JP2005303213A - Solid-state imaging device - Google Patents
Solid-state imaging device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2005303213A JP2005303213A JP2004120953A JP2004120953A JP2005303213A JP 2005303213 A JP2005303213 A JP 2005303213A JP 2004120953 A JP2004120953 A JP 2004120953A JP 2004120953 A JP2004120953 A JP 2004120953A JP 2005303213 A JP2005303213 A JP 2005303213A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- solid
- imaging device
- state imaging
- sealing resin
- state
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 238000003384 imaging method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 166
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 70
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 claims abstract description 70
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 abstract description 52
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 abstract description 11
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 abstract description 10
- 230000008030 elimination Effects 0.000 abstract 1
- 238000003379 elimination reaction Methods 0.000 abstract 1
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 17
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 5
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 239000010931 gold Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000000465 moulding Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 229910000679 solder Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N gold Chemical compound [Au] PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000004593 Epoxy Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000919 ceramic Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000002950 deficient Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229910052737 gold Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000035515 penetration Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008595 infiltration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001764 infiltration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001678 irradiating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000206 photolithography Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229920002120 photoresistant polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000007747 plating Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001681 protective effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229920001187 thermosetting polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/10—Bump connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/15—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/16—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process of an individual bump connector
- H01L2224/161—Disposition
- H01L2224/16151—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/16221—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/16225—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/26—Layer connectors, e.g. plate connectors, solder or adhesive layers; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/31—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/32—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors after the connecting process of an individual layer connector
- H01L2224/321—Disposition
- H01L2224/32151—Disposition the layer connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/32221—Disposition the layer connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/32225—Disposition the layer connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/73—Means for bonding being of different types provided for in two or more of groups H01L2224/10, H01L2224/18, H01L2224/26, H01L2224/34, H01L2224/42, H01L2224/50, H01L2224/63, H01L2224/71
- H01L2224/732—Location after the connecting process
- H01L2224/73201—Location after the connecting process on the same surface
- H01L2224/73203—Bump and layer connectors
- H01L2224/73204—Bump and layer connectors the bump connector being embedded into the layer connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L2224/83—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a layer connector
- H01L2224/83909—Post-treatment of the layer connector or bonding area
- H01L2224/83951—Forming additional members, e.g. for reinforcing, fillet sealant
Landscapes
- Wire Bonding (AREA)
- Structures Or Materials For Encapsulating Or Coating Semiconductor Devices Or Solid State Devices (AREA)
- Solid State Image Pick-Up Elements (AREA)
- Transforming Light Signals Into Electric Signals (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、撮像素子として半導体からなる固体撮像素子を用い、被写体に対応する映像信号を生成する固体撮像装置に関するものである。 The present invention relates to a solid-state imaging device that uses a solid-state imaging device made of a semiconductor as an imaging device and generates a video signal corresponding to a subject.
従来から、被写体に対応する映像信号を生成する撮像装置として、撮像素子に半導体からなる固体撮像素子を用いた固体撮像装置があり、この固体撮像装置は、通常、固体撮像素子をパッケージ内に収容して、その後、保護用のガラス板でカバーして製造されている。 Conventionally, as an imaging device that generates a video signal corresponding to a subject, there is a solid-state imaging device using a solid-state imaging device made of a semiconductor as an imaging device, and this solid-state imaging device usually houses a solid-state imaging device in a package. Then, it is manufactured by covering with a protective glass plate.
以上のような従来の固体撮像装置について、以下に説明する。
図6は従来の固体撮像装置の固体撮像素子がパッケージに収容されたワイヤボンディング方式による構成を示す縦断面図である。この固体撮像装置100は、図6に示すように、セラミックスのパッケージ108の底に、撮像面102を上にして固体撮像素子101を、接着剤105でダイボンディングし、配線回路(図示を省略)との間を例えば金ワイヤ106でワイヤボンディングして電気的に接続した後、気体を封じ込め保護用のガラス板104を封止樹脂109で取り付けて作製されている。この封止樹脂109は接着剤を兼ねるものであり、パッケージ108にはプラスチックスによるものも存在する。
The conventional solid-state imaging device as described above will be described below.
