EP3882012A2 - Sack or bag manufacturing device and method for sack or bag manufacturing - Google Patents
Sack or bag manufacturing device and method for sack or bag manufacturing Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP3882012A2 EP3882012A2 EP21162712.0A EP21162712A EP3882012A2 EP 3882012 A2 EP3882012 A2 EP 3882012A2 EP 21162712 A EP21162712 A EP 21162712A EP 3882012 A2 EP3882012 A2 EP 3882012A2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- sack
- manufacturing device
- belt
- bag manufacturing
- transport
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B31—MAKING ARTICLES OF PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER; WORKING PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER
- B31B—MAKING CONTAINERS OF PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER
- B31B70/00—Making flexible containers, e.g. envelopes or bags
- B31B70/02—Feeding or positioning sheets, blanks or webs
- B31B70/04—Feeding sheets or blanks
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65H—HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL, e.g. SHEETS, WEBS, CABLES
- B65H5/00—Feeding articles separated from piles; Feeding articles to machines
- B65H5/02—Feeding articles separated from piles; Feeding articles to machines by belts or chains, e.g. between belts or chains
- B65H5/021—Feeding articles separated from piles; Feeding articles to machines by belts or chains, e.g. between belts or chains by belts
- B65H5/023—Feeding articles separated from piles; Feeding articles to machines by belts or chains, e.g. between belts or chains by belts between a pair of belts forming a transport nip
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B31—MAKING ARTICLES OF PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER; WORKING PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER
- B31B—MAKING CONTAINERS OF PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER
- B31B2150/00—Flexible containers made from sheets or blanks, e.g. from flattened tubes
- B31B2150/001—Flexible containers made from sheets or blanks, e.g. from flattened tubes with square or cross bottom
- B31B2150/0014—Flexible containers made from sheets or blanks, e.g. from flattened tubes with square or cross bottom having their openings facing transversally to the direction of movement
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B31—MAKING ARTICLES OF PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER; WORKING PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER
- B31B—MAKING CONTAINERS OF PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER
- B31B2150/00—Flexible containers made from sheets or blanks, e.g. from flattened tubes
- B31B2150/002—Flexible containers made from sheets or blanks, e.g. from flattened tubes by joining superimposed sheets, e.g. with separate bottom sheets
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B31—MAKING ARTICLES OF PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER; WORKING PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER
- B31B—MAKING CONTAINERS OF PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER
- B31B2150/00—Flexible containers made from sheets or blanks, e.g. from flattened tubes
- B31B2150/003—Flexible containers made from sheets or blanks, e.g. from flattened tubes made from tubular sheets
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B31—MAKING ARTICLES OF PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER; WORKING PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER
- B31B—MAKING CONTAINERS OF PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER
- B31B2150/00—Flexible containers made from sheets or blanks, e.g. from flattened tubes
- B31B2150/20—Flexible containers made from sheets or blanks, e.g. from flattened tubes the longitudinal axes of the containers being perpendicular to the direction in which the sheets or blanks are fed
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B31—MAKING ARTICLES OF PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER; WORKING PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER
- B31B—MAKING CONTAINERS OF PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER
- B31B2160/00—Shape of flexible containers
- B31B2160/20—Shape of flexible containers with structural provision for thickness of contents
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65H—HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL, e.g. SHEETS, WEBS, CABLES
- B65H2401/00—Materials used for the handling apparatus or parts thereof; Properties thereof
- B65H2401/10—Materials
- B65H2401/11—Polymer compositions
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65H—HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL, e.g. SHEETS, WEBS, CABLES
- B65H2401/00—Materials used for the handling apparatus or parts thereof; Properties thereof
- B65H2401/20—Physical properties, e.g. lubricity
- B65H2401/22—Optical properties, e.g. opacity or transparency
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65H—HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL, e.g. SHEETS, WEBS, CABLES
- B65H2404/00—Parts for transporting or guiding the handled material
- B65H2404/20—Belts
- B65H2404/22—Cross section profile
- B65H2404/222—Flat belt
- B65H2404/2222—Flat belt with protrusions on inner side; Beads
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65H—HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL, e.g. SHEETS, WEBS, CABLES
- B65H2404/00—Parts for transporting or guiding the handled material
- B65H2404/20—Belts
- B65H2404/24—Longitudinal profile
- B65H2404/243—Longitudinal profile with portions of different thickness
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65H—HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL, e.g. SHEETS, WEBS, CABLES
- B65H2404/00—Parts for transporting or guiding the handled material
- B65H2404/20—Belts
- B65H2404/25—Driving or guiding arrangements
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65H—HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL, e.g. SHEETS, WEBS, CABLES
- B65H2404/00—Parts for transporting or guiding the handled material
- B65H2404/20—Belts
- B65H2404/25—Driving or guiding arrangements
- B65H2404/252—Details of idler roller
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65H—HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL, e.g. SHEETS, WEBS, CABLES
- B65H2404/00—Parts for transporting or guiding the handled material
- B65H2404/20—Belts
- B65H2404/26—Particular arrangement of belt, or belts
- B65H2404/261—Arrangement of belts, or belt(s) / roller(s) facing each other for forming a transport nip
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65H—HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL, e.g. SHEETS, WEBS, CABLES
- B65H2701/00—Handled material; Storage means
- B65H2701/10—Handled articles or webs
- B65H2701/19—Specific article or web
- B65H2701/191—Bags, sachets and pouches or the like
Definitions
- the invention relates to a sack or bag production device according to the preamble of claim 1 and a method for sack or bag production according to the preamble of claim 15.
- sacks or bags For the production of sacks or bags, these are processed with at least one processing station for carrying out a work step in the production of sacks or bags. This is about the production of at least one closed base on a material hose or a material sheet, the latter being first formed into a hose piece. To produce the floor, various individual steps are necessary, which can be carried out or are carried out in the respective work stations. Also unfinished sacks or bags are understood in the context of the invention by the term "sacks or bags”. This also includes the material hoses or material sheets as starting elements of the sack or bag production. Different sacks are produced by creating a closed sack on two bottoms, which can later be filled via a valve. An example of such a sack is a cross-bottom valve sack. Such cross-bottom valve bags are often used to transport building materials such as cement, fertilizers or other pourable or free-flowing products.
- a transport system for supplying and removing sacks or bags to and from the processing station, the transport system comprising at least one transport belt with which the sack or bag can be transported by means of frictional engagement.
- the sack or bag is held immovable relative to the transport belt.
- cross-bottom valve bags are often transported orthogonally to their main axis of extension and often lying down, that is, horizontally. Often two parallel transport belts are used, each of which is in contact with one end of the sack near one end of the sack.
- the object of the present invention is therefore to propose a sack or bag production device and a method for sack or bag production which avoids or even overcomes the disadvantages of the prior art.
