EP0286982A2 - Registering device - Google Patents
Registering device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0286982A2 EP0286982A2 EP88105590A EP88105590A EP0286982A2 EP 0286982 A2 EP0286982 A2 EP 0286982A2 EP 88105590 A EP88105590 A EP 88105590A EP 88105590 A EP88105590 A EP 88105590A EP 0286982 A2 EP0286982 A2 EP 0286982A2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- register
- cylinder
- cylinders
- plate
- plate cylinder
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 238000007639 printing Methods 0.000 claims description 23
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 13
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 claims description 4
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000003086 colorant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000018109 developmental process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007645 offset printing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000717 retained effect Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B41—PRINTING; LINING MACHINES; TYPEWRITERS; STAMPS
- B41F—PRINTING MACHINES OR PRESSES
- B41F33/00—Indicating, counting, warning, control or safety devices
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B41—PRINTING; LINING MACHINES; TYPEWRITERS; STAMPS
- B41F—PRINTING MACHINES OR PRESSES
- B41F13/00—Common details of rotary presses or machines
- B41F13/08—Cylinders
- B41F13/10—Forme cylinders
- B41F13/12—Registering devices
- B41F13/14—Registering devices with means for displacing the cylinders
Definitions
- the invention relates to a register setting device for a printing unit with three approximately Y-shaped, plate / blanket cylinder pairs comprising printing units, which have helical gear wheels on their axes, two of which are designed as double gears with opposite pitch on the journal of two rubber blanket cylinders and via a gear are in permanent tooth engagement with one another on the journal of the third rubber blanket cylinder, all cylinders being axially displaceable and the drive being initiated via a gearwheel arranged on a cylinder.
- a printing unit which preferably comprises three approximately Y-shaped printing units 1, 2, 3.
- a blanket cylinder 4 and a plate cylinder 5 are provided
- a blanket cylinder 6 and a plate cylinder 7 and in the printing unit 3 a blanket cylinder 8 and a plate cylinder 9 are provided.
- the cylinders 5 to 9 each have axle journals mounted on both sides in side walls 20, as is indicated for the cylinders 4, 5, 7, 8, 9 by the reference numerals 10 to 14.
- a printing carrier web 69 can preferably be provided with a double face print and an impression by the offset printing method.
- a print carrier web can be provided with four times face printing and double back pressure.
- the basic setting is similar to that described below.
- a triple face print ie a three-color print, can be applied in full use of the principle on which the invention is based, with the advantageous setting and readjustment of the side and circumferential register according to the invention having a particular effect for each color.
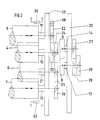
- Fig. 2 shows the cylinders 4, 5, 6, 7 mounted in a side wall 20 with their axle journals 10, 11, 12, 21.
- the cylinders 5 to 9 are driven by means of helical toothed drive gears 22 to 29, wherein in the example shown here in advantageously, the drive of a helical gear 68 is firmly connected to the gear 22 on the journal 11 of the cylinder 5.
- On the journal 10 of the blanket cylinder 4 sits a double gear 23, 24, which drives the gear 26 on the journal 12 of the plate cylinder 7 via a gear 25 on the journal 21 of the rubber blanket cylinder 6.
- a further printing unit 3 with the cylinders 8, 9 can be arranged above the printing units 1 and 2.
- the plate cylinder 9 of the printing unit 3 is driven via the gear 27 arranged on its journal 14, which meshes with a double gear 28, 29 on the journal 13 of the blanket cylinder 8.
- the gear 29 is in engagement with the gear 25 of the blanket cylinder 6.
- the drive is shown side by side for reasons of clarity, while in practice it is in two planes, i.e. is arranged one above the other.
- the gears 27, 28 thus lie in the plane of the gears 22, 23 and the gear 29 in the plane of the gears 24, 25, 26.
- the cylinders 4, 5, 7, 8, 9 are each provided with a register actuating device, preferably in the form of a register actuating motor, as indicated at 15, 16, 17, 18, 19. With the register actuators 15 to 19, the cylinders 4, 5, 7, 8, 9 can be axially displaced. According to the invention, therefore, a blanket cylinder, here the blanket cylinder 6, is not provided with a register actuating device, ie with a register actuating motor. In the context of the invention, it is advantageous to initiate the drive, preferably in the form of a gear 68 on the printing unit 1, ie to bring the drive gear 68 into engagement with the gear 22 of the plate cylinder 5.
- the register setting device comprises 15 to 19 position locking devices, for example linear potentiometers, with the aid of which the lateral position of the cylinders 4, 5, 7, 8, 9 can be determined in each case.
- a position locking device 30 is thus assigned to the plate cylinder 5 directly or to the register actuator 16 assigned to it.
- the blanket cylinder 4 to which or its servomotor 15 a position locking device 33 is assigned, while the plate cylinder 9 or its register servomotor 19 is assigned a position locking device 40.
- the cylinders 7 and 8 and their register actuators 17 and 18 are equipped with position locking devices 43 and 62, respectively.
- the motors 16, 17, 19 are connected to switches 32, 42, 64.
- two position regulators 34, 44 are used in the register actuating device according to the invention, of which the position regulator 34 can control the servomotor 15 and the position regulator 44 can actuate the servomotor 18.
- the position controllers 34, 44 are connected to the Position locking devices 30, 40, 62 connected.
- the position controller 34 receives information via the position locking device 30, ie an electrical signal that provides information about the position of the servomotor 16 or the axial position of the plate cylinder 5, and information about the position of the rubber cylinder 4 via the locking device 33. as at 65 or for the indicated on the cylinders at 66 and 67 due to the helical drive, there is a mechanical or positive connection between the cylinders 4 and 5.