FIG. 6 is a longitudinal sectional view showing a configuration by a wire bonding method in which a solid-state imaging device of a conventional solid-state imaging device is accommodated in a package. As shown in FIG. 6, the solid-
しかし、固体撮像装置は、近年、デジタルカメラや携帯電話用小型カメラ、その他に多用されるに伴って、薄型化、小型化、また低コスト化が要請されるようになり、ワイヤボンディング方式ではなく、回路基板に対して固体撮像素子をフェイスダウンした状態で接続するフリップチップ方式によって製造されるようになっている。 However, as solid-state imaging devices have been frequently used in recent years for digital cameras, small cameras for mobile phones, and the like, thinning, miniaturization, and cost reduction have been demanded. The flip-chip method is used in which a solid-state imaging device is connected face-down to a circuit board.
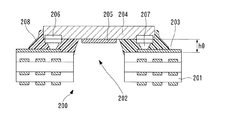
図7はフリップチップ方式によって固体撮像素子が回路基板にフェイスダウンした状態で接続された固体撮像装置を示す縦断面図である。図7に示す固体撮像装置200において、201は開口部202および接続導体203を有する回路基板で、例えばガラスエポキシ基材等からなる多層配線基板である。204は突起電極207を有する固体撮像素子で、その撮像面205を開口部202に位置合わせして、フェイスダウン方式で回路基板201に装着する。
FIG. 7 is a longitudinal sectional view showing a solid-state imaging device in which the solid-state imaging device is connected to the circuit board in a flip-chip manner in a face-down state. In the solid-
その後、固体撮像素子204の信頼性を高めるために、固体撮像素子204の周縁部と回路基板201との間隙に封止樹脂208を注入し加熱硬化する。しかし、突起電極207および接続導体203によって定まる固体撮像素子204と回路基板201との間隙h0は0.03〜0.1mmと小さいので、硬化処理の過程で未硬化の低粘度の封止樹脂208が、毛細管現象によって内部へ浸入し固体撮像素子204の撮像面205に至って、この撮像面205を汚染し易い。
Thereafter, in order to increase the reliability of the solid-
そのために、封止樹脂208の塗布プロセスは、塗布量の厳密な管理を必要としている。
これに対して、絶縁基体上にフェイスダウン方式で装着した固体撮像素子と絶縁基体との間隙部をシールする封止樹脂の形成方法(例えば、特許文献1を参照)が提案されている。
Therefore, the application process of the sealing
On the other hand, a method of forming a sealing resin that seals the gap between the solid-state imaging device mounted on the insulating substrate in a face-down manner and the insulating substrate (see, for example, Patent Document 1) has been proposed.
図8はその製造方法を示したフロー図である。まず、図8(a)に示すように、回路基板301に接続導体303および突起電極307を介して固体撮像素子304を装着し、次に、図8(b)に示すように、回路基板301の固体撮像素子304の装着面とは反対側から、遮光マスク312を介して開口部302を通して、固体撮像素子304の撮像面305に対して、紫外線発生装置311で生成した紫外線309を照射しながら、固体撮像素子304の周縁部と回路基板301との間隙に紫外線・熱両用硬化型封止樹脂310を樹脂注入ノズル313により注入する。これにより、注入した紫外線・熱両用硬化型封止樹脂310が固体撮像素子304の撮像面305側に流動しようとする少なくともその先端部を、紫外線309により硬化させ、それ以上の流出を停止するようにしている。
FIG. 8 is a flowchart showing the manufacturing method. First, as shown in FIG. 8A, the solid-
さらに、所定の量の紫外線・熱両用硬化型封止樹脂310を注入した後、図8(c)に示すように、例えば電気炉等の加熱手段314で加熱することにより、紫外線・熱両用硬化型封止樹脂310の全体を本硬化する。また、不要光が紫外線・熱両用硬化型封止樹脂310を通して固体撮像素子304の撮像面305に入る恐れのある回路基板構成の場合は、図8(d)に示すように、紫外線・熱両用硬化型封止樹脂310の上から、あるいは、紫外線・熱両用硬化型封止樹脂310と固体撮像素子304の裏面全体を遮光性樹脂315で覆うようにする。
Further, after injecting a predetermined amount of ultraviolet / heat
また、回路基板の開口部周囲に、固体撮像素子の撮像面を囲むように枠状構造体を設けて封止樹脂の流れを止めるようにした固体撮像装置(例えば、特許文献2を参照)も提案されている。 In addition, a solid-state imaging device (see, for example, Patent Document 2) in which a frame-like structure is provided around the opening of the circuit board so as to surround the imaging surface of the solid-state imaging device to stop the flow of the sealing resin. Proposed.
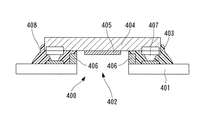
図9はそのような固体撮像装置400を示した図である。接続導体403を設けた回路基板401に、固体撮像素子404が突起電極407を介してフェイスダウンに接続されており、更に、枠状構造体406が撮像面405を囲むように、固体撮像素子404表面と回路基板401表面との双方もしくは片方に固着されている。そして、その外側に封止樹脂408が充填されたものである。
FIG. 9 is a diagram showing such a solid-
このような固体撮像装置400は、封止樹脂408が比較的低い粘度であっても、枠状構造体406が封止樹脂408の流れを止めるので、撮像面405へ浸入することはないとされている。
しかしながら上記のような従来の固体撮像装置では、それぞれ以下のような問題点がある。
図7の固体撮像装置200は、量産化に際して封止樹脂の塗布量の厳密な管理に困難がある。
However, the conventional solid-state imaging device as described above has the following problems.
The solid-
また、図8に示した紫外線・熱両用硬化型封止樹脂310を紫外線309によって硬化し、紫外線・熱両用硬化型封止樹脂310が固体撮像素子304の撮像面305に浸入することを防止する製造方法は、有効な方法であるが、固体撮像素子304の端面と撮像面305の端面との距離が近接した固体撮像素子304の場合、樹脂注入ノズル313によって注入された紫外線・熱両用硬化型封止樹脂310の浸入速度が速くなり、紫外線・熱両用硬化型封止樹脂310が撮像面305に至る前に、その紫外線・熱両用硬化型封止樹脂310を紫外線309で硬化反応させて流動を止めることができない。
Further, the ultraviolet / heat
また、図9に示した固体撮像素子404の撮像面405の周囲、もしくは回路基板401の開口部402周縁に枠状構造体406を設けた固体撮像装置400は、封止樹脂408が撮像面405にまで浸入することを防ぐには有効な方法ではあるが、固体撮像素子404または回路基板401に対して高精度のフォトリソグラフィ技術によるメッキ膜またはフォトレジスト膜の形成を必要とする。
Further, in the solid-
以上のため、固体撮像素子の撮像面が汚染され、撮像品質が低下してしまうとともに、製品の歩留りが悪化して生産性が低下するという問題点を有していた。
本発明は、上記従来の問題点を解決するもので、撮像面を汚染することがなく、良好な撮像品質を得ることができるとともに、製品の歩留りを向上して生産性を高めることができる固体撮像装置を提供する。
For the above reasons, the imaging surface of the solid-state imaging device is contaminated, and the imaging quality is deteriorated. Further, the yield of the product is deteriorated and the productivity is lowered.
The present invention solves the above-mentioned conventional problems, and does not contaminate the imaging surface, can obtain good imaging quality, and can improve the yield of products and increase productivity. An imaging device is provided.
上記の課題を解決するために、本発明の請求項1に記載の固体撮像装置は、撮像面を有する固体撮像素子と、開口部および接続導体を有する絶縁基体とを、前記撮像面が前記絶縁基体に対してフェイスダウンするように接続した固体撮像装置において、前記絶縁基体は、前記開口部の周縁に前記撮像面より広い面積の窪みを有する構成としたことを特徴とする。
In order to solve the above-described problem, a solid-state imaging device according to
また、本発明の請求項2に記載の固体撮像装置は、請求項1記載の固体撮像装置であって、前記絶縁基体が、配線基板からなることを特徴とする。
また、本発明の請求項3に記載の固体撮像装置は、請求項1記載の固体撮像装置であって、前記絶縁基体が、樹脂成形パッケージからなることを特徴とする。
A solid-state imaging device according to claim 2 of the present invention is the solid-state imaging device according to
A solid-state imaging device according to claim 3 of the present invention is the solid-state imaging device according to
以上により、固体撮像素子の表面と窪みの底面との間隙が大きくなり、絶縁基体と固体撮像素子との間隙を低粘度の封止樹脂で封止する際に、塗布される封止樹脂が毛細管現象によって内部へ浸入しても、絶縁基体に形成された窪みによって毛細管現象が断ち切られて、封止樹脂の撮像面への浸入を停止することができる。 As described above, the gap between the surface of the solid-state imaging device and the bottom surface of the recess is increased, and the sealing resin to be applied is sealed when the gap between the insulating substrate and the solid-state imaging device is sealed with a low-viscosity sealing resin. Even if it penetrates into the inside due to the phenomenon, the capillary phenomenon is cut off by the depression formed in the insulating substrate, and the penetration of the sealing resin into the imaging surface can be stopped.
以上のように本発明によれば、固体撮像素子の表面と窪みの底面との間隙が大きくなり、絶縁基体と固体撮像素子との間隙を低粘度の封止樹脂で封止する際に、塗布される封止樹脂が毛細管現象によって内部へ浸入しても、絶縁基体に形成された窪みによって毛細管現象が断ち切られて、封止樹脂の撮像面への浸入を停止することができる。 As described above, according to the present invention, the gap between the surface of the solid-state imaging device and the bottom surface of the recess is increased, and the gap between the insulating substrate and the solid-state imaging device is applied when sealing with the low-viscosity sealing resin. Even if the sealing resin to be infiltrated into the inside due to the capillary phenomenon, the capillary phenomenon is cut off by the depression formed in the insulating substrate, and the infiltration of the sealing resin into the imaging surface can be stopped.
そのため、撮像面を汚染することがなく、良好な撮像品質を得ることができるとともに、製品の歩留りを向上して生産性を高めることができる。 Therefore, the imaging surface is not contaminated and good imaging quality can be obtained, and the yield of products can be improved to increase productivity.
以下、本発明の実施の形態を示す固体撮像装置について、図面を参照しながら具体的に説明する。
(実施の形態1)
本発明の実施の形態1の固体撮像装置を説明する。
Hereinafter, a solid-state imaging device according to an embodiment of the present invention will be specifically described with reference to the drawings.
(Embodiment 1)
A solid-state imaging device according to
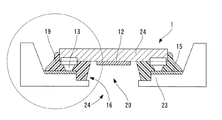
図1は本実施の形態1の固体撮像装置の構成を示す縦断面図である。また、図2は図1に示す固体撮像装置の縦断面図において○印で示した部分の拡大断面図である。
固体撮像装置1は、固体撮像素子11が開口部20を有する回路基板14に対して撮像面12をフェイスダウンにして接続されたものである。すなわち、固体撮像素子11に形成された例えば金による突起電極13と回路基板14に形成されている接続電極15とを位置合わせし、フェイスダウン方式で装着されたものである。この装着は、突起電極13を回路基板14の接続電極15に接合して行い、その接合方法としては、超音波接合、導電接着剤による接着、はんだ接合、あるいは、Auバンプとはんだ接合の併用などが適用される。
FIG. 1 is a longitudinal sectional view showing the configuration of the solid-state imaging device according to the first embodiment. 2 is an enlarged cross-sectional view of a portion indicated by a circle in the vertical cross-sectional view of the solid-state imaging device shown in FIG.
