EP0193108B1 - Dispositif de réglage à intervalle pneumatique - Google Patents
Dispositif de réglage à intervalle pneumatique Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0193108B1 EP0193108B1 EP86102188A EP86102188A EP0193108B1 EP 0193108 B1 EP0193108 B1 EP 0193108B1 EP 86102188 A EP86102188 A EP 86102188A EP 86102188 A EP86102188 A EP 86102188A EP 0193108 B1 EP0193108 B1 EP 0193108B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- obturator
- diaphragm
- switching mechanism
- valve
- mechanism according
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 230000006835 compression Effects 0.000 claims description 8
- 238000007906 compression Methods 0.000 claims description 8
- 239000000696 magnetic material Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000000903 blocking effect Effects 0.000 claims 1
- 230000000717 retained effect Effects 0.000 claims 1
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 abstract description 4
- 238000010411 cooking Methods 0.000 abstract description 3
- 239000012528 membrane Substances 0.000 description 25
- 238000009434 installation Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000001133 acceleration Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000036316 preload Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000002485 combustion reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000446 fuel Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000010354 integration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012423 maintenance Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000004033 plastic Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24C—DOMESTIC STOVES OR RANGES ; DETAILS OF DOMESTIC STOVES OR RANGES, OF GENERAL APPLICATION
- F24C3/00—Stoves or ranges for gaseous fuels
- F24C3/12—Arrangement or mounting of control or safety devices
- F24C3/126—Arrangement or mounting of control or safety devices on ranges
Definitions
- the invention relates to a pneumatic interval switching device, in particular for use in a cooking or heating device, in which in a housing a gas inlet and a gas outlet, a valve arranged in the connecting path thereof with a closing component closing a valve passage, which is composed of two magnetically interacting components a valve seat is held and can be lifted off the valve seat along an axis of movement, and a membrane which can be deflected in the direction of the axis of movement and divides the interior of the housing into two chambers is provided, the first housing chamber with the gas inlet and the second housing chamber via a pressure compensation channel with the Gas outlet is connected.
- a magnetic control valve for space heating gas appliances in which the membrane valve arranged in the connection path between the gas inlet and gas outlet is mechanically prestressed into the closed position and the pressure of the two-sided influence chambers is controlled electromagnetically by means of an additional control valve.
- a bypass is opened via a multi-stage membrane chamber and channel system and externally excited solenoid valves, which first regulates the gas device to be operated to a limited fuel supply.
- This known control arrangement is not readily suitable as an interval switching device.
- the interval switching device of the type mentioned at the beginning in EP-A-0 135 157 which falls under Article 54 (3) EPC, serves as a clock generator for the interval operation of gas burners in cooking and heating appliances. Unlike conventional electromechanical clocks, this pneumatic interval switching device does not require external energy and derives its switching movements from the media pressure. It is characterized by reliable and practically maintenance-free operation and enables easy adjustment the switching cycle, ie the switch-off and switch-on times, for example by simply adjusting a spring preload.
- the object of the present invention is to improve the switching characteristic of the pneumatic interval switching device of the type mentioned which manages without external energy and to achieve a particularly simple and compact design.
- the one of the magnetically interacting components is fixed in position with the stationary valve seat and the other is connected in a fixed manner to the closing component in that the pressure compensation channel runs from the side facing the valve passage through the closing component into the second housing chamber and one Switching interval of the device influencing flow resistance includes that a driving device for lifting the closing component from the valve seat is coupled to the membrane in such a way that it only lifts the closing component from the valve seat after a predetermined movement stroke of the membrane, and that a spring between the membrane and the closing component is effective , which is tensioned by the initial movement stroke of the diaphragm and relaxes after the closing component has been lifted off, with a sudden increase in the opening movement of the closing component.
- This interval switching device only requires two housing parts, one of which, together with the membrane, delimits the first housing chamber and the other, likewise together with the membrane, delimits the second housing chamber.
