EP3808564A1 - Autonomous sheet numbering - Google Patents
Autonomous sheet numbering Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP3808564A1 EP3808564A1 EP19000472.1A EP19000472A EP3808564A1 EP 3808564 A1 EP3808564 A1 EP 3808564A1 EP 19000472 A EP19000472 A EP 19000472A EP 3808564 A1 EP3808564 A1 EP 3808564A1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- printed
- computer
- printing
- sheet
- further processing
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B41—PRINTING; LINING MACHINES; TYPEWRITERS; STAMPS
- B41F—PRINTING MACHINES OR PRESSES
- B41F33/00—Indicating, counting, warning, control or safety devices
- B41F33/0036—Devices for scanning or checking the printed matter for quality control
Definitions
- the present invention is concerned with a method for waste management of printed products by means of an autonomous production line with central printed product detection.
- the invention lies in the technical field of printing logistics.
- a known solution consists, for example, in manually marking printed sheets with a fluorescent pen during the first pass. This pen is then recognized on the second or next pass of the printed sheet and a process such as switching on a good sheet counter in the case of a correctly printed sheet and ejecting the printed sheet in the case of an incorrectly printed sheet is accordingly initiated.
- autonomous printing is not possible on the first print pass.
- the operator has to stop the machine and mark the printed sheet with a fluorescent pen at the exact point where the sensor will later be in the reverse pressure. To do this, he has to take the printed sheet out of the display or mark it in the display. To do this, it is necessary to stop the machine, and when it starts up again, startup waste occurs. Furthermore, there is no comparison between front and back printing. There is a risk here that individual signatures can be mixed in.
- German patent specification DE 10 2010 003 913 B4 is a storage of the stack structure, in the form of waste and good sheets, and the use for a second pass in a printing machine is known, including marking the waste by an inkjet unit and modification of the pallet via an input field on the machine or a terminal, for acknowledgment or Input of manually removed sheets. So here the printed sheet is automatically written with an inkjet unit.
- the marking unit can only distinguish whether the printed sheet is waste or not.
- German patent specification DE 103 49 896 B4 discloses an auto-non-stop in the delivery of the automatic set-up waste and start-up waste separated from the production sheets.
- German patent application DE 10 2005 009 301 A1 again shows how an electronic memory is permanently connected to the substrate and is written with all events that occur during printing.
- the costs for an electronic memory result in higher costs than for a visually applied ID.
- a reader is also required to read this information.
- the European patent application EP 1 939 800 A1 in turn describes the storage of printing material and print information, such as the condition of the sheet, information about the inspection and measuring system, on a data memory or storage on a database with assignment via an ID with feedback in a database or a production system and a corresponding log generation. Furthermore, a location of the position of the substrate pallet is disclosed.
- the object is thus to disclose a method for waste management of printed products which works as completely as possible autonomously and thus much more efficiently than the systems known in the prior art and also avoids their known disadvantages.
- a method for waste management of printed products in a system that processes printing materials, consisting of at least one computer and at least one printing machine, which includes the steps of assigning a central ID for each printed product to be processed in the system by means of a computer, assigning certain events to each ID by the computer, printing of printed products in a printing machine of the system, examination of the correspondingly printed printed products by means of a computer-aided image acquisition system and depending on the assignment of a specific state to each printed product by the computer, assignment of all recorded states to a specific event and triggering of a specific event for all printed products depending on the respectively assigned state of the respective printed product and a specific further processing by the computer.
- a central and unique ID is assigned for each printed product to be processed in the system is therefore fundamental to the method according to the invention.
- a status is also assigned to this print product. Since a set of certain possible events is assigned to each ID at the same time and the activation of the events depends on the respective status of the printed product assigned to the ID, as well as on the respective desired further processing of the printed product created, a specific event is selected and automatically executed depending on this. In the simplest case, this means nothing more than that a printed product is given a specific ID, this printed product is checked and z. B.
- the ID is applied to the respective printed product by means of a writing unit, in particular an inkjet unit, in the form of a machine-readable code, in particular a 1D or 2D code, or an alphanumeric code.
- a writing unit in particular an inkjet unit
- a machine-readable code in particular a 1D or 2D code, or an alphanumeric code.
- the IDs are newly assigned by the computer or specified externally for the system and both the IDs and the assigned events and states are stored by the computer on a local memory of the computer or the printing machine, a central memory of the System or external network storage.
- the computer itself assigns the IDs continuously, usually incrementally, or whether precise IDs are specified accordingly by an external controller, depends on the local place of use, that is to say the print shop in which the method according to the invention is carried out. It is important, however, that in the present system consisting of computer and printing press, each ID with its corresponding event (s) and, if the assigned print product has already been qualitatively examined, the corresponding status is available to the computer at all times.
- the printing press is a sheet-fed printing press and each printed sheet used is assigned an ID accordingly by the computer.
- the method according to the invention can best be used in a sheet-fed printing press. Nevertheless, it can also be used in other forms of printing machines, provided that these can also be separated into individual printed products to which unique IDs can be assigned.
- the events in the case of further processing in the sheet-fed printing press include the activation of a good sheet counter or the stopping of the printing press and, in the case of further processing in a separate further processing unit, the feeding of the printed print product in the separate further processing unit, the separate filing of the printed print product as a sample, the stopping of the separate further processing unit, as well as the loading of configuration data for an autonomous pre-setting of the separate further processing unit and in both cases the ejection of the printed print product as waste.
- the first case of further processing in the printing press normally involves printing the reverse side of the printed product.
- the good sheet counter must be incremented in the case of a good case and, in the case of a bad case, ie the printed product was assessed as waste by the image acquisition system, the printing press is stopped, since in this case no further processing in the form of printing the reverse side is possible. If the printing press in question also has an internal waste gate, the printed product classified as waste can also be ejected directly in this case. Then, under certain circumstances, it is also possible to dispense with stopping the printing press. Furthermore, in the case of further transport of the printed printed product into the further processing unit, actions occurring specifically for this case can be assigned as events, such as those mentioned accordingly.
- the states of the printed and examined printed products include the state of setup waste, production waste or a good sheet.
- an examined printed product being waste
- set-up waste since a certain amount of waste is generated by default when setting up the printing machine, until all the parameters of the printing machine correspond to the desired target parameters, particularly with regard to color control.
- the set-up waste is thus at least partially independent of the quality assessment of the image acquisition system, since a certain amount of waste always occurs when setting up the printing press, while production waste is only the final state if it is generated after the set-up process has been completed and after the actual printing has started
- the printed printed product has been rated as reject by the image acquisition system
- the assigned state as a good sheet automatically results in the assignment of the event of activating the good sheet counter. This applies in particular to the case of further processing in the sheet-fed printing machine, since the good sheet counter must be activated automatically as soon as printed products that are recognized as good sheets enter the printing machine. But even with external further processing, the good sheet counter must be incremented accordingly in the case of an evaluated good sheet.
- a further preferred development of the method according to the invention is that post-processing in the sheet-fed printing machine, in particular printing the back of the printed product or a second printing process, or post-processing in a separate further processing unit of the system, in particular a punch, is used as further processing of the printed product.
- a rotary die cutter, a folding machine or a folder gluer is used as further processing of the printed product.
- the list is not limited to the cases mentioned. Other forms of further processing are also possible; however, the cases mentioned are by far the most frequent and important.
- an inline image acquisition system is used as the image acquisition system, which is located in the printing press behind a last printing or coating unit. It is true that an external image acquisition system can also be used for the method according to the invention, but an inline image acquisition system is to be preferred in the sense of an autonomous production line that requires a high degree of automation.
- Figure 1 shows an example of an image acquisition system 2 which uses the method according to the invention. It consists of at least one image sensor 5, usually a camera 5, which is integrated into the sheet-fed printing press 4. The at least one camera 5 records the print images generated by the printing machine 4 and sends the data to a computer 3, 6 for evaluation.
- This computer 3, 6 can be its own separate computer 6, for example one or more specialized image processing computers 6, or with it the control computer 3 of the printing press 4, at least the control computer 3 of the printing press 4 has a display 7 on which the results of the image inspection are shown to the user 1.
- a sheet-fed printing press 4 is assumed, with which the printed products correspond to printed sheets 9.
- the method according to the invention can in principle be used in all printing machines which produce printed products that are to be clearly separated on a printing substrate that is to be further processed.
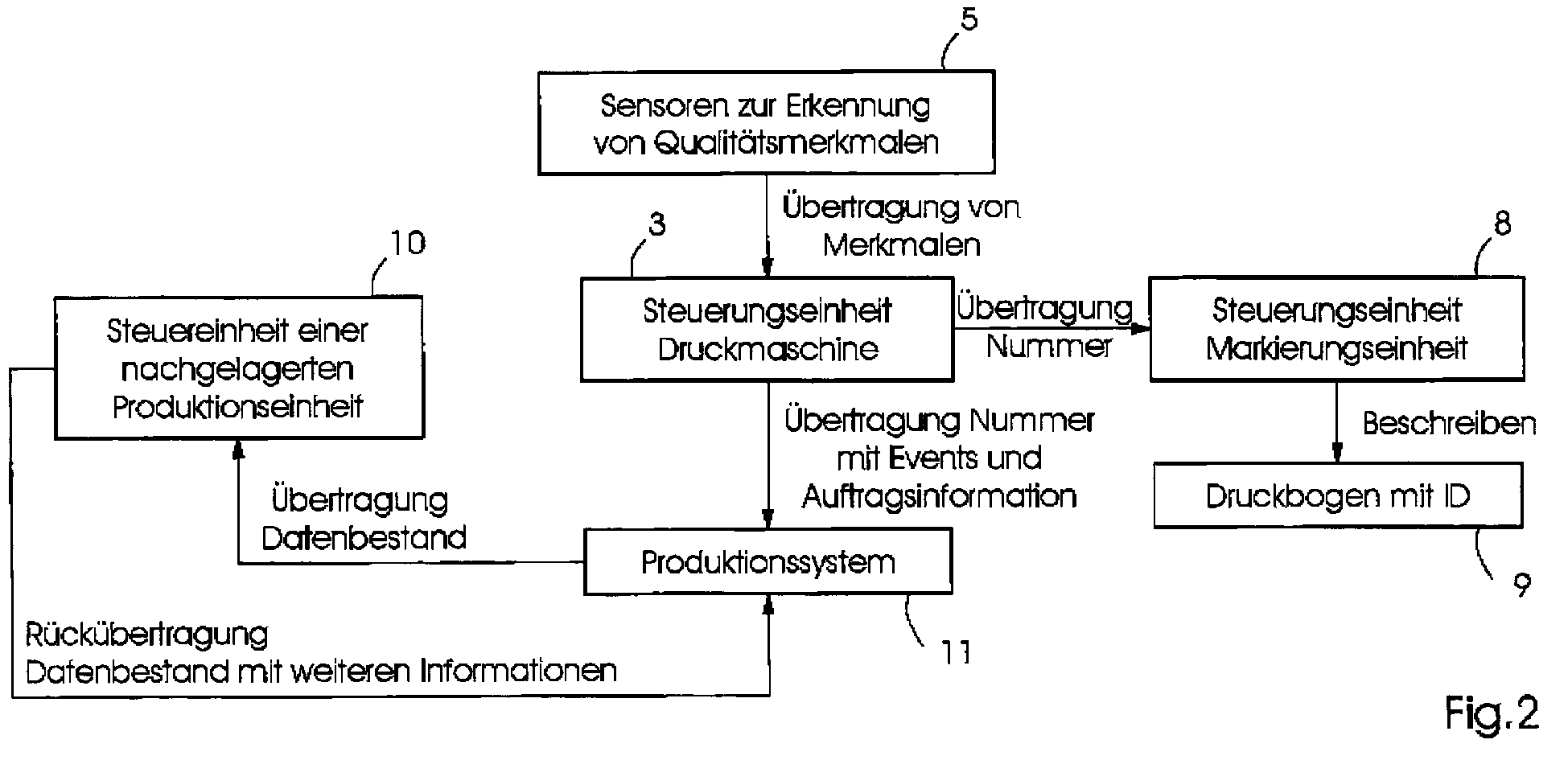
- a unique ID is generally generated for each printed sheet 9. This can be generated by the control computer 3 of the printing press 4 and then transmitted to the control unit of the marking unit 8. Alternatively, the control computer of the marking unit 8 itself can generate the ID and then transmit it to the control unit 3 of the printing press 4. Another alternative is the specification of the ID by a central production system 11 by means of a database and transmission to the control unit 3 of the printing machine 4 and then from this to the control unit of the marking unit 8.
- the ID can be a consecutive number or an arbitrarily generated number.
- This unique ID is applied via a marking unit, such as an inkjet unit on the sheet feeder.
- this marking unit can also be attached at a different position in the printing press 4.
- the ID can be applied in the form of an alphanumeric number that can be read electronically, e.g. via OCR.
- a machine-readable 1D or 2D code e.g. a barcode or a QR code, can also be used.
- This feature automatically modifies the sheet counting device so that the required amount of sheets 9 is produced.
- the printing machine control 3 can receive further parameters and settings that set closer tolerances in order to determine which printed sheets 9 have no or almost no deviations. These are given a further feature, sample sheets, and can be automatically ejected via a separate production line in the downstream post-pressing process and treated separately. In the event of deviations from a reference, the actual deviation is documented so that threshold values can be configured subsequently and thus the properties of each individual sheet 9 can be modified. If there are several panels or elements on a printed sheet 9, the position or the panel number of the deviation is also documented so that subsequent and unambiguous identification is possible. Furthermore, all other job-specific data are assigned to this ID. These can be, for example, order number, work process, signature, face or reverse print page, language, etc.
- the unique ID with all the information is then stored or temporarily stored in a data memory.
- a possible preferred application is a second printing pass of a printed sheet 9 in the same printing press 4.
- the same print side is printed again.
- the sheet ID is read in in the printing press 4 by means of a sensor device on the sheet feed area, in a printing or coating unit or integrated in a color and quality measuring system 2.
- the information behind the associated ID is then expanded by signals in production. For example, a printed sheet 9 that was previously assessed as a good sheet will later be assessed as production waste when a discrepancy is detected.
- the new color and quality information is also assigned to the printed sheet 9 or its stored ID.
- the plausibility check is also carried out.
- the third preferred purpose is to send information generated by the printing press control 3 via the central production system 11 or the cloud to a to transfer downstream production unit.
- a punch, a rotary punch, a folding machine or a folder gluer can be used.
- the sheet-specific ID is read out via an attached sensor unit and compared with the previously generated data. Using the information that the current print sheet 9 then contains, the control computer 3 accordingly initiates an event that happens to the respective print sheet 9
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Quality & Reliability (AREA)
- Inking, Control Or Cleaning Of Printing Machines (AREA)
Abstract
Verfahren zum Makulaturmanagement von Druckprodukten (9) in einem Bedruckstoffe verarbeitenden System, bestehend aus mindestens einem Rechner (3, 8, 10) und mindestens einer Druckmaschine (4), welches die Schritte Vergabe einer zentralen ID für jedes im System zu verarbeitende Druckprodukt (9) mittels eines Rechners, Zuordnung von bestimmten Events zu jeder ID durch den Rechner (3, 8, 10), Bedrucken von Druckprodukten (9) in einer Druckmaschine (4) des Systems, Untersuchung der entsprechend bedruckten Druckprodukte (9) mittels eines rechnergestützten Bilderfassungssystems (2) und abhängig davon Zuordnung eines bestimmten Zustandes zu jedem bedruckten Druckprodukt (9) durch den Rechner (3, 8, 10), Zuordnung aller erfassten Zustände zu jeweils einem bestimmten Event und Auslösen des bestimmten Events für alle bedruckten Druckprodukte (9) abhängig vom jeweils zugeordneten Zustand des jeweiligen Druckproduktes (9) und einer bestimmten Weiterverarbeitung durch den Rechner (3, 8, 10) umfasst. Method for waste management of printed products (9) in a system that processes printing materials, consisting of at least one computer (3, 8, 10) and at least one printing machine (4), which includes the steps of assigning a central ID for each printed product (9 ) by means of a computer, assignment of certain events to each ID by the computer (3, 8, 10), printing of printed products (9) in a printing machine (4) of the system, examination of the correspondingly printed printed products (9) by means of a computer-aided image acquisition system (2) and, depending on this, assignment of a specific state to each printed product (9) by the computer (3, 8, 10), assignment of all recorded states to a specific event and triggering of the specific event for all printed products (9) from the respectively assigned state of the respective printed product (9) and a specific further processing by the computer (3, 8, 10) .
