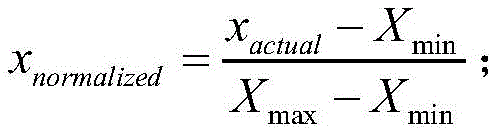CN112257337B - A GMDH neural network-based method for predicting material removal rate of wafer CMP - Google Patents
A GMDH neural network-based method for predicting material removal rate of wafer CMP Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN112257337B CN112257337B CN202011094499.9A CN202011094499A CN112257337B CN 112257337 B CN112257337 B CN 112257337B CN 202011094499 A CN202011094499 A CN 202011094499A CN 112257337 B CN112257337 B CN 112257337B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- hidden layer
- consumption
- data set
- polishing
- value
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 107
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 35
- 238000013528 artificial neural network Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 28
- 238000005498 polishing Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 90
- 238000012549 training Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 63
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 62
- 239000013598 vector Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 51
- 238000003062 neural network model Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 16
- 238000010606 normalization Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 11
- 210000002569 neuron Anatomy 0.000 claims description 72
- 238000005192 partition Methods 0.000 claims description 11
- 238000010219 correlation analysis Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000012528 membrane Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000007619 statistical method Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 abstract description 4
- 230000002159 abnormal effect Effects 0.000 abstract description 2
- 238000012216 screening Methods 0.000 abstract 1
- 235000012431 wafers Nutrition 0.000 description 49
- 230000000875 corresponding effect Effects 0.000 description 30
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 description 15
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 13
- 239000002002 slurry Substances 0.000 description 11
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 7
- 238000004458 analytical method Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000011156 evaluation Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000012530 fluid Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000008570 general process Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000007547 defect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000013450 outlier detection Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000007517 polishing process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000011160 research Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000003044 adaptive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000009286 beneficial effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004422 calculation algorithm Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004364 calculation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003750 conditioning effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002596 correlated effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005530 etching Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000227 grinding Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003862 health status Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002427 irreversible effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001465 metallisation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000002245 particle Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000002161 passivation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004886 process control Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000638 solvent extraction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000009827 uniform distribution Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F30/00—Computer-aided design [CAD]
- G06F30/20—Design optimisation, verification or simulation
- G06F30/27—Design optimisation, verification or simulation using machine learning, e.g. artificial intelligence, neural networks, support vector machines [SVM] or training a model
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/04—Architecture, e.g. interconnection topology
- G06N3/045—Combinations of networks
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/08—Learning methods
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F2111/00—Details relating to CAD techniques
- G06F2111/10—Numerical modelling
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F2113/00—Details relating to the application field
- G06F2113/18—Chip packaging
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F2119/00—Details relating to the type or aim of the analysis or the optimisation
- G06F2119/06—Power analysis or power optimisation
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F2119/00—Details relating to the type or aim of the analysis or the optimisation
- G06F2119/14—Force analysis or force optimisation, e.g. static or dynamic forces
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Evolutionary Computation (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Computational Linguistics (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Geometry (AREA)
- Mechanical Treatment Of Semiconductor (AREA)
Abstract
Description
技术领域technical field
本发明属于半导体材料预测方法技术领域,涉及一种GMDH神经网络的晶圆CMP材料去除率预测方法。The invention belongs to the technical field of semiconductor material prediction methods, and relates to a GMDH neural network wafer CMP material removal rate prediction method.
背景技术Background technique
化学机械抛光(CMP)是晶圆制造的终端下游主流工艺;该工艺的目的是克服晶圆多层金属化的问题。CMP是通过浆料化学品对晶片材料进行钝化和蚀刻,即晶片在向下的压力下使其表面在浆料颗粒上滑动,而使晶片表面平坦化。晶圆CMP工艺过程非常复杂,涉及多种化学和机械现象,例如,表面动力学、电化学界面、接触力学、应力力学、流体动力学和摩擦化学。Chemical Mechanical Polishing (CMP) is the end-stream mainstream process for wafer fabrication; the process is designed to overcome the problem of multi-layer metallization of wafers. CMP is the passivation and etching of the wafer material by slurry chemicals, ie the wafer is flattened by sliding its surface over slurry particles under downward pressure. The wafer CMP process is very complex and involves multiple chemical and mechanical phenomena, such as surface dynamics, electrochemical interfaces, contact mechanics, stress mechanics, fluid dynamics, and tribochemistry.
在晶圆的CMP工艺中,MRR是衡量工艺中性能的重要指标(MRR值即材料去除率)。然而所有晶圆的质量都是根据过程变量的测量值进行控制,需要昂贵的计量工具和生产周期;并且实验室中要求严格的实验工作程序。影响MRR影响因素主要有:下压力、抛光盘及抛光头的转速、温度、抛光液的种类及流速等。目前,为了模拟CMP的物理机制,已经提出了几种模型:一个典型的模型是Preston方程,它将MRR描述为压力和垫与晶片之间的相对速度V的函数,该物理模型的预测精度是均方误差MSE为870.25。还有基于前述的Preston方程进行的改进,例如增加浆料流速、接触应力和化学反应速率到原始的Preston方程中;仅考虑通用工艺参数的深度信念网络DBN,该模型的测试集预测精度是均方误差MSE为7.29。但目前研究工作一直集中在CMP的基于物理学和基于模型的预测建模技术的开发上。In the CMP process of wafers, MRR is an important indicator to measure the performance in the process (MRR value is the material removal rate). However, the quality of all wafers is controlled based on the measurement of process variables, requiring expensive metrology tools and production cycles; and demanding experimental work procedures in the laboratory. The main influencing factors that affect MRR are: down pressure, rotating speed of polishing disc and polishing head, temperature, type and flow rate of polishing liquid, etc. Currently, to simulate the physical mechanism of CMP, several models have been proposed: a typical model is the Preston equation, which describes the MRR as a function of pressure and the relative velocity V between the pad and the wafer, and the prediction accuracy of this physical model is The mean squared error MSE is 870.25. There are also improvements based on the aforementioned Preston equation, such as adding slurry flow rate, contact stress and chemical reaction rate to the original Preston equation; only considering the general process parameters of the deep belief network DBN, the test set prediction accuracy of the model is average The squared error MSE is 7.29. But current research efforts have been focused on the development of physics-based and model-based predictive modeling techniques for CMP.
影响晶圆MRR的因素很多,除了上面模型涉及到的因素,还有抛光盘及抛光头的转速、温度、抛光液的种类等。上面的方法局限于仅考虑通用的工艺参数。根据现有CMP加工过程 MRR的影响因素研实验研究已基本确定上面提到的通用工艺最优参数:如压力、旋转速度和浆料流速等,这些基本参数都受到严格控制。然而在实际抛光过程中,随着时间的推移,抛光垫和修整器等耗损组件的磨损(即消耗量)也会对MRR值产生不可逆影响。现有的方法仅考虑较少的通用工艺变量,且忽视重要消耗变量对MRR值的关键性影响缺陷。There are many factors that affect the MRR of a wafer. In addition to the factors involved in the above model, there are also the rotational speed, temperature, and type of polishing liquid of the polishing disc and polishing head. The above approach is limited to considering only common process parameters. According to the experimental research on the influencing factors of MRR in the existing CMP process, the above-mentioned general process optimal parameters have been basically determined: such as pressure, rotation speed and slurry flow rate, etc., these basic parameters are strictly controlled. However, in the actual polishing process, the wear (i.e., consumption) of wearable components such as polishing pads and dressers over time also has an irreversible effect on the MRR value. Existing methods only consider few general process variables, and ignore the critical influence defect of important consumption variables on MRR value.
在CMP工艺系统中,收集大量过程变量用于过程控制目的。因此,通常建模方法的输入维度非常高,有时涉及数百个输入变量,其中冗余特征的存在会显著影响虚拟度量模型的性能。In a CMP process system, a large number of process variables are collected for process control purposes. Therefore, usually the input dimension of modeling methods is very high, sometimes involving hundreds of input variables, where the existence of redundant features can significantly affect the performance of virtual metric models.
因此,研究一种既可以引入重要消耗变量又可以简化特征选择和模型选择,且度量准确率高的模型具有十分重要的意义。Therefore, it is of great significance to study a model that can introduce important consumption variables, simplify feature selection and model selection, and have high measurement accuracy.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
为解决现有技术中不能精确地获取CMP技术中材料去除率的问题,本发明提供一种 GMDH神经网络的晶圆CMP材料去除率预测方法,基于物理学知识和统计学相结合的复杂系统建模方法;具体是采用GMDH神经网络的自适应模型方法,通过对MRR值的准确预测,确保MRR值在正常范围内以提高去除率精度,例如在晶圆粗抛和精抛模式下,分别控制MRR 值范围140~170nm/min,50~110nm/min,如预测值不符合该范围,及时调整工艺参数,例如及时更换新的修整器和抛光垫等耗损材料。模型的准确预测对评估CMP各组件性能健康状态提供决策性分析依据。In order to solve the problem that the material removal rate in the CMP technology cannot be accurately obtained in the prior art, the present invention provides a GMDH neural network wafer CMP material removal rate prediction method, which is based on a complex system construction combining physical knowledge and statistics. Modulo method; specifically, the adaptive model method of the GMDH neural network is used to ensure that the MRR value is within the normal range to improve the removal rate accuracy through accurate prediction of the MRR value. The MRR value ranges from 140 to 170 nm/min and 50 to 110 nm/min. If the predicted value does not meet this range, adjust the process parameters in time, for example, replace the wearable materials such as new dressers and polishing pads in time. The accurate prediction of the model provides a decision-making analysis basis for evaluating the performance and health status of each component of the CMP.
为达到上述目的,本发明采用的方案如下:For achieving the above object, the scheme that the present invention adopts is as follows:
一种GMDH神经网络的晶圆CMP材料去除率预测方法,包括如下步骤:A method for predicting the removal rate of wafer CMP material by GMDH neural network, comprising the following steps:
(1)获取去除异常值后的抛光样本数据集;其中样本数量为n,每个样本含有a个工艺变量和对应的MRR值(即材料去除率);(1) Obtain a polishing sample data set after removing outliers; the number of samples is n, and each sample contains a process variable and corresponding MRR value (ie, material removal rate);
(2)对抛光样本数据集中由若干个晶圆抛光产生的主要工艺变量进行统计分析,综合考虑各变量分布的均匀性与分布范围,确定b个分布均匀且范围广的有效工艺变量;其中, b<a;(2) Statistically analyze the main process variables generated by several wafer polishing in the polishing sample data set, comprehensively consider the uniformity and distribution range of the distribution of each variable, and determine b effective process variables with uniform distribution and wide range; among them, b < a;
(3)提取每个有效工艺变量的均值、标准差、歪度和峭度,获得4*b个特征向量;(3) Extract the mean, standard deviation, skewness and kurtosis of each effective process variable, and obtain 4*b eigenvectors;
(4)采用回归相关分析法对4*b个特征向量与对应的MRR值进行筛选,且设置相关系数阈值后,即可确定m个特征向量作为GMDH神经网络模型的输入特征向量;其中, m<(4*b);(4) The regression correlation analysis method is used to screen the 4*b eigenvectors and the corresponding MRR values, and after setting the correlation coefficient threshold, m eigenvectors can be determined as the input eigenvectors of the GMDH neural network model; wherein, m <(4*b);
则,确定GMDH神经网络模型的输入维度为m,y为对应输出的MRR值,(输入特征维度m与样本总量n成正比,具体数据的确定是为了提高训练精度,特征越多,精度越高,但是精度随着特征维度的增加而趋于稳定,甚至会降低;为了提高训练精度,同时降低模型复杂度,将输入特征维度在10以内);Then, the input dimension of the GMDH neural network model is determined to be m, and y is the MRR value of the corresponding output. (The input feature dimension m is proportional to the total number of samples n. The specific data is determined to improve the training accuracy. The more features, the better the accuracy. High, but the accuracy tends to be stable as the feature dimension increases, or even decreases; in order to improve the training accuracy and reduce the model complexity, the input feature dimension is within 10);
(5)对m个特征向量形成的数据集A进行归一化处理得到训练特征集A′和测试特征集,其中,训练特征集的样本量为n1,测试特征集的样本量为n2,n=n1+n2。归一化处理的目的是为了降低输入数据的单位量纲不一致对预测精度的影响。(5) Normalize the data set A formed by m feature vectors to obtain a training feature set A' and a test feature set, wherein the sample size of the training feature set is n 1 , and the sample size of the test feature set is n 2 , n=n 1 +n 2 . The purpose of normalization processing is to reduce the impact of the unit dimension inconsistency of the input data on the prediction accuracy.
(6)采用二元二次Volterra多项式回归模型,以样本量为n1的训练特征集A′中m个特征向量为输入层,训练特征集中对应的MRR值为输出层,训练GMDH神经网络模型;即:(6) Using the binary quadratic Volterra polynomial regression model, the m feature vectors in the training feature set A' with a sample size of n 1 are used as the input layer, the corresponding MRR value in the training feature set is the output layer, and the GMDH neural network model is trained. ;which is:
其中,为训练特征集A′中的第b个特征向量,xa′,b为训练特征集 A′中的第a个样本中第b个特征向量中对应的特征值,ya为训练特征集A′中第a个样本对应的实际MRR值,n1为训练样本量,a∈{1,2,…,n1},b∈{1,2, …,m};in, is the b-th feature vector in the training feature set A', x a ' , b is the corresponding feature value in the b-th feature vector in the a-th sample in the training feature set A', y a is the training feature set A The actual MRR value corresponding to the a-th sample in ', n 1 is the training sample size, a∈{1,2,...,n 1 },b∈{1,2,...,m};
(7)将测试特征集(待测样本集)中作为输入的m个特征值输入训练好的GMDH网络模型中,则输出预测的MRR值;(7) input the m eigenvalues as input in the test feature set (sample set to be tested) into the trained GMDH network model, then output the predicted MRR value;
(8)将预测的MRR值和测试特征集中与输入的m个特征值对应的MRR值进行比较,得到该模型预测的准确率。(8) Compare the predicted MRR value with the MRR value corresponding to the input m eigenvalues in the test feature set, and obtain the prediction accuracy of the model.
在粗抛工作模式下,预测结果准确率:均方误差MSE为3.95,均方根误差RMSE为1.99;In the rough throwing working mode, the accuracy of the prediction results: the mean square error MSE is 3.95, and the root mean square error RMSE is 1.99;
在精抛工作模式下,预测结果准确率:均方误差MSE为9.82,均方根误差RMSE为3.31。In the fine polishing working mode, the accuracy of the prediction results: the mean square error MSE is 9.82, and the root mean square error RMSE is 3.31.
作为优选的技术方案:As the preferred technical solution:
如上所述的一种GMDH神经网络的晶圆CMP材料去除率预测方法,步骤(1)中,抛光样本数据集是通过CMP设备上的传感器采集得到,当MRR值为140~170nm/min时,抛光样本数据集是指粗抛样本数据集;当MRR值为50~110nm/min时,抛光样本数据集是指精抛样本数据集;In the above-mentioned method for predicting the removal rate of wafer CMP material by GMDH neural network, in step (1), the polishing sample data set is collected by the sensor on the CMP equipment, and when the MRR value is 140-170 nm/min, The polishing sample data set refers to the rough polishing sample data set; when the MRR value is 50-110 nm/min, the polishing sample data set refers to the fine polishing sample data set;
步骤(1)中,a为25,工艺变量包括腔室压力、主外压力、中心压力、保持环压力、波纹压力、边缘压力、修整器转速、晶圆转速、抛光台转速、A型浆料流速、B型浆料流速、C 型浆料流速、抛光台背衬膜的消耗量、抛光垫的消耗量、晶圆载体柔性板的消耗量、分区膜的消耗量、修整器的消耗量、修整器台的消耗量、修整液状态、用于晶圆加工的腔室、工艺处理阶段、晶圆标识符、时间截、晶圆环位置标识符和抛光机器标识符。选取前18个主要工艺变量进行统计分布分析。其它的标识符变量对目标输出的影响较小,因此不作为预测因子分析。In step (1), a is 25, and the process variables include chamber pressure, main external pressure, center pressure, holding ring pressure, corrugation pressure, edge pressure, conditioner rotation speed, wafer rotation speed, polishing table rotation speed, and A-type slurry Flow rate, Type B slurry flow rate, Type C slurry flow rate, Consumption of polishing table backing film, Consumption of polishing pad, Consumption of wafer carrier flex, Consumption of partition film, Consumption of dresser, Dresser station consumption, dressing fluid status, chambers used for wafer processing, process stages, wafer identifiers, time cuts, wafer ring position identifiers, and polishing machine identifiers. The first 18 main process variables were selected for statistical distribution analysis. Other identifier variables had less effect on the target output and were therefore not analyzed as predictors.
