル画素は、有効表示領域内でランダムに選択されている。このため、これら累積劣化量差の実測値には、表示画面内に偏在する温度ムラや経時変化等の影響が反映されている。
そして、累積劣化量差の実測値と見積もり値との差分を修正する修正係数が算出され、全画素に対応する累積劣化量差の見積もり値が逐次修正される。
The cumulative deterioration amount of the dummy pixel is detected at every measurement timing, and the cumulative deterioration amount difference with respect to the screen average of each sample pixel is calculated. The measurement timing is arbitrary. For example, it may be a fixed cycle or an arbitrary interval.
By the way, as described above, the sample pixels are randomly selected within the effective display area. For this reason, the measured value of the accumulated deterioration amount difference reflects the influence of uneven temperature distribution, change with time, and the like that are unevenly distributed in the display screen.
Then, a correction coefficient for correcting the difference between the actual measurement value and the estimated value of the accumulated deterioration amount difference is calculated, and the estimated value of the accumulated deterioration amount difference corresponding to all pixels is sequentially corrected.
このように、この形態例の場合、累積劣化量差の見積もり値が一律に修正されるのではなく、実測値との乖離度に応じて細かく修正される。従って、使用環境等の不確定要素の影響を反映した高い修正精度を実現できる。また、以上説明したように、事前に用意するのは、階調値と劣化量との基本的な関係を記憶したテーブル(すなわち、階調値/劣化量変換テーブル151)だけで良い。このため、システムの構築に要する手間や作業量を大幅に削減することができる。 Thus, in the case of this embodiment, the estimated value of the accumulated deterioration amount difference is not uniformly corrected, but is finely corrected according to the degree of deviation from the actually measured value. Accordingly, high correction accuracy reflecting the influence of uncertain factors such as the use environment can be realized. Further, as described above, it is sufficient to prepare in advance only a table storing the basic relationship between the gradation value and the deterioration amount (that is, the gradation value / degradation amount conversion table 151). For this reason, it is possible to greatly reduce the labor and the amount of work required to construct the system.
参考までに、図14及び図15に、前述した修正動作により補正精度がどのように改善されるかを模式的に示す。
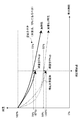
図14は、補正量決定部159が、各画素の劣化量が基準画素の劣化量と一致するように補正動作を実行する場合の動作例に対応する。図中の実線は実際の劣化特性を示し、破線は見積もり値を修正しない場合の劣化特性である。
For reference, FIG. 14 and FIG. 15 schematically show how the correction accuracy is improved by the above-described correction operation.
FIG. 14 corresponds to an operation example in which the correction amount determination unit 159 performs a correction operation so that the deterioration amount of each pixel matches the deterioration amount of the reference pixel. The solid line in the figure indicates the actual deterioration characteristic, and the broken line indicates the deterioration characteristic when the estimated value is not corrected.
補正対象画素の劣化(破線)が一致させるべき基準画素の劣化(破線)に対して5%進んでいると判定された場合、従来手法では、予定する補正期間について補正対象画素の発光を停止させるような制御動作が実行される。破線で示すように、補正期間の終了時点では補正対象画素の劣化特性は、基準画素の劣化特性と一致しているはずである。 When it is determined that the deterioration of the correction target pixel (broken line) is advanced by 5% with respect to the deterioration of the reference pixel to be matched (broken line), the conventional method stops the light emission of the correction target pixel for the scheduled correction period. Such a control operation is executed. As indicated by the broken line, the deterioration characteristic of the correction target pixel should match the deterioration characteristic of the reference pixel at the end of the correction period.
しかし、劣化特性の見積もり精度が悪く、図14に実線で示すように補正開始時点における補正対象画素と基準画素との劣化量の差が実際は3%の場合、補正対象画素の発光を停止することで補正期間終了時点には、補正開始時点とは反対に基準画素の劣化が進んでしまう。このように、累積劣化量差の見積もり精度に問題があると、補正動作が本来の効果(焼き付きの改善)を発揮することができない。
ところが、発明者らの提案する手法を採用すれば、累積劣化量が実際の累積劣化量に一致するように逐次修正されるため、補正対象画素の劣化量は基準画素の劣化量に対して精度良く合わせ込むことができ、補正終了時点には焼き付きを改善することが可能になる。
However, when the estimation accuracy of the deterioration characteristic is poor and the difference in deterioration amount between the correction target pixel and the reference pixel at the start of correction is actually 3% as indicated by the solid line in FIG. 14, the emission of the correction target pixel is stopped. Thus, at the end of the correction period, the deterioration of the reference pixel proceeds in contrast to the correction start time. Thus, if there is a problem in the estimation accuracy of the accumulated deterioration amount difference, the correction operation cannot exhibit the original effect (improving burn-in).
