CN115464348A - Machining process of marine large-cylinder-diameter medium-speed diesel engine crankshaft - Google Patents
Machining process of marine large-cylinder-diameter medium-speed diesel engine crankshaft Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN115464348A CN115464348A CN202211240624.1A CN202211240624A CN115464348A CN 115464348 A CN115464348 A CN 115464348A CN 202211240624 A CN202211240624 A CN 202211240624A CN 115464348 A CN115464348 A CN 115464348A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- crankshaft
- hole
- journal
- connecting rod
- processing
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 238000003754 machining Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 21
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 25
- 238000003801 milling Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 25
- 238000005498 polishing Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 23
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 19
- 238000000227 grinding Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 10
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 8
- 238000009966 trimming Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- 230000007704 transition Effects 0.000 claims description 15
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000000523 sample Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- 229910000831 Steel Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000004140 cleaning Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000010079 rubber tapping Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000010959 steel Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000005553 drilling Methods 0.000 abstract 1
- 238000004080 punching Methods 0.000 abstract 1
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 6
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005520 cutting process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000009434 installation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000009191 jumping Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000003672 processing method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004904 shortening Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000006467 substitution reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000009466 transformation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000844 transformation Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B23—MACHINE TOOLS; METAL-WORKING NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- B23P—METAL-WORKING NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; COMBINED OPERATIONS; UNIVERSAL MACHINE TOOLS
- B23P15/00—Making specific metal objects by operations not covered by a single other subclass or a group in this subclass
- B23P15/14—Making specific metal objects by operations not covered by a single other subclass or a group in this subclass gear parts, e.g. gear wheels
Abstract
The invention discloses a processing technology of a marine large-cylinder-diameter medium-speed diesel engine crankshaft, which comprises the following steps: 1) Milling two end faces of the crankshaft and drilling a central hole; 2) Roughly turning each main journal and roughly and finely turning each crank arm inclined plane; 3) Finish milling a main journal and a connecting rod journal, and finish turning the opening of the main journal and the opening of the connecting rod journal; 4) Marking and punching a crankshaft alignment hole; 5) Processing an inclined oil hole and a straight oil hole; 6) Finely grinding the main journal and the connecting rod journal, the flanges at two ends and the middle flange; 7) Machining a central oil hole; 8) A reamed hole at the connecting end of the matched-reamed crankshaft; 9) Trimming and polishing the hole opening chamfer of each hole; 10 Polishing the main journals and connecting journals. The invention greatly shortens the processing period of the crankshaft, saves the processing and auxiliary time 285.5 hours compared with the traditional process, and greatly improves the processing efficiency of the crankshaft.
Description
Technical Field
The invention relates to a crankshaft machining process of a marine diesel engine, in particular to a crankshaft machining process of a large-cylinder-diameter medium-speed marine diesel engine with a cylinder diameter of 320mm or more and a rotating speed of 300rpm (revolutions per minute) or more and n (revolutions per minute) or less and 1000rpm or less, and belongs to the technical field of metal cutting machining.
Background
The crankshaft is a core part of the diesel engine, a main journal of the crankshaft is horizontally placed in a main bearing hole of the rack during assembly, a main bearing cover is arranged on the main bearing cover and fastened by bolts, a connecting rod neck of the crankshaft is connected with a large end of a connecting rod, a small end of the connecting rod is connected with a piston head by a piston pin to form a power transmission mechanism, the piston reciprocates up and down and is transmitted to the crankshaft through a plurality of connecting rods to drive the crankshaft to rotate, and power of the diesel engine is transmitted out. Therefore, the performance of the crankshaft directly influences the overall performance of the diesel engine.
The cylinder diameter is more than phi 320mm for a large-cylinder-diameter diesel engine, the crankshaft structure of the large-cylinder-diameter diesel engine is complex, the machining processes are multiple, the traditional machining process totally comprises 23 processes, the machining period is long, more tool fixtures and tools are used during machining, auxiliary work such as lifting, clamping, alignment and repeated measurement is multiple, time and labor are wasted, the machining time of one crankshaft is about 440 hours, other auxiliary time is about 22 hours, the total time is 462 hours, and the machining efficiency is very low. In addition, the traditional processing method is adopted, and the quality problems of deformation, shaft neck jumping out-of-tolerance and the like often occur in the grinding process of the large-cylinder-diameter diesel engine crankshaft.
Disclosure of Invention
The invention aims to provide a processing technology of a crankshaft of a marine large-cylinder-diameter medium-speed diesel engine, which has the advantages of simple technological process, short processing period, high processing efficiency and stable and reliable crankshaft processing quality.
The invention is realized by the following technical scheme:
a processing technology of a marine large-cylinder-diameter medium-speed diesel engine crankshaft comprises the following steps:
1) Milling machine: milling two end faces of the crankshaft and punching center holes at two ends;
2) A numerical control lathe: roughly turning each main journal, transition arcs of the main journals and adjacent surfaces and opening of the main journals, and simultaneously roughly and finely turning each crank arm 35-degree inclined surface;
3) Turning and milling the center: measuring the machining allowance of a crankshaft and a phase angle of a connecting rod neck by using a probe, finely milling the main shaft neck and the connecting rod neck, finely turning the opening of the main shaft neck, the opening of the connecting rod neck and various transition arcs, finely milling the excircle and the top circle on two sides of a crank arm, finely turning the flanges at two ends, a middle flange and a thrust stop, finely processing holes on the flange surfaces at two ends, and finely milling a balance block mounting surface at the bottom of the crank arm and holes on a balance block mounting surface;
4) Follow-up grinding machine: the crankshaft is driven to rotate by a machine tool main shaft, simultaneously, the opposite sides of each crank arm are respectively scribed, when the crankshaft rotates for one gear, the crank arm of the corresponding gear is scribed, so that a crankshaft alignment hole is positioned, after all the crank arms are scribed, the crankshaft alignment hole is punched by a sample, and then a main journal and a connecting rod journal are roughly ground and semi-finely ground;
5) Turning and milling the center: processing an inclined oil hole, a straight oil hole, an orifice chamfer, a fillet and threads on a main journal and a connecting rod journal, processing a spigot step on a free end flange face and a hole on a step face, and simultaneously processing a dead point mark line on the excircle of the flanges at two ends;
6) Follow-up grinding machine: the crankshaft is driven to rotate through the main shaft of the machine tool, and the main journal, the connecting rod journal, the flanges at the two ends and the middle flange are finely ground;
7) Milling machine: processing center oil holes of the flanges at two ends and bottom holes and pin holes of threaded holes on the middle flange;
8) A floor type boring machine: assembling the flywheel on the connecting end of the crankshaft, and hinging the reamed hole of the connecting end of the crankshaft according to the flywheel layout corresponding to the project;
9) Bench work: trimming and polishing the hole opening chamfer of each oil hole in the step 5) and the step 7), and polishing the inner hole of each oil hole; removing burrs of each hole on the flanges at the two ends, and filing, chamfering and sanding the orifice of the oil hole; tapping a thread on a bottom hole of a threaded hole on the middle flange;
10 Polishing lathe: polishing each main journal and each connecting rod journal, polishing the transition arc of each main journal and the transition arc of each connecting rod journal, polishing the transition arcs of flanges at two ends, and polishing the side face of a thrust stop;
11 Bench work: and cleaning and checking the appearance quality of the crankshaft, and finally knocking a steel seal and sealing the oil.
The object of the invention is further achieved by the following technical measures.
In the processing technology of the crankshaft of the marine large-cylinder-diameter medium-speed diesel engine, in step 1), step 7) and step 8), the crankshaft is supported by the V-shaped frame during processing.