In the solid-
そして、固体撮像素子11の撮像面12に対向する回路基板14の面には撮像面12よりも面積が広く、かつ開口部20よりも広い面積で窪み16が形成されている。窪み16の上側の空間17は突起電極13と接続電極15とによって定まる固体撮像素子11と回路基板14との間の本来的な空間である。
A
上記の固体撮像素子11と回路基板14とが接続電極15を介して接続された状態において、その周縁部に硬化前の紫外線・熱両用硬化型の封止樹脂19がディスペンサによって塗布される。塗布後に封止樹脂19は紫外線もしくは熱により硬化される。
In a state where the solid-
その過程において、未硬化の低粘度の封止樹脂19は、固体撮像素子11と回路基板14との狭い空間17、ないしは固体撮像素子11と接続電極15との間の空間を毛細管現象によって浸入し内部へ入り込むが、図2に示すように、回路基板14に設けられている窪み16と本来の空間17とによって、固体撮像素子11の表面と窪み16の底面との間には矢印h1で示す大きさの間隙が形成されているので上記の毛細管現象が断ち切られ、封止樹脂19は窪み16へ僅か入った箇所で垂直方向へ垂れて浸入を停止される。そして、硬化が進行することにより、封止樹脂19は図2に示した状態で完全に硬化される。
In the process, the uncured low-
また、特許文献1の製造方法と併用した場合、図3に示すように、紫外線照射装置22から照射される紫外線21の照射角度αが、窪み16がない場合の照射角度βに比較して小さくすることができ、これにより、封止樹脂19を撮像面12から離れた浸入位置で硬化することができ、固体撮像素子11の端面と撮像面12の端面との距離が近接した構成においても、さらに優れた撮像品質が得られる。
Further, when used in combination with the manufacturing method of
このようにして、浸入した封止樹脂19が固体撮像素子11の撮像面12を汚染することを完全に防止することができ、優れた撮像品質が得られる。また、封止樹脂19が撮像面12を汚染した不良品の発生が防止されるので、製品の歩留りが向上し、製造ラインの生産性を高めることができる。
(実施の形態2)
本発明の実施の形態2の固体撮像装置を説明する。
In this way, it is possible to completely prevent the infiltrated sealing
(Embodiment 2)
A solid-state imaging device according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention will be described.
図4は本実施の形態2の固体撮像装置の構成を示す縦断面図である。また、図5は図4に示す固体撮像装置の縦断面図において○印で示した部分の拡大断面図である。なお、図4および図5において、図1および図2と同じ構成要素については同じ符号を用い、ここでの説明は省略する。 FIG. 4 is a longitudinal sectional view showing the configuration of the solid-state imaging device according to the second embodiment. FIG. 5 is an enlarged cross-sectional view of a portion indicated by a circle in the vertical cross-sectional view of the solid-state imaging device shown in FIG. 4 and 5, the same reference numerals are used for the same components as those in FIGS. 1 and 2, and descriptions thereof are omitted here.
実施の形態1の固体撮像装置においては、絶縁基体を接続電極を有する回路基板で構成したが、本実施の形態2の固体撮像装置では、絶縁基体として樹脂成形パッケージ23を使用した点が異なる。従ってここでは、固体撮像装置24は、固体撮像素子11が開口部20を有する樹脂成形パッケージ23に対して撮像面12をフェイスダウンにして接続されたものとなっている。
In the solid-state imaging device of the first embodiment, the insulating base is configured by a circuit board having connection electrodes, but the solid-state imaging device of the second embodiment is different in that a resin molded
すなわち、固体撮像素子11に形成された例えば金による突起電極13と樹脂成形パッケージ23に形成されている接続電極15とを位置合わせし、フェイスダウン方式で装着されたものである。この装着は、突起電極13を樹脂成形パッケージ23の接続電極15に接合して行い、その接合方法としては、超音波接合、導電接着剤による接着、はんだ接合、あるいは、Auバンプとはんだ接合の併用などが適用される。
That is, the protruding
そして、固体撮像素子11の撮像面12に対向する樹脂成形パッケージ23の面には撮像面12よりも面積が広く、かつ開口部20よりも広い面積で窪み16が形成されている。窪み16の上側の空間17は、突起電極13と接続電極15とによって定まる固体撮像素子11と樹脂成形パッケージ23との間の本来的な空間である。
A
上記の固体撮像素子11と樹脂成形パッケージ23とが接続電極15を介して接続された状態において、その周縁部に硬化前の紫外線・熱両用硬化型の封止樹脂19がディスペンサによって塗布される。塗布後に封止樹脂19は紫外線もしくは熱により硬化される。
In a state where the solid-
その過程において、未硬化の低粘度の封止樹脂19は、固体撮像素子11と樹脂成形パッケージ23との狭い空間17、ないしは固体撮像素子11と接続電極15との間の空間を毛細管現象によって浸入し内部へ入り込むが、図5に示すように、樹脂成形パッケージ23に設けられている窪み16と本来の空間17とによって、固体撮像素子11の表面と窪み16の底面との間には矢印h2で示す大きさの間隙が形成されているので上記の毛細管現象が断ち切られ、封止樹脂19は窪み16へ僅か入った箇所で垂直方向へ垂れて浸入を停止される。そして、硬化が進行することにより、封止樹脂19は図5に示した状態で完全に硬化される。
In the process, the uncured low-
また、特許文献1の製造方法と併用した場合には、前述の実施の形態1の固体撮像装置の場合と同様に、固体撮像素子11の端面と撮像面12の端面との距離が近接した構成においても、さらに優れた撮像品質が得られる。
Further, when used in combination with the manufacturing method of
このようにして、浸入した封止樹脂19が固体撮像素子11の撮像面12を汚染することを完全に防止することができ、優れた撮像品質が得られる。また、封止樹脂19が撮像面12を汚染した不良品の発生が防止されるので、製品の歩留りが向上し、製造ラインの生産性を高めることができる。
In this way, it is possible to completely prevent the infiltrated sealing
以上、本発明の固体撮像装置を実施の形態によって具体的に説明したが、勿論、本発明はこれに限られることなく、本発明の技術的思想に基づいて、種々の変形が可能である。
例えば、実施の形態1の固体撮像装置1においては、固体撮像素子11をフェイスダウン方式で装着した後に、封止樹脂19を注入したが、例えば、回路基板14に封止樹脂19を塗布した後に、固体撮像素子11を加熱・加圧による圧着接合で接合させる場合においても、封止樹脂19は窪みにより流速が低下しつつ硬化反応が進行するために、撮像面を汚染せず、同様の効果が得られる。
The solid-state imaging device of the present invention has been specifically described above by way of the embodiments. However, of course, the present invention is not limited to this, and various modifications can be made based on the technical idea of the present invention.
For example, in the solid-
また、各実施の形態においては、固体撮像装置や、その構成要素である固体撮像素子が方形である場合を説明したが、それ以外の多角形や円形または楕円形であってもよく、固体撮像装置や固体撮像素子の形状は限定されない。 In each embodiment, the case where the solid-state imaging device or the solid-state imaging element that is a component thereof is a square has been described. However, other polygons, circles, or ellipses may be used. The shape of the device or the solid-state image sensor is not limited.
また、各実施の形態においては、封止樹脂として紫外線・熱両用硬化型を使用したが、紫外線硬化型樹脂や熱硬化性樹脂を使用してもよいことは言うまでもない。
また、各実施の形態の絶縁基体として、ガラスエポキシ基板やセラミック基板からなる配線基板、あるいは樹脂成形パッケージを使用することができる。
In each embodiment, the ultraviolet / heat curable type is used as the sealing resin, but it goes without saying that an ultraviolet curable resin or a thermosetting resin may be used.
In addition, as the insulating base of each embodiment, a wiring substrate made of a glass epoxy substrate or a ceramic substrate, or a resin molded package can be used.
本発明の固体撮像装置は、撮像面を汚染することがなく、良好な撮像品質を得ることができるとともに、製品の歩留りを向上して生産性を高めることができるものであり、カメラ付き携帯電話などの携帯端末等に内蔵される固体撮像装置に適用することができる。 The solid-state imaging device of the present invention can obtain good imaging quality without contaminating the imaging surface, and can improve the yield of the product and increase the productivity. The present invention can be applied to a solid-state imaging device built in a portable terminal or the like.
1 固体撮像装置
11 固体撮像素子
12 撮像面
13 突起電極
14 回路基板
15 接続電極
16 窪み
17 空間
19 封止樹脂
20 開口部
21 紫外線
22 紫外線照射装置
23 樹脂成形パッケージ
24 固体撮像装置
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (3)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004120953A JP2005303213A (en) | 2004-04-16 | 2004-04-16 | Solid-state imaging device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004120953A JP2005303213A (en) | 2004-04-16 | 2004-04-16 | Solid-state imaging device |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2005303213A true JP2005303213A (en) | 2005-10-27 |
| JP2005303213A5 JP2005303213A5 (en) | 2007-04-26 |
Family
ID=35334319
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004120953A Pending JP2005303213A (en) | 2004-04-16 | 2004-04-16 | Solid-state imaging device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2005303213A (en) |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2007099677A1 (en) * | 2006-03-03 | 2007-09-07 | Sony Chemical & Information Device Corporation | Functional-element-mounted module, process for producing the same, resin sealing plate for use therein, and substrate structure for resin sealing |
| JP2008226895A (en) * | 2007-03-08 | 2008-09-25 | New Japan Radio Co Ltd | Optical semiconductor device and its manufacturing method |
| JP2011086789A (en) * | 2009-10-16 | 2011-04-28 | Japan Radio Co Ltd | Mounting structure and mounting method for electronic component |
| WO2015060345A1 (en) * | 2013-10-23 | 2015-04-30 | 京セラ株式会社 | Imaging element mounted substrate and imaging device |
| JP2017092320A (en) * | 2015-11-12 | 2017-05-25 | 旭化成エレクトロニクス株式会社 | Optical sensor device |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH11220115A (en) * | 1998-01-30 | 1999-08-10 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Manufacture of solid-state image-pickup device |
| JP2002009265A (en) * | 2000-06-21 | 2002-01-11 | Sony Corp | Solid-state image pickup device |
-
2004
- 2004-04-16 JP JP2004120953A patent/JP2005303213A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH11220115A (en) * | 1998-01-30 | 1999-08-10 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Manufacture of solid-state image-pickup device |
| JP2002009265A (en) * | 2000-06-21 | 2002-01-11 | Sony Corp | Solid-state image pickup device |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2007099677A1 (en) * | 2006-03-03 | 2007-09-07 | Sony Chemical & Information Device Corporation | Functional-element-mounted module, process for producing the same, resin sealing plate for use therein, and substrate structure for resin sealing |
| JP2008226895A (en) * | 2007-03-08 | 2008-09-25 | New Japan Radio Co Ltd | Optical semiconductor device and its manufacturing method |
| JP2011086789A (en) * | 2009-10-16 | 2011-04-28 | Japan Radio Co Ltd | Mounting structure and mounting method for electronic component |
| WO2015060345A1 (en) * | 2013-10-23 | 2015-04-30 | 京セラ株式会社 | Imaging element mounted substrate and imaging device |
| JP5988412B2 (en) * | 2013-10-23 | 2016-09-07 | 京セラ株式会社 | Imaging device mounting substrate and imaging apparatus |
| JP2017092320A (en) * | 2015-11-12 | 2017-05-25 | 旭化成エレクトロニクス株式会社 | Optical sensor device |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US7268436B2 (en) | Electronic device with cavity and a method for producing the same | |
| JP5746919B2 (en) | Semiconductor package | |
| CN1324340C (en) | Module for optical devices, and manufacturing method of module for optical devices | |
| JP5095114B2 (en) | Method for manufacturing solid-state imaging device | |
| KR101158139B1 (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| CN1677660A (en) | Semiconductor apparatus, manufacturing method thereof, semiconductor module apparatus using semiconductor apparatus, and wire substrate for semiconductor apparatus | |
| JP2010118634A (en) | Printed circuit board having flow preventing dam and manufacturing method therefor | |
| JP2010165940A (en) | Resin sealing method of semiconductor device | |
| JP2010165940A5 (en) | ||
| JP2007311416A (en) | Solid-state imaging device | |
| JP2013201389A (en) | Imaging module, and manufacturing method of imaging module | |
| JP2007095778A (en) | Function element package and method of manufacturing same | |
| JP2002009265A (en) | Solid-state image pickup device | |
| US8179686B2 (en) | Mounted structural body and method of manufacturing the same | |
| JP3648721B2 (en) | Method for manufacturing solid-state imaging device | |
| JP6971826B2 (en) | Solid-state image sensor and its manufacturing method | |
| JP2006351559A (en) | Wiring board and structure for mounting semiconductor chip on wiring board | |
| JP2005303213A (en) | Solid-state imaging device | |
| KR20130122218A (en) | Method for manufacturing underfill flip chip package | |
| JP2009188275A (en) | Semiconductor chip, semiconductor device, method for manufacturing same, and liquid crystal module | |
| JPWO2009113262A1 (en) | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method of semiconductor device | |
| JP4688443B2 (en) | Manufacturing method of semiconductor device | |
| JPH09186308A (en) | Manufacture of solid-state image pickup module | |
| JP2009070876A (en) | Solid-state imaging device and its manufacturing process | |
| JP2008226895A (en) | Optical semiconductor device and its manufacturing method |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20070312 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20070312 |
|
| RD04 | Notification of resignation of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7424 Effective date: 20080430 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20100402 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20100525 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20100726 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20100907 |