However, if the method proposed by the inventors is adopted, the accumulated deterioration amount is sequentially corrected so as to match the actual accumulated deterioration amount, so that the deterioration amount of the correction target pixel is more accurate than the deterioration amount of the reference pixel. It is possible to match well, and it becomes possible to improve the burn-in at the end of the correction.
図15は、補正量決定部159が、入力階調値が同じ場合に、各画素の発光輝度が基準画素の発光輝度に揃うように補正動作を実行する場合の動作例を表している
図15の場合も、補正対象画素の劣化(破線)が一致させるべき基準画素の劣化(破線)に対して5%進んでいると判定された場合について表している。この場合、従来手法では、補正対象画素の発光輝度を5%上昇させるような制御動作が実行される。破線で示すように、この補正動作の実行により補正対象画素の発光輝度は、基準画素の発光輝度と一致するはずである。
15 illustrates an operation example when the correction amount determination unit 159 performs a correction operation so that the light emission luminance of each pixel matches the light emission luminance of the reference pixel when the input gradation values are the same. This also shows a case where it is determined that the deterioration of the correction target pixel (broken line) is advanced by 5% with respect to the deterioration of the reference pixel (broken line) to be matched. In this case, in the conventional method, a control operation that increases the light emission luminance of the correction target pixel by 5% is executed. As indicated by the broken line, the light emission luminance of the correction target pixel should match the light emission luminance of the reference pixel by executing this correction operation.
しかし、劣化特性の見積もり精度が悪く、図15に実線で示すように補正開始時点における補正対象画素と基準画素との劣化量の差が実際は3%の場合、補正対象画素の発光輝度を5%上昇させると、基準画素の発光輝度よりも2%も大きくなってしまう。このように、劣化量の予測精度に問題があると、補正動作が本来の効果(焼き付きの改善)を発揮することができない。
そしてこの場合も、発明者らの提案する手法を採用すれば、累積劣化量が実際の累積劣化量に一致するように逐次修正されるため、補正対象画素の発光輝度は基準画素の発光輝度に対して精度良く合わせ込むことができ、補正終了時点には焼き付きを改善することが可能になる。
However, when the estimation accuracy of the deterioration characteristic is poor and the difference in deterioration amount between the correction target pixel and the reference pixel at the start of correction is actually 3% as indicated by the solid line in FIG. 15, the emission luminance of the correction target pixel is 5%. When it is raised, it becomes 2% larger than the light emission luminance of the reference pixel. Thus, if there is a problem in the prediction accuracy of the deterioration amount, the correction operation cannot exhibit the original effect (improving burn-in).
In this case as well, if the method proposed by the inventors is adopted, the cumulative deterioration amount is sequentially corrected so as to match the actual cumulative deterioration amount, so the light emission luminance of the correction target pixel becomes the light emission luminance of the reference pixel. On the other hand, it is possible to match with high accuracy, and it is possible to improve the burn-in at the end of the correction.
(e)形態例の効果
以上説明したように、この形態例に係る有機ELディスプレイ装置では、有効表示領域の外側にダミー画素を複数個配置し、その劣化状態を実際に測定して階調値から算出される累積劣化量差の見積もり値を修正する。この仕組みの採用により、修正後累積劣化量差蓄積部157には、実際の劣化状態を正確に反映した累積劣化量差のみが蓄積されることになる。結果として、補正量決定部159で決定される補正量についての信頼性の向上が長期間にわたって保証することができる。
(E) Effect of Embodiment As described above, in the organic EL display device according to this embodiment, a plurality of dummy pixels are arranged outside the effective display area, and the degradation state is actually measured to obtain a gradation value. The estimated value of the cumulative deterioration amount calculated from the above is corrected. By adopting this mechanism, only the accumulated deterioration amount difference that accurately reflects the actual deterioration state is accumulated in the corrected accumulated deterioration amount difference accumulation unit 157. As a result, an improvement in the reliability of the correction amount determined by the correction amount determination unit 159 can be guaranteed over a long period of time.
