JP2007044121A - Medical image display method and apparatus - Google Patents
Medical image display method and apparatus Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2007044121A JP2007044121A JP2005229363A JP2005229363A JP2007044121A JP 2007044121 A JP2007044121 A JP 2007044121A JP 2005229363 A JP2005229363 A JP 2005229363A JP 2005229363 A JP2005229363 A JP 2005229363A JP 2007044121 A JP2007044121 A JP 2007044121A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- image
- images
- cpr
- displaying
- display
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 19
- 210000000056 organ Anatomy 0.000 claims abstract description 36
- 238000002059 diagnostic imaging Methods 0.000 claims abstract 3
- 239000003550 marker Substances 0.000 claims description 8
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 abstract description 4
- 238000003745 diagnosis Methods 0.000 abstract description 3
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 abstract description 3
- 238000009877 rendering Methods 0.000 description 14
- 208000031481 Pathologic Constriction Diseases 0.000 description 7
- 208000037804 stenosis Diseases 0.000 description 7
- 230000036262 stenosis Effects 0.000 description 7
- 238000000605 extraction Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000003086 colorant Substances 0.000 description 3
- 210000004351 coronary vessel Anatomy 0.000 description 3
- 239000000284 extract Substances 0.000 description 3
- 210000004204 blood vessel Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 210000000621 bronchi Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 2
- 210000001035 gastrointestinal tract Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 239000004973 liquid crystal related substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000003325 tomography Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Apparatus For Radiation Diagnosis (AREA)
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging Apparatus (AREA)
- Measuring And Recording Apparatus For Diagnosis (AREA)
- Ultra Sonic Daignosis Equipment (AREA)
- Image Processing (AREA)
- Image Analysis (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明はX線CT装置、MRI装置、超音波装置を含む医用画像診断装置から得られた医用画像を用いた医用画像表示装置およびその方法に係り、注目する管腔臓器について複数の表示法を用いて作成した複数画像を同時表示する場合において、それら複数画像における解剖学的位置関係や、診断に有用な量の計測結果を理解することが可能な技術に関するものである。 The present invention relates to a medical image display apparatus using a medical image obtained from a medical image diagnostic apparatus including an X-ray CT apparatus, an MRI apparatus, and an ultrasonic apparatus, and a method thereof. The present invention relates to a technique capable of understanding the anatomical positional relationship in a plurality of images and the measurement result of an amount useful for diagnosis when simultaneously displaying a plurality of images created by using the images.
血管や気管支、腸管などの管腔臓器を観察、診断する場合、例えば(特許文献1)に記載されているように、観察対象をその対象に沿った曲面で縦切りにした画像(Curved Planar Reconstruction, 以下「CPR像」と呼ぶ)や、前記CPR像を管腔臓器の走行方向に沿って伸展した画像(以下、「展開CPR像」と呼ぶ)で表示する方法がある。
CPR像や展開CPR像とボリュームレンダリング3D画像やサーフェイスレンダリング3D画像などを並べて同時に表示することにより、より多観点からの観察が可能となるが、単純に複数画像を並べて表示するだけでは、操作者の少ない操作で同時表示した画像間において、解剖学的位置が同一の位置を認識したり、管腔臓器の断面積や直径、曲率、狭窄率、管腔臓器内2点間の距離を理解したりすることが困難であった。
本発明は、複数画像間の解剖学的位置関係や、各部位において診断に有用な量の測定結果を表示することを目的としている。
By displaying a CPR image, a developed CPR image, a volume rendering 3D image, a surface rendering 3D image, and the like side by side, it is possible to observe from more perspectives. Recognize the same anatomical position between images displayed simultaneously with few operations, and understand the cross-sectional area, diameter, curvature, stenosis, and distance between two points in the luminal organ. It was difficult to do.
An object of the present invention is to display an anatomical positional relationship between a plurality of images and an amount of measurement results useful for diagnosis at each site.
本発明の医用画像表示方法は、医用画像撮影装置により撮影された画像中の観察対象となる管腔臓器について、その管腔臓器の走行方向に沿って切断した断面像、及び管腔臓器とその周辺臓器の3D画像を含む画像を複数種類作成するステップと、前記作成された画像について所定の標識を設定するステップと、前記設定された標識を前期画像と共に表示するための標識情報を生成するステップと、前記生成された標識情報と前記作成された画像のうちの少なくとも一つとを同時表示するステップとを含む。 The medical image display method of the present invention includes a cross-sectional image cut along a traveling direction of a luminal organ, a luminal organ, and the luminal organ, and the luminal organ, as observed in the image taken by the medical image photographing device Creating a plurality of types of images including 3D images of peripheral organs, setting a predetermined marker for the generated image, and generating marker information for displaying the set marker together with the previous image And simultaneously displaying the generated sign information and at least one of the created images.
また、本発明の医用画像表示装置は、医用画像撮影装置により撮影された画像中の観察対象となる管腔臓器について、その管腔臓器の走行方向に沿って切断した断面像、及び管腔臓器とその周辺臓器の3D画像を含む画像を複数種類作成する手段と、前記作成された画像について所定の標識を設定する手段と、前記設定された標識を前期画像と共に表示するための標識情報を生成する手段と、前記生成された標識情報と前記作成された画像のうちの少なくとも一つとを同時表示する手段とを備える。 In addition, the medical image display device of the present invention is a cross-sectional image of a luminal organ to be observed in an image photographed by a medical image photographing device, cut along the traveling direction of the luminal organ, and a luminal organ. Means for creating a plurality of types of images including 3D images of the surrounding organs, means for setting predetermined markers for the created images, and generating marker information for displaying the set markers together with the previous image And means for simultaneously displaying the generated sign information and at least one of the created images.
本発明により、操作者の煩雑な操作を伴うことなく、複数種類の観察対象管腔臓器画像を表示し、それらの画像間の解剖学的位置関係を表示することができる。 According to the present invention, it is possible to display a plurality of types of observation target luminal organ images and display the anatomical positional relationship between these images without complicated operations by the operator.
本発明について図面を用いて説明する。図1に本発明による医用画像表示装置の一例を示す。 The present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. FIG. 1 shows an example of a medical image display device according to the present invention.
医用画像表示装置は、各種表示法による画像作成や各特徴量計測演算を行うCPU10、医用断層画像撮影装置11により撮影された医用断層画像をLAN12などのネットワークを介して受け取り記憶する磁気ディスク13、各種演算時に医用断層画像データや演算の途中経過を記憶する主メモリ14、操作者が領域抽出にパラメータなどを入力するためのコントローラ15につながれたマウス16やキーボード17、そして各種画像表示に用いる表示メモリ18と液晶ディスプレイやCRTなどのディスプレイ装置19からなる。
The medical image display device is a
図2は図1の主要部を抜粋したブロック図であり、図3は図2の制御装置20の詳細である。
本医用画像表示装置の主要部は入力装置21、記憶装置22、表示装置23と接続された制御装置20からなる。制御装置20は入力装置21および記憶装置22に接続された画像作成部30、特徴量計測部31、標識作成部32からなる。以下に各実施形態について図を用いて説明する。図4に各実施形態に共通なグラフィカルユーザインターフェース(以下GUI)の一例を示す。ここでは、冠状動脈を観察対象臓器とする場合を例にとり説明する。
FIG. 2 is a block diagram excerpting the main part of FIG. 1, and FIG. 3 shows details of the
The main part of the medical image display device is composed of a
[第1の実施形態]
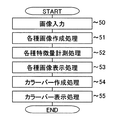
本発明の第1の実施形態について説明する。図5に第1実施形態の処理フローの一例を示す。図5の各ステップについて以下に説明する。
[First embodiment]
A first embodiment of the present invention will be described. FIG. 5 shows an example of the processing flow of the first embodiment. Each step in FIG. 5 will be described below.
(ステップ50)
操作者はマウス16を操作して図4のGUI40上の画像読込ボタン41を押し、観察対象となる管腔臓器を撮影した医用断層画像群を入力する。
(Step 50)
The operator operates the
(ステップ51)
CPU10は、例えば特願2003-313424に記載された管腔臓器領域抽出法を用いて、前記入力された画像から、観察対象となる管腔臓器領域の中心を通る曲線(以下、「芯線」と呼ぶ)を抽出する。さらに抽出した芯線を用いて、(特許文献1)に記載された方法により、前記抽出した芯線に沿った曲面で縦切にした断面像(Curved Planar Reconstruction, 以下「CPR像」と呼ぶ)や、前記CPR像を芯線の方向に伸展した画像(以下、「展開CPR像」と呼ぶ)、ボリュームレンダリング法やサーフェイスレンダリング法を用いた3D画像、前記芯線上の任意の位置で芯線に直交する断面で切断した切断像(Multi Planar Reconstruction、以下「MPR像」と呼ぶ)や前記芯線上の任意の位置での仮想内視鏡像を作成する。ここで、ボリュームレンダリング3D像を作成するか、サーフェイスレンダリング3D像を作成するかなどの条件は、操作者がマウス16などの入力装置を用いて、GUI40上のチェックボックス42を操作することで任意に設定できるようにしてもよい。
(Step 51)
The
(ステップ52)
CPU10は、前記抽出した芯線上に、GUI40上のコンボボックス43内に表示される距離間隔で点をとり、各点上でコンボボックス44内に表示される量を計測する。操作者がマウス16やキーボード17などの入力装置を用いてコンボボックス43を操作することにより、各量を計測する間隔を例えば、5mm間隔、10mm間隔、20mm間隔などと任意に変更できるようにしてもよい。また、操作者がマウス16やキーボード17などの入力装置を用いてコンボボックス44を操作することにより、計測対象となる量を、断面積、直径、曲率、狭窄率など任意に変更できるようにしてもよい。
(Step 52)
The
(ステップ53)
CPU10はステップ51において作成した、CPR像、展開CPR像、3D像、MPR像、仮想内視鏡像などを、それぞれ、GUI40上のCPR像表示領域45、展開CPR像表示領域46、3D像表示領域47、MPR像表示領域48、仮想内視鏡像表示領域49へ表示する。表示された画像はそれぞれ、操作者がマウス16やキーボード17などの入力装置を用いて、CPR、MPR用ウィンドウレベル/幅設定スクロールバー4Aや3D用ウィンドウレベル/幅設定スクロールバー4B、3D用閾値、オパシティ設定エディット4Cを設定することにより、任意に表示階調等を変更することが可能である。また、表示角度設定スクロールバー4D,4Eを操作することによりCPR像および展開CPR像の表示角度を変更して表示することが可能である。また、3D像表示領域47上や仮想内視鏡像表示領域49上でマウスをドラッグすることにより、表示する3D像や仮想内視鏡の方向を回転させることができるようにしてもよい。
(Step 53)
The
(ステップ54)
CPU10はステップ52において計測した量を元にカラーバーを作成する。具体的にはカラーバーの色、長さ、表示位置、表示する方向などを決定する。ここで、カラーバーとは図6に示すように、3D像60、CPR像61、展開CPR像62上にそれぞれ表示される色つきの線分のことであり、図6中では実線、点線、破線などの線分として表現している(線分63,64,65など)。カラーバーの色は展開CPR像62上に示すように場所ごとに異なる色を採用し、3D像60、CPR像61、展開CPR像62とで解剖学的に同一の位置には同一の色を使用することにする。また、カラーバーを表示する間隔はステップ52で設定した5mm,10mm,20mmなどの間隔とする。カラーバーの長さはステップ52で計測した、断面積や直径、曲率、狭窄率の大きさに応じて決定する。カラーバーの向きは芯線に直交する方向とし、この方向に切断したMPR像をMPR像表示領域48に表示するようにしてもよい。
(Step 54)
The
(ステップ55)
CPU10はステップ54において設定した情報を反映したカラーバーを、CPR像、展開CPR像、3D像上にそれぞれ表示する。
操作者がマウス16などの入力装置を用いてGUI40上のバー表示ON/OFF切り替えラジオグループ4Fを操作して、任意にカラーバーの表示/非表示を切り替えられるようにしてもよい。
操作者がマウス16を3D像の回転表示やCPR像、展開CPR像の表示角度の変更などを行うことにより、表示されているカラーバーも相対的に移動するようにしてもよい。
カラーバーの隣に画像の上端側から順に番号を付加して表示するようにしてもよい。また測定した断面積や直径などの量に応じて表示する数値の見た目の大きさを変化させるようにしてもよい。
色の異なる複数のカラーバーを表示する替わりに、間隔の異なる複数の破線や、山の数の異なる複数の波線を表示することにより、解剖学的位置情報を得るようにしてもよい。
(Step 55)
The
The operator may arbitrarily switch the display / non-display of the color bar by operating the bar display ON / OFF switching
The displayed color bar may be moved relatively by the operator performing a rotation display of the 3D image, a change of the display angle of the CPR image, and the developed CPR image by the operator.
You may make it display by adding a number in order from the upper end side of an image next to a color bar. Moreover, you may make it change the magnitude | size of the appearance of the numerical value displayed according to quantities, such as measured cross-sectional area and a diameter.
Instead of displaying a plurality of color bars having different colors, anatomical position information may be obtained by displaying a plurality of broken lines having different intervals or a plurality of wavy lines having different numbers of peaks.
[第2の実施形態]
本発明の第2の実施形態を説明する。図7に第2の実施形態の、処理フローの一例を示す。
各ステップについて以下に説明する。
[Second Embodiment]
A second embodiment of the present invention will be described. FIG. 7 shows an example of the processing flow of the second embodiment.
Each step will be described below.
(ステップ70)
操作者はマウス16を操作して図4のGUI40上の画像読込ボタン41を押し、観察対象となる管腔臓器を撮影した医用断層画像群を入力する。
(Step 70)
The operator operates the
(ステップ71)
CPU10は、例えば特願2003-313424号に記載された管腔臓器領域抽出法を用いて、前記入力された画像から、観察対象となる管腔臓器領域の芯線を抽出する。さらに抽出した芯線を用いて、[特許文献1]に記載された方法により、前記抽出した芯線に沿った曲面で縦切にしたCPR像や、前記CPR像を芯線の方向に伸展した展開CPR像、ボリュームレンダリング法やサーフェイスレンダリング法を用いた3D画像、前記芯線上の任意の位置で芯線に直交する断面で切断したMPR像や前記芯線上の任意の位置での仮想内視鏡像を作成する。ここで、ボリュームレンダリング3D像を作成するか、サーフェイスレンダリング3D像を作成するかなどの条件は、操作者がマウス16などの入力装置を用いて、GUI40上のチェックボックス42を操作することで任意に設定できるようにしてもよい。
(Step 71)
The
(ステップ72)
CPU10は、前記抽出した芯線上に、GUI40上のコンボボックス43内に表示される距離間隔で点をとり、各点上でコンボボックス44内に表示される量を計測する。操作者がマウス16やキーボード17などの入力装置を用いてコンボボックス43を操作することにより、各量を計測する間隔を例えば、5mm間隔、10mm間隔、20mm間隔などと任意に変更できるようにしてもよい。また、操作者がマウス16やキーボード17などの入力装置を用いてコンボボックス44を操作することにより、計測対象となる量を、断面積、直径、曲率、狭窄率など任意に変更できるようにしてもよい。
(Step 72)
The
(ステップ73)
CPU10はステップ71において作成した、CPR像、展開CPR像、3D像、MPR像、仮想内視鏡像などを、それぞれ、GUI40上のCPR像表示領域45、展開CPR像表示領域46、3D像表示領域47、MPR像表示領域48、仮想内視鏡像表示領域49へ表示する。表示された画像はそれぞれ、操作者がマウス16やキーボード17などの入力装置を用いて、CPR、MPR用ウィンドウレベル/幅設定スクロールバー4Aや3D用ウィンドウレベル/幅設定スクロールバー4B、3D用閾値、オパシティ設定エディット4Cを設定することにより、任意に表示階調等を変更することが可能である。また、表示角度設定スクロールバー4D,4Eを操作することによりCPR像および展開CPR像の表示角度を変更して表示することが可能である。また、3D像表示領域47上や仮想内視鏡像表示領域49上でマウスをドラッグすることにより、表示する3D像や仮想内視鏡の方向を回転させることができるようにしてもよい。
(Step 73)
The
(ステップ74)
CPU10はステップ72において計測した量を元にカラーバーを作成する。具体的にはカラーバーの色、長さ、表示位置、表示する方向などを決定する。ここで、カラーバーとは図6に示すように、3D像60、CPR像61、展開CPR像62上にそれぞれ表示される色つきの線分のことであり、図6中では実線、点線、破線などの線分として表現している(線分63,64,65など)。カラーバーの色は展開CPR像62上に示すように場所ごとに異なる色を採用し、3D像60、CPR像61、展開CPR像62とで解剖学的に同一の位置には同一の色を使用することにする。また、カラーバーを表示する間隔はステップ72で設定した5mm、10mm、20mmなどの間隔とする。カラーバーの長さはステップ72で計測した、断面積や直径、曲率、狭窄率の大きさに応じて決定する。カラーバーの向きは芯線に直交する方向とし、この方向に切断したMPR像をMPR像表示領域48に表示するようにしてもよい。
(Step 74)
The
(ステップ75)
CPU10はステップ74において設定した情報を反映したカラーバーを、CPR像、展開CPR像、3D像上にそれぞれ表示する。
(ステップ76)
操作者はマウス16などの入力装置を用いてCPR像表示領域45、展開CPR像表示領域46、3D像表示領域47に表示されているカラーバーのうち任意の1つを選択する。
(Step 75)
The
(Step 76)
The operator uses the input device such as the
(ステップ77)
CPR10は前記選択されたカラーバーの解剖学的位置におけるMPR像や仮想内視鏡像を作成し、MPR像表示領域48、仮想内視鏡像表示領域49に表示する。さらにCPR像、展開CPR像、3D像について、選択された位置周辺の領域での拡大CPR像、拡大展開CPR像、拡大3D像を作成する。もちろん、MPR像や仮想内視鏡像について拡大してもよい。どの程度の周辺領域まで拡大するかは、あらかじめ設定しておいてもよいし、また操作者が任意に選択できるようにしてもよい。拡大の方向は等方的でなく上下方向や左右方向など一定方向にのみ拡大すうようにしてもよい。
(Step 77)
The
(ステップ78)
ステップ77において拡大されたCPR像、展開CPR像、3D像、MPR像、仮想内視鏡像などをそれぞれ、CPR像表示領域45、展開CPR像表示領域46、3D像表示領域47、MPR像表示領域48、仮想内視鏡像表示領域49に表示する。
(Step 78)
The enlarged CPR image, developed CPR image, 3D image, MPR image, virtual endoscopic image, etc. in
操作者がマウス16などの入力装置を用いてGUI40上のバー表示ON/OFF切り替えラジオグループ4Fを操作して、任意にカラーバーの表示/非表示を切り替えられるようにしてもよい。
操作者がマウス16を3D像の回転表示やCPR像、展開CPR像の表示角度の変更などを行うことにより、表示されているカラーバーも相対的に移動するようにしてもよい。
カラーバーの隣に画像の上端側から順に番号を付加して表示するようにしてもよい。また測定した断面積や直径などの量に応じて表示する数値の見た目の大きさを変化させるようにしてもよい。
色の異なる複数のカラーバーを表示する替わりに、間隔の異なる複数の破線や、山の数の異なる複数の波線を表示することにより、解剖学的位置情報を得るようにしてもよい。
The operator may arbitrarily switch the display / non-display of the color bar by operating the bar display ON / OFF switching
The displayed color bar may be moved relatively by the operator performing a rotation display of the 3D image, a change of the display angle of the CPR image, and the developed CPR image by the operator.
You may make it display by adding a number in order from the upper end side of an image next to a color bar. Moreover, you may make it change the magnitude | size of the appearance of the numerical value displayed according to quantities, such as measured cross-sectional area and a diameter.
Instead of displaying a plurality of color bars having different colors, anatomical position information may be obtained by displaying a plurality of broken lines having different intervals or a plurality of wavy lines having different numbers of peaks.
[第3の実施形態]
本発明の第3の実施形態を説明する。図8に第3の実施形態の、処理フローの一例を示す。
各ステップについて以下に説明する。
(ステップ80)
操作者はマウス16を操作して図4のGUI40上の画像読込ボタン41を押し、観察対象となる管腔臓器を撮影した医用断層画像群を入力する。
[Third embodiment]
A third embodiment of the present invention will be described. FIG. 8 shows an example of the processing flow of the third embodiment.
Each step will be described below.
(Step 80)
The operator operates the
(ステップ81)
CPU10は、例えば特願2003-313424号に記載された管腔臓器領域抽出法を用いて、前記入力された画像から、観察対象となる管腔臓器領域の中心を通る芯線を抽出する。さらに抽出した芯線を用いて、特許文献1に記載された方法により、前記抽出した芯線に沿った曲面で縦切にしたCPR像や、前記CPR像を芯線の方向に伸展した展開CPR像、ボリュームレンダリング法やサーフェイスレンダリング法を用いた3D画像、前記芯線上の任意の位置で芯線に直交する断面で切断したMPR像や前記芯線上の任意の位置での仮想内視鏡像を作成する。ここで、ボリュームレンダリング3D像を作成するか、サーフェイスレンダリング3D像を作成するかなどの条件は、操作者がマウス16などの入力装置を用いて、GUI40上のチェックボックス42を操作することで任意に設定できるようにしてもよい。
(Step 81)
CPU10 extracts the core line which passes along the center of the luminal organ area | region used as an observation object from the said input image, for example using the luminal organ area | region extraction method described in Japanese Patent Application No. 2003-313424. Further, using the extracted core wire, by the method described in Patent Document 1, a CPR image obtained by longitudinally cutting the curved surface along the extracted core wire, a developed CPR image obtained by extending the CPR image in the direction of the core wire, a volume A 3D image using a rendering method or a surface rendering method, an MPR image cut at a cross section perpendicular to the core line at an arbitrary position on the core line, and a virtual endoscopic image at an arbitrary position on the core line are created. Here, conditions such as whether to create a volume rendering 3D image or a surface rendering 3D image can be arbitrarily set by the operator operating the
(ステップ82)
CPU10は、前記抽出した芯線上に、GUI40上のコンボボックス43内に表示される距離間隔で点をとり、各点上でコンボボックス44内に表示される量を計測する。操作者がマウス16やキーボード17などの入力装置を用いてコンボボックス43を操作することにより、各量を計測する間隔を例えば、5mm間隔、10mm間隔、20mm間隔などと任意に変更できるようにしてもよい。また、操作者がマウス16やキーボード17などの入力装置を用いてコンボボックス44を操作することにより、計測対象となる量を、断面積、直径、曲率、狭窄率など任意に変更できるようにしてもよい。
(Step 82)
The
(ステップ83)
CPU10はステップ81において作成した、CPR像、展開CPR像、3D像、MPR像、仮想内視鏡像などを、それぞれ、GUI40上のCPR像表示領域45、展開CPR像表示領域46、3D像表示領域47、MPR像表示領域48、仮想内視鏡像表示領域49へ表示する。表示された画像はそれぞれ、操作者がマウス16やキーボード17などの入力装置を用いて、CPR、MPR用ウィンドウレベル/幅設定スクロールバー4Aや3D用ウィンドウレベル/幅設定スクロールバー4B、3D用閾値、オパシティ設定エディット4Cを設定することにより、任意に表示階調等を変更することが可能である。また、表示角度設定スクロールバー4D,4Eを操作することによりCPR像および展開CPR像の表示角度を変更して表示することが可能である。また、3D像表示領域47上や仮想内視鏡像表示領域49上でマウスをドラッグすることにより、表示する3D像や仮想内視鏡の方向を回転させることができるようにしてもよい。
(Step 83)
The
(ステップ84)
CPU10はステップ82において計測した量を元にカラーバーを作成する。具体的にはカラーバーの色、長さ、表示位置、表示する方向などを決定する。ここで、カラーバーとは図6に示すように、3D像60、CPR像61、展開CPR像62上にそれぞれ表示される色つきの線分のことであり、図6中では実線、点線、破線などの線分として表現している(線分63,64,65など)。カラーバーの色は展開CPR像62上に示すように場所ごとに異なる色を採用し、3D像60、CPR像61、展開CPR像62とで解剖学的に同一の位置には同一の色を使用することにする。また、カラーバーを表示する間隔はステップ72で設定した5mm,10mm,20mmなどの間隔とする。カラーバーの長さはステップ82で計測した、断面積や直径、曲率、狭窄率の大きさに応じて決定する。カラーバーの向きは芯線に直交する方向とし、この方向に切断したMPR像をMPR像表示領域48に表示するようにしてもよい。
(Step 84)
The
(ステップ85)
CPU10はステップ84において設定した情報を反映したカラーバーを、CPR像、展開CPR像、3D像上にそれぞれ表示する。
(ステップ86)
操作者はマウス16などの入力装置を用いてCPR像表示領域45、展開CPR像表示領域46、3D像表示領域47に表示されているカラーバーのうち任意の1つを選択する。
(Step 85)
The
(Step 86)
The operator uses the input device such as the
(ステップ87)
CPU10は前記選択したカラーバーと同一色(解剖学的に同一位置)のカラーバーのうち展開CPR像上のカラーバー90(図9)を基準として、CPR像上のカラーバー91および3D像上のカラーバー92の表示位置(高さ)が展開CPR像上の表示位置と合うように、CPR像、3D像全体を平行移動した画像を作成する。
(Step 87)
The
(ステップ88)
ステップ87において作成されたCPR像、3D像をそれぞれ、CPR像表示領域45、展開CPR像表示領域46に表示する。
操作者がマウス16などの入力装置を用いてGUI40上のバー表示ON/OFF切り替えラジオグループ4Fを操作して、任意にカラーバーの表示/非表示を切り替えられるようにしてもよい。
操作者がマウス16を3D像の回転表示やCPR像、展開CPR像の表示角度の変更などを行うことにより、表示されているカラーバーも相対的に移動するようにしてもよい。
カラーバーの隣に画像の上端側から順に番号を付加して表示するようにしてもよい。また測定した断面積や直径などの量に応じて表示する数値の見た目の大きさを変化させるようにしてもよい。
色の異なる複数のカラーバーを表示する替わりに、間隔の異なる複数の破線や、山の数の異なる複数の波線を表示することにより、解剖学的位置情報を得るようにしてもよい。
(Step 88)
The CPR image and 3D image created in
The operator may arbitrarily switch the display / non-display of the color bar by operating the bar display ON / OFF switching
The displayed color bar may be moved relatively by the operator performing a rotation display of the 3D image, a change of the display angle of the CPR image, and the developed CPR image by the operator.
You may make it display by adding a number in order from the upper end side of an image next to a color bar. Moreover, you may make it change the magnitude | size of the appearance of the numerical value displayed according to quantities, such as measured cross-sectional area and a diameter.
Instead of displaying a plurality of color bars having different colors, anatomical position information may be obtained by displaying a plurality of broken lines having different intervals or a plurality of wavy lines having different numbers of peaks.
第1〜3の実施形態では、冠状動脈を観察対象とした場合を例にとり説明したが、冠状動脈以外でも、任意部位の血管、気管支、腸管など他の管腔臓器においても本発明が適用可能である。 In the first to third embodiments, the case where the coronary artery is an observation object has been described as an example. However, the present invention can be applied to other luminal organs such as blood vessels, bronchi, and intestinal tracts other than the coronary artery. It is.
10 CPU、 11 医用断層画像撮影装置、 12 LAN、 13 磁気ディスク、 14 主メモリ、 15 コントローラ、 16 マウス、 17 キーボード、 18 表示メモリ、19 ディスプレイ 10 CPU, 11 medical tomography system, 12 LAN, 13 magnetic disk, 14 main memory, 15 controller, 16 mouse, 17 keyboard, 18 display memory, 19 display
Claims (4)
その管腔臓器の走行方向に沿って切断した断面像、及び管腔臓器とその周辺臓器の3D画像を含む画像を複数種類作成するステップと、
前記作成された画像について所定の標識を設定するステップと、
前記設定された標識を前期画像と共に表示するための標識情報を生成するステップと、
前記生成された標識情報と前記作成された画像のうちの少なくとも一つとを同時表示するステップと
を含むことを特徴とする医用画像表示方法。 About the luminal organ to be observed in the image taken by the medical imaging device,
Creating a plurality of types of images including a cross-sectional image cut along the traveling direction of the luminal organ, and a 3D image of the luminal organ and surrounding organs;
Setting a predetermined sign for the created image;
Generating sign information for displaying the set sign together with the previous period image;
A medical image display method comprising: simultaneously displaying the generated marker information and at least one of the generated images.
複数表示されている画像中の任意の画像内で任意の標識を選択するステップと、
表示されている複数画像について選択された標識周辺の領域を同時に拡大表示するステップと
を備えたことを特徴とする医用画像表示方法。 The medical image display method according to claim 1, further comprising:
Selecting an arbitrary sign in an arbitrary image among the plurality of displayed images;
A method for displaying a medical image, comprising: simultaneously enlarging and displaying an area around a sign selected for a plurality of displayed images.
複数表示されている画像中の任意の画像内で任意の標識を選択するステップと、
表示されている複数画像において前記選択された標識と解剖学的に同一位置にある標識位置が表示領域中で同一の位置となるように、表示画像を平行移動するステップと
を備えたことを特徴とする医用画像表示方法。 The medical image display method according to claim 1, further comprising:
Selecting an arbitrary sign in an arbitrary image among the plurality of displayed images;
Translating the display image so that the marker position that is anatomically identical to the selected marker in the plurality of displayed images is the same position in the display region. And a medical image display method.
その管腔臓器の走行方向に沿って切断した断面像、及び管腔臓器とその周辺臓器の3D画像を含む画像を複数種類作成する手段と、
前記作成された画像について所定の標識を設定する手段と、
前記設定された標識を前期画像と共に表示するための標識情報を生成する手段と、
前記生成された標識情報と前記作成された画像のうちの少なくとも一つとを同時表示する手段と
を備えたことを特徴とする医用画像表示装置。 About the luminal organ to be observed in the image taken by the medical imaging device,
Means for creating a plurality of types of images including cross-sectional images cut along the traveling direction of the luminal organ, and 3D images of the luminal organ and surrounding organs;
Means for setting a predetermined sign for the created image;
Means for generating sign information for displaying the set sign together with the previous period image;
A medical image display device comprising: means for simultaneously displaying the generated marker information and at least one of the generated images.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005229363A JP2007044121A (en) | 2005-08-08 | 2005-08-08 | Medical image display method and apparatus |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005229363A JP2007044121A (en) | 2005-08-08 | 2005-08-08 | Medical image display method and apparatus |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2007044121A true JP2007044121A (en) | 2007-02-22 |
| JP2007044121A5 JP2007044121A5 (en) | 2008-09-25 |
Family
ID=37847511
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005229363A Pending JP2007044121A (en) | 2005-08-08 | 2005-08-08 | Medical image display method and apparatus |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2007044121A (en) |
Cited By (16)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008188116A (en) * | 2007-02-01 | 2008-08-21 | Toshiba It & Control Systems Corp | Mpr display device and computerized tomographic imaging apparatus |
| JP2008259712A (en) * | 2007-04-12 | 2008-10-30 | Fujifilm Corp | Image interpretation support apparatus, method, and program |
| JP2009022411A (en) * | 2007-07-18 | 2009-02-05 | Hitachi Medical Corp | Medical image processor |
| JP2009061028A (en) * | 2007-09-05 | 2009-03-26 | Nemoto Kyorindo:Kk | Image processing apparatus and medical workstation equipped with the same |
| JP2009082470A (en) * | 2007-09-28 | 2009-04-23 | Toshiba Corp | Image display and image display method |
| JP2010082269A (en) * | 2008-09-30 | 2010-04-15 | Toshiba Corp | Radiographing system |
| JP2010154944A (en) * | 2008-12-26 | 2010-07-15 | Toshiba Corp | Medical image diagnostic apparatus and fusion image generation method |
| JP2011030839A (en) * | 2009-08-03 | 2011-02-17 | Nagoya Univ | Medical image observation support device |
| JP2011055922A (en) * | 2009-09-08 | 2011-03-24 | Hitachi Medical Corp | Medical image display, medical image display method and program for performing the same |
| JP2011206155A (en) * | 2010-03-29 | 2011-10-20 | Fujifilm Corp | Diagnosis support system, diagnosis support program and diagnosis support method |
| JP2011212312A (en) * | 2010-03-31 | 2011-10-27 | Fujifilm Corp | Medical diagnostic imaging supporting system and method, and program |
| JP2012212376A (en) * | 2011-03-31 | 2012-11-01 | Fujifilm Corp | Electronic calibration system and electronic calibration method |
| JP2013000431A (en) * | 2011-06-20 | 2013-01-07 | Hitachi Medical Corp | Medical image processor and medical image processing method |
| JP2013027697A (en) * | 2011-06-23 | 2013-02-07 | Toshiba Corp | Medical image processor and medical image diagnostic apparatus |
| WO2013080527A1 (en) * | 2011-11-30 | 2013-06-06 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | Image processing device, method, and program |
| JP2014526927A (en) * | 2011-08-16 | 2014-10-09 | コーニンクレッカ フィリップス エヌ ヴェ | Curved multiplanar reconstruction using optical fiber shape data |
Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0765154A (en) * | 1993-08-31 | 1995-03-10 | Toshiba Corp | Device and method for quantitatively analyzing blood vessel image |
| JPH11318884A (en) * | 1998-03-09 | 1999-11-24 | Hitachi Medical Corp | Image display device |
| JP2003325512A (en) * | 2002-05-16 | 2003-11-18 | Aloka Co Ltd | Ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus |
| JP2004133736A (en) * | 2002-10-11 | 2004-04-30 | Hitachi Medical Corp | Medical image display method and device thereof |
| JP2004283373A (en) * | 2003-03-20 | 2004-10-14 | Toshiba Corp | Analyzer of luminal structure |
| WO2005011501A1 (en) * | 2003-08-01 | 2005-02-10 | Hitachi Medical Corporation | Medical image diagnosis support device and method |
| JP2005198708A (en) * | 2004-01-13 | 2005-07-28 | Toshiba Corp | Vasoconstriction rate analyzer and vasoconstriction rate analyzing method |
| JP2006167287A (en) * | 2004-12-17 | 2006-06-29 | Toshiba Corp | Hemadostenosis rate analysis system |
-
2005
- 2005-08-08 JP JP2005229363A patent/JP2007044121A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0765154A (en) * | 1993-08-31 | 1995-03-10 | Toshiba Corp | Device and method for quantitatively analyzing blood vessel image |
| JPH11318884A (en) * | 1998-03-09 | 1999-11-24 | Hitachi Medical Corp | Image display device |
| JP2003325512A (en) * | 2002-05-16 | 2003-11-18 | Aloka Co Ltd | Ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus |
| JP2004133736A (en) * | 2002-10-11 | 2004-04-30 | Hitachi Medical Corp | Medical image display method and device thereof |
| JP2004283373A (en) * | 2003-03-20 | 2004-10-14 | Toshiba Corp | Analyzer of luminal structure |
| WO2005011501A1 (en) * | 2003-08-01 | 2005-02-10 | Hitachi Medical Corporation | Medical image diagnosis support device and method |
| JP2005198708A (en) * | 2004-01-13 | 2005-07-28 | Toshiba Corp | Vasoconstriction rate analyzer and vasoconstriction rate analyzing method |
| JP2006167287A (en) * | 2004-12-17 | 2006-06-29 | Toshiba Corp | Hemadostenosis rate analysis system |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| 谷口拡樹、永尾朋洋、後藤良洋,林宏光、隈崎達夫: ""Curved Planar Reconstructionシステムの開発"", MEDICAL IMAGING TECHNOLOGY, vol. 第17巻、第4号、OS−49, JPN6010066882, 1 July 1999 (1999-07-01), JP, pages 473 - 474, ISSN: 0001782396 * |
Cited By (18)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008188116A (en) * | 2007-02-01 | 2008-08-21 | Toshiba It & Control Systems Corp | Mpr display device and computerized tomographic imaging apparatus |
| JP2008259712A (en) * | 2007-04-12 | 2008-10-30 | Fujifilm Corp | Image interpretation support apparatus, method, and program |
| JP2009022411A (en) * | 2007-07-18 | 2009-02-05 | Hitachi Medical Corp | Medical image processor |
| JP2009061028A (en) * | 2007-09-05 | 2009-03-26 | Nemoto Kyorindo:Kk | Image processing apparatus and medical workstation equipped with the same |
| JP2009082470A (en) * | 2007-09-28 | 2009-04-23 | Toshiba Corp | Image display and image display method |
| JP2010082269A (en) * | 2008-09-30 | 2010-04-15 | Toshiba Corp | Radiographing system |
| JP2010154944A (en) * | 2008-12-26 | 2010-07-15 | Toshiba Corp | Medical image diagnostic apparatus and fusion image generation method |
| JP2011030839A (en) * | 2009-08-03 | 2011-02-17 | Nagoya Univ | Medical image observation support device |
| JP2011055922A (en) * | 2009-09-08 | 2011-03-24 | Hitachi Medical Corp | Medical image display, medical image display method and program for performing the same |
| JP2011206155A (en) * | 2010-03-29 | 2011-10-20 | Fujifilm Corp | Diagnosis support system, diagnosis support program and diagnosis support method |
| JP2011212312A (en) * | 2010-03-31 | 2011-10-27 | Fujifilm Corp | Medical diagnostic imaging supporting system and method, and program |
| JP2012212376A (en) * | 2011-03-31 | 2012-11-01 | Fujifilm Corp | Electronic calibration system and electronic calibration method |
| JP2013000431A (en) * | 2011-06-20 | 2013-01-07 | Hitachi Medical Corp | Medical image processor and medical image processing method |
| JP2013027697A (en) * | 2011-06-23 | 2013-02-07 | Toshiba Corp | Medical image processor and medical image diagnostic apparatus |
| JP2014526927A (en) * | 2011-08-16 | 2014-10-09 | コーニンクレッカ フィリップス エヌ ヴェ | Curved multiplanar reconstruction using optical fiber shape data |
| US10575757B2 (en) | 2011-08-16 | 2020-03-03 | Koninklijke Philips N.V. | Curved multi-planar reconstruction using fiber optic shape data |
| WO2013080527A1 (en) * | 2011-11-30 | 2013-06-06 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | Image processing device, method, and program |
| US9530238B2 (en) | 2011-11-30 | 2016-12-27 | Fujifilm Corporation | Image processing apparatus, method and program utilizing an opacity curve for endoscopic images |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US10936090B2 (en) | Interactive 3D cursor for use in medical imaging | |
| JP4676021B2 (en) | Diagnosis support apparatus, diagnosis support program, and diagnosis support method | |
| US8994720B2 (en) | Diagnosis assisting apparatus, diagnosis assisting program, and diagnosis assisting method | |
| JP4958901B2 (en) | Medical image display system and medical image display program | |
| JP4845566B2 (en) | Image display device | |
| JP2007044121A (en) | Medical image display method and apparatus | |
| EP2737854A1 (en) | Cutting simulation device and cutting simulation program | |
| CN105956395A (en) | Medical image processing method, device and system | |
| JP5114121B2 (en) | Medical image processing device | |
| JP2008302090A (en) | Medical image display apparatus and program | |
| JP5454841B2 (en) | Medical image processing device | |
| JP4786307B2 (en) | Image processing device | |
| JP5380231B2 (en) | Medical image display apparatus and method, and program | |
| JP2006075216A (en) | Medical image processing system, program and method | |
| JP5305635B2 (en) | Medical image display device | |
| JP2008119252A (en) | Medical image generating apparatus, method, and program | |
| CN106028943A (en) | Ultrasonic virtual endoscopic imaging system and method, and apparatus thereof | |
| JP4686279B2 (en) | Medical diagnostic apparatus and diagnostic support apparatus | |
| JP2007021193A (en) | Image processing apparatus and program | |
| JP2001087228A (en) | Image reading support device | |
| JP5487339B2 (en) | Medical image processing device | |
| JP2009022307A (en) | Medical image display device and its program | |
| JP5472892B2 (en) | Three-dimensional medical image display device and display method thereof |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20080806 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20080806 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20101118 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20101124 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20110120 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20110523 |