JP2006195018A - Three dimensional display method, image generation side apparatus and image display side apparatus - Google Patents
Three dimensional display method, image generation side apparatus and image display side apparatus Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2006195018A JP2006195018A JP2005004637A JP2005004637A JP2006195018A JP 2006195018 A JP2006195018 A JP 2006195018A JP 2005004637 A JP2005004637 A JP 2005004637A JP 2005004637 A JP2005004637 A JP 2005004637A JP 2006195018 A JP2006195018 A JP 2006195018A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- image
- dimensional
- display
- depth
- transmitted
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Abstract
Description
本発明は、3次元表示方法、画像生成側装置、および画像表示側装置に係り、特に、3次元画像を送信する際に有効な技術に関する。 The present invention relates to a three-dimensional display method, an image generation side device, and an image display side device, and more particularly to a technique effective in transmitting a three-dimensional image.
本発明者らは、立体視の生理的要因間での矛盾を抑制でき、かつ、簡便に、立体メガネを用いないで3次元表示が可能な、DFD(Depth-Fused3-D)方式の3次元表示装置を提案している(下記特許文献1、特許文献2参照)。
前述した提案済みの3次元表示装置は、複数の表示面に2次元像を表示し、この複数の表示面に表示される2次元像の、輝度あるいは透過度を各表示面毎に変化させて3次元立体像を表示するものである。
The present inventors have been able to suppress the contradiction between physiological factors of stereoscopic vision, and can easily perform three-dimensional display without using stereoscopic glasses, and the three-dimensional DFD (Depth-Fused3-D) method. A display device has been proposed (see Patent Document 1 and
The proposed three-dimensional display device described above displays a two-dimensional image on a plurality of display surfaces, and changes the brightness or transparency of the two-dimensional image displayed on the plurality of display surfaces for each display surface. A three-dimensional stereoscopic image is displayed.
なお、本願発明に関連する先行技術文献としては以下のものがある。
しかしながら、画像生成側装置から画像表示側装置に対して画像を送信し、画像表示側装置において、DFD方式で3次元立体像を表示する場合に、画像生成側装置から画像表示側装置に送信する画像の伝送路として、従来の2次元表示方式の画像の送信に利用されている伝送路をそのまま利用することができず、専用の伝送路を用意してDFD方式の3次元表示方法に必要な画像を送信する必要があるという問題点があった。
本発明は、前記従来技術の問題点を解決するためになされたものであり、本発明の目的は、3次元表示方法、画像生成側装置、および画像表示側装置において、従来の2次元表示方式の画像の送信に利用されている伝送路を利用してDFD方式の3次元表示方法に必要な画像を送信することが可能となる技術を提供することにある。
本発明の前記ならびにその他の目的と新規な特徴は、本明細書の記述及び添付図面によって明らかにする。
However, when an image is transmitted from the image generation side device to the image display side device, and the 3D stereoscopic image is displayed by the DFD method in the image display side device, the image generation side device transmits the image to the image display side device. As an image transmission line, a conventional transmission line used for transmitting an image in the two-dimensional display method cannot be used as it is, and a dedicated transmission line is prepared and necessary for the three-dimensional display method of the DFD method. There was a problem that it was necessary to send an image.
The present invention has been made to solve the problems of the prior art, and an object of the present invention is to provide a conventional two-dimensional display method in a three-dimensional display method, an image generation side apparatus, and an image display side apparatus. It is an object of the present invention to provide a technique capable of transmitting an image necessary for a three-dimensional display method of the DFD method using a transmission path used for transmitting an image.
The above and other objects and novel features of the present invention will become apparent from the description of this specification and the accompanying drawings.
本願において開示される発明のうち、代表的なものの概要を簡単に説明すれば、下記の通りである。
前述の課題を解決するために、本発明は、画像表示側において、観察者から見て異なった奥行き位置にある複数の表示面に2次元像をそれぞれ表示し、当該各表示面に表示される2次元像の輝度あるいは透過度を前記各表示面毎にそれぞれ独立に変化させて3次元立体像を表示する3次元表示方法であって、画像生成側から2次元画像と奥行き画像とを前記画像表示側に送信し、前記画像表示側において、前記画像生成側から送信された前記2次元画像と奥行き画像から、前記各表示面毎に輝度あるいは透過度をそれぞれに独立に変化させた前記各表示面用の2次元像を生成し、当該各表示面用の2次元像を前記各表示面に表示して3次元立体像を表示することを特徴とする。
また、本発明では、前記2次元画像と奥行き画像が、前記画像生成側から前記画像表示側へ、並列した独立の信号系統で送信されることを特徴とする。
また、本発明では、前記2次元画像と奥行き画像が、前記画像生成側から前記画像表示側へ、交互に時分割して同じ信号系統で送信されることを特徴とする。
また、本発明では、前記時分割の単位は、フレーム単位、フィールド単位、ライン単位、画素単位あるいはブロック単位のいずれか、あるいは複数の組み合わせであることを特徴とする。
また、本発明では、前記2次元画像と奥行き画像は、前記画像生成側から前記画像表示側へ、1枚の画像中に空間分割して同じ信号系統で送信されることを特徴とする。
また、本発明では、前記空間分割は、1枚の画像中の左右あるいは上下で分割することを特徴とする。
また、本発明では、前記空間分割は、1枚の画像中に水平方向あるいは垂直方向に、ライン単位、画素単位あるいはブロック単位で交互に分割することを特徴とする。
Of the inventions disclosed in this application, the outline of typical ones will be briefly described as follows.
In order to solve the above-described problems, the present invention displays two-dimensional images on a plurality of display surfaces at different depth positions as viewed from the observer on the image display side, and displays the two-dimensional images on the respective display surfaces. A three-dimensional display method for displaying a three-dimensional stereoscopic image by independently changing the luminance or transparency of a two-dimensional image for each display surface, wherein the two-dimensional image and the depth image are displayed from the image generation side. Each display that is transmitted to the display side, and on the image display side, the brightness or the transmittance is changed independently for each display surface from the two-dimensional image and the depth image transmitted from the image generation side. A two-dimensional image for a surface is generated, the two-dimensional image for each display surface is displayed on each display surface, and a three-dimensional stereoscopic image is displayed.
In the present invention, the two-dimensional image and the depth image are transmitted from the image generation side to the image display side in parallel independent signal systems.
In the present invention, the two-dimensional image and the depth image are alternately time-divided and transmitted by the same signal system from the image generation side to the image display side.
In the present invention, the time division unit is any one of a frame unit, a field unit, a line unit, a pixel unit, a block unit, or a combination of a plurality of units.
In the present invention, the two-dimensional image and the depth image are divided into a single image and transmitted by the same signal system from the image generation side to the image display side.
Further, in the present invention, the space division is performed by dividing the left and right or top and bottom in one image.
In the present invention, the space division is performed by alternately dividing a single image in the horizontal direction or the vertical direction in units of lines, pixels, or blocks.
また、本発明は、画像生成側装置と、前記画像生成装置側から送信される2次元画像と奥行き画像とに基づき、観察者から見て異なった奥行き位置にある複数の表示面に2次元像をそれぞれ表示し、当該各表示面に表示される2次元像の輝度あるいは透過度を前記各表示面毎にそれぞれ独立に変化させて3次元立体像を表示する画像表示側装置とを有し、前記画像生成側装置が、2次元画像と奥行き画像とを生成し前記画像表示側装置に送信する画像生成手段を有し、前記画像表示側装置が、前記画像生成側装置から送信される2次元画像と奥行き画像とから、前記各表示面毎に輝度あるいは透過度をそれぞれに独立に変化させた前記各表示面用の2次元像を生成し、前記各表示面に表示する輝度分配手段を有する。
ここで、前記2次元画像と奥行き画像は、並列した独立の信号系統で前記画像表示側装置へ送信される。
また、本発明では、前記画像生成側装置が、前記2次元画像と奥行き画像を交互に時分割で多重化する多重化手段を有し、前記2次元画像と奥行き画像を、交互に時分割して同じ信号系統で前記画像表示側装置へ送信し、前記画像表示側装置が、前記交互に時分割で多重化された2次元画像と奥行き画像を、2次元画像と奥行き画像とに分割する分割手段を有することを特徴とする。
また、本発明では、前記画像生成側装置が、前記2次元画像と奥行き画像を、1枚の画像中に空間分割して多重化する多重化手段を有し、前記2次元画像と奥行き画像を、1枚の画像中に空間分割して同じ信号系統で前記画像表示側へ送信し、前記画像表示側装置が、前記1枚の画像中に空間分割して多重化された2次元画像と奥行き画像を、2次元画像と奥行き画像とに分割する分割手段を有することを特徴とする。
In addition, the present invention provides a two-dimensional image on a plurality of display surfaces at different depth positions as viewed from an observer, based on the image generation side device, and the two-dimensional image and depth image transmitted from the image generation device side. An image display-side device that displays a three-dimensional stereoscopic image by independently changing the luminance or transparency of the two-dimensional image displayed on each display surface for each display surface, The image generation side device includes image generation means for generating a two-dimensional image and a depth image and transmitting the two-dimensional image and the depth image to the image display side device, and the image display side device is a two-dimensional image transmitted from the image generation side device Luminance distribution means for generating a two-dimensional image for each display surface in which the luminance or transmissivity is independently changed for each display surface from the image and the depth image, and displaying the two-dimensional image on each display surface .
Here, the two-dimensional image and the depth image are transmitted to the image display side device by a parallel independent signal system.
Further, in the present invention, the image generation side device has multiplexing means for alternately multiplexing the two-dimensional image and the depth image by time division, and alternately time-divides the two-dimensional image and the depth image. The same signal system is transmitted to the image display side device, and the image display side device divides the two-dimensional image and the depth image multiplexed in time division alternately into a two-dimensional image and a depth image. It has the means.
In the present invention, the image generation side device includes multiplexing means for spatially dividing the two-dimensional image and the depth image into a single image and multiplexing the two-dimensional image and the depth image. A two-dimensional image and a depth which are spatially divided into one image and transmitted to the image display side by the same signal system, and the image display side device divides and multiplexes into the one image. It has a dividing means for dividing an image into a two-dimensional image and a depth image.
本願において開示される発明のうち代表的なものによって得られる効果を簡単に説明すれば、下記の通りである。
本発明によれば、従来の2次元表示方式の画像の送信に利用されている伝送路を利用してDFD方式の3次元表示方法に必要な画像を送受信することが可能となる。
The effects obtained by the representative ones of the inventions disclosed in the present application will be briefly described as follows.
According to the present invention, it is possible to transmit and receive an image necessary for a three-dimensional display method using the DFD method by using a transmission path used for transmitting a conventional two-dimensional display method image.
以下、図面を参照して本発明の実施例を詳細に説明する。
なお、実施例を説明するための全図において、同一機能を有するものは同一符号を付け、その繰り返しの説明は省略する。
始めに、DFD型の3次元表示装置について説明する。
[DFD型の3次元表示装置の一例]
図8は、DFD型の3次元表示装置の一例を説明するための図である。
図8に示す3次元表示装置は、観察者100の前面に複数の面、例えば、表示面(101,102)(表示面101が表示面102より観察者100に近い)を設定し、これらの表示面(101,102)に複数の2次元像を表示するために、2次元表示装置と種々の光学素子を用いて光学系103を構築する。
前記2次元表示装置としては、例えば、CRT、液晶ディスプレイ、LEDディスプレイ、プラズマディスプレイ、ELディスプレイ、FEDディスプレイ、DMD、プロジェクション方式ディスプレイ、オシロスコープのような線描画型ディスプレイなどを用い、光学素子としては、例えば、レンズ、全反射鏡、部分反射鏡、曲鏡、プリズム、偏光素子、波長板などを用いる。
なお、図8は、前述の特許文献1に記載されているものと同じ構成のものであり、また、この表示面の設定方法については、前述の特許文献1を参照されたい。
図8に示す3次元表示装置では、図9に示すように、観察者100に提示したい3次元物体104を、観察者100の両眼の視線方向から、前述の表示面(101,102)へ射影した像(以下、「2D化像」と呼ぶ)(105,106)を生成する。
この2D化像の生成方法としては、例えば、視線方向から3次元物体104をカメラで撮影した2次元像を用いる方法、あるいは別の方向から撮影した複数枚の2次元像から合成する方法、あるいはコンピュータグラフィックによる合成技術やモデル化を用いる方法など種々の方法がある。
Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings.
In all the drawings for explaining the embodiments, parts having the same functions are given the same reference numerals, and repeated explanation thereof is omitted.
First, a DFD type three-dimensional display device will be described.
[Example of DFD type 3D display device]
FIG. 8 is a diagram for explaining an example of a DFD type three-dimensional display device.
The three-dimensional display device shown in FIG. 8 sets a plurality of surfaces, for example, display surfaces (101, 102) (the
Examples of the two-dimensional display device include a CRT, a liquid crystal display, an LED display, a plasma display, an EL display, an FED display, a DMD, a projection display, a line drawing type display such as an oscilloscope, and the like as an optical element. For example, a lens, a total reflection mirror, a partial reflection mirror, a curved mirror, a prism, a polarizing element, a wave plate, or the like is used.
Note that FIG. 8 has the same configuration as that described in the above-mentioned Patent Document 1, and refer to the above-mentioned Patent Document 1 for the method of setting the display surface.
In the three-dimensional display device shown in FIG. 8, as shown in FIG. 9, a three-
As a method for generating the 2D image, for example, a method using a two-dimensional image obtained by photographing a three-
図8に示すように、前記2D化像(105,106)を、各々表示面101と表示面102の双方に、観察者100の右眼と左眼とを結ぶ線上の一点から見て重なるように表示する。これは、例えば、2D化像(105,106)の各々の中心位置や重心位置の配置と、各々の像の拡大・縮小を制御することで可能となる。
かかる構成を有する装置上で、2D化像(105,106)の各々の輝度を、観察者100から見た総体的な輝度を一定に保ちつつ、3次元物体104の奥行き位置に対応して変えることで、3次元物体104の3次元立体像を表示する。
その2D化像(105,106)の各々の輝度の変え方の一例について説明する。なお、ここでは、白黒図面であるため、分かりやすいように、以下の図面では、輝度の高い方を濃く示してある。
例えば、3次元物体104が表示面101上にある場合には、図10に示すように、この上の2D化像105の輝度を3次元物体104の輝度に等しくし、表示面102上の2D化像106の輝度はゼロとする。
次に、例えば、3次元物体104が観察者100より少し遠ざかって表示面101より表示面102側に少し寄った位置にある場合には、図11に示すように、2D化像105の輝度を少し下げ、2D化像106の輝度を少し上げる。
As shown in FIG. 8, the 2D image (105, 106) overlaps both the
On the apparatus having such a configuration, the luminance of each of the 2D images (105, 106) is changed in accordance with the depth position of the three-
An example of how to change the luminance of each 2D image (105, 106) will be described. Here, since it is a black and white drawing, for the sake of easy understanding, in the following drawings, the higher luminance is shown darker.
For example, when the three-
Next, for example, when the three-
次に、例えば、3次元物体104が観察者100よりさらに遠ざかって表示面101より表示面102側にさらに寄った位置にある場合には、図12に示すように、2D化像105の輝度をさらに下げ、2D化像106の輝度をさらに上げる。
さらに、例えば、3次元物体104が表示面102上にある場合には、図13に示すように、この上の2D化像106の輝度を3次元物体104の輝度に等しくし、表示面101上の2D化像105の輝度はゼロとする。
このように表示することにより、観察者(人)100の生理的あるいは心理的要因あるいは錯覚により、表示しているのが2D化像(105,106)であっても、観察者100にはあたかも表示面(101,102)の中間に3次元物体104が位置しているように感じられる。
例えば、表示面(101,102)にほぼ等輝度の2D化像(105,106)を表示した場合には、表示面(101,102)の奥行き位置の中間付近に3次元物体104があるように感じられる。この場合に、この3次元物体104は、観察者100には立体感を伴って知覚される。
Next, for example, when the three-
Further, for example, when the three-
By displaying in this way, even if the 2D image (105, 106) is displayed due to the physiological or psychological factors or illusions of the observer (person) 100, it is as if the observer 100 It feels as if the three-
For example, when a 2D image (105, 106) having substantially the same luminance is displayed on the display surface (101, 102), the three-
なお、前記説明においては、例えば、3次元物体全体の奥行き位置を、例えば、表示面(101,102)に表示した2次元像を用いて表現する方法について主に述べたが、図8に示す3次元表示装置は、例えば、3次元物体自体が有する奥行きを表現する方法としても使用できることは明らかである。
3次元物体自体が有する奥行きを表現する場合における重要な要点は、図8に示す構成を有する装置上で、2D化像(105,106)の各々の部位の輝度を、観察者100から見た総体的な輝度を一定に保ちつつ、3次元物体104の各部位が有する奥行き位置に対応して変えることである。
なお、前述の説明では、2次元像を配置する面の中で主に2つの面に関してのみ記述し、かつ観察者に提示する物体が2つの面の間にある場合について述べたが、2次元像を配置する面の個数がこれよりも多く、あるいは提示する物体の位置が異なる場合であっても、同様な手法により3次元立体像を表示することが可能であることは明らかである。
例えば、面が3つで、観察者100に近い面と、中間の面との間に第1の3次元物体が、中間の面と、観察者100に遠い面との間に第2の3次元物体が存在する場合には、観察者100に近い面と、中間の面とに、第1の3次元物体の2D化像を表示し、中間の面と、観察者100に遠い面とに第2の3次元物体の2D化像を表示することで、第1および第2の3次元物体の3次元立体像を表示することができる。
In the above description, for example, the method of expressing the depth position of the entire three-dimensional object using, for example, a two-dimensional image displayed on the display surface (101, 102) has been described. It is obvious that the 3D display device can be used as a method of expressing the depth of the 3D object itself, for example.
An important point in expressing the depth of the three-dimensional object itself is that the brightness of each part of the 2D image (105, 106) is viewed from the observer 100 on the apparatus having the configuration shown in FIG. It is to change corresponding to the depth position of each part of the three-
In the above description, the description has been given of the case where only two surfaces are mainly described among the surfaces on which the two-dimensional image is arranged, and the object to be presented to the observer is between the two surfaces. It is obvious that a three-dimensional stereoscopic image can be displayed by a similar method even when the number of surfaces on which images are arranged is larger than this or when the position of an object to be presented is different.
For example, there are three surfaces, a first three-dimensional object between the surface close to the observer 100 and the intermediate surface, and a second 3 between the intermediate surface and the surface far from the observer 100. When a three-dimensional object exists, a 2D image of the first three-dimensional object is displayed on a surface close to the observer 100 and an intermediate surface, and on the intermediate surface and a surface far from the observer 100. By displaying the 2D image of the second 3D object, it is possible to display 3D images of the first and second 3D objects.
さらに、2D化像が3次元的に移動する場合に関しては、観察者の左右上下方向への移動に関しては通常の2次元表示装置の場合と同様に表示面内での動画再生によって可能であり、奥行き方向への移動に関しては、2D化像(105,106)の各々の輝度を、観察者100から見た総体的な輝度を一定に保ちつつ、3次元立体像の奥行き位置の時間的変化に対応して変化させることにより、3次元像の動画を表現できることは明らかである。
例えば、3次元立体像が表示面101より表示面102まで時間的に移動する場合について説明する。
3次元立体像が表示面101上にある場合には、図10に示すように、表示面101上の2D化像105の輝度を3次元立体像の輝度に等しくし、表示面102上の2D化像106の輝度はゼロとする。
次に、例えば、3次元立体像が、次第に観察者100より時間的に少し遠ざかり、表示面101より表示面102側に時間的に少し寄ってくる場合には、図11に示すように、3次元立体像の奥行き位置の移動に対応させて2D化像105の輝度を時間的に少し下げ、かつ2D化像106の輝度を時間的に少し上げる。
Furthermore, regarding the case where the 2D image is moved three-dimensionally, the movement of the observer in the horizontal and vertical directions can be achieved by moving image reproduction on the display surface as in the case of a normal two-dimensional display device. Regarding the movement in the depth direction, the luminance of each of the 2D images (105, 106) is changed with time in the depth position of the three-dimensional stereoscopic image while keeping the overall luminance viewed from the observer 100 constant. It is clear that a moving image of a three-dimensional image can be expressed by changing it correspondingly.
For example, a case where a three-dimensional stereoscopic image moves from the
When the three-dimensional stereoscopic image is on the
Next, for example, when the three-dimensional stereoscopic image gradually moves away from the observer 100 in time and slightly approaches in time from the
次に、例えば、3次元立体像が観察者100より時間的にさらに遠ざかり、表示面101より表示面102側にさらに寄った位置に時間的に移動する場合には、図12に示すように、3次元立体像の奥行き位置の移動に対応させて2D化像105の輝度を時間的にさらに下げ、かつ2D化像106の輝度を時間的にさらに上げる。
さらに、例えば、3次元立体像が表示面102上まで時間的に移動してきた場合には、図13に示すように、3次元立体像の奥行き位置の移動に対応させてこの上の2D化像106の輝度を3次元立体像の輝度に等しくなるまで時間的に変化させ、かつ表示面101上の2D化像105の輝度がゼロとなるまで変化させる。
このように表示することにより、人の生理的あるいは心理的要因あるいは錯覚により、表示しているのが2D化像(105,106)であっても、観察者100にはあたかも表示面(101,102)の間を、表示面101から表示面102に3次元立体像が奥行き方向に移動するように感じられる。
Next, for example, when the three-dimensional stereoscopic image is further distant from the observer 100 in time and moved to a position closer to the
Furthermore, for example, when the three-dimensional stereoscopic image has moved to the
By displaying in this way, even if a 2D image (105, 106) is displayed due to a human physiological or psychological factor or illusion, the viewer 100 is as if the display surface (101, 101) is displayed. 102), it is felt that the three-dimensional stereoscopic image moves from the
なお、前述の説明では、3次元立体像が表示面101から表示面102まで移動する場合について述べたが、これが表示面(101,102)の間の途中の奥行き位置から表示面102まで移動する場合や、表示面101から表示面(101,102)の間の途中の奥行き位置まで移動する場合や、表示面(101,102)の間の途中の奥行き位置から表示面(101,102)の間の途中の別な奥行き位置まで移動する場合であっても、同様なことが可能なことは明らかである。
なお、前述の説明では、2D化像を配置する面の中で主に2つの面に関してのみ記述し、かつ観察者100に提示する3次元立体像が2つの面の間を移動する場合について述べたが、2次元像を配置する面の個数がこれよりも多く、あるいは提示する3次元物体が複数の面をまたがって移動する場合であっても、同様な手法により、3次元立体像を表示可能であり、同様な効果が期待できることは明らかである。
また、前述の説明では、1個の3次元立体像が2次元像を配置する二つの面内で移動する場合について説明したが、複数個の3次元物体が移動する場合、即ち、表示される2次元像が、それぞれ移動方向の異なる複数の物体像を含む場合には、各表示面に表示される物体像の輝度を、物体像毎に、その物体の移動方向および移動速度に応じて変化させればよいことは明らかである。
In the above description, the case where the three-dimensional stereoscopic image moves from the
In the above description, a description is given of a case where only two surfaces are mainly described among surfaces on which a 2D image is arranged, and a three-dimensional stereoscopic image presented to the observer 100 moves between the two surfaces. However, even if the number of planes on which a two-dimensional image is arranged is larger than this, or even when a three-dimensional object to be presented moves across multiple planes, a three-dimensional stereoscopic image is displayed using the same method. Obviously, similar effects can be expected.
In the above description, the case where one three-dimensional stereoscopic image moves in two planes on which two-dimensional images are arranged has been described. However, when a plurality of three-dimensional objects move, that is, displayed. When the two-dimensional image includes a plurality of object images having different movement directions, the luminance of the object image displayed on each display surface changes for each object image according to the movement direction and movement speed of the object. Obviously, you can do that.
[DFD型の3次元表示装置の他の例]
図14は、本発明の前提となるDFD型の3次元表示装置の他の例を説明するための図である。
図14に示す3次元表示装置は、観察者100の前方に、複数の透過型表示装置、例えば、透過型表示装置(111,112)(透過型表示装置111が透過型表示装置112より観察者100に近い)と、種々の光学素子と、光源110を用いて光学系103を構築する。即ち、本実施例では、前述の図8における表示面(101,102)に代えて、透過形表示装置(111,112)を用いるものである。
前記透過型表示装置(111,112)としては、例えば、ツイストネマティック型液晶ディスプレイ、イン・プレイン型液晶ディスプレイ、ホモジニアス型液晶ディスプレイ、強誘電液晶ディスプレイ、ゲスト−ホスト型液晶ディスプレイ、高分子分散型液晶ディスプレイ、ホログラフィック高分子分散型液晶ディスプレイ、あるいはこれらの組み合わせなどを使用する。また、光学素子としては、例えば、レンズ、全反射鏡、部分反射鏡、曲面鏡、プリズム、偏光素子、波長板などを用いる。
なお、図14では、光源110が、観察者100から見て最も後方に配置された場合を示し、また、図14は、前述の特許文献2に記載されているものと同じ構成のものである。
[Other examples of DFD type 3D display devices]
FIG. 14 is a diagram for explaining another example of the DFD type three-dimensional display device as a premise of the present invention.
The three-dimensional display device shown in FIG. 14 has a plurality of transmissive display devices, for example, transmissive display devices (111, 112) (the transmissive display device 111 is more observable than the transmissive display device 112 in front of the observer 100. The optical system 103 is constructed using various optical elements and a light source 110. That is, in this embodiment, the transmissive display devices (111, 112) are used in place of the display surfaces (101, 102) in FIG.
Examples of the transmissive display device (111, 112) include a twisted nematic liquid crystal display, an in-plane liquid crystal display, a homogeneous liquid crystal display, a ferroelectric liquid crystal display, a guest-host liquid crystal display, and a polymer dispersed liquid crystal. A display, a holographic polymer dispersed liquid crystal display, or a combination thereof is used. In addition, as the optical element, for example, a lens, a total reflection mirror, a partial reflection mirror, a curved mirror, a prism, a polarization element, a wave plate, or the like is used.
FIG. 14 shows a case where the light source 110 is arranged farthest rearward when viewed from the observer 100. FIG. 14 has the same configuration as that described in
図14に示す3次元表示装置においても、前述の図9に示すように、観察者100に提示したい3次元物体104を、観察者100から見て、前記透過型表示装置(111,112)へ射影した2D化像(107,108)を生成する。
前記2D化像(107,108)を、図14に示すように、各々透過型表示装置111と透過型表示装置112との双方に、観察者100の右眼と左眼を結ぶ線上の一点から見て重なるように、2D化像(107,108)として表示する。
これは、例えば、2D化像(107,108)の各々の中心位置や重心位置の配置と、各々の像の拡大/縮小率を制御することで可能となる。
前記構成を有する装置上で、観察者100が見る像は、光源110から射出された光で、2D化像108を透過し、さらに2D化像107を透過した光によって生成される。
図14に示す3次元表示装置では、前記構成を有する装置上で、2D化像(107,108)の各々の透過度の配分を、観察者100から見た総体的な輝度を一定に保ちつつ、3次元物体104の奥行き位置に対応して変えて、透過型表示装置111と透過型表示装置112との間に存在する3次元物体の3次元立体像を表示する。
Also in the three-dimensional display device shown in FIG. 14, as shown in FIG. 9, the three-
As shown in FIG. 14, the 2D image (107, 108) is displayed on each of the transmission display device 111 and the transmission display device 112 from one point on the line connecting the right eye and the left eye of the observer 100. The two-dimensional images (107, 108) are displayed so as to overlap.
This can be achieved, for example, by controlling the arrangement of the center position and the gravity center position of each 2D image (107, 108) and the enlargement / reduction ratio of each image.
On the apparatus having the above-described configuration, an image viewed by the observer 100 is generated by light emitted from the light source 110, transmitted through the 2D image 108, and further transmitted through the 2D image 107.
In the three-dimensional display device shown in FIG. 14, the distribution of the transmittance of each of the 2D images (107, 108) is kept constant on the device having the above-described configuration while keeping the overall luminance as viewed from the observer 100 constant. A three-dimensional stereoscopic image of the three-dimensional object existing between the transmissive display device 111 and the transmissive display device 112 is displayed in accordance with the depth position of the three-
その2D化像(107,108)の各々の透過度の変え方の一例について説明する。
例えば、3次元物体104が透過型表示装置111上にある場合には、透過型表示装置111上の透過度を、2D化像107の輝度が3次元物体104の輝度に等しくなるように設定し、透過型表示装置112上の2D化像108の部分の透過度を、例えば、その透過型表示装置112の最大値とする。
次に、例えば、3次元物体104が観察者100より少し遠ざかって、透過型表示装置111より透過型表示装置112側に少し寄った位置にある場合には、透過型表示装置111上の2D化像107の部分の透過度を少し増加させ、透過型表示装置112上の2D化像108の部分の透過度を少し減少させる。
次に、例えば、3次元物体104が観察者100よりさらに遠ざかって、透過型表示装置111より透過型表示装置112側にさらに寄った位置にある場合には、透過型表示装置111上の2D化像107の部分の透過度をさらに増加させ、透過型表示装置112上の2D化像108の部分の透過度をさらに減少させる。
さらに、例えば、3次元物体104が透過型表示装置112上にある場合には、透過型表示装置112上の透過度を、2D化像108の輝度が3次元物体104の輝度に等しくなるように設定し、透過型表示装置111上の2D化像107の部分の透過度を、例えば、透過型表示装置111の最大値とする。
An example of how to change the transparency of each of the 2D images (107, 108) will be described.
For example, when the three-
Next, for example, when the three-
Next, for example, when the three-
Further, for example, when the three-
このように表示することにより、観察者(人)100の生理的あるいは心理的要因あるいは錯覚により、表示しているのが2D化像(107,108)であっても、観察者100にはあたかも透過型表示装置(111,112)の中間に3次元物体104が位置しているように感じられる。
即ち、例えば、透過型表示装置(111,112)にほぼ等輝度の2D化像(107,108)を表示した場合には、透過型表示装置(111,112)の奥行き位置の中間付近に3次元物体104があるように感じられる。この場合に、この3次元物体104は、観察者100には立体感を伴って知覚される。
なお、前述の説明においては、例えば、3次元物体全体の奥行き位置を、例えば、透過型表示装置(111,112)に表示した2次元像を用いて表現する方法について主に述べたが、図14に示す3次元表示装置においても、図8に示す3次元表示装置で説明した方法と同様の手法により、例えば、3次元物体自体が有する奥行きを表現する方法としても使用できることは明らかである。
また、図14に示す3次元表示装置においても、図8に示す3次元表示装置で説明した方法と同様の手法により、2D化像が3次元的に移動する場合には、観察者100の左右上下方向への移動に関しては通常の2次元表示装置の場合と同様に透過型表示装置内での動画再生によって可能であり、また、奥行き方向への移動に関しては、複数の透過型表示装置における透過度の変化を時間的に行うことで、3次元立体像の動画を表現することができることは明らかである。
By displaying in this way, even if a 2D image (107, 108) is displayed due to a physiological or psychological factor or illusion of the observer (person) 100, the observer 100 is as if it is displayed. It feels as if the three-
That is, for example, when a 2D image (107, 108) having substantially the same luminance is displayed on the transmissive display device (111, 112), 3 near the middle of the depth position of the transmissive display device (111, 112). A
In the above description, for example, the method of expressing the depth position of the entire three-dimensional object using, for example, a two-dimensional image displayed on the transmissive display device (111, 112) has been mainly described. It is obvious that the three-dimensional display device shown in FIG. 14 can also be used as a method of expressing the depth of the three-dimensional object itself, for example, by a method similar to the method described in the three-dimensional display device shown in FIG.
In the three-dimensional display device shown in FIG. 14 as well, when the 2D image is moved three-dimensionally by the same method as that described in the three-dimensional display device shown in FIG. The movement in the vertical direction is possible by moving image reproduction in the transmissive display device as in the case of a normal two-dimensional display device, and the movement in the depth direction is transmitted through a plurality of transmissive display devices. It is obvious that a moving image of a three-dimensional stereoscopic image can be expressed by temporally changing the degree.
DFD型の3次元表示装置では、各表示面における観察者100から見た輝度を、各表示面毎に変化させて3次元立体像を表示する。
即ち、図8に示す3次元表示装置では、2D化像(105,106)の各々の輝度の配分を、観察者100から見た総体的な輝度を一定に保ちつつ、3次元物体104の奥行き位置に対応して変化させて3次元立体像を表示する。
また、図14に示す3次元表示装置では、2D化像(107,108)の各々の透過度の配分を、観察者100から見た総体的な輝度を一定に保ちつつ、3次元物体104の奥行き位置に対応して変化させて3次元立体像を表示する。
このように、図8に示す3次元表示装置では、3次元物体104に近い方の面に表示される2D化像の輝度を、3次元物体104に遠い方の面に表示される2D化像の輝度よりも増加させるのに対して、図14に示す3次元表示装置では、3次元物体104に近い方の透過型表示装置に表示される2D化像の透過度を、3次元物体104に遠い方の透過型表示装置に表示される2D化像の透過度よりも減少させる点で異なっている。
したがって、図14に示す3次元表示装置において、図8に示す3次元表示装置と同様の手法を用いて、3次元物体自体が有する奥行きを表現する場合、あるいは、3次元立体像の動画を表現する場合には、図8に示す3次元表示装置において、各表示面に表示される2D化像の輝度を増加させる場合には、各透過型表示装置に表示される2D化像の透過度を減少させ、また、図14に示す3次元表示装置において、各表示面に表示される2D化像の輝度を減少させる場合には、各透過型表示装置に表示される2D化像の透過度を増加させるようにすればよい。
In the DFD type three-dimensional display device, the luminance viewed from the observer 100 on each display surface is changed for each display surface to display a three-dimensional stereoscopic image.
That is, in the three-dimensional display device shown in FIG. 8, the distribution of the luminance of each 2D image (105, 106) is kept constant in the overall luminance viewed from the observer 100, while the depth of the three-
Further, in the three-dimensional display device shown in FIG. 14, the distribution of the transmissivity of each of the 2D images (107, 108) is kept constant for the three-
As described above, in the 3D display device shown in FIG. 8, the luminance of the 2D image displayed on the surface closer to the
Therefore, in the 3D display device shown in FIG. 14, when the depth of the 3D object itself is expressed using the same method as the 3D display device shown in FIG. 8, or a moving image of a 3D stereoscopic image is expressed. In the case of increasing the luminance of the 2D image displayed on each display surface in the 3D display device shown in FIG. 8, the transmittance of the 2D image displayed on each transmissive display device is increased. In the three-dimensional display device shown in FIG. 14, when the luminance of the 2D image displayed on each display surface is decreased, the transparency of the 2D image displayed on each transmissive display device is increased. It may be increased.
[実施例1]
図1は、本発明の実施例1の3次元表示方法を説明するためのブロック図である。
本実施例では、画像生成側装置203の画像生成手段205から画像出力として、2次元画像201と奥行き画像202を出力し、画像表示側装置204の輝度分配手段206に入力する。
そして、輝度分配手段206にて、輝度(または、透過度)を変化させた2次元画像を生成し、当該2次元画像を表示手段(207,208,209)に表示し、前述のDFD方式の3次元表示方法により3次元立体像を表示する。なお、表示手段の数は、必ずしも図1に示す3個である必要はなく、2個以上の数であればよい。
本実施例では、画像生成側装置203と画像表示側装置204との間の画像の送信方法として2次元画像201と奥行き画像202を用いる。
奥行き画像202とは、3次元物体の奥行き方向の情報(X,Y,ZのZ)を輝度の情報に置き換えて、輝度の濃淡画像として構成したものである。
なお、3次元物体の奥行き方向の情報は、例えば、視線方向から3次元物体をカメラで撮影する際に、カメラ位置から3次元物体までの距離を、距離測定装置で測定し、その距離データに基づき生成することができる。
この方法は、複数の表示手段用の2次元画像を独立して受け渡す方法に比べて、画像のデータ量が少なくなり、表示手段の数が変わっても受け渡す画像は同じであるというメリットがある。
[Example 1]
FIG. 1 is a block diagram for explaining a three-dimensional display method according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
In this embodiment, a two-
Then, the luminance distribution unit 206 generates a two-dimensional image with varying luminance (or transparency), displays the two-dimensional image on the display unit (207, 208, 209), and uses the DFD method described above. A three-dimensional stereoscopic image is displayed by a three-dimensional display method. Note that the number of display means is not necessarily three as shown in FIG. 1, and may be two or more.
In this embodiment, a two-
The
The information about the depth direction of the three-dimensional object is obtained by measuring the distance from the camera position to the three-dimensional object with a distance measuring device when photographing the three-dimensional object with the camera from the line-of-sight direction. Can be generated.
This method has the merit that the amount of image data is smaller than the method of independently transferring two-dimensional images for a plurality of display means, and the transferred images are the same even if the number of display means is changed. is there.
前述したように、本発明の基本となる3次元表示装置の重要な要点は、2D化像(105,106)の各々の輝度、あるいは、2D化像(107,108)の各々の透過度を、観察者100から見た総体的な輝度を一定に保ちつつ、3次元物体104の奥行き位置に対応して変えることである。
したがって、画像生成側装置203から画像表示側装置204へ送信する画像として、2次元画像201と奥行き画像202とを使用することにより、画像表示側装置204において、各表示面に表示する2次元映像データを生成することが可能である。
例えば、表示面(101,102)の奥行き位置の中間に3次元物体104がある場合、画像生成側装置203は、3次元物体104の奥行き方向の情報を輝度の情報に置き換えた奥行き画像202を、画像表示側装置204に対して送信する。
そして、画像表示側装置204が、輝度を変化させる2個の表示手段を有するものである場合に、画像表示側装置204は、当該奥行き画像202に基づき、送信された輝度情報を一対一に分割し、2個の表示手段にほぼ等輝度の2D化像(105,106)を表示することにより、2個の表示手段の奥行き位置の中間付近に3次元物体104があるように、3次元立体像を表示することが可能となる。
As described above, the important point of the three-dimensional display device that is the basis of the present invention is that the luminance of each 2D image (105, 106) or the transmittance of each 2D image (107, 108) is determined. In other words, the overall luminance viewed from the observer 100 is changed in accordance with the depth position of the three-
Therefore, by using the two-
For example, when the three-
When the image display side device 204 has two display means for changing the luminance, the image display side device 204 divides the transmitted luminance information on a one-to-one basis based on the
本実施例では、画像生成側装置203から画像表示側装置204へ送信される画像のデータ量を削減することができる。例えば、2次元画像201が、8ビットが3チャンネル(R、G、B)、奥行き画像202が、8ビットで1チャンネル(単色の階調画像)の時の送信される画像のデータ量は、表示手段の数が2個で、それぞれ2個の表示手段用の2次元画像を送信する場合に比して、2/3に少なくすることができる。
具体的には、R・G・B・R・G・Bで6チャンネル分が、R・G・B・Zの4チャンネル分に減少する。また、表示手段の数が2個以上の場合には、データ量をさらに減少されることが可能である。
また、図2に示すように、従来の2次元画像用の伝送路を2系統利用することで、2次元画像201と奥行き画像202を別々に送信することができ、3次元画像専用の伝送路を用意することなく従来の伝送路を活用することができる。
2次元画像201の伝送は、従来の2次元画像と同様に伝送できるが、奥行き画像202の伝送では、具体的には、例えば、RGBインターフェース(アナログRGB、デジタルRGB、DVIなどR、G、Bが独立なもの)を用いる場合には、R、G、Bの何れかの信号インターフェースを用いて奥行き画像202を伝送する、あるいはR、G、B全てのインターフェースに同じ信号を伝送する等の方法がある。
なお、前述までの説明では、RGBのインターフェースを例に説明したが、2次元画像を伝送できる他の方式のインターフェースを用いても、2次元画像201の伝送は従来の2次元画像と同様に伝送し、奥行き画像202の伝送は単色(グレースケール)画像として扱うことで前記RGBインターフェースと同様に伝送することができる。
In the present embodiment, it is possible to reduce the amount of image data transmitted from the image generation side device 203 to the image display side device 204. For example, when the two-
Specifically, 6 channels of R, G, B, R, G, and B are reduced to 4 channels of R, G, B, and Z. Further, when the number of display means is two or more, the data amount can be further reduced.
In addition, as shown in FIG. 2, two-
The transmission of the two-
In the above description, the RGB interface has been described as an example, but the transmission of the two-
[実施例2]
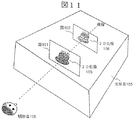
前述の実施例では、2次元画像201と奥行き画像202を、独立して2系統の伝送路を利用して画像生成側装置203から画像表示側装置204へと送信していたが、これを時間軸で時分割して、2次元画像201と奥行き画像202を交互に伝送することで1系統の伝送路にて伝送することができる。
図3に示すように、画像生成側装置203にて2次元画像201と奥行き画像202を時分割で多重する多重化手段210を用いて交互に分割して時間的に多重し、画像表示側装置204の分割手段211にて多重化された画像を2次元画像201と奥行き画像202に分割する。
交互に分割して多重する単位としては、単独のフレーム単位、あるいは、単独のフィールド単位で交互に時分割して同じ1系統の伝送路に多重して受け渡すことができる。
また、単独のライン単位あるいは複数のライン単位で交互に時分割して同じ1系統の伝送路に多重して受け渡すこともできる。
さらに、単独あるいは複数の画素単位で交互に時分割して同じ1系統の伝送路に多重して受け渡すこともできる。あるいは複数の画素が集まったブロック単位で交互に時分割して同じ1系統の伝送路に多重して受け渡すことも可能である。
[Example 2]
In the above-described embodiment, the two-
As shown in FIG. 3, the image generation side device 203 alternately multiplexes the two-
As a unit to be divided and multiplexed alternately, it is possible to multiplex and deliver to the same one-system transmission path by time-division alternately by a single frame unit or a single field unit.
In addition, it is also possible to time-division alternately in a single line unit or a plurality of line units and multiplex them to the same one system transmission path.
Furthermore, it is also possible to multiplex and transfer to the same one system transmission path by time-division alternately or in units of a plurality of pixels. Alternatively, it is also possible to time-division alternately in units of blocks in which a plurality of pixels are collected and to multiplex and transfer them to the same one-system transmission path.
[実施例3]
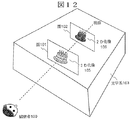
伝送する1つの画像の内部を空間的に分割して2次元画像201と奥行き画像202を空間的に多重することで、1つの画像として、画像生成側装置203から画像表示側装置204へ送信することができる。
図4に示すように、画像生成側装置203にて2次元画像201と奥行き画像202を生成し、多重化手段212にて1つの画像に空間的に多重し、画像生成側装置203から画像表示側装置204へ通常の2次元画像と同様な伝送方法によって伝送し、画像表示側装置204では多重された2次元画像と奥行き画像を分割手段213によって分割する。
これにより、伝送路は従来の2次元画像を伝送できるものをそのまま利用することができ、1系統の伝送路にて伝送することができる。
多重化手段212において、空間的に分割して2次元画像201と奥行き画像202を多重する方法としては、図5に示すように、1つの画像の中を左右に分割する方法、上下に分割する方法がある。もちろん、各々の画像を90度回転させるなどの画像操作をしてから上下あるいは左右に分割するなども可能である。
また、図6に示すように、1つの画像の中に水平方向に単独あるいは複数のライン単位で分割する方法、垂直方向に単独あるいは複数のライン単位で交互に分割する方法も可能である。
さらに、図7に示すように、1つの画像の中に水平方向あるいは垂直方向にブロック単位で交互に分割することもできる。このブロックは、複数の画素が集まったもので構成される。また、ブロックと同様に単独の画素を交互に分割することも可能である。
以上、本発明者によってなされた発明を、前記実施例に基づき具体的に説明したが、本発明は、前記実施例に限定されるものではなく、その要旨を逸脱しない範囲において種々変更可能であることは勿論である。
[Example 3]
The interior of one image to be transmitted is spatially divided, and the two-
As shown in FIG. 4, a two-
As a result, a transmission path that can transmit a conventional two-dimensional image can be used as it is, and transmission can be performed using a single transmission path.
As a method of spatially dividing the two-
Further, as shown in FIG. 6, a method of dividing a single image in the horizontal direction by a single line or a plurality of lines, and a method of dividing by a single line or a plurality of lines in the vertical direction are possible.
Furthermore, as shown in FIG. 7, it is also possible to alternately divide one image into blocks in the horizontal direction or the vertical direction. This block is constituted by a collection of a plurality of pixels. Moreover, it is also possible to divide a single pixel alternately like a block.
As mentioned above, the invention made by the present inventor has been specifically described based on the above embodiments. However, the present invention is not limited to the above embodiments, and various modifications can be made without departing from the scope of the invention. Of course.
100 観察者
101,102 表示面
103 光学系
104 3次元物体
105,106,107,108 2D化像
111,112 透過型表示装置
110 光源
201 2次元画像
202 奥行き画像
203 画像生成側装置
204 画像表示側装置
205 画像生成手段
206 輝度分配手段
207,208,209 表示手段
210,212 多重化手段
211,213 分割手段
DESCRIPTION OF SYMBOLS 100 Observer 101,102 Display surface 103
Claims (14)
画像生成側から2次元画像と奥行き画像とを前記画像表示側に送信し、
前記画像表示側において、前記画像生成側から送信された前記2次元画像と奥行き画像から、前記各表示面毎に輝度あるいは透過度をそれぞれに独立に変化させた前記各表示面用の2次元像を生成し、当該各表示面用の2次元像を前記各表示面に表示して3次元立体像を表示することを特徴とする3次元表示方法。 On the image display side, two-dimensional images are respectively displayed on a plurality of display surfaces at different depth positions as viewed from the observer, and the brightness or transmittance of the two-dimensional images displayed on the display surfaces is displayed on the display surfaces. A three-dimensional display method for displaying a three-dimensional stereoscopic image by changing each independently.
A two-dimensional image and a depth image are transmitted from the image generation side to the image display side;
On the image display side, the two-dimensional image for each display surface in which the luminance or the transmittance is changed independently for each display surface from the two-dimensional image and the depth image transmitted from the image generation side. And displaying a two-dimensional image for each display surface on each display surface to display a three-dimensional stereoscopic image.
2次元画像と奥行き画像とを生成し、前記画像表示側装置に送信する画像生成手段を有することを特徴とする画像生成側装置。 A two-dimensional image is displayed on each of a plurality of display surfaces at different depth positions as viewed from the observer, and the brightness or transmittance of the two-dimensional image displayed on each display surface is independently determined for each display surface. An image generation-side device that transmits a two-dimensional image for displaying a three-dimensional stereoscopic image to an image display-side device that displays a three-dimensional stereoscopic image by changing,
An image generation side device comprising image generation means for generating a two-dimensional image and a depth image and transmitting them to the image display side device.
前記2次元画像と奥行き画像を、交互に時分割して同じ信号系統で前記画像表示側装置へ送信することを特徴とする請求項8に記載の画像生成側装置。 A multiplexing means for alternately multiplexing the two-dimensional image and the depth image in a time division manner;
9. The image generation side device according to claim 8, wherein the two-dimensional image and the depth image are alternately time-divided and transmitted to the image display side device using the same signal system.
前記2次元画像と奥行き画像を、1枚の画像中に空間分割して同じ信号系統で前記画像表示側へ送信することを特徴とする請求項8に記載の画像生成側装置。 Multiplexing means for spatially dividing and multiplexing the two-dimensional image and the depth image into one image;
9. The image generation apparatus according to claim 8, wherein the two-dimensional image and the depth image are spatially divided into one image and transmitted to the image display side using the same signal system.
請求項8または請求項9に記載の画像生成側装置から送信される2次元画像と奥行き画像とから、前記各表示面毎に輝度あるいは透過度をそれぞれに独立に変化させた前記各表示面用の2次元像を生成し、前記各表示面に表示する輝度分配手段を有することを特徴とする画像表示側装置。 A two-dimensional image is displayed on each of a plurality of display surfaces at different depth positions as viewed from the observer, and the brightness or transmittance of the two-dimensional image displayed on each display surface is independently determined for each display surface. An image display side device that displays a three-dimensional stereoscopic image by changing,
For each display surface, the brightness or the transmittance is changed independently for each display surface from the two-dimensional image and the depth image transmitted from the image generation side device according to claim 8 or 9. An image display-side apparatus, comprising: a luminance distribution unit that generates a two-dimensional image of and displays the two-dimensional image on each display surface.
11. A dividing unit that divides a two-dimensional image and a depth image into two-dimensional images and a depth image, which are transmitted from the image generation device side according to claim 10 and are spatially divided and multiplexed in the one image. The image display side device according to claim 12, further comprising:
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005004637A JP2006195018A (en) | 2005-01-12 | 2005-01-12 | Three dimensional display method, image generation side apparatus and image display side apparatus |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005004637A JP2006195018A (en) | 2005-01-12 | 2005-01-12 | Three dimensional display method, image generation side apparatus and image display side apparatus |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2006195018A true JP2006195018A (en) | 2006-07-27 |
| JP2006195018A5 JP2006195018A5 (en) | 2007-03-22 |
Family
ID=36801165
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005004637A Pending JP2006195018A (en) | 2005-01-12 | 2005-01-12 | Three dimensional display method, image generation side apparatus and image display side apparatus |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2006195018A (en) |
Cited By (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009192897A (en) * | 2008-02-15 | 2009-08-27 | Xanavi Informatics Corp | Display device and stereoscopic display method |
| JP2010508691A (en) * | 2006-10-30 | 2010-03-18 | コーニンクレッカ フィリップス エレクトロニクス エヌ ヴィ | Video depth map adjustment |
| JP2010114861A (en) * | 2008-11-10 | 2010-05-20 | Sony Corp | Transmitter, receiver, signal transmission system, and signal transmission method |
| JP2012134732A (en) * | 2010-12-21 | 2012-07-12 | Toshiba Corp | Transmitter, receiver, and transmission system |
| JP2012516071A (en) * | 2009-01-20 | 2012-07-12 | コーニンクレッカ フィリップス エレクトロニクス エヌ ヴィ | Transfer of 3D image data |
| JP2012134634A (en) * | 2010-12-20 | 2012-07-12 | Toshiba Corp | Stereoscopic video signal processing apparatus and method |
| JP2013519286A (en) * | 2010-02-09 | 2013-05-23 | コーニンクレッカ フィリップス エレクトロニクス エヌ ヴィ | 3D video format detection |
| JP2014098827A (en) * | 2012-11-15 | 2014-05-29 | Shimadzu Corp | Head-mounted type display device |
| US8890933B2 (en) | 2010-11-26 | 2014-11-18 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Parallax image conversion apparatus |
| US8933988B2 (en) | 2009-01-28 | 2015-01-13 | Nec Corporation | Picture transmission system and picture transmission method |
| US9179122B2 (en) | 2008-12-04 | 2015-11-03 | Nec Corporation | Image transmission system, image transmission apparatus and image transmission method |
| US10742953B2 (en) | 2009-01-20 | 2020-08-11 | Koninklijke Philips N.V. | Transferring of three-dimensional image data |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS5536240B2 (en) * | 1977-08-12 | 1980-09-19 | ||
| JP2004274642A (en) * | 2003-03-12 | 2004-09-30 | Nippon Telegr & Teleph Corp <Ntt> | Transmission method for three dimensional video image information |
-
2005
- 2005-01-12 JP JP2005004637A patent/JP2006195018A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS5536240B2 (en) * | 1977-08-12 | 1980-09-19 | ||
| JP2004274642A (en) * | 2003-03-12 | 2004-09-30 | Nippon Telegr & Teleph Corp <Ntt> | Transmission method for three dimensional video image information |
Cited By (20)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010508691A (en) * | 2006-10-30 | 2010-03-18 | コーニンクレッカ フィリップス エレクトロニクス エヌ ヴィ | Video depth map adjustment |
| JP2009192897A (en) * | 2008-02-15 | 2009-08-27 | Xanavi Informatics Corp | Display device and stereoscopic display method |
| US8384765B2 (en) | 2008-11-10 | 2013-02-26 | Sony Corporation | Transmitter, receiver, signal transmission system, and signal transmission method |
| CN101742345B (en) * | 2008-11-10 | 2012-06-20 | 索尼株式会社 | Transmitter, receiver, signal transmission system, and signal transmission method |
| JP2010114861A (en) * | 2008-11-10 | 2010-05-20 | Sony Corp | Transmitter, receiver, signal transmission system, and signal transmission method |
| JP4662187B2 (en) * | 2008-11-10 | 2011-03-30 | ソニー株式会社 | Transmitting apparatus, receiving apparatus and signal transmission system |
| US9179122B2 (en) | 2008-12-04 | 2015-11-03 | Nec Corporation | Image transmission system, image transmission apparatus and image transmission method |
| JP2012516071A (en) * | 2009-01-20 | 2012-07-12 | コーニンクレッカ フィリップス エレクトロニクス エヌ ヴィ | Transfer of 3D image data |
| US10742953B2 (en) | 2009-01-20 | 2020-08-11 | Koninklijke Philips N.V. | Transferring of three-dimensional image data |
| US11381800B2 (en) | 2009-01-20 | 2022-07-05 | Koninklijke Philips N.V. | Transferring of three-dimensional image data |
| US10924722B2 (en) | 2009-01-20 | 2021-02-16 | Koninklijke Philips N.V. | Transferring of three-dimensional image data |
| US8933988B2 (en) | 2009-01-28 | 2015-01-13 | Nec Corporation | Picture transmission system and picture transmission method |
| JP2013519286A (en) * | 2010-02-09 | 2013-05-23 | コーニンクレッカ フィリップス エレクトロニクス エヌ ヴィ | 3D video format detection |
| US9325964B2 (en) | 2010-02-09 | 2016-04-26 | Koninklijke Philips N.V. | 3D video format detection |
| US9729852B2 (en) | 2010-02-09 | 2017-08-08 | Koninklijke Philips N.V. | 3D video format detection |
| US8890933B2 (en) | 2010-11-26 | 2014-11-18 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Parallax image conversion apparatus |
| JP2012134634A (en) * | 2010-12-20 | 2012-07-12 | Toshiba Corp | Stereoscopic video signal processing apparatus and method |
| JP2012134732A (en) * | 2010-12-21 | 2012-07-12 | Toshiba Corp | Transmitter, receiver, and transmission system |
| US8497896B2 (en) | 2010-12-21 | 2013-07-30 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Transmitter, receiver and transmission system |
| JP2014098827A (en) * | 2012-11-15 | 2014-05-29 | Shimadzu Corp | Head-mounted type display device |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP2006195018A (en) | Three dimensional display method, image generation side apparatus and image display side apparatus | |
| CN103873844B (en) | Multiple views automatic stereoscopic display device and control the method for its viewing ratio | |
| KR100859694B1 (en) | 2d/3d liquid display device and the driving method thereof | |
| US10313662B2 (en) | Glasses-free autostereoscopic 3D display device | |
| WO2008044858A1 (en) | Autostereoscopic display | |
| KR20130002076A (en) | Stereoscopic image display device and driving method thereof | |
| KR101922722B1 (en) | Stereoscopic image display device | |
| JP3460671B2 (en) | Three-dimensional display method and device | |
| KR101337790B1 (en) | Depth-fused three dimensional display method and apparatus using multi layer | |
| JP2007166277A (en) | Transmission method for three-dimensional image information, transmitting side device, and receiving side device | |
| KR101763942B1 (en) | Stereoscopic Image Display Device | |
| Minami et al. | Portrait and landscape mode convertible stereoscopic display using parallax barrier | |
| US8994791B2 (en) | Apparatus and method for displaying three-dimensional images | |
| JP4283232B2 (en) | 3D display method and 3D display device | |
| JP4451804B2 (en) | Three-dimensional display method, image generation apparatus, and image display apparatus | |
| KR20130066742A (en) | Image display device | |
| US8913077B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus and image processing method | |
| KR101798236B1 (en) | Stereoscopic image display and method of adjusting brightness thereof | |
| JP2014106330A (en) | Three-dimensional display device and three-dimensional display method | |
| JP4481275B2 (en) | 3D video information transmission method | |
| KR20160021650A (en) | Lenticular lens type stereoscopic 3d display device | |
| US20110169916A1 (en) | Method of displaying image and display apparatus for performing the same | |
| JP2006285113A (en) | Three-dimensional display device | |
| JP2004294817A (en) | Three-dimensional display | |
| JP2009237310A (en) | False three-dimensional display method and false three-dimensional display apparatus |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20070201 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20070201 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20100525 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20100608 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20101019 |