かくして、長時間の使用にも焼き付き現象の発生し難い、又は焼き付き現象の改善が可能な有機ELディスプレイ装置を実現することが可能になる。また、この発明の場合、実測値に応じて累積劣化量差が修正される。このため、表示パネル間の個体誤差についても有効である。
勿論、これらの効果は、実測結果を使用した簡単な信号処理だけで実現できるため、従来技術のような、経時変化等の全ての事象を考慮した事前の膨大な実験を不要にできる。このため、製造コストの大幅な削減を実現できる。
Thus, it becomes possible to realize an organic EL display device in which the image sticking phenomenon hardly occurs even when used for a long time or the image sticking phenomenon can be improved. In the case of the present invention, the accumulated deterioration amount difference is corrected according to the actually measured value. For this reason, the individual error between display panels is also effective.
Of course, since these effects can be realized only by simple signal processing using the actual measurement result, it is possible to eliminate the need for an enormous prior experiment in consideration of all events such as changes over time as in the prior art. For this reason, the manufacturing cost can be significantly reduced.
また、形態例で説明した処理手法は、制御内容が単純であるので画面サイズが大型化しても低コストで実現できる。
また、ダミー画素は有効表示領域とまったく同じ画素構成で製造でき、ダミー画素専用の複雑な回路構成や特殊な制御動作を必要としない。この点でも、回路規模の削減と生産難易度の低減との点で有利である。
Further, since the processing method described in the embodiment has simple control contents, it can be realized at low cost even when the screen size is increased.
Further, the dummy pixel can be manufactured with exactly the same pixel configuration as the effective display area, and does not require a complicated circuit configuration dedicated to the dummy pixel or a special control operation. This is also advantageous in terms of reduction in circuit scale and production difficulty.
(C)他の形態例
(a)前述の形態例では、基本発光色がRGBの3色である場合について説明したが、基本発光色は補色を含めて4色以上の場合にも適用できる。この場合、ダミー画素は、これら基本発光色の数だけ用意すれば良い。
(b)前述の形態例では、基本発光色の発色形態について説明しなかったが、基本発光色別に発光素子材料が異なる有機EL素子を用意しても良いし、カラーフィルタ方式や色変換方式を用いて基本発光色を生成しても良い。
(C) Other Embodiments (a) In the above embodiment, the case where the basic emission colors are three colors of RGB has been described. However, the basic emission colors can also be applied to the case where there are four or more colors including complementary colors. In this case, as many dummy pixels as the number of the basic emission colors may be prepared.
(B) In the above-described embodiment, the color generation form of the basic light emission color has not been described. However, an organic EL element having a different light emitting element material for each basic light emission color may be prepared. It may be used to generate a basic emission color.
(c)前述の形態例では、表示画素に対応するダミー画素を自発光パネル上に1つ配置する場合について説明した。また、そのダミー画素の駆動用に新たに1本のゲート駆動線を追加する場合について説明した。しかし、配置するダミー画素の数及び位置は任意であり、配置するダミー画素の数や位置に応じてデータ駆動線とゲート駆動線の本数は最適な数を用意すれば良い。 (C) In the above-described embodiment, the case where one dummy pixel corresponding to the display pixel is arranged on the self-luminous panel has been described. Further, the case where one new gate drive line is added for driving the dummy pixel has been described. However, the number and positions of the dummy pixels to be arranged are arbitrary, and an optimum number of data driving lines and gate driving lines may be prepared according to the number and positions of the dummy pixels to be arranged.
(d)前述の形態例では、自発光表示装置の一例として有機ELディスプレイパネルを例示したが、他の自発光表示装置にも適用できる。例えば、FED(field emission display) 、無機ELディスプレイパネル、LEDパネルその他にも適用できる。 (D) In the above-described embodiment, the organic EL display panel is illustrated as an example of the self-luminous display device, but the present invention can also be applied to other self-luminous display devices. For example, the present invention can be applied to FED (field emission display), inorganic EL display panel, LED panel, and the like.