- the plate cylinder 5 when the plate cylinder 5 is axially displaced, the latter rotates and, since the drive gear 68 does not rotate, the rotation of the plate cylinder 5 as a result of its axial displacement via the gear 22 causes a change in the circumferential register.
- the axial position of the plate cylinder 5 is displayed via the position locking device 30 on the display instrument 31 and the axial position of the blanket cylinder 4 on the display instrument 35. If the plate cylinder 5 now rotates due to axial displacement, this is communicated to the position controller 34 by the position locking device 30, which in the same Directs an axial displacement via the actuator 15 for the blanket cylinder 4, so that the rotation of the plate cylinder 5 is compensated.
- a side register adjustment of the plate cylinder 5 is possible, which automatically results in a compensation of the change in the circumferential register caused thereby.
- a servomotor 37 which together with the potentiometer 36 constitutes a so-called motor potentiometer, activates the position controller 34 by actuating a switch 38, so that the register servomotor 15 is activated correspondingly axially moves the blanket cylinder 4.
- the side register of the plate cylinder 7 is carried out according to the invention by its axial displacement by means of the register servomotor 17.
- the resulting rotation can now only affect the plate cylinder 9 via the cylinders 6 and 8, ie the circumferential setting of the plate cylinder 5 is no longer changed.
- the side register of the plate cylinder 9 is now set thirdly by means of its axial displacement, this only results in a rotation of the circumference of the plate cylinder 9. This also means that the circumference of the plate cylinder 5 is no longer changed.
- the influence on the plate cylinder 7 is compensated.
- the side register of the plate register 5 then the side register of the plate cylinder 7 and then the side register of the plate cylinder 9 are set.
- the plate cylinder 5 is held circumferentially as a result of the drive gear 68
- compensation for the circumferential register setting or a later correction of the side register settings of the plate cylinders 5, 7, 9 results in a compensation according to the invention in that circumferential displacement of the blanket cylinder 4 the plate cylinders 7 and 9 adjustable on the circumference of the plate cylinder 5, that is. are readjustable.
- the circumferential register of the plate cylinder 9 differs, compensation or adjustment is carried out in that the blanket cylinder 8 is axially displaced.
- the rotation of the plate cylinder 7 takes place by the axial displacement of the blanket cylinder 4, which, as already mentioned, the plate cylinder 5 can not rotate, so that by its shift caused rotation itself affects only as a rotation of the plate cylinder 7 and a rotation of the plate cylinder 9 also does not take place, since the blanket cylinder 8 is pushed in the same axial direction as the blanket cylinder 4, so that the axial displacement of the blanket cylinder 4 for adjusting the circumferential register of the plate cylinder 7 does not affect the circumferential register of the plate cylinder 9 affects.
- the setting of the peripheral register of the plate cylinder 5 is shown in FIG. 3, while the setting of the peripheral register of the plate cylinder 9 is shown in FIG. 4. 4, the side position of the plate cylinder 9 is again detected by means of the associated position locking element 40, the value of which is displayed on the instrument 41.
- a displacement of the plate cylinder 9 or the associated register servomotor 19 is communicated via the position fixing device 40, which communicates this value, which is also indicated at 41, to the position controller 44.
- the peripheral register of the plate cylinder 9 is set by the position controller 44 via the register servomotor 18 or the rubber blanket cylinder 8.
- the setpoint value for the circumferential register of the plate cylinder 9 can be adjusted by the potentiometer 46, a desired circumferential register value on the plate cylinder 9 being adjustable by actuating the switch 48 and thus the servomotor 47.
- both position controllers 34, 44 must be activated, which was indicated by the switch 49, if the circumferential register of the plate cylinder 7 is to be set, since, as has already been described above, the blanket cylinders 4 and 8 are axially displaced in this case Need to become. It is therefore sufficient to use only two position controllers 34, 44 for the circumferential register setting of the plate cylinders 5, 7, 9, which are activated individually according to FIGS. 3 and 4 for the circumferential register setting of the plate cylinders 5 and 9, while they are activated together must if the circumferential register of the plate cylinder 7 is to be set according to FIG.
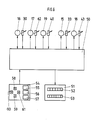
- FIG. 6 which comprises a microcomputer or microprocessor 50
- All actual values of the five cylinders are shown to it by the position locking devices 30, 62, 40; 33, 43 forwarded.
- the microprocessor 50 processes the target and actual values in accordance with the preceding descriptions and outputs the actuating signals to the register actuators 15 to 19 in the manner described above.
- For the compensation of the circumferential register due to the side register adjustment there is also a shift of the blanket cylinder 4 for the plate cylinder 5 of the blanket cylinder 8 for the blanket cylinder 9 and the blanket cylinder 4 and 8 for the plate cylinder 7.
- the circumferential register adjustment of the cylinders 5, 7, 9 can be described in FIG This is done in such a way that the circumferential register of the plate cylinder 5 by shifting the blanket cylinder 4, the circumferential register of the plate cylinder 7 by shifting the blanket cylinder 4 together with the blanket cylinder 8 and the setting of the circumferential register of the plate cylinder 9 by shifting the blanket cylinder 8.
- an operating keyboard 54 is connected to the microprocessor.
- This can advantageously have three buttons 55, 56, 57 for the three colors to be printed on one side of the print carrier web 69. If, for example, the first color is to be set in terms of the side and circumference registers, the button 55 is actuated, after which the circumferential registers on the corresponding plate cylinder in the forward and backward direction by means of Keys 60, 61 and the side register, that is adjustable in the left and right directions by means of the buttons 58, 59.
- the drive i.e. to introduce the drive gear 68 via the drive gear of the plate cylinder 7 or 9, only the setting sequence changing, which can be determined by simple considerations taking into account the preceding description.
