JP2004046870A - Information unit group operation device - Google Patents
Information unit group operation device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2004046870A JP2004046870A JP2003201957A JP2003201957A JP2004046870A JP 2004046870 A JP2004046870 A JP 2004046870A JP 2003201957 A JP2003201957 A JP 2003201957A JP 2003201957 A JP2003201957 A JP 2003201957A JP 2004046870 A JP2004046870 A JP 2004046870A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- information unit
- information
- unit group
- integrated
- group
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Information Retrieval, Db Structures And Fs Structures Therefor (AREA)
Abstract
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、本発明は、情報を検索したり、評価分析するための装置に関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
本明細書において情報単位とは、名称(見出し)を持ったひとかたまりの情報をいう。
情報の最も基本的なものは文字列であるが、画像、音声、動画など電子的に表現できるものであれば、どのようなものでもかまわない。
また、検索の利便性を考慮すれば、その情報の性質を表現するキーワード等の属性値を持っていることが好ましい。
さらに、情報単位群とは、複数の情報単位の集合のことである。
本発明では、情報単位群がファイルシステム上に複数、しかも他のファイルと混在して存在している状況を想定している。
【0003】
例えば、情報単位群の代表的なものは、電子辞書である。
1つの情報単位は例えば『apple』という単語を見出しとして、その発音、意味、用例などの記述を内容とする。
そして、英和辞書の全体が情報単位群ということになる。
さらに、それが複数ある状態とは、英和辞書のみならず、国語辞典、漢和字典、和英辞書、仏和辞書などの様々な辞書データが混在している状態を指す。
辞書データの場合には、通常編集したりはしないが、本発明で扱う情報単位は、編集、変換、移動等の操作を行うことも前提としている。
【0004】
情報単位群の別な例は、データベースである。
データベースの1レコードが1つの情報単位に相当する。
そして、ある分野のデータベース全体が情報単位群に相当する。
【0005】
複数の情報単位群を同時に扱う先行技術文献として、特開昭62−287336や特開平4−195680などがあった。
特開昭62−287336は、複数の辞書をユーザが選択して同時に検索する技術を開示している。
この技術では、ディスク装置および辞書情報サーバに存在する辞書の名称が表示される。
ユーザは、この中から自由な組合せで同時に複数の辞書を利用したり、ある辞書の検索結果から、次の検索条件を指定して、別の辞書を検索したりすることができる。
また、特開平4−195680も同様に、複数の辞書を組み合せて利用する技術である。
この技術では、あらかじめ辞書属性テーブルを設け、変換した結果を用いて辞書をひく連続検索を、一定の基準に基づいて行うことを可能としている。
また、使用すべき辞書とその優先順位を記述したテーブルを設けることで、ユーザが状況に応じたアプリケーションを作成できるようにしている。
【0006】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
しかしながら、これらの技術は、あらかじめ使用可能な情報単位群あるいは情報単位群が存在している位置が決まっていることを前提としている。
さらに、その位置にシステムが扱うことのできない情報が混在していることは想定していない。
このような状況では、システムが扱えない情報を辞書としてユーザに提示する恐れがある。
また、ファイル構成の変更のたびに前記のようなテーブルをユーザがメンテナンスする必要があり、ダイナミックに新しい情報単位群を追加したり分離したりしながら、連続的に検索を行うことはできなかった。
【0007】
そこで、本発明では、通常のファイルシステム内に情報単位群が散在しているような状況においても、システムが使用可能な情報単位群のみを自動的に検索することを課題とする。
また、ユーザが情報単位群の組合せをダイナミックかつ自由に指定して、指定された情報単位群を検索したり分析したりできるようにすることを課題とする。
【0008】
本発明に係る情報単位群操作装置は、様々なファイル形式のファイルが混在するファイルシステムから、所定のファイル形式を持ち、情報単位の集まりである情報単位群を検索する情報単位群検索手段と、前記情報単位群検索手段により検索された情報単位群からユーザが情報単位群を指定する情報単位群指定手段と、検索条件を入力する検索条件入力手段と、前記情報単位群指定手段により指定された情報単位群より、前記検索条件入力手段から入力された検索条件に適合する情報単位を検索する検索手段と、前記検索手段により検索された情報単位を表示する検索結果表示手段とを有する。
【0009】
好適には、前記情報単位群指定手段は、前記情報単位群検索手段により検索された情報単位群の固有識別情報を保持する識別情報保持手段と、前記識別情報保持手段に保持される識別情報を表示する識別情報表示手段と、前記識別情報表示手段による表示に対応して設けられ、前記識別情報保持手段に保持されている識別情報に対応する情報単位群から少なくとも1つの情報単位群を選択する入力を受け付ける情報単位群選択手段と、前記情報単位群選択手段により選択された識別情報を保持する選択結果保持手段を有し、前記検索手段は前記選択結果保持手段に保持された識別情報に対応する情報単位群より、前記検索条件入力手段から入力された検索条件に適合する情報単位を検索するように構成してもよい。
【0010】
好適には、前記検索手段は、更に検索した情報単位が所属する情報単位群の識別情報を取得し、前記検索結果表示手段は、前記検索手段の検索した情報単位とともに、該情報単位が所属する情報単位群の識別情報を表示することができる。
【0011】
好適には、更に、ファイルシステムの中で特に前記所定のファイル形式を持つ情報単位群が存在する可能性が高い場所についての情報を保持する存在場所保持手段を有し、前記情報単位検索手段は存在場所保持手段に保存されている情報に基づいてファイルシステムから所定のファイル形式を持つ情報単位群を検索するようにしてもよい。
【0012】
また、本発明に係る情報単位群操作装置は、様々なファイル形式のファイルが混在するファイルシステムから、所定のファイル形式を持ち、情報単位の集まりである情報単位群を検索する情報単位群検索手段と、前記情報単位群検索手段により検索された情報単位群からユーザが情報単位群を指定する情報単位群指定手段と、情報単位群に属する情報単位を評価するための条件を保持する評価条件保持手段と、評価条件保持手段に保持されている条件に基づいて、前記情報単位群指定手段により指定された情報単位群に属する各情報単位を評価した値を算出する情報単位評価手段と、情報単位評価手段によって算出された評価値に基づいて、情報単位の存在を表現する画像構成要素の位置を決定する位置算出手段と、位置算出手段によって決定された位置に画像構成要素を配置する分析画像生成手段と、分析画像生成手段によって生成された画像を表示する分析画像表示手段とを有する。
【0013】
好適には、前記情報単位群指定手段は、前記情報単位群検索手段により検索された情報単位群の固有識別情報を保持する識別情報保持手段と、前記識別情報保持手段に保持される識別情報を表示する識別情報表示手段と、前記識別情報表示手段による表示に対応して設けられ、前記識別情報保持手段に保持されている識別情報に対応する情報単位群から少なくとも1つの情報単位群を選択する入力を受け付ける情報単位群選択手段と、前記情報単位群選択手段により選択された識別情報を保持する選択結果保持手段とを有し、前記情報単位評価手段は、前記評価条件保持手段に保持されている条件に基づいて、前記選択結果保持手段に保持される情報単位群の識別情報に対応する情報単位群に属する各情報単位を評価した値を算出するように構成してもよい。
【0014】
好適には、ファイルシステムの中で特に前記所定のファイル形式を持つ情報単位群が存在する可能性が高い場所についての情報を保持する存在場所保持手段を有し、前記情報単位検索手段は存在場所保持手段に保存されている情報に基づいてファイルシステムから所定のファイル形式を持つ情報単位群を検索するようにしてもよい。
【0015】
また、本発明に係る情報単位群操作装置は、様々なファイル形式のファイルが混在するファイルシステムから、所定のディレクトリ構造を持つ情報単位群を検索する情報単位群検索手段と、情報単位群検索手段により検索された情報単位群の固有識別情報を保持する識別情報保持手段と、前記識別情報保持手段に保持される識別情報を表示する識別情報表示手段とを有する。
【0016】
好適には、前記情報単位群検索手段はファイルを構成するディレクトリに見出しと該見出しに対応する内容を保持するデータファイルと情報単位の検索時に入力される検索キーと該検索キーに対応するデータの前記データファイル中における存在位置との対応関係を保持するインデックスファイルと前記検索キーを該検索キーに対応するインデックスファイル中のアドレスに変換するハッシュテーブルファイルとを含む情報単位群を検索するようにすることができる。
【0017】
また、本発明に係る情報単位群操作は、情報単位の集まりである情報単位群の識別情報を表示する識別情報表示手段と、前記識別情報表示手段による表示に対応して設けられ、前記情報単位群より少なくとも第1の情報単位群及び第2の情報単位群を順に選択する入力を受け付ける情報単位群選択手段と、前記情報単位群選択手段により選択された前記第1の情報単位群及び第2の情報単位群の識別情報を選択された順序とともに保持する選択結果保持手段と、第1の検索条件を入力する検索条件入力手段と、前記検索条件入力手段から入力された第1の検索条件に適合する情報単位を前記選択結果保持手段に保持された第1の情報単位群から検索し、該検索結果を第2の検索条件として、該第2の検索条件に適合する情報単位を前記第2の情報単位群より検索する検索手段と、前記検索手段により検索された情報単位を表示する検索結果表示手段とを有する。
【0018】
また、本発明に係る情報単位群操作装置は、情報単位の集まりである実情報単位群を統合した統合情報単位群の識別情報を表示する識別情報表示手段と、前記識別情報表示手段による表示に対応して設けられ、前記統合情報単位群の少なくとも一つを選択する入力を受け付ける情報単位群選択手段と、前記情報単位群選択手段により選択された前記統合情報単位群の識別情報を保持する選択結果保持手段と、前記選択結果保持手段に保持された情報単位群を統合して新たな統合情報単位群を生成し、該統合情報単位群の情報を保持する情報単位群統合手段と、検索条件を入力する検索条件入力手段と、前記情報単位群統合手段により統合された新たな統合情報単位群より、前記検索条件入力手段から入力された検索条件に適合する情報単位を検索する検索手段と、前記検索手段により検索された情報単位を表示する検索結果表示手段とを有する。
【0019】
また、本発明に係る情報単位群操作装置は、情報単位の集まりである実情報単位群を統合した統合情報単位群の識別情報を表示する識別情報表示手段と、前記識別情報表示手段による表示に対応して設けられ、前記統合情報単位群の少なくとも一つを選択する入力を受け付ける情報単位群選択手段と、前記情報単位群選択手段により選択された前記統合情報単位群の識別情報を保持する選択結果保持手段と、前記選択結果保持手段に保持された情報単位群を統合して新たな統合情報単位群を生成し、該統合情報単位群の情報を保持する情報単位群統合手段と、情報単位群に属する情報単位を評価するための条件を保持する評価条件保持手段と、評価条件保持手段に保持されている条件に基づいて、前記情報単位群統合手段により統合された統合情報単位群に属する各情報単位を評価した値を算出する情報単位評価手段と、情報単位評価手段によって算出された評価値に基づいて、情報単位の存在を表現する画像構成要素の位置を決定する位置算出手段と、位置算出手段によって決定された位置に画像構成要素を配置する分析画像生成手段と、分析画像生成手段によって生成された画像を表示する分析画像表示手段とを有する。
【0020】
【作用】
ファイルシステム中には、本発明の装置で扱うことができる情報単位群とその他のファイルが混在して保存されている。
情報単位群検索手段は、本発明の装置が扱う情報単位群をファイルシステム内から検索する。
検索条件入力手段は検索条件を入力するための手段である。
ここから入力された条件に基づいて、検索手段は、本発明の装置が扱うものとして検索された情報単位群からユーザが指定した情報単位群に対する検索を行う。