(e)前述の形態例では、基準画素と各画素の累積劣化量差を修正値で修正する場合について説明した。
しかし、各画素についての絶対的な累積劣化量を対応する修正値で修正しても良い。この明細書においては、この累積劣化量と前述した累積劣化量差とを含めて累積劣化情報という。
(E) In the above-described embodiment, a case has been described in which the accumulated deterioration amount difference between the reference pixel and each pixel is corrected with the correction value.
However, the absolute cumulative deterioration amount for each pixel may be corrected with a corresponding correction value. In this specification, the cumulative degradation information and the cumulative degradation amount difference described above are referred to as cumulative degradation information.
(f)前述の形態例では、階調値のみに基づいて算出された累積劣化情報の見積もり値を実測値に基づいて修正する機能を実装する有機ELディスプレイ装置について説明した。
しかし、累積劣化情報の修正機能は、自発光表示装置を搭載する画像処理装置の一部として実装しても良い。例えば、見積もり精度修正部177の修正機能は、ビデオカメラ、デジタルカメラその他の撮像装置(カメラユニットだけでなく、記録装置と一体に構成されているものを含む。)、情報処理端末(携帯型のコンピュータ、携帯電話機、携帯型のゲーム機、電子手帳等)、ゲーム機、プリンタ装置等に実装しても良い。
(F) In the above-described embodiment, the organic EL display device that implements the function of correcting the estimated value of the accumulated deterioration information calculated based only on the gradation value based on the actual measurement value has been described.
However, the function for correcting the accumulated deterioration information may be implemented as a part of an image processing apparatus equipped with a self-luminous display device. For example, the correction function of the estimated
(g)前述の形態例では、階調値のみに基づいて算出された累積劣化情報の見積もり値を実測値に基づいて修正する機能を実装する有機ELディスプレイ装置について説明した。
しかし、累積劣化情報の修正機能は、自発光表示装置や自発光表示装置を搭載する画像処理装置に対して入力表示データ信号を供給する画像処理装置に搭載しても良い。すなわち、ダミー画素の発光輝度や劣化情報を自発光表示装置等から自装置内に取り込む手法を採用しても良い。
(G) In the above-described embodiment, the organic EL display device that has the function of correcting the estimated value of the accumulated deterioration information calculated based only on the gradation value based on the actual measurement value has been described.
However, the function for correcting the accumulated deterioration information may be installed in an image processing device that supplies an input display data signal to a self-luminous display device or an image processing device equipped with the self-luminous display device. In other words, a method may be employed in which the light emission luminance and deterioration information of the dummy pixels are taken into the self device from the self light emitting display device.
(h)前述の形態例では、累積劣化情報の修正機能を機能構成の観点から説明したが、言うまでもなく、同等の機能をハードウェアとしてもソフトウェアとしても実現できる。
また、これらの処理機能の全てをハードウェア又はソフトウェアで実現するだけでなく、その一部はハードウェア又はソフトウェアを用いて実現しても良い。すなわち、ハードウェアとソフトウェアの組み合わせ構成としても良い。
(i)前述の形態例には、発明の趣旨の範囲内で様々な変形例が考えられる。また、本明細書の記載に基づいて創作される又は組み合わせられる各種の変形例及び応用例も考えられる。
(H) In the above-described embodiment, the function for correcting the accumulated deterioration information has been described from the viewpoint of the functional configuration. Needless to say, an equivalent function can be realized as hardware or software.
Further, not only all of these processing functions are realized by hardware or software, but some of them may be realized by using hardware or software. That is, a combination of hardware and software may be used.
(I) Various modifications can be considered for the above-described embodiments within the scope of the gist of the invention. Various modifications and applications created or combined based on the description of the present specification are also conceivable.
