Inter-cloud computing environment value exchange-oriented cross-chain communication method
Technical Field
The invention relates to the field of block chains and distributed cloud computing, in particular to a communication method for performing value exchange in a cross-chain mode by using a block chain as a basic technical support.
Background
The concept of block chain was proposed as the underlying technology of bit currency in the Smart Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System (i.e., bit currency: a point-to-point Electronic Cash System) in 08. In order to realize a point-to-point decentralized trusted accounting system, the intelligent agent puts each transaction information of the bitcoin into a block (namely a block structure for storing transaction data hash values and timestamps), and each block is connected into a chain according to the sequence of the timestamps, which is called a block chain. A user node on a certain blockchain (also referred to as a user node belonging to a certain blockchain) refers to a user terminal that synchronizes all blocks on the certain blockchain to a local server, and in an inter-cloud computing environment, refers to a cloud service consumer and a cloud service provider in particular. A block chain is provided with a plurality of user nodes, and all the user nodes have the functions of broadcasting, verifying, allocating funds in a fund pool and transferring funds. In addition, since the blockchain itself can be regarded as a distributed book, the whole blockchain that synchronizes each user node to the local server is called a local book, and the local book is updated synchronously with the generation of a new block. Therefore, the traditional Chinese intelligent terminal perfectly realizes a decentralized and trusted accounting system under the peer-to-peer network through the form of the block chain. As shown in fig. 2, the block chain is formed by a plurality of blocks (the first block is defined as a creation block) in the order of time stamps for creating the transaction. Each block consists of a block header and three other data fields. The block header contains 6 data fields, which are: chunk ID, random number, last chunk hash value, timestamp of the generated chunk, Merkle root hash value, difficulty value. The block ID is the number of each block and is used for checking the transaction information after the verification module and the transaction are completed; the random number is a number which is subjected to hash operation with transaction information (the hash operation is an operation of mapping data with any length into data with fixed length, SHA-256 hash algorithm is used in a bitcoin, and the hash algorithm is from the safety hash standard issued by the national institute of standards and technology, and is used for a user node to compete for the billing right according to a PoW consensus mechanism; the last block hash value is a value obtained by merging and carrying out hash operation on the data field information of the last block connected with the block to which the last block hash value is 0; generating a time stamp of the block refers to a string of character sequences representing the block generation time; the Merkle root Hash value is formed by combining all transaction information in the transaction information through a Merkle Proof method (Nakamoto S. Bitcin: Apeer-to-peer electronic cash system [ J ].2008, namely Biteh currency: a point-to-point electronic cash system page 4, lines 22-31); the difficulty value is a difficulty coefficient for calculating the hash value when the user contends for the billing right. The other three data fields in the block are: block size, transaction counter, transaction information. The block size is the size of the block in bytes; the transaction counter is the transaction number recorded in the block; the transaction information is information for each transaction record, which is recorded by the user node according to the specific transaction. Later, based on the inspiration of bitcoin, more and more enterprises dedicated to the development of the blockchain infrastructure are launched into the industrial market, and the enterprises include Blockstream, Ripple, Ethereum and the like.
By taking the idea of bitcoin as a reference, Etheng attempts to build an intelligent contract platform on top of bitcoin protocol that does not require a trust base at all. It is an innovative programmable blockchain platform that allows anyone to build and use decentralized applications running through blockchain technology in the platform. In contrast to bitcoin blockchains, which are purely a list of transaction information, etherhouse blockchains are account-based units that track the status of each account, and state transitions across all etherhouse blockchains are transfers of value and information between accounts. The account is divided into an external account and a contract account, wherein the external account is controlled by a user through a private key, and the contract account is controlled by contract code, namely intelligent contract.
As for smart contracts, as early as 1994, the cryptologist nissabo (Nick Szabo) put forward the concept of smart contracts in its own website, but has not been applicable to reality. The development is not continued until the clever bitcoin is proposed. An intelligent CONTRACT is an automatically executable computer program (e.g., "Ethernet White Paper: ANEXT GENERATION SMART CONTACT & DECENTRALIZED APPLICATION PLATFORM", i.e., "ETHERS: Next Generation Intelligent CONTRACTs and DECENTRALIZED APPLICATION PLATFORMs", page 13, line 16-page 17, line 24, which describe the concept of intelligent CONTRACTs in ETHERS, how to write and how to use it. The method is deployed on a block chain, so that automatic control over transaction processes and transaction data can be realized, and interaction with real assets can be realized by executing the program.
If the blockchain is said to solve the problem that the transaction channel is not trusted, the consensus mechanism is to solve the problem of how the blockchain is consistent under the distributed scenario. Representative consensus algorithms include PBFT (Practical Byzantine factory Tolerance), PoW (Proof of Work) consensus algorithm (Nakamoto S. Bitcin: Apeer-to-peer electronic cash system [ J ] 2008, bit currency: a Point-to-Point electronic Cash System, pages 4, lines 1-22), PoS (Proof of rights) consensus algorithm, and the like. PBFT is a message-passing based consensus algorithm generated in the context of the problem of the general of byzantine. The maximum allowable fault tolerance number of the PBFT algorithm in an asynchronous network environment is (n-1)/3(n is the total node number). The PBFT algorithm is consistent through three stages of preparation, preparation and execution, and the three stages are all repeated possibly due to failure. The PoW consensus algorithm based on workload certification is mainly used in accounting right contention for blocks. The hash value of a block (i.e. the result of the hash encryption operation on the transaction record in the block, the transaction record being represented by a string of numbers) is composed of N leading zeros, and the number of zeros depends on the difficulty level of the network. To obtain a reasonable hash value, a large number of trial and error calculations are required, and the calculation time depends on the hash operation speed of the machine. Users on the blockchain compete for billing based on computing power to obtain bitcoin revenue, an operation also known as mine excavation. Since finding the correct hash value is a probabilistic event, when a node has m% of the total network computing power, the node has m% of the probability of finding the hash value of a block, and m is a real number. However, PoW resources are extremely wasteful, and the final operation is not practical. PoS is a rights-based attestation algorithm that considers records and attestations on a blockchain to be maintained and guaranteed by those with economic benefit on the chain. PoS fundamentally breaks away from the waste of computing power of PoW by requiring a prover to provide ownership of a certain amount of cryptocurrency rather than performing a difficult workload proof.
Existing Multi-Cloud service providers, such as Inter-Cloud, SuperCloud, Multi-Cloud, fedeastedcloud, etc., focus primarily on the integration of resources to meet the needs of Cloud service consumers, but lack platform and mechanism support for participant shared collaboration and a service model for cooperative win-win among Cloud service providers.
inter-Cloud Computing (Joint Cloud Computing) is a support technology which is provided for meeting the requirements of future Cloud Computing and adapting to the future development of Cloud Computing and can solve the existing research dilemma, and the Joint Cloud Computing is a new generation Cloud Computing mode which is based on open collaboration among Cloud service providers, integrates multiple Cloud resources deeply, supports self-service collaboration and benefit exchange among Cloud providers, and is convenient for developers to customize Cloud services and create Cloud value in a software definition mode. In an interpyury computing scenario, an interpyury chain coexists with other types of blockchains (user chains and business chains), and a requirement for value exchange exists in a single blockchain.
Under the global development trend of the internet, it is increasingly difficult for a single block link structure to meet the requirements of various transaction services. To address the complex and varied cloud computing transaction service challenges, some companies have proposed the concept of conducting transactions across chains. Representative examples include side chain technology (Sidechain) proposed by Blockstream corporation, and inter-chain protocol proposed by Ripple corporation. The side chain proposed by Blockstream is a chain for realizing the transfer of bitcoin among a plurality of block chains. When transferring funds, a confirmation period and a competition period need to be waited for. The validation period is the time that the funds need to be locked in the chain on which the sender of the funds is located before transferring to the sidechain in order to generate enough work to resist the attack. And the competition period is used for preventing the double-flower attack during the recombination. Both periods require waiting for 1-2 days to lock the funds, respectively. The side chain technique is inefficient due to the excessive time spent for processing the fund verification and cannot meet the requirements of normal transactions.
The Interridge protocol, proposed by Ripple corporation, is a protocol for payments across payment systems. If the two parties of the transaction are in different payment systems, no direct transaction channel is available between the two parties to complete the transaction. Aiming at the situation, the Interridge protocol proposes that middleware (Connectors) is added between a Sender (Sender) and a Receiver (Receiver) of transaction funds to connect, in such a way, a channel capable of direct transaction is established between different payment systems, meanwhile, Escrow and control of the funds during transaction preparation are realized through a third-party funds Escrow platform (Escorow), but the security of the Interridge protocol is doubted by the huge open risk of the Escorow.
Therefore, to implement cross-chain transaction or communication, the following technical problems also exist:
1. the safety problem. The inter-chain communication based on the digital currency needs to guarantee the rights and interests of both communication parties, namely, the effective availability of the transaction currency is ensured; the transaction record is real and traceable; the likelihood of a malicious attack is low. Therefore, a perfect mechanism is needed to maintain traceability and stable operation of the transaction, in the prior art, the transaction is often supervised and maintained by a third party (such as Escrow in the interleaver), and since the third party has a certain potential safety hazard (possibly existing fraud behaviors), the safety of the whole value exchange process cannot be ensured.
2. The efficiency is problematic. To ensure security, it takes a lot of time for currency validation (including verifying whether the source of the currency is valid and whether the currency is available) and accounting (confirming the transaction and recording). Most of the prior art costs a lot of time for verifying the validity of the funds (for example, the side chain spends 2-4 days for locking the funds in one value transfer), and the efficiency of the value exchange is greatly reduced.
Disclosure of Invention
The technical problem to be solved by the invention is to provide a cross-chain communication method for inter-cloud computing environment value exchange, which ensures the safety, reliability and high efficiency of the value exchange process, promotes the transaction and communication between any two chains, and realizes the seamless cross-chain communication between the chains.
The technical scheme of the invention is to facilitate inter-chain value exchange, and particularly provides a cross-chain communication scheme aiming at certain chains without direct connection channels. In an inter-cloud computing environment, there is a blockchain, referred to as inter-cloud chain, that has a need for cross-chain communication with other types of blockchains, including business chains that provide cloud computing services, and user chains that use cloud computing services. According to the idea that middleware is established to connect different payment systems according to an Interridge protocol (APROTOCOL for Interridge Payments, namely Interridge white paper) provided by Ripple company, the invention establishes an intermediate chain for connecting a cloud chain and any chain (as shown in figure 4, taking a service chain A as an example), and performs cross-chain communication through the intermediate chain to further realize value exchange; meanwhile, the fund validity in the value exchange process is verified in an intelligent contract mode, and the safety of the transaction process is guaranteed. The blockchain used in the present invention is the same as the data structure shown in fig. 2, and the contents of the transaction information field in the block are defined. Each transaction message includes the following contents: the transaction record index number, sender address, receiver address, transaction resource content, transaction transfer amount, and transaction generation timestamp. The transaction record index number is a serial number of each transaction record recorded in the ith block in the block chain according to a time sequence and is used for checking transaction information after fund verification and transaction are completed, wherein i is a positive integer; the sender address refers to the IP address of the user node that initiated the transaction; the receiver address refers to the IP address of the user node receiving the transaction; the transaction resource content refers to cloud service resources provided by a cloud service provider to a cloud service consumer in a cloud service transaction; the transaction transfer amount refers to an amount required by a cloud service consumer to purchase a resource provided by a cloud service provider in a cloud service transaction; the time stamp of the generated transaction refers to a string of characters representing the time of generation of the transaction.
The invention comprises the following steps:
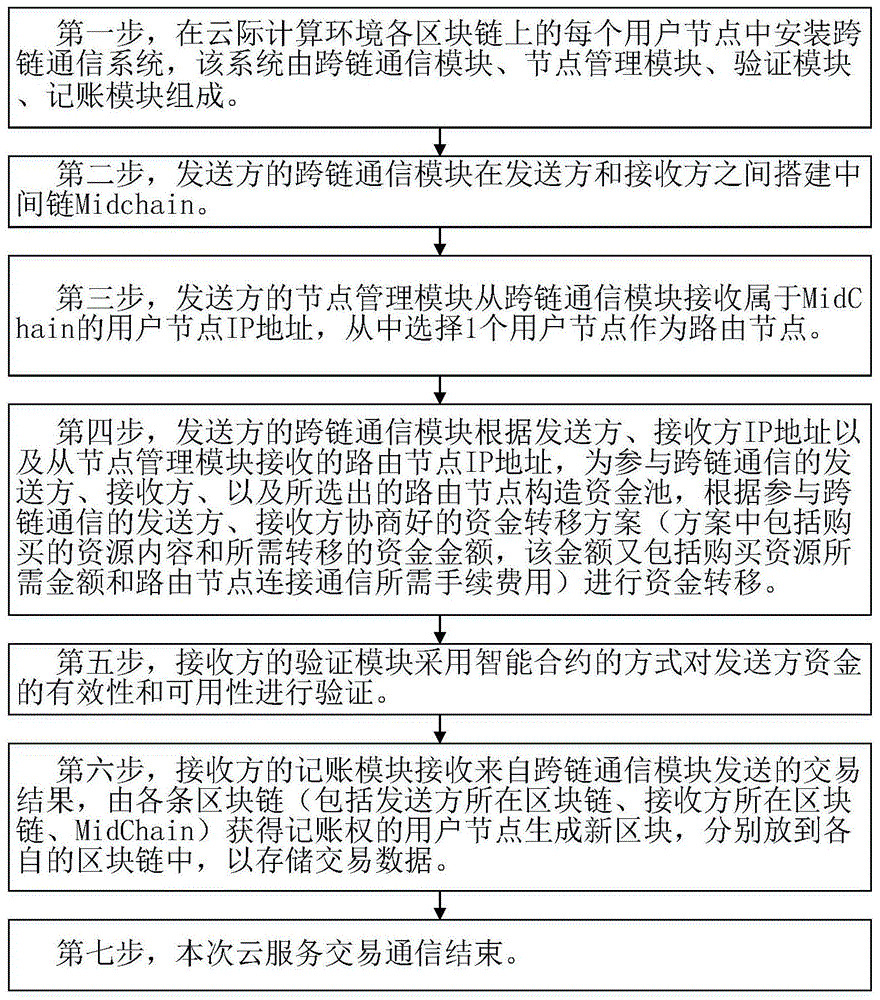
firstly, installing a cross-chain communication system in each user node on each blockchain of the inter-cloud computing environment, wherein the system comprises a cross-chain communication module, a node management module, a verification module and an accounting module.
The cross-chain communication module is connected with a sender (namely a transaction sender, the default transaction sender is a party purchasing resources and paying money), a receiver (namely a transaction receiver, the default transaction receiver is a party providing resources and receiving money), a node management module, a verification module and an accounting module, is responsible for building a middle chain and constructing a routing node fund pool, and is also responsible for communication among the sender, the receiver and the routing node and fund transfer. The method comprises the steps of determining a sender address and a receiver address according to a request sent by a sender, constructing an intermediate chain connecting the sender and the receiver according to the two addresses, and sending IP addresses of all user nodes on the intermediate chain to a node management module; the cross-link communication module receives the IP address of the routing node from the node management module, performs communication connection and cloud service transaction according to the routing node result, and simultaneously sends funds related to the transaction to the verification module; the cross-link communication module receives a transaction acceptance result from the verification module, and continues to execute the transaction or terminate according to the transaction acceptance result; and after the cross-chain communication module finishes the transaction, the transaction information is sent to the accounting module.
The node management module is connected with the cross-chain communication module, receives the IP address of the user node on the intermediate chain from the cross-chain communication module, selects a routing node participating in cross-chain communication from the user node on the intermediate chain, and sends the IP address of the routing node to the cross-chain communication module;
the verification module is connected with the cross-chain communication module, receives the transaction fund from the cross-chain communication module, is responsible for verifying the validity and the availability of the transaction fund and returns the transaction verification result to the cross-chain communication module;
the accounting module is connected with the cross-chain communication module, the sender and the receiver, receives transaction information from the cross-chain communication module, and is responsible for generating an account book for the transaction and synchronizing the account book to all user nodes in a chain where the sender and the receiver are located.
And secondly, a cross-chain communication module of the sender builds an intermediate chain between the sender and the receiver. The method comprises the following steps:
2.1 the cross-chain communication module of the sender constructs an intermediate chain according to the sender address-StartAddr and the receiver address EndAddr, and the constructed intermediate chain is represented by MidChain. The method comprises the following steps:
2.1.1 determine the intermediate chain data structure as a blockchain.
2.1.2 initialize the first block of the intermediate chain:
2.1.2.1 determining the block size to be the byte size occupied by the entire block;
2.1.2.2 initializes the transaction counter to 0;
2.1.2.3 initialize the chunk header of the first chunk of the middle chain:
2.1.2.3.1 initializes the tile ID to 001;
2.1.2.3.2 initializes the random number to 0;
2.1.2.3.3 initializing the last chunk hash value to 0;
2.1.2.3.4 initialize a difficulty value to 0;
2.1.2.3.5 determining the time stamp of the generated block as the time of the block generation time;
2.1.2.3.6 initializing the Merkle root hash value to 0;
2.1.2.4 initializing transaction information in tiles:
2.1.2.4.1 initializing transaction record index number to Mid-1-1 (and growing sequentially in the form of Mid-1-2, Mid-1-3, Mid-1-4);
2.1.2.4.2 initializing transaction resource content to null;
2.1.2.4.3 initializes the transaction transfer amount to 0;
2.1.2.4.4 determining the sender address to be StartAddr;
2.1.2.4.5 determining the receiver address as EndAddr;
2.1.2.4.6 initializes the timestamp of the generated transaction to 0;
2.1.3 creating a user node belonging to MidChain, wherein the method comprises the following steps: and at least 5 different user node servers are randomly selected from the block chain where the sender is located and the block chain where the receiver is located respectively to synchronize the block information on the MidChain, and the synchronized server addresses are recorded as the IP addresses of the user nodes.
2.1.4 the cross-chain communication module of the sender sends all the user node IP addresses on the middle chain to the node management module of the sender.
Thirdly, the node management module of the sender receives the user node IP addresses belonging to MidChain from the cross-link communication module, and 1 user node is selected as a routing node, wherein the method comprises the following steps:
3.1 determining the candidate node range by adopting a PoW consensus algorithm, wherein the method comprises the following steps: performing power competition by adopting a PoW consensus algorithm, and selecting the first five user nodes with the strongest computing power as candidate nodes, wherein the strongest computing power means that the user nodes obtain a random number through operation at the fastest speed, so that the number obtained after the random number and 6 data in a block header are combined together by using a Merkle Proof method meets the set difficulty value, wherein the difficulty value is a maximum target value divided by a current target value (the maximum target value is a fixed hash value and is generally set to be 0x0000 FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF; and the current target value is the block header hash value of the current block (namely the newly generated block).
3.2 because the routing node is used for connecting communication and requires handling fee (the routing node is used as an intermediate connecting node of cross-link communication, the cost is charged for connecting communication between a sender and a receiver, and the specific handling fee amount is self-determined by the routing node), the handling fee required by the communication between the sender and the receiver is sorted from five candidate nodes selected by adopting a PoW consensus algorithm, and the candidate node with the lowest handling fee is selected as the routing node on the MidChain, which is called the routing node for short.
3.3 the node management module of the sender sends the IP address of the routing node to the cross-link communication module of the sender.
Fourthly, the cross-link communication module of the sender constructs a fund pool for the sender, the receiver and the selected routing node participating in the cross-link communication according to the IP address of the sender and the IP address of the receiver and the IP address of the routing node received from the node management module, and fund transfer is carried out according to a fund transfer scheme negotiated by the sender and the receiver participating in the cross-link communication (the scheme comprises purchased resource content and fund amount required to be transferred, and the fund amount comprises the amount required for purchasing the resource and procedure cost required for connecting and communicating with the routing node). The method comprises the following specific steps:
4.1 establishing independent fund pools for a sender, a receiver and a routing node participating in cross-link communication, namely representing the nodes and the corresponding pre-stored fund amount thereof by key value pairs in the form of (node IP addresses and pre-stored fund amounts);
4.2 the three parties of the sender, the receiver and the routing node pre-store a part of funds in the fund pool, namely, the IP addresses of the three parties (the IP address of the node and the pre-stored fund amount) and corresponding pre-stored fund values are respectively given to the three parties.
4.3 the sender broadcasts the fund transfer scheme to the routing node and the receiver, the routing node and the receiver receive the widely broadcast fund transfer scheme, check whether the fund transfer scheme content (fund transfer amount and routing node commission) is correct, if so, the receiver sends a confirmation result (that is, the scheme content is correct) to the routing node, the routing node collects the confirmation result (including the confirmation result of the routing node) and then signs, and returns the fund transfer scheme with the signature to the sender, and meanwhile, the routing node and the receiver send the fund involved in the transaction to the verification module of the routing node and the receiver, and the fifth step is carried out; if not, the receiver sends the error information to the routing node, the routing node collects the error information (including the error information found by the routing node) and attaches the signature of the routing node, the error information is sent to the sender, and the sender broadcasts again after checking and modifying the fund transfer scheme, and then the 4.3 steps are carried out.
And fifthly, the verification module of the receiver verifies the validity and the availability of the funds of the sender in an intelligent contract mode. The specific method for verification is as follows:
5.1 determination conditions for entering funds in a smart contract (i.e. a piece of program automatically performing the determination action deployed in the verification module): it is determined whether the source of funds is available, i.e., whether the sender has sufficient funds to transfer.
5.2 traversing each block of the block chain to which the sender belongs, inquiring transaction information (namely transaction transfer amount and transaction resource content) of the sender, judging whether the sender has enough funds for the transaction (namely whether the total amount of transferred funds minus the total amount of transferred funds of the sender is larger than the amount of funds required to be transferred for the transaction), if not, indicating that the verification fails, the fund transfer scheme is invalidated, the two parties of the transaction coordinate the next operation, and regenerating the fund transfer scheme and broadcasting again by the sender according to the coordination result or 4.3 steps; or turning to the seventh step to terminate the transaction; if sufficient funds exist, the verification is successful, and the result of the successful verification is returned to the cross-link communication module of the sender, and the step is changed to 5.3;
and 5.3, the cross-link communication module of the sender reallocates funds in the fund pool according to the transaction transfer amount related in the fund transfer scheme, namely (the node IP address and the pre-stored fund amount) of the sender is changed into (the node IP address and the existing fund amount) to complete fund transfer, (the existing fund amount is the pre-stored fund amount-the transaction transfer amount), and the transaction information is sent to the accounting module.
Sixthly, the accounting module of the receiver receives the transaction information sent by the cross-chain communication module in the step 5.3, and user nodes which acquire accounting rights by each block chain (including the block chain where the sender is located, the block chain where the receiver is located, and the MidChain) generate new blocks which are respectively put into the respective block chains to store the transaction information, wherein the method comprises the following steps:
6.1 the accounting module performs hash operation on the transaction information (including transaction record index number, transaction resource content, transaction transfer amount, sender address, receiver address and timestamp for generating transaction) (an algorithm for converting target text into hash character strings with the same length, and adopts SHA-256 hash algorithm in safety hash standard issued by national institute of standards and technology), and broadcasts the hash character strings to the block chain where the sender and the receiver are located and each user node on the intermediate chain.
6.2 each user node (including the chain where the sender is located, the chain where the receiver is located and all user nodes on the intermediate chain) contends for the accounting right by adopting a PoW consensus algorithm to perform calculation competition and selecting 1 user node with the strongest calculation. And finally, one user node of each block chain obtains the accounting right, a new block is generated on the block chain to which the user node belongs, and the block size, the transaction counter, the block header and the transaction information are put into the newly generated block. The values of the contents in the block are as follows:
6.2.1 Block size is determined as the byte size occupied by the entire block;
6.2.2 transaction counter is determined as the transaction times contained in the block;
6.2.3 the 6 data contained in the block header are assigned respectively:
6.2.3.1 the block ID is 00i (i is the block serial number, as the blocks increase, the value of i increases progressively according to the rule of n +1, n +2, n +3, …, n is the original number of blocks of the block chain to which the user node obtaining the accounting right belongs, and n is a positive integer);
6.2.3.2 the random number is a random number value obtained by the operation of the user node obtaining the accounting right when competing for the accounting right;
6.2.3.3 the last chunk hash value is the last chunk hash value;
6.2.3.4, the difficulty value is determined by the formula difficulty value is maximum target value ÷ current target value;
6.2.3.5 determining the time stamp of the generated block as the time of the block generation time;
6.2.3.6Merkle root hash is a hash value obtained by combining the transaction information by a Merkle Proof method;
6.2.4 the transaction information contains 6 data assigned values:
6.2.4.1 assigns the transaction record index number Mid- (i-1);
6.2.4.2 determining the transaction resource content as resource content (in the form of a string) for a particular transaction;
6.2.4.3 determining the transaction transfer amount as the amount to be transferred for the particular transaction;
6.2.4.4 determining the sender address to be StartAddr;
6.2.4.5 determining the receiver address as EndAddr;
6.2.4.6 determining the time stamp of the generated transaction as the time of the transaction generation time;
and 6.3, synchronously downloading the newly generated blocks to respective local accounts by each user node on the block chain where the sender and the receiver are located and the intermediate chain.
And step seven, ending the cloud service transaction communication.
The invention can achieve the following technical effects:
1. the accounting module records the transaction information in the local account book of each user node, so that the problem of poor traceability of the transaction information caused by accounting of both transaction parties is avoided, and the problem of high risk of fund exposure of a third-party escrow system is also avoided.
2. And because the fifth step adopts an intelligent contract mode, the efficiency is improved compared with the existing fund verification mode. For example, the side chain technique accomplishes the verification through fund locking of two waiting periods, which take 2-4 days in total, thus seriously affecting the transaction process. And the intelligent contract mode is adopted, rules are preset according to whether the fund is valid (namely whether the transaction record of the previous fund exists) and available (namely whether the fund is used), the fund verification is automatically completed, the unnecessary waiting time is reduced, the account confirming speed is accelerated, and the high efficiency and the order of the transaction are ensured.
3. And in the fourth step, a mode of establishing a fund pool is adopted, and the fund amount in the fund pools of the two parties is redistributed according to the transfer object and the amount described by the fund distribution scheme, so that the safety is improved compared with the mode of directly transferring the specific currency. Meanwhile, the method is also suitable for multiple small-scale transactions, the fund amount is directly modified, unnecessary time delay is reduced, and the efficiency is higher.
Drawings
FIG. 1 is a diagram of a scenario of inter-chain communication between chains in an inter-cloud computing environment.
Fig. 2 is a data structure diagram of the block chain of the present invention.
FIG. 3 is a logic structure diagram of a cross-chain communication system facing the inter-cloud computing environment, which is constructed in the first step of the invention;
fig. 4 is a scenario diagram of a middle chain constructed by the present invention to connect a sender and a receiver to communicate.
Fig. 5 is an overall flow chart of the present invention.
Detailed Description
FIG. 1 is a diagram of a background art scenario for inter-chain communication between chains in an inter-cloud computing environment. In the inter-cloud computing environment, there are various kinds of block chains (the data structure of the block chain is shown in fig. 2), including inter-cloud chains for connecting and cooperating various chains, business chains a and B for providing cloud computing services, and user chains C and D for purchasing and using the cloud computing services. There is a need for transactions for user nodes that are on different chains, including CSPs (cloud service providers), and CSCs (cloud service consumers). For such a cross-chain situation, an intermediate chain needs to be established between two chains of communication to connect.
Fig. 2 is a data structure diagram of the block chain of the present invention. The invention provides for the contents of the transaction information field in the tile. Each transaction message includes the following contents: the transaction record index number, sender address, receiver address, transaction resource content, transaction transfer amount, and transaction generation timestamp. The other information in the block is exactly the same as the existing block chain described in the background.
FIG. 3 is a logic structure diagram of a cross-chain communication system facing the cloud computing environment, which is constructed in the first step of the invention. The cross-chain communication module is connected with a sender (namely a transaction sender, the default transaction sender is a party purchasing resources and paying money), a receiver (namely a transaction receiver, the default transaction receiver is a party providing resources and receiving money), a node management module, a verification module and an accounting module, is responsible for building a middle chain and constructing a routing node fund pool, and is also responsible for communication among the sender, the receiver and the routing node and fund transfer. The method comprises the steps of determining a sender address and a receiver address according to a request sent by a sender, constructing an intermediate chain connecting the sender and the receiver according to the two addresses, and sending IP addresses of all user nodes on the intermediate chain to a node management module; the cross-link communication module receives the IP address of the routing node from the node management module, performs communication connection and cloud service transaction according to the routing node result, and simultaneously sends funds related to the transaction to the verification module; the cross-link communication module receives a transaction acceptance result from the verification module, and continues to execute the transaction or terminate according to the transaction acceptance result; and after the cross-chain communication module finishes the transaction, the transaction information is sent to the accounting module.
The node management module is connected with the cross-chain communication module, receives the IP address of the user node on the intermediate chain from the cross-chain communication module, selects a routing node participating in cross-chain communication from the user node on the intermediate chain, and sends the IP address of the routing node to the cross-chain communication module;
the verification module is connected with the cross-chain communication module, receives the transaction fund from the cross-chain communication module, is responsible for verifying the validity and the availability of the transaction fund and returns the transaction verification result to the cross-chain communication module;
the accounting module is connected with the cross-chain communication module, the sender and the receiver, receives transaction information from the cross-chain communication module, and is responsible for generating an account book for the transaction and synchronizing the account book to all user nodes in a chain where the sender and the receiver are located.
Fig. 4 is a scene diagram of a middle chain constructed by the present invention connecting a sender and a receiver and performing communication. Assuming that there is a communication requirement between the inter-cloud chain and the service chain a, but there is no direct connection channel, an intermediate chain is built between the two chains, Node2 is a routing Node of the intermediate chain, and the routing nodes of the sender, the receiver and the intermediate chain are all provided with a fund pool.
Fig. 5 is an overall flow chart of the present invention. The method comprises the following specific steps:
in the first step, a cross-chain communication system is installed in each user node on each blockchain of the inter-cloud computing environment, and the system is composed of a cross-chain communication module, a node management module, a verification module and an accounting module as shown in fig. 3.
And secondly, a cross-chain communication module of the sender builds an intermediate chain between the sender and the receiver. The method comprises the following steps:
2.1 the cross-chain communication module of the sender constructs an intermediate chain according to the sender address-StartAddr and the receiver address EndAddr, and the constructed intermediate chain is represented by MidChain. The method comprises the following steps:
2.1.1 determine the intermediate chain data structure as a blockchain.
2.1.2 initialize the first block of the intermediate chain:
2.1.2.1 determining the block size to be the byte size occupied by the entire block;
2.1.2.2 initializes the transaction counter to 0;
2.1.2.3 initialize the chunk header of the first chunk of the middle chain:
2.1.2.3.1 initializes the tile ID to 001;
2.1.2.3.2 initializes the random number to 0;
2.1.2.3.3 initializing the last chunk hash value to 0;
2.1.2.3.4 initialize a difficulty value to 0;
2.1.2.3.5 determining the time stamp of the generated block as the time of the block generation time;
2.1.2.3.6 initializing the Merkle root hash value to 0;
2.1.2.4 initializing transaction information in tiles:
2.1.2.4.1 initializing transaction record index number to Mid-1-1 (and growing sequentially in the form of Mid-1-2, Mid-1-3, Mid-1-4);
2.1.2.4.2 initializing transaction resource content to null;
2.1.2.4.3 initializes the transaction transfer amount to 0;
2.1.2.4.4 determining the sender address to be StartAddr;
2.1.2.4.5 determining the receiver address as EndAddr;
2.1.2.4.6 initializes the timestamp of the generated transaction to 0;
2.1.3 creating a user node belonging to MidChain, wherein the method comprises the following steps: and at least 5 different user node servers are randomly selected from the block chain where the sender is located and the block chain where the receiver is located respectively to synchronize the block information on the MidChain, and the synchronized server addresses are recorded as the IP addresses of the user nodes.
2.1.4 the cross-chain communication module of the sender sends all the user node IP addresses on the middle chain to the node management module of the sender.
Thirdly, the node management module of the sender receives the user node IP addresses belonging to MidChain from the cross-link communication module, and 1 user node is selected as a routing node, wherein the method comprises the following steps:
3.1 determining the candidate node range by adopting a PoW consensus algorithm, wherein the method comprises the following steps: performing power competition by adopting a PoW consensus algorithm, and selecting the first five user nodes with the strongest computing power as candidate nodes, wherein the strongest computing power means that the user nodes obtain a random number through operation at the fastest speed, so that the number obtained after the random number and 6 data in a block header are combined together by using a Merkle Proof method meets the set difficulty value, wherein the difficulty value is a maximum target value divided by a current target value (the maximum target value is a fixed hash value and is generally set to be 0x0000 FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF; and the current target value is the block header hash value of the current block (namely the newly generated block).
3.2 because the routing node is used for connecting communication and requires handling fee (the routing node is used as an intermediate connecting node of cross-link communication, the cost is charged for connecting communication between a sender and a receiver, and the specific handling fee amount is self-determined by the routing node), the handling fee required by the communication between the sender and the receiver is sorted from five candidate nodes selected by adopting a PoW consensus algorithm, and the candidate node with the lowest handling fee is selected as the routing node on the MidChain, which is called the routing node for short.
3.3 the node management module of the sender sends the IP address of the routing node to the cross-link communication module of the sender.
And fourthly, constructing a fund pool for the sender, the receiver and the selected routing node participating in the cross-chain communication by the cross-chain communication module of the sender according to the IP addresses of the sender and the receiver and the IP address of the routing node received from the node management module, and transferring funds according to a negotiated fund transfer scheme of the sender and the receiver participating in the cross-chain communication. The method comprises the following specific steps:
4.1 establishing independent fund pools for a sender, a receiver and a routing node participating in cross-link communication, namely representing the nodes and the corresponding pre-stored fund amount thereof by key value pairs in the form of (node IP addresses and pre-stored fund amounts);
4.2 the three parties of the sender, the receiver and the routing node pre-store a part of funds in the fund pool, namely, the IP addresses of the three parties (the IP address of the node and the pre-stored fund amount) and corresponding pre-stored fund values are respectively given to the three parties.
4.3 the sender broadcasts the fund transfer scheme to the routing node and the receiver, the routing node and the receiver receive the widely broadcast fund transfer scheme, check whether the fund transfer scheme is correct, if so, the receiver sends a confirmation result (i.e. the scheme content is correct) to the routing node, the routing node collects the confirmation result (including the confirmation result of the routing node) and then signs, the fund transfer scheme with the signature is returned to the sender, and meanwhile, the routing node and the receiver send the fund involved in the transaction to the verification module of the routing node and the receiver, and the fifth step is carried out; if not, the receiver sends the error information to the routing node, the routing node collects the error information (including the error information found by the routing node) and attaches the signature of the routing node, the error information is sent to the sender, and the sender broadcasts again after checking and modifying the fund transfer scheme, and then the 4.3 steps are carried out.
And fifthly, the verification module of the receiver verifies the validity and the availability of the funds of the sender in an intelligent contract mode. The specific method for verification is as follows:
5.1 judging conditions for inputting funds in the intelligent contract: it is determined whether the source of funds is available, i.e., whether the sender has sufficient funds to transfer.
5.2 traversing each block of the block chain to which the sender belongs, inquiring transaction information (namely transaction transfer amount and transaction resource content) of the sender, judging whether the sender has enough funds for the transaction (namely whether the total amount of transferred funds minus the total amount of transferred funds of the sender is larger than the amount of funds required to be transferred for the transaction), if not, indicating that the verification fails, the fund transfer scheme is invalidated, the two parties of the transaction coordinate the next operation, and regenerating the fund transfer scheme and broadcasting again by the sender according to the coordination result or 4.3 steps; or turning to the seventh step to terminate the transaction; if sufficient funds exist, the verification is successful, and the result of the successful verification is returned to the cross-link communication module of the sender, and the step is changed to 5.3;
and 5.3, the cross-link communication module of the sender reallocates funds in the fund pool according to the transaction transfer amount related in the fund transfer scheme, namely (the node IP address and the pre-stored fund amount) of the sender is changed into (the node IP address and the existing fund amount) to complete fund transfer, and the existing fund amount is the pre-stored fund amount-the transaction transfer amount and the transaction information is sent to the accounting module.
Sixthly, the accounting module of the receiver receives the transaction information sent by the cross-chain communication module in the step 5.3, and user nodes which acquire accounting rights by each block chain (including the block chain where the sender is located, the block chain where the receiver is located, and the MidChain) generate new blocks which are respectively put into the respective block chains to store the transaction information, wherein the method comprises the following steps:
6.1 the accounting module performs hash operation on the transaction information (an algorithm for converting a target text into a hash character string with the same length, and adopts SHA-256 hash algorithm in safety hash standard released by American national standards and technical research institute), and broadcasts the hash operation to the blockchain where the sender and the receiver are located and each user node on the intermediate chain.
6.2 each user node (including the chain where the sender is located, the chain where the receiver is located and all user nodes on the intermediate chain) contends for the accounting right by adopting a PoW consensus algorithm to perform calculation competition and selecting 1 user node with the strongest calculation. And finally, one user node of each block chain obtains the accounting right, a new block is generated on the block chain to which the user node belongs, and the block size, the transaction counter, the block header and the transaction information are put into the newly generated block. The values of the contents in the block are as follows:
6.2.1 Block size is determined as the byte size occupied by the entire block;
6.2.2 transaction counter is determined as the transaction times contained in the block;
6.2.3 the 6 data contained in the block header are assigned respectively:
6.2.3.1 the block ID is 00i (i is the block serial number, as the blocks increase, the value of i increases progressively according to the rule of n +1, n +2, n +3, …, n is the original number of blocks of the block chain to which the user node obtaining the accounting right belongs, and n is a positive integer);
6.2.3.2 the random number is a random number value obtained by the operation of the user node obtaining the accounting right when competing for the accounting right;
6.2.3.3 the last chunk hash value is the last chunk hash value;
6.2.3.4, the difficulty value is determined by the formula difficulty value is maximum target value ÷ current target value;
6.2.3.5 determining the time stamp of the generated block as the time of the block generation time;
6.2.3.6Merkle root hash is a hash value obtained by combining the transaction information by a Merkle Proof method;
6.2.4 the transaction information contains 6 data assigned values:
6.2.4.1 assigns the transaction record index number Mid- (i-1);
6.2.4.2 determining transaction resource content as resource content for a particular transaction;
6.2.4.3 determining the transaction transfer amount as the amount to be transferred for the particular transaction;
6.2.4.4 determining the sender address to be StartAddr;
6.2.4.5 determining the receiver address as EndAddr;
6.2.4.6 determining the time stamp of the generated transaction as the time of the transaction generation time;
and 6.3, synchronously downloading the newly generated blocks to respective local accounts by each user node on the block chain where the sender and the receiver are located and the intermediate chain.
And step seven, ending the cloud service transaction communication.