EP1818261A1 - Apparatus for covering groups of products with tubular stretch film - Google Patents
Apparatus for covering groups of products with tubular stretch film Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP1818261A1 EP1818261A1 EP07101899A EP07101899A EP1818261A1 EP 1818261 A1 EP1818261 A1 EP 1818261A1 EP 07101899 A EP07101899 A EP 07101899A EP 07101899 A EP07101899 A EP 07101899A EP 1818261 A1 EP1818261 A1 EP 1818261A1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- film
- belt
- section
- roller
- arm
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 229920006302 stretch film Polymers 0.000 title claims description 14
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000004566 building material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 235000013305 food Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000009828 non-uniform distribution Methods 0.000 description 1
- FIKAKWIAUPDISJ-UHFFFAOYSA-L paraquat dichloride Chemical compound [Cl-].[Cl-].C1=C[N+](C)=CC=C1C1=CC=[N+](C)C=C1 FIKAKWIAUPDISJ-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 230000003578 releasing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011144 upstream manufacturing Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65B—MACHINES, APPARATUS OR DEVICES FOR, OR METHODS OF, PACKAGING ARTICLES OR MATERIALS; UNPACKING
- B65B9/00—Enclosing successive articles, or quantities of material, e.g. liquids or semiliquids, in flat, folded, or tubular webs of flexible sheet material; Subdividing filled flexible tubes to form packages
- B65B9/10—Enclosing successive articles, or quantities of material, in preformed tubular webs, or in webs formed into tubes around filling nozzles, e.g. extruded tubular webs
- B65B9/13—Enclosing successive articles, or quantities of material, in preformed tubular webs, or in webs formed into tubes around filling nozzles, e.g. extruded tubular webs the preformed tubular webs being supplied in a flattened state
- B65B9/135—Enclosing successive articles, or quantities of material, in preformed tubular webs, or in webs formed into tubes around filling nozzles, e.g. extruded tubular webs the preformed tubular webs being supplied in a flattened state for palletised loads
Definitions
- This invention relates to apparatus for covering groups of products with tubular stretch film.
- hood stretch machines which cover the products with a “hood”, that is to say, a tubular length of film, preferably, but not necessarily, closed at the top end to form a sleeve-like covering that is stretched over the stacked products and allowed to return to its original size, thanks to the elastic properties of the film, in such a way as to tightly hold the products together.
- This type of covering is used, for example, to protect stacked products comprising sacks of loose building material or foods, or to wrap domestic appliances, and is applied by machinery typically consisting of:
- the stretching unit is also equipped with drive means that move the unit down along the frame in such a way as to draw the film over the products, allowing it to gradually release the concertina folds until the film reaches the base of the products at the pallet.
- the film is released completely so that it covers all the products and, if necessary, also the pallet.
- the stretching unit usually consists of four substantially L-shaped arms positioned diagonally on the frame in such a way as to enable the related vertical portion to keep the corner of the film mouth open.
- each arm may comprise:
- the concertina folding means are applied directly to each arm (see patents US 3,902,303 and FR 2.234.509 ).
- This unit normally consists of a power-driven wheel or similar revolving component which, when the film reaches the vertical portion of the arm, is brought into contact with the film and gathers the latter up in concertina fashion. After making the concertina folds, the wheel may be moved away from the film or it may continue to be used to guide the film downwardly along the sides of the product group.
- the frame mounts power-driven rollers for concertina folding the film by pushing it against the second arms or into contact with an idle roller connected to the second arms.
- the Applicant has designed and constructed an apparatus for covering groups of products with tubular stretch film equipped with an extremely functional concertina folding unit capable of overcoming the above mentioned drawback while maintaining a high level of operating flexibility and without encumbering the constructional architecture of the apparatus.
- This invention accordingly provides an apparatus for covering groups of products with tubular stretch film, in particular, an apparatus for covering groups of products with tubular stretch film comprising the technical characteristics defined in one or more of the annexed claims.
- product group 1 will be used, without thereby limiting the scope of the inventive concept, to denote any entity consisting of a single product or two or more stacked products to be wrapped and sealed by the tubular stretch film 2.
- the apparatus is used for palletized product groups 1 of known type and only partly illustrated in schematic form in Figure 3.
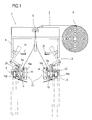
- the apparatus 3 is of the type essentially comprising the following elements of particular relevance to this specification: a frame 4, a roll 5 of stretch film 2, means 8 for gripping and opening the film 2, a unit 9 for stretching the film 2 and means 13 for concertina folding or gathering up the film 2 on the stretching unit 9.
- the frame 4 is usually of the portal type enabling the product group 1 to be positioned inside it.
- the roll 5 of stretch film 2 is mounted outside the frame 4, is provided with film 2 having a tubular cross section with pleated sides (the pleating is not illustrated in the drawings since it is of well known type) to form an initially flattened configuration, and is controlled by film 2 feed means 6 located at the top of the frame 4 itself.
- the gripping and opening means 8 are located inside the frame 4 and usually comprise four clamping gripper units 8a (shown in particular in Figures 1 and 3) acting on the mouth of the film 2 to at least give the mouth a quadrangular cross section.
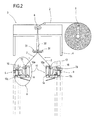
- the above mentioned unit 9 for stretching the film 2 receives the latter from the gripping means 8 in the spread open configuration and then stretches it to a size larger than the perimeter of the product group 1 (see Figure 2).
- the unit 9 comprises a plurality of arms 10 - usually four, arranged in twos, one at each corner formed by two longitudinal walls of the product group 1.
- Each arm 10 comprises a first vertical section 10a for receiving the film 2 on its surface 10b, and a second section 10c by which the arm 10 itself is linked to the frame 4.
- Each arm 10 further comprises horizontal translational drive means 11 and vertical drive means 12 for respectively stretching the film 2 and moving the arms 10 down along the frame 4 in such a way as to cover the product group 1 (see arrows F11 and F12 in Figure 3).
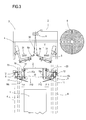
- the above mentioned means 13 for folding the film 2 in concertina fashion gather up a quantity of film 2 sufficient to cover the product group 1 (see Figures 2, 3 and 4); the means 13 are mounted on each arm 10 and act on the film 2 before it is stretched.
- the concertina folding means 13 comprise a power-driven concertina folding belt 14 and an idle roller 16.
- the power-driven belt 14 for folding the film 2 in concertina fashion is associated with each arm 10 and positioned in the area at the back of the above mentioned film 2 contact surface 10b of the vertical arm section 10a.
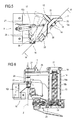
- At least one section 14a of the belt 14 is located at a partial opening 15 in the surface 10b to form a part thereof and in such a way as to engage and feed the film 2 towards the bottom of the contact surface 10b (as indicated by the arrow F14) in combination with the idle roller 16.
- the above mentioned idle roller 16 is positioned to face the contact surface 10b of each arm 10 and is moved by respective drive means 17 between a retracted, idle position, where the roller 16 is away from the section 14a of the belt 14 (as shown by the dashed line in Figure 5), and an advanced, working position, where the roller 16 is in contact with the film 2 interposed between the roller 16 itself and the section 14a of the belt 14 (see Figure 4 and continuous line in Figure 5).
- Figure 4 also shows that the belt 14 is of the endless type and is looped around two wheels 18 and 19, of which at least one, the one labelled 19, is power driven in order to drive the belt in direction F19.
- the part of the belt 14 portion constituting the section 14a for engaging and feeding the film 2 has a predetermined active working height H such that the film 2 is moved towards the contact surface 10b even under the area where it is interposed between the belt and the idle roller 16: in practice, the film 2, which is "flung" from the point of contact between the belt 14 and the roller 16, and as it proceeds, remains in contact with the belt 14, at least partially and then comes into contact with the surface 10b of the vertical section 10 where it is gathered up uniformly.
- At least the active portion of the belt 14 that feeds the film 2 extends, preferably but without restricting the scope of the invention, at an angle to the contact surface 10b.
- the entire belt 14 can be inclined to the contact surface 10b at a divergent angle ⁇ , extending from the top end to the bottom end, so that the film 2 feed section 14a of the belt 14 can project partially from the opening 15.
- the belt 14 section 14a and the roller 16 are in tangential contact with each other, that is to say, they touch at a single point.
- each arm 10 may have an arc-shaped cross section defined by three parts 20, 21, 22 joined to each other without interruption.
- the belt 14 is positioned behind the central part 21 where the partial opening 15 is made.
- the belt 14 may be powered by a drive unit 23 mounted on the arm 10 and kinematically linked through a respective shaft 24 to the bottom wheel 19 of the belt 14.
- each idle roller 16 is rotatably linked to one end of a horizontal rod 25 pivoted at the opposite end to a pin 26 that rotates about a vertical axis Z linked to each joining section 10c of the arm 10.
- Each rod 25 is acted upon by an actuator 27 (constituting the above mentioned drive means 17), located on the joining section 10c and designed to impart to the rod 25 a rotational movement in a horizontal plane between the retracted, idle position and the advanced, working position of the roller 16.
- An apparatus structured in this way therefore, achieves the above mentioned aims thanks to the presence of the belt behind the surface for gathering up the film on each arm.
- the belt Thanks to its position and cooperation with the idle roller at the front, the belt starts gathering up or concertina folding the film on its moving surface at a predetermined rate and then releases it on the unmoving surface of the arm, allowing the concertina folding action to be completed by the force of the remaining film pushing down as the belt feeds it.
- This structure permits better distribution of the concertina folds along the stretching arm, making them more compact and uniform so that the film can subsequently be drawn over the group of products and released in a precisely balanced way.
- the belt does not touch the film because while the film is being drawn over the walls of the product group, the tension created by stretching the film tends to keep the film path clear of the projecting part of the belt, while the roller is in the retracted position.
- the size and position of the belt do not alter the overall dimensions and configurations of the arms during their different operating movements.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Lining Or Joining Of Plastics Or The Like (AREA)
- Wrappers (AREA)
- Making Paper Articles (AREA)
- Shaping Of Tube Ends By Bending Or Straightening (AREA)
- Shaping By String And By Release Of Stress In Plastics And The Like (AREA)
- Basic Packing Technique (AREA)
- Laminated Bodies (AREA)
Abstract
Description
- This invention relates to apparatus for covering groups of products with tubular stretch film.
- Prior technology for wrapping groups of products, including palletised loads, teaches the use of machinery, known in the trade as "hood stretch machines" which cover the products with a "hood", that is to say, a tubular length of film, preferably, but not necessarily, closed at the top end to form a sleeve-like covering that is stretched over the stacked products and allowed to return to its original size, thanks to the elastic properties of the film, in such a way as to tightly hold the products together.
- This type of covering is used, for example, to protect stacked products comprising sacks of loose building material or foods, or to wrap domestic appliances, and is applied by machinery typically consisting of:
- a main portal frame structure inside which the group of products (usually palletised) is placed and which mounts a plurality of units for handling and forming the stretch film;
- a roll of tubular stretch film whose longitudinal edges are pleated to form an initially flat configuration, said roll being positioned on the side of the frame and being controlled by film feed means located at the top of the frame itself;
- a unit, located in the vicinity of the top end of the frame, for spreading open the flattened film tube;
- a unit for opening the mouth of the film to at least form a cross section corresponding to the cross section, usually quadrangular, of the group of products located under the spreading unit;
- a film stretching unit to which the film is fed in the spread open configuration and which is designed to stretch the film to a size larger than the perimeter of the palletised group of products;
- means for "pleating" or folding the film in concertina fashion in such a way as to gather up enough film to cover the palletised group of products in height; these means acting by pressure against the stretching unit, usually before the film is stretched;
- a unit, operating at the top end of the frame, for sealing and separating the film portion to be used from the rest of the film in such a way as to form a sleeve-like cover and usually also equipped with means for joining the top end of the sleeve (for example by sealing).
- The stretching unit is also equipped with drive means that move the unit down along the frame in such a way as to draw the film over the products, allowing it to gradually release the concertina folds until the film reaches the base of the products at the pallet. Here the film is released completely so that it covers all the products and, if necessary, also the pallet.
- Over time, many parts of this general machine structure have developed according to different constructional philosophies.
- Described below is the unit relevant to this specification in particular.
- More specifically, the stretching unit usually consists of four substantially L-shaped arms positioned diagonally on the frame in such a way as to enable the related vertical portion to keep the corner of the film mouth open.
- The horizontal portion of each arm may comprise:
- translational drive means for stretching the film by pulling it in a horizontal direction; and
- the aforementioned vertical drive means for movement along the frame, usually associated with the free end of the arm.
- In some prior art arrangements, the concertina folding means are applied directly to each arm (see patents
US 3,902,303 andFR 2.234.509 - In yet another solution (see patents
DE 3918311 and -
DE 3908957 ), independent power-driven rollers mounted on arms articulated to the frame are used. The arms move the rollers against the vertical portion of the arms in such a way as to make the concertina folds. - Yet another, different arrangement is disclosed in patent applications
EP 1.276.668 andEP 1.353.847 where the concertina folds are made on a specially designed frame placed over, and independent of, the stretching arms and consisting of respective second arms for retaining the film after it has been opened out but before being stretched. - The frame mounts power-driven rollers for concertina folding the film by pushing it against the second arms or into contact with an idle roller connected to the second arms.
- All these solutions are based on the use of power-driven devices with a drive roller or wheel located preferably in front of the stretching arm surface, which may be equipped with one or more idle wheels. Concertina folding units structured in this way may lead to non-uniform distribution of the film gathered up along the surface of the arm: this may in turn lead to overlapping of the film during subsequent stretching, causing parts of the film to stiffen as it is drawn over the group of products.
- This stiffening results in the film tearing or in any case not covering the product groups properly.
- In view of the above, the Applicant has designed and constructed an apparatus for covering groups of products with tubular stretch film equipped with an extremely functional concertina folding unit capable of overcoming the above mentioned drawback while maintaining a high level of operating flexibility and without encumbering the constructional architecture of the apparatus.
- This invention accordingly provides an apparatus for covering groups of products with tubular stretch film, in particular, an apparatus for covering groups of products with tubular stretch film comprising the technical characteristics defined in one or more of the annexed claims.
- The technical characteristics of the invention, with reference to the above aims, are clearly described in the claims below and its advantages are apparent from the detailed description which follows, with reference to the accompanying drawings which illustrate a preferred embodiment of the invention provided merely by way of example without restricting the scope of the inventive concept, and in which:
- Figures 1 to 3 are schematic front views, with some parts cut away in order to better illustrate others, showing an apparatus according to the present invention for covering groups of products with tubular stretch film in different operating configurations;
- Figure 4 is a schematic side view, with some parts others cut away in order to better illustrate others, of a detail A from Figure 2, namely, a stretching arm;
- Figure 5 is a top plan view of the stretching arm of Figure 4;
- Figure 6 is a cross-section through line VI - VI of Figure 5.
- With reference to the accompanying drawings, in particular Figures 1 to 3, the apparatus according to the invention, labelled 3 in its entirety, is used to cover with
tubular stretch film 2 one or more products formingproduct groups 1. - Hereinafter, the
term product group 1 will be used, without thereby limiting the scope of the inventive concept, to denote any entity consisting of a single product or two or more stacked products to be wrapped and sealed by thetubular stretch film 2. - In particular, but without restricting the scope of the invention, the apparatus is used for palletized
product groups 1 of known type and only partly illustrated in schematic form in Figure 3. - The
apparatus 3 according to the invention is of the type essentially comprising the following elements of particular relevance to this specification: aframe 4, aroll 5 ofstretch film 2, means 8 for gripping and opening thefilm 2, aunit 9 for stretching thefilm 2 and means 13 for concertina folding or gathering up thefilm 2 on thestretching unit 9. - The
frame 4 is usually of the portal type enabling theproduct group 1 to be positioned inside it. - The
roll 5 ofstretch film 2 is mounted outside theframe 4, is provided withfilm 2 having a tubular cross section with pleated sides (the pleating is not illustrated in the drawings since it is of well known type) to form an initially flattened configuration, and is controlled byfilm 2 feed means 6 located at the top of theframe 4 itself. - The gripping and
opening means 8 are located inside theframe 4 and usually comprise fourclamping gripper units 8a (shown in particular in Figures 1 and 3) acting on the mouth of thefilm 2 to at least give the mouth a quadrangular cross section. - The above mentioned
unit 9 for stretching thefilm 2 receives the latter from the gripping means 8 in the spread open configuration and then stretches it to a size larger than the perimeter of the product group 1 (see Figure 2). - To do this, the
unit 9 comprises a plurality of arms 10 - usually four, arranged in twos, one at each corner formed by two longitudinal walls of theproduct group 1. - Each
arm 10 comprises a firstvertical section 10a for receiving thefilm 2 on itssurface 10b, and asecond section 10c by which thearm 10 itself is linked to theframe 4. - Each
arm 10 further comprises horizontal translational drive means 11 and vertical drive means 12 for respectively stretching thefilm 2 and moving thearms 10 down along theframe 4 in such a way as to cover the product group 1 (see arrows F11 and F12 in Figure 3). - The above mentioned means 13 for folding the
film 2 in concertina fashion gather up a quantity offilm 2 sufficient to cover the product group 1 (see Figures 2, 3 and 4); themeans 13 are mounted on eacharm 10 and act on thefilm 2 before it is stretched. - The drawings of the preferred embodiment also partly illustrate the following:
- a
unit 30, located near the top end of the frame 4 (upstream of the gripping means 8), for spreading open the pleated sides of thefilm 2 fed in a vertical direction V; and - a
unit 31 for sealing the top of the unwound portion offilm 2, to form a sleeve-like cover, when necessary, and separating it from the rest of thefilm 2; theunit 31 being located at the top end of theframe 4. - As shown in Figure 4, the concertina folding means 13 comprise a power-driven
concertina folding belt 14 and anidle roller 16. - Looking in more detail, the power-driven
belt 14 for folding thefilm 2 in concertina fashion is associated with eacharm 10 and positioned in the area at the back of the above mentionedfilm 2contact surface 10b of thevertical arm section 10a. - At least one
section 14a of thebelt 14 is located at apartial opening 15 in thesurface 10b to form a part thereof and in such a way as to engage and feed thefilm 2 towards the bottom of thecontact surface 10b (as indicated by the arrow F14) in combination with theidle roller 16. - The above mentioned
idle roller 16 is positioned to face thecontact surface 10b of eacharm 10 and is moved by respective drive means 17 between a retracted, idle position, where theroller 16 is away from thesection 14a of the belt 14 (as shown by the dashed line in Figure 5), and an advanced, working position, where theroller 16 is in contact with thefilm 2 interposed between theroller 16 itself and thesection 14a of the belt 14 (see Figure 4 and continuous line in Figure 5). - Figure 4 also shows that the
belt 14 is of the endless type and is looped around twowheels - On the loop defined by the
belt 14, a part of thebelt 14 portion extending at the top of thebelt 14 itself constitutes thesection 14a for engaging and feeding thefilm 2. - More specifically, the part of the
belt 14 portion constituting thesection 14a for engaging and feeding thefilm 2 has a predetermined active working height H such that thefilm 2 is moved towards thecontact surface 10b even under the area where it is interposed between the belt and the idle roller 16: in practice, thefilm 2, which is "flung" from the point of contact between thebelt 14 and theroller 16, and as it proceeds, remains in contact with thebelt 14, at least partially and then comes into contact with thesurface 10b of thevertical section 10 where it is gathered up uniformly. - Again with reference to Figure 4, at least the active portion of the
belt 14 that feeds thefilm 2 extends, preferably but without restricting the scope of the invention, at an angle to thecontact surface 10b. - More precisely, the
entire belt 14 can be inclined to thecontact surface 10b at a divergent angle α, extending from the top end to the bottom end, so that thefilm 2feed section 14a of thebelt 14 can project partially from theopening 15. - As mentioned above, when the
roller 16 is in the advanced, working position, thebelt 14section 14a and theroller 16 are in tangential contact with each other, that is to say, they touch at a single point. - That is because the part of the
belt 14section 14a that comes into contact with theroller 16 is the part at thetop wheel 18 of thebelt 14. - At a constructional level (see Figure 5 in particular) the
vertical section 10a of eacharm 10 may have an arc-shaped cross section defined by threeparts - In this situation, the
belt 14 is positioned behind thecentral part 21 where thepartial opening 15 is made. - As shown in Figure 6, the
belt 14 may be powered by adrive unit 23 mounted on thearm 10 and kinematically linked through arespective shaft 24 to thebottom wheel 19 of thebelt 14. - As shown in Figures 5 and 6, each
idle roller 16 is rotatably linked to one end of ahorizontal rod 25 pivoted at the opposite end to apin 26 that rotates about a vertical axis Z linked to each joiningsection 10c of thearm 10. - Each
rod 25 is acted upon by an actuator 27 (constituting the above mentioned drive means 17), located on the joiningsection 10c and designed to impart to the rod 25 a rotational movement in a horizontal plane between the retracted, idle position and the advanced, working position of theroller 16. - An apparatus structured in this way, therefore, achieves the above mentioned aims thanks to the presence of the belt behind the surface for gathering up the film on each arm.
- Thanks to its position and cooperation with the idle roller at the front, the belt starts gathering up or concertina folding the film on its moving surface at a predetermined rate and then releases it on the unmoving surface of the arm, allowing the concertina folding action to be completed by the force of the remaining film pushing down as the belt feeds it.
- This structure permits better distribution of the concertina folds along the stretching arm, making them more compact and uniform so that the film can subsequently be drawn over the group of products and released in a precisely balanced way.
- Obviously, during the releasing action, the belt does not touch the film because while the film is being drawn over the walls of the product group, the tension created by stretching the film tends to keep the film path clear of the projecting part of the belt, while the roller is in the retracted position.
- Moreover, it should also be noticed that the size and position of the belt do not alter the overall dimensions and configurations of the arms during their different operating movements.
- The invention described has evident industrial applications and may be modified and adapted in several ways without thereby departing from the scope of the inventive concept. Moreover, all the details of the invention may be substituted by technically equivalent elements.
Claims (11)
- An apparatus for covering one or more products forming a product group (1) with tubular stretch film (2), the apparatus (3) being of the type comprising at least:- a roll (5) of tubular stretch film (2) with pleated sides, controlled by film (2) feed means (6) located at the top end of a frame (4);- means (8) for gripping and opening the mouth of the film (2) to at least give the cross section of the mouth a polygonal shape; said gripping means comprising a plurality of gripper elements for each corner of the film;- a film (2) stretching unit (9) which receives the film (2) from the gripping means (8) in the spread open configuration and stretches it to a size larger than the perimeter of the product group (1); the unit (9) comprising a plurality of arms (10) each consisting of a first vertical section (10a) for receiving the film (2) on its surface (10b), and a second section (10c) for linking the arms (10) to the frame (4); each arm (10) being acted upon by horizontal translational drive means (11) and vertical drive means (12) which, respectively, stretch the film (2) and move it downwards along the frame (4) in such a way as to cover the product group (1);- means (13) for "pleating" or folding the film (2) in concertina fashion in such a way as to gather up a quantity of film (2) at least sufficient to cover the product group (1) along its perimetric sides, said means (13) being mounted on each arm (10) and acting on the film (2) before it is stretched, the apparatus (3) being characterised in that the concertina folding means (13) comprise at least:- a power-driven belt (14) for concertina folding the film (2), associated with each arm (10) and positioned in the area at the back of a film (2) contact surface (10b) of the vertical section (10a); at least one section (14a) of the belt (14) being located at a partial opening (15) in the surface (10b) to form a part thereof, in such a way as to engage and feed the film (2) towards the bottom of the contact surface (10b) in combination with- an idle roller (16), positioned to face the contact surface (10b), associated with each arm (10) and driven by respective means (17) between a retracted, idle position, where the roller (16) is away from the section (14a) of the belt (14), and an advanced, working position, where the roller (16) is in contact with the film (2) interposed between the roller (16) itself and the section (14a) of the belt (14).
- The apparatus according to claim 1, characterised in that the belt (14) is of the endless type and is looped around two wheels (18, 19), of which at least the wheel (19) is power driven.
- The apparatus according to claim 1, characterised in that the belt (14) is of the endless type and is looped around two wheels (18, 19), of which at least the wheel (19) is power driven; a part of the belt (14) portion extending at the top of the belt (14) itself constituting the section (14a) for engaging and feeding the film (2).
- The apparatus according to claim 3, characterised in that the part of the belt (14) portion constituting the section (14a) for engaging and feeding the film (2) has a predetermined active working height (H) such that the film (2) is moved towards the contact surface (10b) even under the area where it is interposed between the belt and the idle roller (16).
- The apparatus according to claims 1 to 4, characterised in that at least the active portion of the belt (14) that feeds the film (2) extends at an angle to the contact surface (10b).
- The apparatus according to claims 1 to 4, characterised in that the belt (14) is inclined to the contact surface (10b) at a divergent angle (α), extending from the top end to the bottom end, so that the section (14a) of the film (2) feed belt (14) projects partially from the opening (15).
- The apparatus according to claim 1, characterised in that at the advanced, working position of the roller (16), the belt (14) section (14a) and the roller (16) are in tangential contact with each other, that is to say, they touch at a single point.
- The apparatus according to claims 1 to 4, characterised in that, at the advanced working position, the roller (16) is in tangential contact with, that is to say, touches at a single point, the belt (14) section (14a) located at the upper wheel (18) of the belt (14).
- The apparatus according to claim 1, where the vertical section (10a) of each arm (10) has an arc-shaped cross section defined by three parts (20, 21, 22) joined to each other without interruption, the apparatus being characterised in that the belt (14) is positioned behind the central part (21) where the partial opening (15) is made.
- The apparatus according to claims 1 to 4, characterised in that the belt (14) is powered by a drive unit (23) mounted on the arm (10) and kinematically linked through a respective shaft (24) to the bottom wheel (19) of the belt (14).
- The apparatus according to claim 1, characterised in that each idle roller (16) is rotatably linked to one end of a horizontal rod (25) pivoted at the opposite end to a pin (26) that rotates about a vertical axis (Z) linked to each joining section (10c) of the arm (10); each rod (25) being acted upon by an actuator (27) located on the joining section (10c) and designed to impart to the rod (25) a rotational movement in a horizontal plane between the retracted, idle position and the advanced, working position of the roller (16).
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| IT000096A ITBO20060096A1 (en) | 2006-02-10 | 2006-02-10 | EQUIPMENT FOR COVERING GROUPS OF PRODUCTS WITH EXTENSIBLE TUBULAR FILM |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP1818261A1 true EP1818261A1 (en) | 2007-08-15 |
| EP1818261B1 EP1818261B1 (en) | 2009-06-10 |
Family
ID=37946331
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP07101899A Not-in-force EP1818261B1 (en) | 2006-02-10 | 2007-02-07 | Apparatus for covering groups of products with tubular stretch film |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP1818261B1 (en) |
| AT (1) | ATE433414T1 (en) |
| DE (1) | DE602007001247D1 (en) |
| IT (1) | ITBO20060096A1 (en) |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2014049184A1 (en) * | 2012-09-28 | 2014-04-03 | Innova Maquinaria Cerámica, S.L. | Machine for wrapping palletised loads |
| ITMO20130096A1 (en) * | 2013-04-15 | 2014-10-16 | Bocedi S R L Off | PALLET PACKAGING MACHINE |
| WO2016070883A1 (en) * | 2014-11-04 | 2016-05-12 | Frank Bruhn Aps | Horizontally arranged wrap packaging system |
| CN106314889A (en) * | 2016-10-25 | 2017-01-11 | 安徽永锋智能包装科技有限公司 | Bag opening device for intelligent bagging equipment |
| NL2017863B1 (en) * | 2016-11-24 | 2018-06-01 | F3 Design B V | Packaging machine for applying a foil to an object to be packaged |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4063401A (en) * | 1974-09-24 | 1977-12-20 | Higgins David M | Bagging machine |
| DE9001321U1 (en) * | 1990-02-06 | 1990-04-12 | Develog, Reiner Hannen & Cie, Corgémont | Device for covering a stack of goods with stretch film covers |
| DE19732298C1 (en) * | 1997-07-26 | 1999-02-04 | Moellers Maschf Gmbh | Machine for covering stacked articles with film packaging |
| EP1266829A1 (en) * | 2001-06-13 | 2002-12-18 | Beumer Maschinenfabrik GmbH & Co. KG | Method and apparatus for wrapping articles, particularly stacks of articles, in a stretchfoil, as well as the load obtained |
| EP1580128A1 (en) * | 2004-03-26 | 2005-09-28 | AETNA GROUP S.p.A. | Apparatus for covering groups of products with tubular stretch film |
-
2006
- 2006-02-10 IT IT000096A patent/ITBO20060096A1/en unknown
-
2007
- 2007-02-07 EP EP07101899A patent/EP1818261B1/en not_active Not-in-force
- 2007-02-07 AT AT07101899T patent/ATE433414T1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2007-02-07 DE DE602007001247T patent/DE602007001247D1/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4063401A (en) * | 1974-09-24 | 1977-12-20 | Higgins David M | Bagging machine |
| DE9001321U1 (en) * | 1990-02-06 | 1990-04-12 | Develog, Reiner Hannen & Cie, Corgémont | Device for covering a stack of goods with stretch film covers |
| DE19732298C1 (en) * | 1997-07-26 | 1999-02-04 | Moellers Maschf Gmbh | Machine for covering stacked articles with film packaging |
| EP1266829A1 (en) * | 2001-06-13 | 2002-12-18 | Beumer Maschinenfabrik GmbH & Co. KG | Method and apparatus for wrapping articles, particularly stacks of articles, in a stretchfoil, as well as the load obtained |
| EP1580128A1 (en) * | 2004-03-26 | 2005-09-28 | AETNA GROUP S.p.A. | Apparatus for covering groups of products with tubular stretch film |
Cited By (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2014049184A1 (en) * | 2012-09-28 | 2014-04-03 | Innova Maquinaria Cerámica, S.L. | Machine for wrapping palletised loads |
| EP2902328A4 (en) * | 2012-09-28 | 2015-12-23 | Innova Maquinaria Cerámica S L | Machine for wrapping palletised loads |
| ITMO20130096A1 (en) * | 2013-04-15 | 2014-10-16 | Bocedi S R L Off | PALLET PACKAGING MACHINE |
| EP2792599A1 (en) * | 2013-04-15 | 2014-10-22 | Officina Bocedi S.R.L. | A machine for packaging pallets |
| WO2016070883A1 (en) * | 2014-11-04 | 2016-05-12 | Frank Bruhn Aps | Horizontally arranged wrap packaging system |
| US10800559B2 (en) | 2014-11-04 | 2020-10-13 | Frank Bruhn Aps | Horizontally arranged wrap packaging system |
| CN106314889A (en) * | 2016-10-25 | 2017-01-11 | 安徽永锋智能包装科技有限公司 | Bag opening device for intelligent bagging equipment |
| CN106314889B (en) * | 2016-10-25 | 2019-07-12 | 安徽永锋智能包装科技有限公司 | A kind of bag expanding device for intelligent bagging device |
| NL2017863B1 (en) * | 2016-11-24 | 2018-06-01 | F3 Design B V | Packaging machine for applying a foil to an object to be packaged |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| DE602007001247D1 (en) | 2009-07-23 |
| ITBO20060096A1 (en) | 2007-08-11 |
| ATE433414T1 (en) | 2009-06-15 |
| EP1818261B1 (en) | 2009-06-10 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US8875480B2 (en) | Method of pulling a film tube or hood down over a stack of objects | |
| EP1818261B1 (en) | Apparatus for covering groups of products with tubular stretch film | |
| US20070151211A1 (en) | Device and method for wrapping unit loads or packaged goods | |
| US20040107677A1 (en) | Device for wrapping a stack of goods | |
| JPS5940684B2 (en) | Roll packaging equipment | |
| CN207241005U (en) | Nonwoven fabrics package bag automatic knotting device for pilling | |
| DK178374B1 (en) | HORIZONTALLY ARRANGED WRAP PACKAGING SYSTEM | |
| CN107848642A (en) | Packing machine | |
| CN106144027B (en) | To chartered plane in folded film | |
| US6662535B2 (en) | Apparatus for bagging material | |
| AU613088B2 (en) | Film folding device, method, and product | |
| JPS596764B2 (en) | Automatic packaging method and equipment | |
| EP0020574A1 (en) | Sheet folder | |
| CN207256969U (en) | Nonwoven fabrics package bag automatic knotting device | |
| EP2204323A1 (en) | Wrapping machine | |
| EP1580127A1 (en) | Apparatus for covering groups of products with tubular stretch film | |
| EP1818260B1 (en) | Apparatus for covering groups of products with stretch film | |
| EP3424828B1 (en) | Wrapping system with extensible plastic film and relative improved retaining device, and method for wrapping an item | |
| US3471994A (en) | Wrapper dispenser | |
| JP2668321B2 (en) | Film opening end bending packaging equipment | |
| CN213677477U (en) | Film guide mechanism of full-automatic film sealing and cutting packaging machine | |
| EP1580128A1 (en) | Apparatus for covering groups of products with tubular stretch film | |
| JP3733603B2 (en) | Stretch wrapping machine | |
| GB1591884A (en) | Packaging machines | |
| JP2762961B2 (en) | Stretch film packaging machine |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: AL BA HR MK YU |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20080206 |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid |
Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 602007001247 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20090723 Kind code of ref document: P |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090610 Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090610 Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090610 |
|
| NLV1 | Nl: lapsed or annulled due to failure to fulfill the requirements of art. 29p and 29m of the patents act | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090910 Ref country code: PL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090610 Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090610 Ref country code: SI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090610 Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090610 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20091010 Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090610 Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090610 Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090610 Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090921 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090610 Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090610 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090910 Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20091010 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090610 |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20100311 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20100301 Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090911 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST Effective date: 20101029 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20100301 Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20100207 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20100901 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090610 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20110207 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20110228 Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20110228 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20110207 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090610 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20100207 Ref country code: HU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20091211 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090610 |