Disclosure of Invention
The invention aims to overcome the defects in the prior art, and provides a device and a method for testing the one-dimensional heat exchange phase change process of a wax phase change material, which are capable of carrying out the one-dimensional heat exchange phase change process test and material performance evaluation of the mixture of the phase change material, the phase change material and the enhanced heat conduction nanometer powder under various temperature and pressure conditions. The method has the advantages of accurate measurement, continuous acquisition, high automation degree, strong universality and the like.
The purpose of the invention is realized by the following technical scheme:
a one-dimensional heat exchange phase change process testing device for wax phase change materials comprises a hydraulic system, an upper water tank, a lower water tank and a sealing tank, wherein the hydraulic system comprises an oil tank, a liquid level sensor, a hydraulic pump, a driving motor, a one-way valve, a pressure regulating valve, a stop hand valve, a pressure sensor and a rubber bag; the upper water tank comprises an upper water tank, an upper cold-heat exchanger and an upper temperature sensor; the lower water tank comprises a lower water tank, a lower cold-heat exchanger and a lower temperature sensor; the sealing tank comprises a heat-conducting upper cover, a heat-conducting lower cover, a ceramic pipe wall, a bolt, a fluid inlet one-way valve, a fluid outlet one-way valve, a fluid inlet plug and a fluid outlet plug;
an oil tank of the hydraulic system is connected with an inlet oil path of a hydraulic pump, an outlet oil path of the hydraulic pump is connected with an inlet of a one-way valve, an outlet of the one-way valve is divided into two branches which are respectively connected with an inlet of a pressure regulating valve and an inlet of a stop hand valve, an outlet oil path of the pressure regulating valve returns to the oil tank, and an outlet oil path of the stop hand valve is sequentially connected with a pressure sensor and a rubber bag;
the water feeding tank of the water feeding tank is filled with water, the water temperature in the water feeding tank is monitored by the upper temperature sensor, the upper cold-hot exchanger carries out water temperature compensation in real time according to water temperature data acquired by the upper temperature sensor, and the water temperature in the water feeding tank is kept to be a set target temperature value T1;
The lower water tank of the lower water tank is filled with water, the lower temperature sensor monitors the temperature of the water in the lower water tank, the lower cold-hot exchanger carries out water temperature compensation in real time according to water temperature data acquired by the lower temperature sensor, and the water temperature in the lower water tank is kept to be a set target temperature value T2;
The heat-conducting upper cover, the heat-conducting lower cover and the ceramic pipe wall of the sealed tank form a pressure-bearing sealed cavity. And water, a phase-change material, a rubber leather bag and hydraulic oil are arranged in the pressure-bearing sealing cavity of the sealing tank. In the sealed tank, the phase-change material floats on the water, and a liquid interface exists between the phase-change material and the water. The contact surface of the heat-conducting upper cover and the phase-change material is an upper heat-conducting interface, and the contact surface of the heat-conducting lower cover and the water is a lower heat-conducting interface. The rubber leather bag is completely immersed in water, and the hydraulic oil and the water are physically isolated by the rubber leather bag.
Furthermore, the upper water pool is arranged at the top of the sealing tank, and the bottom of the upper water tank is in contact with the top end face of the heat-conducting upper cover. The oil tank and the seal tank are arranged in the lower water pool. The upper water tank exchanges heat with the heat-conducting upper cover, and the lower water tank exchanges heat with the heat-conducting lower cover and the oil tank.
Furthermore, the rubber leather bag is arranged at the rotary axis of the heat-conducting lower cover and is arranged in the sealing tank. Hydraulic oil is filled in the hydraulic system and the rubber bag. The driving motor drives the hydraulic pump to operate, the one-way valve prevents hydraulic oil from reversely flowing back to the hydraulic pump, and the pressure regulating valve can regulate and keep the oil filling pressure of the rubber bladder at a set value p0And the stop hand valve can close the rubber bag to keep the volume of the hydraulic oil in the rubber bag constant. Pressure sensor capable of monitoring oil filling pressure p of rubber bladder0。
Furthermore, the liquid level of the oil tank floats along with the volume change of hydraulic oil filled in the rubber bag. The oil tank is a uniform-section oil tank, and the cross-sectional area of the oil tank is S. The liquid level sensor is used for detecting the height value h of the liquid level of the oil tank. The change value delta V of the oil-filled volume of the rubber bag can be calculated as S.delta h.
