EP0216831B1 - Echangeur de chaleur - Google Patents
Echangeur de chaleur Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0216831B1 EP0216831B1 EP19860901823 EP86901823A EP0216831B1 EP 0216831 B1 EP0216831 B1 EP 0216831B1 EP 19860901823 EP19860901823 EP 19860901823 EP 86901823 A EP86901823 A EP 86901823A EP 0216831 B1 EP0216831 B1 EP 0216831B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- heat exchanger
- helical
- inlet
- outlet
- cylindrical wall
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired
Links
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 abstract description 7
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 abstract description 7
- 230000008021 deposition Effects 0.000 abstract description 4
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 abstract description 4
- 238000011010 flushing procedure Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000000151 deposition Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000003466 welding Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000009969 flowable effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004140 cleaning Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000855 fermentation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004151 fermentation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001556 precipitation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010408 sweeping Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011144 upstream manufacturing Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F28—HEAT EXCHANGE IN GENERAL
- F28D—HEAT-EXCHANGE APPARATUS, NOT PROVIDED FOR IN ANOTHER SUBCLASS, IN WHICH THE HEAT-EXCHANGE MEDIA DO NOT COME INTO DIRECT CONTACT
- F28D7/00—Heat-exchange apparatus having stationary tubular conduit assemblies for both heat-exchange media, the media being in contact with different sides of a conduit wall
- F28D7/02—Heat-exchange apparatus having stationary tubular conduit assemblies for both heat-exchange media, the media being in contact with different sides of a conduit wall the conduits being helically coiled
- F28D7/022—Heat-exchange apparatus having stationary tubular conduit assemblies for both heat-exchange media, the media being in contact with different sides of a conduit wall the conduits being helically coiled the conduits of two or more media in heat-exchange relationship being helically coiled, the coils having a cylindrical configuration
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a heat exchanger with a double helical passage formed by two helical surfaces which are connected with their inner edges to a core and with their outer edges to a cylindrical wall of a casing so as to create the flows of a first heat exchange medium and a second heat exchange medium, both helical surfaces having the same angle of pitch, and with an inlet and an outlet for each of the flows, which inlet and outlet connects the double helical passage with supply and discharge pipes of the heat exchanger.
- the heat exchanger is especially intended for use in the exchange of heat, preferably in counter flow, between flowable media, particularly between media that are employed as materials in a process for biogas production, and media that have been employed in such a process.
- the heat exchanger according to the invention is not limited to the above mentioned use, but can be used in other fields.
- a heat exchanger of the above mentioned type is principally known from DE-C-178 080.
- no directions are given, however, for the construction of the inlets and the outlets or the connection of the inlets and outlets to the helical passages of the heat exchanger.
- the inlet and outlet may connect the double helical passage with supply and discharge pipes on the heat exchanger.
- the features characteristic of the invention are that the inlet and the outlet are constructed substantially without change of the cross-sectional area from the helical passage through the inlet/outlet to the supply and discharge pipes, that the inlet and the outlet consist of pipe stubs the front walls of which are directed tangentially to the cylindrical wall and disposed in a plane which together with a plane perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the helical passages forms an angle which substantially corresponds to the angle of pitch of the helical surfaces and that at the end of each stub a guide plate is provided between two adjacent helical surfaces, said guide plate extending tangentially from the core towards the cylindrical wall of the casing.
- inlet and the outlet according to the present invention may be connected to the cylindrical wall of the casing or the end of the casing.
- the pipe stubs are connected directly with the mouth of a helical passage, which mouth is provided at the end of the casing and is defined by the end of the cylindrical wall, the core and the ends of the two helical surfaces so that it becomes unnecessary to provide guide plates or the like means.
- the pipe stubs are connected directly with the mouth, care should be taken that the inlet and the outlet are so directed as above mentioned in order to ensure the optimum flow conditions.
- the supply to and discharge from a heat exchanger consisting of a plurality of units can be provided by means of pipe stubs connected directly with the mouths of the helical passages, while the mutual connection of the units is provided by means of pipe stubs connected with the cylindrical walls of the individual casings.
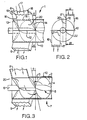
- This heat exchanger 1 has two helical passages 2, 3 formed by two helical surfaces 4, 5, which are provided in the form of two plate strips, which are helically coiled and are welded along their inner edges to a core in the form of a tube 6, while their outer edges are welded to the cylindrical wall 10 of the casing 7.
- the two plate strips 4, 5 have the same angle of pitch 8 and are arranged substantially midway between one another so that the helical passages have approximately equal cross-sectional areas.
- the cylindrical wall 10 may either consist of a cylindrical tube or may be provided in the form of coiled plate strips, which are welded to the outer edges of the plate strips 4, 5 so as to close the spaces between the plate strips 4, 5 and thereby to provide the helical passages 2, 3.
- the plate strips 4, 5 may alternatively be arranged at a displacement relative to one another so that the helical passages 2, 3 will have different cross-sectional areas.
- an inlet 8 and an outlet 9 are welded to the cylindrical wall 10 of the casing 7 in such a manner that there will be no sudden changes of direction, cavities or substantial changes of the cross-sectional area.
- a window is provided in the wall 10 for each of the pipe stubs 8, 9.
- the window which extends across an angle of approximately 90°, is delimited at a first side by a first generatrix 12 of the cylindrical wall 10.
- the first generatrix 12 is located at the line of intersection between a tangential plane to the cylindrical wall and the wall 10 itself.
- the window has a width corresponding to the distance between two adjacent plate strips 4, 5 and is thus delimited in the longitudinal direction of the heat exchanger by two edges 13, 14 located at the welding line between the plate strips and the wall.
- the last side of the window is delimited by a second generatrix 15 of the cylindrical wall 10.
- the second generatrix 15 is located at the point of intersection between the wall 10 and a plane, which is parallel to the beforementioned tangential plane, and which is a tangential plane to the tube 6.
- the pipe stubs 8, 9 are arranged in such a manner that a front wall 16, as viewed from the end (see Fig. 2), is directed tangentially relatively to the wall 10 of the casing 7 and is welded to this wall along the first generatrix 12.
- the pipe stubs 8, 9 have two side walls 18, 19 which connect the front wall and the rear wall and are welded to the wall 10 along the edges 13 and 14.
- the pipe stubs 8, 9 are arranged in a plane, which together with a plane perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the helical passages forms an angle 8 (see Fig. 1), which is identical to the angle of pitch ⁇ of the plate strips 4, 5 (see Fig. 3).
- the pipe stubs 8, 9 are gradually changed to a circular shape (not shown) from the approximately polygonal shape at the connection with the wall 10, whereby it becomes possible to connect the heat exchanger with other equipment by means of conventionally produced cylindrical pipes (not shown).
- the pipe stubs 8, 9 are shown with an exaggerated length and can be shorter than shown.
- two guide plates 20, 21 are connected by welding between two adjacent plate strips 4, 5, and these guide plates are directed tangentially relatively to the tube 6.
- the guide plate 20 is moreover welded to a first generatrix 22 of the tube 6 and the above mentioned second generatrix 15 of the cylindrical wall 10.
- the heat exchanger constructed as above described will have very advantageous flow conditions, and it is particularly suitable for use in the exchange of heat between materials employed in a process for biogas production, and materials that have been used in such a process.
- inhomogenous mass there will be a minimum of precipitation and deposition owing to good flow conditions, and consequently it will rarely be necessary to clean the heat exchanger by flushing. Should it still become necessary to clean the heat exchanger, this can easily be done by flushing, because the cleaning medium can be passed in and out through the pipe stubs 8 and 9 and produce a sweeping of all interior surfaces.
- the heat exchanger according to the invention can also be constructed in other ways.
- the pipe stubs can be welded directly to the mouth of the helical passages as long as the orientation of the pipe stubs in space, as above described, is observed.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Thermal Sciences (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Heat-Exchange Devices With Radiators And Conduit Assemblies (AREA)
Abstract
Claims (5)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| AT86901823T ATE38894T1 (de) | 1985-03-06 | 1986-03-06 | Waermeaustauscher. |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DK102085A DK102085A (da) | 1985-03-06 | 1985-03-06 | Varmeveksler |
| DK1020/85 | 1985-03-06 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0216831A1 EP0216831A1 (fr) | 1987-04-08 |
| EP0216831B1 true EP0216831B1 (fr) | 1988-11-23 |
Family
ID=8100091
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP19860901823 Expired EP0216831B1 (fr) | 1985-03-06 | 1986-03-06 | Echangeur de chaleur |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0216831B1 (fr) |
| DE (1) | DE3661295D1 (fr) |
| DK (1) | DK102085A (fr) |
| WO (1) | WO1986005262A1 (fr) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RU2304580C2 (ru) | 2002-07-29 | 2007-08-20 | Ф.Хоффманн-Ля Рош Аг | Новые бензодиоксолы |
Family Cites Families (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE178080C (fr) * | ||||
| US2060936A (en) * | 1936-02-15 | 1936-11-17 | Todd Comb Equipment Inc | Heat exchange means |
| US2341319A (en) * | 1941-10-31 | 1944-02-08 | Lummus Co | Heat exchanger |
| DE2364500A1 (de) * | 1973-12-24 | 1975-07-03 | Agfa Gevaert Ag | Kombinierter waermeaustauscher und mischer |
| FR2479955A1 (fr) * | 1980-04-04 | 1981-10-09 | Joguet Jean | Dispositif de climatisation d'habitation |
| FR2539498B1 (fr) * | 1983-01-18 | 1988-01-22 | Jcm Ind Sarl | Dispositif de recuperation de chaleur |
-
1985
- 1985-03-06 DK DK102085A patent/DK102085A/da not_active Application Discontinuation
-
1986
- 1986-03-06 DE DE8686901823T patent/DE3661295D1/de not_active Expired
- 1986-03-06 EP EP19860901823 patent/EP0216831B1/fr not_active Expired
- 1986-03-06 WO PCT/DK1986/000019 patent/WO1986005262A1/fr active IP Right Grant
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| DE3661295D1 (en) | 1988-12-29 |
| EP0216831A1 (fr) | 1987-04-08 |
| DK102085A (da) | 1986-09-07 |
| DK102085D0 (da) | 1985-03-06 |
| WO1986005262A1 (fr) | 1986-09-12 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CA1079263A (fr) | Echangeur de chaleur | |
| US6523606B1 (en) | Heat exchanger tube block with multichamber flat tubes | |
| US4211277A (en) | Heat exchanger having internal fittings | |
| US4386652A (en) | Heat exchange assembly | |
| US6935418B1 (en) | Fluid conveying tube and vehicle cooler provided therewith | |
| US9885523B2 (en) | Liquid to liquid multi-pass countercurrent heat exchanger | |
| EP1347258B1 (fr) | Echangeur de chaleur avec supports de tubes | |
| EP0369010B1 (fr) | Echangeur thermique a enveloppe et tube | |
| CN210321338U (zh) | 基于圆形微通道波浪面换热板的板壳式换热器 | |
| US20040182556A1 (en) | High-performance thermal control ducts | |
| US6012514A (en) | Tube-in tube heat exchanger | |
| EP0216831B1 (fr) | Echangeur de chaleur | |
| US4625794A (en) | Plastic heat exchanger construction | |
| US20230175786A1 (en) | Exchanger device | |
| EP1724543A1 (fr) | Unité d'échange de chaleur et échangeur de chaleur qui l'utilise. | |
| US3311166A (en) | Heat exchanger | |
| US3330336A (en) | Heat exchanger tubes with longitudinal ribs | |
| WO2019160521A1 (fr) | Échangeur de chaleur en spirale | |
| CN209745048U (zh) | 一种高效管壳式换热器 | |
| US5894883A (en) | Shell and tube heat exchanger | |
| CN2655156Y (zh) | 一种螺旋折流板管壳式换热器 | |
| CN109900144B (zh) | 换热器和具有该换热器的换热装置 | |
| US4907647A (en) | Heat exchanger | |
| JPH04189A (ja) | カウンタフロー型熱交換器 | |
| US7063135B2 (en) | Heat exchanger |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE FR GB IT LI NL SE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19870311 |
|
| ITCL | It: translation for ep claims filed |
Representative=s name: FUMERO BREVETTI S.N.C. |
|
| TCNL | Nl: translation of patent claims filed | ||
| TCAT | At: translation of patent claims filed | ||
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19870702 |
|
| EL | Fr: translation of claims filed | ||
| DET | De: translation of patent claims | ||
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE FR GB IT LI NL SE |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 38894 Country of ref document: AT Date of ref document: 19881215 Kind code of ref document: T |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 3661295 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19881229 |
|
| ITF | It: translation for a ep patent filed | ||
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| ITTA | It: last paid annual fee | ||
| EAL | Se: european patent in force in sweden |
Ref document number: 86901823.4 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20000228 Year of fee payment: 15 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Payment date: 20000307 Year of fee payment: 15 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Payment date: 20000315 Year of fee payment: 15 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Payment date: 20000317 Year of fee payment: 15 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 20000327 Year of fee payment: 15 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20000329 Year of fee payment: 15 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Payment date: 20000330 Year of fee payment: 15 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20000531 Year of fee payment: 15 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20010306 Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20010306 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20010307 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20010331 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20010331 Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20010331 |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: HOJBOGARD BIOGASTEKNOLOGI Effective date: 20010331 Owner name: BIGADAN A/S Effective date: 20010331 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20011001 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20010306 |
|
| EUG | Se: european patent has lapsed |
Ref document number: 86901823.4 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20011130 |
|
| NLV4 | Nl: lapsed or anulled due to non-payment of the annual fee |
Effective date: 20011001 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20020101 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20050306 |