步骤(1)中,去除异常值的方法为:采用Grubbs检测异常值,目的是提高预测精度,异常值是由传感器测量失败和过程参数发生随机误差产生,为极大值或者极小值。In step (1), the method of removing outliers is as follows: using Grubbs to detect outliers, the purpose is to improve the prediction accuracy, outliers are generated by sensor measurement failure and random errors of process parameters, and are maximum or minimum values.
如上所述的一种GMDH神经网络的晶圆CMP材料去除率预测方法,步骤(2)中,有效工艺变量为统计宽度范围为0.12~11的变量(宽度为变量中的最大值与最小值的差)。分布范围窄的变量不会增加MRR值的精度,因为整个CMP过程转速、压力和流速变量数据分布在很窄的范围内,在实际晶圆CMP中压力、旋转速度和浆料流速都受到严格控制。这些工艺参数基本是一个固定值,以确保晶圆材料去除精度和去除均匀性。从物理学角度看,压力和转速是影响MRR的关键因素,但从计算角度看,将压力和转速包含在GMDH神经网络模型中不会增加MRR预测精度。A kind of GMDH neural network wafer CMP material removal rate prediction method as described above, in step (2), the effective process variable is a variable with a statistical width ranging from 0.12 to 11 (the width is the difference between the maximum value and the minimum value in the variable). Difference). Narrowly distributed variables do not increase the accuracy of the MRR value because the rotational speed, pressure, and flow rate variable data are distributed over a narrow range throughout the CMP process, and pressure, spin speed, and slurry flow rate are tightly controlled in actual wafer CMP . These process parameters are basically fixed values to ensure wafer material removal accuracy and removal uniformity. From a physical point of view, pressure and rotational speed are key factors affecting MRR, but from a computational point of view, including pressure and rotational speed in the GMDH neural network model does not increase the MRR prediction accuracy.
如上所述的一种GMDH神经网络的晶圆CMP材料去除率预测方法,当抛光样本数据集是指粗抛样本数据集时,有效工艺变量为:背衬膜消耗量、抛光垫消耗量、分区膜消耗量和柔性板消耗量;其他无效变量分布较离散,基本为一个常数;因此这些变量不能作为模型的预测因子;A GMDH neural network method for predicting the removal rate of wafer CMP material as described above, when the polishing sample data set refers to the rough polishing sample data set, the effective process variables are: backing film consumption, polishing pad consumption, partition Film consumption and flexible board consumption; the distribution of other invalid variables is relatively discrete and basically a constant; therefore, these variables cannot be used as predictors of the model;
或者,当抛光样本数据集是指精抛样本数据集时,有效工艺变量为:背衬膜消耗量、抛光垫消耗量和分区膜消耗量。Alternatively, when the polishing sample data set refers to the fine polishing sample data set, the effective process variables are: backing film consumption, polishing pad consumption and partition film consumption.
如上所述的一种GMDH神经网络的晶圆CMP材料去除率预测方法,步骤(4)中,当抛光样本数据集是指粗抛样本数据集时,m=8,输入特征向量对应的输入工艺变量特征分别为:背衬膜消耗量的均值、背衬膜消耗量的歪度、抛光垫消耗量的均值、抛光垫消耗量的标准差、抛光垫消耗量的歪度、分区膜消耗量的均值、分区膜消耗量的歪度和柔性板消耗量的均值;The above-mentioned method for predicting the removal rate of wafer CMP material by GMDH neural network, in step (4), when the polishing sample data set refers to the rough polishing sample data set, m=8, and the input process corresponding to the input feature vector The variable features are: the mean of the consumption of the backing film, the skewness of the consumption of the backing film, the mean of the consumption of the polishing pad, the standard deviation of the consumption of the polishing pad, the skewness of the consumption of the polishing pad, the deviation of the consumption of the partitioned film. Average value, skewness of partition film consumption and average value of flexible board consumption;
或者,当抛光样本数据集是指精抛样本数据集时,m=8,输入特征向量对应的输入工艺变量特征分别为:背衬膜消耗量的歪度、抛光垫消耗量的均值、抛光垫消耗量的标准差、抛光垫消耗量的歪度、抛光垫消耗量的峭度、分区膜消耗量的均值、分区膜消耗量的标准差和分区膜消耗量的歪度。Or, when the polishing sample data set refers to the precise polishing sample data set, m=8, and the input process variable characteristics corresponding to the input feature vector are respectively: the skewness of the consumption of the backing film, the average consumption of the polishing pad, the polishing pad Standard deviation of consumption, skewness of pad consumption, kurtosis of pad consumption, mean of zoned film consumption, standard deviation of zoned film consumption and skewness of zoned film consumption.
所述特征值的获取方式均为公知的。The acquisition methods of the eigenvalues are well known.
如上所述的一种GMDH神经网络的晶圆CMP材料去除率预测方法,步骤(5)中,Wafer CMP material removal rate prediction method of a kind of GMDH neural network as above, in step (5),
m个特征向量形成的数据集为A,如下:The dataset formed by m eigenvectors is A, as follows:
其中,(x1,b,x2,b,…,xa,b,…,xn,b)T为数据集A中的第b个特征向量,xa,b为数据集A中的第a个样本中第b个特征向量中对应的特征值,m=8,a∈{1,2,…,n},b∈{1,2,…,m};Among them, (x 1,b ,x 2,b ,…,x a,b ,…,x n,b ) T is the b-th eigenvector in data set A, and x a,b is in data set A The corresponding eigenvalue in the b-th eigenvector in the a-th sample, m=8, a∈{1,2,…,n},b∈{1,2,…,m};
归一化处理是指对数据集A中的特征向量逐一进行归一化处理得到归一化后的数据集,其中,特征向量是指特征向量(x1,b,x2,b,…,xa,b,…,xn,b)T,a∈{1,2,…,n},b∈{1,2,…,m},归一化的计算公式为:The normalization process refers to the normalization of the feature vectors in the data set A one by one to obtain a normalized data set. x a,b ,…,x n,b ) T , a∈{1,2,…,n},b∈{1,2,…,m}, the normalization formula is:
其中,xnormalized为第b个特征向量中归一化后的特征值,xactual为第b个特征向量中的特征值,xmax为第b个特征向量中的最大的特征值,xmin为第b个特征向量中的最小的特征值,b∈{1,2,…,m};Among them, x normalized is the normalized eigenvalue in the b-th eigenvector, x actual is the eigenvalue in the b-th eigenvector, x max is the largest eigenvalue in the b-th eigenvector, and x min is The smallest eigenvalue in the bth eigenvector, b∈{1,2,…,m};
在归一化后的数据集中,随机选择个样本作为训练特征集A′,记为:In the normalized dataset, randomly selected The samples are taken as the training feature set A', denoted as:
其中,为训练特征集A′中的第b个特征向量,x′a,b为训练特征集A′中的第a个样本中第b个特征向量中对应的特征值,n1为训练样本量,m=8, a∈{1,2,…,n1},b∈{1,2,…,m}。in, is the b-th feature vector in the training feature set A', x' a, b are the corresponding eigenvalues in the b-th feature vector in the a-th sample in the training feature set A', n 1 is the training sample size, m=8, a∈{1,2,...,n 1 },b∈{1,2,...,m}.
如上所述的一种GMDH神经网络的晶圆CMP材料去除率预测方法,步骤(6)中,训练GMDH神经网络模型的具体步骤为:The wafer CMP material removal rate prediction method of a kind of GMDH neural network as above, in step (6), the concrete steps of training GMDH neural network model are:
(61)建立第1隐层:(61) Establish the first hidden layer:
(611)对训练特征集A′中8个特征向量中任意取两个特征向量Xi和Xj创建G1个二次多项式方程,并作为基本神经元,即第1隐层基本神经元总数其中,m=8, P为每层隐层中最大神经元总数阈值;(611) Take two eigenvectors X i and X j arbitrarily from the 8 eigenvectors in the training feature set A' to create G1 quadratic polynomial equations, and use them as basic neurons, that is, the total number of basic neurons in the first hidden layer Among them, m=8, P is the threshold of the maximum number of neurons in each hidden layer;
(612)按照Volterra二次多项式回归分别计算获得第1隐层中各个基本神经元对应的模型 (612) Calculate the model corresponding to each basic neuron in the first hidden layer according to Volterra quadratic polynomial regression
其中,为二次多项方程式的目标输出向量预测值,指第1隐层中第r个基本神经元模型中第a个样本的目标输出预测值,x′a,j指从输入中选择第a个样本的第j个输入特征值,且作为连接形成第1隐层第r个基本神经元模型的元素,a∈{1,2,…,n1},b∈{1,2,…,m};in, is the predicted value for the target output vector of the quadratic polynomial equation, refers to the target output prediction value of the a-th sample in the r-th basic neuron model in the first hidden layer, x′ a,j refers to the j-th input feature value of the a-th sample selected from the input, and is formed as a connection The element of the rth basic neuron model of the 1st hidden layer, a∈{1,2,…,n 1 },b∈{1,2,…,m};
{w0,w2,w3,w4,w5}为二次多项式方程的系数,该系数是以与Yr 1的差异最小为目标,采用最小二乘法计算得到;其中,Yr 1为训练特征集A′中n1个训练样本的实际MRR值构成的向量;{w 0 ,w 2 ,w 3 ,w 4 ,w 5 } is the coefficient of the quadratic polynomial equation, the coefficient is The minimum difference with Y r 1 is the target, which is calculated by the least squares method; wherein, Y r 1 is the vector formed by the actual MRR values of n 1 training samples in the training feature set A';
(613)分别计算第1隐层中各个神经元的输出均方根误差值;即(613) Calculate the output root mean square error of each neuron in the first hidden layer respectively value; that is
其中,为第1隐层中第r个基本神经元模型中第a个样本的目标输出预测值,为为第1隐层中第r个基本神经元模型中第a个样本的目标输出真实值;in, is the target output prediction value of the a-th sample in the r-th basic neuron model in the first hidden layer, Output the true value for the target of the a-th sample in the r-th basic neuron model in the first hidden layer;
(614)对第1隐层中所有神经元输出均方根误差从小到大排序,取排序在前的P个神经元作为有效神经元形成第1隐层;(614) Rank the output root mean square errors of all neurons in the first hidden layer from small to large, and take the top P neurons as effective neurons to form the first hidden layer;
(615)以第1隐层中的P个神经元的各项输出作为第2隐层的输入特征向量;则第2隐层形成G2个基本神经元,且G2>P,重复步骤(611)~(614),得到含有P个神经元的第2隐层,其中,第1隐层中参与组合连接形成第2隐层的有U1个有效神经元;(615) Use the outputs of the P neurons in the first hidden layer as the input feature vector of the second hidden layer; then the second hidden layer forms G 2 basic neurons, and G 2 >P, repeat steps (611) to (614) to obtain the second hidden layer containing P neurons, wherein, in the first hidden layer, there are U 1 effective neurons participating in the combined connection to form the second hidden layer ;
(616)计算第1隐层中参与组合连接形成第2隐层的U1个有效神经元的输出的均值E1,即(616) Calculate the output of U 1 effective neurons in the first hidden layer participating in the combined connection to form the second hidden layer The mean E 1 of , namely
(62)建立中间隐层:对第k-1隐层(相当于第1隐层)中的P个神经元的各项输出作为第k隐层(相当于第2隐层)的输入特征向量,重复步骤(611)~(616),得到中间隐层;(62) Establish an intermediate hidden layer: the output of the P neurons in the k-1th hidden layer (equivalent to the 1st hidden layer) is used as the input feature vector of the kth hidden layer (equivalent to the 2nd hidden layer) , repeat steps (611) to (616) to obtain an intermediate hidden layer;
其中,第k隐层中的基本神经元总数k≥2;Among them, the total number of basic neurons in the kth hidden layer k≥2;
第k-1隐层中参与组合连接形成第k隐层的Uk个有效神经元输出的均值Ek,即The output of U k effective neurons in the k-1 hidden layer participating in the combined connection to form the k hidden layer The mean E k of , namely
(63)建立输出层:当Ek-1-Ek≤0.3时(即第k隐层的Ek不在随着隐层数量的增加而明显减少时),训练停止;且以第k隐层中2个输出RMSE较小神经元作为新的输入向量与其对应的目标输出MRR向量构建二次多项方程式,则该方程的输出作为GMDH神经网络模型最终的输出预测值。(63) Establish the output layer: when E k-1 -E k ≤ 0.3 (that is, when the E k of the k-th hidden layer does not decrease significantly with the increase of the number of hidden layers), the training stops; and the k-th hidden layer The two smaller output RMSE neurons are used as new input vectors and their corresponding target output MRR vectors to construct a quadratic polynomial equation, and the output of this equation is used as the final output prediction value of the GMDH neural network model.
如上所述的一种GMDH神经网络的晶圆CMP材料去除率预测方法,P=12。A method for predicting the removal rate of wafer CMP material based on a GMDH neural network as described above, P=12.
有益效果beneficial effect
(1)本发明的一种GMDH神经网络的晶圆CMP材料去除率虚拟预测方法,运用GMDH网络具有单周期预测能力和运行时间短的优点,自组织选择最优特征集建立晶圆MRR预测模型。综合考虑物理学知识和统计学相结合,克服了传统预测方法仅考虑较少变量和忽视重要消耗变量对MRR影响的缺陷。解决了不能快速精确地获取晶圆CMP工艺过程中研磨去除率的问题。(1) The virtual prediction method of wafer CMP material removal rate of a kind of GMDH neural network of the present invention, the use of GMDH network has the advantages of single-cycle prediction ability and short running time, self-organization selects the optimal feature set to establish a wafer MRR prediction model . The combination of comprehensive consideration of physics knowledge and statistics overcomes the defects of traditional prediction methods that only consider fewer variables and ignore the impact of important consumption variables on MRR. It solves the problem that the grinding removal rate during the wafer CMP process cannot be obtained quickly and accurately.
(2)本发明的一种GMDH神经网络的晶圆CMP材料去除率虚拟预测方法,综合考虑抛光过程漂移和不同批次晶圆产品间的差异等误差来源,为提高预测模型的精度,分别对晶圆粗抛和精抛两种模式分别建模。(2) The virtual prediction method of wafer CMP material removal rate of a kind of GMDH neural network of the present invention comprehensively considers error sources such as polishing process drift and difference between different batches of wafer products, in order to improve the accuracy of the prediction model, respectively Two modes of wafer rough polishing and fine polishing are modeled separately.
(3)本发明的一种GMDH神经网络的晶圆CMP材料去除率虚拟预测方法,从粗抛训练的网络结构看出,抛光垫、背衬膜和柔性板消耗变量均值被选为最有效预测因子。此时在输入层多项式方程中广泛使用的最有效的变量是抛光垫消耗量均值。(3) The virtual prediction method of the wafer CMP material removal rate of a GMDH neural network of the present invention, from the network structure of rough polishing training, it can be seen that the average value of the consumption variables of the polishing pad, the backing film and the flexible plate is selected as the most effective prediction factor. The most efficient variable used extensively in the input layer polynomial equation at this time is the pad consumption mean.
(4)本发明的一种GMDH神经网络的晶圆CMP材料去除率虚拟预测方法,从精抛训练的结构看出,抛光垫消耗量均值、标准差和歪度、背衬膜歪度和分区膜消耗变量歪度被选为最有效预测因子,此时在输入层多项式方程中广泛使用的最有效的变量是抛光垫消耗量标准差。(4) The virtual prediction method of the wafer CMP material removal rate of a GMDH neural network of the present invention, from the structure of the fine polishing training, it can be seen that the average value, standard deviation and skewness of the polishing pad consumption, the skewness and partition of the backing film The film consumption variable skew was chosen as the most effective predictor, and the most effective variable widely used in the input layer polynomial equation at this time was the pad consumption standard deviation.
(5)本发明的一种GMDH神经网络的晶圆CMP材料去除率虚拟预测方法,通过该网络模型快速获得MRR值的准确预测,无论是精抛模式还是粗抛模式,都是抛光垫磨损消耗对目标输出MRR影响最大,因此如果预测值不在MRR值范围内,及时调整工艺参数,例如及时更换新的抛光垫和修整器等耗损材料,尤其将抛光垫作为晶圆CMP工艺的重点维护组件。根据2016PHM数据,结合实验预测误差评估指标计算的结果,证明本文提出的MRR预测方法比物理学模型和传统神经网络预测效果更出色。适用于非线性的复杂CMP工艺建模。(5) The virtual prediction method of the wafer CMP material removal rate of a GMDH neural network of the present invention, the accurate prediction of the MRR value is quickly obtained through the network model, whether it is a fine polishing mode or a rough polishing mode, it is the polishing pad wear consumption It has the greatest impact on the target output MRR. Therefore, if the predicted value is not within the range of the MRR value, the process parameters should be adjusted in time, for example, the wearable materials such as new polishing pads and dressers should be replaced in time. According to the 2016PHM data, combined with the calculation results of the experimental prediction error evaluation index, it is proved that the MRR prediction method proposed in this paper is better than the physical model and the traditional neural network prediction effect. Suitable for nonlinear complex CMP process modeling.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1和图2为本发明的晶圆去除率预测的流程图;1 and 2 are flowcharts of wafer removal rate prediction of the present invention;
图3(a)为本发明的4个MRR异常值检测结果;Fig. 3 (a) is 4 MRR abnormal value detection results of the present invention;
图3(b)为本发明的CMP工艺中两种工作模式的MRR值分布图;Fig. 3 (b) is the MRR value distribution figure of two working modes in the CMP process of the present invention;
图4为本发明的晶圆粗抛阶段的训练好的GMDH网络结构示意图;4 is a schematic diagram of a trained GMDH network structure in the rough wafer throwing stage of the present invention;
图5和图6分别为本发明的粗抛阶段和精抛阶段的预测结果;Fig. 5 and Fig. 6 are respectively the prediction result of rough throwing stage and fine throwing stage of the present invention;
图7为本发明在粗抛模式下的工艺变量统计分析图。FIG. 7 is a statistical analysis diagram of process variables in the rough throwing mode of the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面结合具体实施方式,进一步阐述本发明。应理解,这些实施例仅用于说明本发明而不用于限制本发明的范围。此外应理解,在阅读了本发明讲授的内容之后,本领域技术人员可以对本发明作各种改动或修改,这些等价形式同样落于本申请所附权利要求书所限定的范围。The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with specific embodiments. It should be understood that these examples are only used to illustrate the present invention and not to limit the scope of the present invention. In addition, it should be understood that after reading the content taught by the present invention, those skilled in the art can make various changes or modifications to the present invention, and these equivalent forms also fall within the scope defined by the appended claims of the present application.
一种GMDH神经网络的晶圆CMP材料去除率预测方法,其流程示意图如图1~2所示,具体包括如下步骤:A method for predicting the removal rate of wafer CMP materials based on GMDH neural network, the schematic flowchart of which is shown in Figures 1-2, and specifically includes the following steps:
(1)获取去除异常值后的抛光样本数据集;其中样本数量为n,每个样本含有25个工艺变量和对应的MRR值(即材料去除率);(1) Obtain a polishing sample data set after removing outliers; the number of samples is n, and each sample contains 25 process variables and corresponding MRR values (ie, material removal rate);
工艺变量包括腔室压力、主外压力、中心压力、保持环压力、波纹压力、边缘压力、修整器转速、晶圆转速、抛光台转速、A型浆料流速、B型浆料流速、C型浆料流速、抛光台背衬膜的消耗量、抛光垫的消耗量、晶圆载体柔性板的消耗量、分区膜的消耗量、修整器的消耗量、修整器台的消耗量、修整液状态、用于晶圆加工的腔室、工艺处理阶段、晶圆标识符、时间截、晶圆环位置标识符和抛光机器标识符。选取前18个主要工艺变量进行统计分布分析。其它的标识符变量对目标输出的影响较小,因此不作为预测因子分析。Process variables include chamber pressure, main external pressure, center pressure, holding ring pressure, corrugation pressure, edge pressure, dresser rotation speed, wafer rotation speed, polishing table rotation speed, type A slurry flow rate, type B slurry flow rate, type C Slurry flow rate, polishing table backing film consumption, polishing pad consumption, wafer carrier flex board consumption, partitioned film consumption, dresser consumption, dresser table consumption, conditioning fluid status , chamber used for wafer processing, process stage, wafer identifier, time cut, wafer ring position identifier and polishing machine identifier. The first 18 main process variables were selected for statistical distribution analysis. Other identifier variables had less effect on the target output and were therefore not analyzed as predictors.
去除异常值的方法为:采用Grubbs检测异常值,目的是提高预测精度,异常值是由传感器测量失败和过程参数发生随机误差产生,为极大值或者极小值。The method of removing outliers is: using Grubbs to detect outliers, the purpose is to improve the prediction accuracy, outliers are caused by sensor measurement failure and random errors of process parameters, which are maximum or minimum values.
(2)对抛光样本数据集中由若干个晶圆抛光产生的主要工艺变量进行统计分析,确定b 个统计宽度范围为0.12~11(宽度为变量中的最大值与最小值的差)的有效工艺变量;其中, b<a;(2) Statistically analyze the main process variables generated by several wafer polishing in the polishing sample data set, and determine b effective processes with a statistical width ranging from 0.12 to 11 (the width is the difference between the maximum value and the minimum value of the variables). variable; where, b<a;
(3)提取每个有效工艺变量的均值、标准差、歪度和峭度,获得4*b个特征向量;(3) Extract the mean, standard deviation, skewness and kurtosis of each effective process variable, and obtain 4*b eigenvectors;
(4)采用回归相关分析法对4*b个特征向量与对应的MRR值进行筛选,且设置相关系数阈值后,即可确定m个特征向量作为GMDH神经网络模型的输入特征向量;其中,m=8, m<(4*b);(4) The regression correlation analysis method is used to screen the 4*b eigenvectors and the corresponding MRR values, and after setting the correlation coefficient threshold, m eigenvectors can be determined as the input eigenvectors of the GMDH neural network model; wherein, m =8, m<(4*b);
(5)对m个特征向量形成的数据集A进行归一化处理得到训练特征集A′和测试特征集,其中,训练特征集的样本量为n1,测试特征集的样本量为n2,n=n1+n2;具体过程如下:(5) Normalize the data set A formed by m feature vectors to obtain a training feature set A' and a test feature set, wherein the sample size of the training feature set is n 1 , and the sample size of the test feature set is n 2 , n=n 1 +n 2 ; the specific process is as follows:
m个特征向量形成的数据集为A,如下:The dataset formed by m eigenvectors is A, as follows:
其中,(x1,b,x2,b,…,xa,b,…,xn,b)T为数据集A中的第b个特征向量,xa,b为数据集A中的第a 个样本中第b个特征向量中对应的特征值,m=8,a∈{1,2,…,n},b∈{1,2,…,m};Among them, (x 1,b ,x 2,b ,…,x a,b ,…,x n,b ) T is the b-th eigenvector in data set A, and x a,b is in data set A The corresponding eigenvalue in the b-th eigenvector in the a-th sample, m=8, a∈{1,2,…,n},b∈{1,2,…,m};
归一化处理是指对数据集A中的特征向量逐一进行归一化处理得到归一化后的数据集,其中,特征向量是指特征向量(x1,b,x2,b,…,xa,b,…,xn,b)T,a∈{1,2,…,n},b∈{1,2,…,m},归一化的计算公式为:The normalization process refers to the normalization of the feature vectors in the data set A one by one to obtain a normalized data set. x a,b ,…,x n,b ) T , a∈{1,2,…,n},b∈{1,2,…,m}, the normalization formula is:
其中,xnormalized为第b个特征向量中归一化后的特征值,xactual为第b个特征向量中的特征值,xmax为第b个特征向量中的最大的特征值,xmin为第b个特征向量中的最小的特征值, b∈{1,2,…,m};Among them, x normalized is the normalized eigenvalue in the b-th eigenvector, x actual is the eigenvalue in the b-th eigenvector, x max is the largest eigenvalue in the b-th eigenvector, and x min is The smallest eigenvalue in the bth eigenvector, b∈{1,2,…,m};
在归一化后的数据集中,随机选择个样本作为训练特征集A′,记为:In the normalized dataset, randomly selected The samples are taken as the training feature set A', denoted as:
其中,为训练特征集A′中的第b个特征向量,x′a,b为训练特征集 A′中的第a个样本中第b个特征向量中对应的特征值,n1为训练样本量,m=8, a∈{1,2,…,n1},b∈{1,2,…,m};in, is the b-th feature vector in the training feature set A', x' a, b are the corresponding eigenvalues in the b-th feature vector in the a-th sample in the training feature set A', n 1 is the training sample size, m=8, a∈{1,2,...,n 1 },b∈{1,2,...,m};
(6)采用二元二次Volterra多项式回归模型,以样本量为n1的训练特征集A′中m个特征向量为输入层,训练特征集中对应的MRR值为输出层,训练GMDH神经网络模型;即:(6) Using the binary quadratic Volterra polynomial regression model, the m feature vectors in the training feature set A' with a sample size of n 1 are used as the input layer, the corresponding MRR value in the training feature set is the output layer, and the GMDH neural network model is trained. ;which is:
其中,为训练特征集A′中的第b个特征向量,x′a,b为训练特征集 A′中的第a个样本中第b个特征向量中对应的特征值,ya为训练特征集A′中第a个样本对应的实际MRR值,n1为训练样本量,a∈{1,2,…,n1},b∈{1,2,…,m};in, is the b-th feature vector in the training feature set A', x' a, b are the corresponding eigenvalues in the b-th feature vector in the a-th sample in the training feature set A', y a is the training feature set A The actual MRR value corresponding to the a-th sample in ', n 1 is the training sample size, a∈{1,2,...,n 1 },b∈{1,2,...,m};
训练GMDH神经网络模型的具体步骤为:The specific steps for training the GMDH neural network model are:
(61)建立第1隐层:(61) Establish the first hidden layer:
(611)对训练特征集A′中8个特征向量中任意取两个特征向量Xi和Xj创建G1个二次多项式方程,并作为基本神经元,即第1隐层基本神经元总数其中,m=8, P为每层隐层中最大神经元总数阈值;P=12;(611) Take two eigenvectors X i and X j arbitrarily from the 8 eigenvectors in the training feature set A' to create G1 quadratic polynomial equations, and use them as basic neurons, that is, the total number of basic neurons in the first hidden layer Among them, m=8, P is the threshold of the maximum number of neurons in the hidden layer of each layer; P=12;
(612)按照Volterra二次多项式回归分别计算获得第1隐层中各个基本神经元对应的模型 (612) Calculate the model corresponding to each basic neuron in the first hidden layer according to Volterra quadratic polynomial regression
其中,为二次多项方程式的目标输出向量预测值,指第1隐层中第r个基本神经元模型中第a个样本的目标输出预测值,r为第1隐层中基本神经元的序号,x′a,j指从输入中选择第a个样本的第j个输入特征值,且作为连接形成第1隐层第r个基本神经元模型的元素,a∈{1,2,…,n1},b∈{1,2,…,m};P=12。in, is the predicted value for the target output vector of the quadratic polynomial equation, Refers to the target output prediction value of the a-th sample in the r-th basic neuron model in the first hidden layer, r is the serial number of the basic neuron in the first hidden layer, x' a, j refers to selecting the a-th sample from the input The jth input feature value of the sample, and as the element connected to form the rth basic neuron model of the first hidden layer, a∈{1,2,…,n 1 },b∈{1,2,…,m }; P=12.
{w0,w2,w3,w4,w5}为二次多项式方程的系数,该系数是以与Yr 1的差异最小为目标,采用最小二乘法计算得到;其中,Yr 1为训练特征集A′中n1个训练样本的实际MRR值构成的向量;{w 0 ,w 2 ,w 3 ,w 4 ,w 5 } is the coefficient of the quadratic polynomial equation, the coefficient is The minimum difference with Y r 1 is the target, which is calculated by the least squares method; wherein, Y r 1 is the vector formed by the actual MRR values of n 1 training samples in the training feature set A';
(613)分别计算第1隐层中各个神经元的输出均方根误差值;即(613) Calculate the output root mean square error of each neuron in the first hidden layer respectively value; that is
其中,为第1隐层中第r个基本神经元模型中第a个样本的目标输出预测值,为为第1隐层中第r个基本神经元模型中第a个样本的目标输出真实值,r为第1隐层中基本神经元的序号;in, is the target output prediction value of the a-th sample in the r-th basic neuron model in the first hidden layer, is the target output real value of the a-th sample in the r-th basic neuron model in the first hidden layer, and r is the serial number of the basic neuron in the first hidden layer;
(614)对第1隐层中所有神经元输出均方根误差从小到大排序,取排序在前的P个神经元作为有效神经元形成第1隐层;(614) Rank the output root mean square errors of all neurons in the first hidden layer from small to large, and take the top P neurons as effective neurons to form the first hidden layer;
(615)以第1隐层中的P个神经元的各项输出作为第2隐层的输入特征向量,P=12;则第2隐层形成G2个基本神经元,且G2>P,重复步骤(611)~(614),得到含有P个神经元的第2隐层,P=12,其中,第1隐层中参与组合连接形成第2隐层的有U1个有效神经元;(615) Take the outputs of the P neurons in the first hidden layer as the input feature vector of the second hidden layer, P=12; then the second hidden layer forms G 2 basic neurons, and G 2 >P, repeat steps (611) to (614) to obtain the second hidden layer containing P neurons, P=12, wherein U 1 participates in the combined connection to form the second hidden layer in the first hidden layer effective neurons;
(616)计算第1隐层中参与组合连接形成第2隐层的U1个有效神经元的输出的均值E1,即(616) Calculate the output of U 1 effective neurons in the first hidden layer participating in the combined connection to form the second hidden layer The mean E 1 of , namely
其中,r为第1隐层中U1个有效神经元的序号;Among them, r is the serial number of U 1 effective neurons in the first hidden layer;
(62)建立中间隐层:对第k-1隐层中的P个神经元的各项输出作为第k隐层的输入特征向量,重复步骤(611)~(616),得到中间隐层;(62) establishing an intermediate hidden layer: the outputs of the P neurons in the k-1 hidden layer are used as the input feature vector of the k hidden layer, and steps (611) to (616) are repeated to obtain the intermediate hidden layer;
其中,第k隐层中的基本神经元总数k≥2;Among them, the total number of basic neurons in the kth hidden layer k≥2;
第k-1隐层中参与组合连接形成第k隐层的Uk个有效神经元输出的均值Ek,即The output of U k effective neurons in the k-1 hidden layer participating in the combined connection to form the k hidden layer The mean E k of , namely
(63)建立输出层:当Ek-1-Ek≤0.3时(即第k隐层的Ek不在随着隐层数量的增加而明显减少时),训练停止;且以第k隐层中2个输出RMSE较小神经元作为新的输入向量与其对应的目标输出MRR向量构建二次多项方程式,则该方程的输出作为GMDH神经网络模型最终的输出预测值。(63) Establish the output layer: when E k-1 -E k ≤ 0.3 (that is, when the E k of the k-th hidden layer does not decrease significantly with the increase of the number of hidden layers), the training stops; and the k-th hidden layer The two smaller output RMSE neurons are used as new input vectors and their corresponding target output MRR vectors to construct a quadratic polynomial equation, and the output of this equation is used as the final output prediction value of the GMDH neural network model.
(7)将测试特征集(待测样本集)中作为输入的m个特征值输入训练好的GMDH网络模型中,则输出预测的MRR值;(7) input the m eigenvalues as input in the test feature set (sample set to be tested) into the trained GMDH network model, then output the predicted MRR value;
(8)将预测的MRR值和测试特征集中与输入的m个特征值对应的MRR值进行比较,得到该模型预测的准确率。(8) Compare the predicted MRR value with the MRR value corresponding to the input m eigenvalues in the test feature set, and obtain the prediction accuracy of the model.
采用上述的一种GMDH神经网络的晶圆CMP材料去除率预测方法,对通过CMP设备上的传感器采集得到MRR值为140~170nm/min的粗抛样本数据集(MRR值分布图如图3(b) 所示)进行预测,该数据来源于2016PHM挑战赛,其采用Grubbs检测异常值,发现4个 MRR值远大于170nm/min异常值(异常值检测结果如图3(a)所示),获取去除异常值后的粗抛样本数据集;粗抛样本数据集的样本数量为n=102,每个样本含有25个工艺变量和对应的MRR值(即材料去除率);Using the above-mentioned method for predicting the removal rate of wafer CMP materials using a GMDH neural network, the data set of rough samples with an MRR value of 140-170 nm/min collected by sensors on the CMP equipment (the MRR value distribution diagram is shown in Figure 3 (Fig. 3). b)) to predict, the data comes from the 2016 PHM Challenge, which uses Grubbs to detect outliers, and found that 4 MRR values are much larger than 170nm/min outliers (outlier detection results are shown in Figure 3(a)), Obtain the rough-throwing sample data set after removing outliers; the number of samples in the rough-throwing sample data set is n=102, and each sample contains 25 process variables and corresponding MRR values (that is, material removal rate);
在去除异常值后的粗抛样本数据集中,随机选择五个晶圆抛光的样本进行工艺变量统计分析(如图7所示),确定4个有效工艺变量(数据宽度为0.12~11的变量,即背衬膜消耗量、抛光垫消耗量、分区膜消耗量和柔性板消耗量);其中,背衬膜消耗量的分布范围是10.83,抛光垫消耗量的分布范围9.63,分区膜消耗量的分布范围3.25,柔性板消耗量的分布范围是 0.12;其他无效变量分布较离散,基本为一个常数;因此这些变量不能作为模型的预测因子;In the data set of rough polishing samples after removing outliers, five samples of wafer polishing were randomly selected for statistical analysis of process variables (as shown in Figure 7), and 4 effective process variables were determined (variables with a data width of 0.12 to 11, Namely backing film consumption, polishing pad consumption, partitioned film consumption and flexible board consumption); wherein, the distribution range of backing film consumption is 10.83, the distribution range of polishing pad consumption is 9.63, and the consumption of partitioned film is 10.83. The distribution range is 3.25, and the distribution range of flexible board consumption is 0.12; the distribution of other invalid variables is relatively discrete and basically a constant; therefore, these variables cannot be used as predictors of the model;
提取粗抛样本数据集中每个有效工艺变量的均值、标准差、歪度和峭度,获得16个特征向量;Extract the mean, standard deviation, skewness and kurtosis of each effective process variable in the rough throw sample data set, and obtain 16 eigenvectors;
采用回归相关分析法对粗抛样本数据集中16个特征向量与对应的MRR值进行筛选,且设置相关系数阈值(取值为0.65)后,即可确定8个相关性强的特征向量作为GMDH神经网络模型的输入特征向量,见表1,如下:The regression correlation analysis method is used to screen the 16 eigenvectors and the corresponding MRR values in the coarse throwing sample data set, and after setting the correlation coefficient threshold (valued at 0.65), 8 eigenvectors with strong correlation can be determined as the GMDH neural network. The input feature vector of the network model, see Table 1, as follows:
表1Table 1
训练好的GMDH网络结构示意图如图4所示,从输入层看出网络使用最广泛的输入向量是X3(即表1中的抛光垫消耗量均值),是最有效的MRR预测因子。在第1隐层中,是被筛选为剔除的神经元,根据模型评价准则这些神经元组合形成的下一层新神经元输出 RMSE较大,说明这些神经元与输出MRR相关性弱,不参与下一层的网络连接。则是第一隐层的有效神经元。当构筑到第4隐层时,所有有效神经元输出RMSE的均值不再随着隐层数的增加有明显的下降趋势,训练停止,得到含有4个隐层的GMDH神经网络拓扑结构,即得到GMDH网络模型。The schematic diagram of the trained GMDH network structure is shown in Figure 4. From the input layer, it can be seen that the most widely used input vector of the network is X3 (that is, the average polishing pad consumption in Table 1), which is the most effective MRR predictor. In the first hidden layer, is the neuron that was screened out. According to the model evaluation criteria, the output RMSE of the new neurons in the next layer formed by the combination of these neurons is larger, indicating that these neurons are weakly correlated with the output MRR and do not participate in the network connection of the next layer. but is the effective neuron of the first hidden layer. When the fourth hidden layer is constructed, the mean value of the output RMSE of all effective neurons no longer has a significant downward trend with the increase of the number of hidden layers, the training stops, and the topology of the GMDH neural network with 4 hidden layers is obtained, that is, GMDH network model.
将对应的测试特征集中作为输入的8个特征值输入训练好的GMDH网络模型中,则输出预测的MRR值;Input the 8 eigenvalues of the corresponding test feature set as the input into the trained GMDH network model, then output the predicted MRR value;
将预测的MRR值和测试特征集中与输入的8个特征值对应的MRR值进行比较,得到该模型预测的准确率,预测结果示意图如图5所示,在粗抛工作模式下,预测结果准确率:均方误差MSE为3.95,均方根误差RMSE为1.99。The predicted MRR value and the test feature set are compared with the MRR values corresponding to the input 8 eigenvalues, and the accuracy of the model prediction is obtained. The schematic diagram of the prediction result is shown in Figure 5. In the rough throwing mode, the prediction result is accurate. Rate: mean square error MSE is 3.95, root mean square error RMSE is 1.99.
采用上述的一种GMDH神经网络的晶圆CMP材料去除率预测方法,对通过CMP设备上的传感器采集得到MRR值为50~110nm/min的精抛样本数据集(MRR值分布图如图3(b) 所示)进行预测,数据取自2016PHM挑战赛数据,采用Grubbs检测异常值,获取去除异常值后的精抛样本数据集(异常值检测结果如图3(a)所示);其中样本数量为n=105,每个样本含有25个工艺变量和对应的MRR值(即材料去除率);Using the above-mentioned method for predicting the removal rate of wafer CMP materials using a GMDH neural network, the precision polishing sample data set with an MRR value of 50 to 110 nm/min collected by the sensor on the CMP equipment (the MRR value distribution diagram is shown in Figure 3 ( b) shown) to make predictions, the data is taken from the 2016PHM challenge data, Grubbs is used to detect outliers, and the refined sample data set after removing outliers is obtained (outlier detection results are shown in Figure 3(a)); The number is n=105, and each sample contains 25 process variables and corresponding MRR values (ie, material removal rate);
对去除异常值后的精抛样本数据集中由单个晶圆产生的样本进行分析,确定3个有效工艺变量(数据宽度为0.12~11的变量,即背衬膜消耗量、抛光垫消耗量和分区膜消耗量);The samples generated from a single wafer in the refined polishing sample dataset after removing outliers were analyzed to determine 3 valid process variables (variables with a data width of 0.12 to 11, namely backing film consumption, polishing pad consumption and partitioning) membrane consumption);
提取每个有效工艺变量的均值、标准差、歪度和峭度,获得12个特征向量;Extract the mean, standard deviation, skewness and kurtosis of each effective process variable to obtain 12 eigenvectors;
采用回归相关分析法对12个特征向量与对应的MRR值进行筛选,且设置相关系数阈值 (取值为0.7)后,即可确定8个特征向量作为GMDH神经网络模型的输入特征向量,见表2,如下:The 12 eigenvectors and the corresponding MRR values are screened by the regression correlation analysis method, and after setting the correlation coefficient threshold (valued at 0.7), 8 eigenvectors can be determined as the input eigenvectors of the GMDH neural network model, see table 2, as follows:
表2Table 2
将测试特征集中作为输入的8个特征向量样本输入训练好的GMDH网络模型中,则输出预测的MRR值;Input the 8 feature vector samples from the test feature set as input into the trained GMDH network model, then output the predicted MRR value;
将预测的MRR值和测试特征集中与输入的8个特征值对应的MRR值进行比较,得到该模型预测的准确率,预测结果示意图如图6所示,在精抛工作模式下,预测结果准确率:均方误差MSE为9.82,均方根误差RMSE为3.13。Compare the predicted MRR value and the test feature set with the MRR values corresponding to the input 8 eigenvalues to obtain the accuracy of the model prediction. The schematic diagram of the prediction result is shown in Figure 6. In the fine throwing working mode, the prediction result is accurate. Rate: mean square error MSE is 9.82, root mean square error RMSE is 3.13.
表1为在两种不同工作模式下,训练样本和测试样本的详细预测结果Table 1 shows the detailed prediction results of training samples and test samples under two different working modes
表1中的训练样本得到的训练模型也会会与真实值做误差分析,称为训练误差。The training model obtained from the training samples in Table 1 will also perform error analysis with the real value, which is called training error.
预测结果表明GMDH网络得到的MRR预测值与真实测量值符合较好,在建立网络拓扑结构时,通过在训练样本拟合精度和测试集预测精度之间找到平衡点,确保该网络模型即使在小样本或噪声较大时,算法仍能最大限度的反应系统真实的内部关系(各消耗量特征与 MRR值的非线性关系),进而确保所建模型的最优性和泛化性。使该模型能有效监测晶圆CMP 工艺的MRR实时变化。用均方误差(MSE)和均方根误差(RMSE)作为模型性能评估指标。 RMSE越小,模型预测精度更高。The prediction results show that the predicted MRR values obtained by the GMDH network are in good agreement with the real measured values. When establishing the network topology, a balance point is found between the fitting accuracy of the training samples and the prediction accuracy of the test set to ensure that the network model is even in small When the sample or noise is large, the algorithm can still reflect the real internal relationship of the system to the greatest extent (the nonlinear relationship between each consumption feature and the MRR value), thereby ensuring the optimality and generalization of the built model. The model can effectively monitor the real-time variation of MRR of wafer CMP process. The mean square error (MSE) and root mean square error (RMSE) were used as model performance evaluation metrics. The smaller the RMSE, the higher the model prediction accuracy.
Claims (4)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202011094499.9A CN112257337B (en) | 2020-10-14 | 2020-10-14 | A GMDH neural network-based method for predicting material removal rate of wafer CMP |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202011094499.9A CN112257337B (en) | 2020-10-14 | 2020-10-14 | A GMDH neural network-based method for predicting material removal rate of wafer CMP |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN112257337A CN112257337A (en) | 2021-01-22 |
| CN112257337B true CN112257337B (en) | 2022-09-16 |
Family
ID=74243417
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202011094499.9A Active CN112257337B (en) | 2020-10-14 | 2020-10-14 | A GMDH neural network-based method for predicting material removal rate of wafer CMP |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN112257337B (en) |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN114627985B (en) * | 2022-01-26 | 2024-06-21 | 苏州中砥半导体材料有限公司 | Optimization method, system and medium for polishing process of indium phosphide material |
| CN114358443B (en) * | 2022-03-09 | 2022-06-24 | 深圳市信润富联数字科技有限公司 | Average material removal rate prediction method, device, electronic device and storage medium |
| CN118861678A (en) * | 2024-06-25 | 2024-10-29 | 上海集成电路材料研究院有限公司 | Polishing material removal rate distribution prediction model training method, prediction method, storage medium and terminal |
| CN119203799A (en) * | 2024-11-28 | 2024-12-27 | 苏州元脑智能科技有限公司 | A virtual measurement method, product, device and medium |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102799793A (en) * | 2012-07-27 | 2012-11-28 | 中国科学院微电子研究所 | Method and equipment for calculating chemical mechanical polishing removal rate |
| CN102945304A (en) * | 2012-11-14 | 2013-02-27 | 中国科学院微电子研究所 | Method for calculating grinding removal rate of wafer surface |
| TW201539602A (en) * | 2014-03-06 | 2015-10-16 | Kla Tencor Corp | Statistical overlay error prediction for feed forward and feedback correction of overlay errors, root cause analysis and process control |
| CN107214610A (en) * | 2017-05-05 | 2017-09-29 | 天津华海清科机电科技有限公司 | The online flatness control system of copper CMP |
| CN110039440A (en) * | 2019-03-27 | 2019-07-23 | 中国科学院微电子研究所 | A kind of method and device calculating CMP grind clearance |
| CN110555230A (en) * | 2019-07-12 | 2019-12-10 | 北京交通大学 | rotary machine residual life prediction method based on integrated GMDH framework |
-
2020
- 2020-10-14 CN CN202011094499.9A patent/CN112257337B/en active Active
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102799793A (en) * | 2012-07-27 | 2012-11-28 | 中国科学院微电子研究所 | Method and equipment for calculating chemical mechanical polishing removal rate |
| CN102945304A (en) * | 2012-11-14 | 2013-02-27 | 中国科学院微电子研究所 | Method for calculating grinding removal rate of wafer surface |
| TW201539602A (en) * | 2014-03-06 | 2015-10-16 | Kla Tencor Corp | Statistical overlay error prediction for feed forward and feedback correction of overlay errors, root cause analysis and process control |
| CN107214610A (en) * | 2017-05-05 | 2017-09-29 | 天津华海清科机电科技有限公司 | The online flatness control system of copper CMP |
| CN110039440A (en) * | 2019-03-27 | 2019-07-23 | 中国科学院微电子研究所 | A kind of method and device calculating CMP grind clearance |
| CN110555230A (en) * | 2019-07-12 | 2019-12-10 | 北京交通大学 | rotary machine residual life prediction method based on integrated GMDH framework |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| Adaptive virtual metrology for semiconductor chemical mechanical planarization process using GMDH-type polynomial neural networks;Xiaodong Jia, Yuan Di, Jianshe Feng, Qibo Yang, Honghao Dai, Jay;《Journal of Process Control》;20181231;论文第44-54页 * |
| 基于粒子群的RBF神经网络晶圆清洗机过滤器流量预测;王燕燕;《中国优秀博硕士学位论文全文数据库(硕士) 信息科技辑》;20191215;论文第36-44页 * |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN112257337A (en) | 2021-01-22 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN112257337B (en) | A GMDH neural network-based method for predicting material removal rate of wafer CMP | |
| JP4601492B2 (en) | Quality prediction system and method for production process | |
| TWI539298B (en) | Metrology sampling method with sampling rate decision scheme and computer program product thereof | |
| US8437870B2 (en) | System and method for implementing a virtual metrology advanced process control platform | |
| TWI427722B (en) | Advanced process control system and method using virtual measurement with confidence index and computer program product thereof | |
| TWI451336B (en) | Method for screening samples for building prediction model and computer program product thereof | |
| TWI521360B (en) | Metrology sampling method and computer program product thereof | |
| US8452441B2 (en) | Process quality predicting system and method thereof | |
| TW201432479A (en) | Method for searching and analyzing process parameters and computer program product thereof | |
| CN113094893A (en) | Wafer quality virtual measurement method and device, computer equipment and storage medium | |
| CN105702595B (en) | Wafer yield judgment method and multivariate inspection method for wafer qualification test | |
| WO2002031613A2 (en) | System and method for monitoring process quality control | |
| Di et al. | Enhanced virtual metrology on chemical mechanical planarization process using an integrated model and data-driven approach | |
| CN101976045A (en) | Panel quality virtual measurement method and system for TFT-LCD etching process | |
| CN101118422A (en) | Method and system for virtual measurement estimation and estimation model establishment in semiconductor manufacturing | |
| TW201205440A (en) | Virtual measuring system and method thereof for predicting the quality of thin film transistor liquid crystal display processes | |
| TW200401179A (en) | Method of predicting processing device condition or processed result | |
| TWI427487B (en) | Method for sampling workpiece for inspection and computer program product performing the same | |
| CN102262188B (en) | The method of workpiece sampling inspection | |
| TW202147161A (en) | Method for predicting occurrence of tool processing event and virtual metrology application and computer program product thereof | |
| TWI647770B (en) | Yield rate determination method for wafer and method for multiple variable detection of wafer acceptance test | |
| KR20220147036A (en) | Method of performing prediction relating to products manufactured via manufacturing process | |
| CN103278714A (en) | Virtual measurement method and system for mixed manufacturing process | |
| CN111291020A (en) | A Soft Sensing Modeling Method for Dynamic Process Based on Local Weighted Linear Dynamic System | |
| CN115867925B (en) | System and method for controlling measurement of sample parameters |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |