EP0904869A1 - Device for high pressure forming of hollow profiles - Google Patents
Device for high pressure forming of hollow profiles Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0904869A1 EP0904869A1 EP98115208A EP98115208A EP0904869A1 EP 0904869 A1 EP0904869 A1 EP 0904869A1 EP 98115208 A EP98115208 A EP 98115208A EP 98115208 A EP98115208 A EP 98115208A EP 0904869 A1 EP0904869 A1 EP 0904869A1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- support ring
- hollow profile
- stop body
- carrier part
- sealing
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 75
- 238000003780 insertion Methods 0.000 claims description 22
- 230000037431 insertion Effects 0.000 claims description 22
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 12
- 239000012530 fluid Substances 0.000 claims description 10
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 claims description 6
- 229910000639 Spring steel Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 2
- 229920001971 elastomer Polymers 0.000 claims 1
- 239000000806 elastomer Substances 0.000 claims 1
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 10
- 239000004952 Polyamide Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229920002647 polyamide Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000003892 spreading Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000009966 trimming Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000001520 comb Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000013013 elastic material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005429 filling process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003993 interaction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003032 molecular docking Methods 0.000 description 1
- CWQXQMHSOZUFJS-UHFFFAOYSA-N molybdenum disulfide Chemical compound S=[Mo]=S CWQXQMHSOZUFJS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000005192 partition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004033 plastic Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000011084 recovery Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000011265 semifinished product Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010008 shearing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004904 shortening Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001960 triggered effect Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B21—MECHANICAL METAL-WORKING WITHOUT ESSENTIALLY REMOVING MATERIAL; PUNCHING METAL
- B21D—WORKING OR PROCESSING OF SHEET METAL OR METAL TUBES, RODS OR PROFILES WITHOUT ESSENTIALLY REMOVING MATERIAL; PUNCHING METAL
- B21D26/00—Shaping without cutting otherwise than using rigid devices or tools or yieldable or resilient pads, i.e. applying fluid pressure or magnetic forces
- B21D26/02—Shaping without cutting otherwise than using rigid devices or tools or yieldable or resilient pads, i.e. applying fluid pressure or magnetic forces by applying fluid pressure
- B21D26/033—Deforming tubular bodies
- B21D26/045—Closing or sealing means
Definitions
- the invention relates to a device for hydroforming of hollow profiles according to the preamble of the claim 1.
- a generic device is known from DE 43 09 680 A1.
- a sealing head of an axial plunger is the one to be sealed in the engraving of a hydroforming tool inserted hollow profile until a radial Shoulder of the sealing head on the front of the hollow profile comes into play.
- the sealing head bears on its conical trained end two sealing rings in the direction of insertion from a baffle plate attached to the front of the end are secured against slipping out.
- the near the flapper Sealing ring is an O-ring made of a soft rubber-elastic material, while the baffle plate seal made of polyamide exists and has a trapezoidal profile cross section.
- the baffle plate is axial on the face of the sealing head screwed movably and has a bent edge, with which the O-ring can be loaded.
- the sealing rings are like this trained that with little play to the hollow profile the sealing head can be inserted without hindrance.
- the seal after filling the hollow profile with the pressure fluid the pressure fluid channel formed in the sealing head due to the created internal high pressure, which the baffle against presses the O-ring, which due to the slipping up on the contact surface that widens conically towards the axial ram spread the seal head end and thereby radially against the Hollow profile to be pressed.
- the high pressure also affects the polyamide ring of the contact surface slide up, which is then through its wedge-like formation between the contact surface and the hollow profile jammed and by the pressure on the Hollow profile for additional sealing of the hollow profile leads.
- the polyamide ring is placed in this position a stop for the O-ring towards the axial punch, so opposite to the direction of insertion, causing the O-ring by the axial pressure on the polayamide ring by means of the internal high pressure baffle plate deformed elastically and is driven radially apart.
- the invention has for its object a generic To further develop the device so that in a simple manner and a reliable fluid high pressure density without deformation of the hollow profile Sealing is achieved so that a reliable process Forming with regard to stable pressure conditions at Hydroforming is made possible.
- a relative movement of the support part to the sealing arrangement enables this being a stationary with respect to the hollow profile Position takes while the carrier part continues into the hollow profile can be inserted axially further.
- the fixed support ring opposes, by loading the Support ring and the sealing element held thereon by means an actuating means rigidly attached to the carrier part radial expansion of the sealing element almost automatically triggered.
- the sealing element is against the inner wall pressed of the hollow profile, whereby a sufficient fluid high pressure density Sealing of the hollow profile interior against the external environment is reached. This happens before filling so that no leaks occur.
- the fluid high pressure is held at a stable height during forming, since the Preserve the quality of the seal until the end of the forming process remains.
- one is reliable in terms of constant pressure Forming of the hollow profile possible.
- no deformation of the hollow profile end since here only a soft one Radial seal from the inside to the inner wall of the hollow profile is pressed, whereby the hollow profile remains true to size and a any trimming of the squeezed hollow profile in the docking area of the sealing head on the hollow profile after the forming process resource-saving and process time-saving.
- the hollow profile is not squeezed, the withdrawal forces become of the axial ram considerably reduced.
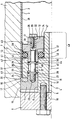
- An internal high-pressure forming tool 1 is shown in the figure, in the engraving 2 a hollow profile 3 is introduced, the internal high-pressure forming tool 1 in the closed position located.
- a sealing head 4 of a hydraulic actuated axial plunger inserted, by means of which the material of the hollow profile 3 during the forming process for reliable forming with a high degree of forming in the direction of the forming location can be replenished.
- the sealing head 4 comprises a hollow cylindrical support member 5, the cavity of which one Pressure fluid channel 6 for introducing the pressure fluid into the hollow profile 3 forms and with a high-pressure fluid generating system is fluidly connected, a sealing arrangement 7, which on the Outer peripheral surface 8 of the carrier part 5 is held axially displaceable and a stop plate 9 facing away from the insertion direction End face 10 of the carrier part 5 screwed is.
- the sealing arrangement 7 includes one with its peripheral shape the circumferential contour of the hollow profile 3 following annular Stop body 11, a support ring 12, an outer that Sealing element forming soft rubber-elastic O-ring 13 and an inner O-ring 14 made of a material with similar Properties like the O-ring 13.
- the O-ring 13 can also consist of a spring steel.
- the stop body 11 lies with a little play with it Circumferential surface 15 all around on the engraving 2 of the forming tool 1 and with its inner wall 16 on the outer peripheral surface 8 of the carrier part 5.
- the stop body 11 On its in the direction of insertion End face 17, the stop body 11 has a coaxial lying sleeve-shaped extension 18 smaller diameter than that of the stop body 11, wherein the extension 18 in one strong press compound circumferentially forming a pressure piece 19 Washer made of a highly wear-resistant material, which abuts the end face 17 of the stop body 11.
- the extension 18 extending in the insertion direction has one starting from its end 29 pointing in the direction of insertion Threaded bore 21 running parallel to the direction of insertion in the manner of a blind hole in which a pin 22 with a screwed to one end 23 of the external thread 24 which is the connecting means between the stop body 11 and the support ring 12 forms.
- an annular collar 25 on which the stop body 11 rests.
- the pin 22 has an axially spaced apart from the collar 25 further ring collar 26 on which a sleeve-shaped extension 27 of the support ring 12 abuts the end face, which with a smaller Diameter than that of the support ring 12 on the opposite of End face 28 of the support ring 12 pointing in the direction of insertion coaxially is arranged.
- the inner circumference and the outer circumference 36 of the extension 27 of the support ring 12 are otherwise in their Connection position with the corresponding circumferences of the extension 18 of the stop body 11, whereby with respect to the in shape and dimension of the same inner circumference of the extensions 18 and 27 of support ring 12 and stop body 11 a manufacturing technology simple colinear guidance can be carried out on the carrier part 5 is.
