EP0048784A2 - Endothermische Hochleistungskolbenkraftmaschine mit einem entsprechenden thermodynamischen Kreisprozess - Google Patents
Endothermische Hochleistungskolbenkraftmaschine mit einem entsprechenden thermodynamischen Kreisprozess Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0048784A2 EP0048784A2 EP80830103A EP80830103A EP0048784A2 EP 0048784 A2 EP0048784 A2 EP 0048784A2 EP 80830103 A EP80830103 A EP 80830103A EP 80830103 A EP80830103 A EP 80830103A EP 0048784 A2 EP0048784 A2 EP 0048784A2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- piston
- combustion
- endothermic engine
- thermodynamic cycle
- ignition
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
- 238000002485 combustion reaction Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 22
- 239000000446 fuel Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 10
- 238000010521 absorption reaction Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 3
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 3
- 239000012530 fluid Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 3
- 230000006835 compression Effects 0.000 claims description 7
- 238000007906 compression Methods 0.000 claims description 7
- 230000002269 spontaneous effect Effects 0.000 claims description 7
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 238000005474 detonation Methods 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000003466 anti-cipated effect Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000011109 contamination Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000002826 coolant Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000012423 maintenance Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000001105 regulatory effect Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000010494 dissociation reaction Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000005593 dissociations Effects 0.000 description 5
- 206010013457 Dissociation Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 239000003153 chemical reaction reagent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 208000018459 dissociative disease Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 230000002349 favourable effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000003112 inhibitor Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000003647 oxidation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000007254 oxidation reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000001174 ascending effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008030 elimination Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003379 elimination reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000009466 transformation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008016 vaporization Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F02—COMBUSTION ENGINES; HOT-GAS OR COMBUSTION-PRODUCT ENGINE PLANTS
- F02B—INTERNAL-COMBUSTION PISTON ENGINES; COMBUSTION ENGINES IN GENERAL
- F02B75/00—Other engines
- F02B75/02—Engines characterised by their cycles, e.g. six-stroke
Definitions
- This invention concerns a new high efficiency alternating endothermic engine based on a new thermodynamic cycle as well as eventual transformation of existing engines.
- Detonation is harmful in that, as an instantaneous combustion (foreseen in the ideal OTTO cycle), it occurs at the wrong moment since it affords maximum pressure in the instant in which the piston is at zero velocity, with the connecting rod perpendicular to the crank arm of the drive shaft, and thus the engine moment is zero.
- Dissociation occurs in the engine to create very rapidly alternating dissociations and reassociations as long as the specific dissociation temperature of the reagents is maintained. By continuing until the exhaust valve is opened, this leads to incomplete combustion since some of these reagents escape still unburned.
- Oxidation inhibitors allow a higher compression ratio to be used, but slow down combustion velocity and cause atmospheric pollution, for the OTTO cycle.
- This goal is achieved by keeping the combustion chamber volume constant for the period required for complete combustion of the operating fluid. In this way, higher maximum pressure is achieved for a pre-established and calculable period so as to obtain a more elevated tangential component and thus a higher engine torque for the same heat absorption and fuel consumption as in current engines.
- the engine consists of a piston or other suitable device advancing with pre-established. and calculable movement as a function of the type and the required performance. This movement occurs through crank mechanisms, cams, rockers or the like positioned or controlled by any type of kinematic chain.
- the invention tends to consider detonation as useful rather than harmful in that occurring after the Maximum Dead Point (M.D.P.), it does not shove the piston but rather pushes it without the characteristic spark knock. With the use of suitable devices, this may even lead to spontaneous ignition of suitably prepared fuel mixtures.
- M.D.P. Maximum Dead Point
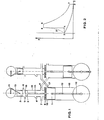
- each element of the engine is composed of a cylinder with two diameters 15 and 16 separated by a diaphragm with a tight stuffing box 5 designed to protect the engine crank mechanism 10 with connecting rod 12 from contamination of the coolant and to seal pistons 1 and 2 in their phases of aspiration and compression of the scavaging air.
- piston 3 connected through connecting rod 13 to crank arm 11, leading to a crank mechanism approximately 90° out of phase with that of 10.
- the volume of combustion chamber 19 is kept nearly constant up to approximately 40° from the M.D.P., where ignition and the onset of combustion occur through spark plug 8.
- the controlled ignition may be anticipated or retarded as in current engines, or the same effect may be achieved by regulating the air intake in the spontaneous ignition variants. Soon after, at the corrent moment, liquid is injected from 9 and in vapourizing lowers the temperature, limits dissociation-reassociation and causes the pressure to increase, using the temperature of the exhaust gases and cylinder walls as well. Contemporaneously, piston 1 sealed with diaphragm 5 begins aspiration through port or valves 18.
- piston 2 covers the exhaust 7 and intake 6 ports, leading to wash out with previously compressed air.
- piston 2 (which is joined to piston 1 via rod 14) covers ports 6 and 7. Liquid or gaseous fuel is then injected through injector 4, compression occurs and the cycle is repeated.
- the wash out operation is greatly facilitated in the engine with two coupled cylinders at 180°, as in figure 1, and air feed is likewise favoured.
- the above-mentioned coupling of the two cylindrical elements is effected through exhaust ports 17 and 7 for compressed air.
- the diagram in figure 2 illustrates the thermodynamic cycle of the controlled ignition engine: 1-2, aspiration; 2-3, compression; 3-4, maintenance of the achieved pressure; 4-5, instantaneous combustion; 5-6, continuation of combustion; 6-7, expansion; 7-2-1, discharge.
- Figure 2 also shows the spontaneous ignition possible using suitable fuels, in the dashed line variant 3-3'-5.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Combustion & Propulsion (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Output Control And Ontrol Of Special Type Engine (AREA)
- Combustion Methods Of Internal-Combustion Engines (AREA)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| IT49751/80A IT1193279B (it) | 1980-09-26 | 1980-09-26 | Motori endotermici alternativi ad alto rendimento con nuovo ciclo termodinamico |
| IT4975180 | 1980-09-26 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0048784A2 true EP0048784A2 (de) | 1982-04-07 |
| EP0048784A3 EP0048784A3 (de) | 1982-09-29 |
Family
ID=11271482
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP80830103A Withdrawn EP0048784A3 (de) | 1980-09-26 | 1980-12-01 | Endothermische Hochleistungskolbenkraftmaschine mit einem entsprechenden thermodynamischen Kreisprozess |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0048784A3 (de) |
| JP (1) | JPS5759028A (de) |
| AU (1) | AU6693981A (de) |
| IT (1) | IT1193279B (de) |
Family Cites Families (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE180037C (de) * | ||||
| US2139457A (en) * | 1935-08-09 | 1938-12-06 | Patchett George William | Internal combustion engine |
| FR891112A (fr) * | 1941-11-08 | 1944-02-28 | Sulzer Ag | Moteur à combustion interne à pistons opposés |
| US3312206A (en) * | 1964-12-09 | 1967-04-04 | Radovic Dusan | Reciprocating engines |
| US4157080A (en) * | 1975-02-11 | 1979-06-05 | Hill Craig C | Internal combustion engine having compartmented combustion chamber |
| GB1516982A (en) * | 1975-09-15 | 1978-07-05 | Jones R | Reciprocating piston heat engines |
| DE7609041U1 (de) * | 1976-03-24 | 1976-11-11 | Salomon, Kurt, 6078 Neu-Isenburg | Wasser-benzin- oder diesel- betriebener kolbenmotor |
| US4169435A (en) * | 1977-06-23 | 1979-10-02 | Faulconer Edward L Jr | Internal combustion engine and method |
| DE2823448A1 (de) * | 1978-05-30 | 1979-12-06 | Dana Corp | Viertakt-brennkraftmaschine |
-
1980
- 1980-09-26 IT IT49751/80A patent/IT1193279B/it active
- 1980-12-01 EP EP80830103A patent/EP0048784A3/de not_active Withdrawn
- 1980-12-17 JP JP55179649A patent/JPS5759028A/ja active Pending
-
1981
- 1981-02-05 AU AU66939/81A patent/AU6693981A/en not_active Abandoned
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| IT8049751A0 (it) | 1980-09-26 |
| IT1193279B (it) | 1988-06-15 |
| JPS5759028A (en) | 1982-04-09 |
| AU6693981A (en) | 1982-04-01 |
| EP0048784A3 (de) | 1982-09-29 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CA2045263C (en) | Internal combustion engine and method | |
| US4565167A (en) | Internal combustion engine | |
| EE02987B1 (et) | Sisepõlemismootor ja sisepõlemismootori töömeetod | |
| US4280451A (en) | High compression vacuum cycle engine | |
| JP2014503740A (ja) | フル拡張内燃機関 | |
| SU1733652A1 (ru) | Двигатель внутреннего сгорани | |
| EP0048784A2 (de) | Endothermische Hochleistungskolbenkraftmaschine mit einem entsprechenden thermodynamischen Kreisprozess | |
| US5230315A (en) | Otto-cycle engine | |
| RU99103574A (ru) | Способ работы двигателя внутреннего сгорания | |
| US2992638A (en) | Internal combustion engine and method of operating same | |
| CN1210199A (zh) | 分缸循环内燃机 | |
| JPS5853668A (ja) | 内燃機関の燃焼方法 | |
| GB2239901A (en) | Engine charge intake control | |
| GB2205900A (en) | Compound I.C. engine | |
| CN211144636U (zh) | 一种节能四冲程内燃机 | |
| WO2001042634A1 (en) | Z-engine | |
| JPS59113239A (ja) | 二段膨張式内燃機関 | |
| RU2163975C1 (ru) | Способ работы двигателя внутреннего сгорания | |
| KR920000052B1 (ko) | 저공해 고출력 내연기관 | |
| RU2022136C1 (ru) | Способ работы двигателя внутреннего сгорания | |
| RU2067193C1 (ru) | Способ работы двухфоркамерного двигателя внутреннего сгорания и двухфоркамерный двигатель внутреннего сгорания | |
| RU2006611C1 (ru) | Способ работы дизельного двигателя внутреннего сгорания | |
| JPS5543260A (en) | Internal combustion engine | |
| RU2684046C1 (ru) | Способ работы двигателя внутреннего сгорания | |
| SU1348542A1 (ru) | Способ работы двигател внутреннего сгорани с наддувом и двигатель внутреннего сгорани с наддувом |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): AT BE DE FR GB NL SE |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): AT BE DE FR GB NL SE |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE APPLICATION HAS BEEN WITHDRAWN |
|
| 18W | Application withdrawn |
Withdrawal date: 19821102 |