EP0303378A2 - Fuel injection pumping apparatus - Google Patents
Fuel injection pumping apparatus Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0303378A2 EP0303378A2 EP88307066A EP88307066A EP0303378A2 EP 0303378 A2 EP0303378 A2 EP 0303378A2 EP 88307066 A EP88307066 A EP 88307066A EP 88307066 A EP88307066 A EP 88307066A EP 0303378 A2 EP0303378 A2 EP 0303378A2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- engine
- fuel
- lever
- pressure pump
- arm
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F02—COMBUSTION ENGINES; HOT-GAS OR COMBUSTION-PRODUCT ENGINE PLANTS
- F02M—SUPPLYING COMBUSTION ENGINES IN GENERAL WITH COMBUSTIBLE MIXTURES OR CONSTITUENTS THEREOF
- F02M59/00—Pumps specially adapted for fuel-injection and not provided for in groups F02M39/00 -F02M57/00, e.g. rotary cylinder-block type of pumps
- F02M59/44—Details, components parts, or accessories not provided for in, or of interest apart from, the apparatus of groups F02M59/02 - F02M59/42; Pumps having transducers, e.g. to measure displacement of pump rack or piston
- F02M59/447—Details, components parts, or accessories not provided for in, or of interest apart from, the apparatus of groups F02M59/02 - F02M59/42; Pumps having transducers, e.g. to measure displacement of pump rack or piston means specially adapted to limit fuel delivery or to supply excess of fuel temporarily, e.g. for starting of the engine
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F02—COMBUSTION ENGINES; HOT-GAS OR COMBUSTION-PRODUCT ENGINE PLANTS
- F02D—CONTROLLING COMBUSTION ENGINES
- F02D1/00—Controlling fuel-injection pumps, e.g. of high pressure injection type
- F02D1/02—Controlling fuel-injection pumps, e.g. of high pressure injection type not restricted to adjustment of injection timing, e.g. varying amount of fuel delivered
- F02D1/04—Controlling fuel-injection pumps, e.g. of high pressure injection type not restricted to adjustment of injection timing, e.g. varying amount of fuel delivered by mechanical means dependent on engine speed, e.g. using centrifugal governors
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F02—COMBUSTION ENGINES; HOT-GAS OR COMBUSTION-PRODUCT ENGINE PLANTS
- F02D—CONTROLLING COMBUSTION ENGINES
- F02D1/00—Controlling fuel-injection pumps, e.g. of high pressure injection type
- F02D1/02—Controlling fuel-injection pumps, e.g. of high pressure injection type not restricted to adjustment of injection timing, e.g. varying amount of fuel delivered
- F02D1/06—Controlling fuel-injection pumps, e.g. of high pressure injection type not restricted to adjustment of injection timing, e.g. varying amount of fuel delivered by means dependent on pressure of engine working fluid
- F02D1/065—Controlling fuel-injection pumps, e.g. of high pressure injection type not restricted to adjustment of injection timing, e.g. varying amount of fuel delivered by means dependent on pressure of engine working fluid of intake of air
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F02—COMBUSTION ENGINES; HOT-GAS OR COMBUSTION-PRODUCT ENGINE PLANTS
- F02M—SUPPLYING COMBUSTION ENGINES IN GENERAL WITH COMBUSTIBLE MIXTURES OR CONSTITUENTS THEREOF
- F02M41/00—Fuel-injection apparatus with two or more injectors fed from a common pressure-source sequentially by means of a distributor
- F02M41/08—Fuel-injection apparatus with two or more injectors fed from a common pressure-source sequentially by means of a distributor the distributor and pumping elements being combined
- F02M41/14—Fuel-injection apparatus with two or more injectors fed from a common pressure-source sequentially by means of a distributor the distributor and pumping elements being combined rotary distributor supporting pump pistons
- F02M41/1405—Fuel-injection apparatus with two or more injectors fed from a common pressure-source sequentially by means of a distributor the distributor and pumping elements being combined rotary distributor supporting pump pistons pistons being disposed radially with respect to rotation axis
- F02M41/1411—Fuel-injection apparatus with two or more injectors fed from a common pressure-source sequentially by means of a distributor the distributor and pumping elements being combined rotary distributor supporting pump pistons pistons being disposed radially with respect to rotation axis characterised by means for varying fuel delivery or injection timing
Definitions
- This invention relates to a fuel injection pumping apparatus for supplying fuel to a compression ignition engine and of the kind comprising a high pressure pump operable in timed relationship with the engine, means including a low pressure pump for supplying fuel to the high pressure pump and a component forming part of the high pressure pump which is adjustable to determine the maximum amount of fuel which can be supplied by the high pressure pump.