- the transport system comprises at least one transport belt with which the sack or the bag can be transported by means of frictional engagement, the transport belt is designed as a flat belt which has notches on at least one of its surfaces.
- the surface acts on the sacks or bags via frictional engagement - also referred to as a transport surface - or a deflection roller or drive pulley acts on the surface for the purpose of guiding or driving (guided surface or drive surface).
- a flat belt is characterized in that said surfaces have a width which is at least three times greater than the thickness of the flat belt. The side faces are therefore not to be understood as surfaces. The notches now have the effect that the flexibility of the flat belt is increased, so that this flat belt can also be guided around rollers or rollers with small diameters without causing damage to the flat belt.
- a flat belt is in particular exclusively frictionally engaged by means of a Drive pulley driven. It is therefore irrelevant whether the drive pulley is in contact with the surface with notches or with the opposite surface.
- the advantage here is that if a surface of the conveyor belt is worn, it can be rotated about its longitudinal axis so that the opposite surface can now take over the functions of the original surface. This means that the conveyor belt has a longer service life, so that ultimately costs can be saved.
- the transport system is designed as a double belt conveyor, the sacks or bags being able to be conveyed in a clamping manner with the surfaces of the transport belts facing one another.
- the frictional engagement between a sack or bag and the transport belt is further increased, which increases the transport reliability.
- both conveyor belts are provided with notches on their surfaces.
- the frictional engagement can be further increased if force supply means are provided which apply a force to the aforementioned transport belts which is directed towards the other transport belt in each case. This can be done in a simple manner by spring-mounted rollers, the spring force pressing the roller onto the transport belt.
- the transport belt comprises at least one inner fiber made of a metal, in particular a steel wire. consists.
- An inner fiber made of metal has the great advantage that it is flexible, but at the same time has high tensile strength, so that it elongates only insignificantly over the course of the operating time. Thus, even after a long operating time of a sack or bag manufacturing device according to the invention, a high quality of the sacks or bags is still guaranteed.
- the transport belt comprises at least one inner fiber which is surrounded by a plastic, in particular a polyurethane.
- a plastic sheathing of the inner fiber can be designed with a suitable choice of the plastic used in the desired hardness.
- the flexibility of the conveyor belt can also be adjusted with a desired hardness so that it can be guided around the drive pulleys provided without damage.
- Polyurethane is a plastic whose properties can be varied greatly, in particular by adding additives, so that the transport belt, in addition to its strength, also has a good frictional connection with the material from which the sacks and bags are made, in particular paper.
- a transport belt that can be used in a sack or bag manufacturing device according to the invention preferably has a width between 10 and 50 mm.
- Its thickness is preferably greater than 3 mm and less than 10 mm. Its coefficient of static friction is preferably between 0.3 and 1, in particular between 0.4 and 0.9. Furthermore, a plastic sheathing, which in particular comprises polyurethane, can be adapted in terms of its abrasion resistance, so that the conveyor belt has a long service life (the time it takes for a worn conveyor belt to be replaced).
- the transport belt is designed as an endless belt, with at least one inner fiber being provided, which is endless, with the inner fiber being encased with plastic.
- the inner fiber can be formed from at least one metal wire by joining its ends to form a continuous fiber. Subsequently, this continuous fiber can be provided with a plastic sheath, thereby creating an endless transport belt.
- An advantage of this configuration of the transport belt is the elimination of a seam or a similar connection point, as is the case with a transport belt Prior art is known. Such a connection point often has particularly large tolerances, so that it is precisely at this point that quality losses can occur.
- the transport belt is designed as an endless belt, the circumferential length being at least 30 meters.
- Such a transport belt is particularly in combination with a device for the production of cross-bottom valve bags, which has a considerable length because of the numerous processing stations required.
- the notches extend as far as the inner fiber.
- the conveyor belt can be bent particularly well, so that smaller drive pulleys can be provided.
- the notches themselves can have a triangular or rectangular cross-section, as will be clarified further below in connection with the drawing.
- the flat belt also has notches on its second surface opposite the first surface. This is accompanied by an even better flexibility of the transport belt. In this case, a surface provided with notches is also in contact with the sacks or bags without any damage being visible.
- the flat belt also has notches on its second surface lying opposite the first surface, the notches being arranged exactly opposite one another. This measure can again increase the flexibility.
- the flat belt also has notches on its second surface opposite the first surface, the notches on the second surface being arranged offset in the longitudinal direction relative to the first surface. This variant improves flexibility, and the transport belt also has good stability.
- the flat belt comprises a groove running in the conveying direction or a web running in the conveying direction on at least one surface.
- At least one deflection pulley and / or one drive pulley and / or at least one further guide element preferably have a complementary profile, so that it is achieved that the transport belt has a very good straight-line ability.
- the plastic material has a hardness of at least 50 Shore A. What is achieved here is that the transport belt is not deformed too much, which could affect the quality of the bags or sacks.
- the plastic material prefferably includes white color pigments. This achieves a light coloring of the transport belt, which means that abrasion of the transport belt which remains on a bag or sack does not lead to strongly visible soiling of the sack or bag. Pollution is also often viewed as a quality defect.
- a signal element can be an element that can be detected by a sensor, for example a magnetic element or any other element which, for example, reacts to radiation from the outside with a reflection of the signal.
- the purpose is to determine the passage of the signal element in order to be able to determine, for example, a changing rotational speed. If there is a deviation from a setpoint speed, the actual speed can be adjusted, for example.
- the above-mentioned object is additionally achieved by a method for sack or pouch production with at least one work step in a processing station, with sacks or bags being fed to and removed from the processing station with a transport system, the transport system comprising at least one transport belt with which the sack or bag is transported by means of frictional engagement.
- the method according to the invention is characterized in that a flat belt is used as the transport belt, which has notches on at least one of its surfaces.
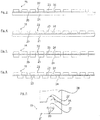
- the Figure 1 shows as an example of bag or sack production a sequence of process steps for forming a base onto a piece of tubing within a sack or bag production device 100.
- Each process step is carried out in an assigned processing station, which are labeled 1. to 7..
- the hose pieces 8, which are already referred to as sacks or bags in the context of the present application, are preferably conveyed to the individual work stations by a double belt conveyor 9, the hose axis running transversely to the conveying direction but in the conveying plane.
- the hose end is pulled open so that the now open bottom 10 lies in a plane which runs essentially orthogonally to the hose axis.
- a valve label 11 is optionally applied to the open floor 10.
- Another valve label 12 can be applied in the work station 3.
- areas of the floor 10 are coated with glue in a manner not shown in detail.
- the floors are then laid in work station 5, with areas of the floors sticking to one another due to the applied glue and thus forming a permanent floor.
- a bottom cover sheet 13 can finally be glued to the laid-up bottom.
- an imprint is optionally printed on the base cover sheet by means of a format cylinder 14.
- the format cylinder 14 can carry raised clichés (not shown).
- the double belt conveyor 9 comprises two revolving, endless transport belts 15 which are guided over deflection rollers 16. To transport the hose pieces, the two conveyor belts 15 are placed one on top of the other in areas of the double belt conveyor and are pressed together by rollers 17 acted on by spring forces, so that a displacement of the hose pieces relative to the conveyor belts is avoided.
- the drive of the The transport belt 15 is shown as an example for the lower transport belt 15.
- the drive comprises a drive motor, not shown, which drives the drive pulley 18.
- the transport belt 15 is guided over the pulleys 19, which are arranged in such a way that the transport belt 15 wraps around the drive pulley 18 preferably over an angle of at least 180 °.
- FIG. 3 now shows a detailed view of a transport belt 15 as it is part of a sack or bag manufacturing device 100 according to the invention.
- This conveyor belt comprises at least one inner fiber 20, which can also be referred to as a neutral fiber, since it is neither elongated nor compressible.
- a lower part 21 of a plastic sheath is arranged below the inner fiber.
- an upper part 22 of a plastic sheath can be seen above the inner fiber.
- the upper part 22 additionally includes notches 24, which preferably extend as far as the inner fiber. As shown, these notches can have a rectangular cross-section. This has the consequence that the remaining webs 23 assume a cuboid shape.
- the lower part 21 can be provided with notches.
- the Figure 4 shows a variant of the embodiment of FIG Figure 3 , in which the notches 24 are triangular or trapezoidal, so that the remaining webs 23 have a trapezoidal shape.
- the Figure 5 shows an embodiment of a conveyor belt 15 in which both the upper 22 and the lower part 21 have notches 24, the notches in the upper part 22 and the notches 24 in the lower part being opposite one another.
- the width of the notches can differ from one another in the upper and lower part.
- FIG. 6 is a variant of a conveyor belt 15 according to FIG Figure 5 to see.
- the notches in the upper part 22 and in the lower part 21 are offset from one another.
- the width of the notches and the ridges can be so be chosen so that the webs in the upper part and the webs in the lower part overlap.
- FIG. 3 shows a cross section of a conveyor belt 15. More than one inner fiber 20 can be provided.
- the upper part 22 has a web 25.
- a guide element 26, for example a roller, a disk or a guide rail, comprises a complementary groove 27 in which the web slides.
- the guide element can also have a web and the transport belt can accordingly have a groove. It is also conceivable that the web or the groove of the conveyor belt is assigned to the lower part 21.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Making Paper Articles (AREA)
Abstract
Die Erfindung beschreibt eine Sack- oder Beutelherstellvorrichtung mit zumindest einer Bearbeitungsstation zur Durchführung eines Arbeitsschrittes bei der Sack- oder Beutelherstellung und einem Transportsystem zum Zu- und Abführen von Säcken oder Beuteln zu und von der Bearbeitungsstation, wobei das Transportsystem zumindest einen Transportriemen umfasst, mit welchem der Sack oder der Beutel mittels Reibschluss transportierbar ist.Der Transportriemen ist als Flachriemen ausgestaltet, welcher zumindest auf einer seiner Oberflächen Einkerbungen umfasst.The invention describes a sack or bag manufacturing device with at least one processing station for carrying out a work step in the sack or bag manufacture and a transport system for feeding and removing sacks or bags to and from the processing station, the transport system comprising at least one transport belt with which the sack or bag can be transported by means of frictional engagement. The transport belt is designed as a flat belt which has notches on at least one of its surfaces.
Description
Die Erfindung betrifft eine des Sack- oder Beutelherstellvorrichtung nach dem Oberbegriff des Anspruchs 1 sowie ein Verfahren zur Sack- oder Beutelherstellung nach dem Oberbegriff des Anspruchs 15.The invention relates to a sack or bag production device according to the preamble of
Zur Herstellung von Säcken oder Beuteln werden diese mit zumindest einer Bearbeitungsstation zur Durchführung eines Arbeitsschrittes bei der Sack- oder Beutelherstellung bearbeitet. Hier geht es um die Herstellung wenigstens eines geschlossenen Bodens an einem Materialschlauch oder einem Materialbogen, wobei letzterer zunächst zu einem Schlauchstück geformt wird. Zur Herstellung des Bodens sind verschiedene Einzelschritte notwendig, die in jeweiligen Arbeitsstationen durchführbar sind bzw. durchgeführt werden. Auch noch nicht fertiggestellte Säcke oder Beutel werden im Sinne der Erfindung unter dem Begriff "Säcke oder Beutel" verstanden. Hierzu zählen demnach auch die Materialschläuche oder Materialbögen als Ausgangselemente der Sack- oder Beutelherstellung. Verschiedene Säcke werden dadurch hergestellt, dass an zwei Böden erzeugt werden, so dass ein geschlossener Sack entsteht, welcher später über ein Ventil befüllt werden kann. Ein Beispiel eines solchen Sacks ist ein Kreuzbodenventilsack. Solche Kreuzbodenventilsäcke werden oft zum Transport von Baumaterialien wie Zement, von Düngern oder anderen schütt- oder rieselfähigen Füllgütern verwendet.For the production of sacks or bags, these are processed with at least one processing station for carrying out a work step in the production of sacks or bags. This is about the production of at least one closed base on a material hose or a material sheet, the latter being first formed into a hose piece. To produce the floor, various individual steps are necessary, which can be carried out or are carried out in the respective work stations. Also unfinished sacks or bags are understood in the context of the invention by the term "sacks or bags". This also includes the material hoses or material sheets as starting elements of the sack or bag production. Different sacks are produced by creating a closed sack on two bottoms, which can later be filled via a valve. An example of such a sack is a cross-bottom valve sack. Such cross-bottom valve bags are often used to transport building materials such as cement, fertilizers or other pourable or free-flowing products.
Zum Zu- und Abführen von Säcken oder Beuteln zu und von der Bearbeitungsstation ist ein Transportsystem vorgesehen, wobei das Transportsystem zumindest ein Transportriemen umfasst, mit welchem der Sack oder der Beutel mittels Reibschluss transportierbar ist. Mit anderen Worten wird der Sack oder der Beutel relativ zum Transportriemen unverschieblich gehalten. Insbesondere Kreuzbodenventilsäcke werden häufig orthogonal zu ihrer Haupterstreckungsachse und oft liegend, also horizontal transportiert. Oft werden zwei parallel laufende Transportriemen genutzt, welche jeweils in der Nähe je eines Endes des Sacks mit diesem in Kontakt stehen.A transport system is provided for supplying and removing sacks or bags to and from the processing station, the transport system comprising at least one transport belt with which the sack or bag can be transported by means of frictional engagement. In other words, the sack or bag is held immovable relative to the transport belt. In particular, cross-bottom valve bags are often transported orthogonally to their main axis of extension and often lying down, that is, horizontally. Often two parallel transport belts are used, each of which is in contact with one end of the sack near one end of the sack.
Bei der Sack- und Beutelherstellung, insbesondere bei der Herstellung von Kreuzbodenventilsäcken haben sich solche Transportsysteme vielfach bewährt.Such transport systems have proven themselves many times in the manufacture of sacks and bags, in particular in the manufacture of cross-bottom valve bags.
Allerdings werden in solchen Transportsystemen Riemen eingesetzt, die hohe Fertigungstoleranzen haben, da unter anderem vulkanisiertes Gummi verwendet wird. Um diese abzumildern, schlägt das Patent
Seit der Anmeldung des genannten Patents sind jedoch die Anforderungen an die Genauigkeiten in der Sackherstellung stark gestiegen, so dass der Einsatz der in dem Patent beschriebenen Transportriemen nicht mehr ausreichend ist. Außerdem ist eine vergrößerte Antriebsscheibe nachteilig, da sie zusätzlichen Bauraum benötigt.Since the application of the patent mentioned, however, the demands on the accuracy of the sack production have risen sharply, so that the use of the conveyor belts described in the patent is no longer sufficient. In addition, an enlarged drive pulley is disadvantageous because it requires additional installation space.
Die Aufgabe der vorliegenden Erfindung ist es daher, eine Sack- oder Beutelherstellvorrichtung sowie Verfahren zur Sack- oder Beutelherstellung vorzuschlagen, welche die genannten Nachteile des Standes der Technik vermeidet oder sogar überwindet.The object of the present invention is therefore to propose a sack or bag production device and a method for sack or bag production which avoids or even overcomes the disadvantages of the prior art.
Erfindungsgemäß wird diese Aufgabe durch sämtliche Merkmale des Anspruchs 1 gelöst. In den abhängigen Ansprüchen sind mögliche Ausgestaltungen der Erfindung angegeben.According to the invention, this object is achieved by all of the features of
Gemäß der vorliegenden Erfindung ist vorgesehen, dass in einer Sack- oder Beutelherstellvorrichtung mit zumindest einer Bearbeitungsstation zur Durchführung eines Arbeitsschrittes bei der Sack- oder Beutelherstellung und mit einem Transportsystem zum Zu- und Abführen von Säcken oder Beuteln zu und von der Bearbeitungsstation, wobei das Transportsystem zumindest ein Transportriemen mit welchem der Sack oder der Beutel mittels Reibschluss transportierbar ist, umfasst, der Transportriemen als Flachriemen ausgestaltet ist, welcher zumindest auf einer seiner Oberflächen Einkerbungen umfasst.According to the present invention it is provided that in a sack or bag manufacturing device with at least one processing station for carrying out a work step in the sack or bag manufacture and with a transport system for feeding and removing sacks or bags to and from the processing station, the transport system comprises at least one transport belt with which the sack or the bag can be transported by means of frictional engagement, the transport belt is designed as a flat belt which has notches on at least one of its surfaces.
Bei einem solchen Transportriemen kann es möglich sein, statt Gummi ein anderes Material einzusetzen, welches sich beispielsweise mit geringeren Toleranzen fertigen lässt, so dass insbesondere beim Transport der Säcke oder Beutel die Gleichlaufschwankungen reduzierbar sind. Gleichlaufschwankungen wirken sich direkt auf die Qualität der Böden aus, so dass verringerte Gleichlaufschwankungen zu einer verbesserten Qualität der Säcke oder Beutel führt. Um ein anderes Material, welches beispielsweise eine höhere Biegesteifigkeit aufweist, auch um Umlenkwalzen und insbesondere Antriebsscheiben führen zu können, ist es erfindungsgemäß vorgesehen, auf zumindest einer seiner Oberflächen Einkerbungen vorzusehen. Unter Oberflächen sind in diesem Fall die Wirkoberflächen zu verstehen. Das bedeutet, dass beispielsweise die Oberfläche per Reibschluss auf die Säcke oder Beutel wirkt - auch als Transportoberfläche bezeichnet -oder eine Umlenkwalze oder Antriebsscheibe zwecks Führung oder Antrieb auf die Oberfläche wirkt (geführte Oberfläche bzw. Antriebsoberfläche). Ein Flachriemen ist dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die genannten Oberflächen eine Breite haben, die mindestens dreimal größer ist als die Dicke des Flachriemens. Die Seitenflächen sind somit nicht als Oberflächen zu verstehen. Die Einkerbungen bewirken nun, dass die Biegefähigkeit des Flachriemens vergrößert ist, so dass dieser Flachriemen auch um Walzen oder Rollen mit kleinen Durchmessern führbar ist, ohne Schäden an dem Flachriemen hervorzurufen.With such a transport belt, it may be possible to use a different material instead of rubber, which material can be manufactured with smaller tolerances, for example, so that the wow and flutter can be reduced, especially when transporting the sacks or bags. Wow and flutter has a direct effect on the quality of the bases, so that reduced wow and flutter leads to an improved quality of the sacks or bags. In order to be able to guide another material, which for example has a higher flexural strength, also around deflection rollers and in particular drive pulleys, it is provided according to the invention to provide notches on at least one of its surfaces. In this case, surfaces are to be understood as meaning the effective surfaces. This means that, for example, the surface acts on the sacks or bags via frictional engagement - also referred to as a transport surface - or a deflection roller or drive pulley acts on the surface for the purpose of guiding or driving (guided surface or drive surface). A flat belt is characterized in that said surfaces have a width which is at least three times greater than the thickness of the flat belt. The side faces are therefore not to be understood as surfaces. The notches now have the effect that the flexibility of the flat belt is increased, so that this flat belt can also be guided around rollers or rollers with small diameters without causing damage to the flat belt.
In einer erfindungsgemäßen Sack- oder Beutelherstellvorrichtung ist insbesondere ein Flachriemen ausschließlich per Reibschluss mittels einer Antriebsscheibe angetrieben. Damit ist es unerheblich, ob die Antriebsscheibe in Kontakt mit der Oberfläche mit Einkerbungen oder er gegenüber liegenden Oberfläche steht. Vorteilhaft ist dabei, dass wenn eine Oberfläche des Transportriemens abgenutzt ist, dieser um seine Längsachse gedreht werden kann, so dass nun die gegenüberliegende Oberfläche die Funktionen der ursprünglichen Oberfläche übernehmen kann. Damit hat der Transportriemen eine höhere Standzeit, so dass letztendlich Kosten eingespart werden können.In a sack or pouch manufacturing device according to the invention, a flat belt is in particular exclusively frictionally engaged by means of a Drive pulley driven. It is therefore irrelevant whether the drive pulley is in contact with the surface with notches or with the opposite surface. The advantage here is that if a surface of the conveyor belt is worn, it can be rotated about its longitudinal axis so that the opposite surface can now take over the functions of the original surface. This means that the conveyor belt has a longer service life, so that ultimately costs can be saved.