- the extension 27 of the support ring 12 has one the support ring 12 common to the threaded bore 21 of the stop body 11 coaxial feedthrough 30 through which the support ring 12 attached to the pin 22 until it rests on the collar 26 is.
- the end 31 of the pin 22 on the support ring side has an internal thread 32 on, whereby by screwing a suitable Screw 33 from the face pointing in the direction of insertion 34 of the support ring 12 from the support ring 12 between the collar 26 and the screw head 35 is screwed.
- the support ring 12 is thus positioned exactly relative to the stop body 11 and also has a defined position on pin 22.
- these two sealing arrangement elements connected by a plurality of pins 22 distributed over their circumference.
- stop body 11 Support ring 12 corresponding screw.
- the lanyard should in any case of the stop body 11 and the Support ring 12 be releasable, because an interchangeability of worn Parts of the seal assembly 7 can be guaranteed got to.
- the outer circumference 36 of the support ring extension 27 lies on the outer circumference O-ring 13 in the radial direction and is supported in the axial Direction on the support ring side on the end face 28 of the support ring 12 from.
- the carrier part 5 has an annular collar 37 which arranged between the stop body 11 and the support ring 12 and with its edge 38 to near the inner wall 39 of the hollow profile 3 extends. This extension close to the hollow profile of the collar 37 or the design of its diameter in such a way that there is a clearance fit with respect to the hollow profile 3 of the collar 37 results, is used for radial support of the Hollow section 3 during a pushing of the hollow section 3 during of the forming process.
- the collar 37 has a collar on both sides in the axial direction 41 on the extension 27 and the extension 18 each engages behind and on the contact surface for the O-ring 13 forming Outer circumference 36 of the extension 27 on the one hand and on the outer circumference of the extension 18 on the other hand.
- the collar 41 closes at its edge 42 facing the edge flush with the Edge 38 of the collar 37 from which the support ring 12 facing Collar in this embodiment with its in the direction of insertion facing end face 43 in a relaxed position the sealing arrangement 7 rests on the O-ring 13. However, this can also axially spaced from the O-ring 13 in the relaxed position be.
- the end face 20 of the hollow profile 3 is used to seal the Hollow profile 3, the carrier part 5 by means of the axial punch pushed in the direction of insertion.
- the O-ring 13 is from Collar 41 of the collar 37 axially squeezed, whereby the O-ring 13 spreads apart radially and on the inner wall 39 of the hollow profile is pressed with high force.
- the Ring collar 37 thus forms the actuating means due to its collar 41 for the sealing ring 13.
- the free displacement mentioned must be so large that the O-ring 13 or in general the sealing element in sufficient for a secure seal Dimensions is compressed, but it may only be so large that the O-ring 13 due to excessive crushing none Takes damage.
- the extensions 18 and 27 and the support ring 12 and the stop body 11 can their inner walls with a wear-resistant sliding film, for example be coated from molybdenum sulfide, what the service life the sealing head 4 increases and the smoothness of the Sealing arrangement 7 significantly increased relative to the carrier part 5.
- the carrier part tapers approximately at the level of the position of the O-ring 13 5 revolving in a stage 46 at which the on the support member 5 inserted O-ring 14 is present. On the opposite Side of the support ring 12 with its end face 28 on the O-ring 14 on.
- the diameter of the support ring 12 is otherwise dimensioned such that that the sealing head 4 with play in the hollow profile 3rd is insertable, however, the clearance 49 between the support ring 12 and hollow section 3 designed so tight that for a sealing Squeezing the O-ring 13 through the collar 41 of the collar 37 there is sufficient resistance and the O-ring 13 with the squeezing impingement not over the edge of the Support ring 12 is pressed, which is a shearing and thus resulting in damage to the O-ring 13.
- the O-ring 13 an elongated one is also conceivable use elastic hollow drilled plugs, which the sealing contact surface on the hollow section 3 is considerably enlarged and thus the security of an adequate seal even after guarantees a long service life.
- the contact surface of the extension 27 of the support ring 12 for the O-ring 13 may differ from the cylindrical design of the embodiment shown also be conical. This is done by applying of the O-ring 13 through the collar 41 of the collar 37 the O-ring 13 alone due to the slipping up expanded in the direction of insertion and spread to the Hollow profile wall 39 pressed, whereby the O-ring 13 only with reduced squeezing force must be applied to the required To achieve sealing. The wear of the O-ring 13 reduced.
- the sealing head 4 together with the axial punch can be done in a simpler manner Track the shortening hollow profile 3 to the same extent are accepted without loss of tightness must become. It is also possible to use the axial ram if necessary to apply an additional axial force to the hollow profile 3, so that the material flow to the forming point during forming is forced with high degrees of deformation, i.e. it will Pushed the hollow profile material to the forming point. To do this unhindered to execute, the stop body 11 and the pressure piece 19 designed in a ring shape, creating an even pressure load when the sealing arrangement 7 is in contact with the stop body 11 given on the end face 20 of the hollow profile 3 is.
- the interaction of carrier part 5 and support ring 12 for spreading the O-ring 13 thereby caused that the carrier part 5 has an external toothing carries that with an internal toothing of the support ring 12 such combs that a simple translatory insertion movement of the Support part 5 after the abutment body 11 abuts the hollow profile 3 spreads the support ring 12 forcibly guided.
- the Support ring 12 is composed of different circular segments, on the outer periphery of the O-ring 13 is held. This form of spreading can also be done by a rotatory Movement of the carrier part 5 take place.
- the carrier part 5 can also be designed as a conical mandrel, the support ring 13 within certain limits as a full body elastic, but with a much greater Shore hardness than the O-ring 13 be formed or in the form of inelastic Circular segments can exist.
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Fluid Mechanics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Gasket Seals (AREA)
- Sealing Devices (AREA)
- Clamps And Clips (AREA)
- Shaping Metal By Deep-Drawing, Or The Like (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Die Erfindung betrifft eine Vorrichtung zum Innenhochdruckumformen von Hohlprofilen gemäß dem Oberbegriff des Patentanspruches 1.The invention relates to a device for hydroforming of hollow profiles according to the preamble of the claim 1.
Eine gattungsgemäße Vorrichtung ist aus der DE 43 09 680 A1 bekannt. Bei dieser wird ein Dichtungskopf eines Axialstempels in das abzudichtende in der Gravur eines Innenhochdruck-Umformwerkzeuges eingelegte Hohlprofil eingeführt, bis eine radiale Schulter des Dichtungskopfes an der Stirnseite des Hohlprofiles zum Anschlag kommt. Der Dichtungskopf trägt an seinem konisch ausgebildeten Ende zwei Dichtringe, die in Einführungsrichtung von einer an der Stirnseite des Endes angebrachten Prallplatte gegen ein Herausrutschen gesichert sind. Der prallplattennahe Dichtring ist ein O-Ring aus einem weichen gummielastischen Material, während der prallplattenferne Dichtring aus Polyamid besteht und einen trapezförmigen Profilquerschnitt aufweist. Die Prallplatte ist an der Stirnseite des Dichtungskopfes axial beweglich angeschraubt und weist einen umgebogenen Rand auf, mit dem der O-Ring beaufschlagbar ist. Die Dichtringe sind derart ausgebildet, daß sie mit geringem Spiel zum Hohlprofil mit dem Dichtungskopf behinderungsfrei einführbar sind. Die Abdichtung soll nach Füllung des Hohlprofiles mit dem Druckfluid über den im Dichtungskopf ausgebildeten Druckfluidkanal aufgrund des angelegten Innenhochdruckes erfolgen, der die Prallplatte gegen den O-Ring preßt, welcher sich infolge des Hochrutschens an der sich zum Axialstempel hin konisch erweiternden Anlagefläche an dem Dichtungskopfende aufspreizen und dadurch radial gegen das Hohlprofil gepreßt werden soll. Des weiteren soll unter der Einwirkung des Innenhochdruckes ebenfalls der Polyamidring an der Anlagefläche hochrutschen, welcher sich dann durch seine keilartige Ausbildung zwischen der Anlagefläche und dem Hohlprofil einklemmt und durch die so erfolgende Anpressung am Hohlprofil zu einer zusätzlichen Abdichtung des Hohlprofiles führt. Darüber hinaus stellt dabei in dieser Lage der Polyamidring einen Anschlag für den O-Ring zum Axialstempel hin, also entgegen der Einführrichtung dar, wodurch sich der O-Ring durch die axiale Anpressung an den Polayamidring mittels der innenhochdruckgetriebenen Prallplatte elastisch deformiert und weiter radial auseinandergetrieben wird. Mit der Vorrichtung wird in günstiger Weise die bislang übliche metallische Abdichtung, die eine plastische Aufweitung des Hohlprofiles zur Folge hat und damit einen Beschnitt des nach Abdichtung anschließend fertigumgeformten Hohlprofiles unweigerlich erfordert, vermieden. Bei der bekannten Vorrichtung ist jedoch nachteilig, daß solange während des Befüllvorganges noch kein Innenhochdruck aufgebaut ist, die Dichtwirkung noch nicht eintritt, so daß eine Leckage entsteht, da über den das Spiel der Dichtringe bildenden Spalt Druckfluid ablaufen kann. Des weiteren ist das Zustandekommen einer Dichtwirkung bei der bekannten Vorrichtung in der Praxis an sich fraglich, da Befüllvolumen und die Befüllgeschwindigkeit extrem hoch sein müssen, damit die Prallscheibe sich bewegt. Anderenfalls ergibt sich ein Druckausgleich der Drücke vor und hinter der Prallscheibe und somit auch während des Innenhochdruckumformens keine Abdichtung des Hohlprofiles, wodurch der Umformvorgang aufgrund von Druckabfall während des Prozesses keine Prozeßsicherheit aufweist. Die Realisierung der besagten hohen Befüllgeschwindigkeit bzw. des hohen Befüllvolumens ist jedoch technisch nicht machbar, insbesondere nicht bei relativ großen Bauteilen wie Kraftfahrzeugachsen usw..A generic device is known from DE 43 09 680 A1. In this a sealing head of an axial plunger is the one to be sealed in the engraving of a hydroforming tool inserted hollow profile until a radial Shoulder of the sealing head on the front of the hollow profile comes into play. The sealing head bears on its conical trained end two sealing rings in the direction of insertion from a baffle plate attached to the front of the end are secured against slipping out. The near the flapper Sealing ring is an O-ring made of a soft rubber-elastic material, while the baffle plate seal made of polyamide exists and has a trapezoidal profile cross section. The baffle plate is axial on the face of the sealing head screwed movably and has a bent edge, with which the O-ring can be loaded. The sealing rings are like this trained that with little play to the hollow profile the sealing head can be inserted without hindrance. The seal after filling the hollow profile with the pressure fluid the pressure fluid channel formed in the sealing head due to the created internal high pressure, which the baffle against presses the O-ring, which due to the slipping up on the contact surface that widens conically towards the axial ram spread the seal head end and thereby radially against the Hollow profile to be pressed. Furthermore, under the The high pressure also affects the polyamide ring of the contact surface slide up, which is then through its wedge-like formation between the contact surface and the hollow profile jammed and by the pressure on the Hollow profile for additional sealing of the hollow profile leads. In addition, the polyamide ring is placed in this position a stop for the O-ring towards the axial punch, so opposite to the direction of insertion, causing the O-ring by the axial pressure on the polayamide ring by means of the internal high pressure baffle plate deformed elastically and is driven radially apart. With the device the metallic seal that has been customary up to now is favorably which results in a plastic widening of the hollow profile has and thus trimming the after sealing fully formed hollow profile inevitably required, avoided. In the known device, however, it is disadvantageous that as long as there is no internal high pressure during the filling process is built up, the sealing effect does not yet occur, so that a Leakage arises because of the play of the sealing rings Gap pressure fluid can drain. Furthermore, it came about a sealing effect in the known device in practice questionable per se because of the filling volume and the filling speed must be extremely high for the baffle plate moves. Otherwise there is pressure equalization the pressures in front of and behind the baffle plate and thus even during hydroforming, no sealing of the Hollow profile, causing the forming process due to pressure drop has no process reliability during the process. The Realization of said high filling speed or high filling volume is not technically feasible, in particular not with relatively large components such as motor vehicle axles etc..
Der Erfindung liegt die Aufgabe zugrunde, eine gattungsgemäße Vorrichtung dahingehend weiterzubilden, daß in einfacher Weise und ohne Verformung des Hohlprofiles eine zuverlässige fluidhochdruckdichte Abdichtung erzielt wird, so daß eine prozeßsichere Umformung hinsichtlich stabiler Druckverhältnisse beim Innenhochdruckumformen ermöglicht wird.The invention has for its object a generic To further develop the device so that in a simple manner and a reliable fluid high pressure density without deformation of the hollow profile Sealing is achieved so that a reliable process Forming with regard to stable pressure conditions at Hydroforming is made possible.
Die Aufgabe ist erfindungsgemäß durch die Merkmale des Patentanspruches 1 gelöst.The task is according to the invention by the features of the claim 1 solved.
Dank der Erfindung wird nach dem Anschlag des Anschlagkörpers des Dichtungskopfes an der Stirnseite des Hohlprofiles eine Relativbewegung des Trägerteils zur Dichtungsanordnung ermöglicht, wobei diese bezüglich des Hohlprofiles eine stationäre Lage einnimmt, während das Trägerteil weiter in das Hohlprofil hinein axial weiter eingeschoben werden kann. Hierbei wird aufgrund der weiteren Einführbewegung des Trägerteils, der der feststehende Stützring entgegensteht, durch Beaufschlagung des Stützringes und des daran gehaltenen Dichtungselementes mittels eines am Trägerteil starr befestigten Betätigungsmittels eine radiale Aufspreizung des Dichtungselementes quasi selbsttätig ausgelöst. Dabei wird das Dichtungselement gegen die Innenwandung des Hohlprofiles gepreßt, wodurch eine ausreichende fluidhochdruckdichte Abdichtung des Hohlprofilinnenraumes gegenüber der äußeren Umgebung erreicht wird. Dies geschieht schon vor dem Befüllen, so daß keine Leckagen auftreten. Der Fluidhochdruck wird beim Umformen in seiner Höhe stabil gehalten, da die Qualität der Abdichtung bis zum Ende des Umformprozesses erhalten bleibt. Somit ist eine hinsichtlich konstanten Druckes prozeßsichere Umformung des Hohlprofiles möglich. Des weiteren tritt mit der erfindungsgemäßen Vorrichtung ebenso wie bei der Vorrichtung aus der gattungsbildenden Druckschrift keine Verformung des Hohlprofilendes auf, da hier lediglich eine weiche Dichtung radial von innen an die Innenwandung des Hohlprofiles gepreßt wird, wodurch das Hohlprofil maßhaltig bleibt und ein etwaiger Beschnitt des gequetschten Hohlprofiles im Andockbereich des Dichtungskopfes am Hohlprofil nach dem Umformprozeß ressourcenschonend und prozeßzeitsparend entfällt. Durch die fehlende Quetschung des Hohlprofiles werden dazu die Rückzugskräfte des Axialstempels erheblich reduziert. Aufgrund des durch die Stirnseite des Hohlprofiles definierten Anschlages stellt sich in einfacher Weise eine exakte Positionierung des Dichtungskopfes zum Hohlprofil von selbst ein. Ein Nachschieben des Materials ohne Faltenbildung oder auch nur ein Nachführen des Hohlprofilmaterials und damit eine Gewährleistung ungehinderten Materialflusses zum Umformungsort hin wird durch die erfindungsgemäße Vorrichtung über die axiale Anlage des Anschlagkörpers an der Stirnseite des Hohlprofiles ebenfalls erreicht, welcher die Nachschiebekraft des Axialstempels auf das Hohlprofil übertragen kann, wohingegen das versagensfreie Nachschieben des Hohlprofilmaterials beim zitierten Stand der Technik aufgrund des Druckabfalles innerhalb des Hohlprofiles infolge der unzureichenden Abdichtung nicht möglich ist. Zum Abdichten wird das Hohlprofil radial mit großer Kraft, axial jedoch nur minimal mit Kraft beaufschlagt, wodurch die bei üblichen Axialabdichtungen hohen erforderlichen Axialkräfte entfallen, die zu einem Knicken des Hohlprofiles, insbesondere eines gebogenen Rohrstückes führen können. Aufgrund der radialen Abdichtung können die Toleranzen des Halbzeugs für die Hohlprofiles sehr grob und daher sehr kostengünstig ausgelegt werden, da die radial wirksame Abdichtungsvorrichtung unempfindlich gegenüber Maßschwankungen ist.Thanks to the invention, after the stop of the stop body of the sealing head on the end face of the hollow profile a relative movement of the support part to the sealing arrangement enables this being a stationary with respect to the hollow profile Position takes while the carrier part continues into the hollow profile can be inserted axially further. This is due to the further insertion movement of the carrier part, the fixed support ring opposes, by loading the Support ring and the sealing element held thereon by means an actuating means rigidly attached to the carrier part radial expansion of the sealing element almost automatically triggered. The sealing element is against the inner wall pressed of the hollow profile, whereby a sufficient fluid high pressure density Sealing of the hollow profile interior against the external environment is reached. This happens before filling so that no leaks occur. The fluid high pressure is held at a stable height during forming, since the Preserve the quality of the seal until the end of the forming process remains. Thus, one is reliable in terms of constant pressure Forming of the hollow profile possible. Furthermore occurs with the device according to the invention as well as in the Device from the generic document no deformation of the hollow profile end, since here only a soft one Radial seal from the inside to the inner wall of the hollow profile is pressed, whereby the hollow profile remains true to size and a any trimming of the squeezed hollow profile in the docking area of the sealing head on the hollow profile after the forming process resource-saving and process time-saving. Through the If the hollow profile is not squeezed, the withdrawal forces become of the axial ram considerably reduced. Because of the stop defined by the end face of the hollow profile the exact positioning of the Sealing head to the hollow profile by itself. A pushing of the material without wrinkling or even tracking of the hollow profile material and thus a guarantee of unimpeded The flow of material to the forming location is determined by the invention Device on the axial contact of the stop body also reached on the front of the hollow profile, which is the pushing force of the axial punch on the hollow profile can transmit, whereas failure-free replenishment the hollow profile material in the cited prior art of the pressure drop within the hollow profile as a result of insufficient sealing is not possible. For sealing the hollow profile radially with great force, but axially only minimally acted upon by force, which is the case with conventional axial seals high required axial forces are eliminated a buckling of the hollow profile, in particular a curved one Can lead pipe section. Because of the radial seal the tolerances of the semi-finished product for the hollow profile can be very coarse and therefore very inexpensive, because the radial effective sealing device insensitive to Dimensional fluctuations.
Zweckmäßige Ausgestaltungen der Erfindung können den Unteransprüchen entnommen werden; im übrigen ist die Erfindung anhand eines in den Zeichnungen dargestellten Ausführungsbeispieles nachfolgend näher erläutert; dabei zeigt die Figur einen Dichtungskopf der erfindungsgemäßen Vorrichtung in einem seitlichen Längsschnitt in einer Einführlage in einem Hohlprofil ohne Abdichtungsfunktion.Advantageous embodiments of the invention can be removed; otherwise the invention is based an embodiment shown in the drawings explained in more detail below; the figure shows a sealing head the device according to the invention in a lateral Longitudinal section in an insertion position in a hollow profile without a sealing function.
In der Figur ist ein Innenhochdruck-Umformwerkzeug 1 dargestellt,
in dessen Gravur 2 ein Hohlprofil 3 eingebracht ist,
wobei das Innenhochdruck-Umformwerkzeug 1 sich in Schließlage
befindet. In das Hohlprofil 3 ist ein Dichtungskopf 4 eines hydraulisch
betätigbaren Axialstempels eingeschoben, mittels dessen
das Material des Hohlprofiles 3 während des Umformprozesses
zur prozeßsicheren Umformung mit hohem Umformgrad in Richtung
des Umformortes nachgeschoben werden kann. Der Dichtungskopf 4
umfaßt ein hohlzylindrisches Trägerteil 5, dessen Höhlung einen
Druckfluidkanal 6 zur Einleitung des Druckfluides in das Hohlprofil
3 bildet und mit einer Fluidhochdruckerzeugungsanlage
fluidisch verbunden ist, eine Dichtungsanordnung 7, die an der
Außenumfangsfläche 8 des Trägerteils 5 axialverschieblich gehalten
ist, und eine Anschlagplatte 9, die an der einführrichtungabgewandten
Stirnseite 10 des Trägerteils 5 angeschraubt
ist.An internal high-pressure forming tool 1 is shown in the figure,
in the engraving 2 a
Die Dichtungsanordnung 7 beinhaltet einen mit seiner Umfangsform
der Umfangskontur des Hohlprofiles 3 folgenden ringförmigen
Anschlagkörper 11, einen Stützring 12, einen äußeren das
Dichtungselement bildenden weichen gummielastischen O-Ring 13
sowie einen inneren O-Ring 14 aus einem Material mit ähnlichen
Eigenschaften wie der O-Ring 13. Der O-Ring 13 kann aber auch
aus einem Federstahl bestehen.The
Der Anschlagkörper 11 liegt bis auf ein geringes Spiel mit seiner
Mantelfläche 15 umlaufend an der Gravur 2 des Umformwerkzeuges
1 und mit seiner Innenwandung 16 an der Außenumfangsfläche
8 des Trägerteils 5 an. An seiner in Einführrichtung weisenden
Stirnseite 17 weist der Anschlagkörper 11 einen koaxial
liegenden hülsenförmigen Fortsatz 18 kleineren Durchmessers als
der des Anschlagkörpers 11 auf, wobei der Fortsatz 18 in einem
starken Preßverbund umfänglich eine ein Druckstück 19 bildende
Ringscheibe aus einem hochverschleißfesten Material trägt, welche
an der Stirnseite 17 des Anschlagkörpers 11 anliegt. In der
Einführlage des Dichtungskopfes 4 in das Hohlprofil 3 liegt das
Druckstück 19 an der Stirnseite 20 des Hohlprofiles 3 an.The
Der in Einführrichtung sich erstreckende Fortsatz 18 weist eine
von seiner in Einführrichtung weisenden Stirnseite 29 ausgehende
parallel zur Einführrichtung verlaufende Gewindebohrung 21
nach Art einer Sackbohrung auf, in die ein Stift 22 mit einem
an dessen einem Ende 23 befindlichen Außengewinde 24 eingeschraubt
ist, welcher das Verbindungsmittel zwischen dem Anschlagkörper
11 und dem Stützring 12 bildet. Zur definierten
Position des Anschlagkörpers 11 auf dem Stift 22 weist dieser
einen Ringbund 25 auf, an dem der Anschlagkörper 11 anliegt.The
Der Stift 22 weist einen zum Ringbund 25 axial beabstandeten
weiteren Ringbund 26 auf, an dem ein hülsenförmiger Fortsatz 27
des Stützringes 12 stirnseitig anliegt, welcher mit kleinerem
Durchmesser als der des Stützringes 12 auf der entgegen der
Einführrichtung weisenden Stirnseite 28 des Stützringes 12 koaxial
angeordnet ist. Der Innenumfang sowie der Außenumfang 36
des Fortsatzes 27 des Stützringes 12 fluchten im übrigen in ihrer
Verbindungslage mit den entsprechenden Umfängen des Fortsatzes
18 des Anschlagkörpers 11, wodurch bezüglich des in Form
und Abmessung gleichgestalteten Innenumfanges der Fortsätze 18
und 27 von Stützring 12 und Anschlagkörper 11 eine fertigungstechnisch
einfache kolineare Führung auf dem Trägerteil 5 ausführbar
ist. Der Fortsatz 27 des Stützringes 12 weist eine mit
dem Stützring 12 gemeinsame zur Gewindebohrung 21 des Anschlagkörpers
11 koaxiale Durchführung 30 auf, über die der Stützring
12 auf den Stift 22 bis zur Anlage am Ringbund 26 aufgesteckt
ist. Das stützringseitige Ende 31 des Stiftes 22 weist ein Innengewinde
32 auf, wodurch mittels Einschrauben einer geeigneten
Schraube 33 von der in Einführrichtung weisenden Stirnseite
34 des Stützringes 12 aus der Stützring 12 zwischen dem Ringbund
26 und dem Schraubenkopf 35 verschraubt ist. Der Stützring
12 ist somit relativ zum Anschlagkörper 11 exakt positioniert
und besitzt auch auf dem Stift 22 eine definierte Lage. Zur mechanischen
Stabilität der Verbindung zwischen Anschlagkörper 11
und Stützring 12 sind diese beiden Dichtanordnungselemente
durch mehrere über deren Umfang verteilte Stifte 22 verbunden.
Alternativ denkbar ist für den Anschlagkörper 11 eine der des
Stützringes 12 entsprechende Verschraubung. Die Verbindungsmittel
sollten auf jeden Fall von dem Anschlagkörper 11 und dem
Stützring 12 lösbar sein, da eine Austauschbarkeit von verschlissenen
Teilen der Dichtungsanordnung 7 gewährleistet sein
muß. The
Am Außenumfang 36 des Stützringfortsatzes 27 liegt der äußere
O-Ring 13 in radialer Richtung an und stützt sich in axialer
Richtung auf Stützringseite an der Stirnseite 28 des Stützringes
12 ab. Das Trägerteil 5 weist einen Ringbund 37 auf, der
zwischen dem Anschlagkörper 11 und dem Stützring 12 angeordnet
ist und sich mit seinem Rand 38 bis nahe der Innenwandung 39
des Hohlprofiles 3 erstreckt. Diese hohlprofilnahe Erstreckung
des Ringbundes 37 bzw. die Auslegung seines Durchmessers derart,
daß sich bezüglich des Hohlprofiles 3 eine Spielpassung
des Ringbundes 37 ergibt, dient zur radialen Abstützung des
Hohlprofiles 3 bei einem Nachschieben des Hohlprofiles 3 während
des Umformprozesses. Somit wird eine für den Umformprozeß
unerwünschte Faltung des Hohlprofiles 3 in dem vom Dichtungskopf
4 abgedeckten Bereich des Hohlprofiles 3, der nicht vom
Innenhochdruck stützend beaufschlagt wird, vermieden. Die erforderlichen
Nachschubkräfte für den Axialstempel werden reduziert,
da der Bereich zwischen der Stirnseite 20 des Hohlprofiles
3 und dem Dichtelement, also dem O-Ring 13 nicht mit Innenhochdruck
beaufschlagt wird und somit keine daraus resultierende
Reibungskraft überwunden werden muß. Der Ringbund 37 bildet
also eine Trennwand zwischen dem Anschlagkörper 11 und dem
Stützring 12, wobei er eine oder mehrere axiale Durchführungen
40 aufweist, die durch das jeweilige Verbindungsmittel zwischen
dem Anschlagkörper 11 und dem Stützring 12, d.h. den Stift 22
durchsetzt wird.The
Der Ringbund 37 weist in axialer Richtung beidseitig einen Kragen
41 auf, der den Fortsatz 27 und den Fortsatz 18 jeweils
hintergreift und am die Anlagefläche für den O-Ring 13 bildenden
Außenumfang 36 des Fortsatzes 27 einerseits und am Außenumfang
des Fortsatzes 18 andererseits anliegt. Der Kragen 41
schließt an seinem hohlprofilzugewandten Rand 42 bündig mit dem
Rand 38 des Ringbundes 37 ab, wobei der dem Stützring 12 Zugewandte
Kragen in diesem Ausführungsbeispiel mit seiner in Einführrichtung
weisenden Stirnseite 43 in entspannter Stellung
der Dichtungsanordnung 7 am O-Ring 13 anliegt. Diese kann jedoch
auch in der entspannten Stellung vom O-Ring 13 axial beabstandet
sein. Wesentlich jedoch ist, daß der Kragen 41 an den
Außenumfängen des Fortsatzes 18 des Anschlagkörpers 11 und des
Fortsatzes 27 des Stützringes 12 axialbeweglich geführt ist.
Bei der gezeigten direkten Anlage beläuft sich Axialbeweglichkeit
im Rahmen der elastischen Deformierbarkeit des Materials
des O-Ringes 13 und des O-Ringes 14. Zur Gewährleistung einer
axialen Beweglichkeit der Ringbundes 37 und damit des Trägerteils
5 relativ zur Dichtungsanordnung 7 ist es ebenfalls notwendig,
daß - ausgehend von der entspannten Lage der Dichtungsanordnung
7 - zwischen der Stirnseite 44 des Fortsatzes 27 und
der in Einführrichtung weisenden Stirnseite 45 des Ringbundes
37 ein freier axialer Verschiebeweg gegeben ist.The
Nach Anlage des Anschlagkörpers 11 über das Druckstück 19 an
der Stirnseite 20 des Hohlprofiles 3 wird zur Abdichtung des
Hohlprofiles 3 das Trägerteil 5 mittels des Axialstempels weiter
in Einführrichtung geschoben. Dabei wird der O-Ring 13 vom
Kragen 41 des Ringbundes 37 axial zusammengequetscht, wodurch
der O-Ring 13 sich radial auseinanderspreizt und an die Innenwandung
39 des Hohlprofiles mit hoher Kraft angepreßt wird. Der
Ringbund 37 bildet aufgrund seines Kragens 41 damit das Betätigungsmittel
für den Dichtring 13. Der erwähnte freie Verschiebeweg
muß dabei so groß sein, daß der O-Ring 13 bzw. allgemein
das Dichtelement in für eine sichere Abdichtung ausreichendem
Maße zusammengedrückt wird, jedoch darf er nur so groß sein,
daß der O-Ring 13 durch zu starkes Zusammenquetschen keinen
Schaden nimmt. Dies wird durch eine geeignete Beabstandung der
bei einer Relativbewegung des Trägerteils 5 einen Gegenanschlag
zum Anschlagkörper 11 bildenden Anschlagplatte 9 von dem Anschlagkörper
11 erreicht, so daß bei Anlage der Anschlagplatte
9 am Anschlagkörper 11 das mit der Anschlagplatte 9 fest verbundene
Trägerteil 5 festgelegt wird und keine weitere Relativbewegung
des Trägerteils 5 in Einführrichtung ausführbar ist.
In gleicher Weise verschiebewegbegrenzend ist eine geeignete
axiale Positionierung des Stützringes 12 auf dem Stift 22, wobei
der Fortsatz 27 des Stützringes 12 und der Ringbund 37 die
beiden korrespondierenden Anschläge bilden. After the
Aufgrund der Anlage der Fortsätze 18 und 27 an der Außenumfangsfläche
8 des Trägerteils 5 ist die Dichtunganordnung 7
kippstabil auf dem Trägerteil 5 gelagert. Die Fortsätze 18 und
27 sowie der Stützring 12 und der Anschlagkörper 11 können an
ihren Innenwandungen mit einem verschleißfesten Gleitfilm, beispielsweise
aus Molybdänsulfid beschichtet sein, was die Standzeit
des Dichtungskopfes 4 erhöht und die Leichtgängigkeit der
Dichtungsanordnung 7 relativ zum Trägerteil 5 erheblich erhöht.Due to the location of the
Etwa auf Höhe der Lage des O-Ringes 13 verjüngt sich das Trägerteil
5 umlaufend in einer Stufe 46, an der der auf das Trägerteil
5 gesteckte O-Ring 14 anliegt. Auf gegenüberliegender
Seite liegt der Stützring 12 mit seiner Stirnseite 28 am O-Ring
14 an. Mit der Relativbewegung des Trägerteils 5 zur Dichtungsanordnung
7 in Einführrichtung wird gleichzeitig zum Zusammenquetschen
des O-Ringes 13 auch der innere O-Ring 14 infolge der
Beaufschlagung der Stufe 46 einerseits und der Stirnseite 28
des Stützringes 12 andererseits sowie von der radial nach außen
begrenzenden Innenumfangsfläche des Fortsatzes 27 des Stützringes
12 quetschend beaufschlagt, wodurch etwaige Leckagen und
Druckabfälle beim Innenhochdruckumformen über den Spielspalt 47
zwischen dem Trägerteil 5 und den auf den verjüngten Abschnitt
48 des Trägerteils 5 gesteckten Stützring 12 vermieden werden.The carrier part tapers approximately at the level of the position of the O-
Der Durchmesser des Stützringes 12 ist im übrigen derart bemessen,
daß der Dichtungskopf 4 zwar mit Spiel in das Hohlprofil 3
einführbar ist, jedoch ist der Spielspalt 49 zwischen Stützring
12 und Hohlprofil 3 so knapp ausgelegt, daß für eine abdichtende
Quetschung des O-Ringes 13 durch den Kragen 41 des Ringbundes
37 ausreichender Widerstand gegeben ist und der O-Ring 13
bei der quetschenden Beufschlagung nicht über die Randkante des
Stützringes 12 gedrückt wird, was eine scherende und damit
schadensträchtige Beanspruchung des O-Ringes 13 zur Folge hat.The diameter of the
Anstatt des O-Ringes 13 ist im übrigen denkbar, einen länglichen
elastischen hohlgebohrten Stopfen einzusetzen, wodurch die
dichtende Anlagefläche am Hohlprofil 3 erheblich vergrößert und
somit die Sicherheit einer ausreichenden Abdichtung auch nach
langer Einsatzzeit gewährleistet. Die Anlagefläche des Fortsatzes
27 des Stützringes 12 für den O-Ring 13 kann abweichend von
der zylindrischen Ausbildung des gezeigten Ausführungsbeispieles
auch konisch ausgebildet sein. Hierbei wird durch Beaufschlagung
des O-Ringes 13 durch den Kragen 41 des Ringbundes 37
der O-Ring 13 allein schon aufgrund des Hochrutschens am sich
in Einführrichtung erweiternden Konus aufgespreizt und an die
Hohlprofilwandung 39 angepreßt, wodurch der O-Ring 13 nur mit
verminderter Quetschkraft beaufschlagt werden muß um die erforderliche
Abdichtung zu erreichen. Dabei wird der Verschleiß des
O-Ringes 13 reduziert.Instead of the O-
Um den Werkstoffluß beim Innenhochdruckumformen nicht zu behindern,
kann der Dichtungskopf 4 samt Axialstempel in einfacher
Weise dem sich verkürzenden Hohlprofil 3 in gleichem Maße nachgeführt
werden ohne daß ein Verlust an Dichtigkeit hingenommen
werden muß. Ebenso ist es möglich bei Bedarf über den Axialstempel
eine zusätzliche Axialkraft auf das Hohlprofil 3 aufzubringen,
so daß der Werkstoffluß zur Umformstelle bei der Umformung
mit hohen Umformgraden forciert wird, d.h. es wird
Hohlprofilmaterial zur Umformstelle nachgeschoben. Um dies ungehindert
auszuführen, ist der Anschlagkörper 11 und das Druckstück
19 ringförmig gestaltet, wodurch eine gleichmäßige Druckbelastung
bei der Anlage der Dichtungsanordnung 7 über den Anschlagkörper
11 an der Stirnseite 20 des Hohlprofiles 3 gegeben
ist.In order not to hinder the material flow during hydroforming,
the sealing head 4 together with the axial punch can be done in a simpler manner
Track the shortening
Im Rahmen der Erfindung kann das Zusammenspiel von Trägerteil 5
und Stützring 12 zur Aufspreizung des O-Ringes 13 auch dadurch
bewirkt werden, daß das Trägerteil 5 eine Außenverzahnung
trägt, die mit einer Innenverzahnung des Stützringes 12 derart
kämmt, daß eine einfache translatorische Einführbewegung des
Trägerteils 5 nach Anlage des Anschlagkörpers 11 am Hohlprofil
3 den Stützring 12 zwangsgeführt aufspreizt. Dazu ist das Trägerteil
5 über seinen verzahnten Abschnitt hinweg konisch auszubilden,
wobei der Konus sich in Einführrichtung verjüngt. Der
Stützring 12 ist dabei aus verschiedenen Kreissegmenten zusammengesetzt,
an deren Außenumfang der O-Ring 13 gehalten wird.
Diese Form von Aufspreizung kann auch durch eine rotatorische
Bewegung des Trägerteils 5 erfolgen. Alternativ zur Verzahnung
kann das Trägerteil 5 auch als konischer Dorn ausgeführt sein,
wobei der Stützring 13 in bestimmten Grenzen als Vollkörper
elastisch, aber mit wesentlich größerer Shore-Härte als der O-Ring
13 ausgebildet sein oder in der Form von unelastischen
Kreissegmenten bestehen kann. Im letzteren Fall bewirkt die
Rückstellkraft des aufgespreizten Stützringes 12 in die entspannte
Lage die elastische Rückverformungskraft des umfänglich
nach Art eines Kolbenringes in den Stützring 12 eingebrachten
O-Ringes 13.In the context of the invention, the interaction of
Claims (13)
dadurch gekennzeichnet,
daß die Dichtungsanordnung (7) einen das Dichtungselement (13) tragenden, am Trägerteil (5) relativ zu diesem axial verschiebbar geführten und in das Hohlprofil (3) beim Andocken des Dichtungskopfes (4) am Hohlprofil (3) eintauchenden Stützring (12) und einen die Anschlagsfläche des Dichtungskopfes (4) am Hohlprofil (3) aufweisenden Anschlagkörper (1) umfaßt, der mit dem Stützring (12) fest verbunden ist, und daß das Trägerteil (5) ein Betätigungsmittel (37) aufweist, das bei Anlage des Anschlagkörpers (11) am Hohlprofil (3) aufgrund einer weitergehenden Axialbewogung des Trägerteils (5) relativ zum Stützring (12) hin in Zusammenwirkung mit dem Stützring (12) das Dichtungselement (13) aufspreizend beaufschlagt. Device for internal high pressure forming of hollow profiles with an internal high pressure forming tool, in the engraving of which the hollow profile can be inserted, and with at least one axial ram which has a sealing head which can be inserted with a section into the hollow profile with play, which has a carrier part provided with a pressure fluid channel, on the one Sealing arrangement is held and which is rigidly connected to the axial plunger, and has a stop face lying against the end in the position of use of the sealing head at the end of the hollow profile, the sealing arrangement including at least one sealing element which can be radially spread apart for circumferentially sealing contact on the inside of the hollow profile,
characterized,
that the sealing arrangement (7) carries the sealing element (13), on the carrier part (5) axially displaceably guided relative to it and in the hollow profile (3) when the sealing head (4) is immersed in the hollow profile (3), the support ring (12) and one of the stop surface of the sealing head (4) on the hollow profile (3) having stop body (1) which is fixedly connected to the support ring (12), and that the carrier part (5) has an actuating means (37) which when the stop body rests (11) on the hollow profile (3) due to a further axial movement of the carrier part (5) relative to the support ring (12) in cooperation with the support ring (12) expands the sealing element (13).
dadurch gekennzeichnet,
daß das Betätigungsmittel ein Ringbund (37) des Trägerteils (6) ist, der eine Axialdurchführung (40) aufweist, die ein den Stützring (12) mit dem Anschlagkörper (11) verbindendes Verbindungsmittel (22) durchragt, und der sich radial zwischen das am Stützring (12) gehaltene Dichtungselement (13) und den Anschlagkörper (11) erstreckt und mit einem in seinem Randbereich gelegenen Kragen (41) die Anlagefläche (36) des Stützringes (12) für das Dichtungselement (13) übergreifend ausgebildet ist, derart, daß das Dichtungselement (13) durch den zwischen dem Dichtungselement (13) und dem Anschlagkörper (11) axialbeweglichen Kragen (41) bei Anlage des Anschlagkörpers (11) am Hohlprofil (3) aufspreizend beaufschlagbar ist.Device according to claim 1,
characterized by
that the actuating means is an annular collar (37) of the carrier part (6), which has an axial passage (40) which projects through a connecting means (22) connecting the support ring (12) to the stop body (11), and which extends radially between the Support ring (12) held sealing element (13) and the stop body (11) extends and with a collar (41) located in its edge region, the contact surface (36) of the support ring (12) for the sealing element (13) is formed such that the sealing element (13) can be acted upon by the collar (41) which is axially movable between the sealing element (13) and the stop body (11) when the stop body (11) lies against the hollow profile (3).
dadurch gekennzeichnet,
daß die Anlagefläche (36) des Stützringes (12) für das Dichtungselement (13) zylindrisch ausgebildet ist.Device according to claim 2,
characterized,
that the contact surface (36) of the support ring (12) for the sealing element (13) is cylindrical.
dadurch gekennzeichnet,
daß die Anlagefläche (36) des Stützringes (12) für das Dichtungselement (13) derart konisch ausgebildet ist, daß sie sich zum Ringbund (37) hin verjüngt.Device according to claim 2,
characterized,
that the contact surface (36) of the support ring (12) for the sealing element (13) is conical in such a way that it tapers towards the ring collar (37).
dadurch gekennzeichnet,
daß das Dichtungselement ein O-Ring (13) aus einem Elastomer oder einem Federstahl ist.Device according to claim 1,
characterized,
that the sealing element is an O-ring (13) made of an elastomer or a spring steel.
dadurch gekennzeichnet,
daß das Dichtungselement ein elastischer länglicher Stopfen ist. Device according to claim 1,
characterized,
that the sealing element is an elastic elongated plug.
dadurch gekennzeichnet,
daß der Anschlagkörper (11) am Trägerteil (5) anliegt und daß der Anschlagkörper (11) sowie der Stützring (12) an ihren am Trägerteil (5) anliegenden Innenwandungen mit einem verschleißfesten Gleitfilm beschichtet sind.Device according to claim 2,
characterized,
that the stop body (11) rests on the carrier part (5) and that the stop body (11) and the support ring (12) are coated on their inner walls lying on the carrier part (5) with a wear-resistant sliding film.
dadurch gekennzeichnet,
daß der Anschlagkörper (11) an seiner dem Hohlprofil (3) zugewandten Stirnseite (17) ein Druckstück (19) aufweist, das aus einem verschleißfesten Material besteht.Device according to claim 2,
characterized,
that the stop body (11) has on its end face (17) facing the hollow profile (3) a pressure piece (19) which consists of a wear-resistant material.
dadurch gekennzeichnet,
daß der Stützring (12) an seiner dem Anschlagkörper (11) zugewandten Stirnseite (28) einen hülsenförmigen Fortsatz (27) aufweist, dessen Stirnseite (44) einen Gegenanschlag zur in Einführungsrichtung weisenden Stirnseite (45) des Ringbundes (37) des Trägerteils (5) bei einer Relativbewegung des Trägerteils (5) bildet.Device according to claim 2,
characterized,
that the support ring (12) has a sleeve-shaped extension (27) on its end face (28) facing the stop body (11), the end face (44) of which has a counter-stop to the end face (45) of the ring collar (37) of the carrier part (5) pointing in the direction of insertion ) forms during a relative movement of the carrier part (5).
dadurch gekennzeichnet,
daß am Trägerteil (5) eine Anschlagplatte (9) befestigt ist, die auf ringbundabgewandter Seite des Anschlagkörpers (11) zu dieser beabstandet angeordnet ist und einen Gegenanschlag zum Anschlagkörper (11) bei einer Relativbewegung des Trägerteils (5) bildet.Device according to claim 2,
characterized,
that a stop plate (9) is fastened to the carrier part (5), which is arranged on the side of the stop body (11) facing away from the collar and forms a counter-stop to the stop body (11) during a relative movement of the carrier part (5).
dadurch gekennzeichnet,
daß der Anschlagkörper (11) der Umfangskontur des Hohlprofiles (3) folgend ringförmig ausgebildet ist. Device according to claim 1,
characterized,
that the stop body (11) following the circumferential contour of the hollow profile (3) is annular.
dadurch gekennzeichnet,
daß das Verbindungsmittel von einem Stift (22) gebildet ist, auf dessen einem mit einem Innengewinde (32) versehenen Ende (31) der eine entsprechende axiale Durchgangsbohrung (30) aufweisende Stützring (12) aufgesteckt ist und in der Stecklage an einem zwischen den Enden (23,31) des Stiftes (22) ausgebildeten Ringbund (26) des Stiftes (22) anliegt sowie von der in Einführungsrichtung weisenden Stirnseite (34) des Stützringes (12) aus mit einer in das Innengewinde (32) des Stiftes (22) eingeschraubten Schraube (33) mit dem Stift (22) verschraubt ist, wobei das andere Ende (23) des Stiftes (22) ein Außengewinde (24) trägt, mit dem dieser in eine Gewindebohrung (21) des Anschlagkörpers (11) eingeschraubt ist.Device according to claim 2,
characterized,
that the connecting means is formed by a pin (22), on one end (31) provided with an internal thread (32) of which the corresponding axial through-bore (30) has a support ring (12) and in the plug-in position at one between the ends (23, 31) of the pin (22) formed ring collar (26) of the pin (22) and from the end face (34) of the support ring (12) pointing in the direction of insertion with a into the internal thread (32) of the pin (22) screwed screw (33) is screwed to the pin (22), the other end (23) of the pin (22) carrying an external thread (24) with which it is screwed into a threaded bore (21) of the stop body (11).
dadurch gekennzeichnet,
daß die Dichtungsanordnung (7) zusätzlich zum Dichtungselement (13) einen inneren Dichtungsring (14) beinhaltet, den das Trägerteil (5) an seiner Außenumfangsfläche (8) trägt und der am Innenumfang des Stützringes (12) anliegt.Device according to claim 2,
characterized,
that the sealing arrangement (7) contains, in addition to the sealing element (13), an inner sealing ring (14) which the carrier part (5) carries on its outer peripheral surface (8) and which bears against the inner periphery of the support ring (12).
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE19742443 | 1997-09-26 | ||
| DE19742443A DE19742443C2 (en) | 1997-09-26 | 1997-09-26 | Device for internal high pressure forming of hollow profiles |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0904869A1 true EP0904869A1 (en) | 1999-03-31 |
| EP0904869B1 EP0904869B1 (en) | 2000-11-29 |
Family
ID=7843656
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP98115208A Expired - Lifetime EP0904869B1 (en) | 1997-09-26 | 1998-08-13 | Device for high pressure forming of hollow profiles |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US6012317A (en) |
| EP (1) | EP0904869B1 (en) |
| AT (1) | ATE197776T1 (en) |
| DE (2) | DE19742443C2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SI1426123T1 (en) * | 2002-12-06 | 2007-06-30 | Thyssen Krupp Automotive Ag | Method and device for internal high pressure forming |
| DE10305074B4 (en) * | 2003-02-07 | 2015-02-05 | Dr. Ing. H.C. F. Porsche Aktiengesellschaft | Transmission shaft and method for producing a gear shaft |
| SE528938C2 (en) * | 2005-02-08 | 2007-03-20 | Ortic Ab | Hydroforming Unit |
| DE102013109880B4 (en) | 2012-09-10 | 2016-11-03 | National Research Council Of Canada | Low-friction end replenishment during hydroforming |
| DE102016209072A1 (en) * | 2016-05-25 | 2017-11-30 | Bayerische Motoren Werke Aktiengesellschaft | Sealing punch for the frontal sealing of a hollow profile |
| US10252389B2 (en) * | 2017-07-05 | 2019-04-09 | Kennametal Inc. | Quick-change clamping unit for toolholder and method of using same |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5233856A (en) * | 1992-05-29 | 1993-08-10 | General Motors Corporation | External seal unit for tube hydroforming |
| DE4309680A1 (en) * | 1993-03-25 | 1994-09-29 | Huber & Bauer Gmbh | Apparatus for the internal high-pressure forming of a tubular blank |
| US5445002A (en) * | 1993-08-16 | 1995-08-29 | Ti Corporate Services Limited | Fill and pressurization apparatus |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US2837810A (en) * | 1955-06-17 | 1958-06-10 | Flexonics Corp | Method of producing fittings |
| US4393674A (en) * | 1981-06-25 | 1983-07-19 | Air-Mo Hydraulics, Inc. | Hydraulic chuck device for engagement with the inside of a tube |
| US5233854A (en) * | 1992-05-11 | 1993-08-10 | General Motors Corporation | Press apparatus for hydroforming a tube |
| US5363544A (en) * | 1993-05-20 | 1994-11-15 | Benteler Industries, Inc. | Multi-stage dual wall hydroforming |
| US5644829A (en) * | 1993-08-16 | 1997-07-08 | T I Corporate Services Limited | Method for expansion forming of tubing |
-
1997
- 1997-09-26 DE DE19742443A patent/DE19742443C2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
1998
- 1998-08-13 DE DE59800360T patent/DE59800360D1/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1998-08-13 EP EP98115208A patent/EP0904869B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1998-08-13 AT AT98115208T patent/ATE197776T1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1998-09-28 US US09/161,471 patent/US6012317A/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5233856A (en) * | 1992-05-29 | 1993-08-10 | General Motors Corporation | External seal unit for tube hydroforming |
| DE4309680A1 (en) * | 1993-03-25 | 1994-09-29 | Huber & Bauer Gmbh | Apparatus for the internal high-pressure forming of a tubular blank |
| US5445002A (en) * | 1993-08-16 | 1995-08-29 | Ti Corporate Services Limited | Fill and pressurization apparatus |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP0904869B1 (en) | 2000-11-29 |
| US6012317A (en) | 2000-01-11 |
| ATE197776T1 (en) | 2000-12-15 |
| DE59800360D1 (en) | 2001-01-04 |
| DE19742443C2 (en) | 1999-07-22 |
| DE19742443A1 (en) | 1999-04-22 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| DE2924707C2 (en) | ||
| DE2923902C2 (en) | ||
| DE3122626C2 (en) | ||
| EP0855243A2 (en) | Clamping arrangement, particularly for workpieces | |
| DE2548626B2 (en) | METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR INSERTING AN O-RING SEAL INTO THE GROOVE OF A SEAT RING | |
| DE3446974A1 (en) | PNEUMATIC CYLINDER ASSEMBLY WITH A LOCKING MECHANISM | |
| EP0733822A1 (en) | Cylinder-piston unit filled with a fluid,especially a gasspring | |
| DE2356186A1 (en) | HYDROPNEUMATIC DEVICE FOR ENERGY CONSUMPTION | |
| DE2553471A1 (en) | GAS SPRING | |
| EP0904869B1 (en) | Device for high pressure forming of hollow profiles | |
| DD298020A5 (en) | VALVE DEVICE | |
| DE1750737A1 (en) | Sealing arrangement in a rotary ball valve | |
| EP0343335B1 (en) | Pneumatic spring | |
| EP0588779B1 (en) | Hydraulic cylinder | |
| DE2534576A1 (en) | SHOCK ABSORBER | |
| DE2926498C2 (en) | Pressure relief valve for a pit ram | |
| DE102015104334A1 (en) | Apparatus for producing a double-walled pipe | |
| DE3307813C1 (en) | Tool for testing pipes in a pipe test press | |
| DE3920161C2 (en) | Expansion wedge device, in particular for motor vehicle brakes | |
| DE2310237A1 (en) | HYDROPNEUMATIC BUMPER, PRESENTLY FOR BUMPER BUMPER OF MOTOR VEHICLES | |
| DE2455901C2 (en) | Device for filling and closing a gas chamber, in particular a gas spring | |
| DE202015104906U1 (en) | Apparatus for producing a double-walled pipe | |
| DE2403852B2 (en) | Hydraulic telescopic ram for pit lining | |
| DE102005055237B4 (en) | Device for fixing a bearing in a housing | |
| WO2005037456A1 (en) | Device for forming a peripherally closed hollow profiled element by means of fluidic internal high pressure |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19990123 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT DE FR GB IT SE |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Free format text: AL;LT;LV;MK;RO;SI |
|
| RAP1 | Party data changed (applicant data changed or rights of an application transferred) |
Owner name: DAIMLERCHRYSLER AG |
|
| GRAG | Despatch of communication of intention to grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS AGRA |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid |
Free format text: AT DE FR GB IT SE |
|
| GRAG | Despatch of communication of intention to grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS AGRA |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19991216 |
|
| ITF | It: translation for a ep patent filed | ||
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT DE FR GB IT SE |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 197776 Country of ref document: AT Date of ref document: 20001215 Kind code of ref document: T |
|
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) |
Effective date: 20001130 |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 59800360 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20010104 |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20010813 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20010814 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: IF02 |
|
| EUG | Se: european patent has lapsed |
Ref document number: 98115208.5 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20050813 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20070822 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20070823 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20070812 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20080813 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST Effective date: 20090430 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20080901 Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20090303 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20080813 |