- the drive can be introduced via the blanket cylinder 6 or in each case via the blanket cylinder, which has only a simple, that is to say no, double gear, although it is somewhat disadvantageous that in this case the blanket cylinders 4, 6, 8 are separated when they are switched off certain problems can occur from each other due to the drive.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Inking, Control Or Cleaning Of Printing Machines (AREA)
- Rotary Presses (AREA)
- Registering Or Overturning Sheets (AREA)
Abstract
Zur Umfangsregistereinstellung von drei Plattenzylindern (5, 7, 9) werden zwei bestimmte Gummituchzylinder (4, 8) axial verschoben. Die bei der Seitenregisterverstellung auftretende Umfangsregisteränderung wird durch einen Positionsregler (34, 44) bzw. einen Mikrorechner automatisch kompensiert. Die Einstellung des Seitenregisters erfolgt in einer vorgegebenen Weise, die von der Einleitung des fest angekoppelten Antriebes abhängt.To set the circumferential register of three plate cylinders (5, 7, 9), two specific blanket cylinders (4, 8) are axially displaced. The change in the circumferential register that occurs during the side register adjustment is automatically compensated by a position controller (34, 44) or a microcomputer. The page register is set in a predetermined manner, which depends on the introduction of the permanently coupled drive.
Description
Die Erfindung betrifft eine Registerstellvorrichtung für eine Druckeinheit mit drei etwa Y-förmig angeordneten, Platten-/Gummituchzylinderpaare umfassende Druckwerken, die schrägverzahnte Antriebsräder auf ihren Achsen aufweisen, von denen zwei als Doppelzahnräder mit entgegengesetzter Steigung ausgebildet auf Achszapfen zweier Gummituchzylinder angeordnet sind und über ein Zahnrad auf dem Achszapfen des dritten Gummituchzylinders miteinander in permanentem Zahneingriff stehen, wobei alle Zylinder axial verschiebbar sind und der Antrieb über ein auf einem Zylinder angeordneten Zahnrad eingeleitet wird.The invention relates to a register setting device for a printing unit with three approximately Y-shaped, plate / blanket cylinder pairs comprising printing units, which have helical gear wheels on their axes, two of which are designed as double gears with opposite pitch on the journal of two rubber blanket cylinders and via a gear are in permanent tooth engagement with one another on the journal of the third rubber blanket cylinder, all cylinders being axially displaceable and the drive being initiated via a gearwheel arranged on a cylinder.
Es ist bekannt, die Registereinstellung durch Verschiebung von Druckwerkzylindern vorzunehmen, wobei sich entsprechend des jeweils eingesetzten schrägverzahnten Antriebes zwangsläufig eine umfangsmäßige Drehung verschiedener Zylinder ergibt, die dann ebenfalls wieder kompensiert werden müssen, was zwangsläufig zeitaufwendig und diffizil ist. Durch die Verwendung von Kupplungen im Antrieb oder durch verschiebbare Zahnräder auf den Achszapfen läßt sich zwar eine einfachere und weniger zeitaufwendige Registereinstellung erreichen, jedoch erfordert dies einen erheblichen Aufwand und ist somit kostspielig.It is known to make the register setting by shifting printing unit cylinders, with a circumferential rotation of various cylinders inevitably corresponding to the helical-toothed drive used in each case, which then also have to be compensated for again, which is inevitably time-consuming and difficult. A simpler and less time-consuming register setting can be achieved by using couplings in the drive or by sliding gearwheels on the axle journal, but this requires considerable effort and is therefore expensive.
Aufgabe der Erfindung ist es, für einem mit auf den Achsstummeln angeordneten schrägverzahnten Zahnrädern aufgebauten Antrieb in einer Druckeinheit eine kostengünstige Registerstellvorrichtung zu schaffen, mit der schnell und sicher die Seiten- und Umfangsregistereinstellung und Nachregelung durchführbar ist. Diese Aufgabe wird durch die Anwendung der Merkmale des kennzeichnenden Teils des Anspruch 1 gelöst. Weiterbildungen der Erfindung ergeben sich aus den Unteransprüchen und aus der Beschreibung in Verbindung mit den Zeichnungen, in diesen zeigen schematisch:
- Fig. 1 Eine Druckeinheit mit der erfindungsgemäßen Registerein- und -nachstellung,
- Fig. 2 eine Darstellung des schrägverzahnten Antriebes der Druckeinheit gemäß Fig. 1,
- Fig. 3 bis 5 Blockschaltbilder der erfindungsgemäßen Registerstellvorrichtung und
- Fig. 6 eine weitere Ausführungsform der Steuerung als Blockschaltbild
- 1 shows a printing unit with the register adjustment and readjustment according to the invention,
- 2 shows the helical drive of the printing unit according to FIG. 1,
- 3 to 5 block diagrams of the register actuating device according to the invention and
- Fig. 6 shows another embodiment of the control as a block diagram
In Fig. 1 ist eine Druckeinheit dargestellt, die vorzugsweise drei etwa Y-förmig angeordnete Druckwerke 1, 2, 3 umfaßt. Im Druckwerk 1 ist ein Gummituchzylinder 4 und ein Plattenzylinder 5, im Druckwerk 2 ein Gummituchzylinder 6 und ein Plattenzylinder 7 und im Druckwerk 3 ein Gummituchzylinder 8 und ein Plattenzylinder 9 vorgesehen. Die Zylinder 5 bis 9 weisen jeweils beidseitig in Seitenwänden 20 gelagerte Achszapfen auf, wie für die Zylinder 4, 5, 7, 8, 9 durch die Bezugszeichen 10 bis 14 angedeutet ist. Vorzugsweise kann mit einer derartigen Druckeinheit eine Druckträgerbahn 69 nach dem Offsetdruckverfahren mit einem zweifachen Schöndruck und einem Widerdruck versehen werden. Bei zwei übereinander stehenden Y-Druckeinheit kann eine Druckträgerbahn mit vierfachem Schöndruck und zweifachem Widerdruck versehen werden. Die Grundeinstellung ist ähnlich wie nachfolgend beschrieben. Im Rahmen der Erfindung ist es jedoch auch möglich die Druckträgerbahn 69 bzw. 69ʹ um einen der Gummituchzylinder zu führen, beispielsweise um den Gummituchzylinder 4 oder 6, wobei dieser dann als Gegendruckzylinder dient und der zugeordnete Plattenzylinder 5 oder 7 mit einer Dilithoplatte belegt ist. Dadurch kann in voller Ausnützung des der Erfindung zugrundeliegenden Prinzips ein dreifacher Schöndruck also ein Dreifarbendruck aufgebracht werden, wobei sich besonders die erfindungsgemäße vorteilhafte Einstellung und Nachregelung des Seiten- und Umfangsregisters für jede Farbe auswirkt.In Fig. 1 a printing unit is shown, which preferably comprises three approximately Y-
Fig. 2 zeigt die in einer Seitenwand 20 mit ihren Achszapfen 10, 11, 12, 21 gelagerten Zylinder 4, 5, 6, 7. Die Zylinder 5 bis 9 werden mittels schrägverzahnter Antriebszahnräder 22 bis 29 angetrieben, wobei in dem hier gezeigten Beispiel in vorteilhafter Weise mit dem Zahnrad 22 auf dem Achszapfen 11 des Zylinders 5 der Antrieb eines schrägverzahnten Zahnrrades 68 fest verbunden ist. Auf dem Achszapfen 10 des Gummituchzylinders 4 sitzt ein Doppelzahnrad 23, 24, das über ein Zahnrad 25 auf dem Achszapfen 21 des Gumituchzylinders 6 das Zahnrad 26 auf dem Achszapfen 12 des Plattenzylinders 7 antreibt. Im Rahmen der Erfindung kann oberhalb der Druckwerke 1 und 2 ein weiteres Druckwerk 3 mit den Zylindern 8, 9 angeordnet werden. Dabei wird der Plattenzylinder 9 des Druckwerks 3 über das auf seinem Achszapfen 14 angeordnete Zahnrad 27 angetrieben, das in Eingriff mit einem Doppelzahnrad 28, 29 auf dem Achszapfen 13 des Gummituchzylinders 8 steht. Das Zahnrad 29 steht in Eingriff mit dem Zahnrad 25 des Gummituchzylinders 6. In Fig. 2 ist der Antrieb aus Übersichtsgründen nebeneinander dargestellt, während er in der Praxis in zwei Ebenen, d.h. übereinander angeordnet ist. Die Zahnräder 27, 28 liegen also in der Ebene der Zahnräder 22, 23 und das Zahnrad 29 in der Ebene der Zahnräder 24, 25, 26.Fig. 2 shows the
Gemäß der Erfindung sind die Zylinder 4, 5, 7, 8, 9 jeweils mit einer Registerstellvorrichtung versehen, und zwar vorzugsweise in Form eines Registerstellmotors, wie bei 15, 16, 17, 18, 19 angedeutet ist. Mit den Registerstellmotoren 15 bis 19 können also die Zylinder 4, 5, 7, 8, 9 axial verschoben werden. Gemäß der Erfindung ist also ein Gummituchzylinder, hier der Gummituchzylinder 6 nicht mit einer Registerstellvorrichtung, d.h. mit einem Registerstellmotor versehen. Im Rahmen der Erfindung ist es vorteilhaft, den Antrieb, vorzugsweise in Form eines Zahnrades 68 am Druckwerk 1 einzuleiten, d.h. das Antriebszahnrad 68 in Eingriff mit dem Zahnrad 22 des Plattenzylinders 5 zu bringen. Es ist jedoch auch möglich, den Antrieb über die Plattenzylinder 7 und 9 oder über den Gummituchzylinder 6 einzuleiten, wobei prinzipiell der gleiche Aufbau der erfindungsgemäßen Registerstellvorrichtung beibehalten werden kann, jedoch ergibt sich eventuell eine andere Abfolge der Einstellvorgänge. Im folgenden wird die Erfindung bei einem über den Plattenzylinder 5 des Druckwerkes 1 eingeleiteten Antriebes 68 beschrieben, d.h., daß bei den nachfolgend beschriebenen Einstellvorgängen durch Verschieben der Zylinder 4, 5, 7, 8, 9 der Plattenzylinder 5 seine Drehung nicht an das Antriebszahnrad 68 "weitergeben" kann, da dieses nicht drehbar bzw. fest mit dem Hauptantrieb verbunden ist.According to the invention, the
Die erfindungsgemäße Registereinstellvorrichtung umfaßt neben den Registerstellmotoren 15 bis 19 Positionsfeststellvorrichtungen, beispielsweise Linearpotentiometer, mit deren Hilfe jeweils die seitliche Position der Zylinder 4, 5, 7, 8, 9 ermittelt werden kann. So ist dem Plattenzylinder 5 direkt oder dem diesem zugeordneten Registerstellmotor 16 eine Positionsfeststellvorrichtung 30 zugeordnet. Das gleiche gilt für den Gummituchzylinder 4 dem oder dessen Stellmotor 15 eine Positionsfeststellvorrichtung 33 zugeordnet ist, während dem Plattenzylinder 9 oder dessen Registerstellmotor 19 eine Positionsfeststellvorrichtung 40 zugeordnet ist. Des weiteren sind die Zylinder 7 und 8 bzw. deren Registerstellmotoren 17 und 18 mit Positionsfeststellvorrichtungen 43 bzw. 62 ausgerüstet. Der Gummituchzylinder 6 weist hingegen weder einen Registerstellmotor noch eine Positionsfeststellvorrichtung im hier beschriebenen Ausführungsbeispiel auf, da gemäß der Erfindung lediglich zwei Gummituchzylinder, hier gummituchzylinder 4 und 8 für die Umfangsregistereinstellung eingesetzt werden, wie im nachfolgenden noch im einzelnen beschrieben wird. Die Motoren 16, 17, 19 sind mit Schaltern 32, 42, 64 verbunden.In addition to the register actuators, the register setting device according to the invention comprises 15 to 19 position locking devices, for example linear potentiometers, with the aid of which the lateral position of the
Des weiteren werden in der erfindungsgemäßen Registerstellvorrichtung zwei Positionsregler 34, 44 verwendet, von denen der Positionsregler 34 den Stellmotor 15 und der Positionsregler 44 den Stellmotor 18 ansteuern kann. Die Positionsregler 34, 44 sind über Leitungen mit den Positionsfeststellvorrichtungen 30, 40, 62 verbunden. Der Positionsregler 34 erhält über die Positionsfeststellvorrichtung 30 eine Information, d.h. ein elektrisches Signal, das Auskunft gibt, über die Position des Stellmotors 16 bzw. die axiale Position des Plattenzylinders 5, sowie über die Feststellvorrichtung 33 Auskunft über die Position des Gummizylinders 4. Da, wie bei 65 bzw. für die an den Zylindern bei 66 und 67 angedeutet infolge des schrägverzahnten Antriebes eine mechanische bzw. formschlüssige Verbindung zwischen den Zylindern 4 und 5 besteht. Dies bedeutet, daß bei beiner Axialverschiebung des Plattenzylinders 5 sich dieser dreht und, da sich das Antriebszahnrad 68 nicht mitdreht, die Drehung des Plattenzylinders 5 infolge seiner Axialverschiebung über das Zahnrad 22 eine Änderung des Umfangsregisters bewirkt. Außerdem wird die Axialposition des Plattenzylinders 5 über die Positionsfeststellvorrichtung 30 am Anzeigeninstrument 31 angezeigt und die Axialposition, des Gummituchzylinders 4 am Anzeigeinstrument 35. Dreht sich nun durch Axialverschiebung der Plattenzylinder 5, so wird dies durch die Positionsfeststellvorrichtung 30 dem Positionsregler 34 mitgeteilt, der in gleicher Richtung eine Axialverschiebung über den Stellmotor 15 für den Gummituchzylinder 4 einleitet, so daß die Drehung des Plattenzylinders 5 kompensiert wird. Somit ist also eine Seitenregistereinstellung des Plattenzylinders 5 möglich, wobei sich automatisch eine Kompensation der dadurch hervorgerufenen Umfangsregisteränderung ergibt. Soll nun das Umfangsregister des Plattenzylinders 5 eingestellt werden, was mittels des Potentiometers 36 möglich ist, wird durch Betätigen eines Schalters 38 ein Stellmotor 37, der zusammen mit dem Potentiometer 36 ein sogenanntes Motorpotentiometer darstellt, der Positionsregler 34 aktiviert, so daß der Registerstellmotor 15 in entsprechender Weise den Gummituchzylinder 4 axial verschiebt. Dadurch ergibt sich eine Drehung des Gummituchzylinders 4, durch die die Zylinder 6, 7, 8, 9 ebenfalls gedreht werden, was bedeutet, das umfangsmäßig die Plattenzylinder 7, 9 auf den Umfang, d.h. auf das Umfangsregister des Plattenzylinders 5 eingestellt werden.Furthermore, two
Nach erfolgter Grundeinstellung des Seitenregisters am Plattenzylinder 5 wird gemäß der Erfindung das Seitenregister des Plattenzylinders 7 durch dessen Axialverschiebung mittels des Registerstellmotors 17 durchgeführt. Die dadurch erfolgte Drehung kann sich nunmehr lediglich noch über die Zylinder 6 und 8 auf den Plattenzylinder 9 auswirken, d.h. die umfangsmäßige Einstellung des Plattenzylinders 5 wird nicht mehr verändert. Wird nunmehr als drittes das Seitenregister des Plattenzylinders 9 durch dessen Axialverschiebung eingestellt, ergibt sich lediglich eine Verdrehung des Umfangs des Plattenzylinders 9. Auch dadurch wird umfangsmäßig der Plattenzylinder 5 nicht mehr verändert. Durch Verschiebung des Gummituchzylinders 8 wird der Einfluß auf den Plattenzylinder 7 kompensiert. Es wird also zunächst das Seitenregister des Plattenregisters 5, dann das Seitenregister des Plattenzylinders 7 und dann das Seitenregister des Plattenzylinders 9 eingestellt. Unter der Berücksichtigung, das infolge des Antriebszahnrades 68 der Plattenzylinder 5 umfangsmäßig festgehalten wird, ergibt sich für die Umfangsmäßige Registereinstellung bzw. bei einer später erforderlichen Korrektur der Seitenregistereinstellungen der Plattenzylinder 5, 7, 9 eine erfindungsgemäße Kompensation dadurch, daß durch Axialverschiebung des Gummituchzylinders 4 umfangsmäßig die Plattenzylinder 7 und 9 auf den Umfang des Plattenzylinders 5 eingstellbar, d h. nachjustierbar sind. Weicht das Umfangsregister des Plattenzylinders 9 ab, so erfolgt eine Kompensation bzw. eine Anpassung dadurch, daß der Gummituchzylinder 8 axial verschoben wird. Die durch diese Verschiebung hervorgerufene Drehung kann dadurch weder eine Drehung des Plattenzylinders 5 noch eine Drehung des Plattenzylinders 7 bewirken. Soll das Umfangsregister des Plattenzylinders 7 nachgestellt werden, so müssen die Gummituchzylinder 4 und 8 axial verschoben werden. Durch den in Fig. 2 dargestellten Antrieb mit den beiden Doppelrädern 23, 24 bzw. 28, 29 erfolgt die Drehung des Plattenzylinders 7 durch die Axialverschiebung des Gummituchzylinders 4, der, wie bereits erwähnt den Plattenzylinder 5 ja nicht drehen kann, so daß die durch seine Verschiebung hervorgerufene Drehung sich ausschließlich als Drehung am Plattenzylinder 7 auswirkt und eine Drehung des Plattenzylinders 9 erfolgt auch nicht, da der Gummituchzylinder 8 in der gleichen Axialrichtung wie der Gummituchzylinder 4 geschoben wird, so daß sich die Axialverschiebung des Gummituchzylinders 4 zur Umfangsregistereinstellung des Plattenzylinders 7 auch nicht auf das Umfangsregister des Plattenzylinders 9 auswirkt.After the basic setting of the side register on the
Die Einstellung des Umfangsregisters des Plattenzylinders 5 geht, wie bereits vorangehend beschrieben wurde aus Fig. 3 hervor, während die Einstellung des Umfangsregisters des Plattenzylinders 9 in Fig. 4 dargestellt ist. Gemäß Fig. 4 wird auch wieder die Seitenposition des Plattenzylinders 9 mittels des zugeordneten Positionsfeststellelementes 40 erfaßt, dessen Wert am Instrument 41 angezeigt wird. Durch die mechanische Verbindung über 66 wird eine Verschiebung des Plattenzylinders 9 bzw. dem zugeordneten Registerstellmotor 19 über die Positionsfeststellvorrichtung 40 mitgeteilt, die diesen Wert, der bei 41 auch angezeigt wird, dem Positionsregler 44 mitteilt. Durch den Positionsregler 44 wird über den Registerstellmotor 18 bzw. über den Gummituchzylinder 8 das Umfangsregister des Plattenzylinders 9 eingestellt. Der Sollwert für das Umfangsregister des Plattenzylinders 9 ist durch das Potentiometer 46 einstellbar, wobei durch Betätigung des Schalters 48 und somit des Stellmotors 47 ein gewünschter Umfangsregisterwert am Plattenzylinder 9 einstellbar ist.As already described above, the setting of the peripheral register of the
Gemäß Fig. 5 müssen beide Positionsregler 34, 44 aktiviert werden, was durch den Schalter 49 angedeutet wurde, wenn das Umfangsregister des Plattenzylinders 7 eingestellt werden soll, da, wie bereits im vorangehenden beschrieben wurde, in diesem Fall die Gummituchzylinder 4 und 8 axial verschoben werden müssen. Es ist also ausreichend, für die Umfangsregistereinstellung der Plattenzylinder 5, 7, 9 lediglich zwei positionsregler 34, 44 zu verwenden, die gemäß Fig. 3 und 4 einzeln für die Umfangsregistereinstellung der Plattenzylinder 5 und 9 aktiviert werden, während sie zusammen aktiviert werden müssen, wenn gemäß Fig.5 das Umfangsregister des Plattenzylinders 7 eingestellt werden soll.5, both
Anstelle der in den Fig. 3 bis 5 dargestellten Schaltungen kann auch die in Fig. 6 dargestellte Anordnung in Rahmen der Erfindung mit Vorteil benutzt werden, die einen Mikrorechner bzw. Mikroprozessor 50 umfaßt. Diesem werden alle Istwerte der fünf Zylinder durch die Positionsfeststellvorrichtungen 30, 62, 40; 33, 43 zugeleitet. Der Mikroprozessor 50 verarbeitet die Soll- und Istwerte entsprechend den vorangehenden Beschreibungen und gibt die Stellsignale an die Registerstellmotoren 15 bis 19 in der vorbeschriebenen Weise. Für die Kompensation des Umfangsregisters infolge der Seitenregistereinstellung erfolgt ebenfalls eine Verschiebung der Gummituchzylinder 4 für den Plattenzylinder 5 des Gummituchzylinders 8 für den Gummituchzylinder 9 und des Gummituchzylinders 4 und 8 für den Plattenzylinder 7. Die Umfangsregistereinstellung der Zylinder 5, 7, 9 kann in der beschriebenen Weise dadurch erfolgen, daß das Umfangsregister des Plattenzylinders 5 durch Verschiebung des Gummituchzylinders 4, das Umfangsregister des Plattenzylinders 7 durch Verschiebung des Gummituchzylinders 4 zusammen mit dem Gummituchzylinder 8 und die Einstellung des Umfangsregisters des Plattenzylinders 9 durch Verschiebung des Gummituchzylinders 8 erfolgt.Instead of the circuits shown in FIGS. 3 to 5, the arrangement shown in FIG. 6, which comprises a microcomputer or
Ein weiterer Vorteil der Schaltung gemäß Fig. 6 besteht darin, daß neben einer Anzeige der Soll- und Istwerte mittels der Rückmeldungsanzeige 51 an einem Sollwertanzeiger 52 und einem Istwertanzeiger 53 mit dem Mikroprozessor 50 eine Bedienungstastatur 54 verbunden ist. Diese kann in vorteilhafter Weise für die drei auf einer Seite der Druckträgerbahn 69 aufzudruckenden drei Farben drei Taster 55, 56, 57 aufweisen. Soll beispielsweise die erste Farbe seiten- und umfangsregistermäßig eingestellt werden, so wird der Taster 55 betätigt, wonach in Vorwärts- und Rückwärtsrichtung das Umfangsregister an dem entsprechenden Plattenzylinder mittels der Tasten 60, 61 und das Seitenregister, d.h. in Linksrichtung und in Rechtsrichtung mittels der Taster 58, 59 einstellbar ist.Another advantage of the circuit according to FIG. 6 is that in addition to displaying the setpoint and actual values by means of the
Im Rahmen der Erfindung ist es möglich, den Antrieb, d.h. das Antriebszahnrad 68 auch über das Antriebszahnrad des Plattenzylinders 7 oder 9 einzubringen, wobei sich lediglich die Einstellfolge ändert, was durch einfache Überlegungen unter Berücksichtigung der vorangehenden Beschreibung ermittelt werden kann. Letztlich kann der Antrieb über den Gummituchzylinder 6 bzw. jeweils über den Gummituchzylinder eingebracht werden, der nur ein einfaches also kein Doppelzahnrad aufweist, wobei es allerdings etwas von Nachteil ist, daß in diesem Fall bei der Abstellung als Trennung der Gummituchzylinder 4, 6, 8 voneinander infolge des Antriebes gewisse Probleme auftreten können.Within the scope of the invention it is possible to drive, i.e. to introduce the
Claims (11)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE19873712702 DE3712702A1 (en) | 1987-04-14 | 1987-04-14 | REGISTER DEVICE |
