JP2005296797A - Coating header, thin film forming apparatus provided with the same, and reverse printing device - Google Patents
Coating header, thin film forming apparatus provided with the same, and reverse printing device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2005296797A JP2005296797A JP2004116678A JP2004116678A JP2005296797A JP 2005296797 A JP2005296797 A JP 2005296797A JP 2004116678 A JP2004116678 A JP 2004116678A JP 2004116678 A JP2004116678 A JP 2004116678A JP 2005296797 A JP2005296797 A JP 2005296797A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- coating
- header
- liquid
- thin film
- coated
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
Images
Abstract
Description
本発明は、相対的に移動する被塗工材の塗工面に対し液状の材料液を供給することにより移動方向に沿って被塗工材に材料液を塗工する薄膜形成装置の塗工ヘッダ、およびそれを備えた薄膜形成装置と反転印刷装置に関する。 The present invention relates to a coating header of a thin film forming apparatus that applies a material liquid to a coating material along a moving direction by supplying a liquid material liquid to a coating surface of the coating material to be moved relatively. And a thin film forming apparatus and a reverse printing apparatus including the same.
最近、液晶表示装置等が広く普及するようになり、この液晶表示装置のガラス板やそのガラス基板に貼られる保護板等の基材に材料液を塗工して、極薄い薄膜を形成する必要が出てきた。そのような場合に用いられる薄膜形成装置の一般的な例の概要構成図を図12に示し説明する。 Recently, liquid crystal display devices and the like have become widespread, and it is necessary to form a very thin thin film by applying a material solution to a substrate such as a glass plate of the liquid crystal display device or a protective plate attached to the glass substrate. Came out. A schematic configuration diagram of a general example of a thin film forming apparatus used in such a case will be described with reference to FIG.
図12において、100は薄膜形成装置であり、塗工ヘッダ101と、塗工ヘッダ101に材料液(塗工液)aを供給する図示しない材料液供給装置と、塗工ヘッダ移動装置102と、各種基板等の基材(被薄膜形成材)110とが所定位置にセットされる台枠103を有している。また。その上方に位置して、塗工ヘッダ101から供給された材料液aを基材110に転写する薄膜塗工ローラ(被塗工材であるシリンダ状部材)104と、薄膜塗工ローラ104を移動するための図示しないローラ移動装置と、薄膜塗工ローラ104を回転するための図示しないローラ回転駆動装置とを備えて構成されている。
In FIG. 12, 100 is a thin film forming apparatus, a
薄膜形成装置100における塗工工程を図12により説明すると、図12(a)に示すように、薄膜塗工ローラ104を、先ずローラ移動装置により塗工ヘッダ101の上方に移動させる。このとき、薄膜塗工ローラ104は回転停止状態とされ、塗工ヘッダ101は薄膜塗工ローラ104と接触しない下降位置とされている。
The coating process in the thin film forming apparatus 100 will be described with reference to FIG. 12. As shown in FIG. 12A, the thin
次いで、(b)に示すように、塗工ヘッダ移動装置102を作動させて塗工ヘッダ101を薄膜塗工ローラ104と接触する上昇位置にとするとともに、ローラ回転駆動装置を作動させて薄膜塗工ローラ104を回転させる。これにより、薄膜塗工ローラ104の周面104aに材料液aが塗工される。
Next, as shown in (b), the coating
薄膜塗工ローラ104の周面104aの全周に亘って材料液が塗工されると、塗工ヘッダ移動装置102の作動により、(c)に示すように、塗工ヘッダ101が薄膜塗工ローラ104と接触しない下降位置とされ、また、ローラ回転駆動装置を停止して薄膜塗工ローラ104の回転を停止させ、薄膜塗工ローラ104の塗工工程が完了する。
When the material liquid is applied over the entire circumference of the
そして、ローラ移動装置の作動により薄膜塗工ローラ104を基材110へと移動させるとともにローラ回転駆動装置を作動させて薄膜塗工ローラ104を回転させる。薄膜塗工ローラ104の高さ位置は、その最下の周面位置が基材110の上面と一致するように設定されており、(d)に示すように、薄膜塗工ローラ104を基材110上で移動させることにより、薄膜塗工ローラ104の周面104a上の材料液が基材110上に転写されることになる。
Then, the thin
上記のような薄膜塗工装置100に用いられ、ガラス基板等の基材(被薄膜形成材)110に極薄い薄膜を形成するための塗工ヘッダとしては、従来、(1)表面張力利用型や、(2)毛細菅現象利用型(例えば、特開2001−62370公報:特許文献1)が提案されている。 Conventionally, as a coating header for forming an extremely thin thin film on a base material (film forming material) 110 such as a glass substrate, which is used in the thin film coating apparatus 100 as described above, conventionally, (1) surface tension utilizing type And (2) a type using a capillary wrinkle phenomenon (for example, Japanese Patent Laid-Open No. 2001-62370: Patent Document 1) has been proposed.
(1)表面張力利用型: 図13は従来の表面張力利用型の塗工ヘッダを用いた薄膜形成装置の一例の構成及び作動を説明するための模式的な要部側断面図である。 (1) Surface Tension Utilizing Type: FIG. 13 is a schematic side sectional view for explaining the configuration and operation of an example of a thin film forming apparatus using a conventional surface tension utilizing type coating header.
この薄膜形成装置200では、図13(a)に示すように、薄膜を形成する材料液(塗工液)aをポンプPにより液供給管202を介して塗工ヘッダとしての円柱体201の空洞(内部)201aへ供給する。この円柱体201の上部には、20μm程度の径の孔が多数形成されたポーラス部(塗工部)203が、周方向に10mm程度の幅をもって形成されており、このポーラス部203においては、円柱体201の外周面と内周面とが連通した状態となっている。したがって、ポンプPにより上記の内部201aへと供給された材料液aは、ポーラス部203において外周面へ供給されるようになるが、この外周面へ供給された材料液aの内、過剰に供給された材料液aは、円柱体201の姿勢がポーラス部203を鉛直上方に向けた姿勢に設定されているため、ポーラス部203を出た後、下方に落下するようになる。
In this thin film forming apparatus 200, as shown in FIG. 13A, a material liquid (coating liquid) a for forming a thin film is pumped by a pump P through a
この結果、ポーラス部203にはその外周面に一定高さ(例えば400μm程度)の材料液aの隆起が得られるようになる。そして、図13(b)に示すように、基材(被薄膜形成材)210を、ポーラス部203における材料液aの隆起に接触させつつ移動させることで、基材210に材料液aの液溜まり(液ビード:液膜)204が形成される。
As a result, the
なお、円柱体201の外周面から落下した材料液aは、円柱体201の下方に配置された液タンク205により回収され、液回収管206を介してポンプPに吸引され、再び円柱体201へと供給されることとなる。
The material liquid a dropped from the outer peripheral surface of the
(2)毛細管現象利用型(キャピラリーコータ型): 図14は従来の毛細管現象利用型の塗工ヘッダを用いた薄膜形成装置の一例の構成及び作動を説明するための模式的な要部側断面図である。 (2) Capillary Phenomenon Utilization Type (Capillary Coater Type): FIG. 14 is a schematic side cross-sectional view for explaining the configuration and operation of an example of a thin film forming apparatus using a conventional capillary phenomenon utilization type coating header. FIG.
この薄膜形成装置300では、非塗工作業時には、塗工ヘッダ301を材料液層302に沈めておき、塗工作業時には、塗工ヘッダ301の先端を、上記材料液層302から基材(被薄膜形成材)310に向けて突出させるようになっている。塗工ヘッダ301には基材310の移動方向に対し略直角方向に配向して開口するスリット303が形成されており、上記材料液層302を形成する材料液aが、毛細現象によりこのスリット303内を伝って塗工ヘッダ301の先端で隆起して液ビード(液溜まり)304を形成する。この液ビード304は材料液aの表面張力によりその隆起高さひいてはその量がほぼ一定に保たれる。
In the thin film forming apparatus 300, the
そして、塗工ヘッダ301の先端に液溜まり304が形成された状態で、塗工ヘッダ301に対し所定の隙間(ギャップ)をあけつつ且つ基材310を液溜まり304に接触させて基材310を移動させることで、基材310に材料液aが塗工される。
Then, with the
このような塗工作業時は、基材310に塗工される分、液溜まり304が減少することとなるが、この減少した分だけ材料液aが、毛細管現象により自然と一定に液溜まり304に供給されるしくみとなっている。
During such a coating operation, the
塗工作業は、図14において(a)〜(f)の順に行われ、先ず、塗工開始前においては、(a)に示すように、塗工ヘッダ301は液タンク305内に沈められており、この液タンク305の上部は蓋306に蓋われている。
The coating work is performed in the order of (a) to (f) in FIG. 14. First, before the start of coating, as shown in (a), the
次いで、(b)に示すように、蓋306がスライドして液タンク305が開放され、塗工ヘッダ301が液タンク305から基材310側へ突出した状態とされる。この時、液タンク305内の材料液aが、毛細管現象により、塗工ヘッダ301に形成されたスリット303を上昇して塗工ヘッダ301の先端で隆起して液溜まり304を形成する。
Next, as shown in (b), the
そして、このような塗工ヘッダ301の状態において、(c)、(d)、(e)に示すように、基材310を塗工ヘッダ301の先端の液溜まり304に接触させながら、基材301のセットされるステージ307と一体に図中左側へとスライドさせて行き、この過程で、基材310に塗工薄膜308が次第に形成されていく。(f)に示すように、基材310が液溜まり304を通過して塗工が完了すると、塗工ヘッダ301は液タンク305内の材料液層302に沈められた後、蓋306がスライドして液タンク305を蓋い、塗工作業が完了する。
And in such a state of the
しかしながら、上述した2つのタイプの従来の薄膜形成装置用の塗工ヘッダには依然以下のような問題があった。 However, the above-described two types of conventional coating headers for thin film forming apparatuses still have the following problems.
(1)表面張力利用型
図15は上述した図13に示すような従来の表面張力利用型の塗工ヘッダとしての円柱体201の問題の説明図であって、(a)は基材210と円柱体201のポーラス部(塗工部)203との最接近部(以下、ニップ部という)の模式的な側面視による断面図であり、(b)は(a)の模式的なA−A矢視断面図である。
(1) Surface Tension Utilization Type FIG. 15 is an explanatory view of the problem of the
図15(a)中の破線207は、基材210とポーラス部203とのニップ部周辺で材料液膜208、209が受ける圧力の圧力分布線を示し、図15(a)中で上にあるほど高い圧力を示している。基材210とポーラス部203との隙間が狭いほど材料液aが受ける圧力は高くなることから、ニップ部において材料液aが絞られる(これを液絞りという)ため材料液aの圧力は急上昇する一方、ニップ部下流側では基材210とポーラス部203との隙間が急に広がるため、材料液の圧力は負圧となる(圧力分布線207における符号207aで示す部分を参照)。
A broken line 207 in FIG. 15A indicates a pressure distribution line of the pressure received by the material
この負圧の発生のため、ニップ部下流側で液膜分裂の際、すなわちポーラス部の材料液膜208の一部が基材210へ材料液膜209として移動する際、上記負圧の作用により材料液膜208、209のメニスカスが基材210とポーラス部203との隙間に引き込まれるような現象が発生し、図15(b)に示すように、材料液膜208、209に規則的なリングパターンと呼ばれる円柱体201円周方向に延びる筋状のムラ(円柱体201軸方向に数mm程度のピッチで繰り返される液厚の凹凸)が発生しやすい。図15(b)中の符号211はリングパターンを形成し基材210に正常に塗工されない余剰液(余剰な材料液)である。リングパターンの凹凸のピッチや高さは、材料液aの表面張力や粘度及びニップ部下流側で発生する負圧207aの程度により異なったものとなる。
Due to the generation of the negative pressure, when the liquid film is split on the downstream side of the nip portion, that is, when a part of the
このようなリングパターンが発生すると、基材210が印刷版である場合には、この印刷版を使用して印刷された印刷物にリングパターンに応じた濃淡ムラが生じ、不良印刷物となる。また、その問題のほかに、表面張力利用型の塗工ヘッダの一般的傾向として、塗工速度はある程度高速化できるが、薄膜形成の精度を十分に上げられない、という問題もあった。
When such a ring pattern is generated, if the
(2)毛細管現象利用型(キャピラリーコータ型)
図16は上述した図14に示すような従来の毛細管現象利用型の塗工ヘッダ301の問題の説明図であって、(a)は基材310と塗工ヘッダ301との最接近部(以下、ニップ部という)の模式的な側面視による断面図であり、(b)は(a)の模式的なB−B矢視断面図である。
(2) Capillary phenomenon type (capillary coater type)
FIG. 16 is an explanatory view of the problem of the conventional capillary phenomenon-based
毛細管現象利用型の塗工ヘッダ301も、上記の表面張力利用型の塗工ヘッダとしての円柱体201と同様の課題を有する。つまり、塗工ヘッダ301の基材310移動方向下流側では、それまで塗工ヘッダ301の上面により規定されていた空間が急激に広がるので、負圧部309が発生し、材料液aの液溜まり304の一部が基材310上の塗工薄膜308へと移動する液膜分裂の際、材料液aのメニスカスが塗工ヘッダ301側に引き込まれてしまう。この結果、(b)に示すような基材310移動方向に対して直角方向において数mmピッチで凹凸が繰り返されるリングパターンが発生しやすくなるのである。(b)中の符号311はリングパターンを形成し基材310に正常に塗工されない余剰液(余剰な材料液)である。
The capillary phenomenon-based
また、この毛細管現象利用型の塗工ヘッダ301では、スリット303の幅(スリット開口幅)と塗工ヘッダ301の先端から基材310の表面までの距離との関係を制御できれば、均一な薄膜の形成(リングパターンの発生を抑制すること)は可能であるが、上記スリット開口幅を装置幅方向[図15(a)において紙面に垂直な方向]に亘って均一に加工するのが難しく、塗工ヘッダ301と基材310との距離に応じてスリット開口幅を適切に調整するのは現実的には難しいという問題があった。また、その問題のほかに、毛細管現象利用型の塗工ヘッダの一般的傾向として、薄膜形成の精度を上げることができ美麗な塗膜が得やすいが、塗工速度が低いという問題があり、材料液aの供給を単に毛細管現象によらずポンプ等圧送手段を用いることである程度速度向上ができるが薄膜精度との関係から限界がある。
Further, in this
以上、従来の(1)表面張力利用型、及び(2)毛細管現象利用型の塗工ヘッダにつき、平板状の基材(被薄膜形成材)に直接薄膜を形成する場合を説明したが、シリンダ状の基材(被薄膜形成材)210、310に薄膜を塗工する場合や、図12で説明したような、被塗工材としての薄膜塗工ローラに一旦塗工した上で薄膜塗工ローラから基材(被薄膜形成材)210、310に転写するときの薄膜塗工ローラへの塗工の場合は、被塗工材(基材または薄膜塗工ローラ等)がシリンダ状物であり、そのシリンダ状物をその軸芯線を中心に回転させつつ、円柱体201又は塗工ヘッダ301により塗工を行うことにより、シリンダ状物の周面に連続的に薄膜を形成するが、同様に上記のリングパターンや薄膜精度、塗工速度の問題を有するものであった。
As described above, the conventional (1) surface tension type and (2) capillary phenomenon type coating headers have been described in the case where a thin film is directly formed on a flat substrate (film forming material). When a thin film is applied to the base materials (film forming materials) 210 and 310, or a thin film coating roller once applied to a thin film coating roller as a coating material as described in FIG. In the case of coating onto a thin film coating roller when transferring from a roller to a substrate (film forming material) 210, 310, the material to be coated (such as a substrate or a thin film coating roller) is a cylinder. The thin film is continuously formed on the peripheral surface of the cylindrical object by coating with the
以上のように、(1)表面張力利用型及び(2)毛細管現象利用型の何れの塗工ヘッダ201、301においても、塗工薄膜の厚みが塗工方向に対する幅方向において不均一になりやすく、リングパターンに応じた濃淡ムラが生じ、不良印刷物(損紙)となる問題があった。
As described above, in any of the
なお、上記問題点の説明においても、被塗工材として平板状の基材(被薄膜形成材)210、310に塗工膜を形成する例を説明したが、リングパターンは被塗工材(基材または薄膜塗工ローラ等)がシリンダ状物の場合にも発生し、シリンダ状の基材(被薄膜形成材)に薄膜を塗工する場合であっても同様であり、また、図12で説明したと同様に、薄膜塗工ローラに一旦塗工した上で薄膜塗工ローラから基材(被薄膜形成材)210、310に転写する場合の、薄膜塗工ローラへの塗工の場合も同様のリングパターンが生じ、その結果、基材(被薄膜形成材)210、310上のリングパターンの問題を発生する。 In the description of the above problem, the example in which the coating film is formed on the flat base materials (thin film forming materials) 210 and 310 as the coating material has been described. This also occurs when the base material or the thin film coating roller is a cylindrical object, and the same applies to the case where a thin film is applied to the cylindrical base material (film forming material). In the same manner as described in the above, in the case of coating on the thin film coating roller when the thin film coating roller is once coated and then transferred from the thin film coating roller to the base material (film forming material) 210, 310 , A similar ring pattern is generated, and as a result, a problem of the ring pattern on the base materials (thin film forming materials) 210 and 310 occurs.
本発明はこのような問題を解決するためになされたものであり、被塗工材(基材または薄膜塗工ローラ等)に均一の厚みで、安定した材料液を塗工でき、塗工速度の向上を可能とする、薄膜形成装置用の材料液の塗工ヘッダと、それを用いた薄膜形成装置を提供することを課題とする。 The present invention has been made to solve such problems, and can apply a stable material solution to a material to be coated (such as a base material or a thin film coating roller) with a uniform thickness, and a coating speed. It is an object of the present invention to provide a coating header of a material liquid for a thin film forming apparatus and a thin film forming apparatus using the same.
本発明は、上記の課題を解決するためになされ、下記の(1)から(8)の手段を提供するものであり、以下、特許請求の範囲に記載の順に説明する。 The present invention has been made to solve the above-described problems, and provides the following means (1) to (8), and will be described below in the order of the claims.
(1)その第1の手段として、液状の材料液を被塗工材の塗工面に塗布し、同塗工面に薄膜を形成する薄膜形成装置用の塗工ヘッダであって、前記材料液を前記被塗工材に供給する前記塗工ヘッダ先端のリップ部におけるリップ下流側面が同塗工ヘッダ中心線に対して0°ないし20°の範囲で前記塗工面側に傾斜して加工されてなることを特徴とする塗工ヘッダを提供する。 (1) As the first means, it is a coating header for a thin film forming apparatus that applies a liquid material solution to a coated surface of a material to be coated and forms a thin film on the coated surface. The lip downstream side surface of the lip portion at the tip of the coating header supplied to the coating material is processed by being inclined toward the coating surface within a range of 0 ° to 20 ° with respect to the coating header center line. A coating header is provided.
(2)第2の手段としては、第1の手段の塗工ヘッダにおいて、下方に向き水平方向に対して20°ないし65°の塗工面角度をつけた前記被塗工材の塗工面に、前記リップ部を上向きに近接配置されてなることを特徴とする塗工ヘッダを提供する。 (2) As the second means, in the coating header of the first means, the coating surface of the material to be coated with a coating surface angle of 20 ° to 65 ° with respect to the horizontal direction facing downward, Provided is a coating header characterized in that the lip portion is closely arranged upward.
(3)また、第3の手段として、第1の手段または第2の手段の塗工ヘッダにおいて、同塗工ヘッダはその中心方向を、前記リップ部が近接配置された箇所の前記塗工面に垂直に向け配置されてなることを特徴とする塗工ヘッダを提供する。 (3) Further, as a third means, in the coating header of the first means or the second means, the coating header has its center direction on the coating surface at the location where the lip portion is disposed in proximity. Provided is a coating header characterized by being arranged vertically.
(4)第4の手段として、第1の手段ないし第3の手段のいずれかの塗工ヘッダにおいて、前記液状の材料液が揮発性の材料液であることを特徴とする塗工ヘッダを提供する。 (4) As a fourth means, in the coating header of any one of the first means to the third means, a coating header is provided in which the liquid material liquid is a volatile material liquid To do.
(5)第5の手段として、第1の手段ないし第4の手段のいずれかの塗工ヘッダにおいて、前記被塗工材は平板状被塗工材であり、前記リップ部が近接配置される前記塗工面は同平板状被塗工材の下面であることを特徴とする塗工ヘッダを提供する。 (5) As a fifth means, in the coating header of any one of the first means to the fourth means, the material to be coated is a flat material to be coated, and the lip portion is disposed in proximity. The coating surface is a lower surface of the flat plate-shaped material to be coated, and provides a coating header.
(6)第6の手段として、第1の手段ないし第4の手段のいずれかの塗工ヘッダにおいて、前記被塗工材はシリンダ状被塗工材であり、前記リップ部が近接配置される塗工面は同シリンダ状被塗工材の下側周面であることを特徴とする塗工ヘッダを提供する。 (6) As a sixth means, in the coating header of any one of the first means to the fourth means, the coated material is a cylindrical coated material, and the lip portion is disposed in proximity. The coating surface is a lower peripheral surface of the cylindrical coated material, and provides a coating header.
(7)第7の手段として、第1の手段ないし第6の手段のいずれかの塗工ヘッダを備えてなることを特徴とする薄膜形成装置を提供する。 (7) As a seventh means, there is provided a thin film forming apparatus comprising the coating header of any one of the first means to the sixth means.
(8)第8の手段として、第1の手段ないし第4の手段、または第6の手段のいずれかの塗工ヘッダを備えてなることを特徴とする反転印刷装置を提供する。 (8) As an eighth means, there is provided a reverse printing apparatus comprising the coating header of any one of the first means to the fourth means or the sixth means.
(1)特許請求の範囲に記載の請求項1の発明によれば、リップ下流側面がシャープエッジまたはそれに近い形状のため、リップ上流側面への液拡張濡れが抑制され、材料液固着が発生しない条件となり、被塗工材に均一の厚みで、安定したビード形状で材料液を塗工でき、リングパターンの問題を回避し塗工速度向上が可能となる。
(1) According to the invention of
(2)請求項2の発明によれば、請求項1の発明の作用効果に加え、鉛直方向液引出し力が大きくなり液ビードが安定、塗工開始前の液だれが防止されて膜厚誤差の増大が防止されるので、さらに、材料液固着が発生しない条件となり、被塗工材に均一の厚みで、安定したビード形状で材料液aを塗工でき、リングパターンの問題を回避し塗工速度向上が可能となる。
(2) According to the invention of claim 2, in addition to the function and effect of the invention of
(3)請求項3の発明によれば、通常の塗工面と垂直な配置方向に取付けた塗工ヘッダにおいて請求項1または請求項2の発明の作用効果をさらに奏することができる。
(3) According to the invention of
(4)請求項4の発明によれば、特に、材料液の固着が生じやすかった揮発性の材料液を塗工する場合において、請求項1ないし請求項3のいずれかの発明の作用効果を顕著に奏することができる。
(4) According to the invention of claim 4, particularly in the case of applying a volatile material liquid in which the material liquid is easily fixed, the effect of the invention of any one of
(5)請求項5の発明によれば、請求項1ないし請求項4のいずれかの発明の作用効果を、平板状被塗工材の下面を塗工面として奏することができる。
(5) According to the invention of claim 5, the effect of the invention of any one of
(6)請求項6の発明によれば、請求項1ないし請求項4のいずれかの発明の作用効果を、シリンダ状被塗工材の下側周面を塗工面として奏することができる。
(6) According to the invention of claim 6, the effect of the invention of any one of
(7)請求項7の発明によれば、薄膜形成装置において、請求項1ないし請求項6のいずれかの発明の作用効果を奏し、基材または薄膜塗工ローラ等の被塗工材に、均一の厚みで、安定した液ビード形状で、材料液を塗工でき、リングパターンの問題を回避し、塗工精度、塗工速度向上が可能な薄膜形成装置となる。
(7) According to the invention of claim 7, in the thin film forming apparatus, the effect of the invention of any one of
(8)請求項8の発明によれば、反転印刷装置において、請求項1ないし請求項4、または請求項6のいずれかの発明の作用効果を奏し、塗布胴等の被塗工材に、均一の厚みで、安定した液ビード形状で材料液を塗布でき、リングパターン等の問題を回避し、塗工精度、塗工速度向上が可能な反転印刷装置となる
(8) According to the invention of
本発明を実施するための最良の形態として、以下に実施例1から実施例3を説明する。 Examples 1 to 3 will be described below as the best mode for carrying out the present invention.