15 入力表示データ補正部
17 見積もり劣化量修正部
155 修正前累積劣化量差蓄積部
157 修正後累積劣化量差蓄積部
175 実劣化量測定部
177 見積もり精度修正部
15 Input Display
Claims (5)
輝度劣化の測定タイミングに、各ダミー画素の発光輝度を検出する輝度検出センサーと、
測定タイミング以外は、有効表示領域内で任意に選択されたサンプル画素に対応する階調値と全画素の平均階調値とをそれぞれ対応するダミー画素に与える一方で、測定タイミングには測定用の階調値を前記複数個のダミー画素全てに与えるダミー画素データ決定部と、
前記輝度検出センサーにより検出された検出輝度に基づいて、各ダミー画素の累積劣化情報を測定する実劣化情報測定部と、
前記複数個のサンプル画素について算出された累積劣化情報の見積もり値と、これらに対応する累積劣化情報の実測値に基づいて各サンプル画素に対応する修正倍率を求めるサンプル画素別修正倍率算出部と、
前記複数個のサンプル画素について算出された累積劣化情報の見積もり値を大きさ順に並べた際に隣接する2つのサンプル画素に対応する各修正倍率の平均値を、対応する見積もり範囲に対する修正値に決定する見積もり範囲別修正値決定部と、
前記修正値による修正済みの累積劣化情報に基づいて、各画素に対応する補正量を決定する補正量決定部と、
決定された補正量に基づいて、有効表示領域に対応する入力階調値を補正する映像信号補正部と
を有することを特徴とする自発光表示装置。 A display panel in which a plurality of dummy pixels are arranged outside the effective display area;
A luminance detection sensor that detects the emission luminance of each dummy pixel at the measurement timing of luminance degradation;
Other than the measurement timing, the gradation value corresponding to the sample pixel arbitrarily selected in the effective display area and the average gradation value of all the pixels are given to the corresponding dummy pixels, while the measurement timing is used for measurement. A dummy pixel data determining unit that gives a gradation value to all of the plurality of dummy pixels;
An actual deterioration information measuring unit that measures cumulative deterioration information of each dummy pixel based on the detected luminance detected by the luminance detection sensor;
An estimated value of cumulative deterioration information calculated for the plurality of sample pixels, and a correction magnification calculation unit for each sample pixel that calculates a correction magnification corresponding to each sample pixel based on an actual measurement value of the cumulative deterioration information corresponding to these,
When the estimated values of the accumulated deterioration information calculated for the plurality of sample pixels are arranged in order of magnitude, the average value of each correction magnification corresponding to two adjacent sample pixels is determined as a correction value for the corresponding estimated range. A correction value determining unit for each estimated range to be
A correction amount determination unit that determines a correction amount corresponding to each pixel based on the cumulative deterioration information corrected by the correction value;
A self-luminous display device, comprising: a video signal correction unit that corrects an input gradation value corresponding to an effective display area based on the determined correction amount.
測定タイミング以外は、有効表示領域内で任意に選択されたサンプル画素に対応する階調値と全画素の平均階調値とをそれぞれ対応するダミー画素に与える一方で、測定タイミングには測定用の階調値を前記複数個のダミー画素全てに与えるダミー画素データ決定部と、
前記輝度検出センサーにより検出された検出輝度に基づいて、各ダミー画素の累積劣化情報を測定する実劣化情報測定部と、
前記複数個のサンプル画素について算出された累積劣化情報の見積もり値と、これらに対応する累積劣化情報の実測値に基づいて各サンプル画素に対応する修正倍率を求めるサンプル画素別修正倍率算出部と、
前記複数個のサンプル画素について算出された累積劣化情報の見積もり値を大きさ順に並べた際に隣接する2つのサンプル画素に対応する各修正倍率の平均値を、対応する見積もり範囲に対する修正値に決定する見積もり範囲別修正値決定部と
を有することを特徴とする見積もり劣化情報修正装置。 An apparatus for correcting an estimated value of cumulative deterioration information calculated for each pixel based on input display data,
Other than the measurement timing, the gradation value corresponding to the sample pixel arbitrarily selected in the effective display area and the average gradation value of all the pixels are given to the corresponding dummy pixels, while the measurement timing is used for measurement. A dummy pixel data determining unit that gives a gradation value to all of the plurality of dummy pixels;
An actual deterioration information measuring unit that measures cumulative deterioration information of each dummy pixel based on the detected luminance detected by the luminance detection sensor;
An estimated value of cumulative deterioration information calculated for the plurality of sample pixels, and a correction magnification calculation unit for each sample pixel that calculates a correction magnification corresponding to each sample pixel based on an actual measurement value of the cumulative deterioration information corresponding to these,
When the estimated values of the accumulated deterioration information calculated for the plurality of sample pixels are arranged in order of magnitude, the average value of each correction magnification corresponding to two adjacent sample pixels is determined as a correction value for the corresponding estimated range. An estimated deterioration information correcting device comprising: a correction value determining unit for each estimated range.
