EP0906885B1 - Brake for textile threads - Google Patents
Brake for textile threads Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0906885B1 EP0906885B1 EP98116792A EP98116792A EP0906885B1 EP 0906885 B1 EP0906885 B1 EP 0906885B1 EP 98116792 A EP98116792 A EP 98116792A EP 98116792 A EP98116792 A EP 98116792A EP 0906885 B1 EP0906885 B1 EP 0906885B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- thread
- clip
- brake according
- thread brake
- bearing
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D04—BRAIDING; LACE-MAKING; KNITTING; TRIMMINGS; NON-WOVEN FABRICS
- D04B—KNITTING
- D04B15/00—Details of, or auxiliary devices incorporated in, weft knitting machines, restricted to machines of this kind
- D04B15/38—Devices for supplying, feeding, or guiding threads to needles
- D04B15/48—Thread-feeding devices
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65H—HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL, e.g. SHEETS, WEBS, CABLES
- B65H59/00—Adjusting or controlling tension in filamentary material, e.g. for preventing snarling; Applications of tension indicators
- B65H59/10—Adjusting or controlling tension in filamentary material, e.g. for preventing snarling; Applications of tension indicators by devices acting on running material and not associated with supply or take-up devices
- B65H59/20—Co-operating surfaces mounted for relative movement
- B65H59/22—Co-operating surfaces mounted for relative movement and arranged to apply pressure to material
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D04—BRAIDING; LACE-MAKING; KNITTING; TRIMMINGS; NON-WOVEN FABRICS
- D04B—KNITTING
- D04B15/00—Details of, or auxiliary devices incorporated in, weft knitting machines, restricted to machines of this kind
- D04B15/38—Devices for supplying, feeding, or guiding threads to needles
- D04B15/44—Tensioning devices for individual threads
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65H—HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL, e.g. SHEETS, WEBS, CABLES
- B65H2701/00—Handled material; Storage means
- B65H2701/30—Handled filamentary material
- B65H2701/31—Textiles threads or artificial strands of filaments
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65H—HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL, e.g. SHEETS, WEBS, CABLES
- B65H59/00—Adjusting or controlling tension in filamentary material, e.g. for preventing snarling; Applications of tension indicators
- B65H59/10—Adjusting or controlling tension in filamentary material, e.g. for preventing snarling; Applications of tension indicators by devices acting on running material and not associated with supply or take-up devices
- B65H59/20—Co-operating surfaces mounted for relative movement
- B65H59/22—Co-operating surfaces mounted for relative movement and arranged to apply pressure to material
- B65H59/225—Tension discs
Definitions
- the invention relates to a thread brake with two resiliently pressed against each other by load means disc or plate-shaped brake elements, between which can be carried out at least one thread to be braked and of which at least one braking element is a central one Has opening.
- disc or plate thread brakes are in various forms in textile technology in use. Particularly advantageous, modern constructions are described, for example, in DE 41 04 663 C1 and in DE 43 01 507 C2, both to the applicant decline.
- the latter of these two publications is the generic term of claim 1. They have pin-shaped storage means throughout on through the central opening at least one Braking element are arranged and on which at least this one braking element is rotatably mounted.
- the diameter a bearing pin forming the pin-shaped bearing means is much smaller than the diameter of the middle Opening the brake elements so that they swing freely are hung from the bearing pin.
- pin-shaped storage means that are in the form of a Bolts are formed, the diameter of which is only slight is smaller than the opening diameter of the brake elements (compare, for example, FIG. 5 of DE 41 04 663 C1), the brake elements are provided with plastic bearing bushes are their storage conditions on the bolt or a ceramic bearing bush pushed onto this improve.
- the brake elements are elastic against each other oppressive burden means are either after conventional type compression springs or there are too permanent magnetic rings are used for this purpose cup-shaped, made of ferromagnetic material existing brake elements are inserted.
- Thread guide means usually provided at least partially directly on the mounting means which the bearing pin or bolt for carry the braking elements.
- the arrangement is mostly hit such that the bearing pin or pin on the Bracket is overhung.
- the braking elements such as mentioned, oscillating on a small diameter bearing pin are suspended, the braking elements at a distance assigned lateral stop elements, which otherwise limit and prevent free movement in the axial direction, that the braking elements are released from their bearing means.
- the holding means with which the thread brake, for example. is attached to the housing of a thread delivery device, are consistently designed to be relatively expensive applies in particular if the thread brake with a Vibration generator cooperates that the Brake elements set in oscillatory movements, the are mainly directed transversely to the bearing axis (DE 41 04 663 C1) or in a direction perpendicular to it act (DE 44 09 450 C2). Because of the braking elements or their bearing means vibrated the lint deposits that otherwise occur, Soiling, etc., originating from difficult to process Yarns can be largely prevented. The The measure has therefore proven itself in practice proven.
- Thread brakes of the aforementioned type are fundamental Bulk item, which means manufacturing cost vital to the economic Success comes. They also have to be easy to maintain and in particular, to be cleaned, what usually through Blow off by means of a compressed air jet. there should be avoided that the braking elements from their Free storage materials or that have blown off Dirt particles, lint and the like in corners or blind spots of mounting elements, bearing parts, etc. accumulate the thread brake and thus in the long run Endanger operational safety.
- the object of the invention is therefore a thread brake to create oneself with simple, inexpensive Construction due to few dirt deposits distinguished and easy cleaning, as well as necessary disassembly and assembly of your parts allowed, while at the same time a perfectly even Braking of the thread guaranteed over long operating periods is.
- the thread brake according to the invention the features of the characterizing part of claim 1 on.
- the holder means on the new thread brake for which the disc or plate-shaped brake elements bearing, pin-shaped bearing means essentially one U-shaped bracket with two spaced apart on both sides of the brake elements trending thighs on a preferred Embodiment is a one-piece wire bent part.
- the pin-shaped bearing means are on this bracket a bearing part which preferably accommodates them on both sides attached that connected to the stirrup legs or on this is trained.
- This bearing part can be in one preferred embodiment in the form of an essentially U-shaped frame formed and made of plastic his.
- the bracket can be two parallel to each other Have bracket sections with which he in a receiving part is stored at a suitable location on a Machine frame or the like but also on the housing a thread delivery device can be attached.
- the Temple sections can be moved longitudinally in the receiving part be stored, which is particularly important is when at least one of the bracket sections for coupling with a back and forth oscillating motion of the bracket issuing vibration generating device is set up. In this way, as already mentioned, effectively prevents the deposition of fluff, etc. become.
- this can be the pin-shaped bearing means receiving bearing part designed to be removable from the bracket so that the bearing means together with the bearing part to be able to exchange.
- the bearing part can the bracket can also be arranged adjustable, for example To facilitate cleaning of the thread brake or around the To change thread travel.
- the bearing part as a U-shaped Frame formed, so the frame on the bracket between an operating position and a folded down position Position pivotable and in the operating position on the Bracket designed to be lockable.
- the correct position on the bracket in the operating position found frame only needs to be folded down be accessible to the pin-shaped storage means to make them blown off on all sides or otherwise can be cleaned.
- the pin-shaped storage means on the frame i.e. more generally on the bearing part, releasably attached, so they can with the frame folded down simply removed and replaced.
- the thread brake can also be designed so that the whole frame with the bearing means and the brake elements can be replaced without the bracket or others Parts of the thread brake are removed or disassembled would. Folding down and, if necessary, removing the Framework, as well as the exchange of storage resources done without tools.
- the bearing pins a much cheaper support the pin-shaped storage means guaranteed. This allows it with straight bearing pins of relatively small diameter to find the end of it without also having to Vibration exposure by a vibration generator accepted an increased risk of breakage should be. Since these bearing pins usually consist of one hard material, for example ceramic, hard material and the like exist and are relatively expensive achieve a significant price advantage in this way. Other developments of the new thread brake are the subject of subclaims.
- the new thread brake is particularly suitable for use suitable for a thread delivery device that with a Housing, a thread delivery drum rotatably mounted on the housing and one connected to the thread delivery drum Drive device, as well as arranged on the housing Thread guide means is formed.
- the thread guide serve the one of a thread supply, for example Spool coming to be supplied to a thread consumer Feed the thread to the thread delivery drum on the input side or from this on the output side the thread to the thread consumer to lead away.
- a thread delivery device is on the housing on the thread inlet side a thread brake according to the invention arranged.
- the bracket two mutually parallel bracket sections with which it is mounted in a receiving part can the parallel bracket sections directly in the Housing or in a part connected to this, for example. the receiving part be stored.
- the thread delivery device with a vibration generating device housed in the housing equipped it follows with the thread brake on the housing immediately a coupling of the bracket with this vibration generating device.
- at least one of the Strap sections for coupling with the one back and forth Vibration generating device which gives rise to the oscillating movement set up.
- one of the bracket sections with it elastic to a predetermined End position for pressing return spring means be loaded so that it is sufficient that the bracket section on a cam or pusher of the vibration generating device supports without being form-fitting to have to be coupled.
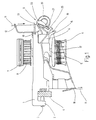
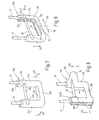
- the thread delivery device shown in Figure 1 is known in its basic structure (compare For example, Figure 1 of DE 43 01 507 C2). It has a housing 1 on that by means of a molded holder 2 and a Clamping screw 3 on a support ring indicated at 4, For example, a circular knitting machine can be attached.
- the housing is vertical in the position of use, through shaft 5 rotatably mounted.
- the wave is on its lower end with one below the housing 1 arranged and designed in the form of a rod cage Thread delivery drum 6 rotatably connected. She is wearing its upper end one rotatably via a coupling 7 couplable pulley 8, the drive device forms and over which the yarn delivery drum 6 from one Endless toothed belt or perforated belt, not shown or the like can be set in rotation.
- Thread brake 9 On the opposite end of the holder 2 Housing 1 is a thread brake 9, the two Identical, essentially disc-shaped brake plates 10, between which a thread to be braked 11 passes through.
- the thread path extends from one thread bobbin not shown by a on the Housing 1 fastens thread eyelet 12, a knot catcher 13 and the thread brake 9 to a base or Receiving part 14 provided via an integrally formed arm 15 Thread inlet eye 16, from the thread 11 on the input side runs onto the thread delivery drum 6.
- Thread delivery drum 6 On the Thread delivery drum 6, the thread 11 forms a storage roll 17, from which it is attached to the housing 1 via a Thread outlet eyelet 18 runs to the thread consumer.
- the thread brake 9 has a one-piece bent wire part trained, substantially U-shaped bracket 19 on which the holding means for the brake discs or plate 10 and their bearing means in the form of a cylindrical Bearing pin 20 forms.
- the bracket 19 has two legs 21 running parallel to each other one end through a crosspiece 22 with each other are connected, each including a right angle to the bracket legs 21.
- On at their other end are the two bracket legs 21 each via a bend 23 of approx. 30 ° and intermediate appropriately designed intermediate sections 24 with two straight bracket sections 25 parallel to one another connected.
- the parallel bracket sections 25 based on the in the Position of use horizontal crossbar 22, in different Height and close the web 22 and the two bracket legs 21 containing imaginary level an angle of approx. 30 °.
- the bracket sections 25 can also optionally with the intermediate sections 24, are at the same level, just a few possible arrangements to mention.
- bracket 19 With its two parallel bracket sections 25 is the bracket 19 in the housing-shaped base or receiving part 14 mounted longitudinally displaceable, as is the case in particular can be seen from Figure 2.
- 14 points two from the front to the back continuous, cylindrical bearing bores 26, in which the bracket sections 25 with in the use position horizontal alignment are guided longitudinally.
- the straight bracket sections 25 are both in height ( Figure 2) and laterally offset from each other ( Figure 5) arranged.
- the overhead bracket section 25 supports its over the back of the base or receptacle 14 protruding end an existing plastic, in Essentially in the form of a cylindrical cap 27 formed coupling part for a in the housing 1st arranged vibration generator, not shown, only one of them in FIG indicated by an arrow 28, back and forth Movement executing drive stamp 29 illustrated is.
- the drive stamp 29 is from one to the shaft 5 the thread delivery device according to FIG. 1, actuated cam, not shown, with which it engages stands.
- the base or receiving part 14 is one compression spring 30 surrounding the upper straight bracket section 26 arranged, which is against an axial spring abutment 31st is supported and endeavors, the coupling piece 27 in plant to hold on the drive stamp 29.
- the compression spring 30 therefore forms return spring means.
- the lower straight bracket section 25 projects, for example the rear of the base or receiving part 14 at 31 something, as indicated by dashed lines in Fig. 2. It is located on the housing 1 base or Receiving part 14 on part of the metallic housing 1 and thus causes electrical grounding of the metallic Bügels 19. Alternatively or in addition to Improvement of the earthing conditions of the bracket 19 also an earth spring (not shown) against the housing 1 press on, and / or the base 14 and / or the cap 27 consists of an electrically conductive material.
- a fastening screw indicated at 32 from the front of the base or receptacle 14 can be actuated.
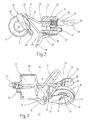
- FIG. 4 On the normal shown in Figure 2 Operating position with the vertical at an angle of approx. 30 ° inclusive, lying on a common level parallel leg 21 of the bracket 19 is a bearing part in Shape of a plastic, essentially U-shaped frame 33 in which the bearing pin 20 for the brake discs 10 at both ends is held, as can be seen in particular from FIG. 4.
- the frame 33 has two mutually parallel, spaced apart frame legs 34, which by an integrally formed frame web 35 at one end are connected.
- the two parallel frame legs 34 are facing the viewer in FIG Inside each with a gutter-shaped Well 36 formed in the vicinity of the free One end of the frame leg protrudes 37.
- the Lugs 37 are on the groove-shaped recesses 36th delimiting on the side of the U-shaped opening of the frame 33 Wall 38 formed. They serve the Frame 33 in the operating position with the legs 21 of the Bracket 19 releasably latch, as is still the case will be explained.
- the frame web 35 is on the outside with a molded bearing shell or claw 39 provided For example, in Fig. 2, 4 is visible and the on the bracket 19 mounted frame 33 elastically engages the crossbar 22, so that the frame 33 is pivotable on the web 22 is stored.
- the bearing shell or claw 39 is there resiliently designed such that the frame 33 overcoming the snap connection formed by her can simply be removed from the bracket 19.
- the frame web 35 On its inside facing the bearing pin 20 is the frame web 35 as a support or support cushion 40 trained for the brake discs or plates 10.
- the frame leg 35 can, for example, inside be provided with a wear-resistant coating.
- one made of wear-resistant Material existing pen or a corresponding one Molding is used in the frame 33, the forms the support or support cushion 40.
- the conditions of use also include cases where a particularly wear-resistant training this in the Rule the entire space between the two frame legs 34 engaging support or support cushion 40 dispensed with becomes.
- the hardened steel, possibly with a wear-resistant coating, made of ceramic or one suitable hard material, thin, cylindrical Bearing pin 20 is on its one, lower in Figure 4 End inserted into a bearing bore 41 which in the Inner wall 38 is formed.
- the bearing pin 20 is in one on the associated side Frame leg 34 provided to the gutter-like Recess 36 open bearing half shell 43 added, which is molded onto the frame leg 34.
- the depth of the Bearing half shell 43 is chosen such that the used bearing pin 20 with its lateral surface somewhat protrudes over the bottom of the groove-shaped recess 36.
- the Bearing pin 20 can also be made of non-conductive material, for example Ceramics exist, which should be mentioned for the sake of order.
- the two brake actuators 10 are on the bearing pin 20 freely suspended. You are in for this purpose in particular from FIGS. 5, 6 each with a central, cylindrical, continuous Opening 44 formed, the diameter of which many times over is larger than the diameter of the bearing pin 20th The diameter ratio is typically about 6: 1 and more.
- the bowl-shaped cambered cross section Brake plate 10 can along the edge of the Opening 44 each formed with a cylindrical lip Hub 45 may be designed to withstand the stress the brake plate 10 and the bearing pin 20 to reduce and cutting the brake plate into the bearing pin 20 to prevent.
- the edges of the Opening 44 in each of the brake actuators 10 also by one used hub ring made of plastic or a suitable bearing pairing with the bearing pin 20 resulting Material can be edged, as is shown in FIG. 10 will be explained.
- the size of the loading force determines the braking effect on the thread running through.
- the two frame legs 34 in the assembled state in considerable lateral distance from the two brake actuators 10.
- the two brake plates 10 resting against each other are therefore considerable in the axial direction Length of the bearing pin 2C freely movable.
- the frame 33 is on the used bearing pin 20 hanging brake actuators 10 with its bearing shell or claw 39 on the horizontal Web 22 of bracket 19 clipped on. Besides, he's around Axis of the web 22 folded up so far that the two Leg 21 in the groove-shaped recesses 36 of the Frame legs 34 are included and the frame 33 with the legs 21 is locked over the locking lugs 37.
- the Thread brake thus has that shown in Figures 1, 2 State in which the between the brake actuators 10 continuous thread 11 in the by the attraction the permanent magnet rings 46 given the amount evenly braked becomes.
- each other Brake actuator 10 of which around the bearing pin 20 or one not shown in the drawing by the Openings 44 of the brake discs 10 extending and in the Frame legs 34 held deflected thread deflecting pin Thread 11 driven frictionally, so that it is a perform a common rotational movement around the bearing pin 20.
- This orbital movement is a wobbling movement in the axial direction superimposed, since, as mentioned, the two brake actuators 10 have no firm lateral guidance. On this ensures that the thread 11 is not in can cut the braking surfaces of the brake plate 10, but that the braking surfaces over their entire circumference progressively engage the thread.
- bracket 19 is over the drive stamp 29 of the vibration generating device vibrating movement issued, under whose Impact of the support points on the opening edge of the Brake actuator 10 on the bearing pin 20 continuously change, so that the brake plate 10 an irregular Carry out movement that the deposit of fluff and the like prevented.
- the bearing pin 20 at one end of the bearing half-shell 43 pushed up out so that he are pulled axially out of the bearing bore 41 can. Since the frame 33 is made of plastic and in unfolded state not by the bracket legs 21 is reinforced, it is elastically deformable so that the described disassembly of the bearing pin 20 easily possible is. A new bearing pin 20 can be reversed be inserted again.
- the arrangement could also be made in such a way that the bearing pin 20 from the frame 33 directly axially is extractable by following it in at least one outside opening bearing bore 41 is supported.
- the bearing pin 20 would then be in its operating position in frame 33 by a locking mechanism, such as in the form of a Locking mechanism or through partial training as a threaded bolt secured.
- a locking mechanism such as in the form of a Locking mechanism or through partial training as a threaded bolt secured.
- Other embodiments that the serve the same purpose are conceivable.
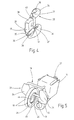
- the two are Bow leg 21 of the U-shaped wire bracket 19a each an eyelet 47 is bent, the cylindrical bearing bore 41 limited.
- the two eyelets 47 are in alignment their bearing bores 41, in which the bearing pin 20th is plugged in.
- the bearing pin 20 is on both sides clamped elastically by the ring eyelets 47. Erforderlichefalls it can be located in the area of at least one bearing bore 41 also a recess, for example in the form of a circumferential one Rastnut, have to additionally or alternatively a form-fitting connection with the respective To produce stirrup legs 21.
- the bearing bore 41 each completely looping eyelets 47
- the bracket legs 21st also be curved so that they have ⁇ -shaped eyelets 47a, as illustrated in Figure 6b, right representation is.
- the bow legs 21 will be loop-shaped.
- the ring eyelets 47 and the eyelets 47a can also be clipped onto the respective stirrup leg 21 and there hook-shaped held frictionally Bracket claw 48 occur, as shown in Figure 6b, left Figure is shown.
- the preferably made of plastic manufactured claws 48 are the end of the Bearing pin 20 attached. They reach around with their jaws 49 the respective stirrup leg 21 on which it is frictionally engaged, are kept immovable.
- one straight bracket section 25 by the compression spring 30 ( Figure 2) in elastic contact with the actuating plunger 29 (or an actuating cam) of the vibration generating device held.
- the coupling part designed as a plastic cap 27 serves the coupling part designed as a plastic cap 27.
- the compression spring 30 it would also be conceivable, the resetting of the bracket 19 or the pressure whose bracket section 25 on the drive tappet 29 to achieve that that the bracket 19 forming Bent wire part with a corresponding elastic prestress is trained.
- positively driven embodiments with two support points of this bent wire part the drive stamp 29 or on the drive cam are possible. Such a variant is indicated in FIG. 6.
- the Temple sections 25 are approximately at right angles to one another at 470 assigning turned. Between the spaced bent bracket parts 470 could, for example Drive stamp or tappet 26 coupled.
- the one-piece, substantially U-shaped frame 33a with a to the back opening, all-round, gutter-shaped Recess 36a formed over the Frame leg 34a and the frame web 35a extends.
- the Frame 33a is through the appropriate dimensioning of the recess 36a on the bracket legs 21 and the bracket web 22 jammed. Overall, he can decrease to the front are, as indicated by the two arrows 480 is.
- the bearing pin 20 is in the frame 33a, similar to in Figure 4.
- a bearing approach and the bearing half shell are designated 42a and 43a.
- FIG. 8 is how by the way, in all embodiments - the frame 33b Made of plastic. His two frame legs 34b and the frame web 35b are each one in the plane of the two stirrup legs 21 lying and towards the outside open, groove-shaped recess 36b formed in the the bracket legs 21 are. In this way it is possible the whole frame 33b in the direction of arrows 490 to move the stirrup legs 21, for example by the operating conditions to change the thread brake.
- the Frame 33b is on the temple legs 21 in its respective Position held by friction.
- the bearing pin 20 is in this case one end in its own, the assigned U-shaped arms 21 encompass and friction with this coupled leg section 340b supported, possibly with the leg 21 also can be locked.
- the bearing pin 20 At its other end is the bearing pin 20 in a groove-like recess open on one side 50 of the associated frame leg 34 recorded and in it locks or jams.
- the bearing pin 20th folded out around the left leg 21 as by an arrow 51 is indicated. He can then from his Leg section 340b are pulled out.
- An actuating tab 52 formed on the frame 33b allows the displacement of the frame 33b in the sense of Arrows 490.
- the frame 33c formed in two parts.
- the frame legs 34c and the Frame web 35c are with a continuous, channel-shaped Provide recess 36c, which corresponds to that of the two stirrup legs 21 limited space towards each other open assigning.
- the whole frame 33c can therefore in Direction of arrows 53 downward on legs 21 moved or subtracted from them entirely.
- Optional can also the two frame legs 34c, the along a parting line 55 in the frame web 35c from one another are separated, laterally subtracted from the legs 21 become. This is indicated by two arrows 56.
- the Support of the bearing pin 20 on the frame legs 34c is solved similarly as in Figure 4. Corresponding parts are provided with corresponding reference symbols.
- the support or support pad 40 for the brake discs 10 not illustrated in detail. It can be similar be designed as in the frame 33 of Figure 4. It in any case serves the brake actuator 10 in operation limit their outer circumference radially in their path of movement.
- the brake actuators 10 hanging on the bearing pin 20 are in their operating position shown in Figure 2 on the bottom of the support or support cushion 40 from which they wobble in the course of their irregular Rotational movement more or less often during operation take off.
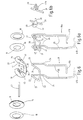
- embodiment a) are on the brake discs or plate 10 consisting of a suitable plastic clipped annular caps 60, with their all-round protruding edge areas 61, 62 the brake plate 10 on the outer circumference and along the circumference of the Overlap opening 44 so that they on the brake actuators 10 are locked.
- the caps 60 cover the cavity the cambered brake actuator 10 in the illustrated Way, while they the permanent magnet rings 46th fix in the correct position so that additional gluing, etc. is generally no longer required.
- the edge 62 bordering the opening 44 forms at the same time a substantially tubular hub, optionally is arched in cross section. To this This results in particularly favorable storage conditions the brake actuator 10 on the bearing pin 20th
- annular disk-shaped inside Mold lip 63 as shown in the illustration b) shows.
- the ring-shaped lips 63 result a small axial width of the bearing surface and thus a increased surface pressure. This can be an advantage if it must be expected that the bearing pin 20 sizing or other resinous or sticky deposits build up.
- FIG Figure c illustrates the washer-shaped Lip also in the form of an annular disc 63a be placed on the permanent magnet ring 46a, the is provided with an annular shoulder 64 for this purpose.
- the permanent magnet rings 46a are with the brake actuators 10 glued, the washers 63a each between its edge and the ring shoulder 64 of the corresponding Permanent magnet rings 46a are inserted.
- Cover 65 can also have an annular disk-shaped lip 65a of a small thickness, which is the hub of the brake actuators 10 forms, so that there are similar storage conditions as in Figures b) and c).
- the invention is not is limited to embodiments in which the Brake actuator 10 oscillating on a thin bearing pin 20 are hung. It can also be used for thread brakes, where the brake plate on a bearing pin or -pin are only rotatably supported with play.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Textile Engineering (AREA)
- Braking Arrangements (AREA)
- Tension Adjustment In Filamentary Materials (AREA)
- Spinning Or Twisting Of Yarns (AREA)
- Portable Nailing Machines And Staplers (AREA)
- Clamps And Clips (AREA)
- Knitting Machines (AREA)
Description
Die Erfindung betrifft eine Fadenbremse mit zwei durch Belastungsmittel nachgiebig gegeneinander gedrückten scheiben- oder tellerförmigen Bremselementen, zwischen denen zumindest ein zu bremsender Faden durchführbar ist und von denen wenigstens ein Bremselement eine mittige Öffnung aufweist.The invention relates to a thread brake with two resiliently pressed against each other by load means disc or plate-shaped brake elements, between which can be carried out at least one thread to be braked and of which at least one braking element is a central one Has opening.
Derartige sogenannte Scheiben- oder Tellerfadenbremsen
sind in der Textiltechnik in vielfältigen Ausführungsformen
im Einsatz. Besonders vorteilhafte, moderne Konstruktionen
sind bspw. beschrieben in der DE 41 04 663 C1
und in der DE 43 01 507 C2, die beide auf die Anmelderin
zurückgehen.
Letztere dieser beiden Druckschriften liegt dem Oberbegriff
des Anspruches 1 zugrunde.
Sie weisen durchgehend stiftförmige Lagermittel
auf, die durch die mittige Öffnung wenigstens eines
Bremselementes verlaufend angeordnet sind und auf denen
wenigstens dieses eine Bremselement drehbar gelagert ist.
Dabei gibt es Ausführungsformen bei denen der Durchmesser
eines die stiftförmigen Lagermittel bildenden Lagerstiftes
wesentlich kleiner ist als der Durchmesser der mittigen
Öffnung der Bremselemente, so dass diese frei pendelnd auf
dem Lagerstift aufgehängt sind. Andere Ausführungsformen
verwenden stiftförmige Lagermittel, die in Gestalt eines
Bolzens ausgebildet sind, dessen Durchmesser nur geringfügig
kleiner ist als der Öffnungsdurchmesser der Bremselemente
(vergleiche bspw. Figur 5 der DE 41 04 663 C1),
wobei die Bremselemente mit Kunststofflagerbuchsen versehen
sind, um ihre Lagerverhältnisse auf dem Bolzen bzw.
einer auf diesen aufgeschobenen keramischen Lagerbuchse zu
verbessern. Die die Bremselemente elastisch gegeneinander
drückenden Belastungsmittel sind hierbei entweder nach
herkömmlicher Art Druckfedern oder es werden aber zu
diesem Zwecke dauermagnetische Ringe verwendet, die in die
schalenförmig gestalteten, aus ferromagnetischem Material
bestehenden Bremselemente eingelegt sind.Such so-called disc or plate thread brakes
are in various forms in textile technology
in use. Particularly advantageous, modern constructions
are described, for example, in
Um den zu bremsenden Faden ordnungsgemäß zwischen den Bremselementen zu führen, sind, abhängig von der jeweiligen Konstruktion, Fadenumlenkstifte, Fadenösen und dergleichen Fadenleitmittel vorgesehen, die in der Regel zumindest teilweise unmittelbar an den Halterungsmitteln vorgesehen sind, welche den Lagerstift oder -bolzen für die Bremselemente tragen. Die Anordnung ist dabei meist derart getroffen, dass der Lagerstift oder -bolzen an den Halterungsmitteln fliegend gelagert ist. Außerdem sind bei den Ausführungsformen, bei denen die Bremselemente, wie erwähnt, auf einem Lagerstift kleinen Durchmessers pendelnd aufgehängt sind, den Bremselementen im Abstand seitliche Anschlagelemente zugeordnet, die deren sonst freie Bewegung in Achsialrichtung begrenzen und verhüten, dass die Bremselemente von ihren Lagermitteln freikommen.In order to properly brake the thread between the Braking elements depend on the respective one Construction, thread deflecting pins, thread eyelets and the like Thread guide means usually provided at least partially directly on the mounting means are provided which the bearing pin or bolt for carry the braking elements. The arrangement is mostly hit such that the bearing pin or pin on the Bracket is overhung. In addition, at the embodiments in which the braking elements, such as mentioned, oscillating on a small diameter bearing pin are suspended, the braking elements at a distance assigned lateral stop elements, which otherwise limit and prevent free movement in the axial direction, that the braking elements are released from their bearing means.
Die Halterungsmittel mit denen die Fadenbremse bspw.
am Gehäuse einer Fadenliefervorrichtung befestigt ist,
sind durchweg verhältnismäßig aufwendig gestaltet, was
insbesondere dann gilt, wenn die Fadenbremse mit einer
Schwingungserzeugungseinrichtung zusammenwirkt, die die
Bremselemente in Schwingungsbewegungen versetzt, die
hauptsächlich quer zu der Lagerachse gerichtet sind (DE 41
04 663 C1) oder in einer rechtwinklig dazu weisenden Richtung
wirken (DE 44 09 450 C2). Dadurch dass die Bremselemente
oder deren Lagermittel in Schwingungen versetzt
werden, können die sonst auftretenden Flusenablagerungen,
Verschmutzungen etc., herrührend von schwierig zu verarbeitenden
Garnen, weitgehend verhindert werden. Die
Maßnahme hat sich deshalb in der Praxis ausgezeichnet
bewährt.The holding means with which the thread brake, for example.
is attached to the housing of a thread delivery device,
are consistently designed to be relatively expensive
applies in particular if the thread brake with a
Vibration generator cooperates that the
Brake elements set in oscillatory movements, the
are mainly directed transversely to the bearing axis (
Fadenbremsen der vorgenannten Art sind grundsätzlich Massenartikel, was bedeutet, dass den Herstellungskosten eine entscheidende Bedeutung für den wirtschaftlichen Erfolg zukommt. Außerdem müssen sie leicht zu warten und insbesondere zu reinigen sein, was in der Regel durch Abblasen mittels eines Druckluftstrahles geschieht. Dabei soll vermieden werden, dass die Bremselemente von ihren Lagermitteln freikommen oder dass sich abgeblasene Schmutzpartikel, Flusen und dergleichen in Ecken oder toten Winkeln von Halterungselementen, Lagerteilen, etc. der Fadenbremse ansammeln und damit auf die Dauer deren Betriebssicherheit gefährden.Thread brakes of the aforementioned type are fundamental Bulk item, which means manufacturing cost vital to the economic Success comes. They also have to be easy to maintain and in particular, to be cleaned, what usually through Blow off by means of a compressed air jet. there should be avoided that the braking elements from their Free storage materials or that have blown off Dirt particles, lint and the like in corners or blind spots of mounting elements, bearing parts, etc. accumulate the thread brake and thus in the long run Endanger operational safety.
Außerdem wird an eine Fadenbremse häufig die Forderung nach leichter Montage und Demontage, zusätzlich zu der Möglichkeit einer bequemen und wirksamen Reinigung gestellt.In addition, the requirement is often a thread brake after easy assembly and disassembly, in addition to the possibility of convenient and effective cleaning posed.
Aufgabe der Erfindung ist es deshalb, eine Fadenbremse zu schaffen, die sich bei einfachem, kostengünstigem Aufbau durch wenig Schmutzablagerungsmöglichkeiten auszeichnet und die eine leichte Reinigung, sowie erforderlichenfalls eine Demontage und Montage ihrer Teile erlaubt, wobei gleichzeitig eine einwandfrei gleichmäßige Bremsung des Fadens über lange Betriebszeiträume gewährleistet ist.The object of the invention is therefore a thread brake to create oneself with simple, inexpensive Construction due to few dirt deposits distinguished and easy cleaning, as well as necessary disassembly and assembly of your parts allowed, while at the same time a perfectly even Braking of the thread guaranteed over long operating periods is.
Zur Lösung dieser Aufgabe weist die Fadenbremse
gemäß der Erfindung die Merkmale des kennzeichnenden Teils des Patentanspruchs 1
auf.To solve this task, the thread brake
according to the invention the features of the characterizing part of
Bei der neuen Fadenbremse weisen die Halterungsmittel für die die scheiben- oder tellerförmigen Bremselemente tragenden, stiftförmigen Lagermittel einen im Wesentlichen U-förmigen Bügel mit zwei im Abstand beidseitig der Bremselemente verlaufenden Schenkeln auf, der in eine bevorzugten Ausführungsform ein einstückiges Drahtbiegeteil ist. An diesem Bügel sind die stiftförmigen Lagermittel mittels eines sie vorzugsweise beidseitig aufnehmenden Lagerteiles befestigt, das mit den Bügelschenkeln verbunden oder an diesen ausgebildet ist. Dieses Lagerteil kann in einer bevorzugten Ausführungsform in Form eines im Wesentlichen U-förmigen Rahmens ausgebildet und aus Kunststoff hergestellt sein. Der Bügel kann zwei zueinander parallele Bügelabschnitte aufweisen, mit denen er in einem Aufnahmeteil gelagert ist, dass an geeigneter Stelle an einen Maschinenrahmen oder dergleichen aber auch an dem Gehäuse einer Fadenliefervorrichtung befestigt werden kann. Die Bügelabschnitte können in dem Aufnahmeteil längsverschieblich gelagert sein, was insbesondere dann von Bedeutung ist, wenn wenigstens einer der Bügelabschnitte zur Kupplung mit einer dem Bügel eine hin- und hergehende Schwingungsbewegung erteilenden Schwingungserzeugungseinrichtung eingerichtet ist. Auf diese Weise kann, wie bereits erwähnt, die Ablagerung von Flusen, etc. wirksam verhindert werden.The holder means on the new thread brake for which the disc or plate-shaped brake elements bearing, pin-shaped bearing means essentially one U-shaped bracket with two spaced apart on both sides of the brake elements trending thighs on a preferred Embodiment is a one-piece wire bent part. The pin-shaped bearing means are on this bracket a bearing part which preferably accommodates them on both sides attached that connected to the stirrup legs or on this is trained. This bearing part can be in one preferred embodiment in the form of an essentially U-shaped frame formed and made of plastic his. The bracket can be two parallel to each other Have bracket sections with which he in a receiving part is stored at a suitable location on a Machine frame or the like but also on the housing a thread delivery device can be attached. The Temple sections can be moved longitudinally in the receiving part be stored, which is particularly important is when at least one of the bracket sections for coupling with a back and forth oscillating motion of the bracket issuing vibration generating device is set up. In this way, as already mentioned, effectively prevents the deposition of fluff, etc. become.
In der Regel kann das die stiftförmigen Lagermitteln aufnehmende Lagerteil von dem Bügel abnehmbar ausgebildet sein, um damit die Lagermittel gemeinsam mit dem Lagerteil austauschen zu können. Abhängig von dem Einsatzzweck und der Konstruktion der Fadenbremse, kann das Lagerteil auf dem Bügel auch verstellbar angeordnet sein, bspw. um die Reinigung der Fadenbremse zu erleichtern oder um den Fadenlaufweg zu verändern. Ist das Lagerteil als U-förmiger Rahmen ausgebildet, so kann der Rahmen an dem Bügel zwischen einer Betriebsstellung und einer abgeklappten Stellung verschwenkbar und in der Betriebsstellung an dem Bügel feststellbar ausgebildet sein.As a rule, this can be the pin-shaped bearing means receiving bearing part designed to be removable from the bracket so that the bearing means together with the bearing part to be able to exchange. Depending on the application and the construction of the thread brake, the bearing part can the bracket can also be arranged adjustable, for example To facilitate cleaning of the thread brake or around the To change thread travel. Is the bearing part as a U-shaped Frame formed, so the frame on the bracket between an operating position and a folded down position Position pivotable and in the operating position on the Bracket designed to be lockable.
Dies ergibt eine besonders einfache Wartungsmöglichkeit der Fadenbremse:This results in a particularly simple maintenance option the thread brake:
Der in der Betriebsstellung lagerichtig an dem Bügel festgestellte Rahmen braucht lediglich abgeklappt zu werden, um damit die stiftförmigen Lagermittel zugänglich zu machen, so dass diese allseitig abgeblasen oder sonstwie gereinigt werden können. Sind die stiftförmigen Lagermittel an dem Rahmen, d.h. allgemeiner an dem Lagerteil, lösbar befestigt, so können sie bei abgeklapptem Rahmen einfach herausgenommen und ausgetauscht werden. Alternativ kann die Fadenbremse auch so gestaltet sein, dass der ganze Rahmen mit den Lagermitteln und den Bremselementen ausgetauscht werden kann, ohne dass der Bügel oder andere Teile der Fadenbremse abgenommen bzw. zerlegt werden müssten. Das Abklappen und gegebenenfalls Abnehmen des Rahmens, wie auch der Austausch der Lagermittel, können ohne Zuhilfenahme von Werkzeugen geschehen. Da die stiftförmigen Lagermittel in dem Lagerteil beidseitig gelagert sind, ist im Vergleich zu der bekannten fliegenden Lagerung der Lagerstifte eine wesentlich günstigere Abstützung der stiftförmigen Lagermittel gewährleistet. Dies erlaubt es mit geraden Lagerstiften verhältnismäßig kleinen Durchmessers das Auslangen zu finden, ohne dass auch bei Schwingungsbeaufschlagung durch eine Schwingungserzeugungseinrichtung eine erhöhte Bruchgefahr in Kauf genommen werden müsste. Da diese Lagerstifte in der Regel aus einem harten Material, bspw. Keramik, Hartstoff und dergleichen bestehen und verhältnismäßig teuer sind, lässt sich auf diese Weise ein beträchtlicher Preisvorteil erzielen. Andere Weiterbildungen der neuen Fadenbremse sind Gegenstand von Unteransprüchen.The correct position on the bracket in the operating position found frame only needs to be folded down be accessible to the pin-shaped storage means to make them blown off on all sides or otherwise can be cleaned. Are the pin-shaped storage means on the frame, i.e. more generally on the bearing part, releasably attached, so they can with the frame folded down simply removed and replaced. alternative the thread brake can also be designed so that the whole frame with the bearing means and the brake elements can be replaced without the bracket or others Parts of the thread brake are removed or disassembled would. Folding down and, if necessary, removing the Framework, as well as the exchange of storage resources done without tools. Because the pen-shaped Storage means stored on both sides in the storage part are compared to the known flying storage the bearing pins a much cheaper support the pin-shaped storage means guaranteed. This allows it with straight bearing pins of relatively small diameter to find the end of it without also having to Vibration exposure by a vibration generator accepted an increased risk of breakage should be. Since these bearing pins usually consist of one hard material, for example ceramic, hard material and the like exist and are relatively expensive achieve a significant price advantage in this way. Other developments of the new thread brake are the subject of subclaims.
Die neue Fadenbremse ist insbesondere zur Verwendung bei einer Fadenliefervorrichtung geeignet, die mit einem Gehäuse, einer an dem Gehäuse drehbar gelagerten Fadenliefertrommel und einer mit der Fadenliefertrommel verbundenen Antriebseinrichtung, sowie mit an dem Gehäuse angeordneten Fadenleitmitteln ausgebildet ist. Die Fadenleitmittel dienen dazu, den von einem Fadenvorrat, bspw. einer Spule kommenden, einem Fadenverbraucher zuzuliefernden Faden der Fadenliefertrommel eingangsseitig zuzuleiten bzw. von dieser ausgangsseitig den Faden zu dem Fadenverbraucher hin wegzuleiten. Bei einer solchen Fadenliefervorrichtung ist an dem Gehäuse auf der Fadeneinlaufseite eine erfindungsgemäße Fadenbremse angeordnet. Bei der erläuterten Ausführungsform der neuen Fadenbremse mit einem als Drahtbiegeteil ausgebildeten U-förmigen Bügel, deren Bügel zwei zueinander parallele Bügelabschnitte aufweist, mit denen er in einem Aufnahmeteil gelagert ist, können die parallelen Bügelabschnitte unmittelbar in dem Gehäuse oder in einem mit diesem verbundenen Teil, bspw. dem Aufnahmeteil gelagert sein. Ist die Fadenliefervorrichtung mit einer in dem Gehäuse untergebrachten Schwingungserzeugungseinrichtung ausgerüstet, so ergibt sich mit dem Aufsetzen der Fadenbremse auf das Gehäuse unmittelbar eine Kopplung des Bügels mit dieser Schwingungserzeugungseinrichtung. Zu diesem Zwecke ist wenigstens einer der Bügelabschnitte zur Kupplung mit der ihm eine hin- und hergehende Schwingungsbewegung erteilenden Schwingungserzeugungseinrichtung eingerichtet. Gleichzeitig kann einer der Bügelabschnitte mit ihn elastisch auf eine vorbestimmte Endstellung zu drückenden Rückstellfedermitteln belastet sein, so dass es genügt, dass der Bügelabschnitt sich auf einem Nocken oder Stössel der Schwingungserzeugungseinrichtung abstützt, ohne mit diesem formschlüssig gekuppelt werden zu müssen. The new thread brake is particularly suitable for use suitable for a thread delivery device that with a Housing, a thread delivery drum rotatably mounted on the housing and one connected to the thread delivery drum Drive device, as well as arranged on the housing Thread guide means is formed. The thread guide serve the one of a thread supply, for example Spool coming to be supplied to a thread consumer Feed the thread to the thread delivery drum on the input side or from this on the output side the thread to the thread consumer to lead away. With such a thread delivery device is on the housing on the thread inlet side a thread brake according to the invention arranged. In the explained embodiment of the new thread brake with a U-shaped bracket designed as a bent wire part, the bracket two mutually parallel bracket sections with which it is mounted in a receiving part, can the parallel bracket sections directly in the Housing or in a part connected to this, for example. the receiving part be stored. Is the thread delivery device with a vibration generating device housed in the housing equipped, it follows with the thread brake on the housing immediately a coupling of the bracket with this vibration generating device. For this purpose, at least one of the Strap sections for coupling with the one back and forth Vibration generating device which gives rise to the oscillating movement set up. At the same time one of the bracket sections with it elastic to a predetermined End position for pressing return spring means be loaded so that it is sufficient that the bracket section on a cam or pusher of the vibration generating device supports without being form-fitting to have to be coupled.
Weiterbildungen der neuen Fadenbremsem sind Gegenstand von Unteransprüchen.Further developments of the new thread brakes are the subject of subclaims.
In der Zeichnung sind Ausführungsbeispiele des Gegenstandes der Erfindung dargestellt. Es zeigen:
Figur 1- eine Fadenliefervorrichtung mit einer Fadenbremse gemäß der Erfindung, in einer Seitenansicht,
Figur 2- die Fadenbremse der Fadenliefervorrichtung nach
Figur 1, in einer Seitenansicht und in einem anderen Maßstab, Figur 3- die Fadenbremse nach
Figur 2, in einer perspektivischen Darstellung bei abgeklapptem Rahmen und in einem anderen Maßstab, Figur 4- den Rahmen mit dem Lagerstift der Fadenbremse
nach
Figur 2, in einer vergrößerten perspektivischen Darstellung, Figur 5- die Fadenbremse nach
Figur 2, in perspektivischer Darstellung, Figur 6- den als Drahtbiegeteil ausgebildeten Bügel, die Bremselemente und deren zugeordneten Dauermagnetringe, in perspektivischer, auseinandergezogener Darstellung, in einem anderen Maßstab,
- Figur 6a
- den Bügel nach Fig. 6 in einer abgewandelten Ausführungsform, in einer entsprechenden perspektivischen Darstellung,
- Figur 6b
- den Bügel nach Fig. 6a, im Ausschnitt unter Veranschaulichung zweier unterschiedlicher Ausbildungen der Lagerteile, jeweils in perspektivischer Darstellung.
Figuren 7bis 9- drei verschiedene Ausführungsbeispiele des Rahmens der Fadenbremse nach Figur 2, jeweils in schematischer, perspektivischer Darstellung, unter Veranschaulichung eines Teils des als Drahtbiegeteil ausgebildeten Bügels, sowie in einem anderen Maßstab und
Figur 10- die Bremsteller und die Lagermittel der Fadenbremse nach Fig. 1 in fünf verschiedenen Ausführungsformen, jeweils in axialen Schnitt, in einer schematischen Seitenansicht und in einem anderen Maßstab.
- Figure 1
- a thread delivery device with a thread brake according to the invention, in a side view,
- Figure 2
- 1, in a side view and on a different scale,
- Figure 3
- 2, in a perspective view with the frame folded down and on a different scale,
- Figure 4
- the frame with the bearing pin of the thread brake according to Figure 2, in an enlarged perspective view,
- Figure 5
- the thread brake according to Figure 2, in a perspective view,
- Figure 6
- the bracket formed as a bent wire part, the brake elements and their associated permanent magnet rings, in a perspective, exploded view, on a different scale,
- Figure 6a
- 6 in a modified embodiment, in a corresponding perspective view,
- Figure 6b
- the bracket of Fig. 6a, in a section illustrating two different designs of the bearing parts, each in a perspective view.
- Figures 7 to 9
- three different embodiments of the frame of the thread brake according to Figure 2, each in a schematic, perspective view, illustrating a part of the bracket designed as a bent wire part, and on a different scale and
- Figure 10
- 1 in five different embodiments, each in an axial section, in a schematic side view and on a different scale.
Die in Figur 1 dargestellte Fadenliefervorrichtung
ist in ihrem grundsätzlichen Aufbau bekannt (vergleiche
bspw. Figur 1 der DE- 43 01 507 C2). Sie weist ein Gehäuse
1 auf, dass mittels eines angeformten Halters 2 und einer
Klemmschraube 3 an einem bei 4 angedeuteten Tragring,
bspw. einer Rundstrickmaschine befestigt werden kann. In
dem Gehäuse ist eine in der Gebrauchslage vertikale,
durchgehende Welle 5 drehbar gelagert. Die Welle ist an
ihrem unteren Ende mit einer unterhalb des Gehäuses 1
angeordneten und in Gestalt eines Stabkäfigs ausgebildeten
Fadenliefertrommel 6 drehfest verbunden. Sie trägt an
ihrem oberen Ende eine über eine Kupplung 7 drehfest
ankuppelbare Riemenscheibe 8, die ihre Antriebseinrichtung
bildet und über die die Fadenliefertrommel 6 von einem
nicht weiter dargestellten, endlosen Zahn- oder Lochriemen
oder dergleichen in Umdrehung versetzt werden kann.The thread delivery device shown in Figure 1
is known in its basic structure (compare
For example, Figure 1 of
An der dem Halter 2 gegenüberliegenden Stirnseite des
Gehäuses 1 ist eine Fadenbremse 9 angeordnet, die zwei
gleichgestaltete, im Wesentlichen scheibenförmige Bremsteller
10 aufweist, zwischen denen ein zu bremsender Faden
11 durchläuft. Der Fadenlaufweg erstreckt sich von einer
nicht weiter dargestellen Fadenspule aus durch eine an dem
Gehäuse 1 befestigt Fadenöse 12, einen Knotenfänger 13
und die Fadenbremse 9 zu einer an einem Sockel- oder
Aufnahmeteil 14 über einen angeformten Arm 15 vorgesehenen
Fadeneinlauföse 16, von der aus der Faden 11 eingangsseitig
auf die Fadenliefertrommel 6 aufläuft. Auf der
Fadenliefertrommel 6 bildet der Faden 11 einen Speicherwickel
17, von dem aus er über eine an dem Gehäuse 1 befestigte
Fadenauslauföse 18 zu dem Fadenverbraucher läuft.On the opposite end of the
Wie insbesondere den Figuren 3 bis 6 zu entnehmen,
weist die Fadenbremse 9 einen als einstückiges Drahtbiegeteil
ausgebildeten, im Wesentlichen U-förmigen Bügel 19
auf, der die Halterungsmittel für die Bremsscheiben oder
-teller 10 und deren Lagermittel in Gestalt eines zylindrischen
Lagerstiftes 20 bildet. Der Bügel 19 verfügt über
zwei parallel zueinander verlaufende Schenkel 21, die an
ihrem einen Ende durch einen Quersteg 22 miteinander
verbunden sind, der sich jeweils unter Einschluss eines
rechten Winkels an die Bügelschenkel 21 anschliesst. An
ihrem anderen Ende sind die beiden Bügelschenkel 21 jeweils
über eine Abkröpfung 23 von ca. 30° und dazwischenliegende,
entsprechend gestaltete Zwischenabschnitte 24
mit zwei zueinander parallelen geraden Bügelabschnitten 25
verbunden. Bei diesem Ausführungsbeispiel liegen die
parallelen Bügelabschnitte 25, bezogen auf den in der
Gebrauchslage horizontalen Quersteg 22, in unterschiedlicher
Höhe und schliessen mit einer den Steg 22 und die
beiden Bügelschenkel 21 enthaltenden, gedachten Ebene
einen Winkel von ca. 30° ein. Die Bügelabschnitte 25
können auch gegebenenfalls mit den Zwischenabschnitten 24,
auf gleicher Höhe liegen, um nur einige Anordnungsmöglichkeiten
zu erwähnen.As can be seen in particular from FIGS. 3 to 6,
the
Mit seinen beiden parallelen Bügelabschnitten 25 ist
der Bügel 19 in dem gehäuseförmigen Sockel- oder Aufnahmeteil
14 längsverschieblich gelagert, wie dies insbesondere
aus Figur 2 zu ersehen ist. Das im Wesentlichen quaderförmige,
aus Kunststoff bestehende Sockel- oder Aufnahmeteil
14 weist zu diesem Zwecke zwei von der Vorder- zur Rückseite
durchgehende, zylindrische Lagerbohrungen 26 auf, in
denen die Bügelabschnitte 25 mit in der Gebrauchslage
horizontaler Ausrichtung längsverschieblich geführt sind.
Die geraden Bügelabschnitte 25 sind sowohl der Höhe nach
(Figur 2) als auch seitlich gegeneinander versetzt (Figur
5) angeordnet. Der obenliegende Bügelabschnitt 25 trägt an
seinem über die Rückseite des Sockel- oder Aufnahmeteils
14 vorragenden Ende ein aus Kunststoff bestehendes, im
Wesentlichen in Gestalt einer zylindrischen Kappe 27
ausgebildetes Kupplungsteil für eine in dem Gehäuse 1
angeordnete, nicht weiter dargestellte Schwingungserzeugungseinrichtung,
von der in Figur 2 lediglich ein eine
durch einen Pfeil 28 angedeutete, hin- und hergehende
Bewegung ausführender Antriebsstempel 29 veranschaulicht
ist. Der Antriebsstempel 29 wird von einem auf die Welle 5
der Fadenliefervorrichtung nach Figur 1 aufgesetzten,
nicht dargestellten Nocken betätigt, mit dem er in Eingriff
steht.With its two
In dem Sockel- oder Aufnahmeteil 14 ist eine den
oberen geraden Bügelabschnitt 26 umgebende Druckfeder 30
angeordnet, die sich gegen ein axiales Federwiderlager 31
abstützt und bestrebt ist, das Kupplungsstück 27 in Anlage
an dem Antriebsstempel 29 zu halten. Die Druckfeder 30
bildet deshalb Rückstellfedermittel.In the base or receiving
Der untere gerade Bügelabschnitt 25 ragt bspw. auf
der Rückseite des Sockel- oder Aufnahmeteils 14 bei 31
etwas vor, wie dies in Fig. 2 gestrichelt angedeutet ist.
Er liegt bei an dem Gehäuse 1 montiertem Sockel- oder
Aufnahmeteil 14 an einem Teil des metallischen Gehäuses 1
an und bewirkt damit eine elektrische Erdung des metallischen
Bügels 19. Alternativ oder zusätzlich kann zur
Verbesserung der Erdungsverhältnisse der Bügel 19 auch
eine (nicht dargestellte) Erdungsfeder gegen das Gehäuse 1
andrücken, und/oder der Sockel 14 und/oder die Kappe 27
besteht aus einem elektrisch leitenden Material. The lower
Zur Befestigung des Sockel- oder Aufnahmeteils 14 an
dem Gehäuse 1 dient eine bei 32 angedeutete Befestigungsschraube,
die von der Vorderseite des Sockel- oder Aufnahmeteils
14 aus betätigbar ist.To attach the base or receiving
Auf die in der in Figur 2 dargestellten normalen
Betriebslage mit der Vertikalen einen Winkel von ca. 30°
einschliessenden, in einer gemeinsamen Ebene liegenden
parallelen Schenkel 21 des Bügels 19 ist ein Lagerteil in
Gestalt eines aus Kunststoff hergestellten, im Wesentlichen
U-förmigen Rahmens 33 aufgesetzt, in dem der Lagerstift
20 für die Bremsscheiben 10 an seinen beiden Enden
gehalten ist, wie dies insbesondere aus Figur 4 hervorgeht.
Der Rahmen 33 weist zwei zueinander parallele,
voneinander beabstandete Rahmenschenkel 34 auf, die durch
einen angeformten Rahmensteg 35 an einem Ende miteinander
verbunden sind. Die beiden zueinander parallelen Rahmenschenkel
34 sind auf der in Figur 4 dem Betrachter zugewandten
Innenseite jeweils mit einer rinnenförmigen
Vertiefung 36 ausgebildet, in die in der Nähe des freien
Rahmenschenkelendes jeweils eine Rastnase 37 ragt. Die
Rastnasen 37 sind an der die rinnenförmige Vertiefungen 36
auf der Seite der U-förmigen Öffnung des Rahmens 33 begrenzenden
Wand 38 ausgebildet. Sie dienen dazu, den
Rahmen 33 in der Betriebsstellung mit den Schenkeln 21 des
Bügels 19 lösbar zu verrasten, wie dies im Einzelnen noch
erläutert werden wird.On the normal shown in Figure 2
Operating position with the vertical at an angle of approx. 30 °
inclusive, lying on a common level
Der Rahmensteg 35 ist auf seiner Außenseite mit einer
angeformten Lagerschale oder -pratze 39 versehen, die
bspw. in Fig. 2, 4 sichtbar ist und die bei auf den Bügel
19 aufgesetztem Rahmen 33 den Quersteg 22 elastisch umgreift,
so dass der Rahmen 33 schwenkbar an dem Steg 22
gelagert ist. Die Lagerschale oder -pratze 39 ist dabei
elastisch nachgiebig derart ausgebildet, dass der Rahmen
33 unter Überwindung der von ihr gebildeten Rastverbindung
einfach von dem Bügel 19 abgenommen werden kann. The
Auf seiner dem Lagerstift 20 zugewandten Innenseite
ist der Rahmensteg 35 als Auflage- oder Abstützkissen 40
für die Bremsscheiben oder -teller 10 ausgebildet. Zu
diesem Zweck kann der Rahmenschenkel 35 innen bspw. mit
einem verschleissfesten Überzug versehen sein. Es sind
auch Ausführungsformen denkbar, bei denen ein aus verschleissfestem
Material bestehender Stift oder ein entsprechendes
Formteil in den Rahmen 33 eingesetzt ist, das
das Auflage- oder Abstützkissen 40 bildet. Abhängig von
den Einsatzbedingungen gibt es auch Fälle, bei denen auf
eine besonders verschleißfeste Ausbildung dieses in der
Regel den ganzen Raum zwischen den beiden Rahmenschenkeln
34 einnehmenden Auflage- oder Abstützkissens 40 verzichtet
wird.On its inside facing the bearing
Der aus gehärtetem Stahl, gegebenenfalls mit einer
verschleißfesten Beschichtung, aus Keramik oder aus einem
geeigneten Hartstoff bestehende, dünne, zylindrische
Lagerstift 20 ist auf seinem einen, in Figur 4 unteren
Ende in eine Lagerbohrung 41 eingesteckt, die in der
Innenwand 38 ausgebildet ist. Auf seiner gegenüberliegenden
Seite ist der Lagerstift 20 in einer an dem zugeordneten
Rahmenschenkel 34 vorgesehen, zu der rinnenartigen
Vertiefung 36 hin offenen Lagerhalbschale 43 aufgenommen,
die an den Rahmenschenkel 34 angeformt ist. Die Tiefe der
Lagerhalbschale 43 ist dabei derart gewählt, dass der
eingesetzte Lagerstift 20 mit seiner Mantelfläche etwas
über den Boden der rinnenförmigen Vertiefung 36 vorragt.
Damit wird erreicht, dass bei in der Gebrauchsstellung mit
den Bügelschenkeln 21 verrastetem Rahmen 33 der in diesem
Falle metallische Lagerstift 20 gegen die Bügelschenkel 21
elektrisch leitend elastisch angepresst ist, so dass eine
einwandfreie Erdung des Lagerstiftes 20 über den metallischen
Bügel 19 und das Gehäuse 1 sichergestellt ist. Der
Lagerstift 20 kann auch aus nichtleitendem Material, etwa
Keramik bestehen, was der Ordnung halber erwähnt sei.The hardened steel, possibly with a
wear-resistant coating, made of ceramic or one
suitable hard material, thin,
An dem Lagerstift 20 sind die beiden Bremsteller 10
frei pendelnd aufgehängt. Sie sind zu diesem Zwecke in der
insbesonders aus den Figuren 5, 6 zu entnehmenden Weise
jeweils mit einer mittigen, zylindrischen, durchgehenden
Öffnung 44 ausgebildet, deren Durchmesser um ein Vielfaches
größer ist als der Durchmesser des Lagerstiftes 20.
Das Durchmesserverhältnis beträgt typischerweise etwa 6:1
und mehr. Die im Querschnitt schalenförmig bombiert ausgebildeten
Bremsteller 10 können längs der Berandung der
Öffnung 44 jeweils mit einer als zylindrische Lippe angeformten
Nabe 45 ausgebildet sein, um damit die Beanspruchung
der Bremsteller 10 und des Lagerstiftes 20 zu verringern
und ein Einschneiden der Bremsteller in den Lagerstift
20 zu verhindern. Alternativ kann die Berandung der
Öffnung 44 bei jedem der Bremsteller 10 auch von einem
eingesetzten Nabenring aus Kunststoff oder einem eine
geeignete Lagerpaarung mit dem Lagerstift 20 ergebenden
Material eingefasst sein, wie dies anhand der Fig. 10 noch
erläutert werden wird. In die torusförmige Vertiefung der
Bremsteller 10 sind von außen her Dauermagnetringe 46
eingesetzt, die so magnetisiert sind, dass sie die Bremsteller
10 aufeinander zu drücken und damit deren Belastungsmittel
bilden, wobei die Größe der Belastungskraft
die Bremswirkung auf den durchlaufenden Faden bestimmt.The two
Wie bspw. aus den Figuren 3, 5 hervorgeht, stehen die
beiden Rahmenschenkel 34 im montierten Zustand in beträchtlichem
seitlichem Abstand von den beiden Bremstellern
10. Die beiden aneinander anliegenden Bremsteller 10
sind deshalb in Achsialrichtung über eine beträchtliche
Länge des Lagerstiftes 2C frei beweglich. Sie können im
Betrieb eine Pendel- und Taumelbewegung ausführen. Sie
sind aber von den beiden Rahmenschenkeln 34 im Zusammenwirken
mit dem dünnen Lagerstift 20 unverlierbar in dem
Rahmen 33 gehalten.As can be seen, for example, from FIGS. 3 and 5, the
two
Im Betriebszustand ist der Rahmen 33 mit den auf dem
eingesetzten Lagerstift 20 hängenden Bremstellern 10 mit
seine Lagerschale oder -pratze 39 auf den horizontalen
Steg 22 des Bügels 19 aufgeklippst. Außerdem ist er um die
Achse des Steges 22 so weit hochgeklappt, dass die beiden
Schenkel 21 in den rinnenförmigen Vertiefungen 36 der
Rahmenschenkel 34 aufgenommen sind und der Rahmen 33 mit
den Schenkeln 21 über die Rastnasen 37 verrastet ist. Die
Fadenbremse weist damit den in den Figuren 1, 2 dargestellten
Zustand auf, in dem der zwischen den Bremstellern
10 durchlaufende Faden 11 in dem durch die Anziehungskraft
der Dauermagnetringe 46 gegebenen Maß gleichmäßig gebremst
wird. Dabei werden die beiden gegeneinander gedrückten
Bremsteller 10 von dem um den Lagerstift 20 oder um einen
in der Zeichnung nicht weiter dargestellten, durch die
Öffnungen 44 der Bremsscheiben 10 verlaufenden und in den
Rahmenschenkeln 34 gehalterten Fadenumlenkstift umgelenkten
Faden 11 reibschlüssig angetrieben, so dass sie eine
gemeinsame Drehbewegung um den Lagerstift 20 ausführen.
Dieser Umlaufbewegung ist eine Taumelbewegung in Achsialrichtung
überlagert, da, wie erwähnt, die beiden Bremsteller
10 keine feste seitliche Führung aufweisen. Auf
diese Weise wird erreicht, dass sich der Faden 11 nicht in
die Bremsflächen der Bremsteller 10 einschneiden kann,
sondern dass die Bremsflächen über ihren gesamten Umfang
fortschreitend mit dem Faden in Eingriff kommen.In the operating state, the
Gleichzeitig wird dem Bügel 19 über den Antriebsstempel
29 der Schwingungserzeugungseinrichtung eine hinund
hergehenden Schwingungsbewegung erteilt, unter deren
Einwirkung die Auflagestellen an der Öffnungsberandung der
Bremsteller 10 auf dem Lagerstift 20 sich fortwährend
verändern, so dass die Bremsteller 10 eine unregelmäßige
Bewegung ausführen, die die Ablagerung von Flusen und
dergleichen verhindert.At the same time the
Da die Bremsteller 10 in der beschriebenen Weise
lediglich von dem U-förmigen Rahmen 33 und dem als Drahtbiegeteil
ausgebildeten U-förmigen Bügel 19 gehaltert
sind, sind an der ganzen Fadenbremse wenig Flächen vorhanden,
auf denen sich überhaupt Flusen absetzen können.
Gleichzeitig sind hervorragende Reinigungsverhältnisse
gegeben, weil die Fadenbremse 9 keine toten Winkel oder
Ecken aufweist, in denen sich beim Abblasen mittels eines
Druckluftstrahls Schmutz oder dergleichen ansammeln könnte.Since the
Beispielsweise um die Reinigung nach dem Verarbeiten
von besonders stark verschmutztem Garn weiter zu vereinfachen
oder um den Lagerstift 20 auszustauschen, kann der
Rahmen 33 aus der Betriebsstellung nach Figur 2 unter
Überwindung der Rastnasen 37 einfach um den Steg 22 in
eine Stellung nach Fig. 3 herabgeklappt werden, in der die
beiden Bremsteller 10 aus dem Raum zwischen den beiden
Bügelschenkeln 21 herausgeklappt sind. In dieser Stellung
sind die beiden Bremsteller 10 frei zugänglich.For example, after cleaning after processing
of particularly heavily soiled yarn
or to replace the
Um die Bremsteller 10 aus dem Rahmen 33 zu entnehmen,
wird der Lagerstift 20 an seinem einem Ende aus der Lagerhalbschale
43 nach oben zu herausgedrückt, so dass er
achsial aus der Lagerbohrung 41 herausgezogen werden
kann. Da der Rahmen 33 aus Kunststoff besteht und im
aufgeklappten Zustand nicht durch die Bügelschenkel 21
verstärkt ist, ist er elastisch so verformbar, dass die
geschilderte Demontage des Lagerstiftes 20 leicht möglich
ist. Ein neuer Lagerstift 20 kann in der umgekehrten Weise
wieder eingefügt werden.In order to remove the
Alternativ kann auch derart vorgegangen werden, dass
der ganze Rahmen 33 mit dem Lagerstift 20 und den
Bremstellern 10, in bereits geschilderter Weise, von dem
Bügelsteg 22 abgenommen und gegebenenfalls durch einen
neuen Rahmen 33 ersetzt wird. Nach Abschluss der Reinigungsarbeiten
oder nach Austausch des Lagerstiftes 20 oder
der Bremsteller 10, etc., wird der Rahmen 33 aus der
abgeklappten Stellung einfach wieder in die Betriebsstellung
nach Figur 2, 5 hochgeklappt und in dieser Stellung
über die Rastnasen 37 mit den Schenkeln 21 des Bügels 19
verrastet. Die Bügelschenkel 21 verlaufen, wie Figur 2
zeigt, in der Betriebsstellung beidseitig der Bremsteller
10, so dass diese in der U-förmigen Öffnung des Bügels 19
zwischen dessen beiden Schenkeln 21 aufgenommen sind.Alternatively, one can also proceed in such a way that
the
Es könnte die Anordnung auch derart getroffen sein,
dass der Lagerstift 20 aus dem Rahmen 33 direkt axial
herausziehbar ist, in dem er in wenigstens einer sich nach
außen öffnenden Lagerbohrung 41 gehaltert ist. Der Lagerstift
20 wäre dann in seiner Betriebsstellung im Rahmen 33
durch einen Feststellmechanismus, etwa in Form eines
Rastmechanismus oder durch teilweise Ausbildung als Gewindebolzen
gesichert. Auch andere Ausführungsformen die dem
gleichen Zweck dienen, sind denkbar.The arrangement could also be made in such a way
that the bearing
Es sind auch Ausführungsformen der neuen Fadenbremse
denkbar, bei denen auf den Rahmen 33 ganz verzichtet ist
und der Lagerstift 20 unmittelbar an den Bügelschenkeln 21
des Drahtbügels gehalten ist. Solche Ausführungsvarianten
sind beispielhaft in den Figuren 6a, 6b dargestellt:There are also embodiments of the new thread brake
conceivable in which the
Bei der Ausführungsform nach Figur 6a sind die beiden
Bügelschenkel 21 des U-förmigen Drahtbügels 19a jeweils zu
einer Ringöse 47 gebogen, die die zylindrische Lagerbohrung
41 begrenzt. Die beiden Ringösen 47 fluchten mit
ihren Lagerbohrungen 41, in welche der Lagerstift 20
eingesteckt ist. Der Lagerstift 20 ist dabei beidseitig
von den Ringösen 47 elastisch festgeklemmt. Erforderlichefalls
kann er im Bereiche wenigstens einer Lagerbohrung 41
auch eine Rastvertiefung, etwa in Gestalt einer ringsumlaufenden
Rastnut, aufweisen, um zusätzlich oder alternativ
eine formschlüssig Verbindung mit dem jeweiligen
Bügelschenkel 21 herzustellen. Anstelle der Ausbildung mit
den geschilderten, die Lagerbohrung 41 jeweils vollständig
umschlingenden Ringösen 47, können die Bügelschenkel 21
auch so gebogen sein, dass sie Ω-förmige Ösen 47a aufweisen,
wie dies in Figur 6b, rechte Darstellung, veranschaulicht
ist. In the embodiment according to FIG. 6a, the two are
Schliesslich kann gegebenenfalls auch darauf verzichtet
werden die Bügelschenkel 21 ösenförmig zu biegen. An
die Stelle der Ringösen 47 bzw. der -förmigen Ösen 47a
kann auch eine auf den jeweiligen Bügelschenkel 21 aufgeklippste
und dort reibschlüssig gehaltene hakenförmige
Halterungsklaue 48 treten, wie sie in Figur 6b, linke
Abbildung, dargestellt ist. Die vorzugsweise aus Kunststoff
hergestellten Halteklauen 48 sind endseitig auf den
Lagerstift 20 aufgesteckt. Sie umgreifen mit ihrem Haltemaul
49 den jeweiligen Bügelschenkel 21, auf dem sie reibschlüssig,
unverschieblich gehalten sind.Finally, it can also be omitted if necessary
the
Bei den beschriebenen Ausführungsformen wird der eine
gerade Bügelabschnitt 25 durch die Druckfeder 30 (Figur 2)
in elastischer Anlage an dem Betätigungsstössel 29 (oder
einem Betätigungsnocken) der Schwingungserzeugungseinrichtung
gehalten. Zur Verschleißminderung an der Kontaktstelle
dient das als Kunststoffkappe ausgebildete Kupplungsteil
27. Anstelle der Druckfeder 30 wäre es auch
vorstellbar, die Rückstellung des Bügels 19 bzw. die Anpressung
dessen Bügelabschnitts 25 an dem Antriebsstössel
29 dadurch zu erzielen, dass das den Bügel 19 bildende
Drahtbiegeteil mit einer entsprechenden elastischen Vorspannung
ausgebildet ist. Auch zwangsgeführte Ausführungsformen
mit zwei Auflagestellen dieses Drahtbiegeteils an
dem Antriebsstempel 29 bzw. an der Antriebsnocke sind möglich.
Eine solche Variante ist in Figur 6 angedeutet. Die
Bügelabschnitte 25 sind bei 470 etwa rechtwinklig aufeinander
zuweisend abgebogen. Zwischen den im Abstand stehenden,
abgebogenen Bügelteilen 470 könnte bspw. der
Antriebsstempel oder -stössel 26 gekuppelt sein.In the described embodiments, one
Wird die Fadenbremse 9 ohne Schwingungserzeugungseinrichtung
verwendet, so werden die geraden Bügelabschnitte
25 in dem Sockel- oder Aufnahmeteil 14, bspw. mittels
Klemmschrauben fixiert.If the
In den Figuren 7 bis 10 sind drei verschiedene alternative
Ausführungsformen des Rahmens 33 veranschaulicht:In Figures 7 to 10 there are three different alternatives
Embodiments of
Bei der Ausführungsform nach Figur 7 ist der einstückige,
im Wesentlichen U-förmige Rahmen 33a mit einer
zur Rückseite hin sich öffnenden, ringsumlaufenden, rinnenförmigen
Vertiefung 36a ausgebildet, die sich über die
Rahmenschenkel 34a und den Rahmensteg 35a erstreckt. Der
Rahmen 33a ist durch die entsprechende Bemessung der Vertiefung
36a auf den Bügelschenkeln 21 und dem Bügelsteg 22
verklemmt. Er kann insgesamt nach vorne zu abgenommen
werden, wie dies durch die beiden Pfeile 480 angedeutet
ist. Der Lagerstift 20 ist in dem Rahmen 33a, ähnlich wie
in Figur 4, gehaltert. Ein Lageransatz und die Lagerhalbschale
sind mit 42a bzw. 43a bezeichnet.In the embodiment according to FIG. 7, the one-piece,
substantially
Bei der Ausführungsform nach Figur 8 ist, - wie
übrigens bei allen Ausführungsformen - der Rahmen 33b aus
Kunststoff hergestellt. Seine beiden Rahmenschenkel 34b
und der Rahmensteg 35b sind jeweils mit einer in der Ebene
der beiden Bügelschenkel 21 liegenden und nach außen hin
offenen, rinnenförmigen Vertiefung 36b ausgebildet, in der
die Bügelschenkel 21 liegen. Auf diese Weise ist es möglich,
den ganzen Rahmen 33b in Richtung der Pfeile 490 auf
den Bügelschenkeln 21 zu verschieben, bspw. um die Betriebsverhältnisse
der Fadenbremse zu verändern. Der
Rahmen 33b ist auf den Bügelschenkeln 21 in seiner jeweiligen
Stellung reibschlüssig gehalten. Der Lagerstift 20
ist in diesem Falle einends in einem eigenen, den zugeordneten
Bügelschenkel 21 U-förmig umfassenden und reibschlüssig
mit diesem gekuppelten Schenkelabschnitt 340b
gehaltert, der gegebenenfalls mit dem Schenkel 21 auch
verrastet sein kann. An seinem anderen Ende ist der Lagerstift
20 in einer einseitig offenen, nutartigen Vertiefung
50 des zugeordneten Rahmenschenkels 34 aufgenommen und in
dieser verrastet oder verklemmt. Um den Lagerstift 20 oder
die Bremsteller 10 auszutauschen, wird der Lagerstift 20
um den linken Schenkel 21 herausgeklappt, wie dies durch
einen Pfeil 51 angedeutet ist. Er kann sodann aus seinem
Schenkelabschnitt 340b herausgezogen werden.In the embodiment of Figure 8 is how
by the way, in all embodiments - the
Eine an dem Rahmen 33b angeformte Betätigungsnase 52
erlaubt die Verschiebung des Rahmens 33b im Sinne der
Pfeile 490.An
Bei der Ausführungsform nach Figur 9 ist der Rahmen
33c zweiteilig ausgebildet. Die Rahmenschenkel 34c und der
Rahmensteg 35c sind mit einer durchgehenden, rinnenförmigen
Vertiefung 36c versehen, die sich zu dem von den
beiden Bügelschenkeln 21 begrenzten Raum hin aufeinander
zuweisend öffnen. Der ganze Rahmen 33c kann deshalb in
Richtung der Pfeile 53 nach unten zu auf den Schenkeln 21
verschoben oder von diesen ganz abgezogen werden. Wahlweise
können aber auch die beiden Rahmenschenkel 34c, die
längs einer Trennfuge 55 in dem Rahmensteg 35c voneinander
getrennt sind, seitlich von den Schenkeln 21 abgezogen
werden. Dies ist durch zwei Pfeile 56 angedeutet. Die
Halterung des Lagerstiftes 20 an den Rahmenschenkeln 34c
ist ähnlich wie in Figur 4 gelöst. Entsprechende Teile
sind mit entsprechenden Bezugsbezeichen versehen.9 is the
Bei den Ausführungsformen nach den Figuren 8, 9 ist
das Auflage- oder Abstützkissen 40 für die Bremsscheiben
10 im Einzelnen nicht veranschaulicht. Es kann ähnlich,
wie bei dem Rahmen 33 nach Figur 4 gestaltet sein. Es
dient in jedem Falle dazu die Bremsteller 10 im Betrieb an
ihrem Außenumfang radial in ihrem Bewegungsweg zu begrenzen.
Die an dem Lagerstift 20 hängenden Bremsteller 10
liegen in ihrer in Figur 2 dargestellten Betriebsstellung
unten auf dem Auflage- oder Abstützkissen 40 auf, von dem
sie sich im Verlaufe ihrer unregelmäßigen Taumel- und
Drehbewegung während des Betriebes mehr oder weniger oft
abheben.In the embodiments according to FIGS. 8, 9
the support or
Wie bereits früher erwähnt, kann es, bspw. abhängig
von den Einsatzbedingungen der Fadenbremse 9, zweckmäßig
sein, insbesondere die Lagerverhältnisse deren Bremsscheiben
oder -teller 10 auf dem Lagerstift 20 an die jeweiligen
Einsatzbedingungen anzupassen. Beispiele dafür sind in
Fig. 10 schematisch dargestellt:As mentioned earlier, it can depend, for example
from the operating conditions of the
Bei der Ausführungsform a) sind auf die Bremsscheiben
oder -teller 10 aus einem geeigneten Kunststoff bestehende
ringförmige Kappen 60 aufgeklippst, die mit ihren ringsumlaufenden
vorstehenden Randbereichen 61, 62 die Bremsteller
10 auf dem Außenumfang und längs des Umfangs der
Öffnung 44 übergreifen, derart, dass sie an den Bremstellern
10 verrastet sind. Die Kappen 60 decken die Höhlung
der bombierten Bremsteller 10 in der dargestellten
Weise ab, wobei sie gleichzeitig die Dauermagnetringe 46
lagerichtig fixieren, so dass ein zusätzliches Einkleben,
etc. derselben in der Regel nicht mehr erforderlich ist.In embodiment a) are on the brake discs
or
Der die Öffnung 44 säumende Rand 62 bildet gleichzeitig
eine im Wesentlichen rohrförmige Nabe, die gegebenenfalls
im Querschnitt gewölbt ausgebildet ist. Auf diese
Weise ergeben sich besonders günstige Lagerungsverhältnisse
der Bremsteller 10 auf dem Lagerstift 20.The
In diesem Zusammenhang kann es auch zweckmäßig sein
an den die Öffnung 44 säumenden Rand 62 innen eine ringscheibenförmige
Lippe 63 anzuformen, wie dies die Abbildung
b) zeigt. Die ringscheibenförmigen Lippen 63 ergeben
eine geringe axiale Breite der Lagerfläche und damit eine
erhöhte Flächenpressung. Dies kann von Vorteil sein, wenn
damit gerechnet werden muss, dass sich auf dem Lagerstift
20 Garnschlichte oder andere harzige oder klebrige Ablagerungen
aufbauen.In this context it can also be useful
on the
Wird auf die Kappen 60 verzichtet, so kann, wie in
Abbildung c) veranschaulicht, die ringscheibenförmige
Lippe auch in Gestalt einer Ringscheibe 63a ausgebildet
sein, die auf den Dauermagnetring 46a aufgesetzt ist, der
zu diesem Zwecke mit einer Ringschulter 64 versehen ist.
Die Dauermagnetringe 46a sind mit den Bremstellern 10
verklebt, wobei die Ringscheiben 63a jeweils zwischen
ihrem Rand und der Ringschulter 64 des entsprechenden
Dauermagnetringen 46a eingefügt sind.If the
Anstelle der die Bremsteller 10 umgreifenden Kappen
60 der Abbildungen a) und b) kann in die bombierten
Bremsteller 10 auch ein ringscheibenförmiger Deckel 65
eingeklippst sein, wie es in den Abbildungen d) und e)
veranschaulicht ist. Dieser insbesondere aus Kunststoff
bestehende Deckel 65 hält den Dauermagnetring 46 lagefest,
wobei die Bremsteller 10 an der Innenberandung ihrer
Öffnung 44 unmittelbar auf den Lagerstift 20 gelagert
sind.Instead of the caps surrounding the
An diese die Dauermagnetringe 46 haltenden eingeklippsten
Deckel 65 kann auch eine ringscheibförmige Lippe
65a geringer Dicke angeformt sein, die die Nabe der Bremstellern
10 bildet, so dass sich ähnliche Lagerungsverhältnisse
wie bei den Abbildungen b) und c) ergeben.The permanent magnet rings 46 are clipped onto them
Cover 65 can also have an annular disk-shaped lip
65a of a small thickness, which is the hub of the
Abschließend sei erwähnt, dass die Erfindung nicht
auf Ausführungsformen beschränkt ist, bei denen die
Bremsteller 10 an einem dünnen Lagerstift 20 pendelnd
aufgehängt sind. Sie ist auch für Fadenbremsen anwendbar,
bei denen die Bremsteller auf einem Lagerbolzen oder
-stift lediglich mit Spiel drehbar gelagert sind.In conclusion, it should be mentioned that the invention is not
is limited to embodiments in which the
Claims (27)
- Thread brake with two disc- or plate-shaped braking elements (10), which are pushed flexibly against one another by biasing means (46) and between which at least one thread (11) to be braked can be passed, at least one braking element of which comprises a central opening (44),
with pin-shaped bearing means (20), which are disposed so as to extend through the central opening (44) of the at least one braking element (10) and on which at least this braking element is rotatably mounted, and
with retaining means for the bearing means (20), characterised in that the retaining means comprise a substantially U-shaped clip (19) with two legs (21) extending at a spacing on both sides of the braking element (10), to which clip the bearing means (20) are fastened by means of at least one bearing part (33, 47) which holds them and which is formed at or connected to at least one of the clip legs (21). - Thread brake according to Claim 1, characterised in that the clip (19) is a one-piece bent wire part.
- Thread brake according to Claim 2, characterised in that eyelet-shaped bearing parts (47, 47a) are moulded onto the clip (19).
- Thread brake according to any one of the preceding Claims, characterised in that the clip (19) comprises two parallel clip portions (25), by means of which it is mounted in a holding part (14).
- Thread brake according to Claim 4, characterised in that the clip portions (25) are mounted so as to be longitudinally displaceable in the holding part (14).
- Thread brake according to Claim 5, characterised in that at least one of the clip portions (25) is adapted for coupling to an oscillation generating device (29) which imparts a reciprocating oscillating movement to the clip.
- Thread brake according to Claim 6, characterised in that at least one of the clip portions (25) is loaded by return spring means (30) for pushing it elastically into a predetermined end position.
- Thread brake according to any one of Claims 2 to 7, characterised in that the two clip legs (21) comprise an angled part (23).
- Thread brake according to any one of Claims 4 to 8, characterised in that the bearing part (33) is formed such that it can be removed from the clip (19).
- Thread brake according to any one of Claims 4 to 9, characterised in that the bearing part (33b) is disposed so as to be adjustable on the clip (19).
- Thread brake according to any one of Claims 4 to 10, characterised in that the bearing part is in the form of a substantially U-shaped frame (33).
- Thread brake according to Claim 11, characterised in that the frame (33, 33a) is disposed such that it can be locked on the clip (19).
- Thread brake according to Claim 11 or 12, characterised in that the frame (33) can be pivoted at the clip (19) between an operating position and a swung-down position and is formed such that it can be fixed to the clip in the operating position.
- Thread brake according to any one of Claims 11 to 13, characterised in that the frame (33) comprises a region (40) which acts as support means for the braking elements (10).
- Thread brake according to any one of Claims 11 to 14, characterised in that the frame (33a) is clamped on the clip (19) in a releasable fashion.
- Thread brake according to any one of Claims 11 to 15, characterised in that the frame (33c) is of split formation.
- Thread brake according to Claim 14, characterised in that the bearing means (20) are disposed at one end at a frame part (340b), which is pivotably mounted on a clip leg, and that the other frame part comprises holding means (50) for the other end of the bearing means.
- Thread brake according to any one of Claims 4 to 17, characterised in that the bearing part (33) is made of a plastics material.
- Thread brake according to any one of the preceding Claims 4, characterised in that the bearing means (20) are fastened to the bearing part (33, 47, 47a) in a releasable fashion.
- Thread brake according to any one of the preceding Claims 4, characterised in that the bearing means (20) are maintained connected in an electrically conductive fashion to the clip (19), and that the clip is adapted for earthing.
- Thread brake according to any one of the preceding Claims, characterised in that the bearing part (33, 47, 47a) is disposed obliquely to the vertical in the operating position.
- Thread brake according to any one of the preceding Claims, characterised in that it comprises at least one thread guide member (16) permanently associated with the clip (19).
- Thread brake according to any one of the preceding Claims, characterised in that the bearing means (20) are retained at the clip (19 at both ends.
- Thread brake according to any one of the preceding Claims, characterised in that the braking elements comprise brake discs or plates (10), with which magnetic loading means (46) are associated, these being covered by attached or inserted covering means (60, 65).
- Thread brake according to any one of the preceding Claims, characterised in that the braking elements comprise brake discs or plates (10), which are in each case mounted on the bearing means (20) via an annular disc-shaped hub (63a, 65a).
- Thread supply apparatus with a housing (1),
a thread supply cylinder (6),
a drive device (8), which is connected to the thread supply cylinder,
thread guide means (12, 18), which are disposed at the housing and via which the thread (11) which is to be supplied can be routed to the thread supply cylinder on the feed side and carried away from the latter on the delivery side to a thread consumer, and with a thread brake (9), which is disposed at the housing on the thread feed side, according to any one of the preceding Claims. - Thread supply apparatus according to Claim 26, characterised in that the thread brake (9) comprises a clip (19) with parallel clip portions (25), which are mounted directly in the housing (1) or in a part (14) which is connected thereto.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE19743573 | 1997-10-02 | ||
| DE19743573A DE19743573A1 (en) | 1997-10-02 | 1997-10-02 | Thread brake |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0906885A2 EP0906885A2 (en) | 1999-04-07 |
| EP0906885A3 EP0906885A3 (en) | 2000-10-25 |
| EP0906885B1 true EP0906885B1 (en) | 2003-04-16 |
Family
ID=7844391
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP98116792A Expired - Lifetime EP0906885B1 (en) | 1997-10-02 | 1998-09-05 | Brake for textile threads |
Country Status (23)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US6135382A (en) |
| EP (1) | EP0906885B1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP2950820B2 (en) |
| KR (1) | KR100308840B1 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN1064644C (en) |
| AR (1) | AR010948A1 (en) |
| BR (1) | BR9803855C1 (en) |
| CO (1) | CO4840533A1 (en) |
| CZ (1) | CZ319398A3 (en) |
| DE (2) | DE19743573A1 (en) |
| EA (1) | EA000426B1 (en) |
| EG (1) | EG22266A (en) |
| ES (1) | ES2192723T3 (en) |
| HK (1) | HK1019346A1 (en) |
| ID (1) | ID21007A (en) |
| MY (1) | MY133051A (en) |
| PE (1) | PE117099A1 (en) |
| PL (1) | PL186630B1 (en) |
| PT (1) | PT906885E (en) |
| SG (1) | SG72862A1 (en) |
| TR (1) | TR199801979A2 (en) |
| TW (1) | TW419542B (en) |
| UA (1) | UA44839C2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN105256454B (en) * | 2015-11-02 | 2017-05-03 | 东莞今富五金机械有限公司 | Yarn pressing mechanism, yarn storage device and stopping device |
| IT201800007866A1 (en) * | 2018-08-06 | 2020-02-06 | Lgl Electronics Spa | WEFT BRAKE DEVICE FOR ACCUMULATION YARN FEEDERS |
| CN108754795A (en) * | 2018-09-12 | 2018-11-06 | 太平洋纺织机械(常熟)有限公司 | Pair of weft heating scissors for a rapier loom device |
| EP4101965A1 (en) * | 2021-06-11 | 2022-12-14 | KARL MAYER STOLL R&D GmbH | Yarn brake |
Family Cites Families (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US1424124A (en) * | 1922-07-25 | Island | ||
| US1462292A (en) * | 1921-06-09 | 1923-07-17 | Foster Machine Co | Device for guiding, clearing, and tensioning yarn |
| US3181569A (en) * | 1964-02-06 | 1965-05-04 | Beacon Mfg Co | Filling yarn control means |
| US4449355A (en) * | 1982-10-18 | 1984-05-22 | Milliken Research Corporation | A.C.-D.C. Slotted type yarn tension control |
| DE4301507C2 (en) * | 1993-01-21 | 1995-01-26 | Memminger Iro Gmbh | Thread brake |
| DE4409450C2 (en) * | 1994-03-18 | 1996-12-05 | Memminger Iro Gmbh | Thread braking device |
-
1997
- 1997-10-02 DE DE19743573A patent/DE19743573A1/en not_active Withdrawn
-
1998
- 1998-09-05 ES ES98116792T patent/ES2192723T3/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1998-09-05 DE DE59807945T patent/DE59807945D1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1998-09-05 PT PT98116792T patent/PT906885E/en unknown
- 1998-09-05 EP EP98116792A patent/EP0906885B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1998-09-09 SG SG1998003591A patent/SG72862A1/en unknown
- 1998-09-14 PL PL98328557A patent/PL186630B1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1998-09-22 CO CO98054617A patent/CO4840533A1/en unknown
- 1998-09-22 ID IDP981275A patent/ID21007A/en unknown
- 1998-09-22 PE PE1998000902A patent/PE117099A1/en not_active Application Discontinuation
- 1998-09-24 MY MYPI98004379A patent/MY133051A/en unknown
- 1998-09-28 JP JP10272663A patent/JP2950820B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1998-09-29 EG EG117998A patent/EG22266A/en active
- 1998-09-30 CN CN98120814A patent/CN1064644C/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1998-09-30 BR BR9803855-9A patent/BR9803855C1/en active Search and Examination
- 1998-09-30 UA UA98095181A patent/UA44839C2/en unknown
- 1998-09-30 TW TW087116206A patent/TW419542B/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1998-10-01 US US09/164,739 patent/US6135382A/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1998-10-01 EA EA199800788A patent/EA000426B1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1998-10-01 KR KR1019980041344A patent/KR100308840B1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1998-10-02 AR ARP980104930A patent/AR010948A1/en active IP Right Grant
- 1998-10-02 TR TR1998/01979A patent/TR199801979A2/en unknown
- 1998-10-02 CZ CZ983193A patent/CZ319398A3/en unknown
-
1999
- 1999-10-06 HK HK99104369A patent/HK1019346A1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CZ319398A3 (en) | 1999-04-14 |
| CO4840533A1 (en) | 1999-09-27 |
| EP0906885A3 (en) | 2000-10-25 |
| JP2950820B2 (en) | 1999-09-20 |
| JPH11165953A (en) | 1999-06-22 |
| TW419542B (en) | 2001-01-21 |
| US6135382A (en) | 2000-10-24 |
| MY133051A (en) | 2007-10-31 |
| KR100308840B1 (en) | 2001-12-28 |
| PL328557A1 (en) | 1999-04-12 |
| PT906885E (en) | 2003-08-29 |
| ES2192723T3 (en) | 2003-10-16 |
| AR010948A1 (en) | 2000-07-12 |
| EA199800788A1 (en) | 1999-04-29 |
| TR199801979A3 (en) | 1999-04-21 |
| HK1019346A1 (en) | 2000-02-03 |
| EP0906885A2 (en) | 1999-04-07 |
| SG72862A1 (en) | 2000-05-23 |
| DE59807945D1 (en) | 2003-05-22 |
| BR9803855A (en) | 2000-03-08 |
| PE117099A1 (en) | 1999-12-13 |
| DE19743573A1 (en) | 1999-04-15 |
| KR19990036762A (en) | 1999-05-25 |
| PL186630B1 (en) | 2004-02-27 |
| EG22266A (en) | 2002-11-30 |
| EA000426B1 (en) | 1999-06-24 |
| ID21007A (en) | 1999-04-08 |
| CN1213718A (en) | 1999-04-14 |
| UA44839C2 (en) | 2002-03-15 |
| TR199801979A2 (en) | 1999-04-21 |
| BR9803855C1 (en) | 2000-11-14 |
| CN1064644C (en) | 2001-04-18 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0499218B1 (en) | Yarn brake | |
| DE60012423T2 (en) | Cutting head for bush mower or edge trimmer | |
| EP3268526B1 (en) | Needle cylinder and circular knitting machine | |
| EP0943023B1 (en) | Device for controlling the transverse movement of at least one thread in a textile machine | |
| EP0190405A1 (en) | Apparatus for removing single bobbins from a container | |
| EP0906885B1 (en) | Brake for textile threads | |
| DE3505913A1 (en) | Yarn-tensioning device on a bobbin creel | |
| DE4301507C2 (en) | Thread brake | |
| CH635137A5 (en) | CIRCULAR COMB FOR COTTON OR WOOL COMBING MACHINE. | |
| EP0446560B1 (en) | Slay mechanism with eccentric slay shaft for a loom | |
| EP0631825B1 (en) | Finger-sieve | |
| DE1785157B1 (en) | Device for cutting through a running textile yarn | |
| EP0529185B1 (en) | Vibratory conveyor | |
| DE4234170A1 (en) | Fastening on vibratory conveyor for tightening conveyor-pots - is mounted on vibratory tray carrier on upper side of driving unit with anchor and actuator moving bottom of conveyor-pot towards carrier | |
| WO1999013145A1 (en) | Thread controlling assembly | |
| DE2701525A1 (en) | ELECTROMAGNETIC PATTERN DEVICE FOR CIRCULAR KNITTING MACHINES | |
| EP3441509B1 (en) | Feed table for a sliver opening device of an open-end spinning device | |
| DE19902465A1 (en) | Yarn feed mechanism for knitter or loom | |
| EP1392900B1 (en) | Attachment for an opening, grading or combing device on textile machinery | |
| DE3144304C2 (en) | ||
| EP0673287A1 (en) | Tension wave strainer | |
| EP0504619B1 (en) | Washing machine | |
| DE8318792U1 (en) | THREAD STORAGE AND DELIVERY DEVICE FOR TEXTILE MACHINES | |
| DE2919916A1 (en) | THREAD FEEDER FOR FLAT KNITTING MACHINES | |
| DE29618765U1 (en) | Elastic deformable rod held at the end in a holder |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AT ES FR GB GR IT PT Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): DE ES FR GB GR IT PT |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Free format text: AL;LT;LV;MK;RO;SI |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Free format text: AL;LT;LV;MK;RO;SI |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20000929 |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid |
Free format text: ES FR GB GR IT PT |
|
| AXX | Extension fees paid |
Free format text: LT PAYMENT 20001122;RO PAYMENT 20001122 |
|
| RBV | Designated contracting states (corrected) |
Designated state(s): AT ES FR GB GR IT PT |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: 8566 |
|
| RBV | Designated contracting states (corrected) |
Designated state(s): DE ES FR GB GR IT PT |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| RTI1 | Title (correction) |
Free format text: BRAKE FOR TEXTILE THREADS |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): DE ES FR GB GR IT PT |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: LT RO |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 59807945 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20030522 Kind code of ref document: P |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GR Ref legal event code: EP Ref document number: 20030402143 Country of ref document: GR |
|
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) | ||
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FG2A Ref document number: 2192723 Country of ref document: ES Kind code of ref document: T3 |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20040119 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GR Payment date: 20050927 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PT Payment date: 20060818 Year of fee payment: 9 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20060922 Year of fee payment: 9 Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20060922 Year of fee payment: 9 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Payment date: 20060926 Year of fee payment: 9 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: PT Ref legal event code: MM4A Free format text: LAPSE DUE TO NON-PAYMENT OF FEES Effective date: 20080305 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20070905 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20080305 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST Effective date: 20080531 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20070404 Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20071001 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20070905 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FD2A Effective date: 20070906 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20070906 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20170921 Year of fee payment: 20 Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20170926 Year of fee payment: 20 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R071 Ref document number: 59807945 Country of ref document: DE |