Description
Die vorliegende Erfindung beschäftigt sich mit einem Verfahren zum Makulaturmanagement von Druckprodukten mittels einer autonomen Produktionsstrecke mit zentraler Druckprodukterfassung.The present invention is concerned with a method for waste management of printed products by means of an autonomous production line with central printed product detection.
Die Erfindung liegt im technischen Gebiet der Druckereilogistik.The invention lies in the technical field of printing logistics.
Im Stand der Technik sind verschiedene Lösungen zur Umsetzung einer vollautomatischen Makulaturausschleusung bekannt Eine bekannte Lösung besteht zum Beispiel darin, bedruckte Druckbogen manuell beim ersten Durchgang mit einem fluoreszierenden Stift zu markieren. Dieser Stift wird beim zweiten bzw. nächsten Durchgang des Druckbogens dann erkannt und dementsprechend ein Prozess wie das Einschalten eines Gutbogenzählers im Fall eines korrekt bedruckten Druckbogens und das Ausschleusen des Druckbogens im Fall eines fehlerhaft bedruckten Druckbogens eingeleitet. Bei diesem Ansatz ist allerdings beim ersten Druckdurchgang kein autonomes Drucken möglich. Der Bediener muss also die Maschine anhalten und den Druckbogen genau an der Stelle mit einem fluoreszierenden Stift markieren, an der Stelle an der später im Widerdruck der Sensor sitzt. Dazu muss er den Druckbogen aus der Auslage heraus nehmen oder ihn in der Auslage markieren. Dazu ist es erforderlich die Maschine anzuhalten, und beim Wiederanlaufen entsteht wieder Anlaufmakulatur. Des Weiteren erfolgt auch kein Abgleich zwischen Schön- und Widerdruck. Hier besteht das Risiko, dass einzelne Signaturen untermischt werden können.Various solutions for implementing fully automatic waste removal are known in the prior art. A known solution consists, for example, in manually marking printed sheets with a fluorescent pen during the first pass. This pen is then recognized on the second or next pass of the printed sheet and a process such as switching on a good sheet counter in the case of a correctly printed sheet and ejecting the printed sheet in the case of an incorrectly printed sheet is accordingly initiated. With this approach, however, autonomous printing is not possible on the first print pass. The operator has to stop the machine and mark the printed sheet with a fluorescent pen at the exact point where the sensor will later be in the reverse pressure. To do this, he has to take the printed sheet out of the display or mark it in the display. To do this, it is necessary to stop the machine, and when it starts up again, startup waste occurs. Furthermore, there is no comparison between front and back printing. There is a risk here that individual signatures can be mixed in.
Aus der deutschen Patentschrift
Allerdings besteht hier der Nachteil, dass die Markierungseinheit nur unterscheiden kann, ob es sich beim bedruckten Druckbogen um Makulatur handelt oder nicht.However, there is the disadvantage here that the marking unit can only distinguish whether the printed sheet is waste or not.
Die deutsche Patentschrift
Die deutsche Patentanmeldung
Die europäische Patentanmeldung
Somit ergibt sich die Aufgabe ein Verfahren zum Makulaturmanagement von Druckprodukten zu offenbaren, welches möglichst vollkommen autonom und damit wesentlich effizienter als die im Stand der Technik bekannten Systeme arbeitet und zudem deren bekannte Nachteile vermeidet.The object is thus to disclose a method for waste management of printed products which works as completely as possible autonomously and thus much more efficiently than the systems known in the prior art and also avoids their known disadvantages.
Gelöst wird diese Aufgabe durch ein Verfahren zum Makulaturmanagement von Druckprodukten in einem Bedruckstoffe verarbeitenden System, bestehend aus mindestens einem Rechner und mindestens einer Druckmaschine, welches die Schritte Vergabe einer zentralen ID für jedes im System zu verarbeitende Druckprodukt mittels eines Rechners, Zuordnung von bestimmten Events zu jeder ID durch den Rechner, Bedruck von Druckprodukten in einer Druckmaschine des Systems, Untersuchung der entsprechend bedruckten Druckprodukte mittels eines rechnergestützten Bilderfassungssystems und abhängig davon Zuordnung eines bestimmten Zustandes zu jedem bedruckten Druckprodukt durch den Rechner, Zuordnung aller erfassten Zustände zu einem bestimmten Event und Auslösen eines bestimmten Events für alle bedruckten Druckprodukte abhängig vom jeweils zugeordneten Zustand des jeweiligen Druckproduktes und einer bestimmten Weiterverarbeitung durch den Rechner umfasst. Grundlegend für das erfindungsgemäße Verfahren ist somit die Merkmalskette, dass eine zentrale und eindeutige ID für jedes im System zu verarbeitende Druckprodukt vergeben wird. Nach Erzeugung dieses Druckprodukts und entsprechender Qualitätsanalyse durch ein Bilderfassungs-System wird diesem Druckprodukt zudem ein Zustand zugeordnet. Da gleichzeitig jeder ID ein Set von bestimmten möglichen Events zugeordnet ist und die Aktivierung der Events abhängig vom jeweiligen Zustand des dem der ID zugeordneten Druckproduktes ist, sowie von der jeweiligen gewünschten Weiterverarbeitung des erzeugten Druckproduktes, wird abhängig davon ein bestimmtes Event ausgewählt und automatisch ausgeführt. Im einfachsten Fall bedeutet das nichts anderes als dass ein Druckprodukt eine bestimmte ID bekommt, dieses Druckprodukt überprüft wird und z. B. als fehlerfreies akzeptiertes Druckprodukt bewertet wird und dementsprechend für eine Weiterverarbeitung in einer Falzmaschine freigegeben wird, zu dieser Weiterverarbeitungseinheit transportiert und dort entsprechend bearbeitet wird. Ein alternatives Szenario wäre, dass ein erzeugtes Druckprodukt mit seiner eindeutigen ID entsprechend als Makulatur vom Bilderfassungssystem eingeschätzt wird und somit als ein mögliches Event die Ausschleusung als Makulatur veranlasst wird. An die ID wird somit die Information über das Druckprodukt gekoppelt und damit, abhängig vom Zustand, seine möglichen Weiterverarbeitungen.This object is achieved by a method for waste management of printed products in a system that processes printing materials, consisting of at least one computer and at least one printing machine, which includes the steps of assigning a central ID for each printed product to be processed in the system by means of a computer, assigning certain events to each ID by the computer, printing of printed products in a printing machine of the system, examination of the correspondingly printed printed products by means of a computer-aided image acquisition system and depending on the assignment of a specific state to each printed product by the computer, assignment of all recorded states to a specific event and triggering of a specific event for all printed products depending on the respectively assigned state of the respective printed product and a specific further processing by the computer. The feature chain that a central and unique ID is assigned for each printed product to be processed in the system is therefore fundamental to the method according to the invention. After this print product has been generated and a corresponding quality analysis has been carried out by an image capture system, a status is also assigned to this print product. Since a set of certain possible events is assigned to each ID at the same time and the activation of the events depends on the respective status of the printed product assigned to the ID, as well as on the respective desired further processing of the printed product created, a specific event is selected and automatically executed depending on this. In the simplest case, this means nothing more than that a printed product is given a specific ID, this printed product is checked and z. B. is evaluated as a faultless accepted printed product and is accordingly released for further processing in a folding machine, transported to this further processing unit and processed there accordingly. An alternative scenario would be that a generated printed product with its unique ID is accordingly assessed as waste by the image capture system and thus, as a possible event, it is triggered as waste. The information about the printed product is thus linked to the ID and, depending on the status, its possible further processing.
Vorteilhafte und daher bevorzugte Weiterbildungen des Verfahrens ergeben sich aus den zugehörigen Unteransprüchen sowie aus der Beschreibung mit den zugehörigen Zeichnungen.Advantageous and therefore preferred developments of the method result from the associated subclaims and from the description with the associated drawings.
Eine bevorzugte Weiterbildung des erfindungsgemäßen Verfahrens ist dabei, dass die ID auf das jeweilige Druckprodukt mittels einer Beschreibeinheit, insbesondere einer Inkjet-Einheit, in Form eines maschinenlesbaren Codes, insbesondere eines 1D- oder 2D-Codes, oder eines alphanumerischen Codes, aufgebracht wird. Dies sind nur die gebräuchlichsten Möglichkeiten, wie die ID dem jeweiligen Druckprodukt zugeordnet werden kann. Alternativ zu diesen analogen Markierungen, in denen das jeweilige Druckprodukt stets mit der ID beschrieben wird, wäre auch eine digitale Zuordnung denkbar, in der lediglich im Rechner bzw. im Speicher des Rechners einem abgezählten Bogen eine entsprechende ID zugeordnet wird. Dies kompliziert jedoch das erfindungsgemäße Verfahren, da hier eine nachgelagerte Identifizierung eines bestimmten Druckproduktes nur schwer möglich ist.A preferred development of the method according to the invention is that the ID is applied to the respective printed product by means of a writing unit, in particular an inkjet unit, in the form of a machine-readable code, in particular a 1D or 2D code, or an alphanumeric code. These are just the most common Options for assigning the ID to the respective print product. As an alternative to these analog markings, in which the respective printed product is always described with the ID, a digital assignment would also be conceivable in which a corresponding ID is assigned to a counted sheet only in the computer or in the memory of the computer. However, this complicates the method according to the invention, since it is difficult to subsequently identify a specific printed product.
Eine weitere bevorzugte Weiterbildung des erfindungsgemäßen Verfahrens ist dabei, dass die IDs vom Rechner neu vergeben oder dem System extern vorgegeben werden und sowohl die IDs als auch die zugeordneten Events und Zustände vom Rechner auf einem lokalen Speicher des Rechners oder der Druckmaschine, einem zentralen Speicher des Systems oder einem externen Netzwerkspeicher gesichert werden. Ob der Rechner selbst die IDs fortlaufend, üblicherweise inkrementell, vergibt oder von einer externen Steuerung genaue IDs entsprechend vorgegeben werden, hängt vom lokalen Einsatzort, also der Druckerei, in welchem das erfindungsgemäße Verfahren durchgeführt wird, ab. Wichtig ist allerdings, dass im vorliegenden System aus Rechner und Druckmaschine jederzeit jede ID mit ihrem entsprechenden Event(s) und, falls das zugeordnete Druckprodukt bereits qualitativ untersucht wurde, auch der entsprechende Zustand dem Rechner zur Verfügung steht.Another preferred development of the method according to the invention is that the IDs are newly assigned by the computer or specified externally for the system and both the IDs and the assigned events and states are stored by the computer on a local memory of the computer or the printing machine, a central memory of the System or external network storage. Whether the computer itself assigns the IDs continuously, usually incrementally, or whether precise IDs are specified accordingly by an external controller, depends on the local place of use, that is to say the print shop in which the method according to the invention is carried out. It is important, however, that in the present system consisting of computer and printing press, each ID with its corresponding event (s) and, if the assigned print product has already been qualitatively examined, the corresponding status is available to the computer at all times.
Eine weitere bevorzugte Weiterbildung des erfindungsgemäßen Verfahrens ist dabei, dass die Druckmaschine eine Bogen-Druckmaschine ist und jedem verwendeten Druckbogen entsprechend vom Rechner eine ID zugeordnet wird. Das erfindungsgemäße Verfahren kann am besten bei einer Bogendruckmaschine eingesetzt werden. Dennoch ist ein Einsatz auch in anderen Formen von Druckmaschinen möglich, sofern auch bei diesen eine Separierung in einzelne Druckprodukte, denen eindeutige IDs zugeordnet werden können, möglich ist.Another preferred development of the method according to the invention is that the printing press is a sheet-fed printing press and each printed sheet used is assigned an ID accordingly by the computer. The method according to the invention can best be used in a sheet-fed printing press. Nevertheless, it can also be used in other forms of printing machines, provided that these can also be separated into individual printed products to which unique IDs can be assigned.
Eine weitere bevorzugte Weiterbildung des erfindungsgemäßen Verfahrens ist dabei, dass die Events im Falle einer Weiterverarbeitung in der Bogen-Druckmaschine das Aktivieren eines Gutbogenzählers oder das Anhalten der Druckmaschine umfassen und im Falle einer Weiterverarbeitung in einer separaten Weiterverarbeitungseinheit das Zuführen des bedruckten Druckproduktes in die separate Weiterverarbeitungseinheit, die separate Ablage des bedruckten Druckproduktes als Muster, das Anhalten der separaten Weiterverarbeitungseinheit, sowie das Laden vorgehaltener Konfigurationsdaten für eine autonome Voreinstellung der separaten Weiterverarbeitungseinheit umfassen und in beiden Fällen das Ausschleusen des bedruckten Druckproduktes als Makulatur. Der erste Fall einer Weiterverarbeitung in der Druckmaschine umfasst dabei normalerweise das Bedrucken der Rückseite des bedruckten Druckproduktes. In diesem Fall muss im Gutfall der Gutbogenzähler inkrementiert werden und im Schlechtfall, d. h. dass das bedruckte Druckprodukt als Makulatur vom Bilderfassungssystem bewertet wurde, die Druckmaschine angehalten wird, da in dem Fall keine Weiterverarbeitung in Form des Bedruckens der Rückseite möglich ist. Falls die betreffende Druckmaschine zudem über eine interne Makulaturweiche verfügt, kann in diesem Fall kann das als Makulatur bewertete Druckprodukt auch direkt ausgeschleust werden. Dann kann unter Umständen auch auf ein Anhalten der Druckmaschine verzichtet werden. Des Weiteren können als Events im Falle eines Weitertransports des bedruckten Druckproduktes in die Weiterverarbeitungseinheit entsprechend spezifisch für diesen Fall auftretende Aktionen als Events zugeordnet werden, wie z.B. die entsprechend genannten.Another preferred development of the method according to the invention is that the events in the case of further processing in the sheet-fed printing press include the activation of a good sheet counter or the stopping of the printing press and, in the case of further processing in a separate further processing unit, the feeding of the printed print product in the separate further processing unit, the separate filing of the printed print product as a sample, the stopping of the separate further processing unit, as well as the loading of configuration data for an autonomous pre-setting of the separate further processing unit and in both cases the ejection of the printed print product as waste. The first case of further processing in the printing press normally involves printing the reverse side of the printed product. In this case, the good sheet counter must be incremented in the case of a good case and, in the case of a bad case, ie the printed product was assessed as waste by the image acquisition system, the printing press is stopped, since in this case no further processing in the form of printing the reverse side is possible. If the printing press in question also has an internal waste gate, the printed product classified as waste can also be ejected directly in this case. Then, under certain circumstances, it is also possible to dispense with stopping the printing press. Furthermore, in the case of further transport of the printed printed product into the further processing unit, actions occurring specifically for this case can be assigned as events, such as those mentioned accordingly.
Eine weitere bevorzugte Weiterbildung des erfindungsgemäßen Verfahrens ist dabei, dass die Zustände der bedruckten und untersuchten Druckprodukte den Zustand einer Einrichtemakulatur, einer Fortdruckmakulatur oder eines Gutbogens umfassen. Für den Fall des Zustandes eines untersuchten Druckproduktes als Makulatur wird demnach zwischen Einrichte- und Fortdruckmakulatur unterschieden, da beim Einrichten der Druckmaschine sowieso standardmäßig eine gewisse Makulatur erzeugt wird, bis sämtliche Parameter der Druckmaschine insbesondere hinsichtlich der Farbsteuerung den gewünschten Zielparametern entsprechen. Die Einrichtemakulatur ist dabei somit zumindest insofern teilweise unabhängig von der Qualitätsbewertung des Bilderfassungssystems, da eben ein gewisser Anteil an Makulatur beim Einrichten der Druckmaschine sowieso immer auftritt, während Fortdruckmakulatur nur dann endgültiger Zustand ist, wenn nach Abschluss des Einrichtevorgangs und nach Beginn des eigentlichen Fortdruckens erzeugtes bedrucktes Druckprodukt vom Bilderfassungssystem als Ausschuss bewertet wurdeAnother preferred development of the method according to the invention is that the states of the printed and examined printed products include the state of setup waste, production waste or a good sheet. In the case of an examined printed product being waste, a distinction is made between set-up and production waste, since a certain amount of waste is generated by default when setting up the printing machine, until all the parameters of the printing machine correspond to the desired target parameters, particularly with regard to color control. The set-up waste is thus at least partially independent of the quality assessment of the image acquisition system, since a certain amount of waste always occurs when setting up the printing press, while production waste is only the final state if it is generated after the set-up process has been completed and after the actual printing has started The printed printed product has been rated as reject by the image acquisition system
Eine weitere bevorzugte Weiterbildung des erfmdungsgemäßen Verfahrens ist dabei, dass der zugeordnete Zustand als Gutbogen automatisch in der Zuordnung des Events des Aktivierens des Gutbogenzählers resultiert. Dies betrifft insbesondere den Fall einer Weiterverarbeitung in der Bogendruckmaschine, da es hier zu einem automatischen Aktivieren des Gutbogenzählers kommen muss, sobald als Gutbogen erkannte Druckprodukte in die Druckmaschine einlaufen. Aber auch bei einer externen Weiterverarbeitung muss der Gutbogenzähler im Falle eines bewerteten Gutbogens entsprechend inkrementiert werden.Another preferred development of the method according to the invention is that the assigned state as a good sheet automatically results in the assignment of the event of activating the good sheet counter. This applies in particular to the case of further processing in the sheet-fed printing machine, since the good sheet counter must be activated automatically as soon as printed products that are recognized as good sheets enter the printing machine. But even with external further processing, the good sheet counter must be incremented accordingly in the case of an evaluated good sheet.
Eine weitere bevorzugte Weiterbildung des erfindungsgemäßen Verfahrens ist dabei, dass als Weiterverarbeitung des bedruckten Druckproduktes eine Nachbearbeitung in der Bogen-Druckmaschine, insbesondere ein Bedruck der Rückseite des Druckproduktes oder ein zweiter Bedruckvorgang, oder eine Nachbearbeitung in einer separaten Weiterverarbeitungseinheit des Systems, insbesondere einer Stanze, einer Rotationsstanze, einer Falzmaschine oder einer Faltschachtelklebemaschine, erfolgt.
Die Aufzählung ist nicht auf die genannten Fälle beschränkt. Es sind auch weitere Formen der Weiterverarbeitung möglich; jedoch sind die genannten Fälle die mit Abstand häufigsten und wichtigsten.A further preferred development of the method according to the invention is that post-processing in the sheet-fed printing machine, in particular printing the back of the printed product or a second printing process, or post-processing in a separate further processing unit of the system, in particular a punch, is used as further processing of the printed product. a rotary die cutter, a folding machine or a folder gluer.
The list is not limited to the cases mentioned. Other forms of further processing are also possible; however, the cases mentioned are by far the most frequent and important.
Eine weitere bevorzugte Weiterbildung des erfindungsgemäßen Verfahrens ist dabei, dass als Bilderfassungssystem ein Inline-Bilderfassungssystem verwendet wird, welches sich in der Druckmaschine hinter einem letzten Druck- oder Lackwerk befindet. Zwar kann auch ein externes Bilderfassungssystem für das erfindungsgemäße Verfahren verwendet werden, im Sinne einer autonomen Produktionsstrecke, die einen hohen Grad an Automatisierung verlangt, ist jedoch ein Inline-Bilderfassungssystem zu bevorzugen.Another preferred development of the method according to the invention is that an inline image acquisition system is used as the image acquisition system, which is located in the printing press behind a last printing or coating unit. It is true that an external image acquisition system can also be used for the method according to the invention, but an inline image acquisition system is to be preferred in the sense of an autonomous production line that requires a high degree of automation.
Eine weitere Lösung der gestellten Aufgabe stellt zudem ein rechnergestütztes automatisiertes Makulaturmanagementsystem für eine Bedruckstoffe verarbeitende Maschine eingerichter zur Ausführung eines Verfahrens nach einem der vorherigen Die Erfindung als solche sowie konstruktiv und/oder funktionell vorteilhafte Weiterbildungen der Erfindung werden nachfolgend unter Bezug auf die zugehörigen Zeichnungen anhand wenigstens eines bevorzugten Ausführungsbeispiels näher beschrieben. In den Zeichnungen sind einander entsprechende Elemente mit jeweils denselben Bezugszeichen versehen.Another solution to the problem posed is a computer-aided, automated waste management system for a machine that processes printing materials, set up to carry out a method according to one of the previous ones The invention as such as well as structurally and / or functionally advantageous developments of the invention are described in more detail below with reference to the associated drawings using at least one preferred exemplary embodiment. In the drawings, elements that correspond to one another are provided with the same reference numerals.
Die Zeichnungen zeigen:
- Figur 1:
- schematisch den Aufbau eines Bilderfassungssystems
- Figur 2:
- den schematischen Ablauf des erfindungsgemäßen Verfahrens
- Figure 1:
- schematically the structure of an image acquisition system
- Figure 2:
- the schematic sequence of the method according to the invention
In
Im Folgenden wird das erfindungsgemäße Verfahren noch einmal näher anhand verschiedener Szenarien erläutert. Bei Bogeneinzug wird grundsätzlich für jeden Druckbogen 9 eine eindeutige ID generiert. Diese kann durch den Steuerungsrechner 3 der Druckmaschine 4 erzeugt und dann an die Steuereinheit der Markierungseinheit 8 übermittelt werden. Alternativ kann auch der Steuerungsrechner der Markierungseinheit 8 selbst die ID erstellen und diese dann an die Steuereinheit 3 der Druckmaschine 4 übermitteln. Weitere Alternative ist die Vorgabe der ID durch ein zentrales Produktionssystem 11 mittels einer Datenbank und Übertragung an die Steuereinheit 3 der Druckmaschine 4 und anschließend von dieser an die Steuereinheit der Markierungseinheit 8. Die ID kann hierbei eine fortlaufende Nummer oder eine willkürlich generierte Nummer sein.In the following, the method according to the invention is explained again in more detail using various scenarios. When sheets are drawn in, a unique ID is generally generated for each printed
Über eine Markierungseinheit, wie zum Beispiel eine Inkjeteinheit am Bogeneinzug, wird diese eindeutige ID auf aufgetragen. Alternativ kann diese Markierungseinheit auch an einer anderen Position in der Druckmaschine 4 angebracht sein. Die ID kann in Form einer alphanumerischen Nummer die elektronisch lesbar ist, z.B. über OCR, aufgetragen werden. In einer alternativen Ausführung kann auch ein maschinenlesbarer 1D- oder 2D-Codes, z.B. ein Barcode oder ein QR-Code, verwendet werden.This unique ID is applied via a marking unit, such as an inkjet unit on the sheet feeder. Alternatively, this marking unit can also be attached at a different position in the
Falls auf dem Bogen 9 schon eine ID vorhanden ist, wird diese mittels der Kamera des Bilderfassungssensors eingelesen, vom Steuerungsrechner 3 der Druckmaschine 4 oder vom Bildverarbeitungsrechner 6 überprüft und entsprechend von diesen verarbeitet, sodass keine Neugenerierung einer ID für diesen Bogen notwendig ist.If there is already an ID on the
Mittels des Inline-Bilderfassungssystems 2 der Druckmaschine 4 und/oder zusätzlicher Farb- und Qualitätsmesssysteme in der Druckmaschine 4 welche den Zustand aktuell verarbeiteter Druckbogen 9 bewerten, werden diese entsprechenden Zustände dann vom Steuerungsrechner 3 der Druckmaschine 4 der zugehörigen ID des jeweiligen Druckbogens 9 zugewiesen. Diese entsprechen bestimmten Eigenschaften, welche durch die Konfiguration und die Voreinstellung der Maschinensteuerung 3 und Erkennen von Merkmalen und Abgleich mit einer vorher definierten Toleranz Eigenschaften wie:
- Einrichtemakulatur - also
Druckbogen 9, die benötigt werden um zu Beginn die Soll Parameter zu erreichen - Fortdruckmakulatur - also
Druckbogen 9, deren Bildqualität innerhalb der Produktionsphase außerhalb der vorgegebenen Toleranzen liegt - Gutbogen -
Druckbogen 9, die innerhalb der vorgegebenen Toleranzen liegen
- Set-up waste - i.e. printed
sheets 9, which are required to achieve the target parameters at the beginning - Production waste - that is, printed
sheets 9, the image quality of which lies outside the specified tolerances during the production phase - Good sheet - printed
sheets 9 that are within the specified tolerances
Diese Eigenschaft modifiziert automatische die Bogen-Zählvorrichtung, sodass die geforderte Menge an Bogen 9 produziert wird.This feature automatically modifies the sheet counting device so that the required amount of
Als Ergänzung kann die Druckmaschinensteuerung 3 weitere Parameter und Einstellungen erhalten, die engere Toleranzen setzen um zu ermitteln, welche Druckbogen 9 keine oder fast keine Abweichungen aufweisen. Diese erhalten ein weiteres Merkmal, Musterbogen, und können im nachgelagerten Postpressprozess automatisch über eine separate Produktionsstrecke ausgeschleust und separat behandelt werden. Bei Abweichungen zu einer Referenz wird die Ist-Abweichung dokumentiert, sodass nachträglich Schwellwerte konfiguriert werden können und somit eine Modifizierung der Eigenschaften jedes einzelnen Bogens 9 erlaubt. Wenn mehrere Nutzen, bzw. Elemente auf einem Druckbogen 9 sind, wird die Position, bzw. die Nutzennummer der Abweichung mit dokumentiert, sodass eine nachträgliche und eindeutige Identifizierung möglich ist. Des Weiteren werden noch alle weiteren jobspezifischen Daten dieser ID zugewiesen. Dies können zum Beispiel Auftragsnummer, Arbeitsgang, Signatur, Schön oder Widerdruckseite, Sprache etc. sein.As a supplement, the
Die eindeutige ID mit den gesamten Informationen wird dann in einem Datenspeicher ab- bzw zwischengespeichert werden.The unique ID with all the information is then stored or temporarily stored in a data memory.
Als Datenspeicher geeignet sind Speicher wie:
- Lokal
auf dem Steuerungsrechner 3der Druckmaschine 4 Zentral im Produktionssystem 11- Global in einer Cloud oder Ähnlichem
- Locally on the
control computer 3 of theprinting press 4 - Central in the
production system 11 - Globally in a cloud or something similar
Diese gesamten Daten werden im Nachgang für verschiedene Einsatzzwecke und hiervon abhängige Verfahren verwendet.All of this data is subsequently used for various purposes and dependent processes.
Ein möglicher bevorzugter Einsatzzweck ein zweiter Druckdurchgang eines bedruckten Bogens 9 in derselben Druckmaschine 4. Bei einem solchen zweiten Durchgang wird die gleiche Druckseite erneut bedruckt. Hierzu wird in der Druckmaschine 4 mittels einer Sensoreinrichtung am Bogeneinzugsbereich, in einem Druck- oder Lackierwerk oder integriert in ein Farb- und Qualitätsmesssystem 2 die Bogen-ID eingelesen. In der Produktion wird dann durch Signale in der Produktion die Information hinter der zugehörigen ID erweitert. Beispielsweise wird dabei ein Druckbogen 9 der vorher als Gutbogen gewertet wurde, später bei erkennen einer Abweichung als Fortdruckmakulatur gewertet werden. Des Weiteren werden auch noch die neuen Farb- und Qualitätsinformationen dem Druckbogen 9, bzw. seiner gespeicherten ID zugewiesen.A possible preferred application is a second printing pass of a printed
Als nächster Schritt werden beim Einrichten eines Auftrags anhand der gespeicherten Information hinter der ID automatisch Events an der Druckmaschine 4 eingeleitet. Diese umfassen zum Beispiel;
- Automatisches Aktivieren des Gutbogenzähler, sobald Gutbogen in
die Druckmaschine 4 einlaufen, Anhalten der Druckmaschine 4, wenn die benötigen Referenzwerte noch nicht erreicht sind, damit aus dem ersten Druckdurchgang keine Gutbogen für das Einrichten verwendet und im Anschluss die vorgegebene Auflage nicht mehr erreicht wird.
- Automatic activation of the good sheet counter as soon as good sheets enter the
printing press 4, - Stopping the
printing press 4 when the required reference values have not yet been reached, so that no good sheets from the first printing pass are used for setting up and the specified number of copies is then no longer achieved.
Als Ergänzung erfolgt noch eine Kontrolle über die Plausibilität um sicherzustellen, dass es sich um den gleichen Auftrag, wie aus dem ersten Durchgang handelt, wodurch eine Untermischung verschiedenster Druckbogen 9, Aufträge und Sprachen entsteht.In addition, there is a plausibility check to ensure that it is the same order as from the first run, which results in a mix of different printed
Ein weiterer, bevorzugter Einsatzzweck ist der Widerdruck bei Geradeausdruckmaschinen. Hier wird bei einem zweiten Durchgang die andere Druckseite bzw. Rückseite des Druckbogens 9 bedruckt. Dabei wird auch hier in der Druckmaschine 4 mittels der Sensoreinrichtung, die am Bogeneinzugsbereiche auf der unteren gegenüberliegenden Seite angebracht ist, die ID eingelesen. In der Produktionsphase der Druckmaschine 4 wird die Information hinter der zugehörigen ID erweitert. Beispielsweise wird ein Druckbogen 9 der vorher als Gutbogen gewertet wurde, bei erkennen einer Abweichung als Fortdrückmakulatur gewertet. Des Weiteren werden auch hier die neuen Farb- und Qualitätsinformationen dem Druckbogen 9, bzw. der gespeicherten ID zugewiesen. Als Ergänzung kann nochmals auf der anderen Bogenseite eine weitere ID aufgedruckt werden, welche durch den Steuerungsrechner 3 der Druckmaschine 4 mit der vorangegangen ID kombiniert wird. Dann werden im nächsten Schritt beim Einrichten eines Auftrags anhand der Information hinter der ID automatisch bestimmte Events an der Druckmaschine 4 eingeleitet Diese umfassen hier:
- Automatisches Aktivieren des Gutbogenzähler, sobald Gutbogen in
die Druckmaschine 4 einlaufen, Anhalten der Druckmaschine 4, wenn die benötigen Referenzwerte noch nicht erreicht sind, womit aus dem ersten Druckdurchgang keine Gutbogen für das Einrichten verwendet und im Anschluss die vorgegeben Auflage nicht mehr erreicht wird.
- Automatic activation of the good sheet counter as soon as good sheets enter the
printing press 4, - Stopping the
printing press 4 when the required reference values have not yet been reached, so that no good sheets are used for the setup from the first printing pass and the specified number of copies is then no longer achieved.
Alternativ oder als Ergänzung erfolgi noch die Kontrolle über die Plausibillität.Alternatively or as a supplement, the plausibility check is also carried out.
Der dritte bevorzugte Einsatzzweck besteht darin, von der Druckmaschinensteuerung 3 generierte Information über das zentrale Produktionssystem 11 oder Cloud an eine nachgelagerte Produktionseinheit zu übertragen. Dabei kommen eine Stanze, ein Rotationsstanze, eine Falzmaschine oder eine Faltschachtelklebemaschine in Frage.The third preferred purpose is to send information generated by the
Auch hier wird bei Bogeneinzug über eine angebrachte Sensoreinheit die bogenspezifische ID ausgelesen und mit den zuvor generierten Daten abgeglichen. Durch die Information die der aktuelle Druckbogen 9 dann beinhaltet, wird dementsprechend vom Steuerungsrechner 3 ein Event eingeleitet, was mit dem jeweiligen Druckbogen 9 passiertHere, too, when sheets are drawn in, the sheet-specific ID is read out via an attached sensor unit and compared with the previously generated data. Using the information that the
Als Events kommen dabei in Frage:
- Das Entsorgen von Makulatur über eine Ausschleusung oder eine separate Ausgabestrecke
- Das Zuführen des Gutbogens zur Produktionsstrecke für die nachgelagerte Produktionseinheit
- Die separate Ablage für Muster, falls ein direkter Versand an den Kunden oder die Ablage in ein Archiv notwendig ist
- Das Stoppen der Produktionseinheit bei nicht plausiblen Jobdaten, damit eine Untermischung verhindert wird
- Das Laden von jobspezifischen Preset-Daten, für eine autonome Voreinstellung der nachgelagerten Produktionseinheit.
- The disposal of waste via a discharge or a separate output line
- The feeding of the good sheet to the production line for the downstream production unit
- The separate storage for samples, if a direct dispatch to the customer or storage in an archive is necessary
- Stopping the production unit in the event of implausible job data, so that mixing up is prevented
- The loading of job-specific preset data for an autonomous presetting of the downstream production unit.
Die folgende Tabelle zeigt ein Beispiel für verschiedene Druckbogen 9, bzw. die ihnen zugeordneten IDs samt der hinterlegten Information.
- 11
- Anwenderuser
- 22
- BilderfassungssystemImage acquisition system
- 33
- Steuerungsrechner der DruckmaschineControl computer of the printing press
- 44th
- DruckmaschinePrinting press
- 55
- BildsensorImage sensor
- 66th
- BildverarbeitungsrechnerImage processing computer
- 77th
- DisplayDisplay
- 88th
- Steuereinheit der MarkierungseinheitControl unit of the marking unit
- 99
- Druckbogen mit IDPrint sheet with ID
- 1010
- Steuereinheit PostpressPostpress control unit
- 1111
- zentrales Produktionssystemcentral production system
Claims (10)
dadurch gekennzeichnet,
dass die ID auf das jeweilige Druckprodukt (9) mittels einer Markierungseinheit, insbesondere einer Inkjet-Einheit, in Form eines maschinenlesbaren Codes, insbesondere eines ID- oder 2D-Codes, oder eines alphanumerischen Codes, aufgebracht wird.Method according to claim 1,
characterized,
that the ID is applied to the respective printed product (9) by means of a marking unit, in particular an inkjet unit, in the form of a machine-readable code, in particular an ID or 2D code, or an alphanumeric code.
dadurch gekennzeichnet,
dass die IDs vom Rechner (3, 8, 10) neu vergeben oder dem System extern vorgegeben werden und sowohl die IDs als auch die zugeordneten Events und Zustände vom Rechner (3, 8, 10) auf einem lokalen Speicher des Rechners (3, 8, 10) oder der Druckmaschine (4), einem zentralen Speicher des Systems oder einem externen Netzwerkspeicher gesichert werdenMethod according to claim 2,
characterized,
that the IDs are newly assigned by the computer (3, 8, 10) or given externally to the system and that both the IDs and the assigned events and states are stored by the computer (3, 8, 10) on a local memory of the computer (3, 8 , 10) or the printing machine (4), a central memory of the system or an external network memory
dadurch gekennzeichnet,
dass die Druckmaschine (4) eine Bogen-Druckmaschine (4) ist und jedem verwendeten Druckbogen (9) entsprechend vom Rechner (3, 8, 10) eine ID zugeordnet wird.Method according to one of the preceding claims,
characterized,
that the printing machine (4) is a sheet-fed printing machine (4) and each printed sheet (9) used is assigned an ID accordingly by the computer (3, 8, 10).
dadurch gekennzeichnet,
dass die Events im Falle einer Weiterverarbeitung in der Bogen-Druckmaschine (4) das Aktivieren eines Gutbogenzählers oder das Anhalten der Druckmaschine (4) umfassen und im Falle einer Weiterverarbeitung in einer separaten Weiterverarbeitungseinheit das Zuführen des bedruckten Druckproduktes (9) in die separate Weiterverarbeitungseinheit, die separate Ablage des bedruckten Druckproduktes (9) als Muster, das Anhalten der separaten Weiterverarbeitungseinheit, sowie das Laden vorgehaltener Konfigurationsdaten für eine autonome Voreinstellung der separaten Weiterverarbeitungseinheit umfassen und in beiden Fällen das Ausschleusen des bedruckten Druckproduktes (9) als Makulatur.Method according to claim 4,
characterized,
that the events in the case of further processing in the sheet printing machine (4) include the activation of a good sheet counter or the stopping of the printing machine (4) and, in the case of further processing in a separate further processing unit, the feeding of the printed product (9) into the separate further processing unit, include the separate filing of the printed product (9) as a sample, the stopping of the separate further processing unit, as well as the loading of stored configuration data for an autonomous presetting of the separate further processing unit and, in both cases, the ejection of the printed product (9) as waste.
dadurch gekennzeichnet,
dass die Zustände der bedruckten und untersuchten Druckprodukte (9) den Zustand einer Einrichtemakulatur, einer Fortdruckmakulatur oder eines Gutbogens umfassenMethod according to one of Claims 4 to 5,
characterized,
that the states of the printed and examined printed products (9) include the state of setup waste, production waste or a good sheet
dadurch gekennzeichnet,
dass der zugeordnete Zustand als Gutbogen automatisch in der Zuordnung des Events des Aktivierens des Gutbogenzählers resultiert.Method according to claim 6,
characterized,
that the assigned status as a good sheet automatically results in the assignment of the event of activating the good sheet counter.
dadurch gekennzeichnet,
dass als Weiterverarbeitung des bedruckten Druckproduktes (9) eine Nachbearbeitung in der Bogen-Druckmaschine (4), insbesondere ein Bedruck der Rückseite des Druckproduktes (9) oder ein zweiter Bedruckvorgang, oder eine Nachbearbeitung in einer separaten Weiterverarbeitungseinheit des Systems, insbesondere einer Stanze, einer Rotationsstanze, einer Falzmaschine oder einer Faltschachtelklebemaschine, erfolgt.Method according to one of Claims 4 to 7,
characterized,
that as further processing of the printed printed product (9) post-processing in the sheet-fed printing machine (4), in particular printing the back of the printed product (9) or a second printing process, or post-processing in a separate further processing unit of the system, in particular a punch, a Rotary die cutter, a folding machine or a folder gluer.
dadurch gekennzeichnet,
dass als Bilderfassungssystem (2) ein Inline-Bilderfassungssystem (2) verwendet wird, welches sich in der Druckmaschine (4) hinter einem letzten Druck- oder Lackwerk befindet.Method according to one of the preceding claims,
characterized,
that the image acquisition system (2) used is an inline image acquisition system (2) which is located in the printing press (4) behind a last printing or coating unit.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP19000472.1A EP3808564B1 (en) | 2019-10-16 | 2019-10-16 | Autonomous sheet numbering |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP19000472.1A EP3808564B1 (en) | 2019-10-16 | 2019-10-16 | Autonomous sheet numbering |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP3808564A1 true EP3808564A1 (en) | 2021-04-21 |
| EP3808564B1 EP3808564B1 (en) | 2023-12-20 |
Family
ID=68280663
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP19000472.1A Active EP3808564B1 (en) | 2019-10-16 | 2019-10-16 | Autonomous sheet numbering |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP3808564B1 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE102022105615A1 (en) | 2022-03-10 | 2023-09-14 | Koenig & Bauer Ag | Sheet processing machine and method for marking and tracking sheets |
Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE10349896B4 (en) | 2003-10-25 | 2005-11-17 | Koenig & Bauer Ag | Sheet-fed printing machine and method for operating a sheet-fed printing machine |
| DE102005009301A1 (en) | 2005-03-01 | 2006-09-07 | Koenig & Bauer Ag | Print substrate and print product data transmission method for manufacturing and marketing of print product, involves directly reading logistics and processing data stored in data memory and transmitting data in process overlapping manner |
| DE102005037497A1 (en) * | 2005-08-09 | 2007-02-15 | Man Roland Druckmaschinen Ag | Method for individually characterizing each copy on a printed sheet comprises applying a printing ink or coating on the sheet using a printing device connected to a laser device with a thermosensitive ink |
| DE102006015828A1 (en) * | 2006-04-03 | 2007-10-04 | Man Roland Druckmaschinen Ag | Image inspection system for e.g. sheet-fed offset press, has sorting device, where data, which are stored in memory and obtained by image processing algorithm, are stored in another memory for analysis by algorithm |
| EP1939800A1 (en) | 2006-12-22 | 2008-07-02 | MAN Roland Druckmaschinen AG | Production flow control for a printer |
| EP3168045A2 (en) * | 2015-11-13 | 2017-05-17 | manroland web systems GmbH | Method for controlling or regulating a production process in the manufacture of printed products |
| DE102010003913B4 (en) | 2010-04-13 | 2019-01-10 | Koenig & Bauer Ag | Method for operating sheet-fed printing machines and a sheet-fed printing machine for printing sheets |
| EP3456535A1 (en) * | 2017-09-14 | 2019-03-20 | Heidelberger Druckmaschinen AG | Image inspection printed products with defect classes |
-
2019
- 2019-10-16 EP EP19000472.1A patent/EP3808564B1/en active Active
Patent Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE10349896B4 (en) | 2003-10-25 | 2005-11-17 | Koenig & Bauer Ag | Sheet-fed printing machine and method for operating a sheet-fed printing machine |
| DE102005009301A1 (en) | 2005-03-01 | 2006-09-07 | Koenig & Bauer Ag | Print substrate and print product data transmission method for manufacturing and marketing of print product, involves directly reading logistics and processing data stored in data memory and transmitting data in process overlapping manner |
| DE102005037497A1 (en) * | 2005-08-09 | 2007-02-15 | Man Roland Druckmaschinen Ag | Method for individually characterizing each copy on a printed sheet comprises applying a printing ink or coating on the sheet using a printing device connected to a laser device with a thermosensitive ink |
| DE102006015828A1 (en) * | 2006-04-03 | 2007-10-04 | Man Roland Druckmaschinen Ag | Image inspection system for e.g. sheet-fed offset press, has sorting device, where data, which are stored in memory and obtained by image processing algorithm, are stored in another memory for analysis by algorithm |
| EP1939800A1 (en) | 2006-12-22 | 2008-07-02 | MAN Roland Druckmaschinen AG | Production flow control for a printer |
| DE102010003913B4 (en) | 2010-04-13 | 2019-01-10 | Koenig & Bauer Ag | Method for operating sheet-fed printing machines and a sheet-fed printing machine for printing sheets |
| EP3168045A2 (en) * | 2015-11-13 | 2017-05-17 | manroland web systems GmbH | Method for controlling or regulating a production process in the manufacture of printed products |
| EP3456535A1 (en) * | 2017-09-14 | 2019-03-20 | Heidelberger Druckmaschinen AG | Image inspection printed products with defect classes |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE102022105615A1 (en) | 2022-03-10 | 2023-09-14 | Koenig & Bauer Ag | Sheet processing machine and method for marking and tracking sheets |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP3808564B1 (en) | 2023-12-20 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP3456535B1 (en) | Image inspection printed products with defect classes | |
| EP2008801B1 (en) | Production system for producing folding boxes and method for feeding spoilage-free blanks to a folder-gluer | |
| CH654428A5 (en) | METHOD FOR CONTROLLING VALUE SHEETS DURING THEIR PRODUCTION. | |
| EP3151176A1 (en) | Method for planning and allocation of productions | |
| DE2559034A1 (en) | FLAT PRINT MULTIPLING DEVICE AND METHOD | |
| EP2090944B1 (en) | Printer and method for wireless RFID-based internal components data recording | |
| DE20010920U1 (en) | Printing machine, in particular sheetfed offset printing machine | |
| CH675853A5 (en) | ||
| EP2960058A1 (en) | Method and device for controlling and regulating a digital printing process | |
| EP3808564B1 (en) | Autonomous sheet numbering | |
| EP2080074A2 (en) | Method for quality assurance during the operation of a paper handling system | |
| DE10023995A1 (en) | Communication system, especially in the production of print media | |
| EP2759405B1 (en) | Method for the capture and transmission of process control data prior to and/or within a print process for the production of printed products in a printing machine | |
| EP3564036B1 (en) | Automatic printing plate sorting | |
| DE3730683A1 (en) | Process and device for monitoring articles | |
| EP3009267A1 (en) | Method for manufacturing printed products | |
| EP3168045B1 (en) | Method for controlling or regulating a production process in the manufacture of printed products | |
| EP2933687A1 (en) | Workflow for web to print printers | |
| EP2001680A1 (en) | Image processing systems for a printing press | |
| DE102018220971B4 (en) | Method for setting up a sheet-fed printing machine with alternating use of waste sheets and unprinted sheets | |
| EP3495295B1 (en) | Method for identification of printed products in print processing | |
| DE102018219734A1 (en) | Improved bowing in the feeder | |
| EP3628490A1 (en) | Improved printing plate logistics | |
| EP3715125B1 (en) | Machine stoppage | |
| DE102006015770B4 (en) | Printing and inserting machine with a retrofittable coupling device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE APPLICATION HAS BEEN PUBLISHED |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: BA ME |
|
| RAP1 | Party data changed (applicant data changed or rights of an application transferred) |
Owner name: HEIDELBERGER DRUCKMASCHINEN INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AG & CO. KG |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: REQUEST FOR EXAMINATION WAS MADE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20211021 |
|
| RBV | Designated contracting states (corrected) |
Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| P01 | Opt-out of the competence of the unified patent court (upc) registered |
Effective date: 20230522 |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: GRANT OF PATENT IS INTENDED |
|
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20230920 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE PATENT HAS BEEN GRANTED |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 502019010147 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: LANGUAGE OF EP DOCUMENT: GERMAN |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20240321 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: LT Ref legal event code: MG9D |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20231220 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: MP Effective date: 20231220 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20231220 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20231220 Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20240321 Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20231220 Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20231220 Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20240320 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20231220 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20231220 Ref country code: RS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20231220 Ref country code: NO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20240320 Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20231220 Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20231220 Ref country code: HR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20231220 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20240420 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20231220 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20231220 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SM Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20231220 Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20231220 Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20231220 Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20231220 Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20240420 Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20231220 Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20231220 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20240422 Ref country code: PL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20231220 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20240422 Ref country code: PL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20231220 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R097 Ref document number: 502019010147 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20231220 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20231220 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20231220 Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20231220 |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20240923 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20231220 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20241031 Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20241016 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20241031 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: BE Ref legal event code: MM Effective date: 20241031 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20241016 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: MM01 Ref document number: 1642164 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20241016 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20251031 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20251024 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20241016 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20251024 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT; INVALID AB INITIO Effective date: 20191016 |