EP0240977A2 - Ventilating device for an air exchange according to the needs - Google Patents
Ventilating device for an air exchange according to the needs Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0240977A2 EP0240977A2 EP87105088A EP87105088A EP0240977A2 EP 0240977 A2 EP0240977 A2 EP 0240977A2 EP 87105088 A EP87105088 A EP 87105088A EP 87105088 A EP87105088 A EP 87105088A EP 0240977 A2 EP0240977 A2 EP 0240977A2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- ventilation
- air
- room
- ventilation device
- humidity
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24F—AIR-CONDITIONING; AIR-HUMIDIFICATION; VENTILATION; USE OF AIR CURRENTS FOR SCREENING
- F24F13/00—Details common to, or for air-conditioning, air-humidification, ventilation or use of air currents for screening
- F24F13/08—Air-flow control members, e.g. louvres, grilles, flaps or guide plates
- F24F13/18—Air-flow control members, e.g. louvres, grilles, flaps or guide plates specially adapted for insertion in flat panels, e.g. in door or window-pane
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24F—AIR-CONDITIONING; AIR-HUMIDIFICATION; VENTILATION; USE OF AIR CURRENTS FOR SCREENING
- F24F11/00—Control or safety arrangements
- F24F11/70—Control systems characterised by their outputs; Constructional details thereof
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24F—AIR-CONDITIONING; AIR-HUMIDIFICATION; VENTILATION; USE OF AIR CURRENTS FOR SCREENING
- F24F11/00—Control or safety arrangements
- F24F11/0001—Control or safety arrangements for ventilation
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24F—AIR-CONDITIONING; AIR-HUMIDIFICATION; VENTILATION; USE OF AIR CURRENTS FOR SCREENING
- F24F11/00—Control or safety arrangements
- F24F11/30—Control or safety arrangements for purposes related to the operation of the system, e.g. for safety or monitoring
- F24F11/46—Improving electric energy efficiency or saving
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24F—AIR-CONDITIONING; AIR-HUMIDIFICATION; VENTILATION; USE OF AIR CURRENTS FOR SCREENING
- F24F11/00—Control or safety arrangements
- F24F11/30—Control or safety arrangements for purposes related to the operation of the system, e.g. for safety or monitoring
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24F—AIR-CONDITIONING; AIR-HUMIDIFICATION; VENTILATION; USE OF AIR CURRENTS FOR SCREENING
- F24F2110/00—Control inputs relating to air properties
- F24F2110/10—Temperature
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24F—AIR-CONDITIONING; AIR-HUMIDIFICATION; VENTILATION; USE OF AIR CURRENTS FOR SCREENING
- F24F2110/00—Control inputs relating to air properties
- F24F2110/20—Humidity
Definitions
- Water vapor which is produced in a room sealed in this way by the people in it and, in addition, by plants as well as by water evaporation, water vapor-separating devices, devices and the like, increases the air humidity in the room, which is disadvantageous for the components enclosing the room can have an impact and adversely affect the indoor climate, ie be normalized again through a temporary, thorough ventilation with intensive air exchange between indoor and outdoor air, the air humidity and possibly also the air temperature.
- this type of ventilation can be the cause of an unfavorable heat balance, because the measure of the ventilation effect is usually the subjective feeling of the person doing the ventilation, which often leads to an unnecessarily long ventilation period with corresponding heat loss.
- the invention is based on a ventilation device for the demand-oriented exchange of air in a room with the outside air by means of a ventilation element having a changeable through opening for the air change. It is based on the task of creating such a device that enables an objective, optimal ventilation control with simple means and without the supply of auxiliary energy, while keeping the heat losses in the room low.
- a sensor which reacts to the humidity of the room air is provided for controlling the air exchange and which is designed as a mechanical actuator for continuously changing opening and closing of the passage opening depending on the room air humidity - or as a valve element itself.
- the invention is based on the principle that a significant simplification of the control of the demand-oriented air exchange can be effected if a sensor reacting to the humidity of the room air does not act via an auxiliary motor, but is designed so that it is designed as an actuator or as a valve closure element .
- the size of the actuating energy in such a ventilation element actuated directly by a sensor is not very large.
- a ventilation element controlled by a humidity sensor which is opened or closed by a sensor that responds to the temperature of the outside air. If the sensors are designed so that the temperature-controlled ventilation element remains closed at a low outside temperature and only opens gradually at higher outside temperatures, the dimensions of both ventilation elements and thus their inertia can be smaller. It also reduces heat loss in the room. It is also advantageous if the ventilation elements are low in friction and inertia me to form roller valves, the hollow cylinders of which can be rotated as control elements by a hygrophile fiber or a bimetal spiral.
- a vertical flat slide can be more appropriate.
- a band of hygrophilic parallel fibers is provided as a moisture sensor. It is reset by the slider's own weight.
- the ventilation device with two ventilation elements is suitable for separate and simultaneous control of air temperature and humidity in a room.
- a further development of the invention is particularly advantageous in which the size of the opening cross section is regulated by a combination of roller valves or slides depending on the humidity of the inside and the temperature of the outside air in such a way that the dew point temperature of the inside air is always lower than the lowest surface temperature of the Space enclosing areas.
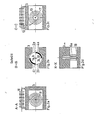
- the ventilation device shown in the figures (1a, 1b, 1c and 2a, 2b, 2c) comprises two roller valves 5a and 3b, respectively, in a common housing 3 about their separate axes, 14a and 14b. are rotatably arranged.
- Each roller valve essentially consists of a hollow cylinder, 1a or 1b, with axially parallel cutouts 2i and 2a, which is accommodated in a coaxial chamber, 31 or 32, housing 3.
- the chambers for housing the hollow cylinders are provided with cutouts, ventilation slots, 4i and 4a, which open to the room to be ventilated or to the outside air.
- the housing 3 forms a component which is to be installed in window frames or other facade areas.
- the roller valve 5a which serves to regulate the temperature, is actuated by the non-positively connected spiral spring 11 made of bimetal according to the principle of a metal thermometer, depending on the temperature of the air, through the ventilation slots 4i and 4a and through the cylinder cutouts 2i and 2a, which are assigned to the roller valve 5a , strokes.
- the intensity of the air change between the interior and outside air depends on the cross section of the free opening which is released for the air passing through through the roller valve 5a; it is dependent on the air temperature via the bimetal spring 11 and is determined by the covering parts of the axially parallel cutouts 2i and 2a of the hollow cylinder 1a and the ventilation slots 4i and 4a, which are assigned to the roller valve 5a.
- the spiral spring 11 provides both the actuating and the restoring force for the roller valve 5a.
- the coil spring shown made of bi-metal come within the scope of the invention as temperature-dependent regulating elements also other temperature springs and bimetals as well as hydraulically operating temperature sensors with liquid, gel or wax filling.
- the roller valve 5a is to be protected against solar radiation and other heat influences which are not directly dependent on the air temperature and which would distort its function.
- the roller valve 6b which is actuated by the regulating element 12 as a moisture-sensitive sensor, is intended for regulating the air humidity in the room to be ventilated.
- fibers or equivalent structures come into consideration which consist of natural or synthetic hair or of natural or synthetic textile materials and / or are provided with coatings and which are overall hygrophilic, capable of desorption or absorption and long-term reversible. 1c and 2c, such a sensor is shown as a fiber 12 extending several times over the length of the housing 3.
- the free end of the fiber 12 is attached to the housing 3 by a spring 15 which gives the fiber a permanent prestress.
- the fiber 12 is then guided several times along the housing 3 via deflection rollers 16 in order to obtain a multiple change in length when the air humidity changes.
- the fiber 12 is attached to a winding wheel 17 connected to the axis 14b of the roller valve 5b.
- the moisture-dependent changes in length of the fiber 12 cause corresponding rotations of the roller valve 5b; the fiber 12 provides the actuating force, while the required restoring force is introduced by a spiral spring 13 connected to the winding wheel 17 or by an opposing regulating element (not shown here).
- FIGS. 1d, 1e, 1f and 2a, 2b and 2d differs from the one described above in that instead of the roller valve 5a regulating the air humidity, a slide 6a is provided with the moisture-sensitive sensor 12, which is equipped with a moisture sensor 19 interacts in the form of a band of many parallel, hygrophilic fibers.
- the slide 6a is guided vertically in the housing part 3a by molded strips 18.
- a thin rope or wire 20 engages, which leads via a deflection roller 16 to one end of the sliver 19 stiffened with crossbars 21.
- the other end of the band 19 is connected by a wire 22 to a holder 23 attached to the housing 3.
- the slide arrangement described above does require larger actuating forces than the roller valve. But it has the advantage that it is less disturbed by strong winds. Rather, the pressure of the wind can press the slide against the guide 18 inwards and thereby improve a seal. There is also no need for a return spring, since the slider keeps the band 19 taut due to its own weight.
- closure elements such as flaps or grilles, can also be used as ventilation elements.
- the ventilation device When using the ventilation device for the simultaneous regulation of air temperature and humidity in a room to be ventilated, the following cases should be considered, from which the relationship to be specified for the ventilation device results, according to which the total cross-section of the openings between indoor and outdoor air is to be regulated.
- the ventilation device stands out now as a device for basic and on-demand ventilation.
- the roller valve 5a At high outside air temperatures, the roller valve 5a is fully open.
- the roller valve 5b supports the air exchange only when there are high internal moisture loads.
- overheating effects in strong sunlight are reduced, as a result of which the ventilation device according to the invention leads to a more comfortable room climate.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Combustion & Propulsion (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Building Environments (AREA)
- Air-Conditioning For Vehicles (AREA)
- Ventilation (AREA)
- Air Humidification (AREA)
- Vaporization, Distillation, Condensation, Sublimation, And Cold Traps (AREA)
Abstract
Lüftungseinrichtung für den bedarfsorientierten Austausch der Luft in einem Raum mit der Außenluft mittels eines eine veränderbare Durchgangsöffnung für den Luftwechsel aufweisenden Lüftungselementes mit einem als mechanisches Stellorgan oder als Ventilelement ausgebildeten Feuchtesensors, wobei ein zweites Lüftungselement vorgesehen sein kann, das einen auf die Temperatur der Außenluft reagierenden Sensor aufweist. Vorteilhafte Ausbildung der Lüftungselemente als Walzenventile mit Steuerung durch hygrophile Faser 12 bzw. durch Bimetallspirale 11, oder Ausführung des Lüftungselementes als Flachschieber 6a mit Steuerung durch ein Band hygrophiler Fasern 19. Ventilation device for the demand-oriented exchange of air in a room with the outside air by means of a ventilation element having a changeable through opening for the air exchange with a moisture sensor designed as a mechanical actuator or as a valve element, wherein a second ventilation element can be provided which reacts to the temperature of the outside air Has sensor. Advantageous design of the ventilation elements as roller valves with control by hygrophile fiber 12 or by bimetal spiral 11, or execution of the ventilation element as flat slide 6a with control by a band of hygrophilic fibers 19.
Description
Ein unkontrollierter Luftaustausch zwischen der Luft in einem Raum und der Außenluft, wie er nicht nur beim üblichen Öffnen von Türen und Fenstern stattfindet, sondern bislang sich auch als "latenter" bzw. "natürlicher" Luftaustausch durch undichte Tür- und Fensterfugen abgespielt hat, führt in der Regel zu einem unerwünschten Verlust der mit der Raumluft fortgeführten Wärme. Aus Gründen der Energieeinsparung hat man daher Wert auf optimale Abdichtung der Tür- und insbesondere der Fensterfugen gelegt; der "natürliche" Luftaustausch wird dadurch unterbrochen oder zumindest gehemmt.
Wasserdampf, der in einem dergestalt abgedichteten Raum von der darin sich aufhaltenden Personen und darüber hinaus von Pflanzen sowie durch Wasserverdunstung, Wasserdampf ausscheidende Einrichtungen, Geräte und dergl. produziert wird, läßt die Luftfeuchte im Raum steigen, was sich auf die den Raum einschließenden Bauteile nachteilig auswirken kann und das Raumklima ungünstig beeinflußt, d.h. durch eine zeitlich begrenzte, gründliche Lüftung mit intensivem Luftaustausch zwischen Innen- und Außenluft, die Luftfeuchte und gegebenenfalls auch die Lufttemperatur wieder normalisiert werden. Diese Art der Lüftung kann aber Ursache einer ungünstigen Wärmebilanz sein, weil Gradmesser für den Luftungseffekt in der Regel das subjektive Empfinden der die Lüftung vornehmenden Person ist, was oft zu einer unnötig langen Lüftungsdauer mit entsprechendem Wärmeverlust führt.An uncontrolled exchange of air between the air in a room and the outside air, which not only occurs when doors and windows are opened normally, but has also previously taken place as "latent" or "natural" air exchange through leaky door and window joints usually to an undesirable loss of the heat carried away with the room air. For reasons of energy saving, great value has therefore been placed on optimal sealing of the door and in particular the window joints; the "natural" air exchange is interrupted or at least inhibited.
Water vapor, which is produced in a room sealed in this way by the people in it and, in addition, by plants as well as by water evaporation, water vapor-separating devices, devices and the like, increases the air humidity in the room, which is disadvantageous for the components enclosing the room can have an impact and adversely affect the indoor climate, ie be normalized again through a temporary, thorough ventilation with intensive air exchange between indoor and outdoor air, the air humidity and possibly also the air temperature. However, this type of ventilation can be the cause of an unfavorable heat balance, because the measure of the ventilation effect is usually the subjective feeling of the person doing the ventilation, which often leads to an unnecessarily long ventilation period with corresponding heat loss.
Es ist bekannt, Fenster, gegebenenfalls auch Türen, mit Lüftungsklappen, Lüftungsgittern oder dergl. zu versehen, die von Hand verstellbar sind, un eine Verbindung mit veränderbarem Querschnitt zwischen Innen- und Außenluft herzustellen. Mit diesen von Hand zu bedienenden Mitteln läßt sich ein kontinuierlicher Austausch der Luft in einem Raum mit der Außenluft bewerkstelligen. Auch hier besteht aber die Gefahr einer ungünstigen Wärmebilanz, weil Gradmesser für die den Lüftungseffekt bedingende Bedienung der Lüftungsklappen u.ä. auch jetzt das subjektive Empfinden der Bedienungsperson ist und weil überdies mit einer theoretisch notwendigen dauernden Beobachtung des Lüftungserfolgs in der Regel nicht zu rechnen ist.It is known to provide windows, possibly also doors, with ventilation flaps, ventilation grilles or the like, which can be adjusted by hand, and to produce a connection with a variable cross section between inside and outside air. With these manually operated means, a continuous exchange of the air in a room with the outside air can be accomplished. However, here too there is a risk of an unfavorable heat balance, because a gauge for the operation of the ventilation flaps and the like, which results in the ventilation effect. is also the subjective feeling of the operator and because, moreover, a theoretically necessary permanent observation of the ventilation success is generally not to be expected.
Es ist ferner auch bekannt, Lüftungsklappen und dergl. durch mechanische Stellglieder, die motorisch, also unter Zufuhr von Hilfsenergie, betrieben werden, zu betätigen. Hier besteht die Möglichkeit, die Stellmotoren durch Sensoren, z.B. für die Lufttemperatur, zu schalten und so eine objektive, optimale Lüftungsregelung durchzuführen. Diese Art der automatischen Lüftungsregelung mit Zufuhr von Hilfsenergie ist indessen apparativ sehr aufwendig und mit tragbaren Kosten in bestehende Gebäude in der Regel nicht nachträglich einzuführen.It is also known to actuate ventilation flaps and the like by mechanical actuators which are operated by a motor, that is to say with the supply of auxiliary energy. Here it is possible to switch the servomotors using sensors, eg for the air temperature, and thus to carry out an objective, optimal ventilation control. This type of automatic ventilation control with supply of auxiliary energy is, however, very complex in terms of equipment and generally cannot be introduced retrospectively into existing buildings at affordable costs.
Die Erfindung geht aus von einer Lüftungseinrichtung zum bedarfsorientierten Austausch der Luft in einem Raum mit der Außenluft mittels eines eine veränderbare Durchgangsöffnung für den Luftwechsel aufweisenden Lüftungselementes. Ihr liegt die Aufgabe zugrunde, eine solche Einrichtung zu schaffen, die ständig eine objektive, optimale Lüftungsregelung mit einfachen Mitteln und ohne Zufuhr von Hilfsenergie ermöglicht, wobei die Wärmeverluste im Raum gering gehalten werden sollen.The invention is based on a ventilation device for the demand-oriented exchange of air in a room with the outside air by means of a ventilation element having a changeable through opening for the air change. It is based on the task of creating such a device that enables an objective, optimal ventilation control with simple means and without the supply of auxiliary energy, while keeping the heat losses in the room low.
Die Aufgabe wird erfindungsgemäß dadurch gelöst, daß für die Steuerung des Luftaustausches ein auf die Feuchte der Raumluft reagierender Sensor vorgesehen ist, der als mechanisches Stellorgan zum stetig veränderbaren Öffnen und Schließen der Durchgangsöffnung in Abhängigkeit von der Raumluftfeuchte - oder als Ventilelement selbst ausgebildet ist.The object is achieved in that a sensor which reacts to the humidity of the room air is provided for controlling the air exchange and which is designed as a mechanical actuator for continuously changing opening and closing of the passage opening depending on the room air humidity - or as a valve element itself.
Der Erfindung liegt die Oberlegung zugrunde, daß eine wesentliche Vereinfachung der Steuerung des bedarfsorientierten Luftaustausches bewirkt werden kann, wenn ein auf die Feuchtigkeit der Raumluft reagierender Sensor nicht über einen Hilfsmotor wirkt, sondern so ausgebildet ist, daß er selbst als Stellorgan oder als Ventilverschlußelement ausgebildet ist.The invention is based on the principle that a significant simplification of the control of the demand-oriented air exchange can be effected if a sensor reacting to the humidity of the room air does not act via an auxiliary motor, but is designed so that it is designed as an actuator or as a valve closure element .
Die Größe der Stellenergie bei einem solchen unmittelbar von einem Sensor betätigten Lüftungselement ist nicht sehr groß. Um trotzdem kurze Steuerzeiten und ausreichende Lüftungsquerschnitte bei allen Betriebsverhältnissen zu erreichen, kann es zweckmäßig sein, zusätzlich zu dem von einem Feuchtesensor gesteuerten Lüftungselement ein weiteres Lüftungselement vorzusehen, das durch einen auf die Temperatur der Außenluft reagierenden Sensor geöffnet oder geschlossen wird. Wenn dabei die Sensoren so ausgebildet sind, daß bei niedriger Außentemperatur das temperaturgesteuerte Lüftungselement geschlossen bleibt und sich erst bei höheren Außentemperaturen allmählich öffnet, können die Abmessungen beider Lüftungselemente und damit deren Trägheit kleiner sein. Außerdem werden dadurch die Wärmeverluste im Raum verringert. Vorteilhaft ist es weiter, die Lüftungselemente als reibungs- und trägheitsar me Walzenventile auszubilden, deren Hohlzylinder durch eine hygrophile Faser oder eine Bimetallspirale als Stellelemente verdrehbar sein können.The size of the actuating energy in such a ventilation element actuated directly by a sensor is not very large. In order to achieve short control times and adequate ventilation cross-sections in all operating conditions, it may be advisable to provide a ventilation element controlled by a humidity sensor, which is opened or closed by a sensor that responds to the temperature of the outside air. If the sensors are designed so that the temperature-controlled ventilation element remains closed at a low outside temperature and only opens gradually at higher outside temperatures, the dimensions of both ventilation elements and thus their inertia can be smaller. It also reduces heat loss in the room. It is also advantageous if the ventilation elements are low in friction and inertia me to form roller valves, the hollow cylinders of which can be rotated as control elements by a hygrophile fiber or a bimetal spiral.
Für Anwendungen, bei denen ein dichter Abschluß der Lüftungselemente auch bei starker Windanströmung notwendig ist, kann ein senkrechter Flachschieber zweckmäßiger sein. Für die dabei erforderlichen höheren Stellkräfte ist als Feuchtesensor ein Band aus hygrophilen parallelen Fasern vorgesehen. Die Rückstellung erfolgt durch das Eigengewicht des Schiebers.For applications in which a tight seal of the ventilation elements is necessary even with strong wind, a vertical flat slide can be more appropriate. For the higher positioning forces required, a band of hygrophilic parallel fibers is provided as a moisture sensor. It is reset by the slider's own weight.
Die Lüftungseinrichtung mit zwei Lüftungselementen ist zur getrennten wie zur simultanen Regelung von Lufttemperatur und Luftfeuchte in einem Raum geeignet.The ventilation device with two ventilation elements is suitable for separate and simultaneous control of air temperature and humidity in a room.
Besonders vorteilhaft ist eine Weiterbildung der Erfindung, bei der durch eine Kombination von Walzenventilen oder Schiebern die Größe des Öffnungsquerschnitts abhängig von der Feuchte der Innen- und der Temperatur der Außenluft dergestalt geregelt wird, daß die Taupunktstemperatur der Innenluft stets niedriger ist als die niedrigste Oberflächentemperatur der Raumumschließungsflächen. Dadurch läßt sich die sonst zur Kondenswasser- und bis zur Schimmelbildung an den den Raum einschließenden Bauteilen führende, besonders kritische Situation beherrschen, die auftritt, wenn der Taupunkt der feuchten Innenluft unterschritten wird.A further development of the invention is particularly advantageous in which the size of the opening cross section is regulated by a combination of roller valves or slides depending on the humidity of the inside and the temperature of the outside air in such a way that the dew point temperature of the inside air is always lower than the lowest surface temperature of the Space enclosing areas. As a result, the particularly critical situation which otherwise leads to the formation of condensation and to the formation of mold on the components enclosing the room can be mastered, which occurs when the dew point of the humid indoor air falls below.
Ausführungsformen der Erfindung sind nachstehend anhand der Figuren beispielsweise beschrieben. Es zeigen:
Figur 1a einen Längsschnitt durch eine Lüftungseinrichtung mit zwei LüftungselementenFigur 1b einen waagerechten Schnitt längs der Linie D-D inFigur 1a- Figur 1c eine Aufsicht in Richtung E-E in
Figur 1a - Figur 1d einen Längsschnitt durch eine andere Ausführungsform einer Lüftungseinrichtung
- Figur 1e einen waagerechten Schnitt längs der Linie I-I in Figur 1d
- Figur 1f eine Aufsicht in der Richtung H-H in Figur 1d
Figur 2a einen Querschnitt längs der Linie A-A in derFigur 1a- Figur 2b einen Querschnitt längs der Linie B-B in den
Figuren 1a und 1d - Figur 2c einen Querschnitt längs der Linie C-C in der
Figur 1a - Figur 2d einen Querschnitt längs der Linie K-K in der Figur 1d
- Figure 1a shows a longitudinal section through a ventilation device with two ventilation elements
- Figure 1b is a horizontal section along the line DD in Figure 1a
- Figure 1c is a plan view in the direction EE in Figure 1a
- Figure 1d shows a longitudinal section through another embodiment of a ventilation device
- Figure 1e is a horizontal section along the line II in Figure 1d
- Figure 1f is a plan view in the direction HH in Figure 1d
- Figure 2a shows a cross section along the line AA in Figure 1a
- 2b shows a cross section along the line BB in FIGS. 1a and 1d
- Figure 2c shows a cross section along the line CC in Figure 1a
- Figure 2d shows a cross section along the line KK in Figure 1d
Die in den Figuren (1a, 1b, 1c und 2a, 2b, 2c) dargestellte Lüftungseinrichtung umfaßt zwei Walzenventile 5a bzw. 3b, die in einem gemeinsamen Gehäuse 3 um ihre voneinander getrennten Achsen, 14a bzw. 14b. drehbar angeordnet sind. Jedes Walzenventil besteht im wesentlichen aus einem Hohlzylinder, 1a bzw. 1b, mit achsparallelen Ausschnitten 2i und 2a, der in einer koaxialen Kammer, 31 bzw. 32, Gehäuses 3 untegebracht ist. Die Kammern für die Unterbringung der Hohlzylinder sind mit Ausschnitten, Lüftungsschlitzen, 4i bzw. 4a, versehen, die sich zu dem zu lüftenden Raum bzw. zur Außenluft öffnen. Das Gehäuse 3 bildet ein Bauteil, welches in Fensterrahmen oder andere Fassadenbereiche einzubauen ist. Das der Temperaturregulierung dienende Walzenventil 5a wird durch die kraftschlüssig damit verbundene Spiralfeder 11 aus Bimetall nach dem Prinzip eines Metallthermometers abhängig von der Temperatur der Luft betätigt, die durch die Lüftungsschlitze 4i und 4a sowie durch die Zylinderausschnitte 2i und 2a, die dem Walzenventil 5a zugeordnet sind, streicht. Die Intensität des Luftwechsels zwischen Innenraum und Außenluft hängt von dem Querschnitt der freien Öffnung ab, die für die durchstreichende Luft durch das Walzenventil 5a freigegeben wird; sie ist über die Bimetallfeder 11 von der Lufttemperatur abhängig und durch die sich dekkenden Teile der achsparallelen Ausschnitte 2i und 2a des Hohlzylinders 1a und der Lüftungsschlitze 4i und 4a, die dem Walzenventil 5a zugeordnet sind, bestimmt.The ventilation device shown in the figures (1a, 1b, 1c and 2a, 2b, 2c) comprises two
Die Spiralfeder 11 liefert sowohl die Stell- als auch die Rückstellkraft für das Walzenventil 5a. Außer der gezeigten Spiralfeder aus Bi-Metall kommen in Rahmen der Erfindung als temperaturabhängige Regulierelemente auch andere Temperaturfedern und Bimetalle sowie hydraulisch arbeitende Temperatursensoren mit Flüssigkeits- Gel- oder Wachsfüllung in Betracht. Je nach den örtlichen Verhältnissen ist das Walzenventil 5a gegen Sonneneinstrahlung und andere nicht unmittelbar von der Lufttemperatur abhängige Wärmeeinflüsse, die seine Funktion verfälschen würden, zu schützen.The
Zur Regulierung der Luftfeuchte in dem zu lüftenden Raum ist das Walzenventil 6b bestimmt, welches durch das Regulierelement 12 als feuchtigkeitsempfindlichen Sensor betätigt wird. Hierfür kommen im Rahmen der Erfindung insbesondere Fasern oder äquivalente Gebilde in Betracht, die aus Natur- oder Kunsthaar bzw. aus natürlichen oder synthetischen Spinnstoffen bestehen und/oder mit Beschichtungen versehen sind und die insgesamt hygrophil, desorptions- bzw. absorptionsfähig und langzeitig reversibel sind. In den Fig. 1c und 2c ist ein solcher Sensor als sich mehrfach über die Länge des Gehäuses 3 erstreckende Faser 12 dargestellt.The roller valve 6b, which is actuated by the regulating
Das frei Ende der Faser 12 ist mit einer Feder 15, die der Faser eine dauernde Vorspannung erteilt, am Gehäuse 3 eingehängt. Über Umlenkrollen 16 ist die Faser 12 sodann mehrmals längs des Gehäuses 3 geführt, um eine vielfache Längenänderung bei Änderung die Luftfeuchte zu erhalten. Schließlich ist die Faser 12 an einem mit der Achse 14b des Walzenvertils 5b verbundenen Wickelrad 17 befestigt. Die feuchtigkeitsabhängigen Längenänderungen der Faser 12 bewirken entsprechende Drehungen des Walzenventils 5b; dabei liefert die Faser 12 die Stellkraft, während die erforderliche Rückstellkraft durch eine mit dem Wickelrad 17 verbundene Spiralfeder 13 oder durch ein, hier nicht dargestelltes, gegenläufiges Regulierelement eingeleitet wird. Bei der Anbringung der Lüftungseinrichtung ist darauf zu achten, daß der Feuchtigkeitssensor so plaziert wird, daß er einer konvektiven Strömung der Raumluft ausgesetzt wird.The free end of the
Die in den Figuren 1d, 1e, 1f und 2a, 2b und 2d dargestellte Ausführungsform der Erfindung unterscheidet sich von der vorstehend beschriebenen dadurch, daß anstelle des die Luftfeuchte regulierenden Walzenventiles 5a mit dem feuchtigkeitsempfindlichen Sensor 12 ein Schieber 6a vorgesehen ist, der mit einem Feuchtesensor 19 in Form eines Bandes aus vielen parallelen, hygrophilen Fasern zusammenwirkt. Der Schieber 6a ist in dem Gehäuseteil 3a durch angeformte Leisten 18 senkrecht geführt. An seinem oberen Ende greift ein dünnes Seil oder ein Draht 20 an, der über eine Umlenkrolle 16 zu dem einen Ende des mit Querstegen 21 versteiften Faserbandes 19 führt. Das andere Ende des Bandes 19 ist durch einen Draht 22 mit einem am Gehäuse 3 befestigten Halter 23 verbunden.The embodiment of the invention shown in FIGS. 1d, 1e, 1f and 2a, 2b and 2d differs from the one described above in that instead of the
Die vorstehend beschriebene Schieberanordnung benötigt zwar größere Stellkräfte als das Walzenventil. Sie hat aber den Vorteil, daß sie weniger durch starke Windanströmung gestört wird. Der Druck des Windes kann vielmehr den Schieber an die Führung 18 nach innen andrücken und dadurch ein Abdichtung verbessern. Es wird auch keine Rückholfeder benötigt, da der Schieber das Band 19 durch sein Eigengewicht immer straff hält.The slide arrangement described above does require larger actuating forces than the roller valve. But it has the advantage that it is less disturbed by strong winds. Rather, the pressure of the wind can press the slide against the
Außer dem beschriebenen Walzenventil und dem Schieber können auch andere Verschlußrogane, wie Klappen oder Gitter sinngemäß als Lüftungselemente Verwendung finden.In addition to the roller valve and the slide described, other closure elements, such as flaps or grilles, can also be used as ventilation elements.
Beim Einsatz der Lüftungseinrichtung zur simultanen Regulierung von Lufttemperatur und -feuchte in einem zu lüftenden Raum sind folgende Fälle in Betracht zu ziehen, aus denen sich die der Lüftungseinrichtung vorzugebende Beziehung ergibt, nach welcher der Gesamtquerschnitt der Öffnungen zwischen Innen- und Außenluft zu regulieren ist.When using the ventilation device for the simultaneous regulation of air temperature and humidity in a room to be ventilated, the following cases should be considered, from which the relationship to be specified for the ventilation device results, according to which the total cross-section of the openings between indoor and outdoor air is to be regulated.
