EP0906514B1 - Rotor for a turbomachine with blades insertable into grooves and blades for a rotor - Google Patents
Rotor for a turbomachine with blades insertable into grooves and blades for a rotor Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0906514B1 EP0906514B1 EP97928110A EP97928110A EP0906514B1 EP 0906514 B1 EP0906514 B1 EP 0906514B1 EP 97928110 A EP97928110 A EP 97928110A EP 97928110 A EP97928110 A EP 97928110A EP 0906514 B1 EP0906514 B1 EP 0906514B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- rotor
- blade root
- turbomachine
- blade
- slot
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F04—POSITIVE - DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS FOR LIQUIDS OR ELASTIC FLUIDS
- F04D—NON-POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT PUMPS
- F04D29/00—Details, component parts, or accessories
- F04D29/26—Rotors specially for elastic fluids
- F04D29/32—Rotors specially for elastic fluids for axial flow pumps
- F04D29/38—Blades
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F01—MACHINES OR ENGINES IN GENERAL; ENGINE PLANTS IN GENERAL; STEAM ENGINES
- F01D—NON-POSITIVE DISPLACEMENT MACHINES OR ENGINES, e.g. STEAM TURBINES
- F01D5/00—Blades; Blade-carrying members; Heating, heat-insulating, cooling or antivibration means on the blades or the members
- F01D5/30—Fixing blades to rotors; Blade roots ; Blade spacers
- F01D5/3007—Fixing blades to rotors; Blade roots ; Blade spacers of axial insertion type
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F01—MACHINES OR ENGINES IN GENERAL; ENGINE PLANTS IN GENERAL; STEAM ENGINES
- F01D—NON-POSITIVE DISPLACEMENT MACHINES OR ENGINES, e.g. STEAM TURBINES
- F01D5/00—Blades; Blade-carrying members; Heating, heat-insulating, cooling or antivibration means on the blades or the members
- F01D5/30—Fixing blades to rotors; Blade roots ; Blade spacers
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F04—POSITIVE - DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS FOR LIQUIDS OR ELASTIC FLUIDS
- F04D—NON-POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT PUMPS
- F04D29/00—Details, component parts, or accessories
- F04D29/26—Rotors specially for elastic fluids
- F04D29/32—Rotors specially for elastic fluids for axial flow pumps
- F04D29/321—Rotors specially for elastic fluids for axial flow pumps for axial flow compressors
- F04D29/322—Blade mountings
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a rotor for a turbomachine with blades which can be fitted in grooves, the grooves are attached obliquely to the axis of rotation of the rotor, and a blade for a rotor.
- a rotor for example known from US-A-2 643 853.
- GB-A-2 237 846 relates to a gas turbine for an aircraft engine, reducing the mass of the turbine rotor to increase safety when operating a maximum speed is described. This mass reduction takes place in that the blade root of a turbine blade two separated by a continuous groove and has spaced parts. These parts of the Blade root are spaced from each other by two partitions, which lead to a spreading of the blade root.
- the object of the present invention is now that in operation to reduce a strength problem occurring in a rotor and specify a suitable combination of blade root and groove.
- a rotor for a turbomachine is used to solve this task with the features of claim 1 and with a shovel the features of claim 6.
- Advantageous features and combinations result from the in the respective dependent claims disclosed features.
- a preferred embodiment provides that a corresponding adapted area of the blade root and a stiffer in contrast Area of the groove to each other or opposite. Thereby is achieved that the corresponding stiffness of the groove and Blade base correspond so that there is an equalization of the tensions that occur.
- the flow of force when transmitting power from the blade root in the groove can be designed inexpensively with appropriate adaptation. It is also favorable if the highest occurring in the groove area Voltage, in particular in the area of sharp corners of the groove in the rotor, an area diminished Stiffness of the blade root is present, so that when the Turbomachine no tensions occur, leading to destruction or material fatigue from prolonged operation of the turbomachine to lead.
- An advantageous and preferred embodiment of the invention is based on a gas turbine compressor, which is a preferred turbomachine for applying the invention, shown.
- the rotor 1 of the turbomachine is preferably off axially arranged one behind the other, interlocked (Serration), by a tie rod, not shown interconnected rotor disks 1 are formed.
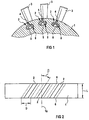
- FIG. 1 shows a section of a rotor disk 1 with a groove. 2 inserted blades 3.
- Each blade 3 has areas with different stiffness. Suitable for this is in Blade foot 4 has a recess 5 so that the groove 2, which have an unevenly high rigidity across their groove depth has an adapted rigidity of the blade root 4 opposite. Since one in particular at the sharp corner 6 (see FIG. 2) Groove 2, which is located at the end of the groove, during operation of the gas turbine increased voltages occur in the compressor Area of the blade root 4, the recess 5 is formed on that, at this point, he is slightly compliant. An advantageous one Design of the recess 5 sees this in the form a cutout on the front 8 of the blade root 4 runs out of it at an angle downwards.
- FIG. 2 shows the rotor disk 1 from FIG. 1 in a top view.
- the grooves 2 are at an installation angle ⁇ to the axis of rotation the rotor disc 1 attached, due to the adapted Bucket feet 4 can be much larger compared to conventional installation angles. This is especially important for Gas turbines and their compressors with a low mass flow special role. There can be larger blade angles and thus larger installation angles ⁇ may be required. This leads in turn to increased local stresses in the groove 2, especially in the sharp corners 6 stiffness reduced by the increased angle available.
- the pointed corners 6 are places higher locally Tension. They are the ends of the dashed lines, groove width D located on the inside of the rotor 1. Seen over the groove length L, it is not only in their depth, but also different in their extent Areas of different voltages, therefore different Influence on the strength when the blade root is installed 4 and operation of the turbomachine.
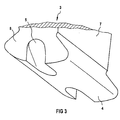
- Figure 3 shows a blade root 4 according to the invention with indicated Extension of the blade 7 of the blade 3.
- This has a recess 5 starting at both End faces 8, which are inclined downward from the blade root 4 run out.
- This reduction in material in the blade root 4 leads to reduced stiffness in areas of the end faces 8 and also in adjacent areas of the blade root 4.
- Such adapted areas have greater elasticity, so that deformations occurring in operation, especially also the sharp corners 6 can be caught cheaper.
- FIG. 4 shows the blade 3 from FIG. 3 in the installed state.
- the reduction in material 5 in the blade root 4 leads to that lines of force in the blade root 4 are interrupted and on these places the blade root 4 against loads on Arise on the blade 7 due to the acting blade forces, over the adapted blade root 4 in the middle area the groove length L is deflected and received there via the groove 2 become.
- FIG. 5 shows a further embodiment of the invention.
- the built-in blade root 4 has a recess 5 in a rather elongated shape that extends towards the center of the groove depth pulls out of the blade root 4 below.
- This recess can not only by means of milling but also through a hole or similar machining methods can be achieved.
- For the purpose of of the invention are not only recesses 5 as adjustments to understand the rigidity of areas of the blade root 4. Rather, all measures that affect the rigidity of a Change blade root in at least one area, applicable. For example, inserting or processing one other material in the blade root possible, which opposite this has a higher elasticity. Is particularly cheap it that in compressors or generally turbomachinery, which in alternating operation, an adjustment of the areas of the blade root 4 to that operating area of the turbomachine is ajar, in which this is mostly driven becomes.
- the invention creates in this example depending on Size of the recess and slope of the installation angle a reduction of local stresses of 30% and more.
- the advantage The invention is its low cost, its effectiveness as well as the subsequent rigidity adjustment of blade feet with turbo machines already in operation.
- Another advantage of the invention is the interchangeability Shovels. This means that shovel feet can be made with and without material reduction be mounted together in a rotor disk.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Structures Of Non-Positive Displacement Pumps (AREA)
- Turbine Rotor Nozzle Sealing (AREA)
Description
Die vorliegende Erfindung betrifft einen Rotor für eine Turbomaschine mit in Nuten anbringbaren Schaufeln, wobei die Nuten schräg zur Rotationsachse des Rotors angebracht sind, sowie eine Schaufel für einen Rotor. Ein solcher Rotor ist zum Beispiel aus der US-A-2 643 853 bekannt.The present invention relates to a rotor for a turbomachine with blades which can be fitted in grooves, the grooves are attached obliquely to the axis of rotation of the rotor, and a blade for a rotor. One such rotor is for example known from US-A-2 643 853.
Bei Rotoren von Turbomaschinen können aufgrund der Rotation hohe Fliehkräfte auftreten. Bei in einem Rotor anbringbaren Schaufeln besteht zudem die Schwierigkeit, den Rotor so auszulegen, daß er zum einen eine genügende Festigkeit aufweist, zum anderen aber gewisse Abmessungsgrenzen, die von den Belastungen der Turbomaschine abhängen, nicht überschreitet. Die Schaufeln, die in Nuten anbringbar sind, müssen dazu einen geeigneten Schaufelfuß aufweisen. Je nach Konstruktionsprinzip der Verbindung zwischen Schaufelfuß und Rotor treten zwischen diesen unterschiedliche Spannungen auf. Diese verteilen sich über den Schaufelfuß unterschiedlich. Ein Einflußparameter auf die auftretenden Spannungen beim Betrieb der Turbomaschine ist beispielsweise der Einbauwinkel des Schaufelfußes in die Welle. With rotors of turbomachinery, due to the rotation high centrifugal forces occur. When attachable in a rotor Blades are also difficult to design the rotor so that on the one hand it has sufficient strength, on the other others but certain dimensional limits from the loads depend on the turbomachine, do not exceed. The shovels, that can be attached in grooves must be suitable Have blade root. Depending on the construction principle of the connection between blade root and rotor occur between them different voltages. These are spread over the Blade base different. An influencing parameter on the occurring For example, voltages during the operation of the turbomachine the installation angle of the blade root in the shaft.
Die GB-A-2 237 846 betrifft eine Gasturbine für ein Flugzeugtriebwerk, bei der eine Reduzierung der Masse des Turbinenläufers zur Erhöhung der Sicherheit beim Betrieb bei einer maximalen Geschwindigkeit beschrieben ist. Diese Massenreduktion findet dadurch statt, daß der Schaufelfuß einer Turbinenschaufel zwei voneinander durch eine durchgehende Nut getrennte und beabstandete Teile aufweist. Diese Teile des Schaufelfußes werden durch zwei Trennwände voneinander beabstandet, welche zu einer Spreizung des Schaufelfußes führen. GB-A-2 237 846 relates to a gas turbine for an aircraft engine, reducing the mass of the turbine rotor to increase safety when operating a maximum speed is described. This mass reduction takes place in that the blade root of a turbine blade two separated by a continuous groove and has spaced parts. These parts of the Blade root are spaced from each other by two partitions, which lead to a spreading of the blade root.
Aufgabe der vorliegenden Erfindung ist es nun, die im Betrieb eines Rotors auftretenden Festigkeitsprobleme zu mindern'und eine dazu geeignete Kombination von Schaufelfuß und Nut anzugeben.The object of the present invention is now that in operation to reduce a strength problem occurring in a rotor and specify a suitable combination of blade root and groove.
Zur Lösung dieser Aufgabe dienen ein Rotor für eine Turbomaschine mit den Merkmalen des Anspruches 1 und eine Schaufel mit den Merkmalen des Anspruches 6. Vorteilhafte Merkmale und Kombinationen ergeben sich aus den in den jeweils abhängigen Ansprüchen offenbarten Merkmalen.A rotor for a turbomachine is used to solve this task with the features of claim 1 and with a shovel the features of claim 6. Advantageous features and combinations result from the in the respective dependent claims disclosed features.
Ein erfindungsgemäßer Rotor mit in Nuten anbringbaren Schaufeln, bei dem die Nuten schräg zu der Rotationsachse des Rotors angebracht sind, weist bei zumindest einem Teil seiner Schaufeln einen Schaufelfuß mit mindestens zwei Bereichen mit unterschiedlicher Steifigkeit auf, die an unterschiedliche Bereiche der Steifigkeit der Nut, in die der Schaufelfuß anbringbar ist, angepaßt, vorzugsweise angeglichen, sind.A rotor according to the invention with blades which can be fitted in grooves, where the grooves are oblique to the axis of rotation of the rotor are attached, points to at least part of its blades a blade root with at least two areas with different Stiffness based on different areas the rigidity of the groove in which the blade root can be attached, adapted, preferably aligned.
Eine bevorzugte Ausgestaltung sieht vor, daß ein entsprechend angepaßter Bereich des Schaufelfußes und ein demgegenüber steiferer Bereich der Nut aneinander- oder gegenüberliegen. Dadurch wird erreicht, daß entsprechende Steifigkeiten von Nut und Schaufelfuß sich so entsprechen, daß es zu einer Vergleichmäßigung der auftretenden Spannungen insgesamt kommt. Insbesondere der Kraftfluß bei der Kraftübertragung vom Schaufelfuß in die Nut ist bei entsprechender Anpassung günstig gestaltbar. Günstig ist es weiterhin, wenn im Nutbereich höchster auftretender Spannung, im allgemeinen insbesondere im Bereich der spitzen Ecken der Nut in dem Rotor, ein Bereich verminderter Steifigkeit des Schaufelfußes anliegt, so daß bei Betrieb der Turbomaschine keine Spannungen auftreten, die zur Zerstörung oder Materialermüdung über längeren Betrieb der Turbomaschine führen.A preferred embodiment provides that a corresponding adapted area of the blade root and a stiffer in contrast Area of the groove to each other or opposite. Thereby is achieved that the corresponding stiffness of the groove and Blade base correspond so that there is an equalization of the tensions that occur. In particular the flow of force when transmitting power from the blade root in the groove can be designed inexpensively with appropriate adaptation. It is also favorable if the highest occurring in the groove area Voltage, in particular in the area of sharp corners of the groove in the rotor, an area diminished Stiffness of the blade root is present, so that when the Turbomachine no tensions occur, leading to destruction or material fatigue from prolonged operation of the turbomachine to lead.