検索結果は検索結果表示手段によって表示される。
以上によって、ファイルシステム中に散在する情報単位群の中から、適当なものを選択し、検索することが可能となる。
【0021】
また情報単位群検索手段の検索結果は識別情報保持手段に保存され、識別情報表示手段はユーザに対して識別情報保持手段の内容を表示する。
ユーザは情報単位群選択手段を通じて、識別情報表示手段に表示されている情報単位群を選択し、その選択結果は選択結果保持手段に保存される。
検索手段は、選択結果保持手段に保持された選択結果に基づいて情報単位群に対する検索を行う。
これにより、グラフィカルな取り扱いができ、ユーザフレンドリな構成になる。
【0022】
また検索手段は、検索結果とともにその検索結果がどの情報単位群に所属するものであるのかを取得する。
そして、検索結果表示手段は、検索された情報単位の情報とともに、その情報単位がどの情報単位群に所属するものかを提示する。
以上によって、複数の情報単位群を統合的に検索した場合に、検索結果の情報単位がどの情報単位群に所属するものであるのかを容易に知ることが可能となる。
【0023】
情報単位群検索手段は、ファイルシステム中に散在する本発明の装置で扱うことができる情報単位群を検索する。
ユーザは検索された情報単位群から幾つかを指定する。
情報単位群評価手段は、指定された情報単位群に含まれる情報単位を順次読み込んで、評価条件保持手段に保存されている条件に照らした評価値を算出する。そして、その評価値を位置算出手段が画面上の位置情報へと変換し、分析画像生成手段が情報単位の存在を表現する画像構成要素を位置算出手段によって算出された位置に配置した画像を生成する。
生成された画像は、分析画像表示手段に表示される。
以上により、ファイルシステム中に散在する情報単位群の中から、適当なものを選択し、選択された情報単位群を様々な条件に基づいて、分析した画像を得ることが可能となる。
【0024】また情報単位群検索手段の検索結果は識別情報保持手段に保存され、識別情報表示手段はユーザに対して識別情報保持手段の内容を表示する。ユーザは情報単位群選択手段を通じて、識別情報表示手段に表示されている情報単位群を選択し、その選択結果は選択結果保持手段に保存される。
情報単位評価手段は選択結果保持手段に保持された選択結果に基づいて情報単位の評価を行う。
これにより、グラフィカルな取り扱いができ、ユーザフレンドリな構成になる。
【0025】
更に、存在場所保持手段がファイルシステム中で情報単位群が配置されている確率の高い位置を保存している。
これは、通常ユーザーからの指示によって行われる。
この存在場所保持手段の情報を利用して、情報単位群検索手段は、使用可能な情報単位群を検索する。
以上により、ファイルシステムを全て検索することなしに、ファイルシステム中に散在する情報単位群の中から適当なものを選択し、検索・分析することが可能となる。
【0026】
本発明の装置で取り扱うことの出来る情報単位群は所定のディレクトリ構造を持っていることが考えられる。
そこで、ディレクトリ構造に基づいて本装置で使用可能か否かを判定することで、場合に応じた情報単位群の検索ができる。
特に検索用の情報単位群である場合には情報を格納したデータファイル以外に検索を高速化するためのファイルを同時に保持していることがあるので、このようなファイルの存在を判定基準とすることができる。
【0027】
識別情報表示手段は情報単位群を識別するための情報を表示する。
ユーザは表示された情報単位群を指定する。
選択順序は保存され、検索時にはその検索順序に従って、先に検索された情報単位群の検索結果を次の情報単位群の検索条件として検索する。
以上により、情報単位群の中から依存関係のある自由な組合せをダイナミックに指定して、連続的に検索出来る。
【0028】
識別情報表示手段は実情報単位群を統合した統合情報単位群の識別情報を表示する。
ユーザは示された統合情報単位群を指定する。
選択された統合情報単位群は更に統合され、新たな統合情報単位群が構成される。
検索手段は統合された情報単位群に含まれ、検索条件に適合する情報単位を検索する。
これにより、複数の情報単位群を自由に組み合せて情報単位群の検索ができるとともに、複数の情報単位群の指定を容易に行うことができ、指定の追加変更等が柔軟に容易に行える。
【0029】
識別情報表示手段は実情報単位群を統合した統合情報単位群の識別情報を表示する。
ユーザは示された統合情報単位群を指定する。
選択された統合情報単位群は更に統合され、新たな統合情報単位群が構成される。
情報単位評価手段は統合された情報単位群に含まれる情報単位を順次読み込んで評価条件保持手段に保持されている条件に照らした評価値を算出する。
そして評価値を位置算出手段が画面上の位置情報へと変換し、分析画像表示手段によって表示される。
これにより、複数の情報単位群を自由に組み合せて分析ができるとともに、複数の情報単位群の指定を容易に行うことができ、指定の追加変更等が柔軟に容易に行える。
【0030】
【発明の実施の形態】
以下、図面を参照しながら実施例に基づいて本発明の特徴を具体的に説明する。
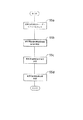
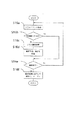
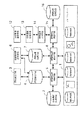
(実施例1:検索のための全体の構成)図1は、本発明を実施するための一実施例である情報単位群操作装置の全体構成を示すブロック図である。
本発明は、ファイルシステム1、このファイルシステム1の中から本装置で使用可能な情報単位群を検索する情報単位群検索手段5、情報単位群検索手段5が検索中に参考にする存在場所保持手段2、この情報単位群検索手段5の検索結果を保持する群名保持手段4、この群名保持手段4の内容を表示する群名表示手段3、この群名表示手段3に表示されている情報群の中から検索対象を選択する情報単位群選択手段6、この情報単位群選択手段6の選択結果を保持する選択結果保持手段7、この選択結果保持手段7の内容に基づいて、選択された情報単位群を統合し、統合した結果を保持する情報単位群統合手段8、検索条件を入力する検索条件入力手段9、検索条件入力手段9から入力された検索条件を用い、情報単位群統合手段8によって統合された情報単位群を検索する検索手段10、この検索手段10の検索結果を表示する検索結果表示手段11とからなる。
【0031】
(使用可能情報単位群の検索)本実施例の情報単位群操作装置は、図2に示されるようなディレクトリ管理されたファイルシステム中に、本装置で使用可能な情報単位群が分散して配置されており、且つそれ以外のファイルと混在しているものとする。
図2において、「情報単位群」と記載されている2a、2b等は本装置で使用可能な情報単位群であるとする。
また、二重の矩形で囲まれた2c、2d等はディレクトリを示し、実践の矩形で示されている2e、2f等は文書ファイル、画像ファイル等である。
以下ではこれらをすべてまとめてファイルアイテムと呼ぶ。
ここでいうファイルシステムは本装置に直結したものでもよいし、ネットワークで結合されたものでもよい。
最近では、ネットワーク上の他のファイルシステムであっても、あたかも自分自身のファイルシステムであるかのように扱う技術が普及しているからである。
【0032】
次に、本実施例における情報単位群の構成について述べる。
本装置で扱うことの出来る情報単位群は図3(a)図に示すように、ファイルアイテム(ディレクトリ)下に、Data、Index、Tableという3つのファイルアイテム(サブファイル)を持つ構造であるとする。
ここで、Dataはデータの見出しとその見出しに対応する内容部を有するデータ単位の集合からなっている。
IndexとTableはデータの検索を高速化するために設けられたファイルである。
Tableは、与えられた検索キーから求められるハッシュ値に対応するファイルIndexを指すアドレス値に変換する。
Indexのファイルは検索キーとその検索キーを持つデータが存在するDataのファイルの中のアドレスとの組をリストにした構造を持つハッシュテーブルであって、Tableファイルで示されるアドレスは同じハッシュ値を持つデータが格納されるアドレスのリストの先頭アドレスを示している。
以上の構成の概略を図3(b)に示す。
例えば、検索キーとして「パセリ」が入力されたとき、そのハッシュ値を1とすると、まずファイルTableを用いて対応するハッシュ値からファイルIndexのアドレスを計算し、次にファイルIndexを用いて、そのハッシュ値の示すアドレスを先頭にするリストを順にチェックして、ファイルDataのアドレスを取り出し、検索結果の内容部のデータを得る。
【0033】
次に本実施例の情報単位群統合手段に保持されている情報単位群の統合結果について説明する。
情報単位群の間の関係は二分木により管理されている。
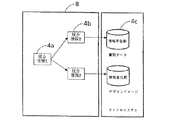
図4はその様子を示す概念図である。
図において4cは情報単位群、4a、4bは統合情報である。
二分木の葉の統合情報はファイルシステム中に存在する情報単位群に対応して設けられ、葉以外の統合情報は2つの統合情報を指すように構成されている。
2つの統合情報をさすポインタに順序付けをしておけば、統合順序を記憶しておくことができる。
各統合情報は固有の名前を持っている。
情報単位群統合手段には、二分木が複数格納されていてもよい。
【0034】
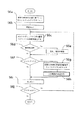
図5及び図6のフローチャートに従って、情報単位群検索手段5がファイルシステムの中を全てチェックして、本装置で使用可能な情報単位群を検索し、リストアップする処理の流れを説明する。
図5は処理の概略を示したものである。
まず、カレントディレクトリの値を保存する変数CURDIRの値にルートディレクトリをセットする(ステップS5a)。
そして、図6により後述する本装置で使用可能な情報単位群を検索する関数を呼び出す(ステップS5b)。
続いて、情報単位群統合手段を参照する(ステップS5c)。
最後に群名表示手段3が、ステップS5bで検索された本装置で使用可能な情報単位群の群名をリストアップして処理を終了する(ステップS5d)。
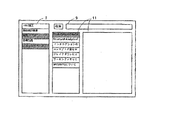
図9は群名表示手段3により群名がリストアップされた様子を示す一例である。
「1993論文」から「デザインイメージ」まではファイルシステム中に実在する情報単位群の群名であって、「書誌データ+デザインイメージ」は情報単位群を統合した統合情報の識別子である。
【0035】
図6は図5のステップS5bで呼び出される本装置で使用可能な情報単位群を検索する関数である。
まず、変数CURDIRの値に基づいて、カレントディレクトリをセットする(ステップS6a)。
そして、カレントディレクトリの何番目のファイルアイテムかを示す変数Nに1を代入する(ステップS6b)。
以下の処理では、N番目のファイルアイテムを処理対象とする(ステップS6c)。
次に、N番目のファイルアイテムが本装置で使用可能な情報単位群であるかどうかを後述するような方法により判定する(ステップS6d)。
本装置で使用可能な情報単位群であると判断された場合には群名保持手段4に、そのファイルアイテムの名称と存在する場所の情報を順次追加していく(ステップS6e)。
具体的には情報単位群の名称は各情報単位群が個別に持つファイルアイテム名称を読み出すことにより獲得し、場所情報はカレントディレクトリの位置により得ることができる。
例えば図2では情報単位群2aには「他社特許概要」、情報単位群2bには「各種引用」という名称が予め付けられている。
次に、このN番目のファイルアイテムが下位にファイルアイテムを含むかどうかを判断する(ステップS6f)。
下位にファイルアイテムを含む場合には、変数CURDIRの値にN番目のファイルアイテムをセットして(ステップS6g)、この図6の関数を再帰的に呼び出す(ステップS6h)。
変数Nの値をインクリメント(ステップS6i)した後、N番目のファイルアイテムが存在する限り(ステップS6j)、ステップS6cからステップS6iの処理を繰り返す。
カレントディレクトリ内に未判断のファイルアイテムが無くなった場合にはこの関数を終了する。
そして、最初に変数CURDIRにルートディレクトリをセットした関数が終了した時点で、制御は図5のフローチャートで示される処理へと戻る。
このとき、群名保持手段4にはファイルシステム中に存在する、本装置で使用可能な情報単位群の群名がすべて記憶されている。
図8(a)は図2のファイルシステムを検索した結果、群名保持手段4に保持される情報の一例である。
【0036】
ステップS6dにおいて、ファイルアイテムが本装置で使用可能な情報単位群であるかの判定は以下のように行われる。
本実施例の装置で扱うことのできる情報単位群は、図3に示したようにファイルアイテム(ディレクトリ)下に、Data,Index,Tableという3つのファイルアイテム(サブファイル)を持つ構造である。
そこで、ファイルアイテムの中にこの3つのサブファイルを持つものは、本装置で扱うことができる情報単位群であると判断することができる。
この例に基づいて図6のS6d及びS6eを詳細に示したフローチャートが図7である。
【0037】