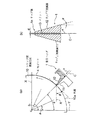
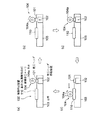
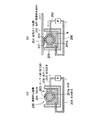
本発明の実施例1に係る塗工ヘッダを図1に基づき説明する。図1(a)はシリンダ状被塗工材に対する本実施例の塗工ヘッダの配置図であり、(b)は本実施例の塗工ヘッダの拡大断面図である。本実施例の塗工ヘッダは、図12に示すと同様の薄膜形成装置に用いられる塗工ヘッダであり、薄膜形成装置全体は図12を参照することとし、改めて図示することは省略する。なお、本実施例において、薄膜形成装置100は図12に図示のものに限定されることなく、種々の態様のものであってよい。 The coating header which concerns on Example 1 of this invention is demonstrated based on FIG. FIG. 1A is an arrangement view of a coating header of this embodiment with respect to a cylindrical coated material, and FIG. 1B is an enlarged cross-sectional view of the coating header of this embodiment. The coating header of the present embodiment is a coating header used in the same thin film forming apparatus as shown in FIG. 12, and the entire thin film forming apparatus will be referred to FIG. 12, and will not be illustrated again. In this embodiment, the thin film forming apparatus 100 is not limited to the one shown in FIG.
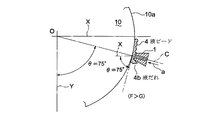
図1において、1は本実施例の塗工ヘッダであり、10は塗工ヘッダ1により材料液(塗工液)aの薄膜を塗工されるシリンダ状被塗工材である。材料液aは揮発性の材料液も含むものとする。シリンダ状被塗工材10は、例えば、各種基板等の基材(被薄膜形成材)であり、または、材料液aを基材に転写する薄膜塗工ローラ等であって、シリンダ状に形成され、その軸芯線O回りに図中矢印方向に回転しつつ、その周面10a(塗工面)に近接する塗工ヘッダ1によって塗工され、周面10a上に材料液aの液ビード4が形成される。
In FIG. 1,
塗工ヘッダ1は、図14で説明したと同様に毛細管現象利用型の塗工ヘッダであり、その内部に設けられスリット13を有し、スリット13は塗工ヘッダ1の先端部(以下、「リップ部」という)1aに開口を有し、毛細管現象を利用して材料液aをシリンダ状被塗工材10の周面10aに供給する。なお、毛細管現象による以上に塗工速度を増大させる必要のある場合は材料液aをポンプ等により加圧して供給することがある。
The
塗工ヘッダ1のリップ部1aが位置するシリンダ状被塗工材10の下側の周面10aの点の、シリンダ状被塗工材10の下側の周面10aの真下の位置からの角度、すなわちシリンダ状被塗工材10の軸芯Oと塗工ヘッダ1とを結ぶ線と鉛直方向Yとのなす角度をθとすると、塗工ヘッダ1のリップ部1aに相対し、塗工されるシリンダ状被塗工材10の周面10a(塗工面)の傾斜角度、すなわち接線方向の角度は、水平方向Xに対してθとなる(以下、「塗工面角度θ」という)。
The angle of the point on the lower
本実施例において、塗工ヘッダ1のリップ部1a(以下、単に「塗工ヘッダ1」とも記載する)は、シリンダ状被塗工材10の下側の周面10aの真下の位置から鉛直方向Yに対してθ回った点の周面10aに位置しており、θは、θ1=25°からθ2=65°の範囲、θ=25〜65°に設定される。すなわち塗工面角度θ=25〜65°に設定される。
In the present embodiment, the
なお、通常、塗工ヘッダ1は、塗工ヘッダ中心線Cを略シリンダ状被塗工材10の軸芯線Oに向けて、リップ部1aが近接配置された箇所の周面10a(塗工面)の方向、すなわち同箇所の接線方向と略垂直に配向されるから、塗工ヘッダ中心線Cの鉛直方向Yに対する角度もθ=25〜65°の範囲になる。
Normally, the
塗工ヘッダ1の断面形状は図1(b)に示すように、シリンダ状被塗工材10の回転方向における上流側のリップ上流側面11と、下流側のリップ下流側面12の間に、塗工ヘッダ中心線Cに沿ってスリット13が形成されている。スリット13はリップ部1aにおいて、周面10aに面してシリンダ状被塗工材10の軸方向に延在する開口を有し、そこから周面10aへの材料液aの供給を行う。
As shown in FIG. 1B, the cross-sectional shape of the
スリット13の開口幅dは例えば0.5〜0.8mmであり、スリット13を挟むリップ上流側面11側とリップ下流側面12側の先端部材厚さはそれぞれ5mm程度である。リップ下流側面12は塗工ヘッダ中心線Cに対し、角度αの周面10a(塗工面)側に傾斜した面をなすように加工されており、α=0〜20°の範囲、さらに好ましくはα=5〜20°の範囲としてある。
The opening width d of the slit 13 is, for example, 0.5 to 0.8 mm, and the tip member thicknesses on the lip
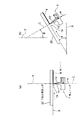
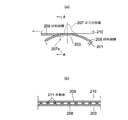
本発明の実施例2に係る塗工ヘッダを図2(a)に基づき説明する。図2(a)は平板状被塗工材に対する本実施例の塗工ヘッダの配置図である。本実施例の塗工ヘッダも、実施例1と同じく、図12に示すと同様の薄膜形成装置に用いられる塗工ヘッダ1であり、平板状被塗工材に対するものである以外は、塗工ヘッダ1の構造も薄膜形成装置全体も実施例1で記載したと同様であり、繰り返しの記載は省略する。
The coating header which concerns on Example 2 of this invention is demonstrated based on Fig.2 (a). FIG. 2A is a layout view of the coating header of this embodiment with respect to the flat plate-shaped material to be coated. Similarly to Example 1, the coating header of this example is a
図2(a)において、20は塗工ヘッダ1により材料液aの薄膜を塗工される平板状被塗工材である。材料液aは揮発性の材料液もである含むものとする。平板状被塗工材20は、例えば、各種基板等の平板状の基材(被薄膜形成材)であり、水平軸Xに沿って配置され、水平軸X方向に移動されつつ、その下面(塗工面)に略垂直上向きに近接する塗工ヘッダ1によって塗工され、面上に材料液aの液ビード4が形成される。従って、平板状被塗工材20の水平方向Xに対する塗工面角度θ=0°である。
In FIG. 2A,
なお、通常、塗工ヘッダ1は、塗工ヘッダ中心線Cを平板状被塗工材20の下面(塗工面)に略垂直に配向されるから、塗工ヘッダ中心線Cの鉛直方向Yに対する角度もθ=0°になる。
In general, the
塗工ヘッダ1は、実施例1と同様のものであり、内部に設けられ毛細管現象を利用して材料液aを供給するスリット13を有し、塗工ヘッダ中心線Cを平板状被塗工材20に略垂直に向けてリップ部1aを近接させて設置されている。塗工ヘッダ1の断面形状は図1(b)に示すものと同じであり、リップ下流側面12は塗工ヘッダ中心線Cに対し塗工面側に傾斜する、角度αの傾斜面をなし、α=0〜20°、さらに好ましくはα=5〜20°としてある。
The
本発明の実施例3に係る塗工ヘッダを図2(b)に基づき説明する。図2(b)は平板状被塗工材に対する本実施例の塗工ヘッダの配置図である。本実施例の塗工ヘッダも、実施例1、実施例2と同じく、図12に示すと同様の薄膜形成装置に用いられる塗工ヘッダであり、平板状被塗工材に対するものである以外は、塗工ヘッダの構造も薄膜形成装置全体も実施例1で説明したと同様であり、繰り返しの記載は省略する。本実施例が実施例2と異なるのは、平板状被塗工材20が水平方向Xに対して傾斜して配置されるものである点であり、それ以外は引例1と同様である。
The coating header which concerns on Example 3 of this invention is demonstrated based on FIG.2 (b). FIG. 2B is a layout view of the coating header of the present embodiment with respect to the flat plate-shaped material to be coated. The coating header of this example is also a coating header used in the same thin film forming apparatus as shown in FIG. 12 as in Example 1 and Example 2, except that it is for a flat coated material. The structure of the coating header and the entire thin film forming apparatus are the same as described in the first embodiment, and repeated description is omitted. The present embodiment is different from the second embodiment in that the flat plate-shaped
図2(b)において、20は塗工ヘッダ1により材料液aの薄膜を塗工される平板状被塗工材である。平板状被塗工材20は、例えば、各種基板等の平板状の基材(被薄膜形成材)であり、水平軸Xに対してθ傾斜して設置され、その角度θの方向に移動しつつ、その下面(塗工面)に垂直向きに近接する塗工ヘッダ1によって塗工され、面上に材料液aの液ビード4が形成される。材料液aは揮発性の材料液もである含むものとする。したがって、平板状被塗工材20の塗工面角度はθである。
In FIG. 2 (b),
本実施例において、塗工面角度θは、θ=25〜65°の範囲になるように設置してある。なお、通常、塗工ヘッダ1は、塗工ヘッダ中心線Cを平板状被塗工材20の下面(塗工面)と略垂直に配向されるから、塗工ヘッダ中心線Cの鉛直方向Yに対する角度もθ=25〜65°の範囲になる。
In this embodiment, the coating surface angle θ is set to be in the range of θ = 25 to 65 °. In general, the
塗工ヘッダ1は、実施例1と同様のものであり、内部に設けられ毛細管現象を利用して材料液aを供給するスリット13を有し、塗工ヘッダ中心線Cを平板状被塗工材20に略垂直に向けてリップ部1aを近接させて設置されている。塗工ヘッダ1の断面形状は図1(b)に示すものと同じであり、リップ下流側面12は塗工ヘッダ中心線Cに対し塗工面側に傾斜する、角度αの傾斜面をなし、α=0〜20°、さらに機械工作上、好ましくはα=5〜20°としてある。
The
上記の各実施例に係る塗工ヘッダ1の形状と、配置の特徴についてまとめて以下説明する。
The shape of the
(1)塗工ヘッダのリップ部形状(先端形状)について:
本発明者の研究により、塗工ヘッダ1のリップ部1aの形状が、材料液(塗工液)aの塗工状態の安定化に影響することが判明し、研究・試験の結果、リップ部形状の最適化につき下記のことを見出した。
(1) About the lip shape (tip shape) of the coating header:
As a result of research by the present inventor, it has been found that the shape of the
塗工ヘッダ1の中心線Cをシリンダ状被塗工材10の周面10aに対して略垂直に向けリップ部1aを近接させ、シリンダ状被塗工材10をその軸芯O回りに回転させつつ材料液aを周面10a上に塗工したもので、基本的な試験条件は次の通りである。
・材料液(揮発性インキ):粘度≦4mPa・s
・被塗工材:シリコンブランケット
・塗工速度:0.03m/s、0.05m/s
・塗工被膜厚さ:10〜20μm
・ヘッダ、リップ部の材料:SCM材
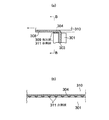
図3は、リップ部1aのリップ下流側面12が周面10a(塗工面)側に傾斜し、塗工ヘッダ1中心線Cとなす角度(リップ下流側面角度)αを変えて塗工した試験結果の例であり、塗工状態図である。
The center line C of the
・ Material liquid (volatile ink): Viscosity ≦ 4 mPa · s
・ Coating material: Silicon blanket ・ Coating speed: 0.03 m / s, 0.05 m / s
-Coating film thickness: 10-20 μm
-Material of header and lip portion: SCM material Fig. 3 shows an angle formed by the lip
(リップ下流側面角度α=0度の場合) 図3(a)に示すように、リップ下流側面12が塗工ヘッダ1中心線Cに対して0°で、リップ端面に対して直角でシャープエッジとなるため、リップ上流側面11への液拡張濡れが抑制される。またリップ部1a下流側のビード位置が安定する。そのため安定した液ビード4が得られている。
(When the lip downstream side surface angle α = 0 °) As shown in FIG. 3A, the lip
(リップ下流側面角度α=12度の場合) 図3(b)に示すように、この場合もリップ下流側面12が塗工ヘッダ1中心線Cに対して12度と、シャープエッジに近い形状のため、リップ上流側面11への液拡張濡れが抑制されており、良好で安定した液ビードが得られている。
(In the case of the lip downstream side surface angle α = 12 degrees) As shown in FIG. 3B, the lip
(リップ下流側面角度α=30度の場合) 図3(c)に示すように、リップ下流側面12を塗工ヘッダ1中心線Cに対し30度と大きく、リップ下流側面角度αが大きくなると、液がリップ下流側面12に材料液aが付着しやすくなる。この付着した材料液aは揮発性インキのため、すぐ硬化してリップ部1aに固着する。この固着した材料液aに、新たに塗工した材料液aが付着し、図示のようにリップ部1a下流側のビード位置5が乱れてくる。その結果として塗工された液ビード4は不均一で安定性のない液ビードとなる。
(In the case of the lip downstream side surface angle α = 30 degrees) As shown in FIG. 3 (c), when the lip
以上の試験結果をまとめたグラフを図4に示す。横軸はリップ下流側面角度αを示し、左縦軸は「(イ)材料液固着防止効果」(液ビード安定性)、右縦軸は「(ロ)リップ先端形状加工性の難易度」を示す。リップ先端形状の機械加工性の難易度は、リップ部1aの先端は非常に小さく、また硬い材料を使用するが、実際の装置に利用するためには塗工方向に対し幅方向に精度良く、均一に加工する必要があり、実際にはこの加工が困難な事から考慮したものである。
A graph summarizing the above test results is shown in FIG. The horizontal axis indicates the lip downstream side surface angle α, the left vertical axis indicates “(b) material liquid adhesion prevention effect” (liquid bead stability), and the right vertical axis indicates “(b) difficulty level of lip tip shape workability”. Show. The difficulty of the machinability of the lip tip shape is that the tip of the
図4に示すように、(イ)材料液固着防止効果(液ビード安定性)は、リップ下流側面角度αが0°で、リップ下流側面12がシャープエッジ(直角)になるほど良いビードが得られが、リップ下流側面角度αが30°の場合は、材料液aの固着が発生し、適していない。またリップ部1aの機械加工の難易度は、シャープエッジになるほど困難になり、リップ下流側面角度αが大きくなるほど容易になる。
As shown in FIG. 4, (a) the material liquid sticking prevention effect (liquid bead stability) is such that a better bead is obtained when the lip downstream side surface angle α is 0 ° and the lip
そこで、実際に機械加工でき、また良好な液ビードが得られる適正領域としては、リップ下流側面角度α=0〜20度、機械加工上から、より望ましくはα=5〜20度の範囲である。その場合、塗工する材料液aが揮発性インキ液の場合でもインキ液がリップ先端に固着しないので、良好で安定した塗工が可能となる。 Therefore, an appropriate region where the actual machining can be performed and a good liquid bead can be obtained is a lip downstream side surface angle α = 0 to 20 °, and more preferably α = 5 to 20 ° from the viewpoint of machining. . In that case, even when the material liquid a to be applied is a volatile ink liquid, the ink liquid does not adhere to the tip of the lip, so that a good and stable coating can be achieved.
(2)塗工ヘッダの配置について:
本発明者の研究により、塗工ヘッダ1により塗工される被塗工材の傾斜角度、すなわち塗工面角度θが、材料液(塗工液)aの厚み等、塗工状態の安定化に影響することが判明し、研究・試験の結果、塗工面角度θの最適化につき(また、塗工ヘッダ1は通常、塗工面に略垂直に配置されるから、塗工ヘッダ1の配置の最適化につき)、下記のことを見出した。
(2) About the layout of the coating header:
According to the inventor's research, the inclination angle of the material to be coated applied by the
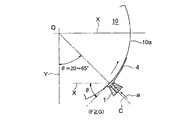
図5に基づき、塗工ヘッダ1の最適配置を決定するための試験を説明する。図5は、塗工面角度θ最適化のための試験におけるシリンダ状被塗工材10に対する塗工ヘッダの配置図であり、シリンダ状被塗工材10の周面10aに対して塗工ヘッダ1の中心線Cを垂直に向け、すなわちシリンダ状被塗工材10の軸芯Oに向けて、リップ部1aを近接させ、リンダ状被塗工材10を回転させつつ、材料液aを周面10a上に塗工したもので、基本的な試験条件は次の通りである。
・材料液(揮発性インキ):粘度≦4mPa・s
・被塗工材:シリコンブランケット
・塗工速度:0.03m/s、0.05m/s
・塗工被膜厚さ:10〜20μm
・ヘッダ、リップ部の材料:SCM材
塗工ヘッダ1は、シリンダ状被塗工材10の真下の位置で上向き配置の場合、すなわち、シリンダ状被塗工材10の塗工面角度θ=0°、鉛直方向Yに対する塗工ヘッダ1の方向Cの角度θ=0°の位置から、シリンダ状被塗工材10の真横の位置で水平向き配置の場合、すなわち、塗工面角度θ=90°、周面10a上の塗工ヘッダ1の位置の鉛直方向Yに対する角度θ=90°の位置まで、塗工ヘッダ1の位置を変えて、シリンダ状被塗工材10に塗工される材料液aの液ビードの塗工状況を試験した。
Based on FIG. 5, the test for determining the optimal arrangement | positioning of the
・ Material liquid (volatile ink): Viscosity ≦ 4 mPa · s
・ Coating material: Silicon blanket ・ Coating speed: 0.03 m / s, 0.05 m / s
-Coating film thickness: 10-20 μm
-Header and lip material: SCM material When the
塗工ヘッダ1から供給された材料液aがシリンダ状被塗工材10の周面10a(塗工面)に塗工される時、材料液aには、重量Gで落下する力と、シリンダ状被塗工材10の移動により材料液aの粘度に基づく塗工面に沿う方向(接線方向)の液引出し力f(以下、「塗工面方向液引出し力f」という)が作用する。
When the material liquid a supplied from the
この試験は、上記の重量Gと、塗工面方向液引出し力fの鉛直方向成分F(以下、「鉛直方向液引出し力F」という)との関係が、被塗工材に塗工される液ビードの安定性を左右すると着目したものである。 In this test, a liquid in which the relationship between the weight G and the vertical component F of the liquid drawing force f in the coating surface (hereinafter referred to as “vertical liquid drawing force F”) is applied to the material to be coated. It focuses on the stability of the bead.
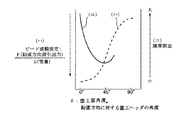
図5に示すように、F=f・sinθであるから、θ=0°でF=f・sin0°=0、θ=90°でF=f・sin90°=fとなり、塗工状況の試験結果の代表例を、下記のように図6〜図8に示す。
As shown in FIG. 5, since F = f · sin θ, F = f ·
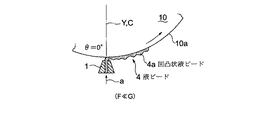
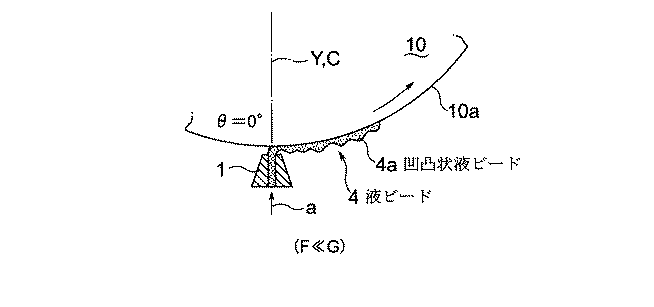
(塗工ヘッダ1をシリンダ状被塗工材10の軸芯真下に上向きに配置した場合) 図6(及び図5)に示すように、塗工ヘッダ1に相対する周面10aの接線方向の水平方向Xに対する角度が塗工面角度θであり、塗工ヘッダ1の周面10a上の位置の鉛直方向Yに対する角度もθ=0°である。従って、塗工ヘッダ1をシリンダ状被塗工材10に対し真下から塗工する場合は、鉛直方向液引出し力F=sin0°=0 であり、一方、重量Gは大きく作用し(F≪G)、しかも材料液供給速度が減少する方向に作用するので、シリンダ状被塗工材10に塗工された液ビード4は、幅方向にも、進行方向にも均一性がなく、図示のように凹凸状液ビード4aとなりやすい。
(When the
(塗工ヘッダ1をシリンダ状被塗工材10の周面上、真下の位置から鉛直方向Yに対してθ回った位置に配置した場合) 図7(及び図5)に示すように、塗工ヘッダ1に相対する周面10aの接線方向の水平方向Xに対する角度が塗工面角度θであり、塗工ヘッダ1の周面10a上の位置の鉛直方向Yに対する角度はθである。
(When the
塗工面角度θ=20°〜65°の場合は重力Gと塗工面方向液引出し力fの鉛直方向成分が発生し、鉛直方向液引出し力F=fsinθ が重量Gとほぼ同等かやや大の力(F≧G)としやすいので、液だれも発生せず、均一なビードが塗布できる。 When the coating surface angle θ = 20 ° to 65 °, vertical components of the gravity G and the liquid drawing force f in the coating surface are generated, and the vertical liquid drawing force F = fsinθ is almost equal to the weight G or slightly larger force. Since it is easy to set it as (F> = G), a dripping does not generate | occur | produce and a uniform bead can be apply | coated.
(塗工ヘッダ1をシリンダ状被塗工材10の真横に近い、真下から75°の位置に配置した場合) 図8(及び図5)に示すように、塗工ヘッダ1に相対する周面10aの接線方向の水平方向Xに対する角度が塗工面角度θ=75°であり、塗工ヘッダ1の周面10a上の位置の鉛直方向Yに対する角度もθ=75°である。この場合は、鉛直方向液引出し力F=fsin75°は、塗工面角度θ=20°〜65°の場合よりもさらに大きくなり、F>Gとなりやすいので、液ビード4の形成はさらに安定する。
(When the
すなわち、上記のように水平位置に近づき、塗工ヘッダ1の取り付け位置の塗工面角度θ、すなわち周面10a上の角度θが大きくなり90°に近づき、塗工面角度θが90°に近づくほど、鉛直方向液引出し力Fが大きくなり、液ビード4が安定する。
That is, as it approaches the horizontal position as described above, the coating surface angle θ at the mounting position of the
しかし、実際の運用においては、塗工面角度θが大きくなるにつれ、塗工ヘッダ1の中心線方向Cが鉛直方向Y上向きから水平方向Xへと傾くため、塗工開始前に液だれ4bが発生し、リップ部1a(塗工ヘッダ1の先端部)の裏側に回り込み、上流側のビード位置(液溜まり)が乱れる。そのため液ビード4も不均一な塗工状態となってくる。そのため、塗工面角度θが45°を越えると膜厚誤差が増大する。
However, in actual operation, as the coating surface angle θ increases, the center line direction C of the
ちなみに、塗工ヘッダ1をシリンダ状被塗工材10に対して下向きに配置すると、重量Gが大きく作用し、しかも材料液供給速度が増大する方向に作用するので、液だれが発生し易く、安定した塗工が困難となり、通常用いられない。
By the way, when the
図9は、以上の試験結果をまとめたグラフであり、図9において、横軸は水平面方向Xに対する「塗工面角度θ」〔シリンダ状被塗工材10の場合は、塗工ヘッダ1の位置の鉛直方向に対する周面10a上の角度であり、塗工ヘッダ中心線Cを塗工面方向(周面10a接線方向)に対して垂直に配置した場合は、鉛直方向Yに対する塗工ヘッダの角度〕、縦軸(ハ)は塗工した液ビードのビード液膜の安定性を示し、縦軸(ニ)は液ビードの膜厚誤差を示す。
FIG. 9 is a graph summarizing the above test results. In FIG. 9, the horizontal axis represents “coating surface angle θ” with respect to the horizontal plane direction X [in the case of the
また、図9に示す結果の評価を、〔表1〕にまとめて示す。 Moreover, evaluation of the result shown in FIG. 9 is collectively shown in [Table 1].
(3)以上の試験結果に示されることから、上記実施例は以下の作用効果を奏すると言える。 (3) From the above test results, it can be said that the above example has the following effects.
(シリンダ状被塗工材10の場合:実施例1) 上記したように、リップ下流側面12をリップ下流側面角度α=0〜20°、さらに好ましくはα=5〜20°の範囲となるように加工したリップ部1aを設けた塗工ヘッダ1とする。また、塗工ヘッダ1の取付位置は、塗工面角度θ=25〜65°となるように、塗工ヘッダ1の位置をシリンダ状被塗工材10に対し真下からの周面10a上の角度θ=25〜65°の領域で設置し、鉛直方向液引出し力Fを重力G以上(F≧G)とし、上流側のビード位置を固定した方が良い。
(In the case of the cylindrical coating material 10: Example 1) As described above, the lip
これにより実施例1においては、材料液固着が発生しない条件となり、シリンダ状被塗工材10に均一の厚みで、安定したビード形状で材料液aを塗工でき、リングパターンの問題を回避し塗工速度向上が可能となる。特に、材料液aの固着が生じやすかった揮発性インキを材料液aとして塗工する場合、その作用効果が顕著である。
Thus, in Example 1, the material liquid does not stick, and the material liquid a can be applied to the cylindrical
(平板状被塗工材20の場合:実施例2、実施例3) 平板状被塗工材20は、ハンドリングの都合上、水平に配置し、水平方向に移動させつつ塗工する場合が多いが、その場合、実施例1のように平板状被塗工材20下面(塗工面)に対して垂直で上向きに塗工ヘッダ1を配置し、リップ下流側面角度α=0〜20°、さらに好ましくはα=5〜20°の範囲となるように加工したリップ部1aを設けた塗工ヘッダ1とする。これにより実施例2においては、材料液固着が発生しない条件となり、揮発性インキを材料液aとした場合でも、平板状被塗工材20に均一の厚みで、安定したビード形状で材料液aを塗工でき、リングパターンの問題を回避し塗工速度向上が可能となる。
(In the case of the flat coated material 20: Example 2 and Example 3) The flat
平板状被塗工材20の下面(塗工面)と同下面に対する塗工ヘッダ1との関係は、シリンダ状被塗工材10における周面10a(塗工面)と同周面1aに対する塗工ヘッダ1との関係と同様である。そこで実施例3のように、実施例2と同様にリップ下流側面角度α=0〜20°、さら機械加工上に好ましくはα=5〜20°の範囲となるように加工したリップ部1aを設けた塗工ヘッダ1を用い、さらに、平板状被塗工材20を水平方向Xに対してθ傾斜して設置し塗工面角度θとし、その塗工面角度θの方向に移動させつつ、平板状被塗工材20の下面に近接する塗工ヘッダ1によって塗工する場合は、塗工面角度θ=20〜65°に設定すると、実施例1と同様に材料液固着が発生しない条件となり、被塗工材に均一の厚みで、安定したビード形状で材料液aを塗工でき、リングパターンの問題を回避し塗工速度向上が可能となる。特に、材料液aの固着が生じやすかった揮発性インキを材料液aとして塗工する場合、その作用効果が顕著である。
The relationship between the lower surface (coating surface) of the flat
なお、その場合、平板状被塗工材20の下面に対し塗工ヘッダ1の中心軸方向Cを垂直に配向させて設置すれば、鉛直方向Yに対して塗工ヘッダ中心線Cのなす角度もθである。
In this case, if the central axis direction C of the
従って、上記実施例1から実施例3のいずれかの塗工ヘッダを備えた薄膜形成装置は、基材または薄膜塗工ローラ等の被塗工材に、均一の厚みで、安定した液ビード形状で、材料液を塗工でき、リングパターンの問題を回避し塗工精度、塗工速度向上が可能な薄膜形成装置となる。 Therefore, the thin film forming apparatus including the coating header according to any of the first to third embodiments has a uniform liquid bead shape with a uniform thickness on a substrate or a material to be coated such as a thin film coating roller. Thus, the material liquid can be applied, and a thin film forming apparatus capable of improving the coating accuracy and the coating speed by avoiding the ring pattern problem.
なお、本実施例の薄膜形成装置は、図12に図示の薄膜形成装置100に限られず、図12を参照して説明すれば、図示とは逆に、薄膜塗工ローラ104を位置固定とし、基材110を移動させるものでもよく、また、基材110を塗工ヘッダ101と接触するような高さ位置に設定するとともに、その高さ位置において基材110を図中で左右に移動させる移動装置を設け、薄膜塗工ローラ104無しで塗工ヘッダ101から基材110へ直接塗工を行うものでもよく、基材110が平板状のものでなくシリンダ状のものの場合は、塗工ヘッダ101と接触した状態で回転させる回転駆動装置を設けたものでもよい。
Note that the thin film forming apparatus of the present embodiment is not limited to the thin film forming apparatus 100 illustrated in FIG. 12, and will be described with reference to FIG. 12. The base 110 may be moved, and the
また、薄膜形成装置100は、塗工ヘッダ101が1基のものではなく、材料液の色等の種類によって塗工ヘッダ101を複数基備え、合わせて薄膜塗工ローラ104も複数基備えたものでもよい。
Further, the thin film forming apparatus 100 is not provided with a
以上述べたように、各実施例の塗工ヘッダ1は、一般的に薄膜形成装置用の塗工ヘッダとして用いられるものであるが、特に薄膜形成装置の一つとしての反転印刷装置において、その塗工ヘッダとして、有効に実施し得るものとなる。
As described above, the
一般的にカラーフィルタ等を形成する方法としては、印刷法、フォトリソ法等の方法が知られているが、印刷法においては反転印刷装置を用いることが有効であり、以下、一般的な反転印刷装置と、反転印刷装置による印刷法で薄膜(カラーフィルタ等)を形成する原理について図10、図11により説明する。図10は一般的な反転印刷装置の概要構成図、図11(a)〜(c)は一般的な反転印刷装置の動作と原理の説明図である。 In general, methods such as a printing method and a photolithographic method are known as methods for forming a color filter, etc., but it is effective to use a reversal printing apparatus in the printing method. The principle of forming a thin film (color filter or the like) by a printing method using an apparatus and a reverse printing apparatus will be described with reference to FIGS. FIG. 10 is a schematic configuration diagram of a general reverse printing apparatus, and FIGS. 11A to 11C are explanatory views of the operation and principle of the general reverse printing apparatus.