Eine vorteilhafte Ausgestaltung der Erfindung wird anhand der Ausführungsbeispiele der folgenden Zeichnungen erläutert. Weitere vorteilhafte Ausgestaltungen ergeben sich durch geeignete Kombinationen der offenbarten Markmale der Erfindung. Es zeigen:
- Figur 1
- einen Rotor mit erfindungsgemäß angepaßten und eingesetzten Schaufeln im Querschnitt,
Figur 2- den Rotor aus Figur 1 in einer Aufsicht ohne eingesetzte Schaufeln,
Figur 3- einen erfindungsgemäßen Schaufelfuß,
Figur 4- den in einer Läuferscheibe eingesetzten Schaufelfuß
aus
Figur 3, Figur 5- einen weiteren erfindungsgemäßen eingesetzten Schaufelfuß.
- Figure 1
- a rotor with blades adapted and used according to the invention in cross section,
- Figure 2
- 2 the rotor from FIG. 1 in a top view without inserted blades,
- Figure 3
- a blade root according to the invention,
- Figure 4
- the blade root from FIG. 3 used in a rotor disk,
- Figure 5
- another blade root used according to the invention.
Eire vorteilhafte und bevorzugte Ausgestaltung der Erfindung wird im folgenden anhand eines Gasturbinenverdichters, welcher eine bevorzugte Turbomaschine zur Anwendung der Erfindung ist, dargestellt. Der Rotor 1 der Turbomaschine ist vorzugsweise aus axial hintereinander angeordneten, miteinander verzahnten (Hirthverzahnung), durch einen nicht dargestellten Zuganker miteinander verbundenen Läuferscheiben 1 gebildet.An advantageous and preferred embodiment of the invention is based on a gas turbine compressor, which is a preferred turbomachine for applying the invention, shown. The rotor 1 of the turbomachine is preferably off axially arranged one behind the other, interlocked (Serration), by a tie rod, not shown interconnected rotor disks 1 are formed.
Figur 1 zeigt einen Abschnitt einer Läuferscheibe 1 mit in Nuter.
2 eingesetzten Schaufeln 3. Jede Schaufel 3 weist Bereiche
mit unterschiedlicher Steifigkeit auf. Passend dazu ist im
Schaufelfuß 4 eine Aussparung 5 so angebracht, daß der Nut 2,
die eine ungleichmäßig große Steifigkeit über ihre Nuttiefe
aufweist, eine angepaßte Steifigkeit des Schaufelfußes 4 gegenüberliegt.
Da insbesondere am spitzen Eck 6 (siehe Figur 2) einer
Nut 2, welches am Nutende liegt, im Betrieb des Gasturbiner
verdichters erhöhte Spannungen auftreten, weist in diesem
Bereich der Schaufelfuß 4 die Aussparung 5 so ausgebildet auf,
daß, er an dieser Stelle leicht nachgiebig ist. Eine vorteilhafte
Ausgestaltung der Aussparung 5 sieht diese in der Form
einer Ausfräsung vor, die an der Stirnseite 8 des Schaufelfußes
4 schräg nach unten aus diesem herausläuft.FIG. 1 shows a section of a rotor disk 1 with a groove.
2 inserted
Figur 2 zeigt die Läuferscheibe 1 aus der Figur 1 in einer Aufsicht.
Die Nuten 2 sind in einem Einbauwinkel β zur Rotationsachse
der Läuferscheibe 1 angebracht, der auf Grund der angepaßten
Schaufelfüße 4 sehr viel größer sein kann gegenüber
herkömmlichen Einbauwinkeln. Dieses spielt insbesondere für
Gasturbinen und deren Verdichter mit geringem Massenstrom eine
besondere Rolle. Dort können größere Schaufelwinkel und damit
größere Einbauwinkel β erforderlich sein. Dieses führt wiederum
zu erhöhten lokalen Spannungen in der Nut 2, da insbesondere in
den spitzen Ecken 6 durch die erhöhten Winkel reduzierte Steifigkeiten
vorliegen. Die spitzen Ecken 6 sind Orte lokaler hoher
Spannung. Sie sind als Enden der gestrichelt angedeuteten,
in der Läuferscheibe 1 innenliegenden Nutbreite D eingezeichnet.
Über die Nutlänge L gesehen, besitzt diese nicht nur in
ihrer Tiefe, sondern auch in ihrer Erstreckung unterschiedliche
Bereiche unterschiedlicher Spannungen, die daher unterschiedlichen
Einfluß auf die Festigkeit bei eingebautem Schaufelfuß 4
und Betrieb der Turbomaschine haben.FIG. 2 shows the rotor disk 1 from FIG. 1 in a top view.
The
Figur 3 zeigt einen erfindungsgemäßen Schaufelfuß 4 mit angedeuteter
Verlängerung des Schaufelblattes 7 der Schaufel 3.
Dieser weist eine Aussparung 5 beginnend jeweils an beiden
Stirnflächen 8 auf, die schräg nach unten aus dem Schaufelfuß 4
herauslaufen. Diese Materialverminderung im Schaufelfuß 4 führt
zu einer verminderten Steifigkeit in Bereichen der Stirnflächen
8 und auch in anliegenden Bereichen des Schaufelfußes 4. Derartig
angepaßte Bereiche weisen eine größere Elastizität auf, so
daß auftretende Verformungen im Betrieb, insbesondere auch an
den spitzen Ecken 6 günstiger aufgefangen werden.Figure 3 shows a
Figur 4 zeigt die Schaufel 3 aus Figur 3 in eingebautem Zustand.
Die Materialverminderung 5 im Schaufelfuß 4 führt dazu,
daß Kraftlinien im Schaufelfuß 4 unterbrochen werden und an
diesen Stellen der Schaufelfuß 4 gegenüber Belastungen, die auf
Grund der wirkenden Schaufelkräfte am Schaufelblatt 7 aufkommen,
über den angepaßten Schaufelfuß 4 in den mittleren Bereich
der Nutlänge L umgelenkt und dort über die Nut 2 aufgenommen
werden.FIG. 4 shows the
Figur 5 zeigt eine weitere Ausführungsform der Erfindung. Der
eingebaute Schaufelfuß 4 weist eine Aussparung 5 in einer eher
länglichen Form auf, die sich zur Mitte der Nuttiefe hin nach
unten aus dem Schaufelfuß 4 herauszieht. Diese Aussparung kann
nicht nur mittels Fräsung sondern auch über eine Bohrung oder
ähnliche spanende Bearbeitungsweisen erzielt werden. Im Sinne
der Erfindung sind aber nicht nur Aussparungen 5 als Anpassungen
der Steifigkeit von Bereichen des Schaufelfußes 4 zu verstehen.
Vielmehr sind alle Maßnahmen, die die Steifigkeit eines
Schaufelfußes in mindestens einem Bereich ändern, anwendbar.
Beispielsweise ist auch das Einsetzen oder Verarbeiten eines
anderen Materials im Schaufelfuß möglich, welches diesem gegenüber
eine höhere Elastizität aufweist. Insbesondere günstig ist
es, daß bei Verdichtern bzw. allgemein Turbomaschinen, die in
wechselndem Betrieb gefahren werden, eine Anpassung der Bereiche
des Schaufelfußes 4 an denjenigen Betriebsbereich der Turbomaschine
angelehnt ist, in dem dieser überwiegend gefahren
wird.Figure 5 shows a further embodiment of the invention. The
built-in
Die Erfindung schafft bei diesem angeführten Beispiel je nach Größe der Aussparung und Schräge des Einbauwinkels eine Reduzierung von lokalen Spannungen von 30 % und mehr. Der Vorteil der Erfindung ist ihr geringer Kostenaufwand, ihre Effektivität sowie auch die nachträgliche Steifigkeitsanpassung von Schaufelfüßen bei schon in Betrieb genommenen Turbomaschinen. Ein weiterer Vorteil der Erfindung ist die Austauschbarkeit der Schaufeln. So können auch Schaufelfüße mit und ohne Materialverminderung in einer Läuferscheibe gemeinsam angebracht sein.The invention creates in this example depending on Size of the recess and slope of the installation angle a reduction of local stresses of 30% and more. The advantage The invention is its low cost, its effectiveness as well as the subsequent rigidity adjustment of blade feet with turbo machines already in operation. On Another advantage of the invention is the interchangeability Shovels. This means that shovel feet can be made with and without material reduction be mounted together in a rotor disk.
Claims (7)
- Rotor (1) for a turbomachine having an axis (1a) of rotation, in particular a turbocompressor, having blades (3) which can be fitted into slots (2), the slots (2) being made at an angle to the axis (1a) of rotation, characterized in that at least one blade root (4) has at least two regions of different rigidity which are adapted, preferably matched, to different regions of the rigidity of the slot (2) into which the blade root (4) can be fitted.
- Rotor (1) according to Claim 1, characterized in that a correspondingly adapted region of the blade root (4) and a more rigid region, in comparison thereto, of the slot (2) bear against one another or are located opposite one another.
- Rotor (1) according to Claim 1 or 2, characterized in that a region of reduced rigidity of the blade root (4) bears against a slot region of maximum stress, especially during operation of the turbomachine.
- Rotor (1) according to Claim 1, 2 or 3, characterized in that a region of reduced rigidity of the installed blade root (4) bears against a slot end, especially against an acute corner (6).
- Rotor (1) according to one of the preceding claims, characterized in that the loads at the slot (2) and the loads at the blade root (4) are matched in accordance with the forces which prevail in the turbomachine operating range mainly used.
- Blade (3) for a rotor (1) of a turbomachine, in particular according to one of the preceding claims, characterized in that, in addition to its form adapted to a slot geometry, the blade root (4) has two opposite end faces (8), a material reduction reducing the rigidity, preferably at least one recess (5), being provided in the region of the end faces (8).
- Blade (3) according to Claim 6, characterized in that a recess (5), preferably a bore or a milled-out portion, runs from the end face (8) of the blade root (4) into the interior of the latter.
Applications Claiming Priority (5)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE19624924 | 1996-06-21 | ||
| DE19624924 | 1996-06-21 | ||
| DE19642537 | 1996-10-15 | ||
| DE19642537 | 1996-10-15 | ||
| PCT/DE1997/001159 WO1997049921A1 (en) | 1996-06-21 | 1997-06-09 | Rotor for a turbomachine with blades insertable into grooves and blades for a rotor |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0906514A1 EP0906514A1 (en) | 1999-04-07 |
| EP0906514B1 true EP0906514B1 (en) | 2001-10-24 |
Family
ID=26026814
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP97928110A Expired - Lifetime EP0906514B1 (en) | 1996-06-21 | 1997-06-09 | Rotor for a turbomachine with blades insertable into grooves and blades for a rotor |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US6065938A (en) |
| EP (1) | EP0906514B1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP2000512707A (en) |
| KR (1) | KR20000022064A (en) |
| DE (1) | DE59705094D1 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO1997049921A1 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2018077589A1 (en) | 2016-10-26 | 2018-05-03 | Siemens Aktiengesellschaft | Turbine rotor arrangement and method for manufacturing a turbine rotor blade |
Families Citing this family (37)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP1136654A1 (en) * | 2000-03-21 | 2001-09-26 | Siemens Aktiengesellschaft | Turbine rotor blade |
| US6439851B1 (en) * | 2000-12-21 | 2002-08-27 | United Technologies Corporation | Reduced stress rotor blade and disk assembly |
| US6428279B1 (en) * | 2000-12-22 | 2002-08-06 | General Electric Company | Low windage loss, light weight closure bucket design and related method |
| US6846159B2 (en) * | 2002-04-16 | 2005-01-25 | United Technologies Corporation | Chamfered attachment for a bladed rotor |
| US6769877B2 (en) * | 2002-10-18 | 2004-08-03 | General Electric Company | Undercut leading edge for compressor blades and related method |
| EP1426553A1 (en) * | 2002-12-03 | 2004-06-09 | Techspace Aero S.A. | Weight reduction of rotor blades |
| US6902376B2 (en) * | 2002-12-26 | 2005-06-07 | General Electric Company | Compressor blade with dovetail slotted to reduce stress on the airfoil leading edge |
| US7121803B2 (en) * | 2002-12-26 | 2006-10-17 | General Electric Company | Compressor blade with dovetail slotted to reduce stress on the airfoil leading edge |
| US20040213672A1 (en) * | 2003-04-25 | 2004-10-28 | Gautreau James Charles | Undercut leading edge for compressor blades and related method |
| SE526255C2 (en) * | 2003-03-14 | 2005-08-09 | Sandvik Intellectual Property | Tools and indexable inserts for fine turning of rotationally symmetrical grooves in workpieces |
| DE10357134A1 (en) * | 2003-12-06 | 2005-06-30 | Alstom Technology Ltd | Rotor for a compressor |
| US7156621B2 (en) * | 2004-05-14 | 2007-01-02 | Pratt & Whitney Canada Corp. | Blade fixing relief mismatch |
| US7252481B2 (en) * | 2004-05-14 | 2007-08-07 | Pratt & Whitney Canada Corp. | Natural frequency tuning of gas turbine engine blades |
| JP4869616B2 (en) * | 2005-04-01 | 2012-02-08 | 株式会社日立製作所 | Steam turbine blade, steam turbine rotor, steam turbine using the same, and power plant |
| JP4584102B2 (en) * | 2005-09-30 | 2010-11-17 | 株式会社日立製作所 | Turbine rotor, inverted Christmas tree type turbine blade, low pressure steam turbine and steam turbine power plant using the same |
| FR2900989B1 (en) * | 2006-05-12 | 2008-07-11 | Snecma Sa | AIRCRAFT ENGINE COMPRESSOR ASSEMBLY COMPRISING AUBES WITH FOOT HAMMER ATTACHMENT |
| FR2903138B1 (en) * | 2006-06-28 | 2017-10-06 | Snecma | MOBILE AUB AND ROTOR DISC OF TURBOMACHINE, AND DEVICE FOR ATTACHING SUCH A DAWN TO SUCH A DISK |
| FR2905139B1 (en) * | 2006-08-25 | 2012-09-28 | Snecma | ROTOR BLADE OF A TURBOMACHINE |
| FR2911632B1 (en) | 2007-01-18 | 2009-08-21 | Snecma Sa | ROTOR DISC OF TURBOMACHINE BLOWER |
| US8313289B2 (en) | 2007-12-07 | 2012-11-20 | United Technologies Corp. | Gas turbine engine systems involving rotor bayonet coverplates and tools for installing such coverplates |
| US8075280B2 (en) * | 2008-09-08 | 2011-12-13 | Siemens Energy, Inc. | Composite blade and method of manufacture |
| JP5395455B2 (en) * | 2009-02-20 | 2014-01-22 | 三菱重工業株式会社 | Rotor blade for axial compressor |
| EP2282010A1 (en) | 2009-06-23 | 2011-02-09 | Siemens Aktiengesellschaft | Rotor blade for an axial flow turbomachine |
| FR2981132B1 (en) * | 2011-10-10 | 2013-12-06 | Snecma | DISCHARGE COOLING TURBOMACHINE ASSEMBLY |
| FR3001646B1 (en) * | 2013-02-01 | 2015-09-11 | Turbomeca | SPINDLE PIN AND METHOD FOR PARTS SUCH AS TURBINE ROTOR DISKS OR TURBOMACHINE COMPRESSOR DISKS |
| JP2016035209A (en) * | 2014-08-01 | 2016-03-17 | 三菱日立パワーシステムズ株式会社 | Axial-flow compressor and gas turbine with axial-flow compressor |
| GB2529681B (en) * | 2014-08-29 | 2019-02-20 | Rolls Royce Plc | Gas turbine engine rotor arrangement |
| CN104265377B (en) * | 2014-09-16 | 2016-01-20 | 上海金通灵动力科技有限公司 | A kind of structure reducing vertical tree type wheel hub molded line place stress |
| US9896947B2 (en) * | 2014-12-15 | 2018-02-20 | United Technologies Corporation | Turbine airfoil attachment with multi-radial serration profile |
| US10400784B2 (en) | 2015-05-27 | 2019-09-03 | United Technologies Corporation | Fan blade attachment root with improved strain response |
| FR3062875B1 (en) * | 2017-02-10 | 2021-07-02 | Safran Aircraft Engines | MOBILE TURBOMACHINE DAWN INCLUDING HOLES IN THE FOOT |
| JP7031270B2 (en) * | 2017-12-08 | 2022-03-08 | 株式会社リコー | Inspection equipment, inspection system and inspection method |
| FR3087479B1 (en) | 2018-10-23 | 2022-05-13 | Safran Aircraft Engines | DAWN OF TURBOMACHINE |
| US10815799B2 (en) * | 2018-11-15 | 2020-10-27 | General Electric Company | Turbine blade with radial support, shim and related turbine rotor |
| JP7385992B2 (en) * | 2018-12-28 | 2023-11-24 | 川崎重工業株式会社 | Rotating blades and disks |
| CN111412183B (en) * | 2020-04-24 | 2021-05-18 | 上海应达风机股份有限公司 | Fan impeller and machining and manufacturing process thereof |
| KR20230081267A (en) | 2021-11-30 | 2023-06-07 | 두산에너빌리티 주식회사 | Turbine blade, turbine and gas turbine including the same |
Family Cites Families (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US2643853A (en) * | 1948-07-26 | 1953-06-30 | Westinghouse Electric Corp | Turbine apparatus |
| US4191509A (en) * | 1977-12-27 | 1980-03-04 | United Technologies Corporation | Rotor blade attachment |
| WO1991001433A1 (en) * | 1989-07-25 | 1991-02-07 | Allied-Signal Inc. | Dual alloy turbine blade |
| GB2237846B (en) * | 1989-11-09 | 1993-12-15 | Rolls Royce Plc | Rim parasitic weight reduction |
| FR2697051B1 (en) * | 1992-10-21 | 1994-12-02 | Snecma | Turbomachine rotor comprising a disk whose periphery is occupied by oblique cells which alternate with teeth of variable cross section. |
| US5372481A (en) * | 1993-11-29 | 1994-12-13 | Solar Turbine Incorporated | Ceramic blade attachment system |
| FR2725239B1 (en) * | 1994-09-30 | 1996-11-22 | Gec Alsthom Electromec | PROVISION FOR THE SHARPING OF STRESS SPIKES IN THE ANCHORAGE OF A TURBINE BLADE, COMPRISING A ROOT CALLED IN "FOOT-FIR" |
| US5846054A (en) * | 1994-10-06 | 1998-12-08 | General Electric Company | Laser shock peened dovetails for disks and blades |
-
1997
- 1997-06-09 DE DE59705094T patent/DE59705094D1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1997-06-09 JP JP10502063A patent/JP2000512707A/en active Pending
- 1997-06-09 WO PCT/DE1997/001159 patent/WO1997049921A1/en not_active Application Discontinuation
- 1997-06-09 KR KR1019980710467A patent/KR20000022064A/en not_active Application Discontinuation
- 1997-06-09 EP EP97928110A patent/EP0906514B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
-
1998
- 1998-12-21 US US09/217,862 patent/US6065938A/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2018077589A1 (en) | 2016-10-26 | 2018-05-03 | Siemens Aktiengesellschaft | Turbine rotor arrangement and method for manufacturing a turbine rotor blade |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US6065938A (en) | 2000-05-23 |
| JP2000512707A (en) | 2000-09-26 |
| DE59705094D1 (en) | 2001-11-29 |
| KR20000022064A (en) | 2000-04-25 |
| EP0906514A1 (en) | 1999-04-07 |
| WO1997049921A1 (en) | 1997-12-31 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0906514B1 (en) | Rotor for a turbomachine with blades insertable into grooves and blades for a rotor | |
| DE602004001531T2 (en) | Stator scoop with double curvature | |
| DE68907555T2 (en) | Liquefying centrifugal pump or impeller for such a pump. | |
| DE60022003T2 (en) | A blade attachment assembly and method for reducing stresses in a blade attachment assembly | |
| DE4132332C2 (en) | ||
| DE19828817C2 (en) | Rotor for a turbo machine | |
| EP2045444A1 (en) | Rotor blade, method for producing a rotor blade, and compressor with such a rotor blade | |
| EP1135578B1 (en) | Support devices for the vanes of power units | |
| DE602005001231T2 (en) | Locking means for gas turbine engines | |
| DE3148985C2 (en) | ROTOR ASSEMBLY | |
| EP1522678B1 (en) | Fixing method for the blading of a turbomachine | |
| EP3702620A1 (en) | Axial fan with noise reducing fan impeller vanes having bores | |
| DE19736333C1 (en) | Mounting for turbine wheel for fluid pump | |
| DE69919459T2 (en) | Attachment of an airfoil to a rotor | |
| EP1524409B1 (en) | Blade-locking system | |
| EP1657404B1 (en) | Turbomachine rotor, in particular gas turbine rotor | |
| EP0918938B1 (en) | Friction vacuum pump | |
| CH660207A5 (en) | Device for the damping of blade vibrations in axial flow turbo engines | |
| DE19654471B4 (en) | Rotor of a turbomachine | |
| DD288649A5 (en) | RADIAL FAN | |
| DE29715035U1 (en) | Friction vacuum pump | |
| EP3309359A1 (en) | Blade assembly for a gas turbine engine | |
| EP2149677A1 (en) | Attachment device for attaching a rotor blade to a rotor of a turbomachine | |
| EP1350924B1 (en) | Fastening of nozzle segments in a gas turbine | |
| DE19544313B3 (en) | Blade with slotted shaft |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19981204 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): CH DE FR GB IT LI |
|
| GRAG | Despatch of communication of intention to grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS AGRA |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20010201 |
|
| GRAG | Despatch of communication of intention to grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS AGRA |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): CH DE FR GB IT LI |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 59705094 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20011129 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: IF02 |
|
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) |
Effective date: 20020118 |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20020630 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20020630 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20120626 Year of fee payment: 16 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20130609 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 19 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20150608 Year of fee payment: 19 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20150610 Year of fee payment: 19 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20150821 Year of fee payment: 19 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R119 Ref document number: 59705094 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20160609 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST Effective date: 20170228 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20160630 Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170103 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20160609 |