まず、注目するファイルアイテムの下の何番目のサブファイルかを示す変数Jに1を代入するとともに、サブファイルDataの存在の有無を示すフラグDF、サブファイルIndexの存在の有無を示すフラグIF、サブファイルTableの存在の有無を示すフラグTFをそれぞれ0に初期化する(ステップS7a)。
以下の処理ではJ番目のサブファイルを処理対象とする(ステップS7b)。J番目のサブファイルがDataであるかどうかチェックし(ステップS7c)、Dataであれば、フラグDFの値を1にセットする(ステップS7d)。同様に、Indexであるかどうか(ステップS7e)、Tableであるかどうか(ステップS7g)をチェックし、それぞれ該当するサブファイルであれば、対応するフラグIF(ステップS7f)、フラグTF(ステップS7h)を1にセットする。
この3つのサブファイルのチェックの順番は任意で良い。
次に、フラグDF、IF、TFの3つ全てが1になっているかどうかをチェックする(ステップS7j)。
全てが1になっている場合には、注目するファイルアイテムは、本装置で使用可能な情報単位群であるので、その名称と存在場所の情報を群名保持手段4に記録する(ステップS7k)。
全てが1でない場合には、変数Jの値をインクリメントし、次のサブファイルが存在すれば、そのサブファイルについてステップS7bからステップS7iを繰り返す(ステップS7l)。
サブファイルが無くなったら、そのファイルアイテムは本装置で使用可能な情報単位群でないので、処理を終了する。
【0038】
これ以外にも判定の方法はいくつか存在する。
例えば、最も単純な方法として、本装置が扱う情報単位群の名称を、「×××.DAT」等と決めておき、判断の対象となるファイルアイテムがこの規則に沿ったものかどうかを判定する方法である。
また、ファイルシステムによっては、各ファイルがどのアプリケーションで取り扱われるものかを示すファイルタイプを規定できるものもある。
そのようなファイルシステムにおいては、ファイルアイテムごとにファイルタイプをチェックして判定基準にすることもできる。
より正確に判断しようとすれば、実際にそのファイルアイテムを検索対象としてオープンして、一度検索し、実際にその対象が検索可能で、かつ正当な情報単位群であるかどうかを判定するといった方法もある。
その際に、どの情報単位群も共通に持っている管理用情報単位を検索してもよい。
管理用情報単位はキーボードなどを用いてユーザが入力することができない固有の検索キーにより検索される情報単位である。
【0039】
次に、本装置で使用可能な情報単位群が保持されている可能性の高いディレクトリを存在場所保持手段2に、あらかじめ保持しておく場合の処理を図10に示すフローチャートを用いて説明する。
本実施例においては、存在場所保持手段2は図12のように構成されているものとする。
【0040】
図10において、まず変数Kの値を0にセットする(ステップS10a)。
次に存在場所保持手段2に保存されている指定ディレクトリのK番目を読み込んで、カレントディレクトリとする(ステップS10b)。
変数Nの値を0にセットし(ステップS10c)、カレントディレクトリのN番目のファイルアイテムを処理対象として指定する(ステップS10d)。
次にこのファイルアイテムが装置で使用可能な情報単位群であるかを判定し(ステップS10e)、そうである場合には、群名保持手段4にそのファイルアイテムの名称を記録する(ステップS10f)。
変数Nの値を1つづつインクリメントしながら(ステップS10g)、ファイルアイテムがなくなるまでステップS10cからステップS10gの処理を繰り返す(ステップS10h)。
そして、変数Kの値を1つづつインクリメントし(ステップS10i)、指定されたディレクトリが全てなくなるまで、ステップS10bからステップS10iの処理を繰り返す(ステップS10j)。
最後に、群名表示手段3が、使用可能な情報単位群の名称をリストアップして処理を終了する(ステップS10k)。
【0041】
図10の処理では、指定されたディレクトリの一階層のみを調べるように構成したが、指定されたディレクトリが更に下位のディレクトリを含んでいる場合には、図6のフローチャートに示したような再帰的な処理により、指定ディレクトリ以下のディレクトリを検索するように構成してもよい。
その場合には、検索された情報単位群に重複が生じないように、群名保持手段4への群名の記録の際に、既に同じ群名のものが含まれていないかチェックしてから書き込むようにしたり、後処理により、群名保持手段4の内容から重複しているものを省くように構成するのがよい。
【0042】
次に、図11を用いて図5のステップS5cで行われる情報単位群統合手段の参照について述べる。
最初に情報単位群統合手段に格納されている統合情報のうちで、ルートになっているものを1つ選択して図11の処理に移る。
まず、カレントの統合情報を設定する。
スタートではルートの統合情報となる(ステップS11a)。
カレントの統合情報の名前とアドレスを一時的に記録しておく(ステップS11b)。
次にカレントの統合情報の子の順序を計数する変数Nに0を代入し(ステップS11c)、N番目の子に当たる統合情報を処理対象とする(ステップS11d)。
処理対象の統合情報が二分木の葉であるかどうかをチェックし(ステップS11e)、処理対象の統合情報が葉であるときには、その統合情報に対応する情報単位群が存在しているかどうかをチェックする。
チェックの方法として、例えば、統合情報に対応している情報単位群の群名に一致する群名が群名保持手段に保持されているかどうかを調べることができる(ステップS11f)。
このとき情報単位群が存在しなければ、一時的に記憶した統合情報の名前をクリアして、ルートの統合情報から始まったこの関数を強制終了する(ステップS11g)。
ステップS11eにおいて葉でない場合は、その統合情報をカレントの統合情報として(ステップS11h)この関数を再帰的に呼び出す(ステップS11i)。
変数Nをインクリメントして(ステップS11j)、Nの値が2未満であれば,ステップS11dから繰り返し、そうでなければ、処理を終了する(ステップS11k)。
図11の関数が1つのルートの統合情報に付いて終了すると、一時的に記憶しておいた統合情報の名前と統合情報のアドレスを群名保持手段に移動する。
そして、ルートとなっている統合情報がなくなるまで、以上の処理を繰り返す。
図8(b)は図5のフローチャートに示す処理が終了したときの群名保持手段の状態の一例を示したものである。
【0043】
なお、ここでは二分木の各ノードに当たる統合情報をすべて、抽出するようにしたが、統合情報が多くなると煩雑になることもあるので、例えば、ルートにあたる統合情報についてのみ抽出するようにしてもよい。
この場合、二分木で統合する必要はなく、リスト構造等を用いてもよい。
また、ステップS5cの処理を行うかどうかをユーザが指定できるようにしてもよい。
ステップS11f、S11gの処理では、統合された情報単位群の中で、存在しないものがあれば、それを検出して表示しないようにしているので、既に価値のなくなった統合情報を処理対象として指定することがない。
このとき、削除された情報単位群を含む統合情報は、自動的に削除するように構成してもよい。
【0044】
(情報単位群の選択)図9のようにリストアップされた情報単位群または統合情報から、操作対象とする情報単位群を選択する処理について述べる。
【0045】
図13は、情報単位群選択手段6が、選択順序を記録せず情報単位群を選択する処理を表現したフローチャートである。
この処理によれば、複数の情報単位群を同時に選択することが可能である。
ただし、選択順序を記録しないので、複数の情報単位群を順序を付けて組み合せることはできない。
ここでは、マウスクリックによって、ユーザーが情報単位群を選択するものとする。
【0046】
まず、マウスイベントを取得し(ステップS13a)、それが使用可能な情報単位群を表示したリスト内で起きたものかをチェックする(ステップS13b)。
リスト内で起きたものの場合には、リストの選択処理として、選択されたアイテムをユーザが認識できるように表示を変更する。
ここでは、図14のように選択されたアイテムの表示部分にシェードをかける。
各アイテムの表示に対応してフラグが設けられており、シェードのかかったアイテムにはフラグが立つようになっている(ステップS13c)。
そして、選択処理が終了するまで、ステップS13aからステップS13cの処理を繰り返す(ステップS13d)。
【0047】
次に、選択結果を取り出して記録する。
まず、変数Nに0をセットし(ステップS13e)、ステップS13cで設定されたフラグをチェックして、リストのアイテムのN番目が選択されているかをチェックする(ステップS13f)。
選択されていたとすると、選択内容を選択結果保持手段7に情報単位群名称、場所情報等を記録する(ステップS13g)。
図15は選択結果保持手段の記憶状態を示した一例である。
そして、変数Nを1づつインクリメントしながら(ステップS13h)、リストのアイテムが終了するまでステップS13fからステップS13hの処理を繰り返す(ステップS13i)。
最終的に、情報単位群統合手段8が、選択結果保持手段7の情報を用いて、1つ以上の情報単位群を統合し、統合された結果に基づいて対象となる情報単位群をオープンする(ステップS13j)。
なお、オープンするとは情報単位群を操作可能な状態にすることをいう。
【0048】
以降、このオープンされた情報単位群が操作対象となる。
本実施例では、情報単位群統合手段8は選択結果保持手段7に保持された情報単位群または統合情報に基づいて二分木を構成する。
まず、初期設定として、選択結果保持手段7に保持されたリストから情報単位群または統合情報を取り出す。
情報単位群であった場合は、その情報単位群を例えばポインタ等で指し示すような新たな統合情報を1つ作成し、その統合情報を指定統合情報Aとする。
統合情報であった場合は、その統合情報を指定統合情報Aとする。
次に、選択結果保持手段7に保持された情報単位群または統合情報を取り出し、情報単位群であった場合は、その情報単位群を例えばポインタ等で指し示すような新たな統合情報を1つ作成し、その統合情報を指定統合情報Bとする。
統合情報であった場合は、その統合情報を指定統合情報Bとする。
指定統合情報AとBが揃ったら、指定統合情報AとBを指す新しい統合情報を作成し、この新しい統合情報を指定統合情報Aとする。
そして、選択結果保持手段7に保持されたリストが終了するまで、指定統合情報Bを決定するところから処理を繰り返す。
後述する検索時または分析時には、生成された統合情報を、ルートノードとして処理を開始する。
【0049】
図16は、情報単位群選択手段6が、選択順序を記録しながら情報単位群を選択する処理を表現したフローチャートである。
この処理によれば、複数の情報単位群を同時に選択したり、複数の情報単位群を順序を付けて組み合せることができる。
まず、マウスイベントを取得し(ステップS16a)、それが使用可能情報単位群を表示したリスト内で起きたものかをチェックする(ステップS16b)。リスト内で起きたものの場合には、リストの選択処理として、ここでは図14のように選択されたアイテムにシェードをかける(ステップS16c)。
同時に、選択内容を選択結果保持手段7に選択順序、情報単位群名称、場所情報等を追加記録する(ステップS16d)。
図17にこの場合の選択結果保持手段の記憶形態の一例を示す。
そして、選択処理が終了するまで、ステップS16aからステップS16dの処理を繰り返す(ステップS16e)。
最終的に、選択結果保持手段7の情報を用いて、情報単位群統合手段8が1つ以上の情報単位群を統合しオープンする(ステップS16f)。
【0050】
この実施例の場合は、選択順序情報を保持しているので、順序情報を利用したオープンが可能となる。
具体的には、検索キーが入力された場合、ある情報単位群に対して行った検索結果を、次に指定された情報単位群に対する検索キーとして利用するといった検索である。
前述の二分木による統合は、その順序を保持するように構成する。
例えば、二分木を作成するときに、選択結果保持手段7のリストの最後から順に読み出し、指定統合情報Bに順序2、指定統合情報Aに順序1を割当てれば、順序が維持される。
【0051】
(オープンされた情報単位群の検索)オープンされた情報単位群の検索処理について述べる。
ここでは、前述の処理により複数の情報単位群が情報単位群統合手段8によって、前記の二分木構造を用い、あたかも1つの情報単位群として取り扱えるように統合されているものとする。
【0052】
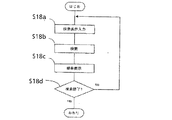
図18は、検索処理について表現したフローチャートである。
まず、ユーザーは検索条件入力手段9から、検索条件を入力する。
ここでは、各情報単位に付与されているキーワードに対する検索を行うものとする。
ユーザーは検索条件入力手段9に検索キーを入力する(ステップS18a)。ここでは、検索方法としてキーワード検索を用いるが、全文検索などの一般的検索に置き換えても、基本的な機能や処理フローは全く同様である。
検索手段10は、この検索キーに基づいて、統合されている複数の情報単位群を検索し、図19のような検索結果を得る(ステップS18b)。
この場合は、条件に適合した情報単位の名称、所属情報単位群の名称、情報単位実体のファイル中での存在位置の情報が検索結果である。
そして、この結果を検索結果表示手段11に、図20のように見出し語リストの形態でユーザーに提示する(ステップS18c)。
ユーザーから、検索終了の指示が出るまで、この処理を繰り返す(ステップS18d)。