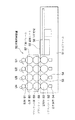
図10に示すように反転印刷装置50の固定フレーム51には、シリコンシート52を表面に貼り付けた塗布胴53、塗布胴53表面に接して材料液として樹脂(インキ)a′を塗布(塗工)する塗布装置54を1ユニットとし、各色分、すなわち、ブラックマトリクス、レッド、グリーン、ブルーの4ユニット(ブラックマトリクス用ユニットU1、レッド用ユニットU2、グリーン用ユニットU3、ブルー用ユニットU4)分と基板シート55を設置する印刷定盤56が設けてある。また、固定フレーム51上には移動する可動フレーム57があり、可動フレーム57にはシリコンブランケット58が巻き付けてあるブランケット胴59、同ブランケット胴59と接して、凸版60を表面に取り付けた回転する版胴61を1ユニットとし、固定フレーム51の塗布胴53に対応して設けてある。
As shown in FIG. 10, the fixed frame 51 of the reverse printing apparatus 50 is coated with a
図11は、図10に示す反転印刷装置50の動作及び原理を示す図である。塗布装置54により塗布胴53上に貼り付けてあるシリコンシート52上に着色された樹脂(インキ)a′を塗布し、この樹脂a′をブランケット胴59、上のシリコンブランケット58に転写する(a)。次に版胴61上に樹脂版を露光、現像し、所定の形状に凸部を形成した凸版60を取り付け、凸版60を押圧しブランケット58上の塗布面から凸部分の樹脂a′を除去する(b)。ブランケット58面上の残りの樹脂a′を可動フレームの移動により印刷定盤上の基板シート55上に転写する(c)。この原理によって、ブラックマトリクス、レッド、グリーン、ブルーにつき可動フレームが往復することにより基板シート55にブラックマトリクスとレッド(R)、グリーン(G)、ブルー(B)の画素のカラーフィルタ層を形成することができる。
FIG. 11 is a diagram showing the operation and principle of the reverse printing apparatus 50 shown in FIG. A colored resin (ink) a ′ is applied on the
以上のような反転印刷装置50において、塗布胴53は、上記実施例における「シリンダ状被塗工材10」に相当するので、塗布装置54に、上記実施例の「塗工ヘッダ1」を適用することで、上述の実施例1の塗工ヘッダ1の作用効果を反転印刷装置50において奏することができる。(なお、図10、図11は一般的な反転印刷装置を示すものであるので、図中の塗布装置54は、本発明の実施例の塗工ヘッダ1を明示するものではない。)
すなわち、上記実施例1の塗工ヘッダ1を備えた反転印刷装置50は、被塗工材となる塗布胴53に、均一の厚みで、安定した液ビード形状で、材料液としての樹脂(インキ)a′を塗布(塗工)でき、リングパターン等の問題を回避し、塗工精度、塗工速度向上が可能な反転印刷装置となる
以上、本発明を図示の実施例について説明したが、本発明は上記の実施例に限定されず、本発明の範囲内でその具体的構造に種々の変更を加えてよいことはいうまでもない。
In the reverse printing apparatus 50 as described above, the
That is, the reversal printing apparatus 50 provided with the
1 塗工ヘッダ
1a ニップ部
4 液ビード
4a 凹凸状液ビード
4b 液だれ
10 シリンダ状被塗工材
10a 周面
11 リップ上流側面
12 リップ下流側面
13 スリット
20 平板状被塗工材
50 反転印刷装置
51 固定フレーム
53 塗布胴
54 塗布装置
55 基板シート
57 可動フレーム
59 ブランケット胴
61 版胴
100 薄膜形成装置
101 塗工ヘッダ
102 塗工ヘッダ移動装置
104 薄膜塗工ローラ
104a 周面
θ 塗工面角度
G 重量
F 鉛直方向液引出し力
f 塗工面方向液引出し力
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (8)
A reverse printing apparatus comprising the coating header according to any one of claims 1 to 4 and claim 6.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004116678A JP2005296797A (en) | 2004-04-12 | 2004-04-12 | Coating header, thin film forming apparatus provided with the same, and reverse printing device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004116678A JP2005296797A (en) | 2004-04-12 | 2004-04-12 | Coating header, thin film forming apparatus provided with the same, and reverse printing device |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2005296797A true JP2005296797A (en) | 2005-10-27 |
Family
ID=35328991
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004116678A Withdrawn JP2005296797A (en) | 2004-04-12 | 2004-04-12 | Coating header, thin film forming apparatus provided with the same, and reverse printing device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2005296797A (en) |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE102013215265A1 (en) | 2013-08-02 | 2015-02-05 | Windmöller & Hölscher Kg | doser |
| DE102013215264A1 (en) | 2013-08-02 | 2015-02-05 | Windmöller & Hölscher Kg | inking |
| DE102013215267A1 (en) | 2013-08-02 | 2015-02-05 | Windmöller & Hölscher Kg | doser |
| US9873937B2 (en) | 2009-05-22 | 2018-01-23 | Samsung Display Co., Ltd. | Thin film deposition apparatus |
-
2004
- 2004-04-12 JP JP2004116678A patent/JP2005296797A/en not_active Withdrawn
Cited By (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US9873937B2 (en) | 2009-05-22 | 2018-01-23 | Samsung Display Co., Ltd. | Thin film deposition apparatus |
| US10689746B2 (en) | 2009-05-22 | 2020-06-23 | Samsung Display Co., Ltd. | Thin film deposition apparatus |
| US11624107B2 (en) | 2009-05-22 | 2023-04-11 | Samsung Display Co., Ltd. | Thin film deposition apparatus |
| US11920233B2 (en) | 2009-05-22 | 2024-03-05 | Samsung Display Co., Ltd. | Thin film deposition apparatus |
| DE102013215265A1 (en) | 2013-08-02 | 2015-02-05 | Windmöller & Hölscher Kg | doser |
| DE102013215264A1 (en) | 2013-08-02 | 2015-02-05 | Windmöller & Hölscher Kg | inking |
| DE102013215267A1 (en) | 2013-08-02 | 2015-02-05 | Windmöller & Hölscher Kg | doser |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP1342508B1 (en) | Coating apparatus and coating method | |
| JP2005296797A (en) | Coating header, thin film forming apparatus provided with the same, and reverse printing device | |
| JP2010005543A (en) | Reverse gravure coating method and device using this method | |
| JP2006281103A (en) | Ink supply apparatus, pattern formation method, pattern formation apparatus, color filter formation method, and pattern formation apparatus | |
| US7862864B2 (en) | Bar coating method and apparatus | |
| JP2003190870A (en) | Method for coating cylindrical body surface and fixation roller formed by the method | |
| JP2006255660A (en) | Coating method and coater | |
| JP2007181811A (en) | Production method for improving uniformity of quality of coating layer | |
| JPH0677709B2 (en) | Transfer device | |
| JP2013166089A (en) | Method for applying coating material and coating apparatus | |
| JP2013208826A (en) | Thin film printing method and thin film printer | |
| JP4353681B2 (en) | Die head for coating | |
| JP3482112B2 (en) | Coating method and device | |
| JP2006218433A (en) | Method and device of blade coating | |
| JP2009233501A (en) | Roll coating method and roll coating apparatus | |
| CN219856474U (en) | Liquid supply mechanism and printing device comprising same | |
| JP3881268B2 (en) | Coating method and coating apparatus | |
| JP2005058869A (en) | Material liquid application header for thin film forming apparatus and thin film forming apparatus | |
| JP2019130859A (en) | Doctor blade and printing device | |
| JP5367322B2 (en) | Coating equipment | |
| JP2006198475A (en) | Blade coating method and disk coating method using this | |
| JP2017021386A (en) | Alignment film printing plate and manufacturing method of liquid crystal display device | |
| JP2006205010A (en) | Blade coater and printing surface coater for disk | |
| JPH10202156A (en) | Roll coater | |
| JP2009028638A (en) | Coating method and coating apparatus |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A300 | Withdrawal of application because of no request for examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A300 Effective date: 20070703 |