In the processing technology of the crankshaft of the marine large-cylinder-diameter medium-speed diesel engine, in the step 2), the step 3) and the step 5), the crankshaft is supported by the movable center frame during processing, and two ends of the crankshaft are tightly pressed through the three-jaw chuck and the double-top points on the machine tool.
In the processing technology of the marine crankshaft of the large-cylinder-diameter medium-speed diesel engine, in the step 4) and the step 6), the crankshaft is supported by the plurality of movable center frames during processing, two ends of the crankshaft are tightly propped by the double centers, and the measurement is assisted by the Marbos measuring instrument.
The method has the advantages of totaling eleven working procedures, having less working procedure flows, short process route and fewer times of machine tool installation, saving twelve working procedures compared with the traditional process and greatly shortening the processing period of the crankshaft. The processing time of one crankshaft is about 165.5 hours, the other auxiliary time is about 11 hours, the total time is 176.5 hours, the processing and auxiliary time is saved by 285.5 hours compared with the traditional process, and the processing efficiency of the crankshaft is greatly improved. In addition, the crankshaft machining method can effectively ensure the machining quality of the crankshaft, and greatly reduces the labor intensity of operators and saves time and labor for operation because part of procedures are changed from common machine tools to numerical control machine tool machining.
Advantages and features of the invention will be illustrated and explained by the following non-restrictive description of preferred embodiments thereof, given by way of example only with reference to the accompanying drawings.
Drawings
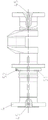
FIG. 1 is a process diagram of the present invention 1;
FIG. 2 is a process diagram of the present invention FIG. 2;
FIG. 3 is an enlarged cross-sectional view D-D of FIG. 2;
FIG. 4 is an enlarged view from the direction A of FIG. 2;
FIG. 5 is an enlarged view from the direction B of FIG. 2;
FIG. 6 is a process diagram of the present invention FIG. 3;
FIG. 7 is a process diagram of the present invention of FIG. 4;
FIG. 8 is an enlarged cross-sectional view taken along line C-C of FIG. 7;
FIG. 9 is an enlarged cross-sectional S-S view of FIG. 7;
FIG. 10 is a process diagram of the present invention FIG. 5;
FIG. 11 is a process diagram of the present invention FIG. 6;
Detailed Description
The invention is further illustrated by the following examples in conjunction with the drawings.
The invention takes a 9L32/40 model as an example, the crankshaft length of the 9L32/40 model is 5820mm, the net weight is 4307kg, and the diameters of a main journal and a connecting journal are phi 290mm.
The invention relates to a processing technology of a marine large-cylinder-diameter medium-speed diesel engine crankshaft, which comprises the following steps:
1) Planer type milling machine: the crankshaft is supported by a V-shaped frame, two end faces of the crankshaft are milled, and center holes at two ends are punched;
2) A numerical control lathe: the crankshaft is supported by a movable center frame, and two ends of the crankshaft are tightly pressed by a three-jaw chuck and double tips on a machine tool. As shown in fig. 1, roughly turning each main journal 1, a transition arc 11 of the main journal 1 and an adjacent surface, and an opening 12 of the main journal 1, and roughly and finely turning a 35-degree inclined surface 21 of each crank arm 2;