【0053】
ステップS18bにおいて、統合されている情報単位群の検索の際には、先だって作成した統合情報のルートノードから二分木を順次探索し、たどり着いた葉の統合情報に対応する情報単位群に対して検索条件を与え、検索をかける。
また、情報単位群を統合した二分木は、検索処理が終わっても通常、すなわち、選択結果保持手段のリストが1つの要素からなっている時以外は保持されるようにする。
前述のように二分木の各ノードに対応する統合情報を指定することが出来るような構成とすれば、指定された統合情報の下位に存在する情報単位群をあたかも一つの情報単位群であるかのように検索・分析を行うことができ、予めファイルの存在状況を管理する手続きやユーザインタフェースをを別個に設けなくても、必要な時に必要な情報単位群の編成ができるというメリットを持つ。
また、必要な時だけ二分木を保持するようなコマンドを設けてもよい。
統合された情報単位群を後に利用することを考えない場合には、情報単位群統合手段8に二分木による統合の機能を持たせなくてもよい。
情報単位群統合手段8は統合選択結果保持手段7を参照しながら、そこに記憶されて利得情報単位群の1つをオープンして検索を行った後、次の情報単位群に移り、同様な処理を繰り返すことができる。
【0054】
次に情報単位群の選択順序を用いて、連続的な検索を行う例を述べる。
図21は統合を行わない場合において、情報単位群が順序付けされたときの、検索手続きをしめしたフローチャートである。
まず、検索条件を入力する(ステップS21a)。
次に選択順序を示す変数Nに1をセットする(ステップS21b)。
選択順序の情報単位群をオープンする(ステップS21c)。
検索条件でオープンした情報単位群を検索し(ステップS21d)、検索結果を記録しておく(ステップSe)。
情報単位群をクローズする(ステップS21f)。
Nをインクリメントし(ステップS21g)、次の情報単位群が存在すれば(ステップS21h)、記憶保持している検索結果を検索条件として,ステップScから繰り返す(ステップS21i)。
次の情報単位群が存在しなければ、検索結果を表示して終了する(ステップS21j)。
統合されている場合は、Nの個数をカウントする代わりに、統合情報のルートノードから二分木を順次探索し、たどり着いた葉の統合情報に対応する情報単位群に対して検索をかけるように構成すればよい。
子に対応する統合情報をさす枝に順序を保持していれば、順序1の付いているほうから検索することにより選択の順序が守られる。
以上述べた処理により、ファイルシステム内に他のファイルと混在する情報単位群の中から、自由な組合せに対して検索を加えることが可能となる。
【0055】
(検索結果の詳細と所属情報単位群の表示)検索結果の詳細情報とともに、詳細情報を表示した情報単位がどの情報単位群に所属するものであるかを表示する処理について述べる。
図22は、この処理を表現したフローチャートである。
まず、マウスイベントを取得し(ステップS22a)、そのイベントが検索結果を表示したリストの内部で発生したものかどうかをチェックする(ステップS22b)。
もし、リスト内のものであれば、リスト選択処理として、ここではリスト中の選択されたアイテムにシェードをかける(ステップS22c)。
そして、図19の検索結果の情報単位群名とファイル位置から、選択されたアイテムの内容を読み込んで、表示する(ステップS22d)。
次に、この情報単位が所属する情報単位群の名称を図19の検索結果から取り出し(ステップS22e)、同時に表示する。
所属情報単位群とともに内容を提示した例が図23である(ステップS22f)。
以上の処理をユーザーが終了の指示を出すまで繰り返す(ステップS22g)。
この処理で、情報単位の詳細な内容とともに、それがどの情報単位群に属するものなのかについて知ることができる。
【0056】
(実施例2:分析のための全体構成)図24は、複数の情報単位群に含まれる情報単位の分析を行なうための情報操作装置の一例の全体構成を示すブロック図である。
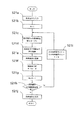
本実施例は、ファイルシステム1、ファイルシステムの中から、本装置が使用可能な情報単位群を検索する情報単位群検索手段5、情報単位群検索手段5が検索中に参考にする存在場所保持手段2、情報単位群検索手段5の検索結果を保持する群名保持手段4、群名保持手段4の内容を表示する群名表示手段3、群名表示手段3に表示されている情報単位群の中から検索対象とする情報単位群を選択する情報単位群選択手段6、情報単位群選択手段6の選択結果を保持する選択結果保持手段7、選択結果保持手段7の内容に基づいて、選択された情報単位群を統合し、一つの情報単位群として構成する情報単位群統合手段8、情報単位群統合手段8によって統合された情報単位群に属する各情報単位を評価した値を算出するための条件を保持する評価条件保持手段16、評価条件保持手段16の条件に基づいて情報単位を評価する情報単位評価手段15、情報単位評価手段15によって算出された評価値に基づいて、情報単位の存在を表現する画像構成要素の位置を決定する位置算出手段14、位置算出手段14によって決定された位置に画像構成要素を配置する分析画像生成手段13、分析画像生成手段13によって生成された画像を表示する分析画像表示手段12とからなる。
【0057】
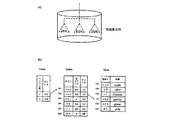
(分析画像の生成)選択した情報単位群を検索し、その情報単位に含まれる情報単位の存在を表現する点などの画像構成要素を各情報単位の性質に応じて配置することにより、選択した情報単位群を分析することができる。
ここでは、横方向に評価アイテム(検索キーワード群)を配置し、情報単位がその評価アイテムをキーワードに含む場合には点を配置する。
縦方向はランダムに配置するものとする。
【0058】
図25は、この処理を表現したフローチャートである。
選択された情報単位群が選択結果保持手段に格納され、1つの情報単位群と同様な扱いができるように統合されるまでの動作は実施例1と同様なので省略し、以下ではそれ以降の処理について述べる。
まず、検索対象として選択され、統合されている情報単位群に含まれる情報単位を順次1つづつ読み込む。
統合されている情報単位群の取扱いについては実施例1の検索の説明で述べたのと同様に二分木を探索する(ステップS25a)。
そして、評価条件保持手段16に保存されている評価アイテムを順次一つづつ取り出し、情報単位評価手段15は、読み込んだ情報単位と評価アイテムを比較する。
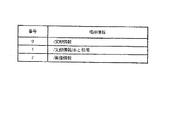
図26は評価条件保持手段に保持される評価アイテムの例である。
この場合、『デザイン』『イメージ』『感性』が横方向の評価アイテムとなる。
評価アイテムに続いて示されている数字の10、20、30等は評価値を示し、後述するように使用される。
縦方向は条件が指定されないで、評価値のみ乱数により発生されることを示している(ステップS25b)。
もしも、条件が適合する場合、即ちこの例においては情報単位のキーワードの中に評価アイテムが含まれる場合には、その情報単位について横方向評価値(例えば10)をセットする(ステップS25c)。
さらに、縦方向の評価値(この例の場合は乱数を取得する)もセットする(ステップS25d)。
そして、この両方の評価値に基づいて、位置算出手段14が、実際の画面上の点の位置に変換する(ステップS25e)。
続いて分析画像生成手段13が、この位置に新たに点を付加した画像を生成し(ステップS25f)、分析画像表示手段12に表示する(ステップS25g)。
1つの情報単位に付き、このステップS25bからステップS25gの処理を評価アイテムが終了するまで繰り返す(ステップS25h)。
さらに、ステップS25aからステップS25hの処理を統合された情報単位群に含まれる全ての情報単位を読み込むまで繰り返す(ステップS25i)。
【0059】
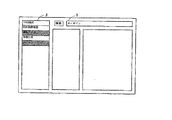
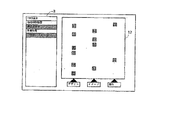
以上の処理によって、生成された画像の例を図27に示す。
この図では、3つの評価アイテムそれぞれをキーワードに含む情報単位の存在を表現する画像構成要素(点)が、画面上に配置されている。
なお、評価条件保持手段に保持される評価条件は幾つかのグループに分かれていてもよく、どの評価条件で表示させるか予め選択させるような構成にしてもよいし、ユーザが適当に組み合せたり、任意に指定できるようにしてもよい。
その場合、図27の軸の表示部分もそれに応じて書き換えればよい。
以上述べた処理により、ファイルシステム内に他のファイルと混在する情報単位群の中から、自由な組合せに対して、分析を加えることが可能となる。
【0060】
なお、情報単位群としては、上記実施例に示したようなファイル形式に従って構成されたものであれば、辞書データベースや、音声、画像等の混在したマルチメディアデータベースなどを利用することができる。
【0061】
【発明の効果】
本発明により、通常のファイルシステム内に他のファイルとともに散在する複数の情報単位群を、自由に組み合せ、容易に検索や分析を行うことができるようになった。
特に、複数の情報単位群を同時に選択して検索した場合には、検索結果がどの情報単位群に所属するものなのかを知ることが容易となった。
あらかじめ情報単位群が存在する可能性の高い場所を指定しておき、その中を検証することにより、効果的に使用可能な情報単位群をユーザーに提示することが可能となった。
また、本装置で使用可能な情報単位群の検索時にファイルのディレクトリ構造を利用することができるようになった。
また、情報単位群の検索順序を自由に、かつダイナミックに指定して連続検索が容易に行えるようになった。
更に、検索、分析対象とする情報単位群の統合を行い、保持しておくことにより、情報単位群の編成をより柔軟にかつ容易に行えるようになった。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】本発明の情報単位群操作装置を実現するための構成を示すブロック図である。
【図2】本発明で対象としているファイルシステムの例を示す図である。
【図3】本発明で対象とする情報単位群の構成の一例を示す図である。
【図4】情報単位群統合手段に保持される統合情報の一例を示す図である。
【図5】全ファイルシステムをチェックし、使用可能な情報単位群を検索するための処理を表現するフローチャートである。
【図6】図5の処理によって再帰的に利用される使用可能情報単位群抽出関数を示す図である。
【図7】ファイルアイテムが本装置で使用可能な情報単位群であるかの判定の例を示すフローチャートである。
【図8】群名保持手段に保存される情報の例を示す図である。
【図9】使用可能情報単位群を表示した例である。
【図10】指定されたディレクトリに存在する使用可能な情報単位群を検索するための処理を表現するフローチャートである。
【図11】統合情報を検索するフローチャートである。
【図12】存在場所保持手段に保存される情報の例を示す図である。
【図13】選択順序を保存しない場合の情報単位群選択処理を表現するフローチャートである。
【図14】情報単位群を選択した例を示す図である。
【図15】選択結果保持手段に保存される情報の例(順序なし)を示す図である。
【図16】選択順序を保存する場合の情報単位群選択処理を表現するフローチャートである。
【図17】選択結果保持手段に保存される情報の例(順序あり)を示す図である。
【図18】情報単位群の検索処理を表現するフローチャートである。
【図19】検索結果の例を示す図である。
【図20】検索結果の表示例を示す図である。
【図21】情報単位群が順序付けされて指定された時の検索手続きを示すフローチャートである。
【図22】検索結果の見出し語を選択し詳細な内容を提示する処理を表現するフローチャートである。
【図23】情報単位の詳細な内容を提示した例を示す図である。
【図24】本発明の情報操作装置を実現するための構成を示すブロック図である。
【図25】情報単位を順次読み込んで評価し、分析画像を提示するための処理を表現するフローチャートである。
【図26】評価値算出手段に保存される情報の例を示す図である。
【図27】分析画像を表示した例を示す図である。
【符号の説明】
1…ファイルシステム、2…存在場所保持手段、3…群名表示手段、4…群名保持手段、5…情報単位群検索手段、6…情報単位群選択手段、7…選択結果保持手段、8…情報単位群統合手段、9…検索条件入力手段、10…検索手段、11…検索結果表示手段、12…分析画像表示手段、13…分析画像生成手段、14…位置算出手段、15…情報単位評価手段、16…評価条件保持手段、2a,2b…情報単位群、2c,2d…ディレクトリ、2e…文書ファイル、2f…画像ファイル[0001]
TECHNICAL FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to an apparatus for searching for information and performing evaluation analysis.
[0002]
[Prior art]
In this specification, an information unit refers to a group of information having a name (heading).
The most basic type of information is a character string, but any type of information such as an image, a sound, or a moving image can be used as long as it can be expressed electronically.
Also, in consideration of the convenience of the search, it is preferable to have an attribute value such as a keyword expressing the property of the information.
Further, the information unit group is a set of a plurality of information units.
In the present invention, it is assumed that a plurality of information unit groups exist on the file system and are mixed with other files.
[0003]
For example, a typical information unit group is an electronic dictionary.
One information unit has, for example, a word “apple” as a heading and a description of its pronunciation, meaning, example, and the like.
The entire English-Japanese dictionary is an information unit group.
Further, a state in which there are a plurality of them means a state in which not only English-Japanese dictionaries but also various dictionary data such as Japanese-language dictionaries, Chinese-Japanese dictionaries, Japanese-English dictionaries, and French-Japanese dictionaries are mixed.
In the case of dictionary data, editing is not normally performed, but it is also assumed that the information unit handled in the present invention performs operations such as editing, conversion, and movement.
[0004]
Another example of the information unit group is a database.
One record in the database corresponds to one information unit.
The entire database in a certain field corresponds to an information unit group.
[0005]
Prior art documents dealing with a plurality of information unit groups simultaneously include JP-A-62-287336 and JP-A-4-195680.
Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 62-287336 discloses a technique in which a user selects a plurality of dictionaries and searches them simultaneously.
In this technique, the names of the dictionaries existing in the disk device and the dictionary information server are displayed.
The user can use a plurality of dictionaries simultaneously in a free combination from among them, or can specify another search condition from a search result of one dictionary and search another dictionary.
Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 4-195680 is also a technique for using a plurality of dictionaries in combination.
In this technique, a dictionary attribute table is provided in advance, and it is possible to perform a continuous search using a result of the conversion based on a certain standard.
Further, by providing a table in which dictionaries to be used and their priorities are described, the user can create an application according to the situation.
[0006]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
However, these techniques are based on the premise that a usable information unit group or a position where an information unit group exists is determined in advance.
Further, it is not assumed that information that cannot be handled by the system is mixed at the position.
In such a situation, information that cannot be handled by the system may be presented to the user as a dictionary.
In addition, the table needs to be maintained by the user every time the file configuration is changed, and it is not possible to continuously search while dynamically adding or separating a new information unit group. .
[0007]
Therefore, an object of the present invention is to automatically search for only information unit groups that can be used by the system, even in a situation where information unit groups are scattered in a normal file system.
It is another object of the present invention to allow a user to dynamically and freely specify a combination of information unit groups to search and analyze the specified information unit group.
[0008]
The information unit group operation device according to the present invention, from a file system in which files of various file formats are mixed, an information unit group search unit that has a predetermined file format and searches for an information unit group that is a collection of information units, The information unit group specified by the information unit group specified by the user from the information unit group searched by the information unit group search unit, the search condition input unit to input search conditions, and the information unit group specified by the information unit group specification unit The information processing system includes a search unit for searching an information unit group that matches the search condition input from the search condition input unit, and a search result display unit for displaying the information unit searched by the search unit.
[0009]
Preferably, the information unit group designation means includes: identification information holding means for holding unique identification information of the information unit group searched by the information unit group search means; and identification information held by the identification information holding means. Identification information display means for displaying, and at least one information unit group selected from information unit groups provided corresponding to the display by the identification information display means and corresponding to the identification information held in the identification information holding means. An information unit group selection unit that receives an input; and a selection result holding unit that holds the identification information selected by the information unit group selection unit, wherein the search unit corresponds to the identification information held by the selection result holding unit. A search may be made for an information unit that matches the search condition input from the search condition input means from the information unit group to be searched.
[0010]
Preferably, the search unit further acquires identification information of an information unit group to which the searched information unit belongs, and the search result display unit includes the information unit searched by the search unit and the information unit to which the search unit belongs. The identification information of the information unit group can be displayed.
[0011]
Preferably, the information system further includes an existence place holding unit that holds information on a place where there is a high possibility that the information unit group having the predetermined file format particularly exists in the file system. An information unit group having a predetermined file format may be searched from the file system based on the information stored in the existence location holding unit.
[0012]
Further, the information unit group operation device according to the present invention is an information unit group search means for searching an information unit group having a predetermined file format and being a collection of information units from a file system in which files of various file formats are mixed. An information unit group designating means for a user to designate an information unit group from the information unit group searched by the information unit group searching means, and an evaluation condition holding for holding a condition for evaluating an information unit belonging to the information unit group Means, information unit evaluation means for calculating a value obtained by evaluating each information unit belonging to the information unit group designated by the information unit group designation means, based on the condition held in the evaluation condition holding means; A position calculating unit that determines a position of an image component expressing the existence of the information unit based on the evaluation value calculated by the evaluating unit; Having an analysis image generating means for arranging the image component, and an analysis image display means for displaying the image generated by the analysis image generating means to the position.
[0013]
Preferably, the information unit group designation means includes: identification information holding means for holding unique identification information of the information unit group searched by the information unit group search means; and identification information held by the identification information holding means. Identification information display means for displaying, and at least one information unit group selected from information unit groups provided corresponding to the display by the identification information display means and corresponding to the identification information held in the identification information holding means. An information unit group selecting unit that receives an input; and a selection result holding unit that holds identification information selected by the information unit group selecting unit. The information unit evaluating unit is held by the evaluation condition holding unit. Calculating a value that evaluates each information unit belonging to the information unit group corresponding to the identification information of the information unit group held in the selection result holding unit, based on the condition that It may form.
[0014]
Preferably, the information processing apparatus further includes a location storage unit that retains information about a location where the information unit group having the predetermined file format is particularly likely to exist in the file system. An information unit group having a predetermined file format may be searched from the file system based on the information stored in the holding unit.
[0015]
Further, an information unit group operation device according to the present invention includes an information unit group search unit for searching an information unit group having a predetermined directory structure from a file system in which files of various file formats are mixed, and an information unit group search unit. It has identification information holding means for holding the unique identification information of the information unit group searched by the above, and identification information display means for displaying the identification information held in the identification information holding means.
[0016]
Preferably, the information unit group search means includes a data file holding a heading and contents corresponding to the heading in a directory constituting a file, a search key input at the time of searching for an information unit, and data of the data corresponding to the search key. A search is made for an information unit group including an index file that holds a correspondence relationship with an existing position in the data file and a hash table file that converts the search key into an address in the index file corresponding to the search key. can do.
[0017]
Further, the information unit group operation according to the present invention is provided with identification information display means for displaying identification information of an information unit group, which is a group of information units, and provided in correspondence with the display by the identification information display means, An information unit group selecting unit that receives an input for sequentially selecting at least a first information unit group and a second information unit group from a group; and the first information unit group and the second information unit selected by the information unit group selecting unit. Selection result holding means for holding the identification information of the information unit group together with the selected order, search condition input means for inputting a first search condition, and first search condition input from the search condition input means. A matching information unit is searched from the first information unit group held in the selection result holding unit, and the search result is set as a second search condition, and an information unit matching the second search condition is set as the second information condition. of A search means for searching from multicast unit group, and a search result display means for displaying the information unit searched by the searching means.
[0018]
Further, the information unit group operation device according to the present invention includes an identification information display unit that displays identification information of an integrated information unit group obtained by integrating a real information unit group that is a group of information units, and a display performed by the identification information display unit. An information unit group selecting unit that is provided correspondingly and receives an input for selecting at least one of the integrated information unit groups; and a selection unit that holds identification information of the integrated information unit group selected by the information unit group selecting unit. A result holding unit, an information unit group integrating unit that integrates the information unit groups held in the selection result holding unit to generate a new integrated information unit group, and holds information of the integrated information unit group; From the new integrated information unit group integrated by the information unit group integrating unit, and an information unit that matches the search condition input from the search condition input unit. A search means for search, the search result display means for displaying the information unit searched by the searching means.
[0019]
Further, the information unit group operation device according to the present invention includes an identification information display unit that displays identification information of an integrated information unit group obtained by integrating a real information unit group that is a group of information units, and a display performed by the identification information display unit. An information unit group selecting unit that is provided correspondingly and receives an input for selecting at least one of the integrated information unit groups; and a selection unit that holds identification information of the integrated information unit group selected by the information unit group selecting unit. A result holding unit, an information unit group integrating unit that integrates the information unit groups held in the selection result holding unit to generate a new integrated information unit group, and holds information of the integrated information unit group; An evaluation condition holding unit for holding a condition for evaluating an information unit belonging to a group; and a management unit integrated by the information unit group integration unit based on the condition held in the evaluation condition holding unit. An information unit evaluation unit for calculating a value obtained by evaluating each information unit belonging to the information unit group; and a position of an image component expressing the existence of the information unit is determined based on the evaluation value calculated by the information unit evaluation unit. The apparatus includes a position calculation unit, an analysis image generation unit that arranges image components at the positions determined by the position calculation unit, and an analysis image display unit that displays an image generated by the analysis image generation unit.
[0020]
[Action]
In the file system, a group of information units that can be handled by the apparatus of the present invention and other files are mixed and stored.
The information unit group search means searches the file system for an information unit group handled by the apparatus of the present invention.
The search condition input means is a means for inputting a search condition.
Based on the conditions input from here, the search means performs a search for the information unit group specified by the user from the information unit group searched as handled by the apparatus of the present invention.
The search result is displayed by the search result display means.
As described above, an appropriate unit can be selected from the information unit group scattered in the file system and searched.
[0021]
The search result of the information unit group search means is stored in the identification information holding means, and the identification information display means displays the contents of the identification information holding means to the user.
The user selects the information unit group displayed on the identification information display means through the information unit group selection means, and the selection result is stored in the selection result holding means.
The search unit searches the information unit group based on the selection result held in the selection result holding unit.
Thereby, a graphical handling can be performed and a user-friendly configuration is obtained.
[0022]
Further, the search means acquires the search result and the information unit group to which the search result belongs.
Then, the search result display means presents the information of the searched information unit and to which information unit group the information unit belongs.
As described above, when a plurality of information unit groups are integratedly searched, it is possible to easily know which information unit group the information unit of the search result belongs to.
[0023]
The information unit group search means searches for an information unit group that can be handled by the device of the present invention scattered in the file system.
The user specifies some from the retrieved information unit group.
The information unit group evaluation unit sequentially reads information units included in the specified information unit group, and calculates an evaluation value based on the condition stored in the evaluation condition holding unit. Then, the position calculation means converts the evaluation value into position information on the screen, and the analysis image generation means generates an image in which image components representing the existence of the information unit are arranged at the positions calculated by the position calculation means. I do.
The generated image is displayed on the analysis image display means.
As described above, it is possible to select an appropriate one from among the information unit groups scattered in the file system, and obtain an image obtained by analyzing the selected information unit group based on various conditions.
The search result of the information unit group search means is stored in the identification information holding means, and the identification information display means displays the contents of the identification information holding means to the user. The user selects the information unit group displayed on the identification information display means through the information unit group selection means, and the selection result is stored in the selection result holding means.
The information unit evaluation means evaluates the information unit based on the selection result held in the selection result holding means.
Thereby, a graphical handling can be performed and a user-friendly configuration is obtained.
[0025]
Further, the location storage means stores a position where the information unit group is likely to be arranged in the file system.
This is usually performed according to an instruction from a user.
Using the information of the location storage means, the information unit group search means searches for a usable information unit group.
As described above, it is possible to select an appropriate information unit group among the information unit groups scattered in the file system and search and analyze the information unit without searching the entire file system.
[0026]
The information unit group that can be handled by the device of the present invention may have a predetermined directory structure.
Therefore, it is possible to search for the information unit group according to the case by determining whether or not the information unit can be used in the present apparatus based on the directory structure.
In particular, in the case of an information unit group for search, since a file for speeding up search may be held at the same time other than the data file storing the information, the existence of such a file is used as a criterion. be able to.
[0027]
The identification information display means displays information for identifying the information unit group.
The user specifies the displayed information unit group.
The selection order is saved, and at the time of the search, the search result of the information unit group previously searched is searched as the search condition of the next information unit group in accordance with the search order.
As described above, a free combination having a dependency relationship can be dynamically specified from the information unit group and can be continuously searched.
[0028]
The identification information display means displays identification information of the integrated information unit group obtained by integrating the real information unit group.
The user specifies the indicated integrated information unit group.
The selected integrated information unit group is further integrated to form a new integrated information unit group.
The search means searches for an information unit that is included in the integrated information unit group and matches the search condition.
Thereby, the information unit group can be searched by freely combining the plurality of information unit groups, and the plurality of information unit groups can be easily specified, and the addition and change of the specification can be flexibly and easily performed.
[0029]
The identification information display means displays identification information of the integrated information unit group obtained by integrating the real information unit group.
The user specifies the indicated integrated information unit group.
The selected integrated information unit group is further integrated to form a new integrated information unit group.
The information unit evaluation unit sequentially reads the information units included in the integrated information unit group and calculates an evaluation value based on the condition held in the evaluation condition holding unit.
Then, the evaluation value is converted by the position calculation means into position information on the screen, and displayed by the analysis image display means.
Accordingly, the analysis can be performed by freely combining a plurality of information unit groups, the plurality of information unit groups can be easily specified, and the addition and change of the specification can be performed flexibly and easily.
[0030]
BEST MODE FOR CARRYING OUT THE INVENTION
Hereinafter, the features of the present invention will be specifically described based on embodiments with reference to the drawings.
(Embodiment 1: Overall Configuration for Searching) FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing the overall configuration of an information unit group operation device according to an embodiment for implementing the present invention.
The present invention relates to a
[0031]
(Search for Available Information Unit Group) The information unit group operation device of the present embodiment is arranged such that information unit groups usable by the present device are dispersed in a directory-managed file system as shown in FIG. It is assumed that the file is mixed with other files.
In FIG. 2, 2a, 2b, and the like described as “information unit group” are assumed to be information unit groups that can be used in the present apparatus.
2c, 2d, etc., enclosed by double rectangles indicate directories, and 2e, 2f, etc. indicated by practice rectangles are document files, image files, and the like.
Hereinafter, all of them are collectively called a file item.
The file system referred to here may be one directly connected to the present apparatus or one connected via a network.
This is because recently, a technology that treats another file system on a network as if it were its own file system has become widespread.
[0032]
Next, the configuration of the information unit group in this embodiment will be described.
As shown in FIG. 3A, the information unit group that can be handled by this apparatus has a structure having three file items (sub files) of Data, Index, and Table under a file item (directory). I do.
Here, Data consists of a set of data units having a data heading and a content part corresponding to the heading.
Index and Table are files provided to speed up data retrieval.
Table is converted into an address value indicating a file Index corresponding to a hash value obtained from a given search key.
The Index file is a hash table having a structure in which a set of a search key and an address in the Data file in which data having the search key exists is listed, and the address indicated in the Table file has the same hash value. It shows the head address of the list of addresses where the stored data is stored.
An outline of the above configuration is shown in FIG.
For example, when “parsley” is input as a search key and its hash value is 1, first, the address of the file Index is calculated from the corresponding hash value using the file table, and then the address is calculated using the file index. The list starting with the address indicated by the hash value is checked in order, the address of the file Data is extracted, and the data of the content part of the search result is obtained.
[0033]
Next, the integration result of the information unit group held in the information unit group integration unit of the present embodiment will be described.
The relationship between the information unit groups is managed by a binary tree.
FIG. 4 is a conceptual diagram showing this state.
In the figure, 4c is an information unit group, and 4a and 4b are integrated information.
The integrated information of the leaves of the binary tree is provided corresponding to the information unit group existing in the file system, and the integrated information other than the leaves is configured to indicate two integrated information.
If the pointers indicating the two pieces of integrated information are ordered, the integrated order can be stored.
Each integrated information has a unique name.
A plurality of binary trees may be stored in the information unit group integration means.
[0034]
The flow of the process in which the information unit group search means 5 checks the entire file system, searches for an information unit group that can be used by the present apparatus, and lists them will be described with reference to the flowcharts of FIGS.
FIG. 5 shows an outline of the processing.
First, the root directory is set to the value of the variable CURDIR that stores the value of the current directory (step S5a).
Then, a function for searching for an information unit group that can be used in the present apparatus, which will be described later with reference to FIG. 6, is called (step S5b).
Subsequently, the information unit group integration unit is referred to (step S5c).
Finally, the group name display means 3 lists the group names of the information unit groups that can be used in the apparatus searched in step S5b, and ends the processing (step S5d).
FIG. 9 is an example showing a state where the group names are listed by the group name display means 3.
“1993 dissertation” to “design image” are group names of information unit groups that actually exist in the file system, and “bibliographic data + design image” is an identifier of integrated information obtained by integrating information unit groups.
[0035]
FIG. 6 is a function called in step S5b of FIG. 5 to search for an information unit group usable in the apparatus.
First, the current directory is set based on the value of the variable CURDIR (step S6a).
Then, 1 is assigned to a variable N indicating the number of the file item in the current directory (step S6b).
In the following processing, the N-th file item is set as a processing target (step S6c).
Next, it is determined whether or not the N-th file item is an information unit group that can be used in the present apparatus by a method described later (step S6d).
If it is determined that the information unit group can be used by the present apparatus, the name of the file item and information on the location where the file item exists are sequentially added to the group name holding means 4 (step S6e).
Specifically, the name of the information unit group can be obtained by reading out the file item name individually owned by each information unit group, and the location information can be obtained by the position of the current directory.
For example, in FIG. 2, the
Next, it is determined whether or not the N-th file item includes a lower-level file item (step S6f).
If a file item is included in the lower order, the Nth file item is set to the value of the variable CURDIR (step S6g), and the function of FIG. 6 is recursively called (step S6h).
After incrementing the value of the variable N (Step S6i), the processes from Step S6c to Step S6i are repeated as long as the N-th file item exists (Step S6j).
If there are no undetermined file items in the current directory, this function ends.
Then, when the function in which the root directory is set in the variable CURDIR is completed, the control returns to the process shown in the flowchart of FIG.
At this time, the group name holding means 4 stores all the group names of the information unit groups which exist in the file system and can be used in the present apparatus.
FIG. 8A shows an example of information held in the group name holding unit 4 as a result of searching the file system of FIG.
[0036]
In step S6d, determination as to whether the file item is an information unit group that can be used in the present apparatus is performed as follows.
The information unit group that can be handled by the apparatus of this embodiment has a structure having three file items (sub-files) Data, Index, and Table under a file item (directory) as shown in FIG.
Therefore, a file item having these three sub-files can be determined to be an information unit group that can be handled by the present apparatus.
FIG. 7 is a flowchart showing S6d and S6e of FIG. 6 in detail based on this example.
[0037]
First, while substituting 1 for a variable J indicating the number of the sub-file under the file item of interest, a flag DF indicating the existence of the sub-file Data, a flag IF indicating the existence of the sub-file Index, The flag TF indicating the existence of the subfile Table is initialized to 0 (step S7a).
In the following processing, the J-th sub file is set as a processing target (step S7b). It is checked whether the J-th subfile is Data (step S7c). If it is Data, the value of the flag DF is set to 1 (step S7d). Similarly, it is checked whether the file is an Index (step S7e) and whether it is a Table (step S7g). If the file is a corresponding subfile, the corresponding flag IF (step S7f) and flag TF (step S7h) Is set to 1.
The order of checking these three sub-files may be arbitrary.
Next, it is checked whether all three of the flags DF, IF, and TF are set to 1 (step S7j).
If all of them are 1, the file item of interest is an information unit group that can be used in the present apparatus, so that its name and location information are recorded in the group name holding means 4 (step S7k). .
If all are not 1, the value of the variable J is incremented. If the next subfile exists, steps S7b to S7i are repeated for that subfile (step S71).
If there are no more sub-files, the file item is not an information unit group that can be used in this apparatus, and the process ends.
[0038]
There are several other determination methods.
For example, as the simplest method, the name of the information unit group handled by the present apparatus is determined as “xxx.DAT” or the like, and it is determined whether the file item to be determined conforms to this rule. How to
Further, some file systems can define a file type indicating which application handles each file.
In such a file system, the file type can be checked for each file item and used as a criterion.
If you want to make a more accurate determination, you can actually open the file item as a search target, search once, and determine whether the target is actually a searchable and valid information unit group. There is also.
At this time, a management information unit that is common to all information unit groups may be searched.
The management information unit is an information unit searched by a unique search key that cannot be input by a user using a keyboard or the like.
[0039]
Next, a process in which a directory that is likely to hold an information unit group that can be used in this apparatus is stored in the
In the present embodiment, it is assumed that the location storage means 2 is configured as shown in FIG.
[0040]
In FIG. 10, first, the value of the variable K is set to 0 (step S10a).
Next, the K-th directory in the designated directory stored in the
The value of the variable N is set to 0 (step S10c), and the Nth file item in the current directory is specified as a processing target (step S10d).
Next, it is determined whether or not this file item is an information unit group that can be used in the device (step S10e). If so, the name of the file item is recorded in the group name holding unit 4 (step S10f). .
While incrementing the value of the variable N one by one (step S10g), the processing from step S10c to step S10g is repeated until there is no more file item (step S10h).
Then, the value of the variable K is incremented one by one (step S10i), and the processing from step S10b to step S10i is repeated until all the designated directories are exhausted (step S10j).
Finally, the group name display means 3 lists the names of the available information unit groups and ends the processing (step S10k).
[0041]
In the process of FIG. 10, the configuration is such that only one level of the specified directory is checked. However, if the specified directory includes a lower directory, the recursive process as shown in the flowchart of FIG. By a simple process, a directory under the designated directory may be searched.
In that case, when recording the group name in the group name holding means 4, it is checked whether or not the same group name is already included so that the searched information unit group does not overlap. It is preferable that the content of the group name holding means 4 be omitted by writing or by post-processing.
[0042]
Next, reference to the information unit group integrating means performed in step S5c of FIG. 5 will be described with reference to FIG.
First, one of the integrated information stored in the information unit group integrating means, which is the root, is selected, and the process proceeds to FIG.
First, the current integrated information is set.
At the start, it becomes route integration information (step S11a).
The name and address of the current integrated information are temporarily recorded (step S11b).
Next, 0 is substituted into a variable N for counting the order of children of the current integrated information (step S11c), and the integrated information corresponding to the Nth child is processed (step S11d).
It is checked whether or not the integrated information to be processed is a leaf of a binary tree (step S11e). If the integrated information to be processed is a leaf, it is checked whether or not an information unit group corresponding to the integrated information exists.
As a checking method, for example, it can be checked whether or not a group name that matches the group name of the information unit group corresponding to the integrated information is held in the group name holding unit (step S11f).
At this time, if the information unit group does not exist, the name of the temporarily stored integrated information is cleared, and this function started from the root integrated information is forcibly terminated (step S11g).
If it is not a leaf in step S11e, the function is recursively called (step S11i) using the integrated information as current integrated information (step S11h).
The variable N is incremented (step S11j), and if the value of N is less than 2, the process is repeated from step S11d; otherwise, the process is terminated (step S11k).
When the function of FIG. 11 is completed for one route of integrated information, the temporarily stored integrated information name and integrated information address are moved to the group name holding unit.
Then, the above processing is repeated until there is no integrated information serving as the root.
FIG. 8B shows an example of the state of the group name holding means when the processing shown in the flowchart of FIG. 5 is completed.
[0043]
Here, all the integrated information corresponding to each node of the binary tree is extracted. However, if the integrated information increases, it may be complicated. For example, only the integrated information corresponding to the root may be extracted. .
In this case, there is no need to perform integration using a binary tree, and a list structure or the like may be used.
Further, the user may be able to specify whether or not to perform the process of step S5c.
In the processing of steps S11f and S11g, if any of the integrated information unit groups does not exist, it is detected and prevented from being displayed, so that the integrated information that has already lost its value is designated as the processing target. I can't.
At this time, the integrated information including the deleted information unit group may be automatically deleted.
[0044]
(Selection of Information Unit Group) A process of selecting an information unit group to be operated from an information unit group or integrated information listed as shown in FIG. 9 will be described.
[0045]
FIG. 13 is a flowchart showing a process in which the information unit group selecting means 6 selects an information unit group without recording the selection order.
According to this processing, a plurality of information unit groups can be selected at the same time.
However, since the selection order is not recorded, a plurality of information unit groups cannot be ordered and combined.
Here, it is assumed that the user selects the information unit group by clicking the mouse.
[0046]
First, a mouse event is acquired (step S13a), and it is checked whether the mouse event has occurred in a list displaying available information unit groups (step S13b).
In the case of an occurrence in the list, the display is changed so that the user can recognize the selected item as a list selection process.
Here, as shown in FIG. 14, the display portion of the selected item is shaded.
Flags are provided corresponding to the display of each item, and flags are set for shaded items (step S13c).
Then, the processing from step S13a to step S13c is repeated until the selection processing ends (step S13d).
[0047]
Next, the selection result is taken out and recorded.
First, the variable N is set to 0 (step S13e), the flag set in step S13c is checked, and it is checked whether the Nth item in the list is selected (step S13f).
If it has been selected, the contents of the selection are recorded in the selection result holding means 7 such as the information unit group name and the location information (step S13g).
FIG. 15 is an example showing the storage state of the selection result holding means.
Then, while incrementing the variable N by one (step S13h), the processing from step S13f to step S13h is repeated until the items in the list are completed (step S13i).
Finally, the information unit group integrating means 8 integrates one or more information unit groups using the information of the selection result holding means 7 and opens a target information unit group based on the integrated result. (Step S13j).
Note that opening means to make the information unit group operable.
[0048]
Thereafter, the opened information unit group is an operation target.
In the present embodiment, the information unit group integrating means 8 forms a binary tree based on the information unit group or the integrated information held in the selection result holding means 7.
First, as an initial setting, an information unit group or integrated information is extracted from the list held in the selection result holding means 7.
If it is an information unit group, one piece of new integrated information that points to the information unit group with, for example, a pointer is created, and the integrated information is designated as designated integrated information A.
If it is integrated information, the integrated information is designated as designated integrated information A.
Next, the information unit group or the integrated information held in the selection result holding means 7 is taken out, and if it is the information unit group, one piece of new integrated information is created which points to the information unit group with, for example, a pointer. Then, the integrated information is designated as designated integrated information B.
If it is integrated information, the integrated information is designated as designated integrated information B.
When the specified integrated information A and B are completed, new integrated information indicating the specified integrated information A and B is created, and this new integrated information is designated as specified integrated information A.
Until the list held in the selection result holding means 7 ends, the process is repeated from the point where the designated integrated information B is determined.
At the time of search or analysis, which will be described later, processing is started using the generated integrated information as a root node.
[0049]
FIG. 16 is a flowchart showing a process in which the information unit group selecting means 6 selects an information unit group while recording the selection order.
According to this processing, a plurality of information unit groups can be selected at the same time, or a plurality of information unit groups can be ordered and combined.
First, a mouse event is acquired (step S16a), and it is checked whether the mouse event has occurred in the list displaying the usable information unit group (step S16b). If the item has occurred in the list, the selected item is shaded as shown in FIG. 14 as a list selection process (step S16c).
At the same time, the selection contents, the selection order, the information unit group name, the location information and the like are additionally recorded in the selection result holding means 7 (step S16d).
FIG. 17 shows an example of the storage form of the selection result holding means in this case.
Then, the processing from step S16a to step S16d is repeated until the selection processing ends (step S16e).
Finally, using the information of the selection
[0050]
In the case of this embodiment, since the selection order information is held, it is possible to open using the order information.
Specifically, when a search key is input, a search is performed in which a search result performed on a certain information unit group is used as a search key for the next specified information unit group.
The integration using the binary tree described above is configured to maintain the order.
For example, when creating a binary tree, the order is maintained by sequentially reading from the end of the list of the selection result holding means 7 and assigning
[0051]
(Search for Open Information Unit Group) A search process for an opened information unit group will be described.
Here, it is assumed that a plurality of information unit groups have been integrated by the information unit group integrating means 8 using the above-described binary tree structure as if they were handled as one information unit group.
[0052]
FIG. 18 is a flowchart expressing the search processing.
First, the user inputs search conditions from the search condition input means 9.
Here, it is assumed that a search is performed for a keyword assigned to each information unit.
The user inputs a search key into the search condition input means 9 (step S18a). Here, a keyword search is used as a search method. However, even if a general search such as a full-text search is used, the basic functions and processing flow are exactly the same.
The
In this case, the name of the information unit that meets the conditions, the name of the belonging information unit group, and the information on the location of the information unit entity in the file are search results.
Then, this result is presented to the user on the search result display means 11 in the form of a headword list as shown in FIG. 20 (step S18c).
This process is repeated until the user issues an instruction to end the search (step S18d).
[0053]
In step S18b, when searching for the integrated information unit group, a binary tree is sequentially searched from the root node of the integrated information created earlier, and the information unit group corresponding to the integrated information of the leaf that has been reached is searched. Give a condition and search.
Further, the binary tree obtained by integrating the information unit groups is normally retained even after the search processing is completed, that is, except when the list of the selection result retaining unit is composed of one element.
As described above, if the configuration is such that the integrated information corresponding to each node of the binary tree can be specified, whether the information unit group existing under the specified integrated information is one information unit group It is possible to perform the search and analysis as described above, and it is possible to organize a necessary information unit group when necessary without separately providing a procedure and a user interface for managing the file existence status in advance.
Also, a command that holds the binary tree only when necessary may be provided.
If it is not considered that the integrated information unit group will be used later, the information unit group integration means 8 does not have to have the function of integration using a binary tree.
The information unit group integrating means 8 refers to the integrated selection result holding means 7, opens one of the gain information unit groups stored therein and performs a search, and then moves to the next information unit group and performs the same operation. The process can be repeated.
[0054]
Next, an example of performing a continuous search using the selection order of the information unit group will be described.
FIG. 21 is a flowchart showing a search procedure when the information unit groups are ordered when integration is not performed.
First, a search condition is input (step S21a).
Next, 1 is set to a variable N indicating the selection order (step S21b).
The information unit group in the selection order is opened (step S21c).
The information unit group opened according to the search condition is searched (step S21d), and the search result is recorded (step Se).
The information unit group is closed (step S21f).
N is incremented (step S21g), and if the next information unit group exists (step S21h), the process is repeated from step Sc using the stored search result as a search condition (step S21i).
If the next information unit group does not exist, the search result is displayed and the process ends (step S21j).
When integrated, instead of counting the number of N, a binary tree is sequentially searched from the root node of the integrated information, and a search is performed on the information unit group corresponding to the integrated information of the reached leaf. do it.
If the branch indicating the integrated information corresponding to the child has the order, the order of selection is maintained by searching from the one with the
Through the processing described above, it is possible to perform a search for a free combination from the information unit group that is mixed with other files in the file system.
[0055]
(Details of Search Result and Display of Affiliation Information Unit Group) A process of displaying which information unit group the information unit displaying the detailed information belongs to along with the detailed information of the search result will be described.
FIG. 22 is a flowchart showing this processing.
First, a mouse event is acquired (step S22a), and it is checked whether the event has occurred in the list displaying the search result (step S22b).
If the item is in the list, the selected item in the list is shaded as a list selection process (step S22c).
Then, the content of the selected item is read from the information unit group name and the file position of the search result shown in FIG. 19 and displayed (step S22d).
Next, the name of the information unit group to which this information unit belongs is extracted from the search result of FIG. 19 (step S22e) and displayed at the same time.
FIG. 23 shows an example in which the contents are presented together with the belonging information unit group (step S22f).
The above processing is repeated until the user issues an end instruction (step S22g).
Through this processing, it is possible to know the detailed contents of the information unit and to which information unit group it belongs.
[0056]
(Embodiment 2: Overall Configuration for Analysis) FIG. 24 is a block diagram showing an overall configuration of an example of an information operating device for analyzing information units included in a plurality of information unit groups.
In the present embodiment, an information unit
[0057]
(Generation of analysis image) The selected information unit group was searched, and image components such as points expressing the existence of the information unit included in the information unit were selected according to the properties of each information unit. The information unit group can be analyzed.
Here, an evaluation item (search keyword group) is arranged in the horizontal direction, and a point is arranged when the information unit includes the evaluation item in the keyword.
The vertical direction is randomly arranged.
[0058]
FIG. 25 is a flowchart expressing this processing.
The operation until the selected information unit group is stored in the selection result holding means and integrated so as to be able to be handled in the same manner as one information unit group is the same as in the first embodiment, so that the description is omitted, and the subsequent processing will be omitted. Is described.
First, the information units included in the integrated information unit group selected as a search target are sequentially read one by one.
As for the handling of the integrated information unit group, a binary tree is searched in the same manner as described in the description of the search in the first embodiment (step S25a).
Then, the evaluation items stored in the evaluation
FIG. 26 is an example of an evaluation item held in the evaluation condition holding means.
In this case, "design", "image", and "sensitivity" are evaluation items in the horizontal direction.
The vertical direction indicates that the condition is not specified and only the evaluation value is generated by random numbers (step S25b).
If the condition is satisfied, that is, if the evaluation item is included in the keyword of the information unit in this example, a horizontal evaluation value (for example, 10) is set for the information unit (step S25c).
Further, an evaluation value in the vertical direction (a random number is obtained in this example) is also set (step S25d).
Then, based on these two evaluation values, the position calculating means 14 converts the values into actual point positions on the screen (step S25e).
Subsequently, the analysis
The processing from step S25b to step S25g is repeated for one information unit until the evaluation item ends (step S25h).
Further, the processing from step S25a to step S25h is repeated until all the information units included in the integrated information unit group are read (step S25i).
[0059]
FIG. 27 shows an example of an image generated by the above processing.
In this figure, image components (dots) expressing the existence of an information unit including each of three evaluation items in a keyword are arranged on the screen.
The evaluation conditions held in the evaluation condition holding means may be divided into several groups, may be configured to select in advance which evaluation conditions are to be displayed, or the user may combine them appropriately, Any designation may be made.
In this case, the axis display portion in FIG. 27 may be rewritten accordingly.
With the above-described processing, it is possible to add an analysis to a free combination from an information unit group mixed with other files in the file system.
[0060]
As the information unit group, a dictionary database, a multimedia database in which voices, images, and the like are mixed, and the like can be used as long as the information unit group is configured according to the file format as described in the above embodiment.
[0061]
【The invention's effect】
According to the present invention, a plurality of information unit groups scattered together with other files in an ordinary file system can be freely combined and searched and analyzed easily.
In particular, when a plurality of information unit groups are selected and searched at the same time, it becomes easy to know to which information unit group the search result belongs.
By specifying in advance a place where an information unit group is likely to exist, and verifying the location, it is possible to present an effectively usable information unit group to a user.
Further, the directory structure of a file can be used when searching for an information unit group that can be used in the present apparatus.
Further, continuous search can be easily performed by freely and dynamically designating the search order of the information unit group.
Further, by integrating and retaining information unit groups to be searched and analyzed, it is possible to more flexibly and easily organize information unit groups.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a configuration for realizing an information unit group operation device of the present invention.
FIG. 2 is a diagram illustrating an example of a file system targeted by the present invention.
FIG. 3 is a diagram showing an example of a configuration of an information unit group targeted in the present invention.
FIG. 4 is a diagram showing an example of integrated information held in an information unit group integrating means.
FIG. 5 is a flowchart showing a process for checking all file systems and searching for usable information unit groups.
FIG. 6 is a diagram showing a usable information unit group extraction function used recursively by the processing of FIG. 5;
FIG. 7 is a flowchart illustrating an example of determining whether a file item is an information unit group usable in the present apparatus.
FIG. 8 is a diagram showing an example of information stored in a group name holding unit.
FIG. 9 is an example in which a usable information unit group is displayed.
FIG. 10 is a flowchart illustrating a process for searching for a usable information unit group existing in a specified directory.
FIG. 11 is a flowchart for searching for integrated information.
FIG. 12 is a diagram illustrating an example of information stored in an existence location holding unit.
FIG. 13 is a flowchart illustrating an information unit group selection process when the selection order is not stored.
FIG. 14 is a diagram showing an example in which an information unit group is selected.
FIG. 15 is a diagram illustrating an example (no order) of information stored in a selection result holding unit.
FIG. 16 is a flowchart illustrating an information unit group selection process when the selection order is stored.
FIG. 17 is a diagram illustrating an example (in order) of information stored in a selection result holding unit;
FIG. 18 is a flowchart illustrating a search process of an information unit group.
FIG. 19 is a diagram illustrating an example of a search result.
FIG. 20 is a diagram illustrating a display example of a search result.
FIG. 21 is a flowchart showing a search procedure when an information unit group is ordered and specified.
FIG. 22 is a flowchart illustrating a process of selecting a headword of a search result and presenting detailed contents.
FIG. 23 is a diagram showing an example in which detailed contents of an information unit are presented.
FIG. 24 is a block diagram showing a configuration for realizing the information operation device of the present invention.
FIG. 25 is a flowchart showing a process for sequentially reading and evaluating information units and presenting an analysis image.
FIG. 26 is a diagram showing an example of information stored in an evaluation value calculation unit.
FIG. 27 is a diagram showing an example in which an analysis image is displayed.
[Explanation of symbols]
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (4)
前記識別情報表示手段による表示に対応して設けられ、前記統合情報単位群の少なくとも一つを選択する入力を受け付ける情報単位群選択手段と、
前記情報単位群選択手段により選択された前記統合情報単位群の識別情報を保持する選択結果保持手段と、
前記選択結果保持手段に保持された情報単位群を統合して新たな統合情報単位群を生成し、該統合情報単位群の情報を保持する情報単位群統合手段と、
検索条件を入力する検索条件入力手段と、
前記情報単位群統合手段により統合された新たな統合情報単位群より、前記検索条件入力手段から入力された検索条件に適合する情報単位を検索する検索手段と、
前記検索手段により検索された情報単位を表示する検索結果表示手段と
を有することを特徴とする情報単位群操作装置。Identification information display means for displaying identification information of an integrated information unit group obtained by integrating a real information unit group which is a group of information units;
An information unit group selection unit provided corresponding to the display by the identification information display unit and receiving an input for selecting at least one of the integrated information unit groups;
Selection result holding means for holding identification information of the integrated information unit group selected by the information unit group selection means,
An information unit group integrating unit that integrates the information unit group held in the selection result holding unit to generate a new integrated information unit group, and holds information of the integrated information unit group;
Search condition input means for inputting search conditions;
Search means for searching, from the new integrated information unit group integrated by the information unit group integration means, for an information unit that matches the search condition input from the search condition input means,
An information unit group operation device, comprising: a search result display unit for displaying an information unit searched by the search unit.
前記識別情報表示手段による表示に対応して設けられ、前記統合情報単位群の少なくとも一つを選択する入力を受け付ける情報単位群選択手段と、
前記情報単位群選択手段により選択された前記統合情報単位群の識別情報を保持する選択結果保持手段と、
前記選択結果保持手段に保持された情報単位群を統合して新たな統合情報単位群を生成し、該統合情報単位群の情報を保持する情報単位群統合手段と、
情報単位群に属する情報単位を評価するための条件を保持する評価条件保持手段と、
評価条件保持手段に保持されている条件に基づいて、前記情報単位群統合手段により統合された統合情報単位群に属する各情報単位を評価した値を算出する情報単位評価手段と、
情報単位評価手段によって算出された評価値に基づいて、情報単位の存在を表現する画像構成要素の位置を決定する位置算出手段と、
位置算出手段によって決定された位置に画像構成要素を配置する分析画像生成手段と、分析画像生成手段によって生成された画像を表示する分析画像表示手段と
を有することを特徴とする情報単位群操作装置。Identification information display means for displaying identification information of an integrated information unit group obtained by integrating a real information unit group which is a group of information units;
An information unit group selection unit provided corresponding to the display by the identification information display unit and receiving an input for selecting at least one of the integrated information unit groups;
Selection result holding means for holding identification information of the integrated information unit group selected by the information unit group selection means,
An information unit group integrating unit that integrates the information unit group held in the selection result holding unit to generate a new integrated information unit group, and holds information of the integrated information unit group;
Evaluation condition holding means for holding conditions for evaluating information units belonging to the information unit group,
Information unit evaluation means for calculating a value obtained by evaluating each information unit belonging to the integrated information unit group integrated by the information unit group integration means, based on the condition held in the evaluation condition holding means,
Based on the evaluation value calculated by the information unit evaluation means, a position calculation means for determining the position of the image component expressing the presence of the information unit,
An information unit group operating device comprising: an analysis image generation unit that arranges image components at positions determined by a position calculation unit; and an analysis image display unit that displays an image generated by the analysis image generation unit. .
前記表示に対応して設けられ、前記統合情報単位群の少なくとも一つを選択する入力を受け付け、
前記選択された前記統合情報単位群の識別情報を保持し、
前記保持された情報単位群を統合して新たな統合情報単位群を生成し、該統合情報単位群の情報を保持し、
検索条件を入力し、
前記統合された新たな統合情報単位群より、前記入力された検索条件に適合する情報単位を検索し、
前記検索された情報単位を表示する
ことを特徴とする情報単位群操作方法。Displays the identification information of the integrated information unit group obtained by integrating the real information unit group, which is a set of information units,
Provided corresponding to the display, accepts an input to select at least one of the integrated information unit group,
Holding identification information of the selected integrated information unit group,
Integrating the held information unit group to generate a new integrated information unit group, holding the information of the integrated information unit group,
Enter search criteria,
From the integrated new integrated information unit group, search for an information unit that matches the input search condition,
An information unit group operation method, wherein the searched information units are displayed.
前記表示に対応して設けられ、前記統合情報単位群の少なくとも一つを選択する入力を受け付け、
前記選択された前記統合情報単位群の識別情報を保持し、
前記選択結果保持手段に保持された情報単位群を統合して新たな統合情報単位群を生成し、該統合情報単位群の情報を保持し、
情報単位群に属する情報単位を評価するための条件を保持し、
前記保持されている条件に基づいて、前記統合された統合情報単位群に属する各情報単位を評価した値を算出し、
前記算出された評価値に基づいて、情報単位の存在を表現する画像構成要素の位置を決定し、
前記決定された位置に画像構成要素を配置し、
前記配置された画像を表示する
ことを特徴とする情報単位群操作方法。Displays the identification information of the integrated information unit group obtained by integrating the real information unit group, which is a set of information units,
Provided corresponding to the display, accepts an input to select at least one of the integrated information unit group,
Holding identification information of the selected integrated information unit group,
A new integrated information unit group is generated by integrating the information unit groups held in the selection result holding unit, and the information of the integrated information unit group is held,
Holding conditions for evaluating information units belonging to the information unit group,
Based on the held conditions, calculate a value that evaluates each information unit belonging to the integrated integrated information unit group,
Based on the calculated evaluation value, determine the position of the image component expressing the presence of the information unit,
Placing an image component at the determined position,
An information unit group operating method, characterized by displaying the arranged image.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003201957A JP2004046870A (en) | 2003-07-25 | 2003-07-25 | Information unit group operation device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003201957A JP2004046870A (en) | 2003-07-25 | 2003-07-25 | Information unit group operation device |
Related Parent Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP7142697A Division JPH08314973A (en) | 1995-05-17 | 1995-05-17 | Operation device for information unit group |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2004046870A true JP2004046870A (en) | 2004-02-12 |
Family
ID=31712524
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003201957A Pending JP2004046870A (en) | 2003-07-25 | 2003-07-25 | Information unit group operation device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2004046870A (en) |
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008505376A (en) * | 2004-05-03 | 2008-02-21 | マイクロソフト コーポレーション | System and method for dynamically generating selectable search extensions |
| US7925682B2 (en) | 2003-03-27 | 2011-04-12 | Microsoft Corporation | System and method utilizing virtual folders |
| US8555199B2 (en) | 2003-03-24 | 2013-10-08 | Microsoft Corporation | System and method for user modification of metadata in a shell browser |
| US8615717B2 (en) | 2003-04-17 | 2013-12-24 | Microsoft Corporation | Address bar user interface control |
| US8707209B2 (en) | 2004-04-29 | 2014-04-22 | Microsoft Corporation | Save preview representation of files being created |
| US8972342B2 (en) | 2004-04-29 | 2015-03-03 | Microsoft Corporation | Metadata editing control |
| US9361312B2 (en) | 2003-03-27 | 2016-06-07 | Microsoft Technology Licensing, Llc | System and method for filtering and organizing items based on metadata |
| US10489044B2 (en) | 2005-07-13 | 2019-11-26 | Microsoft Technology Licensing, Llc | Rich drag drop user interface |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0793196A (en) * | 1993-09-27 | 1995-04-07 | Fuji Xerox Co Ltd | Information managing device |
| JPH07121564A (en) * | 1993-10-26 | 1995-05-12 | Fuji Xerox Co Ltd | Information presenting device |
-
2003
- 2003-07-25 JP JP2003201957A patent/JP2004046870A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0793196A (en) * | 1993-09-27 | 1995-04-07 | Fuji Xerox Co Ltd | Information managing device |
| JPH07121564A (en) * | 1993-10-26 | 1995-05-12 | Fuji Xerox Co Ltd | Information presenting device |
Cited By (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US8555199B2 (en) | 2003-03-24 | 2013-10-08 | Microsoft Corporation | System and method for user modification of metadata in a shell browser |
| US7925682B2 (en) | 2003-03-27 | 2011-04-12 | Microsoft Corporation | System and method utilizing virtual folders |
| US8117226B2 (en) | 2003-03-27 | 2012-02-14 | Microsoft Corporation | System and method for virtual folder sharing including utilization of static and dynamic lists |
| US9361312B2 (en) | 2003-03-27 | 2016-06-07 | Microsoft Technology Licensing, Llc | System and method for filtering and organizing items based on metadata |
| US9361313B2 (en) | 2003-03-27 | 2016-06-07 | Microsoft Technology Licensing, Llc | System and method for filtering and organizing items based on common elements |
| US8615717B2 (en) | 2003-04-17 | 2013-12-24 | Microsoft Corporation | Address bar user interface control |
| US8707209B2 (en) | 2004-04-29 | 2014-04-22 | Microsoft Corporation | Save preview representation of files being created |
| US8972342B2 (en) | 2004-04-29 | 2015-03-03 | Microsoft Corporation | Metadata editing control |
| JP2008505376A (en) * | 2004-05-03 | 2008-02-21 | マイクロソフト コーポレーション | System and method for dynamically generating selectable search extensions |
| US8024335B2 (en) | 2004-05-03 | 2011-09-20 | Microsoft Corporation | System and method for dynamically generating a selectable search extension |
| US10489044B2 (en) | 2005-07-13 | 2019-11-26 | Microsoft Technology Licensing, Llc | Rich drag drop user interface |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5105802B2 (en) | Information processing device | |
| US20020143797A1 (en) | File classification management system and method used in operating systems | |
| US20060230334A1 (en) | Visual thesaurus as applied to media clip searching | |
| JP3362125B2 (en) | Information processing method | |
| KR20000062514A (en) | Method for automatically sorting and searching patent materials and analyzing searched data | |
| US20080140608A1 (en) | Information Managing Apparatus, Method, and Program | |
| JPH1145284A (en) | Preparation method for profile and computer readable recording medium recording program for making computer execute respective processes of the method | |
| JP2004046870A (en) | Information unit group operation device | |
| JP5447484B2 (en) | Information processing device | |
| JP7104390B2 (en) | Document creation device, document creation method, database construction device, database construction method, and program | |
| JP3588507B2 (en) | Information filtering device | |
| JP2008027134A (en) | Document management device, document management method, and program of executing document management method | |
| JPH08314973A (en) | Operation device for information unit group | |
| JP3429225B2 (en) | Storage medium storing data search program | |
| JP3531344B2 (en) | Information retrieval device | |
| JP2000330979A (en) | Method for analyzing electronic document to be retrieved and electronic document registration system | |
| JP2004062901A (en) | Operating device of information unit group | |
| JPH10162011A (en) | Information retrieval method, information retrieval system, information retrieval terminal equipment, and information retrieval device | |
| KR100718745B1 (en) | Patent retrieve system and method by using text mining | |
| KR20080039864A (en) | User interface system for analysing documents | |
| JPH10228488A (en) | Information retrieval collecting method and its system | |
| JP2004234582A (en) | Dictionary construction method, system, and screen | |
| JPH07175811A (en) | Electronic document control device | |
| JP3933407B2 (en) | Document processing apparatus, document processing method, and storage medium storing document processing program | |
| JP2002117043A (en) | Device and method for document retrieval, and recording medium with recorded program for implementing the same method |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20040603 |