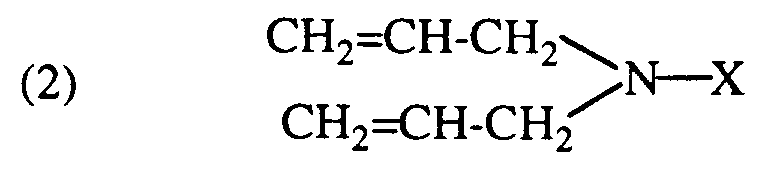EP0447352B1 - Process for improving the yield and the wet fastness of the dyeing or printing with anionic dyes of cellulosic fibrous material - Google Patents
Process for improving the yield and the wet fastness of the dyeing or printing with anionic dyes of cellulosic fibrous material Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0447352B1 EP0447352B1 EP91810016A EP91810016A EP0447352B1 EP 0447352 B1 EP0447352 B1 EP 0447352B1 EP 91810016 A EP91810016 A EP 91810016A EP 91810016 A EP91810016 A EP 91810016A EP 0447352 B1 EP0447352 B1 EP 0447352B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- formula
- process according
- dyeing
- carried out
- methyl
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 29
- 238000004043 dyeing Methods 0.000 title claims description 27
- 239000000975 dye Substances 0.000 title claims description 24
- 125000000129 anionic group Chemical group 0.000 title claims description 4
- 239000002657 fibrous material Substances 0.000 title description 9
- 150000003242 quaternary ammonium salts Chemical class 0.000 claims description 20
- 229920003043 Cellulose fiber Polymers 0.000 claims description 9
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 8
- 239000000982 direct dye Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- JZMJDSHXVKJFKW-UHFFFAOYSA-M methyl sulfate(1-) Chemical compound COS([O-])(=O)=O JZMJDSHXVKJFKW-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 claims description 6
- DYUWTXWIYMHBQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-prop-2-enylprop-2-en-1-amine Chemical group C=CCNCC=C DYUWTXWIYMHBQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- KIWBPDUYBMNFTB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethyl hydrogen sulfate Chemical compound CCOS(O)(=O)=O KIWBPDUYBMNFTB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 125000002496 methyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])* 0.000 claims description 4
- 125000001495 ethyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 claims description 3
- LSNNMFCWUKXFEE-UHFFFAOYSA-M Bisulfite Chemical compound OS([O-])=O LSNNMFCWUKXFEE-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 claims description 2
- 150000001450 anions Chemical class 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000003118 aryl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 2
- 150000005840 aryl radicals Chemical class 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000000835 fiber Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000005843 halogen group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 2
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-L Sulfate Chemical compound [O-]S([O-])(=O)=O QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 claims 1
- 150000008052 alkyl sulfonates Chemical class 0.000 claims 1
- XENVCRGQTABGKY-ZHACJKMWSA-N chlorohydrin Chemical group CC#CC#CC#CC#C\C=C\C(Cl)CO XENVCRGQTABGKY-ZHACJKMWSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium hydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[Na+] HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 45
- XSQUKJJJFZCRTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Urea Chemical compound NC(N)=O XSQUKJJJFZCRTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 18
- -1 imidazolium salts Chemical class 0.000 description 12
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 10
- 229920000742 Cotton Polymers 0.000 description 9
- ONMOULMPIIOVTQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 98-47-5 Chemical compound OS(=O)(=O)C1=CC=CC([N+]([O-])=O)=C1 ONMOULMPIIOVTQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- 150000001412 amines Chemical class 0.000 description 8
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 8
- 229920002678 cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 6
- 239000001913 cellulose Substances 0.000 description 6
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 description 6
- 239000004202 carbamide Substances 0.000 description 5
- 125000002091 cationic group Chemical group 0.000 description 5
- 239000007795 chemical reaction product Substances 0.000 description 5
- 239000004593 Epoxy Substances 0.000 description 4
- YIQKLZYTHXTDDT-UHFFFAOYSA-H Sirius red F3B Chemical compound C1=CC(=CC=C1N=NC2=CC(=C(C=C2)N=NC3=C(C=C4C=C(C=CC4=C3[O-])NC(=O)NC5=CC6=CC(=C(C(=C6C=C5)[O-])N=NC7=C(C=C(C=C7)N=NC8=CC=C(C=C8)S(=O)(=O)[O-])S(=O)(=O)[O-])S(=O)(=O)O)S(=O)(=O)O)S(=O)(=O)[O-])S(=O)(=O)[O-].[Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[Na+] YIQKLZYTHXTDDT-UHFFFAOYSA-H 0.000 description 4
- 239000000834 fixative Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000010409 ironing Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000000985 reactive dye Substances 0.000 description 4
- 159000000000 sodium salts Chemical class 0.000 description 4
- QTTDXDAWQMDLOF-UHFFFAOYSA-J tetrasodium 3-[[4-[[4-[(6-amino-1-hydroxy-3-sulfonatonaphthalen-2-yl)diazenyl]-6-sulfonatonaphthalen-1-yl]diazenyl]naphthalen-1-yl]diazenyl]naphthalene-1,5-disulfonate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[Na+].Nc1ccc2c(O)c(N=Nc3ccc(N=Nc4ccc(N=Nc5cc(c6cccc(c6c5)S([O-])(=O)=O)S([O-])(=O)=O)c5ccccc45)c4ccc(cc34)S([O-])(=O)=O)c(cc2c1)S([O-])(=O)=O QTTDXDAWQMDLOF-UHFFFAOYSA-J 0.000 description 4
- JOXIMZWYDAKGHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N toluene-4-sulfonic acid Chemical compound CC1=CC=C(S(O)(=O)=O)C=C1 JOXIMZWYDAKGHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- BRLQWZUYTZBJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Epichlorohydrin Chemical compound ClCC1CO1 BRLQWZUYTZBJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- ZMXDDKWLCZADIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N N,N-Dimethylformamide Chemical compound CN(C)C=O ZMXDDKWLCZADIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- KWYUFKZDYYNOTN-UHFFFAOYSA-M Potassium hydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[K+] KWYUFKZDYYNOTN-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 3
- 150000001767 cationic compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 3
- VAYGXNSJCAHWJZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N dimethyl sulfate Chemical compound COS(=O)(=O)OC VAYGXNSJCAHWJZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000004744 fabric Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000003756 stirring Methods 0.000 description 3
- XEPXTKKIWBPAEG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,1-dichloropropan-1-ol Chemical compound CCC(O)(Cl)Cl XEPXTKKIWBPAEG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- UWOFGIXNNCPENM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3,3-difluoropentan-2-one Chemical compound CCC(F)(F)C(C)=O UWOFGIXNNCPENM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- MCSXGCZMEPXKIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-hydroxy-4-[(4-methyl-2-nitrophenyl)diazenyl]-N-(3-nitrophenyl)naphthalene-2-carboxamide Chemical compound Cc1ccc(N=Nc2c(O)c(cc3ccccc23)C(=O)Nc2cccc(c2)[N+]([O-])=O)c(c1)[N+]([O-])=O MCSXGCZMEPXKIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- CSCPPACGZOOCGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetone Chemical compound CC(C)=O CSCPPACGZOOCGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethanol Chemical compound CCO LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- PEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Glycerine Chemical compound OCC(O)CO PEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- CDBYLPFSWZWCQE-UHFFFAOYSA-L Sodium Carbonate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[O-]C([O-])=O CDBYLPFSWZWCQE-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 2
- FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium chloride Chemical compound [Na+].[Cl-] FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- 230000000740 bleeding effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000004040 coloring Methods 0.000 description 2
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- DENRZWYUOJLTMF-UHFFFAOYSA-N diethyl sulfate Chemical compound CCOS(=O)(=O)OCC DENRZWYUOJLTMF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229940008406 diethyl sulfate Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 238000005470 impregnation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 2
- HTPJPKXFBLUBPI-UHFFFAOYSA-I pentasodium 5-[[4-[[4-anilino-6-[[8-hydroxy-7-[[4-[(8-hydroxy-3,6-disulfonatonaphthalen-1-yl)diazenyl]-2-methoxy-5-methylphenyl]diazenyl]-3,6-disulfonatonaphthalen-1-yl]amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl]amino]phenyl]diazenyl]-2-hydroxybenzoate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[Na+].COc1cc(N=Nc2cc(cc3cc(cc(O)c23)S([O-])(=O)=O)S([O-])(=O)=O)c(C)cc1N=Nc1c(O)c2c(Nc3nc(Nc4ccccc4)nc(Nc4ccc(cc4)N=Nc4ccc(O)c(c4)C([O-])=O)n3)cc(cc2cc1S([O-])(=O)=O)S([O-])(=O)=O HTPJPKXFBLUBPI-UHFFFAOYSA-I 0.000 description 2
- BWHMMNNQKKPAPP-UHFFFAOYSA-L potassium carbonate Chemical compound [K+].[K+].[O-]C([O-])=O BWHMMNNQKKPAPP-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 2
- 239000000047 product Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000005956 quaternization reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000004753 textile Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000002759 woven fabric Substances 0.000 description 2
- 125000006273 (C1-C3) alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- SPXOTSHWBDUUMT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 138-42-1 Chemical class OS(=O)(=O)C1=CC=C([N+]([O-])=O)C=C1 SPXOTSHWBDUUMT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WYCOJIVDCGJKDB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3,4-dimethylbenzenesulfonic acid Chemical compound CC1=CC=C(S(O)(=O)=O)C=C1C WYCOJIVDCGJKDB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PXACTUVBBMDKRW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-bromobenzenesulfonic acid Chemical class OS(=O)(=O)C1=CC=C(Br)C=C1 PXACTUVBBMDKRW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RJWBTWIBUIGANW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-chlorobenzenesulfonic acid Chemical class OS(=O)(=O)C1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1 RJWBTWIBUIGANW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZCYVEMRRCGMTRW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7553-56-2 Chemical compound [I] ZCYVEMRRCGMTRW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HRPVXLWXLXDGHG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acrylamide Chemical compound NC(=O)C=C HRPVXLWXLXDGHG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WKBOTKDWSSQWDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Bromine atom Chemical compound [Br] WKBOTKDWSSQWDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OTNQPBUDBBSHIN-UHFFFAOYSA-N CS(Nc1cccc(Nc2nc(Cl)nc(N)n2)c1)(=O)=O Chemical compound CS(Nc1cccc(Nc2nc(Cl)nc(N)n2)c1)(=O)=O OTNQPBUDBBSHIN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OUVDUAPUDZNDJQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N C[N](CCO)(CC=C)CC=C Chemical compound C[N](CCO)(CC=C)CC=C OUVDUAPUDZNDJQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 244000025254 Cannabis sativa Species 0.000 description 1
- 235000012766 Cannabis sativa ssp. sativa var. sativa Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 235000012765 Cannabis sativa ssp. sativa var. spontanea Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- ZAMOUSCENKQFHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chlorine atom Chemical compound [Cl] ZAMOUSCENKQFHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 240000000491 Corchorus aestuans Species 0.000 description 1
- 235000011777 Corchorus aestuans Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 235000010862 Corchorus capsularis Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 206010016334 Feeling hot Diseases 0.000 description 1
- PXGOKWXKJXAPGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Fluorine Chemical compound FF PXGOKWXKJXAPGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004952 Polyamide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000297 Rayon Polymers 0.000 description 1
- PMZURENOXWZQFD-UHFFFAOYSA-L Sodium Sulfate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[O-]S([O-])(=O)=O PMZURENOXWZQFD-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 229920002472 Starch Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000010521 absorption reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004480 active ingredient Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000654 additive Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000002411 adverse Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229920000615 alginic acid Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 235000010443 alginic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 150000008044 alkali metal hydroxides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 125000000217 alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 150000003863 ammonium salts Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- SRSXLGNVWSONIS-UHFFFAOYSA-M benzenesulfonate Chemical compound [O-]S(=O)(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 SRSXLGNVWSONIS-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 229940077388 benzenesulfonate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- SRSXLGNVWSONIS-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzenesulfonic acid Chemical class OS(=O)(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 SRSXLGNVWSONIS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000009835 boiling Methods 0.000 description 1
- GDTBXPJZTBHREO-UHFFFAOYSA-N bromine Substances BrBr GDTBXPJZTBHREO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052794 bromium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000006227 byproduct Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000009120 camo Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 235000013877 carbamide Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 235000005607 chanvre indien Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000003638 chemical reducing agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052801 chlorine Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000000460 chlorine Substances 0.000 description 1
- JOYKCMAPFCSKNO-UHFFFAOYSA-N chloro benzenesulfonate Chemical compound ClOS(=O)(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 JOYKCMAPFCSKNO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000004140 cleaning Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229920001577 copolymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 150000008050 dialkyl sulfates Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000002270 dispersing agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003792 electrolyte Substances 0.000 description 1
- GKIPXFAANLTWBM-UHFFFAOYSA-N epibromohydrin Chemical compound BrCC1CO1 GKIPXFAANLTWBM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000002170 ethers Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910052731 fluorine Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011737 fluorine Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000011187 glycerol Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229920000578 graft copolymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229910052736 halogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000002367 halogens Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000011487 hemp Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920001519 homopolymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 150000004693 imidazolium salts Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000012535 impurity Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052740 iodine Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011630 iodine Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000001449 isopropyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])(*)C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 230000014759 maintenance of location Effects 0.000 description 1
- FQPSGWSUVKBHSU-UHFFFAOYSA-N methacrylamide Chemical compound CC(=C)C(N)=O FQPSGWSUVKBHSU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000012454 non-polar solvent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000012074 organic phase Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004033 plastic Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002798 polar solvent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000058 polyacrylate Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920002647 polyamide Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000728 polyester Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229910000027 potassium carbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 125000001436 propyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 239000011541 reaction mixture Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910000029 sodium carbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011780 sodium chloride Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000002639 sodium chloride Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229910052938 sodium sulfate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 235000011152 sodium sulphate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000008107 starch Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000019698 starch Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000003459 sulfonic acid esters Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000012209 synthetic fiber Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920002994 synthetic fiber Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000002562 thickening agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000080 wetting agent Substances 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D06—TREATMENT OF TEXTILES OR THE LIKE; LAUNDERING; FLEXIBLE MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- D06P—DYEING OR PRINTING TEXTILES; DYEING LEATHER, FURS OR SOLID MACROMOLECULAR SUBSTANCES IN ANY FORM
- D06P1/00—General processes of dyeing or printing textiles, or general processes of dyeing leather, furs, or solid macromolecular substances in any form, classified according to the dyes, pigments, or auxiliary substances employed
- D06P1/44—General processes of dyeing or printing textiles, or general processes of dyeing leather, furs, or solid macromolecular substances in any form, classified according to the dyes, pigments, or auxiliary substances employed using insoluble pigments or auxiliary substances, e.g. binders
- D06P1/52—General processes of dyeing or printing textiles, or general processes of dyeing leather, furs, or solid macromolecular substances in any form, classified according to the dyes, pigments, or auxiliary substances employed using insoluble pigments or auxiliary substances, e.g. binders using compositions containing synthetic macromolecular substances
- D06P1/5207—Macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions involving only carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds
- D06P1/5214—Polymers of unsaturated compounds containing no COOH groups or functional derivatives thereof
- D06P1/5242—Polymers of unsaturated N-containing compounds
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D06—TREATMENT OF TEXTILES OR THE LIKE; LAUNDERING; FLEXIBLE MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- D06P—DYEING OR PRINTING TEXTILES; DYEING LEATHER, FURS OR SOLID MACROMOLECULAR SUBSTANCES IN ANY FORM
- D06P1/00—General processes of dyeing or printing textiles, or general processes of dyeing leather, furs, or solid macromolecular substances in any form, classified according to the dyes, pigments, or auxiliary substances employed
- D06P1/44—General processes of dyeing or printing textiles, or general processes of dyeing leather, furs, or solid macromolecular substances in any form, classified according to the dyes, pigments, or auxiliary substances employed using insoluble pigments or auxiliary substances, e.g. binders
- D06P1/52—General processes of dyeing or printing textiles, or general processes of dyeing leather, furs, or solid macromolecular substances in any form, classified according to the dyes, pigments, or auxiliary substances employed using insoluble pigments or auxiliary substances, e.g. binders using compositions containing synthetic macromolecular substances
- D06P1/5264—Macromolecular compounds obtained otherwise than by reactions involving only unsaturated carbon-to-carbon bonds
- D06P1/5278—Polyamides; Polyimides; Polylactames; Polyalkyleneimines
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D06—TREATMENT OF TEXTILES OR THE LIKE; LAUNDERING; FLEXIBLE MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- D06P—DYEING OR PRINTING TEXTILES; DYEING LEATHER, FURS OR SOLID MACROMOLECULAR SUBSTANCES IN ANY FORM
- D06P1/00—General processes of dyeing or printing textiles, or general processes of dyeing leather, furs, or solid macromolecular substances in any form, classified according to the dyes, pigments, or auxiliary substances employed
- D06P1/44—General processes of dyeing or printing textiles, or general processes of dyeing leather, furs, or solid macromolecular substances in any form, classified according to the dyes, pigments, or auxiliary substances employed using insoluble pigments or auxiliary substances, e.g. binders
- D06P1/655—Compounds containing ammonium groups
- D06P1/66—Compounds containing ammonium groups containing quaternary ammonium groups
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D06—TREATMENT OF TEXTILES OR THE LIKE; LAUNDERING; FLEXIBLE MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- D06P—DYEING OR PRINTING TEXTILES; DYEING LEATHER, FURS OR SOLID MACROMOLECULAR SUBSTANCES IN ANY FORM
- D06P3/00—Special processes of dyeing or printing textiles, or dyeing leather, furs, or solid macromolecular substances in any form, classified according to the material treated
- D06P3/58—Material containing hydroxyl groups
- D06P3/60—Natural or regenerated cellulose
- D06P3/62—Natural or regenerated cellulose using direct dyes
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10S—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10S8/00—Bleaching and dyeing; fluid treatment and chemical modification of textiles and fibers
- Y10S8/916—Natural fiber dyeing
- Y10S8/918—Cellulose textile
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a process for improving the yield and the wet fastness properties of dyeings or prints produced with anionic dyes on cellulose fiber material. From DE-A-3 626 410 it is known that monomeric cationic compounds, such as imidazolium salts, can be used to improve the coloration of cellulose fibers.
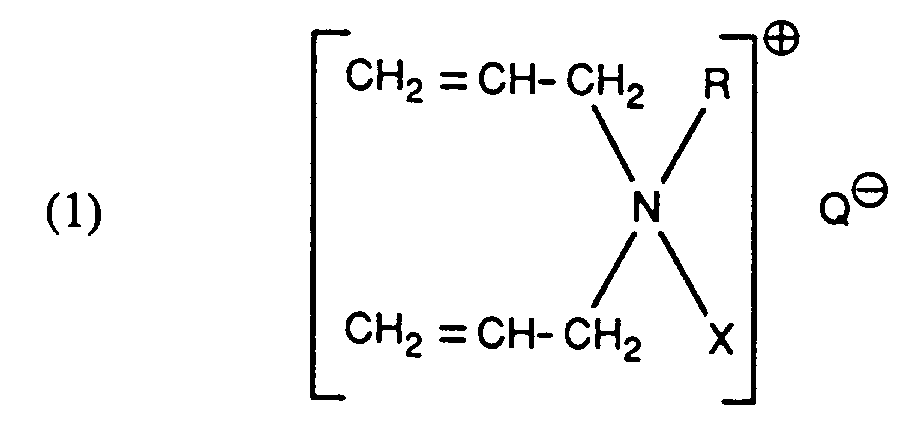
- the process according to the invention is characterized in that cellulose fiber material is dyed with a quaternary ammonium salt of the formula before dyeing or during dyeing wherein R C1-C3-alkyl, X the group Hal is a halogen atom and Q ⁇ the anion of an aromatic sulfonic acid or especially a C1-C3 alkyl sulfate ion, such as, for example, benzenesulfonate, p-toluenesulfonate, chlorobenzenesulfonate, ethyl sulfate (CH3CH2SO4) or especially methyl sulfate (CH3SO4), mean treated.
- a quaternary ammonium salt of the formula before dyeing or during dyeing wherein R C1-C3-alkyl, X the group Hal is a halogen atom and Q ⁇ the anion of an aromatic sulfonic acid or especially a C1-C3 alkyl
- Suitable alkyl groups for R are methyl, ethyl, propyl, isopropyl. Ethyl and especially methyl are preferred.
- Halogen means, for example, bromine, fluorine, iodine or preferably chlorine.
- Specific ammonium salts of formula (1) that can be used in the present invention are N-epoxy-2,3-propyl-N-methyl-N, N-diallylammonium methyl sulfate, N- (3-chloro-2-hydroxypropyl) -N-methyl-N, N-diallylammonium methyl sulfate, N- (3-chloro-2-hydroxypropyl) -N-ethyl-N, N-diallylammonium ethyl sulfate, N- (3-chloro-2-hydroxypropyl) -N-methyl-N, N-diallylammonium p-toluenesulfonate, N-epoxy-2,3-propyl-N-ethyl-N, N-diallylammonium ethyl sulfate and N-epoxy-2,3-propyl-N-methyl-N, N-diallylammonium p-toluen
- the first two representatives are particularly preferred.
- the quaternary ammonium salts of the formula (1) are prepared by adding a tertiary diallylamine of the formula wherein X has the meaning given, with a sulfonic acid alkyl ester of the formula (3) Z-SO2-OR wherein Z represents an aryl radical or -OR and R has the meaning given.
- the quaternary ammonium salt thus produced contains practically no dihalopropanol like dichloropropanol.
- sulfonic acid esters are e.g. Benzenesulfonates, p-toluenesulfonates, p-bromobenzenesulfonates, p-chlorobenzenesulfonates, p-nitrobenzenesulfonates and especially dialkyl sulfates such as diethyl sulfate and especially dimethyl sulfate.
- reaction is conveniently carried out at 30-90 ° C, preferably at 30-60 ° C.
- the quaternization can be carried out in a non-polar or polar solvent, such as water, dimethylformamide or ethanol.
- the quaternized product is isolated in the usual way.
- the diallylamine compound of the formula (2) is prepared in a manner known per se by reacting diallylamine with an ⁇ -epihalohydrin, whereupon the halohydrin compound obtained is isolated. If one sets the reaction product e.g. an alkali metal hydroxide such as sodium hydroxide, the 1-diallylamino-2,3-epoxypropane is formed.
- an alkali metal hydroxide such as sodium hydroxide
- the epihalohydrin which is reacted with diallylamine can be any ⁇ -epihalohydrin, e.g. Epibromohydrin, Epifluorhydrin, Epijodhydrin, ß-Methylepichlorhydrin or preferably epichlorohydrin.
- Quaternary ammonium salts which can be used according to the invention are particularly suitable for improving the color yield and the wet fastness of dyeings or prints which are based on cellulose fiber materials with anionic dyes, such as e.g. Reactive or direct dyes are generated.
- the treatment of the cellulose material is preferably carried out semi-continuously by the cold residence method.
- the cellulose material is impregnated with the treatment agent (fixative) e.g. subjected to a fixing process by printing or preferably padding and then by storage.
- This application can be carried out before dyeing or during dyeing.
- the treatment is preferably carried out by the block-cold dwell process and in particular during the dyeing.
- the impregnation can be carried out at 20 to 50 ° C, but preferably at room temperature.
- the fixing process is carried out by storing the impregnated goods for 4 to 48 hours, preferably 10 to 25 hours at room temperature.
- the preparations advantageously contain the quaternary ammonium salt of the formula (1) in an amount of 10 to 70 g / l, preferably 25 to 50 g / l, of active ingredient.
- the squeezing effect is expediently 60 to 120% by weight.
- these preparations expediently also contain alkaline compounds, such as, for example, potassium hydroxide or preferably sodium hydroxide.
- alkaline compounds such as, for example, potassium hydroxide or preferably sodium hydroxide.
- a 30% aqueous sodium hydroxide solution is preferred, which is added to the preparation in an amount of 20 to 50 ml / l, preferably 25 to 40 ml / l.
- the pH of the preparations can therefore generally be 8 to 13.5, preferably 10 to 12.
- the preparations can also contain other conventional additives e.g. Electrolytes, e.g. Sodium chloride or sodium sulfate, urea, glycerin, thickeners such as e.g. Alginates, starch ethers or polyacrylates, reducing agents, dispersants and wetting agents, homopolymers or copolymers of acrylamide or methacrylamide or graft polymers, as described in EP-A-111 454 and EP-A-363 319, and also contain defoamers and other cationic fixing agents , which the latter can also be fiber-reactive.
- Electrolytes e.g. Sodium chloride or sodium sulfate, urea, glycerin
- thickeners such as e.g. Alginates, starch ethers or polyacrylates, reducing agents, dispersants and wetting agents, homopolymers or copolymers of acrylamide or methacrylamide or graft polymers, as described in EP-A
- Regenerated or in particular natural cellulose can be considered as fiber material, such as e.g. Cellulose, viscose silk, hemp, linen, jute or preferably cotton, as well as fiber blends with synthetic fibers e.g. those made of polyamide / cotton or in particular polyester / cotton.
- the textile can be used in any form, e.g. Yarns, skeins of yarn, woven fabrics, knitted fabrics, felts, preferably in the form of textile fabrics, such as woven fabrics, knitted fabrics or carpets, which consist entirely or partially of native, regenerated or modified cellulose.
- the pretreatment of the cellulose fiber material with the cationic compounds of the formula (1) can be coupled with other pretreatment operations.
- the treatment of the cellulose fiber material is preferably carried out simultaneously with the dyeing.
- the dyeings are carried out with reactive dyes or preferably with substantive dyes by the cold residence process, it being possible for the impregnation to be carried out both by printing and by padding.
- the amount of the dyes generally depends on the desired color strength and is expediently 0.1 to 100 g per liter of liquor, preferably 5 to 40 g / l of liquor.
- the dyeing can be carried out by the exhaust process or by two-stage processes, e.g. the padding process or printing can be produced, the padding process, in particular the so-called pad-steam process, pad-fix process or the pad-cold retention process being possible.
- the usual direct dyes are suitable as noun dyes, for example the "Direct Dyes” mentioned in Color Index, 3rd edition (1971) Volume 2 on pages 2005-2478.
- Reactive dyes are understood to be the usual dyes which form a chemical bond with the cellulose, e.g. the "Reactive Dyes” listed in Color Index, Volume 3 (3rd Edition, 1971) on pages 3391-3560 and Volume 6 (Revised 3rd Edition, 1975) on Pages 6268-6345.
- the process according to the invention gives uniform and vivid colorations both in the pretreatment with subsequent dyeing and in the simultaneous application of the cationic fixative and dye, which are distinguished from known dyeing options by an improved color yield.
- dyeings on cellulose fiber material with substantive dyes are produced, which show a considerable improvement in wet fastness properties.
- the shade and lightfastness of the dyeings are not adversely affected.
- the process is particularly environmentally friendly, since the cationic, fiber-reactive fixing agent does not contain a disruptive by-product like the dichloropropanol.
- the percentages relate to the weight, unless stated otherwise.
- the quantities relate to commercially available, that is to say coupe goods for the dyes and to the pure substance for the auxiliaries.
- the five-digit Color Index numbers (CI) refer to the 3rd edition of the Color Index.
- Example 1 247.6 g of dimethyl sulfate are added to 360 g of 1-diallylamino-3-chloro-2-hydroxypropane with stirring in 60 minutes at 20-40 ° C. and the mixture is stirred for 3 1/2 hours at room temperature.
- the reaction product of the formula is viscous, clear and soluble in water.
- the N, N-diallyl-N- (3-chloro-2-hydroxypropyl) amine used in Example 1 is produced as follows.
- the reaction product of the formula is viscous, clear and soluble in water. Amine number: 0.012, epoxy number: 3.52.
- the 1-diallylamino-2,3-epoxypropane used in Example 2 is produced as follows.
- diallylamine 230 g are heated to 28 ° C. together with 222 g of ⁇ -epichlorohydrin and 7 g of water.
- the reaction mixture is stirred at 28-30 ° C. for 7 hours.
- a solution of 112 g of sodium hydroxide in 182 g of water is then added at 20 ° C.
- the mixture is stirred at 22-25 ° C for 16 hours.
- the mixture is then diluted with 400 g of water and the organic phase is separated off. The latter is dried over potassium carbonate and at Distilled at 40-42 ° C.
- the 1-diallylamino-2,3-epoxypropane obtained has an amine number of 6.48 and an epoxy number of 6.23.
- Example 3 108.9 g of diethyl sulfate are added to 108.8 g of 1-diallylamino-2,3-epoxypropane with stirring in 70 minutes at 60-85 ° C. and the mixture is stirred at 75 ° C. for 1 1/2 hours.
- the product of the formula is viscous, clear and soluble in water.
- Example 4 189.5 g of 1-diallylamino-3-chloro-2-hydroxypropane are dissolved in 126 g of acetone, 186 g of methyl p-toluenesulfonic acid are added at 30-40 ° C. in 2 hours and the mixture is stirred for 1 1/2 hours this temperature. The solvent is then removed.
- reaction product of the formula is viscous, clear and soluble in water. Amine number: 0.014.
- Table 1 The authenticity assessments are listed in Table 1 below.
- Table 1 Coloring g / l dye Fastness to wet ironing ISO C2S wash Change the nuance Bleeding on cotton (1) without 45 3-4 4th 2nd With 20th 5 5 3-4 (2) without 16 2nd 4th 2nd With 12th 5 5 5 (3) without 25th 2-3 4-5 4th With 12th 4-5 5 5 (4) without 35 4-5 4-5 3-4 With 20th 5 5 5
- the goods are then rinsed cold and hot and dried.
- Example 3 20 g of cotton tricot, bleached and mercerized, are padded with a preparation in a liter of 90% with a liquor absorption 35 g of the quaternary ammonium salt of the formula (4) 30 ml sodium hydroxide solution (30%) contains. After padding, the tricot is rolled up wet and stored in a plastic bag for 18 hours at room temperature. The goods are then rinsed cold and hot.
- the pretreated tricot is wetted together with 20 g of untreated tricot in an aqueous dye liquor at 50 ° C., which, at a liquor ratio of 1:40, 1% of the dye Direct Blue 71 C.I. 43140 contains.
- the temperature is raised to 98 ° C. within 30 minutes and dyeing is carried out at this temperature for 45 minutes.
- Example 4 The tricot pretreated according to example 3 is wetted together with 20 g of untreated tricot at 98 ° C. in an aqueous liquor which has a liquor ratio of 1:30 1% of the dye of the formula contains. The temperature is then reduced to 85 ° C. within 30 minutes, adds 5 g / l sodium carbonate calc. 2 ml / l sodium hydroxide solution (30%) and treat the material for a further 45 minutes at 85 ° C. The dyeings are then rinsed in boiling water for 5 minutes.
- Example 5 The tricot pretreated according to example 3 is wetted together with 20 g of non-pretreated tricot and 20 g of tricot treated in the same way, but only with 30 ml / l sodium hydroxide solution (30%) in an aqueous liquor at 50.degree a liquor ratio of 1:40, 1% of a dye of the formula contains. The material is then dyed for 40 minutes at 50 ° C and then rinsed warm for 5 minutes.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Textile Engineering (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Coloring (AREA)
- Epoxy Compounds (AREA)
- Organic Low-Molecular-Weight Compounds And Preparation Thereof (AREA)
Description
Die vorliegende Erfindung betrifft ein Verfahren zur Verbesserung der Ausbeute und der Nassechtheiten von mit anionischen Farbstoffen auf Cellulosefasermaterial erzeugten Färbungen oder Drucken. Aus der DE-A-3 626 410 ist es bekannt, daß zur Verbesserüng der Färbung von Cellulose fasern monomere Kationische Verbindungen, wie Imidazoliumsalze, eingesetzt werden können.The present invention relates to a process for improving the yield and the wet fastness properties of dyeings or prints produced with anionic dyes on cellulose fiber material. From DE-A-3 626 410 it is known that monomeric cationic compounds, such as imidazolium salts, can be used to improve the coloration of cellulose fibers.
Das erfindungsgemäße Verfahren ist dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass man Cellulosefasermaterial vor dem Färben oder während des Färbens mit einem quaternären Ammoniumsalz der Formel
worin
R C₁-C₃-Alkyl,
X die Gruppe
Hal ein Halogenatom und
Q⊖ das Anion einer aromatischen Sulfonsäure oder besonders ein C₁-C₃-Alkylsulfation, wie z.B. Benzolsulfonat, p-Toluolsulfonat, Chlorbenzolsulfonat, Ethylsulfat (CH₃CH₂SO₄) oder vor allem das Methylsulfat (CH₃SO₄),
bedeuten, behandelt.The process according to the invention is characterized in that cellulose fiber material is dyed with a quaternary ammonium salt of the formula before dyeing or during dyeing
wherein
R C₁-C₃-alkyl,
X the group
Hal is a halogen atom and
Q ⊖ the anion of an aromatic sulfonic acid or especially a C₁-C₃ alkyl sulfate ion, such as, for example, benzenesulfonate, p-toluenesulfonate, chlorobenzenesulfonate, ethyl sulfate (CH₃CH₂SO₄) or especially methyl sulfate (CH₃SO₄),
mean treated.
Geeignete Alkylgruppen für R sind Methyl, Ethyl, Propyl, Isopropyl. Bevorzugt sind Ethyl und besonders Methyl.Suitable alkyl groups for R are methyl, ethyl, propyl, isopropyl. Ethyl and especially methyl are preferred.
Halogen bedeutet beispielsweise Brom, Fluor, Jod oder vorzugsweise Chlor.Halogen means, for example, bromine, fluorine, iodine or preferably chlorine.
Spezifische Ammoniumsalze der Formel (1), die erfindungsgemäss verwendet werden können, sind
N-Epoxy-2,3-propyl-N-methyl-N,N-diallylammoniummethylsulfat,
N-(3-Chlor-2-hydroxypropyl)-N-methyl-N,N-diallylammoniummethylsulfat,
N-(3-Chlor-2-hydroxypropyl)-N-ethyl-N,N-diallylammoniumethylsulfat,
N-(3-Chlor-2-hydroxypropyl)-N-methyl-N,N-diallylammonium-p-toluolsulfonat,
N-Epoxy-2,3-propyl-N-ethyl-N,N-diallylammoniumethylsulfat und
N-Epoxy-2,3-propyl-N-methyl-N,N-diallylammonium-p-toluolsulfonat.Specific ammonium salts of formula (1) that can be used in the present invention are
N-epoxy-2,3-propyl-N-methyl-N, N-diallylammonium methyl sulfate,
N- (3-chloro-2-hydroxypropyl) -N-methyl-N, N-diallylammonium methyl sulfate,
N- (3-chloro-2-hydroxypropyl) -N-ethyl-N, N-diallylammonium ethyl sulfate,
N- (3-chloro-2-hydroxypropyl) -N-methyl-N, N-diallylammonium p-toluenesulfonate,
N-epoxy-2,3-propyl-N-ethyl-N, N-diallylammonium ethyl sulfate and
N-epoxy-2,3-propyl-N-methyl-N, N-diallylammonium p-toluenesulfonate.
Die zwei erstgenannten Vertreter sind besonders bevorzugt.The first two representatives are particularly preferred.
Die Herstellung der quaternären Ammoniumsalze der Formel (1) erfolgt dadurch, dass man ein tertiäres Diallylamin der Formel
worin X die angegebene Bedeutung hat, mit einem Sulfonsäurealkylester der Formel
(3) Z-SO₂-OR
worin Z einen Arylrest oder -OR bedeutet und R die angegebene Bedeutung hat, umsetzt.The quaternary ammonium salts of the formula (1) are prepared by adding a tertiary diallylamine of the formula
wherein X has the meaning given, with a sulfonic acid alkyl ester of the formula
(3) Z-SO₂-OR
wherein Z represents an aryl radical or -OR and R has the meaning given.
Das so hergestellte quaternäre Ammoniumsalz enthält praktisch kein Dihalogenpropanol wie Dichlorpropanol.The quaternary ammonium salt thus produced contains practically no dihalopropanol like dichloropropanol.
Gut geeignet unter den Sulfonsäureestern sind z.B. Benzolsulfonate, p-Toluolsulfonate, p-Brombenzolsulfonate, p-Chlorbenzolsulfonate, p-Nitrobenzolsulfonate und insbesondere Dialkylsulfate wie Diethylsulfat und vor allem Dimethylsulfat.Well suited among the sulfonic acid esters are e.g. Benzenesulfonates, p-toluenesulfonates, p-bromobenzenesulfonates, p-chlorobenzenesulfonates, p-nitrobenzenesulfonates and especially dialkyl sulfates such as diethyl sulfate and especially dimethyl sulfate.
Die Umsetzung (Quaternisierung) erfolgt zweckmässigerweise bei 30-90°C, vorzugsweise bei 30-60°C.The reaction (quaternization) is conveniently carried out at 30-90 ° C, preferably at 30-60 ° C.
Die Quaternisierung kann in einem nichtpolaren oder polaren Lösungsmittel, wie z.B. Wasser, Dimethylformamid oder Ethanol durchgeführt werden.The quaternization can be carried out in a non-polar or polar solvent, such as water, dimethylformamide or ethanol.
Die Isolierung des quaternisierten Produktes erfolgt auf übliche Weise.The quaternized product is isolated in the usual way.
Die Herstellung der Diallylaminverbindung der Formel (2) erfolgt in an sich bekannte Weise durch Umsetzung von Diallylamin mit einem α-Epihalogenhydrin, worauf die erhaltene Halogenhydrinverbindung isoliert wird. Setzt man dem Reaktionsprodukt z.B. ein Alkalimetallhydroxid wie Natriumhydroxid zu, so entsteht das 1-Diallylamino-2,3-epoxypropan.The diallylamine compound of the formula (2) is prepared in a manner known per se by reacting diallylamine with an α-epihalohydrin, whereupon the halohydrin compound obtained is isolated. If one sets the reaction product e.g. an alkali metal hydroxide such as sodium hydroxide, the 1-diallylamino-2,3-epoxypropane is formed.
Das Epihalogenhydrin, das mit Diallylamin umgesetzt wird, kann jedes beliebige α-Epihalogenhydrin, wie z.B. Epibromhydrin, Epifluorhydrin, Epijodhydrin, ß-Methylepichlorhydrin oder vorzugsweise Epichlorhydrin sein.The epihalohydrin which is reacted with diallylamine can be any α-epihalohydrin, e.g. Epibromohydrin, Epifluorhydrin, Epijodhydrin, ß-Methylepichlorhydrin or preferably epichlorohydrin.
Erfindungsgemäss verwendbare quaternäre Ammoniumsalze eignen sich insbesondere zur Verbesserung der Farbausbeute und der Nassechtheiten von Färbungen oder Drucken, welche auf Cellulosefasermaterialien mit anionischen Farbstoffen, wie z.B. Reaktiv- oder Direktfarbstoffen erzeugt werden.Quaternary ammonium salts which can be used according to the invention are particularly suitable for improving the color yield and the wet fastness of dyeings or prints which are based on cellulose fiber materials with anionic dyes, such as e.g. Reactive or direct dyes are generated.
Die Behandlung des Cellulosematerials wird vorzugsweise halbkontinuierlich nach der Kaltverweilmethode durchgeführt. Dabei wird das Cellulosematerial mit dem Behandlungsmittel (Fixiermittel) imprägniert z.B. durch Bedrucken oder vorzugsweise Klotzen und dann durch Lagerung einem Fixierprozess unterworfen. Diese Applikation kann vor dem Färben oder während des Färbens durchgeführt werden. Vorzugsweise erfolgt die Behandlung nach dem Klotz-Kaltverweilverfahren und insbesondere während des Färbens.The treatment of the cellulose material is preferably carried out semi-continuously by the cold residence method. The cellulose material is impregnated with the treatment agent (fixative) e.g. subjected to a fixing process by printing or preferably padding and then by storage. This application can be carried out before dyeing or during dyeing. The treatment is preferably carried out by the block-cold dwell process and in particular during the dyeing.
Die Imprägnierung kann bei 20 bis 50°C, vorzugsweise jedoch bei Raumtemperatur vorgenommen werden. Der Fixierprozess erfolgt durch Lagern der imprägnierten Ware während 4 bis 48 Stunden, vorzugsweise 10 bis 25 Stunden bei Raumtemperatur.The impregnation can be carried out at 20 to 50 ° C, but preferably at room temperature. The fixing process is carried out by storing the impregnated goods for 4 to 48 hours, preferably 10 to 25 hours at room temperature.
Die Zubereitungen (Klotzflotten oder Druckpasten) enthalten das quaternäre Ammoniumsalz der Formel (1) vorteilhafterweise in einer Menge von 10 bis 70 g/l, vorzugsweise 25 bis 50 g/l Wirkstoffgehalt. Bei den Klotzflotten beträgt der Abquetscheffekt zweckmässig 60 bis 120 Gew.-%.The preparations (padding liquors or printing pastes) advantageously contain the quaternary ammonium salt of the formula (1) in an amount of 10 to 70 g / l, preferably 25 to 50 g / l, of active ingredient. In the padding liquors, the squeezing effect is expediently 60 to 120% by weight.
Ausser der kationischen, reaktiven Verbindung der Formel (1) enthalten diese Zubereitungen zweckmässigerweise noch alkalisch reagierende Verbindungen, wie z.B. Kaliumhydroxid oder vorzugsweise Natriumhydroxid. Bevorzugt wird eine 30%-ige wässerige Natriumhydroxidlösung, die in einer Menge von 20 bis 50 ml/l, vorzugsweise 25 bis 40 ml/l der Zubereitung zugesetzt wird.In addition to the cationic, reactive compound of the formula (1), these preparations expediently also contain alkaline compounds, such as, for example, potassium hydroxide or preferably sodium hydroxide. A 30% aqueous sodium hydroxide solution is preferred, which is added to the preparation in an amount of 20 to 50 ml / l, preferably 25 to 40 ml / l.
Der pH-Wert der Zubereitungen kann somit in der Regel 8 bis 13,5, vorzugsweise 10 bis 12 betragen.The pH of the preparations can therefore generally be 8 to 13.5, preferably 10 to 12.
Die Zubereitungen können auch weitere übliche Zusätze z.B. Elektrolyte, wie z.B. Natriumchlorid oder Natriumsulfat, Harnstoff, Glycerin, Verdicker, wie z.B. Alginate, Stärkeether oder Polyacrylate, Reduktionsschutzmittel, Dispergier- und Netzmittel, Homopolymerisate oder Mischpolymerisate des Acrylamids oder Methacrylamids oder Pfropfpolymerisate, wie sie in EP-A-111 454 und EP-A-363 319 beschrieben sind, sowie auch Entschäumer und weitere kationische Fixiermittel enthalten, welch letztere auch faserreaktiv sein können.The preparations can also contain other conventional additives e.g. Electrolytes, e.g. Sodium chloride or sodium sulfate, urea, glycerin, thickeners such as e.g. Alginates, starch ethers or polyacrylates, reducing agents, dispersants and wetting agents, homopolymers or copolymers of acrylamide or methacrylamide or graft polymers, as described in EP-A-111 454 and EP-A-363 319, and also contain defoamers and other cationic fixing agents , which the latter can also be fiber-reactive.
Als Fasermaterial kann regenerierte oder insbesondere natürliche Cellulose in Betracht kommen, wie z.B. Zellwolle, Viskoseseide, Hanf, Leinen, Jute oder vorzugsweise Baumwolle, sowie auch Fasermischungen mit synthetischen Fasern z.B. solche aus Polyamid/Baumwolle oder insbesondere aus Polyester/Baumwolle.Regenerated or in particular natural cellulose can be considered as fiber material, such as e.g. Cellulose, viscose silk, hemp, linen, jute or preferably cotton, as well as fiber blends with synthetic fibers e.g. those made of polyamide / cotton or in particular polyester / cotton.
Das Textilgut ist in jeglicher Form anwendbar, wie z.B. Garne, Garnstränge, Gewebe, Gewirke, Filze, vorzugsweise in Form von textilen Flächengebilden, wie Gewebe, Maschenware oder Teppich, die ganz oder teilweise aus nativer, regenerierter oder modifizierter Cellulose bestehen.The textile can be used in any form, e.g. Yarns, skeins of yarn, woven fabrics, knitted fabrics, felts, preferably in the form of textile fabrics, such as woven fabrics, knitted fabrics or carpets, which consist entirely or partially of native, regenerated or modified cellulose.
Die Vorbehandlung des Cellulosefasermaterials mit den kationischen Verbindungen der Formel (1) kann mit anderen Vorbehandlungsoperationen gekoppelt werden. Man kann z.B. dem alkalischen Bad, in dem Rohbaumwolle zur Entfernung von Verunreinigungen üblicherweise vor dem Färben abgekocht wird, das kationische, reaktive Fixiermittel zusetzen und so die Reinigung und die Vorbehandlung mit dem Fixiermittel in einem Arbeitsgang durchführen.The pretreatment of the cellulose fiber material with the cationic compounds of the formula (1) can be coupled with other pretreatment operations. You can e.g. Add the cationic, reactive fixative to the alkaline bath, in which raw cotton is usually boiled before dyeing to remove impurities, and thus carry out cleaning and pretreatment with the fixative in one operation.
Vorzugsweise erfolgt die Behandlung des Cellosefasermaterials gleichzeitig mit dem Färben. Die Färbungen erfolgen mit Reaktivfarbstoffen oder vorzugsweise mit Substantivfarbstoffen nach dem Kaltverweilverfahren, wobei die Imprägnierung sowohl durch Bedrucken als auch durch Klotzen durchgeführt werden kann.The treatment of the cellulose fiber material is preferably carried out simultaneously with the dyeing. The dyeings are carried out with reactive dyes or preferably with substantive dyes by the cold residence process, it being possible for the impregnation to be carried out both by printing and by padding.
Die Menge der Farbstoffe richtet sich in der Regel nach der gewünschten Farbstärke und beträgt zweckmässig 0,1 bis 100 g pro Liter Flotte, vorzugsweise 5 bis 40 g/l Flotte.The amount of the dyes generally depends on the desired color strength and is expediently 0.1 to 100 g per liter of liquor, preferably 5 to 40 g / l of liquor.
Im Falle der Verwendung der kationischen Verbindung in einer Vorbehandlung des Cellulosefasermaterials kann die Färbung nach dem Ausziehverfahren oder durch zweistufige Prozesse, wie z.B. das Foulardierverfahren oder Bedrücken erzeugt werden, wobei als Foulardierverfahren, besonders das sogenannte Pad-Steam-Verfahren, Pad-Fix-Verfahren oder das Klotz-Kaltverweilverfahren in Frage kommen können.In the case of using the cationic compound in a pretreatment of the cellulose fiber material, the dyeing can be carried out by the exhaust process or by two-stage processes, e.g. the padding process or printing can be produced, the padding process, in particular the so-called pad-steam process, pad-fix process or the pad-cold retention process being possible.
Als Substantivfarbstoffe sind die üblichen Direktfarbstoffe geeignet, beispielsweise die in Colour Index, 3. Auflage (1971) Band 2 auf den Seiten 2005-2478 genannten "Direct Dyes".The usual direct dyes are suitable as noun dyes, for example the "Direct Dyes" mentioned in Color Index, 3rd edition (1971) Volume 2 on pages 2005-2478.
Unter Reaktivfarbstoffen werden die üblichen Farbstoffe verstanden, welche mit der Cellulose eine chemische Bindung eingehen, z.B. die in Colour Index, in Band 3(3. Auflage, 1971) auf den Seiten 3391-3560 und in Band 6 (revidierte 3. Auflage, 1975) auf den Seiten 6268-6345 aufgeführten "Reactive Dyes".Reactive dyes are understood to be the usual dyes which form a chemical bond with the cellulose, e.g. the "Reactive Dyes" listed in Color Index, Volume 3 (3rd Edition, 1971) on pages 3391-3560 and Volume 6 (Revised 3rd Edition, 1975) on Pages 6268-6345.
Man erhält nach dem erfindungsgemässen Verfahren sowohl bei der Vorbehandlung mit anschliessendem Färben als auch bei gleichzeitiger Applikation des kationischen Fixiermittels und Farbstoffes gleichmässige und farbkräftige Ausfärbungen, die sich gegenüber bekannten Färbemöglichkeiten durch eine verbesserte Farbausbeute auszeichnen. Insbesondere werden Färbungen auf Cellulosefasermaterial mit Substantivfarbstoffen erzeugt, welche eine erhebliche Verbesserung der Nassechtheiten zeigen. Nuance und Lichtechtheit der Färbungen werden nicht negativ beeinflusst. Das Verfahren ist besonders umweltfreundlich, da das kationische, faserreaktive Fixiermittel kein störendes Nebenprodukt wie das Dichlorpropanol enthält.The process according to the invention gives uniform and vivid colorations both in the pretreatment with subsequent dyeing and in the simultaneous application of the cationic fixative and dye, which are distinguished from known dyeing options by an improved color yield. In particular, dyeings on cellulose fiber material with substantive dyes are produced, which show a considerable improvement in wet fastness properties. The shade and lightfastness of the dyeings are not adversely affected. The process is particularly environmentally friendly, since the cationic, fiber-reactive fixing agent does not contain a disruptive by-product like the dichloropropanol.
In den folgenden Herstellungs- und Anwendungsbeispielen beziehen sich die Prozentansätze, wenn nichts anderes angegeben ist, auf das Gewicht. Die Mengen beziehen sich bei den Farbstoffen auf handelsübliche, d.h. coupierte Ware und bei den Hilfsmitteln auf Reinsubstanz. Die fünfstelligen Colour-Index Nummern (C.I) beziehen sich auf die 3. Auflage des Colour-Index.In the following manufacturing and application examples, the percentages relate to the weight, unless stated otherwise. The quantities relate to commercially available, that is to say coupe goods for the dyes and to the pure substance for the auxiliaries. The five-digit Color Index numbers (CI) refer to the 3rd edition of the Color Index.
Beispiel 1: Zu 360 g 1-Diallylamino-3-chlor-2-hydroxypropan gibt man unter Rühren in 60 Minuten bei 20-40°C 247,6 g Dimethylsulfat und rührt 3 1/2 Stunden bei Raumtemperatur. Das Reaktionsprodukt der Formel
ist viskos, klar und löslich in Wasser. Aminzahl: 0,015
Das im Beispiel 1 verwendete N,N-Diallyl-N-(3-chlor-2-hydroxypropyl)-amin wird folgendermassen hergestellt. Example 1: 247.6 g of dimethyl sulfate are added to 360 g of 1-diallylamino-3-chloro-2-hydroxypropane with stirring in 60 minutes at 20-40 ° C. and the mixture is stirred for 3 1/2 hours at room temperature. The reaction product of the formula
is viscous, clear and soluble in water. Amine number: 0.015
The N, N-diallyl-N- (3-chloro-2-hydroxypropyl) amine used in Example 1 is produced as follows.
230 g Diallylamin werden zusammen mit 222 g α-Epichlorhydrin und 7 g Wasser auf 28°C erwärmt. Man rührt das Gemisch 7 Stunden bei 28-30°C. Anschliessend wird das Reaktionsprodukt bei
68-70°C destilliert.230 g of diallylamine are heated to 28 ° C. together with 222 g of α-epichlorohydrin and 7 g of water. The mixture is stirred at 28-30 ° C for 7 hours. The reaction product is then at
Distilled at 68-70 ° C.
Man erhält 361 g N,N-Diallyl-N-(3-chlor-2-hydroxypropyl)-amin. Aminzahl: 5,4; Epoxyzahl:-.361 g of N, N-diallyl-N- (3-chloro-2-hydroxypropyl) amine are obtained. Amine number: 5.4; Epoxy number: -.
Zu 270 g 1-Diallylamino-2,3-epoxypropan gibt man unter Rühren in 60 Minuten bei 20°C 223 g Dimethylsulfat und rührt eine Stunde bei Raumtemperatur.223 g of dimethyl sulfate are added to 270 g of 1-diallylamino-2,3-epoxypropane with stirring in 60 minutes at 20 ° C. and the mixture is stirred for one hour at room temperature.
Das Reaktionsprodukt der Formel
ist viskos, klar und löslich in Wasser. Aminzahl: 0,012, Epoxyzahl: 3,52.The reaction product of the formula
is viscous, clear and soluble in water. Amine number: 0.012, epoxy number: 3.52.
Das im Beispiel 2 verwendete 1-Diallylamino-2,3-epoxypropan wird folgendermassen hergestellt.The 1-diallylamino-2,3-epoxypropane used in Example 2 is produced as follows.
230 g Diallylamin werden zusammen mit 222 g α-Epichlorhydrin und 7 g Wasser auf 28°C erwärmt. Man rührt das Reaktionsgemisch während 7 Stunden bei 28-30°C. Hierauf gibt man bei 20°C eine Lösung von 112 g Natriumhydroxyd in 182 g Wasser zu. Bei 22-25°C rührt man 16 Stunden. Anschliessend wird mit 400 g Wasser verdünnt und die organische Phase abgetrennt. Letztere wird über Kaliumcarbonat getrocknet und bei
40-42°C destilliert Das erhaltene 1-Diallylamino-2,3-epoxypropan weist eine Aminzahl von 6,48 und eine Epoxyzahl von 6,23 auf.230 g of diallylamine are heated to 28 ° C. together with 222 g of α-epichlorohydrin and 7 g of water. The reaction mixture is stirred at 28-30 ° C. for 7 hours. A solution of 112 g of sodium hydroxide in 182 g of water is then added at 20 ° C. The mixture is stirred at 22-25 ° C for 16 hours. The mixture is then diluted with 400 g of water and the organic phase is separated off. The latter is dried over potassium carbonate and at
Distilled at 40-42 ° C. The 1-diallylamino-2,3-epoxypropane obtained has an amine number of 6.48 and an epoxy number of 6.23.
Beispiel 3: Zu 108,8 g 1-Diallylamino-2,3-epoxypropan gibt man unter Rühren in 70 Minuten bei 60-85°C 108,9 g Diethylsulfat und rührt 1 1/2 Stunden bei 75°C. Das Rekationsprodukt der Formel
ist viskos, klar und löslich in Wasser. Aminzahl: 0,044, Epoxyzahl: 3,15. Example 3: 108.9 g of diethyl sulfate are added to 108.8 g of 1-diallylamino-2,3-epoxypropane with stirring in 70 minutes at 60-85 ° C. and the mixture is stirred at 75 ° C. for 1 1/2 hours. The product of the formula
is viscous, clear and soluble in water. Amine number: 0.044, epoxy number: 3.15.
Beispiel 4: 189,5 g 1-Diallylamino-3-chlor-2-hydroxypropan werden in 126 g Aceton gelöst, dazu gibt man in 2 Stunden 186 g p-Toluolsulfonsäuremethylester bei 30-40°C und rührt 1 1/2 Stunden bei dieser Temperatur.
Anschliessend wird das Lösungsmittel entfernt. Example 4: 189.5 g of 1-diallylamino-3-chloro-2-hydroxypropane are dissolved in 126 g of acetone, 186 g of methyl p-toluenesulfonic acid are added at 30-40 ° C. in 2 hours and the mixture is stirred for 1 1/2 hours this temperature.
The solvent is then removed.
Das Reaktionsprodukt der Formel:
ist viskos, klar und löslich in Wasser. Aminzahl: 0,014.The reaction product of the formula:
is viscous, clear and soluble in water. Amine number: 0.014.
Beispiel 1: Jeweils 20 g Baumwoll-Cretonne, gebleicht und nicht mercerisiert, werden getrennt auf einem Foulard mit einer der 4 folgenden Flotten, welche im Liter
- 1) 20 g des Farbstoffes Direct Red 80 C.I. 35780
32 ml Natriumhydroxidlösung (30 %)
35 g des quaternären Ammoniumsalzes der Formel (4) - 2) 12g des Farbstoffes Direct Blue 71 C.I. 34140
32 ml Natriumhydroxidlösung (30 %)
35 g des quaternären Ammoniumsalzes der Formel (4) - 3) 12 g des Farbstoffes Direct Violet 66 C.I. 29125
32 ml Natriumhydroxidiösung (30 %)
35 g des quaternären Ammoniumsalzes der Formel (4) - 4) 20g des Farbstoffes Direct Green 26 C.I. 34045
32 ml Natriumhydroxidiösung (30 %)
35 g des quaternären Ammoniumsalzes der Formel (4)
- 1) 20 g of the Direct Red 80 CI 35780 dye
32 ml sodium hydroxide solution (30%)
35 g of the quaternary ammonium salt of the formula (4) - 2) 12 g of the Direct Blue 71 CI 34140 dye
32 ml sodium hydroxide solution (30%)
35 g of the quaternary ammonium salt of the formula (4) - 3) 12 g of the Direct Violet 66 CI 29125 dye
32 ml sodium hydroxide solution (30%)
35 g of the quaternary ammonium salt of the formula (4) - 4) 20g of the Direct Green 26 CI 34045 dye
32 ml sodium hydroxide solution (30%)
35 g of the quaternary ammonium salt of the formula (4)
Von diesen 4 Färbungen werden folgende Echtheiten geprüft:
- Nassbügelechtheit (SN ISO 105-X11)
- ISO C2S-Wäsche (ISO 105-C06)
- Fastness to wet ironing (SN ISO 105-X11)
- ISO C2S wash (ISO 105-C06)
In der folgenden Tabelle 1 sind die Echtheitsbewertungen aufgeführt.
Aehnliche Ergebnisse werden erhalten, wenn beim Färben anstelle des quaternären Ammoniumsalzes der Formel (4) jeweils die gleiche Menge der quaternären Ammoniumsalze der Formeln (6) und (7) verwendet wird.Similar results are obtained if the same amount of the quaternary ammonium salts of the formulas (6) and (7) is used in each case for dyeing instead of the quaternary ammonium salt of the formula (4).
Beispiel 2: Jeweils 20 g Baumwoll-Tricot, gebleicht und mercerisiert, werden getrennt auf einem Foulard mit einer der 4 folgenden Flotten, welche im Liter
- 1) 25 g eines Farbstoffes der Formel
40 ml Natriumhydroxidlösung (30 %)
100 g Harnstoff und
3 g Natriumsalz der 3-Nitrobenzolsulfonsäure - 2) 25 g eines Farbstoffes der Formel
40 ml Natriumhydroxidlösung (30 %)
100 g Harnstoff und
3 g Natriumsalz der 3-Nitrobenzolsulfonsäure - 3) 25 g eines Farbstoffes der Formel
40 ml Natriumhydroxidlösung (30 %)
100g Harnstoff und
3 g Natriumsalz der 3-Nitrobenzolsulfonsäure - 4) 25 g eines Farbstoffes der Formel
40 ml Natriumhydroxidlösung (30 %)
100g Harnstoff und
3 g Natriumsalz der 3-Nitrobenzolsulfonsäure
- 1) 25 g of a dye of the formula
40 ml sodium hydroxide solution (30%)
100 g urea and
3 g of sodium salt of 3-nitrobenzenesulfonic acid - 2) 25 g of a dye of the formula
40 ml sodium hydroxide solution (30%)
100 g urea and
3 g of sodium salt of 3-nitrobenzenesulfonic acid - 3) 25 g of a dye of the formula
40 ml sodium hydroxide solution (30%)
100g urea and
3 g of sodium salt of 3-nitrobenzenesulfonic acid - 4) 25 g of a dye of the formula
40 ml sodium hydroxide solution (30%)
100g urea and
3 g of sodium salt of 3-nitrobenzenesulfonic acid
Anschliessend wird die Ware kalt und heiss gespült und getrocknet.The goods are then rinsed cold and hot and dried.
Von diesen 4 Färbungen werden die Nassbügelechtheit und die ISO C2S-Wäsche geprüft, wobei auch entsprechende stärkegleiche, jeweils mit mehr Farbstoff erhaltenen Färbungen, die jeweils ohne Zusatz des quaternären Ammoniumsalzes der Formel (5) erhalten worden sind, mitgeprüft werden.Of these 4 dyeings, the fastness to wet ironing and the ISO C2S wash are tested, and corresponding dyeings of the same strength, each obtained with more dye and obtained without the addition of the quaternary ammonium salt of the formula (5), are also checked.
In der folgenden Tabelle 2 sind die Echtheitsbewertungen gegenübergestellt.
Beispiel 3: Je 20 g Baumwolltricot, gebleicht und mercerisiert, werden bei einer Flottenaufnahme von 90 % mit einer Zubereitung foulardiert, die im Liter
35 g des quaternären Ammoniumsalzes der Formel (4)
30 ml Natriumhydroxidlösung (30 %)
enthält. Nach dem Foulardieren wird das Tricot nass aufgerollt und in einem Plastiksack 18 Stunden bei Raumtemperatur gelagert. Anschliessend wird die Ware kalt und heiss gespült. Example 3: 20 g of cotton tricot, bleached and mercerized, are padded with a preparation in a liter of 90% with a liquor absorption
35 g of the quaternary ammonium salt of the formula (4)
30 ml sodium hydroxide solution (30%)
contains. After padding, the tricot is rolled up wet and stored in a plastic bag for 18 hours at room temperature. The goods are then rinsed cold and hot.
Das vorbehandelte Tricot wird zusammen mit 20 g nicht-behandeltem Tricot in einer wässerigen Färbeflotte bei 50°C eingenetzt, welche bei einem Flottenverhältnis von 1:40 1 % des Farbstoffes Direct Blue 71 C.I. 43140 enthält Man steigert innert 30 Minuten die Temperatur auf 98°C und färbt 45 Minuten bei dieser Temperatur.The pretreated tricot is wetted together with 20 g of untreated tricot in an aqueous dye liquor at 50 ° C., which, at a liquor ratio of 1:40, 1% of the dye Direct Blue 71 C.I. 43140 contains. The temperature is raised to 98 ° C. within 30 minutes and dyeing is carried out at this temperature for 45 minutes.
Man erhält 2 Tricotstücke, wobei das vorbehandelte Stück tiefblau gefärbt ist, während das nicht-vorbehandelte Material nur leicht angefärbt ist.2 pieces of tricot are obtained, the pretreated piece being colored deep blue, while the non-pretreated material is only slightly stained.
Beispiel 4: Das gemäss Beispiel 3 vorbehandelte Tricot wird zusammen mit 20 g nichtvorbehandeltem Tricot bei 98°C in einer wässerigen Flotte eingenetzt, welche bei einem Flottenverhältnis von 1:30
1 % des Farbstoffes der Formel
enthält. Hierauf senkt man die Temperatur innert 30 Minuten auf 85°C, fügt
5 g/l Natriumcarbonat calc.
2 ml/l Natriumhydroxidlösung (30 %)
hinzu und behandelt das Material weitere 45 Minuten bei 85°C. Anschliessend werden die Färbungen 5 Minuten in kochendem Wasser gespült. Example 4: The tricot pretreated according to example 3 is wetted together with 20 g of untreated tricot at 98 ° C. in an aqueous liquor which has a liquor ratio of 1:30
1% of the dye of the formula
contains. The temperature is then reduced to 85 ° C. within 30 minutes, adds
5 g / l sodium carbonate calc.
2 ml / l sodium hydroxide solution (30%)
and treat the material for a further 45 minutes at 85 ° C. The dyeings are then rinsed in boiling water for 5 minutes.
Man erhält 2 Tricots, wobei das vorbehandelte Tricot tiefrot gefärbt ist, während das nichtvorbehandelte Material nur leicht rosa gefärbt ist.Two tricots are obtained, the pretreated tricot having a deep red color, while the non-pretreated material is only slightly pink in color.
Beispiel 5: Das gemäss Beispiel 3 vorbehandelte Tricot wird zusammen mit 20 g nichtvorbehandeltem Tricot und 20 g von auf gleiche Weise, jedoch nur mit 30 ml/l Natriumhydroxidlösung (30 %) behandeltem Tricot in einer wässerigen Flotte bei 50°C eingenetzt, die bei einem Flottenverhältnis von 1:40, 1 % eines Farbstoffes der Formel
enthält. Hierauf färbt man das Material 40 Minuten bei 50°C und spült es anschliessend 5 Minuten warm. Example 5: The tricot pretreated according to example 3 is wetted together with 20 g of non-pretreated tricot and 20 g of tricot treated in the same way, but only with 30 ml / l sodium hydroxide solution (30%) in an aqueous liquor at 50.degree a liquor ratio of 1:40, 1% of a dye of the formula
contains. The material is then dyed for 40 minutes at 50 ° C and then rinsed warm for 5 minutes.
Man erhält 3 Tricotstücke, wobei das gemäss Beispiel 3 vorbehandelte Tricot tiefrot gefärbt ist, während die 2 übrigen Tricotstücke nur leicht angefärbt sind.3 tricot pieces are obtained, the tricot pretreated according to example 3 being colored deep red, while the other 2 tricot pieces are only slightly colored.
Claims (10)
- A process for improving the colour yield and the wet fastness properties of dyeings or prints produced with anionic dyes on cellulose fibre material, which comprises treating the fibre material before dyeing or during dyeing with a quaternary ammonium salt of the formula
R is C₁-C₃alkyl, X is the group - A process according to claim 1, wherein R in formula (1) is methyl or ethyl.
- A process according to any one of claims 1 to 3, wherein Q- in formula (1) is the methyl sulfate ion or ethyl sulfate ion.
- A process according to any one of claims 1 to 5, wherein the treatment is carried out semicontinuously in accordance with the cold pad-batch method.
- A process according to any one of claims 1 to 6, wherein the treatment is carried out in accordance with the cold pad-batch method and during the dyeing.
- A process according to any one of claims 1 to 7, wherein the treatment is carried out from an alkaline medium.
- A process according to any one of claims 1 to 8, wherein the treatment is carried out to improve the colour yield and the wet fastness properties of dyeings produced with direct dyes.
- A process according to any one of claims 1 to 9, wherein the quaternary ammonium salt of the formula (1) is obtained by reacting a tertiary diallylamine of the formula
(3) Z-SO₂-OR
in which Z is an aryl radical or -OR and R is as defined in claims 1 to 9.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CH84890 | 1990-03-15 | ||
| CH848/90 | 1990-03-15 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0447352A1 EP0447352A1 (en) | 1991-09-18 |
| EP0447352B1 true EP0447352B1 (en) | 1994-12-21 |
Family
ID=4196621
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP91810016A Expired - Lifetime EP0447352B1 (en) | 1990-03-15 | 1991-01-10 | Process for improving the yield and the wet fastness of the dyeing or printing with anionic dyes of cellulosic fibrous material |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US5147411A (en) |
| EP (1) | EP0447352B1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JPH04214479A (en) |
| DE (1) | DE59103947D1 (en) |
| PT (1) | PT96523B (en) |
| ZA (1) | ZA91377B (en) |
Families Citing this family (16)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB9120227D0 (en) * | 1991-09-23 | 1991-11-06 | Ici Plc | Printing process and pretreatment composition |
| AU677587B2 (en) * | 1992-06-04 | 1997-05-01 | Ciba Specialty Chemicals Holding Inc. | Process for the fixation of dyes containing at least one polymerisable double bond by means of ionising radiation |
| EP0591108B1 (en) * | 1992-10-01 | 1996-06-05 | Ciba-Geigy Ag | Process for dyeing of wool containing fiber materials |
| EP0719357B1 (en) * | 1993-09-16 | 1998-01-14 | Ciba SC Holding AG | Thermofixing of dyes in presence of polymerizable compound and an initiator |
| US5698476A (en) * | 1995-03-01 | 1997-12-16 | The Clorox Company | Laundry article for preventing dye carry-over and indicator therefor |
| DE19509982A1 (en) * | 1995-03-18 | 1996-09-19 | Sandoz Ag | Textile aftertreatment |
| US5667533A (en) * | 1996-02-07 | 1997-09-16 | The Virkler Company | Heather dyed fabric and method of producing same |
| US5833720A (en) * | 1996-04-29 | 1998-11-10 | Kent; Johnny Joe | Energy efficient dyeing method |
| GB9703813D0 (en) * | 1997-02-24 | 1997-04-16 | Ici Plc | Dyeing of textiles |
| US6323306B1 (en) | 1998-09-08 | 2001-11-27 | Ciba Specialty Chemicals Water Treatments Ltd. | Preparation of water-soluble cross-linked cationic polymers |
| KR101129505B1 (en) * | 2003-07-14 | 2012-03-29 | 시바 홀딩 인크 | Hydrogen peroxide catalyzed process for the preparation of sterically hindered N-hydrocarbyloxyamines |
| WO2005123581A1 (en) * | 2004-06-09 | 2005-12-29 | University Of Florida Research | Ultralyophobe interfaces |
| CN101360764B (en) * | 2005-11-14 | 2011-12-14 | 西巴控股公司 | Preparation of functionalized cationic polymers and their preparation and application in personal care |
| BRPI0821229A2 (en) * | 2007-12-20 | 2017-01-10 | Basf Se | personal care composition, method for treating mammalian keratin-containing fiber conditioning, and cationic terpolymer |
| JP6453239B2 (en) * | 2013-01-25 | 2019-01-16 | カラーゼン、エルエルシー | Fiber processing for improved dyeability |
| KR102513061B1 (en) * | 2017-04-14 | 2023-03-22 | 니토 보세키 가부시기가이샤 | Wet friction fastness improver for cellulosic fibers, method for producing dyed cellulosic fibers using the same, and uses thereof |
Family Cites Families (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE2812307A1 (en) * | 1978-03-21 | 1979-10-04 | Basf Ag | DISPERSION COLOR PREPARATIONS |
| JPS6071786A (en) * | 1983-09-28 | 1985-04-23 | 第一工業製薬株式会社 | Dyeing fastness enhancing method |
| JPS60110987A (en) * | 1983-11-15 | 1985-06-17 | 日東紡績株式会社 | Enhancement of dyeing fastness |
| JPS61133213A (en) * | 1984-11-30 | 1986-06-20 | Sumitomo Chem Co Ltd | Diallylamine copolymer, production thereof and color fastness enhancer containing same |
| JPS61231283A (en) * | 1985-04-01 | 1986-10-15 | 日東紡績株式会社 | Enhancement of dye fastness |
| DE3626410A1 (en) * | 1985-08-08 | 1987-02-19 | Ciba Geigy Ag | Process for pad dyeing cellulose textile materials |
| DE3720508A1 (en) * | 1986-07-02 | 1988-01-07 | Sandoz Ag | Water-soluble polymer of diallylamine |
| CH677857B5 (en) * | 1986-07-02 | 1992-01-15 | Sandoz Ag | |
| DE3706176A1 (en) * | 1987-02-26 | 1988-09-08 | Sandoz Ag | MIX WITH SYNERGISTIC PROPERTIES |
-
1991
- 1991-01-10 DE DE59103947T patent/DE59103947D1/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1991-01-10 EP EP91810016A patent/EP0447352B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1991-01-18 PT PT96523A patent/PT96523B/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1991-01-18 JP JP3004459A patent/JPH04214479A/en active Pending
- 1991-01-18 ZA ZA91377A patent/ZA91377B/en unknown
- 1991-03-11 US US07/667,720 patent/US5147411A/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| PT96523B (en) | 1998-06-30 |
| DE59103947D1 (en) | 1995-02-02 |
| US5147411A (en) | 1992-09-15 |
| JPH04214479A (en) | 1992-08-05 |
| EP0447352A1 (en) | 1991-09-18 |
| ZA91377B (en) | 1991-08-28 |
| PT96523A (en) | 1991-10-15 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0447352B1 (en) | Process for improving the yield and the wet fastness of the dyeing or printing with anionic dyes of cellulosic fibrous material | |
| EP0040790B2 (en) | Process for dyeing and printing textile materials containing hydroxyl and/or carbon-amide groups | |
| EP1247842B1 (en) | Fiber-reactive anthraquinone dyes, their preparation and use | |
| DE2726433A1 (en) | PROCESS FOR IMPROVING THE COLOR YIELD AND THE FASTENNESSES OF COLORS, CATIONIC FIBER-REACTIVE COMPOUNDS AND THEIR PRODUCTION | |
| EP0359188B1 (en) | Dyeing and printing process of cellulose fibres in the absence of alkali or reducing agents | |
| CH525997A (en) | Method for reserving textile fiber material made from synthetic polyamides | |
| DE2407147A1 (en) | QUARTER N-(2,3-EPOXYALKYL)AMMONIUM COMPOUNDS | |
| EP0259251B1 (en) | Cationic compounds from the reaction of carbamides with epihalogen hydrines | |
| DE3539117A1 (en) | Bis-imidazolium salts | |
| EP0250365B1 (en) | Process for the after-treatment of dyed cellulosic fibrous material | |
| DE2238552A1 (en) | METHOD OF DYING CELLULOSE TEXTILES | |
| DE2527962A1 (en) | METHOD FOR TREATMENT OF CELLULOSE FIBERS | |
| DE3829974A1 (en) | QUATERNATED CONDENSATION PRODUCTS | |
| EP0438380B1 (en) | Polymerized quaternary diallylammonium compounds | |
| EP0225282A1 (en) | Process for the post-treatment of dyed cellulosic fibrous material | |
| DE2124617B2 (en) | METHOD FOR GENERATING MULTITONE EFFECTS ON FIBER MATERIAL MADE FROM POLYACRYLNITRILE OR POLYACRYLNITRILE COPOLYMERS | |
| EP0012294B1 (en) | Quaternary reactive compounds, their preparation and their application to increase the affinity of anionic dyestuffs to fibres containing nitrogen or hydroxyl groups | |
| EP0188999B1 (en) | Cationic reaction products from 1-aminoalkyl imidazole compounds and epihalogen hydrins | |
| DE3539116A1 (en) | Process for improving the dye yield and the wet fastnesses of dyeings or prints produced on cellulose fibre material using anionic dyestuffs | |
| EP0950751B1 (en) | Process for the treatment of cellulose fibers | |
| DE2343317C3 (en) | ||
| EP0591108B1 (en) | Process for dyeing of wool containing fiber materials | |
| DE2343317A1 (en) | TEXTILE COLORING AND PRINTING PROCESS | |
| EP0474594B1 (en) | Process for dyeing of wool and mixtures thereof with other fibres with reactive dyestuffs | |
| DE3626410A1 (en) | Process for pad dyeing cellulose textile materials |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19910114 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): BE CH DE ES FR GB IT LI |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19940223 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): BE CH DE ES FR GB IT LI |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: THE PATENT HAS BEEN ANNULLED BY A DECISION OF A NATIONAL AUTHORITY Effective date: 19941221 |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 59103947 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19950202 |
|
| ITF | It: translation for a ep patent filed | ||
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) |
Effective date: 19950209 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| ITTA | It: last paid annual fee | ||
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PUE Owner name: CIBA-GEIGY AG TRANSFER- CIBA SC HOLDING AG |
|
| BECN | Be: change of holder's name |
Effective date: 19961129 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: TP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PFA Free format text: CIBA SC HOLDING AG TRANSFER- CIBA SPECIALTY CHEMICALS HOLDING INC. |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: 732E |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: CD |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 19981130 Year of fee payment: 9 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Payment date: 19981207 Year of fee payment: 9 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 19981210 Year of fee payment: 9 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 19981216 Year of fee payment: 9 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Payment date: 19990324 Year of fee payment: 9 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20000110 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20000131 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20000131 Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20000131 |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: CIBA SPECIALTY CHEMICALS HOLDING INC. Effective date: 20000131 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20000110 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20000929 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20001101 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES;WARNING: LAPSES OF ITALIAN PATENTS WITH EFFECTIVE DATE BEFORE 2007 MAY HAVE OCCURRED AT ANY TIME BEFORE 2007. THE CORRECT EFFECTIVE DATE MAY BE DIFFERENT FROM THE ONE RECORDED. Effective date: 20050110 |