Im Winter herrschen niedrige Außentemperaturen und hohe relative Luftfeuchtigkeiten. Der absolute Wassergehalt, d. h. die Wassermenge je m³ Luft, ist dagegen sehr klein. Daher kann die auf Raumtemperatur erwärmte Außenluft sehr viel Wasser aufnehmen. Zum Ab führen der im Raum produzierten Feuchtigkeit genügt daher ein geringer Luftaustausch. Bei niedrigen Außenlufttemperaturen bleibt daher das temperaturgesteuerte Walzenventil 5a geschlossen, und das feuchtgesteuerte Walzenventil 5b öffnet nur bei Feuchteproduktion im Raum. Bei voreingestellter relativer Grenzfeuchte im Raum, z. B. bei 50 %, schließt das Walzenventil 5b vollständig, während es bei relativen Feuchten von z. B. über 80 % vollständig öffnet. Der Übergang dazwischen ist stetig und reversibel. Ein erhöhter Luftaustausch liegt also nur zu Zeiten hoher innerer Feuchteproduktionen vor, wodurch die Lüftungseinrichtung mit dem Walzenventil 5b als Bedarfslüftung funtioniert und somit energiesparend wirkt.In winter there are low outside temperatures and high relative humidity. In contrast, the absolute water content, ie the amount of water per m³ of air, is very small. Therefore, the outside air warmed to room temperature can absorb a lot of water. For Ab Because of the humidity produced in the room, a low air exchange is sufficient. At low outside air temperatures, the temperature-controlled
In der Übergangsjahreszeit herrschen hohe relative Feuchten bei milden Temperaturen. Der absolute Feuchtegehalt der Außenluft ist sehr groß. Die in den Raum wechselnde Außenluft kann daher nur wenig Wasserdampf aufnehmen. Bei konstanter Feuchteproduktion ist somit in der Übergangszeit ein größerer Luftaustausch vorzunehmen als in der Winterzeit. Wegen der relativ hohen Außenlufttemperatur wirkt sich dies jedoch nicht stark auf den Wärmeverbrauch und mögliche verminderte Energieeinsparung aus. Bei optimaler Auslegung des Walzenventils 5b reicht der Luftaustausch über dieses Element alleine nicht mehr zum Abbau der Feuchtigkeit im Raum aus. Daher wird mit ansteigenden Außenlufttemperaturen das Walzenventil 5a selbsttätig geöffnet. Der erforderliche Luftaustausch ist somit freigegeben. Die Lüftungseinrichtung gemäß der Erfindung zeichnet sich jetzt als Einrichtung zur Grund- und Bedarfslüftung aus.In the transition season, there are high relative humidities at mild temperatures. The absolute moisture content of the outside air is very large. The outside air that changes into the room can therefore only absorb a little water vapor. With constant moisture production, a larger air exchange is to be carried out in the transitional period than in winter. However, due to the relatively high outside air temperature, this does not have a major impact on heat consumption and possible reduced energy savings. If the
Bei hohen Außenlufttemperaturen ist das Walzenventil 5a vollständig geöffnet. Das Walzenventil 5b unterstützt den Luftaustausch nur bei hohen inneren Feuchtebelastungen. Durch den erhöhten Grundlüftungsstrom werden Überhitzungseffekte bei starker Sonneneinstrahlung vermindert, wodurch die Lüftungseinrichtung gemäß der Erfindung zu einem behaglicheren Raumklima führt.At high outside air temperatures, the
Beispiele für den Einsatz der Lüftungseinrichtung gemäß der Erfindung: Examples of the use of the ventilation device according to the invention:
Innenlufttemperatur: 16° C
mittlere Feuchteproduktion: 60 g/h
erforderl. Luftaustausch
Winter (-10 °C): 10 m³/h (nur Ventil 5b)
Übergangszeit (+10 °C): 14 m³/h (Ventile 5b + 5a)Indoor air temperature: 16 ° C
average moisture production: 60 g / h
required Air exchange
Winter (-10 ° C): 10 m³ / h (
Transition time (+10 ° C): 14 m³ / h (
Innenlufttemperatur: 20 ° C
mittlere Feuchteproduktion: 100 g/h
erforderl. Luftaustausch
Winter (-10 °C) 12 m³/h (nur Ventil 5b)
Übergangszeit (+10 °C): 15 m³/h (Ventile 5b + 5a)Indoor air temperature: 20 ° C
average moisture production: 100 g / h
required Air exchange
Winter (-10 ° C) 12 m³ / h (
Transition time (+10 ° C): 15 m³ / h (
Claims (9)
dadurch gekennzeichnet,
daß für die Steuerung des Luftaustausches ein auf die relative Feuchte der Raumluft reagierender Feuchtensensor vorgesehen ist, der gleichzeitig als mechanisches Stellorgan zum stetigen Öffnen und Schließen der Durchgangsöffnung des Lüftungselementes in Abhängigkeit von der Raumluftfeuchte ausgebildet ist.1. Ventilation device for the demand-oriented exchange of air in a room with the outside air by means of a ventilation element having a changeable through opening for the air change
characterized,
that a humidity sensor reacting to the relative humidity of the room air is provided for controlling the air exchange, which is designed at the same time as a mechanical actuator for the constant opening and closing of the through opening of the ventilation element depending on the room air humidity.
dadurch gekennzeichnet,
daß für die Regelung des Luftaustausches zwei getrennt arbeitende Lüftungselemente vorgesehen sind, von denen das eine durch einen auf die Raumfeuchte und das andere durch einen auf die Temperatur der Außenluft reagierenden Sensor steuerbar ist.2. Ventilation device according to claim 1,
characterized,
that two separately working ventilation elements are provided for the regulation of the air exchange, one of which can be controlled by a sensor which reacts to the room humidity and the other by a sensor which responds to the temperature of the outside air.
gekennzeichnet,
durch eine solche Ausbildung der Sensoren, daß bei niedriger Außentemperatur, z. B. im Winter, nur das durch die Feuchte der Raumluft gesteuerte Lüftungselement betätigt wird, während bei höherer Außentemperatur auch das temperaturgesteuerte Lüftungselement sich zusätzlich oder allein öffnet.3. Ventilation device according to claim 2,
featured,
by such a design of the sensors that at low outside temperatures, for. B. in winter, only the ventilation element controlled by the humidity of the room air is actuated, while at higher outside temperatures the temperature-controlled ventilation element opens additionally or alone.
dadurch gekennzeichnet,
daß mindestens ein Lüftungselement, als Walzenventil (5a, 5b) ausgebildet ist, das in an sich bekannter Weise aus einem Hohlzylinder (1a, 1b) mit achsparallelen Ausschnitten (2i, 2a) besteht, der innerhalb eines koaxialen, mit Lüftungsschlitzen (4i, 4a) für die Raum- und die Außenluft versehenen Gehäuses (3) so hin und her drehbar gelagert ist, daß die sich jeweils deckenden Teile der Ausschnitte (2i, 2a) und der Lüftungsschlitze (4i, 4a) die veränderbare Durchgangsöffnung bilden.4. Ventilation device according to claim 1, 2 or 3,
characterized,
that at least one ventilation element is designed as a roller valve (5a, 5b) which, in a manner known per se, consists of a hollow cylinder (1a, 1b) with axially parallel cutouts (2i, 2a) which is located within a coaxial, with ventilation slots (4i, 4a ) for the room and outside air provided housing (3) is rotatably mounted so that the overlapping parts of the cutouts (2i, 2a) and the ventilation slots (4i, 4a) form the variable through opening.
dadurch gekennzeichnet,
daß der Feuchtesensor eine sich mehrfach über die Länge des Gehäuses (3) erstreckende hygrophile Faser (12) ist, die über mehrere Rollen (16) geleitet gegen die Kraft einer Spiralfeder (13) ihre Längenänderungen mittels eines Wickelrades (17) als Drehbewegung auf den Hohlzylinder (5b) überträgt.5. Ventilation device according to claim 1 to 4,
characterized,
that the moisture sensor is a multiple over the length of the housing (3) extending hygrophilic fiber (12) which is guided over several rollers (16) against the force of a coil spring (13) their changes in length by means of a winding wheel (17) as a rotational movement on the Hollow cylinder (5b) transmits.
dadurch gekennzeichnet,
daß der der Außenluft ausgesetzte Temperatursensor eine an sich bekannte Bimetallspirale (11) ist.6. Ventilation device according to claim 2 to 4,
characterized,
that the temperature sensor exposed to the outside air is a bimetal spiral (11) known per se.
dadurch gekennzeichnet,
daß ein Lüftungselement (33) ein Flachschieber (6a) ist, der in einer senkrechten Führung (18) eines Gehäuseteiles (3a) verschiebbar gelagert und oben über eine Umlenkrolle (16) mit einem Band (19) aus zueinander parallelen, hygrophilen Fasern verbunden ist.7. Ventilation device according to claim 1, 2 or 3,
characterized,
that a ventilation element (33) is a flat slide (6a) which is slidably mounted in a vertical guide (18) of a housing part (3a) and is connected at the top via a deflection roller (16) to a band (19) made of parallel, hygrophilic fibers .
dadurch gekennzeichnet,
daß der Feuchtesensor eine hygrophile Substanz, z. B. ein Salz, ist, deren feuchtigkeitsabhängige Volumenänderung, z. B. über einen Kolben die Veränderung der Durchgangsöffnung des Lüftungselementes bewirkt.8. Ventilation device according to claim 1, 2 or 3,
characterized,
that the moisture sensor is a hygrophilic substance, e.g. B. is a salt, the moisture-dependent volume change, z. B. causes a change in the passage opening of the ventilation element via a piston.
dadurch gekennzeichnet,
daß der Feuchtesensor eine hygrophile Beschichtung auf einer biegsamen Platte ist und nach Art eines Bimetallelementes als Verschlußteil ausgebildet ist.9. Ventilation device according to claim 1, 2 or 3,
characterized,
that the moisture sensor is a hygrophilic coating on a flexible plate and is designed in the manner of a bimetallic element as a closure part.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| AT87105088T ATE54026T1 (en) | 1986-04-08 | 1987-04-06 | VENTILATION DEVICE FOR NEEDS-ORIENTED AIR EXCHANGE. |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE19863611709 DE3611709A1 (en) | 1986-04-08 | 1986-04-08 | VENTILATION DEVICE FOR DEMAND-ORIENTED AIR EXCHANGE |
| DE3611709 | 1986-04-08 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0240977A2 true EP0240977A2 (en) | 1987-10-14 |
| EP0240977A3 EP0240977A3 (en) | 1988-08-24 |
| EP0240977B1 EP0240977B1 (en) | 1990-06-20 |
Family
ID=6298179
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP87105088A Expired - Lifetime EP0240977B1 (en) | 1986-04-08 | 1987-04-06 | Ventilating device for an air exchange according to the needs |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0240977B1 (en) |
| AT (1) | ATE54026T1 (en) |
| DE (2) | DE3611709A1 (en) |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0495464A3 (en) * | 1991-01-15 | 1993-05-05 | Thermo King Corporation | Refrigeration temperature control system |
| EP0638775A1 (en) * | 1993-08-10 | 1995-02-15 | Conseils Etudes Et Recherches En Gestion De L'air C.E.R.G.A. | Process and device for the cross-section control of an air inlet opening in a room |
| GB2292454A (en) * | 1994-08-18 | 1996-02-21 | Titon Hardware | Temperature-responsive slot ventilator |
| GB2359618A (en) * | 2000-02-22 | 2001-08-29 | Geoff Smith | Automatic portable vent responding to temperature and/or humidity changes |
| FR2817327A1 (en) * | 2000-11-24 | 2002-05-31 | Anjos | Control for ventilation flap comprises parallel braids whose length varies according to moisture content of air, slide attached to one end of braids, second slide which moves at right angles to axis of flap and lever connecting slides |
| FR2958730A1 (en) * | 2010-04-12 | 2011-10-14 | Somfy Sas | CONNECTING HYGROREGLABLE AIR INTAKE |
Families Citing this family (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE19727318A1 (en) * | 1997-06-27 | 1999-01-07 | Guenter Dipl Ing Waldow | Device for avoiding condensation and steaming up of windows of habitable buildings |
| DE10110383A1 (en) * | 2001-03-03 | 2002-09-12 | Hilmar Niklaus | Ventilation appliance for hermetically sealed rooms has shutter pivot shaft with bearing elements formed by sleeve and axle journal with intermediate seal |
| DE10358472B4 (en) * | 2003-12-08 | 2011-02-10 | Maico Elektroapparate-Fabrik Gmbh | Ventilation device for connecting an exhaust air line and central ventilation device |
| DE102009009109B3 (en) * | 2009-02-16 | 2010-10-07 | Howatherm-Klimatechnik Gmbh | Method for providing ventilation to area via supply air openings and exhaust air openings, involves loading supply air openings with supply air alternatively, where supply air openings are spaced apart distance from each other |
| DE102014104063A1 (en) * | 2014-03-25 | 2015-10-01 | Maco Technologie Gmbh | VENTILATION DEVICE |
| DE102015219302A1 (en) * | 2015-10-06 | 2017-04-06 | Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft zur Förderung der angewandten Forschung e.V. | breather |
Family Cites Families (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE717397C (en) * | 1937-09-19 | 1942-02-13 | Askania Werke Ag | Process for air humidification in gas-heated rooms |
| FR1539936A (en) * | 1967-08-10 | 1968-09-20 | Lagarde Ets Joseph | New process for regulating the hygrometry of an enclosure and new device for implementing this process |
| SE335790B (en) * | 1968-12-20 | 1971-06-07 | Husqvarna Vapenfabriks Ab | |
| CH612852A5 (en) * | 1976-07-29 | 1979-08-31 | Luwa Ag | Automatic fire protection shut-off member for ventilating ducts, in particular of shelters |
| DE2730417A1 (en) * | 1977-07-06 | 1979-01-25 | Rimu Lueftungstechnik Philipp | Air feed control for air conditioning in stables - with outside air feed ratio dependent upon heat content of stable air |
| DE2923734C2 (en) * | 1979-06-12 | 1982-09-02 | Westfälisches Metallwerk Franz Schneider, 3492 Brakel | Ventilation device for installation in window or door frames |
-
1986
- 1986-04-08 DE DE19863611709 patent/DE3611709A1/en active Granted
-
1987
- 1987-04-06 DE DE8787105088T patent/DE3763338D1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1987-04-06 AT AT87105088T patent/ATE54026T1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1987-04-06 EP EP87105088A patent/EP0240977B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Cited By (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0495464A3 (en) * | 1991-01-15 | 1993-05-05 | Thermo King Corporation | Refrigeration temperature control system |
| EP0638775A1 (en) * | 1993-08-10 | 1995-02-15 | Conseils Etudes Et Recherches En Gestion De L'air C.E.R.G.A. | Process and device for the cross-section control of an air inlet opening in a room |
| FR2708992A1 (en) * | 1993-08-10 | 1995-02-17 | Cerga | Method and device for adjusting the section of a ventilation air inlet in a room. |
| US5507433A (en) * | 1993-08-10 | 1996-04-16 | Conseils Etudes Et Recherches En Gestion De L'air (C.E.R.G.A) | Method and device for adjusting the cross section of a ventilation air inlet in premises |
| GB2292454A (en) * | 1994-08-18 | 1996-02-21 | Titon Hardware | Temperature-responsive slot ventilator |
| GB2292454B (en) * | 1994-08-18 | 1998-12-09 | Titon Hardware | Ventilator |
| GB2359618A (en) * | 2000-02-22 | 2001-08-29 | Geoff Smith | Automatic portable vent responding to temperature and/or humidity changes |
| FR2817327A1 (en) * | 2000-11-24 | 2002-05-31 | Anjos | Control for ventilation flap comprises parallel braids whose length varies according to moisture content of air, slide attached to one end of braids, second slide which moves at right angles to axis of flap and lever connecting slides |
| FR2958730A1 (en) * | 2010-04-12 | 2011-10-14 | Somfy Sas | CONNECTING HYGROREGLABLE AIR INTAKE |
| WO2011128840A1 (en) | 2010-04-12 | 2011-10-20 | Somfy Sas | Communicating hydraulically controllable air inlet |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| ATE54026T1 (en) | 1990-07-15 |
| DE3611709C2 (en) | 1990-02-08 |
| DE3763338D1 (en) | 1990-07-26 |
| EP0240977A3 (en) | 1988-08-24 |
| DE3611709A1 (en) | 1987-10-15 |
| EP0240977B1 (en) | 1990-06-20 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0240977B1 (en) | Ventilating device for an air exchange according to the needs | |
| EP0691494A1 (en) | Sanitary valve | |
| EP0001615A1 (en) | Regulating means for central heating system | |
| DE2501626A1 (en) | VARIABLE FLOW CONTROL BOX AND SYSTEM INCLUDING THIS | |
| DE69409311T2 (en) | Method and device for regulating the cross-section of the entrance of a room ventilation opening | |
| DE2934501C2 (en) | ||
| EP0447944B1 (en) | Fire protection flap | |
| EP0027933A1 (en) | Thermostatic valve, especially thermostatic valve for a heating radiator | |
| DE2915260A1 (en) | Animal stall ventilation system - has fresh and stale air shutters adjusted dependent on wind and temp. respectively | |
| EP3658733B1 (en) | Building facade system having hygroscopic and auto-reactive dehumidification mechanism | |
| CH330963A (en) | Thermostatic regulator | |
| DE19909097A1 (en) | Thermostatic valve attachment | |
| DE2621959C3 (en) | Device for regulating the air discharge in self-ventilation systems | |
| DE3444658A1 (en) | Actuating member for ventilation flaps, hoods and slides on cold frames and greenhouses | |
| DE2520109C3 (en) | Thermostatic control device for an air conditioning system | |
| DE2619413B2 (en) | Thermostatically operated control arrangement for a four-pipe air conditioning system | |
| DE1679547A1 (en) | Device for influencing the temperature of rooms | |
| DE2821147A1 (en) | DEVICE WITH TEMPERATURE SENSOR FOR REGULATING AN ACTUATOR IN A VENTILATION SYSTEM | |
| DE2926599A1 (en) | Heating radiator thermostat assembly - has additional heat sensor between valve and main heat sensor working in opposite direction | |
| DE3121080A1 (en) | Air outlet with displaceable jet-guide devices | |
| AT219245B (en) | Device for controlling an air curtain system | |
| DE1043704B (en) | Devices for automatic heat regulation by ventilation in greenhouses, flowerbeds, halls and other rooms | |
| EP0615102A1 (en) | Air transfer system | |
| AT345694B (en) | DOOR CLOSER | |
| DE1222197B (en) | Thermostat regulator for regulating the fuel supply to a burner device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE FR GB IT LI NL |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE FR GB IT LI NL |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19880705 |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19891027 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE FR GB IT LI NL |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 54026 Country of ref document: AT Date of ref document: 19900715 Kind code of ref document: T |
|
| ITF | It: translation for a ep patent filed | ||
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 3763338 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19900726 |
|
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) | ||
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Payment date: 19910319 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| PLBI | Opposition filed |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009260 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 19910327 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 19910328 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Payment date: 19910409 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Payment date: 19910415 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 19910430 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| 26 | Opposition filed |
Opponent name: ROTO FRANK AKTIENGESELLSCHAFT Effective date: 19910316 |
|
| NLR1 | Nl: opposition has been filed with the epo |
Opponent name: ROTO FRANK AKTIENGESELLSCHAFT. |
|
| RDAG | Patent revoked |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009271 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: PATENT REVOKED |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| 27W | Patent revoked |
Effective date: 19911230 |
|
| GBPR | Gb: patent revoked under art. 102 of the ep convention designating the uk as contracting state | ||
| NLR2 | Nl: decision of opposition | ||
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: FRAUNHOFER-G.- ZUR FORDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORD Effective date: 19920430 |