| DE3712702 | 1987-04-14 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0286982A2 true EP0286982A2 (en) | 1988-10-19 |
| EP0286982A3 EP0286982A3 (en) | 1989-11-29 |
| EP0286982B1 EP0286982B1 (en) | 1992-06-10 |
Family
ID=6325635
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP88105590A Expired - Lifetime EP0286982B1 (en) | 1987-04-14 | 1988-04-08 | Registering device |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US4821640A (en) |
| EP (1) | EP0286982B1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JPS63264355A (en) |
| DE (2) | DE3712702A1 (en) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE3933666A1 (en) * | 1989-10-09 | 1991-04-18 | Heidelberger Druckmasch Ag | DEVICE AND METHOD FOR ADJUSTING THE REGISTER ON A PRINTING MACHINE WITH MULTIPLE PRINTING UNITS |
| DE4038510A1 (en) * | 1990-12-03 | 1992-06-04 | Roland Man Druckmasch | Index adjustment for printing unit with pref. three printing mechanisms - involves each mechanism having platen cylinder, and rubber sheet cylinder with inclined toothed drive gearwheels |
| NL2001608C2 (en) * | 2008-05-22 | 2009-11-24 | Mps Holding B V | Printing module for use in an offset printing device and offset printing device provided with such a printing module. |
Families Citing this family (17)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE3918127C1 (en) * | 1989-06-03 | 1990-12-13 | Man Roland Druckmaschinen Ag, 6050 Offenbach, De | |
| DE4021895C2 (en) * | 1990-07-10 | 1994-02-17 | Roland Man Druckmasch | Printing unit of an offset printing machine for performing a flying printing plate change |
| DE4110035C2 (en) * | 1991-03-27 | 1995-04-13 | Roland Man Druckmasch | Device for adjusting elements in folding cylinders of rotary printing machines |
| EP0652104B1 (en) * | 1993-11-05 | 2002-04-10 | MAN Roland Druckmaschinen AG | Printing unit for waterless offset printing |
| DE4430693B4 (en) | 1994-08-30 | 2005-12-22 | Man Roland Druckmaschinen Ag | Drives for a web-fed rotary offset printing machine |
| US6644184B1 (en) | 1995-02-09 | 2003-11-11 | Man Roland Druckmaschinen Ag | Offset printing machine |
| US5668455A (en) * | 1994-09-16 | 1997-09-16 | Gotz; Fritz Rainer | Angle encoder for rotating equipment |
| DE19508516A1 (en) * | 1995-03-10 | 1996-09-12 | Roland Man Druckmasch | Alignment mechanism for multicolour press printing on both sides |
| DE19508517A1 (en) * | 1995-03-10 | 1996-09-12 | Roland Man Druckmasch | Alignment adjustment esp. for offset printing press |
| DE10119140A1 (en) * | 2000-05-17 | 2001-11-22 | Heidelberger Druckmasch Ag | Printing and coating machine for processing printed sheets uses a modular run, a counter-pressure cylinder, a cylinder to adjust to it with tools to handle sheets of printed material and a circumferential register adjuster. |
| DE10164651A1 (en) | 2001-04-17 | 2002-10-31 | Koenig & Bauer Ag | Method and device for register control |
| DE10118759A1 (en) * | 2001-04-17 | 2002-11-07 | Koenig & Bauer Ag | Method for register control of a cylinder causes a drive to make the cylinder shift in an axial position for adjusting a side register after a change in the position of a rotational angle in a cylinder drive. |
| KR100501959B1 (en) * | 2003-02-06 | 2005-07-20 | 조충 | Rotary press |
| EP1593504A1 (en) * | 2004-05-04 | 2005-11-09 | Müller Martini Holding AG | Device with a frame and a coating unit attached thereon. |
| DE102005019566A1 (en) * | 2005-04-27 | 2006-11-09 | Bosch Rexroth Aktiengesellschaft | Printing machine and method for register correction |
| DE102018201968A1 (en) * | 2017-03-08 | 2018-09-13 | Heidelberger Druckmaschinen Ag | Method for reducing quasi-static registration differences in a printing machine |
| CN109501440B (en) * | 2018-09-28 | 2020-09-18 | 陕西北人印刷机械有限责任公司 | Version roller drive and horizontal automatic register set |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO1983004219A1 (en) * | 1982-06-01 | 1983-12-08 | Web Printing Controls Co., Inc. | Register control system |
| EP0154836A2 (en) * | 1984-03-14 | 1985-09-18 | Heidelberger Druckmaschinen Aktiengesellschaft | Registering device for rotary printing machines |
Family Cites Families (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4222325A (en) * | 1978-08-25 | 1980-09-16 | White Consolidated Industries, Inc. | Mounting means for movable carriage on an offset press |
| SE426153B (en) * | 1979-01-22 | 1982-12-13 | Wifag Maschf | DRIVE DEVICE FOR A ROLLER OFFSET PRESSURE MACHINE |
| US4572074A (en) * | 1984-11-14 | 1986-02-25 | Harris Graphics Corporation | Multi-unit press register |
| DD235049A1 (en) * | 1985-03-04 | 1986-04-23 | Polygraph Leipzig | CONTROL CIRCUIT |
| DD235050B1 (en) * | 1985-03-04 | 1988-09-21 | Polygraph Leipzig | CONTROL CIRCUIT |
| DE3614029C1 (en) * | 1986-04-25 | 1987-04-02 | Roland Man Druckmasch | Web-fed rotary offset printing machine with a printing unit for flying plate changes |
-
1987
- 1987-04-14 DE DE19873712702 patent/DE3712702A1/en not_active Ceased
-
1988
- 1988-04-08 DE DE8888105590T patent/DE3871845D1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1988-04-08 EP EP88105590A patent/EP0286982B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1988-04-13 US US07/181,310 patent/US4821640A/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1988-04-13 JP JP63089174A patent/JPS63264355A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO1983004219A1 (en) * | 1982-06-01 | 1983-12-08 | Web Printing Controls Co., Inc. | Register control system |
| EP0154836A2 (en) * | 1984-03-14 | 1985-09-18 | Heidelberger Druckmaschinen Aktiengesellschaft | Registering device for rotary printing machines |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE3933666A1 (en) * | 1989-10-09 | 1991-04-18 | Heidelberger Druckmasch Ag | DEVICE AND METHOD FOR ADJUSTING THE REGISTER ON A PRINTING MACHINE WITH MULTIPLE PRINTING UNITS |
| US5327826A (en) * | 1989-10-09 | 1994-07-12 | Heidelberger Druckmaschinen Ag | Register adjustment device on a printing machine with a plurality of printing units and method of operating the device |
| DE4038510A1 (en) * | 1990-12-03 | 1992-06-04 | Roland Man Druckmasch | Index adjustment for printing unit with pref. three printing mechanisms - involves each mechanism having platen cylinder, and rubber sheet cylinder with inclined toothed drive gearwheels |
| NL2001608C2 (en) * | 2008-05-22 | 2009-11-24 | Mps Holding B V | Printing module for use in an offset printing device and offset printing device provided with such a printing module. |
| WO2009142495A1 (en) * | 2008-05-22 | 2009-11-26 | Mps Holding B.V. | Printing module for use in an offset printing apparatus and offset printing apparatus provided with such a printing module |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP0286982B1 (en) | 1992-06-10 |
| DE3712702A1 (en) | 1988-11-03 |
| DE3871845D1 (en) | 1992-07-16 |
| JPS63264355A (en) | 1988-11-01 |
| EP0286982A3 (en) | 1989-11-29 |
| US4821640A (en) | 1989-04-18 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0286982B1 (en) | Registering device | |
| DE3435487C2 (en) | ||
| DE2818662C2 (en) | Device for setting the page and circumferential register of a plate cylinder of a rotary printing press | |
| EP0154836B1 (en) | Registering device for rotary printing machines | |
| EP0531675B1 (en) | Method and device for adjusting ink zone duct keys into their respective positions | |
| DE3432572A1 (en) | ROTARY PRESS PRESS | |
| DE3743646C2 (en) | Device for setting an amount of printing ink supplied in a printing press | |
| EP1243414A1 (en) | Printing method | |
| DE3045611C2 (en) | Register setting device of a sheet-fed rotary offset printing machine for simultaneous front and back printing | |
| EP1291175B1 (en) | Plate cylinder for several images | |
| DE3917919C2 (en) | ||
| DE3504435A1 (en) | BOW PRINTING MACHINE WITH BOWING SYSTEM ON A PRINTING MACHINE CYLINDER | |
| EP0705689B2 (en) | Drive for a multicolour sheet printing press | |
| DE3336792C2 (en) | ||
| DE2609513B2 (en) | Device for turning on and off an impression roller acting on the forme cylinder of a gravure printing machine | |
| DE3620152C2 (en) | Circuit arrangement for an offset printing press inking system | |
| EP0196019A2 (en) | Web-fed rotary offset printing machine with a printing unit for the flying-plate change | |
| DE4219147C5 (en) | Circumferential register setting device for an offset printing machine | |
| DE2364858C3 (en) | Mechanical control element with the option to save selected setting positions | |
| DE3832891A1 (en) | OFFSET PRINTING MACHINE FOR PRINTING A CONTINUOUS TRAIN | |
| DE4038510A1 (en) | Index adjustment for printing unit with pref. three printing mechanisms - involves each mechanism having platen cylinder, and rubber sheet cylinder with inclined toothed drive gearwheels | |
| DE4436584C2 (en) | Plate cylinder storage | |
| DE3246938A1 (en) | Printing machine having a forme cylinder, a forme inking roller and a back pressure cylinder | |
| DE3224649C2 (en) | ||
| DE102023110050B3 (en) | Method for producing a transmission actuator and a transmission actuator |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): CH DE FR IT LI SE |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): CH DE FR IT LI SE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19891028 |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19910325 |
|
| ITF | It: translation for a ep patent filed | ||
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): CH DE FR IT LI SE |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 3871845 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19920716 |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Payment date: 19930315 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 19930317 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Payment date: 19930322 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Effective date: 19940409 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Effective date: 19940430 Ref country code: CH Effective date: 19940430 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Effective date: 19941229 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| EUG | Se: european patent has lapsed |
Ref document number: 88105590.9 Effective date: 19941110 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 19980318 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20000201 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20050408 |