In einer weiteren Ausführungsform ist vorgesehen, dass das Transportsystem als Doppelbandförderer ausgestaltet ist, wobei mit den einander zugewandten Oberflächen der Transportriemen die Säcke oder Beutel klemmend förderbar sind. Das bedeutet, dass zumindest entlang eines Transportweges der Säcke oder Beutel zumindest zwei Transportriemen vorgesehen sind, deren Transportoberflächen einander zugewandt sind und an Stellen, an denen kein Sack anliegt, in berührendem Kontakt stehen. Mit einer solchen Anordnung ist der Reibschluss zwischen einem Sack oder Beutel und dem Transportriemen weiter erhöht, was die Transportzuverlässigkeit steigert. In diesem Fall sind beide Transportriemen mit Einkerbungen an ihren Oberflächen versehen. Der Reibschluss lässt sich weiter erhöhen, wenn Kraftbereitstellungsmittel vorgesehen sind, welche die genannten Transportriemen mit einer Kraft beaufschlagen, welche jeweils auf den anderen Transportriemen gerichtet ist. In einfacher Weise kann das durch federn gelagerte Rollen erfolgen, wobei die Federkraft die Rolle auf den Transportriemen drückt.In a further embodiment it is provided that the transport system is designed as a double belt conveyor, the sacks or bags being able to be conveyed in a clamping manner with the surfaces of the transport belts facing one another. This means that at least two transport belts are provided along a transport path of the sacks or bags, the transport surfaces of which face one another and are in touching contact at points where no sack is in contact. With such an arrangement, the frictional engagement between a sack or bag and the transport belt is further increased, which increases the transport reliability. In this case, both conveyor belts are provided with notches on their surfaces. The frictional engagement can be further increased if force supply means are provided which apply a force to the aforementioned transport belts which is directed towards the other transport belt in each case. This can be done in a simple manner by spring-mounted rollers, the spring force pressing the roller onto the transport belt.
In einer vorteilhaften Ausgestaltung der Erfindung umfasst der Transportriemen zumindest eine Innenfaser, welche aus einem Metall, insbesondere aus einem Stahldraht. besteht. Eine Innenfaser aus Metall hat den großen Vorteil, dass sie biegsam ist, aber gleichzeitig eine hohe Dehnfestigkeit, so dass sie sich im Laufe der Betriebszeit nur unwesentlich längt. Somit ist auch nach langer Betriebszeit einer erfindungsgemäßen Sack- oder Beutelherstellvorrichtung noch eine hohe Qualität der Säcke oder Beutel gewährleistet.In an advantageous embodiment of the invention, the transport belt comprises at least one inner fiber made of a metal, in particular a steel wire. consists. An inner fiber made of metal has the great advantage that it is flexible, but at the same time has high tensile strength, so that it elongates only insignificantly over the course of the operating time. Thus, even after a long operating time of a sack or bag manufacturing device according to the invention, a high quality of the sacks or bags is still guaranteed.
Weiterhin kann es vorgesehen sein, dass der Transportriemen zumindest eine Innenfaser umfasst, welche von einem Kunststoff, insbesondere einem Polyurethan, umgeben ist. Eine Kunststoffummantelung der Innenfaser kann durch eine passende Wahl des verwendeten Kunststoffes in gewünschter Härte gestaltet werden. Mit einer gewünschten Härte kann auch die Biegefähigkeit des Transportriemens eingestellt werden, so dass dieser um die vorgesehenen Antriebsscheiben beschädigungslos führbar ist. Polyurethan ist dabei ein Kunststoff, welcher insbesondere durch Zugabe von Additiven in seinen Eigenschaften stark variierbar ist, so dass der Transportriemen neben seiner Festigkeit auch einen guten Reibschluss mit dem Material, aus welchem die Säcke und Beutel hergestellt sind, insbesondere Papier, hervor bringt. Ein Transportriemen, der in einer erfindungsgemäßen Sack- oder Beutelherstellvorrichtung verwendbar ist, weist bevorzugt eine Breite zwischen 10 und 50 mm auf. Seine Dicke ist bevorzugt größer als 3 mm und kleiner als 10 mm. Seine Haftreibungzahl liegt bevorzugt zwischen 0,3 und 1, insbesondere zwischen 0,4 und 0,9. Ferner kann eine Kunststoffummantelung, die insbesondere Polyurethan umfasst, in seiner Abriebfestigkeit angepasst sein, so dass eine lange Standzeit des Transportriemens (die Zeit, die bis zum Ersetzen eines verschlissenen Transportriemens verstreicht) gegeben ist.Furthermore, it can be provided that the transport belt comprises at least one inner fiber which is surrounded by a plastic, in particular a polyurethane. A plastic sheathing of the inner fiber can be designed with a suitable choice of the plastic used in the desired hardness. The flexibility of the conveyor belt can also be adjusted with a desired hardness so that it can be guided around the drive pulleys provided without damage. Polyurethane is a plastic whose properties can be varied greatly, in particular by adding additives, so that the transport belt, in addition to its strength, also has a good frictional connection with the material from which the sacks and bags are made, in particular paper. A transport belt that can be used in a sack or bag manufacturing device according to the invention preferably has a width between 10 and 50 mm. Its thickness is preferably greater than 3 mm and less than 10 mm. Its coefficient of static friction is preferably between 0.3 and 1, in particular between 0.4 and 0.9. Furthermore, a plastic sheathing, which in particular comprises polyurethane, can be adapted in terms of its abrasion resistance, so that the conveyor belt has a long service life (the time it takes for a worn conveyor belt to be replaced).
Bei dem im vorherigen Absatz beschriebenen Aufbau des Transportriemens lässt sich zudem eine vergleichsweise konstante Dicke erzeugen, so dass die im Vergleich zum Stand der Technik geringeren Fertigungstoleranzen zu einer besseren Qualität der Beutel oder Säcke führen.With the structure of the conveyor belt described in the previous paragraph, a comparatively constant thickness can also be produced, so that the lower manufacturing tolerances compared to the prior art lead to a better quality of the bags or sacks.
Ferner kann es vorteilhaft sein, wenn der Transportriemen als Endlosriemen ausgestaltet ist, wobei zumindest eine Innenfaser vorgesehen ist, welche endlos ist, wobei die Innenfaser mit Kunststoff umhüllt ist. Dabei kann die Innenfaser aus wenigstens einem Metalldraht geformt werden, indem dessen Enden zu einer Endlosfaser zusammengefügt werden. Anschließend kann diese Endlosfaser mit einer Kunststoffumhüllung versehen werden, wobei damit ein endloser Transportriemen geschaffen ist. Ein Vorteil bei dieser Ausgestaltung des Transportriemens ist der Wegfall einer Naht oder einer ähnlichen Verbindungsstelle, wie sie von einem Transportriemen aus dem Stand der Technik bekannt ist. Eine solche Verbindungsstelle weist oft besonders große Toleranzen auf, so dass es gerade an dieser Stelle zu Qualitätseinbußen kommen kann.Furthermore, it can be advantageous if the transport belt is designed as an endless belt, with at least one inner fiber being provided, which is endless, with the inner fiber being encased with plastic. The inner fiber can be formed from at least one metal wire by joining its ends to form a continuous fiber. Subsequently, this continuous fiber can be provided with a plastic sheath, thereby creating an endless transport belt. An advantage of this configuration of the transport belt is the elimination of a seam or a similar connection point, as is the case with a transport belt Prior art is known. Such a connection point often has particularly large tolerances, so that it is precisely at this point that quality losses can occur.
Bevorzugt ist es, wenn der Transportriemen als Endlosriemen ausgestaltet ist, wobei die Umlauflänge zumindest 30 Meter beträgt. Ein solcher Transportriemen ist insbesondere in Kombination mit einer Vorrichtung zur Herstellung von Kreuzbodenventilsäcken, die wegen der zahlreichen benötigten Bearbeitungsstationen eine beträchtliche Länge aufweist.It is preferred if the transport belt is designed as an endless belt, the circumferential length being at least 30 meters. Such a transport belt is particularly in combination with a device for the production of cross-bottom valve bags, which has a considerable length because of the numerous processing stations required.
In einer bevorzugten Ausgestaltung ist vorgesehen, dass die Einkerbungen bis zur Innenfaser reichen. In diesem Fall ist eine besonders gute Biegbarkeit des Transportriemens gegeben, so dass kleinere Antriebsscheiben vorgesehen werden können. Die Einkerbungen selbst können einen dreieckigen oder rechteckigen Querschnitt aufweisen, wie es weiter unten im Zusammenhang mit der Zeichnung verdeutlicht wird.In a preferred embodiment it is provided that the notches extend as far as the inner fiber. In this case, the conveyor belt can be bent particularly well, so that smaller drive pulleys can be provided. The notches themselves can have a triangular or rectangular cross-section, as will be clarified further below in connection with the drawing.
In einer vorteilhaften Weiterbildung der Erfindung ist es vorgesehen, dass der Flachriemen auch auf seiner zweiten, der ersten Oberfläche gegenüber liegenden Oberfläche Einkerbungen aufweist. Damit geht eine noch bessere Biegsamkeit des Transportriemens einher. In diesem Fall steht eine mit Einkerbungen versehene Oberfläche auch mit den Säcken oder Beuteln in Kontakt, ohne dass eine Beschädigung sichtbar wird.In an advantageous development of the invention it is provided that the flat belt also has notches on its second surface opposite the first surface. This is accompanied by an even better flexibility of the transport belt. In this case, a surface provided with notches is also in contact with the sacks or bags without any damage being visible.
In einer weiteren Ausführungsform kann vorgesehen sein, dass der Flachriemen auch auf seiner zweiten, der ersten Oberfläche gegenüber liegenden Oberfläche Einkerbungen aufweist, wobei die Einkerbungen genau gegenüber liegend angeordnet sind. Diese Maßnahme kann abermals die Biegsamkeit erhöhen.In a further embodiment it can be provided that the flat belt also has notches on its second surface lying opposite the first surface, the notches being arranged exactly opposite one another. This measure can again increase the flexibility.
In einer Variante der Erfindung kann es vorteilhaft sein, wenn der Flachriemen auch auf seiner zweiten, der ersten Oberfläche gegenüber liegenden Oberfläche Einkerbungen aufweist, wobei die Einkerbungen auf der zweiten Oberfläche in Längsrichtung versetzt zur ersten Oberfläche angeordnet sind. Diese Variante verbessert die Biegsamkeit, wobei der Transportriemen zusätzlich eine gute Stabilität aufweist.In a variant of the invention, it can be advantageous if the flat belt also has notches on its second surface opposite the first surface, the notches on the second surface being arranged offset in the longitudinal direction relative to the first surface. This variant improves flexibility, and the transport belt also has good stability.
Es kann vorteilhaft sein, wenn der Flachriemen an zumindest einer Oberfläche eine in Förderrichtung verlaufende Nut oder einen in Förderrichtung verlaufenden Steg umfasst. Zumindest eine Umlenkrolle und/oder eine Antriebsscheibe und/oder zumindest ein weiteres Führungselement weisen bevorzugt ein Komplementärprofil auf, so dass erreicht wird, dass der Transportriemen eine sehr gute Geradeauslauffähigkeit zeigt.It can be advantageous if the flat belt comprises a groove running in the conveying direction or a web running in the conveying direction on at least one surface. At least one deflection pulley and / or one drive pulley and / or at least one further guide element preferably have a complementary profile, so that it is achieved that the transport belt has a very good straight-line ability.
Ferner ist es bevorzugt, wenn das Kunststoffmaterial eine Härte von mindestens 50 Shore A aufweist. Dabei wird erreicht, dass der Transportriemen sich nicht zu stark verformt, was zulasten der Qualität der Beutel oder Säcke gehen könnte.It is also preferred if the plastic material has a hardness of at least 50 Shore A. What is achieved here is that the transport belt is not deformed too much, which could affect the quality of the bags or sacks.
Weiterhin ist es möglich, dass das Kunststoffmaterial weiße Farbpigmente umfasst. Damit wird eine helle Färbung des Transportriemens erreicht, was dazu führt, dass ein Abrieb des Transportriemens, der auf einem Beutel oder Sack verbleibt, nicht zu stark sichtbaren Verschmutzungen des Sack oder Beutels führt. Auch eine Verschmutzung wird oft als Qualitätsmangel angesehen.It is also possible for the plastic material to include white color pigments. This achieves a light coloring of the transport belt, which means that abrasion of the transport belt which remains on a bag or sack does not lead to strongly visible soiling of the sack or bag. Pollution is also often viewed as a quality defect.
Weiterhin ist denkbar, dass in dem Flachriemen zumindest ein Signalelement eingebettet ist. Ein Signalelement kann dabei ein von einem Sensor detektierbares Element sein, beispielsweise ein Magnetelement oder ein beliebiges anderes Elemente, das beispielsweise auf eine Strahlung von außen mit einer Reflektion des Signals reagiert. Zweck ist es, den Durchlauf des Signalelements festzustellen, um beispielsweise eine sich ändernde Umlaufgeschwindigkeit feststellen zu können. Bei einer Abweichung von einer Sollgeschwindigkeit kann beispielsweise die Ist-Geschwindigkeit angepasst werden.It is also conceivable that at least one signal element is embedded in the flat belt. A signal element can be an element that can be detected by a sensor, for example a magnetic element or any other element which, for example, reacts to radiation from the outside with a reflection of the signal. The purpose is to determine the passage of the signal element in order to be able to determine, for example, a changing rotational speed. If there is a deviation from a setpoint speed, the actual speed can be adjusted, for example.
Die oben genannte Aufgabe wird zusätzlich gelöst durch ein Verfahren zur Sack- oder Beutelherstellung mit zumindest einem Arbeitsschritt in einer Bearbeitungsstation, wobei mit einem Transportsystem Säcken oder Beuteln zu und von der Bearbeitungsstation zu- oder abgeführt werden, wobei das Transportsystem zumindest ein Transportriemen umfasst, mit welchem der Sack oder der Beutel mittels Reibschluss transportiert werden.The above-mentioned object is additionally achieved by a method for sack or pouch production with at least one work step in a processing station, with sacks or bags being fed to and removed from the processing station with a transport system, the transport system comprising at least one transport belt with which the sack or bag is transported by means of frictional engagement.
Das erfindungsgemäße Verfahren zeichnet sich dadurch aus, dass als Transportriemen ein Flachriemen genutzt wird, welcher zumindest auf einer seiner Oberflächen Einkerbungen umfasst.The method according to the invention is characterized in that a flat belt is used as the transport belt, which has notches on at least one of its surfaces.
Mit diesem Verfahren werden die gleichen Vorteile erzielt, wie sie bereits im Zusammenhang mit einer erfindungsgemäßen Sack- oder Beutelherstellvorrichtung beschrieben worden sind.With this method, the same advantages are achieved as have already been described in connection with a sack or bag manufacturing device according to the invention.
Weitere Vorteile, Merkmale und Einzelheiten der Erfindung gehen aus der nachfolgenden Beschreibung hervor, in der unter Bezugnahme auf die Figuren verschiedene Ausführungsbeispiele im Einzelnen erläutert sind. Dabei können die in den Ansprüchen und in der Beschreibung erwähnten Merkmale jeweils einzeln für sich oder beliebige Kombinationen erwähnter Merkmale erfindungswesentlich sein. Im Rahmen der gesamten Offenbarung gelten Merkmale und Einzelheiten, die im Zusammenhang mit dem erfindungsgemäßen Verfahren beschrieben sind, selbstverständlich auch im Zusammenhang mit der erfindungsgemäßen Sack- oder Beutelherstellvorrichtung und jeweils umgekehrt, so dass bezüglich der Offenbarung zu den einzelnen Aspekten der Erfindung stets wechselseitig Bezug genommen wird beziehungsweise werden kann. Die einzelnen Figuren zeigen:
- Fig. 1
- Abfolge der Schritte zur Herstellung von Säcken
- Fig. 2
- Ansicht einer Sack- oder Beutelherstellvorrichtung
- Fig. 3
- Ausführungsform eines Transportriemens in einer erfindungsgemäßen Sack- oder Beutelherstellvorrichtung
- Fig. 4
- eine Abwandlung der Ausführungsform gemäß
Figur 3 - Fig. 5
- eine weitere Ausführungsform eines Transportriemens in einer erfindungsgemäßen Sack- oder Beutelherstellvorrichtung
- Fig. 6
- eine Abwandlung der Ausführungsform gemäß
Figur 5
- Fig. 1
- Sequence of steps for making bags
- Fig. 2
- View of a sack or bag manufacturing device
- Fig. 3
- Embodiment of a transport belt in a sack or bag manufacturing device according to the invention
- Fig. 4
- a modification of the embodiment according to
Figure 3 - Fig. 5
- a further embodiment of a transport belt in a sack or bag manufacturing device according to the invention
- Fig. 6
- a modification of the embodiment according to
Figure 5
Die
In der
Die
Die
Die
In der
Die
Die Ausführungsformen der
Claims (15)
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass
der Transportriemen als Flachriemen ausgestaltet ist, welcher zumindest auf einer seiner Oberflächen Einkerbungen umfasst.Sack or bag manufacturing device with at least one processing station for carrying out a work step in the sack or bag manufacture and a transport system for supplying and removing sacks or bags to and from the processing station, the transport system comprising at least one transport belt with which the sack or the The bag can be transported by means of a friction fit,
characterized in that
the transport belt is designed as a flat belt which comprises notches on at least one of its surfaces.
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass
das Transportsystem als Doppelförderer ausgestaltet ist, weicher zumindest zwei Transportriemen umfasst, wobei mit den einander zugewandten Oberflächen der Transportriemen die Säcke oder Beutel klemmend förderbar sind.Sack or bag manufacturing device according to claim 1,
characterized in that
the transport system is designed as a double conveyor, which comprises at least two transport belts, the sacks or bags being able to be conveyed in a clamping manner with the surfaces of the transport belts facing one another.
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass
der Transportriemen zumindest eine Innenfaser umfasst, welche aus Metall besteht, insbesondere aus einem Stahldraht.Sack or bag manufacturing device according to one of the preceding claims,
characterized in that
the conveyor belt comprises at least one inner fiber made of metal, in particular of a steel wire.
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass
der Transportriemen zumindest eine Innenfaser umfasst, welche von einem Kunststoff, insbesondere einem Polyurethan, umgeben ist.Sack or bag manufacturing device according to one of the preceding claims,
characterized in that
the conveyor belt comprises at least one inner fiber which is surrounded by a plastic, in particular a polyurethane.
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass
der Transportriemen als Endlosriemen ausgestaltet ist, wobei zumindest eine Innenfaser vorgesehen ist, welche endlos ist, wobei die Innenfaser mit Kunststoff umhüllt ist.Sack or bag manufacturing device according to one of the preceding claims,
characterized in that
the transport belt is designed as an endless belt, at least one inner fiber being provided, which is endless, the inner fiber being coated with plastic.
der Transportriemen als Endlosriemen ausgestaltet ist, wobei die Umlauflänge zumindest 30 Meter beträgt.Sack or bag manufacturing device according to one of the preceding claims, characterized in that
the transport belt is designed as an endless belt, the circumferential length being at least 30 meters.
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass
die Einkerbungen bis zur Innenfaser reichen.Sack or bag manufacturing device according to one of the preceding claims,
characterized in that
the notches extend to the inner fiber.
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass
der Flachriemen auch auf seiner zweiten, der ersten Oberfläche gegenüber liegenden Oberfläche Einkerbungen aufweist.Sack or bag manufacturing device according to one of the preceding claims,
characterized in that
the flat belt also has notches on its second surface opposite the first surface.
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass
der Flachriemen auch auf seiner zweiten, der ersten Oberfläche gegenüber liegenden Oberfläche Einkerbungen aufweist, wobei die Einkerbungen genau gegenüber liegend angeordnet sind.Sack or bag manufacturing device according to one of the preceding claims,
characterized in that
the flat belt also has notches on its second surface opposite the first surface, the notches being arranged exactly opposite one another.
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass
der Flachriemen auch auf seiner zweiten, der ersten Oberfläche gegenüber liegenden Oberfläche Einkerbungen aufweist, wobei die Einkerbungen auf der zweiten Oberfläche in Längsrichtung versetzt zur ersten Oberfläche angeordnet sind.Sack or bag manufacturing device according to one of the preceding claims,
characterized in that
the flat belt also has notches on its second surface opposite the first surface, the notches on the second surface being arranged offset in the longitudinal direction with respect to the first surface.
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass
der Flachriemen an zumindest einer Oberfläche eine in Förderrichtung verlaufende Nut oder einen in Förderrichtung verlaufenden Steg umfasst.Sack or bag manufacturing device according to one of the preceding claims,
characterized in that
the flat belt comprises a groove running in the conveying direction or a web running in the conveying direction on at least one surface.
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass
das Kunststoffmaterial eine Härte von mindestens 50 Shore A aufweist.Sack or bag manufacturing device according to one of the preceding claims,
characterized in that
the plastic material has a hardness of at least 50 Shore A.
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass
das Kunststoffmaterial weiße Farbpigmente umfasst.Sack or bag manufacturing device according to one of the preceding claims,
characterized in that
the plastic material comprises white color pigments.
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass
in den Flachriemen zumindest ein Signalelement eingebettet ist.Sack or bag manufacturing device according to one of the preceding claims,
characterized in that
at least one signal element is embedded in the flat belt.
dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass
als Transportriemen ein Flachriemen genutzt wird, welcher zumindest auf einer seiner Oberflächen Einkerbungen umfasst.Method for sack or pouch production with at least one work step in a processing station, with a transport system being used to supply or remove sacks or bags to and from the processing station, the transport system comprising at least one transport belt with which the sack or bag is transported by means of frictional engagement will,
characterized in that
a flat belt is used as a transport belt, which comprises notches on at least one of its surfaces.
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE102020203493 | 2020-03-18 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP3882012A2 true EP3882012A2 (en) | 2021-09-22 |
| EP3882012A3 EP3882012A3 (en) | 2022-01-05 |
Family
ID=74884806
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP21162712.0A Pending EP3882012A3 (en) | 2020-03-18 | 2021-03-16 | Sack or bag manufacturing device and method for sack or bag manufacturing |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP3882012A3 (en) |
Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP1578596B1 (en) | 2002-12-20 | 2006-06-14 | Windmöller & Hölscher KG | Bottom positioning device for cross bottom bags |
Family Cites Families (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATE136867T1 (en) * | 1989-12-04 | 1996-05-15 | Interbold | LEAF HANDLING DEVICE |
| JPH0780262B2 (en) * | 1992-11-12 | 1995-08-30 | 株式会社藤田機械 | Conveying structure of bags in bag making machine |
| US5807194A (en) * | 1996-10-31 | 1998-09-15 | The Gates Corporation | Toothed belt |
| DE10028831A1 (en) * | 1999-06-22 | 2001-01-04 | Norddeutsche Seekabelwerk Gmbh | Belt, in particular, conveyor belt comprises an outside surface whose coefficient of friction at least over certain regions has a reduced value |
| DE10011680C2 (en) * | 2000-03-10 | 2003-10-30 | Boewe Systec Ag | Device for transporting flat goods |
| CN108162491A (en) * | 2017-11-22 | 2018-06-15 | 昆明理工大学 | A kind of test paper bag seals fold device |
| DE102018113631A1 (en) * | 2018-06-07 | 2019-12-12 | Windmöller & Hölscher Kg | transport device |
-
2021
- 2021-03-16 EP EP21162712.0A patent/EP3882012A3/en active Pending
Patent Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP1578596B1 (en) | 2002-12-20 | 2006-06-14 | Windmöller & Hölscher KG | Bottom positioning device for cross bottom bags |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP3882012A3 (en) | 2022-01-05 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| DE3877307T2 (en) | CONVEYOR AND / OR SUPPORTING BAND. | |
| DE69219977T2 (en) | Method and device for the continuous production of an object | |
| EP3571145B1 (en) | Drive device, drive element, and conveyor wagon drive | |
| DE3404006A1 (en) | DEVICE FOR APPLYING AN ADHESIVE STRING OF PLASTIC TO A GLASS PANEL | |
| DD229350A5 (en) | CONTINUOUS METHOD FOR PRESSING A COMPOSITION ASSEMBLY | |
| EP2415700A2 (en) | Device for aligning a flat product | |
| DE102016221271B4 (en) | Method and apparatus for applying a flexible seal to the perimeter of a component | |
| EP0138745A2 (en) | Driving pulley for a slat conveyor | |
| EP0416213A1 (en) | Process for making flexible impermeable bands | |
| DE102008057463B4 (en) | Spring made of a fiber composite material and method and apparatus for producing the same | |
| EP0771643B1 (en) | Process and conveyor table for continuously conveying a strip-like plastic material | |
| DE69307921T2 (en) | DEVICE AND METHOD FOR PRODUCING A STRING OF DOUGH | |
| DE2643346C3 (en) | Press for exerting a surface pressure with circumferential belts and controlling the lateral position of the same | |
| EP3882012A2 (en) | Sack or bag manufacturing device and method for sack or bag manufacturing | |
| DE69028080T2 (en) | PRODUCTION OF TIRE LINK AND DEVICE THEREFOR | |
| DE9002430U1 (en) | Device for guiding goods, in particular for automatic cutting and sewing systems for textile webs or the like. | |
| DE2805870A1 (en) | Shearing rubber web sections for tyre carcasses - with cutter bar moved above and below plane of conveyor | |
| DE3875625T2 (en) | AMPLIFIER POLYMER OBJECT. | |
| DE3903599A1 (en) | MACHINE FOR APPLYING ADHESIVE ON LONG-STRETCHED RAILWAY MATERIAL | |
| DE10233483B4 (en) | transport device | |
| EP1776215B1 (en) | Device for drawing in veneer strips | |
| DE2632337A1 (en) | DEVICE FOR COATING THE SIDE OF A SPACER FRAME FOR INSULATING GLASS PANELS WITH A DURABLE ADHESIVE LAYER | |
| WO1995027799A1 (en) | Skiving machine for flat supple material, particularly leather, as well as use of the machine and process for relief skiving and appropriate template | |
| DE3744107C2 (en) | ||
| WO2011101421A1 (en) | Installation for producing steel cord conveyor belts |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE APPLICATION HAS BEEN PUBLISHED |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| RIC1 | Information provided on ipc code assigned before grant |
Ipc: B31B 160/20 20170101ALN20211126BHEP Ipc: B31B 150/20 20170101ALN20211126BHEP Ipc: B31B 150/00 20170101ALN20211126BHEP Ipc: B65H 5/02 20060101ALI20211126BHEP Ipc: B65H 29/12 20060101ALI20211126BHEP Ipc: B31B 70/04 20170101AFI20211126BHEP |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: REQUEST FOR EXAMINATION WAS MADE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20220705 |
|
| RBV | Designated contracting states (corrected) |
Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |