EP0822011B1 - Process for forming decorative paint film exhibiting metallic effect - Google Patents
Process for forming decorative paint film exhibiting metallic effect Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0822011B1 EP0822011B1 EP97113357A EP97113357A EP0822011B1 EP 0822011 B1 EP0822011 B1 EP 0822011B1 EP 97113357 A EP97113357 A EP 97113357A EP 97113357 A EP97113357 A EP 97113357A EP 0822011 B1 EP0822011 B1 EP 0822011B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- paint film
- decorative
- paint
- preferred
- base
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B05—SPRAYING OR ATOMISING IN GENERAL; APPLYING FLUENT MATERIALS TO SURFACES, IN GENERAL
- B05D—PROCESSES FOR APPLYING FLUENT MATERIALS TO SURFACES, IN GENERAL
- B05D5/00—Processes for applying liquids or other fluent materials to surfaces to obtain special surface effects, finishes or structures
- B05D5/06—Processes for applying liquids or other fluent materials to surfaces to obtain special surface effects, finishes or structures to obtain multicolour or other optical effects
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B05—SPRAYING OR ATOMISING IN GENERAL; APPLYING FLUENT MATERIALS TO SURFACES, IN GENERAL
- B05D—PROCESSES FOR APPLYING FLUENT MATERIALS TO SURFACES, IN GENERAL
- B05D5/00—Processes for applying liquids or other fluent materials to surfaces to obtain special surface effects, finishes or structures
- B05D5/06—Processes for applying liquids or other fluent materials to surfaces to obtain special surface effects, finishes or structures to obtain multicolour or other optical effects
- B05D5/067—Metallic effect
- B05D5/068—Metallic effect achieved by multilayers
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B44—DECORATIVE ARTS
- B44C—PRODUCING DECORATIVE EFFECTS; MOSAICS; TARSIA WORK; PAPERHANGING
- B44C1/00—Processes, not specifically provided for elsewhere, for producing decorative surface effects
Definitions
- the present invention relates to process for forming a decorative paint film in which a decorative layer is formed by drawing, for example, color images on a surface to be painted, such as a surface of an automobile body, and the like.
- a decorative paint film forming process according to the present invention it is possible to readily form a vivid decorative paint film which exhibits a metallic effect.
- ink-jet type printers have been utilized as a printing apparatus for computers.
- four color inks are injected through a nozzle, respectively, in accordance with hues of pixels in the image data which are stored in a memory of a computer.
- the four color inks are, for instance, red, blue, and yellow (i.e., the three primary colors) inks in addition to a black ink.
- the four color inks are deposited on a printing paper in dotted fashions, and are superimposed on the printing paper.
- the hues of the pixels are reproduced on the printing paper.
- the nozzles are driven in horizontal directions, and simultaneously the printing paper is driven in vertical directions. As a result, the image data can be drawn on the printing paper.
- the printers are applicable only to paper-like substances to be coated. However, if image data can be drawn, for example, on automobile bodies, complicated decorations can be mass-produced industrially.
- metallic coatings are employed widely to paint automobile outer panels.
- the metallic coatings include aluminum pigments, mica pigments, and so on.
- the metallic coatings are prepared by the following 2-coat-and-1-bake coating method: namely; a base paint is first applied on a surface of an intermediate paint film.
- the base paint involves a glossy substance.
- gloss substance hereinafter means an aluminum pigment, a mica pigment, etc.
- a clear paint is applied on a surface of the resulting base paint film by a wet-on-wet coating method, and subsequently the base paint and clear paint are baked and dried to an integral two-layer paint film by heating.
- Japanese Unexamined Patent Publication (KOKAI) No. 7-108,216 discloses such a process. In the process, a decorative coating is carried out on a surface of an intermediate paint film, and thereafter a base paint and a clear paint is applied on the resulting decorative layer entirely.
- the present invention has been developed in view of the aforementioned circumstances. It is therefore an object of the present to provide a process for forming a decorative paint film which exhibits vivid hues together with a metallic effect, and which has superb decorativeness.
- a first aspect of the present invention can carry out the aforementioned object, and is a process for forming a decorative paint film exhibiting a metallic effect.
- the present process comprises:
- a second aspect of the present invention can carry out the aforementioned object, and is a process for forming a decorative paint film exhibiting a metallic effect.
- the present process comprises:
- a base paint film is first formed, and subsequently a decorative layer is formed.
- the base paint film can be uncured (i.e., in a wet state), or can be cured to a certain extent by heating it preliminarily. Alternatively, the base paint film can be cared completely.
- a decorative layer can be cured to prepare a decorative paint film.
- a clear paint film can preferably be formed on a surface of the decorative layer to prepare a decorative paint film. In this instance, a clear paint can be applied on an uncured decorative layer, and then the resulting clear paint film and the decorative layer can be baked and dried integrally.
- a decorative layer can be cured, and thereafter a clear paint film can be formed on the cured decorative layer.
- the base paint film is visible through the decorative layer, because the decorative layer is formed so as to have a thickness of less than a hiding thickness.
- light transmits through the decorative layer to arrive at the base paint film, and reflects at the glossy substance.
- the reflected light again transmits through the decorative layer, and finally comes into eyes.
- a novel decoration can be produced in which a metallic effect is superimposed on the hues of the decorative layer.
- the clear paint film is further formed on the decorative layer, a large refractive index of the clear paint film and an extended optical-path furthermore enhances the metallic effect, and the clear paint film can also protect the decorative layer.
- a base paint film and a clear paint film are formed in advance, and subsequently a decorative layer is formed on the surface of the clear paint film.
- the decorative layer can be formed.
- a base paint film, a clear paint film and a decorative layer can be baked and dried integrally by a 3-coat-and-1-bake coating method.
- a second or outermost clear paint film can be formed on a surface of the decorative layer.
- the base paint film is visible through the clear paint film and the decorative layer, because the decorative layer is formed so as to have a thickness of less than a hiding thickness.
- light transmits through the decorative layer to arrive at the clear paint film, and further transmits through the clear paint film to arrive at the base paint film. Then, the light reflects at the glossy substance. The reflected light again transmits through the clear paint film and decorative layer, and finally comes into eyes.
- a novel decoration can be produced in which a metallic effect is superimposed on the hues of the decorative layer.
- a large refractive index of the second clear paint film and an extended optical-path furthermore enhances the metallic effect, and the second clear paint film can also protect the decorative layer.
- the present process can be modified as set forth in the aforementioned fourth option.
- a paint film formed of a water based paint, and a paint film formed of an organic solvent based paint can preferably be coated alternately.
- the paints are inhibited from mingling with each other at the interface between the paint films. As a result, it is possible to form a vivid decorative layer which is free from the blur.
- the first and second aspects of the present invention are a process for forming a decorative paint film exhibiting a metallic effect, respectively.
- the present process can readily produce a decorative paint film which exhibits a unique metallic effect, and which involves a vivid pattern.
- the unique metallic effect has not been produced by conventional methods so far.
- the unique metallic effect which is exhibited through the decorative layer, can be enhanced furthermore vividly.
- the blurredness is inhibited from occurring.
- the hues of the resulting decorative layer, and the profile thereof can be upgraded furthermore vividly.
- the base paint can be a conventional base paint which includes at least a glossy substance selected from the group consisting of an aluminum pigment, a mica pigment, and a pearl mica pigment.
- the mica pigment can include a silver plating layer formed thereon.
- the pearl mica pigment can include a titanium oxide layer formed thereon.
- the base paint can preferably be applied on a substrate so as to form a base paint film having a thickness of from 10 to 30 ⁇ m.
- the glossy substance can preferably have an average particle diameter of from 10 to 30 ⁇ m.
- the glossy substance has an average particle diameter of less than 10 ⁇ m, no satisfactory metallic effect can be given to the resulting base paint film.
- the glossy substance has an average particle diameter of more than 30 ⁇ m, the glossy substance is less likely to parallelly orient in the resulting base film so that no satisfactory metallic effect can be given to the resulting base paint film.
- the glossy substance can further preferably have an average particle diameter of from 15 to 20 ⁇ m.
- the base paint includes non-volatile compositions, and the non-volatile compositions can preferably contain the glossy substance in an amount of from 10 to 50% by weight.
- the non-volatile compositions contain the glossy substance in an amount of less than 10% by weight, no satisfactory metallic effect is given to the resulting base paint film.
- the non-volatile compositions contain the glossy substance in an amount of more than 50% by weight, no satisfactory metallic effect is given to the resulting base paint film because the excessively included glossy substance is less likely to parallelly orient in the resulting base paint film.
- the non-volatile compositions can further preferably contain the glossy substance in an amount of from 20 to 40% by weight.
- the base paint film can preferably exhibit a lightness of 20 or more expressed as an "L" value.
- the base paint film exhibits a lightness of less than 20 expressed as an "L” value, no metallic effect is given to the resulting base paint film because the glossy substance, involved in the base paint film, is less likely to be observed through the decorative layer.
- the "L” value herein means an "L” value of the base paint film through which the underlying layer is visible.
- the decorative paint is not limited to specific paints in particular.
- the decorative paint can be inks which have been employed by ink-jet methods conventionally.
- the decorative paint is applied to form a decorative layer having a thickness of less than a hiding thickness.
- the decorative layer can further preferably have a thickness of 5 ⁇ m or less, furthermore preferably from 0.1 to 3 ⁇ m. Accordingly, the base paint film, underlying the decorative layer, is visible through the decorative layer. As a result, the resulting decorative paint film exhibits the unique metallic effect.
- the hiding thickness of the decorative paint depends on a specific pigment included in the decorative paint, and on a concentration of the specific pigment.
- the decorative paint includes non-volatile compositions, and the non-volatile compositions can preferably contain the specific pigment in a concentration of from 30 to 70% by weight, further preferably from 40 to 50% by weight.
- the decorative paint includes non-volatile compositions, and the non-volatile compositions can preferably contain the specific pigment in a concentration of from 10 to 60% by weight, further preferably from 20 to 30% by weight
- the decorative paint includes non-volatile compositions, and the non-volatile compositions can preferably contain the specific pigment in a concentration of from 5 to 30% by weight, further preferably from 10 to 20% by weight.
- the resulting decorative paint When the concentration of the specific pigments is more than the upper limits, the resulting decorative paint exhibits a considerably thin hiding thickness so that it is hard to apply the decorative paint to prepare a decorative layer having a thin thickness less than the hiding thickness.
- the concentration of the specific pigments When the concentration of the specific pigments is less than the lower limits, and when the resulting decorative paint is applied so as to give a decorative layer desired hues, the resultant decorative layer may occasionally cause running.
- the concentration of the specific pigments falls between the upper and lower limits, the decorative paints can be applied to form the decorative layer, which has a thickness of less than a hiding thickness, by applying the decorative paints of the specific colors one after another while controlling the injection amounts of the decorative paints. Note that the thickness of the thus prepared decorative layer is also an optimum thickness which gives the resulting decorative layer desired hues, and which hardly causes the resulting decorative layer to run.
- a clear paint can be further applied on the surface of the decorative layer to form a clear paint film.
- the dear paint film can preferably have a thickness of from 20 to 100 ⁇ m.
- a steel plate was subjected to an electrodeposition coating and subsequently to an intermediate coating, thereby preparing a coated plate. Then, an acrylic-melamine organic solvent based paint was applied onto the coated plate in a thickness of about 15 ⁇ m.
- the acrylic-melamine organic solvent based paint exhibited a silver metallic color, and included 40% by weight of non-volatile compositions.
- the non-volatile compositions contained an aluminum pigment in an amount of 14% by weight, a blue pigment in an amount of 1% by weight, and a black pigment in a trace amount with respect to the whole base paint taken as 100% by weight, respectively.
- the coated plate with the base paint was heated for 5 minutes to preliminarily cure the base paint.
- a decorative paint film was carried out onto a surface of the resulting base paint film by an ink-jet method with water based inks.
- Each of the water based inks had a composition as set forth in Table 1 below.
- the resulting decorative layer involved a flower pattern which was derived from image data.
- the image data had been produced by scanning a photograph of a flower with an image scanner.
- the thus formed decorative layer had a thickness of about 1.5 ⁇ m at the maximum (i.e., less than the hiding thickness).
- an acrylic-melamine organic solvent based clear paint was applied onto a surface of the thus formed decorative layer, and onto a surface of the base paint film on which the decorative layer was not formed, respectively, in a thickness of about 30 ⁇ m.
- the coated plate with the clear paint applied was baked and dried at 140 °C for 30 minutes, thereby completing a decorative paint film of a First Preferred Embodiment.
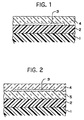
- Fig. 1 illustrates the thus prepared decorative paint film schematically.
- the decorative paint film comprised an intermediate paint film 1, a base paint film 2, a decorative layer 3, and a clear paint film 4.
- the base paint film 2 was formed on a surface of the intermediate paint film 1.
- the decorative layer 3 was partially formed on a surface of the base paint film 2.
- the clear paint film 4 was formed on a surface of the decorative layer 3, and on a surface of the base paint film 2.
- the decorative layer 3 could be observed through the clear paint film 4. Further, the base paint film 2 could be observed through the decorative layer 3. Furthermore, concerning the portions where the decorative layer 3 was not formed, the base paint film 2 could be observed through the clear paint film 4. Accordingly, the flower pattern, involved in the decorative layer 3, can be observed vividly in the silver metallic color, which was exhibited by the base paint film 2. At the same time, the metallic glossiness, resulting from the aluminum pigment, could be observed in the decorative layer 3. Thus, the decorative paint film was of decorativeness which had not been available so far.
- the base paint was baked and dried at 140 °C for 30 minutes after applying the base paint. Unless otherwise specified, a decorative paint film of a Second Preferred Embodiment was completed in the same manner as the First Preferred Embodiment.
- the decorative paint film was carried out without preliminary heating the base paint after applying the base paint, and the three layers were baked and dried at 140 °C for 30 minutes in order to integrate the three layers (i.e., the base paint film, the decorative layer and the clear paint film) after applying the clear paint.
- a decorative paint film of a Third Preferred Embodiment was completed in the same manner as the First Preferred Embodiment.
- the thus prepared decorative paint film was of decorativeness which had not been available so far, though it exhibited slight blurredness.
- the slight blurredness apparently resulted from the decorative layer, which was stained by the base paint and clear paint.
- a plate-shaped workpiece was prepared.
- the workpiece was made from polypropylene, and was coated with a primer.
- the primer predominantly contained chlorinated polypropylene.
- an acrylic-melamine organic solvent based paint was applied onto the plate-shaped workpiece in a thickness of about 15 ⁇ m.
- the acrylic-melamine organic solvent based paint exhibited a red mica metallic color, and included 40% by weight of non-volatile compositions.
- the non-volatile compositions contained an aluminum pigment in an amount of 2% by weight, a mica pigment in an amount of 6% by weight, and a red pigment in an amount of 20% by weight with respect to the whole base paint taken as 100% by weight, respectively.
- an acrylic-melamine organic solvent based clear paint was applied onto the plate-shaped workpiece with the base paint applied in a thickness of about 30 ⁇ m. Subsequently, the workpiece was heated at 120°C for 30 minutes in order to integrally bake and dry the base paint film and clear paint film.
- a geometric pattern was applied onto a surface of the clear paint film by an ink-jet method with water based inks.
- the water based inks had the same composition as that of the First Preferred Embodiment.
- the geometric pattern had been produced on a computer monitor.
- the thus formed decorative layer had a thickness of about 2 ⁇ m at the maximum (i.e., less than the hiding thickness).
- an acrylic-melamine organic solvent based clear paint was applied onto a surface of the thus formed decorative layer, and onto a surface of the first (or intermediate) clear paint film on which the decorative layer was not formed, respectively, in a thickness of about 30 ⁇ m.
- the plate-shaped workpiece was subsequently heated at 120 °C for 30 minutes, thereby completing a decorative paint film of a Fourth Preferred Embodiment.
- Fig. 2 illustrates the thus prepared decorative paint film schematically.
- a decorative layer 3 could be observed through a clear paint film 4.
- a base paint film 2 could be observed through the decorative layer 3 and an intermediate clear paint film 5.
- the base paint film 2 could be observed through the clear paint film 4 and intermediate clear paint film 5. Accordingly, the geometric pattern, involved in the decorative layer 3, could be observed vividly in the red mica metallic color, exhibited by the base paint film 2.
- the metallic glossiness, resulting from the aluminum pigment and mica pigment could be observed in the decorative layer 3.
- the decorative paint film was of decorativeness which had not been available so far.
- a decorative paint film of Tenth through Fourteenth Preferred Embodiments was prepared in the same manner as the Fourth Preferred Embodiment. It is apparent from Table 2 that decorative paint films of decorativeness which had not been available so far were prepared in the Fifth through Fourteenth Preferred Embodiments. Note that the decorative paint film of the Fifth through Fourteenth Preferred Embodiments had a thickness of less than the hiding thickness even at portions where the multiple color inks were superimposed.
- the acrylic-melamine mica metallic base paint included 40% by weight of non-volatile compositions.
- the non-volatile compositions contained an aluminum pigment in an amount of 4.4% by weight, a white mica pigment in an amount of 4.3% by weight, a red pigment in an amount of 0.1% by weight, a yellow pigment in an amount of 0.2% by weight, and a white pigment in an amount of 3.4% by weight with respect to the whole base paint taken as 100% by weight, respectively.
- the aluminum pigment had an average particle diameter of 15 ⁇ m.
- the white mica pigment had an average particle diameter of 18 ⁇ m.
- a decorative paint film of a Fifteenth Preferred Embodiment was prepared in the same manner as the First Preferred Embodiment. Note that the base paint film of the Fifteenth Preferred Embodiment exhibited a lightness of 55 expressed as an "L" value, and that the decorative layer had a thickness of about 2 ⁇ m at the maximum (i.e., less than the hiding thickness).
- the flower pattern exhibiting a unique metallic effect was depicted on the mica metallic color.
- the decorative paint film was of decorativeness which had not been available so far.
- the acrylic-melamine mica metallic base paint included 40% by weight of non-volatile compositions.
- the non-volatile compositions contained an aluminum pigment in an amount of 1.0% by weight, a red mica pigment in an amount of 3.0% by weight, and a red pigment in an amount of 8.0% by weight with respect to the whole base paint taken as 100% by weight, respectively.
- the aluminum pigment had an average particle diameter of 11 ⁇ m.
- the red mica pigment had an average particle diameter of 15 ⁇ m.
- a decorative paint film of a Sixteenth Preferred Embodiment was prepared in the same manner as the First Preferred Embodiment. Note that the base paint film of the Sixteenth Preferred Embodiment exhibited a lightness of 25 expressed as an "L" value, and that the decorative layer had a thickness of about 2 ⁇ m at the maximum (i.e., less than the hiding thickness).
- the flower pattern exhibiting a unique metallic effect was depicted on the red mica metallic color.
- the decorative paint film was of decorativeness which had not been available so far.
- the acrylic-melamine metallic base paint included 40% by weight of non-volatile compositions.
- the non-volatile compositions contained an aluminum pigment in an amount of 19.0% by weight, a blue pigment in an amount of 1.0% by weight, and a black pigment in a trace amount with respect to the whole base paint taken as 100% by weight, respectively.
- the aluminum pigment had an average particle diameter of 11 ⁇ m.
- a decorative paint film of a Seventeenth Preferred Embodiment was prepared in the same manner as the First Preferred Embodiment.
- the base paint film of the Seventeenth Preferred Embodiment exhibited a lightness of 74 expressed as an "L" value, and that the decorative layer had a thickness of about 2 ⁇ m at the maximum (i.e., less than the hiding thickness).
- the flower pattern exhibiting a unique metallic effect was depicted on the blue metallic color.
- the decorative paint film was of decorativeness which had not been available so far.
- the acrylic-melamine metallic base paint included 40% by weight of non-volatile compositions.
- the non-volatile compositions contained an aluminum pigment in an amount of 4.2% by weight, a blue pigment in an amount of 1.0% by weight, and a white pigment in an amount of 4.0% by weight with respect to the whole base paint taken as 100% by weight, respectively.
- the aluminum pigment had an average particle diameter of 22 ⁇ m.
- a decorative paint film of an Eighteenth Preferred Embodiment was prepared in the same manner as the First Preferred Embodiment.
- the base paint film of the Eighteenth Preferred Embodiment exhibited a lightness of 68 expressed as an "L" value, and that the decorative layer had a thickness of about 2 ⁇ m at the maximum (i.e., less than the hiding thickness).
- the flower pattern exhibiting a unique metallic effect was depicted on the blue metallic color.
- the decorative paint film was of decorativeness which had not been available so far.
- a base paint As a base paint, another acrylic-melamine mica metallic base paint was used.
- the acrylic-melamine mica metallic base paint included 40% by weight of non-volatile compositions.
- the non-volatile compositions contained a red mica pigment in an amount of 10.0% by weight, and a red pigment in an amount of 9.0% by weight with respect to the whole base paint taken as 100% by weight, respectively.
- the red mica pigment had an average particle diameter of 15 ⁇ m.
- a decorative paint film of a Nineteenth Preferred Embodiment was prepared in the same manner as the First Preferred Embodiment. Note that the base paint film of the Nineteenth Preferred Embodiment exhibited a lightness of 46 expressed as an "L" value, and that the decorative layer had a thickness of about 2 ⁇ m at the maximum (i.e., less than the hiding thickness).
- the flower pattern exhibiting a unique metallic effect was depicted on the red mica metallic color.
- the decorative paint film was of decorativeness which had not been available so far.
- a steel plate was subjected to an electrodeposition coating and subsequently to an intermediate coating, thereby preparing a coated plate. Then, a white color polyester-melamine paint was applied onto the coated plate in a thickness of about 35 ⁇ m, and was baked at 140 °C for 30 minutes. Subsequently, a mica base paint was applied onto a surface of the white color polyester-melamine paint film in a thickness of about 15 ⁇ m.
- the mica base paint included 40% by weight of non-volatile compositions.
- the non-volatile compositions contained a white mica pigment in an amount of 6.0% by weight with respect to the whole base paint taken as 100% by weight.
- the white mica pigment had an average particle diameter of 18 ⁇ m.
- a decorative paint film of a Twentieth Preferred Embodiment was prepared in the same manner as the First Preferred Embodiment. Note that the base paint film of the Twentieth Preferred Embodiment, which was formed on the white color polyester-melamine paint film, exhibited a lightness of 79 expressed as an "L" value, and that the decorative layer had a thickness of about 2 ⁇ m at the maximum (i.e., less than the hiding thickness).
- the flower pattern exhibiting a unique metallic effect was depicted on the white mica metallic color.
- the decorative paint film was of decorativeness which had not been available so far.
- the acrylic-melamine metallic base paint included 40% by weight of non-volatile compositions.
- the non-volatile compositions contained an aluminum pigment in an amount of 3.0% by weight, a red pigment in an amount of 0.1% by weight, a yellow pigment in an amount of 0.2% by weight, and a white pigment in an amount of 3.4% by weight with respect to the whole base paint film taken as 100% by weight, respectively.
- the aluminum pigment had an average particle diameter of 15 ⁇ m.
- a decorative paint film of a Twenty-first Preferred Embodiment was prepared in the same manner as the Fist Preferred Embodiment. Note that the base paint film of the Twenty-first Preferred Embodiment exhibited a lightness of 48 expressed as an "L" value, and that the decorative layer had a thickness of about 2 ⁇ m at the maximum (i.e., less than the hiding thickness).
- the decorative paint film was of decorativeness which was not exactly equivalent to that of the Fifteenth through Twentieth Preferred Embodiments, but which had not been available so far.
- the acrylic-melamine metallic base paint included 40% by weight of non-volatile compositions.
- the non-volatile compositions contained an aluminum pigment in an amount of 25.0% by weight, a red pigment in an amount of 0.1% by weight, a yellow pigment in an amount of 0.2% by weight, and a white pigment in an amount of 3.4% by weight with respect to the whole base paint taken as 100% by weight, respectively.
- the aluminum pigment had an average particle diameter of 11 ⁇ m.
- a decorative paint film of a Twenty-second Preferred Embodiment was prepared in the same manner as the First Preferred Embodiment. Note that the base paint film of the Twenty-second Preferred Embodiment exhibited a lightness of 65 expressed as an "L" value, and that the decorative layer had a thickness of about 2 ⁇ m at the maximum (i.e., less than the hiding thickness).
- the decorative paint film was of decorativeness which was not exactly equivalent to that of the Fifteenth through Twentieth Preferred Embodiments, but which had not been available so far.
- the acrylic-melamine metallic base paint included 40% by weight of non-volatile compositions.
- the non-volatile compositions contained an aluminum pigment in an amount of 20.0% by weight, a red pigment in an amount of 0.1% by weight, a yellow pigment in an amount of 0.2% by weight, and a white pigment in an amount of 3.4% by weight with respect to the whole base paint taken as 100% by weight, respectively.
- the aluminum pigment had an average particle diameter of 8 ⁇ m.
- a decorative paint film of a Twenty-third Preferred Embodiment was prepared in the same manner as the First Preferred Embodiment. Note that the base paint film of the Twenty-third Preferred Embodiment exhibited a lightness of 52 expressed as an "L" value, and that the decorative layer had a thickness of about 2 ⁇ m at the maximum (i.e., less than the hiding thickness).
- the decorative paint film was of decorativeness which was not exactly equivalent to that of the Fifteenth through Twentieth Preferred Embodiments, but which had not been available so far.
- a base paint As a base paint, another acrylic-melamine mica metallic base paint was used.
- the acrylic-melamine mica metallic base paint included 40% by weight of non-volatile compositions.
- the non-volatile compositions contained a red mica pigment in an amount of 10.0% by weight, and a red pigment in an amount of 9.0% by weight with respect to the whole base paint taken as 100% by weight, respectively.
- the red mica pigment had an average particle diameter of 35 ⁇ m.
- a decorative paint film of a Twenty-fourth Preferred Embodiment was prepared in the same manner as the First Preferred Embodiment. Note that the base paint film of the Twenty-third Preferred Embodiment exhibited a lightness of 34 expressed as an "L" value, and that the decorative layer had a thickness of about 2 ⁇ m at the maximum (i.e., less than the hiding thickness).
- the flower pattern exhibiting a unique metallic effect was depicted on the red mica metallic color.
- the decorative paint film was of decorativeness which was not exactly equivalent to that of the Fifteenth through Twentieth Preferred Embodiments, but which had not been available so far.
- the acrylic-melamine mica metallic base paint included 40% by weight of non-volatile compositions.
- the non-volatile compositions contained a white mica pigment in an amount of 3.0% by weight, a blue mica pigment in an amount of 3.0% by weight, a black pigment in an amount of 2.0% by weight, a green pigment in an amount of 0.2% by weight, and a blue pigment in an amount of 2.0% by weight with respect to the whole base paint taken as 100% by weight, respectively.
- the white mica pigment had an average particle diameter of 17 ⁇ m.
- the blue mica pigment had an average particle diameter of 17 ⁇ m.
- a decorative paint film of a Twenty-fifth Preferred Embodiment was prepared in the same manner as the First Preferred Embodiment. Note that the base paint film of the Twenty-fifth Preferred Embodiment exhibited a lightness of 14 expressed as an "L" value, and that the decorative layer had a thickness of about 2 ⁇ m at the maximum (i.e., less than the hiding thickness).
- the decorative paint film was of decorativeness which was not exactly equivalent to that of the Fifteenth through Twentieth Preferred Embodiments, but which had not been available so far.
- Table 3 summarizes the content of the glossy substances in the base paints which were employed in the Fifteenth through Twenty-fifth Preferred Embodiments, the average particle diameter of the glossy substances thereof, and the "L" value of the resultant base paint films.
- a content of a glossy substance can preferably fall in a range of from 10 to 50% by weight, further preferably from 20 to 40% by weight, with respect to non-volatile compositions of a base paint taken as 100% by weight.
- An average particle diameter of a glossy substance can preferably fall in a range of from 10 to 30 ⁇ m, further preferably from 15 to 20 ⁇ m.
- An "L" value exhibited by a base paint film can preferably be 20 or more.
- a plate-shaped workpiece was prepared.
- the workpiece was made from polypropylene, and was coated with a primer.
- the primer predominantly contained chlorinated polypropylene.
- the workpiece was heated preliminarily at 120 °C for 5 minutes.
- an acrylic-melamine organic solvent based paint was applied onto the workpiece in a thickness of about 15 ⁇ m.
- the acrylic-melamine organic solvent based paint exhibited a silver metallic color, and included 40% by weight of non-volatile compositions.
- the non-volatile compositions contained an aluminum pigment in an amount of 14% by weight, a blue pigment in an amount of 1% by weight, and a black pigment in a trace amount with respect to the whole base paint taken as 100% by weight, respectively.
- an acrylic-melamine organic solvent based clear paint was applied onto the plate-shaped workpiece with the base paint applied in a thickness of about 30 ⁇ m. Subsequently, the base paint and clear paint were baked at 120 °C for 30 minutes.
- a decorative layer was formed onto the plate-shaped workpiece with the base paint film and intermediate clear paint film by an ink-jet method with water based inks.
- the water based inks included pigments in the same concentrations as set forth in Table 1 above.
- the resulting decorative layer involved a flower pattern which was derived from image data.
- the image data had been produced by scanning a photograph of a flower with an image scanner.
- the thus formed decorative layer had a thickness of about 1.5 ⁇ m at the maximum (i.e., less than the hiding thickness).
- an acrylic-melamine organic solvent based clear paint was applied onto the plate-shaped workpiece with the base paint film, intermediate clear paint film and decorative layer coated in a thickness of about 30 ⁇ m.
- the clear paint was subsequently baked at 120 °C for 30 minutes, thereby completing a decorative paint film of a Twenty-sixth Preferred Embodiment.
- the thus prepared decorative paint film involved the flower pattern which was depicted vividly in the silver metallic color.
- the flower pattern exhibited a unique metallic effect as well.
- the decorative paint film was of decorativeness which had not been produced by conventional coating processes so far.
- a decorative paint film of a Twenty-seventh Preferred Embodiment was completed in the same manner as the Twenty-sixth Preferred Embodiment.
- the thus prepared decorative paint film involved the flower pattern which was depicted vividly in the silver metallic color.
- the flower pattern exhibited a unique metallic effect as well.
- the decorative paint film was of decorativeness which had not been produced by conventional coating processes so far.
- a plate-shaped workpiece was prepared.
- the workpiece was made from polypropylene, and was coated with a primer.
- the primer predominantly contained chlorinated polypropylene.
- the workpiece was heated preliminarily at 120 °C for 5 minutes.
- an acrylic-melamine organic solvent based paint was applied onto the workpiece in a thickness of about 15 ⁇ m, and was preliminarily heated at 120 °C for 5 minutes.
- the acrylic-melamine organic solvent based paint exhibited a silver metallic color, and included 40% by weight of non-volatile compositions.
- the non-volatile compositions contained an aluminum pigment in an amount of 14% by weight, a blue pigment in an amount of 1% by weight, and a black pigment in a trace amount with respect to the whole base paint taken as 100% by weight, respectively.
- a decorative layer was formed onto the plate-shaped workpiece with the base paint film by an ink-jet method with water based inks.
- the water based inks included pigments in the same concentrations as set forth in Table 1 above.
- the resulting decorative layer involved a flower pattern which was derived from image data.
- the image data had been produced by scanning a photograph of a flower with an image scanner.
- the thus formed decorative layer bad a thickness of about 1.5 ⁇ m at the maximum (i.e., less than the hiding thickness).
- an acrylic-melamine organic solvent based clear paint was applied onto the plate-shaped workpiece with the base paint film and decorative layer in a thickness of about 30 ⁇ m.
- the clear paint film, base paint film and decorative layer were subsequently baked at 120 °C for 30 minutes, thereby completing a decorative paint film of a Twenty-eighth Preferred Embodiment.
- the thus prepared decorative paint film involved the flower pattern which was depicted vividly in the silver metallic color.
- the flower pattern exhibited a unique metallic effect as well.
- the decorative paint film was of decorativeness which had not been produced by conventional coating processes so far.
- a silver metallic base paint film was not dried preliminarily, and a decorative layer was formed by using water based inks immediately after a silver metallic base paint was applied onto the plate-shaped workpiece, a decorative paint film of a Twenty-ninth Preferred Embodiment was completed in the same manner as the Twenty-eighth Preferred Embodiment.
- the thus prepared decorative paint film involved the flower pattern which was depicted vividly in the silver metallic color.
- the flower pattern exhibited a unique metallic effect as well.
- the decorative paint film was of decorativeness which had not been produced by conventional coating processes so far.
- a silver metallic base paint film was formed by using a water based paint
- a decorative layer was formed by using organic solvent based inks
- a clear paint film was formed by using a water based clear paint
- a decorative paint film of a Thirtieth Preferred Embodiment was completed in the same manner as the Twenty-eighth Preferred Embodiment.
- the thus prepared decorative paint film involved the flower pattern which was depicted vividly in the silver metallic color.
- the flower pattern exhibited a unique metallic effect as well.
- the decorative paint film was of decorativeness which had not been produced by conventional coating processes so far.
- a silver metallic base paint film was formed by using water based paint
- a silver metallic base paint film was not dried preliminarily
- a decorative layer was formed by using organic solvent based inks immediately after a silver metallic base paint was applied onto the plate-shaped workpiece
- a clear paint film was formed by using a water based clear paint
- a decorative paint film of a Thirty-first Preferred Embodiment was completed in the same manner as the Twenty-eighth Preferred Embodiment.
- the thus prepared decorative paint film involved the flower pattern which was depicted vividly in the silver metallic color.
- the flower pattern exhibited a unique metallic effect as well.
- the decorative paint film was of decorativeness which had not been produced by conventional coating processes so far.
- the thus prepared decorative paint film involved the flower pattern which was depicted vividly in the silver metallic color.
- the flower pattern exhibited a unique metallic effect as well.
- the vividness and metallic effect of the flower pattern, involved in the decorative paint film of the Thirty-second Preferred Embodiment were not precisely correspondent with those of the Twenty-eighth through Thirty-first Preferred Embodiment, the decorative paint film was of decorativeness which had not been produced by conventional coating processes so far.
- the thus prepared decorative paint film involved the flower pattern which was depicted vividly in the silver metallic color.
- the flower pattern exhibited a unique metallic effect as well.
- the vividness and metallic effect of the flower pattern, involved in the decorative paint film of the Thirty-third Preferred Embodiment were not precisely correspondent with those of the Twenty-eighth through Thirty-first Preferred Embodiment, the decorative paint film was of decorativeness which had not been produced by conventional coating processes so far.
- a silver metallic paint film was formed by using an organic solvent based paint
- a decorative layer was formed by using organic solvent based inks
- a clear paint film was formed by using a water based clear paint
- a decorative paint film of a Thirty-fourth Preferred Embodiment was completed in the same manner as the Twenty-eighth Preferred Embodiment.
- the thus prepared decorative paint film involved the flower pattern which was depicted vividly in the silver metallic color.
- the flower pattern exhibited a unique metallic effect as welt
- the vividness and metallic effect of the flower pattern, involved in the decorative paint film of the Thirty-fourth Preferred Embodiment were not precisely correspondent with those of the Twenty-eighth through Thirty-first Preferred Embodiment, the decorative paint film was of decorativeness which had not been produced by conventional coating processes so far.
- a silver metallic paint film was formed by using an organic solvent based paint
- a decorative layer was formed by using water based inks
- a clear paint film was formed by using a water based clear paint
- a decorative paint film of a Thirty-fifth Preferred Embodiment was completed in the same manner as the Twenty-eighth Preferred Embodiment.
- the thus prepared decorative paint film involved the flower pattern which was depicted vividly in the silver metallic color.
- the flower pattern exhibited a unique metallic effect as well.
- the vividness and metallic effect of the flower pattern, involved in the decorative paint film of the Thirty-fifth Preferred Embodiment were not precisely correspondent with those of the Twenty-eighth through Thirty-first Preferred Embodiment, the decorative paint film was of decorativeness which had not been produced by conventional coating processes so far.
- a silver metallic paint film was formed by using a water based paint
- a decorative layer was formed by using water based inks
- a clear paint film was formed by using an organic solvent based clear paint
- a decorative paint film of a Thirty-sixth Preferred Embodiment was completed in the same manner as the Twenty-eighth Preferred Embodiment.
- the thus prepared decorative paint film involved the flower pattern which was depicted vividly in the silver metallic color.
- the flower pattern exhibited a unique metallic effect as well.
- the vividness and metallic effect of the flower pattern, involved in the decorative paint film of the Thirty-sixth Preferred Embodiment were not precisely correspondent with those of the Twenty-eighth through Thirty-first Preferred Embodiment, the decorative paint film was of decorativeness which had not been produced by conventional coating processes so far.
- a silver metallic base paint film was formed by using an organic solvent based paint
- a silver metallic base paint film was not dried
- a decorative layer was formed by using organic solvent based inks immediately after a silver metallic base paint was applied onto the plate-shaped workpiece
- a clear paint film was formed by using a water based clear paint
- a decorative paint film of a Thirty-seventh Preferred Embodiment was completed in the same manner as the Twenty-eighth Preferred Embodiment.
- the thus prepared decorative paint film involved the flower pattern which was depicted vividly in the silver metallic color.
- the flower pattern exhibited a unique metallic effect as well.
- the vividness and metallic effect of the flower pattern, involved in the decorative paint film of the Thirty-seventh Preferred Embodiment were not precisely correspondent with those of the Twenty-eighth through Thirty-first Preferred Embodiment, the decorative paint film was of decorativeness which had not been produced by conventional coating processes so far.
- a silver metallic base paint film was formed by using an organic solvent based paint
- a silver metallic base paint film was not dried
- a decorative layer was formed by using water based inks immediately after a silver metallic base paint was applied onto the plate-shaped workpiece
- a clear paint film was-formed by using a water based clear paint
- a decorative paint film of a Thirty-eighth Preferred Embodiment was completed in the same manner as the Twenty-eighth Preferred Embodiment.
- the thus prepared decorative paint film involved the flower pattern which was depicted vividly in the silver metallic color.
- the flower pattern exhibited a unique metallic effect as well.
- the vividness and metallic effect of the flower pattern, involved in the decorative paint film of the Thirty-eighth Preferred Embodiment were not precisely correspondent with those of the Twenty-eighth through Thirty-first Preferred Embodiment, the decorative paint film was of decorativeness which had not been produced by conventional coating processes so far.
- a silver metallic base paint film was formed by using a water based paint
- a silver metallic base paint film was not dried
- a decorative layer was formed by using water based inks immediately after a silver metallic base paint was applied onto the plate-shaped workpiece
- a clear paint film was formed by using an organic solvent based clear paint
- a decorative paint film of a Thirty-ninth Preferred Embodiment was completed in the same manner as the Twenty-eighth Preferred Embodiment.
- the thus prepared decorative paint film involved the flower pattern which was depicted vividly in the silver metallic color.
- the flower pattern exhibited a unique metallic effect as well.
- the vividness and metallic effect of the flower pattern, involved in the decorative paint film of the Thirty-ninth Preferred Embodiment were not precisely correspondent with those of the Twenty-eighth through Thirty-first Preferred Embodiment, the decorative paint film was of decorativeness which had not been produced by conventional coating processes so far.
- a silver metallic paint film was formed by using an organic solvent based paint
- a decorative paint film was formed by using organic solvent based inks
- a clear paint film was formed by using an organic solvent based clear paint
- a decorative paint film of a Fortieth Preferred Embodiment was completed in the same manner as the Twenty-eighth Preferred Embodiment.
- the thus prepared decorative paint film involved the flower pattern which was depicted vividly in the silver metallic color.
- the flower pattern exhibited a unique metallic effect as well.
- the vividness and metallic effect of the flower pattern, involved in the decorative paint film of the Fortieth Preferred Embodiment were not precisely correspondent with those of the Twenty-eighth through Thirty-first Preferred Embodiment, the decorative paint film was of decorativeness which had not been produced by conventional coating processes so far.
- a silver metallic paint film was formed by using an organic solvent based paint
- a silver metallic base paint film was not dried
- a decorative layer was formed by using organic solvent based inks immediately after a silver metallic base paint was applied onto the plate-shaped workpiece
- a clear paint film was formed by using an organic solvent based clear paint
- a decorative paint film of a Forty-first Preferred Embodiment was completed in the same manner as the Twenty-eighth Preferred Embodiment.
- the thus prepared decorative paint film involved the flower pattern which was depicted vividly in the silver metallic color.
- the flower pattern exhibited a unique metallic effect as well.
- the vividness and metallic effect of the flower pattern, involved in the decorative paint film of the Forty-first Preferred Embodiment were not precisely correspondent with those of the Twenty-eighth through Thirty-first Preferred Embodiment, the decorative paint film was of decorativeness which had not been produced by conventional coating processes so far.
- a silver metallic paint film was formed by using a water based paint
- a decorative layer was formed by using water based inks
- a clear paint film was formed by using a water based clear paint
- a decorative paint film of a Forty-second Preferred Embodiment was completed in the same manner as the Twenty-eighth Preferred Embodiment.
- the thus prepared decorative paint film involved the flower pattern which was depicted vividly in the silver metallic color.
- the flower pattern exhibited a unique metallic effect as well.
- the vividness and metallic effect of the flower pattern, involved in the decorative paint film of the Forty-second Preferred Embodiment were not precisely correspondent with those of the Twenty-eighth through Thirty-first Preferred Embodiment, the decorative paint film was of decorativeness which had not been produced by conventional coating processes so far.
- a silver metallic paint film was formed by using a water based paint
- a silver metallic base paint film was not dried
- a decorative layer was formed by using water based inks immediately after a silver metallic base paint was applied onto the plate-shaped workpiece
- a clear paint film was formed by using a water based clear paint
- a decorative paint film of a Forty-third Preferred Embodiment was completed in the same manner as the Twenty-eighth Preferred Embodiment.
- the thus prepared decorative paint film involved the flower pattern which was depicted vividly in the silver metallic color.
- the flower pattern exhibited a unique metallic effect as well.
- the vividness and metallic effect of the flower pattern, involved in the decorative paint film of the Forty-third Preferred Embodiment were not precisely correspondent with those of the Twenty-eighth through Thirty-first Preferred Embodiment, the decorative paint film was of decorativeness which had not been produced by conventional coating processes so far.
- a decorative paint film forming process includes the steps of applying a base paint, including a glossy substance, to form a base paint film, and applying a decorative paint on a surface of the base paint film to form a decorative layer having a thickness of less than a hiding thickness.
- a clear paint can be applied on the base paint film to form a clear paint film, and the decorative layer can be formed on the clear paint film.
- the resulting decorative paint film involves a noble decoration in which a metallic effect is superimposed on the hues of the decorative layer.
Landscapes
- Application Of Or Painting With Fluid Materials (AREA)
- Laminated Bodies (AREA)
Description
Claims (18)
- A process for forming a decorative paint film exhibiting a metallic effect, the process comprising the steps of:applying a base paint to form a base paint film having a surface, the base paint including a glossy substance; andapplying a decorative paint with an ink-jet on the surface of the base paint film to form a decorative layer, the decorative layer having a surface and a thickness of less than a hiding thickness.
- The process according to Claim 1, wherein the glossy substance has an average particle diameter of from 10 to 30 µm.
- The process according to claim 1, wherein the base paint includes non-volatile compositions and the non-volatile compositions contain the glossy substance in an amount of from 10 to 50% by weight.
- The process according to Claim 1, wherein the base paint film exhibits a lightness of 20 or more expressed as an "L" value.
- The process according to Claim 1, wherein, when the decorative layer is laminated on the base paint film in a wet manner, a paint film formed of a water based paint, and a paint film formed of an organic solvent based paint are coated alternately.
- The process according to claim 1, wherein the decorative paint includes non-volatile compositions, and the non-volatile compositions contain a yellow pigment in an amount of from 30 to 70% by weight.
- The process according to claim 1, wherein the decorative paint includes non-volatile compositions, and the non-volatile compositions contain a red pigment in an amount of from 30 to 70% per weight.
- The process according to Claim 1, wherein the decorative paint includes non-volatile compositions, and the non-volatile compositions contain a blue pigment in an amount of from 10 to 60% by weight.
- The process according to Claim 1, wherein the decorative paint includes non-volatile compositions, and the non-volatile compositions contain a black pigment in an amount of from 5 to 30% by weight.
- The process according to Claim 1, wherein the base paint film has a thickness of from 10 to 30 µm.
- The process according to Claim 1, wherein the decorative layer has a thickness of 5 µm or less.
- The process according to Claim 1 further comprising a step of applying a clear paint on the surface of the decorative layer to form a clear paint film.
- The process according to Claim 12, wherein the clear paint film has a thickness of from 20 to 100 µm.
- The process according to Claim 12, wherein the decorative paint is heated preliminarily before applying the clear paint
- The process according to Claim 12, wherein the decorative paint is baked before applying the clear paint paint.
- The process according to Claim 1, wherein the base paint is heated preliminarily before applying the decorative paint.
- The process according to Claim 1, wherein the base paint is baked before applying the decorative paint.
- A process for forming a decorative paint film exhibiting a metallic effect, the process comprising the steps of:applying a base paint to form a base paint film having a surface, the base paint including a glossy substance;applying a clear paint on the surface of the base paint film to form a clear paint film having a surface; andapplying a decorative paint on the surface of the clear paint film to form a decorative layer, the decorative layer having a surface and a thickness of less than a hiding thickness.
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP20452096 | 1996-08-02 | ||
| JP8204520A JPH1043675A (en) | 1996-08-02 | 1996-08-02 | Formation of patterned coating film giving metallic impression |
| JP204520/96 | 1996-08-02 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0822011A2 EP0822011A2 (en) | 1998-02-04 |
| EP0822011A3 EP0822011A3 (en) | 1999-05-12 |
| EP0822011B1 true EP0822011B1 (en) | 2002-12-04 |
Family
ID=16491900
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP97113357A Expired - Lifetime EP0822011B1 (en) | 1996-08-02 | 1997-08-01 | Process for forming decorative paint film exhibiting metallic effect |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0822011B1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JPH1043675A (en) |
| KR (1) | KR100244574B1 (en) |
| CA (1) | CA2211726A1 (en) |
| DE (1) | DE69717556T2 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US8507077B1 (en) | 2012-09-12 | 2013-08-13 | Krow Innovation, Llc | Camouflage branding system and method |
Families Citing this family (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6376016B1 (en) | 2000-06-14 | 2002-04-23 | Ford Global Tech., Inc. | Method for painting a vehicle with at least two colors |
| US6451117B1 (en) | 2000-08-11 | 2002-09-17 | Ford Global Tech., Inc. | Paint mask and a method for utilizing the same |
| KR20030042765A (en) * | 2001-11-23 | 2003-06-02 | 주식회사 엘지이아이 | Painting method of refrigerator door |
| JP2007154431A (en) * | 2005-11-30 | 2007-06-21 | Kubota Matsushitadenko Exterior Works Ltd | Decorative building board |
| CA2572900C (en) * | 2006-01-23 | 2011-03-15 | Kansai Paint Co., Ltd. | Method of forming multi-layered patterned coating film |
| FR2905914B1 (en) * | 2006-09-20 | 2008-11-14 | Renault Sas | MOTOR VEHICLE WITH BODY COVERED BY AN OUTSIDE DECORATION AND PROTECTION ASSEMBLY |
| EP1927633A1 (en) | 2006-11-30 | 2008-06-04 | Seiko Epson Corporation | Ink composition, two-pack curing ink composition set, and recording method and recorded matter using these |
| JP6078430B2 (en) * | 2007-01-29 | 2017-02-08 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | Ink set, ink jet recording method and recorded matter |
| US8894197B2 (en) | 2007-03-01 | 2014-11-25 | Seiko Epson Corporation | Ink set, ink-jet recording method, and recorded material |
| DE102008053178A1 (en) | 2008-10-24 | 2010-05-12 | Dürr Systems GmbH | Coating device and associated coating method |
| JP5368967B2 (en) * | 2009-12-25 | 2013-12-18 | 関西ペイント株式会社 | Multi-layer coating formation method |
| DE102013002433A1 (en) * | 2013-02-11 | 2014-08-14 | Dürr Systems GmbH | Painting process and painting plant for decorative stripes |
Family Cites Families (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS591111B2 (en) * | 1979-02-28 | 1984-01-10 | 凸版印刷株式会社 | Decorative board manufacturing method |
| US4551491A (en) * | 1983-07-29 | 1985-11-05 | Inmont Corporation | Pearlescent automotive paint compositions |
| JPS60118266A (en) * | 1983-11-29 | 1985-06-25 | Toyota Motor Corp | Two-tone coating method |
| US4598015A (en) * | 1984-12-11 | 1986-07-01 | Inmont Corporation | Multilayer satin finish automotive paint system |
| JPS62216671A (en) * | 1986-03-17 | 1987-09-24 | Nippon Paint Co Ltd | Metallic coating method |
| AU5138090A (en) * | 1989-03-22 | 1990-09-27 | Basf Corporation | Coating system with metallic basecoat exhibiting dichromatic hue shift effects |
| CA2010818A1 (en) * | 1989-03-22 | 1990-09-22 | Sol Panush | Coating system exhibiting color travel and opalescent color effects |
| US5106682A (en) * | 1989-03-25 | 1992-04-21 | Sumitomo Electric Industries Ltd. | Fluororesin-coated article |
| US4971841A (en) * | 1989-06-08 | 1990-11-20 | Basf Corporation | Reflective automotive coating compositions |
| JPH0312263A (en) * | 1989-06-12 | 1991-01-21 | Nissan Motor Co Ltd | Method for forming urushi like film |
| GB2257929A (en) * | 1991-06-19 | 1993-01-27 | Tudor Hart George Henry | Distressed paint finishes |
| JPH07108216A (en) * | 1993-10-08 | 1995-04-25 | Toyota Auto Body Co Ltd | Metallic painted product and production thereof |
-
1996
- 1996-08-02 JP JP8204520A patent/JPH1043675A/en active Pending
-
1997
- 1997-07-30 CA CA002211726A patent/CA2211726A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 1997-08-01 KR KR1019970036800A patent/KR100244574B1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1997-08-01 EP EP97113357A patent/EP0822011B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1997-08-01 DE DE69717556T patent/DE69717556T2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US8507077B1 (en) | 2012-09-12 | 2013-08-13 | Krow Innovation, Llc | Camouflage branding system and method |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JPH1043675A (en) | 1998-02-17 |
| DE69717556D1 (en) | 2003-01-16 |
| DE69717556T2 (en) | 2003-04-17 |
| EP0822011A3 (en) | 1999-05-12 |
| KR100244574B1 (en) | 2000-02-15 |
| EP0822011A2 (en) | 1998-02-04 |
| KR19980018278A (en) | 1998-06-05 |
| CA2211726A1 (en) | 1998-02-02 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0822011B1 (en) | Process for forming decorative paint film exhibiting metallic effect | |
| CN1208185C (en) | Adhesive tape for coating decoration | |
| US10486348B2 (en) | Decorative resin molded article and its production method | |
| US6756108B2 (en) | Heat transcription film and manufacturing method thereof | |
| KR19990022744A (en) | Control of metallic appearance of automotive cast paint films | |
| EP2204239A1 (en) | Process for the production of multi-layer coatings | |
| JP4324705B2 (en) | How to paint resin parts | |
| JP4412884B2 (en) | High brightness decorative film | |
| JP2001290429A (en) | Colorimetric color card and method for repairing coating film using the same | |
| CN1098363A (en) | The method of transfer printing image-text | |
| JP2003118064A (en) | Light reflecting film decorative material | |
| JP2005144338A (en) | Coating method | |
| JPH07214888A (en) | Stereoscopic pattern coating plate and manufacture thereof | |
| JPH10156279A (en) | Deep color metallic tone coating method and coated material | |
| CN107107402A (en) | Method for producing the elastomer skin with textured surface | |
| JP4712630B2 (en) | Method for repairing multilayer coating film and article obtained therefrom | |
| JPS6315029B2 (en) | ||
| JP2019084711A (en) | Coating repaired article and coating repairing method | |
| JP2001240807A (en) | Coating material for forming dot pattern and method for forming coating film | |
| JPH07241520A (en) | Method for making designed coating film | |
| JPS62289272A (en) | Dry type transfer article | |
| KR102404801B1 (en) | Decoration having ink receptive layer for concealing substrate and method for manufacturing the same | |
| JP3211369B2 (en) | Resin molded painted product and method of manufacturing the same | |
| JP2000095973A (en) | Clear coating composition for contaier outside surface | |
| JPH10235282A (en) | Colored coating film with double clear coating film |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19970801 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): DE FR GB |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid |
Free format text: DE FR GB |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20000828 |
|
| GRAG | Despatch of communication of intention to grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS AGRA |
|
| GRAG | Despatch of communication of intention to grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS AGRA |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): DE FR GB |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 69717556 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20030116 |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20030801 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20030929 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20030905 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20030801 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20040430 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20050301 |