EP2394699A2 - Vorrichtung zur Vermeidung der Blutoxidation - Google Patents
Vorrichtung zur Vermeidung der Blutoxidation Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP2394699A2 EP2394699A2 EP20110168210 EP11168210A EP2394699A2 EP 2394699 A2 EP2394699 A2 EP 2394699A2 EP 20110168210 EP20110168210 EP 20110168210 EP 11168210 A EP11168210 A EP 11168210A EP 2394699 A2 EP2394699 A2 EP 2394699A2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- insertion hole
- finger insertion
- yubi
- irradiation
- fluid activating
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
- 239000008280 blood Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 39
- 210000004369 blood Anatomy 0.000 title claims abstract description 39
- 230000002401 inhibitory effect Effects 0.000 title claims abstract description 22
- 238000007254 oxidation reaction Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 21
- 230000003647 oxidation Effects 0.000 title claims abstract description 20
- 238000003780 insertion Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 46
- 230000037431 insertion Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 46
- 239000012530 fluid Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 45
- 230000003213 activating effect Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 41
- 239000003822 epoxy resin Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 7
- 229920000647 polyepoxide Polymers 0.000 claims abstract description 7
- 230000036542 oxidative stress Effects 0.000 abstract description 18
- 241001465754 Metazoa Species 0.000 description 63
- 230000037023 motor activity Effects 0.000 description 49
- 210000003811 finger Anatomy 0.000 description 36
- 238000002474 experimental method Methods 0.000 description 27
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 23
- 241000699666 Mus <mouse, genus> Species 0.000 description 21
- 241000699670 Mus sp. Species 0.000 description 18
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 10
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 8
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 7
- 230000005855 radiation Effects 0.000 description 6
- 238000011084 recovery Methods 0.000 description 6
- 230000002829 reductive effect Effects 0.000 description 6
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 5
- 208000013738 Sleep Initiation and Maintenance disease Diseases 0.000 description 4
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N atomic oxygen Chemical compound [O] QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 4
- 206010022437 insomnia Diseases 0.000 description 4
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 239000001301 oxygen Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000004913 activation Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000002888 effect on disease Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000006742 locomotor activity Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000033764 rhythmic process Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 3
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Diethyl ether Chemical compound CCOCC RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- CWYNVVGOOAEACU-UHFFFAOYSA-N Fe2+ Chemical compound [Fe+2] CWYNVVGOOAEACU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 241000282412 Homo Species 0.000 description 2
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000010171 animal model Methods 0.000 description 2
- 210000004204 blood vessel Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910001448 ferrous ion Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000002560 therapeutic procedure Methods 0.000 description 2
- 210000003813 thumb Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 210000003462 vein Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 206010002091 Anaesthesia Diseases 0.000 description 1
- HTTJABKRGRZYRN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Heparin Chemical compound OC1C(NC(=O)C)C(O)OC(COS(O)(=O)=O)C1OC1C(OS(O)(=O)=O)C(O)C(OC2C(C(OS(O)(=O)=O)C(OC3C(C(O)C(O)C(O3)C(O)=O)OS(O)(=O)=O)C(CO)O2)NS(O)(=O)=O)C(C(O)=O)O1 HTTJABKRGRZYRN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 101000836873 Homo sapiens Nucleotide exchange factor SIL1 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 206010028980 Neoplasm Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 238000009825 accumulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000037005 anaesthesia Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003963 antioxidant agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003078 antioxidant effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000004071 biological effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 201000011510 cancer Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 238000005260 corrosion Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007797 corrosion Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 201000010099 disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000037265 diseases, disorders, signs and symptoms Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 230000004907 flux Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229960002897 heparin Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229920000669 heparin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 102000052329 human SIL1 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 238000010030 laminating Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910044991 metal oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000004706 metal oxides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000012544 monitoring process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001590 oxidative effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003389 potentiating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000843 powder Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000003254 radicals Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000003642 reactive oxygen metabolite Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000011160 research Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012827 research and development Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000284 resting effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000009758 senescence Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005245 sintering Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001629 suppression Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000004083 survival effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012353 t test Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012795 verification Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61N—ELECTROTHERAPY; MAGNETOTHERAPY; RADIATION THERAPY; ULTRASOUND THERAPY
- A61N2/00—Magnetotherapy
- A61N2/06—Magnetotherapy using magnetic fields produced by permanent magnets
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61N—ELECTROTHERAPY; MAGNETOTHERAPY; RADIATION THERAPY; ULTRASOUND THERAPY
- A61N1/00—Electrotherapy; Circuits therefor
- A61N1/40—Applying electric fields by inductive or capacitive coupling ; Applying radio-frequency signals
- A61N1/403—Applying electric fields by inductive or capacitive coupling ; Applying radio-frequency signals for thermotherapy, e.g. hyperthermia
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61N—ELECTROTHERAPY; MAGNETOTHERAPY; RADIATION THERAPY; ULTRASOUND THERAPY
- A61N2/00—Magnetotherapy
- A61N2/002—Magnetotherapy in combination with another treatment
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61N—ELECTROTHERAPY; MAGNETOTHERAPY; RADIATION THERAPY; ULTRASOUND THERAPY
- A61N5/00—Radiation therapy
- A61N5/06—Radiation therapy using light
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a blood oxidation inhibiting apparatus.
- This apparatus includes fluid activating bodies disposed around the outside periphery of a pipe in order to activate a fluid flowing in the pipe.
- Each of the fluid activating bodies is composed of a black radiation sintered body made by sintering the powder of a plurality of kinds of metal oxides at high temperature and an electromagnetic wave converging body for converging the electromagnetic wave radiated from the black radiation sintered body to a specific wavelength.
- the electromagnetic wave converging body is formed by laminating at least six magnets with the N-poles and the S-poles thereof disposed alternately, and an electromagnetic wave passing-through hole is formed to the laminated magnets so as to pass therethrough.
- the object thereof is merely to solve the problem of fluid activation, and thus the effect on the blood of a human body is not completely expected.
- the present inventors organized a collaborative team and carried out experiments for examining whether the above-described prior art can exert an effect on the blood of a human body as later described.
- the above-described prior art if used in conjunction with electromagnetic wave irradiation, can lower and eliminate the oxidative stress, exerting an effect on diseases attributed to the oxidative stress, and is applicable to therapy of insomnia, and the like.
- a blood oxidation inhibiting apparatus a finger insertion hole for inserting a finger being formed therein, comprising a plurality of fluid activating bodies being disposed around the finger insertion hole, the fluid activating bodies being integrally fixed to a cover with an epoxy resin, the cover being formed of straight line portions extending substantially at right angles to each other and a circular arc portion connecting between the ends of both straight line portions in the shape of a circular arc, and the fluid activating bodies being constituted by a set of at least three fluid activating bodies, two thereof being disposed between one of both ends of the circular arc portion and the finger insertion hole, and between the other both ends of the circular arc portion and the finger insertion hole, respectively, with the electromagnetic wave converging body thereof being oriented toward the finger insertion hole, and one thereof being disposed between the corner formed by both straight line portions and the finger insertion hole with the electromagnetic wave converging body thereof being oriented toward the finger insertion hole.
- a blood oxidation inhibiting apparatus a finger insertion hole for inserting a finger being formed therein, comprising a plurality of fluid activating bodies being disposed around the finger insertion hole, with the electromagnetic wave converging body thereof being oriented toward the finger insertion hole, the fluid activating bodies being integrally fixed to a cover with an epoxy resin, the cover being formed substantially in the shape of a square, and the fluid activating bodies being constituted by a set of at least four fluid activating bodies each disposed between one of the four corners of the cover and the finger insertion hole with the electromagnetic wave converging body thereof being oriented toward the finger insertion hole.
- the blood vessels in the finger are irradiated with a specific laser-like electromagnetic wave from any of the three or four fluid activating bodies.
- the oxidative stress in the blood is lowered and eliminated, which exerts an effect on the diseases attributed to the oxidative stress, thereby insomnia, and the like, being treated.
- the blood oxidation inhibiting apparatus of the present invention is of finger insertion type, and has a simple construction containing fluid activating bodies, thus it is compact and light weight, and can be manufactured inexpensively.
- the blood oxidation inhibiting apparatus is adapted to be of finger insertion type such that it is compact and light weight, and can be inexpensively manufactured, and used in home.
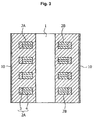
- the fluid activating bodies 2A, 2B, 2C are each constituted as stated in the patent document 1.
- the fluid activating bodies 2A, 2B, 2C are each constituted by a black radiation sintered body 3 and an electromagnetic wave converging body 4 for converging the electromagnetic wave generated by this black radiation sintered body 3 to a specific wavelength.
- the fluid activating bodies 2A, 2B, 2C are each disposed such that the electromagnetic wave converging body 4 is oriented toward the finger insertion hole 1.
- the fluid activating bodies 2A, 2B, 2C are integrally fixed to a cover 10 with an epoxy resin 5.
- the cover 10 is formed of straight line portions 11, 12 extending substantially at right angles to each other and a circular arc portion 13 connecting between the ends of both straight line portions 11, 12 in the shape of a circular arc, the straight line portion 12 is fixed to a supporting plate 14.
- the supporting plate 14 need not always be provided.
- the finger insertion hole 1 is formed in the central portion on the line connecting between both ends of the circular arc portion 13.
- the fluid activating bodies 2A, 2B are disposed on the line connecting between the ends of the circular arc portion 13, being oriented toward the finger insertion hole 1, and the fluid activating body 2C is disposed between the corner formed by the straight line portions 11, 12 and the finger insertion hole 1, being oriented toward the finger insertion hole 1.
- the blood oxidation inhibiting apparatus is of finger insertion type, and has a simple construction containing the fluid activating bodies 2A, 2B, 2C, thus it is compact and light weight, and can be manufactured inexpensively.
- Fig. 4 illustrates another embodiment of a blood oxidation inhibiting apparatus according to the present invention.
- the same or equivalent components as those in the above-described embodiment will be provided with the same symbols in the following explanation.
- a set of four fluid activating bodies 2A, 2B, 2C, 2D are provided.
- the cover 10 is formed in the shape of a square, and the fluid activating bodies 2A, 2B, 2C, 2D are each disposed between one the four corners of the cover 10 and the finger insertion hole 1, being oriented from toward the finger insertion hole 1. Even if the blood oxidation inhibiting apparatus is configured in this way, the same effect as that described above can be obtained.
- the blood oxidation inhibiting apparatus of the present embodiment can eliminate the oxidative stress on a human and an animal, exerting an effect on diseases attributed to the oxidative stress, and is applicable to therapy to insomnia and the like.
- the "Yubi-MR" refers to a blood oxidation inhibiting apparatus of the present embodiment as shown in Fig. 1 to Fig. 3 in which a set of three fluid activating bodies 2A, 2B, 2C is provided.
- the "Yubi-MR for animal use” refers to a fluid activation apparatus which uses a "Pipetector” (the name of a product of Japan System Planning Co., Ltd.) and is configured as stated in claim 4 in the patent document 1 (Japanese Patent No. 3952477 ).
- the "dummy apparatus” refers to an apparatus loaded only with wiggler magnets, which was manufactured for comparison with the "Yubi-MR for animal use”.
- the "BAP” is an acronym of biological antioxidant potential.
- the "dROM” is an acronym of diacron reactive oxygen metabolites, meaning the oxidative stress.
- the BAP and dROM were measured, using FRAS4 (Free Radical Analytical System 4) manufactured by Wismerll Co., Ltd.
- Table 1 gives the changes in BAP and dROM before and after Yubi-MR irradiation for 9 subjects
- Fig. 5 shows the changes in BAP/dROM ratio before and after Yubi-MR irradiation for 9 subjects.
- the BAP value was not significantly changed before and after the Yubi-MR irradiation, while the dROM value was significantly reduced (at a critical rate of 5% or less) before and after the Yubi-MR irradiation.
- the Yubi-MR irradiation gives no significant change to the BAP value, but has an effect of decreasing the dROM value. It was considered that the effect was brought about by the reduction action based on the Yubi-MR.
- Fig. 6 shows the influence of the Yubi-MR for animal use on the BAP/dROM ratio for mice.
- the mice exhibited the BAP/dROM ratio ranging from 14 to 26, which was different from the BAP/dROM ratio ranging from 6 to 13 for the humans, however, it was recognized that the irradiation with the Yubi-MR for animal use caused an increase in BAP/dROM in the same manner as with the Yubi-MR irradiation onto the humans.
- the number of mice was as small as two, thus it is necessary to make a verification by increasing the number of mice.
- mice irradiated for 1 min. to 30 min. with the Yubi-MR for animal use was compared with that of the mice irradiated with the dummy apparatus.
- Table 3 shows the suppression of the mouse motor activity by the irradiation with the Yubi-MR for animal use and that with the dummy apparatus;
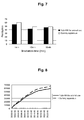
- Fig. 7 shows the relationship between the time period of irradiation and the motor activity for the Yubi-MR for animal use and the dummy apparatus;
- Fig. 8 shows the comparison of the integrated value of the mouse motor activity on the irradiation with the Yubi-MR for animal use with that with the magnet.
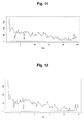
- mice with which the time period of motor activity interruption was extended on the irradiation with the Yubi-MR for animal use tend to restore the motor activity thereof with the irradiation being changed over to that with the magnet.
- Fig. 10 shows the recovery from the reduction in motor activity on the irradiation with the Yubi-MR for animal use.
- the ordinate denotes the motor activity (points) per one mouse, while the abscissa denotes the time period.
- the Yubi-MR has the ability to irradiate a special electromagnetic wave that is possessed by the Yubi-MR for animal use.
- the value of the ability has already been extremely highly appreciated, providing the advantages of removing the ferrous ion from the service water and preventing corrosion.
- the principle might be based on that the electromagnetic wave radiated from the black body acts on the water molecules, ionizing them on the NMR effect.
- Such a powerful effect can be expected to give electrons not only to the ferrous ions in the water, but also to the oxidized substances in the living body for making reduction.
- the present researchers took notice of it, and observed the influence of the Yubi-MR on the oxidative stress in the blood.
- the Yubi-MR is a novel apparatus which utilizes a physical phenomenon, and is capable of reducing the oxidative stress in the living body.
- This apparatus is based on the fact that use of the electromagnetic wave (a special wave) can reduce the oxidative stress.
- the present inventors observed the influence of doing the same on the motor activity of animals. In conducting this experiment, it is necessary to take the influence of the magnet into account. This is because, in order to amplify and filter the wave radiated from the black body, the wiggler magnet is used. It has been reported that the living beings are influenced by the magnetic field, thus the inventors tried to eliminate the influence of the magnetic field as much as possible.
- the following problems were posed: (1) examination of the proper period of time for irradiation, (2) examination of the proper irradiation site of the animal body, and (3) setting the proper time of day when the experiment is to be started.
- a dummy apparatus the magnetic flux density of which is tuned with that of the Yubi-MR for animal use was used as a control for examining the effect of the Yubi-MR for animal use.
- the irradiation for one minute with the Yubi-MR for animal use obviously suppressed the mouse motor activity, compared to that with the dummy apparatus.
- Such effect of the irradiation with the Yubi-MR for animal use was temporary, and when the irradiation was interrupted, the motor activity was increased.
- the effect of the Yubi-MR for animal use was not so great as to change the motor activity rhythm of the living beings.
- the living creatures have evolved over three billion and six hundred thousand years, having obtained energy by oxidizing the substance with the use of oxygen. With the earth having been changed from that with no oxygen to that with oxygen, organisms capable of utilizing an enormous amount of energy were born. The current number of living beings on the earth relates the benefit of oxygen.
- the oxidative stress can be accumulated in the body, causing senescence, accelerating arterioscelerosis, increasing the incidence of cancer, and hastening death. Therefore, it is natural to consider that, if the oxidative stress can be reduced even in some degree, it would provide a survival benefit for the living beings.
- the present inventors are convinced that the Yubi-MR proposed herein is a biologically significant apparatus which provides the living beings with the reducing power to inhibit the oxidization of the blood.
- the safety of the Yubi-MR is enhanced, a more potent biological effect is exhibited, the research and development are advanced so as for the Yubi-MR to be popularized on the market.
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Radiology & Medical Imaging (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Magnetic Treatment Devices (AREA)
- External Artificial Organs (AREA)
- Electrotherapy Devices (AREA)
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010134233A JP2011255094A (ja) | 2010-06-11 | 2010-06-11 | 血液酸化抑制器具 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP2394699A2 true EP2394699A2 (de) | 2011-12-14 |
| EP2394699A3 EP2394699A3 (de) | 2012-09-12 |
Family
ID=44118057
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP20110168210 Withdrawn EP2394699A3 (de) | 2010-06-11 | 2011-05-31 | Vorrichtung zur Vermeidung der Blutoxidation |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20110307022A1 (de) |
| EP (1) | EP2394699A3 (de) |
| JP (1) | JP2011255094A (de) |
| CN (1) | CN102274587A (de) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20130296440A1 (en) * | 2012-05-01 | 2013-11-07 | ChromaDex Inc. | Pterostilbene and curcumin combination for treatment of oxidative stress and inflammation |
Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006068621A (ja) | 2004-09-01 | 2006-03-16 | Nippon System Kikaku Kk | 流体活性化装置 |
Family Cites Families (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4367143A (en) * | 1981-06-03 | 1983-01-04 | Aqua Magnetics, Inc. | Apparatus for magnetically treating liquid flowing through a pipe and clamping means therefor |
| JPH02131186A (ja) * | 1988-11-10 | 1990-05-18 | Fuji Keiki:Kk | 簡易型水処理装置 |
| US5024759A (en) * | 1988-12-21 | 1991-06-18 | Hydroquip Technologies, Inc. | Magnetic treatment of fluids |
| US5131904A (en) * | 1990-05-04 | 1992-07-21 | Richard Markoll | Treatment of arthritis with magnetic field therapy and apparatus therefor |
| US5078870A (en) * | 1990-08-17 | 1992-01-07 | Carpenter Roland K | Unpotted apparatus for magnetically treating liquids flowing through relatively large pipes and the manner of attaching same to the exterior of such pipes |
| US5129382A (en) * | 1990-09-12 | 1992-07-14 | Eagle Research And Development, Inc. | Combustion efficiency improvement device |
| US6231759B1 (en) * | 1996-12-24 | 2001-05-15 | Takashi Sato | Water treatment device |
| US5989178A (en) * | 1997-04-02 | 1999-11-23 | Chiu; Alexander Y. C. | Magnetic ring |
| US6707362B1 (en) * | 2002-11-22 | 2004-03-16 | Az Industries, Inc. | Method and apparatus for focusing a magnetic field to treat liquids |
| JP2005081037A (ja) * | 2003-09-11 | 2005-03-31 | Kunihiro Kishida | 磁気発生装置 |
| US7104948B2 (en) * | 2003-10-06 | 2006-09-12 | Create Co., Ltd. | Bracelet that radiates anion and far infrared rays |
| US7229561B1 (en) * | 2004-02-27 | 2007-06-12 | Hiroyoshi Hamanaka | Method of in-pipe activation of running water and in-pipe activator for running water as well as method of maintaining body temperature by way of promoting blood flow |
-
2010
- 2010-06-11 JP JP2010134233A patent/JP2011255094A/ja active Pending
-
2011
- 2011-05-31 EP EP20110168210 patent/EP2394699A3/de not_active Withdrawn
- 2011-06-09 CN CN201110152829XA patent/CN102274587A/zh active Pending
- 2011-06-10 US US13/157,674 patent/US20110307022A1/en not_active Abandoned
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006068621A (ja) | 2004-09-01 | 2006-03-16 | Nippon System Kikaku Kk | 流体活性化装置 |
| JP3952477B2 (ja) | 2004-09-01 | 2007-08-01 | 日本システム企画株式会社 | 流体活性化装置 |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| NAOMASA YAMAMOTO, NORIFUMI YONEHARA, YUUICHI KOIKE, EFFECT OF YUBI-MR FOR ANIMAL USE ON MOTOR ACTIVITY OF MOUSEEXPERIMENTERS, 26 May 2009 (2009-05-26) |
| NAOMASA YAMAMOTO, YUUICHI KOIKE, EXPERIMENT USING BLOOD OF HUMAN EXPERIMENTERS, 10 November 2009 (2009-11-10) |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN102274587A (zh) | 2011-12-14 |
| EP2394699A3 (de) | 2012-09-12 |
| US20110307022A1 (en) | 2011-12-15 |
| JP2011255094A (ja) | 2011-12-22 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Wilson et al. | Ultra-high dose rate (FLASH) radiotherapy: Silver bullet or fool's gold? | |
| Sørensen et al. | Relative biological effectiveness (RBE) and distal edge effects of proton radiation on early damage in vivo | |
| Marcu et al. | Translational research in FLASH radiotherapy—from radiobiological mechanisms to in vivo results | |
| Pollycove | Radiobiological basis of low-dose irradiation in prevention and therapy of cancer | |
| Decauchy et al. | Cold plasma endoscopy applied to biliary ducts: feasibility risk assessment on human-like and porcine models for the treatment of cholangiocarcinoma | |
| Bell et al. | Whole abdominal pencil beam scanned proton FLASH increases acute lethality | |
| Fowler et al. | VIII General review | |
| Xin et al. | Transdermal delivery of topical lidocaine in a mouse model is enhanced by treatment with cold atmospheric plasma | |
| EP2394699A2 (de) | Vorrichtung zur Vermeidung der Blutoxidation | |
| Yao et al. | Feasibility study of range verification based on proton-induced acoustic signals and recurrent neural network | |
| Clements et al. | Monte Carlo optimization of a GRID collimator for preclinical megavoltage ultra-high dose rate spatially-fractionated radiation therapy | |
| Ware et al. | Effects of proton radiation dose, dose rate and dose fractionation on hematopoietic cells in mice | |
| WO2021261443A1 (ja) | 放射線治療装置の線量評価アルゴリズム | |
| Leith et al. | Comparison of skin responses of mice after single or fractionated exposure to cyclotron-accelerated helium ions and 230 kV X-irradiation | |
| Anikina et al. | An Experimental Model of Proton-Beam-Induced Radiation Dermatitis In Vivo | |
| Masunaga et al. | Radiobiologic significance of response of intratumor quiescent cells in vivo to accelerated carbon ion beams compared with γ-rays and reactor neutron beams | |
| Bewley | The 8 MeV linear accelerator at the MRC Cyclotron Unit Hammersmith Hospital, London | |
| Feder | High radiation dose rates may improve cancer therapy | |
| Giovannini et al. | In vivo radiobiological investigations with the TOP-IMPLART proton beam on a medulloblastoma mouse model | |
| Zhao et al. | Key Magnetized Exosomes for Effective Targeted Delivery of Doxorubicin Against Breast Cancer Cell Types in Mice Model | |
| Shahbazi-Gahrouei et al. | The correlation between high background radiation and blood level of the trace elements (copper, zinc, iron and magnesium) in workers of Mahallat's hot springs | |
| Hartel et al. | Chromosome Aberrations in Lymphocytes of Prostate Cancer Patients Treated with IMRT and Carbon Ions | |
| NOVALDI et al. | PEMANFAATAN MEDAN ELEKTROMAGNETIK DALAM TEKNOLOGI PENGOBATAN MODERN | |
| Gadhban et al. | Effects of in-vivo application of cold atmospheric plasma on the leukocyte of balb/c mice | |
| Lawson | The Effect of Electrical Stimulation on Blood Flow in Chronic Wounds in Patients with and without Diabetes |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: BA ME |
|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: BA ME |
|
| RIC1 | Information provided on ipc code assigned before grant |
Ipc: A61N 1/40 20060101ALI20120806BHEP Ipc: A61N 2/08 20060101AFI20120806BHEP Ipc: A61N 5/06 20060101ALI20120806BHEP |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE APPLICATION IS DEEMED TO BE WITHDRAWN |
|
| 18D | Application deemed to be withdrawn |
Effective date: 20130313 |