- the high pressure pump comprises a plunger which is located within a transverse bore formed in a rotary distributor member which is driven in timed relationship with the associated engine.
- the plunger is moved outwardly by fuel supplied to the bore and inwardly to deliver fuel through an outlet to the associated engine, by a cam lobe formed on the internal peripheral surface of an annular cam.
- the aforesaid component comprises a stop ring which is angularly adjustable about the axis of rotation of the distributor member and which defines an internal stop surface which limits the outward movement of the plunger and thereby the amount of fuel which can flow into the bore for subsequent delivery to the associated engine.
- torque control means the modification of the maximum amount of fuel which can be supplied by the apparatus in accordance with the engine speed.
- torque control is to reduce the maximum amount of fuel which can be supplied by the apparatus as the engine speed approaches its allowed maximum value.
- other adjustments of the maximum fuel quantity may also be required in accordance with a varying engine operating parameter. For example in a turbo supercharged engine it is desirable to be able to adjust the fuel quantity in accordance with the air pressure in the engine air inlet manifold so that when the air pressure is low the maximum amount of fuel which can be supplied is reduced as compared with the situation when the turbo supercharger is in full operation. In another example it may be necessary to provide additional torque control in another part of the engine speed range.
- the object of the present invention is to provide an apparatus of the kind specified in a simple and convenient form.
- an apparatus of the kind specified comprises a three arm pivotal lever, the first and second arms being operatively connected to first and second engine operating parameter responsive devices which impart pivotal movement to the lever in response to a change in the engine operating parameter to which they are responsive, the third arm being connected to said component.
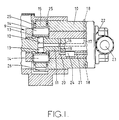
- the apparatus comprises a body part 10 in which is journalled a rotary cylindrical distributor member 11 in which is formed a transversely extending bore 12.
- the distributor member in use is driven in timed relationship with an associated engine, the distributor member for this purpose being coupled to a drive shaft shown.
- a pair of pumping plungers 13 Located in the bore is a pair of pumping plungers 13 at the outer ends of which are located cam followers each of which includes a roller 14.
- the rollers are engaged by cam lobes formed on the internal peripheral surface of an annular cam ring 15 which is located within the body part and which for the purpose of timing adjustment, may be angularly adjustable within the body part.
- the plungers and cam lobes form a high pressure pump 9.
- the longitudinal passage 16 communicates with a plurality of inlet passages 19 which are positioned to register in turn with an inlet port 20 formed in the body part and connected to the outlet 21 of a low pressure fuel supply pump 22 which has an inlet 23.
- the communication of the inlet port 20 with an inlet passage 19 occurs during the time when the plungers are allowed to move outwardly by the cam lobes and the quantity of fuel which is supplied to the bore during this period is controlled by a control device 24 which may for example be an adjustable throttle.
- a control device 24 which may for example be an adjustable throttle.
- a pair of stop rings 25 is provided, these being positioned on the opposite sides of the cam ring 15 and being mounted for angular adjustment within the body part.
- the internal surfaces of the stop rings are shaped to define stop surfaces for engagement by the rollers during outward movement of the plungers. The extent of outward movement of the plungers and therefore the maximum amount of fuel which can be supplied to the associated engine is determined by the angular setting of the stop rings.
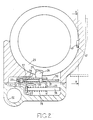
- the stop rings are connected together so that they move angularly in unison, by means of a saddle member 26 which, as shown in Figure 2, includes a base section 27 upstanding from which are a pair of spaced tongues 28 which engage within slots 29 respectively formed in the stop rings 25.
- the saddle member is located on one side of a support plate 30 which is secured within the body part and which is provided with a slot 31.
- a support plate 30 On the opposite side of the support plate 30 is a generally U-shaped member 32, the U-shaped member and the base section of the saddle member being secured together by rivets 33, there being located about each rivet, spacers 34 which slide in the slot 31.
- One limb 35 of the U-shaped member is provided with an aperture through which extends a spring locating rod 36 the rod being carried on a support 37 secured within the body part.
- a spring 38 Interposed between the support 37 and the limb 35 is a spring 38 the effect of which is to bias the saddle member and therefore the stop rings, towards a position to reduce the maximum amount of fuel which can be supplied to the associated engine.
- a stop means 39 is provided for engagement with the other limb 40 of the member 32 to determine the movement of the saddle member under the action of the spring 38 and the stop means forms part of a device responsive to an engine operating parameter and which will be explained.
- a pin 42 movable in a slot 43 is provided the pin being biased by means of a spring which is stronger than the spring 38.
- a fluid pressure operable piston (not shown) responsive to the outlet pressure of the low pressure pump 22 and which moves the pin against the action of the spring to allow the stop plates to move to the normal maximum fuel position as determined by the stop 39.
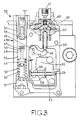
- the stop means 39 is seen to be one end of the one arm of a three armed lever 44 which carries a pivot pin 45 slidable in an elongated slot 46 in the support plate 30.
- the lever 44 is of "T" shaped form and the two other arms 47, 48 are of equal length and each terminate in an upstanding tang.
- the arm 47 its tang extends within a transverse opening formed in a piston 49 located within a cylinder 50.
- the piston forms part of a first engine operating parameter responsive device 49A.
- the ends of the cylinder are closed by plugs 51, 52, the plug 51 forming an abutment for a spring 54 interposed between the plug and a flanged tubular abutment against which bears a further spring 53 the other end of which engages the piston 49.
- a pin 55 is fixed in a bore in the piston and terminates in a spherical end in the opening therein.
- the pin external of the piston defines an enlarged portion about which is located the spring 53 and a reduced portion which guides the adjacent end of the tubular abutment and the spring 54.
- the plug 52 is formed in two parts the outer part 56 forming an adjustable stop for the piston 49 and the inner part 57 forming an adjustable abutment for a coiled spring 58 which acts on the piston in opposition to the springs 53, 54.
- a passage (not shown) is provided to allow fuel under pressure from the outlet of the supply pump 22 to act on the face of the piston 49 engaged by the spring 58.
- the tang on the arm 48 of the lever 44 is engaged by the spherical end of a push rod 59 which is operatively connected to a pressure responsive device 60 which includes an inlet 61.
- the inlet 61 is an air inlet which in use, is connected to the air inlet manifold of the associated engine which in this case is a turbo supercharged engine.
- the device includes a diaphragm 62 of annular form the outer peripheral rim of which is trapped between two parts of the housing of the apparatus.
- the inner peripheral rim of the diaphragm is sealed to a resiliently loaded carrier 63 which when the pressure of air in the inlet increases, urges the push rod 59 downwardly as seen in the drawing.
- Figures 2 and 3 show the parts in the position which they adopt for the purpose of excess fuel supply.
- the axes of movement of the pin 55 and the rod 59 are parallel to each other and to the slot 46, the slot being disposed midway between said axes.
- the piston 49 In operation, and ignoring for the moment the pressure responsive device 60, with an increase in the output pressure of the low pressure pump and when the preloading of the springs 53, 54 is overcome, the piston 49 will move and allow anti-clockwise movement of the lever 44 under the action of the spring 38. This allows the spring 38 to move the stop plates to reduce the maximum amount of fuel which can be supplied to the engine thereby providing torque control.
- the spring 58 and the inner part 57 of the plug 52 are provided for the purpose of adjusting the fuel pressure and therefore the engine speed, at which the piston 49 starts to move.
- the pin 45 slides along the slot 46 and the lever pivots about the spherical end of the push rod 59.
- the pressure responsive device may be replaced by a fuel pressure responsive device which modifies the maximum fuel quantity at a lower engine speed. It is also possible to reverse the piston 49 and the associated springs in the cylinder 50.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Combustion & Propulsion (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Fuel-Injection Apparatus (AREA)
- High-Pressure Fuel Injection Pump Control (AREA)
Abstract
Description
- This invention relates to a fuel injection pumping apparatus for supplying fuel to a compression ignition engine and of the kind comprising a high pressure pump operable in timed relationship with the engine, means including a low pressure pump for supplying fuel to the high pressure pump and a component forming part of the high pressure pump which is adjustable to determine the maximum amount of fuel which can be supplied by the high pressure pump.
- In one form of apparatus of the aforesaid kind the high pressure pump comprises a plunger which is located within a transverse bore formed in a rotary distributor member which is driven in timed relationship with the associated engine. The plunger is moved outwardly by fuel supplied to the bore and inwardly to deliver fuel through an outlet to the associated engine, by a cam lobe formed on the internal peripheral surface of an annular cam. The aforesaid component comprises a stop ring which is angularly adjustable about the axis of rotation of the distributor member and which defines an internal stop surface which limits the outward movement of the plunger and thereby the amount of fuel which can flow into the bore for subsequent delivery to the associated engine.
- It is known to provide such apparatus in a form in which what is known the art as "torque control" is obtained. Essentially this means the modification of the maximum amount of fuel which can be supplied by the apparatus in accordance with the engine speed. Usually the effect of torque control is to reduce the maximum amount of fuel which can be supplied by the apparatus as the engine speed approaches its allowed maximum value. However, other adjustments of the maximum fuel quantity may also be required in accordance with a varying engine operating parameter. For example in a turbo supercharged engine it is desirable to be able to adjust the fuel quantity in accordance with the air pressure in the engine air inlet manifold so that when the air pressure is low the maximum amount of fuel which can be supplied is reduced as compared with the situation when the turbo supercharger is in full operation. In another example it may be necessary to provide additional torque control in another part of the engine speed range.
- The object of the present invention is to provide an apparatus of the kind specified in a simple and convenient form.
- According to the invention an apparatus of the kind specified comprises a three arm pivotal lever, the first and second arms being operatively connected to first and second engine operating parameter responsive devices which impart pivotal movement to the lever in response to a change in the engine operating parameter to which they are responsive, the third arm being connected to said component.
- In the accompanying drawings:-
- Figure 1 is a diagrammatic sectional side elevation of one example of a pump,
- Figure 2 is a section to an enlarged scale of part of the pump shown in Figure 1, and
- Figure 3 is an inverted plan view of a part of the apparatus not seen in Figure 1.
- Referring to Figure 1 of the drawings the apparatus comprises a
body part 10 in which is journalled a rotarycylindrical distributor member 11 in which is formed a transversely extendingbore 12. The distributor member in use is driven in timed relationship with an associated engine, the distributor member for this purpose being coupled to a drive shaft shown. - Located in the bore is a pair of
pumping plungers 13 at the outer ends of which are located cam followers each of which includes aroller 14. The rollers are engaged by cam lobes formed on the internal peripheral surface of anannular cam ring 15 which is located within the body part and which for the purpose of timing adjustment, may be angularly adjustable within the body part. The plungers and cam lobes form ahigh pressure pump 9. - The portion of the bore lying intermediate the
plungers 13, communicates with apassage 16 extending longitudinally within the distributor member and at one point thepassage 16 communicates with adelivery passage 17 which is positioned to register in turn with a plurality ofoutlet ports 18 formed in the body part, the outlets in use being connected to the injection nozzles of the associated engine respectively. - At another point the
longitudinal passage 16 communicates with a plurality ofinlet passages 19 which are positioned to register in turn with aninlet port 20 formed in the body part and connected to theoutlet 21 of a low pressurefuel supply pump 22 which has aninlet 23. The communication of theinlet port 20 with aninlet passage 19 occurs during the time when the plungers are allowed to move outwardly by the cam lobes and the quantity of fuel which is supplied to the bore during this period is controlled by acontrol device 24 which may for example be an adjustable throttle. As the distributor member continues to rotate theinlet passage 19 moves out of register with theinlet port 20 and thedelivery passage 17 moves into register with anoutlet 18 to allow fuel displaced during the inward movement of the plungers to flow to the appropriate outlet. - In order to control the maximum amount of fuel which can be supplied by the pump to the associated engine, a pair of
stop rings 25 is provided, these being positioned on the opposite sides of thecam ring 15 and being mounted for angular adjustment within the body part. The internal surfaces of the stop rings are shaped to define stop surfaces for engagement by the rollers during outward movement of the plungers. The extent of outward movement of the plungers and therefore the maximum amount of fuel which can be supplied to the associated engine is determined by the angular setting of the stop rings. - The stop rings are connected together so that they move angularly in unison, by means of a
saddle member 26 which, as shown in Figure 2, includes abase section 27 upstanding from which are a pair of spacedtongues 28 which engage withinslots 29 respectively formed in thestop rings 25. The saddle member is located on one side of asupport plate 30 which is secured within the body part and which is provided with aslot 31. On the opposite side of thesupport plate 30 is a generally U-shapedmember 32, the U-shaped member and the base section of the saddle member being secured together byrivets 33, there being located about each rivet,spacers 34 which slide in theslot 31. - One
limb 35 of the U-shaped member is provided with an aperture through which extends aspring locating rod 36 the rod being carried on asupport 37 secured within the body part. Interposed between thesupport 37 and thelimb 35 is aspring 38 the effect of which is to bias the saddle member and therefore the stop rings, towards a position to reduce the maximum amount of fuel which can be supplied to the associated engine. Astop means 39 is provided for engagement with theother limb 40 of themember 32 to determine the movement of the saddle member under the action of thespring 38 and the stop means forms part of a device responsive to an engine operating parameter and which will be explained. - For the purpose of starting the associated engine an excess of fuel must be supplied, the excess quantity being greater than the normal maximum quantity of fuel. In order to move the stop rings to permit an excess of fuel to be supplied, a
pin 42 movable in aslot 43 is provided the pin being biased by means of a spring which is stronger than thespring 38. Associated with the pin is a fluid pressure operable piston (not shown) responsive to the outlet pressure of thelow pressure pump 22 and which moves the pin against the action of the spring to allow the stop plates to move to the normal maximum fuel position as determined by thestop 39. - With reference to Figure 3, the stop means 39 is seen to be one end of the one arm of a three
armed lever 44 which carries a pivot pin 45 slidable in an elongated slot 46 in thesupport plate 30. Thelever 44 is of "T" shaped form and the twoother arms - In the case of the
arm 47 its tang extends within a transverse opening formed in apiston 49 located within acylinder 50. The piston forms part of a first engine operating parameter responsive device 49A. The ends of the cylinder are closed byplugs plug 51 forming an abutment for aspring 54 interposed between the plug and a flanged tubular abutment against which bears afurther spring 53 the other end of which engages thepiston 49. Apin 55 is fixed in a bore in the piston and terminates in a spherical end in the opening therein. The pin external of the piston defines an enlarged portion about which is located thespring 53 and a reduced portion which guides the adjacent end of the tubular abutment and thespring 54. Theplug 52 is formed in two parts theouter part 56 forming an adjustable stop for thepiston 49 and theinner part 57 forming an adjustable abutment for a coiledspring 58 which acts on the piston in opposition to thesprings supply pump 22 to act on the face of thepiston 49 engaged by thespring 58. - The tang on the
arm 48 of thelever 44 is engaged by the spherical end of apush rod 59 which is operatively connected to a pressureresponsive device 60 which includes aninlet 61. In the example theinlet 61 is an air inlet which in use, is connected to the air inlet manifold of the associated engine which in this case is a turbo supercharged engine. The device includes adiaphragm 62 of annular form the outer peripheral rim of which is trapped between two parts of the housing of the apparatus. The inner peripheral rim of the diaphragm is sealed to a resiliently loadedcarrier 63 which when the pressure of air in the inlet increases, urges thepush rod 59 downwardly as seen in the drawing. Figures 2 and 3 show the parts in the position which they adopt for the purpose of excess fuel supply. - The axes of movement of the
pin 55 and therod 59 are parallel to each other and to the slot 46, the slot being disposed midway between said axes. - In operation, and ignoring for the moment the pressure
responsive device 60, with an increase in the output pressure of the low pressure pump and when the preloading of thesprings piston 49 will move and allow anti-clockwise movement of thelever 44 under the action of thespring 38. This allows thespring 38 to move the stop plates to reduce the maximum amount of fuel which can be supplied to the engine thereby providing torque control. Thespring 58 and theinner part 57 of theplug 52 are provided for the purpose of adjusting the fuel pressure and therefore the engine speed, at which thepiston 49 starts to move. During the movement of the piston the pin 45 slides along the slot 46 and the lever pivots about the spherical end of thepush rod 59. - In like manner when the air pressure in the inlet manifold of the engine increases the
diaphragm 62 will cause thepush rod 59 to move downwardly thereby causing movement of the lever in the clockwise direction. This movement of the lever moves the U shapedmember 32 against the action of thespring 38 and the stop plates are moved to increase the maximum amount of fuel which can be supplied to the associated engine. The lever in this case pivots about its point of contact with the spherical end ofpin 55 with some sliding therebetween. - In practice the lever moves under the influence of both the
piston 49 and also the pressureresponsive device 60 in response to changes of engine speed and the air pressure in the air inlet manifold. If the distance between the lines of action of the piston and the push rod is made equal to the length of thearm 39 as measured from the pin 45, the ratio of 1:1 will be obtained for both air pressure and speed changes as compared with the movement of thesaddle member 26. - In the example increases in the engine speed and the inlet manifold pressure result in movement of the
lever 44 in the opposite direction. In some engine installations for example normally aspirated engines the pressure responsive device may be replaced by a fuel pressure responsive device which modifies the maximum fuel quantity at a lower engine speed. It is also possible to reverse thepiston 49 and the associated springs in thecylinder 50.
Claims (5)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| GB8718853 | 1987-08-08 | ||
| GB878718853A GB8718853D0 (en) | 1987-08-08 | 1987-08-08 | Fuel injection pumping apparatus |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0303378A2 true EP0303378A2 (en) | 1989-02-15 |
| EP0303378A3 EP0303378A3 (en) | 1989-07-19 |
Family
ID=10622042
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP88307066A Withdrawn EP0303378A3 (en) | 1987-08-08 | 1988-08-01 | Fuel injection pumping apparatus |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US4903661A (en) |
| EP (1) | EP0303378A3 (en) |
| JP (1) | JPH01187362A (en) |
| GB (1) | GB8718853D0 (en) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5957101A (en) * | 1997-07-09 | 1999-09-28 | Kohler Co. | Automatic compression release mechanism for an internal combustion engine |
| DE102013204327A1 (en) * | 2013-03-13 | 2014-09-18 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Cylinder head blank, cylinder head and high-pressure pump for fuel injection systems |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4120275A (en) * | 1975-06-28 | 1978-10-17 | Diesel Kiki Co., Ltd. | Engine fuel injection pump governor |
| GB2034814A (en) * | 1978-11-02 | 1980-06-11 | Bosch Gmbh Robert | Fuel injection pump for super charged diesel internal combustion engines |
| GB2061402A (en) * | 1979-10-20 | 1981-05-13 | Lucas Industries Ltd | Fuel injection pump |
| EP0118385A1 (en) * | 1983-03-04 | 1984-09-12 | Stanadyne Inc. | Fuel injection pump with plunger stroke control |
Family Cites Families (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB482864A (en) * | 1936-08-24 | 1938-04-06 | Saurer Ag Adolph | Improvements in and relating to the control of the fuel supply to internal combustion engines |
| FR2278928A1 (en) * | 1973-10-30 | 1976-02-13 | Sigma Diesel | IMPROVEMENTS TO THE FUEL FLOW CONTROL DEVICES FOR INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES |
| DE2526148C2 (en) * | 1975-06-12 | 1983-08-25 | Robert Bosch Gmbh, 7000 Stuttgart | Control device for the fuel supply of internal combustion engines |
| DE2747083A1 (en) * | 1977-10-20 | 1979-05-03 | Bosch Gmbh Robert | DEVICE FOR LIMITING THE FULL-LOAD INJECTION QUANTITY IN A CHARGED AIR-COMPRESSING INJECTION COMBUSTION ENGINE |
| DE2849093C2 (en) * | 1978-11-11 | 1987-01-22 | Klöckner-Humboldt-Deutz AG, 5000 Köln | Mechanical speed controller for an injection pump |
| GB2070134B (en) * | 1980-02-14 | 1983-08-17 | Lucas Industries Ltd | Liquid fuel injection pumping apparatus |
| DE3430141A1 (en) * | 1984-08-16 | 1986-02-27 | Robert Bosch Gmbh, 7000 Stuttgart | FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM FOR DIESEL INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES, ESPECIALLY FOR VEHICLE DIESEL ENGINES |
-
1987
- 1987-08-08 GB GB878718853A patent/GB8718853D0/en active Pending
-
1988
- 1988-08-01 EP EP88307066A patent/EP0303378A3/en not_active Withdrawn
- 1988-08-03 US US07/227,655 patent/US4903661A/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1988-08-08 JP JP63196208A patent/JPH01187362A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4120275A (en) * | 1975-06-28 | 1978-10-17 | Diesel Kiki Co., Ltd. | Engine fuel injection pump governor |
| GB2034814A (en) * | 1978-11-02 | 1980-06-11 | Bosch Gmbh Robert | Fuel injection pump for super charged diesel internal combustion engines |
| GB2061402A (en) * | 1979-10-20 | 1981-05-13 | Lucas Industries Ltd | Fuel injection pump |
| EP0118385A1 (en) * | 1983-03-04 | 1984-09-12 | Stanadyne Inc. | Fuel injection pump with plunger stroke control |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| GB8718853D0 (en) | 1987-09-16 |
| JPH01187362A (en) | 1989-07-26 |
| EP0303378A3 (en) | 1989-07-19 |
| US4903661A (en) | 1990-02-27 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0016718B1 (en) | Fuel injection system snubber valve assembly | |
| US4098249A (en) | Fuel injection pumping apparatus | |
| US4074667A (en) | Liquid fuel injection pumping apparatus | |
| GB2036381A (en) | Timing control for fuel injection pump | |
| US4903661A (en) | Fuel injection pumping apparatus | |
| US4358255A (en) | Liquid fuel injection pumping apparatus | |
| US4359995A (en) | Fuel injection pumping apparatus | |
| US4299542A (en) | Fuel injection pumping apparatus | |
| US4055387A (en) | Liquid fuel injection pumping apparatus | |
| AU570877B2 (en) | Fuel injection pump with plunger stroke control | |
| US4050437A (en) | Liquid fuel injection pumping apparatus | |
| US3913546A (en) | Horsepower limiter and overfueling control mechanism | |
| US4380223A (en) | Liquid fuel injection pumping apparatus | |
| US4358256A (en) | Fuel injection pumping apparatus | |
| GB2068591A (en) | Fuel Injection Pumping Apparatus | |
| US2815741A (en) | Timing apparatus for fuel injection pump | |
| CA1047339A (en) | Liquid fuel injection pumping apparatus for internal combustion engines | |
| US4320733A (en) | Fuel pumping apparatus | |
| US4751903A (en) | Fuel pumping apparatus | |
| US5197441A (en) | Fuel injection pumping apparatus | |
| US4348995A (en) | Fuel pumping apparatus | |
| GB1569265A (en) | Fuel injection pumping apparatus | |
| US4930998A (en) | Fuel pump | |
| US3937199A (en) | Fuel injection pump | |
| EP0402014A2 (en) | Fuel injection pumping apparatus |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): DE ES FR GB IT |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): DE ES FR GB IT |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19891124 |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19910220 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE APPLICATION IS DEEMED TO BE WITHDRAWN |
|
| 18D | Application deemed to be withdrawn |
Effective date: 19910703 |