- the locking component is in the invention hanging on the spring and arranged without any other side guide, so that the device is housed in a compact and simple housing can be. Since the closing component is held in each end position by defined forces and the switching functions are also carried out by pneumatic and / or mechanical (springs) forces, the interval switching device according to the invention is not tied to a specific installation position, that is to say it is effective regardless of position.
- the switching device has the advantage that it ensures a sudden full opening of the valve passage immediately after the beginning of the lifting of the closure component after the driving device has taken effect.
- This extremely steep front flank of the switch-on or fire interval of the switching cycle is particularly advantageous in the case of so-called over-stoichiometric premixing gas burners, in particular injector burners.
- a preferred exemplary embodiment of the invention is characterized in that the closing component has a valve plate which consists at least partially of magnetizable or magnetic material and a shaft which is fixedly connected to it and ends in the second housing chamber and through which the pressure compensation channel runs coaxially.
- the shaft is passed through a central opening of the membrane and is firmly connected to one end of the spring in the region of its outer end.
- the spring is preferably a gas-tight rubber bellows surrounding the locking component, which is connected on the one hand to the locking component and on the other hand to the membrane. This integration of the spring in the rubber bellows simplifies the construction and makes an additional spring, for example a helical spring for rapid acceleration the opening movement of the closing component is unnecessary. Leakage losses between the two housing chambers along the valve stem are also avoided.
- valve disc is attached to the bellows via the stem.
- one-sided centering of the closing component on the bellows is sufficient; the attractive force of the permanent magnet, which is preferably arranged in the valve passage itself, ensures that the valve disk is reliably seated on the valve seat.
- a capillary tube is arranged in the pressure compensation channel, the opening cross section and length of which determine the flow resistance of the pressure compensation channel and influence the switching time constant of the interval switching device.
- a capillary tube of a correspondingly changed length is preferably used to change the switching time constant.
- a change in the throttle cross section to change the flow resistance is problematic below a certain opening cross section because of the risk of nozzle clogging.
- an adjustable throttle in the pressure equalization channel can also be used instead of the capillary tube.
- the valve passage preferably has a bore which is coaxial with the axis of movement of the closing component and concentric with the valve seat and in which a permanent magnet is permanently installed.
- the permanent magnet is arranged between pole shoes, the ends of which face the closing component protrude beyond the end face of the permanent magnet.
- the bore has an annular groove communicating with the gas outlet in the area of the projecting ends of the two pole shoes.
- the diaphragm is preferably biased by a compression spring supported against the housing into the end position corresponding to the closed position of the closing component.
- This compression spring urges the membrane into the position corresponding to the closed position of the closing component and therefore ensures that the valve closes properly and reliably. Without this spring, the membrane would have to be positioned precisely depending on the effective magnetic force. In this respect, the compression spring reduces installation and maintenance effort.
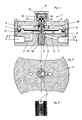
- the interval switching device shown in FIG. 1 in a sectional view has a housing 1 with two housing shells 2 and 3.
- a between the two housing shells 2 and 3 clamped rubber membrane 4 divides the approximately cylindrical interior of the housing 1 into a first housing chamber 5 and a second housing chamber 6.
- In the lower housing shell 2 are a gas inlet 7, a gas outlet 8, connecting channels 9 and 10 and stationary components of a valve arranged in the connecting path between the gas inlet and gas outlet.
- the valve has a valve plate 11 serving as a closing component, which in the closed position of the valve shown in FIG. 1 is in contact with a valve seat 12 provided with a seal and closes a valve passage 13 between the first housing chamber 5 and the gas outlet 8.
- the valve passage 13 merges into a blind bore 15 coaxial with the housing axis 14.
- a permanent magnet package consisting of a permanent magnet 20 and pole pieces 21 (FIG. 3) is fastened.
- the pole shoes 21 protrude from the end adjacent to the valve plate 11 via the permanent magnet 20.
