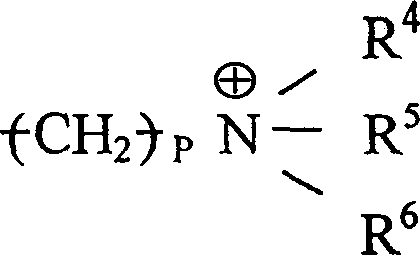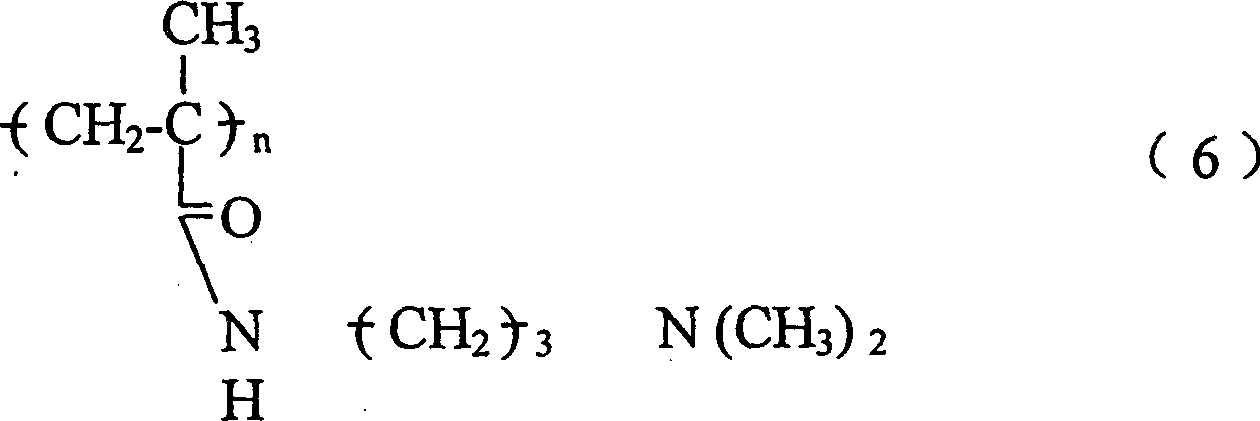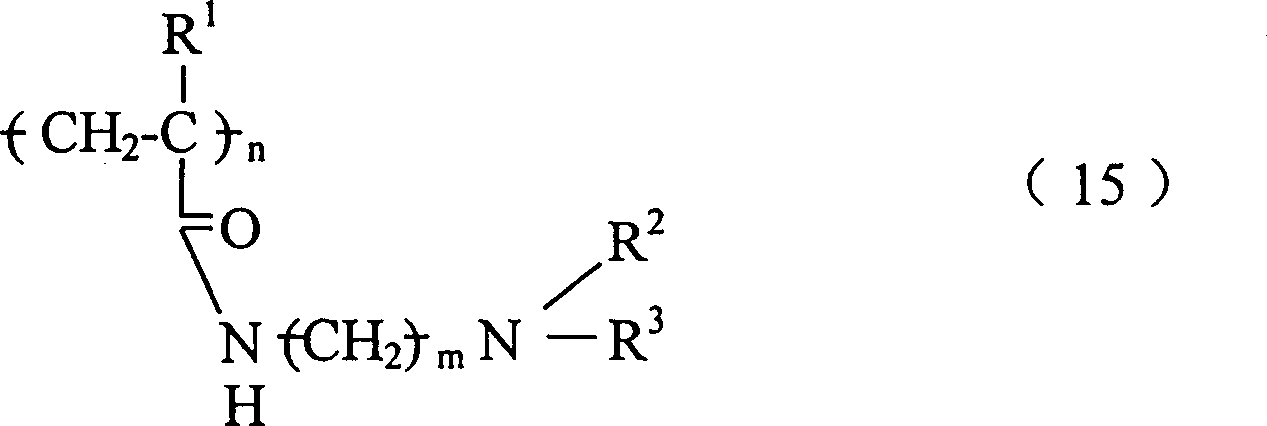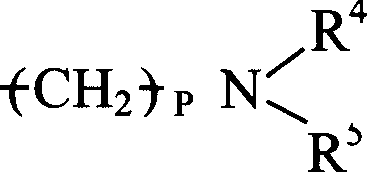CN1136855C - Cross-linked polymers for removing bile salts from patient - Google Patents
Cross-linked polymers for removing bile salts from patient Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN1136855C CN1136855C CNB951935224A CN95193522A CN1136855C CN 1136855 C CN1136855 C CN 1136855C CN B951935224 A CNB951935224 A CN B951935224A CN 95193522 A CN95193522 A CN 95193522A CN 1136855 C CN1136855 C CN 1136855C
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- alkyl
- formula
- polymer
- polymer composition
- copolymer
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/74—Synthetic polymeric materials
- A61K31/785—Polymers containing nitrogen
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/74—Synthetic polymeric materials
- A61K31/785—Polymers containing nitrogen
- A61K31/787—Polymers containing nitrogen containing heterocyclic rings having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/74—Synthetic polymeric materials
- A61K31/795—Polymers containing sulfur
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P3/00—Drugs for disorders of the metabolism
- A61P3/06—Antihyperlipidemics
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08F—MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS OBTAINED BY REACTIONS ONLY INVOLVING CARBON-TO-CARBON UNSATURATED BONDS
- C08F8/00—Chemical modification by after-treatment
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08F—MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS OBTAINED BY REACTIONS ONLY INVOLVING CARBON-TO-CARBON UNSATURATED BONDS
- C08F220/00—Copolymers of compounds having one or more unsaturated aliphatic radicals, each having only one carbon-to-carbon double bond, and only one being terminated by only one carboxyl radical or a salt, anhydride ester, amide, imide or nitrile thereof
- C08F220/02—Monocarboxylic acids having less than ten carbon atoms; Derivatives thereof
- C08F220/52—Amides or imides
- C08F220/54—Amides, e.g. N,N-dimethylacrylamide or N-isopropylacrylamide
- C08F220/60—Amides, e.g. N,N-dimethylacrylamide or N-isopropylacrylamide containing nitrogen in addition to the carbonamido nitrogen
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10S—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10S210/00—Liquid purification or separation
- Y10S210/902—Materials removed
- Y10S210/903—Nitrogenous
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Polymers & Plastics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Diabetes (AREA)
- Obesity (AREA)
- Hematology (AREA)
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
- Addition Polymer Or Copolymer, Post-Treatments, Or Chemical Modifications (AREA)
- External Artificial Organs (AREA)
- Medicines Containing Antibodies Or Antigens For Use As Internal Diagnostic Agents (AREA)
- Medicines That Contain Protein Lipid Enzymes And Other Medicines (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本发明的背景技术Background Art of the Invention
本发明涉及从患者体内除去胆汁盐。The present invention relates to the removal of bile salts from a patient.
从患者体内螯合和除去胆汁盐(例如胆酸盐,甘胆酸盐,甘鹅胆酸盐,中磺胆酸盐和脱氧胆酸盐)可以降低患者的胆固醇水平。经过消化系统服用后除去胆汁盐的离子交换树脂己经用于该目的。除去胆汁盐将导致体内产生更多的胆汁盐。因为胆汁盐的生物前体是胆固醇,所以胆固醇代谢为胆汁盐就伴随有病人体内的胆固醇的减少。Sequestration and removal of bile salts (eg, cholate, glycocholate, glycochechilate, mesosulfocholate, and deoxycholate) from the patient can reduce the patient's cholesterol levels. Ion exchange resins that remove bile salts after administration through the digestive system have been used for this purpose. Removing bile salts will cause more bile salts to be produced in the body. Since the bioprecursor of bile salts is cholesterol, the metabolism of cholesterol to bile salts is accompanied by a decrease in cholesterol in the patient.
本发明的技术方案Technical scheme of the present invention
第一方面,本发明特征在于通过离子交换从患者体内除去胆汁盐的方法,包括给患者服用无毒和稳定的治疗有效量的一种或多种高交联聚合物。聚合物的特征在于具有下式重复单元或其共聚物。In a first aspect, the invention features a method of removing bile salts from a patient by ion exchange comprising administering to the patient a nontoxic and stable therapeutically effective amount of one or more highly crosslinked polymers. Polymers are characterized by repeating units of the formula or its copolymers.
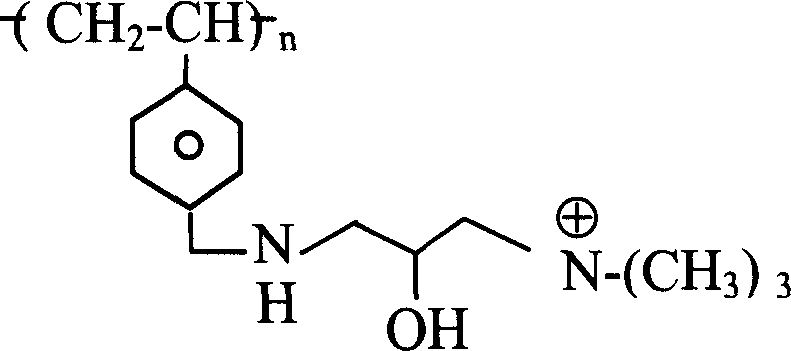
其中n为整数;R1是H或C1-C8烷基(可以是直链或支链、取代的或未取代的,例如甲基);M是 或-Z-R2;Z是O,NR3,S,或(CH2)m;m=0-10;R3是H或C1-C8烷基(可以是直链或支链、取代的或未取代的,例如甲基);及R2是或 wherein n is an integer; R 1 is H or C 1 -C 8 alkyl (which may be linear or branched, substituted or unsubstituted, such as methyl); M is or -ZR 2 ; Z is O, NR 3 , S, or (CH 2 ) m ; m=0-10; R 3 is H or C 1 -C 8 alkyl (can be linear or branched, substituted or unsubstituted, such as methyl); and R is or
其中P=0-10,且每个R4、R5和R6各自是H,C1-C8烷基(可以是直链或支链,取代的或未取代的,例如甲基),或芳基(例如具有一个或多个环并且可被取代或未被取代,例如苯基,萘基,咪唑基,或吡啶基)。Wherein P = 0-10, and each R 4 , R 5 and R 6 is independently H, C 1 -C 8 alkyl (which may be linear or branched, substituted or unsubstituted, such as methyl), or aryl (eg, having one or more rings and which may be substituted or unsubstituted, eg, phenyl, naphthyl, imidazolyl, or pyridyl).
“无毒”意指当治疗有效量被消化时,聚合物或任何释放到体内的离子都是无害的。优选地,实际上这种释放到体内的离子对患者是有利的。例如,可交换的离子为天然营养物如氨基酸。"Nontoxic" means that the polymer or any ions released into the body are not harmful when a therapeutically effective amount is ingested. Preferably, such released ions into the body are actually beneficial to the patient. For example, the exchangeable ions are natural nutrients such as amino acids.
“稳定”意指当聚合物以治疗有效量被吸收时不会被溶解,也不分解形成有害的副产物,并且基本上保持完整以便将完成了离子交换的离子排出体外。"Stable" means that the polymer does not dissolve when absorbed in therapeutically effective amounts, does not decompose to form deleterious by-products, and remains substantially intact for excretion of ion-exchanged ions from the body.
在优选实例中,聚合物通过多功能交联共聚单体交联而完成,其中共聚单体的量约为单位总重量的1-25%(更优选2.5-20%)。In a preferred embodiment, the polymer is completed by crosslinking a multifunctional crosslinking comonomer in an amount of about 1-25% (more preferably 2.5-20%) of the total weight of the unit.
聚合物还优选包括一种或多种疏水性共聚单体,例如苯乙烯,乙烯基萘,乙基乙烯基苯,丙烯酰胺和甲基丙烯酰胺的N-烷基和N-芳基衍生物,丙烯酸烷基酯和芳基酯,甲基丙烯酸烷基酯和芳基酯,4-乙烯基联苯基,4-乙烯基茴香醚,4-氨基苯乙烯,和任何这些共聚单体的氟化衍生物(例如对一氟苯乙烯,全氟苯乙烯,六氟异丙基丙烯酸酯,六氟丁基甲基丙烯酸酯,或十七氟癸基甲基丙烯酸酯)。烷基优选为C1-C15烷基,可以是直链,支链或环状的(例如环己基),并且可进一步被取代或未取代。芳基优选具有一外或多个环并且可被取代或未取代,例如苯基,萘基,咪唑基,或吡啶基。聚合物还可以包括一种或多种带正电荷的共聚单体,例如乙烯基吡啶,二甲氨基甲基苯乙烯,或乙烯基咪唑。The polymer also preferably comprises one or more hydrophobic comonomers such as N-alkyl and N-aryl derivatives of styrene, vinylnaphthalene, ethylvinylbenzene, acrylamide and methacrylamide, Alkyl and aryl acrylates, alkyl and aryl methacrylates, 4-vinyl biphenyl, 4-vinyl anisole, 4-aminostyrene, and fluorinated comonomers of any of these Derivatives (such as p-fluorostyrene, perfluorostyrene, hexafluoroisopropyl acrylate, hexafluorobutyl methacrylate, or heptadecylfluorodecyl methacrylate). Alkyl is preferably C 1 -C 15 alkyl, may be linear, branched or cyclic (eg cyclohexyl), and may be further substituted or unsubstituted. Aryl preferably has one or more rings and can be substituted or unsubstituted, eg phenyl, naphthyl, imidazolyl, or pyridyl. The polymer may also include one or more positively charged comonomers, such as vinylpyridine, dimethylaminomethylstyrene, or vinylimidazole.
第一个优选的聚合物实例的特征在于具有下式重复单元或其共聚物 A first preferred polymer example is characterized by repeating units of the formula or copolymers thereof
该聚合物还可以包括以下一种或多种下述成份作为共聚单体:n-丁基甲基丙烯酰胺,六氟丁基甲基丙烯酸酯,十七氟癸基甲基丙烯酸酯,苯乙烯或其氟化衍生物,2-乙烯基萘,4-乙烯基咪唑,乙烯基吡啶,乙基甲基丙烯酸酯三甲铵,乙基丙烯酸酯三甲铵,4-乙烯基联苯基,4-乙烯基茴香醚,或4-氨基苯乙烯。The polymer may also include as comonomers one or more of the following: n-butyl methacrylamide, hexafluorobutyl methacrylate, heptadecafluorodecyl methacrylate, styrene or its fluorinated Derivatives, 2-Vinylnaphthalene, 4-Vinylimidazole, Vinylpyridine, Trimethylammonium Ethylmethacrylate, Trimethylammonium Ethacrylate, 4-Vinylbiphenyl, 4-Vinylanisole, or 4-aminostyrene.
第二个优选聚合物的实例的特征在于具有下式重复单元或其共聚物 A second example of a preferred polymer is characterized by repeating units of the formula or copolymers thereof
该聚合物可以包括以下一种或多种下述成份作为共聚单体:异丙基丙烯酰胺,苯乙烯或其氟化物,六氟异丙基丙烯酸酯,和乙基甲基丙烯酸酯三甲铵。The polymer may include as comonomers one or more of the following: isopropylacrylamide, styrene or its fluoride, hexafluoroisopropylacrylate, and trimethylammonium ethyl methacrylate.
第三个优选聚合物的实例的特征在于具有下式重复单元或其共聚物 A third example of a preferred polymer is characterized by repeating units of the formula or copolymers thereof
该聚合物还可以包括苯乙烯或其氟化衍生物作为共聚单体。The polymer may also comprise styrene or its fluorinated derivatives as comonomer.
第四个优选聚合物的实例的特征在于具有下式重复单元或其共聚物。 A fourth preferred example of the polymer is characterized by a repeating unit of the formula below or a copolymer thereof.
第五个优选聚合物的实例的特征在于具有下式重复单元或其共聚物。 A fifth preferred example of the polymer is characterized by a repeating unit of the following formula or a copolymer thereof.
第六个优选聚合物的实例的特征在于具有下式重复单元或其共聚物 An example of a sixth preferred polymer is characterized by repeating units of the formula or copolymers thereof
该聚合物还可以包括乙基乙烯基苯乙烯作为共聚单体。The polymer may also comprise ethyl vinyl styrene as a comonomer.
第七个优选聚合物实例的特征在于具有下式重复单元或其共聚物。 A seventh preferred polymer example is characterized by a repeating unit of the formula or a copolymer thereof.
第八个优选聚合物实例的特征在于具有下式重复单元或其共聚物 An eighth preferred polymer example is characterized by repeating units of the formula or copolymers thereof
该聚合物还可以包括苯乙烯或其氟化衍生物作为共聚单体。The polymer may also comprise styrene or its fluorinated derivatives as comonomer.
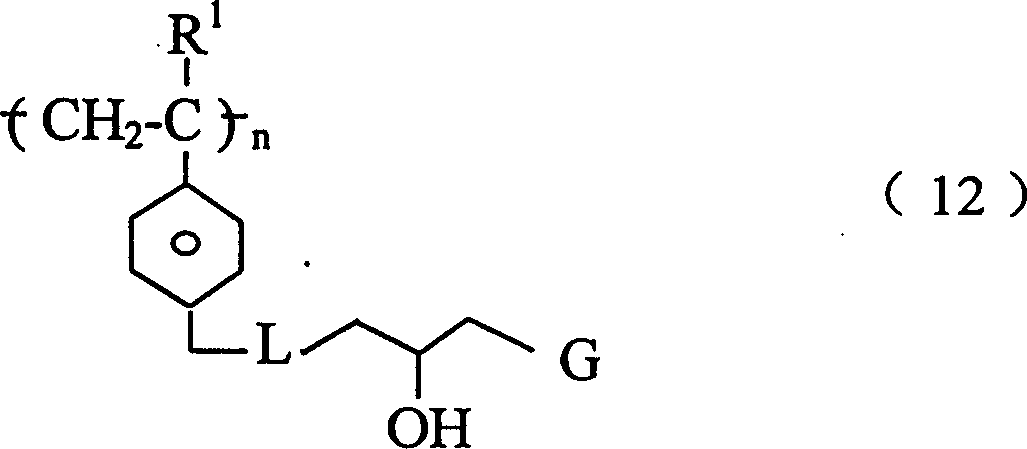
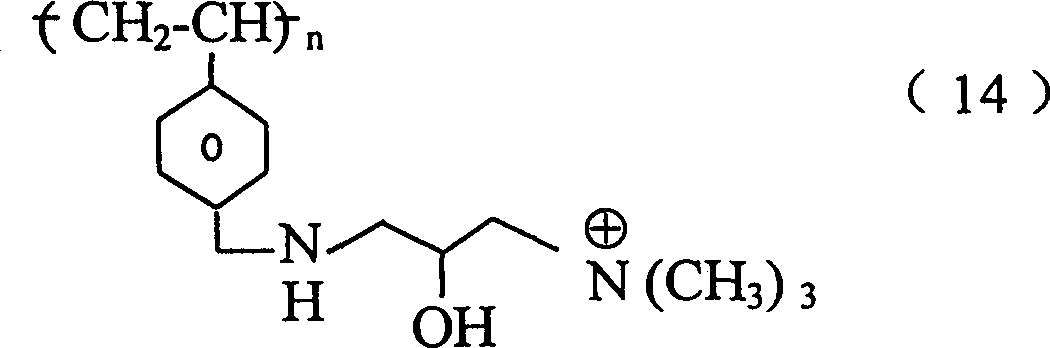
第二方面,本发明特征在于通过离子交换从患者体内除去胆汁盐的方法,包括给患者服用的治疗有效量的一种或多种高交联聚合物,该聚合物具有下式重复单元或其共聚物, In a second aspect, the invention features a method of removing bile salts from a patient by ion exchange comprising administering to the patient a therapeutically effective amount of one or more highly cross-linked polymers having repeating units of the formula or copolymer,
其中n为整数;R1是H或C1-C8烷基;L是-NH-或 G是 或 并且,每个R2、R3和R4各自为H,C1-C8烷基,或芳基,该聚合物服用后无毒并且稳定。Where n is an integer; R 1 is H or C 1 -C 8 alkyl; L is -NH- or G is or In addition, each of R 2 , R 3 and R 4 is H, C 1 -C 8 alkyl, or aryl, and the polymer is nontoxic and stable after ingestion.
在优选实例中,聚合物通过多功能交联共聚单体交联,其中共聚单体的量约为单体总重量的1-25%(更优选2.5-20%)。该聚合物还优选包括一种或多种上述疏水性共聚单体。In a preferred embodiment, the polymer is crosslinked by a multifunctional crosslinking comonomer in an amount of about 1-25% (more preferably 2.5-20%) based on the total weight of the monomers. The polymer also preferably includes one or more of the aforementioned hydrophobic comonomers.
第一种优选聚合物的实例的特征在于具有下式重复单元或其共聚物该聚合物还可以包括苯乙烯或其氟化衍生物作为共聚单体。Examples of a first preferred polymer are characterized by repeating units of the formula or copolymers thereof The polymer may also comprise styrene or its fluorinated derivatives as comonomer.
第二种优选聚合物的实例的特征在于具有下式重复单元或其共聚物。 Examples of a second preferred polymer are characterized by repeating units of the formula or copolymers thereof.
根据本发明第一和第二方面,聚合物可以带有正电荷,或者在服用后的生理pH下能变为带电荷。对于后者,带电荷的离子在服用后结合能与胆汁盐交换的带负电荷的平衡离子。如果聚合物带有正电荷,则该聚合物可被提供一种或多种可交换的平衡离子。适宜平衡离子的实例包括Cl-,Br-,CH3OSO3 -,HSO4 -,HO4 2-,HCO3 -,CO3 2-,乙酸盐,乳酸盐,琥珀酸盐,丙酸盐,丁酸盐,抗坏血酸盐,柠檬酸盐,马来酸盐,叶酸盐,氨基酸衍生物,核苷酸,类脂,或磷脂。平衡离子之间可以相同或不同。例如,聚合物可以含有二种不同类型的平衡离子,这两种离子被交换用于除去胆汁盐。也可以服用一种以上聚合物,这些聚合物各自具有结合不同的其固有电荷平衡离子。According to the first and second aspects of the invention, the polymer may be positively charged, or be capable of becoming charged at physiological pH after ingestion. For the latter, the charged ions are bound to negatively charged counterions that can be exchanged with bile salts after ingestion. If the polymer is positively charged, the polymer may be provided with one or more exchangeable counterions. Examples of suitable counterions include Cl − , Br − , CH 3 OSO 3 − , HSO 4 − , HO 4 2− , HCO 3 − , CO 3 2− , acetate, lactate, succinate, propionic acid Salt, butyrate, ascorbate, citrate, maleate, folate, amino acid derivatives, nucleotides, lipids, or phospholipids. The counter ions may be the same or different. For example, a polymer may contain two different types of counterions that are exchanged for the removal of bile salts. It is also possible to administer more than one polymer, each having a different combination of its intrinsic charge-balancing ions.
本发明还包括用于除去胆汁盐的治疗组合物,该组合物包括治疗有效量的一种或多种上述聚合物。The present invention also includes therapeutic compositions for the removal of bile salts comprising a therapeutically effective amount of one or more of the polymers described above.
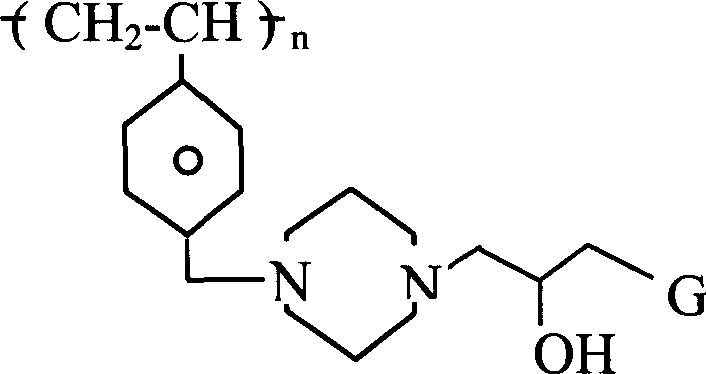
另一方面,本发明涉及高交联聚合物组合物,该组合物包括具有下重复单元的聚合物 In another aspect, the present invention relates to a highly crosslinked polymer composition comprising a polymer having the following repeating unit
其中R1是H或甲基,Q是-NH-(CH2)3-或-O-(CH2)2,n为整数,以及至少一种选自乙烯基萘,乙烯基咪唑,苯乙烯氟化衍生物,氟化烷基甲基丙烯酸酯的附加共聚单体。wherein R 1 is H or methyl, Q is -NH-(CH 2 ) 3 - or -O-(CH 2 ) 2 , n is an integer, and at least one selected from vinylnaphthalene, vinylimidazole, styrene Fluorinated derivative, additional comonomer for fluorinated alkyl methacrylates.
在这方面的一些优选实例中,R1是甲基,Q是-NH-(CH2)3-。该聚合物还可以包括作为共聚单体的乙基丙烯酸酯三甲铵或乙基甲基丙烯酸酯三甲铵。在另一个优选实例中,Q是-O-(CH2)2。In some preferred examples of this aspect, R1 is methyl and Q is -NH-( CH2 ) 3- . The polymer may also include trimethylammonium ethacrylate or trimethylammonium ethylmethacrylate as comonomers. In another preferred embodiment, Q is -O-(CH 2 ) 2 .
适宜的氟化苯乙烯衍生物的实例包括对-氟苯乙烯和五氟苯乙烯。适宜的氟化烷基甲基丙烯酸酯的实例包括六氟丁基甲基丙烯酸酯和十七氟癸基甲基丙烯酸酯。Examples of suitable fluorinated styrene derivatives include p-fluorostyrene and pentafluorostyrene. Examples of suitable fluorinated alkyl methacrylates include hexafluorobutyl methacrylate and heptadecafluorodecyl methacrylate.
在本发明的另一方面,还涉及高交联聚合物组合物,该组合物包括特征为具有下述重复单元的聚合物, In another aspect of the present invention, it also relates to a highly crosslinked polymer composition comprising a polymer characterized by having the following repeating units,
其中R1是H或甲基,Q是-NH-(CH2)3-或-O-(CH2)2,n为整数,以及作为附加共聚单体的(a)苯乙烯(b)乙基丙烯酸酯三甲铵或乙基甲基丙烯酸酯三甲铵,其中R1是甲基,Q是-NH-(CH2)3-。wherein R 1 is H or methyl, Q is -NH-(CH 2 ) 3 - or -O-(CH 2 ) 2 , n is an integer, and (a) styrene (b) B as an additional comonomer trimethylammonium acrylate or trimethylammonium ethylmethacrylate, wherein R 1 is methyl and Q is -NH-(CH 2 ) 3 -.
再一方面,本发明涉及合成具有疏水和亲水单元高交联聚合物的方法,该方法包括在醇溶剂存在下与亲水性单体或疏水性单体反应。In yet another aspect, the present invention relates to a method for synthesizing highly crosslinked polymers having hydrophobic and hydrophilic units, the method comprising reacting a hydrophilic monomer or a hydrophobic monomer in the presence of an alcoholic solvent.
再又一方面,本发明涉及从患者体内除去胆汁盐的方法,该方法包括给患者服用治疗有效量的以下物质的反应产物:In yet another aspect, the invention relates to a method of removing bile salts from a patient, the method comprising administering to the patient a therapeutically effective amount of a reaction product of:
(a)具有下式重复单元的一种或多种高交联聚合物: (a) one or more highly crosslinked polymers having repeating units of the formula:
及其盐和共聚物,其中n和m是整数,每个R1、R2和R3各自是H,或C1-C8烷基;及and salts and copolymers thereof, wherein n and m are integers, and each R 1 , R 2 and R 3 is independently H, or C 1 -C 8 alkyl; and
(b)至少一种烷基化试剂。该反应产物服用后无毒并且稳定。(b) at least one alkylating agent. The reaction product is nontoxic and stable after ingestion.
“盐”意指在重复单元中胺氮被质子化后得到的带正电荷氮原子与它的带负电荷的平衡离子相结合。"Salt" means the protonation of the amine nitrogen in the repeat unit resulting in a positively charged nitrogen atom associated with its negatively charged counterion.
“烷基化试剂”意指与交联聚合物反应时,以共价键在一个或多个聚合物氮原子上连接有烷基或其衍生物(例如芳烷基,羟基烷基,烷基铵盐,烷基酰胺,或它们的结合物)。"Alkylating agent" means, when reacted with a crosslinked polymer, an alkyl group or derivative thereof (e.g., aralkyl, hydroxyalkyl, alkyl ammonium salts, alkylamides, or combinations thereof).
在优选实例中,这种反应产物通过多功能交联共聚单体交联,其中共聚单体约为单体总重量的1-25%(更优选2.5-20%)。In preferred embodiments, this reaction product is crosslinked by a multifunctional crosslinking comonomer, wherein the comonomer is about 1-25% (more preferably 2.5-20%) of the total weight of the monomers.
第一个优选聚合物的特征在于具有下式重复单元:或其盐或其共聚物。A first preferred polymer is characterized by repeating units of the formula: or its salt or its copolymer.
第二个优选聚合物的特征在于具有下式重复单元:或其盐或其共聚物。A second preferred polymer is characterized by repeating units of the formula: or its salt or its copolymer.
优选烷基化试剂具有式RX,其中R是C1-C20烷基,C1-C20羟基烷基,C1-C20芳烷基,C1-C20烷基铵,或C1-C20烷基酰氨基,X包括一种或多种亲电子离去基团。“亲电子离去基团”意指在烷基化期间,可被交联聚合物中的氮原子置换的基团。优选离去基团的实例包括卤化物,环氧化物,甲苯磺酸盐,甲磺酸盐基团。例如,对于环氧基团,烷基化反应将引起三员环氧环开环。Preferred alkylating agents have the formula RX, wherein R is C 1 -C 20 alkyl, C 1 -C 20 hydroxyalkyl, C 1 -C 20 aralkyl, C 1 -C 20 alkyl ammonium, or C 1 -C 20 alkylamido, X includes one or more electrophilic leaving groups. "Electrophilic leaving group" means a group that can be displaced by a nitrogen atom in a crosslinked polymer during alkylation. Examples of preferred leaving groups include halide, epoxide, tosylate, mesylate groups. For example, for an epoxy group, an alkylation reaction will cause the three-membered epoxy ring to open.
优选烷基化试剂的实例包括C1-C20烷基卤化物(例如正丁基卤,正-己基卤,正-辛基卤,正-癸基卤,正-十二烷基卤,正-十四烷基卤,正-十八烷基卤,及其结合物);C1-C20卤代烷(例如1,10-二卤代癸烷;C1-C20羟基烷基卤(例如11-卤代-1-十一烷醇);C1-C20芳烷基卤(例如苄基卤);C1-C20烷基卤铵盐(例如(4-卤代丁基)三甲铵盐,(6-卤代己基)三甲铵盐,(8-卤代辛基)三甲铵盐,(10-卤代癸基)三甲铵盐,(12-卤代-十二烷基)三甲铵盐及它们的结合物);C1-C20烷基环氧铵盐(例如(缩水甘油基丙基)三甲铵盐);和C1-C20环氧烷基酰胺(例如N-(2,3-环氧丙烷)丁酰胺,N-(2,3-环氧丙烷)己酰胺,及其结合物)。Examples of preferred alkylating agents include C 1 -C 20 alkyl halides (e.g. n-butyl halide, n-hexyl halide, n-octyl halide, n-decyl halide, n-dodecyl halide, n-dodecyl halide, n- -tetradecyl halide, n-octadecyl halide, and combinations thereof); C 1 -C 20 alkyl halides (e.g. 1,10-dihalodecane; C 1 -C 20 hydroxyalkyl halides (e.g. 11-halo-1-undecanol); C 1 -C 20 aralkyl halides (e.g. benzyl halides); C 1 -C 20 alkyl halide ammonium salts (e.g. (4-halobutyl) trimethyl Ammonium salt, (6-halohexyl)trimethylammonium salt, (8-halogenoctyl)trimethylammonium salt, (10-halogenodecanyl)trimethylammonium salt, (12-halogeno-dodecyl)trimethylammonium salt ammonium salts and combinations thereof); C 1 -C 20 alkyl epoxy ammonium salts (eg (glycidyl propyl) trimethyl ammonium salt); and C 1 -C 20 epoxy alkyl amides (eg N-( 2,3-propylene oxide) butanamide, N-(2,3-propylene oxide) hexanamide, and combinations thereof).
聚合物与至少二种烷基化试剂反应是特别优选的。在一个优选实例中,烷基化试剂之一是式RX,其中R是C1-C20烷基,X包括一种或多种亲水性离去基团(例如烷基卤),另一个烷基化试剂是式R’X,其中R’是C1-C20烷基铵基,X包括一种或多种亲水性离去基团(例如烷基卤化铵盐)。It is especially preferred to react the polymer with at least two alkylating agents. In a preferred embodiment, one of the alkylating agents is of the formula RX, wherein R is C 1 -C 20 alkyl, X includes one or more hydrophilic leaving groups (e.g., alkyl halides), and the other The alkylating agent is of the formula R'X, wherein R' is a C1 - C20 alkylammonium group and X includes one or more hydrophilic leaving groups (eg, alkylammonium halide salts).
在另一个优选实例中,烷基化试剂之一是RX,其中R是C1-C20烷基,X包括一种或多种亲水性离去基团(例如烷基卤),另一个烷基化试剂是R’X,其中R’是C1-C20羟基烷基,X包括一种或多种亲水性离去基团(例如羟基烷基卤)。In another preferred embodiment, one of the alkylating agents is RX, wherein R is C 1 -C 20 alkyl, X includes one or more hydrophilic leaving groups (e.g., alkyl halides), and the other The alkylating agent is R'X, wherein R' is C1 - C20 hydroxyalkyl, and X includes one or more hydrophilic leaving groups (eg, hydroxyalkyl halides).
再一个优选实例中,烷基化试剂之一是C1-C20二卤代烷,另一个烷基化试剂是C1-C20烷基铵盐。In yet another preferred embodiment, one of the alkylating agents is a C 1 -C 20 dihaloalkane, and the other alkylating agent is a C 1 -C 20 alkylammonium salt.
本发明提供了一种从患者体内除去胆汁盐的有效治疗方法(从而降低患者胆固醇的水平)。以治疗有效量服用这种组合物是无毒的并用稳定。The present invention provides an effective therapeutic method for removing bile salts from a patient (thus lowering the patient's cholesterol level). Such compositions are nontoxic and stable when administered in therapeutically effective amounts.
本发明还提供了具有亲水性和疏水性单元的聚合物有效合成,即该反应在醇溶剂存在下进行,这种醇溶剂由于其链转移性质通常认为不是好的聚合溶剂。The present invention also provides efficient synthesis of polymers with both hydrophilic and hydrophobic units, ie the reaction is carried out in the presence of alcoholic solvents which are generally not considered good polymerization solvents due to their chain transfer properties.
其它特征和优点将从以下优选实施方案及权利要求中看清楚。Other features and advantages will be apparent from the following preferred embodiments and claims.
本发明的最佳实施例组合物 BEST EXAMPLE COMPOSITIONS OF THE INVENTION
优选聚合物具有在上述发明概述部分给出的结构式。该聚合物是高交联的。高交联水平使得聚合物完全不溶并且限制烷基化反应产物仅在胃肠道有活性。因此,该组合物是非系统活性的,这样将减小对患者的副作用。Preferred polymers have the formula given in the Summary of the Invention section above. The polymer is highly crosslinked. The high level of crosslinking renders the polymer completely insoluble and limits the activity of the alkylation reaction product only in the gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, the composition is not systemically active, which will reduce side effects on the patient.
聚合物优选通过在聚合期间在反应混合物中加入交联共聚单体进行交联。适宜交联共聚单体的实例包括二丙烯酸酯和二甲基丙烯酸酯(例如二丙烯酸乙二醇酯,二丙烯酸丙二醇酯,二丙烯酸丁二醇酯,二甲基丙烯酸乙二醇酯,二甲基丙烯酸丙二醇酯,二甲基丙烯酸丁二醇酯,二甲基丙烯酸聚乙二醇酯,二丙烯酸聚乙二醇酯),亚甲双丙烯酰胺,亚甲双甲基丙烯酰胺,亚乙双丙烯酰胺,亚乙双甲基丙烯酰胺,亚乙(H3CH2)双甲基丙烯酰胺,亚乙基双丙烯酰胺,二乙烯基苯,双酚A二甲基丙烯酸酯,和双酚A二丙烯酸酯。这些交联共聚单体即可以是商品也可用Mandeville等人“Process for Adjusting Ion Concentration in a Patient andCompositions Therefor,”U.S.S.N.08/065,113,申请日1993年5月20(转让给本专利申请相同受让人,这里引作参考)所述方法制备。典型地,交联剂的量为交联剂和单体总重量的1.0-25%,优选为2.5-20%。The polymer is preferably crosslinked by adding a crosslinking comonomer to the reaction mixture during the polymerization. Examples of suitable crosslinking comonomers include diacrylates and dimethacrylates (e.g. ethylene glycol diacrylate, propylene glycol diacrylate, butylene glycol diacrylate, ethylene glycol dimethacrylate, dimethyl propylene glycol acrylate, butylene glycol dimethacrylate, polyethylene glycol dimethacrylate, polyethylene glycol diacrylate), methylene bisacrylamide, methylene bismethacrylamide, ethylene bis Acrylamide, ethylene bismethacrylamide, ethylene (H 3 CH 2 ) bismethacrylamide, ethylene bisacrylamide, divinylbenzene, bisphenol A dimethacrylate, and bisphenol A Diacrylate. These crosslinking comonomers are either commercially available or available in Mandeville et al. "Process for Adjusting Ion Concentration in a Patient and Compositions Therefor," USSN 08/065,113, filed May 20, 1993 (assigned to the same assignee of this patent application, Cited here as a reference) method for preparation. Typically, the amount of crosslinker is 1.0-25%, preferably 2.5-20%, based on the total weight of crosslinker and monomer.
优选地,聚合物包括一种或多种增加聚合物总疏水性的共聚单体。由于胆汁盐是疏水的,疏水性单体可以使聚合物与胆汁盐之间相互作用的选择性达到最大。Preferably, the polymer includes one or more comonomers that increase the overall hydrophobicity of the polymer. Since bile salts are hydrophobic, hydrophobic monomers can maximize the selectivity of the interaction between the polymer and bile salts.
适宜的疏水性共聚单体的实例包括,例如丙烯酰胺,甲基丙烯酰胺,及其N-烷基(例如甲基,乙基,异丙基,丁基,己基,十二烷基,环己基,二环己基)和N-芳基(例如苯基,二苯基)衍生物;烷基和芳基丙烯酸酯及甲基丙烯酸酯(例如乙基,丙基,丁基,十二烷基),及其氟化衍生物(例如六氟异丙基丙烯酸酯,六氟丁基甲基丙烯酸酯,十七氟癸基丙烯酸酯);苯乙烯及其衍生物(例如二甲氨基甲基苯乙烯,4氨基苯乙烯,及其氟化衍生物,例如对-氟苯乙烯,五氟苯乙烯);乙基乙烯基苯;乙烯基萘;乙烯基吡啶;乙烯基咪唑;4-乙烯基联苯,4,4-乙烯基茴香醚;及其结合物。在制备这些聚合物中所用疏水性共聚单体的量为1-75%重量,优选3-65%。Examples of suitable hydrophobic comonomers include, for example, acrylamide, methacrylamide, and N-alkyl groups thereof (e.g., methyl, ethyl, isopropyl, butyl, hexyl, dodecyl, cyclohexyl , dicyclohexyl) and N-aryl (e.g. phenyl, diphenyl) derivatives; alkyl and aryl acrylates and methacrylates (e.g. ethyl, propyl, butyl, dodecyl) , and its fluorinated derivatives (such as hexafluoroisopropyl acrylate, hexafluorobutyl methacrylate, heptadecafluorodecyl acrylate); styrene and its derivatives (such as dimethylaminomethylstyrene, 4 Aminostyrene, and its fluorinated derivatives, such as p-fluorostyrene, pentafluorostyrene); ethylvinylbenzene; vinylnaphthalene; vinylpyridine; vinylimidazole; 4-vinylbiphenyl, 4 , 4-Vinylanisole; and combinations thereof. The amount of hydrophobic comonomer used in the preparation of these polymers is from 1 to 75% by weight, preferably from 3 to 65%.
所需疏水水平也可以通过适当选择交联共聚单体而方便地获得。例如二乙烯基苯是适宜的交联共聚单体并且也是疏水性的。另外,在二乙烯基苯中的主要“杂质”是乙基乙烯基苯,这种疏水性的可聚合的共聚单体也对聚合物总疏水性作出贡献。其它疏水性交联共聚单体包括双酚A二丙烯酸酯和双酚A二甲基丙烯酸酯。The desired level of hydrophobicity can also be conveniently obtained by appropriate choice of crosslinking comonomers. For example divinylbenzene is a suitable crosslinking comonomer and is also hydrophobic. Additionally, the major "impurity" in divinylbenzene is ethylvinylbenzene, a hydrophobic polymerizable comonomer that also contributes to the overall hydrophobicity of the polymer. Other hydrophobic crosslinking comonomers include bisphenol A diacrylate and bisphenol A dimethacrylate.
交联聚合物可与一种或多种烷基化试剂反应。优选的烷基化试剂的实例己在发明概述中给出。A.聚合物的制备实施例1.聚(甲基丙烯酰氨基丙基三甲氯化铵)(聚MAPTAC)的制备Crosslinked polymers can be reacted with one or more alkylating agents. Examples of preferred alkylating agents are given in the Summary of the Invention. A. Preparation of polymer Example 1. Preparation of poly(methacrylamidopropyltrimethylammonium chloride) (polyMAPTAC)
向1000mL的3颈园底烧瓶中加入下列物质:甲基丙烯酰氨基丙基三甲基氯化铵(MAPTAC)(40mL,50%水溶液,21g),二甲基丙烯酸乙二醇酯交联共聚单体(5.00g,4.76mL),乙酸乙酯(200mL),2-丙醇(200mL)。所得溶液是澄清的。接着加入聚合引发剂AIBN(0.1g)并将反应混合物加热至65℃。当温度达到65℃时,用氮气将溶液脱气5分钟,这时溶液变为混蚀,说明聚合正在进行。将反应在65℃再保持3小时,然后冷却至室温。Into a 1000 mL 3-neck round bottom flask was added the following: methacrylamidopropyltrimethylammonium chloride (MAPTAC) (40 mL, 50% aqueous solution, 21 g), ethylene glycol dimethacrylate cross-linked copolymer Monomer (5.00 g, 4.76 mL), ethyl acetate (200 mL), 2-propanol (200 mL). The resulting solution was clear. The polymerization initiator AIBN (0.1 g) was then added and the reaction mixture was heated to 65°C. When the temperature reached 65°C, the solution was degassed with nitrogen for 5 minutes, at which point the solution became mixed, indicating that polymerization was in progress. The reaction was maintained at 65°C for an additional 3 hours, then cooled to room temperature.
将所得聚合物(坚硬而粘)与500mL水合并以便软化聚合物,然后将其转移至混合器中并与1500mL 2-丙醇共混并离心。滗析混合物并借助100mL水转移至另一个混合机中。加入800mL2-丙醇并将混合物渗合,沉降然后滗析。将混合物与1000mL2-丙醇合并,掺合,过滤并真空干燥,得到12.6g聚合物。The resulting polymer (hard and sticky) was combined with 500 mL of water to soften the polymer, which was then transferred to a mixer and blended with 1500 mL of 2-propanol and centrifuged. The mixture was decanted and transferred to another mixer with 100 mL of water. 800 mL of 2-propanol was added and the mixture was blended, settled and then decanted. The mixture was combined with 1000 mL of 2-propanol, blended, filtered and dried under vacuum to yield 12.6 g of polymer.
用类似方法制备与0.5%亚甲双甲基丙烯酰胺交联共聚单体交联的聚MAPTAC,与10%亚甲双甲基丙烯酰胺交联共聚单体交联的聚MAPTAC;和与10%二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体交联的聚MAPTAC。实施例2.聚(乙烯胺)的制备PolyMAPTAC crosslinked with 0.5% methylenebismethacrylamide crosslinking comonomer, polyMAPTAC crosslinked with 10% methylenebismethacrylamide crosslinking comonomer; and 10% Divinylbenzene cross-linked comonomer cross-linked poly-MAPTAC. Embodiment 2. Preparation of poly(vinylamine)
第一步为亚乙基双乙酰胺的制备。将乙酰胺(118g),乙醛(44.06g),乙酸铜(0.2g),和水(300mL)装在1L带有冷凝器、温度计和机械搅拌的三颈烧瓶中。加入浓HCl(34mL)并将混合物加热至45-50℃搅拌24小时。真空除去水得到稠淤渣,将其冷却至5℃时结晶。加入丙酮(200mL)并搅拌几分钟,滤出固体并弃去。将丙醇冷却至0℃并滤出固体。将该固体用500mL丙酮冲洗并空气干燥18小时,得到31.5g亚乙基双乙酰胺。The first step is the preparation of ethylene bis-acetamide. Acetamide (118 g), acetaldehyde (44.06 g), copper acetate (0.2 g), and water (300 mL) were charged in a 1 L three-necked flask equipped with a condenser, thermometer, and mechanical stirring. Concentrated HCl (34 mL) was added and the mixture was heated to 45-50 °C and stirred for 24 hours. The water was removed in vacuo to give a thick sludge which crystallized on cooling to 5°C. Acetone (200 mL) was added and stirred for several minutes, the solid was filtered and discarded. The propanol was cooled to 0 °C and the solid was filtered off. The solid was rinsed with 500 mL of acetone and air dried for 18 hours to yield 31.5 g of ethylenebisacetamide.
第二步为从亚乙基双乙酰胺制备乙烯基乙酰胺,将亚乙基双乙酰胺(31.05g),碳酰钙(2g)和硅藻土541(2g)装入带有温度计、机械搅拌和顶部Vigreux柱的蒸馏头的500mL三颈烧瓶中。通过加热烧瓶至180-225℃在35mmHg真空蒸馏混合物。收集除了产物之外还含有大部分乙酰胺(由NMR测定)的单一组分(10.8g)。将该固体产物溶于异丙醇(30mL)以形成聚合用粗乙烯基乙酰胺溶液。The second step is to prepare vinylacetamide from ethylenebisacetamide, ethylenebisacetamide (31.05g), calcium carbonate (2g) and diatomaceous earth 541 (2g) are loaded with thermometer, mechanical Stir and top the 500 mL three-necked flask with the distillation head of the Vigreux column. The mixture was vacuum distilled at 35 mmHg by heating the flask to 180-225°C. A single fraction (10.8 g) was collected which contained most of the acetamide (determined by NMR) in addition to the product. The solid product was dissolved in isopropanol (30 mL) to form a crude vinylacetamide solution for polymerization.
将粗乙烯基乙酰胺溶液(15mL),二乙烯基苯(1g,技术级,纯度55%,混合异构体),和AIBN(0.3g)混合并在氮气氛下加热至回流90分钟,形成固体沉淀。冷却溶液,加入异丙醇(50mL),并用离心收集固体。用异丙醇冲洗该固体两次,用水冲洗一次,并在真空箱中干燥得到0.8g聚(乙烯基乙酰胺),该物质用于制备以下的聚(乙烯胺)。Crude vinylacetamide solution (15 mL), divinylbenzene (1 g, technical grade, 55% purity, mixed isomers), and AIBN (0.3 g) were combined and heated to reflux for 90 minutes under nitrogen to form Solids precipitated. The solution was cooled, isopropanol (50 mL) was added, and the solid was collected by centrifugation. The solid was washed twice with isopropanol, once with water, and dried in a vacuum oven to yield 0.8 g of poly(vinylacetamide), which was used to prepare the following poly(vinylamine).
将聚(乙烯基乙酰胺)(0.79g)装入含有水(25mL)和浓HCl(25mL)的100mL单颈烧瓶中。将混合物回流5天,并滤出固体,用水冲洗一次,用异丙醇冲洗两次,在真空箱中干燥得到0.77g产物。红外光谱分析表明还有大量酰胺(1656cm-1)存在,没有形成很多的胺(1606cm-1)。将反应物(约0.84g)悬浮在NaOH(46g)和水(46g)中并加热至沸点(约140℃)。由于发泡温度被降低,保持在约100℃2小时。加水(100mL)并过滤收集固体。用水冲洗固体一次后将其悬浮在水(500mL)中并用乙酸调节pH至5。再滤出固体,用水、异丙醇冲洗,并在真空箱中干燥得到0.51g产物。红外光谱分析表明已经开成大量胺。实施例3.聚(3-二甲氨基丙基丙烯酰胺)(DMAPA)的制备Poly(vinylacetamide) (0.79 g) was charged to a 100 mL single neck flask containing water (25 mL) and concentrated HCl (25 mL). The mixture was refluxed for 5 days and the solid was filtered off, rinsed once with water, twice with isopropanol and dried in a vacuum oven to give 0.77 g of product. Infrared spectroscopy analysis showed that there was still a large amount of amides (1656cm -1 ), but not much amines (1606cm -1 ). The reactant (ca. 0.84 g) was suspended in NaOH (46 g) and water (46 g) and heated to boiling point (ca. 140° C.). Since the foaming temperature is lowered, it is maintained at about 100°C for 2 hours. Water (100 mL) was added and the solid was collected by filtration. After rinsing the solid once with water, it was suspended in water (500 mL) and the pH was adjusted to 5 with acetic acid. The solid was then filtered off, rinsed with water, isopropanol, and dried in a vacuum oven to yield 0.51 g of product. Infrared spectroscopic analysis showed that a large number of amines had been synthesized. Embodiment 3. Preparation of poly(3-dimethylaminopropylacrylamide) (DMAPA)
在100mL三颈烧瓶中,将二甲氨基丙基丙烯酰胺(10g)和亚甲双丙烯酰胺交联共聚单体(1.1g)溶解在50mL水中。将该溶液在氮气下搅拌10分钟。将过硫酸钾(0.3g)和偏亚硫酸氢钠(0.3g)分别溶于2-3mL水中然后混合。几秒钟之后仍在氮气下将上述溶液加到单体溶液中。这时立即形成胶状物并被置过夜。除去胶状物并与500mL异丙醇混合。滤出固体并用丙酮冲洗三次。滤出白色固体粉末并在真空箱中干燥得到6.1g。实施例4.聚(二甲氨基丙基丙烯酰胺盐酸化物)(DMAPA·HCl)的制备In a 100 mL three-neck flask, dimethylaminopropylacrylamide (10 g) and methylenebisacrylamide crosslinking comonomer (1.1 g) were dissolved in 50 mL of water. The solution was stirred under nitrogen for 10 minutes. Potassium persulfate (0.3 g) and sodium metabisulfite (0.3 g) were each dissolved in 2-3 mL of water and mixed. After a few seconds, the above solution was added to the monomer solution, still under nitrogen. At this point a gel formed immediately and was left overnight. The gum was removed and mixed with 500 mL of isopropanol. The solid was filtered off and rinsed three times with acetone. A white solid powder was filtered off and dried in a vacuum oven to yield 6.1 g. Embodiment 4. Preparation of poly(dimethylaminopropylacrylamide hydrochloride) (DMAPA·HCl)
将二甲氨基丙基丙烯酰胺(20.10g)溶解在水(100mL)中并用浓HCl中和至pH6.95。加入亚甲双丙烯酰胺交联共聚单体(2.2g)和水(100mL)并温热(34°)以便溶解。在搅拌下加入过硫酸钾(0.2g)和偏亚硫酸氢钾(0.2g)。凝胶化后,将溶液放置6小时,并与异丙醇(600mL)混合3次,真空箱中干燥得到14.47g标题聚合物。Dimethylaminopropylacrylamide (20.10 g) was dissolved in water (100 mL) and neutralized to pH 6.95 with concentrated HCl. Methylenebisacrylamide crosslinking comonomer (2.2 g) and water (100 mL) were added and warmed (34°) to dissolve. Potassium persulfate (0.2 g) and potassium metabisulfite (0.2 g) were added with stirring. After gelation, the solution was left for 6 hours, mixed 3 times with isopropanol (600 mL), and dried in a vacuum oven to obtain 14.47 g of the title polymer.
用类似方法制备与10%亚甲双甲基丙烯酰胺交联共聚单体交联的聚DMAPA·HCl。实施例5.聚(二甲氨基丙基甲基丙烯酰胺盐酸化物)(DMAPMA.HCl)PolyDMAPA·HCl crosslinked with 10% methylenebismethacrylamide crosslinking comonomer was prepared in a similar manner. Example 5. Poly(dimethylaminopropylmethacrylamide hydrochloride) (DMAPMA.HCl)
的制备Preparation of
将二甲氨基丙基甲基丙烯酸胺(20.0g)溶解在水(100mL)中并用浓HCl中和至pH6.94。加入亚甲双丙烯酰胺交联共聚单体(2.2g)并将该溶液温热(39℃)以便溶解。在搅拌和氮气氛下加入过硫酸钾(0.3g)和偏亚硫酰氢钾(0.3g)。凝胶化后,将溶液放置过夜,并与异丙醇(500mL)混合两次,真空箱中干燥得到27.65g产物。将一些固体(3.2g;以-80/+200目筛子过筛)在水(100mL)中搅拌50分钟。再加水(100mL)并将溶液搅拌36分钟。离心收集固体,再悬浮在水(400mL)中,搅拌15分钟,再离心收集固体。最后将固体悬浮在水(500mL)中,搅拌90分钟,过滤收集。将固体在真空箱中干燥得出0.28g标题聚合物。实施例6.聚(甲基丙烯酰氨基丙基三甲基氯化铵)共聚(正-丁基甲基丙Dimethylaminopropylmethacrylamine (20.0 g) was dissolved in water (100 mL) and neutralized to pH 6.94 with concentrated HCl. Methylenebisacrylamide crosslinking comonomer (2.2 g) was added and the solution was warmed (39°C) to dissolve. Potassium persulfate (0.3 g) and potassium metasulfite (0.3 g) were added with stirring under a nitrogen atmosphere. After gelation, the solution was left overnight, mixed twice with isopropanol (500 mL), and dried in a vacuum oven to yield 27.65 g of product. Some of the solid (3.2 g; sieved through a -80/+200 mesh sieve) was stirred in water (100 mL) for 50 minutes. Additional water (100 mL) was added and the solution was stirred for 36 minutes. The solid was collected by centrifugation, resuspended in water (400 mL), stirred for 15 minutes, and collected by centrifugation again. Finally the solid was suspended in water (500 mL), stirred for 90 minutes and collected by filtration. The solid was dried in a vacuum oven to give 0.28 g of the title polymer. Example 6. Poly(methacrylamidopropyltrimethylammonium chloride)copoly(n-butylmethylpropane
烯酰胺)(MAPTAC共聚-BuMA)的制备Preparation of enamide) (MAPTAC copolymerization-BuMA)
共聚单体正-丁基甲基丙烯酰胺(BuMA)制备如下:The comonomer n-butylmethacrylamide (BuMA) was prepared as follows:
在1L烧瓶中,将甲基丙烯酰氯(48.4mL,52.3g,0.500mol)溶解在四氢呋喃(300mL)中并将其放在冰浴中。在保持温度5-15℃时滴加含有丁胺(36.6g)和三乙胺(55.6g)的溶液。将溶液搅拌5分钟后,滤出固体三乙胺盐酸化物并弃去。从母液中真空除去溶剂并将所得黄色油用于下步制备,无需进一步纯化。产生71.58g BuMA共聚单体。In a 1 L flask, methacryloyl chloride (48.4 mL, 52.3 g, 0.500 mol) was dissolved in tetrahydrofuran (300 mL) and placed in an ice bath. A solution containing butylamine (36.6 g) and triethylamine (55.6 g) was added dropwise while maintaining the temperature at 5-15°C. After the solution was stirred for 5 minutes, the solid triethylamine hydrochloride was filtered off and discarded. The solvent was removed from the mother liquor in vacuo and the resulting yellow oil was used in the next preparation without further purification. Yield 71.58 g BuMA comonomer.
向1000mL三颈园底烧瓶中加入下列物质:甲基丙烯酰氨基丙基三甲基氯化铵(MAPTAC)(108mL,50%水溶液,56.8g),二甲基丙烯酸乙二醇酯交联共聚单体(19.62g),BuMA共聚单体(12.12g)和2-丙醇(850mL)。所得溶液为澄清的。接着将反应混合物加热至40℃,同时用氮气脱气。当溶液达到40℃时,加入催化剂,即过硫酸钾(0.75g)和偏硫酸氢钾(0.75g)的25mL水溶液。这时溶液立即开始变混浊,表明聚合正在进行。将反应在40℃保持24小时,然后冷却至室温。Into a 1000 mL three-neck round bottom flask was added the following: methacrylamidopropyltrimethylammonium chloride (MAPTAC) (108 mL, 50% aqueous solution, 56.8 g), ethylene glycol dimethacrylate cross-linked copolymer Monomer (19.62 g), BuMA comonomer (12.12 g) and 2-propanol (850 mL). The resulting solution was clear. The reaction mixture was then heated to 40°C while degassing with nitrogen. When the solution reached 40°C, the catalyst, 25 mL of an aqueous solution of potassium persulfate (0.75 g) and potassium metabisulfate (0.75 g), was added. At this point the solution immediately began to turn cloudy, indicating that polymerization was in progress. The reaction was maintained at 40°C for 24 hours, then cooled to room temperature.
过滤所得聚合物并在漏斗上用异丙醇洗涤,真空干燥得到64.54g标题聚合物。The resulting polymer was filtered and washed on the funnel with isopropanol and dried in vacuo to yield 64.54 g of the title polymer.
将用于试验的聚合物每次用800mL水洗涤共两次,随后每次用500mL甲醇洗涤两次,得到34.5g纯化过的聚合物。The polymer used in the test was washed twice with 800 mL each of water, followed by two washes each with 500 mL of methanol to obtain 34.5 g of purified polymer.
交联的MAPTAC共聚-BuMA共聚物也被用作为交联共聚单体的二甲基丙烯酸丙二醇酯制备,而不是用二甲基丙烯酸乙二醇酯制备,具体制备如下:Crosslinked MAPTAC co-BuMA copolymers were also prepared using propylene glycol dimethacrylate as the crosslinking comonomer instead of ethylene glycol dimethacrylate as follows:
向1000mL三颈园底烧瓶中加入以下物质:甲基丙烯酰氨基丙基三甲基氯化铵(MAPTAC)(60mL,50%水溶液,31.5g),二甲基丙烯酸丙二醇酯交联共聚单体(9.81g),BuMA共聚单体(6.06g),和2-丙醇(300mL)。所得溶液是澄清的。接着将反应混合物加热至70℃,同时用氮气脱气。当溶液被加热至70℃时,加入催化剂AIBN(0.50g)。这时溶液立即开始变混浊,说明聚合正在进行。将反应在70℃保持6小时然后冷却至室温。To a 1000 mL three-neck round bottom flask was added the following: methacrylamidopropyltrimethylammonium chloride (MAPTAC) (60 mL, 50% in water, 31.5 g), propylene glycol dimethacrylate crosslinking comonomer (9.81 g), BuMA comonomer (6.06 g), and 2-propanol (300 mL). The resulting solution was clear. The reaction mixture was then heated to 70°C while degassing with nitrogen. When the solution was heated to 70°C, catalyst AIBN (0.50 g) was added. At this point the solution immediately began to turn cloudy, indicating that polymerization was in progress. The reaction was maintained at 70°C for 6 hours and then cooled to room temperature.
过滤所得聚合物并在漏斗上用异丙醇洗涤,真空干燥得到23.3g聚合物。The resulting polymer was filtered and washed on the funnel with isopropanol and dried under vacuum to yield 23.3 g of polymer.
用类似方法并通过调整起始单体的比例制备与24%二甲基丙烯酸乙二醇酯交联共聚单体交联的MAPTAC共聚BuMA(5%),与0.5%亚甲双甲基丙烯酰胺交联共聚单体交联的MAPTAC共聚BuMA(2%)和与22%二甲基丙烯酸丙二醇酯交联共聚单体交联的MAPTAC共聚BuMA(14%)。实施例7.聚(甲基丙烯酰氨基丙基三甲基氯化铵)共聚(苯乙烯)MAPTAC copolymerized BuMA (5%) cross-linked with 24% ethylene glycol dimethacrylate cross-linking comonomer was prepared in a similar manner and by adjusting the ratio of starting monomers, and 0.5% methylenebismethacrylamide Crosslinked comonomer crosslinked MAPTAC copolymerized BuMA (2%) and MAPTAC copolymerized BuMA crosslinked with 22% propylene glycol dimethacrylate crosslinked comonomer (14%). Example 7. Poly(methacrylamidopropyltrimethylammonium chloride)copoly(styrene)
(MAPTAC共聚苯乙烯)的制备Preparation of (MAPTAC Copolystyrene)
向1000mL三颈园底烧瓶中加入以下物质,甲基丙烯酰氨基丙基三甲基氯化铵(MAPTAC)(60mL,50%水溶液,31.5g),二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体(2.00g),苯乙烯共聚单体(1.75g),和2-丙醇(300mL)。所得溶液是澄清的。接着将反应混合物加热至60℃,并用氮气脱气。当溶液温度达到60℃时,加入催化剂AIBN(0.50g)。这时该溶液立即开始变混浊,说明聚合正在进行。将反应在60℃保持24小时,然后冷却至室温。7小时后,该混合物变得非常粘稠,为了更好搅拌加入100mL异丙醇。To a 1000 mL three necked round bottom flask was added the following, methacrylamidopropyltrimethylammonium chloride (MAPTAC) (60 mL, 50% in water, 31.5 g), divinylbenzene crosslinking comonomer (2.00 g), styrene comonomer (1.75 g), and 2-propanol (300 mL). The resulting solution was clear. The reaction mixture was then heated to 60°C and degassed with nitrogen. When the solution temperature reached 60°C, catalyst AIBN (0.50 g) was added. At this point the solution immediately began to turn cloudy, indicating that polymerization was in progress. The reaction was maintained at 60°C for 24 hours, then cooled to room temperature. After 7 hours, the mixture became very viscous and 100 mL of isopropanol was added for better stirring.
过滤所得聚合物并在漏斗上用异丙醇洗涤,真空干燥得到30.9g标题聚合物。The resulting polymer was filtered and washed on the funnel with isopropanol and dried in vacuo to give 30.9 g of the title polymer.
将用于试验的聚合物每次用1000mL水洗涤两次,接着每次用800mL甲醇洗涤两次得到纯化过的28.0g聚合物。The polymer used in the test was washed twice with 1000 mL each of water followed by 28.0 g of purified polymer twice with 800 mL each of methanol.
用类似方法并通过变化起始单体的比例制备与7.5%二甲基丙烯酸丁二醇酯交联共聚单体交联的MAPTAC共聚-苯乙烯(19%),与7%二乙烯基苯共聚单体交联的MAPTAC共聚-苯乙烯(23%),与6%二乙烯基苯共聚单体交联的MAPTAC共聚-苯乙烯(30%),和与6%二乙烯基苯共聚单体交联的MAPTAC共聚-苯乙烯(38%)。实施例8.聚(甲基丙烯酰氨基丙基三甲基氯化铵)共聚(乙烯基萘)MAPTAC copoly-styrene (19%) crosslinked with 7.5% butanediol dimethacrylate crosslinking comonomer was prepared in a similar manner and by varying the ratio of starting monomers, copolymerized with 7% divinylbenzene Monomer cross-linked MAPTAC co-styrene (23%), MAPTAC co-styrene cross-linked with 6% divinylbenzene comonomer (30%), and cross-linked with 6% divinylbenzene comonomer Linked MAPTAC Co-Styrene (38%). Example 8. Poly(methacrylamidopropyltrimethylammonium chloride)copoly(vinylnaphthalene)
(MAPTAC共聚-VN)的制备Preparation of (MAPTAC copolymerization-VN)
向1000mL三颈园底烧瓶中加入以下物质:甲基丙烯酰氨基丙基三甲基氯化铵(MAPTAC)(40mL的50%水溶液,21.0g),二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体(2.25g),2-乙烯基萘共聚单体(10.5g),和2-丙醇(320mL)。所得溶液是澄清的。接着将反应混合物加热至65℃,同时用氮气脱气。当溶液达到65℃时,加入催化剂AIBN(0.50g)。这时溶液立即开始变混浊,说明聚合正在进行。将反应在65℃保持20小时,然后冷却至室温。To a 1000 mL three-neck round bottom flask was added the following: methacrylamidopropyltrimethylammonium chloride (MAPTAC) (40 mL of a 50% aqueous solution, 21.0 g), divinylbenzene crosslinking comonomer (2.25 g), 2-vinylnaphthalene comonomer (10.5 g), and 2-propanol (320 mL). The resulting solution was clear. The reaction mixture was then heated to 65°C while degassing with nitrogen. When the solution reached 65°C, catalyst AIBN (0.50 g) was added. At this point the solution immediately began to turn cloudy, indicating that polymerization was in progress. The reaction was maintained at 65°C for 20 hours, then cooled to room temperature.
过滤所得聚合物并用异丙醇在漏斗上洗涤,然后立即在400mL蒸馏水中浆化。将混合物搅拌0.5小时然后过滤。重复水洗涤一次。将滤饼在400mL甲醇中浆化并搅拌0.5小时。过滤混合物并重复甲醇浆化一次。真空干燥得到22.11g,65.5%标题聚合物。The resulting polymer was filtered and washed on the funnel with isopropanol, then immediately slurried in 400 mL of distilled water. The mixture was stirred for 0.5 hours then filtered. Repeat the water wash once. The filter cake was slurried in 400 mL of methanol and stirred for 0.5 hours. The mixture was filtered and methanol slurrying was repeated once. Drying in vacuo gave 22.11 g, 65.5% of the title polymer.
用类似方法通过改变起始单体的比例制备与5%二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体交联的MAPTAC共聚-VN(39%)。实施例9.聚(甲基丙烯酰氨基丙基三甲基氯化铵)共聚(1-乙烯基咪唑)MAPTAC Copolymer-VN (39%) crosslinked with 5% divinylbenzene crosslinking comonomer was prepared in a similar manner by varying the ratio of starting monomers. Example 9. Poly(methacrylamidopropyltrimethylammonium chloride)copoly(1-vinylimidazole)
(MAPTAC共聚-VI)的制备Preparation of (MAPTAC copolymer-VI)
向1000mL三颈园底烧瓶中加入以下物质:甲基丙烯酰氨基丙基三甲基氯化铵(MAPTAC)(40mL的50%水溶液,21.0g),二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体(2.25g),1-乙烯基咪唑共聚单体(12.54g),和2-丙醇(300mL)。所得溶液是澄清的。接着将反应混合物加热至65℃,同时用氮气脱气。当溶液达到65℃时,加入催化剂AIBN(0.50g)。这时溶液立即开始变混浊,说明聚合正在进行。将反应在65℃保持20小时,然后冷却至室温。To a 1000 mL three-neck round bottom flask was added the following: methacrylamidopropyltrimethylammonium chloride (MAPTAC) (40 mL of a 50% aqueous solution, 21.0 g), divinylbenzene crosslinking comonomer (2.25 g), 1-vinylimidazole comonomer (12.54 g), and 2-propanol (300 mL). The resulting solution was clear. The reaction mixture was then heated to 65°C while degassing with nitrogen. When the solution reached 65°C, catalyst AIBN (0.50 g) was added. At this point the solution immediately began to turn cloudy, indicating that polymerization was in progress. The reaction was maintained at 65°C for 20 hours, then cooled to room temperature.
过滤所得聚合物并用异丙醇在漏斗上洗涤,然后立即在400mL蒸馏水中浆化。将混合物搅拌0.5小时然后过滤。重复水洗涤一次。将滤饼在400mL甲醇中浆化并搅拌0.5小时。过滤混合物并重复甲醇浆化一次。真空干燥得到7.34g,20.5%标题聚合物。实施例10.聚(三甲基氯化铵丙烯酸乙酯)共聚(苯乙烯)(TMAEAC共聚-The resulting polymer was filtered and washed on the funnel with isopropanol, then immediately slurried in 400 mL of distilled water. The mixture was stirred for 0.5 hours then filtered. Repeat the water wash once. The filter cake was slurried in 400 mL of methanol and stirred for 0.5 hours. The mixture was filtered and methanol slurrying was repeated once. Drying in vacuo yielded 7.34 g, 20.5% of the title polymer. Example 10. Poly(trimethylammonium chloride ethyl acrylate) copolymer(styrene)(TMAEAC copolymer-
Sty)的制备Preparation of Sty)
向1000mL三颈园底烧瓶中加入以下物质:三甲基氯化铵丙烯酸乙酯(TMAEAC)(99.4mL的50%水溶液,53.0g),二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体(7.00g),苯乙烯共聚单体(40.0g),和2-丙醇(800mL)。所得溶液是澄清的。接着将反应混合物加热至65℃,同时用氮气脱气。当溶液达到65℃时,加入催化剂AIBN(1.50g)。这时溶液立即开始变混浊,说明聚合正在进行。将反应在65℃保持6小时,冷却至60℃并再搅拌18小时,然后冷却至室温。To a 1000 mL three necked round bottom flask was added the following: trimethylammonium chloride ethyl acrylate (TMAEAC) (99.4 mL of a 50% aqueous solution, 53.0 g), divinylbenzene crosslinking comonomer (7.00 g), Styrene comonomer (40.0 g), and 2-propanol (800 mL). The resulting solution was clear. The reaction mixture was then heated to 65°C while degassing with nitrogen. When the solution reached 65°C, catalyst AIBN (1.50 g) was added. At this point the solution immediately began to turn cloudy, indicating that polymerization was in progress. The reaction was maintained at 65°C for 6 hours, cooled to 60°C and stirred for an additional 18 hours, then cooled to room temperature.
过滤所得聚合物并用异丙醇在漏斗上洗涤,然后立即在1000mL蒸馏水中浆化。将混合物搅拌0.5小时然后加入800mL甲醇并再搅拌0.5小时。将混合物沉降并滗析上清液,得到750mL剩余物。将剩余物再用750mL甲醇浆化并搅拌0.5小时。每次用800mL甲醇将甲醇浆化和滗析重复两次。随后加入800mL异丙醇,将混合物搅拌0.5小时并过滤。最后加入600mL异丙醇并搅拌0.5小时。真空干燥滤液得到49.2g,49.2%标题聚合物。The resulting polymer was filtered and washed on the funnel with isopropanol, then immediately slurried in 1000 mL of distilled water. The mixture was stirred for 0.5 hours then 800 mL of methanol was added and stirred for another 0.5 hours. The mixture was settled and the supernatant was decanted to give a residue of 750 mL. The residue was slurried with an additional 750 mL of methanol and stirred for 0.5 h. Methanol slurrying and decanting were repeated twice with 800 mL each of methanol. Then 800 mL of isopropanol was added, the mixture was stirred for 0.5 hours and filtered. Finally 600 mL of isopropanol was added and stirred for 0.5 hours. The filtrate was dried in vacuo to yield 49.2 g, 49.2% of the title polymer.
用类似方法通过改变起始单体的比例制备与8%二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体交联的TMAEAC共聚-苯乙烯(31%)和与6%二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体交联的TMAEAC共聚-苯乙烯(46%)。实施例11.聚(三甲基氯化铵甲基丙烯酸乙酯)共聚(苯乙烯)(TMAEMCTMAEAC copoly-styrene (31%) crosslinked with 8% divinylbenzene crosslinking comonomer and crosslinked with 6% divinylbenzene crosslinking comonomer were prepared in a similar manner by varying the ratio of starting monomers. Linked TMAEAC co-styrene (46%). Example 11. Poly(trimethylammonium chloride ethyl methacrylate) copoly(styrene) (TMAEMC
共聚-苯乙烯)的制备 Preparation of Co-Styrene)
向1000mL三颈园底烧瓶中加入以下物质:三甲基氯化铵甲基丙烯酸乙酯(TMAEMAC)(38.8mL的50%水溶液,21.7g),二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体(3.72g),苯乙烯共聚单体(15.66g),和2-丙醇(2500mL)。所得溶液是澄清的。接着将反应混合物加热至65℃,同时用氮气脱气。当溶液达到65℃时,加入催化剂AIBN(0.50g)。这时溶液立即开始变混浊,说明聚合正在进行。2小时后混合物变得非常粘稠,再加入100mL异丙醇。5小时后,混合物再次变得非常粘稠,所以再加入100mL异丙醇。将反应在65℃保持6小时,然后冷却至室温。To a 1000 mL three necked round bottom flask was added the following: trimethylammonium chloride ethyl methacrylate (TMAEMAC) (38.8 mL of a 50% aqueous solution, 21.7 g), divinylbenzene crosslinking comonomer (3.72 g ), styrene comonomer (15.66 g), and 2-propanol (2500 mL). The resulting solution was clear. The reaction mixture was then heated to 65°C while degassing with nitrogen. When the solution reached 65°C, catalyst AIBN (0.50 g) was added. At this point the solution immediately began to turn cloudy, indicating that polymerization was in progress. After 2 hours the mixture became very viscous and another 100 mL of isopropanol was added. After 5 hours, the mixture became very viscous again, so another 100 mL of isopropanol was added. The reaction was maintained at 65°C for 6 hours, then cooled to room temperature.
过滤所得聚合物并用异丙醇在漏斗上洗涤,然后立即在1000mL蒸馏水中浆化。将混合物搅拌0.5小时然后转移至混合器中并混合5分钟。过滤聚合物浆状物并加入1000mL蒸馏水并再将混合物搅拌0.5小时。过滤混合物,每次用500mL甲醇浆化滤饼两次。真空干燥滤液得到30.2g,75.9%标题聚合物。The resulting polymer was filtered and washed on the funnel with isopropanol, then immediately slurried in 1000 mL of distilled water. The mixture was stirred for 0.5 hours then transferred to a mixer and mixed for 5 minutes. The polymer slurry was filtered and 1000 mL of distilled water was added and the mixture was stirred for an additional 0.5 hours. The mixture was filtered and the filter cake was slurried twice with 500 mL each of methanol. The filtrate was dried in vacuo to yield 30.2 g, 75.9% of the title polymer.
用类似方法通过改变起始单体的比例制备与4%二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体交联的TMAEMC共聚-苯乙烯(58%),与4%二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体交联的TMAEMC共聚-苯乙烯(33%)和与4%二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体交联的TMAEMC共聚-苯乙烯(24%)。实施例12.聚(甲基丙烯酰氨基丙基-3-(三甲基氯化铵)),共聚(2,3,4,5,6-TMAEMC co-poly-styrene (58%) cross-linked with 4% divinylbenzene cross-linking comonomer was prepared in a similar manner by varying the ratio of starting monomers, cross-linked with 4% divinylbenzene cross-linking comonomer Linked TMAEMC co-styrene (33%) and TMAEMC co-styrene crosslinked with 4% divinylbenzene crosslinking comonomer (24%). Example 12. Poly(methacrylamidopropyl-3-(trimethylammonium chloride)), copoly(2,3,4,5,6-
五氟乙烯基苯乙烯)(MAPTAC共聚-StyF5)的制备Preparation of pentafluorovinylstyrene) (MAPTAC copolymer-StyF 5 )
向1000mL三颈园底烧瓶中加入以下物质:甲基丙烯酰氨基丙基-3-(三甲基氯化铵)(MAPTAC)(24.5mL的50%水溶液,13.00g),二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体(1.00g),五氟苯乙烯共聚单体(6.00g),和2-丙醇(150mL)和AIBN(0.50g)。所得溶液是澄清的。接着将反应混合物加热至65℃,同时用氮气脱气。很短一段时间后溶液开始变混浊,说明聚合正在进行。5小时后混合物变得非常粘稠,所以再加入100mL异丙醇。将反应在65℃保持24小时,然后冷却至室温。To a 1000 mL three necked round bottom flask was added the following: methacrylamidopropyl-3-(trimethylammonium chloride) (MAPTAC) (24.5 mL of a 50% solution in water, 13.00 g), divinylbenzene Co-co-monomer (1.00 g), pentafluorostyrene comonomer (6.00 g), and 2-propanol (150 mL) and AIBN (0.50 g). The resulting solution was clear. The reaction mixture was then heated to 65°C while degassing with nitrogen. After a short time the solution started to become cloudy, indicating that polymerization was in progress. After 5 hours the mixture became very viscous, so an additional 100 mL of isopropanol was added. The reaction was maintained at 65°C for 24 hours and then cooled to room temperature.
过滤所得聚合物并用异丙醇在漏斗上洗涤,然后立即在500mL蒸馏水中浆化。将混合物搅拌0.5小时,加入500mL蒸馏水并将混合物搅拌0.5小时。过滤聚合物,并将滤饼每次用300mL甲醇浆化两次。真空干燥滤液得到7.74g标题聚合物。The resulting polymer was filtered and washed on the funnel with isopropanol, then immediately slurried in 500 mL of distilled water. The mixture was stirred for 0.5 hours, 500 mL of distilled water was added and the mixture was stirred for 0.5 hours. The polymer was filtered and the filter cake was slurried twice with 300 mL methanol each. The filtrate was dried in vacuo to give 7.74 g of the title polymer.
用类似方法通过改变起始单体的比例制备与5%二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体交联的MAPTAC共聚-StyF5(20%),与5%二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体交联的MAPTAC共聚-StyF5(40%)和与5%二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体交联的MAPTAC共聚-StyF5(45%)。实施例13.聚(甲基丙烯酰氨基丙基-3-(三甲基氯化铵)),共聚2-(三甲基MAPTAC copoly-StyF 5 (20%) cross-linked with 5% divinylbenzene cross-linking comonomer was prepared in a similar manner by changing the ratio of starting monomers, cross-linked with 5% divinylbenzene cross-linking comonomer Linked MAPTAC co- StyF5 (40%) and MAPTAC co- StyF5 crosslinked with 5% divinylbenzene crosslinking comonomer (45%). Example 13. Poly(methacrylamidopropyl-3-(trimethylammonium chloride)), copolymerized 2-(trimethylammonium chloride)
氯化铵)甲基丙烯酸乙酯共聚-苯乙烯(MAPTAC共聚- Ammonium chloride) ethyl methacrylate copolymer-styrene (MAPTAC copolymer-
TMAEMC共聚-Sty)的制备Preparation of TMAEMC copolymerization-Sty)
向1000mL三颈园底烧瓶中加入以下物质:甲基丙烯酰氨基丙基-3-(三甲基氯化铵)(MAPTAC)(10.40g的50%水溶液,5.20g),2-(三甲基氯化铵)甲基丙烯酸乙酯(TMAEMC)(4.86g,70%水溶液,3.40g),二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体(1.00g),苯乙烯共聚单体(10.40g),2-丙醇(150mL)和AIBN(0.50g)。所得溶液是澄清的。接着将反应混合物加热至70℃,同时用氮气脱气。很短一段时间后溶液开始变混浊,说明聚合正在进行。将反应在70℃保持24小时,然后冷却至室温。To a 1000 mL three necked round bottom flask was added the following: methacrylamidopropyl-3-(trimethylammonium chloride) (MAPTAC) (10.40 g of a 50% solution in water, 5.20 g), 2-(trimethylammonium ammonium chloride) ethyl methacrylate (TMAEMC) (4.86g, 70% aqueous solution, 3.40g), divinylbenzene crosslinking comonomer (1.00g), styrene comonomer (10.40g), 2 - Propanol (150 mL) and AIBN (0.50 g). The resulting solution was clear. The reaction mixture was then heated to 70°C while degassing with nitrogen. After a short time the solution started to become cloudy, indicating that polymerization was in progress. The reaction was maintained at 70°C for 24 hours and then cooled to room temperature.
过滤所得聚合物并用异丙醇在漏斗上洗涤,然后立即在500mL甲醇中浆化。将混合物搅拌0.5小时。过滤聚合物浆状物并加入400mL蒸馏水并再将混合物搅拌0.5小时。过滤混合物并重复水浆化。过滤混合物并将滤饼每次用400mL甲醇浆化两次。真空干燥滤液得到5.39g标题聚合物。The resulting polymer was filtered and washed on the funnel with isopropanol, then immediately slurried in 500 mL of methanol. The mixture was stirred for 0.5 hours. The polymer slurry was filtered and 400 mL of distilled water was added and the mixture was stirred for an additional 0.5 hours. The mixture was filtered and water slurrying repeated. The mixture was filtered and the filter cake was slurried twice with 400 mL methanol each. The filtrate was dried in vacuo to yield 5.39 g of the title polymer.
用类似方法通过改变起始单体的比例制备与5%二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体交联的MAPTAC共聚-TMAEMC(34%)共聚-Sty(36%),与5%二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体交联的MAPTAC共聚-TMAEMC(31%)共聚-Sty(41%),与5%二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体交联的MAPTAC共聚-TMAEMC(28%)共聚-Sty(46%),与5%二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体交联的MAPTAC共聚-TMAEMC(23%)共聚-Sty(48%),与4%二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体交联的MAPTAC共聚-TMAEMC(26%)共聚-Sty(52%),与4%二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体交联的MAPTAC共聚-TMAEMC(17%)共聚-Sty(53%),与4%二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体交联的MAPTAC共聚-TMAEMC(15%)共聚-Sty(55%),与4%二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体交联的MAPTAC共聚-TMAEMC(13%)共聚-Sty(61.5%)。实施例14.聚(三甲基氯化铵甲基丙烯酸乙酯共聚-(异丙基丙烯酰胺))MAPTAC copoly-TMAEMC (34%) copoly-Sty (36%) crosslinked with 5% divinylbenzene crosslinking comonomer was prepared in a similar manner by changing the ratio of starting monomers, and 5% divinylbenzene Cross-linked comonomer cross-linked MAPTAC-TMAEMC (31%) co-Sty (41%), MAPTAC co-TMAEMC (28%) cross-linked with 5% divinylbenzene cross-linked comonomer-Sty (46%), MAPTAC Co-TMAEMC (23%) cross-linked with 5% divinylbenzene cross-linking comonomer, Co-Sty (48%), cross-linked with 4% divinylbenzene cross-linking comonomer MAPTAC Co-TMAEMC (26%) Co-Sty (52%), MAPTAC Co-TMAEMC (17%) Co-Sty (53%) cross-linked with 4% divinylbenzene cross-linked comonomer, with 4 % MAPTAC co-TMAEMC (15%) cross-linked with divinylbenzene cross-linking comonomer (15%) Co-Sty (55%), MAPTAC co-TMAEMC cross-linked with 4% divinylbenzene cross-linking comonomer (13 %) Co-Sty (61.5%). Example 14. Poly(trimethylammonium chloride ethyl methacrylate copolymer-(isopropylacrylamide))
(TMAEMAC共聚-IPA)的制备Preparation of (TMAEMAC copolymerization-IPA)
首先,共聚单体异丙基丙烯酰胺(IPA)的制备如下:First, the preparation of comonomer isopropylacrylamide (IPA) is as follows:
在1L烧瓶中将丙烯酰氯(63mL,70.2g,0.775mol)溶解于四氢呋喃(200mL)并置于冰浴。滴加含异丙胺(127.7mL,88.67g,1.50mol)溶液,保持温度在5-15℃。将溶液搅拌10分钟后将固体异丙胺盐酸化物滤除。从母液中真空除去溶剂,得到几乎无色的油,经过放置使其固化,无需进一步纯化即可用于下面标题共聚物的制备。Acryloyl chloride (63 mL, 70.2 g, 0.775 mol) was dissolved in tetrahydrofuran (200 mL) in a 1 L flask and placed in an ice bath. A solution containing isopropylamine (127.7 mL, 88.67 g, 1.50 mol) was added dropwise, keeping the temperature at 5-15°C. The solution was stirred for 10 minutes and the solid isopropylamine hydrochloride was filtered off. The solvent was removed in vacuo from the mother liquor to give an almost colorless oil which solidified on standing and was used without further purification in the preparation of the title copolymer below.
向1000mL三颈园底烧瓶中加入以下物质:三甲基氯化铵甲基丙烯酸乙酯(76.5mL的50%水溶液,41.18g,0.213mol),亚甲基双丙烯酰胺交联共聚单体(2.40g),IPA共聚单体(4.52g,0.070mol),和水(200mL)。所得溶液是澄清的。搅拌反应混合物,同时用氮气脱气。当溶液脱气时加入过硫酸钾(0.3g)和焦亚磷酸钾(0.3g)组成的催化剂。聚合反应2分钟后开始,3分钟后凝结成胶。To a 1000 mL three necked round bottom flask was added the following: trimethylammonium chloride ethyl methacrylate (76.5 mL of a 50% aqueous solution, 41.18 g, 0.213 mol), methylenebisacrylamide crosslinking comonomer ( 2.40 g), IPA comonomer (4.52 g, 0.070 mol), and water (200 mL). The resulting solution was clear. The reaction mixture was stirred while degassing with nitrogen. A catalyst consisting of potassium persulfate (0.3 g) and potassium pyrophosphite (0.3 g) was added while the solution was degassing. Polymerization started after 2 minutes and gelled after 3 minutes.
第二天早晨,将该胶转到混合机中并加入1000mL水。混合几秒钟后聚合物吸进全部的水。膨胀的聚合物分几批用异丙醇混合几次以将其脱水。过滤所得聚合物并用异丙醇在漏斗上洗涤,真空干燥滤液得到36.8g标题共聚物。实施例15.聚(甲基丙烯酰氨基丙基-3-(三甲基氯化铵))共聚-(乙烯基吡啶)The next morning, the gum was transferred to a mixer and 1000 mL of water was added. The polymer absorbed all the water after mixing for a few seconds. The swollen polymer was dehydrated by mixing several batches with isopropanol several times. The resulting polymer was filtered and washed on the funnel with isopropanol, and the filtrate was dried in vacuo to yield 36.8 g of the title copolymer. Example 15. Poly(methacrylamidopropyl-3-(trimethylammonium chloride))co-(vinylpyridine)
(MAPTAC共聚-VP)的制备Preparation of (MAPTAC copolymerization-VP)
向1000mL三颈园底烧瓶中加入以下物质:甲基丙烯酰氨基丙基-3-(三甲基氯化铵)(MAPTAC)(40mL的50%水溶液,21.0g),二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体(2.25g),乙烯基吡啶(14.0g,0.133mol),浓盐酸(11mL,0.133mol),2-丙醇(300mL),和AIBN(0.67g)。所得溶液是澄清的。接着,将反应混合物加热至60℃,同时用氮气脱气。短时间后该溶液开始混浊,表明聚合反应正在进行。将反应混合物在60℃保持20小时,然后冷却至室温。To a 1000 mL three-neck round bottom flask was added the following: methacrylamidopropyl-3-(trimethylammonium chloride) (MAPTAC) (40 mL of a 50% solution in water, 21.0 g), divinylbenzene cross-linked Comonomer (2.25 g), vinylpyridine (14.0 g, 0.133 mol), concentrated hydrochloric acid (11 mL, 0.133 mol), 2-propanol (300 mL), and AIBN (0.67 g). The resulting solution was clear. Next, the reaction mixture was heated to 60°C while degassing with nitrogen. After a short time the solution became cloudy, indicating that polymerization was in progress. The reaction mixture was maintained at 60°C for 20 hours and then cooled to room temperature.
过滤所得聚合物并在漏斗上用异丙醇洗涤,然后立即在1000mL蒸馏水中浆化。将混合物搅拌1小时。过滤聚合物浆液,在漏斗上用甲醇洗涤,然后在600mL甲醇中浆化1小时。过滤并空气干燥,得到20.4g共聚物。实施例16.聚(三甲基氯化铵甲基丙烯酸乙酯)共聚-(对氟苯乙烯)The resulting polymer was filtered and washed on the funnel with isopropanol, then immediately slurried in 1000 mL of distilled water. The mixture was stirred for 1 hour. The polymer slurry was filtered, washed with methanol on the funnel, and then slurried in 600 mL of methanol for 1 hour. Filtration and air drying yielded 20.4 g of copolymer. Example 16. Poly(trimethylammonium chloride ethyl methacrylate) copolymer-(p-fluorostyrene)
(TMAEMC共聚-F1Sty)的制备Preparation of (TMAEMC Copolymerization-F 1 Sty)
向500mL烧瓶中加入以下物质:三甲基氯化铵甲基丙烯酸乙酯(TMAEMC)(11.0g的70%水溶液,7.70g),二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体(0.50g),对氟苯乙烯共聚单体(4.00g),2-丙醇(125mL)和AIBN(0.25g)。所得溶液是澄清的。接着,将反应混合物加热至65℃,同时用氮气脱气。溶液马上开始混浊,表明聚合反应正在进行。反应在65℃保持6小时,然后冷却至室温。To a 500 mL flask was added the following: trimethylammonium chloride ethyl methacrylate (TMAEMC) (11.0 g of a 70% solution in water, 7.70 g), divinylbenzene crosslinking comonomer (0.50 g), p-fluoro Styrene comonomer (4.00 g), 2-propanol (125 mL) and AIBN (0.25 g). The resulting solution was clear. Next, the reaction mixture was heated to 65°C while degassing with nitrogen. The solution immediately became cloudy, indicating that polymerization was in progress. The reaction was maintained at 65°C for 6 hours, then cooled to room temperature.
通过滗析除去溶剂,聚合物立即在250mL蒸馏水中浆化。搅拌该混合物0.5小时,然后滗析。如此用水浆化3次。最后,用400mL甲醇浆化聚合物。过滤并真空干燥,得到5.42g,44.4%标题共聚物。The solvent was removed by decantation and the polymer was immediately slurried in 250 mL of distilled water. The mixture was stirred for 0.5 hours then decanted. This was slurried 3 times with water. Finally, the polymer was slurried with 400 mL of methanol. Filtration and vacuum drying afforded 5.42 g, 44.4% of the title copolymer.
用类似方法通过改变起始单体的比例制备与4%二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体交联的TMAEMC共聚-F1Sty(24%)。实施例17.聚(甲基丙烯酰氨基丙基-3-(三甲基氯化铵))共聚-(六氟甲基丙TMAEMC co-F 1 Sty (24%) crosslinked with 4% divinylbenzene crosslinking comonomer was prepared in a similar manner by varying the ratio of starting monomers. Example 17. Poly(methacrylamidopropyl-3-(trimethylammonium chloride))copoly-(hexafluoromethylpropane
烯酸丁酯)(MAPTAC共聚-F6BMA)的制备Butyl acrylate) (MAPTAC copolymerization-F 6 BMA)
向1000mL三颈园底烧瓶中加入以下物质:甲基丙烯酰氨基丙基-3-(三甲基氯化铵)(MAPTAC)(28.5mL的50%水溶液,15.0g),二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体(1.00g),六氟甲基丙烯酸丁酯(4.00g),2-丙醇(150mL)和AIBN(0.50g)。所得溶液是澄清的。接着,将反应混合物加热至60℃,同时用氮气脱气。短时间后溶液开始混浊,表明聚合反应正在进行。反应在60℃保持24小时,然后冷却至室温。To a 1000 mL three necked round bottom flask was added the following: methacrylamidopropyl-3-(trimethylammonium chloride) (MAPTAC) (28.5 mL of a 50% solution in water, 15.0 g), divinylbenzene Co-co-monomer (1.00 g), butyl hexafluoromethacrylate (4.00 g), 2-propanol (150 mL) and AIBN (0.50 g). The resulting solution was clear. Next, the reaction mixture was heated to 60°C while degassing with nitrogen. After a short time the solution became cloudy, indicating that the polymerization reaction was in progress. The reaction was maintained at 60°C for 24 hours, then cooled to room temperature.
将所得聚合物过滤并在漏斗上用异丙醇洗涤,随即用500mL蒸馏水浆化。将混合物搅拌1小时。过滤聚合物浆液,并再用水浆化一次。将聚合物在500mL甲醇中浆化1小时并过滤,并重复一次。最后将该混合物在400mL异丙醇中浆化并搅拌过夜。过滤及空气干燥,得到7.52g标题共聚物。实施例18.聚(三甲基氯化铵丙烯酸乙酯)共聚-(六氟丙烯酸异丙酯)The resulting polymer was filtered and washed on the funnel with isopropanol, then slurried with 500 mL of distilled water. The mixture was stirred for 1 hour. The polymer slurry was filtered and reslurried with water. The polymer was slurried in 500 mL of methanol for 1 hour and filtered, and repeated once. Finally the mixture was slurried in 400 mL of isopropanol and stirred overnight. Filtration and air drying yielded 7.52 g of the title copolymer. Example 18. Poly(trimethylammonium chloride ethyl acrylate) copoly-(isopropyl hexafluoroacrylate)
(TMAEAC共聚-F6IA)的制备Preparation of (TMAEAC copolymer- F6IA )
向1000mL三颈园底烧瓶中加入以下物质:三甲基氯化铵丙烯酸乙酯(30.0mL的50%水溶液,15.0g),二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体(1.00g),F6IPA(4.00g),AIBN(0.50g)和2-丙醇(150mL)。所得溶液是澄清的。将反应混合物搅拌,同时用氮气脱气,并加热至60℃。18小时后反应混合物允许被冷却至室温,滗析除去溶剂。剩下的聚合物在400mL水中浆化,搅拌1小时后过滤。再用水浆化一次,然后用甲醇浆化两次。最后,将聚合物在200mL异丙醇中浆化,搅拌2小时并过滤。空气干燥,得到5.59g标题聚合物。实施例19.聚(甲基丙烯酰氨基丙基-3-(三甲基氯化铵))共聚-(十七氟甲基To a 1000 mL three-neck round bottom flask was added the following: trimethylammonium chloride ethyl acrylate (30.0 mL of a 50% solution in water, 15.0 g), divinylbenzene crosslinking comonomer (1.00 g), F6IPA (4.00g), AIBN (0.50g) and 2-propanol (150mL). The resulting solution was clear. The reaction mixture was stirred while degassing with nitrogen and heated to 60°C. After 18 hours the reaction mixture was allowed to cool to room temperature and the solvent was removed by decantation. The remaining polymer was slurried in 400 mL of water, stirred for 1 hour and filtered. Slurry again with water and twice with methanol. Finally, the polymer was slurried in 200 mL of isopropanol, stirred for 2 hours and filtered. Air drying gave 5.59 g of the title polymer. Example 19. Poly(methacrylamidopropyl-3-(trimethylammonium chloride))copoly-(heptadecafluoromethyl
丙烯酸癸酯)(MAPTAC共聚-F17DecMA)的制备Preparation of Decyl Acrylate)(MAPTAC Copolymerization-F 17 DecMA)
向1000mL三颈园底烧瓶中加入以下物质:甲基丙烯酰氨基丙基-3-(三甲基氯化铵)(MAPTAC)(28.5mL的50%水溶液,15.0g),二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体(1.00g),十七氟甲基丙烯酸癸酯(4.00g),2-丙醇(1 50mL)和AIBN(0.40g)。所得溶液是澄清的。然后,将反应混合物加热至65℃,同时用氮气脱气。短时间后溶液开始混浊,表明聚合反应正在进行。4小时后反应混合物已经非常稠,再加入100mL异丙醇,将反应在65℃保持18小时,然后冷却至室温。To a 1000 mL three necked round bottom flask was added the following: methacrylamidopropyl-3-(trimethylammonium chloride) (MAPTAC) (28.5 mL of a 50% solution in water, 15.0 g), divinylbenzene Co-co-monomer (1.00 g), heptadecylfluorodecyl methacrylate (4.00 g), 2-propanol (1 50 mL) and AIBN (0.40 g). The resulting solution was clear. Then, the reaction mixture was heated to 65°C while degassing with nitrogen. After a short time the solution became cloudy, indicating that the polymerization reaction was in progress. After 4 hours the reaction mixture had become very thick and another 100 mL of isopropanol was added and the reaction was maintained at 65°C for 18 hours and then cooled to room temperature.
过滤所得聚合物,并在漏斗上用异丙醇洗涤,然后立即在600mL蒸馏水中浆化。将混合物搅拌1小时。过滤聚合物浆液,再用水浆化一次。然后将混合物在500mL甲醇中浆化1小时并过滤。空气干燥,得到17.73g标题聚合物。实施例20.聚(甲基丙烯酰氨基丙基-3-(三甲基氯化铵))共聚-(2-(三甲基氯The resulting polymer was filtered and washed on the funnel with isopropanol, then immediately slurried in 600 mL of distilled water. The mixture was stirred for 1 hour. The polymer slurry was filtered and slurried once more with water. The mixture was then slurried in 500 mL of methanol for 1 hour and filtered. Air drying gave 17.73 g of the title polymer. Example 20. Poly(methacrylamidopropyl-3-(trimethylammonium chloride))copoly-(2-(trimethylammonium chloride)
化铵)丙烯酸乙酯),共聚-苯乙烯(MAPTAC共聚-TMAEAC共Ammonium chloride) ethyl acrylate), copolymer-styrene (MAPTAC copolymer-TMAEAC copolymer
聚-Sty)的制备Preparation of poly-Sty)
向1000mL三颈园底烧瓶中加入以下物质:甲基丙烯酰氨基丙基-3-(三甲基氯化铵)(MAPTAC)(10.00g的50%水溶液,5.00g),2-(三甲基氯化铵)丙烯酸乙酯(TMAEAC)(6.00g的50%水溶液,3.00g),二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体(1.00g),苯乙烯(11.00g),2-丙醇(150mL)和AIBN(0.25g)。所得溶液是澄清的。然后,将反应混合物加热至70℃,同时用氮气脱气。短时间后溶液开始混浊,表明聚合反应正在进行。将反应在70℃保持24小时,然后冷却至室温。To a 1000 mL three-neck round bottom flask was added the following: methacrylamidopropyl-3-(trimethylammonium chloride) (MAPTAC) (10.00 g in 50% water, 5.00 g), 2-(trimethylammonium chloride) ammonium chloride) ethyl acrylate (TMAEAC) (6.00 g in 50% aqueous solution, 3.00 g), divinylbenzene crosslinking comonomer (1.00 g), styrene (11.00 g), 2-propanol (150 mL ) and AIBN (0.25g). The resulting solution was clear. Then, the reaction mixture was heated to 70°C while degassing with nitrogen. After a short time the solution became cloudy, indicating that the polymerization reaction was in progress. The reaction was maintained at 70°C for 24 hours and then cooled to room temperature.
过滤所得聚合物,并在漏斗上用异丙醇洗涤,然后立即在500mL甲醇中浆化。将混合物搅拌0.5小时。沉降和滗析聚合物浆液。加入200mL蒸馏水并将混合物搅拌0.5小时。滗析混合物,然后再用400mL水浆化。滗析混合物,聚合物每次用200mL甲醇浆化两次。过滤并空气干燥,得到2.76g标题共聚物。The resulting polymer was filtered and washed on the funnel with isopropanol, then immediately slurried in 500 mL of methanol. The mixture was stirred for 0.5 hours. Settling and decanting the polymer slurry. 200 mL of distilled water was added and the mixture was stirred for 0.5 hours. The mixture was decanted and then reslurried with 400 mL of water. The mixture was decanted and the polymer was slurried twice with 200 mL methanol each. Filtration and air drying afforded 2.76 g of the title copolymer.
用类似方法通过改变起始单体的比例制备与5%二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体交联的MAPTAC共聚-TMAEAC(10%)共聚-Sty(60%)。实施例21.聚(2-(三甲基氯化铵)丙烯酸乙酯),共聚-(2,3,4,5,6-五氟苯乙烯)MAPTAC co-TMAEAC (10%) co-Sty (60%) crosslinked with 5% divinylbenzene crosslinking comonomer was prepared in a similar manner by varying the ratio of starting monomers. Example 21. Poly(2-(trimethylammonium chloride) ethyl acrylate), copoly-(2,3,4,5,6-pentafluorostyrene)
(TMAEAC共聚-StyF5)的制备Preparation of (TMAEAC copolymerization-StyF 5 )
向1000mL三颈园底烧瓶中加入以下物质:2-(三甲基氯化铵)丙烯酸乙酯(TMAEAC)(24.0mL的50%水溶液,13.00g),二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体(1.00g),五氟苯乙烯(6.00g),2-丙醇(150mL)和AIBN(0.50g)。所得溶液是澄清的。然后,将反应混合物加热至65℃,同时用氮气脱气。短时间后溶液开始混浊,表明聚合反应正在进行。2小时后混合物已经非常稠,因此加入100mL异丙醇。将反应在65℃保持22小时,然后冷却至室温。To a 1000 mL three necked round bottom flask was added the following: 2-(Trimethylammonium chloride) ethyl acrylate (TMAEAC) (24.0 mL of a 50% solution in water, 13.00 g), divinylbenzene crosslinking comonomer ( 1.00 g), pentafluorostyrene (6.00 g), 2-propanol (150 mL) and AIBN (0.50 g). The resulting solution was clear. Then, the reaction mixture was heated to 65°C while degassing with nitrogen. After a short time the solution became cloudy, indicating that the polymerization reaction was in progress. After 2 hours the mixture was already very thick, so 100 mL of isopropanol was added. The reaction was maintained at 65°C for 22 hours, then cooled to room temperature.
过滤所得聚合物,并在漏斗上用异丙醇洗涤,然后立即在400mL蒸馏水中浆化。将混合物搅拌0.5小时。将聚合物浆液过滤并加入600mL蒸馏水,再将混合物搅拌0.5小时。过滤混合物,滤饼在400mL甲醇中浆化。过滤并空气干燥,得到7.26g标题共聚物。The resulting polymer was filtered and washed on the funnel with isopropanol, then immediately slurried in 400 mL of distilled water. The mixture was stirred for 0.5 hours. The polymer slurry was filtered and 600 mL of distilled water was added, and the mixture was stirred for 0.5 hours. The mixture was filtered and the filter cake was slurried in 400 mL of methanol. Filtration and air drying yielded 7.26 g of the title copolymer.
用类似方法通过改变起始单体的比例制备与5%二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体交联的TMAEAC共聚-StyF5(20%)。实施例22.聚(2-(三甲基氯化铵)甲基丙烯酸乙酯),共聚-(2,3,4,5,6-五氟苯TMAEAC co-StyF 5 (20%) crosslinked with 5% divinylbenzene crosslinking comonomer was prepared in a similar manner by varying the ratio of the starting monomers. Example 22. Poly(2-(trimethylammonium chloride)ethyl methacrylate), copoly-(2,3,4,5,6-pentafluorobenzene
乙烯)(TMAEMC共聚-StyF5)的制备Preparation of ethylene) (TMAEMC copolymerization-StyF 5 )
向1000mL三颈园底烧瓶中加入以下物质:2-(三甲基氯化铵)甲基丙烯酸乙酯(TMAEMC)(19.52mL的70%水溶液,13.66g),二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体(1.00g),五氟苯乙烯(9.18g),2-丙醇(150mL)和AIBN(0.40g)。所得溶液是澄清的。然后,将反应混合物加热至70℃,同时用氮气脱气。短时间后溶液开始混浊,表明聚合反应正在进行。1.5小时后混合物已经非常稠,因此加入50mL异丙醇。将反应在70℃保持5小时,然后冷却至室温。To a 1000 mL three necked round bottom flask was added the following: 2-(Trimethylammonium chloride) ethyl methacrylate (TMAEMC) (19.52 mL of a 70% solution in water, 13.66 g), divinylbenzene cross-linked copolymer solid (1.00g), pentafluorostyrene (9.18g), 2-propanol (150mL) and AIBN (0.40g). The resulting solution was clear. Then, the reaction mixture was heated to 70°C while degassing with nitrogen. After a short time the solution became cloudy, indicating that the polymerization reaction was in progress. After 1.5 hours the mixture was already very thick, so 50 mL of isopropanol was added. The reaction was maintained at 70°C for 5 hours and then cooled to room temperature.
过滤所得聚合物,并在漏斗上用异丙醇洗涤,然后立即在500mL蒸馏水中浆化。将混合物搅拌0.25小时。将聚合物浆液过滤并加入500mL蒸馏水,再将混合物搅拌0.25小时。聚合物再用水浆化一次。过滤混合物,滤饼在每次300mL的甲醇中浆化三次。过滤并空气干燥,得到1.26g标题共聚物。The resulting polymer was filtered and washed on the funnel with isopropanol, then immediately slurried in 500 mL of distilled water. The mixture was stirred for 0.25 hours. The polymer slurry was filtered and 500 mL of distilled water was added, and the mixture was stirred for 0.25 hours. The polymer was slurried once more with water. The mixture was filtered, and the filter cake was slurried three times in 300 mL portions of methanol. Filtration and air drying afforded 1.26 g of the title copolymer.
用类似方法通过改变起始单体的比例制备与4%二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体交联的TMAEMC共聚-StyF5(24%)以及与4%二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体交联的TMAEMC共聚-StyF5(39%)。实施例23.聚(吖丙啶)的制备TMAEMC copoly-StyF 5 (24%) cross-linked with 4% divinylbenzene cross-linking comonomer and cross-linked with 4% divinylbenzene cross-linking comonomer were prepared in a similar manner by changing the ratio of starting monomers Linked TMAEMC co-StyF 5 (39%). Example 23. Preparation of poly(ethyleneimine)
将聚吖丙啶(120g的50%水溶液;Scientific Polymer Products)溶解于水(250mL)。滴加表氯醇(22.1mL)。将溶液加热至60℃4小时。之后,形成胶体。移出胶体,用水(1.5L)调合,并滤出固体,用水(3L)漂洗三次和用异丙醇(3L)漂洗两次。所得胶体在真空炉中干燥,得到81.2g标题聚合物。实施例24.聚(甲基丙烯酰氨基丙基-3-(三甲基氯化铵)),共聚-(2-(三甲基Polyethyleneimine (120 g of a 50% aqueous solution; Scientific Polymer Products) was dissolved in water (250 mL). Epichlorohydrin (22.1 mL) was added dropwise. The solution was heated to 60°C for 4 hours. Afterwards, a colloid is formed. The gel was removed, taken up with water (1.5 L), and the solid was filtered off, rinsed three times with water (3 L) and twice with isopropanol (3 L). The resulting gel was dried in a vacuum oven to yield 81.2 g of the title polymer. Example 24. Poly(methacrylamidopropyl-3-(trimethylammonium chloride)), copoly-(2-(trimethylammonium chloride)
氯化铵)甲基丙烯酸乙酯),共聚-(2,3,4,5,6-五氟苯乙烯) Ammonium chloride) ethyl methacrylate), copolymer-(2,3,4,5,6-pentafluorostyrene)
(MAPTAC共聚-TMAEMC共聚-StyF5)的制备Preparation of (MAPTAC Copolymerization-TMAEMC Copolymerization-StyF 5 )
向1000mL三颈园底烧瓶中加入以下物质:甲基丙烯酰氨基丙基-3-(三甲基氯化铵)(MAPTAC)(10.00g的50%水溶液,5.00g),2-(三甲基氯化铵)甲基丙烯酸乙酯(TMAEMC)(5.71g的70%水溶液,4.00g),二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体(1.00g),五氟苯乙烯(10.00g),2-丙醇(1 50mL)和AIBN(0.50g)。所得溶液是澄清的。然后,将反应混合物加热至70℃,同时用氮气脱气。短时间后溶液开始混浊,表明聚合反应正在进行。将反应在70℃保持24小时,然后冷却至室温。To a 1000 mL three-neck round bottom flask was added the following: methacrylamidopropyl-3-(trimethylammonium chloride) (MAPTAC) (10.00 g in 50% water, 5.00 g), 2-(trimethylammonium chloride) ammonium chloride) ethyl methacrylate (TMAEMC) (5.71 g in 70% aqueous solution, 4.00 g), divinylbenzene crosslinking comonomer (1.00 g), pentafluorostyrene (10.00 g), 2- Propanol (1 50mL) and AIBN (0.50g). The resulting solution was clear. Then, the reaction mixture was heated to 70°C while degassing with nitrogen. After a short time the solution became cloudy, indicating that the polymerization reaction was in progress. The reaction was maintained at 70°C for 24 hours and then cooled to room temperature.
过滤所得聚合物,并在漏斗上用异丙醇洗涤,然后立即在500mL甲醇中浆化。将混合物搅拌0.25小时。过滤浆状聚合物,然后每次用300mL水浆化,共三次。将最后一次浆状聚合物搅合5分钟。过滤混合物,然后每次用300mL甲醇浆化滤饼,共两次。过滤并真空干燥,得到9.74g共聚物。实施例25.聚(2-(三甲基氯化铵)丙烯酸乙酯),共聚-(2-(三甲基氯化铵)甲The resulting polymer was filtered and washed on the funnel with isopropanol, then immediately slurried in 500 mL of methanol. The mixture was stirred for 0.25 hours. The slurry polymer was filtered and slurried three times with 300 mL of water each time. The final slurry of polymer was blended for 5 minutes. The mixture was filtered, and the filter cake was slurried twice with 300 mL of methanol each. Filtration and vacuum drying yielded 9.74 g of copolymer. Example 25. Poly(2-(trimethylammonium chloride) ethyl acrylate), copoly-(2-(trimethylammonium chloride) formazan
基丙烯酸乙酯),共聚-苯乙烯(TMAEAC共聚-TMAEMC共聚Ethyl Acrylate), Co-Styrene (TMAEAC Co-TMAEMC Co-polymer
-Sty)的制备-Sty) preparation
向1000mL三颈园底烧瓶中加入以下物质:2-(三甲基氯化铵)丙烯酸乙酯(TMAEAC)(6.00g的50%水溶液,3.00g),2-(三甲基氯化铵)甲基丙烯酸乙酯(TMAEMC)(4.29g的70%水溶液,3.00g),二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体(1.00g),苯乙烯(13.00g),2-丙醇(150mL)和AIBN(0.50g)。所得溶液是澄清的。然后,将反应混合物加热至70℃,同时用氮气脱气。短时间后溶液开始混浊,表明聚合反应正在进行。将反应在70℃保持24小时,然后冷却至室温。To a 1000 mL three necked round bottom flask was added the following: 2-(Trimethylammonium chloride) ethyl acrylate (TMAEAC) (6.00 g of a 50% solution in water, 3.00 g), 2-(Trimethylammonium chloride) Ethyl methacrylate (TMAEMC) (4.29 g in 70% water, 3.00 g), divinylbenzene crosslinking comonomer (1.00 g), styrene (13.00 g), 2-propanol (150 mL) and AIBN (0.50g). The resulting solution was clear. Then, the reaction mixture was heated to 70°C while degassing with nitrogen. After a short time the solution became cloudy, indicating that the polymerization reaction was in progress. The reaction was maintained at 70°C for 24 hours and then cooled to room temperature.
滗析所得聚合物,然后立即在500mL甲醇中浆化。将混合物搅拌0.5小时。过滤浆状聚合物并加入500mL蒸馏水。将混合物搅拌0.5小时并混合10分钟。将混合物沉降并滗析水。重复水浆化两次,每次用400mL甲醇浆化滗析剩余物,并每次沉降和滗析。真空干燥得到8.03g标题共聚物。实施例26.聚(甲基丙烯酰氨基丙基-3-(三甲基氯化铵)),共聚-(2-(三甲基The resulting polymer was decanted and immediately slurried in 500 mL of methanol. The mixture was stirred for 0.5 hours. The slurry polymer was filtered and 500 mL of distilled water was added. The mixture was stirred for 0.5 hour and mixed for 10 minutes. The mixture was settled and the water was decanted. Repeat the water slurrying twice, each time with 400 mL of methanol to decant the residue, and each time to settle and decant. Drying in vacuo yielded 8.03 g of the title copolymer. Example 26. Poly(methacrylamidopropyl-3-(trimethylammonium chloride)), copoly-(2-(trimethylammonium chloride)
氯化铵)丙烯酸乙酯),共聚-(2,3,4,5,6-五氟苯乙烯)(MAPTAC Ammonium chloride) ethyl acrylate), copolymer-(2,3,4,5,6-pentafluorostyrene) (MAPTAC
共聚-TMAEAC共聚-StyF5)的制备Preparation of Co-TMAEAC Co-StyF 5 )
向1000mL三颈园底烧瓶中加入以下物质:甲基丙烯酸乙酯-3-(三甲基氯化铵)(MAPTA)(8.00g,50%水溶液,4.00g),2-(三甲基氯化铵)丙烯酸乙酯(TMAEMA)(6.00g的50%水溶液,3.00g),二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体(1.00g),五氟苯乙烯(12.00g),2-丙醇(150mL)和AIBN(0.50g)。所得溶液是澄清的。然后,将反应混合物加热至70℃,同时用氮气脱气。短时间后溶液开始混浊,表明聚合反应正在进行。将反应在70℃保持24小时,然后冷却至室温。To a 1000 mL three-neck round bottom flask was added the following: ethyl methacrylate-3-(trimethylammonium chloride) (MAPTA) (8.00 g, 50% in water, 4.00 g), 2-(trimethylammonium chloride Ammonium chloride) ethyl acrylate (TMAEMA) (6.00 g in 50% aqueous solution, 3.00 g), divinylbenzene crosslinking comonomer (1.00 g), pentafluorostyrene (12.00 g), 2-propanol (150 mL ) and AIBN (0.50 g). The resulting solution was clear. Then, the reaction mixture was heated to 70°C while degassing with nitrogen. After a short time the solution became cloudy, indicating that the polymerization reaction was in progress. The reaction was maintained at 70°C for 24 hours and then cooled to room temperature.
过滤所得聚合物,并在漏斗上用异丙醇洗涤,然后立即在400mL甲醇中浆化。将混合物搅拌0.5。将浆状聚合物过滤然后每次用250mL水浆化,共两次。将最后一次浆状聚合物混合5分钟。过滤混合物,然后每次用250mL甲醇浆化,共两次。真空干燥滤液得到7.80g共聚物。实施例27.聚(2-(三甲基氯化铵)丙烯酸乙酯),共聚-(2-(三甲基氯化铵)甲The resulting polymer was filtered and washed on the funnel with isopropanol, then immediately slurried in 400 mL of methanol. The mixture was stirred for 0.5. The slurry polymer was filtered and slurried twice with 250 mL of water each time. The final slurry of polymer was mixed for 5 minutes. The mixture was filtered and then slurried twice with 250 mL of methanol each. The filtrate was dried in vacuo to yield 7.80 g of copolymer. Example 27. Poly(2-(trimethylammonium chloride) ethyl acrylate), copoly-(2-(trimethylammonium chloride) formazan
基丙烯酸乙酯),共聚-(2,3,4,5,6-五氟苯乙烯)(TMAEAC共聚ethyl acrylate), copolymer-(2,3,4,5,6-pentafluorostyrene) (TMAEAC copolymer
-TMAEMC共聚-Sty F5)的制备-TMAEMC copolymerization-Sty F 5 ) Preparation
向1000mL三颈园底烧瓶中加入以下物质:2-(三甲基氯化铵)丙烯酸乙酯(TMAEAC)(6.00g的50%水溶液,3.00g),2-(三甲基氯化铵)甲基丙烯酸乙酯(TMAEMC)(4.29g的,70%水溶液,3.00g),二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体(1.00g),五氟苯乙烯(13.00g),2-丙醇(150mL)和AIBN(0.50g)。所得溶液是澄清的。然后,将反应混合物加热至70℃,同时用氮气脱气。短时间后溶液开始混浊,表明聚合反应正在进行。将反应在70℃保持24小时,然后冷却至室温。To a 1000 mL three necked round bottom flask was added the following: 2-(Trimethylammonium chloride) ethyl acrylate (TMAEAC) (6.00 g of a 50% solution in water, 3.00 g), 2-(Trimethylammonium chloride) Ethyl methacrylate (TMAEMC) (4.29 g, 70% aqueous solution, 3.00 g), divinylbenzene crosslinking comonomer (1.00 g), pentafluorostyrene (13.00 g), 2-propanol (150 mL ) and AIBN (0.50 g). The resulting solution was clear. Then, the reaction mixture was heated to 70°C while degassing with nitrogen. After a short time the solution became cloudy, indicating that the polymerization reaction was in progress. The reaction was maintained at 70°C for 24 hours and then cooled to room temperature.
滗析所得聚合物,然后立即在400mL甲醇中浆化。将混合物搅拌0.5小时。过滤浆状聚合物,然后每次用200mL水浆化,共两次。将第二次浆状聚合物混合5分钟。过滤混合物并每次用200mL甲醇浆化,共两次。真空干燥得到6.87g标题共聚物。实施例28.聚(甲基丙烯酰氨基丙基三甲基氯化铵)共聚(4-乙烯基联苯)The resulting polymer was decanted and immediately slurried in 400 mL of methanol. The mixture was stirred for 0.5 hours. The slurry polymer was filtered and then slurried twice with 200 mL of water each time. The second slurry polymer was mixed for 5 minutes. The mixture was filtered and slurried twice with 200 mL of methanol each. Drying in vacuo yielded 6.87 g of the title copolymer. Example 28. Poly(methacrylamidopropyltrimethylammonium chloride)copoly(4-vinylbiphenyl)
(MAPTAC共聚-VBPh)的制备Preparation of (MAPTAC copolymerization-VBPh)
向1000mL三颈园底烧瓶中加入以下物质:甲基丙烯酰氨基丙基三甲基氯化铵(MAPTAC)(10.49g的50%水溶液,0.0475mol),4-乙烯基联苯(VBPh)(9.01g,0.050mol),二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体(1.47g),2-丙醇(150mL),聚合引发剂AIBN(0.25g)。所得混合物含有不溶的VBPh(加热后溶解)。然后,将反应混合物加热至70℃,同时用氮气脱气。短时间后溶液开始混浊,表明聚合反应正在进行。将反应在70℃保持24小时小时,然后冷却至室温。To a 1000 mL three-neck round bottom flask was added the following: methacrylamidopropyltrimethylammonium chloride (MAPTAC) (10.49 g of a 50% aqueous solution, 0.0475 mol), 4-vinylbiphenyl (VBPh) ( 9.01 g, 0.050 mol), divinylbenzene crosslinking comonomer (1.47 g), 2-propanol (150 mL), polymerization initiator AIBN (0.25 g). The resulting mixture contained insoluble VBPh (dissolved upon heating). Then, the reaction mixture was heated to 70°C while degassing with nitrogen. After a short time the solution became cloudy, indicating that the polymerization reaction was in progress. The reaction was maintained at 70°C for 24 hours and then cooled to room temperature.
过滤所得聚合物,并在漏斗上用异丙醇洗涤,然后立即在200mL甲醇中浆化,接着搅拌1小时。过滤浆状聚合物,然后重复甲醇浆化步骤。接着每次用200mL水浆化聚合物,共两次。过滤所得混合物然后将滤饼然后每次用200mL甲醇浆化,共两次。过滤所得混合物并真空干燥得到9.59g共聚物。实施例29.聚(甲基丙烯酰氨基丙基三甲基氯化铵)共聚(4-乙烯基联苯)The resulting polymer was filtered and washed on the funnel with isopropanol, then immediately slurried in 200 mL of methanol followed by stirring for 1 hour. The slurry polymer was filtered and the methanol slurrying step was repeated. The polymer was then slurried twice with 200 mL of water each time. The resulting mixture was filtered and the filter cake was then slurried twice with 200 mL each of methanol. The resulting mixture was filtered and dried under vacuum to yield 9.59 g of copolymer. Example 29. Poly(methacrylamidopropyltrimethylammonium chloride)copoly(4-vinylbiphenyl)
(MAPTAC共聚-VA)的制备Preparation of (MAPTAC copolymerization-VA)
向1000mL三颈园底烧瓶中加入以下物质:甲基丙烯酰氨基丙基三甲基氯化铵(MAPTAC)(10.49g的50%水溶液,0.0475mol),4-乙烯基茴香醚(VA)(6.71g,0.050mol),二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体(1.30g),2-丙醇(200mL),聚合引发剂AIBN(0.40g)。然后,将所得澄清溶液加热至70℃,同时用氮气脱气。几小时后溶液开始混浊,表明聚合反应正在进行。将反应在70℃保持36小时,然后冷却至室温。To a 1000 mL three necked round bottom flask was added the following: methacrylamidopropyltrimethylammonium chloride (MAPTAC) (10.49 g of a 50% aqueous solution, 0.0475 mol), 4-vinylanisole (VA) ( 6.71 g, 0.050 mol), divinylbenzene crosslinking comonomer (1.30 g), 2-propanol (200 mL), polymerization initiator AIBN (0.40 g). The resulting clear solution was then heated to 70°C while degassing with nitrogen. After a few hours the solution became cloudy, indicating that polymerization was in progress. The reaction was maintained at 70°C for 36 hours and then cooled to room temperature.
过滤所得聚合物,并在漏斗上用异丙醇洗涤,然后立即在200mL甲醇中浆化,接着搅拌1小时。过滤浆状聚合物。接着每次用200mL水浆化聚合物两次。过滤所得混合物,将滤饼用200mL甲醇浆化,然后用200异丙醇浆化。过滤所得混合物并真空干燥得到5.19g共聚物。实施例30.聚[(N-(4-甲基苯乙烯)-N’-(3-三甲基氯化铵-2-羟基丙基)哌嗪]The resulting polymer was filtered and washed on the funnel with isopropanol, then immediately slurried in 200 mL of methanol followed by stirring for 1 hour. Filter slurry polymer. The polymer was then slurried twice with 200 mL each of water. The resulting mixture was filtered and the filter cake was slurried with 200 mL of methanol followed by 200 mL of isopropanol. The resulting mixture was filtered and dried under vacuum to yield 5.19 g of copolymer. Example 30. Poly[(N-(4-methylstyrene)-N'-(3-trimethylammonium chloride-2-hydroxypropyl)piperazine]
的制备Preparation of
第一步是制备4-(哌嗪基甲基)苯乙烯的反应。The first step is the reaction to prepare 4-(piperazinylmethyl)styrene.
向500mL烧瓶中加入乙烯基苄基氯(7.63g,0.050mol),哌嗪(8.61g,0.100mol)和异丙醇(50mL)。将所得混合物在70℃加热45分钟,然后慢慢冷却至室温以便形成结晶物质的浆。将该浆状物放在冰箱中约3小时,然后过滤。将固体哌嗪盐酸盐真空干燥,然后称重(5.55g)并弃去。在旋转蒸发器上将母液浓缩至约25mL并加入乙酸乙酯(50mL)。将所得混合物放在冰箱中约10分钟,然后将第二次得到的哌嗪盐酸盐过滤并弃去。在旋转蒸发器上蒸发母液至干得到10.35g粗4-(哌嗪甲基)苯乙烯,将其用于制备以下N-(4-甲基苯乙烯)-N’-(3-三甲基氯化铵-2-羟基丙基)哌嗪,并且无需进一步纯化。向500mL烧瓶中加入4-(哌嗪甲基)苯乙烯(10.35g,约0.45mol),缩水甘油基三甲基氯化铵(7.58g,0.045mol)和异丙醇(50mL)。将所得混合物加热至60℃并搅拌20小时,然后冷却至室温,并用于以下聚合反应且无需进一步纯化。To a 500 mL flask was added vinylbenzyl chloride (7.63 g, 0.050 mol), piperazine (8.61 g, 0.100 mol) and isopropanol (50 mL). The resulting mixture was heated at 70°C for 45 minutes, then slowly cooled to room temperature to form a slurry of crystalline material. The slurry was placed in the refrigerator for about 3 hours, then filtered. The solid piperazine hydrochloride was dried in vacuo, then weighed (5.55 g) and discarded. The mother liquor was concentrated to about 25 mL on a rotary evaporator and ethyl acetate (50 mL) was added. The resulting mixture was placed in the refrigerator for about 10 minutes, then the piperazine hydrochloride obtained a second time was filtered and discarded. Evaporation of the mother liquor to dryness on a rotary evaporator yielded 10.35 g of crude 4-(piperazinemethyl)styrene, which was used to prepare the following N-(4-methylstyrene)-N'-(3-trimethyl Ammonium chloride-2-hydroxypropyl)piperazine and without further purification. To a 500 mL flask was added 4-(piperazinemethyl)styrene (10.35 g, about 0.45 mol), glycidyltrimethylammonium chloride (7.58 g, 0.045 mol) and isopropanol (50 mL). The resulting mixture was heated to 60°C and stirred for 20 hours, then cooled to room temperature and used in the following polymerization without further purification.
将二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体(0.93g)加到0.40mol N-(4-甲基苯乙烯)-N’-(3-三甲基氯化铵-2-羟基丙基)哌嗪中。用氮气将所得溶液脱气,然后加入聚合引发剂AIBN(0.20g)。将温度升至70℃继续用氮气脱气并放置3小时,这时大量的交联聚合物沉淀。然后将混合物冷却至40℃并过滤。Add divinylbenzene crosslinking comonomer (0.93 g) to 0.40 mol N-(4-methylstyrene)-N'-(3-trimethylammonium chloride-2-hydroxypropyl)piperazine middle. The resulting solution was degassed with nitrogen, and then AIBN (0.20 g), a polymerization initiator, was added. The temperature was raised to 70°C and degassed with nitrogen was continued for 3 hours, at which time a large amount of cross-linked polymer precipitated. The mixture was then cooled to 40°C and filtered.
过滤所得聚合物,并在漏斗上用异丙醇洗涤,然后立即在200mL甲醇中浆化,接着搅拌1小时。过滤浆状聚合物,然后重复甲醇浆化步骤。每次用200mL水浆化聚合物,共两次。接着过滤,将滤饼每次用200mL甲醇浆化,共两次,真空干燥得到7.90g共聚物。实施例31.聚(N-(4-甲基苯乙烯)-N’-(3-三甲基氯化铵-2-羟基丙基)哌嗪,The resulting polymer was filtered and washed on the funnel with isopropanol, then immediately slurried in 200 mL of methanol followed by stirring for 1 hour. The slurry polymer was filtered and the methanol slurrying step was repeated. The polymer was slurried twice with 200 mL of water each time. Then filtered, the filter cake was slurried twice with 200 mL of methanol each time, and vacuum-dried to obtain 7.90 g of copolymer. Example 31. Poly(N-(4-methylstyrene)-N'-(3-trimethylammonium chloride-2-hydroxypropyl)piperazine,
共聚苯乙烯的制备 Preparation of Copolystyrene
向0.022mol N-(4-甲基苯乙烯)-N’-(3-三甲基氯化铵-2-羟基丙基)哌嗪(按实施例30所述制备)中加入苯乙烯共聚单体(2.29g,0.022mol)和二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体(0.50g,0.004mol)。用氮气将所得溶液脱气,然后加入聚合引发剂AIBN(0.3g)。将温度升至70℃,继续用氮气脱气并放置4小时,这时大量的交联聚合物沉淀。然后添加25mL异丙醇并继续加热19小时。之后,将混合物冷却至室温并过滤,得到固体聚合物。To 0.022 mol of N-(4-methylstyrene)-N'-(3-trimethylammonium chloride-2-hydroxypropyl)piperazine (prepared as described in Example 30) was added styrene copolymerized monomer monomer (2.29 g, 0.022 mol) and divinylbenzene crosslinking comonomer (0.50 g, 0.004 mol). The resulting solution was degassed with nitrogen, and then AIBN (0.3 g), a polymerization initiator, was added. The temperature was raised to 70°C, degassing with nitrogen was continued and allowed to stand for 4 hours, at which time a large amount of cross-linked polymer precipitated. Then 25 mL of isopropanol was added and heating was continued for 19 hours. Afterwards, the mixture was cooled to room temperature and filtered to obtain a solid polymer.
过滤所得聚合物,并在漏斗上用异丙醇洗涤,然后立即在200mL甲醇中浆化。接着,将混合物搅拌0.5小时。过滤浆状聚合物,每次用250mL水浆化聚合物,共两次。过滤混合物,滤饼在200mL甲醇中浆化,过滤,然后在200mL异丙醇中浆化。过滤并真空干燥,得到4.98g共聚物。The resulting polymer was filtered and washed on the funnel with isopropanol, then immediately slurried in 200 mL of methanol. Next, the mixture was stirred for 0.5 hours. Filter the slurry polymer, and slurry the polymer with 250 mL of water each time, twice in total. The mixture was filtered, and the filter cake was slurried in 200 mL of methanol, filtered, and then slurried in 200 mL of isopropanol. Filtration and vacuum drying yielded 4.98 g of copolymer.
含有2∶1摩尔比的苯乙烯:季铵单体也被用类似方法制备。实施例32.聚(N-(3-三甲基氯化铵-2-羟基丙基)-4-氨基苯乙烯的制备A styrene:quaternary ammonium monomer containing a 2:1 molar ratio was similarly prepared. Example 32. Preparation of poly(N-(3-trimethylammonium chloride-2-hydroxypropyl)-4-aminostyrene
第一步是按下面所述制备4-氨基甲基苯乙烯。The first step is to prepare 4-aminomethylstyrene as described below.
向250mL烧瓶中加入乙烯基苄基氯(7.63g,0.050mol),浓氨水(9.8mL)和异丙醇(40mL)。将混合物搅拌1星期,这时大量结晶物质(氯化铵)沉淀下来。滤出固体并用异丙醇洗涤。母液在旋转蒸发器上蒸发直到闻不到氨味。加入异丙醇(50mL),然后将混合物冷冻几小时。冷冻之后,已经沉淀的4-氨基甲基苯乙烯氯化铵被滤出,得到4-氨基甲基苯乙烯,无需进一步纯化即可使用。To a 250 mL flask was added vinylbenzyl chloride (7.63 g, 0.050 mol), concentrated ammonia (9.8 mL) and isopropanol (40 mL). The mixture was stirred for 1 week, at which time a large amount of crystalline material (ammonium chloride) precipitated. The solid was filtered off and washed with isopropanol. The mother liquor was evaporated on a rotary evaporator until there was no smell of ammonia. Isopropanol (50 mL) was added and the mixture was refrigerated for several hours. After freezing, the 4-aminomethylstyrene ammonium chloride which had precipitated was filtered off to give 4-aminomethylstyrene which was used without further purification.
在500mL烧瓶中加入4-氨基甲基苯乙烯(0.050mol),缩水甘油基三甲基氯化铵(7.62g,0.050mol)和水(约2mL)形成溶液,并加入二乙烯基交联共聚单体(0.98g)。将所得溶液在70℃加热5小时,之后,加入少量水(约5-10mL)以溶解一些沉淀的盐。加入聚合引发剂AIBN(0.20g),同时用氮气给溶液脱气。反应混合物这时已变得非常稠,需要添加异丙醇使聚合物可以搅拌。Add 4-aminomethylstyrene (0.050mol), glycidyltrimethylammonium chloride (7.62g, 0.050mol) and water (about 2mL) into a 500mL flask to form a solution, and add divinyl cross-linking copolymer Monomer (0.98 g). The resulting solution was heated at 70°C for 5 hours, after which a small amount of water (about 5-10 mL) was added to dissolve some of the precipitated salts. The polymerization initiator AIBN (0.20 g) was added while degassing the solution with nitrogen. The reaction mixture had become very thick by this point and it was necessary to add isopropanol to make the polymer stirrable.
在70℃搅拌约16小时后,将混合物冷却至室温并过滤。所得聚合物在漏斗上用甲醇洗涤,然后立即在200mL甲醇中浆化。接着,将所得混合物搅拌1小时。过滤浆状聚合物,用甲醇再重复一次浆化过程。然后,聚合物用每次200mL甲醇浆化,共两次。过滤混合物,滤饼在200mL甲醇中浆化。过滤并真空干燥,得到8.68g聚合物。实施例33.用1-碘辛烷烷基化剂将与亚甲基双甲基丙烯酰胺交联的聚(二After stirring at 70°C for about 16 hours, the mixture was cooled to room temperature and filtered. The resulting polymer was washed with methanol on the funnel and immediately slurried in 200 mL of methanol. Next, the resulting mixture was stirred for 1 hour. The slurry polymer was filtered and the slurrying process was repeated one more time with methanol. The polymer was then slurried with two 200 mL portions of methanol. The mixture was filtered and the filter cake was slurried in 200 mL of methanol. Filtration and vacuum drying yielded 8.68 g of polymer. Example 33. Poly(bismethacrylamide) crosslinked with 1-iodooctane alkylating agent
甲氨基丙基甲基丙烯酰胺)烷基化 Alkylation of methylaminopropyl methacrylamide
用实施例5所述方法制备的与亚甲基双甲基丙烯酰胺交联的聚(二甲氨基丙基甲基丙烯酰胺)(1.0g)悬浮在甲醇(100mL)中,并加入氢氧化钠(0.2g)。搅拌15分钟后,加入1-碘辛烷(1.92mL),并将混合物在60℃搅拌20小时。然后,冷却混合物,滤出固体。通过将固体悬浮在异丙醇(500mL)中来洗涤它。之后,搅拌1小时并通过过滤收集。用氯化钠水溶液(500mL的1M溶液)重复洗涤过程两次,用水(500mL)洗涤,共两次,用异丙醇(500mL)洗涤一次。在50℃真空炉中干燥24小时,得到0.1g烷基化产品。实施例34.用1-碘辛烷烷基化剂将与亚甲基双甲基丙烯酰胺交联的聚(二Poly(dimethylaminopropylmethacrylamide) (1.0 g) cross-linked with methylenebismethacrylamide prepared by the method described in Example 5 was suspended in methanol (100 mL), and sodium hydroxide was added (0.2g). After stirring for 15 minutes, 1-iodooctane (1.92 mL) was added, and the mixture was stirred at 60°C for 20 hrs. Then, the mixture was cooled and the solid was filtered off. The solid was washed by suspending it in isopropanol (500 mL). Afterwards, it was stirred for 1 hour and collected by filtration. The washing process was repeated twice with aqueous sodium chloride (500 mL of a 1M solution), twice with water (500 mL), and once with isopropanol (500 mL). Drying in a vacuum oven at 50°C for 24 hours yielded 0.1 g of the alkylated product. Example 34. Poly(bismethacrylamide) crosslinked with 1-iodooctane alkylating agent
甲氨基丙基丙烯酰胺)烷基化 Methylaminopropyl acrylamide) Alkylation
根据实施例33所述方法将用实施例4所述方法制备的与亚甲基双甲基丙烯酰胺交联的聚(二甲氨基丙基丙烯酰胺)(10g)烷基化,得到2.95g烷基化产品。实施例35.聚(2-(甲基丙烯酰氨基)乙基三甲基碘化铵)共聚-苯乙烯的制Poly(dimethylaminopropylacrylamide) (10 g) prepared by the method described in Example 4 and crosslinked with methylenebismethacrylamide (10 g) was alkylated according to the method described in Example 33 to obtain 2.95 g of alkanes. base products. Example 35. Preparation of poly(2-(methacrylamido)ethyltrimethylammonium iodide)copoly-styrene
备Prepare
第一步是按下面所述制备2-(N’,N’-二甲基氨基)-N-乙基甲基丙烯酰胺盐酸盐。The first step is to prepare 2-(N',N'-dimethylamino)-N-ethylmethacrylamide hydrochloride as described below.
向1000mL烧瓶中加入甲基丙烯酰氯(52.3g,0.5mol)和四氢呋喃(300mL)。将溶液冷却至10℃以下,然后滴加N,N-二甲基氨基乙胺(30.5g,0.35mol)的四氢呋喃(100mL),同时保持温度在8-10℃。添加完成后过滤混合物,用冷四氢呋喃洗涤,真空干燥,得到65.69g 2-(N’,N’-二甲基氨基)-N-乙基甲基丙烯酰胺盐酸盐。To a 1000 mL flask was added methacryloyl chloride (52.3 g, 0.5 mol) and tetrahydrofuran (300 mL). The solution was cooled below 10°C, then N,N-dimethylaminoethylamine (30.5 g, 0.35 mol) in tetrahydrofuran (100 mL) was added dropwise while maintaining the temperature at 8-10°C. After the addition was complete, the mixture was filtered, washed with cold tetrahydrofuran, and dried in vacuo to obtain 65.69 g of 2-(N',N'-dimethylamino)-N-ethylmethacrylamide hydrochloride.
下一步是如下所述制备2-(甲基丙烯酰氨基)乙基三甲基碘化铵。The next step is to prepare 2-(methacrylamido)ethyltrimethylammonium iodide as described below.
将氢氧化钾(15.4g,0.24mol)和甲醇(240mL)放入500mL烧瓶,然后将混合物充分搅拌使氢氧化钾完全溶解。在溶液中加入2-(N’,N’-二甲基氨基)-N-乙基甲基丙烯酰胺盐酸盐(46.35g,0.24mol),并将所得混合物搅拌0.5小时。过滤混合物以除去氯化钾。滤液在旋转蒸发器中浓缩。将异丙醇(400mL)和甲基碘(18.7mL,42.6g,0.30mol)加到浓缩的滤液中,然后将混合物在室温搅拌过夜。第二天早晨,滤出的固体产物,用异丙醇洗涤,真空干燥,得到61.08g 2-(甲基丙烯酰氨基)乙基三甲基碘化铵,为白色晶状固体。Potassium hydroxide (15.4 g, 0.24 mol) and methanol (240 mL) were put into a 500 mL flask, and the mixture was stirred well to completely dissolve potassium hydroxide. 2-(N',N'-dimethylamino)-N-ethylmethacrylamide hydrochloride (46.35 g, 0.24 mol) was added to the solution, and the resulting mixture was stirred for 0.5 hours. The mixture was filtered to remove potassium chloride. The filtrate was concentrated on a rotary evaporator. Isopropanol (400 mL) and methyl iodide (18.7 mL, 42.6 g, 0.30 mol) were added to the concentrated filtrate, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight. The next morning, the solid product was filtered, washed with isopropanol, and dried in vacuo to obtain 61.08 g of 2-(methacrylamido)ethyltrimethylammonium iodide as a white crystalline solid.
接着,将2-(甲基丙烯酰氨基)乙基三甲基碘化铵(12.24g,0.050mol),苯乙烯(5.2g,0.050mol),二乙烯基苯交联共聚单体(0.65g,0.005mol),异丙醇(150mL),水(20mL),和聚合引发剂AIBN(0.4g)加到1000mL烧瓶中。用氮气给所得溶液脱气,同时加热至70℃。然后,将溶液在70℃及氮气下搅拌24小时,之后,将其冷却至室温。这时,滗析溶剂,然后将200mL甲醇加到烧瓶中形成浆液,并搅拌过夜。过滤产物,然后加到搅拌器中与500mL水混合。搅合所得混合物15分钟,然后过滤。依次用水(200mL)和甲醇(200mL)洗涤留下的固体物质。过滤并真空干燥,得到3.22g标题聚合物。聚合物试验A.人造肠液的制备试验方法1Next, 2-(methacrylamido)ethyltrimethylammonium iodide (12.24g, 0.050mol), styrene (5.2g, 0.050mol), divinylbenzene crosslinking comonomer (0.65g , 0.005mol), isopropanol (150mL), water (20mL), and polymerization initiator AIBN (0.4g) were added to a 1000mL flask. The resulting solution was degassed with nitrogen while heating to 70°C. The solution was then stirred at 70°C under nitrogen for 24 hours, after which it was cooled to room temperature. At this point, the solvent was decanted, then 200 mL of methanol was added to the flask to form a slurry and stirred overnight. The product was filtered, then added to a blender and mixed with 500 mL of water. The resulting mixture was stirred for 15 minutes, then filtered. The remaining solid material was washed successively with water (200 mL) and methanol (200 mL). Filtration and vacuum drying afforded 3.22 g of the title polymer. Polymer Test A. Preparation of Artificial Intestinal Fluid Test Method 1
将碳酸钠(1.27g)和氯化钠(1.87g)溶解于400mL蒸馏水中。向此溶液加入纯胆汁酸混合物,该混合物由牛磺胆酸(0.138g,0.24mmol),甘氨胆酸(0.292g,0.60mmol),甘氨脱氧胆酸(0.085g,0.18mmol)和甘氨鹅脱氧胆酸(glycochenodeoxycholic)(0.085g,0.18mmol)组成。用乙酸将溶液的pH调至7.20。该溶液被用于多种聚合物的试验。该溶液中全部胆汁盐的浓度为3毫摩尔,该浓度近似等于十二指肠中正常体液的浓度。Sodium carbonate (1.27 g) and sodium chloride (1.87 g) were dissolved in 400 mL of distilled water. To this solution was added a pure bile acid mixture consisting of taurocholic acid (0.138g, 0.24mmol), glycocholic acid (0.292g, 0.60mmol), glycodeoxycholic acid (0.085g, 0.18mmol) and glycine Composition of glycochenodeoxycholic acid (0.085g, 0.18mmol). The pH of the solution was adjusted to 7.20 with acetic acid. This solution was used for testing various polymers. The concentration of total bile salts in this solution is 3 millimolar, which is approximately equal to that of normal body fluid in the duodenum.
聚合物试验如下。The polymer tests were as follows.
在40mL离心管中加入0.25g聚合物和上文制备的20mL人造小肠液。将混合物在保持于37℃的水浴中搅拌3小时。将混合物离心,并过滤有点儿混浊的上清液。通过用3a-羟基甾族脱氢酶进行酶测定来分析滤液的总3-羟基甾族化合物含量(如下所述)。试验方法2Add 0.25 g of the polymer and 20 mL of the artificial small intestine fluid prepared above into a 40 mL centrifuge tube. The mixture was stirred for 3 hours in a water bath maintained at 37°C. The mixture was centrifuged and the slightly cloudy supernatant was filtered. The filtrates were analyzed for total 3-hydroxysteroid content by enzymatic assay with 3a-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (described below). Test method 2
将碳酸钠(1.27g)和氯化钠(1.87g)溶解于400mL蒸馏水中。在此溶液中加入甘氨胆酸(1.95g,4.0mmol)或甘氨鹅脱氧胆酸(1.89g,4.0mmol),制成10mM溶液。用乙酸将溶液的pH调至6.8。这些储备溶液被用于多种聚合物的试验。Sodium carbonate (1.27 g) and sodium chloride (1.87 g) were dissolved in 400 mL of distilled water. Glycocholic acid (1.95 g, 4.0 mmol) or glycochenodeoxycholic acid (1.89 g, 4.0 mmol) was added to this solution to make a 10 mM solution. The pH of the solution was adjusted to 6.8 with acetic acid. These stock solutions were used for testing of various polymers.
聚合物试验如下。The polymer tests were as follows.
在14mL离心管中加入10mg聚合物和从10mM储液(制备如上)制备的,浓度为0.1-10mM的10mL胆汁盐溶液,以及适量无胆汁盐缓冲液。将混合物在保持于37℃的水浴中搅拌3小时。过滤混合物。通过用3α-羟基甾族脱氢酶进行酶测定来分析滤液的总3-羟基甾族化合物含量(如下所述)。Into a 14 mL centrifuge tube was added 10 mg of polymer and 10 mL of bile salt solution prepared from the 10 mM stock solution (prepared as above) at a concentration of 0.1-10 mM, and appropriate amount of bile salt-free buffer. The mixture was stirred for 3 hours in a water bath maintained at 37°C. Filter the mixture. Filtrates were analyzed for total 3-hydroxysteroid content by enzymatic assay with 3α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (described below).
总胆汁盐含量的酶测定Enzymatic determination of total bile salt content
制备四种储液。Four stock solutions were prepared.
溶液1:Tris-HCl缓冲液,含0.133M Tris,0.666mM EDTA,Solution 1: Tris-HCl buffer containing 0.133M Tris, 0.666mM EDTA,
pH9.5。 pH9.5.
溶液2:肼水合物溶液,含1M pH为9.5的肼水合物。Solution 2: Hydrazine hydrate solution, containing 1M hydrazine hydrate at pH 9.5.
溶液3:NAD+溶液,含7mM NAD+,pH7.0。Solution 3: NAD+ solution, containing 7mM NAD+, pH 7.0.
溶液4:HSD溶液,含2单位/mL的Tris-HCl缓冲液(0.03M Tris,Solution 4: HSD solution containing 2 units/mL of Tris-HCl buffer (0.03M Tris,
1mM EDTA),pH7.2。1mM EDTA), pH7.2.
在3mL比色杯中加入1.5mL溶液1,1.0mL溶液2,0.3mL溶液3,0.1mL溶液4和0.1mL上述聚合物试验得到的上清液/滤液。将该溶液置于UV-VIS分光光度计并测量其在340nm处的NADH吸收(O.D.)。胆汁盐浓度由上面制备的人造肠液稀释度刻度曲线来测定。Add 1.5 mL of solution 1, 1.0 mL of solution 2, 0.3 mL of solution 3, 0.1 mL of solution 4 and 0.1 mL of the supernatant/filtrate from the above polymer assay in a 3 mL cuvette. The solution was placed in a UV-VIS spectrophotometer and its NADH absorption (O.D.) at 340 nm was measured. Bile salt concentrations were determined from the artificial intestinal fluid dilution calibration curve prepared above.
前面所述的全部聚合物都参加了上述一个或两个试验,并且全部对从人造肠液中除去胆汁盐有效。使用 All of the aforementioned polymers participated in one or both of the above tests and all were effective in removing bile salts from artificial intestinal fluid. use
本发明聚合物可以约1mg/kg/天至约10g/kg/天剂量给患者口服给药。具体的剂量取决于每个患者的情况,如患者的重量和所要除去的胆汁盐的范围。聚合物可以水合物或非水合物形式给药,如果需要,还可以添加调味剂以增加患者的接受能力。另外可以添加的成份还有如人造色素。The polymers of the present invention can be administered orally to a patient at a dose of about 1 mg/kg/day to about 10 g/kg/day. The specific dosage will depend on the circumstances of each patient, such as the patient's weight and the range of bile salts to be removed. The polymers can be administered in hydrated or non-hydrated form and, if desired, flavored to increase patient acceptance. In addition, ingredients that can be added include artificial colors.
适于给药的实例包括丸剂,片剂,囊剂和粉剂(如喷洒在食物上)。这些丸剂,片剂,囊剂,或粉剂可以用有保护能力的物质包衣,该物质保护组合物不受患者胃中的胃酸影响,以获得足够长时间不被分解地抵达患者小肠。该聚合物可以独自或与药物上可接受的载体物质如碳酸镁或乳糖一起给药,或聚合物与磷脂形成微胞。Examples suitable for administration include pills, tablets, sachets and powders (eg sprayed on food). These pills, tablets, sachets, or powders may be coated with a protective substance that protects the composition from gastric acid in the patient's stomach long enough to reach the patient's small intestine without being broken down. The polymer may be administered alone or with a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier material such as magnesium carbonate or lactose, or the polymer forms micelles with phospholipids.
其它具体说明包括在本发明的权利要求中。Other specific descriptions are included in the claims of the present invention.
Claims (29)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US08/258,477 | 1994-06-10 | ||
| US08/258,477 US5624963A (en) | 1993-06-02 | 1994-06-10 | Process for removing bile salts from a patient and compositions therefor |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN1155287A CN1155287A (en) | 1997-07-23 |
| CN1136855C true CN1136855C (en) | 2004-02-04 |
Family
ID=22980711
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNB951935224A Expired - Lifetime CN1136855C (en) | 1994-06-10 | 1995-05-24 | Cross-linked polymers for removing bile salts from patient |
Country Status (15)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US5624963A (en) |
| EP (1) | EP0764177B1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JPH10501264A (en) |
| CN (1) | CN1136855C (en) |
| AT (1) | ATE205508T1 (en) |
| AU (1) | AU694777B2 (en) |
| CA (1) | CA2192592C (en) |
| DE (1) | DE69522687T2 (en) |
| DK (1) | DK0764177T3 (en) |
| ES (1) | ES2164152T3 (en) |
| MX (1) | MX9606172A (en) |
| NZ (1) | NZ285979A (en) |
| PT (1) | PT764177E (en) |
| RU (1) | RU2146266C1 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO1995034588A1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (69)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5607669A (en) * | 1994-06-10 | 1997-03-04 | Geltex Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Amine polymer sequestrant and method of cholesterol depletion |
| US5618530A (en) * | 1994-06-10 | 1997-04-08 | Geltex Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Hydrophobic amine polymer sequestrant and method of cholesterol depletion |
| US5929184A (en) * | 1993-06-02 | 1999-07-27 | Geltex Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Hydrophilic nonamine-containing and amine-containing copolymers and their use as bile acid sequestrants |
| US5703188A (en) * | 1993-06-02 | 1997-12-30 | Geltex Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Process for removing bile salts from a patient and compositions therefor |
| US5900475A (en) * | 1994-06-10 | 1999-05-04 | Geltex Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Hydrophobic sequestrant for cholesterol depletion |
| US6129910A (en) * | 1993-06-02 | 2000-10-10 | Geltex Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Water-insoluble noncrosslinked bile acid sequestrants |
| TW474813B (en) * | 1994-06-10 | 2002-02-01 | Geltex Pharma Inc | Alkylated composition for removing bile salts from a patient |
| FR2757866B1 (en) * | 1996-12-30 | 2004-12-17 | Catalyse | POLYMERS COMPRISING QUATERNARY AMMONIUM GROUPS, THEIR USE FOR THE MANUFACTURE OF AN ANTIBACTERIAL PROPERTY MATERIAL AND THEIR PREPARATION METHODS |
| US6203785B1 (en) | 1996-12-30 | 2001-03-20 | Geltex Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Poly(diallylamine)-based bile acid sequestrants |
| DE19705963A1 (en) * | 1997-02-17 | 1998-08-20 | Hoechst Ag | Crosslinked vinyl polymers with bile acid adsorber effect |
| US5925379A (en) * | 1997-03-27 | 1999-07-20 | Geltex Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Interpenetrating polymer networks for sequestration of bile acids |
| US6423754B1 (en) * | 1997-06-18 | 2002-07-23 | Geltex Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Method for treating hypercholesterolemia with polyallylamine polymers |
| US5900233A (en) * | 1997-10-16 | 1999-05-04 | Day; Charles E. | Epichlorohydrin and 1-(3-aminopropyl) imidazole copolymer and its use in treating irritable bowel syndrome |
| US6083497A (en) | 1997-11-05 | 2000-07-04 | Geltex Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Method for treating hypercholesterolemia with unsubstituted polydiallylamine polymers |
| US6566407B2 (en) | 1997-11-05 | 2003-05-20 | Geltex Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Method for reducing oxalate |
| US5985938A (en) * | 1997-11-05 | 1999-11-16 | Geltex Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Method for reducing oxalate |
| US6726905B1 (en) | 1997-11-05 | 2004-04-27 | Genzyme Corporation | Poly (diallylamines)-based phosphate binders |
| US6299868B1 (en) | 1999-07-14 | 2001-10-09 | Geltex Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Fat-binding polymers |
| US6267952B1 (en) | 1998-01-09 | 2001-07-31 | Geltex Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Lipase inhibiting polymers |
| US7048917B1 (en) | 1998-01-09 | 2006-05-23 | Genzyme Corporation | Fat-binding polymers |
| US6264937B1 (en) | 1998-01-09 | 2001-07-24 | Geltex Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Fat-binding polymers |
| AU4369499A (en) * | 1998-06-30 | 2000-01-17 | Aventis Research & Technologies Gmbh & Co. Kg | Novel method for producing cross-linked vinyl polymers based on quaternary ammonium groups exhibiting a bile acid adsorbent effect |
| DE69912389T2 (en) * | 1998-08-05 | 2004-07-22 | Hisamitsu Pharmaceutical Co., Inc., Tosu | METHOD FOR PRODUCING CATIONIC POLYMER |
| US6294163B1 (en) | 1998-10-02 | 2001-09-25 | Geltex Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Polymers containing guanidinium groups as bile acid sequestrants |
| US6271264B1 (en) | 1998-12-01 | 2001-08-07 | Geltex Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Polymers containing spirobicyclic ammonium moieties as bile acid sequestrants |
| US6190649B1 (en) | 1999-04-23 | 2001-02-20 | Geltex Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Polyether-based bile acid sequestrants |
| AU774636B2 (en) * | 1999-07-14 | 2004-07-01 | Genzyme Corporation | Fat-binding polymers, optionally combined with lipase inhibitors |
| US6733780B1 (en) | 1999-10-19 | 2004-05-11 | Genzyme Corporation | Direct compression polymer tablet core |
| US20020054903A1 (en) * | 1999-10-19 | 2002-05-09 | Joseph Tyler | Direct compression polymer tablet core |
| WO2002081528A1 (en) * | 2001-04-05 | 2002-10-17 | Sekisui Chemical Co., Ltd. | Polymer specifically recognizing bile acid, process for producing the same, bile acid-absorbing polymer and cholesterol-lowering agents |
| EP1923064B1 (en) | 2001-04-18 | 2017-06-28 | Genzyme Corporation | Use of amine polymer for lowering serum glucose |
| KR20040018357A (en) * | 2001-04-18 | 2004-03-03 | 젠자임 코포레이션 | Low salt forms of polyallylamine |
| WO2002085380A1 (en) * | 2001-04-18 | 2002-10-31 | Geltex Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Method for treating gout and reducing serum uric acid |
| WO2002085379A1 (en) * | 2001-04-18 | 2002-10-31 | Geltex Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Method for improving vascular access in patients with vascular shunts |
| ES2304437T3 (en) * | 2001-04-18 | 2008-10-16 | Genzyme Corporation | USE OF COLESEVELAM OR SEVELAMER HYDROCLORIDE TO REDUCE SERIOUS GLUCOSE. |
| MXPA03009562A (en) * | 2001-04-18 | 2004-02-12 | Genzyme Corp | Methods of treating syndrome x with aliphatic polyamines. |
| US7041280B2 (en) * | 2001-06-29 | 2006-05-09 | Genzyme Corporation | Aryl boronate functionalized polymers for treating obesity |
| US7049345B2 (en) * | 2001-06-29 | 2006-05-23 | Genzyme Corporation | Fat-binding polymers |
| AT411463B (en) | 2002-09-03 | 2004-01-26 | Dsm Fine Chem Austria Gmbh | High yield production of alkylated nitrogen containing crosslinked polymer gels, e.g. epichlorohydrin crosslinked poly allylamine hydrochloride, comprises washing with methanol, sodium chloride and water |
| WO2004037274A1 (en) * | 2002-10-22 | 2004-05-06 | Genzyme Corporation | Amine polymers for promoting bone formation |
| AT412473B (en) | 2003-01-15 | 2005-03-25 | Dsm Fine Chem Austria Gmbh | METHOD FOR THE CONTINUOUS DRYING OF N- BZW. AMINO, AMMONIUM OR SPIROBICYCLIC AMMONIUM GROUPS OF POLYMERS |
| US20070212325A1 (en) | 2004-03-26 | 2007-09-13 | Mitsubishi Pharma Corporation | Insulin Resistance-Improving Agent |
| US20060177415A1 (en) * | 2004-11-01 | 2006-08-10 | Burke Steven K | Once a day formulation for phosphate binders |
| US7985418B2 (en) | 2004-11-01 | 2011-07-26 | Genzyme Corporation | Aliphatic amine polymer salts for tableting |
| EP1951266A2 (en) * | 2005-09-02 | 2008-08-06 | Genzyme Corporation | Method for removing phosphate and polymer used therefore |
| KR101547925B1 (en) | 2005-09-15 | 2015-08-27 | 젠자임 코포레이션 | Shaset Formulation for Amine Polymers |
| DE102005063339B4 (en) * | 2005-10-18 | 2012-01-12 | Henkel Ag & Co. Kgaa | Use of halide-poor polymer solutions with cationic amino groups |
| JP2009536246A (en) * | 2006-05-05 | 2009-10-08 | ゲンズイメ コーポレーション | Amine condensation polymers as phosphate scavengers. |
| EP2039363B1 (en) | 2006-06-16 | 2013-01-02 | Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation | Agent for prevention and/or treatment of glomerulopathy |
| MX2009000611A (en) * | 2006-07-18 | 2009-04-16 | Genzyme Corp | Amine dendrimers. |
| EP2066293A2 (en) | 2006-09-29 | 2009-06-10 | Genzyme Corporation | Amide dendrimer compositions |
| WO2008076242A1 (en) * | 2006-12-14 | 2008-06-26 | Genzyme Corporation | Amido-amine polymer compositions |
| JP2010519298A (en) * | 2007-02-23 | 2010-06-03 | ゲンズイメ コーポレーション | Amine polymer composition |
| EP2131820A1 (en) * | 2007-03-08 | 2009-12-16 | Genzyme Corporation | Sulfone polymer compositions |
| WO2008133954A1 (en) * | 2007-04-27 | 2008-11-06 | Genzyme Corporation | Amido-amine dendrimer compositions |
| JP5043501B2 (en) * | 2007-05-09 | 2012-10-10 | 日油株式会社 | Random copolymer containing phosphorylcholine-like groups |
| EP2217215A1 (en) * | 2007-12-14 | 2010-08-18 | Genzyme Corporation | Coated pharmaceutical compositions |
| US20110142952A1 (en) * | 2008-06-20 | 2011-06-16 | Harris David J | Pharmaceutical Compositions |
| US8673272B2 (en) * | 2009-07-27 | 2014-03-18 | Isp Investments Inc. | Ultraviolet-absorbing compounds |
| JP5865847B2 (en) * | 2010-02-24 | 2016-02-17 | レリプサ, インコーポレイテッド | Cross-linked polyvinylamine, polyallylamine and polyethyleneimine for use as bile acid scavengers |
| WO2012027331A1 (en) | 2010-08-27 | 2012-03-01 | Ironwood Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Compositions and methods for treating or preventing metabolic syndrome and related diseases and disorders |
| US20130123433A1 (en) | 2011-11-14 | 2013-05-16 | Formosa Laboratories, Inc. | Method for preparing poly(allylamine) hydrochloride and derivatives therefrom |
| US9475891B2 (en) | 2013-09-19 | 2016-10-25 | Navinta, Llc | Process for the preparation of colesevelam hydrochloride |
| PL229768B1 (en) | 2015-06-10 | 2018-08-31 | Univ Jagiellonski | Adaptation of block polymer containing the block of poly(3-(methacryloylamino)propyltrimethyloammonium chloride (PMAPTAC) for neutralization of heparin |
| GB201515602D0 (en) * | 2015-09-03 | 2015-10-21 | Biocompatibles Uk Ltd | Polymers and microspheres |
| KR102019785B1 (en) * | 2017-04-11 | 2019-11-04 | 단국대학교 천안캠퍼스 산학협력단 | pH-temperature responsive copolymer and drug carrier for delivery to small intestine using it |
| EP3998295A4 (en) * | 2019-07-12 | 2023-08-09 | GC Corporation | ANTIBACTERIAL POLYMER PARTICLES, COMPOSITION AND ARTICLE |
| DE102019008024A1 (en) * | 2019-11-18 | 2021-05-20 | Universität Stuttgart | Cation exchange and anion exchange polymers and (blend) membranes made from polymers containing highly fluorinated aromatic groups by means of nucleophilic substitution |
| CN111521705B (en) * | 2020-05-05 | 2021-04-20 | 大连润生康泰医学检验实验室有限公司 | Method for enriching bile acid in serum |
Family Cites Families (45)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BE580490A (en) * | 1958-07-15 | 1960-01-08 | Merck & Co Inc | Compositions and methods for lowering the cholesterol content of the blood |
| US3383281A (en) * | 1961-09-22 | 1968-05-14 | Merck & Co Inc | Method for binding bile acids in vivo |
| US3308020A (en) * | 1961-09-22 | 1967-03-07 | Merck & Co Inc | Compositions and method for binding bile acids in vivo including hypocholesteremics |
| BE756035A (en) * | 1969-09-12 | 1971-03-11 | Inveresk Res Int | POLYMERS BRIDGES |
| US3803237A (en) * | 1969-11-03 | 1974-04-09 | Upjohn Co | Reaction products of polyethylenepolyamines and chlorohydrins or epoxy containing compounds |
| US3980770A (en) * | 1971-06-04 | 1976-09-14 | Pharmacia Aktiebolag | Polymerization products containing amino groups useful in serum cholesterol level control |
| US3923972A (en) * | 1971-10-12 | 1975-12-02 | Monsanto Co | Method of lowering blood cholesterol level |
| US3953406A (en) * | 1973-01-26 | 1976-04-27 | California Institute Of Technology | Water-insoluble, swellable polyurethanes |
| US4205064A (en) * | 1973-06-11 | 1980-05-27 | Merck & Co., Inc. | Bile acid sequestering composition containing poly[{alkyl-(3-ammoniopropyl)imino}-trimethylenedihalides] |
| US4217429A (en) * | 1973-06-11 | 1980-08-12 | Merck & Co., Inc. | Poly-[(methylimino)trimethylene] |
| US4027009A (en) * | 1973-06-11 | 1977-05-31 | Merck & Co., Inc. | Compositions and methods for depressing blood serum cholesterol |
| CS187563B1 (en) * | 1974-02-08 | 1979-02-28 | Petr Strop | Method of preparation of the hydrophilic homogeneous or macroporous annexes |
| CS173201B1 (en) * | 1974-02-13 | 1977-02-28 | ||
| US4198396A (en) * | 1974-07-03 | 1980-04-15 | Warren-Teed Laboratories, Inc. | Dissolution of gallstones |
| US4016209A (en) * | 1975-04-23 | 1977-04-05 | Merck & Co., Inc. | 3-[N'-(3-Halopropyl)-N-'-methylamino]-N,N,N-trimethyl-1-propanaminium halide and acid addition salts thereof |
| US4071478A (en) * | 1976-06-07 | 1978-01-31 | Merck & Co., Inc. | Controlled partially cross-linked 3,3-ionenes |
| FI67483C (en) * | 1977-02-17 | 1985-04-10 | Merck & Co Inc | PROCEDURE FOR THE FRAMEWORK OF ETHCYCLE ADMINISTRATION OF PHARMACOLOGICAL PRODUCT AGAINST GALLSYRAK COMPLEX BILDANDE ADSORBATE PREPARATION |
| IT1106718B (en) * | 1978-12-21 | 1985-11-18 | Alfa Farmaceutici Spa | PHARMACOLOGICALLY ACTIVE SALONIZED ANIONIC RESIN BASED COMPOSITIONS |
| JPS57142920A (en) * | 1981-03-02 | 1982-09-03 | Mitsubishi Petrochem Co Ltd | Cholesterol depressant |
| JPS5879022A (en) * | 1981-11-04 | 1983-05-12 | Bitamin Kenkyusho:Kk | Novel metal-crosslinked polymer compound containing quaternary nitrogen atom, its preparation, and remedy for hyperlipemia containing said polymer compound as active component |
| WO1983002392A1 (en) * | 1982-01-18 | 1983-07-21 | Kihara, Kunio | Cholesterol lowering drug |
| JPS6090243A (en) * | 1983-10-25 | 1985-05-21 | Nitto Boseki Co Ltd | Method for producing small spherical monoallylamine cross-linked polymer |
| JPS60106803A (en) * | 1983-11-14 | 1985-06-12 | Nitto Boseki Co Ltd | Production of allylurea polymer |
| EP0142962A3 (en) * | 1983-11-14 | 1986-01-15 | Nitto Boseki Co., Ltd. | Process for producing poly (allylamine) derivatives |
| US4540760A (en) * | 1984-01-11 | 1985-09-10 | Nitto Boseki Co. Ltd. | Process for producing polymers of monoallylamine |
| JPS60209523A (en) * | 1984-04-03 | 1985-10-22 | Mitsubishi Petrochem Co Ltd | Antilipemic agent |
| DE3572985D1 (en) * | 1984-05-11 | 1989-10-19 | Bristol Myers Co | Novel bile sequestrant resin and uses |
| US4837015A (en) * | 1987-03-05 | 1989-06-06 | Carolina Medical Products Company, Inc. | Alkali metal ion-charged, cation exchanger and use thereof to adjust sodium, potassium and calcium body fluid levels |
| US4759923A (en) * | 1987-06-25 | 1988-07-26 | Hercules Incorporated | Process for lowering serum cholesterol using poly(diallylmethylamine) derivatives |
| GB8829088D0 (en) * | 1988-12-13 | 1989-01-25 | Smith Kline French Lab | Compounds |
| US5236701A (en) * | 1989-07-19 | 1993-08-17 | Lowchol Scientific Inc. | Ingestible hydrophilic polymeric amines useful for lowering blood cholesterol |
| GB8928278D0 (en) * | 1989-12-14 | 1990-02-21 | Smith Kline French Lab | Compounds |
| CA2040996A1 (en) * | 1990-05-02 | 1991-11-03 | Robert L. Albright | Composition and method for controlling cholesterol |
| GB9011332D0 (en) * | 1990-05-21 | 1990-07-11 | Smith Kline French Lab | Compounds |
| FI106800B (en) * | 1990-12-06 | 2001-04-12 | Hoechst Ag | Process for the preparation of novel therapeutically useful dimeric bile acid derivatives |
| IE914179A1 (en) * | 1990-12-07 | 1992-06-17 | Ici Plc | Nitrogen derivatives |
| US5055197A (en) * | 1991-04-05 | 1991-10-08 | Rohm And Haas Company | Process for removing residual monomers and oligemers from amine-containing polymers |
| CA2042870C (en) * | 1991-05-17 | 1996-11-26 | Leon Edward St. Pierre | Metal ion coordinated polyamine resins for the lowering of blood cholesterol |
| WO1993005084A1 (en) * | 1991-09-06 | 1993-03-18 | Commonwealth Scientific And Industrial Research Organisation | Composition and method for reducing cholesterol concentration |
| DE69326231T2 (en) * | 1992-01-14 | 1999-12-30 | Hisamitsu Pharmaceutical Co., Inc. | CHOLESTEROL-LOWING AGENT |
| WO1993025595A1 (en) * | 1992-06-17 | 1993-12-23 | Isp Investments Inc. | Cationic polymer compositions |
| DK0580078T3 (en) * | 1992-07-22 | 1998-05-25 | Hoechst Ag | Polyvinylamine derivatives with hydrophilic centers, process for their preparation as well as the use of the compounds as drugs, carriers of active substances and food aid. |
| RU95107405A (en) * | 1992-08-20 | 1997-02-10 | Е. И. Дюпон Де Немур энд Компани (US) | Cross-linked polymer ammonium salt, pharmaceutical composition, method for decreasing of cholesterol content in blood plasma, method for promotion of excretion of cholic acids |
| US5451397A (en) * | 1992-12-21 | 1995-09-19 | Rohm And Haas Company | Bile acid sequestrant |
| EP0706399A4 (en) * | 1993-06-02 | 1998-08-12 | Geltex Pharma Inc | Compositions and process for removing bile salts |
-
1994
- 1994-06-10 US US08/258,477 patent/US5624963A/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
1995
- 1995-05-24 RU RU96124822A patent/RU2146266C1/en active
- 1995-05-24 CN CNB951935224A patent/CN1136855C/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1995-05-24 CA CA002192592A patent/CA2192592C/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1995-05-24 EP EP95919914A patent/EP0764177B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1995-05-24 DE DE69522687T patent/DE69522687T2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1995-05-24 PT PT95919914T patent/PT764177E/en unknown
- 1995-05-24 NZ NZ285979A patent/NZ285979A/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1995-05-24 ES ES95919914T patent/ES2164152T3/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1995-05-24 AU AU25560/95A patent/AU694777B2/en not_active Expired
- 1995-05-24 JP JP8502188A patent/JPH10501264A/en not_active Ceased
- 1995-05-24 DK DK95919914T patent/DK0764177T3/en active
- 1995-05-24 AT AT95919914T patent/ATE205508T1/en active
- 1995-05-24 WO PCT/US1995/006542 patent/WO1995034588A1/en not_active Ceased
-
1996
- 1996-12-06 MX MX9606172A patent/MX9606172A/en unknown
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP0764177B1 (en) | 2001-09-12 |
| CA2192592C (en) | 2009-11-24 |
| CN1155287A (en) | 1997-07-23 |
| ATE205508T1 (en) | 2001-09-15 |
| AU694777B2 (en) | 1998-07-30 |
| CA2192592A1 (en) | 1995-12-21 |
| DE69522687D1 (en) | 2001-10-18 |
| DE69522687T2 (en) | 2002-06-20 |
| WO1995034588A1 (en) | 1995-12-21 |
| HK1001611A1 (en) | 1998-07-03 |
| DK0764177T3 (en) | 2002-01-14 |
| RU2146266C1 (en) | 2000-03-10 |
| ES2164152T3 (en) | 2002-02-16 |
| JPH10501264A (en) | 1998-02-03 |
| EP0764177A1 (en) | 1997-03-26 |
| AU2556095A (en) | 1996-01-05 |
| PT764177E (en) | 2002-03-28 |
| US5624963A (en) | 1997-04-29 |
| NZ285979A (en) | 1998-08-26 |
| MX9606172A (en) | 1998-06-30 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN1136855C (en) | Cross-linked polymers for removing bile salts from patient | |
| CN1150217C (en) | A kind of cross-linked polymer and its application | |
| US5703188A (en) | Process for removing bile salts from a patient and compositions therefor | |
| CN1511039A (en) | Methods of Lowering Plasma Glucose | |
| CA2349620C (en) | Use of aliphatic polyamines for reducing oxalate | |
| CN1245425A (en) | Poly(diallylamine)-based bile acid sequestrants | |
| US6566407B2 (en) | Method for reducing oxalate | |
| WO1994027620A1 (en) | Compositions and process for removing bile salts | |
| CN1509180A (en) | Methods of treating syndrome X with aliphatic polyamines | |
| JP2004528332A (en) | Method of treating gout and binding uric acid | |
| CN1056056A (en) | Cholesterol controlling composition and controlling method thereof | |
| CN1103871A (en) | bile acid sequestrant | |
| CN101065409A (en) | Crosslinked amine polymers | |
| HK1001611B (en) | Cross-linked polymers for removing bile salts from a patient | |
| HK1025912A (en) | Poly(diallylamine)-based bile acid sequestrants | |
| CN1222855A (en) | Ionic polymers as anti-infective agents | |
| CN1189168A (en) | Hydrophobic heteroatom-containing sequestrant for cholesterol depletion | |
| HK1110341A (en) | Crosslinked amine polymers | |
| HK1009820A (en) | Hydrophobic heteroatom-containing sequestrant for cholesterol depletion | |
| HK1034044A1 (en) | Fat-binding polymers | |
| HK1034044B (en) | Fat-binding polymers |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| ASS | Succession or assignment of patent right |
Owner name: ENZYME CO., LTD. Free format text: FORMER OWNER: GELTEX PHARMACEUTICALS INC. Effective date: 20031010 |
|
| C41 | Transfer of patent application or patent right or utility model | ||
| TR01 | Transfer of patent right |
Effective date of registration: 20031010 Patentee after: Genzyme Corp. Patentee before: Geltex Pharmaceuticals Inc. |
|
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| C17 | Cessation of patent right | ||
| CX01 | Expiry of patent term |
Expiration termination date: 20150524 Granted publication date: 20040204 |