測定タイミング以外は、有効表示領域内で任意に選択されたサンプル画素に対応する階調値と全画素の平均階調値とをそれぞれ対応するダミー画素に与える一方で、測定タイミングには測定用の階調値を前記複数個のダミー画素全てに与えるダミー画素データ決定部と、
前記輝度検出センサーにより検出された検出輝度に基づいて、各ダミー画素の累積劣化情報を測定する実劣化情報測定部と、
前記複数個のサンプル画素について算出された累積劣化情報の見積もり値と、これらに対応する累積劣化情報の実測値に基づいて各サンプル画素に対応する修正倍率を求めるサンプル画素別修正倍率算出部と、
前記複数個のサンプル画素について算出された累積劣化情報の見積もり値を大きさ順に並べた際に隣接する2つのサンプル画素に対応する各修正倍率の平均値を、対応する見積もり範囲に対する修正値に決定する見積もり範囲別修正値決定部と、
前記修正値による修正済みの累積劣化情報に基づいて、各画素に対応する補正量を決定する補正量決定部と、
決定された補正量に基づいて、有効表示領域に対応する入力階調値を補正する映像信号補正部と
を有することを特徴とする入力表示データ補正装置。 A device for correcting input display data input to a display panel in which a plurality of dummy pixels and corresponding luminance detection sensors are arranged outside an effective display area,
Other than the measurement timing, the gradation value corresponding to the sample pixel arbitrarily selected in the effective display area and the average gradation value of all the pixels are given to the corresponding dummy pixels, while the measurement timing is used for measurement. A dummy pixel data determining unit that gives a gradation value to all of the plurality of dummy pixels;
An actual deterioration information measuring unit that measures cumulative deterioration information of each dummy pixel based on the detected luminance detected by the luminance detection sensor;
An estimated value of cumulative deterioration information calculated for the plurality of sample pixels, and a correction magnification calculation unit for each sample pixel that calculates a correction magnification corresponding to each sample pixel based on an actual measurement value of the cumulative deterioration information corresponding to these,
When the estimated values of the accumulated deterioration information calculated for the plurality of sample pixels are arranged in order of magnitude, the average value of each correction magnification corresponding to two adjacent sample pixels is determined as a correction value for the corresponding estimated range. A correction value determining unit for each estimated range to be
A correction amount determination unit that determines a correction amount corresponding to each pixel based on the cumulative deterioration information corrected by the correction value;
An input display data correction device comprising: a video signal correction unit that corrects an input gradation value corresponding to an effective display area based on the determined correction amount.
測定タイミング以外は、有効表示領域内で任意に選択されたサンプル画素に対応する階調値と全画素の平均階調値とをそれぞれ対応するダミー画素に与える一方で、測定タイミングには測定用の階調値を前記複数個のダミー画素全てに与えるダミー画素データ決定処理と、
前記輝度検出センサーにより検出された検出輝度に基づいて、各ダミー画素の累積劣化情報を測定する実劣化量測定処理と、
前記複数個のサンプル画素について算出された累積劣化情報の見積もり値と、これらに対応する累積劣化情報の実測値に基づいて各サンプル画素に対応する修正倍率を求めるサンプル画素別修正倍率算出処理と、
前記複数個のサンプル画素について算出された累積劣化情報の見積もり値を大きさ順に並べた際に隣接する2つのサンプル画素に対応する各修正倍率の平均値を、対応する見積もり範囲に対する修正値に決定する見積もり範囲別修正値決定処理と
をコンピュータに実行させるコンピュータプログラム。 A computer program for correcting an estimated value of section deterioration amount information calculated based on input display data,
Other than the measurement timing, the gradation value corresponding to the sample pixel arbitrarily selected in the effective display area and the average gradation value of all the pixels are given to the corresponding dummy pixels, while the measurement timing is used for measurement. Dummy pixel data determination processing for giving a gradation value to all the plurality of dummy pixels;
Based on the detected luminance detected by the luminance detection sensor, an actual deterioration amount measurement process for measuring cumulative deterioration information of each dummy pixel;
An estimated value of cumulative deterioration information calculated for the plurality of sample pixels, and a correction magnification calculation process for each sample pixel for obtaining a correction magnification corresponding to each sample pixel based on an actual measurement value of the cumulative deterioration information corresponding to these,
When the estimated values of the accumulated deterioration information calculated for the plurality of sample pixels are arranged in order of magnitude, the average value of each correction magnification corresponding to two adjacent sample pixels is determined as a correction value for the corresponding estimated range. A computer program that causes a computer to execute correction value determination processing for each estimated range.
測定タイミング以外は、有効表示領域内で任意に選択されたサンプル画素に対応する階調値と全画素の平均階調値とをそれぞれ対応するダミー画素に与える一方で、測定タイミングには測定用の階調値を前記複数個のダミー画素全てに与えるダミー画素データ決定処理と、
前記輝度検出センサーにより検出された検出輝度に基づいて、各ダミー画素の累積劣化情報を測定する実劣化量測定処理と、
前記複数個のサンプル画素について算出された累積劣化情報の見積もり値と、これらに対応する累積劣化情報の実測値に基づいて各サンプル画素に対応する修正倍率を求めるサンプル画素別修正倍率算出処理と、
前記複数個のサンプル画素について算出された累積劣化情報の見積もり値を大きさ順に並べた際に隣接する2つのサンプル画素に対応する各修正倍率の平均値を、対応する見積もり範囲に対する修正値に決定する見積もり範囲別修正値決定処理と、
前記修正値による修正済みの累積劣化情報に基づいて、各画素に対応する補正量を決定する補正量決定処理と、
決定された補正量に基づいて、有効表示領域に対応する入力階調値を補正する映像信号補正処理と
をコンピュータに実行させるコンピュータプログラム。
A computer program for correcting an estimated value of section deterioration amount information calculated based on input display data,
Other than the measurement timing, the gradation value corresponding to the sample pixel arbitrarily selected in the effective display area and the average gradation value of all the pixels are given to the corresponding dummy pixels, while the measurement timing is used for measurement. Dummy pixel data determination processing for giving a gradation value to all the plurality of dummy pixels;
Based on the detected luminance detected by the luminance detection sensor, an actual deterioration amount measurement process for measuring cumulative deterioration information of each dummy pixel;
An estimated value of cumulative deterioration information calculated for the plurality of sample pixels, and a correction magnification calculation process for each sample pixel for obtaining a correction magnification corresponding to each sample pixel based on an actual measurement value of the cumulative deterioration information corresponding to these,
When the estimated values of the accumulated deterioration information calculated for the plurality of sample pixels are arranged in order of magnitude, the average value of each correction magnification corresponding to two adjacent sample pixels is determined as a correction value for the corresponding estimated range. Correction value determination processing for each estimated range to be performed,
A correction amount determination process for determining a correction amount corresponding to each pixel based on the cumulative deterioration information corrected by the correction value;
A computer program for causing a computer to execute a video signal correction process for correcting an input gradation value corresponding to an effective display area based on a determined correction amount.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006026419A JP2007206464A (en) | 2006-02-02 | 2006-02-02 | Spontaneous display device, estimation degradation information correction device, input display data compensation device, and program |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006026419A JP2007206464A (en) | 2006-02-02 | 2006-02-02 | Spontaneous display device, estimation degradation information correction device, input display data compensation device, and program |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2007206464A true JP2007206464A (en) | 2007-08-16 |
| JP2007206464A5 JP2007206464A5 (en) | 2009-01-29 |
Family
ID=38485983
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006026419A Pending JP2007206464A (en) | 2006-02-02 | 2006-02-02 | Spontaneous display device, estimation degradation information correction device, input display data compensation device, and program |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2007206464A (en) |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011065048A (en) * | 2009-09-18 | 2011-03-31 | Sony Corp | Display device |
| JP2011221305A (en) * | 2010-04-09 | 2011-11-04 | Sony Corp | Image display device and image display method |
| US8902263B2 (en) | 2010-09-02 | 2014-12-02 | Samsung Display Co., Ltd. | Display device and driving method thereof |
| KR20190050887A (en) * | 2017-11-03 | 2019-05-14 | 삼성디스플레이 주식회사 | Display device |
| US10803827B2 (en) | 2015-07-24 | 2020-10-13 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Display apparatus and display method |
| US11587505B2 (en) | 2017-11-02 | 2023-02-21 | Samsung Display Co., Ltd. | Display device |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003330418A (en) * | 2002-05-14 | 2003-11-19 | Sony Corp | Display device and its driving method |
| JP2004146936A (en) * | 2002-10-22 | 2004-05-20 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Color display apparatus |
| JP2004234011A (en) * | 2003-01-31 | 2004-08-19 | Eastman Kodak Co | Organic light emitting diode (oled) display |
| JP2005017520A (en) * | 2003-06-24 | 2005-01-20 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | El color display device |
-
2006
- 2006-02-02 JP JP2006026419A patent/JP2007206464A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003330418A (en) * | 2002-05-14 | 2003-11-19 | Sony Corp | Display device and its driving method |
| JP2004146936A (en) * | 2002-10-22 | 2004-05-20 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Color display apparatus |
| JP2004234011A (en) * | 2003-01-31 | 2004-08-19 | Eastman Kodak Co | Organic light emitting diode (oled) display |
| JP2005017520A (en) * | 2003-06-24 | 2005-01-20 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | El color display device |
Cited By (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011065048A (en) * | 2009-09-18 | 2011-03-31 | Sony Corp | Display device |
| JP2011221305A (en) * | 2010-04-09 | 2011-11-04 | Sony Corp | Image display device and image display method |
| US8791931B2 (en) | 2010-04-09 | 2014-07-29 | Sony Corporation | Image display apparatus and image displaying method |
| US8902263B2 (en) | 2010-09-02 | 2014-12-02 | Samsung Display Co., Ltd. | Display device and driving method thereof |
| US10803827B2 (en) | 2015-07-24 | 2020-10-13 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Display apparatus and display method |
| US11587505B2 (en) | 2017-11-02 | 2023-02-21 | Samsung Display Co., Ltd. | Display device |
| US11900871B2 (en) | 2017-11-02 | 2024-02-13 | Samsung Display Co., Ltd. | Display device |
| KR20190050887A (en) * | 2017-11-03 | 2019-05-14 | 삼성디스플레이 주식회사 | Display device |
| KR102473211B1 (en) * | 2017-11-03 | 2022-12-05 | 삼성디스플레이 주식회사 | Display device |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5124939B2 (en) | Self-luminous display device, conversion table update device, and program | |
| JP5440340B2 (en) | Image display device and image display method | |
| TW201445537A (en) | Video image signal processing circuit, method for processing video image signal, and display device | |
| JP2007156044A (en) | Spontaneous light emission display device, gray scale value/deterioration rate conversion table update device, and program | |
| JP2005539252A (en) | Display device | |
| JP2011065048A (en) | Display device | |
| KR20100038394A (en) | Display device | |
| JP2011065047A (en) | Display device | |
| JP2007163712A (en) | Display panel, self-luminous display device, gradation value/degradation rate conversion table updating device, input display data correction device, and program | |
| JP4946062B2 (en) | Self-luminous display device, estimated deterioration information correction device, input display data correction device, and program | |
| JP2008176115A (en) | Display apparatus, control computation unit, and display driving method | |
| CN105225621B (en) | System and method for extracting correlation curve of organic light emitting device | |
| KR20080100124A (en) | Method for uneven light emission correction of organic el panel and display correction circuit of organic el panel | |
| JP2010048939A (en) | Display apparatus, display control apparatus, and display control method as well as program | |
| KR20100015772A (en) | Display correcting circuit for organic el panel, display correcting circuit and display device | |
| JP2007164003A (en) | Self-luminous display device, image processing device, lighting time length control device, and program | |
| JP2014013335A (en) | Display device and driving method of display panel | |
| JP2007206464A (en) | Spontaneous display device, estimation degradation information correction device, input display data compensation device, and program | |
| JP2007240803A (en) | Spontaneous light emission display device, black level correcting device and program | |
| US9001099B2 (en) | Image display and image display method | |
| JP4830495B2 (en) | Self-luminous display device, conversion table update device, and program | |
| CN110729214B (en) | Method for determining efficiency degradation of organic light emitting device and display system | |
| CN110710195B (en) | Image display apparatus and control method thereof | |
| JP2011082213A (en) | Display panel, module, and electronic apparatus | |
| JP2008145835A (en) | Self-luminous display apparatus, white balance adjustment circuit, and white balance adjustment method |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20081205 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20081205 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A821 Effective date: 20081219 |
|
| RD02 | Notification of acceptance of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7422 Effective date: 20081219 |
|
| RD04 | Notification of resignation of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7424 Effective date: 20081225 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20110830 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20111227 |