- annular groove 16 is formed which, when the valve is open, ensures unimpeded gas passage from the gas inlet 7 via the connecting channel 9, the first housing chamber 5, the valve passage 13 to the connecting channel 10 of the gas outlet 8, regardless of the installation position of the magnet combination 20, 21.
- the valve disk 11 consists at least partially of magnetizable material and is therefore attracted to the valve seat 12 by the permanent magnet 20 in the closed position shown.
- a ring magnet could also be installed in the valve plate or in the closing component 11, which magnet magnet interacts either with a corresponding opposite pole of a magnet assigned to the valve seat or with a magnetizable component of the valve seat.
- the valve disk 11 is connected in a hanging arrangement via a rigid shaft 23 to one end of a gas-tight rubber bellows 24.
- the other end of the rubber bellows 24 put over the shaft is gas-tightly connected to the membrane 4.
- a pressure equalization channel 25 runs concentrically to the housing axis 14 through the entire closing component shaft 23 and connects the valve passage 13 open to the gas outlet 8 with the second housing chamber 6.
- a capillary tube 28, the length and cross section of which is the flow resistance of the pressure equalization channel, is permanently installed in the pressure equalization channel 25, which is designed as a through bore determine and, as will be explained below in the functional description, significantly influence the switching time constant.
- valve plate 11 The closing component consisting of valve plate 11 and shaft 23 is displaceable along the housing axis 14 for opening and closing the valve.
- a rigid sleeve 26 made of plastic or metal is slidably mounted on the shaft 23.
- This sleeve 26 is motionally coupled to the deflectable part 40 of the membrane 4. After executing a predetermined movement stroke of the membrane 4 or the deflectable part 40, the sleeve 26 abuts with its upper end face against a stop 27 which is fixedly connected to the shaft 23 and takes the entire closing component in the direction of the housing axis 14 via the stop 27. The magnetic force holding the valve plate 11 on the seat 12 is overcome.
- the bellows 24 is designed as a resilient component and, in the exemplary embodiment shown in FIG. 1, acts as a compression spring which, when compressed in the direction of the housing axis 14, charges and suddenly discharges from the seat surface 12 when the valve plate 11 is torn off. This spring function of the bellows 24 leads to an abrupt opening movement of the valve plate 11 as soon as the sleeve 26 comes into contact with the stop 27.
- a set screw 31 is screwed into a housing bore 30, on which a compression spring 32, which urges part 40 of the membrane 4 into the end position shown in FIG. 1, is supported. By turning the screw 31, the preload of the spring 32 and thus the deflection characteristic of the membrane 4 and the switching time constant of the interval switching device can be changed.
- the entire closing component 11, 23 is raised in the direction of the housing axis 14 and the valve plate 11 is lifted off the seat.
- the previously charged spring assigned to the bellows 24 is released and relaxes with sudden acceleration of the opening movement of the valve plate 11.
- the valve passage 13 is therefore suddenly released completely and the gas can flow from the gas inlet 7 to the gas outlet 8.
- the pressure in the first housing chamber 5 can compensate for itself via the pressure compensation channel 25 to the second housing chamber 6.
- the flow resistance formed by the capillary tube 28 determines the time until the pressure is completely equalized between the chambers 5 and 6.
- the bellows 24 can also be designed as a helical spring in a modification of the embodiment described above.
- a sufficiently gas-tight seal must be provided between the shaft 23 of the closing component and the sleeve 26 connected to the membrane 4, 40.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Combustion & Propulsion (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Fluid-Pressure Circuits (AREA)
- Fluid-Driven Valves (AREA)
- Magnetically Actuated Valves (AREA)
- Paper (AREA)
- Fittings On The Vehicle Exterior For Carrying Loads, And Devices For Holding Or Mounting Articles (AREA)
- Multiple-Way Valves (AREA)
- Advancing Webs (AREA)
- Switches Operated By Changes In Physical Conditions (AREA)
- Details Of Valves (AREA)
- External Artificial Organs (AREA)
Claims (13)
- Dispositif de réglage à intervalle pneumatique en particulier pour l'utilisation dans des appareils de cuisson ou de chauffage, comprenant un corps (1) avec une entrée (7) et une sortie (8) du gaz, un robinet situé sur la voie de connexion entre les deux, muni d'un obturateur (11, 23) fermant le passage du robinet et retenu sur le siège de celui-ci (12) par deux éléments (20, 21) à interaction magnétique, ledit obturateur pouvant être soulevé de ce siège (12) le long d'un axe de mouvement (14), ainsi qu'un diaphragme (4) déplaçable dans le sens de l'axe de mouvement (14) et séparant l'intérieur du corps en deux chambres (5, 6) dont la première (5) communique avec l'entrée du gaz (7) et la seconde (6) par l'intermédiaire d'un canal de compensation de la pression (25) avec la sortie du gaz (8) caractérisé par le fait que l'un des éléments à interaction magnétique (20, 21) est fixé de manière permanente sur le siège stationnaire (12) du robinet et l'autre est fixé de manière à effectuer un mouvement correspondant à celui de l'obturateur (11, 23), que le canal de compensation de la pression (25) passe du côté faisant face au passage du robinet (13) par l'obturateur (11, 23) dans la seconde chambre (6) et qu'il est doté d'une résistance d'écoulement (28) influençant l'intervalle d'enclenchement du dispositif de réglage, qu'un mécanisme d'entraînement (26, 27) pour soulever l'obturateur (11, 23) du siège (12) du robinet est accouplé au diaphragme (4) effectuant un mouvement correspondant à celui du diaphragme de telle façon qu'il (26, 27) ne souleve l'opérateur du siège (12) qu'après un déplacement prédéterminé du diaphragme et qu'un ressort (24) est en action entre le diaphragme (4, 40) et l'obturateur (11, 23), ledit ressort étant tendu par un déplacement initial du diaphragme et se détend quand l'obturateur (11, 23) est soulevé du siège, accélérant ainsi brusquement le mouvement d'ouverture de l'obturateur.
- Dispositif de réglage à intervalle pneumatique selon la revendication 1, caractérisé par le fait que l'obturateur comprend une soupape (11) consistant au moins en partie d'un matériau magnétisable ou magnétique et une tige (23) rigidement fixée à cette soupape et se terminant dans la seconde chambre (6), tige traversée coaxialement par le canal de compensation de la pression (25), que la tige (23) passe par une ouverture centrale du diaphragme (4, 40) et que l'une de ses extrémités est fixée à l'une des extrémités du ressort (24).
- Dispositif de réglage à intervalle pneumatique selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 et 2, caractérisé par le fait qu'un soufflet (24) étanche au gaz et gonflable dans le sens de l'axe de mouvement (14) est raccordé d'un côté avec l'obturateur (11, 23) et de l'autre côté avec le diaphragme (4, 40).
- Dispositif de réglage à intervalle pneumatique selon la revendication 3, caractérisé par le fait que le soufflet est un soufflet en caoutchouc entourant l'obturateur (23) dont la paroi fait office de ressort entre le diaphragme (4, 40) et l'obturateur (11, 23).
- Dispositif de réglage à intervalle pneumatique selon la revendication 4, caractérisé par le fait que la soupape (11) est par l'intermédiaire de la tige (23) suspendue à ce soufflet (24).
- Dispositif de réglage à intervalle pneumatique selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 5, caractérisé par le fait qu'un tube capillaire est disposé dans le canal de compensation de la pression (25), tube dont la section d'ouverture et la longueur déterminent la résistance d'écoulement du canal.
- Dispositif de réglage à intervalle pneumatique selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 5, caractérisé par le fait que le canal de compensation de la pression (25) est muni d'un organe d'étranglement ajustable, déterminant la résistance à écoulement à l'intérieur du canal.
- Dispositif de réglage à intervalle pneumatique selon l'une quelconque des revendications 2 à 6, caractérisé par le fait que le mécanisme d'entraînement comprend une douille (26) déplaçable le long de la tige (23) de l'obturateur et accouplée au diaphragme (4, 40), effectuant un mouvement correspondant à celui du diaphragme, ainsi qu'une butée (27) disposée sur la voie de déplacement de la douille et rigidement fixée à la tige.
- Dispositif de réglage à intervalle pneumatique selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 8, caractérisé par le fait que le passage du robinet (13) comporte concentriquement par rapport au siège (12) un alésage (15) coaxialement à l'axe de mouvement (14) et dans lequel est monté un aimant permanent (20).
- Dispositif de réglage à intervalle pneumatique selon la revendication 9, caractérisé par le fait que l'aimant permanent (20) est dispose entre deux épanouissements polaires (21) dont les extrémités faisant face à l'obturateur saillissent de la surface frontale de l'aimant permanent et que l'alésage (15) est muni d'un rainure annulaire (16) communiquant avec la sortie du gaz (8) dans la zone de saillie des deux épanouissements polaires (21).
- Dispositif de réglage à intervalle pneumatique selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 10, caractérisé par le fait que le diaphragme (4) est comprimé en position finale correspondant à la position de fermeture de l'obturateur (11, 23) par un ressort travaillant en compression (32) appuyé par le corps (1).
- Dispositif de réglage à intervalle pneumatique selon la revendication 11, caractérisé par le fait que le ressort (32) est maintenu par une vis de serrage (31), serrée de façon étanche au gaz coaxialement ou parallèlement dans le corps (1) et que la force excercée par ce ressort sur le diaphragme (4, 40) peut être ajustée dans le sens de l'axe de mouvement (14) de l'obturateur (11, 23) en modifiant la position de la vis de serrage.
- Dispositif de réglage à intervalle pneumatique selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 12, caractérisé par le fait que le corps (1) se compose de deux parties (2, 3) entre lesquelles est tendu le diaphragme (4,40).
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| AT86102188T ATE63630T1 (de) | 1985-02-25 | 1986-02-20 | Pneumatische intervallschaltvorrichtung. |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE19853506612 DE3506612A1 (de) | 1985-02-25 | 1985-02-25 | Pneumatische intervallschaltvorrichtung |
| DE3506612 | 1985-02-25 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0193108A2 EP0193108A2 (fr) | 1986-09-03 |
| EP0193108A3 EP0193108A3 (en) | 1988-07-20 |
| EP0193108B1 true EP0193108B1 (fr) | 1991-05-15 |
Family
ID=6263519
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP86102188A Expired - Lifetime EP0193108B1 (fr) | 1985-02-25 | 1986-02-20 | Dispositif de réglage à intervalle pneumatique |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0193108B1 (fr) |
| AT (1) | ATE63630T1 (fr) |
| DE (2) | DE3506612A1 (fr) |
| ES (1) | ES8704615A1 (fr) |
| HU (1) | HU195302B (fr) |
| IN (1) | IN167246B (fr) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AT398474B (de) * | 1991-04-26 | 1994-12-27 | Vaillant Gmbh | Gasbrenner |
| DE102004001221B4 (de) * | 2004-01-07 | 2009-02-12 | Rational Ag | Gargerät mit einer Vorrichtung zum Verschließen / Öffnen zumindest einer Öffnung und Verfahren hierzu |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3247868A (en) * | 1962-07-13 | 1966-04-26 | Itt | Fluid control means |
| FR1445304A (fr) * | 1965-08-25 | 1966-07-08 | Junkers & Co | Soupape commandée par thermostat pour régler l'amenée du gaz à un appareil chauffé au gaz |
| FR2524965A1 (fr) * | 1982-04-09 | 1983-10-14 | Carl Yves | Obturateur automatique detecteur de fuites |
| DE3330318A1 (de) * | 1983-08-23 | 1985-03-07 | Ruhrgas Ag, 4300 Essen | Gas-koch- oder heizgeraet |
-
1985
- 1985-02-25 DE DE19853506612 patent/DE3506612A1/de not_active Withdrawn
-
1986
- 1986-02-20 EP EP86102188A patent/EP0193108B1/fr not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1986-02-20 AT AT86102188T patent/ATE63630T1/de not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1986-02-20 DE DE8686102188T patent/DE3679216D1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1986-02-24 HU HU86758A patent/HU195302B/hu unknown
- 1986-02-25 ES ES552371A patent/ES8704615A1/es not_active Expired
- 1986-04-17 IN IN288/MAS/86A patent/IN167246B/en unknown
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| IN167246B (fr) | 1990-09-29 |
| ES552371A0 (es) | 1987-04-16 |
| EP0193108A3 (en) | 1988-07-20 |
| HUT43163A (en) | 1987-09-28 |
| HU195302B (en) | 1988-04-28 |
| EP0193108A2 (fr) | 1986-09-03 |
| ES8704615A1 (es) | 1987-04-16 |
| ATE63630T1 (de) | 1991-06-15 |
| DE3506612A1 (de) | 1986-08-28 |
| DE3679216D1 (de) | 1991-06-20 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| DE69224621T2 (de) | Ein schnelles impulsion erzeugende membranventil | |
| DE69612144T2 (de) | Verbessertes electromagnetisches Dosierventil für ein Kraftstoffeinspritzventil | |
| EP0195261B1 (fr) | Soupape magnétique, en particulier soupape de commande de quantité de combustible | |
| CH655984A5 (de) | Magnetventil mit leistungsverstaerker. | |
| DE19907998C1 (de) | Gasdruckeinstellvorrichtung mit einem direkt modulierenden Gasdruckeinstellventil | |
| DE10044822C1 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Prüfen der Dichtheit von Ventilen in einer Gasstrecke | |
| DE112009004389T5 (de) | Pilotbetätigtes Wasserventil | |
| DE3739337A1 (de) | Ventilanordnung | |
| DE3244840C2 (fr) | ||
| CH661107A5 (de) | Vorgesteuertes ventil. | |
| EP0193108B1 (fr) | Dispositif de réglage à intervalle pneumatique | |
| EP0462583B1 (fr) | Régulateur de pression de gaz commandé par une membrane | |
| EP0811795B1 (fr) | Robinet d'eau piloté | |
| DE3942437C2 (fr) | ||
| DE3811358A1 (de) | Selbstschlussventil | |
| DE3619840C2 (de) | Gashahn | |
| DE4038736A1 (de) | Eigenmediumbetaetigtes, durch einen magnetanker gesteuertes servoventil | |
| DE2723178C2 (de) | Sicherheits- und Steuersystem für die Luftzufuhr zur Verbrennungskammer eines Gasbrenners mit Zwangsabzug | |
| EP0135157B1 (fr) | Appareil à gaz pour la cuisson ou pour le chauffage | |
| EP0058741A1 (fr) | Soupape combinée | |
| DE4341997A1 (de) | Gasbrenner | |
| DE3211889C2 (fr) | ||
| DE102011053152A1 (de) | Vorrichtung zur Steuerung der Brennstoffmenge durch eine Brennstoffleitung | |
| DE2518335C3 (de) | Gasventil | |
| EP0109978A1 (fr) | Appareil de régulation de gaz avec un servorégulateur de pression |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AT CH DE FR GB LI |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AT CH DE FR GB LI |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19881224 |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19891228 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT CH DE FR GB LI |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 63630 Country of ref document: AT Date of ref document: 19910615 Kind code of ref document: T |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 3679216 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19910620 |
|
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) | ||
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Effective date: 19920220 Ref country code: AT Effective date: 19920220 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Effective date: 19920229 Ref country code: CH Effective date: 19920229 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Effective date: 19921030 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 19930113 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Effective date: 19941101 |