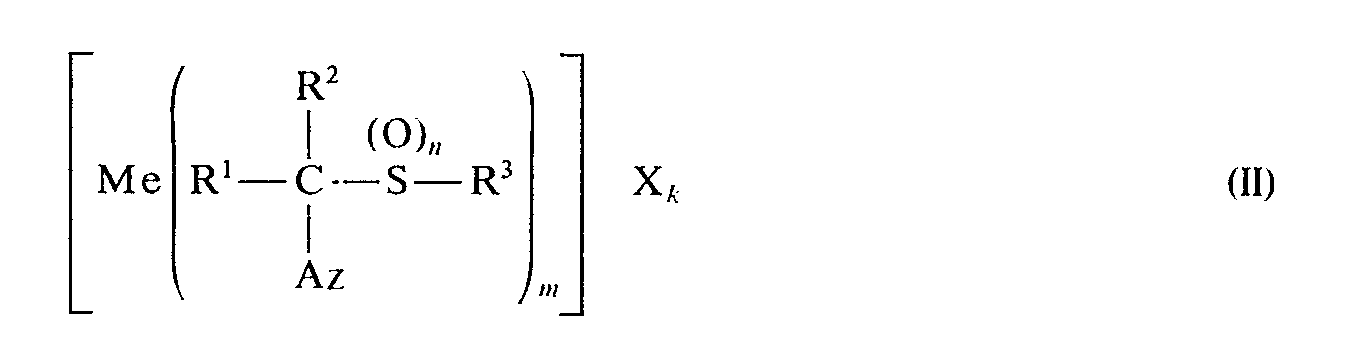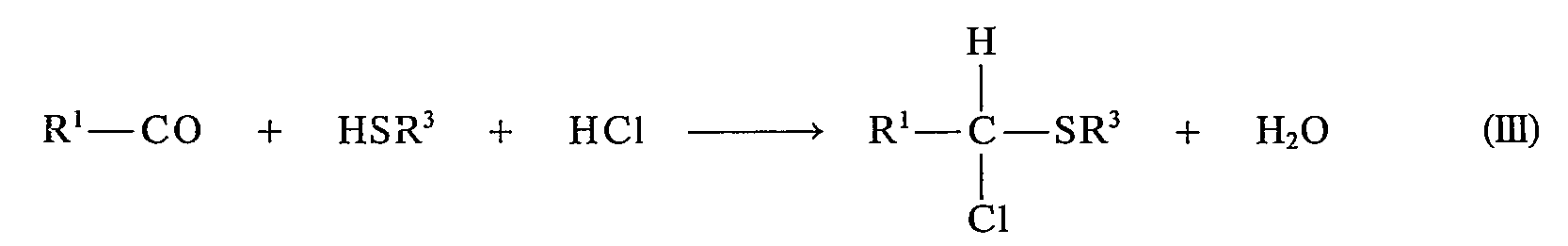EP0000752B1 - Alpha-azolylsulphides, sulphoxides and sulphones, their salts and metal complexes, method for their production and fungizides containing them - Google Patents
Alpha-azolylsulphides, sulphoxides and sulphones, their salts and metal complexes, method for their production and fungizides containing them Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0000752B1 EP0000752B1 EP78100538A EP78100538A EP0000752B1 EP 0000752 B1 EP0000752 B1 EP 0000752B1 EP 78100538 A EP78100538 A EP 78100538A EP 78100538 A EP78100538 A EP 78100538A EP 0000752 B1 EP0000752 B1 EP 0000752B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- sulfide
- chlorophenyl
- weight
- triazol
- parts
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired
Links
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D257/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing rings having four nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms
- C07D257/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing rings having four nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms not condensed with other rings
- C07D257/04—Five-membered rings
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01N—PRESERVATION OF BODIES OF HUMANS OR ANIMALS OR PLANTS OR PARTS THEREOF; BIOCIDES, e.g. AS DISINFECTANTS, AS PESTICIDES OR AS HERBICIDES; PEST REPELLANTS OR ATTRACTANTS; PLANT GROWTH REGULATORS
- A01N43/00—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing heterocyclic compounds
- A01N43/48—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing heterocyclic compounds having rings with two nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms
- A01N43/50—1,3-Diazoles; Hydrogenated 1,3-diazoles
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01N—PRESERVATION OF BODIES OF HUMANS OR ANIMALS OR PLANTS OR PARTS THEREOF; BIOCIDES, e.g. AS DISINFECTANTS, AS PESTICIDES OR AS HERBICIDES; PEST REPELLANTS OR ATTRACTANTS; PLANT GROWTH REGULATORS
- A01N43/00—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing heterocyclic compounds
- A01N43/48—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing heterocyclic compounds having rings with two nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms
- A01N43/58—1,2-Diazines; Hydrogenated 1,2-diazines
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01N—PRESERVATION OF BODIES OF HUMANS OR ANIMALS OR PLANTS OR PARTS THEREOF; BIOCIDES, e.g. AS DISINFECTANTS, AS PESTICIDES OR AS HERBICIDES; PEST REPELLANTS OR ATTRACTANTS; PLANT GROWTH REGULATORS
- A01N43/00—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing heterocyclic compounds
- A01N43/64—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing heterocyclic compounds having rings with three nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms
- A01N43/647—Triazoles; Hydrogenated triazoles
- A01N43/653—1,2,4-Triazoles; Hydrogenated 1,2,4-triazoles
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01N—PRESERVATION OF BODIES OF HUMANS OR ANIMALS OR PLANTS OR PARTS THEREOF; BIOCIDES, e.g. AS DISINFECTANTS, AS PESTICIDES OR AS HERBICIDES; PEST REPELLANTS OR ATTRACTANTS; PLANT GROWTH REGULATORS
- A01N43/00—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing heterocyclic compounds
- A01N43/713—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing heterocyclic compounds having rings with four or more nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D231/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,2-diazole or hydrogenated 1,2-diazole rings
- C07D231/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,2-diazole or hydrogenated 1,2-diazole rings not condensed with other rings
- C07D231/10—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,2-diazole or hydrogenated 1,2-diazole rings not condensed with other rings having two or three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D231/12—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,2-diazole or hydrogenated 1,2-diazole rings not condensed with other rings having two or three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with only hydrogen atoms, hydrocarbon or substituted hydrocarbon radicals, directly attached to ring carbon atoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D233/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazole or hydrogenated 1,3-diazole rings, not condensed with other rings
- C07D233/54—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazole or hydrogenated 1,3-diazole rings, not condensed with other rings having two double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D233/56—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazole or hydrogenated 1,3-diazole rings, not condensed with other rings having two double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with only hydrogen atoms or radicals containing only hydrogen and carbon atoms, attached to ring carbon atoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D249/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings having three nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms
- C07D249/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings having three nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms not condensed with other rings
- C07D249/08—1,2,4-Triazoles; Hydrogenated 1,2,4-triazoles
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07F—ACYCLIC, CARBOCYCLIC OR HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS CONTAINING ELEMENTS OTHER THAN CARBON, HYDROGEN, HALOGEN, OXYGEN, NITROGEN, SULFUR, SELENIUM OR TELLURIUM
- C07F1/00—Compounds containing elements of Groups 1 or 11 of the Periodic System
- C07F1/005—Compounds containing elements of Groups 1 or 11 of the Periodic System without C-Metal linkages
Definitions
- the invention relates to new ⁇ -azolyl sulfides, ⁇ -azolyl sulfoxides and a-azolyl sulfones and their salts and metal complexes, processes for their preparation and agents for combating fungi containing them.
- imidazole derivatives for example 1- [2,4-dichlorophenyl- ⁇ -allylethyl ether] imidazole (DE-OS 2063857)
- the effect is not always satisfactory at low application rates and application concentrations.
- the fungitoxic effect is often associated with a high level of phytotoxicity, so that the crops are also damaged in the concentrations required for combating rust fungi. For these reasons, they are not always suitable for use as crop protection agents for combating fungi and not for all types of plants.
- R 1 means, for example, hydrogen, methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, n-pentyl, n-hexyl, n-heptyl (3), methoxycarbonyl, phenyl, 4-nitrophenyl, 4-bromophenyl, 4-cyanophenyl , 2-methylphenyl, 4-t-butylphenyl, 3-trifluoromethylphenyl, 4-trifluoromethylphenyl, 4-fluorophenyl, 2-chlorophenyl, 4-chlorophenyl, 2,4-dichlorophenyl, 2,6-dichlorophenyl, 3,4-dichlorophenyl, - Naphthyl.
- R 2 means, for example, hydrogen, methyl, n-propyl.
- R 3 means, for example, methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, t-butyl, n-pentyl, n-hexyl, allyl, propargyl, phenyl, 4-methoxyphenyl, 4-tolyl, 4-chlorophenyl, 3, 4-dichlorophenyl, 2,4-dichlorophenyl, 2,3,6-trichlorophenyl, benzyl, 3-trifluoromethylbenzyl, 4-chlorobenzyl, 4-bromobenzyl, 3,4-dichlorobenzyl, 2,4-dichlorobenzyl, 2,3,6- Trichlorobenzyl, 2-phenylethyl.
- salts are the hydrochlorides, bromides, sulfates, nitrates, phosphates, oxalates or dodecylbenzenesulfonates.
- the effectiveness of the salts is due to the cation, so that the choice of the anion is arbitrary.
- a diluent such as methanol, ethanol, isopropanol, n-butanol, diethyl ether, tetrahydrofuran, dioxane, acetone, acetonitrile, dimethylformamide, dimethyl sulfoxide, chloroform, methylene chloride or toluene can be used.
- Potassium permanganate, hydrogen peroxide or percarboxylic acids such as peracetic acid, perbenzoic acid or 3-chloroperbenzoic acid can be used as the oxidizing agent.
- a diluent such as water, acetic acid, methanol, acetone, chloroform or methylene chloride can be used.
- the metal salts of formula IV are well known, easily accessible compounds.
- All water-miscible solvents are suitable for the preparation of the metal complexes of the formula II. These preferably include methanol, ethanol, isopropanol, acetone, tetrahydrofuran and dioxane. It is generally carried out at temperatures between 0 and 100 ° C, preferably between 10 and 35 ° C.
- separation of the enantiomers or diastereomers is normally not required for use as fungicides or as an agent for regulating plant growth.
- a solution of 6.0 g of 1-pentyl- [1- (1,2,4-triazol-1-yl) pentyl is added dropwise to the solution of 10.0 g of 85 percent 3-chloroperbenzoic acid in 140 ml of methyl chloride with stirring and ice-cooling - (1)] - sulfide. After the initial heating has subsided, the mixture is stirred for a further 2 days at 25 ° C. The mixture is then washed with sodium carbonate solution, sodium sulfite solution and water and the organic phase is dried. After concentration, a light yellow oil remains, from which 3.5 g of colorless crystals of mp 69 ° to 71 ° C. are obtained when rubbed with diisopropyl ether.
- 82 g of tert-butyl - [(2-methylphenyl) chloromethyl] sulfide are added dropwise to the solution of 43.6 g of imidazole in 300 ml of acetone with stirring. After adding 88 g of finely powdered potassium carbonate, the mixture is heated under reflux for 5 hours. The undissolved constituents are then filtered off and the filtrate is concentrated. The residue mixed with 300 ml of water is extracted with 3 x 200 ml of methylene chloride. After washing with water, drying and concentrating, 69 g of a brownish oil remain from the combined organic phases, which are dissolved in 1 l of diisopropyl ether.
- the colorless, insoluble residue of the hexane extractions consists of 27 g (12%) 2,4-dichlorobenzyl - [(2 ', 4'-dichlorophenyl) - (1,2,4-triazol-4-yl) methyl] sulfide from mp. 132-133 ° C.
- a solution of 7.1 g of 85 percent 3-chloroperbenzoic acid in 70 is added dropwise to the solution of 9.7 g of tert-butyl - [(4-chlorophenyl) -1,2,4-triazolylmethyl] sulfide in 20 ml of methylene chloride while cooling with ice ml of methylene chloride.
- the new a-azolyl sulfides, a-azolyl sulfoxides and a-azolyl sulfones and their salts show a considerably broader fungicidal activity and a superior plant tolerance than the known 1- [2,4-dichlorophenyl-ß-allylethyl ether] imidazole.
- the new active ingredients can also be in the form of their salts, e.g. B. hydrochlorides, oxalates or nitrates can be used.
- crop plants mean wheat, rye, barley, oats, rice, corn, apple tree, cucumber, beans, coffee, sugar cane, grapevine, strawberries and ornamental plants in horticulture.
- the active compounds according to the invention are systemically active.
- the systemic effectiveness of these agents is of particular interest in connection with the control of internal plant diseases, for. B. grain rust, powdery mildew.
- the agents according to the invention can simultaneously suppress the growth of two or more of the fungi mentioned and are highly tolerated by plants.
- the application rates required to control the phytopathogenic fungi are between 0.05 and 2 kg of active ingredient / ha of cultivated area.
- the active compounds according to the invention can be converted into the customary formulations, such as solutions, emulsions, suspensions, powders, pastes and granules. These are manufactured in a known manner, e.g. B. by mixing the active ingredient with solvents and / or carriers, optionally using emulsifiers and dispersants, and in the case of using water as a diluent also other organic solvents as auxiliary solvents! can be used.
- solvents such as aromatics (e.g. xylene, benzene), chlorinated armates (e.g. chlorobenzenes), paraffins (e.g. petroleum fractions), alcohols (e.g.
- ⁇ ⁇
- Carriers such as natural rock powder (e.g. kaolins, clays, talc, chalk) and synthetic rock powder (e.g. highly disperse silica, silicates); Emulsifiers such as nonionic and anionic emulsifiers (e.g. polyoxyethylene fatty alcohol ether, alkyl sulfonates and aryl sulfonates) and dispersants such as lignin, sulfite liquor and methyl cellulose.
- Carriers such as natural rock powder (e.g. kaolins, clays, talc, chalk) and synthetic rock powder (e.g. highly disperse silica, silicates)
- Emulsifiers such as nonionic and anionic emulsifiers (e.g. polyoxyethylene fatty alcohol ether, alkyl sulfonates and aryl sulfonates) and dispersants such as lignin, sulfite liquor and methyl
- the formulations generally contain between 0.1 and 95 percent by weight of active compound, preferably between 0.5 and 90%.
- the formulations or the ready-to-use preparations produced therefrom, such as solutions, emulsions, suspensions, powders, pastes or granules, are used in a known manner, for example by spraying, atomizing, dusting, scattering, pickling or pouring.
- agents according to the invention can also be present in these use forms together with other active ingredients, e.g. B. herbicides, insecticides, growth regulators and fungicides or with fertilizers.
- active ingredients e.g. B. herbicides, insecticides, growth regulators and fungicides or with fertilizers.
- Leaves of »Firlbeck's Union « barley seedlings grown in pots are sprayed with aqueous emulsions of 80% (% by weight) active ingredient and 20% emulsifier and after the Drying the spray coating with oidia (spores) of the barley powdery mildew (Erysiphe graminis var. Hordei) dusted.
- the test plants are then placed in a greenhouse at temperatures between 20 and 22 ° C and 75 to 80% relative humidity. After 10 days, the extent of the development of mildew is determined.
- Leaves of »Jubilar « wheat seedlings grown in pots are artificially infected with spores of the wheat brown rust (Puccinia recondita) 24 hours before spraying and placed at 20 to 25 ° C in a water vapor-saturated chamber.
- the plants are then sprayed with aqueous emulsions of 80% (weight percent) active ingredient and 20% emulsifier. After the spray coating has dried on, the test plants are placed in the greenhouse at temperatures between 20 and 22 ° C. and 75 to 80% relative atmospheric humidity. After 10 days, the extent of the rust fungus development is determined.
- active ingredient 2 20 parts by weight of active ingredient 2 are mixed well with 3 parts by weight of the sodium salt of diisobutylnaphthalene- ⁇ -sulfonic acid, 17 parts by weight of the sodium salt of lignosulfonic acid from a sulfite waste liquor and 60 parts by weight of powdered silica gel and ground in a hammer mill.
- a spray liquor is obtained which contains 0.1% by weight of the active ingredient.
- active ingredient 1 40 parts by weight of active ingredient 1 are intimately mixed with 10 parts of sodium salt of a phenolsulfonic acid-urea-formaldehyde condensate, 2 parts of silica gel and 48 parts of water. A stable aqueous dispersion is obtained. Dilution with 100,000 parts by weight of water gives an aqueous dispersion which contains 0.04% by weight of active ingredient.
- active ingredient 2 20 parts are intimately mixed with 2 parts of calcium salt of dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid, 8 parts of fatty alcohol polyglycol ether, 2 parts of sodium salt of a phenolsulfonic acid-urea-formaldehyde condensate and 68 parts of a paraffinic mineral oil. A stable oily dispersion is obtained.
Description
Die Erfindung betrifft neue α-Azolylsulfide, α-Azolyl-sulfoxide und a-Azolyl-sulfone sowie deren Salze und Metallkomplexe, Verfahren zu ihrer Herstellung sowie sie enthaltende Mittel zur Bekämpfung von Pilzen.The invention relates to new α-azolyl sulfides, α-azolyl sulfoxides and a-azolyl sulfones and their salts and metal complexes, processes for their preparation and agents for combating fungi containing them.
Es ist bekannt, daß Imidazol-Derivate, zum Beispiel das 1-[2,4-Dichlorphenyl-ß-allyläthyläther]-imidazol (DE-OS 2063857), eine gute fungizide Wirksamkeit zeigen. Die Wirkung ist bei niedrigen Aufwandmengen und Anwendungskonzentrationen nicht immer befriedigend. Darüber hinaus ist die fungitoxische Wirkung oft mit einer hohen Phytotoxizität verbunden, so daß in den für die Bekämpfung von Rostpilzen notwendigen Konzentrationen auch die Kulturpflanzen geschädigt werden. Aus diesen Gründen sind sie für den Gebrauch als Pflanzenschutzmittel zur Bekämpfung von Pilzen nicht immer und nicht bei allen Pflanzenarten geeignet.It is known that imidazole derivatives, for example 1- [2,4-dichlorophenyl-β-allylethyl ether] imidazole (DE-OS 2063857), show good fungicidal activity. The effect is not always satisfactory at low application rates and application concentrations. In addition, the fungitoxic effect is often associated with a high level of phytotoxicity, so that the crops are also damaged in the concentrations required for combating rust fungi. For these reasons, they are not always suitable for use as crop protection agents for combating fungi and not for all types of plants.
Es wurde gefunden, daß die neuen α-Azolylsulfide, -sulfoxide und -sulfone der Formel
- R1 Wasserstoff, Alkyl, Alkoxycarbonyl oder gegebenenfalls substituiertes Aryl,
- R2 Wasserstoff oder Alkyl,
- R3 Alkyl, Alkenyl, Alkinyl, gegebenenfalls substituiertes Phenyl oder gegebenenfalls substituiertes Aralkyl,
- Az Imidazol-1-yl, Pyrazol-1-yl, 1,2,4-Triazo)-1-y), 1,2,4-Triazo)-4-y), Tetrazot-1-y) oder Tetrazol-2-yl und
- n 0, 1 oder 2 bedeuten und deren Salze und Metallkomplexe gut wirksam gegen Schadpilze, insbesondere aus der Klasse derAscomyceten und Basidiomyceten sind.
- R 1 is hydrogen, alkyl, alkoxycarbonyl or optionally substituted aryl,
- R 2 is hydrogen or alkyl,
- R 3 is alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, optionally substituted phenyl or optionally substituted aralkyl,
- Az imidazol-1-yl, pyrazol-1-yl, 1,2,4-triazo) -1-y), 1,2,4-triazo) -4-y), tetrazot-1-y) or tetrazole- 2-yl and
- n is 0, 1 or 2 and their salts and metal complexes are effective against harmful fungi, in particular from the classes of the ascomycetes and basidiomycetes.
R1 bedeutet beispielsweise Wasserstoff, Methyl, Ethyl, n-Propyl, Isopropyl, n-Butyl, n-Pentyl, n-Hexyl, n-Heptyl(3), Methoxycarbonyl, Phenyl, 4-Nitrophenyl, 4-Bromphenyl, 4-Cyanphenyl, 2-Methylphenyl, 4-t-Butylphenyl, 3-Trifluormethylphenyl, 4-Trifluormethylphenyl, 4-Fluorphenyl, 2-Chlorphenyl, 4-Chlorphenyl, 2,4-Dichlorphenyl, 2,6-Dichlorphenyl, 3,4-Dichlorphenyl, -Naphthyl.R 1 means, for example, hydrogen, methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, n-pentyl, n-hexyl, n-heptyl (3), methoxycarbonyl, phenyl, 4-nitrophenyl, 4-bromophenyl, 4-cyanophenyl , 2-methylphenyl, 4-t-butylphenyl, 3-trifluoromethylphenyl, 4-trifluoromethylphenyl, 4-fluorophenyl, 2-chlorophenyl, 4-chlorophenyl, 2,4-dichlorophenyl, 2,6-dichlorophenyl, 3,4-dichlorophenyl, - Naphthyl.
R2 bedeutet beispielsweise Wasserstoff, Methyl, n-Propyl.R 2 means, for example, hydrogen, methyl, n-propyl.
R3 bedeutet beispielsweise Methyl, Ethyl, n-Propyl, Isopropyl, n-Butyl, t-Butyl, n-Pentyl, n-Hexyl, Allyl, Propargyl, Phenyl, 4-Methoxyphenyl, 4-Tolyl, 4-Chlorphenyl, 3,4-Dichlorphenyl, 2,4-Dichlorphenyl, 2,3,6-Trichlorphenyl, Benzyl, 3-Trifluormethylbenzyl, 4-Chlorbenzyl, 4-Brombenzyl, 3,4-Dichlorbenzyl, 2,4-Dichlorbenzyl, 2,3,6-Trichlorbenzyl, 2-Phenylethyl.R 3 means, for example, methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, t-butyl, n-pentyl, n-hexyl, allyl, propargyl, phenyl, 4-methoxyphenyl, 4-tolyl, 4-chlorophenyl, 3, 4-dichlorophenyl, 2,4-dichlorophenyl, 2,3,6-trichlorophenyl, benzyl, 3-trifluoromethylbenzyl, 4-chlorobenzyl, 4-bromobenzyl, 3,4-dichlorobenzyl, 2,4-dichlorobenzyl, 2,3,6- Trichlorobenzyl, 2-phenylethyl.
Salze sind beispielsweise die Hydrochloride, Bromide, Sulfate, Nitrate, Phosphate, Oxalate oder Dodecylbenzolsulfonate. Die Wirksamkeit der Salze geht auf das Kation zurück, so daß die Wahl des Anions beliebig ist.Examples of salts are the hydrochlorides, bromides, sulfates, nitrates, phosphates, oxalates or dodecylbenzenesulfonates. The effectiveness of the salts is due to the cation, so that the choice of the anion is arbitrary.
Metallkomplexe sind Verbindungen der Formel
- R1, R2, R3, Az und n die oben angegebene Bedeutung haben und
- Me ein Metall, z. B. Kupfer, Zink, Zinn, Mangan, Eisen, Cobalt oder Nickel bedeutet,
- X das Anion einer anorganischen Säure bedeutet, z. B. Salzsäure, Schwefelsäure, Phosphorsäure, Bromwasserstoffsäure,
- m und k 1,2,3 oder 4 bedeuten.
- R 1 , R 2 , R 3 , Az and n have the meaning given above and
- Me a metal, e.g. B. copper, zinc, tin, manganese, iron, cobalt or nickel,
- X represents the anion of an inorganic acid, e.g. B. hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, phosphoric acid, hydrobromic acid,
- m and k mean 1, 2, 3 or 4.
Weiterhin wurde gefunden, daß man α-Azolylsulfide der Formel I (mit n=0) erhält, wenn man α-Chlorsulfide der Formel
- R1, R2 und R3 die oben angegebenen Bedeutungen haben, mit den Azolen H-Az, in denen Az die oben angegebene Bedeutung hat, gegebenenfalls in Gegenwart einer Base und gegebenenfalls in Gegenwart eines Verdünnungsmittels umsetzt. Durch Oxidation der so erhaltenen α-Azolylsulfide der Formel I (n=0) erhält man die α-Azolyl-sulfoxide der Formel I (n=1) und die α-Azolyl-sulfone der Formel I (n=2).
- R 1 , R 2 and R 3 have the meanings given above, with the azoles H-Az, in which Az has the meaning given above, optionally in the presence of a base and optionally in the presence of a diluent. By oxidation of the α-azolyl sulfides of the formula I (n = 0) thus obtained, the α-azolyl sulfoxides of the formula I (n = 1) and the α-azolyl sulfones of the formula I (n = 2) are obtained.
Zur Herstellung der α-Azolylsulfide der Formel I (n=0) ist es zweckmäßig, die α-Chlorsulfide der Formel III ohne Verdünnungsmittel oder in Gegenwart eines Verdünnungsmittels mit etwa 0,5 bis 2 Äquivalenten eines Alkalisalzes des jeweiligen Azols oder mit etwa 0,5 bis 4 Äquivalenten des jeweiligen Azols, gegebenenfalls unter Zusatz von 0,5 bis 4 Äquivalenten einer Base bei Temperaturen von etwa 0 bis 200°C, vorzugsweise +20 bis +160°C in homogener oder inhomogener Phase umzusetzen.To prepare the α-azolyl sulfides of the formula I (n = 0), it is advantageous to use the α-chlorosulfides of the formula III without a diluent or in the presence of a diluent with about 0.5 to 2 equivalents of an alkali metal salt of the respective azole or with about 0. 5 to 4 equivalents of the respective azole, optionally with the addition of 0.5 to 4 equivalents of a base at temperatures of about 0 to 200 ° C, preferably +20 to + 160 ° C in a homogeneous or inhomogeneous phase.
Als Verdünnungsmittel können z. B. Methanol, Äthanol, Isopropanol, n-Butanol, Diäthyläther, Tetrahydrofuran, Dioxan, Aceton, Acetonitril, Dimethylformamid, Dimethylsulfoxid, Chloroform, Methylenchlorid oder Toluol verwendet werden. Als Basen können z. B. organische Amine wie Triäthylamin, Pyridin oder anorganische Verbindungen, z. B. Kaliumcarbonat oder Natriumhydroxid verwendet werden.As a diluent such. As methanol, ethanol, isopropanol, n-butanol, diethyl ether, tetrahydrofuran, dioxane, acetone, acetonitrile, dimethylformamide, dimethyl sulfoxide, chloroform, methylene chloride or toluene can be used. As bases z. B. organic amines such as triethylamine, pyridine or inorganic compounds, eg. As potassium carbonate or sodium hydroxide can be used.
Die als Ausgangsstoffe verwendeten α-Chlorsulfide III sind z. T. aus der Literatur bekannt oder können nach literaturbekannten Verfahren hergestellt werden, z. B.
- a) durch Chlorierung von Sulfiden mit N-Chlorsuccinimid (siehe z. B. B. L. Tuleen und T. B. Stephens, J. Org. Chem., 34,31 [1969]) nach dem Schema
- b) durch Umsetzung von Aldehyden mit Thiolen in Gegenwart von Chlorwasserstoff (siehe z. B. H. Böhme, H. Fischer und R. Frank, Liebigs Apn. Chem., 563, 54 [1949]) nach dem Schema
- a) by chlorination of sulfides with N-chlorosuccinimide (see, for example, BBL Tuleen and TB Stephens, J. Org. Chem., 34.31 [1969]) according to the scheme
- b) by reacting aldehydes with thiols in the presence of hydrogen chloride (see, for example, BH Böhme, H. Fischer and R. Frank, Liebigs A p . Chem., 563, 54 [1949]) according to the scheme
Zur Herstellung der α-Azolylsulfoxide der Formel I (n=1) setzt man die α-Azolylsulfide gegebenenfalls in Gegenwart eines Verdünnungsmittels mit etwa einem Äquivalent eines geeigneten Oxidationsmittels bei-Temperaturen zwischen etwa -30 und +100°C um. Die α-Azolylsulfone (Formel I, n =2) erhält man in ähnlicher Weise bei der Oxidation der α-Azolylsulfide (I, n=0) mit mindestens zwei Äquivalenten eines geeigneten Oxidationsmittels oder bei der Oxidation der a-Azolylsulfoxide (I, n = 1) mit mindestens einem Äquivalent eines Oxidationsmittels.To prepare the α-azolyl sulfoxides of the formula I (n = 1), the α-azolyl sulfides are reacted, if appropriate in the presence of a diluent with about one equivalent of a suitable oxidizing agent at temperatures between about -30 and + 100 ° C. The α-azolyl sulfones (formula I, n = 2) are obtained in a similar manner in the oxidation of the α-azolyl sulfides (I, n = 0) with at least two equivalents of a suitable oxidizing agent or in the oxidation of the a-azolyl sulfoxides (I, n = 1) with at least one equivalent of an oxidizing agent.
Als Oxidationsmittel können beispielsweise Kaliumpermanganat, Wasserstoffperoxid oder Percarbonsäuren wie Peressigsäure, Perbenzoesäure oder 3-Chlorperbenzoesäure verwendet werden. Als Verdünnungsmittel können z. B. Wasser, Essigsäure, Methanol, Aceton, Chloroform oder Methylenchlorid verwendet werden. Ein bevorzugtes Verfahren zur Herstellung der Sulfoxide (I, n = 1) ist die Umsetzung der Sulfide (I, n=0) mit einem Äquivalent 3-Chlorperbenzoesäure in Methylenchlorid bei 0 bis 25°C. Ein bevorzugtes Verfahren zur Herstellung der Sulfone ist die Umsetzung der Sulfide (I, n=0) mit zwei Äquivalenten 3-Chlorperbenzoesäure in Methylenchlorid bei 15bis41°C.Potassium permanganate, hydrogen peroxide or percarboxylic acids such as peracetic acid, perbenzoic acid or 3-chloroperbenzoic acid can be used as the oxidizing agent. As a diluent such. As water, acetic acid, methanol, acetone, chloroform or methylene chloride can be used. A preferred method for producing the sulfoxides (I, n = 1) is to react the sulfides (I, n = 0) with an equivalent of 3-chloroperbenzoic acid in methylene chloride at 0 to 25 ° C. A preferred method for producing the sulfones is the reaction of the sulfides (I, n = 0) with two equivalents of 3-chloroperbenzoic acid in methylene chloride at 15 to 41 ° C.
Die Verbindungen der Formel I (n=0, 1, 2) sind in vielen organischen Lösungsmitteln, z. B. in Essigester, Aceton, Äthanol, Methylenchlorid, Chloroform, Dimethylsulfoxid, Dimethylformamid und N-Methylpyrrolidon leicht lösliche Substanzen. Die α-Azolylsulfide (I=0) sind darüber hinaus auch in Toluol gut löslich.The compounds of formula I (n = 0, 1, 2) are found in many organic solvents, e.g. B. in ethyl acetate, acetone, ethanol, methylene chloride, chloroform, dimethyl sulfoxide, dimethylformamide and N-methylpyrrolidone easily soluble substances. The α-azolyl sulfides (I = 0) are also readily soluble in toluene.
Sie lassen sich mit Säuren in ihre Salze, z. B. Hydrochloride, Sulfate, Nitrate, Oxalate, Formiate, Acetate oder Dodecylbenzylsulfonate überführen.You can with acids in their salts, for. B. hydrochlorides, sulfates, nitrates, oxalates, formates, acetates or dodecylbenzyl sulfonates.
Ferner wurde gefunden, daß man die Metall-Komplexe der Formel II erhält, wenn man α-Azolylsulfide bzw. deren Derivate der Formel mit Metallsalzen der Formel
- Me, X und k die oben angegebene Bedeutung haben und a 0,1,2,3 und 4 bedeutet, in Gegenwart eines Lösungsmittels umsetzt. Hier steht Me vorzugsweise für Metalle der I., II. und IV. bis VIII. Nebengruppe des Periodensystems der Elemente sowie für Metalle der II. und IV. Hauptgruppe, insbesondere für Kupfer, Zink, Zinn, Mangan, Eisen, Cobalt oder Nickel.
- Me, X and k have the meaning given above and a denotes 0.1, 2, 3 and 4, in the presence of a solvent. Here Me preferably stands for metals of subgroups I, II and IV to VIII of the Periodic Table of the Elements and for metals of main groups II and IV, in particular for copper, zinc, tin, manganese, iron, cobalt or nickel.
Die Metallsalze der Formel IV sind allgemein bekannte, leicht zugängliche Verbindungen.The metal salts of formula IV are well known, easily accessible compounds.
Für die Herstellung der Metall-Komplexe der Formel II kommen alle mit Wasser mischbaren Lösungsmittel in Frage. Hierzu gehören vorzugsweise Methanol, Äthanol, Isopropanol, Aceton, Tetrahydrofuran und Dioxan. Dabei arbeitet man im allgemeinen bei Temperaturen zwischen 0 und 100° C, vorzugsweise zwischen 10 und 35° C.All water-miscible solvents are suitable for the preparation of the metal complexes of the formula II. These preferably include methanol, ethanol, isopropanol, acetone, tetrahydrofuran and dioxane. It is generally carried out at temperatures between 0 and 100 ° C, preferably between 10 and 35 ° C.
Die Suifide (I, n=0) und Sulfone (I, n = 2) enthalten jeweils ein Asymmetrisches Kohlenstoffatom und fallen demgemäß als Enantiomerengemische an, die in die optisch aktiven Verbindungen getrennt werden können. Im Falle der Sulfoxide I (n=1) treten durch das dem Asymmetrischen Kohlenstoff benachbarte Asymmetrische Schwefeistom Diastereomerengemische auf, die in üblicher Weise, z. B. durch Kristallisation oder Chromatographie in die einzelnen Komponenten getrennt werden können. Für die Anwendung als Fungizide oder als Mittel zur Regulierung des Pflanzenwachstums ist jedoch eine Trennung der Enantiomeren oder Diastereomeren normalerweise nicht erforderlich.The suifides (I, n = 0) and sulfones (I, n = 2) each contain an asymmetric carbon atom and are accordingly obtained as enantiomer mixtures which can be separated into the optically active compounds. In the case of sulfoxides I (n = 1), the asymmetric sulfur atom adjacent to the asymmetric carbon gives rise to diastereomer mixtures which are used in the customary manner, for. B. can be separated by crystallization or chromatography in the individual components. However, separation of the enantiomers or diastereomers is normally not required for use as fungicides or as an agent for regulating plant growth.
Zur Lösung von 22,1 g 1,2,4-Triazol in 500 ml wasserfreiem Aceton gibt man 60,5 g tert.-Butyl-[(2,4-dichlorphenyl)-chlormethyl]-sulfid. Nach Zugabe von 44,2 g feingepulvertem Kaliumcarbonat erhitzt man die Mischung unter Rühren sieben Stunden unter Rückfluß. Danach filtriert man die unlöslichen Bestandteile ab, engt das Filtrat im Vakuum zur Trockene ein und versetzt den Rückstand mit 300 ml Wasser. Man extrahiert die wäßrige Phase 3mal mit je 200 ml Methylenchlorid, wäscht die vereinigten Extrakte mit 200 ml Wasser, trocknet sich und engt im Vakuum ein. Nach Zugabe von 100 ml Diisopropyläther gewinnt man aus dem Rückstand 35,6 g (53%) farblose Kristalle vom Schmp. 95 bis 97° C.60.5 g of tert-butyl - [(2,4-dichlorophenyl) chloromethyl] sulfide are added to the solution of 22.1 g of 1,2,4-triazole in 500 ml of anhydrous acetone. After 44.2 g of finely powdered potassium carbonate have been added, the mixture is heated under reflux with stirring for seven hours. The insoluble constituents are then filtered off, the filtrate is evaporated to dryness in vacuo and 300 ml of water are added to the residue. The aqueous phase is extracted 3 times with 200 ml of methylene chloride, the combined extracts are washed with 200 ml of water, dried and concentrated in vacuo. After adding 100 ml of diisopropyl ether, 35.6 g (53%) of colorless crystals of mp 95 ° to 97 ° C. are obtained from the residue.
1H-NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ=1,3 (s, 9 H), 6,95 (s, 1 H), 7,0-7,4 (m, 3 H, ABX), 8,0 (s, 1 H), 8,8 ppm (s, 1 H). 1 H-NMR (100 MHz, CDCl 3 ): δ = 1.3 (s, 9 H), 6.95 (s, 1 H), 7.0-7.4 (m, 3 H, ABX), 8.0 (s, 1H), 8.8ppm (s, 1H).
Zur Lösung von 9,5g tert.-Butyl-[(2,4-dichlorphenyl)-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl-methyl]-sulfid in 100 ml Äthanol tropft man 15 ml einer molaren äthanolischen Lösung von Kupfer(II)-chlorid-dihydrat. Aus dieser tiefblauen Lösung isoliert man nach zweitägigem Stehen bei 0°C 9,8 g blaue Kristalle, die mit Äthanol und Äther gewaschen werden. Schmp. 130°C.15 ml of a molar ethanolic solution of copper are added dropwise to the solution of 9.5 g of tert-butyl - [(2,4-dichlorophenyl) -1,2,4-triazol-1-yl-methyl] sulfide in 100 ml of ethanol (II) chloride dihydrate. After standing for two days at 0 ° C., 9.8 g of blue crystals are isolated from this deep blue solution, which are washed with ethanol and ether. Mp 130 ° C.
Zur Suspension von 13,0 g Natriumhydrid in 100 ml Dimethylformamid tropft man unter Rühren eine Lösung von 43,5 g Triazol in 200 ml Dimethylformamid. Nach Beendigung der Wasserstoffentwicklung tropft man zu der auf Raumtemperatur abgekühlten Mischung 97,0 g 1-Pentyl-[1-chlorpentyl-(1)]-sulfid hinzu, wobei sich das Gemisch erwärmt. Anschließend rührt man noch acht Stunden bei 80°C. Die Reaktionsmischung wird sodann im Vakuum eingeengt, mit 500 ml Wasser versetzt und 5mal mit Methylenchlorid extrahiert. Die vereinigten und eingeengten Extrakte chromatographiert man an Kieselgel (5 x 70 cm) zunächst unter Verwendung von Methylenchlorid als Laufmittel. Nach Durchlauf der ersten bräunlichen Zone werden steigende Mengen Aceton zugesetzt (bis 10% Aceton). Als zweite Zone isoliert man so 15,0 g Produkt als blaßgelbes Öl. IR (Film): 2955, 2925, 2860, 1496, 1460, 1271, 1190, 1133,1008,677 cm-1.A solution of 43.5 g of triazole in 200 ml of dimethylformamide is added dropwise to the suspension of 13.0 g of sodium hydride in 100 ml of dimethylformamide. When the evolution of hydrogen has ended, 97.0 g of 1-pentyl- [1-chloropentyl- (1)] sulfide are added dropwise to the mixture, which has cooled to room temperature, and the mixture heats up. The mixture is then stirred at 80 ° C for eight hours. The reaction mixture is then concentrated in vacuo, mixed with 500 ml of water and extracted 5 times with methylene chloride. The combined and concentrated extracts are chromatographed on silica gel (5 × 70 cm) first using methylene chloride as the eluent. After passing through the first brownish zone, increasing amounts of acetone are added (up to 10% acetone). The second zone thus isolated 15.0 g of product as a pale yellow oil. IR (film): 2955, 2925, 2860, 1496, 1460, 1271, 1190, 1133, 1008.677 cm -1 .
1H-NMR (270 MHz, CDCl3): δ=0,9 (»tr«, 6 H), 1,3 (m, 8 H), 1,5 (m, 2 H), 2,1 (m, 2 H), 2,4 (m, 2 H), 5,4 (tr, 1 H), 8,0 (s, 1 H), 8,4 ppm (s, 1 H). 1 H-NMR (270 MHz, CDCl 3 ): δ = 0.9 ("tr", 6 H), 1.3 (m, 8 H), 1.5 (m, 2 H), 2.1 ( m, 2 H), 2.4 (m, 2 H), 5.4 (tr, 1 H), 8.0 (s, 1 H), 8.4 ppm (s, 1 H).
Zur Lösung von 10,0 g 85prozentiger 3-Chlorperbenzoesäure in 140 ml Methylchlorid tropft man unter Rühren und Eiskühlung eine Lösung von 6,0 g 1-Pentyl-[1-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-pentyl-(1)]-sulfid. Nach Abklingen der anfänglichen Erwärmung rührt man noch 2 Tage bei 25° C. Die Mischung wird dann mit Natriumcarbonatlösung, Natriumsulfitlösung und Wasser gewaschen und die organische Phase getrocknet. Nach dem Einengen bleibt ein hellgelbes Öl, aus dem beim Anreiben mit Diisopropyläther 3,5 g farblose Kristalle vom Schmp. 69 bis 71 ° C gewonnen werden.A solution of 6.0 g of 1-pentyl- [1- (1,2,4-triazol-1-yl) pentyl is added dropwise to the solution of 10.0 g of 85 percent 3-chloroperbenzoic acid in 140 ml of methyl chloride with stirring and ice-cooling - (1)] - sulfide. After the initial heating has subsided, the mixture is stirred for a further 2 days at 25 ° C. The mixture is then washed with sodium carbonate solution, sodium sulfite solution and water and the organic phase is dried. After concentration, a light yellow oil remains, from which 3.5 g of colorless crystals of mp 69 ° to 71 ° C. are obtained when rubbed with diisopropyl ether.
NMR (CDCl3, 100 MHz): 6=0,9 (m, 6 H), 1,4 (m, 8 H), 1,8 (m, 2 H), 2,5 (m, 2 H), 2,8 (»dd«, 2 H), 5,4 (dd, 1 H), 8,1 (s, 1 H), 5 ppm (s, 1 H).NMR (CDCl 3 , 100 MHz): 6 = 0.9 (m, 6 H), 1.4 (m, 8 H), 1.8 (m, 2 H), 2.5 (m, 2 H) , 2.8 ("dd", 2 H), 5.4 (dd, 1 H), 8.1 (s, 1 H), 5 ppm (s, 1 H).
Zur Lösung von 43,6 g Imidazol in 300 ml Aceton tropft man unter Rühren 82 g tert.-Butyl-[(2-methylphenyl)-chlormethyl]-sulfid. Nach Zugabe von 88 g feingepulvertem Kaliumcarbonat erhitzt man 5 Stunden unter Rückfluß. Danach wird von den ungelösten Bestandteilen abfiltriert und das Filtrat eingeengt. Der mit 300 ml Wasser versetzte Rückstand wird mit 3 x 200 ml Methylenchlorid extrahiert. Aus den vereinigten organischen Phasen bleiben nach Waschen mit Wasser, Trocknen und Einengen 69 g eines bräunlichen Öls zurück, die in 1 I Diisopropyläther gelöst werden. Durch tropfenweise Zugabe von 90 ml einer 2,85molaren Lösung von Chlorwasserstoff in Diisopropyläther unter Rühren fallen aus dieser Lösung blaßgelbe Kristalle des Hydrochlorids, die aus Aceton umkristallisiert werden, an. Man erhält so 51 g farbloses tert.-Butyl-[(2-methylphenyl)-imidazol-1-yl-methyl]-sulfidhydrochlo- rid vom Schmp. 168 bis 170°C (Verbindung Nr. 110).82 g of tert-butyl - [(2-methylphenyl) chloromethyl] sulfide are added dropwise to the solution of 43.6 g of imidazole in 300 ml of acetone with stirring. After adding 88 g of finely powdered potassium carbonate, the mixture is heated under reflux for 5 hours. The undissolved constituents are then filtered off and the filtrate is concentrated. The residue mixed with 300 ml of water is extracted with 3 x 200 ml of methylene chloride. After washing with water, drying and concentrating, 69 g of a brownish oil remain from the combined organic phases, which are dissolved in 1 l of diisopropyl ether. The dropwise addition of 90 ml of a 2.85 molar solution of hydrogen chloride in diisopropyl ether with stirring gives pale yellow crystals of the hydrochloride, which are recrystallized from acetone, from this solution. This gives 51 g of colorless tert-butyl - [(2-methylphenyl) imidazol-1-ylmethyl] sulfide hydrochloride, mp. 168 to 170 ° C. (compound no. 110).
Nach Übergießen des Hydrochlorids mit einer wäßrigen Lösung von 25 g Natriumhydrogencarbonat extrahiert man die freie Base mit 3 x 200 ml Äther. Nach dem Trocknen und Einengen fällt sie als blaßgelbes Öl (27 g) an, das allmählich durchkristallisiert (Fp. 93-95°).After pouring the hydrochloride with an aqueous solution of 25 g of sodium hydrogen carbonate, the free base is extracted with 3 x 200 ml of ether. After drying and concentration, it is obtained as a pale yellow oil (27 g), which gradually crystallizes through (mp. 93-95 °).
1H-NMR (60 MHz, CDCl3): δ=1,3 (s, 9 H), 2,4 (s, 3 H), 6,25 (s, 1 H), 6,7-7,1 (m, 6 H), 7,65 ppm (dd, 1 H). 1 H-NMR (60 MHz, CDCl 3 ): δ = 1.3 (s, 9 H), 2.4 (s, 3 H), 6.25 (s, 1 H), 6.7-7, 1 (m, 6H), 7.65 ppm (dd, 1H).
Die Mischung von 60,7 g 4-Clilorphenyl-(chlormethyl-(4'-chlorphenyl))-sulfid, 27,2 g Imidazol und 55,4 g Kaliumcarbonat in 400 ml Aceton wird unter Rühren 5 Stunden unter Rückfluß erhitzt. Danach wird filtriert, das Filtrat zur Trockne eingeengt und mit 500 ml Wasser versetzt. Man extrahiert diese Mischung 3mal mit je 200 ml Methylenchlorid. Die vereinigten Extrakte werden über Natriumsulfat getrocknet. Aus der im Vakuum zur Trockene eingeengten Lösung werden nach Anreiben mit Diisopropyläther 26 g (38%) farblose Kristalle vom Schmp. 88° C isoliert.The mixture of 60.7 g of 4-clilorphenyl- (chloromethyl- (4'-chlorophenyl)) sulfide, 27.2 g of imidazole and 55.4 g of potassium carbonate in 400 ml of acetone is heated under reflux with stirring for 5 hours. It is then filtered, the filtrate is evaporated to dryness and 500 ml of water are added. This mixture is extracted 3 times with 200 ml of methylene chloride. The combined extracts are dried over sodium sulfate. 26 g (38%) of colorless crystals having a melting point of 88 ° C. are isolated from the solution, which has been evaporated to dryness in a vacuum, after rubbing with diisopropyl ether.
1H-NMR (60 MHz, CDCI3): 8=6,3 (s, 1H), 6,9-7,4 (m, 1OH), 7,5 (br. s,1 1 H). 1 H NMR (60 MHz, CDCI 3 ): 8 = 6.3 (s, 1H), 6.9-7.4 (m, 1OH), 7.5 (br. S, 1 1 H).
Zur Lösung von 193 g tert.-Butyl-(chlormethyl-(2,6-dichlorphenyl))-sulfid und 44 g Pyrazol in 1 I Toluol tropft man 66 g Triäthylamin und erhitzt nach Abklingen der schwach exothermen Reaktion noch 1 Stunde unter Rückfluß. Man filtriert vom Ungelösten ab, engt das Filtrat ein und versetzt den Rückstand mit 500 ml Wasser. Nach Extraktion mit 3mal 200 ml Methylenchlorid erhält man beim Einengen der vereinigten Extrakte einen festen Rückstand, der nach dem Waschen mit Diisopropyläther 117 g (57%) farblose Kristalle vom Schmp. 97-98°C ergibt.66 g of triethylamine are added dropwise to the solution of 193 g of tert-butyl- (chloromethyl- (2,6-dichlorophenyl)) sulfide and 44 g of pyrazole in 1 l of toluene and, after the weakly exothermic reaction has subsided, the mixture is heated under reflux for 1 hour. The undissolved solution is filtered off, the filtrate is concentrated and the residue is mixed with 500 ml of water. After extraction with 3 times 200 ml of methylene chloride, when the combined extracts are concentrated, a solid residue is obtained which, after washing with diisopropyl ether, gives 117 g (57%) of colorless crystals, mp. 97-98 ° C.
1H-NMR (60 MHz, CDCl3): δ=1,4 ppm (s, 9 H), 6,2 (»tr.«, 1 H), 7,0-7,3 (m, 3 H), 7,4 (»d«, 1 H), 8,2 (»d«, 2 H). 1 H-NMR (60 MHz, CDCl 3 ): δ = 1.4 ppm (s, 9 H), 6.2 ("tr.", 1 H), 7.0-7.3 (m, 3 H ), 7.4 ("d", 1 H), 8.2 ("d", 2 H).
Eine Mischung von 60,4 g Chlormethyl-(2,4-dichlorbenzyl)-sulfid, 35 g 1,2,4-Triazol und 69 g gepulvertem Kaliumcarbonat in 300 ml wasserfreiem Aceton wird 10 Stunden unter Rückfluß zum Sieden erhitzt. Danach filtriert man die unlöslichen Bestandteile ab, engt das Filtrat im Vakuum zur Trockne ein und versetzt den Rückstand mit 300 ml Wasser. Dann wird 3mal mit je 200 ml Methylenchlorid extrahiert, die vereinigten Extrakte getrocknet und im Vakuum eingeengt. Aus dem zurückbleibenden braunen Öl werden durch Kristallisation aus Diisopropyläther/Methanol bei -60°C 39,8 g (58%) farblose Kristalle vom Schmp. 68-70°C gewonnen.A mixture of 60.4 g of chloromethyl (2,4-dichlorobenzyl) sulfide, 35 g of 1,2,4-triazole and 69 g of powdered potassium carbonate in 300 ml of anhydrous acetone is heated to boiling under reflux for 10 hours. The insoluble constituents are then filtered off, the filtrate is evaporated to dryness in vacuo and 300 ml of water are added to the residue. Then it is extracted 3 times with 200 ml of methylene chloride, the combined extracts are dried and concentrated in vacuo. 39.8 g (58%) of colorless crystals of melting point 68-70 ° C. are obtained from the remaining brown oil by crystallization from diisopropyl ether / methanol at -60 ° C.
1H-NMR (60 MHz, CDCl3): δ=3,8 (s, 2 H), 5,0 (s, 2 H), 7,0-7,5 (m, 3 H), 7,9 (s, 1 H), 8,2 (s, 1 H). 1 H-NMR (60 MHz, CDCl 3 ): δ = 3.8 (s, 2 H), 5.0 (s, 2 H), 7.0-7.5 (m, 3 H), 7, 9 (s, 1H), 8.2 (s, 1H).
Eine Mischung von 200 g 2,4-Dichlorbenzyl-[(2',4'-dichlorphenyl)-chlormethyl]-sulfid, 145 g 1,2,4-Triazol und 138 g gepulvertem Kaliumcarbonat in 2 wasserfreiem Aceton wird unter kräftigem Rühren 9 Stunden unter Rückfluß erhitzt. Danach werden die festen Bestandteile durch Filtration entfernt, das Filtrat im Vakuum zur Trockne eingeengt und der ölige Rückstand nach Zusatz von 500 ml Wasser fünfmal mit je 200 ml Methylenchlorid extrahiert. Die vereinigten organischen Phasen werden über Natriumsulfat getrocknet und dann im Vakuum zur Trockne eingeengt. Beim Anreiben des Rückstandes mit Diisopropyläther erhält man 157 farblose Kristalle, die die isomeren Triazolylverbindungen im Verhältnis 8 : 2 enthalten.A mixture of 200 g of 2,4-dichlorobenzyl - [(2 ', 4'-dichlorophenyl) chloromethyl] sulfide, 145 g of 1,2,4-triazole and 138 g of powdered potassium carbonate in 2 anhydrous acetone becomes 9 with vigorous stirring Heated under reflux for hours. The solid constituents are then removed by filtration, the filtrate is evaporated to dryness in vacuo and the oily residue is extracted five times with 200 ml of methylene chloride after the addition of 500 ml of water. The combined organic phases are dried over sodium sulfate and then evaporated to dryness in vacuo. Rubbing the residue with diisopropyl ether gives 157 colorless crystals which contain the isomeric triazolyl compounds in a ratio of 8: 2.
Dieses Gemisch wird mehrfach mit heißem Hexan extrahiert. Aus den vereinigten Hexanlösungen erhält man beim Abziehen des Lösungsmittels im Vakuum 122 g (65%), 2,4-Dichlorbenzyl-[(2',4'-dichlorphenyl)-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl-methyl]-sulfid in Form farbloser Kristalle vom Schmp. 120-125° C.This mixture is extracted several times with hot hexane. When the solvent is removed in vacuo, 122 g (65%), 2,4-dichlorobenzyl - [(2 ', 4'-dichlorophenyl) -1,2,4-triazol-1-yl-methyl] are obtained from the combined hexane solutions. -sulfide in the form of colorless crystals with a melting point of 120-125 ° C.
1H-NMR (220 MHz, CDCI3): δ=3,9 ppm (breites s, 2 H), 6,65 (s, 1 H), 7,0-7,5 (m, 6 H), 8,0 (s, 1 H), 8,6 (s, 1 H). 1 H-NMR (220 MHz, CDCI 3 ): δ = 3.9 ppm (broad s, 2 H), 6.65 (s, 1 H), 7.0-7.5 (m, 6 H), 8.0 (s, 1H), 8.6 (s, 1H).
Der farblose, unlösliche Rückstand der Hexanextraktionen besteht aus 27 g (12%) 2,4-Dichlorbenzyl-[(2',4'-dichlorphenyl)-(1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)-methyl]-sulfid vom Schmp. 132-133°C.The colorless, insoluble residue of the hexane extractions consists of 27 g (12%) 2,4-dichlorobenzyl - [(2 ', 4'-dichlorophenyl) - (1,2,4-triazol-4-yl) methyl] sulfide from mp. 132-133 ° C.
1H-NMR (220 MHz, CDCl3): δ=3,9 ppm (s, 2 H), 6,5 (s, 1 H), 7,0-7,5 (m, 6 H), 8,45 (s, 2 H). 1 H-NMR (220 MHz, CDCl 3 ): δ = 3.9 ppm (s, 2 H), 6.5 (s, 1 H), 7.0-7.5 (m, 6 H), 8 , 45 (s, 2H).
Zu einer Lösung von 78 g tert.-Butyl-[(4-chlorphenyl)-chlormethyl]-sulfid in 175 ml trockenem Dimethylformamid (DMF) tropft man unter Rühren 350 ml einer molaren Lösung 1,2,4-Triazolylnatrium in DMF (hergestellt aus 0,35 Mol Natriumhydrid und 0,35 Mol 1,2,4-Triazol in 350 ml DMF). Nach Abklingen der schwach exothermen Reaktion rührt man noch 4 Stunden bei 80°C nach. Der Ansatz wird in 1 I Wasser gegossen und mit 3mal 200 ml Methylenchlorid extrahiert. Die vereinigten organischen Phasen werden mit Wasser gewaschen, über Natriumsulfat getrocknet und m Vakuum eingedampft. Der Rückstand bildet beim Verreiben mit 150 ml Diisopropyläther 40,0 g (46%) farblose Kristalle vom Schmp. 95° C.350 ml of a molar solution of 1,2,4-triazolyl sodium in DMF (prepared) are added dropwise to a solution of 78 g of tert-butyl - [(4-chlorophenyl) chloromethyl] sulfide in 175 ml of dry dimethylformamide (DMF) from 0.35 mol sodium hydride and 0.35 mol 1,2,4-triazole in 350 ml DMF). After the weakly exothermic reaction has subsided, stirring is continued at 80 ° C. for 4 hours. The mixture is poured into 1 liter of water and extracted with 3 times 200 ml of methylene chloride. The combined organic phases are washed with water, dried over sodium sulfate and in vacuo evaporated. When triturated with 150 ml of diisopropyl ether, the residue forms 40.0 g (46%) of colorless crystals with a melting point of 95 ° C.
1H-NMR (60 MHz, CDCI3): d=1,3 ppm (s, 9 H), 6,6 (s,1 H), 7,2 (AA'BB', 4 H), 8,0 (s,1 H),8,7(s,1 1 H). 1 H NMR (60 MHz, CDCI3): d = 1.3 ppm (s, 9 H), 6.6 (s, 1 H), 7.2 (AA'BB ', 4 H), 8.0 (s, 1H), 8.7 (s, 1 1H).
Zur Lösung von 9,7 g tert.-Butyl-[(4-chlorphenyl)-1,2,4-triazolylmethyl]-sulfid in 20 ml Methylenchlorid tropft man unter Eiskühlung eine Lösung von 7,1 g 85prozentiger 3-Chlorperbenzoesäure in 70 ml Methylenchlorid. Man rührt noch 2 Stunden bei 0°C nach bis laut Dünnschichtchromatogramm (Si02, Methylenchlorid/Aceton 7:3) kein Sulfid (RF=0,57) mehr vorhanden ist und nur noch die beiden diastereomeren Sulfoxide erkennbar sind (RF=0,38 und 0,20). Die Lösung wird sodann bis zur Beendigung der C02-Entwicklung mit wäßriger Natriumhydrogencarbonatlösung gewaschen. Nach dem Waschen der organischen Phase mit Wasser wird diese getrocknet, eingeengt und der feste Rückstand mit wenig Äther gewaschen. Man erhält 7,0 g (67%) farblose Kristalle vom Schmp. 125-128° C.A solution of 7.1 g of 85 percent 3-chloroperbenzoic acid in 70 is added dropwise to the solution of 9.7 g of tert-butyl - [(4-chlorophenyl) -1,2,4-triazolylmethyl] sulfide in 20 ml of methylene chloride while cooling with ice ml of methylene chloride. The mixture is stirred for 2 hours at 0 ° C until, according to the thin layer chromatogram (Si0 2 , methylene chloride / acetone 7: 3), no sulfide (R F = 0.57) is present and only the two diastereomeric sulfoxides can be seen (R F = 0.38 and 0.20). The solution is then washed with aqueous sodium bicarbonate solution until the CO 2 evolution has ended. After washing the organic phase with water, it is dried, concentrated and the solid residue is washed with a little ether. 7.0 g (67%) of colorless crystals of mp 125-128 ° C. are obtained.
1H-NMR (220 MHZ, CDCI3): δ=1,10 und 1,15 (zwei s, zus. 9 H), 6,18 und 6,24 (zwei s, zus. 1 H), 7,3-7,7 (m, 4 H), 8,01 und 8,07 (zwei s, zus. 1H), 8,41 und 8,51 (zwei s, zus. 1 H). 1 H-NMR (220 MHz, CDCI 3 ): δ = 1.10 and 1.15 (two s, together 9 H), 6.18 and 6.24 (two s, together 1 H), 7, 3-7.7 (m, 4 H), 8.01 and 8.07 (two s, together 1H), 8.41 and 8.51 (two s, together 1 H).
Zur Lösung von 10,7 g tert.-Butyl-[(4-chlorphenyl)-1,2,4-triazolylmethyl]-sulfoxid in 50 ml Methylenchlorid tropft man bei 20°C eine Lösung von 7,3 g 85prozentiger 3-Chlorperbenzoesäure in 100 ml Methylenchlorid zu. Nach dem Ergebnis der Dünnschichtchromatographie (DC) wird das weniger polare Sulfoxid schneller oxidiert; erst durch längeres Nachrühren bei Raumtemperatur wird auch das stärker polare Sulfoxid oxidiert. Nach 18 Stunden ist nach DC (Si02, Methylenchlorid/Aceton 7 : 3) die Umsetzung beendet. Das Sulfon (RF=0,46) wird durch Waschen der Lösung mit Natriumhydrogencarbonatlösung und Wasser, Trocknen und Einengen der organischen Phase isoliert. Nach dem Waschen des Rückstandes der organischen Phase isoliert. Nach dem Waschen des Rückstandes mit Diisopropyläther erhält man 8,7 g (77%) farblose Kristalle vom Schmp. 150° C.A solution of 7.3 g of 85 percent 3-chloroperbenzoic acid is added dropwise at 20 ° C. to dissolve 10.7 g of tert-butyl - [(4-chlorophenyl) -1,2,4-triazolylmethyl] sulfoxide in 50 ml of methylene chloride in 100 ml of methylene chloride. According to the result of thin layer chromatography (TLC), the less polar sulfoxide is oxidized faster; The more polar sulfoxide is only oxidized by stirring for a longer period at room temperature. After 18 hours after TLC (Si0 2 , methylene chloride / acetone 7: 3) the reaction is complete. The sulfone (R F = 0.46) is isolated by washing the solution with sodium hydrogen carbonate solution and water, drying and concentrating the organic phase. After washing the residue of the organic phase isolated. After washing the residue with diisopropyl ether, 8.7 g (77%) of colorless crystals with a melting point of 150 ° C. are obtained.
1H-NMR (220 MHz, CDCI3): δ=1,3 ppm (s, 9 H), 6,75 (s, 1 H), 7,5 (AA'BB', 4 H), 8,03 (s, 1 H), 8,84 (s, 1 H). 1 H-NMR (220 MHz, CDCI 3 ): δ = 1.3 ppm (s, 9 H), 6.75 (s, 1 H), 7.5 (AA'BB ', 4 H), 8, 03 (s, 1H), 8.84 (s, 1H).
Zu einer Mischung von 26,1 g Tetrazol und 102 g 4-Chlorphenyl-[(4'-chlorphenyl)-chlormethyl]-sulfid in 3,5 I Toluol tropft man bei Raumtemperatur 37,4 g Triäthylamin unter Rühren zu. Die Mischung wird danach 4 Stunden unter Rückfluß erhitzt. Man filtriert vom Unlöslichen ab, wäscht das Filtrat mit Wasser und trocknet die organische Phase über Natriumsulfat. Nach Abziehen des Lösungsmittels im Vakuum bleibt ein fester Rückstand, aus dem nach Zusatz von 50 ml Diisopropyläther 74,7 g (67%) gelbstichige Kristalle vom Schmp. 104-106°C isoliert werden.37.4 g of triethylamine are added dropwise at room temperature to a mixture of 26.1 g of tetrazole and 102 g of 4-chlorophenyl - [(4'-chlorophenyl) chloromethyl] sulfide in 3.5 l of toluene, with stirring. The mixture is then refluxed for 4 hours. The insoluble matter is filtered off, the filtrate is washed with water and the organic phase is dried over sodium sulfate. After the solvent has been stripped off in vacuo, a solid residue remains, from which, after addition of 50 ml of diisopropyl ether, 74.7 g (67%) of yellowish crystals of mp. 104-106 ° C. are isolated.
1H-NMR (60 MHz, CDCl3): δ=6,7-7,6 ppm (m, 9 H), 8,4 und 8,9 (zwei s, zus. 2 H). 1 H-NMR (60 MHz, CDCl 3 ): δ = 6.7-7.6 ppm (m, 9 H), 8.4 and 8.9 (two s, together 2 H).
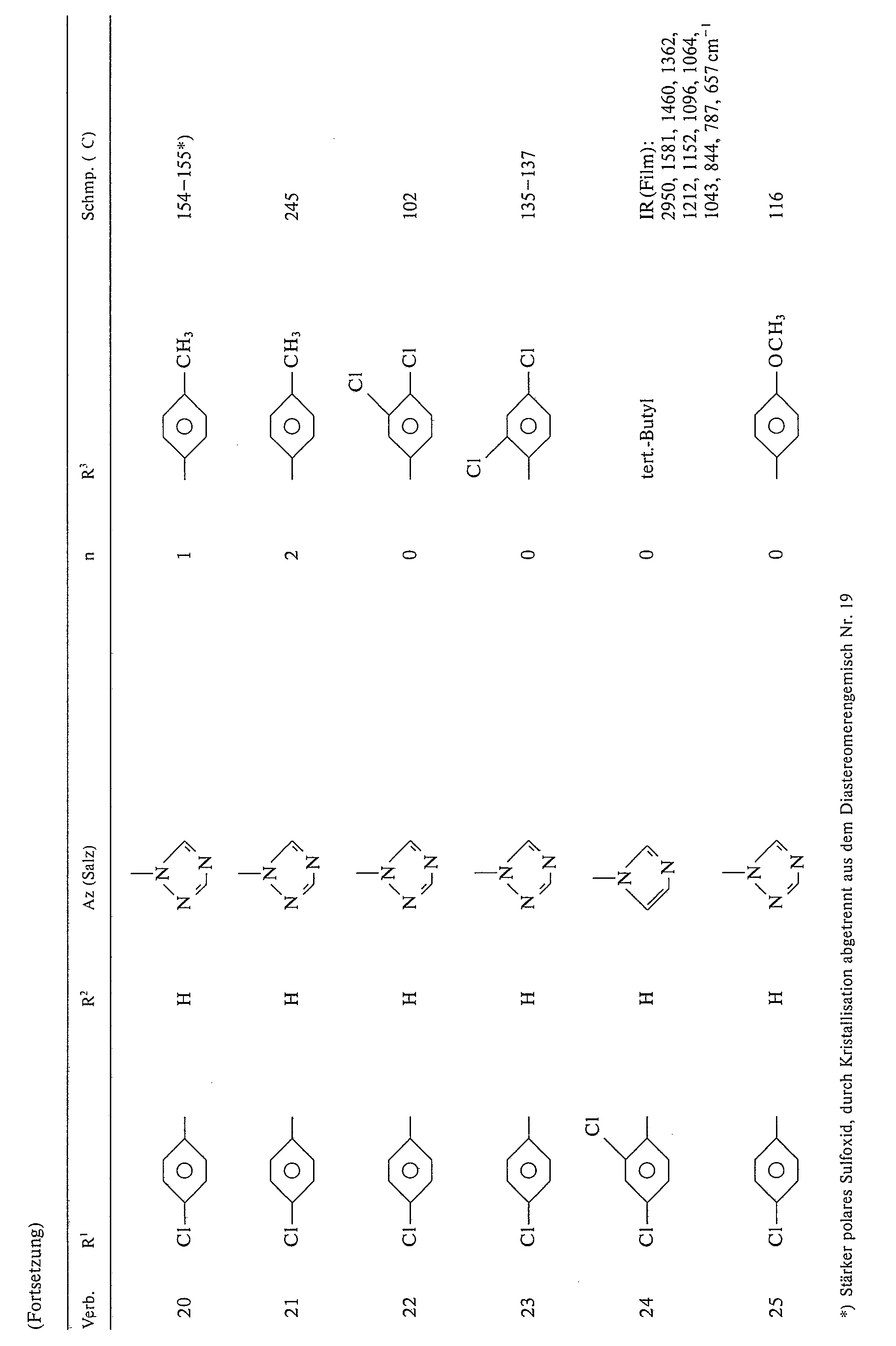
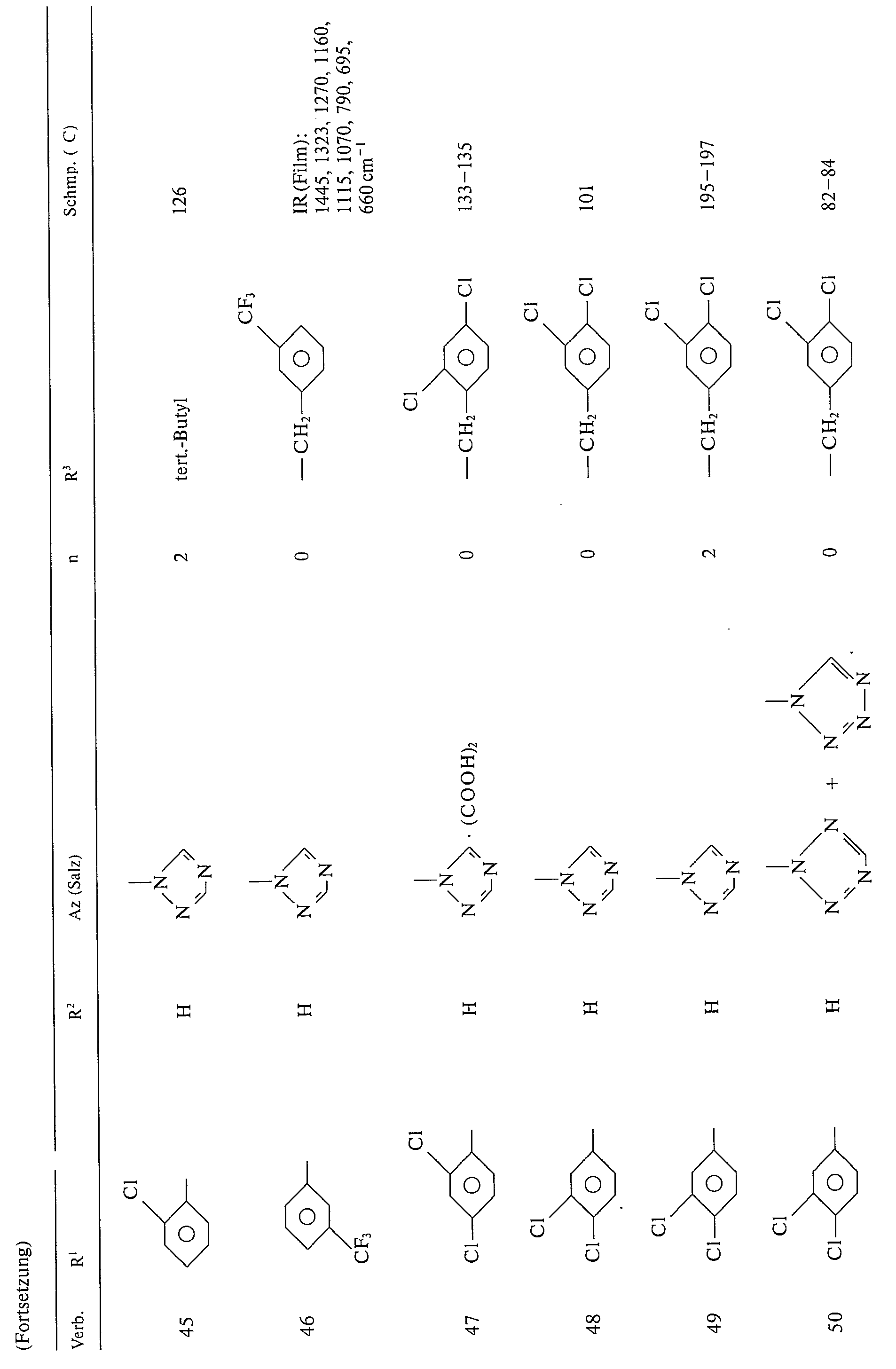
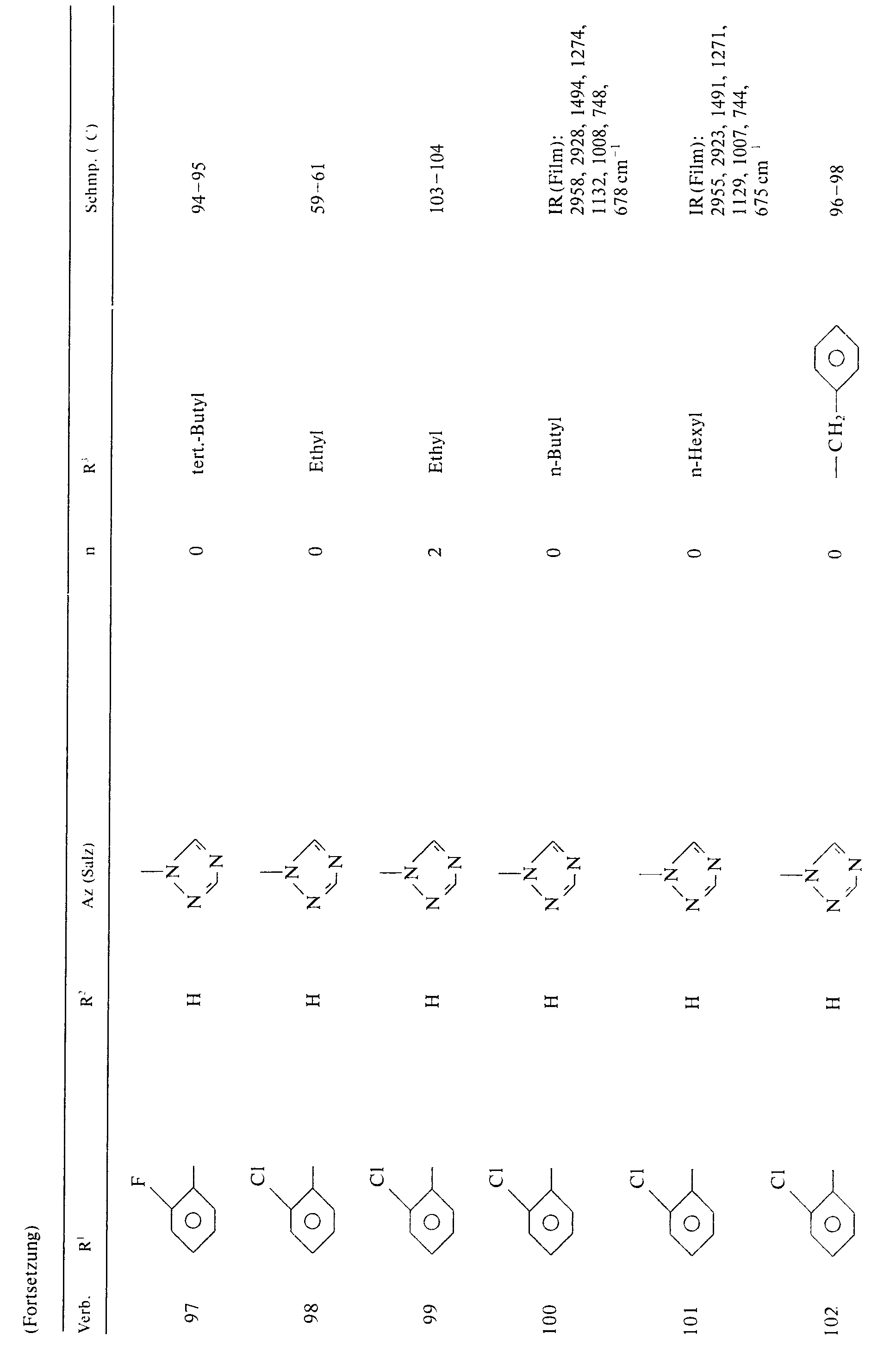
Beispiele für die erfindungsgemäßen Verbindungen der Formel I seien in folgender Tabelle 1 genannt:
Die neuen a-Azolylsulfide, a-Azolyl-sulfoxide und a-Azolyl-sulfone und ihre Salze zeigen eine erheblich breitere fungizide Wirkung und eine überlegene Pflanzenverträglichkeit als das bekannte 1-[2,4-Dichlorphenyl-ß-allyläthyläther]-imidazol. Die neuen Wirkstoffe können auch in Form ihrer Salze, z. B. Hydrochloride, Oxalate oder Nitrate verwendet werden.The new a-azolyl sulfides, a-azolyl sulfoxides and a-azolyl sulfones and their salts show a considerably broader fungicidal activity and a superior plant tolerance than the known 1- [2,4-dichlorophenyl-ß-allylethyl ether] imidazole. The new active ingredients can also be in the form of their salts, e.g. B. hydrochlorides, oxalates or nitrates can be used.
Von großem Interesse sind die erfindungsgemäßen fungiziden Mittel bei Pilzerkrankungen an verschiedenen Kulturpflanzen, z. B. bei
- Ustilago scitaminea (Zuckerrohrbrand),
- Hemileia vastatrix (Kaffeerost),
- Uromyces fabae bzw. appendiculatus (Bohenrost),
- Puccinia Arten (Getreiderost),
- Erysiphe graminis (Getreidemehltau),
- Botrytis cinerea an Rebe, Erdbeeren,
- Unicula necator,
- Sphaerotheca fuliginea,
- Erysiphe cichoracearum,
- Podosphaera leucotricha.
- Ustilago scitaminea (sugar cane fire),
- Hemileia vastatrix (coffee rust),
- Uromyces fabae or appendiculatus (broom rust),
- Puccinia species (grain rust),
- Erysiphe graminis (powdery mildew),
- Botrytis cinerea on vine, strawberries,
- Unicula necator,
- Sphaerotheca fuliginea,
- Erysiphe cichoracearum,
- Podosphaera leucotricha.
Unter Kulturpflanzen verstehen wir in diesem Zusammenhang insbesondere Weizen, Roggen, Gerste, Hafer, Reis, Mais, Apfelbaum, Gurken, Bohnen, Kaffee, Zuckerrohr, Weinrebe, Erdbeeren sowie Zierpflanzen im Gartenbau.In this context, crop plants mean wheat, rye, barley, oats, rice, corn, apple tree, cucumber, beans, coffee, sugar cane, grapevine, strawberries and ornamental plants in horticulture.
Die erfindungsgemäßen Wirkstoffe sind systemisch wirksam. Die systemische Wirksamkeit dieser Mittel ist von besonderem Interesse im Zusammenhang mit der Bekämpfung von inneren Pflanzenkrankheiten, z. B. Getreiderost, Getreidemehltau.The active compounds according to the invention are systemically active. The systemic effectiveness of these agents is of particular interest in connection with the control of internal plant diseases, for. B. grain rust, powdery mildew.
Die erfindungsgemäßen Mittel können gleichzeitig das Wachstum von zwei oder mehr der genannten Pilze unterdrücken und besitzen eine hohe Pflanzenverträglichkeit. Die zur Bekämpfung der phytopathogenen Pilze erforderlichen Aufwandmengen liegen zwischen 0,05 und 2 kg Wirkstoff/ha Kulturfläche.The agents according to the invention can simultaneously suppress the growth of two or more of the fungi mentioned and are highly tolerated by plants. The application rates required to control the phytopathogenic fungi are between 0.05 and 2 kg of active ingredient / ha of cultivated area.
Die erfindungsgemäßen Wirkstoffe können in die üblichen Formulierungen übergeführt werden, wie Lösungen, Emulsionen, Suspensionen, Pulver, Pasten und Granulate. Diese werden in bekannter Weise hergestellt, z. B. durch Vermischen des Wirkstoffes mit Lösungsmitteln und/oder Trägerstoffen, gegebenenfalls unter Verwendung von Emulgiermitteln und Dispergiermitteln, wobei im Falle der Benutzung von Wasser als Verdünnungsmittel auch andere organische Lösungsmittel als Hilfslösungsmitte! verwendet werden können. Als Hilfsstoffe kommen dafür im wesentlichen in Frage: Lösungsmittel, wie Aromaten (z. B. Xylol, Benzol), chlorierte Armaten (z. B. Chlorbenzole), Paraffine (z. B. Erdölfraktionen), Alkohole (z. B. Methanol, Butanol), Amine (z. B. Äthanolamin, Dimethylformamid) und Wasser; Trägerstoffe wie natürliche Gesteinsmehle (z. B. Kaoline, Tonerden, Talkum, Kreide) und synthetische Gesteinsmehle (z. B. hochdisperse Kieselsäure, Silikate); Emulgiermittel, wie nichtionogene und anionische Emulgatoren (z. B. Polyoxyäthylen-Fettalkohol-Äther, Alkylsulfonate und Arylsulfonate) und Dispergiermittel, wie Lignin, Sulfitablaugen und Methylcellulose.The active compounds according to the invention can be converted into the customary formulations, such as solutions, emulsions, suspensions, powders, pastes and granules. These are manufactured in a known manner, e.g. B. by mixing the active ingredient with solvents and / or carriers, optionally using emulsifiers and dispersants, and in the case of using water as a diluent also other organic solvents as auxiliary solvents! can be used. The following are essentially suitable as auxiliaries: solvents, such as aromatics (e.g. xylene, benzene), chlorinated armates (e.g. chlorobenzenes), paraffins (e.g. petroleum fractions), alcohols (e.g. methanol, Butanol), amines (e.g. ethanolamine, dimethylformamide) and water; Carriers such as natural rock powder (e.g. kaolins, clays, talc, chalk) and synthetic rock powder (e.g. highly disperse silica, silicates); Emulsifiers such as nonionic and anionic emulsifiers (e.g. polyoxyethylene fatty alcohol ether, alkyl sulfonates and aryl sulfonates) and dispersants such as lignin, sulfite liquor and methyl cellulose.
Die Formulierungen enthalten im allgemeinen zwischen 0,1 und 95 Gewichtsprozent Wirkstoff, vorzugsweise zwischen 0,5 und 90%. Die Formulierungen bzw. die daraus hergestellten gebrauchsfertigen Zubereitungen, wie Lösungen, Emulsionen, Suspensionen, Pulver, Pasten oder Granulate, werden in bekannter Weise angewendet, beispielsweise durch Versprühen, Vernebeln, Verstäuben, Verstreuen, Beizen oder Gießen.The formulations generally contain between 0.1 and 95 percent by weight of active compound, preferably between 0.5 and 90%. The formulations or the ready-to-use preparations produced therefrom, such as solutions, emulsions, suspensions, powders, pastes or granules, are used in a known manner, for example by spraying, atomizing, dusting, scattering, pickling or pouring.
Die erfindungsgemäßen Mittel können in diesen Anwendungsformen auch zusammen mit anderen Wirkstoffen vorliegen, z. B. Herbiziden, Insektiziden, Wachstumsregulatoren und Fungiziden oder auch mit Düngemitteln vermischt werden.The agents according to the invention can also be present in these use forms together with other active ingredients, e.g. B. herbicides, insecticides, growth regulators and fungicides or with fertilizers.
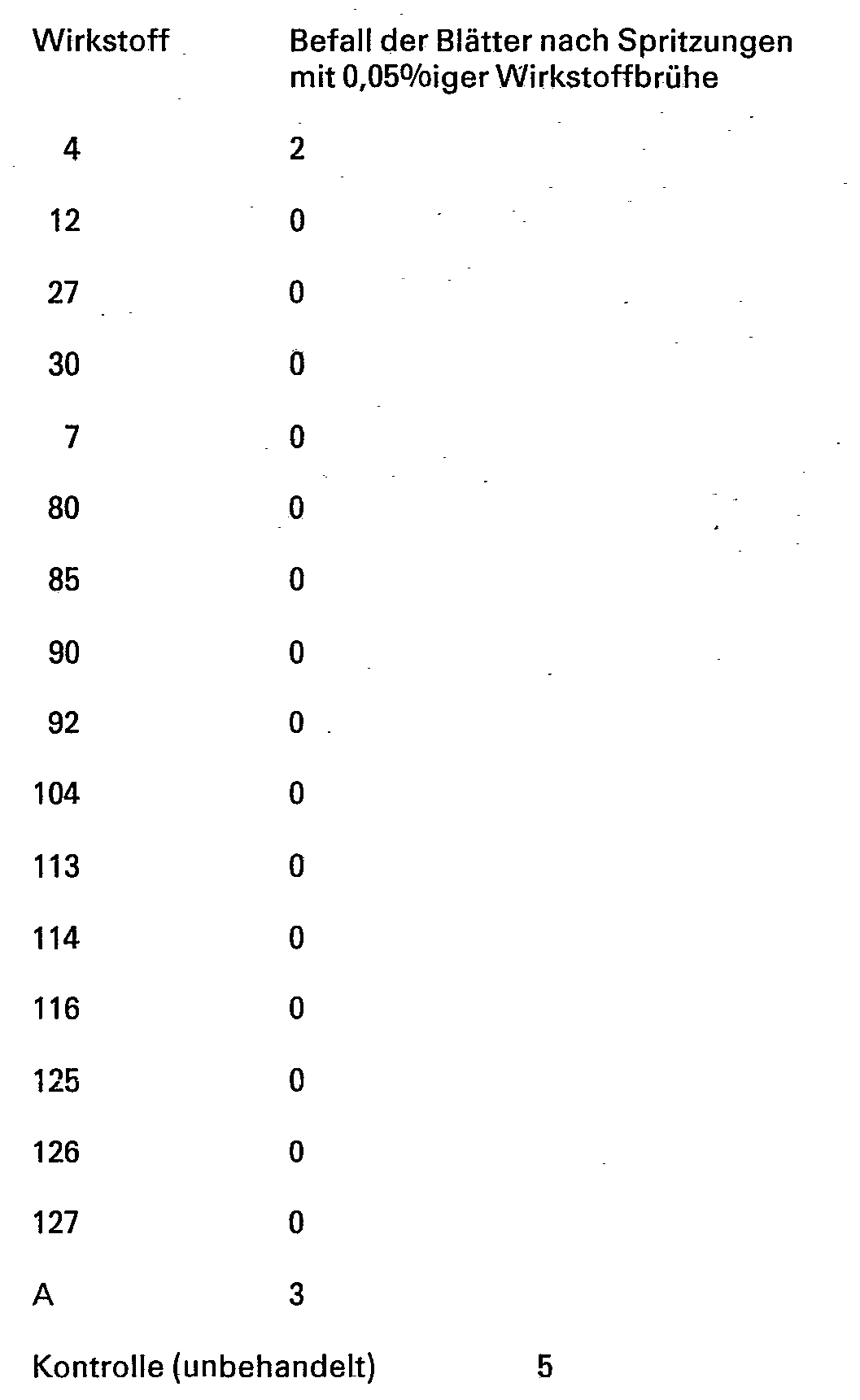
Für die folgenden Versuche, die die fungizide Wirksamkeit der erfindungsgemäßen Verbindungen belegen, wurde zu Vergleichszwecken der folgende bekannte Wirkstoff verwendet
Blätter von in Töpfen gewachsenen Gerstenkeimlingen der Sorte »Firlbecks Union« werden mit wäßrigen Emulsionen aus 80% (Gew.-%) Wirkstoff und 20% Emulgiermittel besprüht und nach dem Antrocknen des Spritzbelages mit Oidien (Sporen) des Gerstenmehltaus (Erysiphe graminis var. hordei) bestäubt. Die Versuchspflanzen werden anschließend im Gewächshaus bei Temperaturen zwischen 20 und 22°C und 75 bis 80% relativer Luftfeuchtigkeit aufgestellt. Nach 10 Tagen wird das Ausmaß der Mehltaupilzentwicklung ermittelt.
Entsprechend wie in Beispiel 9 beschrieben, werden Blätter, von in Töpfen gewachsenen Weizenkeimlingen der Sorte »Jubilar« behandelt und mit Oidien (Sporen) des Weizenmehltaus (Erysiphe graminis var. tritici) infiziert und im übrigen wie in Beispiel 9 behandelt.
Blätter von in Töpfen gewachsenen Weizenkeimlingen der Sorte »Jubilar« werden 24 Stunden vor der Spritzung künstlich mit Sporen des Weizenbraunrostes (Puccinia recondita) infiziert und bei 20 bis 25° C in einer wasserdampfgesättigten Kammer aufgestellt. Danach werden die Pflanzen mit wäßrigen Emulsionen aus 80% (Gewichtsprozent) Wirkstoff und 20% Emulgiermittel besprüht. Nach dem Antrocknen des Spritzbelages werden die Versuchspflanzen im Gewächshaus bei Temperaturen zwischen 20 und 22°C und 75 bis 80% relativer Luftfeuchtigkeit aufgestellt. Nach 10 Tagen wird das Ausmaß der Rostpilzentwicklung ermittelt.
Man vermischt 90 Gewichtsteile der Verbindung 1 mit 10 Gewichtsteilen N-Methyl-α-pyrrolidon und erhält eine Lösung, die zur Anwendung in Form kleinster Tropfen geeignet ist.90 parts by weight of compound 1 are mixed with 10 parts by weight of N-methyl-α-pyrrolidone, and a solution is obtained which is suitable for use in the form of tiny drops.
20 Gewichtsteile der Verbindung 2 werden in einer Mischung gelöst, die aus 80 Gewichtsteilen Xylol, 10 Gewichtsteilen des Anlagerungsproduktes von 8 bis 10 Mol Äthylenoxid an 1 Mol Ölsäure-N-monoäthanolamid, 5 Gewichtsteilen Calciumsalz der Dodecylbenzolsulfonsäure und 5 Gewichtsteilen des Anlagerungsproduktes von 40 Mol Äthylenoxid an 1 Mol Ricinusöl besteht. Durch Ausgießen und feines Verteilen der Lösung in 100 000 Gewichtsteilen Wasser erhält man eine wäßrige Dispersion, die 0,02 Gewichtsprozent des Wirkstoffs enthält.20 parts by weight of compound 2 are dissolved in a mixture consisting of 80 parts by weight of xylene, 10 parts by weight of the adduct of 8 to 10 mol of ethylene oxide and 1 mol of oleic acid-N-monoethanolamide, 5 parts by weight of calcium salt of dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid and 5 parts by weight of the adduct of 40 mol of ethylene oxide of 1 mole of castor oil. By pouring the solution into 100,000 parts by weight of water and finely distributing it therein, an aqueous dispersion is obtained which contains 0.02% by weight of the active ingredient.
20 Gewichtsteile der Verbindung 3 werden in einer Mischung gelöst, die aus 40 Gewichtsteilen Cyclohexanon, 30 Gewichtsteilen Isobutanol, 20 Gewichtsteilen des Anlagerungsproduktes von 7 Mol Äthylenoxid an 1 Mol Isooctylphenol und 10 Gewichtsteilen des Anlagerungsproduktes von 40 Mol Äthylenoxid an 1 Mol Ricinusöl besteht. Durch Eingießen und feines Verteilen der Lösung in 100 000 Gewichtsteilen Wasser erhält man eine wäßrige Dispersion, die 0,02 Gewichtsprozent des Wirkstoffs enthält.20 parts by weight of compound 3 are dissolved in a mixture consisting of 40 parts by weight of cyclohexanone, 30 parts by weight of isobutanol, 20 parts by weight of the adduct of 7 mol of ethylene oxide and 1 mol of isooctylphenol and 10 parts by weight of the adduct of 40 mol of ethylene oxide and 1 mol of castor oil. Pouring the solution into 100,000 parts by weight of water and finely distributing it therein gives an aqueous dispersion which comprises 0.02% by weight of the active ingredient.
20 Gewichtsteile der Verbindung 1 werden in einer Mischung gelöst, die aus 25 Gewichtsteilen Cyclohexanol, 65 Gewichtsteilen einer Mineralölfraktion vom Siedepunkt 210 bis 280°C und 10 Gewichtsteilen des Anlagerungsproduktes von 40 Mol Äthylenoxid an 1 Mol Ricinusöl besteht. Durch Eingießen und feines Verteilen der Lösung in 100 000 Gewichtsteilen Wasser erhält man eine wäßrige Dispersion, die 0,02 Gewichtsprozent des Wirkstoffs enthält.20 parts by weight of compound 1 are dissolved in a mixture consisting of 25 parts by weight of cyclohexanol, 65 parts by weight of a mineral oil fraction with a boiling point of 210 to 280 ° C. and 10 parts by weight of the adduct of 40 moles of ethylene oxide and 1 mole of castor oil. Pouring the solution into 100,000 parts by weight of water and finely distributing it therein gives an aqueous dispersion which comprises 0.02% by weight of the active ingredient.
20 Gewichtsteile des Wirkstoffs 2 werden mit 3 Gewichtsteilen des Natriumsalzes der Diisobutylnaphthalin-α-sulfonsäure, 17 Gewichtsteilen des Natriumsalzes einer Ligninsulfonsäure aus einer Sulfit-Ablauge und 60 Gewichtsteilen pulverförmigem Kieselsäuregel gut vermischt und in einer Hammermühle vermahlen. Durch feines Verteilen der Mischung in 20 000 Gewichtsteilen Wasser erhält man eine Spritzbrühe, die 0,1 Gewichtsprozent des Wirkstoffs enthält.20 parts by weight of active ingredient 2 are mixed well with 3 parts by weight of the sodium salt of diisobutylnaphthalene-α-sulfonic acid, 17 parts by weight of the sodium salt of lignosulfonic acid from a sulfite waste liquor and 60 parts by weight of powdered silica gel and ground in a hammer mill. By finely distributing the mixture in 20,000 parts by weight of water, a spray liquor is obtained which contains 0.1% by weight of the active ingredient.
3 Gewichtsteile der Verbindung 3 werden mit 97 Gewichtsteilen feinteiligem Kaolin innig vermischt. Man erhält auf diese Weise ein Stäubmittel, das 3 Gewichtsprozent des Wirkstoffs enthält.3 parts by weight of compound 3 are intimately mixed with 97 parts by weight of finely divided kaolin. In this way, a dusting agent is obtained which contains 3% by weight of the active ingredient.
30 Gewichtsteile der Verbindung 4 werden mit einer Mischung aus 92 Gewichtsteilen pulverförmigem Kieselsäuregel und 8 Gewichtsteilen Paraffinöl, das auf die Oberfläche dieses Kieselsäuregels gesprüht wurde, innig vermischt. Man erhält auf diese Weise eine Aufbereitung des Wirkstoffs mit guter Haftfähigkeit.30 parts by weight of compound 4 are intimately mixed with a mixture of 92 parts by weight of powdered silica gel and 8 parts by weight of paraffin oil which has been sprayed onto the surface of this silica gel. In this way, a preparation of the active ingredient with good adhesiveness is obtained.
40 Gewichtsteile des Wirkstoffs 1 werden mit 10 Teilen Natriumsalz eines Phenolsulfonsäure-harnstoff-formaldehyd-Kondensats, 2 Teilen Kieselgel und 48 Teilen Wasser innig vermischt. Man erhält eine stabile wäßrige Dispersion. Durch Verdünnen mit 100 000 Gewichtsteilen Wasser erhält man eine wäßrige Dispersion, die 0,04 Gewichtsprozent Wirkstoff enthält.40 parts by weight of active ingredient 1 are intimately mixed with 10 parts of sodium salt of a phenolsulfonic acid-urea-formaldehyde condensate, 2 parts of silica gel and 48 parts of water. A stable aqueous dispersion is obtained. Dilution with 100,000 parts by weight of water gives an aqueous dispersion which contains 0.04% by weight of active ingredient.
20 Teile des Wirkstoffs 2 werden mit 2 Teilen Calciumsalz der Dodecylbenzolsulfonsäure, 8 Teilen Fettalkohol-polyglykoläther, 2 Teilen Natriumsalz eines Phenolsulfonsäure-harnstoff-formaldehyd-Kondensats und 68 Teilen eines paraffinischen Mineralöls innig vermischt. Man erhält eine stabile ölige Dispersion.20 parts of active ingredient 2 are intimately mixed with 2 parts of calcium salt of dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid, 8 parts of fatty alcohol polyglycol ether, 2 parts of sodium salt of a phenolsulfonic acid-urea-formaldehyde condensate and 68 parts of a paraffinic mineral oil. A stable oily dispersion is obtained.
Claims (10)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE2735314 | 1977-08-05 | ||
| DE19772735314 DE2735314A1 (en) | 1977-08-05 | 1977-08-05 | ALPHA-AZOLYL SULPHIDES AND THEIR DERIVATIVES |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0000752A2 EP0000752A2 (en) | 1979-02-21 |
| EP0000752A3 EP0000752A3 (en) | 1979-04-04 |
| EP0000752B1 true EP0000752B1 (en) | 1981-01-14 |
Family
ID=6015701
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP78100538A Expired EP0000752B1 (en) | 1977-08-05 | 1978-07-28 | Alpha-azolylsulphides, sulphoxides and sulphones, their salts and metal complexes, method for their production and fungizides containing them |
Country Status (14)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0000752B1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JPS5430174A (en) |
| AT (1) | AT360279B (en) |
| CA (1) | CA1112647A (en) |
| CS (1) | CS200238B2 (en) |
| DD (1) | DD137525A5 (en) |
| DE (2) | DE2735314A1 (en) |
| DK (1) | DK145597C (en) |
| FI (1) | FI64360C (en) |
| HU (1) | HU180205B (en) |
| IL (1) | IL55241A (en) |
| IT (1) | IT1107959B (en) |
| PL (1) | PL107615B1 (en) |
| SU (1) | SU795436A3 (en) |
Cited By (19)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0005754A1 (en) * | 1978-05-19 | 1979-12-12 | BASF Aktiengesellschaft | Compositions and process for regulating plant growth |
| EP0056860A1 (en) * | 1981-01-08 | 1982-08-04 | BASF Aktiengesellschaft | Substituted azolyl-glycolsulfonates, fungicides containing them and process for their preparation |
| EP0091219A2 (en) * | 1982-04-01 | 1983-10-12 | Schering Agrochemicals Limited | Heterocyclic fungicidal and growth regulant compounds, and compositions containing them |
| EP0098243A1 (en) * | 1982-06-25 | 1984-01-11 | Ciba-Geigy Ag | Acid derivatives, method for their preparation and their use in combating microorganisms |
| EP0107392A1 (en) * | 1982-10-09 | 1984-05-02 | Pfizer Limited | Triazole antifungal agents |
| EP0140571A1 (en) * | 1983-09-30 | 1985-05-08 | Schering Agrochemicals Limited | Diazole and triazole compounds |
| US4636514A (en) * | 1982-08-13 | 1987-01-13 | The Dow Chemical Company | Aryl(aryloxy or arylthio)azolomethanes |
| US4701463A (en) * | 1982-08-13 | 1987-10-20 | The Dow Chemical Company | Pyridyl (pyridyloxy or pyriolylthio) azolomethanes |
| US4701207A (en) * | 1982-08-13 | 1987-10-20 | The Dow Chemical Company | Phenyl (phenoxy or phenylthio) azolomethanes |
| US4716174A (en) * | 1982-08-13 | 1987-12-29 | The Dow Chemical Company | Aryl(aryloxy or arylthio)azolomethanes and their use as pesticides |
| US4717733A (en) * | 1982-08-13 | 1988-01-05 | The Dow Chemical Company | Aryl(aryloxy or arylthio)azolomethanes and their use as pesticides |
| US4717732A (en) * | 1982-08-13 | 1988-01-05 | The Dow Chemical Company | Aryl(aryloxy or arylthio)azolomethanes and their use as pesticides |
| US4717734A (en) * | 1982-08-13 | 1988-01-05 | The Dow Chemical Company | Aryl(aryloxy or arylthio)azolomethanes and their use as pesticides |
| US4720502A (en) * | 1982-08-13 | 1988-01-19 | The Dow Chemical Company | Aryl(aryloxy or arylthio)azolomethanes and their use as pesticides |
| US4728657A (en) * | 1982-08-13 | 1988-03-01 | The Dow Chemical Company | Aryl(aryloxy or arylthio)azolomethanes |
| US4731372A (en) * | 1982-08-13 | 1988-03-15 | The Dow Chemical Company | Aryl(aryloxy or arylthio) azolomethanes, and their use as pesticides |
| US4767752A (en) * | 1985-03-18 | 1988-08-30 | S.D.S. Biotech K.K. | Imidazolyl or triazolyl substituted propionate derivative and nonmedical fungicide containing the same |
| FR2677983A1 (en) * | 1991-06-24 | 1992-12-24 | Oreal | ALKYLTHIOPOLY (ETHYLIMIDAZOLIUM) COMPOUNDS, PREPARATION METHOD AND THEIR USE AS BIOCIDAL AGENTS. |
| CN100562516C (en) * | 2001-12-27 | 2009-11-25 | 第一制药株式会社 | Amyloid-beta produces and the excretory inhibitor |
Families Citing this family (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0061835B1 (en) * | 1981-03-18 | 1989-02-01 | Imperial Chemical Industries Plc | Triazole compounds, a process for preparing them, their use as plant fungicides and fungicidal compositions containing them |
| DK348883A (en) * | 1982-08-13 | 1984-02-14 | Dow Chemical Co | ARYL (ARYLOXY OR ARYLTHIO) AZOLOMETHANES, THEIR PREPARATION AND USE |
| US4978672A (en) * | 1986-03-07 | 1990-12-18 | Ciba-Geigy Corporation | Alpha-heterocyclc substituted tolunitriles |
| US4937250A (en) * | 1988-03-07 | 1990-06-26 | Ciba-Geigy Corporation | Alpha-heterocycle substituted tolunitriles |
| US4749713A (en) * | 1986-03-07 | 1988-06-07 | Ciba-Geigy Corporation | Alpha-heterocycle substituted tolunitriles |
| GB0108592D0 (en) * | 2001-04-05 | 2001-05-23 | Merck Sharp & Dohme | Therapeutic agents |
| AU2004251987C1 (en) | 2003-06-30 | 2010-11-18 | Daiichi Sankyo Company, Limited | Heterocyclic methyl sulfone derivative |
| US7314875B2 (en) * | 2004-04-13 | 2008-01-01 | Cephalon, Inc. | Tricyclic aromatic and bis-phenyl sulfinyl derivatives |
-
1977
- 1977-08-05 DE DE19772735314 patent/DE2735314A1/en active Pending
-
1978
- 1978-07-28 IL IL55241A patent/IL55241A/en unknown
- 1978-07-28 DE DE7878100538T patent/DE2860325D1/en not_active Expired
- 1978-07-28 EP EP78100538A patent/EP0000752B1/en not_active Expired
- 1978-07-31 CA CA308,484A patent/CA1112647A/en not_active Expired
- 1978-08-01 IT IT50557/78A patent/IT1107959B/en active
- 1978-08-02 CS CS785091A patent/CS200238B2/en unknown
- 1978-08-02 DD DD20708978A patent/DD137525A5/en unknown
- 1978-08-03 SU SU782646293A patent/SU795436A3/en active
- 1978-08-03 PL PL1978208828A patent/PL107615B1/en unknown
- 1978-08-04 HU HU78BA3683A patent/HU180205B/en unknown
- 1978-08-04 AT AT568678A patent/AT360279B/en active
- 1978-08-04 JP JP9469478A patent/JPS5430174A/en active Pending
- 1978-08-04 DK DK345678A patent/DK145597C/en active
- 1978-08-04 FI FI782403A patent/FI64360C/en not_active IP Right Cessation
Cited By (21)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0005754A1 (en) * | 1978-05-19 | 1979-12-12 | BASF Aktiengesellschaft | Compositions and process for regulating plant growth |
| EP0056860A1 (en) * | 1981-01-08 | 1982-08-04 | BASF Aktiengesellschaft | Substituted azolyl-glycolsulfonates, fungicides containing them and process for their preparation |
| EP0091219A3 (en) * | 1982-04-01 | 1984-06-27 | Fbc Limited | Heterocyclic fungicidal and growth regulant compounds, and compositions containing them |
| EP0091219A2 (en) * | 1982-04-01 | 1983-10-12 | Schering Agrochemicals Limited | Heterocyclic fungicidal and growth regulant compounds, and compositions containing them |
| EP0098243A1 (en) * | 1982-06-25 | 1984-01-11 | Ciba-Geigy Ag | Acid derivatives, method for their preparation and their use in combating microorganisms |
| US4716174A (en) * | 1982-08-13 | 1987-12-29 | The Dow Chemical Company | Aryl(aryloxy or arylthio)azolomethanes and their use as pesticides |
| US4717732A (en) * | 1982-08-13 | 1988-01-05 | The Dow Chemical Company | Aryl(aryloxy or arylthio)azolomethanes and their use as pesticides |
| US4636514A (en) * | 1982-08-13 | 1987-01-13 | The Dow Chemical Company | Aryl(aryloxy or arylthio)azolomethanes |
| US4701463A (en) * | 1982-08-13 | 1987-10-20 | The Dow Chemical Company | Pyridyl (pyridyloxy or pyriolylthio) azolomethanes |
| US4701207A (en) * | 1982-08-13 | 1987-10-20 | The Dow Chemical Company | Phenyl (phenoxy or phenylthio) azolomethanes |
| US4731372A (en) * | 1982-08-13 | 1988-03-15 | The Dow Chemical Company | Aryl(aryloxy or arylthio) azolomethanes, and their use as pesticides |
| US4717733A (en) * | 1982-08-13 | 1988-01-05 | The Dow Chemical Company | Aryl(aryloxy or arylthio)azolomethanes and their use as pesticides |
| US4728657A (en) * | 1982-08-13 | 1988-03-01 | The Dow Chemical Company | Aryl(aryloxy or arylthio)azolomethanes |
| US4717734A (en) * | 1982-08-13 | 1988-01-05 | The Dow Chemical Company | Aryl(aryloxy or arylthio)azolomethanes and their use as pesticides |
| US4720502A (en) * | 1982-08-13 | 1988-01-19 | The Dow Chemical Company | Aryl(aryloxy or arylthio)azolomethanes and their use as pesticides |
| EP0107392A1 (en) * | 1982-10-09 | 1984-05-02 | Pfizer Limited | Triazole antifungal agents |
| EP0140571A1 (en) * | 1983-09-30 | 1985-05-08 | Schering Agrochemicals Limited | Diazole and triazole compounds |
| US4767752A (en) * | 1985-03-18 | 1988-08-30 | S.D.S. Biotech K.K. | Imidazolyl or triazolyl substituted propionate derivative and nonmedical fungicide containing the same |
| FR2677983A1 (en) * | 1991-06-24 | 1992-12-24 | Oreal | ALKYLTHIOPOLY (ETHYLIMIDAZOLIUM) COMPOUNDS, PREPARATION METHOD AND THEIR USE AS BIOCIDAL AGENTS. |
| EP0520873A1 (en) * | 1991-06-24 | 1992-12-30 | L'oreal | Alkylthiopoly(ethylimidazolium)compounds, process of preparation and their use as biocide agents |
| CN100562516C (en) * | 2001-12-27 | 2009-11-25 | 第一制药株式会社 | Amyloid-beta produces and the excretory inhibitor |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| PL208828A1 (en) | 1979-05-21 |
| EP0000752A2 (en) | 1979-02-21 |
| PL107615B1 (en) | 1980-02-29 |
| DE2860325D1 (en) | 1981-03-12 |
| JPS5430174A (en) | 1979-03-06 |
| DD137525A5 (en) | 1979-09-12 |
| IT7850557A0 (en) | 1978-08-01 |
| EP0000752A3 (en) | 1979-04-04 |
| DE2735314A1 (en) | 1979-02-22 |
| CS200238B2 (en) | 1980-08-29 |
| DK145597C (en) | 1983-08-15 |
| CA1112647A (en) | 1981-11-17 |
| IL55241A (en) | 1982-01-31 |
| AT360279B (en) | 1980-12-29 |
| IT1107959B (en) | 1985-12-02 |
| SU795436A3 (en) | 1981-01-07 |
| FI64360C (en) | 1983-11-10 |
| DK145597B (en) | 1982-12-20 |
| IL55241A0 (en) | 1978-09-29 |
| DK345678A (en) | 1979-02-06 |
| HU180205B (en) | 1983-02-28 |
| FI782403A (en) | 1979-02-06 |
| FI64360B (en) | 1983-07-29 |
| ATA568678A (en) | 1980-05-15 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0000752B1 (en) | Alpha-azolylsulphides, sulphoxides and sulphones, their salts and metal complexes, method for their production and fungizides containing them | |
| EP0196038B1 (en) | Azolyl methyl oxiranes, their preparation and use as plant-protecting agents | |
| EP0061051B1 (en) | Substituted triazolylmethyl oxiranes, process for their preparation and their application as intermediates | |
| EP0110048B1 (en) | Substituated 1-hydroxy-ethyl-triazolyl derivatives | |
| EP0054865B1 (en) | Substituted 1-azolyl-butan-2-ones, their preparation and their application as fungicides as well as intermediates | |
| EP0121171B1 (en) | Fungicides, process for their preparation and their use | |
| EP0131845B1 (en) | Use of substituted diazolylalkylcarbinols in plant protection for the control of fungi | |
| EP0104549B1 (en) | Azolyl butanoles | |
| EP0071009B1 (en) | Fungicidal alkinyl-azole derivatives and their use | |
| EP0121888B1 (en) | 1-azolyl-3-pyrazolyl-2-propanol derivatives, process for their preparation and their use as fungicides | |
| US4154842A (en) | Fungicidally and bactericidally active 1-azolyl-4-hydroxy-1-phenoxy-butane derivatives | |
| EP0025882A1 (en) | N-Phenylpropyl-substituted azoles, process for their preparation and fungicides containing them | |
| EP0334035B1 (en) | Azolyl propenyl and azolyl methyloxiran derivatives, and fungicides containing them | |
| DE2944223A1 (en) | FUNGICIDAL ENTRIAZOLES, THEIR PRODUCTION AND USE | |
| EP0047405A2 (en) | Azolylalkyl derivatives, process for their preparation and their use as fungicides | |
| EP0102578B1 (en) | 2-aryl-2-azolyl-methyl-1,3-dioxepines | |
| DE2821829A1 (en) | MEANS OF REGULATING PLANT GROWTH | |
| DD141255A5 (en) | FUNGICIDAL AGENTS | |
| EP0042980A2 (en) | 4-Substituted 1-azolyl-1-phenoxy-3,3-dimethyl-butan-2-ones and ols, process for their preparation and their application as fungicides | |
| EP0000112A1 (en) | Triazol-substituted sulphur derivatives, their preparation and their utilisation as fungicides | |
| EP0056089B1 (en) | Azolylalkyl-2,3-dihydrobenzofurans, fungicides containing them and methods for their preparation | |
| EP0119572B1 (en) | Substituted phenethyl-triazolyl derivatives, process for their preparation and their use as fungicides | |
| EP0057864A2 (en) | 2-Azolylmethyl-1,3-dioxolane and dioxane derivatives, process for their preparation and their application as fungicides | |
| EP0073331B1 (en) | 5-aryloxy-5-azolyl-3,3-dimethyl-1-penten-4-ones and -ols, process for their preparation and their use as fungicides | |
| EP0001571B1 (en) | Phenylazophenyloxy-triazolyl derivatives and fungicides containing them |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): BE CH DE FR GB LU NL SE |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): BE CH DE FR GB LU NL SE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed | ||
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): BE CH DE FR GB LU NL SE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Effective date: 19810114 |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 2860325 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19810312 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19810731 |
|
| KL | Correction list |
Free format text: 81/01 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Payment date: 19830628 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 19840622 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 19840625 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Payment date: 19840630 Year of fee payment: 7 Ref country code: BE Payment date: 19840630 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 19870731 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Effective date: 19880728 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Effective date: 19880729 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Effective date: 19880731 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Effective date: 19880901 |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: BASF A.G. Effective date: 19880731 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Effective date: 19890201 |
|
| NLV4 | Nl: lapsed or anulled due to non-payment of the annual fee | ||
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19890331 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST |
|
| EUG | Se: european patent has lapsed |
Ref document number: 78100538.4 Effective date: 19890510 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |