EP0902406B1 - Method for transmitting traffic data and for analysing the road traffic network, traffic-evaluating central unit and terminal therefor - Google Patents
Method for transmitting traffic data and for analysing the road traffic network, traffic-evaluating central unit and terminal therefor Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0902406B1 EP0902406B1 EP98250299A EP98250299A EP0902406B1 EP 0902406 B1 EP0902406 B1 EP 0902406B1 EP 98250299 A EP98250299 A EP 98250299A EP 98250299 A EP98250299 A EP 98250299A EP 0902406 B1 EP0902406 B1 EP 0902406B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- route
- routes
- borders
- traffic
- vehicle
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08G—TRAFFIC CONTROL SYSTEMS
- G08G1/00—Traffic control systems for road vehicles
- G08G1/01—Detecting movement of traffic to be counted or controlled
- G08G1/0104—Measuring and analyzing of parameters relative to traffic conditions
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08G—TRAFFIC CONTROL SYSTEMS
- G08G1/00—Traffic control systems for road vehicles
- G08G1/09—Arrangements for giving variable traffic instructions
- G08G1/0962—Arrangements for giving variable traffic instructions having an indicator mounted inside the vehicle, e.g. giving voice messages
- G08G1/0968—Systems involving transmission of navigation instructions to the vehicle
- G08G1/096805—Systems involving transmission of navigation instructions to the vehicle where the transmitted instructions are used to compute a route
- G08G1/096811—Systems involving transmission of navigation instructions to the vehicle where the transmitted instructions are used to compute a route where the route is computed offboard
- G08G1/096822—Systems involving transmission of navigation instructions to the vehicle where the transmitted instructions are used to compute a route where the route is computed offboard where the segments of the route are transmitted to the vehicle at different locations and times
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08G—TRAFFIC CONTROL SYSTEMS
- G08G1/00—Traffic control systems for road vehicles
- G08G1/09—Arrangements for giving variable traffic instructions
- G08G1/0962—Arrangements for giving variable traffic instructions having an indicator mounted inside the vehicle, e.g. giving voice messages
- G08G1/0968—Systems involving transmission of navigation instructions to the vehicle
- G08G1/096833—Systems involving transmission of navigation instructions to the vehicle where different aspects are considered when computing the route
- G08G1/096844—Systems involving transmission of navigation instructions to the vehicle where different aspects are considered when computing the route where the complete route is dynamically recomputed based on new data
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08G—TRAFFIC CONTROL SYSTEMS
- G08G1/00—Traffic control systems for road vehicles
- G08G1/09—Arrangements for giving variable traffic instructions
- G08G1/0962—Arrangements for giving variable traffic instructions having an indicator mounted inside the vehicle, e.g. giving voice messages
- G08G1/0968—Systems involving transmission of navigation instructions to the vehicle
- G08G1/096877—Systems involving transmission of navigation instructions to the vehicle where the input to the navigation device is provided by a suitable I/O arrangement
- G08G1/096888—Systems involving transmission of navigation instructions to the vehicle where the input to the navigation device is provided by a suitable I/O arrangement where input information is obtained using learning systems, e.g. history databases
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Radar, Positioning & Navigation (AREA)
- Remote Sensing (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Analytical Chemistry (AREA)
- Databases & Information Systems (AREA)
- Traffic Control Systems (AREA)
- Navigation (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
- Monitoring And Testing Of Exchanges (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Die Erfindung betrifft ein Verfahren zur Übertragung von Wegedaten sowie eine Verkehrserfassungszentrale und ein Endgerät.The invention relates to a method for transmitting route data and a Traffic control center and a terminal.
Die Übermittlung von Wegedaten zwischen einem Fahrzeug und einer Zentrale, also
insbesondere die Übertragung von einen jeweils von einem Fahrzeug zurückgelegten Weg
betreffenden Daten (FCD) vom Fahrzeug an die Zentrale oder z.B. die Übertragung von in
einer Zentrale einem übermittelten Weg zuordnenbaren weiteren übertragenen Daten, wie
Reisezeiten von Fahrzeugen belastet wegen der sehr hohen Anzahl von Fahrzeugen den
Übertragungsweg sehr stark. Insbesondere durch die Übertragung von von vielen einzelnen
Fahrzeugen bestimmten Wegedaten zu jeweils zurückgelegten Wegen sowie von
Reisezeiten etc. für den jeweiligen übermittelten Weg, bedingt aufgrund der Vielzahl von
Fahrzeugen eine sehr große zu übertragende Datenmenge. Die zur Übertragung zur
Verfügung stehenden Übertragungskanäle sind jedoch hinsichtlich ihrer Kapazität nicht
unbegrenzt.
Die DE 195 08 486 A1 offenbart ein Verfahren zur Übermittlung von Positionsdaten per
Mobilfunk zwischen einem Fahrzeug und einer Zentrale, bei welchem jeweils nach einem
bestimmten Intervall mit einem GPS-Empfänger Positionsdaten in Form eines Punktes
(unter Angabe von Länge und Breite) erfasst werden, wobei jeweils zwei Punkte zu einem
Vektor verbunden werden und aus allen derart erhaltenen Vektoren ein erster Vektorzug
gebildet wird. Zur Datenreduktion wird der erste Vektor durch Geradenzüge mit jeweils
ansteigender Anzahl von Geraden solange approximiert, bis der maximale Abstand der
tatsächlichen Positionsdaten vom Geradenzug unterhalb eines vorbestimmten
Schwellenwertes liegt, worauf die derart reduzierten Positionsdaten übertragen werden.
Ein Zugriff auf Informationen in einer digitalen Karte des Verkehrswegnetzes wird zur
Datenreduktion nicht empfohlen. The transmission of route data between a vehicle and a control center, in particular the transmission of data (FCD) relating to a path covered by a vehicle in each case from the vehicle to the control center or, for example, the transmission of further transmitted data which can be assigned to a transmitted path in a control center, such as Travel times of vehicles put a heavy burden on the transmission route due to the very high number of vehicles. In particular, due to the transmission of route data determined by many individual vehicles to the distances traveled in each case, and of travel times etc. for the respective route transmitted, due to the large number of vehicles, a very large amount of data to be transmitted is required. However, the transmission channels available for transmission are not unlimited in terms of their capacity.
DE 195 08 486 A1 discloses a method for transmitting position data by mobile radio between a vehicle and a control center, in which position data in the form of a point (with the specification of length and width) are recorded with a GPS receiver after a specific interval, whereby two points are connected to a vector and a first vector train is formed from all the vectors obtained in this way. For data reduction, the first vector is approximated by straight lines with an increasing number of straight lines until the maximum distance of the actual position data from the straight line lies below a predetermined threshold value, whereupon the position data reduced in this way are transmitted.
Access to information in a digital map of the traffic network is not recommended for data reduction.
Die Schrift EP-A-0 263 332 betrifft einen Empfänger für Verkehrsfunksendungen, bei dem
einem Ausgangsstraßennetz ein groberes Raster in Form von Segmenten übergelegt wird,
die wiederum mehrere Streckensegmente enthalten. Die sich daraus ergebende Liste
enthält die Bezeichnungen der Segmente und der darin enthaltenen Streckensegmente.
Durch die Übertragung des jeweiligen Streckensegments wird das jeweilige Segment
festgelegt.The document EP-A-0 263 332 relates to a receiver for traffic radio broadcasts, in which a coarser grid in the form of segments is superimposed on an exit road network, which segments in turn contain a plurality of route segments. The resulting list contains the names of the segments and the route segments contained therein.
The respective segment is determined by the transmission of the respective route segment.
Aufgabe der vorliegenden Erfindung ist die Optimierung der Übermittlung von Wegedaten zwischen jeweils einem Fahrzeug und einer Zentrale.The object of the present invention is to optimize the transmission of route data between a vehicle and a control center.
Diese Aufgabe wird durch ein Verfahren nach Anspruch 1 sowie durch eine Verkehrserfassungszentrale und ein Endgerät nach den Ansprüchen 19 und 22 gelöst. This object is achieved by a method according to claim 1 and by a Traffic detection center and a terminal according to claims 19 and 22 solved.
Die Erfindung optimiert die Übertragung von Wegedaten durch Verringerung der Redundanz, also durch Erhöhung der lnformationsdichte bei der Übertragung. Hierzu werden jeweils eine oder mehrere Kanten in der digitalen Karte des Verkehrswegenetzes, in welchem sich Fahrzeuge bewegen, zu Teilwegen zusammengefaßt. Wegedaten können mit einer Bezeichnung des Teilweges, auf welchen sie sich beziehen, übertragen werden. Sonstige Daten wie Reisezeiten, Umweltdaten, Temperaturen etc. können z.B. durch Bezeichnung eines Teilweges und des Ortes auf dem Teilweg bezeichnet werden. Somit ist lediglich ein eindimensionaler Bahnparameter wie z.B. der Abstand vom Anfang des Teilweges zur Bezeichnung eines genauen Ortes von bahnbezogenen Informationen wie Reisezeiten oder Umweltdaten innerhalb eines Teilweges erforderlich, was mit einer geringeren Redundanz als bei einer zweidimensionalen (geographische Länge und Breite) Ortsangabe möglich ist; die Ortsbezeichnung ist also eine relativ kurze Information.The invention optimizes the transmission of route data by reducing the Redundancy, i.e. by increasing the information density during transmission. For this will each have one or more edges in the digital map of the Traffic route network, in which vehicles move, to partial routes summarized. Route data can be identified with a description of the partial route which they relate to are transferred. Other dates such as travel times, Environmental data, temperatures etc. can e.g. by designating a partial route and of the location on the partial route. So it's just a one-dimensional one Path parameters such as the distance from the beginning of the partial route to the description an exact location of train-related information such as travel times or Environmental data required within a partial route, which with a lower Redundancy than with a two-dimensional (geographical longitude and latitude) Location is possible; the place name is therefore a relatively short piece of information.
Kanten des Verkehrswegenetzes, in welchem sich Fahrzeuge bewegen, sind Teilabschnitte von Straßen, Fahrbahnen oder Fahrbahngruppen oder dgl. in einer Ausgangs-Verkehrsnetzkarte und mit anderen Kanten durch Knoten verbunden. An Knoten eines Verkehrswegenetzes können eine, zwei oder mehrere Kanten anliegen. Wenn an einem Knoten nur eine Kante anliegt, handelt es sich um einen Endpunkt des Verkehrswegenetzes. Wenn an einem Knoten zwei Kanten anliegen, kann es sich um eine Unterteilung einer Straße, Fahrbahn, Fahrbahngruppe etc. in Längsrichtung in mehrere Kanten handeln, wobei jeweils zwei Kanten dort durch einen Knoten verbunden sind. Wenn an einem Knoten drei oder mehr Kanten anliegen, handelt es sich um eine Abzweigung oder Kreuzung von Straßen, Fahrbahnen, Fahrbahngruppen etc. Eine Kreuzung, an welcher mehr als drei Kanten anliegen, kann durch mehrere Knoten mit drei Kanten ersetzt werden. Die unterschiedlichen Richtungen einer Straße können durch eine oder mehrere Kanten dargestellt sein. Wegedaten im Sinne der Ansprüche umfassen Daten, welche den von jeweils einem Fahreug zurückgelegten Weg identifizieren, nämlich die Kanten oder die Teilwege, welche jeweils eine oder mehrere aneinandergrenzende Kanten umfassen und zusammen den zurückgelegten Weg bilden. Wenn aufgrund übertragener Wegedaten der Weg eines Fahrzeuges in einer digitalen Karte eines Verkehrsnetzes in der Zentrale bestimmt ist, können auch weitere Daten wie Reisezeiten diesem Weg zugeordnet werden. Edges of the traffic network in which vehicles are moving Sections of roads, lanes or lane groups or the like in one Exit traffic network map and connected to other edges by nodes. On The nodes of a traffic route network can lie on one, two or more edges. If there is only one edge at a node, it is an end point of the Infrastructure network. If there are two edges on a node, it can be a subdivision of a street, roadway, lane group etc. in the longitudinal direction in act several edges, two edges each by a node are connected. If there are three or more edges on a node, it acts is a junction or intersection of roads, lanes, lane groups etc. An intersection with more than three edges can be divided by several Knots with three edges to be replaced. The different directions of a street can be represented by one or more edges. Route data in the sense of Claims include data that is covered by one vehicle at a time Identify the path, namely the edges or the partial paths, each one or include several contiguous edges and together the covered Make way. If, based on transmitted route data, the route of a vehicle in a digital map of a transport network in the head office can also Further data such as travel times can be assigned to this route.
Besonders vorteilhafte Ausgestaltungen der Erfindung ergeben sich aus den Unteransprüchen.Particularly advantageous embodiments of the invention result from the Dependent claims.
Übertragene Wegedaten können insbesondere einen von einem Fahrzeug mit einem Verkehrsdetektor durchfahrenen Weg betreffen und vom Fahrzeug an die Zentrale übermittelt werden. Die derart in der Zentrale ermittelten Daten können insbesondere für Reisezeitenstatistiken und für spätere Empfehlungen zur Wahl von Wegen durch Fahrzeuge verwendet werden.Route data transmitted can in particular be one from a vehicle with one Traffic detector traveled route and from vehicle to headquarters be transmitted. The data determined in this way in the central office can in particular for travel time statistics and for later recommendations on the choice of routes Vehicles are used.
Auch können sich die Wegedaten insbesondere auf einen dem Fahrzeug von der Zentrale empfohlenen Weg beziehen und von der Zentrale an das Fahrzeug bzw. auch an mehrere Fahrzeuge übermittelt werden. Damit kann ein Fahrzeug über für einen oder mehrere Wege aufgrund von Reisezeitenstatiken in einer Zentrale ermittelte Reisezeiten informiert und über die Auswahl von Wegen beraten werden.The route data can also relate in particular to one of the vehicles Head office recommended route and from the head office to the vehicle respectively can be transmitted to several vehicles. So that a vehicle can be used for one or determined several routes based on travel time statistics in a central office Travel times are informed and advice on the selection of routes.
Die Übermittlung eines Weges erfolgt zweckmäßig durch die Übermittlung von Bezeichnungen der ihn bildenden Teilwege. Ein Weg kann dabei aus einem oder mehreren Teilwegen bestehen. Die Bezeichnungen der Teilwege können in der Zentrale und im Fahrzeug in identischen oder unterschiedlichen Datenbanken abgespeichert vorliegen mit einer Zuordnung von einen Teilweg bildenden Kanten zu jeweils einem Teilweg; stattdessen kann auch in der Zentrale und im Fahrzeug jeweils mindestens ein Satz von Vorschriften zur Bildung von Teilwegen aus Kanten gespeichert sein und zur Identifikation von Teilwegen eines zu übermittelnden Weges auf diese Vorschriften zurückgegriffen werden. Auch können mehrere unterschiedliche Datenbanken und/oder Sätze von Vorschriften zur Bildung von Teilwegen jeweils im Fahrzeug und in der Zentrale gespeichert sein, wobei bei der Übermittlung von einen Weg betreffenden Daten der Satz von Vorschriften oder die Datenbank, auf welche sich die Wegedaten beziehen, mit übermittelt werden, was die Universalität erhöht.The transmission of a route is expediently carried out by the transmission of Designations of the partial routes forming it. A way can be from one or exist several partial routes. The names of the partial routes can be found in the Central and in the vehicle in identical or different databases stored with an assignment of edges forming a partial path one partial route each; instead can also be used in the head office and in the vehicle at least one set of rules for the formation of partial paths from edges be saved and for the identification of partial routes of a route to be transmitted these rules are used. Also several different ones Databases and / or sets of regulations for the formation of partial routes in each case Vehicle and be stored in the headquarters, with the transmission of one Path related data the set of regulations or the database to which the route data relate to it, which increases the universality.
Ferner können bei der Zuordnung von jeweils einer oder mehreren Kanten zu Teilwegen die Straßentypen dieser Kanten berücksichtigt werden; somit können beispielsweise Teilwege aus Autobahnabschnitte repräsentierenden Kanten oder aus Autobahnabschnitte und Landstraßen repräsentierenden Kanten gebildet werden. Furthermore, when assigning one or more edges each Partly because of the road types of these edges are taken into account; thus can for example, partial routes from edges representing highway sections or from Edges representing highway sections and country roads are formed.
Zweckmäßig wird von der Zentrale an mindestens ein Fahrzeug zu einem empfohlenen Weg die dafür erwartete Reisezeit übermittelt. Von einem Fahrzeug wird an die Zentrale zweckmäßig die für einen zurückgelegten Weg oder Teilwege des Weges benötigte Zeit übermittelt. Damit lassen sich über Belegungsstatistiken von Strecken hinaus direkt Reisezeiten für bestimmte Wege ermitteln.At least one vehicle expediently becomes one from the control center recommended route communicates the expected travel time. From a vehicle expedient to the head office for the distance or partial routes covered by the Path time needed transmitted. This means that occupancy statistics from In addition to routes, directly determine travel times for certain routes.
Vorzugsweise wird zu Wegedaten der zugehörige Zeitraum oder Zeitpunkt übermittelt. Zu von einem Fahrzeug ermittelten Wegedaten kann also die genaue Zeit oder eine quantifizierte Zeitspanne übermittelt werden und in der Zentrale abgespeichert werden. Ebenso kann von der Zentrale zur Übermittlung von Wegedaten übermittelt werden, welchen Zeitraum, also beispielsweise welche Tageszeit, welchen Wochentag oder welchen Tag im Jahr diese Wegedaten betreffen, womit beispielsweise Wegempfehlungen bei zu bestimmten Jahreszeiten auftretenden Staus präzise übermittelt werden können.The associated period or time is preferably transmitted for route data. The exact time or a time can thus be determined for route data determined by a vehicle quantified period of time are transmitted and stored in the headquarters. The control center can also transmit route data, what time period, for example what time of day, what day of the week or which day of the year these route data relate to, for example Precise route recommendations for traffic jams occurring at certain times of the year can be transmitted.
Durch eine Analyse eines Kanten und Knoten aufweisenden Verkehrswegenetzes unter Generierung einer in den Ansprüchen angegebenen Zieldatei aus einer Ausgangsdatei wird eine zur Referenzierung von Teilwegen bei der Übertragung von Wegedaten zwischen einer Zentrale und einem Fahrzeug geeignete Zieldatei erzeugt. Für die Erzeugung der Zieldatei können unterschiedliche Vorgehensweisen gewählt werden. Beispielsweise können, ausgehend von einem als Anfangsknoten gewählten Knoten des Netzes, Teilwege derart definiert werden, daß mit aufsteigender Numerierung der Teilwege jeweils ein Teilweg durch möglichst langes Linksabbiegen, ausgehend vom Anfangsknoten, definiert wird. Diese Vorschrift ist sehr einfach implementierbar.By analyzing an edge and knot Traffic route network generating one specified in the claims The target file from a source file is used to reference partial routes in the Suitable transmission of route data between a control center and a vehicle Target file created. Different can be used to generate the target file Approaches can be chosen. For example, starting from a as Starting nodes selected nodes of the network, partial routes are defined in such a way that with ascending numbering of the partial routes, one partial route through if possible long left turn, starting from the starting node. This regulation is very easy to implement.
In einer Verkehrserfassungszentrale oder einem Endgerät kann ein erfindungsgemäßes Verfahren in Form eines Programms vorteilhaft implementiert werden.In a traffic recording center or a terminal, a The inventive method advantageously implemented in the form of a program become.
Weitere Merkmale und Vorteile ergeben sich aus den weiteren Ansprüchen und aus der nachfolgenden Beschreibung eines Ausführungsbeispiels anhand der Zeichnung. Dabei zeigt:
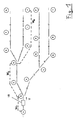
- Fig. 1
- als einzige Figur schematisch eine digitale Straßenkarte eines Verkehrswegenetzes.
- Fig. 1
- the only figure schematically shows a digital road map of a traffic route network.
Figur 1 zeigt eine digitale Straßenkarte eines Kanten 1 bis 17 und Knoten A bis T umfassenden Verkehrswegenetzes. Eine Kante umfaßt hier einen Streckenabschnitt einer Straße. Alternativ wäre es auch möglich, für einen Streckenabschnitt mehrere Kanten, beispielsweise für beide Fahrtrichtungen jeweils eine Kante oder für jede Fahrspur jeweils eine Kante oder für Abbiegespuren eine eigene Kante etc. zu definieren. Die Kante 1 befindet sich zwischen den beiden Knoten A und B, die Kante 2 befindet sich zwischen den Knoten B und C, die Kante 3 befindet sich zwischen den Knoten C und D usw. Im dargestellten sehr kleinen Verkehrswegenetz sind die Knoten A, G, J, P, T jeweils Anfangsknoten der digitalen Karte des Verkehrswegenetzes, also Knoten, von welchen jeweils nur eine Kante oder nur eine Kante der betrachteten Straßenklassen ausgeht. Die Knoten B, D, L sind Abzweigungsknoten, also Knoten mit mindestens drei anliegenden Kanten; dies bedeutet, daß beispielsweise von der Kante 1 am Knoten B ein Fahrzeug in Richtung der Kante 2 oder der Kante 10 weiterfahren kann, daß also eine echte Abzweigungsmöglichkeit besteht. Anstelle von wie hier jeweils drei Kanten, kann ein Abzweigungsknoten auch mit mehr als drei Kanten, beispielsweise an einer Kreuzung, verbunden sein; jedoch ist es auch möglich, um die hier gewählte Darstellung mit Abzweigungsknoten mit jeweils genau drei Kanten zu erhalten, auch an Kreuzungen mit mehr als drei Kanten mehrere Abzweigungsknoten zu definieren, von welchen jeweils genau drei Kanten ausgehen. Die Knoten C, E, F, H, I, K M, N, Q R sind Knoten, von welchen jeweils nur zwei Kanten, beispielsweise vom Knoten C die Kante 2 und 3, ausgehen. Diese Kanten können in einer ein Verkehrswegenetz repräsentierenden digitalen Straßenkarte für bestimmte Zwecke, wie z.B. Stauerfassung, von Bedeutung sein, jedoch sind sie zur Analyse eines Weges und Übertragung von diesen Weg betreffenden Wegedaten, wie insbesondere Reisezeiten, nicht von Bedeutung. Femer können aus einer ein Verkehrswegenetz repräsentierenden digitalen Karte, also Ausgangsdatei, zur Bildung einer Teilwege des Verkehrswegenetzes mit geringer Redundanz darstellenden Zieldatei unter Berücksichtigung von Kanten und/oder Knoten nur einer bestimmten Straßenklasse, also beispielsweise Autobahn, berücksichtigt werden; auch können z.B. aus einer Ausgangsdatei mehrere Zieldateien für jeweils eine Straßenklasse gebildet werden. Figure 1 shows a digital road map of an edge 1 to 17 and node A to T. extensive traffic network. An edge here comprises a section of the route a street. Alternatively, it would also be possible to have several for one section of the route Edges, for example one edge for each direction of travel or one for each One lane or one edge for turning lanes, etc. define. The edge 1 is between the two nodes A and B, the edge 2 is between nodes B and C, edge 3 is between the Nodes C and D etc. In the very small traffic network shown, the nodes are A, G, J, P, T each start node of the digital map of the traffic network, ie Knots, of which only one edge or only one edge of the considered Street classes. The nodes B, D, L are branch nodes, i.e. nodes with at least three adjacent edges; this means, for example, from the edge 1 At node B, drive a vehicle in the direction of edge 2 or edge 10 can that there is a real possibility of branching off. Instead of like here three edges each, a junction node can also have more than three edges, for example at an intersection; however, it is also possible to order the here selected representation with branch nodes with exactly three edges each preserved, even at intersections with more than three edges, several junction nodes to define from which exactly three edges each originate. The nodes C, E, F, H, I, K M, N, Q R are nodes, of which only two edges, for example Edge 2 and 3 start from node C. These edges can be in one Digital road map representing traffic route network for specific purposes, such as. Congestion detection may be important, however, they are used to analyze a route and transmission of route data relating to this route, in particular Travel times, not important. A network of traffic routes can also be found representative digital map, i.e. output file, to form a partial route of the Traffic network with target file representing low redundancy Consideration of edges and / or nodes of only a certain road class, for example, freeway, are taken into account; also e.g. from one Output file, several target files can be created for each street class.
Wenn mit der als Ausgangsdatei vorliegenden, ein Verkehrswegenetz
repräsentierenden digitalen Straßenkarte in Figur 1 ein Weg und diesen Weg
betreffende weitere Wegedaten übermittelt werden sollen, kann dies durch
Übermittlung der passierten Knoten und/oder der passierten Kanten erfolgen.
Beispielsweise kann sich ein in der Kante 1 in Richtung des Pfeiles V vom
Anfangsknoten A zum Anfangsknoten J fortbewegendes Fahrzeug 18 über die Kanten
1, 2, 3, 7, 8, 9 fortbewegen. Dieser Weg kann in einem Endgerät im Fahrzeug
aufgrund eines Positionserfassungsystems (beispielsweise GPS) und/oder eines
Kilometerzählers und/oder eines Geschwindigkeitszählers und/oder der Erfassung der
Lenkbewegungen des Fahrzeugs und/oder einer digitalen Straßenkarte etc. erfaßt
werden. Ferner kann zum Weg eine Gesamtzeit, welche für diesen Weg benötigt wird
und für Teilwege des Weges Teilweg-Zeiten erfaßt werden. Diese Wegedaten sollen
vom Fahrzeug 18 an eine Zentrale übermittelt werden. Dies kann von einem Endgerät
im Fahrzeug 18 zur Zentrale, beispielsweise per Funk, insbesondere Mobilfunk,
erfolgen. Hierzu kann beispielsweise eine Übertragung nach GSM, insbesondere
GSM-SMS, in Form einer Kurznachricht gewählt werden.If with the existing as an output file, a traffic network
representing digital road map in Figure 1 a way and this way
further route data in question should be transmitted by
The passed nodes and / or the passed edges are transmitted.
For example, in the edge 1 in the direction of arrow V from
Starting node A to the starting
Im in Figur 1 dargestellten Beispiel können für einen vom Fahrzeug 18 zurückgelegten
Weg von A nach J die Kanten 1, 2, 3, 7, 8, 9 und die dafür benötigte Zeit als
Wegedaten an eine Zentrale übertragen werden. Aufgrund der Vielzahl von
Fahrzeugen fällt dabei jedoch eine sehr große Datenmenge an. Die Kapazität des zur
Verfügung stehenden Übertragungsmediums ist jedoch begrenzt. Deshalb soll die
anfallende Datenmenge möglichst gering gehalten werden.In the example shown in FIG. 1, a
Hierzu wird das Verkehrswegenetz in Teilwege zerlegt. Dabei können jeweils eine oder mehrere Kanten 1 - 17 einen Teilweg bilden. Im Endgerät und in der Zentrale kann mindestens ein Satz von Vorschriften zur Bildung von Teilwegen in einem Verkehrswegenetz oder eine nach einem Satz von Vorschriften aus der digitalen Straßenkarte eines Verkehrswegenetzes (Ausgangsdatei) gebildete, weniger redundante (informationstechnisch komprimierte) digitale Straßenkarte des Verkehrswegenetzes (also Zieldatei) gespeichert sein. Die Identifikation eines Weges bei der Übermittlung eines zurückgelegten Weges und ihn betreffenden Reisezeiten etc. vom Fahrzeug an die Zentrale oder von der Zentrale an ein Fahrzeug kann dabei, falls im Fahrzeug und in der Zentrale mehrere Sätze von Vorschriften zur Bildung von Teilwegen oder mehrere nach diesen Vorschriftensätzen gebildete Zieldateien vorliegen, unter Benennung des für die Teilwege geltenden Vorschriftensatzes oder der dafür geltenden Zieldatei übermittelt werden.For this, the traffic route network is broken down into partial routes. One or each can be used several edges 1 - 17 form a partial path. In the terminal and in the control center at least one set of regulations for the formation of partial routes in one Traffic network or one according to a set of regulations from the digital Road map of a traffic route network (output file) less formed redundant (information technology compressed) digital road map of the Traffic route network (i.e. destination file) must be saved. The identification of a path when transmitting a route covered and travel times relating to it etc. from the vehicle to the control center or from the control center to a vehicle, if there are several sets of regulations for the formation of Partial or multiple target files created according to these sets of rules are available, stating the set of regulations applicable to the partial routes or the applicable target file.
Die Vorschriften zur Zerlegung des Verkehrsnetzes in Teilwege können so gewählt werden, daß Unabhängigkeit von den digitalen Straßenkarten besteht, die im Endgerät und der Zentrale verwendet werden. Insbesondere muß im Endgerät und in der Zentrale nicht notwendigerweise die gleiche digitale Straßenkarte oder die gleiche Version (Aktualisierung) einer digitalen Straßenkarte vorliegen. Das Verfahren ist auch für unterschiedliche Karten oder Kartenversionen im Endgerät und in der Zentrale ausbildbar.The regulations for dividing the transport network into partial routes can be chosen in this way be independent of the digital road maps that exist in the terminal and the headquarters can be used. In particular, in the terminal and in the Central does not necessarily have the same digital street map or the same Version (update) of a digital road map is available. The procedure is too for different cards or card versions in the terminal and in the head office formable.
Für die Datenreduktion eines Verkehrswegenetzes durch Bildung von Teilwegen aus mehreren Kanten und/oder Knoten sind unterschiedliche Sätze von Vorschriften möglich.For data reduction of a traffic route network by forming partial routes Multiple edges and / or nodes are different sets of rules possible.
Beispielsweise kann ein Teilweg jeweils zwischen zwei Knoten definiert werden, die jeweils entweder Ausgangsknoten A, G, J, P, T oder Abzweigungsknoten B, D, L, sind. Nach dieser Version ergeben sich die Teilwege der in Figur 1 dargestellten digitalen Straßenkarte eines Verkehrswegenetzes folgendermaßen:For example, a partial route can be defined between two nodes each are either output nodes A, G, J, P, T or branch nodes B, D, L, respectively. The partial routes of the digital channels shown in FIG. 1 result from this version Road map of a traffic network as follows:
Der Teilweg W1 umfaßt die Kante 1, der Teilweg W2 umfaßt die Kanten 2, 3, W3 = 4, 5, 6, W4 = 7, 8, 9, W5 = 10, 11, W6 = 12, 13, 14, W7 = 15, 16, 17. Es kann abgespeichert werden, nach welchem Satz von Vorschriften Teilweige W1 bis W7 gebildet werden. Auch kann in einer Zieldatei abgespeichert werden, welche Kanten jeweils in einem Teilweg W1 bis W7 enthalten sind und/oder welche Knoten das Ende eines Teilweges W1 bis W7 bilden.The partial route W 1 comprises the edge 1, the partial route W 2 comprises the edges 2, 3, W 3 = 4, 5, 6, W 4 = 7, 8, 9, W 5 = 10, 11, W 6 = 12, 13, 14, W 7 = 15, 16, 17. It can be saved according to which set of rules partial branches W 1 to W 7 are formed. It can also be stored in a target file which edges are contained in a partial route W 1 to W 7 and / or which nodes form the end of a partial route W 1 to W 7 .
Ein weiterer Satz von Vorschriften zur Bildung von Teilwegen in einer ein Verkehrswegenetz repräsentierenden digitalen Straßenkarte kann lauten: Ein Teilweg wird ausgehend von einem beliebigen Ausgangsknoten A mit aufsteigender Knotennumerierung jeweils gebildet, indem möglichst lange nach links abgebogen wird bis zu einem weiteren Ausgangsknoten G, J, P, T. Damit werden Wege zwischen diesem Ausgangsknoten A und den weiteren Ausgangsknoten erfaßt. Eine weitere Vorschrift kann nach Abarbeitung aller möglichen Wege vom Ausgangsknoten A in der Wahl eines weiteren Ausgangsknotens G liegen, wobei von diesem alle Wege außer dem Weg zum bereits betrachteten Ausgangsknoten A entsprechend als Teilwege definiert werden. Eine weitere Vorschrift kann darin liegen, darauf mit den restlichen Ausgangsknoten entsprechend weiterzuverfahren. Nach diesen Verfahren ergäben sich die Teilwege X1 für den Weg vom Knoten A zum Knoten G, X2 = A, J; X3 = A, P; X4= A, T; X5 = G, J; X6 = G, P; X7 = G, T; X8 = J, P; X9 = J, T; X10 = P, T, so daß die Anzahl der Teilwege X1 bis X10 die fakultierte Anzahl der Ausgangsknoten ist. Hier würde ein Weg als übermittelte Wegedaten nur jeweils einen Teilweg beinhalten.Another set of regulations for the formation of partial routes in a digital road map representing a traffic route network can be as follows: A partial route is formed starting from any exit node A with increasing node numbering, by turning left for as long as possible until a further exit node G, J, P, T. Paths between this output node A and the other output nodes are thus detected. After all possible routes from the output node A have been processed, a further rule can lie in the choice of a further output node G, all of which except the route to the output node A already considered being defined accordingly as partial routes. Another requirement may be to proceed accordingly with the remaining exit nodes. According to these methods, the partial routes X 1 would result for the route from node A to node G, X 2 = A, J; X 3 = A, P; X 4 = A, T; X 5 = G, J; X 6 = G, P; X 7 = G, T; X 8 = J, P; X 9 = J, T; X 10 = P, T, so that the number of partial routes X 1 to X 10 is the faculted number of output nodes. Here, a route as transmitted route data would only contain a partial route.
Ein weiterer Satz von Vorschriften zur Bildung von Teilwegen kann auch folgendermaßen definiert werden: Von einem beliebig gewählten Ausgangsknoten A wird möglichst lange links abbiegend bis zu einem anderen Ausgangsknoten G, J, P, T analysiert; dabei werden Teilwege nur für Wege zwischen Ausgangsknoten und Ausgangsknoten sowie eventuell zusätzlich zwischen Ausgangsknoten und Kreuzungsknoten definiert, wenn sich aufgrund erfaßter Verkehrsdaten von Fahrzeugen ergibt, daß eine relevante Anzahl von Fahrzeugen diesen Weg fährt. Damit ergeben sich im Verkehrswegenetz nur einige Wege, welche jeweils nur einen oder mehrere definierte Teilwege umfassen, so daß nur für diese Wege die Übertragung der sie betreffenden Wegedaten optimiert ist; da jedoch ein sehr großer Teil der Fahrzeuge zumindest zu bestimmten Zeiten Wege zurücklegt, welche sehr stark befahrende Teilwege umfassen, ergibt sich auch damit eine sehr gute Optimierung der bei der Übertragung von Wegedaten von Fahrzeugen anfallenden Datenmenge.Another set of regulations for the formation of partial routes can also are defined as follows: From an arbitrarily selected output node A turns left as long as possible to another exit node G, J, P, T analyzed; partial routes are only used for routes between exit nodes and Output node and possibly additionally between output node and Intersection node defined when from traffic data recorded by Vehicles shows that a relevant number of vehicles are traveling this route. This means that there are only a few routes in the traffic route network, each only one or include several defined partial routes, so that only for these routes Transmission of the route data concerning them is optimized; since, however, a very large one Some of the vehicles travel at least at certain times, which is a lot include heavily trafficked partial routes, this also results in a very good one Optimization of those involved in the transmission of route data from vehicles Amount of data.
Beispielsweise kann ein Satz von Vorschriften zur Bildung von Teilwegen
folgendermaßen aussehen: Der erste Teilweg Y1 umfaßt die Kanten 1, 2, 3, 7, 8, 9, der
Teilweg Y2 umfaßt die Kanten 15, 16, 17, der Teilweg Y3 umfaßt die Kanten 10, 11, 12,
13, 14, der Teilweg Y4 umfaßt die Kanten 4, 5, 6. Damit lassen sich alle Wege, welche
ein Fahrzeug 18 vom Ausgangsknoten A aus befahren kann, mit sehr geringer
Datenmenge definieren und übertragen. Jedoch können nach diesem Satz von
Vorschriften Wege zwischen beispielsweise dem Knoten C und dem Knoten D nicht in
Form von Teilwege mit geringer Redundanz übertragen werden, was jedoch
unproblematisch ist, wenn sich wenige Fahrzeuge von C nach D fortbewegen.For example, a set of regulations for the formation of partial routes may look as follows: the first partial route Y 1 comprises the
Claims (24)
- Method of transmitting route data, in particular by mobile phone, between a vehicle (18) and a control centre,
where route data are transmitted with designations of part-routes (W1, W2, W4), each comprising one or more adjoining borders (1;2, 3;7, 8, 9),
where at least some of the part-routes (W1, W2, W4) comprise a number of borders (2,3; 7, 8, 9) in the digital map of the traffic route network. - Method as in Claim 1,
characterised in that
route data on a route travelled through by the vehicle (18) with a traffic sensor are transmitted from the vehicle (18) to the control centre. - Method as in one of the preceding Claims,
characterised in that
route data on a route are transmitted from the control centre to the vehicle (18). - Method as in one of the preceding Claims,
characterised in that
the transmission of a route is effected by transmitting the designations of the part-routes that form it, the designations (W1 to W8) being held in memory in the control centre and in the vehicle (18) in the same (W1 to W7; W1 to W7) or different (W1 to W8 ; X1 to X10) databases, in particular in the form of target files created in accordance with Claim 14, with an assignment in each case to a part-route (W4) of borders (7, 8, 9) which form in each case one part-route (W4). - Method as in one of the preceding Claims,
characterised in that
the transmission of a route is effected by transmitting the designations of at least the part-routes that form it, at least one set of instructions for forming part-routes from borders being stored in both the control centre and the vehicle. - Method as in Claim 5,
characterised in that
a number of sets of instructions for the formation of part-routes are stored, and in that, together with route data for a route, the relevant set of instructions or a designation of this set of instructions is also transmitted. - Method as in one of the preceding Claims,
characterised in that
between one node, from which at least three borders branch off, and another node, from which at least three borders likewise branch off, a part-route is formed. - Method as in one of the preceding Claims,
characterised in that,
when assigning borders to part-routes, the types of road (motorway) of the borders are taken into consideration. - Method as in Claim 8,
characterised in that
each part-route is formed only from borders of the same type of road, preferably only part-routes between terminal nodes of this road class being defined. - Method as in one of the preceding Claims,
characterised in that
the expected journey time for a route is transmitted from the control centre to a vehicle for this route. - Method as in one of the preceding Claims,
characterised in that
the journey time needed for the route and/or for part-routes is transmitted from the vehicle to the control centre for a route covered by the vehicle. - Method as in one of the preceding Claims,
characterised in that,
for route data, the period or time at which the route data were recorded, or for which period or time the route data were established, are transmitted. - Method as in one of the preceding Claims,
characterised in that,
in the case of route data recorded by a number of vehicles for a number of routes, assigned journey times and assigned recording periods or recording times are saved in the control centre in a statistics file. - Method as in one of the preceding Claims,
characterised in that
for the purpose of analysing a traffic route network which has borders (1 to 17) and nodes (A to T) and which is present in the form of a source file comprising at least details of connections between borders and/or nodes, a target file is created representing the traffic route network, by forming each of a number of part-routes by combining, in each case, one or more borders or nodes from the source file which are linked to each other; and, for each of these part-routes, a designation of the part-route and a list of the borders and/or nodes it includes are saved in the target file. - Method as in Claim 14,
characterised in that
borders or nodes which are not included in a part-route are also saved in the target file. - Method as in Claim 14 or 15,
characterised in that
borders for a specific class of road (motorway) are analysed separately in each case and are stored in their own target file or target part-file. - Method as in one of Claims 14 to 16,
characterised in that,
between a node from which at least three borders branch off and another node from which at least three borders likewise branch off, a part-route is defined in each case. - Method as in one of Claims 14 to 17,
characterised in that,
starting from a selectable initial node (A), the part-route numbered 1 is formed by turning off to the left from it and at other nodes, and that other part-routes, in each case with the next lowest number, are each formed by turning off to the left for as long as possible. - Traffic recording centre for recording traffic, with a memory, a receiver, a program stored in the memory for implementing the method as in one of the preceding Claims, and a control system for processing the program.
- Traffic recording centre as in Claim 19,
characterised in that
it has a target file created in accordance with Claim 14. - Traffic recording centre as in Claim 19 or 20,
characterised in that
it has a transmitter. - Terminal, in particular for a vehicle, for recording traffic information, with a memory, a transmitter, a program stored in the memory for implementing the method as in one of Claims 1 to 18, and a control system for processing the program.
- Terminal as in Claim 22,
with a receiver. - Terminal as in Claim 22 or 23,
with a target file generated in accordance with Claim 14.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE19741116 | 1997-09-12 | ||
| DE19741116A DE19741116B4 (en) | 1997-09-12 | 1997-09-12 | Method for the transmission of route data, method for analyzing a traffic route network, traffic detection center and terminal |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0902406A2 EP0902406A2 (en) | 1999-03-17 |
| EP0902406A3 EP0902406A3 (en) | 2000-08-16 |
| EP0902406B1 true EP0902406B1 (en) | 2004-03-17 |
Family
ID=7842784
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP98250299A Expired - Lifetime EP0902406B1 (en) | 1997-09-12 | 1998-08-25 | Method for transmitting traffic data and for analysing the road traffic network, traffic-evaluating central unit and terminal therefor |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US6314360B1 (en) |
| EP (1) | EP0902406B1 (en) |
| AT (1) | ATE262204T1 (en) |
| DE (2) | DE19741116B4 (en) |
| ES (1) | ES2213874T3 (en) |
Families Citing this family (29)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB2360421B (en) * | 1999-11-10 | 2004-02-18 | Ibm | Transmission of geographic information to mobile devices |
| WO2001035370A1 (en) * | 1999-11-11 | 2001-05-17 | Gedas Telematics Gmbh | Method of describing and generating road networks and corresponding road network |
| DE10052109B4 (en) * | 1999-11-11 | 2014-10-30 | Deutsche Telekom Ag | Method for describing and generating road networks and road network |
| GB2361545A (en) * | 2000-01-27 | 2001-10-24 | Trafficmaster Developments Ltd | Traffic monitoring |
| US6353795B1 (en) * | 2000-02-01 | 2002-03-05 | Infospace, Inc. | Method and system for matching an incident to a route |
| US6615130B2 (en) * | 2000-03-17 | 2003-09-02 | Makor Issues And Rights Ltd. | Real time vehicle guidance and traffic forecasting system |
| DE10015935A1 (en) * | 2000-03-30 | 2001-10-04 | Bosch Gmbh Robert | Method for transmitting a position of traffic information, in particular a traffic disruption |
| US6587781B2 (en) * | 2000-08-28 | 2003-07-01 | Estimotion, Inc. | Method and system for modeling and processing vehicular traffic data and information and applying thereof |
| MXPA03007168A (en) | 2001-01-12 | 2013-05-28 | Gates Corp | Low growth power transmission belt |
| JP4663136B2 (en) * | 2001-01-29 | 2011-03-30 | パナソニック株式会社 | Method and apparatus for transmitting location information of digital map |
| JP3990641B2 (en) * | 2002-03-27 | 2007-10-17 | 松下電器産業株式会社 | Road information providing system and apparatus and road information generation method |
| DE10231833A1 (en) * | 2002-07-12 | 2004-01-22 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Procedure for updating route data |
| ATE390679T1 (en) * | 2002-08-29 | 2008-04-15 | Itis Holdings Plc | DEVICE AND METHOD FOR PROVIDING TRAFFIC INFORMATION |
| US7254481B2 (en) * | 2002-12-27 | 2007-08-07 | Fujitsu Limited | Action support method and apparatus |
| JP4255007B2 (en) * | 2003-04-11 | 2009-04-15 | 株式会社ザナヴィ・インフォマティクス | Navigation device and travel time calculation method thereof |
| KR100703444B1 (en) * | 2003-06-03 | 2007-04-03 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Device and method for downloading and displaying a images of global position information in navigation system |
| US7620402B2 (en) | 2004-07-09 | 2009-11-17 | Itis Uk Limited | System and method for geographically locating a mobile device |
| DE102006000643A1 (en) | 2006-01-03 | 2007-07-05 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Method for transmitting route information |
| JP4591395B2 (en) * | 2006-03-31 | 2010-12-01 | アイシン・エィ・ダブリュ株式会社 | Navigation system |
| GB0901588D0 (en) | 2009-02-02 | 2009-03-11 | Itis Holdings Plc | Apparatus and methods for providing journey information |
| GB2492369B (en) | 2011-06-29 | 2014-04-02 | Itis Holdings Plc | Method and system for collecting traffic data |
| US9053636B2 (en) | 2012-12-30 | 2015-06-09 | Robert Gordon | Management center module for advanced lane management assist for automated vehicles and conventionally driven vehicles |
| US9286800B2 (en) | 2012-12-30 | 2016-03-15 | Robert Gordon | Guidance assist vehicle module |
| CN104217579B (en) * | 2013-07-23 | 2016-08-24 | 同济大学 | Transportation network key road segment searching method based on section sub-network redundancy |
| US9799218B1 (en) | 2016-05-09 | 2017-10-24 | Robert Gordon | Prediction for lane guidance assist |
| US9911329B1 (en) | 2017-02-23 | 2018-03-06 | Robert Gordon | Enhanced traffic sign information messaging system |
| FR3093976A1 (en) * | 2019-03-19 | 2020-09-25 | Continental Automotive | Method of adaptive routing of a vehicle in a road network |
| DE102019006103B4 (en) * | 2019-08-29 | 2022-03-17 | Joynext Gmbh | Transferring the history of a route |
| CN111798660B (en) * | 2020-06-30 | 2021-12-07 | 腾讯科技(深圳)有限公司 | Vehicle information display and acquisition method and device and related equipment |
Family Cites Families (15)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE3633881A1 (en) * | 1986-10-04 | 1988-04-07 | Bosch Gmbh Robert | RECEIVER FOR TRAFFIC RADIO BROADCASTING |
| DE3810177C2 (en) * | 1988-03-25 | 1999-06-17 | Bosch Gmbh Robert | Radio receivers, in particular vehicle receivers |
| JP2792210B2 (en) * | 1990-07-03 | 1998-09-03 | 富士電機株式会社 | Control method and control device for automatic guided vehicle |
| NL9001810A (en) * | 1990-08-13 | 1992-03-02 | Philips Nv | METHOD FOR DETERMINING THE POSITION OF A VEHICLE, DEVICE FOR DETERMINING THE POSITION OF A VEHICLE AND VEHICLE PROVIDED WITH THE DEVICE. |
| US5845227A (en) * | 1991-02-01 | 1998-12-01 | Peterson; Thomas D. | Method and apparatus for providing shortest elapsed time route and tracking information to users |
| GB2271420A (en) * | 1992-10-07 | 1994-04-13 | Ford Motor Co | Vehicle navigation system |
| JPH07234994A (en) * | 1994-02-24 | 1995-09-05 | Toshiba Corp | Route display device |
| US5543789A (en) * | 1994-06-24 | 1996-08-06 | Shields Enterprises, Inc. | Computerized navigation system |
| DE19508486A1 (en) * | 1995-03-09 | 1996-09-12 | Mannesmann Ag | Method and device for reducing the amount of data to be transmitted from a vehicle |
| JPH08339162A (en) * | 1995-06-12 | 1996-12-24 | Alpine Electron Inc | Map plotting method |
| KR100198813B1 (en) * | 1996-06-12 | 1999-06-15 | 정선종 | Post trajectory system |
| JP3223240B2 (en) * | 1996-11-19 | 2001-10-29 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | Vehicle control device |
| US5893081A (en) * | 1996-11-25 | 1999-04-06 | Etak, Inc. | Using multiple levels of costs for a pathfinding computation |
| US5916299A (en) * | 1996-11-25 | 1999-06-29 | Etak, Inc. | Method for determining exits and entrances for a region in a network |
| US5978730A (en) * | 1997-02-20 | 1999-11-02 | Sony Corporation | Caching for pathfinding computation |
-
1997
- 1997-09-12 DE DE19741116A patent/DE19741116B4/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
1998
- 1998-08-25 DE DE59810980T patent/DE59810980D1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1998-08-25 ES ES98250299T patent/ES2213874T3/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1998-08-25 AT AT98250299T patent/ATE262204T1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1998-08-25 EP EP98250299A patent/EP0902406B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1998-09-11 US US09/151,491 patent/US6314360B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US6314360B1 (en) | 2001-11-06 |
| EP0902406A3 (en) | 2000-08-16 |
| DE59810980D1 (en) | 2004-04-22 |
| ES2213874T3 (en) | 2004-09-01 |
| DE19741116A1 (en) | 1999-03-18 |
| DE19741116B4 (en) | 2004-02-26 |
| ATE262204T1 (en) | 2004-04-15 |
| EP0902406A2 (en) | 1999-03-17 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0902406B1 (en) | Method for transmitting traffic data and for analysing the road traffic network, traffic-evaluating central unit and terminal therefor | |
| EP1026649B1 (en) | Method and device to prepare traffic information | |
| DE19539641C2 (en) | Method and device for traffic situation-dependent vehicle route guidance | |
| EP0944893B1 (en) | Process for selecting the traffic information transmitted by a traffic information centre which concerns a route of a vehicle equipped with a terminal in a road network | |
| EP0730726B1 (en) | Process for producing a digitised road map | |
| EP1145210B1 (en) | Method for identifying events which cover more than one segment using segments | |
| EP0884709B1 (en) | Device to obtain information about the predetermined maximum speed in a vehicle | |
| EP2507589A1 (en) | Method for simplifying a description of a route | |
| EP0803852B1 (en) | Method and device to guide a vehicle | |
| EP0889454A2 (en) | Method and central unit for forecasting and analysis of a traffic network | |
| EP1245017B1 (en) | Method of describing and generating road networks and corresponding road network | |
| EP0790591B1 (en) | Locationdatabase for determining routes within a road traffic network | |
| EP1397643B1 (en) | Method for generating navigating data for route guidance and navigation system | |
| DE102018202970A1 (en) | Method for determining topological information of a road intersection | |
| DE19753170A1 (en) | Method for transmitting route information relating to a recommended route of a vehicle in a traffic network from a traffic control center to a terminal in a vehicle, terminal and control center | |
| DE19816585B4 (en) | Method for route information of a terminal user by transmitting route information from a center to the terminal | |
| DE102019103671A1 (en) | Control of a motor vehicle | |
| DE19750775A1 (en) | Method for selecting a route of a vehicle with a terminal in a traffic network, traffic information transmitted from a central, terminal and central for carrying out the method | |
| EP0261450A1 (en) | Guiding system for individual traffic | |
| DE10052934A1 (en) | Method for determining a path between a starting point and an end point of a network, such as a road network | |
| WO1998027530A1 (en) | Process for transmitting route information concerning the recommended route of a vehicle in a road network between a traffic information centre and a terminal mounted in a vehicle, terminal and traffic information centre | |
| DE10234367B3 (en) | Traffic situation imaging method for traffic flow organization system uses correlation of flow lines dependent on measured traffic parameters | |
| DE19810126A1 (en) | Computer-assisted route-finding method for vehicle driver | |
| DE60106857T2 (en) | Method and device for reference sites in transport telematics | |
| DE10052109B4 (en) | Method for describing and generating road networks and road network |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI NL PT SE |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Free format text: AL;LT;LV;MK;RO;SI |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Free format text: AL;LT;LV;MK;RO;SI |
|
| RIC1 | Information provided on ipc code assigned before grant |
Free format text: 7G 08G 1/01 A, 7G 08G 1/0969 B, 7G 08G 1/09 B |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20000810 |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid |
Free format text: AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI NL PT SE |
|
| RAP1 | Party data changed (applicant data changed or rights of an application transferred) |
Owner name: VODAFONE AG |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20021022 |
|
| RAP1 | Party data changed (applicant data changed or rights of an application transferred) |
Owner name: VODAFONE HOLDING GMBH |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| RAP1 | Party data changed (applicant data changed or rights of an application transferred) |
Owner name: ATX EUROPE GMBH |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI NL PT SE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20040317 Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20040317 Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20040317 Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20040317 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) |
Effective date: 20040317 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: GERMAN |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 59810980 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20040422 Kind code of ref document: P |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20040617 Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20040617 Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20040617 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20040730 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20040809 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Payment date: 20040819 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20040825 |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20040831 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20040831 Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20040831 |
|
| NLV1 | Nl: lapsed or annulled due to failure to fulfill the requirements of art. 29p and 29m of the patents act | ||
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FG2A Ref document number: 2213874 Country of ref document: ES Kind code of ref document: T3 |
|
| RAP2 | Party data changed (patent owner data changed or rights of a patent transferred) |
Owner name: ATX EUROPE GMBH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FD4D |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: *ATX EUROPE G.M.B.H. Effective date: 20040831 |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20041220 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES;WARNING: LAPSES OF ITALIAN PATENTS WITH EFFECTIVE DATE BEFORE 2007 MAY HAVE OCCURRED AT ANY TIME BEFORE 2007. THE CORRECT EFFECTIVE DATE MAY BE DIFFERENT FROM THE ONE RECORDED. Effective date: 20050825 Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20050825 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20050826 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20050825 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20060428 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST Effective date: 20060428 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FD2A Effective date: 20050826 |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: *ATX EUROPE G.M.B.H. Effective date: 20040831 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20040817 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20150821 Year of fee payment: 18 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R119 Ref document number: 59810980 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170301 |