Furthermore, the phase-change material has a phase-change temperature of 0-100 ℃ and a density of less than 1g/cm-3And the waxy material is insoluble in water, wherein the waxy material is composed of one or more of paraffin material, n-heptadecane, n-hexadecane, n-pentadecane and n-tetradecane.
Furthermore, the heat-conducting upper cover and the heat-conducting lower cover are of rotary stepped cylindrical structures, grooves are designed on the circumferential surfaces of the heat-conducting upper cover and the heat-conducting lower cover, and the sealing rings in the grooves realize radial sealing of the pressure-bearing sealing cavity. Bolt mounting holes are uniformly distributed on the periphery of the edge of the end face of the heat-conducting upper cover and the heat-conducting lower cover, and the heat-conducting upper cover and the heat-conducting lower cover are tightly and fixedly connected with the wall of the ceramic tube by bolts.
Further, the heat conduction lower cover is provided with a fluid inlet and a fluid outlet. Water and phase-change materials are injected into the sealing tank through the fluid inlet, and simultaneously air in the sealing tank is discharged through the fluid outlet in the process of injecting water and phase-change material liquid into the sealing tank. A fluid inlet single valve is installed in the fluid inlet, and a fluid outlet single valve is installed in the fluid outlet. The fluid inlet single-way valve and the fluid outlet single-way valve are used for keeping the fluid to flow in a single direction. The fluid inlet plug is arranged on the end face of the heat-conducting lower cover to seal the fluid inlet, and the fluid outlet plug is arranged on the end face of the heat-conducting lower cover to seal the fluid outlet.
Furthermore, the ceramic pipe wall is a circular pipe structure made of heat insulation ceramic, and the rotation axis of the ceramic pipe wall is arranged along the vertical direction, so that the heat dissipation or the heat absorption of the sealed tank along the circumferential direction can be avoided. The phase-change material generates heat exchange with the outside at an upper heat conduction interface and a liquid interface, and the heat exchange process is a one-dimensional process only carried out along the vertical rotation axis direction of the seal tank.
Furthermore, the testing device for the one-dimensional heat exchange phase change process of the waxy phase change material is used for testing in a thermostatic chamber, and the temperature of water in the thermostatic chamber and the temperature of water in a lower water pool are kept consistent and are T2。
Furthermore, the testing temperature condition T of the testing device for the one-dimensional heat exchange phase change process of the waxy phase change material0、T1、T2Satisfy the relation T1<T0<T2。
Further, the liquid volume V of the phase change material in the sealed tank0Much less than the volume of water, the volume V of the phase change material liquid0Is the nominal volume V of the rubber bladder150% of the total.
A test method for one-dimensional heat exchange phase change process of waxy phase change material comprises the following steps:
s1: the rotary axis of the cylinder of the sealing tank is placed along the vertical direction, and the heat-conducting lower cover is positioned above the heat-conducting upper cover. And unscrewing the fluid inlet plug and the fluid outlet plug, injecting water into the inner cavity of the sealed tank through the fluid inlet, discharging air in the inner cavity of the sealed tank through the fluid outlet, and discharging air in the rubber bag through the rubber bag interface. When the water continuously flows out of the fluid outlet, the air in the inner cavity of the seal pot and the rubber bag is completely discharged, the inner cavity of the seal pot is filled with the water, the rubber bag is crushed, and the fluid inlet plug and the fluid outlet plug are screwed down.
S2: after the water injection of the seal tank is completed, the rubber bag is connected with a hydraulic system, the stop hand valve and the pressure sensor are opened, the pressure regulating valve is adjusted to enable the pressure of an oil path to be in a zero state, the driving motor is started and the hydraulic pump is driven to continuously run, hydraulic oil is gradually circulated into a pipeline of the hydraulic system from the oil tank, and residual air in the pipeline is discharged from an outlet of the pressure regulating valve. When the outlet of the pressure regulating valve continuously flows out hydraulic oil, and the liquid level sensor detects that the liquid level height value h of the oil tank is kept constant, the fact that air in the hydraulic system is completely discharged and filled with the hydraulic oil is indicated, and then the driving motor, the stop hand valve and the pressure sensor are closed.
S3: the sealed tank keeps the cylinder rotation axis to be placed along the vertical direction, and the heat conduction upper cover is located above the heat conduction lower cover. Unscrewing the fluid inlet plug and the fluid outlet plug, and injecting the fluid into the inner cavity of the sealed tank through the fluid inlet with the volume V0The phase change material liquid of (2). The phase-change material is lower than water and insoluble in water due to density, after entering the inner cavity, the phase-change material floats on the upper layer of the water, and in the process of injecting the phase-change material, the sealing tank discharges the same volume V through the fluid outlet0The fluid inlet and outlet plugs are then tightened.
S4: the sealed tank keeps the cylinder rotation axis to be placed along the vertical direction, and the heat conduction upper cover is located above the heat conduction lower cover. Starting the stop hand valve and the pressure sensor, starting the driving motor and driving the hydraulic pump to continuously operate, and adjusting the pressure regulating valve to make the oil charging pressure of the rubber bladder be p0Unscrewing a fluid outlet plug, injecting hydraulic oil into the rubber leather bag by a hydraulic system, wherein the injection volume is the nominal volume V of the rubber leather bag150% of the total amount of the components, and simultaneously discharging 50% V from the sealed tank through a fluid outlet1The volume of water is then screwed down to close the fluid outlet plug, the stop hand valve, the pressure sensor, and the drive motor.
S5: the ambient temperature in the thermostatic chamber is regulated to T2The storage temperature in the lower water tank is T2The water tank is filled with the sealing tank filled with the phase-change materials and the oil tank, the cylinder rotation axis is kept to be placed along the vertical direction, and the heat-conducting upper cover of the sealing tank is positioned above the heat-conducting lower cover. Opening the stop hand valve and the pressure sensor, starting the driving motor and driving the hydraulic pump to continuously operate, and adjusting the pressure regulating valve to the inflation of the rubber bagOil pressure p0. The sealed tank and the oil tank are kept stand in the water tank for a long time until the liquid level height of the oil tank detected by the liquid level sensor is constant h, and the temperatures of hydraulic oil, water and phase-change materials are all T2The equilibrium state of (1).
S6: the temperature of the upper water pool is T1The water of (2). The temperature of hydraulic oil, water and phase-change material is T2And then, starting the test, and placing the upper water pool on the top of the heat-conducting upper cover.
S7: at a temperature T1<T0<T2Under the condition, under the action of the temperature difference between the upper water tank and the lower water tank, the heat-conducting interface, the phase-change material and the liquid interface generate heat exchange along the axis direction, the phase-change material gradually generates one-dimensional phase change from liquid to solid from the upper heat-conducting interface and along the vertical axis downwards, the volume of the phase-change material gradually shrinks, the height of the liquid interface gradually rises, the rubber leather bag gradually expands, hydraulic oil is supplemented into the rubber leather bag, the height of the liquid level of the oil tank drops, the liquid level sensor continuously collects the change process of the height h of the liquid level of the oil tank, and the height change quantity delta h curve of the liquid level is recorded. And when the phase change material and the water reach the equilibrium state again, the liquid level h of the oil tank stops changing.
S8: by repeating the above-mentioned operations S1-S7, the present invention can be used at various pressures p0Under the condition of and T1、T2And carrying out comparison tests on different phase-change materials under the condition of a temperature boundary.
S9: rate of change of volume of phase change material to be at pressure p0Temperature T1And T2Under the condition, after carrying out the heat exchange test of the time length t, calculating S.DELTA.h.V0 -1The value is evaluated, and the heat conductivity of the phase change material is evaluated according to the time point t0The rate of change of the liquid level h dh/dt0Evaluation was performed.
Compared with the prior art, the technical scheme of the invention has the following beneficial effects:
1. the invention realizes the square sealing of the phase-change material on the top of the inner cavity of the sealed tank and floating on the water by utilizing the incompatibility and different densities of the water and the phase-change material. The soft characteristic of the rubber bag is utilized to realize the physical isolation of the hydraulic oil and the water. The liquid interface between water and phase-change material moves in vertical direction along with phase-change process, and the rubber bag changes shape along with the change of oil-filled volume, and has no friction resistance loss.
2. The phase change material is filled by water, and the phase change material is in close contact with water on a liquid interface without additional contact thermal resistance; the oil charging pressure applied by the hydraulic system helps to improve the contact tightness between the phase change material and the upper heat conducting cover at the upper heat conducting interface.
3. In the testing process, the liquid level height change value of the oil tank is measured only by collecting the data of the liquid level sensor, so that the volume change data of the phase change material in the phase change process can be indirectly obtained, and the method has high automation degree and strong data continuity.
4. The ceramic pipe wall avoids circumferential heat exchange, the upper water pool and the lower water pool which are used as heat sources and cold sources, the heat conduction upper cover and the heat conduction lower cover, the phase-change material and water are arranged in the vertical direction, the heat exchange of the device is carried out along the direction of a vertical rotation axis, the phase-change material is subjected to a phase-change process in the device in an ideal one-dimensional heat exchange mode, and the comparative evaluation of the heat conduction capacity and the volume change rate of different phase-change materials is facilitated.
5. The invention can set various constant temperature difference conditions through the upper water pool and the lower water pool, and can set various phase change pressure conditions through the hydraulic system, thereby realizing the test under various temperature and pressure conditions.
6. The device has the advantages of simple structure, easy realization, low manufacturing cost and strong universality, and is suitable for various waxy phase-change materials and mixtures thereof.
Detailed Description
The invention is described in further detail below with reference to the figures and specific examples. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described herein are merely illustrative of the invention and are not intended to limit the invention.
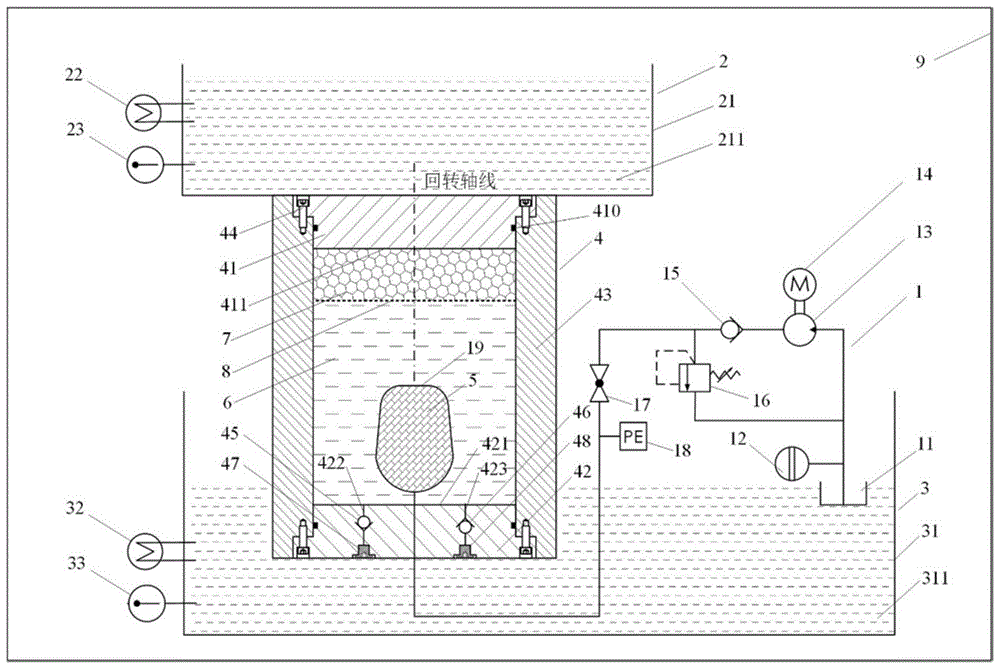
As shown in fig. 1, a testing device for one-dimensional heat exchange phase change process of wax phase change material comprises four parts of a hydraulic system 1, an upper water pool 2, a lower water pool 3 and a seal tank 4, wherein the hydraulic system 1 comprises an oil tank 11, a liquid level sensor 12, a hydraulic pump 13, a driving motor 14, a one-way valve 15, a pressure regulating valve 16, a stop hand valve 17, a pressure sensor 18 and a rubber bag 19; the upper water pool 2 comprises an upper water tank 21, an upper cold and heat exchanger 22 and an upper temperature sensor 23; the lower water tank 3 comprises a lower water tank 31, a lower heat exchanger 32 and a lower temperature sensor 33; the sealed tank 4 comprises a heat-conducting upper cover 41, a heat-conducting lower cover 42, a ceramic pipe wall 43, a bolt 44, a fluid inlet check valve 45, a fluid outlet check valve 46, a fluid inlet plug 47 and a fluid outlet plug 48.
An oil tank 11 of the hydraulic system 1 is connected with an inlet oil path of a hydraulic pump 13, an outlet oil path of the hydraulic pump 13 is connected with an inlet of a one-way valve 15, an outlet of the one-way valve 15 is divided into two branches which are respectively connected with an inlet of a pressure regulating valve 16 and an inlet of a stop hand valve 17, an outlet oil path of the pressure regulating valve 16 returns to the oil tank 11, and an outlet oil path of the stop hand valve 17 is sequentially connected with a pressure sensor 18 and a rubber bag 19. The rubber bag 19 is arranged at the rotation axis of the heat-conducting lower cover 42 and is arranged in the sealing tank 4. The hydraulic system 1 and the rubber bag 19 are filled with hydraulic oil 5. The driving motor 14 drives the hydraulic pump 13 to operate, the one-way valve 15 prevents the hydraulic oil 5 from reversely flowing back to the hydraulic pump 13, and the pressure regulating valve 16 can regulate and keep the oil filling pressure of the rubber bag 19 at a set value p0The stop hand valve 17 can close the rubber bladder 19 to keep the volume of the hydraulic oil 5 in the rubber bladder 19 constant. The pressure sensor 18 can monitor the oil filling pressure p of the rubber bag 190。
The water 211 is filled in the upper water tank 21 of the upper water tank 2, the upper temperature sensor 23 monitors the temperature of the water 211 in the upper water tank 21, the upper cold and hot exchanger 22 carries out real-time water temperature compensation according to the water temperature data acquired by the upper temperature sensor 23, and the water temperature in the upper water tank 21 is kept to be a set target temperature value T1. The lower water tank 31 of the lower water tank 3 is filled with water 311, the lower temperature sensor 33 monitors the temperature of the water 311 in the lower water tank 31, and the lower heat exchanger 32 performs real-time water temperature compensation according to the water temperature data acquired by the lower temperature sensor 33 to keep the water temperature in the lower water tank 31 at the set target temperature value T2。
The heat-conducting upper cover 41, the heat-conducting lower cover 42 and the ceramic pipe wall 43 of the sealed tank 4 form a pressure-bearing sealed cavity, the ceramic pipe wall 43 is of a circular pipe structure, the rotation axis of the ceramic pipe wall is arranged along the vertical direction, the heat-conducting upper cover 41 and the heat-conducting lower cover 42 are of a rotary stepped cylindrical structure, grooves are designed on the circumferential surface of the heat-conducting upper cover and the heat-conducting lower cover, and the sealing rings 410 in the grooves realize radial sealing of the pressure-bearing sealed cavity. The heat-conducting upper cover 41 and the heat-conducting lower cover 42 are evenly provided with bolt mounting holes on the circumference of the edge of the end face and are fixedly connected with the ceramic pipe wall 43 by bolts 44.
The pressure-bearing sealed cavity of the sealed tank 4 is internally provided with water 6, a phase-change material 7, a rubber bag 19 and hydraulic oil 5. Inside the sealed tank 4, the phase change material 7 floats on top of the water 6, and the phase change material 7 and the water 6 have a liquid interface 8. The contact surface of the upper heat-conducting cover 41 and the phase-change material 7 is an upper heat-conducting interface 411, and the contact surface of the lower heat-conducting cover 42 and the water 6 is a lower heat-conducting interface 421. The rubber bladder 19 is completely immersed in the water 6, and the hydraulic oil 5 is physically separated from the water 6 by the rubber bladder 19.
Preferably, the phase-change material 7 has a phase-change temperature of 0-100 deg.C and a density of less than 1g/cm-3And water insoluble waxy materials. Wherein the waxy material is composed of one or more of paraffin wax material, n-heptadecane, n-hexadecane, n-pentadecane and n-tetradecane.
Preferably, the upper water tank 2 is arranged on the top of the sealed tank 4, and the bottom of the upper water tank 21 is in contact with the top end face of the heat-conducting upper cover 41. The oil tank 11 and the seal tank 4 are placed in the lower water tank 3. The upper water tank 2 exchanges heat with the heat-conducting upper cover 41, and the lower water tank 3 exchanges heat with the heat-conducting lower cover 42 and the oil tank 11.
Preferably, the ceramic pipe wall 43 is made of heat-insulating ceramic, so as to prevent the sealed tank 4 from radiating or absorbing heat along the circumferential direction. The phase-change material 7 generates heat exchange with the outside at the upper heat conducting interface 411 and the liquid interface 8, and the heat exchange process is a one-dimensional process only along the vertical rotation axis direction of the seal tank 4.
Preferably, the liquid level of the oil tank 11 is floated according to the volume change of the hydraulic oil 5 filled in the rubber bag 19. The tank 11 is a constant-section tank having a cross-sectional area S. The liquid level sensor 12 is used for detecting the liquid level height value h of the oil tank 11. The change value DeltaV of the oil-filled volume of the rubber bag 19 can be calculated as S.Deltah.
Preferably, the thermally conductive lower cover 42 is provided with a fluid inlet 422, a fluid outlet 423. The water 6 and the phase-change material 7 are injected into the seal tank 4 through the fluid inlet 422, and simultaneously, the air in the seal tank 4 is discharged through the fluid outlet 423 in the process that the water 6 and the phase-change material 7 are injected into the seal tank 4. A fluid inlet one-way valve 45 is installed in the fluid inlet 422, and a fluid outlet one-way valve 46 is installed in the fluid outlet 423. The fluid inlet single-way valve 45 and the fluid outlet single-way valve 46 are used for keeping the fluid flowing in a single direction. The fluid inlet plug 47 is mounted to the end surface of the thermally conductive lower cover 42 to seal the fluid inlet 422, and the fluid outlet plug 48 is mounted to the end surface of the thermally conductive lower cover 42 to seal the fluid outlet 423.
Preferably, the testing device of the present invention can be used for performing a test in the thermostatic chamber 9, and the temperature of the water 311 in the thermostatic chamber 9 and the lower water pool 3 are kept consistent and are T2. Test temperature condition T of the test device of the invention0、T1、T2Satisfy the relation T1<T0<T2. Liquid volume V of phase change material 7 in sealed tank 40Much less than 6 volumes of water and 7 volumes of liquid V of phase-change material0Is a nominal volume V of the rubber bladder 19150% of the total.
The measuring method of the testing device comprises the following steps:
1. the axis of rotation of the cylinder of the sealed can 4 is placed in the vertical direction, and the heat conductive lower lid 42 is located above the heat conductive upper lid 41. The fluid inlet plug 47 and the fluid outlet plug 48 are unscrewed, water 6 is injected into the inner cavity of the sealed tank 4 through the fluid inlet 422, air in the inner cavity of the sealed tank 4 is discharged through the fluid outlet 423, and air in the rubber bag 19 is discharged through the interface of the rubber bag 19. When the fluid outlet 423 continuously flows out of the water 6, indicating that the air in the inner cavity of the sealed tank 4 and the rubber bladder 19 is completely discharged, the inner cavity of the sealed tank 4 is filled with the water 6, the rubber bladder 19 is crushed, and the fluid inlet plug 47 and the fluid outlet plug 48 are tightened.
2. After the sealed tank 4 finishes water injection, the rubber bag 19 is connected with the hydraulic system 1, the stop hand valve 17 and the pressure sensor 18 are opened, the pressure regulating valve 16 is adjusted to enable the pressure of an oil path to be in a zero state, the driving motor 14 is started and drives the hydraulic pump 13 to continuously run, the hydraulic oil 5 is gradually circulated into a pipeline of the hydraulic system 1 from the oil tank 11, and residual air in the pipeline is discharged from an outlet of the pressure regulating valve 16. When the outlet of the pressure regulating valve 16 continuously flows out of the hydraulic oil 5, and the liquid level sensor 12 detects that the liquid level height value h of the oil tank 11 is kept constant, the air in the hydraulic system 1 is completely discharged and the hydraulic oil 5 is filled, and then the driving motor 14, the stop hand valve 17 and the pressure sensor 18 are closed.
3. The sealed can 4 keeps the cylinder rotation axis placed in the vertical direction, and the heat-conductive upper lid 41 is located above the heat-conductive lower lid 42. Unscrewing the fluid inlet plug 47 and the fluid outlet plug 48, and injecting the volume V into the inner cavity of the sealed tank 4 through the fluid inlet 4220The phase change material 7 liquid. The phase-change material 7 is lower than the water 6 and insoluble in the water 6, after entering the inner cavity, the phase-change material 7 floats on the upper layer of the water 6, and in the process of injecting the phase-change material 7, the sealed tank 4 discharges the volume V with the same volume through the fluid outlet 4230Then the fluid inlet plug 47 and the fluid outlet plug 48 are tightened.
4. The sealed can 4 keeps the cylinder rotation axis placed in the vertical direction, and the heat-conductive upper lid 41 is located above the heat-conductive lower lid 42. The stop hand valve 17 and the pressure sensor 18 are opened, the driving motor 14 is started and drives the hydraulic pump 13 to continuously run, and the pressure regulating valve 16 is regulated to ensure that the oil filling pressure of the rubber bag 19 is p0The fluid outlet plug 48 is unscrewed, the hydraulic system 1 injects the hydraulic oil 5 into the rubber leather bag 19, and the injection volume is the nominal volume V of the rubber leather bag 19150% of the amount of the component (b) and at the same time, the seal pot 4 discharges 50% V through the fluid outlet 4231The volume of water 6, then the fluid outlet plug 48 is tightened, closing the shut off hand valve 17, the pressure sensor 18, the drive motor 14.
5. The ambient temperature in the thermostatic chamber is regulated to T2The temperature of the lower water tank 3 is T2The sealed tank 4 into which the phase change material 7 has been injected and the oil tank 11 are placed in the water tank 31 while keeping the axis of rotation of the cylinder in a vertical direction, and the heat-conductive upper lid 41 of the sealed tank 4 is positioned above the heat-conductive lower lid 42. The stop hand valve 17 and the pressure sensor 18 are opened, the driving motor 14 is started and drives the hydraulic pump 13 to continuously run, and the oil charging pressure from the pressure regulating valve 16 to the rubber leather bag 19 is adjusted to be p0. The seal tank 4 and the oil tank 11 are kept still in the water pool 3 for a long enough time until the liquid level of the oil tank 11 detected by the liquid level sensor 12 is constantThe value h is T, the temperatures of the hydraulic oil 5, the water 6 and the phase-change material 7 are all T2The equilibrium state of (1).
6. The temperature of the upper water pool 2 is stored as T1Of water 211. The temperature of the hydraulic oil 5, the water 6 and the phase-change material 7 is T2Thereafter, the test is started and the upper basin 2 is placed on top of the thermally conductive upper lid 41.
7. At a temperature T1<T0<T2Under the condition, under the action of the temperature difference between the upper water tank 2 and the lower water tank 3, the heat conduction interface 411, the phase-change material 7 and the liquid interface 8 generate heat exchange along the axial direction, the phase-change material 7 gradually generates one-dimensional phase change from liquid to solid from the upper heat conduction interface 411 and downwards along a vertical axis, the volume of the phase-change material 7 gradually shrinks, the height of the liquid interface 8 gradually rises, the rubber leather bag 19 gradually expands, the hydraulic oil 5 is supplemented into the rubber leather bag 19, the liquid level of the oil tank 11 drops, the liquid level sensor 12 continuously collects the change process of the liquid level h of the oil tank 11, and a liquid level change quantity delta h curve is recorded. When the phase change material 7 and the water 6 reach the equilibrium state again, the liquid level h of the oil tank 11 stops changing.
8. The above-described 1 st to 7 th working processes are repeated, and the present invention can be used at various pressures p0Under the condition of and T1、T2And carrying out comparison tests on different phase-change materials 7 under the condition of temperature boundary.
9. Rate of change of volume of phase change material to be at pressure p0Temperature T1And T2Under the condition, after carrying out the heat exchange test of the time length t, calculating S.DELTA.h.V0 -1The value is evaluated, and the heat conductivity of the phase change material is evaluated according to the time point t0The rate of change of the liquid level h dh/dt0Evaluation was performed.
The present invention is not limited to the above-described embodiments. The foregoing description of the specific embodiments is intended to describe and illustrate the technical solutions of the present invention, and the above specific embodiments are merely illustrative and not restrictive. Those skilled in the art can make many changes and modifications to the invention without departing from the spirit and scope of the invention as defined in the appended claims.