EP0788976B1 - Container and heat-resistant cap for use with same - Google Patents
Container and heat-resistant cap for use with same Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0788976B1 EP0788976B1 EP97101824A EP97101824A EP0788976B1 EP 0788976 B1 EP0788976 B1 EP 0788976B1 EP 97101824 A EP97101824 A EP 97101824A EP 97101824 A EP97101824 A EP 97101824A EP 0788976 B1 EP0788976 B1 EP 0788976B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- container
- tube
- ridge
- heat
- intermediate tube
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 229920003002 synthetic resin Polymers 0.000 claims abstract description 15
- 239000000057 synthetic resin Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 15
- 238000009835 boiling Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 11
- -1 e.g. Polymers 0.000 description 8
- 238000004064 recycling Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 description 5
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000005489 elastic deformation Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000004698 Polyethylene Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000004743 Polypropylene Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229920000573 polyethylene Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 229920001155 polypropylene Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 235000013334 alcoholic beverage Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000012141 concentrate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000006185 dispersion Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000011389 fruit/vegetable juice Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000014347 soups Nutrition 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65D—CONTAINERS FOR STORAGE OR TRANSPORT OF ARTICLES OR MATERIALS, e.g. BAGS, BARRELS, BOTTLES, BOXES, CANS, CARTONS, CRATES, DRUMS, JARS, TANKS, HOPPERS, FORWARDING CONTAINERS; ACCESSORIES, CLOSURES, OR FITTINGS THEREFOR; PACKAGING ELEMENTS; PACKAGES
- B65D41/00—Caps, e.g. crown caps or crown seals, i.e. members having parts arranged for engagement with the external periphery of a neck or wall defining a pouring opening or discharge aperture; Protective cap-like covers for closure members, e.g. decorative covers of metal foil or paper
- B65D41/32—Caps or cap-like covers with lines of weakness, tearing-strips, tags, or like opening or removal devices, e.g. to facilitate formation of pouring openings
- B65D41/46—Snap-on caps or cap-like covers
- B65D41/48—Snap-on caps or cap-like covers non-metallic, e.g. made of paper or plastics
- B65D41/485—Snap-on caps or cap-like covers non-metallic, e.g. made of paper or plastics with integral internal sealing means
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65D—CONTAINERS FOR STORAGE OR TRANSPORT OF ARTICLES OR MATERIALS, e.g. BAGS, BARRELS, BOTTLES, BOXES, CANS, CARTONS, CRATES, DRUMS, JARS, TANKS, HOPPERS, FORWARDING CONTAINERS; ACCESSORIES, CLOSURES, OR FITTINGS THEREFOR; PACKAGING ELEMENTS; PACKAGES
- B65D47/00—Closures with filling and discharging, or with discharging, devices
- B65D47/04—Closures with discharging devices other than pumps
- B65D47/06—Closures with discharging devices other than pumps with pouring spouts or tubes; with discharge nozzles or passages
- B65D47/08—Closures with discharging devices other than pumps with pouring spouts or tubes; with discharge nozzles or passages having articulated or hinged closures
- B65D47/0857—Closures with discharging devices other than pumps with pouring spouts or tubes; with discharge nozzles or passages having articulated or hinged closures made separately from the base element provided with the spout or discharge passage
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65D—CONTAINERS FOR STORAGE OR TRANSPORT OF ARTICLES OR MATERIALS, e.g. BAGS, BARRELS, BOTTLES, BOXES, CANS, CARTONS, CRATES, DRUMS, JARS, TANKS, HOPPERS, FORWARDING CONTAINERS; ACCESSORIES, CLOSURES, OR FITTINGS THEREFOR; PACKAGING ELEMENTS; PACKAGES
- B65D47/00—Closures with filling and discharging, or with discharging, devices
- B65D47/04—Closures with discharging devices other than pumps
- B65D47/06—Closures with discharging devices other than pumps with pouring spouts or tubes; with discharge nozzles or passages
- B65D47/10—Closures with discharging devices other than pumps with pouring spouts or tubes; with discharge nozzles or passages having frangible closures
- B65D47/103—Membranes with a tearing element
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a container for containing juice, alcoholic drink, soup or the like that is heated when filled in the container, and a heat-resistant cap for use with the container.
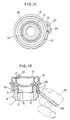
- Fig. 13 denoted by reference numeral 51 is a container illustrated as, by way of example, a bottle.
- the container 51 has a mouth 52 provided with an annular recess 53 formed in an outer circumferential surface of its upper portion and an annular boss 54 formed below the annular recess 53.
- Denoted by 55 is an intermediate stopper made of synthetic resin, e.g., polyethylene, and comprising an inner tube 56, an intermediate tube 57 and an upper wall 58.
- a mouth wall 60 having an endless rippable groove 59 formed therein is provided at the center.
- the intermediate stopper 55 also comprises a ripping member 61, a lower support portion 62, a pouring tube 63 and a latching portion 64.
- Denoted by 65 is an annular ridge engaging the annular recess 53.
- denoted by 66 is an outer lid made of highly heat-resistant synthetic resin, e.g., polypropylene, and comprising an outer tube 67 and a lid member 68 formed integrally with each other through a hinge 69.
- the outer tube 67 has a lower end 70 positioned to rest on an upper end of the lower support portion 62, and also has an annular engagement portion 71 formed on an inner circumferential surface of its upper portion to project radially inward.
- the engagement portion 71 is engaged in vertical relation with the latching portion 64 annularly formed above the upper wall 58 of the intermediate stopper 55.
- the lid member 68 is held in place such that a locked portion 72 formed in a part of an inner circumferential surface of the lid member is lightly locked in vertical relation by a locking portion 73 formed in an upper part of the engagement portion 71 when the lid member is closed.
- denoted by 74 is an annular intermediate leg coming into close contact with the pouring tube 63.
- the container and the heat-resistant cap for use with the container are suitably employed to contain liquid goods as mentioned above which are heated when filled in the container.
- the outer tube 67 made of heat-resistant synthetic resin and held in pressure contact with the intermediate tube 57 serves to prevent the intermediate tube 57 from reducing elasticity, i.e., losing a proper elastic deformation, due to heat transmitted through the mouth 52 from a heated liquid (not shown) filled in the container 51, and hence to compensate for a reduction in degree of sealing.
- the container 51 is prevented from lowering a degree of sealing by the presence of the outer tube 67.
- the heat-resistant cap When the liquid commodity in the container 51 is used up and the container 51 is recovered for recycling of resources, it is required to separate the container 51 and the heat-resistant cap from each other. Stated otherwise, the heat-resistant cap must be removed from the container mouth 52. However, the heat-resistant cap cannot be easily removed from the container mouth 52 because the ridge 65 of the intermediate tube 57 is tightly engaged in vertical relation with the recess 53 of the mouth 52. Also, even in an attempt to remove the heat-resistant cap by using an uncapping tool such as a cap opener, the use of an uncapping tool such as a cap opener will be in vain because an access to a lower end of the lower support portion 62 is blocked off by the boss 54 of the container mouth 52.
- the present invention has been made with a view of solving the problem stated above, and its object is to provide a container and a heat-resistant cap for use with the container, which heat-resistant cap is of hit-capping type that can be easily fitted to the container by simple hitting when capped over a mouth of the container, and can also be very easily removed from the container mouth, and which container is suitable for recycling of resources.
- the lower end of the outer tube is located in a position corresponding to the upper edge of the ridge of the intermediate tube, and the embrittled line is formed in the inner circumferential surface of the intermediate tube in a position contiguous to the upper edge of the ridge.
- the lower end of the outer tube is located in a position corresponding to the upper edge of the ridge of the intermediate tube, and the embrittled line is formed in the inner circumferential surface of the intermediate tube in a position contiguous to the lower edge of the ridge.
- the lower end of the outer tube is located in a position corresponding to the ridge of the intermediate tube, and the embrittled line is formed in the inner circumferential surface of the intermediate tube in a position contiguous to the lower edge of the ridge.
- the embrittled portion is formed in the form of a slit.
- the lower end of the outer tube is located in a position corresponding to substantially the lower edge of the ridge of the intermediate tube, and a part of the intermediate tube below an upper end of the lower support portion is formed to be dislocated radially outward of the remaining part thereof to form an embrittled line in the dislocated position.
- the ridge is held in pressure contact with the recess in the vertical direction by the lower end of the outer tube.
- the ridge is located in a position above a bottom portion of the recess.
- the outer tube and the lid member are joined to each other through a hinge.
- the lower support portion includes a tab provided contiguous to or in the vicinity of the embrittled portion.
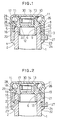
- Fig. 1 is cross-sectional view, partly omitted, of a container and a heat-resistant cap for use with the container, the view showing a first embodiment of the present invention and a state where the cap is fitted to the container.
- Fig. 2 is cross-sectional view similar to Fig. 1, the view showing a second embodiment of the present invention.
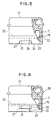
- Fig. 3 is cross-sectional view similar to Fig. 1, the view showing a third embodiment of the present invention.
- Fig. 4 is a side view, partly sectioned, of the heat -resistant cap shown in Fig. 1.
- Fig. 5 is a side view, partly sectioned, of a heat-resistant cap shown in Fig. 3.
- Fig. 6 is a side view, partly sectioned, of a heat-resistant cap, the view showing a fourth embodiment of the present invention.
- Fig. 7 is a side view, partly sectioned, of a heat-resistant cap, the view showing a fifth embodiment of the present invention.
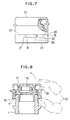
- Fig. 8 is a view showing a state where the heat-resistant cap shown in Fig. 1 is being removed from the container.
- Fig. 9 is a view showing a state where a heat-resistant cap shown in Fig. 2 is being removed from a container.
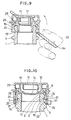
- Fig. 10 is cross-sectional view, partly omitted, of a container and a heat-resistant cap for use with the container, the view showing a sixth embodiment of the present invention and a state where the cap is fitted to the container.
- Fig. 11 is a bottom view of the heat-resistant cap shown in Fig. 10.
- Fig. 12 is a view showing a state where the heat-resistant cap shown in Fig. 10 is being removed from the container.
- Fig. 13 is cross-sectional view, partly omitted, of a conventional container and a conventional heat-resistant cap for use with the container.
- the container 1 has a mouth 2 provided in its outer circumferential surface with an annular recess 3 and an annular boss 4 formed in the order named from above with a spacing therebetween.
- Denoted by 5 is a stopper fitted over the mouth 2 and made of synthetic resin, e.g., polyethylene.
- the stopper 5 has a gripping portion 9 comprising an inner tube 6, an intermediate tube 7 and an upper wall 8. The gripping portion 9 grips the mouth 2 in such a manner that the inner tube 6, the intermediate tube 7 and the upper wall 8 are held in pressure contact with inner, outer and top surfaces of the mouth 2, respectively, thereby keeping the stopper 5 fitted over the mouth 2.
- Denoted by 10 is a pouring tube extending upward from the upper wall 8, and a mouth wall 14 having an endless rippable groove 12 formed therein is provided integrally with the upper wall 8 and within the pouring tube 10.
- the mouth wall 14 includes a ripping member 13 in the form of a pull ring provided inside the rippable groove 12.
- the intermediate tube 7 has an annular ridge 15 formed on its inner circumferential surface. When the heat-resistant cap is capped over the mouth 2 of the container by hitting, the annular ridge 15 is engaged with the annular recess 3 formed in the outer circumferential surface of the mouth 2 in its upper end portion.
- Denoted by 11 is a latching portion formed above the upper wall 8 to extend radially outward and engaged with an engagement portion 19 of an outer lid 18, described later, for latching the same.
- denoted by 18 is an outer lid made of synthetic resin, e.g., polypropylene, having a softening temperature against heat that is higher than not only the softening temperature of the synthetic resin as material of the stopper 5, but also the boiling point of water, and having hardness higher than the material of the stopper 5.
- the outer lid 18 comprises an outer tube 16 held in pressure contact with an outer circumferential surface of the intermediate tube 7 and a lid member 17.
- the outer tube 16 and the lid member 17 are integrally formed with each other through a hinge 26.
- the outer tube 16 has an annular engagement portion 19 formed on an inner circumferential surface of its upper part and, as seen from the drawing, the engagement portion 19 is engaged in vertical relation with the latching portion 11 annularly formed above the upper wall 8 of the intermediate stopper 5.
- the outer tube 16 has a lower end 20 located around the intermediate tube 7 in a position corresponding to any one of upper and lower edges and a middle point of the ridge 15 on the inner circumferential surface of the intermediate tube 7. More specifically, the lower end 20 of the outer tube 16 is positioned corresponding to the upper edge of the ridge 15 in the first and second embodiments shown in Figs. 1 and 2, while it is positioned corresponding to substantially the middle point of the ridge 15 in the third embodiment shown in Fig. 3.
- the lower end 20 of the outer tube 16 located in any of the above positions can serve to urge the ridge 15 toward the mouth 2 for pressure contact therewith.
- Denoted by 28 is a locked portion and 29 is a locking portion, the former 28 being lightly locked in vertical relation by the latter 29 when the lid member 17 is closed.
- the intermediate tube 7 has an embrittled line 22 formed therein contiguous to any one of the upper and lower edges of the ridge 15.
- the embrittled line 22 is formed as a thin-walled portion, for example, and may be formed entirely or partly over the circumference of the intermediate tube 7. In the first embodiment shown in Fig. 1, the embrittled line 22 is formed contiguous to the upper edge of the ridge 15, while in the second and third embodiments shown in Figs. 2 and 3, it is formed contiguous to the lower edge of the ridge 15. Note that the embrittled line 22 may be in the form of perforations, successive holes or notches, or combinations thereof other than the thin-walled portion.
- denoted by 30 is an annular intermediate leg formed on an inner surface of the lid member 17 and coming into close contact with the pouring tube 10 when the outer lid 18 is closed.
- an embrittled portion formed as a thin-walled portion, for example, to extend from a lower end 23 of the intermediate tube 7 to the embrittled line 22.
- the embrittled portion 24 may be in the form of perforations, successive holes or notches, or combinations thereof other than the thin-walled portion.
- the embrittled portion 24 may be in the form of a slit as shown in Fig. 6.
- the intermediate tube 7 also includes a tab 27 provided on its outer circumferential surface near the embrittled portion 22. When the tab 27 is pulled, a part of the intermediate tube is ripped off along the embrittled portion 24 and the embrittled line 22.
- 31 is a connecting piece formed to be easily rippable
- 32 is a secured portion ofthe connecting piece 31.
- the outer tube 16 of the outer lid 18, which is made of synthetic resin having a softening temperature against heat that is higher than not only the softening temperature of the material of the intermediate tube 7, but also the boiling point of water, and having hardness higher than the material of the intermediatetube 7, is held in pressure contact with the outer circumferential surface of the intermediate tube 7, such a reduction in strength of the pressure contact of the intermediate tube 7 is compensated by the pressure contact of the outer tube 16. As a result, a reduction in degree of sealing can be kept within a practically allowable range.
- a cap of another embodiment such as shown in Fig. 10 also operates in the same manner as described above.
- Denoted by 21 is a lower support portion.
- the embrittled portion 24 of the intermediate tube 7 and then the embrittled line 22 connecting to the former are ripped up.
- the embrittled line 22 is formed contiguous to selected one of the upper and lower edges of the ridge 15, the intermediate tube 7 is ripped up circumferentially at the upper or lower edge of th e ridge 15.
- the lower end 20 of the outer tube 16 is not extended to reach the lower end 23 of the intermediate tube 7, but it is terminated in a position adjacent to the ridge 15.
- the outer tube 16 can serve to press the ridge 15 inward on one hand, and allows the intermediate tube 16 to be ripped up along the embrittled line 22 in spite of the presence of itself on the other hand.
- the intermediate tube 16 may be ripped up completely when the embrittled line 22 is formed all over the circumference thereof, or partly when it is formed over a part of the circumference thereof.
- the embrittled line 22 is formed contiguous to the upper edge of the ridge 15
- forces urging the ridge 15 into the pressure contact state are weakened by partly ripping up the intermediate tube 7 along the embrittled line, or are completely eliminated by ripping up same all over the circumference thereof.
- the heat-resistant cap can be easily removed from the mouth by placing a finger 33 against the ripped-up edge of the intermediate tube 7 and pushing it upward, as shown in Fig. 8.
- the heat-resistant cap can be easily removed from the mouth by placing an uncapping tool 34 such as a cap opener against the ripped-up edge of the intermediate tube 7 and pushing it upward, as shown in Fig. 9.
- an uncapping tool 34 such as a cap opener against the ripped-up edge of the intermediate tube 7 and pushing it upward, as shown in Fig. 9.
- the ripping-up can be more easily started by the presence of the tab 27 provided contiguous to or in the vicinity of the embrittled portion 24 as shown in Figs. 4 to 7. In other words, by gripping the tab 27 and pulling it outward, ripping forces can be easily applied to the embrittled portion 24.
- the cap when removing the heat-resistant cap from the container, the cap can be removed by placing the finger 33 or the uncapping tool such as a cap opener in contact with the outer lid 18 having higher hardness, i.e., rigidity, than the stopper 5, because the latching portion 11 of the stopper 5 is so tightly engaged with the engagement portion 19 of the outer tube 16 in its upper portion that the stopper 5 and the outer tube 16 are integrally fitted to each other over a wide circumferential region. Therefore, in comparison with the case of applying forces to a part of the relatively soft stopper 5 through direct dispersion of the forces due to a partial elastic deformation of the stopper 5 is less, thus enabling flexible and easy removal of the cap.
- the uncapping tool such as a cap opener
- a container and a heat-resistant cap for use with the container, shown in Fig. 10, according to a sixth embodiment of the present invention will be described below.
- a part of the intermediate tube 7 below an upper end of its lower support portion 21 is formed to be dislocated radially outward of the remaining part thereof,and the lower end 20 of the outer tube 16 is positioned substantially at the same level as the ridge 15.
- the outer circumferential surface of the mouth 2 includes a slope 35 extended from the recess 3 to the boss 4.
- the ridge 15 of the intermediate tube 7 is located midway the recess 3 in the vertical direction and is held in pressure contact with the recess 3 in a position above a bottom portion 25 of the recess 3.
- the container and the heat-resistant cap for use with the container which are constructed as described above, operate essentially in the same manner as with the other embodiments shown in Figs. 1 to 9.
- a liquid commodity filled in the container 1 can be used by opening the lid member 17, pulling the ripping member 13 and ripping off the mouth wall 14 along the rippable groove 12.
- the tab 27 is pulled so as to rip up the intermediate tube 7 along the embrittled portion 24 and then the embrittled line 22.
- the ripping-up causes the lower ends of the intermediate tube 7 and the outer tube 16 to appear substantially at the same level, as shown in Fig. 12.
- the heat-resistant cap can be easily removed from the container 1 by placing the uncapping tool 34 such as a cap opener against the lower ends of the intermediate tube 7 and the outer tube 16.
- the uncapping tool 34 such as a cap opener
- the cap can also be easily removed from the container 1 by applying forces directly with the finger 33.
- the heat-resistant cap of this embodiment since the part of the intermediate tube 7 below the upper end of the lower support portion 21 is formed to be dislocated radially outward of the remaining part thereof, ripping forces are concentrated on the outwardly dislocated portion when applied to rip up the intermediate tube 7 along the embrittled line 22, so that the intermediate tube 7 can be easily ripped up along the embrittled line 22. Also, since the ridge 15 of the intermediate tube 7 is located midway the recess 3 in the vertical direction, the heat-resistant cap can be more easily removed from the container 1 when uncapped.
- the heat-resistant cap when the heat-resistant cap is fitted to the mouth 2 of the container 1 filled with a heated liquid commodity, a reduction in degree of sealing due to heat of the liquid commodity transmitted through the mouth 2 can be kept within a practically allowable range. Also, when the container 1 is recovered for recycling of resources, the heat-resistant cap can be very easily removed from the mouth 2 of the container 1 by such a simple operation as ripping up the intermediate tube 7 along the embrittled portion 24 and then the embrittled line 22 connecting to the former.
- the heat-resistant cap can be very easily removed by the finger 33 without using the uncapping tool 34 such as a cap opener.
- the heat-resistant cap can be very easily removed by using the uncapping tool 34 such as a cap opener.
- the outer tube 16 can satisfactorily bring the ridge 15 of the intermediate tube 7 into pressure contact with the mouth 2, and the heat-resistant cap can be very easily removed by using the uncapping tool 34 such as a cap opener.
- the embrittled portion 24 is in the form of a slit, it is very easy to start ripping up the intermediate tube 7 along the embrittled line 22.
- the heat-resistant cap can be more easily removed from the mouth 2.
- the tab 27 is provided contiguous to or in the vicinity of the embrittled portion 24, the part of the intermediate tube 7 below the upper end of the lower support portion 21 can be easily ripped away along the embrittled line 22 by gripping the tab 27, although the intermediate tube 7 has a less grippable portion and is more hard to grip by the presence of the outer tube 16 held in pressure contact with the intermediate tube 7.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Closures For Containers (AREA)
- Packages (AREA)
- Details Of Rigid Or Semi-Rigid Containers (AREA)
Abstract
Description
- The present invention relates to a container for containing juice, alcoholic drink, soup or the like that is heated when filled in the container, and a heat-resistant cap for use with the container.
- Heretofore, containers and heat-resistant caps for use with the containers, which are adapted for the purpose mentioned above, have been generally constructed as shown in Fig. 13. Referring to Fig. 13, denoted by
reference numeral 51 is a container illustrated as, by way of example, a bottle. Thecontainer 51 has amouth 52 provided with anannular recess 53 formed in an outer circumferential surface of its upper portion and anannular boss 54 formed below theannular recess 53. Denoted by 55 is an intermediate stopper made of synthetic resin, e.g., polyethylene, and comprising aninner tube 56, anintermediate tube 57 and anupper wall 58. Amouth wall 60 having an endlessrippable groove 59 formed therein is provided at the center. Theintermediate stopper 55 also comprises a rippingmember 61, alower support portion 62, apouring tube 63 and alatching portion 64. Denoted by 65 is an annular ridge engaging theannular recess 53. Further, denoted by 66 is an outer lid made of highly heat-resistant synthetic resin, e.g., polypropylene, and comprising anouter tube 67 and alid member 68 formed integrally with each other through ahinge 69. - The
outer tube 67 has alower end 70 positioned to rest on an upper end of thelower support portion 62, and also has anannular engagement portion 71 formed on an inner circumferential surface of its upper portion to project radially inward. Theengagement portion 71 is engaged in vertical relation with thelatching portion 64 annularly formed above theupper wall 58 of theintermediate stopper 55. Further, thelid member 68 is held in place such that a lockedportion 72 formed in a part of an inner circumferential surface of the lid member is lightly locked in vertical relation by alocking portion 73 formed in an upper part of theengagement portion 71 when the lid member is closed. In addition, denoted by 74 is an annular intermediate leg coming into close contact with thepouring tube 63. - Because of the foregoing construction, the container and the heat-resistant cap for use with the container are suitably employed to contain liquid goods as mentioned above which are heated when filled in the container. More specifically, the
outer tube 67 made of heat-resistant synthetic resin and held in pressure contact with theintermediate tube 57 serves to prevent theintermediate tube 57 from reducing elasticity, i.e., losing a proper elastic deformation, due to heat transmitted through themouth 52 from a heated liquid (not shown) filled in thecontainer 51, and hence to compensate for a reduction in degree of sealing. In other words, thecontainer 51 is prevented from lowering a degree of sealing by the presence of theouter tube 67. - But the conventional container and the conventional heat-resistant cap for use with the container, which are constructed as described above, have a problem as follows.
- When the liquid commodity in the
container 51 is used up and thecontainer 51 is recovered for recycling of resources, it is required to separate thecontainer 51 and the heat-resistant cap from each other. Stated otherwise, the heat-resistant cap must be removed from thecontainer mouth 52. However, the heat-resistant cap cannot be easily removed from thecontainer mouth 52 because theridge 65 of theintermediate tube 57 is tightly engaged in vertical relation with therecess 53 of themouth 52. Also, even in an attempt to remove the heat-resistant cap by using an uncapping tool such as a cap opener, the use of an uncapping tool such as a cap opener will be in vain because an access to a lower end of thelower support portion 62 is blocked off by theboss 54 of thecontainer mouth 52. - The present invention has been made with a view of solving the problem stated above, and its object is to provide a container and a heat-resistant cap for use with the container, which heat-resistant cap is of hit-capping type that can be easily fitted to the container by simple hitting when capped over a mouth of the container, and can also be very easily removed from the container mouth, and which container is suitable for recycling of resources.
- This object is achieved by the features of
claim 1. - In the container and the heat-resistant cap for use with the container, preferably, the lower end of the outer tube is located in a position corresponding to the upper edge of the ridge of the intermediate tube, and the embrittled line is formed in the inner circumferential surface of the intermediate tube in a position contiguous to the upper edge of the ridge.
- In the container and the heat-resistant cap for use with the container, preferably, the lower end of the outer tube is located in a position corresponding to the upper edge of the ridge of the intermediate tube, and the embrittled line is formed in the inner circumferential surface of the intermediate tube in a position contiguous to the lower edge of the ridge.
- In the container and the heat-resistant cap for use with the container, preferably, the lower end of the outer tube is located in a position corresponding to the ridge of the intermediate tube, and the embrittled line is formed in the inner circumferential surface of the intermediate tube in a position contiguous to the lower edge of the ridge.
- In the container and the heat-resistant cap for use with the container, preferably, the embrittled portion is formed in the form of a slit. Also, in the container and the heat-resistant cap for use with the container, preferably, the lower end of the outer tube is located in a position corresponding to substantially the lower edge of the ridge of the intermediate tube, and a part of the intermediate tube below an upper end of the lower support portion is formed to be dislocated radially outward of the remaining part thereof to form an embrittled line in the dislocated position.
- In the container and the heat-resistant cap for use with the container, preferably, the ridge is held in pressure contact with the recess in the vertical direction by the lower end of the outer tube.
- In the container and the heat-resistant cap for use with the container, preferably, the ridge is located in a position above a bottom portion of the recess.
- In the container and the heat-resistant cap for use with the container, preferably, the outer tube and the lid member are joined to each other through a hinge.
- In the container and the heat-resistant cap for use with the container, preferably, the lower support portion includes a tab provided contiguous to or in the vicinity of the embrittled portion.
- Fig. 1 is cross-sectional view, partly omitted, of a container and a heat-resistant cap for use with the container, the view showing a first embodiment of the present invention and a state where the cap is fitted to the container.
- Fig. 2 is cross-sectional view similar to Fig. 1, the view showing a second embodiment of the present invention.
- Fig. 3 is cross-sectional view similar to Fig. 1, the view showing a third embodiment of the present invention.
- Fig. 4 is a side view, partly sectioned, of the heat -resistant cap shown in Fig. 1.
- Fig. 5 is a side view, partly sectioned, of a heat-resistant cap shown in Fig. 3.
- Fig. 6 is a side view, partly sectioned, of a heat-resistant cap, the view showing a fourth embodiment of the present invention.
- Fig. 7 is a side view, partly sectioned, of a heat-resistant cap, the view showing a fifth embodiment of the present invention.
- Fig. 8 is a view showing a state where the heat-resistant cap shown in Fig. 1 is being removed from the container.
- Fig. 9 is a view showing a state where a heat-resistant cap shown in Fig. 2 is being removed from a container.
- Fig. 10 is cross-sectional view, partly omitted, of a container and a heat-resistant cap for use with the container, the view showing a sixth embodiment of the present invention and a state where the cap is fitted to the container.
- Fig. 11 is a bottom view of the heat-resistant cap shown in Fig. 10.
- Fig. 12 is a view showing a state where the heat-resistant cap shown in Fig. 10 is being removed from the container.
- Fig. 13 is cross-sectional view, partly omitted, of a conventional container and a conventional heat-resistant cap for use with the container.
- Referring to Figs. 1 to 3, denoted by
reference numeral 1 is a container illustrated as, by way of example, a glass bottle. Thecontainer 1 has amouth 2 provided in its outer circumferential surface with anannular recess 3 and anannular boss 4 formed in the order named from above with a spacing therebetween. Denoted by 5 is a stopper fitted over themouth 2 and made of synthetic resin, e.g., polyethylene. Thestopper 5 has agripping portion 9 comprising aninner tube 6, anintermediate tube 7 and anupper wall 8. The grippingportion 9 grips themouth 2 in such a manner that theinner tube 6, theintermediate tube 7 and theupper wall 8 are held in pressure contact with inner, outer and top surfaces of themouth 2, respectively, thereby keeping thestopper 5 fitted over themouth 2. - Denoted by 10 is a pouring tube extending upward from the
upper wall 8, and amouth wall 14 having an endlessrippable groove 12 formed therein is provided integrally with theupper wall 8 and within thepouring tube 10. Themouth wall 14 includes a rippingmember 13 in the form of a pull ring provided inside therippable groove 12. Theintermediate tube 7 has anannular ridge 15 formed on its inner circumferential surface. When the heat-resistant cap is capped over themouth 2 of the container by hitting, theannular ridge 15 is engaged with theannular recess 3 formed in the outer circumferential surface of themouth 2 in its upper end portion. - Denoted by 11 is a latching portion formed above the
upper wall 8 to extend radially outward and engaged with anengagement portion 19 of anouter lid 18, described later, for latching the same. - Further, denoted by 18 is an outer lid made of synthetic resin, e.g., polypropylene, having a softening temperature against heat that is higher than not only the softening temperature of the synthetic resin as material of the
stopper 5, but also the boiling point of water, and having hardness higher than the material of thestopper 5. Theouter lid 18 comprises anouter tube 16 held in pressure contact with an outer circumferential surface of theintermediate tube 7 and alid member 17. Theouter tube 16 and thelid member 17 are integrally formed with each other through ahinge 26. Theouter tube 16 has anannular engagement portion 19 formed on an inner circumferential surface of its upper part and, as seen from the drawing, theengagement portion 19 is engaged in vertical relation with the latchingportion 11 annularly formed above theupper wall 8 of theintermediate stopper 5. Theouter tube 16 has alower end 20 located around theintermediate tube 7 in a position corresponding to any one of upper and lower edges and a middle point of theridge 15 on the inner circumferential surface of theintermediate tube 7. More specifically, thelower end 20 of theouter tube 16 is positioned corresponding to the upper edge of theridge 15 in the first and second embodiments shown in Figs. 1 and 2, while it is positioned corresponding to substantially the middle point of theridge 15 in the third embodiment shown in Fig. 3. Thelower end 20 of theouter tube 16 located in any of the above positions can serve to urge theridge 15 toward themouth 2 for pressure contact therewith. Denoted by 28 is a locked portion and 29 is a locking portion, the former 28 being lightly locked in vertical relation by the latter 29 when thelid member 17 is closed. - Further, the
intermediate tube 7 has an embrittledline 22 formed therein contiguous to any one of the upper and lower edges of theridge 15. The embrittledline 22 is formed as a thin-walled portion, for example, and may be formed entirely or partly over the circumference of theintermediate tube 7. In the first embodiment shown in Fig. 1, the embrittledline 22 is formed contiguous to the upper edge of theridge 15, while in the second and third embodiments shown in Figs. 2 and 3, it is formed contiguous to the lower edge of theridge 15. Note that the embrittledline 22 may be in the form of perforations, successive holes or notches, or combinations thereof other than the thin-walled portion. Additionally, denoted by 30 is an annular intermediate leg formed on an inner surface of thelid member 17 and coming into close contact with the pouringtube 10 when theouter lid 18 is closed. - Next, referring to Figs. 4 to 7, denoted by 24 is an embrittled portion formed as a thin-walled portion, for example, to extend from a
lower end 23 of theintermediate tube 7 to the embrittledline 22. The embrittledportion 24 may be in the form of perforations, successive holes or notches, or combinations thereof other than the thin-walled portion. As an alternative, the embrittledportion 24 may be in the form of a slit as shown in Fig. 6. Theintermediate tube 7 also includes atab 27 provided on its outer circumferential surface near the embrittledportion 22. When thetab 27 is pulled, a part of the intermediate tube is ripped off along the embrittledportion 24 and the embrittledline 22. Incidentally, denoted by 31 is a connecting piece formed to be easily rippable, and 32 is a secured portion ofthe connectingpiece 31. In the heat-resistant cap of the foregoing construction, as mentioned before, when the cap isfitted to thecontainer 1 filled with a heated liquid commodity, heat of the liquid commodity is transmitted to theintermediate tube 7 of thestopper 5 through themouth 2, whereupon theintermediate tube 7 held in pressure contact with themouth 2 under its elastic deformation is heated to tend to reduce the strength of the pressure contact. However, because theouter tube 16 of theouter lid 18, which is made of synthetic resin having a softening temperature against heat that is higher than not only the softening temperature of the material of theintermediate tube 7, but also the boiling point of water, and having hardness higher than the material of theintermediatetube 7, is held in pressure contact with the outer circumferential surface of theintermediate tube 7, such a reduction in strength of the pressure contact of theintermediate tube 7 is compensated by the pressure contact of theouter tube 16. As a result, a reduction in degree of sealing can be kept within a practically allowable range. - It is to be noted that a cap of another embodiment such as shown in Fig. 10 also operates in the same manner as described above. Denoted by 21 is a lower support portion.
- When the liquid commodity in the
container 1 is used up and thecontainer 1 is recovered for recycling of resources, the embrittledportion 24 of theintermediate tube 7 and then the embrittledline 22 connecting to the former are ripped up. At this time, since the embrittledline 22 is formed contiguous to selected one of the upper and lower edges of theridge 15, theintermediate tube 7 is ripped up circumferentially at the upper or lower edge ofth e ridge 15. Further, unlike the conventional cap described above, thelower end 20 of theouter tube 16 is not extended to reach thelower end 23 of theintermediate tube 7, but it is terminated in a position adjacent to theridge 15. Thus, theouter tube 16 can serve to press theridge 15 inward on one hand, and allows theintermediate tube 16 to be ripped up along the embrittledline 22 in spite of the presence of itself on the other hand. Theintermediate tube 16 may be ripped up completely when the embrittledline 22 is formed all over the circumference thereof, or partly when it is formed over a part of the circumference thereof. In the case where the embrittledline 22 is formed contiguous to the upper edge of theridge 15, forces urging theridge 15 into the pressure contact state are weakened by partly ripping up theintermediate tube 7 along the embrittled line, or are completely eliminated by ripping up same all over the circumference thereof. Accordingly, the heat-resistant cap can be easily removed from the mouth by placing afinger 33 against the ripped-up edge of theintermediate tube 7 and pushing it upward, as shown in Fig. 8. - In the case where the embrittled
line 22 is formed contiguous to the lower edge of theridge 15, the heat-resistant cap can be easily removed from the mouth by placing an uncappingtool 34 such as a cap opener against the ripped-up edge of theintermediate tube 7 and pushing it upward, as shown in Fig. 9. - Furthermore, in the cap wherein the embrittled
line 22 and thelower end 20 of theouter tube 16 are substantially aligned with each other in the radial direction, ripping forces are just directly transmitted to the embrittledline 22, enabling starting of the ripping up in a snap, because theintermediate tube 7 is less deformed due to the rigidity of theouter tube 16 having hardness higher than theintermediate tube 7. - In the cap wherein the
lower end 20 of theouter tube 16 is positioned corresponding to the upper edge of theridge 15 and the embrittledline 22 is formed along the lower edge of theridge 15, ripping forces are also directly transmitted to the embrittledline 22, enabling starting of the ripping up in a snap, because thelower end 20 of theouter tube 16 is present near the embrittledline 22 and theintermediate tube 7 is less deformed for essentially theintermediate tube 7 is less deformed for essentially the same reason as in the above cap. - In the cap, wherein the
lower end 20 of theouter tube 16 is positioned corresponding to substantially the middle point of theridge 15 and the embrittledline 22 is formed contiguous to the lower edge of theridge 15, as shown in Fig. 3, it is also possible to start the ripping up in a snap for essentially the same reason as in the above cap. - The ripping-up can be more easily started by the presence of the
tab 27 provided contiguous to or in the vicinity of the embrittledportion 24 as shown in Figs. 4 to 7. In other words, by gripping thetab 27 and pulling it outward, ripping forces can be easily applied to the embrittledportion 24. - In addition, when removing the heat-resistant cap from the container, the cap can be removed by placing the
finger 33 or the uncapping tool such as a cap opener in contact with theouter lid 18 having higher hardness, i.e., rigidity, than thestopper 5, because the latchingportion 11 of thestopper 5 is so tightly engaged with theengagement portion 19 of theouter tube 16 in its upper portion that thestopper 5 and theouter tube 16 are integrally fitted to each other over a wide circumferential region. Therefore, in comparison with the case of applying forces to a part of the relativelysoft stopper 5 through direct dispersion of the forces due to a partial elastic deformation of thestopper 5 is less, thus enabling confortable and easy removal of the cap. - Next, a container and a heat-resistant cap for use with the container, shown in Fig. 10, according to a sixth embodiment of the present invention will be described below. Referring to Fig. 10, a part of the
intermediate tube 7 below an upper end of itslower support portion 21 is formed to be dislocated radially outward of the remaining part thereof,and thelower end 20 of theouter tube 16 is positioned substantially at the same level as theridge 15. The outer circumferential surface of themouth 2 includes a slope 35 extended from therecess 3 to theboss 4. Theridge 15 of theintermediate tube 7 is located midway therecess 3 in the vertical direction and is held in pressure contact with therecess 3 in a position above abottom portion 25 of therecess 3. - The container and the heat-resistant cap for use with the container, which are constructed as described above, operate essentially in the same manner as with the other embodiments shown in Figs. 1 to 9. A liquid commodity filled in the
container 1 can be used by opening thelid member 17, pulling the rippingmember 13 and ripping off themouth wall 14 along therippable groove 12. When the liquid commodity in thecontainer 1 is used up and thecontainer 1 is recovered for recycling of resources, thetab 27 is pulled so as to rip up theintermediate tube 7 along the embrittledportion 24 and then the embrittledline 22. The ripping-up causes the lower ends of theintermediate tube 7 and theouter tube 16 to appear substantially at the same level, as shown in Fig. 12. Therefore, the heat-resistant cap can be easily removed from thecontainer 1 by placing the uncappingtool 34 such as a cap opener against the lower ends of theintermediate tube 7 and theouter tube 16. Note that, instead of using theuncapping tool 34 such as a cap opener, the cap can also be easily removed from thecontainer 1 by applying forces directly with thefinger 33. - In the heat-resistant cap of this embodiment, since the part of the
intermediate tube 7 below the upper end of thelower support portion 21 is formed to be dislocated radially outward of the remaining part thereof, ripping forces are concentrated on the outwardly dislocated portion when applied to rip up theintermediate tube 7 along the embrittledline 22, so that theintermediate tube 7 can be easily ripped up along the embrittledline 22. Also, since theridge 15 of theintermediate tube 7 is located midway therecess 3 in the vertical direction, the heat-resistant cap can be more easily removed from thecontainer 1 when uncapped. - Advantages of the present invention are as follows.
- According to the present invention constructed as described above, when the heat-resistant cap is fitted to the
mouth 2 of thecontainer 1 filled with a heated liquid commodity, a reduction in degree of sealing due to heat of the liquid commodity transmitted through themouth 2 can be kept within a practically allowable range. Also, when thecontainer 1 is recovered for recycling of resources, the heat-resistant cap can be very easily removed from themouth 2 of thecontainer 1 by such a simple operation as ripping up theintermediate tube 7 along the embrittledportion 24 and then the embrittledline 22 connecting to the former. - According to the feature defined in
Claim 2, the heat-resistant cap can be very easily removed by thefinger 33 without using theuncapping tool 34 such as a cap opener. - According to the feature defined in
Claim 3, the heat-resistant cap can be very easily removed by using theuncapping tool 34 such as a cap opener. - According to the feature defined in
Claim 4, theouter tube 16 can satisfactorily bring theridge 15 of theintermediate tube 7 into pressure contact with themouth 2, and the heat-resistant cap can be very easily removed by using theuncapping tool 34 such as a cap opener. - According to the feature defined in
Claim 5, since the embrittledportion 24 is in the form of a slit, it is very easy to start ripping up theintermediate tube 7 along the embrittledline 22. - According to the feature defined in
Claim 6, since the part of theintermediate tube 7 below the upper end of thelower support portion 21 is formed to be dislocated radially outward of the remaining part thereof, ripping forces tend to concentrate on the outwardly dislocated portion so that theintermediate tube 7 can be more easily ripped up along the embrittledline 22. - According to the feature defined in
Claim 7, since theridge 15 is held in pressure contact with midway therecess 3 in the vertical direction, the heat-resistant cap can be easily removed from themouth 2. - According to the feature defined in
Claim 8, since theridge 15 is located in a position above thebottom portion 25 of therecess 3, the heat-resistant cap can be more easily removed from themouth 2. - According to the feature defined in
Claim 9, since theouter tube 16 and thelid member 17 are joined to each other through thehinge 26, the rigidity of theouter lid 18 can be maintained by such a structure when a heated liquid commodity is filled in the container and the cap is fitted to the container. As a result, a reduction in degree of sealing of thestopper 5 is compensated by the pressure contact of theouter lid 18 with theintermediate stopper 5. - According to the feature defined in
Claim 10, since thetab 27 is provided contiguous to or in the vicinity of the embrittledportion 24, the part of theintermediate tube 7 below the upper end of thelower support portion 21 can be easily ripped away along the embrittledline 22 by gripping thetab 27, although theintermediate tube 7 has a less grippable portion and is more hard to grip by the presence of theouter tube 16 held in pressure contact with theintermediate tube 7.
Claims (10)
- A container and a heat-resistant cap for use with said container, comprising a recess (3) and a boss (4) formed in and on an outer circumferential surface of a mouth (2) of a container (1) to extend circumferentially with a vertical spacing therebetween; a stopper (5) made of synthetic resin and fitted over said mouth (2); a gripping portion (9) provided in said stopper (5) and comprising an inner tube (6), an intermediated tube (7) and an upper wall (8) which are held in pressure contact with inner, outer and top surfaces of said mouth (2), respectively; a pouring tube (10) extending upward from said upper wall (8) and a latching portion (11) formed to extend radially outward from said pouring portion (10); a mouth wall (14) provided integrally with said upper wall (8) within said pouring tube (10) for closing said mouth (2) and including a ripping member (13) in the form of a pull ring located above an upper surface of said mouth wall (14) inside an annular groove (12) thereof for separating said mouth wall (14) from said upper wall (8) along said annular groove (12); a ridge (15) provided on an inner circumferential surface of said intermediate tube (7) and held in pressure contact with said recess (3); an outer lid (18) comprising an outer tube (16) held in pressure contact with a part of an outer circumferential surface of said intermediate tube (7) and a lid member (17), said outer lid (18) being made of synthetic resin having a softening temperature higher than both the softening temperature of the synthetic resin of said stopper (5) and the boiling point of water, and having a higher hardness than the synthetic resin of said stopper (5); an engagement portion (19) provided on said outer lid (18) and engaged in vertical relation with said latching portion (11); a lower end (20) of said outer tube (16) located around said intermediate tube (7) in a position corresponding to any one of upper and lower edges and a middle region of said ridge (15); a lower support portion (21) formed in said intermediate tube (7) for supporting the lower end (20) of said outer tube (16); an embrittled line (22) formed to extend circumferentially in the inner circumferential surface of said intermediate tube (7) in a position contiguous to selected one of the upper and lower edges of said ridge (15); and an embrittled portion (24) formed to extend from a lower end (23) of said intermediate tube (7) to said embrittled line (22).
- A container and a heat-resistant cap for use with said container according to claim 1, wherein the lower end (20) of said outer tube (16) is located in a position corresponding to the upper edge of said ridge (15) of said intermediate tube (7), and said embrittled line (22) is formed in the inner circumferential surface of said intermediate tube (7) in a position contiguous to the upper edge of said ridge (15).
- A container and a heat-resistant cap for use with said container according to claim 1, wherein the lower end (20) of said outer tube (16) is located in a position corresponding to the upper edge of said ridge (15) of said intermediate tube (7), and said embrittled line (22) is formed in the inner circumferential surface of said intermediate tube (7) in a position contiguous to the lower edge of said ridge (15).
- A container and a heat-resistant cap for use with said container according to claim 1, wherein the lower end (20) of said outer tube (16) is located in a position corresponding to said ridge (15) of said intermediate tube (7), and said embrittled line (22) is formed in the inner circumferential surface of said intermediate tube (7) in a position contiguous to the lower edge of said ridge (15).
- A container and a heat-resistant cap for use with said container according to any one of claims 1 to 4, wherein said embrittled portion (24) is formed in the form of a slit.
- A container and a heat-resistant cap for use with said container according to claim 1, wherein the lower end (20) of said outer tube (16) is located in a position corresponding to substantially the lower edge of said ridge (15) of said intermediate tube (7), and said intermediate tube (7) below an upper end of said lower support portion (21) is formed to be dislocated radially outward of the remaining part thereof to form an embrittled line (22) in the dislocated position.
- A container and a heat-resistant cap for use with said container according to claim 6, wherein said ridge (15) is held in pressure contact with said recess (3) in the vertical direction by the lower end (20) of said outer tube (16).
- A container and a heat-resistant cap for use with said container according to claim 7, wherein said ridge (15) is located in a position above a bottom portion (25) of said recess (3).
- A container and a heat-resistant cap for use with said container according to claim 1 to 8, wherein said outer tube (16) and said lid member (17) are joined to each other through a hinge (26).
- A container and a heat-resistant cap for use with said container according to any one of claims 1 to 9, wherein said lower support portion (21) includes a tab (27) provided contiguous to or in the vicinity of said embrittled portion (24).
Applications Claiming Priority (6)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP22686/96 | 1996-02-08 | ||
| JP2268696 | 1996-02-08 | ||
| JP02268696A JP4069263B2 (en) | 1996-02-08 | 1996-02-08 | Heat resistant cap |
| JP15110396A JP3873174B2 (en) | 1996-06-12 | 1996-06-12 | Cap used for container |
| JP151103/96 | 1996-06-12 | ||
| JP15110396 | 1996-06-12 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0788976A1 EP0788976A1 (en) | 1997-08-13 |
| EP0788976B1 true EP0788976B1 (en) | 2001-12-05 |
Family
ID=26359944
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP97101824A Expired - Lifetime EP0788976B1 (en) | 1996-02-08 | 1997-02-05 | Container and heat-resistant cap for use with same |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0788976B1 (en) |
| AT (1) | ATE210054T1 (en) |
| DE (1) | DE69708718T2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AU760708B2 (en) * | 1998-11-27 | 2003-05-22 | Wellman Industrial Plastics Co Pty Limited | A closure |
| DE102006001322A1 (en) * | 2006-01-09 | 2007-07-12 | Bericap Gmbh & Co. Kg | Cap with snap hinge and modified snap rim |
| GB201716075D0 (en) * | 2017-10-02 | 2017-11-15 | Obrist Closures Switzerland | A closure |
| EP4416071A4 (en) * | 2021-10-21 | 2025-03-12 | AptarGroup, Inc. | DISPENSING CLOSURE |
Family Cites Families (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH669575A5 (en) * | 1985-08-20 | 1989-03-31 | Alfatechnic Ag | |
| US4815618A (en) * | 1988-04-25 | 1989-03-28 | Sunbeam Plastics Corporation | Tamper indicating dispenser closure |
-
1997
- 1997-02-05 EP EP97101824A patent/EP0788976B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1997-02-05 AT AT97101824T patent/ATE210054T1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1997-02-05 DE DE69708718T patent/DE69708718T2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| DE69708718T2 (en) | 2002-09-05 |
| EP0788976A1 (en) | 1997-08-13 |
| DE69708718D1 (en) | 2002-01-17 |
| ATE210054T1 (en) | 2001-12-15 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US5810207A (en) | Container and heat-resistant cap for use with same | |
| US5048709A (en) | Straw-containing cover attachment and assembly for a beverage container | |
| US5176278A (en) | Beverage can resealing device | |
| CA2266118C (en) | Valved bottle cap | |
| US5957316A (en) | Valved bottle cap | |
| US8360256B2 (en) | Storage and drinking container having cap and retaining ring | |
| US6241114B1 (en) | Closure cap for drink can | |
| EP0214799B1 (en) | Closure for a container | |
| EA000651B1 (en) | Cover | |
| US7568586B2 (en) | Easy open container closure | |
| GB2264110A (en) | Resealable bottle cap with push-pull closure | |
| US4482070A (en) | Safety closure cap for bottles | |
| US3142403A (en) | Reusable sealing caps | |
| WO2004069666A2 (en) | Linerless sealing closure for a container | |
| EP0788976B1 (en) | Container and heat-resistant cap for use with same | |
| US4562932A (en) | Cap closure for a container with pharmaceutical contents | |
| US7007816B2 (en) | Cap with angled upper skirt | |
| JPH0440268B2 (en) | ||
| US20010037989A1 (en) | Cap with angled upper skirt | |
| RU83492U1 (en) | BOTTLE LID COVER (OPTIONS) | |
| RU102208U1 (en) | BOTTLE LID COVER (OPTIONS) | |
| US3288320A (en) | Reusable bottle cap | |
| KR20080009250A (en) | Container with bottle lid loss prevention structure | |
| US20110062159A1 (en) | Beverage container closure with pressure release | |
| JPH1095450A (en) | Container and heat resistant cap for the container |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE DK ES FR GB IT LI NL PT SE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19971006 |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19990805 |
|
| GRAG | Despatch of communication of intention to grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS AGRA |
|
| GRAG | Despatch of communication of intention to grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS AGRA |
|
| GRAG | Despatch of communication of intention to grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS AGRA |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE DK ES FR GB IT LI NL PT SE |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 210054 Country of ref document: AT Date of ref document: 20011215 Kind code of ref document: T |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: NV Representative=s name: KIRKER & CIE SA Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: IF02 |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 69708718 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20020117 |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20020305 Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20020305 Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20020305 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20020627 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 20060215 Year of fee payment: 10 Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20060215 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Payment date: 20060220 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Payment date: 20060221 Year of fee payment: 10 Ref country code: BE Payment date: 20060221 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20060228 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20060427 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20070228 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20070228 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20070205 |
|
| NLV4 | Nl: lapsed or anulled due to non-payment of the annual fee |
Effective date: 20070901 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20070205 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST Effective date: 20071030 |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: *MIKASA INDUSTRY CO. LTD Effective date: 20070228 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20070228 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20070901 Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20070901 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20070205 Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20070228 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20060221 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20070205 |