3) Turning and milling the center: the crankshaft is supported by a movable center frame, and two ends of the crankshaft are tightly propped through a three-jaw chuck and double-tip on a machine tool. Measuring the machining allowance of the crankshaft and the phase angle of the connecting rod neck 3 by using a probe, as shown in fig. 2 to 5, finely milling a main journal 1 and the connecting rod neck 3, finely turning a main journal open 12, a connecting rod neck open 31 and transition arcs 11, finely milling an outer circle 22 and a top circle 23 on two sides of the connecting rod neck 2, finely turning two-end flanges 4, a middle flange 5 and a thrust stop open 6, finely turning holes 41 on flange surfaces on two ends, and finely milling a balance block mounting surface 24 on the bottom of the connecting rod neck 2 and holes 25 on a balance block mounting surface;
4) Follow-up grinding machine: the crankshaft is supported by a plurality of movable center frames, two ends of the crankshaft are tightly pressed by double centers, and the measurement is assisted by a Marburg measuring instrument. As shown in fig. 6, the crankshaft is driven to rotate by the main shaft of the machine tool, simultaneously, the opposite sides of each crank arm 2 are respectively marked, and the crankshaft is marked on the crank arm 2 of the corresponding gear when rotating for one gear, so that a crankshaft alignment hole 26 is positioned, all the crank arms 2 are marked after marking, then the crankshaft alignment hole 26 is punched, and then the main journal 1 and the connecting journal 3 are roughly ground and semi-finely ground, the shaft diameter size is checked after finishing fine grinding, and the shaft diameter run-out is checked;
5) Turning and milling the center: the crankshaft is supported by a movable center frame, and two ends of the crankshaft are tightly propped through a three-jaw chuck and double-tip on a machine tool. As shown in fig. 7, 8 and 9, the oblique oil hole 13, the straight oil hole 14 and the chamfer, the fillet and the thread of the orifice on the main journal 1 and the connecting rod journal 3 are processed, the spigot step 42 on the flange surface of the free end and the hole 43 on the step surface are processed, and simultaneously, a dead point mark line 44 is processed on the excircle of the flange at the two ends;
6) Follow-up grinding machine: the crankshaft is clamped by double tips, a plurality of movable center frames are supported, and auxiliary measurement is carried out through a Marbos measuring instrument, as shown in figure 10, the crankshaft is driven to rotate through a machine tool main shaft, the main shaft neck 1, the connecting rod neck 3, the flanges 4 at two ends and the middle flange 5 are finely ground, the shaft diameter size is checked after the fine grinding is finished, and the shaft diameter runout is checked;
7) Planer type milling machine: the crankshaft is supported by a V-shaped frame, and as shown in FIG. 11, central oil holes 45 of the flanges 4 at two ends and bottom holes 51 and pin holes 52 of threaded holes on the middle flange are processed;
8) A floor type boring machine: the crankshaft is supported by a V-shaped frame, the flywheel is assembled at the connecting end of the crankshaft, and a reaming hole at the connecting end of the crankshaft is matched according to a flywheel layout corresponding to a project;
9) Bench work: trimming and polishing the hole opening chamfer of each oil hole in the step 5) and the step 7), and polishing the inner hole of each oil hole; removing burrs of each hole on flanges at two ends, filing, chamfering and sanding the orifice of the oil hole; tapping on a bottom hole 51 of the threaded hole on the intermediate flange;
10 Polishing lathe: polishing each main journal 1 and each connecting rod journal 3, polishing the transition arc 11 of each main journal 1 and the transition arc of each connecting rod journal 3, polishing the transition arcs of the flanges 4 at two ends, and polishing the side face of the anti-thrust gear;
11 ) bench work: and cleaning and checking the appearance quality of the crankshaft, and finally knocking a steel seal and sealing the oil.
In addition to the above embodiments, the present invention may have other embodiments, and any technical solutions formed by equivalent substitutions or equivalent transformations fall within the scope of the claims of the present invention.
Claims (4)
1. A processing technology of a marine large-cylinder-diameter medium-speed diesel engine crankshaft is characterized by comprising the following steps:
1) Milling machine: milling two end faces of the crankshaft and punching center holes at two ends;
2) A numerical control lathe: roughly turning each main journal, transition arcs of the main journals and adjacent surfaces and opening of the main journals, and roughly and finely turning each crank arm inclined plane of 35 degrees;
3) Turning and milling the center: measuring the machining allowance of a crankshaft and a phase angle of a connecting rod neck by using a probe, finely milling the main shaft neck and the connecting rod neck, finely turning the opening of the main shaft neck, the opening of the connecting rod neck and various transition arcs, finely milling the excircle and the top circle on two sides of a crank arm, finely turning the flanges at two ends, a middle flange and a thrust stop, finely processing holes on the flange surfaces at two ends, and finely milling a balance block mounting surface at the bottom of the crank arm and holes on a balance block mounting surface;
4) Follow-up grinding machine: the crankshaft is driven to rotate by a machine tool main shaft, simultaneously, the opposite sides of each crank arm are respectively scribed, when the crankshaft rotates for one gear, the crank arm of the corresponding gear is scribed, so that a crankshaft alignment hole is positioned, after all the crank arms are scribed, the crankshaft alignment hole is punched by a sample, and then a main journal and a connecting rod journal are roughly ground and semi-finely ground;
5) Turning and milling the center: processing an inclined oil hole, a straight oil hole, an orifice chamfer, a fillet and threads on a main journal and a connecting rod journal, processing a spigot step on a free end flange face and a hole on a step face, and simultaneously processing a dead point mark line on the excircle of the flanges at two ends;
6) Follow-up grinding machine: the crankshaft is driven to rotate through the main shaft of the machine tool, and the main journal, the connecting rod journal, the flanges at the two ends and the middle flange are finely ground;
7) Milling machine: processing center oil holes of the flanges at two ends and bottom holes and pin holes of threaded holes on the middle flange;
8) A floor type boring machine: assembling the flywheel on the connecting end of the crankshaft, and hinging the hinged hole of the connecting end of the crankshaft according to the flywheel layout corresponding to the project;
9) Performing bench work: trimming and polishing the chamfer angle of the orifice of each oil hole in the step 5) and the step 7), and polishing the inner hole of each oil hole; removing burrs of each hole on the flanges at the two ends, and filing, chamfering and sanding the orifice of the oil hole; tapping a thread on a bottom hole of a threaded hole on the middle flange;
10 Polishing lathe: polishing each main journal and each connecting rod journal, polishing the transition arc of each main journal and the transition arc of each connecting rod journal, polishing the transition arcs of flanges at two ends, and polishing the side face of a thrust stop;
11 Bench work: and cleaning and checking the appearance quality of the crankshaft, and finally knocking a steel seal and sealing the oil.
2. The process for machining the crankshaft of the marine large-cylinder-diameter medium-speed diesel engine according to claim 1, wherein the process comprises the following steps: in the steps 1), 7) and 8), the crankshaft is supported by a V-shaped frame during processing.
3. The process for machining the crankshaft of the marine large-cylinder-diameter medium-speed diesel engine according to claim 1, wherein the process comprises the following steps: in the step 2), the step 3) and the step 5), the crankshaft is supported by a movable center frame during processing, and two ends of the crankshaft are tightly pressed through a three-jaw chuck and double-top tips on a machine tool.
4. The process for machining the crankshaft of the marine large-cylinder-diameter medium-speed diesel engine according to claim 1, wherein the process comprises the following steps: in the steps 4) and 6), the crankshaft is supported by a plurality of movable center frames during processing, two ends of the crankshaft are tightly pressed by double centers, and the measurement is assisted by a Marbos measuring instrument.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211240624.1A CN115464348B (en) | 2022-10-11 | 2022-10-11 | Processing technology of crankshaft of marine large-cylinder-diameter medium-speed diesel engine |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211240624.1A CN115464348B (en) | 2022-10-11 | 2022-10-11 | Processing technology of crankshaft of marine large-cylinder-diameter medium-speed diesel engine |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN115464348A true CN115464348A (en) | 2022-12-13 |
| CN115464348B CN115464348B (en) | 2024-01-02 |
Family
ID=84336305
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202211240624.1A Active CN115464348B (en) | 2022-10-11 | 2022-10-11 | Processing technology of crankshaft of marine large-cylinder-diameter medium-speed diesel engine |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN115464348B (en) |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB1417065A (en) * | 1972-03-02 | 1975-12-10 | Maschf Augsburg Nuernberg Ag | Process for manufacturing a crankshaft |
| CN103009021A (en) * | 2012-12-31 | 2013-04-03 | 四川绵竹鑫坤机械制造有限责任公司 | Segmented crankshaft machining process |
| CN103551855A (en) * | 2013-11-14 | 2014-02-05 | 上海中船三井造船柴油机有限公司 | Method and device for simultaneous drilling and reaming processing of crankshaft and flywheel of marine low-speed diesel engine |
| CN105196012A (en) * | 2015-09-23 | 2015-12-30 | 四川飞亚汽车零部件有限公司 | Novel process for processing crankshaft |
| CN113601119A (en) * | 2021-08-13 | 2021-11-05 | 陕西柴油机重工有限公司 | Machining method for high-power diesel engine camshaft |
-
2022
- 2022-10-11 CN CN202211240624.1A patent/CN115464348B/en active Active
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB1417065A (en) * | 1972-03-02 | 1975-12-10 | Maschf Augsburg Nuernberg Ag | Process for manufacturing a crankshaft |
| CN103009021A (en) * | 2012-12-31 | 2013-04-03 | 四川绵竹鑫坤机械制造有限责任公司 | Segmented crankshaft machining process |
| CN103551855A (en) * | 2013-11-14 | 2014-02-05 | 上海中船三井造船柴油机有限公司 | Method and device for simultaneous drilling and reaming processing of crankshaft and flywheel of marine low-speed diesel engine |
| CN105196012A (en) * | 2015-09-23 | 2015-12-30 | 四川飞亚汽车零部件有限公司 | Novel process for processing crankshaft |
| CN113601119A (en) * | 2021-08-13 | 2021-11-05 | 陕西柴油机重工有限公司 | Machining method for high-power diesel engine camshaft |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN115464348B (en) | 2024-01-02 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN210099460U (en) | Drilling equipment convenient to deburring | |
| CN101941131A (en) | Method for repairing cylinder screw holes and special scraper and screw tap for implementing method | |
| CN110977342B (en) | Split machining process for connecting rod | |
| CN103551855A (en) | Method and device for simultaneous drilling and reaming processing of crankshaft and flywheel of marine low-speed diesel engine | |
| CN109128723B (en) | Method for machining V-shaped through lightening hole of crankshaft connecting rod neck | |
| CN112025204A (en) | Method for repairing embedded back hinge of ejector rod hole of machine body | |
| CN111531319A (en) | Method for repairing main shaft hole of internal combustion engine body and application | |
| CN115464348A (en) | Machining process of marine large-cylinder-diameter medium-speed diesel engine crankshaft | |
| CN202291479U (en) | Rotary type numerical control vertical drilling machine | |
| CN211219921U (en) | Combined positioning fixture | |
| CN208408772U (en) | A kind of machine for cutting thread for steel bar | |
| CN203696170U (en) | Built-up jig for machining main body and sleeve of lathe wrench | |
| CN211219841U (en) | Full-automatic turntable | |
| CN213672031U (en) | Drilling chamfering machine tool | |
| CN205763963U (en) | One prevents workpiece lathe chuck device in axial sliding | |
| CN204171544U (en) | A kind of full metal screw pump stator auxiliary machining device | |
| CN102785064A (en) | Method for processing cross axle | |
| CN220362231U (en) | Numerical control drilling and milling counter bore chamfering all-in-one machine for metal aluminum material | |
| CN112372236A (en) | Method for processing lubricating oil scale inclined hole of diesel engine frame | |
| CN218947034U (en) | Automatic tool changing device on right-angle accessory head of planer boring and milling machine | |
| CN105880936A (en) | Bolt machining method | |
| CN211438968U (en) | Rotary table | |
| CN113369529B (en) | Large engine cam shaft hole boring method and boring auxiliary device | |
| CN216927465U (en) | Hand-operated wheel for machine tool | |
| CN213888539U (en) | Tool for machining trapezoidal threads through lathe |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |